The Effect of Dopant Additions on the Microstructure of Boron Fibers Before and After Reaction to MgB 2
|
|
|
- Rebecca Wilkinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol Materials Research Society FF6.2.1 The Effect of Dopant Additions on the Microstructure of Boron Fibers Before and After Reaction to MgB 2 James V. Marzik 1, Raymond J. Suplinskas 1, William J. Croft 2, Warren J. MoberlyChan 2, John D. DeFouw 3, and David C. Dunand 3 1 Specialty Materials, Inc., Lowell, MA, U.S.A. 2 Harvard University, Cambridge MA, U.S.A. 3 Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, U.S.A. ABSTRACT Boron fibers made by a commercial chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process have been used as precursors for the formation of magnesium diboride (MgB 2 ) superconducting wires. Prior to a reaction with magnesium, the addition of dopants such as carbon and titanium to the boron fiber has been shown to enhance the superconducting properties of MgB 2. These dopants also influence the kinetics of the reaction with magnesium. In this study, the effect of carbon dopant additions on the microstructure of boron fibers was investigated using powder x-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Additionally, bundles of boron fibers were pressure infiltrated with molten magnesium and reacted at elevated temperatures. The microstructure and microchemistry of the fiber-metal interfaces were investigated by TEM and energy dispersive x-ray analysis (EDS). INTRODUCTION Chemically vapor deposited (CVD) boron fibers [1] have been used for over three decades as a composite reinforcement in a number of structural aerospace applications. Of more recent interest is the use of CVD boron (B) fibers as precursors for the synthesis of MgB 2 superconductors. The discovery of superconductivity in MgB 2 at temperatures near 40K [2] has provided a technical opportunity to achieve high performance superconductors with lower fabrication and operating costs. B fibers can be converted to MgB 2 via reaction with Mg vapor [3], in principle eliminating a separate wire-forming manufacturing step. It has been shown [4-7] that doping the B starting material by co-deposition of the dopant and boron through CVD yields improved superconductor properties when the material is converted to MgB 2. Significant increases in both the critical current density, (J c ~ 5 x 10 6 A cm -2 at 5K) and the upper critical magnetic field (H c2 (0)>32T) have been demonstrated. Further, CVD B fibers have been infiltrated with liquid magnesium, and subsequently reacted to continuous MgB 2 fibers resulting in Mg/MgB 2 composites after solidification of the excess metal [8]. Hence, the potential exists for a process, based on existing commercial technology, to produce continuous, optimally doped MgB 2 superconducting wires embedded within a ductile, conductive metallic matrix (Figure 1). The introduction of carbon impurities into B fibers by CVD methods results in homogeneous dopant distribution and predictable dopant concentrations, based on the reported superconducting properties [6] of doped B fibers that were converted to Mg(B 1-x C) 2. However, it was observed that increases in the dopant concentration in B fibers resulted in significant decreases in the reaction rates during the formation of doped MgB 2 by the reaction with Mg vapor. This change in reaction rates motivated the work reported here, in which doped B fibers are characterized prior to and after their conversion to MgB 2.
2 FF6.2.2 Payout spool for tungsten wire BCl 3 + H 2 + dopant(s) Glass tube Doped boron fiber Mg vapor Individual doped MgB 2 superconducting fiber Variable DC supply C Pressure cast in molten Mg Exhaust gases Mercury electrode (top & bottom) Take-up spool for boron fiber on tungsten boride substrate Wire consisting of doped MgB 2 superconducting fibers in Mg matrix Figure 1. Process diagram showing CVD synthesis of boron fiber [1] and conversion to MgB 2 by reaction with magnesium vapor [3-7, 9] or molten Mg [8] EXPERIMENTAL The B fibers used here were synthesized using a modification of a commercial CVD process [1]. A 12µm diameter tungsten wire was drawn continuously through a 2-meter vertical glass reactor that was sealed at the top and bottom by pools of mercury. The mercury forms both an electrical contact and a gas seal. A mixture of boron trichloride (BCl 3 ) and hydrogen (H 2 ) was admitted through an inlet at the top and spent process gases were exhausted through an outlet near the bottom. The wire in the reactor is resistively heated to C by application of a DC voltage to the mercury seals. At this temperature, the BCl 3 is reduced by the H 2 ; pure, solid, amorphous elemental boron was deposited and byproduct hydrogen chloride was exhausted. The diameter of the boron produced is controlled by the draw rate of the wire through the reactor; a rate of 3-4 m/min results in a 100µm B fiber (with a reacted tungsten boride core, primarily W 2 B 5 ) being spooled continuously at the bottom. Carbon-doped B fibers were prepared similarly to undoped B fibers described above, with the addition of methane to the BCl 3 and H 2 reaction mixture. The composition (atomic %) of carbon in the gas mixture relative to boron was 0.5, 1.0, 1.4, 2.0, and 3.0%. Continuous lengths of 80µm diameter C-doped B fibers were produced. In this paper, the values used for dopant levels were the gas phase atomic ratios of carbon to boron. Initial analytical work indicates that the actual concentrations of carbon in the deposit may be approximately 50% higher than the gas phase concentration.
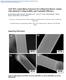
3 FF6.2.3 SEM/EDS analyses were carried out on a digital SEM (JEOL 5610), and a ThermoNoran System Six EDS system. TEM analyses were performed on a JEOL 2010-FEG (field emission gun) microscope operating at 200kV and a Philips EM420 operating at 100kV. EDS analyses were carried out in STEM (scanning transmission electron microscopy) mode, using an EDAX EDAM-III detector with Emispec Cynapse software. X-ray diffraction patterns were obtained using a Scintag Model XDS-2000 x-ray diffractometer calibrated with a NIST silicon standard. Copper Kα radiation was detected with a germanium crystal cooled to 77K. The diffraction patterns were taken in the range of 2 2θ 70 with a scan rate of 0.1 2θ per minute. B/Mg composite samples were prepared by placing bundles of boron fibers into titanium crucibles and infiltrating under pressure with molten magnesium according to a previously reported method [8]. The typical infiltration temperature and time was 800 C for 30 min. Select samples were heated at C to facilitate further reaction between the boron fibers (doped and undoped) and the Mg matrix. RESULTS A series of SEM micrographs of boron fiber surfaces (Figure 2) shows fiber surface morphology as a function of carbon doping level. Undoped CVD B fibers appear amorphous by TEM. X-ray diffraction patterns (Figure 3a) are indicative of an amorphous phase. The corncob surface texture (insets to Figures 2a and 2b) is indicative of macroscopic growth morphology and not the size of individual grains. Below a carbon dopant level of 2%, the fiber surface morphology remained relatively unchanged and the boron phase remained x-ray amorphous. At the 2% dopant level, however (Figure 2c) there were isolated occurrences of much larger grains,10-50µm in size, that were most likely seeded by a threshold concentration of carbon dopant. At the 3% dopant level (Figure 2d) rapid crystal growth dominates and the fiber no longer retained a regular cylindrical shape, but rather was a string of larger 10-50µm crystals irregularly arrayed around the tungsten boride substrate. X-ray diffraction of the 3% carbondoped boron fiber indicates that it is well-crystallized tetragonal boron (Figure 3c). TEM was performed on fiber surfaces, broken shards of fibers, and samples prepared by ion beam thinning. High resolution TEM did not detect crystalline grains in the undoped B fibers. Tilting dark field imaging also did not exhibit significant crystallinity, indicating that the undoped B fibers are primarily amorphous, which is consistent with the above x-ray diffraction results. TEM observation of the crystallized fibers doped with 3% carbon showed grains >10-20µm in size at the surface of the fiber. Selected area diffraction (SAD) showed that the fibers doped with high levels of carbon crystallized with the tetragonal phase of boron [10]. High resolution TEM images acquired at the [111] orientation were consistent with tetragonally crystallized boron formation in the 3% carbon- doped boron fiber. Quantitative EDS performed on spectra acquired from several thicknesses of crystallized B determined that carbon is present within the crystal and was not merely a surface contaminant during the analysis. Quantitative EDS also established that the carbon concentration is significantly less than 20 atomic %, thereby indicating the crystalline phase is not B 4 C. Although over twenty B(low-C) phases are reported in the Powder Diffraction File (PDF) [11], the electron diffraction data of these crystallized fibers match best to results reported for pure tetragonal boron (PDF ). It is thus suggested that some of the many "pure" boron phases reported in the PDF may have some solubility for carbon.
