Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering. Department of Civil Engineering. Hydrology and Hydraulics. Final Exam, April 21, 2017
|
|
|
- Garey Ford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 F Name: Student #: University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Department of Civil Engineering C1V250 - Hydrology and Hydraulics Final Exam, April 21, 2017 Duration: 2 and V2 hrs The test is 11 pages and graded out of 70 marks. Test is closed book, only a non-progranirnable calculator, rulers and a two-sided 8 ½" x 11" aid sheet is permitted. All work must be neat and legible. Show all your calculations and state any assumptions. Answers are to be written in exam booklets. Your equation sheet must be submitted with your exam at the end of the examination period. Page! of 11
2 14 TERMS AND CONCEPTS marks] Define and describe 3 of the following (use sketches when appropriate): Effective Rainfall Field Capacity Stage Lysimeter CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS 14 mark] What are the two resistance factors caused by plants that affect evapotranspiration? Describe these two types of resistance factors and how they affect evapotranspiration rates. Use sketches where appropriate. 14 marksl What function do the weirs provide in the Humber River? Many of the weirs along the Humber River have trapezoidal notches removed from the center of the weir. Why was this done? Was this intervention successful? Why or why not? Page 2 of 11
3 COMPUTATION QUESTIONS. 4. The stormwater management system of a proposed 1.8 ha commercial development needs to be designed for a storm with a 25 year return period. The 25-year IDF curve is given by: t + 33 Where i is the rainfall intensity in cm/hr and t is the storm duration in minutes. Local regulations require a minimum time of concentration of 10 minutes. The development has a Manning's n for overland flow of 0.016, an average overland flow length of 90 m and an average slope of 0.6%. 110 marks] Determine the flow rate that will govern the design of the storm sewer. The time of concentration can be modelled using the kinematic wave equation. 18 marks] The developer is considering directing the runoff to a reservoir for storage. In order to size the reservoir you need to determine the total volume of runoff that needs to be stored. Use the NRCS curve number method to estimate the total volume of runoff for a 2 hr design storm, assuming the soil has an average condition at the beginning of the design storm. An infiltration test on the soil shows that the minimum infiltration rate is 2 mm/hr. Page 3 of!!
4 5. Discharge data was recorded during a 2-hr rain event at the outlet of a 200 km2 watershed. The data is plotted in Figure 1. The stream outflows into a 50 ha lake. Hydrograph D Time (hrs) Figure 1-2-hr Streamfiow Hydrograph (i) [15 marks] Create the hydrograph for a 7 hour, 4.5 mm rainfall event. You may draw on Figure 1 on this page to show your work. Include a sketch that graphically represents your process using the graph paper provided in Figure 2 and label each series. Clearly show all intermediary steps and calculations for creating this hydro,iraph. Page 4 of!!
5 Figure 2- Graph Paper for Question 5 (i) [4 marks] The municipality is considering diverting a portion of the river for a microhydroelectric project. They require a 10 m3/s discharge through the diversion channel for the project to be successful. They have designed a 3 m wide rectangular concrete lined diversion channel with a slope of 0.1 % to be used to divert the water for this project. What depth of channel is required to accommodate this discharge? [2 marks] Will the flow in the channel designed above be sub-critical or supercritical flow? Page of!!
6 6. A site consists entirely of a sandy loam soil and has 4 mm of depression storage. Assume the initial moisture content is Using the Green and An-pt Method, [2 marks] Determine if and when ponding begins during the storm. 115 marks] Determine the incremental and cumulative runoff from the site using the following design storm. Interval (mm) Average Rainfall (mm/hr) End of Exam Page 6 of 11
7 Flow Wetted Hydraulic Shape Section Area A Perimeter P Radius R 77 (b + zy)y Trapezoidal y y(h+zy) b +2y1+z2 b+v1+z2 Triangular NI Z Y 7 zy 2 2y v1 + ZY Rectangular E _ by by b + b 2v - A V Wide flat I by b y -b >>y-- Circular b S (0 sino ç - sin 0 Copynght 32O13 Pearson Education, publishing as Prentice Hall Page 7ofll
8 Table 16.5 Rational Runoff Coefficient Urban Catchments General Description C Surface C City Asphalt paving Suburban business Roofs Industrial 0.5-0,9 Lawn heavy soil >7 slope Residential multiunits Housing estates < Bungalows Lawn sandy soil > Parks, cemeteries < Rural Catchments (less than 10 km2) Ground Cover Basic Factor Corrections: Add or Subtract Bare surface 0.40 Slope < 5%:-0.05 Grassland 0.35 Slope> 10%: Cultivated land 0.30 Recurrence interval <20 yr: Timber 0.18 Recurrence interval > SO yr: Mean annual precipitation <600 mm: Mean annual precipitation> 900 mm: Source: Stephenson (1981). Page 8 of 11
9 Table 4.6 Green-Ampt Infiltration Parameters Wetting front soil Effective hydraulic Soil texture class Porosity, 9 suction head, S1, cm conductivity, K, cm/h Sand 0,437 4, ( ) ( ) Loamy sand 0, ( ) ( ) Sandy loam ( ) ( ) Loam ( ) ( ) Silt loam 0,501 16,68 0,34 ( ) ( ) Sandy clay loam 0, ( ) ( ) Clay loam ( ) ( ) Silty clay loam ( ) ( ) Sandy clay 0, ( ) ( ) Silty clay 0, ( ) ( ) Clay , ( ,523) ( ) Source: Rawls and 8rakensiek (1983). Table 4.10 Hydrologic Soil Groups Minimum Infiltration Rate Group Range (rnm.hr) Texture' A Sand, loamy sand, or sandy loam Silt loam or loam C Sandy clay loam D Clay loam, silty clay Foam, sandy clay, silty clay, or clay a Reproduced from U.S..Soil Conservation Service (1986. Page 9 of It
10 Table 2-1 Runoff Curve Numbers for Selected Agricultural, Suburban, and Urban Land Use (Antecedent Moisture Condition II; 0.25) Hydrologic Soil Group Land Use Description A B C D Cultivated land' Without conservation treatment With conservation treatment Pasture or range land Poor condition Good condition Meadow Good condition Wood or forest land Thin stand, poor cover, no mulch Good cover Open spaces, lawns, parks, golf courses, cemeteries, etc. Good condition: grass cover on 75% or more of the area Fair condition: grass cover on 50%-75% of the areai Commercial and business areas (85% impervious) Industrial districts (72% impervious) Residential3 Average lot size Average % impervious4 1/8 ac or less ac /3 ac /2 ac lac Paved parking lots, roofs, driveways, etc Streets and roads Paved with curbs and storm sewers Gravel Dirt Factor to convert runoff volume to depth Unit of Runoff Unit of Unit of Unit of Unit of K Ordinate Time Base Volume Area depth m3/s day m3/s*day km2 mm 86.4 m3/s hour m2/s*-hr km2 mm 3.6 Conversions: 1 ha = 10,000 m2 1 nun = in Page 10 of 11
