open access Hypothesis Volume 9(11)
|
|
|
- Clinton Brown
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hypothesis Volume 9(11) Molecular modeling and docking characterization of CzR1, a CC-NBS-LRR R-gene from Curcuma zedoaria Loeb. that confers resistance to Pythium aphanidermatum Raj Kumar Joshi 1 *, Satyabrata Nanda 1, Ellojita Rout 1, Basudeba Kar 1, Pradeep Kumar Naik 2 & Sanghamitra Nayak 1 1Centre of Biotechnology, Siksha O Anusandhan University, Bhubaneswar , India; 2Dept. of Biotechnology and Bioinformatics, Jaypee University of Information Technology, Waknaghat, Solan, Himachal Pradesh, India; Raj Kumar Joshi rajkumar.joshi@yahoo.co.in; Phone: ; *Corresponding author Received May 25, 2013; Accepted May 27, 2013; Published June 29, 2013 Abstract: Plant NBS-LRR R-genes recognizes several pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and limit pathogen infection through a multifaceted defense response. CzR1, a coiled-coil-nucleotide-binding-site-leucine-rich repeat R-gene isolated from Curcuma zedoaria L exhibit constitutive resistance to different strains of P. aphanidermatum. Majority of the necrotrophic oomycetes are characterized by the presence of carbohydrate PAMPs β-glucans in their cell walls which intercat with R-genes. In the present study, we predicted the 3D (three dimensional) structure of CzR1 based on homology modeling using the homology module of Prime through the Maestro interface of Schrodinger package ver 2.5. The docking investigation of CzR1 with β-glucan using the Glide software suggests that six amino acid residues, Ser186, Glu187, Ser263, Asp264, Asp355 and Tyr425 act as catalytic residues and are involved in hydrogen bonding with ligand β-(1,3)-d-glucan. The calculated distance between the carboxylic oxygen atoms of Glu187 Asp355 pair is well within the distance of 5Å suggesting a positive glucanase activity of CzR1. Elucidation of these molecular characteristics will help in in silico screening and understanding the structural basis of ligand binding to CzR1 protein and pave new ways towards a broad spectrum rhizome rot resistance development in the cultivated turmeric. Key words: Curcuma zedoaria, Pythium aphanidermatum, CC-NBS-LRR, molecular docking, β-(1, 3)-D-Glucan. Background: Curcuma longa L. (turmeric) of the family Zingiberaceae is one of the most important crop with great medicinal and economic significance [1]. India is the world s largest producer, and exporter of turmeric followed by China, Indonesia, Bangladesh and Thailand [2]. The International Trade Centre, Geneva, has estimated an annual growth rate of 10% in the world demand for turmeric. However, turmeric yield is not up to the demand because continuous domestication of the preferred genotypes coupled with their exclusive vegetative nature seems to have eroded the genetic base of this crop and as a result all of its cultivars available today are equally suceptible to major fungal and bacterial diseases. Crop losses to the tune of 60% has been realized in the recent times mainly due to the infection by a necrotrophic oomycetic fungus Pythium aphanidermatum causing the rhizome rot disease in turmeric [2]. Due to several constraint associated with the utilization of chemical pesticides and host resistance breeding, a genetic transformation approach using alien genes could be the most likely solution towards development of rhizome rot resistance. Our lab has recently identified and characterized a coiled-coil-nucleotide-bindingsite-leucine-rich repeat (CC-NBS-LRR) R-gene, CzR1 from wild Bioinformation 9(11): (2013) Biomedical Informatics
2 turmeric genotype Curcuma zedoaria that exhibit constitutive upregulated expressions in response to different strains of P. aphanidermatum [3]. The conceptual protein has 906 amino acids, a predicted molecular weight of Da and a calculated isoelectric point (pi) of Before utilization in long term turmeric improvement programmes, it is essential to determine the three dimensional (3D) model of CzR1 to assess its structural integrity and biological relevance. A homology modeling based protein structure perdiction of CzR1 could be an efficient strategy taking into account the time consuming and cumbersome nature of X-ray diffraction or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) [4]. Further, several evidences suggest that various R-genes and pathogenesis related proteins play major role in neutralizing the oomycetic cell wall to kill the pathogen in line of defense signaling [5]. Beta-1,3-glucan, the major cellwall constituents of necrotrophic oomycetes often acts as elicitors of defence reactions and serve as pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) [6]. Thus, the recognition of these PAMPs by R-genes are crucial to activate defense reactions in plants. However, there is no report on the interaction between R-gene and β-1,3-glucan to study the presence of a possible glucanase activity in R-gene dependent pathogen defense. Thus the present study was designed to predict the 3D structure of CzR1 based on homology modeling and molecular docking of the R-protein with β-1, 3(D)-glucan. Methodology: A BLASTX search of the Protein Data Bank (PDB) using CzR1 predcited protein as query showed high sequence identity (61%) with human APAF-1 protein (PDB ID: 1Z6T) and significant homology with coiled coil domain of MLA10 gene of Hordeum vulgare (PDB ID: 3QFL) and leucine rich repeat domain from Xanthomonas oryzae (PDB ID: 4FCG). Models of CzR1 protein were constructed based on the crystal structure coordinates of 1Z6T along with other two sequences at a resolution of 2.21 Å. The pair wise alignment of CzR1 was done with 1Z6T as reference using the homology module of Prime through the Maestro interface (Schrodinger, LLC, and New York, USA). The pair wise alignment was improved manually by minor editing based on the secondary structure predictions as well as the pair wise superposition of the NB-ARC domain to develop the three dimensional structure of CzR1. The model was screened for unfavorable steric contacts and remodeled using a rotamer library database of Prime. Explicit hydrogen was added to the protein and the model was subjected to energy minimization using the force-field OPLS-2005 using 300 iterations in a simple minimization method. The steepest descent energy minimization was performed until the energy showed stability in the sequential repetition. CzR1 model structure was evaluated for its backbone conformation by inspecting the Psi/Phi angles in a Ramachandran plot generated using the software PROCHECK version 3.5 [7]. Z score of CzR1 and the template (1Z6T) was estimated using the software Prosa2003 [8]. Nevertheless, PROCHECK assured the reliability of the structure and the protein was subjected to VERIFY3D [9] available from NIH MBI Laboratory Servers. The root mean square deviation (RMSD) was calculated by superposing the predicted Cα traces and backbone atoms of Cz1R structure onto the template (1Z6T) in order to assess the the deviation of the modeled structure from the template. The protein structure image of the model was illustrated using the software PyMOL. Molecular docking was performed in order to determine the binding affinity of polymer of β-(1,3)-d-glucan onto Cz1R protein. The chemical structure β-(1,3)-d-glucan was extracted from Chemical Book ( and its three dimensional structure was developed using the molecular builder tool of Maestro (Schrodinger package, ver 8.5). Initially different binding sites were predicted on CzR1 protein using SiteMap (Schrodinger, ver 2.4), out of which only the binding site from the NB-ARC domain was considered for docking study. The receptor-grid file was generated at the centre of the predicted binding site using Glide (Schrodinger, ver 2.5). A bounding box of size 14Å x 14Å x 14Å was defined and centered on the mass center of each binding site in order to confine the mass center of the docked ligand. β-(1,3)-d-glucan was then docked into each predicted binding site using Glide XP (extra precision) docking [10-11]. Out of the 5,000 poses that were sampled initially through exhaustive search of the torsional minima 800 poses per ligand were selected for energy minimization (conjugate gradients 1,000 steps). The 10 lowestenergy poses obtained were subjected to post docking minimization (Monte Carlo sampling based on torsional minima and refining the orientation of side groups of ligand). A single best conformation of the ligand was considered for further analysis