4 FF6.2.4 a b c 50µm 50µm d Figure 2. Surface morphology of boron fibers at the following carbon dopant levels in atomic percent: a) 0% b) 1.4% c) 2% and d) 3%. Insets to 2a and 2b show a 25µm wide area of the fiber surface. 50µm 20µm Intensity (arb. Units) Undoped CVD boron fiber a CVD boron fiber b doped with 1.4% C CVD boron fiber doped with 3% C c Deg 2θ Deg 2θ Deg 2θ Figure 3. X-ray diffraction patterns of undoped and carbon-doped B fibers. Undoped boron and boron doped with 1.4% carbon consist of amorphous boron plus crystalline tungsten boride substrate material. Boron doped with 3% carbon is a well crystallized tetragonal boron phase. TEM samples were prepared in cross section of the Mg-infiltrated B fibers, using polishing, dimpling and ion-beam thinning. The B fibers strongly resist thinning as compared to the surrounding matrix metal grains. Figure 4a is a bright field image of the interface between undoped B fiber and matrix in a composite infiltrated at 800 C. Four regions are visible: (i) the fiber interior (top region of 4a) is amorphous B; (ii) closer to the fiber-matrix interface is 0.5µm zone of fine grains (20-50nm); (iii) the fiber surface consists of a 1-2µm zone of coarser ~1µm grains; (iv) the bottom region in Figure 4a consists of the Mg matrix which was preferentially removed by TEM sample preparation. Figure 4b exhibits SAD of the fine-grain zone, with ring diffraction consistent with several B-Mg phases (such as MgB 4 or MgB 12 ). Figure 4c exhibits SAD of the next region with a [-1100] zone axis of the MgB 2 hexagonal phase. TEM analysis of the Mg matrix showed Mg metal grains >10-20µm in size extending across the entire matrix region between fibers. As infiltrated at 800 C, the reaction between B and Mg was limited to two thin layers indicated in Figure 4. Figure 5 shows optical micrographs of cross sections of composites that were heat treated at 1000 C (after the initial 800 C infiltration). A significant
5 FF6.2.5 a Amorphous boron b c Mg matrix (removed) Figure 4. Bright-field TEM image (4a) at interface of undoped boron fiber and Mg matrix. 4b shows SAD of the finer-grained phase (SAD ring pattern consistent with MgB 4 or MgB 12 ), and EDS was consistent with a phase that is more boron-rich than the MgB 2 phase. 4c shows SAD indexed with the [-1100] zone orientation of the MgB 2 hexagonal phase. Pure Mg (from EDS) 50µm 15µm Pure boron (from EDS) Partially reacted zone (EDS showed MgB 2, MgB 4, and possibly MgB 7 ) Figure 5. Polarized optical micrographs of composites made with undoped (left) and 0.5% C-doped (right) boron fibers. Undoped boron was heat treated at 1000 C for 15 min. C- doped boron (right) was heat treated at 1000 C for 16 hr. The Mg matrix partially reacted with the boron, although the C-doped boron fiber reacted much more slowly than the undoped fiber. fraction of the undoped boron fibers reacted with the Mg after 15 min at 1000 C. The 0.5% C- doped boron fibers reacted much more slowly with the Mg matrix, exhibiting a reaction zone of <5 µm after more than 16 hr at 1000 C. The presence of carbon apparently inhibits the reaction between B and Mg, although the reason for this is not clear. The undoped and 0.5% C-doped boron fibers are both amorphous with similar crystallite sizes. Carbide phases at the C-doped fiber-matrix interface were not observed by TEM examination, although partial material loss
6 FF6.2.6 during sample preparation could explain this. SEM/EDS analysis of the partially reacted zones indicated a boron-rich composition suggesting that MgB 4 and/or MgB 7 form prior to complete reaction of the fiber to form MgB 2. This is consistent with previous reports [3] in which boron fibers were reacted with Mg vapor. TEM analysis of Mg-B composites that were annealed at 950 C for 1 hour after the initial infiltration showed evidence of MgB 2 formation in the Mg matrix >100µm from the fiber-matrix interface. CONCLUSIONS The microstructure of boron fibers made by CVD was examined as a function of carbon dopant level. Undoped fibers and fibers doped with carbon at levels of <2 atomic % were found to be amorphous. At carbon dopant levels at 2%, the growth of large (10-50µm) grains of crystalline tetragonal boron was observed. It is suggested that there may be carbon present in the crystalline tetragonal phase of boron observed in fibers that were doped with higher concentrations ( 2%) of carbon. Doped and undoped fibers were infiltrated with molten magnesium to form boron/magnesium metal matrix composites. At the 800 C infiltration temperature, a layer of MgB 2 was observed adjacent to the Mg matrix and a layer of boron-rich phase or phases (MgB 4 and/or higher borides) were observed adjacent to the boron fiber. Additional reaction at C resulted in further conversion of the fibers into a mixture of MgB 2 and higher borides (e.g. MgB 4 ), as well as increased formation of MgB 2 further into the Mg matrix. It was observed that C-doped boron fibers reacted with Mg much more slowly than undoped B fibers. Carbides were not observed at the fiber-matrix interface of the carbon-doped boron fibers reacted with Mg at C. REFERENCES 1. R.J. Suplinskas and J.V. Marzik, Boron and Silicon Carbide Filaments, in Handbook of Reinforcements for Plastics, edited by J.V. Milewski and H.S. Katz (New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Co., 1987) pp J. Nagamatsu, N. Nakagawa, T. Muranaka, Y. Zenitani, and J. Akimitsu, Nature 410, 63 (2001). 3. P.C. Canfield, D.K. Finnemore, S.L. Bud ko, J.E. Ostenson, G. Lapertot, C.E. Cunningham, and C. Petrovic, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 2423, (2001). 4. D.K. Finnemore, W.E. Straszhiem, S.L. Bud ko, P.C. Canfield, N.E. Anderson Jr., and R.J. Suplinskas, Physica C, 385, 278 (2003). 5. N.E. Anderson Jr., W.E. Straszhiem, S.L. Bud ko, P.C. Canfield, D.K. Finnemore, and R.J. Suplinskas, Physica C, 390, 11 (2003). 6. R.H.T. Wilke, S.L. Bud ko, P.C. Canfield, D.K. Finnemore, R.J. Suplinskas, and S.T. Hannahs, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, (2004). 7. R.H.T. Wilke, S.L. Bud ko, P.C. Canfield, M.J. Kramer, Y.Q. Wu, D.K. Finnemore, R.J. Suplinskas, J.V. Marzik, S.T. Hannahs, Superconductivity in MgB 2 doped with Ti and C, Physica C, in press (2004). 8. John D. DeFouw and David C. Dunand, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 120 (2003). 9. P.C. Canfield and G.W. Crabtree, Physics Today 56(3), 34 (2003). 10. J.L. Hoard, R.E. Hughes, D.E. Sands, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80, 4507 (1958). 11. International Center for Diffraction Data: Newtown Square, PA (2004).
High critical current densities in superconducting MgB 2 thin films
 High critical current densities in superconducting MgB 2 thin films S. H. Moon a), J. H. Yun, H. N. Lee, J. I. Kye, H. G. Kim, W. Chung, and B. Oh LG Electronics Institute of Technology, Seoul 137-724,
High critical current densities in superconducting MgB 2 thin films S. H. Moon a), J. H. Yun, H. N. Lee, J. I. Kye, H. G. Kim, W. Chung, and B. Oh LG Electronics Institute of Technology, Seoul 137-724,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 High Electrochemical Activity of the Oxide Phase in Model Ceria- and Ceria-Ni Composite Anodes William C. Chueh 1,, Yong Hao, WooChul Jung, Sossina M. Haile Materials Science, California Institute of Technology,
High Electrochemical Activity of the Oxide Phase in Model Ceria- and Ceria-Ni Composite Anodes William C. Chueh 1,, Yong Hao, WooChul Jung, Sossina M. Haile Materials Science, California Institute of Technology,
EFFECTS OF SINTERING TEMPERATURE ON SUPERCONDUCTIVITY IN Ti-SHEATHED MgB 2 WIRES. G. Liang 1, H. Fang 1, S. Guchhait 2, C. Hoyt 1, J. T.