11 Table 14.4 Values of Manning's Roughness Coefficient' Material Closed conduit or built-up channel 1.1 Metal Manning n Brass 0.01 Copper Steel welded Steel riveted Cast iron coated Wrought iron galvanized Corrugated metal (storm drain) Nonmetal Glass 0.01 Cement Cement mortar Concrete culvert Concrete lined channel/pipe Wood Clay Brickwork 0,013 Brickwork with cement mortar Masonry/ rubble masonry Sanitary sewer coated with slime Asphalt Plastic PVC ,011 Polyethylene Excavated or Dredged Channel Straight and clean Winding and sluggish Dredged Rock cut/stony Earth bottom, rubble sides 0.03 Unmaintained/uncut brush 0.08 Natural streams On plain, clean, straight, no pools 0.03 On plain, clean, winding, some pools 0.04 On plain, sluggish, weedy, deep pools 0.07 On mountain, few boulders 0,04 On mountain, large boulders 0.05 a For overland flow roughness coefficient see Table Note: Judgment must be used to determine n for channel characteristics that fall in between these categories. See Chow (1959) for a detailed reference. Page!! of 11
ORDINANCE APPENDIX F STORMWATER MANAGEMENT DESIGN CRITERIA
 ORDINANCE APPENDIX F STORMWATER MANAGEMENT DESIGN CRITERIA TABLE F-1 DESIGN STORM RAINFALL AMOUNT FIGURE F-1 ALTERNATING BLOCK METHOD FOR RAINFALL DISTRIBUTION FIGURE F-2 PENNDOT DELINEATED REGIONS FIGURE
ORDINANCE APPENDIX F STORMWATER MANAGEMENT DESIGN CRITERIA TABLE F-1 DESIGN STORM RAINFALL AMOUNT FIGURE F-1 ALTERNATING BLOCK METHOD FOR RAINFALL DISTRIBUTION FIGURE F-2 PENNDOT DELINEATED REGIONS FIGURE
Runoff Calculations. Time of Concentration (T c or t c ) from one location to another within a watershed. Travel
 Runoff Calculations Bob Pitt University of Alabama and Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Time of Concentration and Travel Time (based on Chapter 3 of TR-55) Time of Concentration (T c ): time required
Runoff Calculations Bob Pitt University of Alabama and Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Time of Concentration and Travel Time (based on Chapter 3 of TR-55) Time of Concentration (T c ): time required
MODULE 1 RUNOFF HYDROGRAPHS WORKSHEET 1. Precipitation
 Watershed MODULE 1 RUNOFF HYDROGRAPHS WORKSHEET 1 A watershed is an area of land thaaptures rainfall and other precipitation and funnels it to a lake or stream or wetland. The area within the watershed
Watershed MODULE 1 RUNOFF HYDROGRAPHS WORKSHEET 1 A watershed is an area of land thaaptures rainfall and other precipitation and funnels it to a lake or stream or wetland. The area within the watershed
ORDINANCE APPENDIX C RUNOFF COEFFICIENTS AND CURVE NUMBERS
 ORDINANCE APPENDIX C RUNOFF COEFFICIENTS AND CURVE NUMBERS TABLE C-1. RUNOFF CURVE NUMBERS Source: Table 2-2a, Table 2-2b, and Table 2-2c from U. S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation
ORDINANCE APPENDIX C RUNOFF COEFFICIENTS AND CURVE NUMBERS TABLE C-1. RUNOFF CURVE NUMBERS Source: Table 2-2a, Table 2-2b, and Table 2-2c from U. S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation
0.0. Pervious CN = 40. (Unconnected impervious) (Total impervious) Total impervious area (percent) Composite CN
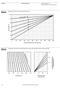 Figure 2-3 Composite CN with connected impervious area. 100 Composite CN 90 80 70 60 Pervious CN = 90 80 70 60 50 40 50 40 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Connected impervious area (percent) Figure 2-4
Figure 2-3 Composite CN with connected impervious area. 100 Composite CN 90 80 70 60 Pervious CN = 90 80 70 60 50 40 50 40 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Connected impervious area (percent) Figure 2-4
What is runoff? Runoff. Runoff is often defined as the portion of rainfall, that runs over and under the soil surface toward the stream
 What is runoff? Runoff Runoff is often defined as the portion of rainfall, that runs over and under the soil surface toward the stream 1 COMPONENTS OF Runoff or STREAM FLOW 2 Cont. The types of runoff
What is runoff? Runoff Runoff is often defined as the portion of rainfall, that runs over and under the soil surface toward the stream 1 COMPONENTS OF Runoff or STREAM FLOW 2 Cont. The types of runoff
APPENDIX E APPENDIX E ESTIMATING RUNOFF FOR SMALL WATERSHEDS
 APPENDIX E ESTIMATING RUNOFF FOR SMALL WATERSHEDS March 18, 2003 This page left blank intentionally. March 18, 2003 TABLES Table E.1 Table E.2 Return Frequencies for Roadway Drainage Design Rational Method
APPENDIX E ESTIMATING RUNOFF FOR SMALL WATERSHEDS March 18, 2003 This page left blank intentionally. March 18, 2003 TABLES Table E.1 Table E.2 Return Frequencies for Roadway Drainage Design Rational Method
Learning objectives. Upon successful completion of this lecture, the participants will be able to describe:
 Solomon Seyoum Learning objectives Upon successful completion of this lecture, the participants will be able to describe: The different approaches for estimating peak runoff for urban drainage network
Solomon Seyoum Learning objectives Upon successful completion of this lecture, the participants will be able to describe: The different approaches for estimating peak runoff for urban drainage network
APPENDIX E ESTIMATING RUNOFF FROM SMALL WATERSHEDS
 ESTIMATING RUNOFF FROM SMALL WATERSHEDS June 2011 THIS PAGE LEFT BLANK INTENTIONALLY. June 2011 TABLES Table E.1 Table E.2 Return Frequencies for Roadway Drainage Design Rational Method Values June 2011
ESTIMATING RUNOFF FROM SMALL WATERSHEDS June 2011 THIS PAGE LEFT BLANK INTENTIONALLY. June 2011 TABLES Table E.1 Table E.2 Return Frequencies for Roadway Drainage Design Rational Method Values June 2011
APPENDIX F RATIONAL METHOD
 7-F-1 APPENDIX F RATIONAL METHOD 1.0 Introduction One of the most commonly used procedures for calculating peak flows from small drainages less than 200 acres is the Rational Method. This method is most
7-F-1 APPENDIX F RATIONAL METHOD 1.0 Introduction One of the most commonly used procedures for calculating peak flows from small drainages less than 200 acres is the Rational Method. This method is most
Chapter Introduction. 5.2 Computational Standard Methods HYDROLOGY
 Chapter 5. HYDROLOGY 5.1 Introduction The definition of hydrology is the scientific study of water and its properties, distribution, and effects on the earth s surface, in the soil and the atmosphere.
Chapter 5. HYDROLOGY 5.1 Introduction The definition of hydrology is the scientific study of water and its properties, distribution, and effects on the earth s surface, in the soil and the atmosphere.