and the binding affinity between the protein and ligand was estimated using the GlideScore function [12]. The mode of protein-ligand interaction was plotted using the program LIGPLOT [13]. Results & Discussion: The CzR1 protein from C. zedoaria with 906 amino acids contains NB-ARC domain (168 to 465) and LRR-1 domain (630 to 651) predicted from Pfam database [3]. Although Mla1 protein from Hordeum vulgare shared 62% similarity with CzR1, it could not be used as a template due to non-availability of its structure information in the PDB database. Hence, the crystal structures of MLA10 coiled coil domain (3QFL), human APAF-1 protein (1Z6T) and Xanthomonas oryzae leucine rich repeat domain (4FCG) were combinedly used as templates for developing a homology based model of CzR1 (Figure 1A). The overall stereo chemical quality of the model was assessed by PROCHECK. The Ramachandran plot showed 96.6% amino acid residues from the main chain conformation of CzR1 within the favored or allowed regions suggesting that majority of the amino acids are in a phi-psi distribution that is consistent with a righthanded α-helix. The G-factors, indicating the quality of the covalent bond length and overall bond angles, were 0.10 for dihedrals, 0.42 for covalent bonds, and 0.11 as overall value. Although, a calculated RMSD value of Å (Figure 1B) was obtained by super positioning of the Cα atoms of the CzR1 and the template protein (1Z6T), the RMSD between the NB-ARC domain structures between both the proteins was only Å. Prosa2003 analysis yielded a Z score of 4.32 for CzR1 and 4.63 for the central template (1Z6T). The final model, which we took for further analysis, consisted of 631 amino acid residues. The overall main-chain and side-chain parameters, as evaluated by PROCHECK, are all very favorable. The assessment with VERIFY3D, which derives a 3D-1D profile based on the local environment of each residue, described by the statistical preferences for: the area of the residue that is buried, the Bioinformation 9 (11): (2013) Biomedical Informatics
3 fraction of side-chain area that is covered by polar atoms (oxygen and nitrogen) and the local secondary structure, also substantiated the reliability of the three dimensional structure. Figure 1: Homology model structure of CzR1. A) The NB-ARC domain of CzR1 is represented in red colour and the LRRs were represented in green colour; B) Super positioning of CzR1 and the template 1Z6T (yellow colour). The RMSD between both the structures was Å. The RMSD between the NB-ARC domains between both the proteins was Å. S2). β-(1,3)-d-glucan shares higher values of electrostatic interaction (E coul, kcal/mol), hydrogen bonding energy (H bond, kcal/mol) and Van der Waals interaction (E vdw, kcal/mol) energies Table 2 (see supplementary material) predicted by Glide-XP because of the polar and non polar interactions with the binding site amino acids. The model produced by GlideXP predicts that six amino acid residues, Ser186, Glu187, Ser263, Asp264, Asp355 and Tyr425 are involved in hydrogen bonding with docked polymer β-(1,3)-d- Glucan (Figure 2A & 2B). The calculated distance between the carboxylic oxygen atoms of the Glu187 Asp355 pair is 4.38Å, which is well within the distance of 5Å required between the two catalytic residues for glucanase activity [15]. Furthermore, polymer of β-(1,3)-d-glucan showed desirable hydrophobic interactions with the hydrophobic residues within the binding cavity (Figure 3). The favourable H-bonding, columbic, and hydrophobic interaction energies make polymer of β-(1,3)-d- Glucan highly active and selective for CzR1. Previous to our studies, there is no data on the possible glucanase or hydrolytic activity of the R-genes. However, many PR-proteins with antifungal activity exhibits such interdomain surface cleft for glycoside hydrolase enzymes and binding by (1,3)-b-D-glucan [16-17]. Further research on binding interactions between variable NBS-LRR class R-genes and different pathogen /microbe associated molecular patterns (PAMPs/MAMPs) is needed to get a decisive conclusion on the global functioning and regulation of such R-genes. Figure 2: A) Molecular docking snapshot of β-(1,3)-d-glucan bound to site 4 of NB_ARC domain in CzR1; B) Enlarge view of bound β-(1,3)-d-glucan along with the interacting amino acids. β-(1, 3)-D-Glucan is represented in yellow carbon colour while the binding site amino acids were represented in green colour To examine the glucanase prospective of CzR1, we subjected it to molecular docking with the polymeric carbohydrate β-(1,3)- D-Glucan which is a major constituent of cell wall in most of the necrotrophic oomycetes [14]. Five different binding sites with different site scores were predicted with different physiochemical properties in Table 1 (see supplementary material). However, the binding site (site 4) that includes amino acids from the NB-ARC domain with good site score, volume, enclosure, hydrophilicity and donor/acceptor ratio was considered for molecular docking of β-(1,3)-d-glucan. The docking show better docking score ( kcal/mol) and Emodel energy ( kcal/mol) of β-(1, 3)-D-Glucan with the binding site 4 located at the NB-ARC domain of CzR1 (Table Figure 3: Ligand plot demonstrating the interacting amino acids of CzR1 (site 4) with β-(1,3)-d-glucan. The hydrogen bonds were represented with dotted green line along with the bond length in Å. Conclusion: In conclusions, molecular modeling procedures revealed the presence of a narrow cleft near the ATP-GTP binding site of the highly charged NBS domain of CzR1, a CC-NBS-LRR class R- gene from C. zedoaria. Molecular docking predicted high affinity between CzR1 and (1, 3)-β-D-glucan, a major component of the oomycete cell wall with favorable pairing of two negatively charged amino acid residues Glu187-Asp (355) within the Bioinformation 9 (11): (2013) Biomedical Informatics
4 docked complex. This suggest that CzR1 could be possibly having a β-1, 3-glucanase activity in vivo besides the regular ATP-GTP binding function in initiating pathogen defense. Revelation of these molecular characteristic of CzR1 controlling the resistance of C. zedoaria against P.aphanidermatum together with studies on the significance of hydrolytic activity of CzR1 will be highly informative towards the development of a broad spectrum rhizome rot resistance in the cultivated turmeric. Acknowledgment: SN gratefully acknowledges the financial assistance in the form of Institutional research fellowship from Siksha O Anusandhan University. ER acknowledges financial support in the form of junior research fellowship from Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India. BK is thankful to Council of Scientific and Industrial research (CSIR), Govt. of India for providing senior research fellowship. The authors are grateful to Dr. Manoj Ranjan Nayak, President,Siksha O Anusandhan University for his encouragement and support. References: [1] Ravindran PN et al. Turmeric-the genus Curcuma CRC Press 2007 [2] Selvan et al. Indian Spices- production and utilization [3] Kar B et al. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol Doi: /j.pmpp [4] Yadav BS et al. Exp Mol Pathol : 7 [PMID: ] [5] Asselbergh B et al. Plant Physiol : 1863 [PMID: ] [6] Altenbach D & Robatzek S, Mol Plant Microbe Interact : 1031 [PMID: ]. [7] Laskowski RA et al. J Appl Crystallogr : 283 [8] Sippl MJ, Proteins : 355 [PMID: ] [9] Eisenberg D et al. Methods Enzymol : 396 [PMID: ] [10] Friesner et al. J Med Chem : 1739 [PMID: ] [11] Halgren TA et al. J Med Chem : 1750 [PMID: ] [12] Eldridge MD et al. J Comput Aided Mol Des : 425 [PMID: ] [13] Wallace AC et al. Protein Eng : 127 [PMID: ] [14] Latijnhouwers M et al. Trends Microbiol : 462 [PMID: ] [15] Zechel DL & Withers SG, Curr Opin Chem Biol : 643 [PMID: ] [16] Osmond RI et al. Eur J Biochem : 4190 [PMID: ] [17] Ghosh R & Chakrabarti C, Planta : 883 [PMID: ] Edited by P Kangueane Citation: Joshi et al. Bioinformation 9(11): (2013) License statement: This is an open-access article, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, for non-commercial purposes, provided the original author and source are credited Bioinformation 9 (11): (2013) Biomedical Informatics