 EFFECTS OF SINTERING TEMPERATURE ON SUPERCONDUCTIVITY IN Ti-SHEATHED MgB 2 WIRES G. Liang 1, H. Fang 1, S. Guchhait 2, C. Hoyt 1, J. T. Markert 2 1 Department of Physics, Sam Houston State University,
EFFECTS OF SINTERING TEMPERATURE ON SUPERCONDUCTIVITY IN Ti-SHEATHED MgB 2 WIRES G. Liang 1, H. Fang 1, S. Guchhait 2, C. Hoyt 1, J. T. Markert 2 1 Department of Physics, Sam Houston State University,
Enhancement of connectivity and flux pinning in MgB2 superconducting bulks and wires
 University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection 1954-2016 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2009 Enhancement of connectivity and flux pinning in MgB2 superconducting
University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection 1954-2016 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2009 Enhancement of connectivity and flux pinning in MgB2 superconducting
Sr and Pb additions. L. Affleck, C. Leach *
 Microstructures of BaTiO 3 based PTC thermistors with Ca, Sr and Pb additions Abstract L. Affleck, C. Leach * Manchester Materials Science Centre University of Manchester and UMIST Grosvenor Street, Manchester
Microstructures of BaTiO 3 based PTC thermistors with Ca, Sr and Pb additions Abstract L. Affleck, C. Leach * Manchester Materials Science Centre University of Manchester and UMIST Grosvenor Street, Manchester
CHAPTER 4. SYNTHESIS OF ALUMINIUM SELENIDE (Al 2 Se 3 ) NANO PARTICLES, DEPOSITION AND CHARACTERIZATION
 40 CHAPTER 4 SYNTHESIS OF ALUMINIUM SELENIDE (Al 2 Se 3 ) NANO PARTICLES, DEPOSITION AND CHARACTERIZATION 4.1 INTRODUCTION Aluminium selenide is the chemical compound Al 2 Se 3 and has been used as a precursor
40 CHAPTER 4 SYNTHESIS OF ALUMINIUM SELENIDE (Al 2 Se 3 ) NANO PARTICLES, DEPOSITION AND CHARACTERIZATION 4.1 INTRODUCTION Aluminium selenide is the chemical compound Al 2 Se 3 and has been used as a precursor
Weak links and phase slip centers in superconducting MgB 2 wires
 Weak links and phase slip centers in superconducting MgB 2 wires Maya Bar-Sadan, Gregory Leitus and Shimon Reich* Department of Materials and Interfaces, The Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel
Weak links and phase slip centers in superconducting MgB 2 wires Maya Bar-Sadan, Gregory Leitus and Shimon Reich* Department of Materials and Interfaces, The Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel
MICROSTRUCTURAL CHARACTERIZATION OF MODIFIED COMMERCIAL 2219 ALUMINUM ALLOY
 Association of Metallurgical Engineers Serbia and Montenegro Scientific paper AME UDC:669.715.17.2:62.192.4=2 MICROSTRUCTURAL CHARACTERIZATION OF MODIFIED COMMERCIAL 2219 ALUMINUM ALLOY V. MAKSIMOVIĆ 1,
Association of Metallurgical Engineers Serbia and Montenegro Scientific paper AME UDC:669.715.17.2:62.192.4=2 MICROSTRUCTURAL CHARACTERIZATION OF MODIFIED COMMERCIAL 2219 ALUMINUM ALLOY V. MAKSIMOVIĆ 1,
CHAPTER 4 THE STUDIES OF THE CVD GROWTH PROCESS FOR EPITAXIAL DIAMOND (100) FILMS USING UHV STM
 CHAPTER 4 THE STUDIES OF THE CVD GROWTH PROCESS FOR EPITAXIAL DIAMOND (100) FILMS USING UHV STM 4.1 Introduction This chapter presents studies of the CVD diamond growth process using UHV STM. It has been
CHAPTER 4 THE STUDIES OF THE CVD GROWTH PROCESS FOR EPITAXIAL DIAMOND (100) FILMS USING UHV STM 4.1 Introduction This chapter presents studies of the CVD diamond growth process using UHV STM. It has been
Microstructural Characterization of Materials
 Microstructural Characterization of Materials 2nd Edition DAVID BRANDON AND WAYNE D. KAPLAN Technion, Israel Institute of Technology, Israel John Wiley & Sons, Ltd Contents Preface to the Second Edition
Microstructural Characterization of Materials 2nd Edition DAVID BRANDON AND WAYNE D. KAPLAN Technion, Israel Institute of Technology, Israel John Wiley & Sons, Ltd Contents Preface to the Second Edition
Preparation and structural characterization of thin-film CdTe/CdS heterojunctions
 JOURNAL OF OPTOELECTRONICS AND ADVANCED MATERIALS Vol. 8, No., June 006, p. 96-940 Preparation and structural characterization of thin-film CdTe/ heterojunctions I. SALAORU a, P. A. BUFFAT b, D. LAUB b,
JOURNAL OF OPTOELECTRONICS AND ADVANCED MATERIALS Vol. 8, No., June 006, p. 96-940 Preparation and structural characterization of thin-film CdTe/ heterojunctions I. SALAORU a, P. A. BUFFAT b, D. LAUB b,
Biomimetic synthesis of gold nanocrystals using a reducing amphiphile. Ferdinand Gonzaga, Sherdeep Singh and Michael A. Brook. Department of Chemistry
 Biomimetic synthesis of gold nanocrystals using a reducing amphiphile. Ferdinand Gonzaga, Sherdeep Singh and Michael A. Brook Department of Chemistry 1280 Main St. W. Hamilton ON L8S 4M1 Canada Outline
Biomimetic synthesis of gold nanocrystals using a reducing amphiphile. Ferdinand Gonzaga, Sherdeep Singh and Michael A. Brook Department of Chemistry 1280 Main St. W. Hamilton ON L8S 4M1 Canada Outline
Growth and Doping of SiC-Thin Films on Low-Stress, Amorphous Si 3 N 4 /Si Substrates for Robust Microelectromechanical Systems Applications
 Journal of ELECTRONIC MATERIALS, Vol. 31, No. 5, 2002 Special Issue Paper Growth and Doping of SiC-Thin Films on Low-Stress, Amorphous Si 3 N 4 /Si Substrates for Robust Microelectromechanical Systems
Journal of ELECTRONIC MATERIALS, Vol. 31, No. 5, 2002 Special Issue Paper Growth and Doping of SiC-Thin Films on Low-Stress, Amorphous Si 3 N 4 /Si Substrates for Robust Microelectromechanical Systems
Thermodynamics of the Mg-B system: Implications for the deposition of MgB 2 thin films
 Thermodynamics of the Mg-B system: Implications for the deposition of MgB 2 thin films Zi-Kui Liu and D. G. Schlom Department of Materials Science and Engineering The Pennsylvania State University University
Thermodynamics of the Mg-B system: Implications for the deposition of MgB 2 thin films Zi-Kui Liu and D. G. Schlom Department of Materials Science and Engineering The Pennsylvania State University University
Direct Observation of nm-scale Mg- and B-Oxide Phases at Grain Boundaries in MgB 2
 Direct Observation of nm-scale Mg- and B-Oxide Phases at Grain Boundaries in MgB 2 R. F. Klie, J. C. Idrobo and N. D. Browning Department of Physics (M/C 273), University of Illinois at Chicago, 845 West
Direct Observation of nm-scale Mg- and B-Oxide Phases at Grain Boundaries in MgB 2 R. F. Klie, J. C. Idrobo and N. D. Browning Department of Physics (M/C 273), University of Illinois at Chicago, 845 West
Effect of aromatic hydrocarbon addition on in situ powder-in-tube processed MgB 2
 Effect of aromatic hydrocarbon addition on in situ powder-in-tube processed MgB 2 tapes H. Yamada General Technology Division, Central Japan Railway Company, 1545-33, Ohyama, Komaki, Aichi 485-0801, Japan
Effect of aromatic hydrocarbon addition on in situ powder-in-tube processed MgB 2 tapes H. Yamada General Technology Division, Central Japan Railway Company, 1545-33, Ohyama, Komaki, Aichi 485-0801, Japan
Influence of Ball-Milled Low Purity Boron Powder on the Superconductivity of MgB2
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2007 Influence of Ball-Milled Low Purity Boron Powder on the Superconductivity
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2007 Influence of Ball-Milled Low Purity Boron Powder on the Superconductivity
Effect of Heat Treatment on Interfacial Strengthening Mechanisms of Second Phase Particulate Reinforced Aluminium Alloy
 24-26.5.2005, Hradec nad Moravici Effect of Heat Treatment on Interfacial Strengthening Mechanisms of Second Phase Particulate Reinforced Aluminium Alloy S.T. Hasan Faculty of Arts, Computing, Engineering
24-26.5.2005, Hradec nad Moravici Effect of Heat Treatment on Interfacial Strengthening Mechanisms of Second Phase Particulate Reinforced Aluminium Alloy S.T. Hasan Faculty of Arts, Computing, Engineering
Oxidation Behavior of In Situ Synthesized TiB/Ti Composite in Air Environment
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 5, No. 12 (2) pp. 321 to 326 #2 The Japan Institute of Metals Oxidation Behavior of In Situ Synthesized TiB/Ti Composite in Air Environment Yexia Qin*, Weijie Lu, Jining Qin
Materials Transactions, Vol. 5, No. 12 (2) pp. 321 to 326 #2 The Japan Institute of Metals Oxidation Behavior of In Situ Synthesized TiB/Ti Composite in Air Environment Yexia Qin*, Weijie Lu, Jining Qin
The growth of patterned ceramic thin films from polymer precursor solutions Göbel, Ole
 University of Groningen The growth of patterned ceramic thin films from polymer precursor solutions Göbel, Ole IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
University of Groningen The growth of patterned ceramic thin films from polymer precursor solutions Göbel, Ole IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
Characterization of Nanoscale Electrolytes for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Membranes