Names: ESS 315. Lab #6, Floods and Runoff Part I Flood frequency
 Names: ESS 315 Lab #6, Floods and Runoff Part I Flood frequency A flood is any relatively high flow of water over land that is not normally under water. Floods occur at streams and rivers but can also
Names: ESS 315 Lab #6, Floods and Runoff Part I Flood frequency A flood is any relatively high flow of water over land that is not normally under water. Floods occur at streams and rivers but can also
DRAINAGE & DESIGN OF DRAINAGE SYSTEM
 Drainage on Highways DRAINAGE & DESIGN OF DRAINAGE SYSTEM P. R.D. Fernando Chartered Engineer B.Sc.(Hons), M.Eng. C.Eng., MIE(SL) Drainage Requirement of Highway Drainage System Introduction Drainage means
Drainage on Highways DRAINAGE & DESIGN OF DRAINAGE SYSTEM P. R.D. Fernando Chartered Engineer B.Sc.(Hons), M.Eng. C.Eng., MIE(SL) Drainage Requirement of Highway Drainage System Introduction Drainage means
LAKE COUNTY HYDROLOGY DESIGN STANDARDS
 LAKE COUNTY HYDROLOGY DESIGN STANDARDS Lake County Department of Public Works Water Resources Division 255 N. Forbes Street Lakeport, CA 95453 (707)263-2341 Adopted June 22, 1999 These Standards provide
LAKE COUNTY HYDROLOGY DESIGN STANDARDS Lake County Department of Public Works Water Resources Division 255 N. Forbes Street Lakeport, CA 95453 (707)263-2341 Adopted June 22, 1999 These Standards provide
UPDATE OF ARC TP108 RUN-OFF CALCULATION GUIDELINE
 UPDATE OF ARC TP108 RUN-OFF CALCULATION GUIDELINE Bodo Hellberg, Stormwater Action Team, Auckland Regional Council Matthew Davis, Stormwater Action Team, Auckland Regional Council ABSTRACT This paper focuses
UPDATE OF ARC TP108 RUN-OFF CALCULATION GUIDELINE Bodo Hellberg, Stormwater Action Team, Auckland Regional Council Matthew Davis, Stormwater Action Team, Auckland Regional Council ABSTRACT This paper focuses
STORMWATER MANAGEMENT: Emerging Planning Approaches and Control Technologies
 STORMWATER MANAGEMENT: Emerging Planning Approaches and Control Technologies Chapter 5 " HYDROLOGIC SYSTEMS " CHAPTER 5 5.1 INTRODUCTION 5.1.1 Training Objectives The objectives of this module are:! to
STORMWATER MANAGEMENT: Emerging Planning Approaches and Control Technologies Chapter 5 " HYDROLOGIC SYSTEMS " CHAPTER 5 5.1 INTRODUCTION 5.1.1 Training Objectives The objectives of this module are:! to
CHAPTER 3 STORMWATER HYDROLOGY. Table of Contents SECTION 3.1 METHODS FOR ESTIMATING STORMWATER RUNOFF
 CHAPTER 3 STORMWATER HYDROLOGY Table of Contents SECTION 3.1 METHODS FOR ESTIMATING STORMWATER RUNOFF 3.1.1 Introduction to Hydrologic Methods...3.1-1 3.1.2 Symbols and Definitions...3.1-3 3.1.3 Rainfall
CHAPTER 3 STORMWATER HYDROLOGY Table of Contents SECTION 3.1 METHODS FOR ESTIMATING STORMWATER RUNOFF 3.1.1 Introduction to Hydrologic Methods...3.1-1 3.1.2 Symbols and Definitions...3.1-3 3.1.3 Rainfall
Rational Method Hydrological Calculations with Excel COURSE CONTENT
 Rational Method Hydrological Calculations with Excel Harlan H. Bengtson, PhD, P.E. COURSE CONTENT 1. Introduction Calculation of peak storm water runoff rate from a drainage area is often done with the
Rational Method Hydrological Calculations with Excel Harlan H. Bengtson, PhD, P.E. COURSE CONTENT 1. Introduction Calculation of peak storm water runoff rate from a drainage area is often done with the
Cumulative Precipitation
 Problem 1: Hyetograph Construction (4 pts) Use the rainfall information below to construct both the cumulative (inch) and incremental (in/hr) hyetographs. Note: the incremental hyetograph must be formatted
Problem 1: Hyetograph Construction (4 pts) Use the rainfall information below to construct both the cumulative (inch) and incremental (in/hr) hyetographs. Note: the incremental hyetograph must be formatted
FORT COLLINS STORMWATER CRITERIA MANUAL Hydrology Standards (Ch. 5) 1.0 Overview
 Chapter 5: Hydrology Standards Contents 1.0 Overview... 1 1.1 Storm Runoff Determination... 1 1.2 Design Storm Frequencies... 1 1.3 Water Quality Storm Provisions... 2 1.4 Design Storm Return Periods...
Chapter 5: Hydrology Standards Contents 1.0 Overview... 1 1.1 Storm Runoff Determination... 1 1.2 Design Storm Frequencies... 1 1.3 Water Quality Storm Provisions... 2 1.4 Design Storm Return Periods...
Appendix I OFFICE OF THE MORGAN COUNTY SURVEYOR STORMWATER DESIGN MANUAL 7/1/2008
 Appendix I OFFICE OF THE MORGAN COUNTY SURVEYOR This Page Left Intentionally Blank OFFICE OF THE MORGAN COUNTY SURVEYOR APPENDIX I PAGE 1 Appendix II OFFICE OF THE MORGAN COUNTY SURVEYOR This Page Left
Appendix I OFFICE OF THE MORGAN COUNTY SURVEYOR This Page Left Intentionally Blank OFFICE OF THE MORGAN COUNTY SURVEYOR APPENDIX I PAGE 1 Appendix II OFFICE OF THE MORGAN COUNTY SURVEYOR This Page Left
The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Sanitary Engineering- ECIV 4325 L5. Storm water Management
 The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Sanitary Engineering- ECIV 4325 L5. Storm water Management Husam Al-Najar Storm water management : Collection System Design principles The Objectives
The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Sanitary Engineering- ECIV 4325 L5. Storm water Management Husam Al-Najar Storm water management : Collection System Design principles The Objectives
iswm TM Technical Manual Hydrology:
 : 1.0 2.0 Downstream Assessment 3.0 Streambank Protection 4.0 Water Balance 5.0 Rainfall Tables 6.0 Hydrologic Soils Data Table of Contents 1.0... HO-1 1.1 Estimating Runoff... HO-1 1.1.1 Introduction
: 1.0 2.0 Downstream Assessment 3.0 Streambank Protection 4.0 Water Balance 5.0 Rainfall Tables 6.0 Hydrologic Soils Data Table of Contents 1.0... HO-1 1.1 Estimating Runoff... HO-1 1.1.1 Introduction
STORMWATER HYDROLOGY
 ..CHAPTER.. STORMWATER HYDROLOGY 3.1 Introduction to Hydrologic Methods Hydrology is the science dealing with the characteristics, distribution, and movement of water on and below the earth's surface and
..CHAPTER.. STORMWATER HYDROLOGY 3.1 Introduction to Hydrologic Methods Hydrology is the science dealing with the characteristics, distribution, and movement of water on and below the earth's surface and
Table of Contents CHAPTER. Chapter 2 Hydrologic Analysis. 2.1 Estimating Runoff
 CHAPTER Table of Contents 2 Chapter 2 Hydrologic Analysis 2.1 Estimating Runoff 2.1.1 Introduction to Hydrologic Methods...2.1-1 2.1.2 Symbols and Definitions...2.1-4 2.1.3 Rainfall Estimation...2.1-5
CHAPTER Table of Contents 2 Chapter 2 Hydrologic Analysis 2.1 Estimating Runoff 2.1.1 Introduction to Hydrologic Methods...2.1-1 2.1.2 Symbols and Definitions...2.1-4 2.1.3 Rainfall Estimation...2.1-5
APPENDIX A: STORMWATER HYDROLOGY
 APPENDIX A: STORMWATER HYDROLOGY In low impact development (LID), the objective of stormwater control measures (SCMs) is to mimic or replicate the hydrologic function of a natural system. This approach