5 Supplementary material: Table 1: Different binding sites predicted by SiteMap (Schrödinger Inc.) longwith their physicochemical properties: site score, volume, enclosure, hydrophilicity and lower value of donor/acceptor ratio from CzR1 modeled structure. Site 4, located at the NB- ARC domain was used for the molecular docking of β-(1,3)-d-glucan. Site ID Site score Volume(Å) 3 Exposure Enclosure Hydrophobic Hydrophilic Donor/Acceptor Table 2: Glide XP docking pose of β-(1,3)-d-glucan onto CzR1 and their energy scores. Glide XP docking generated more precise binding conformation of β-(1,3)-d-glucan with good binding affinity. Glide XPscore Glide energy Glide E vdw Glide E coul Glide H bond Glide E model Bioinformation 9 (11): (2013) Biomedical Informatics
Homology modeling and structural validation of tissue factor pathway inhibitor
 www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 9(16) Homology modeling and structural validation of tissue factor pathway inhibitor Piyush Agrawal, Zoozeal Thakur & Mahesh Kulharia* Centre for Bioinformatics,
www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 9(16) Homology modeling and structural validation of tissue factor pathway inhibitor Piyush Agrawal, Zoozeal Thakur & Mahesh Kulharia* Centre for Bioinformatics,
ABSTRACT. tropical and sub-tropical countries. Recent utility of turmeric by the pharmaceutical
 ABSTRACT Turmeric (Curcuma longa L; Zingiberaceae) is one of the most important herb in the tropical and sub-tropical countries. Recent utility of turmeric by the pharmaceutical industries as a source
ABSTRACT Turmeric (Curcuma longa L; Zingiberaceae) is one of the most important herb in the tropical and sub-tropical countries. Recent utility of turmeric by the pharmaceutical industries as a source
Suppl. Figure 1: RCC1 sequence and sequence alignments. (a) Amino acid
 Supplementary Figures Suppl. Figure 1: RCC1 sequence and sequence alignments. (a) Amino acid sequence of Drosophila RCC1. Same colors are for Figure 1 with sequence of β-wedge that interacts with Ran in
Supplementary Figures Suppl. Figure 1: RCC1 sequence and sequence alignments. (a) Amino acid sequence of Drosophila RCC1. Same colors are for Figure 1 with sequence of β-wedge that interacts with Ran in
Bioinformation Volume 5 open access
 Molecular docking analysis of new generation cephalosporins interactions with recently known SHV-variants Asad Ullah Khan 1 *, Mohd Hassan Baig 1, Gulshan Wadhwa 2 1 Interdisciplinary Biotechnology Unit,
Molecular docking analysis of new generation cephalosporins interactions with recently known SHV-variants Asad Ullah Khan 1 *, Mohd Hassan Baig 1, Gulshan Wadhwa 2 1 Interdisciplinary Biotechnology Unit,
Molecular docking of glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase in Rhizopus oryzae
 www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 7(6) Molecular docking of glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase in Rhizopus oryzae Kamalika Banerjee 1, Utkarsh Gupta 1, Sanjay Gupta 1, Gulshan Wadhwa 2, Reema Gabrani
www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 7(6) Molecular docking of glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase in Rhizopus oryzae Kamalika Banerjee 1, Utkarsh Gupta 1, Sanjay Gupta 1, Gulshan Wadhwa 2, Reema Gabrani
In-silico comparative study of inhibitory mechanism of Plant Serine Proteinase Inhibitors
 www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 8(14) In-silico comparative study of inhibitory mechanism of Plant Serine Proteinase Inhibitors Chekkara Venkata Sathya Siva Prasad 1 *, Saurabh Gupta 1, Alex Gaponenko
www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 8(14) In-silico comparative study of inhibitory mechanism of Plant Serine Proteinase Inhibitors Chekkara Venkata Sathya Siva Prasad 1 *, Saurabh Gupta 1, Alex Gaponenko
Ligand docking. CS/CME/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 22 and 27, 2015 Ron Dror
 Ligand docking CS/CME/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 22 and 27, 2015 Ron Dror 1 Outline Goals of ligand docking Defining binding affinity (strength) Computing binding affinity: Simplifying the problem Ligand docking
Ligand docking CS/CME/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 22 and 27, 2015 Ron Dror 1 Outline Goals of ligand docking Defining binding affinity (strength) Computing binding affinity: Simplifying the problem Ligand docking
Molecular differentiation of Peroxysome proliferator activated receptor coactivator-1 among different breeds of Bubalus bubalis
 www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 8(13) Molecular differentiation of Peroxysome proliferator activated receptor coactivator-1 among different breeds of Bubalus bubalis Anil Kumar 1, Ravinder Kumar
www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 8(13) Molecular differentiation of Peroxysome proliferator activated receptor coactivator-1 among different breeds of Bubalus bubalis Anil Kumar 1, Ravinder Kumar
Molecular design principles underlying β-strand swapping. in the adhesive dimerization of cadherins
 Supplementary information for: Molecular design principles underlying β-strand swapping in the adhesive dimerization of cadherins Jeremie Vendome 1,2,3,5, Shoshana Posy 1,2,3,5,6, Xiangshu Jin, 1,3 Fabiana
Supplementary information for: Molecular design principles underlying β-strand swapping in the adhesive dimerization of cadherins Jeremie Vendome 1,2,3,5, Shoshana Posy 1,2,3,5,6, Xiangshu Jin, 1,3 Fabiana
Comparative Modeling Part 1. Jaroslaw Pillardy Computational Biology Service Unit Cornell Theory Center
 Comparative Modeling Part 1 Jaroslaw Pillardy Computational Biology Service Unit Cornell Theory Center Function is the most important feature of a protein Function is related to structure Structure is
Comparative Modeling Part 1 Jaroslaw Pillardy Computational Biology Service Unit Cornell Theory Center Function is the most important feature of a protein Function is related to structure Structure is
Homology modeling, comparative genomics and functional annotation of Mycoplasma genitalium hypothetical protein MG_237
 www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 7(6) Homology modeling, comparative genomics and functional annotation of Mycoplasma genitalium hypothetical protein MG_237 Azeem Mehmood Butt 1, Maria Batool 2,
www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 7(6) Homology modeling, comparative genomics and functional annotation of Mycoplasma genitalium hypothetical protein MG_237 Azeem Mehmood Butt 1, Maria Batool 2,
Protein Structure Prediction
 Homology Modeling Protein Structure Prediction Ingo Ruczinski M T S K G G G Y F F Y D E L Y G V V V V L I V L S D E S Department of Biostatistics, Johns Hopkins University Fold Recognition b Initio Structure
Homology Modeling Protein Structure Prediction Ingo Ruczinski M T S K G G G Y F F Y D E L Y G V V V V L I V L S D E S Department of Biostatistics, Johns Hopkins University Fold Recognition b Initio Structure
Bioinformatics & Protein Structural Analysis. Bioinformatics & Protein Structural Analysis. Learning Objective. Proteomics
 The molecular structures of proteins are complex and can be defined at various levels. These structures can also be predicted from their amino-acid sequences. Protein structure prediction is one of the
The molecular structures of proteins are complex and can be defined at various levels. These structures can also be predicted from their amino-acid sequences. Protein structure prediction is one of the
Supplementary materials. Computational study of β-n-acetylhexosaminidase from. Talaromyces flavus, a glycosidase with high substrate flexibility
 Supplementary materials Computational study of β-n-acetylhexosaminidase from Talaromyces flavus, a glycosidase with high substrate flexibility Natallia Kulik 1,*, Kristýna Slámová 2, Rüdiger Ettrich 1,3,
Supplementary materials Computational study of β-n-acetylhexosaminidase from Talaromyces flavus, a glycosidase with high substrate flexibility Natallia Kulik 1,*, Kristýna Slámová 2, Rüdiger Ettrich 1,3,
Design of inhibitors of the HIV-1 integrase core domain using virtual screening
 www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 10(2) Design of inhibitors of the HIV-1 integrase core domain using virtual screening Preetom Regon 1, Dhrubajyoti Gogoi 2 *, Ashok Kumar Rai 1, Manabjyoti Bordoloi
www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 10(2) Design of inhibitors of the HIV-1 integrase core domain using virtual screening Preetom Regon 1, Dhrubajyoti Gogoi 2 *, Ashok Kumar Rai 1, Manabjyoti Bordoloi
Molecular Structures
 Molecular Structures 1 Molecular structures 2 Why is it important? Answers to scientific questions such as: What does the structure of protein X look like? Can we predict the binding of molecule X to Y?