 Characterization of Nanoscale Electrolytes for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Membranes Cynthia N. Ginestra 1 Michael Shandalov 1 Ann F. Marshall 1 Changhyun Ko 2 Shriram Ramanathan 2 Paul C. McIntyre 1 1 Department
Characterization of Nanoscale Electrolytes for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Membranes Cynthia N. Ginestra 1 Michael Shandalov 1 Ann F. Marshall 1 Changhyun Ko 2 Shriram Ramanathan 2 Paul C. McIntyre 1 1 Department
Growth of monocrystalline In 2 O 3 nanowires by seed orientation dependent vapour-solid-solid mechanism
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Growth of monocrystalline In
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Growth of monocrystalline In
Princeton University, Princeton NJ. Abstract. materials is reported. Reaction temperatures between 600 C and 800 C, encompassing the
 The Reactivity of MgB 2 with Common Substrate and Electronic Materials T. He 1, John M. Rowell 2, and R.J. Cava 1 1 Department of Chemistry and Princeton Materials Institute Princeton University, Princeton
The Reactivity of MgB 2 with Common Substrate and Electronic Materials T. He 1, John M. Rowell 2, and R.J. Cava 1 1 Department of Chemistry and Princeton Materials Institute Princeton University, Princeton
Supplimentary Information. Large-Scale Synthesis and Functionalization of Hexagonal Boron Nitride. Nanosheets
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplimentary Information Large-Scale Synthesis and Functionalization of Hexagonal Boron Nitride
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplimentary Information Large-Scale Synthesis and Functionalization of Hexagonal Boron Nitride
Growth Of TiO 2 Films By RF Magnetron Sputtering Studies On The Structural And Optical Properties
 Journal of Multidisciplinary Engineering Science and Technology (JMEST) Growth Of TiO 2 Films By RF Magnetron Sputtering Studies On The Structural And Optical Properties Ahmed K. Abbas 1, Mohammed K. Khalaf
Journal of Multidisciplinary Engineering Science and Technology (JMEST) Growth Of TiO 2 Films By RF Magnetron Sputtering Studies On The Structural And Optical Properties Ahmed K. Abbas 1, Mohammed K. Khalaf
6. DENSIFICATION BY ULTRA-HIGH PRESSURE SINTERING (UHP)
 6. DENSIFICATION BY ULTRA-HIGH PRESSURE SINTERING (UHP) Different sintering cycles were used in an attempt to optimise the sintering conditions for the LPSSiC system under ultra-high pressure. A summary
6. DENSIFICATION BY ULTRA-HIGH PRESSURE SINTERING (UHP) Different sintering cycles were used in an attempt to optimise the sintering conditions for the LPSSiC system under ultra-high pressure. A summary
STUDYING AMORPHOUS-CRYSTALLINE TRANSITIONS IN POWDERS CAUSED BY BALL-MILLING
 STUDYING AMORPHOUS-CRYSTALLINE TRANSITIONS IN POWDERS CAUSED BY BALL-MILLING K. Tomolya 1, D. Janovszky 2, A. Sycheva 3, A. Roósz 4 1 Ph.D. Research fellow, 2 Ph.D. Senior research fellow, 3 Ph.D. Research
STUDYING AMORPHOUS-CRYSTALLINE TRANSITIONS IN POWDERS CAUSED BY BALL-MILLING K. Tomolya 1, D. Janovszky 2, A. Sycheva 3, A. Roósz 4 1 Ph.D. Research fellow, 2 Ph.D. Senior research fellow, 3 Ph.D. Research
The lowest quality of silicon is the so- called metallurgical silicon. The source material of making metallurgical silicon is quartzite.
 ET3034TUx - 4.2 - Manufacturing of crystalline silicon We have various types of silicon wafers such as monocrystalline silicon and polycrystalline silicon. In this block I will give an answer to the question:
ET3034TUx - 4.2 - Manufacturing of crystalline silicon We have various types of silicon wafers such as monocrystalline silicon and polycrystalline silicon. In this block I will give an answer to the question:
Microstructural study of titanium carbide coating on cemented carbide
 JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 17 (1982) 589-594 Microstructural study of titanium carbide coating on cemented carbide S. VUORINEN, A. HORSEWELL* Laboratory of Applied Physics I, Technical University of
JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 17 (1982) 589-594 Microstructural study of titanium carbide coating on cemented carbide S. VUORINEN, A. HORSEWELL* Laboratory of Applied Physics I, Technical University of
Microstructures and dislocations in the stressed AZ91D magnesium alloys
 Materials Science and Engineering A344 (2002) 279/287 www.elsevier.com/locate/msea Microstructures and dislocations in the stressed AZ91D magnesium alloys R.M. Wang a,b,, A. Eliezer a, E. Gutman a a Ben-Gurion
Materials Science and Engineering A344 (2002) 279/287 www.elsevier.com/locate/msea Microstructures and dislocations in the stressed AZ91D magnesium alloys R.M. Wang a,b,, A. Eliezer a, E. Gutman a a Ben-Gurion
Composite. Department of Physics, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi , India
 1 Improved Critical Current Density of MgB 2 Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) Composite Chandra Shekhar *, Rajiv Giri, S.K. Malik a and O N Srivastava* Department of Physics, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi-221005,
1 Improved Critical Current Density of MgB 2 Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) Composite Chandra Shekhar *, Rajiv Giri, S.K. Malik a and O N Srivastava* Department of Physics, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi-221005,
needed for the SOFC electrolyte membrane application. Few directed vapor deposition
 Chapter 3 Experimental Procedure 3.1 Overview Prior to this study, DVD has not been used to create the type of dense metal oxide layers needed for the SOFC electrolyte membrane application. Few directed
Chapter 3 Experimental Procedure 3.1 Overview Prior to this study, DVD has not been used to create the type of dense metal oxide layers needed for the SOFC electrolyte membrane application. Few directed
In operandi observation of dynamic annealing: a case. Supplementary Material
 In operandi observation of dynamic annealing: a case study of boron in germanium nanowire devices Supplementary Material Maria M. Koleśnik-Gray, 1,3,4 Christian Sorger, 1 Subhajit Biswas, 2,3 Justin D.
In operandi observation of dynamic annealing: a case study of boron in germanium nanowire devices Supplementary Material Maria M. Koleśnik-Gray, 1,3,4 Christian Sorger, 1 Subhajit Biswas, 2,3 Justin D.
Improvement of the critical current of in situ Cu-sheathed MgB 2 wires by copper additions and toluene doping
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 36 (2012 ) 1594 1598 Superconductivity Centennial Conference Improvement of the critical current of in situ Cu-sheathed MgB 2 wires by copper
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 36 (2012 ) 1594 1598 Superconductivity Centennial Conference Improvement of the critical current of in situ Cu-sheathed MgB 2 wires by copper
Preparation and Characterization of Micro-Crystalline Hydrogenated Silicon Carbide p-layers
 Preparation and Characterization of Micro-Crystalline Hydrogenated Silicon Carbide p-layers Erten Eser, Steven S. Hegedus and Wayne A. Buchanan Institute of Energy Conversion University of Delaware, Newark,
Preparation and Characterization of Micro-Crystalline Hydrogenated Silicon Carbide p-layers Erten Eser, Steven S. Hegedus and Wayne A. Buchanan Institute of Energy Conversion University of Delaware, Newark,
Cu(In,Ga)Se 2 FILM FORMATION FROM SELENIZATION OF MIXED METAL/METAL-SELENIDE PRECURSORS
 Cu(In,Ga)Se 2 FILM FORMATION FROM SELENIZATION OF MIX METAL/METAL-SELENIDE PRECURSORS Rui Kamada, William N. Shafarman, and Robert W. Birkmire Institute of Energy Conversion University of Delaware, Newark,
Cu(In,Ga)Se 2 FILM FORMATION FROM SELENIZATION OF MIX METAL/METAL-SELENIDE PRECURSORS Rui Kamada, William N. Shafarman, and Robert W. Birkmire Institute of Energy Conversion University of Delaware, Newark,
Nanocrystalline structure and Mechanical Properties of Vapor Quenched Al-Zr-Fe Alloy Sheets Prepared by Electron-Beam Deposition
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 44, No. 10 (2003) pp. 1948 to 1954 Special Issue on Nano-Hetero Structures in Advanced Metallic Materials #2003 The Japan Institute of Metals Nanocrystalline structure and
Materials Transactions, Vol. 44, No. 10 (2003) pp. 1948 to 1954 Special Issue on Nano-Hetero Structures in Advanced Metallic Materials #2003 The Japan Institute of Metals Nanocrystalline structure and
Comparison of the transformation sequence from ),-A1OOH (boehmite) to o~-a12o 3 (corundum) induced by heating and by ball milling
 Materials Science and Engineering, A181/A 182 (1994) 1227-1231 1227 Comparison of the transformation sequence from ),-A1OOH (boehmite) to o~-a12o 3 (corundum) induced by heating and by ball milling A.