APPENDIX A: STORMWATER HYDROLOGY In low impact development (LID), the objective of stormwater control measures (SCMs) is to mimic or replicate the hydrologic function of a natural system. This approach
Ponds Planning, Design, Construction
 United States Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service Ponds Planning, Design, Construction Agriculture Handbook Number 590 Estimating storm runoff The amount of precipitation,
United States Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service Ponds Planning, Design, Construction Agriculture Handbook Number 590 Estimating storm runoff The amount of precipitation,
Activity Calculating Property Drainage
 Page 1 of 5 Activity 2.3.11 Calculating Property Drainage Introduction When a property is developed, it is important to understand that changes to watershed characteristics (i.e., land use, slope, soil
Page 1 of 5 Activity 2.3.11 Calculating Property Drainage Introduction When a property is developed, it is important to understand that changes to watershed characteristics (i.e., land use, slope, soil
Chapter 6. The Empirical version of the Rational Method
 Chapter 6 The Empirical version of the Rational Method The Empirical version is named because the parameters it uses (apart from rainfall data) are arbitrary and are generally based on experience or observation
Chapter 6 The Empirical version of the Rational Method The Empirical version is named because the parameters it uses (apart from rainfall data) are arbitrary and are generally based on experience or observation
PART 3 - STANDARDS FOR SEWERAGE FACILITIES DESIGN OF STORM SEWERS
 PART 3 - STANDARDS FOR SEWERAGE FACILITIES 3.3 - DESIGN OF STORM SEWERS 3.301 Design of Storm Sewers A. General Information B. Investigations and Surveys C. Special Projects 3.302 Design Criteria for Storm
PART 3 - STANDARDS FOR SEWERAGE FACILITIES 3.3 - DESIGN OF STORM SEWERS 3.301 Design of Storm Sewers A. General Information B. Investigations and Surveys C. Special Projects 3.302 Design Criteria for Storm
HYDROLOGY WORKSHEET 1 PRECIPITATION
 HYDROLOGY WORKSHEET 1 PRECIPITATION A watershed is an area of land that captures rainfall and other precipitation and funnels it to a lake or stream or wetland. The area within the watershed where the
HYDROLOGY WORKSHEET 1 PRECIPITATION A watershed is an area of land that captures rainfall and other precipitation and funnels it to a lake or stream or wetland. The area within the watershed where the
6.0 Runoff. 6.1 Introduction. 6.2 Flood Control Design Runoff
 October 2003, Revised February 2005 Chapter 6.0, Runoff Page 1 6.1 Introduction 6.0 Runoff The timing, peak rates of discharge, and volume of stormwater runoff are the primary considerations in the design
October 2003, Revised February 2005 Chapter 6.0, Runoff Page 1 6.1 Introduction 6.0 Runoff The timing, peak rates of discharge, and volume of stormwater runoff are the primary considerations in the design
Introduction to Storm Sewer Design
 A SunCam online continuing education course Introduction to Storm Sewer Design by David F. Carter Introduction Storm sewer systems are vital in collection and conveyance of stormwater from the upstream
A SunCam online continuing education course Introduction to Storm Sewer Design by David F. Carter Introduction Storm sewer systems are vital in collection and conveyance of stormwater from the upstream
CVEN 339 Summer 2009 Final Exam. 120 minutes allowed. 36 Students. No curve applied to grades. Median 70.6 Mean 68.7 Std. Dev High 88 Low 24.
 CVEN 339 Final Exam 120 minutes allowed 36 Students No curve applied to grades Median 70.6 Mean 68.7 Std. Dev. 13.7 High 88 Low 24.5 Name: CVEN 339 Water Resources Engineering Summer Semester 2009 Dr.
CVEN 339 Final Exam 120 minutes allowed 36 Students No curve applied to grades Median 70.6 Mean 68.7 Std. Dev. 13.7 High 88 Low 24.5 Name: CVEN 339 Water Resources Engineering Summer Semester 2009 Dr.
Module 3: Rainfall and Hydrology for Construction Site Erosion Control
 Module 3: Rainfall and Hydrology for Construction Site Erosion Control Robert Pitt Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental Engineering University of Alabama Tuscaloosa, AL Rainfall and Hydrology
Module 3: Rainfall and Hydrology for Construction Site Erosion Control Robert Pitt Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental Engineering University of Alabama Tuscaloosa, AL Rainfall and Hydrology
Hydrologic Engineering Center Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS) Sunil KUMAR Director, National Water Academy
 Hydrologic Engineering Center Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS) Sunil KUMAR Director, National Water Academy 22 April 2015 NWA, Pune Exercise Objective: To determine hydrological Response of the given
Hydrologic Engineering Center Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS) Sunil KUMAR Director, National Water Academy 22 April 2015 NWA, Pune Exercise Objective: To determine hydrological Response of the given
Effect of Land Surface on Runoff Generation
 Effect of Land Surface on Runoff Generation Context: Hydrologic Cycle Runoff vs Infiltration Infiltration: Process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil Runoff: Water (from rain, snowmelt,
Effect of Land Surface on Runoff Generation Context: Hydrologic Cycle Runoff vs Infiltration Infiltration: Process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil Runoff: Water (from rain, snowmelt,
1. Stream Network. The most common approach to quantitatively describing stream networks was postulated by Strahler (1952).
 1. Stream Network The most common approach to quantitatively describing stream networks was postulated by Strahler (1952). First Order Streams streams with no tributaries. Second Order Streams begin at
1. Stream Network The most common approach to quantitatively describing stream networks was postulated by Strahler (1952). First Order Streams streams with no tributaries. Second Order Streams begin at
Highway Drainage 1- Storm Frequency and Runoff 1.1- Runoff Determination
 Highway Drainage Proper drainage is a very important consideration in design of a highway. Inadequate drainage facilities can lead to premature deterioration of the highway and the development of adverse
Highway Drainage Proper drainage is a very important consideration in design of a highway. Inadequate drainage facilities can lead to premature deterioration of the highway and the development of adverse
RUNOFF CALCULATIONS RATIONAL METHOD. To estimate the magnitude of a flood peak the following alternative methods are available:
 RUNOFF CALCULATIONS To estimate the magnitude of a flood peak the following alternative methods are available: 1. Unit-hydrograph technique 2. Empirical method 3. Semi-Empirical method (such rational method).
RUNOFF CALCULATIONS To estimate the magnitude of a flood peak the following alternative methods are available: 1. Unit-hydrograph technique 2. Empirical method 3. Semi-Empirical method (such rational method).