Molecular Structures 1 Molecular structures 2 Why is it important? Answers to scientific questions such as: What does the structure of protein X look like? Can we predict the binding of molecule X to Y?
BMB/Bi/Ch 170 Fall 2017 Problem Set 1: Proteins I
 BMB/Bi/Ch 170 Fall 2017 Problem Set 1: Proteins I Please use ray-tracing feature for all the images you are submitting. Use either the Ray button on the right side of the command window in PyMOL or variations
BMB/Bi/Ch 170 Fall 2017 Problem Set 1: Proteins I Please use ray-tracing feature for all the images you are submitting. Use either the Ray button on the right side of the command window in PyMOL or variations
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) Conformational Analysis Protein Folding Protein Structure Prediction
 Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) Conformational Analysis Protein Folding Protein Structure Prediction Conformational Analysis 2 Conformational Analysis Properties of molecules depend on their three-dimensional
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) Conformational Analysis Protein Folding Protein Structure Prediction Conformational Analysis 2 Conformational Analysis Properties of molecules depend on their three-dimensional
Molecular Structures
 Molecular Structures 1 Molecular structures 2 Why is it important? Answers to scientific questions such as: What does the structure of protein X look like? Can we predict the binding of molecule X to Y?
Molecular Structures 1 Molecular structures 2 Why is it important? Answers to scientific questions such as: What does the structure of protein X look like? Can we predict the binding of molecule X to Y?
Docking studies of piperine - iron conjugate with human CYP450 3A4
 www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 9(7) Docking studies of piperine - iron conjugate with human CYP450 3A4 Veerabrahmam Alugolu 1 *, Satyanarayana Rentala 2, Aruna Lakshmi Komarraju 2 & Uma Devi
www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 9(7) Docking studies of piperine - iron conjugate with human CYP450 3A4 Veerabrahmam Alugolu 1 *, Satyanarayana Rentala 2, Aruna Lakshmi Komarraju 2 & Uma Devi
4/10/2011. Rosetta software package. Rosetta.. Conformational sampling and scoring of models in Rosetta.
 Rosetta.. Ph.D. Thomas M. Frimurer Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Potein Reseach Center for Basic Metabilic Research Breif introduction to Rosetta Rosetta docking example Rosetta software package Breif
Rosetta.. Ph.D. Thomas M. Frimurer Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Potein Reseach Center for Basic Metabilic Research Breif introduction to Rosetta Rosetta docking example Rosetta software package Breif
NNvPDB: Neural Network based Protein Secondary Structure Prediction with PDB Validation
 www.bioinformation.net Web server Volume 11(8) NNvPDB: Neural Network based Protein Secondary Structure Prediction with PDB Validation Seethalakshmi Sakthivel, Habeeb S.K.M* Department of Bioinformatics,
www.bioinformation.net Web server Volume 11(8) NNvPDB: Neural Network based Protein Secondary Structure Prediction with PDB Validation Seethalakshmi Sakthivel, Habeeb S.K.M* Department of Bioinformatics,
Molecular Modeling 9. Protein structure prediction, part 2: Homology modeling, fold recognition & threading
 Molecular Modeling 9 Protein structure prediction, part 2: Homology modeling, fold recognition & threading The project... Remember: You are smarter than the program. Inspecting the model: Are amino acids
Molecular Modeling 9 Protein structure prediction, part 2: Homology modeling, fold recognition & threading The project... Remember: You are smarter than the program. Inspecting the model: Are amino acids
Docking studies on short and ultra-short peptides against beta-secretase (BACE1) enzyme
 Research Article Docking studies on short and ultra-short peptides against beta-secretase (BACE1) enzyme Pandurangan Perumal 1, Liew Chun Lap 1, Ling Yu Luong 1, Tan Ling Hoi 1, Pavadai Parasuraman 2 ABSTRACT
Research Article Docking studies on short and ultra-short peptides against beta-secretase (BACE1) enzyme Pandurangan Perumal 1, Liew Chun Lap 1, Ling Yu Luong 1, Tan Ling Hoi 1, Pavadai Parasuraman 2 ABSTRACT
Structural Validation and Homology Modeling of Lea 2 Protein in Bread Wheat
 American-Eurasian J. Agric. & Environ. Sci., 14 (10): 1044-1048, 2014 ISSN 1818-6769 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.aejaes.2014.14.10.12424 Structural Validation and Homology Modeling of Lea
American-Eurasian J. Agric. & Environ. Sci., 14 (10): 1044-1048, 2014 ISSN 1818-6769 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.aejaes.2014.14.10.12424 Structural Validation and Homology Modeling of Lea
An insilico Approach: Homology Modelling and Characterization of HSP90 alpha Sangeeta Supehia
 259 Journal of Pharmaceutical, Chemical and Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-7658 Impact Factor (SJIF): 2.092 December 2014-February 2015; 2(4):259-264 Available online at http://www.jpcbs.info Online published
259 Journal of Pharmaceutical, Chemical and Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-7658 Impact Factor (SJIF): 2.092 December 2014-February 2015; 2(4):259-264 Available online at http://www.jpcbs.info Online published
LIST OF ACRONYMS & ABBREVIATIONS
 LIST OF ACRONYMS & ABBREVIATIONS ALA ARG ASN ATD CRD CYS GLN GLU GLY GPCR HIS hstr ILE LEU LYS MET mglur1 NHDC PDB PHE PRO SER T1R2 T1R3 TMD TRP TYR THR 7-TM VFTM ZnSO 4 Alanine, A Arginine, R Asparagines,
LIST OF ACRONYMS & ABBREVIATIONS ALA ARG ASN ATD CRD CYS GLN GLU GLY GPCR HIS hstr ILE LEU LYS MET mglur1 NHDC PDB PHE PRO SER T1R2 T1R3 TMD TRP TYR THR 7-TM VFTM ZnSO 4 Alanine, A Arginine, R Asparagines,
STRUM: Structure-based stability change prediction on. single-point mutation
 STRUM: Structure-based stability change prediction on single-point mutation Lijun Quan, Qiang Lv, Yang Zhang Supplemental Information Figure S1. Histogram distribution of TM-score of the I-TASSER models
STRUM: Structure-based stability change prediction on single-point mutation Lijun Quan, Qiang Lv, Yang Zhang Supplemental Information Figure S1. Histogram distribution of TM-score of the I-TASSER models
Structure formation and association of biomolecules. Prof. Dr. Martin Zacharias Lehrstuhl für Molekulardynamik (T38) Technische Universität München
 Structure formation and association of biomolecules Prof. Dr. Martin Zacharias Lehrstuhl für Molekulardynamik (T38) Technische Universität München Motivation Many biomolecules are chemically synthesized
Structure formation and association of biomolecules Prof. Dr. Martin Zacharias Lehrstuhl für Molekulardynamik (T38) Technische Universität München Motivation Many biomolecules are chemically synthesized
Introduction to Proteins
 Introduction to Proteins Lecture 4 Module I: Molecular Structure & Metabolism Molecular Cell Biology Core Course (GSND5200) Matthew Neiditch - Room E450U ICPH matthew.neiditch@umdnj.edu What is a protein?
Introduction to Proteins Lecture 4 Module I: Molecular Structure & Metabolism Molecular Cell Biology Core Course (GSND5200) Matthew Neiditch - Room E450U ICPH matthew.neiditch@umdnj.edu What is a protein?