Materials Science and Engineering, A181/A 182 (1994) 1227-1231 1227 Comparison of the transformation sequence from ),-A1OOH (boehmite) to o~-a12o 3 (corundum) induced by heating and by ball milling A.
Ag 2 S: Fabrication and Characterization Techniques
 2 2 S: Fabrication and Characterization Techniques This chapter describes two fabrication methods used for the growth of 2 S thin films. The specific growth parameters are presented for each method as
2 2 S: Fabrication and Characterization Techniques This chapter describes two fabrication methods used for the growth of 2 S thin films. The specific growth parameters are presented for each method as
Integrated Silicon Heater for Tip-Based. Nanomanufacturing
 Supporting Information Wear Resistant Diamond Nanoprobe Tips with Integrated Silicon Heater for Tip-Based Nanomanufacturing Patrick C. Fletcher 1, Jonathan R. Felts 1, Zhenting Dai 1, Tevis T.B. Jacobs
Supporting Information Wear Resistant Diamond Nanoprobe Tips with Integrated Silicon Heater for Tip-Based Nanomanufacturing Patrick C. Fletcher 1, Jonathan R. Felts 1, Zhenting Dai 1, Tevis T.B. Jacobs
Polycrystalline and microcrystalline silicon
 6 Polycrystalline and microcrystalline silicon In this chapter, the material properties of hot-wire deposited microcrystalline silicon are presented. Compared to polycrystalline silicon, microcrystalline
6 Polycrystalline and microcrystalline silicon In this chapter, the material properties of hot-wire deposited microcrystalline silicon are presented. Compared to polycrystalline silicon, microcrystalline
Heteroepitaxy of Monolayer MoS 2 and WS 2
 Supporting Information Seed Crystal Homogeneity Controls Lateral and Vertical Heteroepitaxy of Monolayer MoS 2 and WS 2 Youngdong Yoo, Zachary P. Degregorio, James E. Johns* Department of Chemistry, University
Supporting Information Seed Crystal Homogeneity Controls Lateral and Vertical Heteroepitaxy of Monolayer MoS 2 and WS 2 Youngdong Yoo, Zachary P. Degregorio, James E. Johns* Department of Chemistry, University
Microstructural Characterization of Ti 20 Zr 20 Cu 40 Ni 20 Metallic Glass
 Engineering Physics 2018; 2(1): 6-10 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ep doi: 10.11648/j.ep.20180201.12 Microstructural Characterization of Ti 20 Zr 20 Cu 40 Ni 20 Metallic Glass Panugothu Rama
Engineering Physics 2018; 2(1): 6-10 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ep doi: 10.11648/j.ep.20180201.12 Microstructural Characterization of Ti 20 Zr 20 Cu 40 Ni 20 Metallic Glass Panugothu Rama
Title: Electroplating of superconducting films of MgB 2 from molten salts
 Title: Electroplating of superconducting films of MgB 2 from molten salts Authors: Hideki Abe, 1 Kenji Yoshii, 2 Kenji Nishida, 1 & Motoharu Imai 1 1 National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), Tsukuba,
Title: Electroplating of superconducting films of MgB 2 from molten salts Authors: Hideki Abe, 1 Kenji Yoshii, 2 Kenji Nishida, 1 & Motoharu Imai 1 1 National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), Tsukuba,
Degradation of superconducting properties in MgB 2 films by exposure to water
 Degradation of superconducting properties in MgB 2 films by exposure to water H Y Zhai, H M Christen, L Zhang, M Paranthaman, P H Fleming and D H Lowndes Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN 37931-6056
Degradation of superconducting properties in MgB 2 films by exposure to water H Y Zhai, H M Christen, L Zhang, M Paranthaman, P H Fleming and D H Lowndes Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN 37931-6056
Structural changes of polycrystalline silicon layers during high temperature annealing
 Structural changes of polycrystalline silicon layers during high temperature annealing D. Lysáček, L. Válek ON SEMICONDUCTOR CZECH REPUBLIC, Rožnov p. R., david.lysacek@onsemi.com Abstract The structure
Structural changes of polycrystalline silicon layers during high temperature annealing D. Lysáček, L. Válek ON SEMICONDUCTOR CZECH REPUBLIC, Rožnov p. R., david.lysacek@onsemi.com Abstract The structure
Development of New Generation Of Coatings with Strength-Ductility Relationship, Wear, Corrosion and Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance Beyond the
 Development of New Generation Of Coatings with Strength-Ductility Relationship, Wear, Corrosion and Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance Beyond the Current Materials Accomplishments till date As the structural
Development of New Generation Of Coatings with Strength-Ductility Relationship, Wear, Corrosion and Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance Beyond the Current Materials Accomplishments till date As the structural
Observation in the GB (Gentle Beam) Capabilities
 A field-emission cathode in the electron gun of a scanning electron microscope provides narrower probing beams at low as well as high electron energy, resulting in both improved spatial resolution and
A field-emission cathode in the electron gun of a scanning electron microscope provides narrower probing beams at low as well as high electron energy, resulting in both improved spatial resolution and
Carnegie Mellon MRSEC
 Carnegie Mellon MRSEC Texture, Microstructure & Anisotropy, Fall 2009 A.D. Rollett, P. Kalu 1 ELECTRONS SEM-based TEM-based Koseel ECP EBSD SADP Kikuchi Different types of microtexture techniques for obtaining
Carnegie Mellon MRSEC Texture, Microstructure & Anisotropy, Fall 2009 A.D. Rollett, P. Kalu 1 ELECTRONS SEM-based TEM-based Koseel ECP EBSD SADP Kikuchi Different types of microtexture techniques for obtaining
Specimen configuration
 APPLICATIONNOTE Model 1040 NanoMill TEM specimen preparation system Specimen configuration Preparing focused ion beam (FIB) milled specimens for submission to Fischione Instruments. The Model 1040 NanoMill
APPLICATIONNOTE Model 1040 NanoMill TEM specimen preparation system Specimen configuration Preparing focused ion beam (FIB) milled specimens for submission to Fischione Instruments. The Model 1040 NanoMill
MA-SHS of ZrC and ZrB2 in Air from The Zr/B/C Powder. the original is available online at Instructions for use
 Title MA-SHS of ZrC and ZrB2 in Air from The Zr/B/C Powder Author(s)Tsuchida, Takeshi; Yamamoto, Satoshi CitationEURO CERAMICS VIII, PTS 1-3: 85-88 Issue Date 2004 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/15876
Title MA-SHS of ZrC and ZrB2 in Air from The Zr/B/C Powder Author(s)Tsuchida, Takeshi; Yamamoto, Satoshi CitationEURO CERAMICS VIII, PTS 1-3: 85-88 Issue Date 2004 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/15876
Structure and optical properties of M/ZnO (M=Au, Cu, Pt) nanocomposites
 Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells 8 () 339 38 Structure and optical properties of M/ (M=Au, Cu, Pt) nanocomposites U. Pal a,b, *, J. Garc!ıa-Serrano a, G. Casarrubias-Segura a, N. Koshizaki c, T. Sasaki
Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells 8 () 339 38 Structure and optical properties of M/ (M=Au, Cu, Pt) nanocomposites U. Pal a,b, *, J. Garc!ıa-Serrano a, G. Casarrubias-Segura a, N. Koshizaki c, T. Sasaki
Effect of Volume Spray Rate on Highly Conducting Spray Deposited Fluorine Doped SnO2 Thin Films
 Effect of Volume Spray Rate on Highly Conducting Spray Deposited Fluorine Doped SnO2 Thin Films Dr.R.N. ARLE 1, B.L.KHATIK 2 1 Department of Physics, Jijamata College of Science and Arts, Bhende Bk.India
Effect of Volume Spray Rate on Highly Conducting Spray Deposited Fluorine Doped SnO2 Thin Films Dr.R.N. ARLE 1, B.L.KHATIK 2 1 Department of Physics, Jijamata College of Science and Arts, Bhende Bk.India
LASER SURFACE ALLOYING (LSA) OF ALUMINIUM (AA 1200) WITH TiB 2 FOR HARDNESS IMPROVEMENT Paper (802)