Assessment of MIDS Performance Goal Alternatives: Runoff Volumes, Runoff Rates, and Pollutant Removal Efficiencies
 Assessment of MIDS Performance Goal Alternatives: Runoff Volumes, Runoff Rates, and Pollutant Removal Efficiencies Prepared for Minnesota Pollution Control Agency June 30, 2011 p-gen3-12w Assessment of
Assessment of MIDS Performance Goal Alternatives: Runoff Volumes, Runoff Rates, and Pollutant Removal Efficiencies Prepared for Minnesota Pollution Control Agency June 30, 2011 p-gen3-12w Assessment of
Treatment Volume: Curve Numbers. Composite CN or Not? Treatment Volume: Curve Numbers. Treatment Volume: Calculation. Treatment Volume: Calculation
 Stormwater Engineering Bioretention Design Bill Hunt, PE, Ph.D. Extension Specialist & Assistant Professor NCSU-BAE www.bae.ncsu.edu/stormwater Bioretention Design Six Step Process 1 Determine Volume to
Stormwater Engineering Bioretention Design Bill Hunt, PE, Ph.D. Extension Specialist & Assistant Professor NCSU-BAE www.bae.ncsu.edu/stormwater Bioretention Design Six Step Process 1 Determine Volume to
Drainage Analysis. Appendix E
 Drainage Analysis Appendix E The existing and proposed storm drainage systems have been modeled with Bentley CivilStorm V8 computer modeling software. The peak stormwater discharge was determined for
Drainage Analysis Appendix E The existing and proposed storm drainage systems have been modeled with Bentley CivilStorm V8 computer modeling software. The peak stormwater discharge was determined for
HYDROLOGIC CONSIDERATIONS. 22 nd Annual Nonpoint Source Pollution Conference Saratoga Springs, NY
 LOW IMPACT DEVELOPMENT HYDROLOGIC CONSIDERATIONS 22 nd Annual Nonpoint Source Pollution Conference Saratoga Springs, NY May 18, 2011 PRESENTATION AGENDA Introduction Definitions Discuss Impacts to Hydrologic
LOW IMPACT DEVELOPMENT HYDROLOGIC CONSIDERATIONS 22 nd Annual Nonpoint Source Pollution Conference Saratoga Springs, NY May 18, 2011 PRESENTATION AGENDA Introduction Definitions Discuss Impacts to Hydrologic
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS
 Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Methods of Streamflow Analysis
 4 Methods of Streamflow Analysis CHAPTER 4 Streamflow Measurements Danielle M. Andrews Department of Crop and Soil Sciences, The Pennsylvania State University I. INTRODUCTION Perennial carries water all
4 Methods of Streamflow Analysis CHAPTER 4 Streamflow Measurements Danielle M. Andrews Department of Crop and Soil Sciences, The Pennsylvania State University I. INTRODUCTION Perennial carries water all
Sixth Semester B. E. (R)/ First Semester B. E. (PTDP) Civil Engineering Examination
 CAB/2KTF/EET 1221/1413 Sixth Semester B. E. (R)/ First Semester B. E. (PTDP) Civil Engineering Examination Course Code : CV 312 / CV 507 Course Name : Engineering Hydrology Time : 3 Hours ] [ Max. Marks
CAB/2KTF/EET 1221/1413 Sixth Semester B. E. (R)/ First Semester B. E. (PTDP) Civil Engineering Examination Course Code : CV 312 / CV 507 Course Name : Engineering Hydrology Time : 3 Hours ] [ Max. Marks
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS
 Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
54 MODERN SEWER DESIGN
 54 MODERN SEWER DESIGN 7 m diameter steel sewer being installed in wet conditions. 3. HYDROLOGY CHAPTER 3 Hydrology 55 Introduction The hydrologic cycle is a continuous process whereby water is transported
54 MODERN SEWER DESIGN 7 m diameter steel sewer being installed in wet conditions. 3. HYDROLOGY CHAPTER 3 Hydrology 55 Introduction The hydrologic cycle is a continuous process whereby water is transported
Water Resources Management Plan
 B u r n s v i l l e M i n n e s o t a Water Resources Management Plan - Volume Control / Infiltration Worksheet This Appendix contains a worksheet and related information that can be used for evaluating
B u r n s v i l l e M i n n e s o t a Water Resources Management Plan - Volume Control / Infiltration Worksheet This Appendix contains a worksheet and related information that can be used for evaluating
Precipitation Surface Cover Topography Soil Properties
 Precipitation Surface Cover Topography Soil Properties Intrinsic capacity of rainfall to cause erosion Influenced by Amount, intensity, terminal velocity, drop size and drop size distribution of rain.
Precipitation Surface Cover Topography Soil Properties Intrinsic capacity of rainfall to cause erosion Influenced by Amount, intensity, terminal velocity, drop size and drop size distribution of rain.
Unit 2: Geomorphologic and Hydrologic Characteristics of Watersheds. ENVS 435: Watershed Management INSTR.: Dr. R.M. Bajracharya
 Unit 2: Geomorphologic and Hydrologic Characteristics of Watersheds ENVS 435: Watershed Management INSTR.: Dr. R.M. Bajracharya Watersheds are hydro-geologic units Water flow and cycling are basic and
Unit 2: Geomorphologic and Hydrologic Characteristics of Watersheds ENVS 435: Watershed Management INSTR.: Dr. R.M. Bajracharya Watersheds are hydro-geologic units Water flow and cycling are basic and
Quantity of sewage. Dry weather flow: Domestic and industrial wastewater (Base flow) including inflow, infiltration and exfiltration
 Quantity of sewage Quantity of sewage depends on Dry weather flow and storm water Dry weather flow: Domestic and industrial wastewater (Base flow) including inflow, infiltration and exfiltration Infiltration
Quantity of sewage Quantity of sewage depends on Dry weather flow and storm water Dry weather flow: Domestic and industrial wastewater (Base flow) including inflow, infiltration and exfiltration Infiltration
Runoff Processes. Daene C. McKinney
 CE 374 K Hydrology Runoff Processes Daene C. McKinney Watershed Watershed Area draining to a stream Streamflow generated by water entering surface channels Affected by Physical, vegetative, and climatic
CE 374 K Hydrology Runoff Processes Daene C. McKinney Watershed Watershed Area draining to a stream Streamflow generated by water entering surface channels Affected by Physical, vegetative, and climatic
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS
 Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
San Francisco State University Site 1 Vegetated Infiltration Basin Monitoring Report: Rainy Seasons and
 San Francisco State University Site 1 Vegetated Infiltration Basin Monitoring Report: Rainy Seasons 2011-12 and 2012-13 Project Overview San Francisco State University (SFSU) has implemented several green
San Francisco State University Site 1 Vegetated Infiltration Basin Monitoring Report: Rainy Seasons 2011-12 and 2012-13 Project Overview San Francisco State University (SFSU) has implemented several green
WASTEWATER & STORM WATER COLLECTION AND REMOVAL
 CVE 471 WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING WASTEWATER & STORM WATER COLLECTION AND REMOVAL Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ Civil Engineering Program Middle East Technical University Northern Cyprus Campus CVE
CVE 471 WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING WASTEWATER & STORM WATER COLLECTION AND REMOVAL Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ Civil Engineering Program Middle East Technical University Northern Cyprus Campus CVE
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS
 Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Design of Stormwater Wetlands
 Hydraulic & Hydrologic Stormwater Engineering Design of Stormwater Wetlands Jon Hathaway, EI Extension Associate NCSU Bio. And Ag. Engineering 6 Step Process 1. Watershed Analysis (Runoff Volume and Peak
Hydraulic & Hydrologic Stormwater Engineering Design of Stormwater Wetlands Jon Hathaway, EI Extension Associate NCSU Bio. And Ag. Engineering 6 Step Process 1. Watershed Analysis (Runoff Volume and Peak
Highway Surface Drainage
 Highway Surface Drainage R obert D. M iles, Research Engineer Joint Highway Research Project, and Assistant Professor of Highway Engineering, School of Civil Engineering Purdue University IN T R O D U
Highway Surface Drainage R obert D. M iles, Research Engineer Joint Highway Research Project, and Assistant Professor of Highway Engineering, School of Civil Engineering Purdue University IN T R O D U
Index. Page numbers followed by f indicate figures.