Homology Modelling. Thomas Holberg Blicher NNF Center for Protein Research University of Copenhagen
 Homology Modelling Thomas Holberg Blicher NNF Center for Protein Research University of Copenhagen Why are Protein Structures so Interesting? They provide a detailed picture of interesting biological features,
Homology Modelling Thomas Holberg Blicher NNF Center for Protein Research University of Copenhagen Why are Protein Structures so Interesting? They provide a detailed picture of interesting biological features,
Protein Folding Problem I400: Introduction to Bioinformatics
 Protein Folding Problem I400: Introduction to Bioinformatics November 29, 2004 Protein biomolecule, macromolecule more than 50% of the dry weight of cells is proteins polymer of amino acids connected into
Protein Folding Problem I400: Introduction to Bioinformatics November 29, 2004 Protein biomolecule, macromolecule more than 50% of the dry weight of cells is proteins polymer of amino acids connected into
Docking. Why? Docking : finding the binding orientation of two molecules with known structures
 Docking : finding the binding orientation of two molecules with known structures Docking According to the molecules involved: Protein-Ligand docking Protein-Protein docking Specific docking algorithms
Docking : finding the binding orientation of two molecules with known structures Docking According to the molecules involved: Protein-Ligand docking Protein-Protein docking Specific docking algorithms
Bioinformatics Practical Course. 80 Practical Hours
 Bioinformatics Practical Course 80 Practical Hours Course Description: This course presents major ideas and techniques for auxiliary bioinformatics and the advanced applications. Points included incorporate
Bioinformatics Practical Course 80 Practical Hours Course Description: This course presents major ideas and techniques for auxiliary bioinformatics and the advanced applications. Points included incorporate
Model based design of inhibitors for c-jun
 Model based design of inhibitors for c-jun Pallavi Chauhan 1, *, Madhvi Shakya 2 1 Department of Bioinformatics, 2 Department of Mathematics, MANIT, Bhopal, MP, India; Pallavi Chauhan - Email: pallavi.chauhan2006@gmail.com;
Model based design of inhibitors for c-jun Pallavi Chauhan 1, *, Madhvi Shakya 2 1 Department of Bioinformatics, 2 Department of Mathematics, MANIT, Bhopal, MP, India; Pallavi Chauhan - Email: pallavi.chauhan2006@gmail.com;
Homology Modeling of Mouse orphan G-protein coupled receptors Q99MX9 and G2A
 Quality in Primary Care (2016) 24 (2): 49-57 2016 Insight Medical Publishing Group Research Article Homology Modeling of Mouse orphan G-protein Research Article Open Access coupled receptors Q99MX9 and
Quality in Primary Care (2016) 24 (2): 49-57 2016 Insight Medical Publishing Group Research Article Homology Modeling of Mouse orphan G-protein Research Article Open Access coupled receptors Q99MX9 and
Molecular Docking Study of Some Novel Nitroimidazo[1,2-b]pyridazine
![Molecular Docking Study of Some Novel Nitroimidazo[1,2-b]pyridazine Molecular Docking Study of Some Novel Nitroimidazo[1,2-b]pyridazine](/thumbs/95/125396186.jpg) DOI:10.7598/cst2016.1227 Chemical Science Transactions ISSN:2278-3458 2016, 5(3), 700-710 RESEARCH ARTICLE Molecular Docking Study of Some Novel Nitroimidazo[1,2-b]pyridazine based Heterocyclics on Methicillin
DOI:10.7598/cst2016.1227 Chemical Science Transactions ISSN:2278-3458 2016, 5(3), 700-710 RESEARCH ARTICLE Molecular Docking Study of Some Novel Nitroimidazo[1,2-b]pyridazine based Heterocyclics on Methicillin
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Unraveling the effects of amino acid substitutions
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Unraveling the effects of amino acid substitutions
Rational Drug Designing for Drug Target Alanine Racemase (Alr) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Infectious Diseases Volume 8 Number 1 Rational Drug Designing for Drug Target Alanine Racemase (Alr) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis S Kushwaha, P Chauhan Citation S Kushwaha,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Infectious Diseases Volume 8 Number 1 Rational Drug Designing for Drug Target Alanine Racemase (Alr) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis S Kushwaha, P Chauhan Citation S Kushwaha,
STRUCTURE, DYNAMICS AND INTERACTIONS OF PROTEINS BY NMR SPECTROSCOPY
 STRUCTURE, DYNAMICS AND INTERACTIONS OF PROTEINS BY NMR SPECTROSCOPY Constantin T. Craescu INSERM & Institut Curie - Recherche Orsay, France A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE Chemical composition
STRUCTURE, DYNAMICS AND INTERACTIONS OF PROTEINS BY NMR SPECTROSCOPY Constantin T. Craescu INSERM & Institut Curie - Recherche Orsay, France A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE Chemical composition
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London)
 BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) SCHOOL OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES M.Sc. EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS ON: Postgraduate Certificate in Principles of Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) SCHOOL OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES M.Sc. EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS ON: Postgraduate Certificate in Principles of Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology
Supplementary information for Small molecule inhibitors block Gas6-inducible TAM activation and tumorigenicity
 Supplementary information for Small molecule inhibitors block Gas6-inducible TAM activation and tumorigenicity Stanley G. Kimani 1 *, Sushil Kumar 1 *, Nitu Bansal 2 *, Kamalendra Singh 3, Vladyslav Kholodovych
Supplementary information for Small molecule inhibitors block Gas6-inducible TAM activation and tumorigenicity Stanley G. Kimani 1 *, Sushil Kumar 1 *, Nitu Bansal 2 *, Kamalendra Singh 3, Vladyslav Kholodovych
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Structure of a tyrosyl-trna synthetase splicing factor bound to a group I intron RNA Paul J. Paukstelis 1, Jui-Hui Chen 2, Elaine Chase 2, Alan M. Lambowitz 1,*, and Barbara L. Golden 2,*,. 1 Institute
Structure of a tyrosyl-trna synthetase splicing factor bound to a group I intron RNA Paul J. Paukstelis 1, Jui-Hui Chen 2, Elaine Chase 2, Alan M. Lambowitz 1,*, and Barbara L. Golden 2,*,. 1 Institute
Algorithms in Bioinformatics ONE Transcription Translation
 Algorithms in Bioinformatics ONE Transcription Translation Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University sami.khuri@sjsu.edu Biology Review DNA RNA Proteins Central Dogma Transcription
Algorithms in Bioinformatics ONE Transcription Translation Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University sami.khuri@sjsu.edu Biology Review DNA RNA Proteins Central Dogma Transcription
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 3 v Nucleic acids Ø Polymers specialized for the storage transmission and use of genetic information Ø Two types DNA
 AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 3 v Nucleic acids Ø Polymers specialized for the storage transmission and use of genetic information Ø Two types DNA Encodes hereditary information Used to specify the amino
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 3 v Nucleic acids Ø Polymers specialized for the storage transmission and use of genetic information Ø Two types DNA Encodes hereditary information Used to specify the amino
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) DNA and RNA Structure
 Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) DNA and RNA Structure Importance of DNA/RNA 3D Structure Nucleic acids are essential materials found in all living organisms. Their main function is to maintain and transmit
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) DNA and RNA Structure Importance of DNA/RNA 3D Structure Nucleic acids are essential materials found in all living organisms. Their main function is to maintain and transmit
Structural bioinformatics
 Structural bioinformatics Why structures? The representation of the molecules in 3D is more informative New properties of the molecules are revealed, which can not be detected by sequences Eran Eyal Plant
Structural bioinformatics Why structures? The representation of the molecules in 3D is more informative New properties of the molecules are revealed, which can not be detected by sequences Eran Eyal Plant
Protein-Protein Docking
 Protein-Protein Docking Goal: Given two protein structures, predict how they form a complex Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University CS597A, Fall 2005 Applications: Quaternary structure prediction Protein
Protein-Protein Docking Goal: Given two protein structures, predict how they form a complex Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University CS597A, Fall 2005 Applications: Quaternary structure prediction Protein
Computational Methods for Protein Structure Prediction