 LASER SURFACE ALLOYING (LSA) OF ALUMINIUM (AA 200) WITH TiB 2 FOR HARDNESS IMPROVEMENT Paper (802) Abimbola Patricia Popoola *, Sisa Pityana,2 Department of Chemical and Metallurgical Engineering, Tshwane
LASER SURFACE ALLOYING (LSA) OF ALUMINIUM (AA 200) WITH TiB 2 FOR HARDNESS IMPROVEMENT Paper (802) Abimbola Patricia Popoola *, Sisa Pityana,2 Department of Chemical and Metallurgical Engineering, Tshwane
Supporting Information. Solution-Processed 2D PbS Nanoplates with Residual Cu 2 S. Exhibiting Low Resistivity and High Infrared Responsivity
 Supporting Information Solution-Processed 2D PbS Nanoplates with Residual Cu 2 S Exhibiting Low Resistivity and High Infrared Responsivity Wen-Ya Wu, Sabyasachi Chakrabortty, Asim Guchhait, Gloria Yan
Supporting Information Solution-Processed 2D PbS Nanoplates with Residual Cu 2 S Exhibiting Low Resistivity and High Infrared Responsivity Wen-Ya Wu, Sabyasachi Chakrabortty, Asim Guchhait, Gloria Yan
A study aimed at characterizing the interfacial structure in a tin silver solder on nickel-coated copper plate during aging
 Sādhanā Vol. 33, Part 3, June 2008, pp. 251 259. Printed in India A study aimed at characterizing the interfacial structure in a tin silver solder on nickel-coated copper plate during aging D C LIN 1,
Sādhanā Vol. 33, Part 3, June 2008, pp. 251 259. Printed in India A study aimed at characterizing the interfacial structure in a tin silver solder on nickel-coated copper plate during aging D C LIN 1,
Hahn-Meitner-Institut Berlin, Glienicker Str. 100, D-14109, Berlin, Germany
 Journal of Metastable and Nanocrystalline Materials Vols. 20-21 (2004) pp. 35-40 online at http://www.scientific.net (2004) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Crystallization of Pd 40 Cu 30 Ni 10 P 20
Journal of Metastable and Nanocrystalline Materials Vols. 20-21 (2004) pp. 35-40 online at http://www.scientific.net (2004) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Crystallization of Pd 40 Cu 30 Ni 10 P 20
Non-agglomerated iron oxyhydroxide akaganeite nanocrystals incorporating extraordinary high amounts of different dopants
 Supporting Information Non-agglomerated iron oxyhydroxide akaganeite nanocrystals incorporating extraordinary high amounts of different dopants Ksenia Fominykh 1, Daniel Böhm 1, Siyuan Zhang 2, Alena Folger
Supporting Information Non-agglomerated iron oxyhydroxide akaganeite nanocrystals incorporating extraordinary high amounts of different dopants Ksenia Fominykh 1, Daniel Böhm 1, Siyuan Zhang 2, Alena Folger
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012154 TITLE: Structural Characterization of GaN Nanowires Fabricated via Direct Reaction of Ga Vapor and Ammonia DISTRIBUTION:
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012154 TITLE: Structural Characterization of GaN Nanowires Fabricated via Direct Reaction of Ga Vapor and Ammonia DISTRIBUTION:
ALD TiO 2 coated Silicon Nanowires for Lithium Ion Battery Anodes with enhanced Cycling Stability and Coulombic Efficiency
 ALD TiO 2 coated Silicon Nanowires for Lithium Ion Battery Anodes with enhanced Cycling Stability and Coulombic Efficiency Elmira Memarzadeh Lotfabad a, Peter Kalisvaart a,*, Kai Cui b, Alireza Kohandehghan
ALD TiO 2 coated Silicon Nanowires for Lithium Ion Battery Anodes with enhanced Cycling Stability and Coulombic Efficiency Elmira Memarzadeh Lotfabad a, Peter Kalisvaart a,*, Kai Cui b, Alireza Kohandehghan
The Effect of Heat Treatment on Ni/Au Ohmic Contacts to p-type GaN
 Li-Chien Chen et al.: The Effect of Heat Treatment on Ni/Au Ohmic Contacts 773 phys. stat. sol. (a) 176, 773 (1999) Subject classification: 73.40.Cg; S7.14 The Effect of Heat Treatment on Ni/Au Ohmic Contacts
Li-Chien Chen et al.: The Effect of Heat Treatment on Ni/Au Ohmic Contacts 773 phys. stat. sol. (a) 176, 773 (1999) Subject classification: 73.40.Cg; S7.14 The Effect of Heat Treatment on Ni/Au Ohmic Contacts
Electrochemical synthesis of superconducting MgB 2 thin films: a novel potential technique
 Electrochemical synthesis of superconducting MgB 2 thin films: a novel potential technique S H Pawar*, A B Jadhav, P M Shirage and D D Shivagan Superconductivity Lab., School of Energy Studies, Department
Electrochemical synthesis of superconducting MgB 2 thin films: a novel potential technique S H Pawar*, A B Jadhav, P M Shirage and D D Shivagan Superconductivity Lab., School of Energy Studies, Department
Microstructured Optical Fibers as New Nanotemplates for High Pressure CVD
 Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 988 2007 Materials Research Society 0988-QQ04-02 Microstructured Optical Fibers as New Nanotemplates for High Pressure CVD Neil Baril 1, John Badding 1, Pier Savio 2,
Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 988 2007 Materials Research Society 0988-QQ04-02 Microstructured Optical Fibers as New Nanotemplates for High Pressure CVD Neil Baril 1, John Badding 1, Pier Savio 2,
Practical 2P8 Transmission Electron Microscopy
 Practical 2P8 Transmission Electron Microscopy Originators: Dr. N.P. Young and Prof. J. M. Titchmarsh What you should learn from this practical Science This practical ties-in with the lecture course on
Practical 2P8 Transmission Electron Microscopy Originators: Dr. N.P. Young and Prof. J. M. Titchmarsh What you should learn from this practical Science This practical ties-in with the lecture course on
ISSN GANENDRA, Vol. V, No. 1. PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TRANSPARENT CONDUCTIVE ZnO THIN FILMS BY DC MAGNETRON SPUTTERING
 PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TRANSPARENT CONDUCTIVE ZnO THIN FILMS BY DC MAGNETRON SPUTTERING Sudjatmoko, Suryadi, Widdi Usada, Tono Wibowo, and Wirjoadi Centre for Research and Development of Advanced
PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TRANSPARENT CONDUCTIVE ZnO THIN FILMS BY DC MAGNETRON SPUTTERING Sudjatmoko, Suryadi, Widdi Usada, Tono Wibowo, and Wirjoadi Centre for Research and Development of Advanced
5. A New Crystalline Form o f Carbon under Shock Compression
 22 Proc. Japan Acad., 67, Ser. B (1991) [Vol. 67(B), 5. A New Crystalline Form o f Carbon under Shock Compression By Hisako HIRAI and Ken-ichi KONDO Research Laboratory of Engineering Materials, Tokyo
22 Proc. Japan Acad., 67, Ser. B (1991) [Vol. 67(B), 5. A New Crystalline Form o f Carbon under Shock Compression By Hisako HIRAI and Ken-ichi KONDO Research Laboratory of Engineering Materials, Tokyo
Microstructural Evolution of Ti-Mo-Ni-C Powder by Mechanical Alloying
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 50, No. 1 (2009) pp. 117 to 122 #2009 The Japan Institute of Metals Microstructural Evolution of -Mo-Ni-C Powder by Mechanical Alloying Hiroyuki Hosokawa, Kiyotaka Kato, Koji
Materials Transactions, Vol. 50, No. 1 (2009) pp. 117 to 122 #2009 The Japan Institute of Metals Microstructural Evolution of -Mo-Ni-C Powder by Mechanical Alloying Hiroyuki Hosokawa, Kiyotaka Kato, Koji
Amorphous and Polycrystalline Thin-Film Transistors
 Part I Amorphous and Polycrystalline Thin-Film Transistors HYBRID AMORPHOUS AND POLYCRYSTALLINE SILICON DEVICES FOR LARGE-AREA ELECTRONICS P. Mei, J. B. Boyce, D. K. Fork, G. Anderson, J. Ho, J. Lu, Xerox
Part I Amorphous and Polycrystalline Thin-Film Transistors HYBRID AMORPHOUS AND POLYCRYSTALLINE SILICON DEVICES FOR LARGE-AREA ELECTRONICS P. Mei, J. B. Boyce, D. K. Fork, G. Anderson, J. Ho, J. Lu, Xerox
Dual Catalytic Purpose of the Tungsten Filament During the. Synthesis of Single-Helix Carbon Microcoils by Hot-Wire CVD
 Dual Catalytic Purpose of the Tungsten Filament During the Synthesis of Single-Helix Carbon Microcoils by Hot-Wire CVD C. J. Oliphant 1,2, C. J. Arendse 1,, G. F. Malgas 1, D. E. Motaung 1,2, T. F. G.