 Index Aerodynamic method, 103, 110 111 Algae, 131, 173, 175 Alternate depth, 88 Alternating block method, 132, 140 141 Attenuation, 106, 107f, 118, 120 Page numbers followed by f indicate figures. Baseflow
Index Aerodynamic method, 103, 110 111 Algae, 131, 173, 175 Alternate depth, 88 Alternating block method, 132, 140 141 Attenuation, 106, 107f, 118, 120 Page numbers followed by f indicate figures. Baseflow
Overland Flow Time of Concentration on Very Flat Terrains
 Overland Flow Time of Concentration on Very Flat Terrains Ming-Han Li and Paramjit Chibber Two types of laboratory experiments were conducted to measure overland flow times on surfaces with very low slopes.
Overland Flow Time of Concentration on Very Flat Terrains Ming-Han Li and Paramjit Chibber Two types of laboratory experiments were conducted to measure overland flow times on surfaces with very low slopes.
A Stormwater Management Plan and Sediment Control Plan are required for all proposed developments within the City of Richmond.
 Engineering Page 3-1 3.0 STORM DRAINAGE 3.1 GENERAL Good drainage is vital to flat urban areas such as Lulu Island. It is essential that every storm sewer must be designed accurately minimizing conflicts
Engineering Page 3-1 3.0 STORM DRAINAGE 3.1 GENERAL Good drainage is vital to flat urban areas such as Lulu Island. It is essential that every storm sewer must be designed accurately minimizing conflicts
Stormwater Drainage Criteria Manual. City Of Clearwater Engineering Department Effective July 1, 2015
 Stormwater Drainage Criteria Manual City Of Clearwater Engineering Department Effective July 1, 2015 Engineering Department STORMWATER DRAINAGE CRITERIA MANUAL Table of Contents STORMWATER DRAINAGE CRITERIA
Stormwater Drainage Criteria Manual City Of Clearwater Engineering Department Effective July 1, 2015 Engineering Department STORMWATER DRAINAGE CRITERIA MANUAL Table of Contents STORMWATER DRAINAGE CRITERIA
APPENDIX IV. APPROVED METHODS FOR QUANTIFYING HYDROLOGIC CONDITIONS OF CONCERN (NORTH ORANGE COUNTY)
 APPENDIX IV. APPROVED METHODS FOR QUANTIFYING HYDROLOGIC CONDITIONS OF CONCERN (NORTH ORANGE COUNTY) Hydromodification design criteria for the North Orange County permit area are based on the 2- yr, 24-hr
APPENDIX IV. APPROVED METHODS FOR QUANTIFYING HYDROLOGIC CONDITIONS OF CONCERN (NORTH ORANGE COUNTY) Hydromodification design criteria for the North Orange County permit area are based on the 2- yr, 24-hr
The Texas A&M University and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Hydrologic Modeling Inventory (HMI) Questionnaire
 The Texas A&M University and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Hydrologic Modeling Inventory (HMI) Questionnaire May 4, 2010 Name of Model, Date, Version Number Dynamic Watershed Simulation Model (DWSM) 2002
The Texas A&M University and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Hydrologic Modeling Inventory (HMI) Questionnaire May 4, 2010 Name of Model, Date, Version Number Dynamic Watershed Simulation Model (DWSM) 2002
Detention Pond Design Considering Varying Design Storms. Receiving Water Effects of Water Pollutant Discharges
 Detention Pond Design Considering Varying Design Storms Land Development Results in Increased Peak Flow Rates and Runoff Volumes Developed area Robert Pitt Department of Civil, Construction and Environmental
Detention Pond Design Considering Varying Design Storms Land Development Results in Increased Peak Flow Rates and Runoff Volumes Developed area Robert Pitt Department of Civil, Construction and Environmental
Module 3 and Module 4 Watershed Analysis and RUSLE Calculation. Noboru Togawa. Presented to: Dr. Pitt Construction Site Erosion Control
 Module 3 and Module 4 Watershed Analysis and RUSLE Calculation by Presented to: Dr. Pitt Construction Site Erosion Control Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental Engineering The University
Module 3 and Module 4 Watershed Analysis and RUSLE Calculation by Presented to: Dr. Pitt Construction Site Erosion Control Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental Engineering The University
Estimating Stormwater Runoff from the 3D-model of an Urban Area in Istanbul
 198 Estimating Stormwater Runoff from the 3D-model of an Urban Area in Istanbul Muhammed Ali Örnek 1, Melike Ersoy 2, Yasin Çağatay Seçkin 3 1 Istanbul Technical University, Istanbul/Turkey maornek@itu.edu.tr
198 Estimating Stormwater Runoff from the 3D-model of an Urban Area in Istanbul Muhammed Ali Örnek 1, Melike Ersoy 2, Yasin Çağatay Seçkin 3 1 Istanbul Technical University, Istanbul/Turkey maornek@itu.edu.tr
EART 204. Water. Dr. Slawek Tulaczyk. Earth Sciences, UCSC
 EART 204 Water Dr. Slawek Tulaczyk Earth Sciences, UCSC 1 Water is an amazing liquid, (high heat capacity - particularly in phase transitions, maximum density at ca. 4 deg. C) 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Basin Hydrologic
EART 204 Water Dr. Slawek Tulaczyk Earth Sciences, UCSC 1 Water is an amazing liquid, (high heat capacity - particularly in phase transitions, maximum density at ca. 4 deg. C) 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Basin Hydrologic
Stormwater Analysis Report
 Stormwater Analysis Report Solar Panel Array Temple Street (Rt. 14) West Boylston, MA February 24, 216 SITE Prepared for: West Boylston Municipal Lighting Plant 4 Crescent Street West Boylston, MA 1583
Stormwater Analysis Report Solar Panel Array Temple Street (Rt. 14) West Boylston, MA February 24, 216 SITE Prepared for: West Boylston Municipal Lighting Plant 4 Crescent Street West Boylston, MA 1583
Computation of excess stormflow at the basin scale. Prof. Pierluigi Claps. Dept. DIATI, Politecnico di Torino
 Computation of excess stormflow at the basin scale Prof. Pierluigi Claps Dept. DIATI, Politecnico di Torino Pierluigi.claps@polito.it losses include: interception, evapotranspiration, storage infiltration,
Computation of excess stormflow at the basin scale Prof. Pierluigi Claps Dept. DIATI, Politecnico di Torino Pierluigi.claps@polito.it losses include: interception, evapotranspiration, storage infiltration,
Appendix C Little Calumet River Watershed Curve Number Calculation
 Little Calumet River Watershed Curve Number Calculation Introduction SCS hydrology uses the empirical curve number (CN) parameter as a part of calculating runoff volumes based on landscape characteristics
Little Calumet River Watershed Curve Number Calculation Introduction SCS hydrology uses the empirical curve number (CN) parameter as a part of calculating runoff volumes based on landscape characteristics
SPATIAL-TEMPORAL ADJUSTMENTS OF TIME OF CONCENTRATION
 JOURNAL O LOOD ENGINEERING J E 1(1) January June 2009; pp. 21 28 SPATIAL-TEMPORAL ADJUSTMENTS OF TIME OF CONCENTRATION Kristin L. Gilroy & Richard H. McCuen Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
JOURNAL O LOOD ENGINEERING J E 1(1) January June 2009; pp. 21 28 SPATIAL-TEMPORAL ADJUSTMENTS OF TIME OF CONCENTRATION Kristin L. Gilroy & Richard H. McCuen Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
Table of Contents. Overview... 1
 Chapter 3 Chapter 3 Table of Contents Overview... 1 Rainfall... 2 3-2-1 Rainfall Depths and Intensities... 2 3-2-2 Design Storm Distribution for Colorado Urban Hydrograph Procedure (CUHP)... 5 3-2-3 Temporal
Chapter 3 Chapter 3 Table of Contents Overview... 1 Rainfall... 2 3-2-1 Rainfall Depths and Intensities... 2 3-2-2 Design Storm Distribution for Colorado Urban Hydrograph Procedure (CUHP)... 5 3-2-3 Temporal
Chapter Description. Describe the hydraulic principles and apply the fundamental concept in analyzing flow in open channels.