 Computational Methods for Protein Structure Prediction Ying Xu 2017/12/6 1 Outline introduction to protein structures the problem of protein structure prediction why it is possible to predict protein structures
Computational Methods for Protein Structure Prediction Ying Xu 2017/12/6 1 Outline introduction to protein structures the problem of protein structure prediction why it is possible to predict protein structures
Protocol S1: Supporting Information
 Protocol S1: Supporting Information Basis for the specificity of the kinase domain of Abl for peptide substrates The crystal structures reported in this work were obtained using two different ATP analog-peptide
Protocol S1: Supporting Information Basis for the specificity of the kinase domain of Abl for peptide substrates The crystal structures reported in this work were obtained using two different ATP analog-peptide
Protein 3D Structure Prediction
 Protein 3D Structure Prediction Michael Tress CNIO ?? MREYKLVVLGSGGVGKSALTVQFVQGIFVDE YDPTIEDSYRKQVEVDCQQCMLEILDTAGTE QFTAMRDLYMKNGQGFALVYSITAQSTFNDL QDLREQILRVKDTEDVPMILVGNKCDLEDER VVGKEQGQNLARQWCNCAFLESSAKSKINVN
Protein 3D Structure Prediction Michael Tress CNIO ?? MREYKLVVLGSGGVGKSALTVQFVQGIFVDE YDPTIEDSYRKQVEVDCQQCMLEILDTAGTE QFTAMRDLYMKNGQGFALVYSITAQSTFNDL QDLREQILRVKDTEDVPMILVGNKCDLEDER VVGKEQGQNLARQWCNCAFLESSAKSKINVN
X-ray structures of fructosyl peptide oxidases revealing residues responsible for gating oxygen access in the oxidative half reaction
 X-ray structures of fructosyl peptide oxidases revealing residues responsible for gating oxygen access in the oxidative half reaction Tomohisa Shimasaki 1, Hiromi Yoshida 2, Shigehiro Kamitori 2 & Koji
X-ray structures of fructosyl peptide oxidases revealing residues responsible for gating oxygen access in the oxidative half reaction Tomohisa Shimasaki 1, Hiromi Yoshida 2, Shigehiro Kamitori 2 & Koji
Phytopathogenic bacteria. review of arms race Effector-triggered immunity Effector diversification
 Phytopathogenic bacteria review of arms race Effector-triggered immunity Effector diversification Arms race of plant-pathogen interactions plants have different layers of immunity 1 st layer: PAMP-triggered
Phytopathogenic bacteria review of arms race Effector-triggered immunity Effector diversification Arms race of plant-pathogen interactions plants have different layers of immunity 1 st layer: PAMP-triggered
Molecular Modeling Lecture 8. Local structure Database search Multiple alignment Automated homology modeling
 Molecular Modeling 2018 -- Lecture 8 Local structure Database search Multiple alignment Automated homology modeling An exception to the no-insertions-in-helix rule Actual structures (myosin)! prolines
Molecular Modeling 2018 -- Lecture 8 Local structure Database search Multiple alignment Automated homology modeling An exception to the no-insertions-in-helix rule Actual structures (myosin)! prolines
Ligand docking and binding site analysis with pymol and autodock/vina
 International Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4 (2) (2015) 168-177 www.sciencepubco.com/index.php/ijbas Science Publishing Corporation doi: 10.14419/ijbas.v4i2.4123 Research Paper Ligand docking
International Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4 (2) (2015) 168-177 www.sciencepubco.com/index.php/ijbas Science Publishing Corporation doi: 10.14419/ijbas.v4i2.4123 Research Paper Ligand docking
Outline. Background. Background. Background and past work Introduction to present work ResultsandDiscussion Conclusions Perspectives BIOINFORMATICS
 Galactosemia Foundation 2012 Conference Breakout Session G July 20th, 2012, 14:15 15:15 Computational Biology Strategy for the Development of Ligands of GALK Enzyme as Potential Drugs for People with Classic
Galactosemia Foundation 2012 Conference Breakout Session G July 20th, 2012, 14:15 15:15 Computational Biology Strategy for the Development of Ligands of GALK Enzyme as Potential Drugs for People with Classic
Protein-Ligand Analysis with SID
 Protein-Ligand Analysis with SID A new post-simulation analysis tool Dmitry Lupyan, PhD Understanding molecular processes with MD Drug discovery and design Protein-protein interactions + Protein-DNA interactions
Protein-Ligand Analysis with SID A new post-simulation analysis tool Dmitry Lupyan, PhD Understanding molecular processes with MD Drug discovery and design Protein-protein interactions + Protein-DNA interactions
In silico analysis of onion chitinases using transcriptome data
 www.bioinformation.net Volume 14(8) Hypothesis In silico analysis of onion chitinases using transcriptome data Rupesh Kumar Mohapatra 1 & Satyabrata Nanda 1,2* 1Center for Biotechnology, Siksha O Anusandhan
www.bioinformation.net Volume 14(8) Hypothesis In silico analysis of onion chitinases using transcriptome data Rupesh Kumar Mohapatra 1 & Satyabrata Nanda 1,2* 1Center for Biotechnology, Siksha O Anusandhan
CSE : Computational Issues in Molecular Biology. Lecture 19. Spring 2004
 CSE 397-497: Computational Issues in Molecular Biology Lecture 19 Spring 2004-1- Protein structure Primary structure of protein is determined by number and order of amino acids within polypeptide chain.
CSE 397-497: Computational Issues in Molecular Biology Lecture 19 Spring 2004-1- Protein structure Primary structure of protein is determined by number and order of amino acids within polypeptide chain.
Clamping down on pathogenic bacteria how to shut down a key DNA polymerase complex
 Clamping down on pathogenic bacteria how to shut down a key DNA polymerase complex Bacterial DNA-replication machinery Pathogenic bacteria that are resistant to the current armoury of antibiotics are an
Clamping down on pathogenic bacteria how to shut down a key DNA polymerase complex Bacterial DNA-replication machinery Pathogenic bacteria that are resistant to the current armoury of antibiotics are an
Prediction of Protein-Protein Binding Sites and Epitope Mapping. Copyright 2017 Chemical Computing Group ULC All Rights Reserved.
 Prediction of Protein-Protein Binding Sites and Epitope Mapping Epitope Mapping Antibodies interact with antigens at epitopes Epitope is collection residues on antigen Continuous (sequence) or non-continuous
Prediction of Protein-Protein Binding Sites and Epitope Mapping Epitope Mapping Antibodies interact with antigens at epitopes Epitope is collection residues on antigen Continuous (sequence) or non-continuous
Sequence analysis and homology modeling of peroxidase from Medicago sativa
 www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 8(20) Sequence analysis and homology modeling of peroxidase from Medicago sativa Vinita Hooda 1 *, Prasada babu Gundala 2 & Paramageetham Chinthala 3 1Department
www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 8(20) Sequence analysis and homology modeling of peroxidase from Medicago sativa Vinita Hooda 1 *, Prasada babu Gundala 2 & Paramageetham Chinthala 3 1Department
Solutions to 7.02 Quiz II 10/27/05
 Solutions to 7.02 Quiz II 10/27/05 Class Average = 83 Standard Deviation = 9 Range Grade % 87-100 A 43 74-86 B 39 55-73 C 17 > 54 D 1 Question 1 (56 points) While studying deep sea bacteria, you discover
Solutions to 7.02 Quiz II 10/27/05 Class Average = 83 Standard Deviation = 9 Range Grade % 87-100 A 43 74-86 B 39 55-73 C 17 > 54 D 1 Question 1 (56 points) While studying deep sea bacteria, you discover
Structure Prediction. Modelado de proteínas por homología GPSRYIV. Master Dianas Terapéuticas en Señalización Celular: Investigación y Desarrollo
 Master Dianas Terapéuticas en Señalización Celular: Investigación y Desarrollo Modelado de proteínas por homología Federico Gago (federico.gago@uah.es) Departamento de Farmacología Structure Prediction
Master Dianas Terapéuticas en Señalización Celular: Investigación y Desarrollo Modelado de proteínas por homología Federico Gago (federico.gago@uah.es) Departamento de Farmacología Structure Prediction
Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
Bioinformation by Biomedical Informatics Publishing Group
 Algorithm to find distant repeats in a single protein sequence Nirjhar Banerjee 1, Rangarajan Sarani 1, Chellamuthu Vasuki Ranjani 1, Govindaraj Sowmiya 1, Daliah Michael 1, Narayanasamy Balakrishnan 2,
Algorithm to find distant repeats in a single protein sequence Nirjhar Banerjee 1, Rangarajan Sarani 1, Chellamuthu Vasuki Ranjani 1, Govindaraj Sowmiya 1, Daliah Michael 1, Narayanasamy Balakrishnan 2,
Homology Modelling. Thomas Holberg Blicher NNF Center for Protein Research University of Copenhagen
 Homology Modelling Thomas Holberg Blicher NNF Center for Protein Research University of Copenhagen Why are Protein Structures so Interesting? They provide a detailed picture of interesting biological features,
Homology Modelling Thomas Holberg Blicher NNF Center for Protein Research University of Copenhagen Why are Protein Structures so Interesting? They provide a detailed picture of interesting biological features,
2018 Protein Modeling Exam Key
 2018 Protein Modeling Exam Key Multiple Choice: 1. Which of the following amino acids has a negative charge at ph 7? a. Gln b. Glu c. Ser d. Cys 2. Which of the following is an example of secondary structure?