Dual Catalytic Purpose of the Tungsten Filament During the Synthesis of Single-Helix Carbon Microcoils by Hot-Wire CVD C. J. Oliphant 1,2, C. J. Arendse 1,, G. F. Malgas 1, D. E. Motaung 1,2, T. F. G.
CHARACTERISATION OF INTERMETALLIC INCLUSIONS OBTAINED BY DISSOLUTION OF IRON ALLOYING ADDITIVES IN MOLTEN ALUMINIUM. Varužan Kevorkijan *
 Association of Metallurgical Engineers of Serbia AMES Scientific paper UDC: 669.13'71 CHARACTERISATION OF INTERMETALLIC INCLUSIONS OBTAINED BY DISSOLUTION OF IRON ALLOYING ADDITIVES IN MOLTEN ALUMINIUM
Association of Metallurgical Engineers of Serbia AMES Scientific paper UDC: 669.13'71 CHARACTERISATION OF INTERMETALLIC INCLUSIONS OBTAINED BY DISSOLUTION OF IRON ALLOYING ADDITIVES IN MOLTEN ALUMINIUM
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of precursor coated on salt template. (a) SEM image of Mo precursor coated on NaCl. Scale bar, 50 μm. (b) EDS of Mo precursor coated on
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of precursor coated on salt template. (a) SEM image of Mo precursor coated on NaCl. Scale bar, 50 μm. (b) EDS of Mo precursor coated on
A cheap liquid additive from acetone for strong in-field J c enhancement in MgB 2 conductors
 A cheap liquid additive from acetone for strong in-field J c enhancement in MgB 2 conductors Dongliang Wang 1, Yanwei Ma 1, #, Zhaoshun Gao 1, Xianping Zhang 1, Lei Wang 1, S. Awaji 2, K. Watanabe 2, E.
A cheap liquid additive from acetone for strong in-field J c enhancement in MgB 2 conductors Dongliang Wang 1, Yanwei Ma 1, #, Zhaoshun Gao 1, Xianping Zhang 1, Lei Wang 1, S. Awaji 2, K. Watanabe 2, E.
The Preparation of Fine Particulate for Electron Microscopy Investigations Using Dental Amalgam
 Ames Laboratory Conference Papers, Posters, and Presentations Ames Laboratory 4-1990 The Preparation of Fine Particulate for Electron Microscopy Investigations Using Dental Amalgam L. Scott Chumbley Iowa
Ames Laboratory Conference Papers, Posters, and Presentations Ames Laboratory 4-1990 The Preparation of Fine Particulate for Electron Microscopy Investigations Using Dental Amalgam L. Scott Chumbley Iowa
FORMATION OF BURIED OXIDE IN MEV OXYGEN IMPLANTED SILICON
 73 FORMATION OF BURIED OXIDE IN MEV OXYGEN IMPLANTED SILICON C.W.NIEH, F. XIONG, C. C. AHN, Z. ZHOU*, D. N. JAMIESON, T. VREELAND JR., B. FULTZ, and T. A. TOMBRELLO. Materials Research Group California
73 FORMATION OF BURIED OXIDE IN MEV OXYGEN IMPLANTED SILICON C.W.NIEH, F. XIONG, C. C. AHN, Z. ZHOU*, D. N. JAMIESON, T. VREELAND JR., B. FULTZ, and T. A. TOMBRELLO. Materials Research Group California
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Materials. GdCl 3 xh 2 O, (99.99%), YCl 3 6H 2 O (99.99%), YbCl 3 6H 2 O (99.99%), ErCl 3 6H 2 O (99.9%), NaOH (98+%), NH 4 F (98+%), 1 octadecene (90%), and oleic acid (90%) were all purchased from Sigma
Materials. GdCl 3 xh 2 O, (99.99%), YCl 3 6H 2 O (99.99%), YbCl 3 6H 2 O (99.99%), ErCl 3 6H 2 O (99.9%), NaOH (98+%), NH 4 F (98+%), 1 octadecene (90%), and oleic acid (90%) were all purchased from Sigma
Densification and grain growth of TiO 2 -doped ZnO
 Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 25, No. 4, 2007 Densification and grain growth of TiO 2 -doped ZnO K. YILDIZ *, N. KARAKU, N. TOPLAN, H. Ö. TOPLAN Sakarya University, Metallurgy and Materials Engineering,
Materials Science-Poland, Vol. 25, No. 4, 2007 Densification and grain growth of TiO 2 -doped ZnO K. YILDIZ *, N. KARAKU, N. TOPLAN, H. Ö. TOPLAN Sakarya University, Metallurgy and Materials Engineering,
Continuous Synthesis of Carbon Nanoclusters Using Well-Controlled Thermal Plasmas
 Continuous Synthesis of Carbon Nanoclusters Using Well-Controlled Thermal Plasmas T. Ohishi*, Y. Yoshihara and O. Fukumasa Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Yamaguchi University, 2-16-1 Tokiwadai,
Continuous Synthesis of Carbon Nanoclusters Using Well-Controlled Thermal Plasmas T. Ohishi*, Y. Yoshihara and O. Fukumasa Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Yamaguchi University, 2-16-1 Tokiwadai,
Physics and Material Science of Semiconductor Nanostructures
 Physics and Material Science of Semiconductor Nanostructures PHYS 570P Prof. Oana Malis Email: omalis@purdue.edu Today Bulk semiconductor growth Single crystal techniques Nanostructure fabrication Epitaxial
Physics and Material Science of Semiconductor Nanostructures PHYS 570P Prof. Oana Malis Email: omalis@purdue.edu Today Bulk semiconductor growth Single crystal techniques Nanostructure fabrication Epitaxial
Microstructure and Microhardness of an Al-Zr-Ti-Fe Alloy
 Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, September 5-9, 2010, Yokohama, Japan 2010 2010 The Japan Institute of Light Metals pp. 1004-1008 1004 Microstructure and Microhardness
Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, September 5-9, 2010, Yokohama, Japan 2010 2010 The Japan Institute of Light Metals pp. 1004-1008 1004 Microstructure and Microhardness
ELECTROLYTIC PHASE EXTRACTION: AN OLD TECHNIQUE TO EVALUATE PRECIPITATES IN NITINOL
 80 ELECTROLYTIC PHASE EXTRACTION: AN OLD TECHNIQUE TO EVALUATE PRECIPITATES IN NITINOL Roy G. Baggerly Boeing Research & Technology, Northwest Analytical Laboratories ABSTRACT: Nitinol is a shape memory
80 ELECTROLYTIC PHASE EXTRACTION: AN OLD TECHNIQUE TO EVALUATE PRECIPITATES IN NITINOL Roy G. Baggerly Boeing Research & Technology, Northwest Analytical Laboratories ABSTRACT: Nitinol is a shape memory
Chapter 3: Powders Production and Characterization
 Chapter 3: Powders Production and Characterization Course Objective... To introduce selective powder production processes and characterization methods. This course will help you : To understand properties
Chapter 3: Powders Production and Characterization Course Objective... To introduce selective powder production processes and characterization methods. This course will help you : To understand properties
Interface studies in a Ti-6Al-4VJsigma fiber composite
 JOURNAL DE PHYSIQUE IV Colloque C7, supplkment au Journal de Physique 111, Volume 3, novembre 1993 Interface studies in a Ti-6Al-4VJsigma fiber composite D. UPADHYAYA, M.A. BAKER*, C.M. WARD-CLOSE**, I?
JOURNAL DE PHYSIQUE IV Colloque C7, supplkment au Journal de Physique 111, Volume 3, novembre 1993 Interface studies in a Ti-6Al-4VJsigma fiber composite D. UPADHYAYA, M.A. BAKER*, C.M. WARD-CLOSE**, I?
The Evolution of Superconducting Phase MgB x
 Vol. 114 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 1 Proceedings of the XIII National School of Superconductivity, L adek Zdrój 2007 The Evolution of Superconducting Phase MgB x Sz. Loś a, W. Kempiński a, J.
Vol. 114 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 1 Proceedings of the XIII National School of Superconductivity, L adek Zdrój 2007 The Evolution of Superconducting Phase MgB x Sz. Loś a, W. Kempiński a, J.