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my HYDRAULICS UNIFORM FLOW IN OPEN CHANNEL TOPIC 2.1 by Nadiatul Adilah Ahmad Abdul Ghani Faculty of Civil Engineering and Earth Resources nadiatul@ump.edu.my
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my HYDRAULICS UNIFORM FLOW IN OPEN CHANNEL TOPIC 2.1 by Nadiatul Adilah Ahmad Abdul Ghani Faculty of Civil Engineering and Earth Resources nadiatul@ump.edu.my
HYDROLOGIC-HYDRAULIC STUDY ISABELLA OCEAN RESIDENCES ISLA VERDE, CAROLINA, PR
 HYDROLOGIC-HYDRAULIC STUDY ISABELLA OCEAN RESIDENCES ISLA VERDE, CAROLINA, PR 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Project Description and Location Isabella Ocean Residences is a residential development to be constructed
HYDROLOGIC-HYDRAULIC STUDY ISABELLA OCEAN RESIDENCES ISLA VERDE, CAROLINA, PR 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Project Description and Location Isabella Ocean Residences is a residential development to be constructed
Basics of Wastewater Collection System
 Basics of Wastewater Collection System PDH: 3.0 Hours 1 OUTLINE Introduction Definition of Terms Types of Collections Systems Types of Sewers Shapes of Sewers Collection System Appurtenances Basic Considerations
Basics of Wastewater Collection System PDH: 3.0 Hours 1 OUTLINE Introduction Definition of Terms Types of Collections Systems Types of Sewers Shapes of Sewers Collection System Appurtenances Basic Considerations
Module 3. Lecture 6: Synthetic unit hydrograph
 Lecture 6: Synthetic unit hydrograph Synthetic Unit Hydrograph In India, only a small number of streams are gauged (i.e., stream flows due to single and multiple storms, are measured) There are many drainage
Lecture 6: Synthetic unit hydrograph Synthetic Unit Hydrograph In India, only a small number of streams are gauged (i.e., stream flows due to single and multiple storms, are measured) There are many drainage
1 Precipitation: Water that comes from clouds. Most precipitation falls as rain, but it can also fall as frozen water such as snow.
 AEN-127 University of Kentucky College of Agriculture, Food and Environment Cooperative Extension Hydrologic Models Tyler Mahoney, Civil Engineering, and Carmen Agouridis and Richard Warner, Biosystems
AEN-127 University of Kentucky College of Agriculture, Food and Environment Cooperative Extension Hydrologic Models Tyler Mahoney, Civil Engineering, and Carmen Agouridis and Richard Warner, Biosystems
Module 10b: Gutter and Inlet Designs and Multiple Design Objectives
 Module 10b: Gutter and Inlet Designs and Multiple Design Objectives Bob Pitt University of Alabama and Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Evening traffic plows through high water at the intersection of
Module 10b: Gutter and Inlet Designs and Multiple Design Objectives Bob Pitt University of Alabama and Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Evening traffic plows through high water at the intersection of
MVP 17.3 WATER BAR END TREATMENT SIZING AND DETAILS 1/22/18
 MVP 17.3 WATER BAR END TREATMENT SIZING AND DETAILS 1/22/18 The purpose of this detail is to document the methodology developed to size the length of the water bar end treatments to ensure flow leaving
MVP 17.3 WATER BAR END TREATMENT SIZING AND DETAILS 1/22/18 The purpose of this detail is to document the methodology developed to size the length of the water bar end treatments to ensure flow leaving
Land Development and Soil Characteristics Affects on Runoff
 Land Development and Soil Characteristics Affects on Runoff Robert Pitt, Celina Bochis, and Pauline Johnson Department of Civil, Construction and Environmental Engineering The University of Alabama Tuscaloosa,
Land Development and Soil Characteristics Affects on Runoff Robert Pitt, Celina Bochis, and Pauline Johnson Department of Civil, Construction and Environmental Engineering The University of Alabama Tuscaloosa,
Appendix J: Storm Conveyance Design Parameters
 Appendix J: Storm Conveyance Design Parameters Drain Commissioner 39 February 2005 STORM DRAINAGE DESIGN CRITERIA A. STORM SEWERS 1. The required discharge capacity shall be determined by the Rational
Appendix J: Storm Conveyance Design Parameters Drain Commissioner 39 February 2005 STORM DRAINAGE DESIGN CRITERIA A. STORM SEWERS 1. The required discharge capacity shall be determined by the Rational
the 2001 season. Allison brought high winds and street flooding to Houston, after
 Module 10b: Gutter and Inlet Designs and Multiple Design Objectives Bob Pitt University of Alabama and Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Evening traffic plows through high water at the intersection of
Module 10b: Gutter and Inlet Designs and Multiple Design Objectives Bob Pitt University of Alabama and Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Evening traffic plows through high water at the intersection of
WinTR-55 Small Watershed Hydrology
 WinTR-55 Small Watershed Hydrology Modeling Single Sub-area Watersheds (Part 2) We ve looked at the minimum data entry requirements and how we can enter curve numbers and times of concentration directly
WinTR-55 Small Watershed Hydrology Modeling Single Sub-area Watersheds (Part 2) We ve looked at the minimum data entry requirements and how we can enter curve numbers and times of concentration directly
Hydrology for Drainage Design. Design Considerations Use appropriate design tools for the job at hand:
 Hydrology for Drainage Design Robert Pitt Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Alabama Tuscaloosa, AL Objectives for Urban Drainage Systems are Varied Ensure personal safety
Hydrology for Drainage Design Robert Pitt Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Alabama Tuscaloosa, AL Objectives for Urban Drainage Systems are Varied Ensure personal safety
Design Example Residential Subdivision
 Design Example Residential Subdivision Rhode Island Stormwater Design and Installation Standards Manual December 2010 Public Training March 22, 2010 Richard Claytor, P.E. 508-833-6600 Appendix D: Site