2018 Protein Modeling Exam Key Multiple Choice: 1. Which of the following amino acids has a negative charge at ph 7? a. Gln b. Glu c. Ser d. Cys 2. Which of the following is an example of secondary structure?
ProBiS: a web server for detection of structurally similar protein binding sites
 W436 W440 Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, Vol. 38, Web Server issue Published online 26 May 2010 doi:10.1093/nar/gkq479 ProBiS: a web server for detection of structurally similar protein binding sites Janez
W436 W440 Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, Vol. 38, Web Server issue Published online 26 May 2010 doi:10.1093/nar/gkq479 ProBiS: a web server for detection of structurally similar protein binding sites Janez
PROTEINS & NUCLEIC ACIDS
 Chapter 3 Part 2 The Molecules of Cells PROTEINS & NUCLEIC ACIDS Lecture by Dr. Fernando Prince 3.11 Nucleic Acids are the blueprints of life Proteins are the machines of life We have already learned that
Chapter 3 Part 2 The Molecules of Cells PROTEINS & NUCLEIC ACIDS Lecture by Dr. Fernando Prince 3.11 Nucleic Acids are the blueprints of life Proteins are the machines of life We have already learned that
Protein Structure Databases, cont. 11/09/05
 11/9/05 Protein Structure Databases (continued) Prediction & Modeling Bioinformatics Seminars Nov 10 Thurs 3:40 Com S Seminar in 223 Atanasoff Computational Epidemiology Armin R. Mikler, Univ. North Texas
11/9/05 Protein Structure Databases (continued) Prediction & Modeling Bioinformatics Seminars Nov 10 Thurs 3:40 Com S Seminar in 223 Atanasoff Computational Epidemiology Armin R. Mikler, Univ. North Texas
Information Page. A List of Secondary Structure Prediction Servers
 Introduction to Bioinformatics Information Page Chapter 5, page 1/4, 2012/11/09 A List of Secondary Structure Prediction Servers Name APSSP PredictProtein GOR IV Jpred 3 CFSSP NNPREDICT JUFO BCM Search
Introduction to Bioinformatics Information Page Chapter 5, page 1/4, 2012/11/09 A List of Secondary Structure Prediction Servers Name APSSP PredictProtein GOR IV Jpred 3 CFSSP NNPREDICT JUFO BCM Search
Virtual screening of ABCC1 transporter nucleotidebinding domains as a therapeutic target in multidrug resistant cancer
 www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 8(19) Virtual screening of ABCC1 transporter nucleotidebinding domains as a therapeutic target in multidrug resistant cancer Kanin Rungsardthong, Sergio Mares-
www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 8(19) Virtual screening of ABCC1 transporter nucleotidebinding domains as a therapeutic target in multidrug resistant cancer Kanin Rungsardthong, Sergio Mares-
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
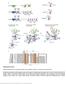 Supplementary Figure 1 Domain architecture and conformational states of the decapping complex, as revealed by structural studies. (a) Domain organization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp) and Saccharomyces
Supplementary Figure 1 Domain architecture and conformational states of the decapping complex, as revealed by structural studies. (a) Domain organization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp) and Saccharomyces
Highly-efficient T4 DNA ligase-based SNP analysis using a ligation fragment containing a modified nucleobase at the end
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Highly-efficient T4 DNA ligase-based SNP analysis using
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Highly-efficient T4 DNA ligase-based SNP analysis using
NSave Nature to Survive
 ISSN: 0973-7049 : Special issue, Vol. 1; 151-157; 2010 NSave Nature to Survive APPLICATION OF BIOINFORMATICS IN GREEN ENERGY TECHNOLOGY: JATROPHA CURCAS ACCASE ENZYME AS CASE STUDY Raghunath Satpathy et
ISSN: 0973-7049 : Special issue, Vol. 1; 151-157; 2010 NSave Nature to Survive APPLICATION OF BIOINFORMATICS IN GREEN ENERGY TECHNOLOGY: JATROPHA CURCAS ACCASE ENZYME AS CASE STUDY Raghunath Satpathy et
Navigating BioLuminate for PyMOL Users: A Practical Approach. 2nd European Life Science Bootcamp Ana Negri, PhD
 Navigating BioLuminate for PyMOL Users: A Practical Approach 2nd European Life Science Bootcamp Ana Negri, PhD Agenda Introduction to BioLuminate PyMOL-like features in the BioLuminate interface: Basic
Navigating BioLuminate for PyMOL Users: A Practical Approach 2nd European Life Science Bootcamp Ana Negri, PhD Agenda Introduction to BioLuminate PyMOL-like features in the BioLuminate interface: Basic
Bacteriophages get a foothold on their prey
 Bacteriophages get a foothold on their prey Long and thin, the receptor-binding needle of bacteriophage T4 Bacterial viruses, bacteriophages or phages, have served as a tool to decipher principles of molecular
Bacteriophages get a foothold on their prey Long and thin, the receptor-binding needle of bacteriophage T4 Bacterial viruses, bacteriophages or phages, have served as a tool to decipher principles of molecular
If you wish to have extra practice with swiss pdb viewer or to familiarize yourself with how to use the program here is a tutorial:
 Name (s): Swiss PDB viewer assignment chapter 4. If you wish to have extra practice with swiss pdb viewer or to familiarize yourself with how to use the program here is a tutorial: http://spdbv.vital-it.ch/themolecularlevel/spvtut/index.html
Name (s): Swiss PDB viewer assignment chapter 4. If you wish to have extra practice with swiss pdb viewer or to familiarize yourself with how to use the program here is a tutorial: http://spdbv.vital-it.ch/themolecularlevel/spvtut/index.html
Authors: Antonio Macchiarulo, Antimo Gioiello, Charles Thomas, Thijs W.H. Pols, Roberto Nuti,
 Supporting Information. Probing the Binding Site of Bile Acids in TGR5 Authors: Antonio Macchiarulo, Antimo Gioiello, Charles Thomas, Thijs W.H. Pols, Roberto Nuti, Cristina Ferrari, Nicola Giacchè, Francesca
Supporting Information. Probing the Binding Site of Bile Acids in TGR5 Authors: Antonio Macchiarulo, Antimo Gioiello, Charles Thomas, Thijs W.H. Pols, Roberto Nuti, Cristina Ferrari, Nicola Giacchè, Francesca
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
Chapter 8 DNA Recognition in Prokaryotes by Helix-Turn-Helix Motifs
 Chapter 8 DNA Recognition in Prokaryotes by Helix-Turn-Helix Motifs 1. Helix-turn-helix proteins 2. Zinc finger proteins 3. Leucine zipper proteins 4. Beta-scaffold factors 5. Others λ-repressor AND CRO
Chapter 8 DNA Recognition in Prokaryotes by Helix-Turn-Helix Motifs 1. Helix-turn-helix proteins 2. Zinc finger proteins 3. Leucine zipper proteins 4. Beta-scaffold factors 5. Others λ-repressor AND CRO
Specificity: Induced Fit
 Specificity: Induced Fit Conformational changes may occur upon ligand binding (Daniel Koshland in 1958) This adaptation is called the induced fit Induced fit allows for tighter binding of the ligand Induced
Specificity: Induced Fit Conformational changes may occur upon ligand binding (Daniel Koshland in 1958) This adaptation is called the induced fit Induced fit allows for tighter binding of the ligand Induced
Molecular docking studies on inhibition of Stat3 dimerization by curcumin natural derivatives and its conjugates with amino acids
 www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 8(20) Molecular docking studies on inhibition of Stat3 dimerization by curcumin natural derivatives and its conjugates with amino acids Anil Kumar 1 & Utpal Bora
www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 8(20) Molecular docking studies on inhibition of Stat3 dimerization by curcumin natural derivatives and its conjugates with amino acids Anil Kumar 1 & Utpal Bora