Preparation and characterization of Co BaTiO 3 nano-composite films by the pulsed laser deposition
 Journal of Crystal Growth 289 (26) 48 413 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcrysgro Preparation and characterization of Co BaTiO 3 nano-composite films by the pulsed laser deposition Wu Weidong a,b,, He Yingjie
Journal of Crystal Growth 289 (26) 48 413 www.elsevier.com/locate/jcrysgro Preparation and characterization of Co BaTiO 3 nano-composite films by the pulsed laser deposition Wu Weidong a,b,, He Yingjie
Accumulation (%) Amount (%) Particle Size 0.1
 100 10 Amount (%) 5 50 Accumulation (%) 0 0.1 1 Particle Size (µm) 10 0 Supplementary Figure 1. The particle size distribution of W-15 at% Cr after 20 hours milling. Supplementary Figure 2. a,b, X-ray
100 10 Amount (%) 5 50 Accumulation (%) 0 0.1 1 Particle Size (µm) 10 0 Supplementary Figure 1. The particle size distribution of W-15 at% Cr after 20 hours milling. Supplementary Figure 2. a,b, X-ray
Synthesis of diamond-like carbon films with super-low friction and wear properties
 Synthesis of diamond-like carbon films with super-low friction and wear properties MSE 676 All Things Carbon / 09-29-2009 A. Erdemir, O.L. Eryilmaz, and G. Fenske J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 18(4), Jul/Aug
Synthesis of diamond-like carbon films with super-low friction and wear properties MSE 676 All Things Carbon / 09-29-2009 A. Erdemir, O.L. Eryilmaz, and G. Fenske J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 18(4), Jul/Aug
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Prof.Dr.Figen KAYA
 Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Prof.Dr.Figen KAYA Transmission Electron Microscope A transmission electron microscope, similar to a transmission light microscope, has the following components along
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Prof.Dr.Figen KAYA Transmission Electron Microscope A transmission electron microscope, similar to a transmission light microscope, has the following components along
Chemically Tunable Full Spectrum Optical Properties of 2D Silicon Telluride Nanoplates
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Chemically Tunable Full Spectrum Optical Properties of 2D Silicon Telluride Nanoplates Mengjing Wang,, Gabriella Lahti, David Williams, and Kristie J. Koski * Department of Chemistry,
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Chemically Tunable Full Spectrum Optical Properties of 2D Silicon Telluride Nanoplates Mengjing Wang,, Gabriella Lahti, David Williams, and Kristie J. Koski * Department of Chemistry,
STRUCTURAL AND ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF Sb 2 O 3 THIN FILMS
 STRUCTURAL AND ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF Sb 2 O 3 THIN FILMS NICOLAE ÞIGÃU Faculty of Sciences, Dunãrea de Jos University of Galaþi, 47 Domneascã Street, 800201, Romania e-mail: ntigau@ugal.ro Received
STRUCTURAL AND ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF Sb 2 O 3 THIN FILMS NICOLAE ÞIGÃU Faculty of Sciences, Dunãrea de Jos University of Galaþi, 47 Domneascã Street, 800201, Romania e-mail: ntigau@ugal.ro Received
Preparation of Ultra-fine Alumina Powders by D. C. Plasma Jet
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 17(3), 299-303 (2000) Preparation of Ultra-fine Alumina Powders by D. C. Plasma Jet Seung-Min Oh and Dong-Wha Park Department of Chemical Engineering, Inha University, 253 Yonghyun-Dong,
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 17(3), 299-303 (2000) Preparation of Ultra-fine Alumina Powders by D. C. Plasma Jet Seung-Min Oh and Dong-Wha Park Department of Chemical Engineering, Inha University, 253 Yonghyun-Dong,
Silver Diffusion Bonding and Layer Transfer of Lithium Niobate to Silicon
 Chapter 5 Silver Diffusion Bonding and Layer Transfer of Lithium Niobate to Silicon 5.1 Introduction In this chapter, we discuss a method of metallic bonding between two deposited silver layers. A diffusion
Chapter 5 Silver Diffusion Bonding and Layer Transfer of Lithium Niobate to Silicon 5.1 Introduction In this chapter, we discuss a method of metallic bonding between two deposited silver layers. A diffusion
N-doped Graphite Carbon Derived from Carbon Foam for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Ruthenium @ N-doped Graphite Carbon Derived from Carbon Foam for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Ruthenium @ N-doped Graphite Carbon Derived from Carbon Foam for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
Effect of barrier layers on the texture and microstructure of Copper films
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 766 2003 Materials Research Society E2.2.1 Effect of barrier layers on the texture and microstructure of Copper films Tejodher Muppidi and David P Field School of MME, Washington
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 766 2003 Materials Research Society E2.2.1 Effect of barrier layers on the texture and microstructure of Copper films Tejodher Muppidi and David P Field School of MME, Washington
Evidence of nanopores in sol gel based TiO 2 and TiN ultrafiltration membranes
 Materials Chemistry and Physics 63 (2000) 139 144 Evidence of nanopores in sol gel based TiO 2 and TiN ultrafiltration membranes G. Tomandl a, M. Mangler a, E. Pippel b, J. Woltersdorf b, a University
Materials Chemistry and Physics 63 (2000) 139 144 Evidence of nanopores in sol gel based TiO 2 and TiN ultrafiltration membranes G. Tomandl a, M. Mangler a, E. Pippel b, J. Woltersdorf b, a University
Ruthenium Oxide Films Prepared by Reactive Biased Target Sputtering
 Ruthenium Oxide Films Prepared by Reactive Biased Target Sputtering Hengda Zhang Anthony Githinji 1. Background RuO2 in both crystalline and amorphous forms is of crucial importance for theoretical as
Ruthenium Oxide Films Prepared by Reactive Biased Target Sputtering Hengda Zhang Anthony Githinji 1. Background RuO2 in both crystalline and amorphous forms is of crucial importance for theoretical as
Soft Magnetic Properties of Nanocystalline Fe Si B Nb Cu Rod Alloys Obtained by Crystallization of Cast Amorphous Phase
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 9 (2002) pp. 2337 to 2341 c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals EXPRESS REGULAR ARTICLE Soft Magnetic Properties of Nanocystalline Fe Si B Nb Cu Rod Alloys Obtained
Materials Transactions, Vol. 43, No. 9 (2002) pp. 2337 to 2341 c 2002 The Japan Institute of Metals EXPRESS REGULAR ARTICLE Soft Magnetic Properties of Nanocystalline Fe Si B Nb Cu Rod Alloys Obtained
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/336/6084/1007/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Unidirectional Growth of Microbumps on (111)-Oriented and Nanotwinned Copper Hsiang-Yao Hsiao, Chien-Min Liu, Han-wen Lin,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/336/6084/1007/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Unidirectional Growth of Microbumps on (111)-Oriented and Nanotwinned Copper Hsiang-Yao Hsiao, Chien-Min Liu, Han-wen Lin,
Supplementary Material for. Dual-functional Memory and Threshold. Resistive Switching Based on the Push-Pull. Mechanism of Oxygen Ions
 Supplementary Material for Dual-functional Memory and Threshold Resistive Switching Based on the Push-Pull Mechanism of Oxygen Ions Yi-Jen Huang 1, Shih-Chun Chao 2, Der-Hsien Lien 1, Cheng-Yen Wen 2,4,
Supplementary Material for Dual-functional Memory and Threshold Resistive Switching Based on the Push-Pull Mechanism of Oxygen Ions Yi-Jen Huang 1, Shih-Chun Chao 2, Der-Hsien Lien 1, Cheng-Yen Wen 2,4,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Atmospheric microplasma-functionalized 3D microfluidic strips within dense carbon nanotube arrays confine Au nanodots for SERS sensing Samuel Yick, Zhao Jun Han and Kostya (Ken)
Supplementary Information Atmospheric microplasma-functionalized 3D microfluidic strips within dense carbon nanotube arrays confine Au nanodots for SERS sensing Samuel Yick, Zhao Jun Han and Kostya (Ken)
Preparation and Physical Properties of Tl 0.65 Hg 0.35 Ba 2 Ca n-1 Cu n O 2n+3 δ (n = 1, 2, 3) Superconductors
 Applied Physics Research; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2013 ISSN 1916-9639 E-ISSN 1916-9647 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Preparation and Physical Properties of Tl 0.65 Hg 0.35 Ba 2 Ca n-1 Cu
Applied Physics Research; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2013 ISSN 1916-9639 E-ISSN 1916-9647 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Preparation and Physical Properties of Tl 0.65 Hg 0.35 Ba 2 Ca n-1 Cu