Design Example Residential Subdivision Rhode Island Stormwater Design and Installation Standards Manual December 2010 Public Training March 22, 2010 Richard Claytor, P.E. 508-833-6600 Appendix D: Site
Section 600 Runoff Table of Contents
 Section 600 Runoff Table of Contents 601 INTRODUCTION...600-1 602 RATIONAL METHOD...600-1 602.1 Rational Method Formula...600-2 602.2 Time of Concentration...600-2 602.3 Intensity...600-4 602.4 Runoff
Section 600 Runoff Table of Contents 601 INTRODUCTION...600-1 602 RATIONAL METHOD...600-1 602.1 Rational Method Formula...600-2 602.2 Time of Concentration...600-2 602.3 Intensity...600-4 602.4 Runoff
Presented by: Peter Spal, IBI Group. OECS Regional Engineering Workshop October 1, 2014
 Presented by: Peter Spal, IBI Group OECS Regional Engineering Workshop October 1, 2014 Presentation Topics Principles of Hydrology rational formula, unit hydrograph Modeling Methods SWMMHYMO Synthetic
Presented by: Peter Spal, IBI Group OECS Regional Engineering Workshop October 1, 2014 Presentation Topics Principles of Hydrology rational formula, unit hydrograph Modeling Methods SWMMHYMO Synthetic
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Engineering Hydrology Chapter 1 Introduction 2016-2017 Hydrologic Cycle Hydrologic Cycle Processes Processes Precipitation Atmospheric water Evaporation Infiltration Surface Runoff Land Surface Soil water
Engineering Hydrology Chapter 1 Introduction 2016-2017 Hydrologic Cycle Hydrologic Cycle Processes Processes Precipitation Atmospheric water Evaporation Infiltration Surface Runoff Land Surface Soil water
Chapter 4 "Hydrology"
 Chapter 4 "Hydrology" Revised TxDOT Hydraulics Manual Jorge A. Millan, P.E., CFM TxDOT Design Division/Hydraulics 2012 Transportation Short Course October 17, 2012 Chapter 4 Sections 1 Hydrology s Role
Chapter 4 "Hydrology" Revised TxDOT Hydraulics Manual Jorge A. Millan, P.E., CFM TxDOT Design Division/Hydraulics 2012 Transportation Short Course October 17, 2012 Chapter 4 Sections 1 Hydrology s Role
FAST WATER / SLOW WATER AN EVALUATION OF ESTIMATING TIME FOR STORMWATER RUNOFF
 FAST WATER / SLOW WATER AN EVALUATION OF ESTIMATING TIME FOR STORMWATER RUNOFF Factors Affecting Stormwater Runoff: Rainfall intensity % Impervious surfaces Watershed size Slope Soil type, soil compaction
FAST WATER / SLOW WATER AN EVALUATION OF ESTIMATING TIME FOR STORMWATER RUNOFF Factors Affecting Stormwater Runoff: Rainfall intensity % Impervious surfaces Watershed size Slope Soil type, soil compaction
This page intentionally left blank
 REFERENCE DOCUMENTS This page intentionally left blank TABLE OF CONTENTS REFERENCE DOCUMENTS REFERENCE DOCUMENT A: MEAN SEASONAL PRECIPITATION MAP R 1 REFERENCE DOCUMENT B: K FACTOR R 2 REFERENCE DOCUMENT
REFERENCE DOCUMENTS This page intentionally left blank TABLE OF CONTENTS REFERENCE DOCUMENTS REFERENCE DOCUMENT A: MEAN SEASONAL PRECIPITATION MAP R 1 REFERENCE DOCUMENT B: K FACTOR R 2 REFERENCE DOCUMENT
Introduction. Keywords: Oil Palm, hydrology, HEC-HMS, HEC-RAS. a * b*
 The Effect of Land Changes Towards in Sg. Pandan Perwira Bin Khusairi Rahman 1,a* and Kamarul Azlan bin Mohd Nasir 1,b 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia a * wirakhusairirahman@gmail.com,
The Effect of Land Changes Towards in Sg. Pandan Perwira Bin Khusairi Rahman 1,a* and Kamarul Azlan bin Mohd Nasir 1,b 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia a * wirakhusairirahman@gmail.com,
UMLALAZI-NKANDLA SMART GROWTH DEVELOPMENT CENTRE PROVISION OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SERVICES
 UMLALAZI-NKANDLA SMART GROWTH DEVELOPMENT CENTRE PROVISION OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SERVICES PROPOSED STORMWATER RETICULATION DESIGN AND MANAGEMENT DATE: OCTOBER 2011 PREPARED FOR: PREPARED BY: DEPARTMENT
UMLALAZI-NKANDLA SMART GROWTH DEVELOPMENT CENTRE PROVISION OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SERVICES PROPOSED STORMWATER RETICULATION DESIGN AND MANAGEMENT DATE: OCTOBER 2011 PREPARED FOR: PREPARED BY: DEPARTMENT
Appendix F. Flow Duration Basin Design Guidance
 Appendix F Flow Duration Basin Design Guidance Appendix F FINAL REPORT F:\SC46\SC46.31\HMP Mar 05\Appendices\Appendix F FLY_HMP.doc MARCH 2005 Appendix F Flow Duration Basin Design Guidance Prepared by
Appendix F Flow Duration Basin Design Guidance Appendix F FINAL REPORT F:\SC46\SC46.31\HMP Mar 05\Appendices\Appendix F FLY_HMP.doc MARCH 2005 Appendix F Flow Duration Basin Design Guidance Prepared by
RETENTION BASIN EXAMPLE
 -7 Given: Total Tributary Area = 7.5 ac o Tributary Area within Existing R/W = 5.8 ac o Tributary Area, Impervious, Outside of R/W = 0.0 ac o Tributary Area, Pervious, Outside of R/W = 1.7 ac o Tributary
-7 Given: Total Tributary Area = 7.5 ac o Tributary Area within Existing R/W = 5.8 ac o Tributary Area, Impervious, Outside of R/W = 0.0 ac o Tributary Area, Pervious, Outside of R/W = 1.7 ac o Tributary
Example 1: Pond Design in a residential development (Water Quantity calculations for a Wet Pond and Wet Extended Detention Pond)
 Chapter 10 Design Examples Example 1: Pond Design in a residential development (Water Quantity calculations for a Wet Pond and Wet Extended Detention Pond) Example 2: Filter Design in a commercial development
Chapter 10 Design Examples Example 1: Pond Design in a residential development (Water Quantity calculations for a Wet Pond and Wet Extended Detention Pond) Example 2: Filter Design in a commercial development
TABLE OF CONTENTS PART III - MINIMUM DESIGN STANDARDS Section 105 DRAINAGE SYSTEM DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS AND SCOPE 105.1
 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART III - MINIMUM DESIGN STANDARDS Section 105 DRAINAGE SYSTEM DESIGN SECTION TITLE PAGE 105.1. SPECIFICATIONS AND SCOPE 105.1 105.2. METHODS OF ANALYSIS 105.1 105.2.1. Rational Method
TABLE OF CONTENTS PART III - MINIMUM DESIGN STANDARDS Section 105 DRAINAGE SYSTEM DESIGN SECTION TITLE PAGE 105.1. SPECIFICATIONS AND SCOPE 105.1 105.2. METHODS OF ANALYSIS 105.1 105.2.1. Rational Method