Interaction of nalidixic acid and ciprofloxacin with wild type and mutated quinolone-resistance-determining region of DNA gyrase A
 Indian Journal of Biochemistry & Biophysics Vol. 46, April 2009, pp 147-153 Interaction of nalidixic acid and ciprofloxacin with wild type and mutated quinolone-resistance-determining region of DNA gyrase
Indian Journal of Biochemistry & Biophysics Vol. 46, April 2009, pp 147-153 Interaction of nalidixic acid and ciprofloxacin with wild type and mutated quinolone-resistance-determining region of DNA gyrase
Structure and Function of the First Full-Length Murein Peptide Ligase (Mpl) Cell Wall Recycling Protein
 Paper Presentation PLoS ONE 2011 Structure and Function of the First Full-Length Murein Peptide Ligase (Mpl) Cell Wall Recycling Protein Debanu Das, Mireille Herve, Julie Feuerhelm, etc. and Dominique
Paper Presentation PLoS ONE 2011 Structure and Function of the First Full-Length Murein Peptide Ligase (Mpl) Cell Wall Recycling Protein Debanu Das, Mireille Herve, Julie Feuerhelm, etc. and Dominique
MOLECULAR DOCKING STUDIES FOR IDENTIFICATION OF POTENT PHOSPHOINOSITIDE 3-KINASES (PI3KS) INHIBITORS
 CHAPTER 7 MLECULAR DCKIG STUDIES FR IDETIFICATI F PTET PHSPHISITIDE 3-KIASES (PI3KS) IHIBITRS 7.1 Introduction Phosphoinositide 3 kinases (PI3Ks) constitute a class of enzymes that catalyse phosphorylation
CHAPTER 7 MLECULAR DCKIG STUDIES FR IDETIFICATI F PTET PHSPHISITIDE 3-KIASES (PI3KS) IHIBITRS 7.1 Introduction Phosphoinositide 3 kinases (PI3Ks) constitute a class of enzymes that catalyse phosphorylation
Virtual bond representation
 Today s subjects: Virtual bond representation Coordination number Contact maps Sidechain packing: is it an instrumental way of selecting and consolidating a fold? ASA of proteins Interatomic distances
Today s subjects: Virtual bond representation Coordination number Contact maps Sidechain packing: is it an instrumental way of selecting and consolidating a fold? ASA of proteins Interatomic distances
CMSE 520 BIOMOLECULAR STRUCTURE, FUNCTION AND DYNAMICS
 CMSE 520 BIOMOLECULAR STRUCTURE, FUNCTION AND DYNAMICS (Computational Structural Biology) OUTLINE Review: Molecular biology Proteins: structure, conformation and function(5 lectures) Generalized coordinates,
CMSE 520 BIOMOLECULAR STRUCTURE, FUNCTION AND DYNAMICS (Computational Structural Biology) OUTLINE Review: Molecular biology Proteins: structure, conformation and function(5 lectures) Generalized coordinates,
Solving Structure Based Design Problems using Discovery Studio 1.7 Building a Flexible Docking Protocol
 Solving Structure Based Design Problems using Discovery Studio 1.7 Building a Flexible Docking Protocol C. M. (Venkat) Venkatachalam Fellow, Life Sciences Dipesh Risal Marketing, Life Sciences Overview
Solving Structure Based Design Problems using Discovery Studio 1.7 Building a Flexible Docking Protocol C. M. (Venkat) Venkatachalam Fellow, Life Sciences Dipesh Risal Marketing, Life Sciences Overview
2/23/16. Protein-Protein Interactions. Protein Interactions. Protein-Protein Interactions: The Interactome
 Protein-Protein Interactions Protein Interactions A Protein may interact with: Other proteins Nucleic Acids Small molecules Protein-Protein Interactions: The Interactome Experimental methods: Mass Spec,
Protein-Protein Interactions Protein Interactions A Protein may interact with: Other proteins Nucleic Acids Small molecules Protein-Protein Interactions: The Interactome Experimental methods: Mass Spec,
Fundamentals of Protein Structure
 Outline Fundamentals of Protein Structure Yu (Julie) Chen and Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University CS597A, Fall 2005 Protein structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Forces and factors Levels
Outline Fundamentals of Protein Structure Yu (Julie) Chen and Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University CS597A, Fall 2005 Protein structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Forces and factors Levels
Bioinformatics Prof. M. Michael Gromiha Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 5a Protein sequence databases
 Bioinformatics Prof. M. Michael Gromiha Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 5a Protein sequence databases In this lecture, we will mainly discuss on Protein Sequence
Bioinformatics Prof. M. Michael Gromiha Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 5a Protein sequence databases In this lecture, we will mainly discuss on Protein Sequence
Introduction to Bioinformatics
 Introduction to Bioinformatics http://1.51.212.243/bioinfo.html Dr. rer. nat. Jing Gong Cancer Research Center School of Medicine, Shandong University 2011.10.19 1 Chapter 4 Structure 2 Protein Structure
Introduction to Bioinformatics http://1.51.212.243/bioinfo.html Dr. rer. nat. Jing Gong Cancer Research Center School of Medicine, Shandong University 2011.10.19 1 Chapter 4 Structure 2 Protein Structure
Nanobiotechnology. Place: IOP 1 st Meeting Room Time: 9:30-12:00. Reference: Review Papers. Grade: 50% midterm, 50% final.
 Nanobiotechnology Place: IOP 1 st Meeting Room Time: 9:30-12:00 Reference: Review Papers Grade: 50% midterm, 50% final Midterm: 5/15 History Atom Earth, Air, Water Fire SEM: 20-40 nm Silver 66.2% Gold
Nanobiotechnology Place: IOP 1 st Meeting Room Time: 9:30-12:00 Reference: Review Papers Grade: 50% midterm, 50% final Midterm: 5/15 History Atom Earth, Air, Water Fire SEM: 20-40 nm Silver 66.2% Gold
CABIOS. Objectively judging the quality of a protein structure from a Ramachandran plot. Rob W.W.Hooft, Chris Sander and Gerrit Vriend
 CABIOS Vol. 13 no. 4 1997 Pages 425-430 Objectively judging the quality of a protein structure from a Ramachandran plot Rob W.W.Hooft, Chris Sander and Gerrit Vriend Abstract Motivation: Statistical methods
CABIOS Vol. 13 no. 4 1997 Pages 425-430 Objectively judging the quality of a protein structure from a Ramachandran plot Rob W.W.Hooft, Chris Sander and Gerrit Vriend Abstract Motivation: Statistical methods
Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
Molecular docking based screening of a simulated HIF-1 protein model for potential inhibitors
 www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(11) Hypothesis Molecular docking based screening of a simulated HIF-1 protein model for potential inhibitors Mundla Sri Latha 3, Madhu Sudhana Saddala 1, 2 * 1Centre for
www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(11) Hypothesis Molecular docking based screening of a simulated HIF-1 protein model for potential inhibitors Mundla Sri Latha 3, Madhu Sudhana Saddala 1, 2 * 1Centre for
What s New in LigandScout 4.4
 What s New in LigandScout 4.4 What's New in LigandScout 4.4? 2D Molecule editor for convenient structure editing Binding affinity prediction and atom contribution display Automated protein binding site
What s New in LigandScout 4.4 What's New in LigandScout 4.4? 2D Molecule editor for convenient structure editing Binding affinity prediction and atom contribution display Automated protein binding site
Supplementary Information for. Structure of human tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase-2 reveals the mechanism of protein tyrosine sulfation reaction
 Supplementary Information for Structure of human tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase-2 reveals the mechanism of protein tyrosine sulfation reaction Takamasa Teramoto, Yukari Fujikawa, Yoshirou Kawaguchi, Katsuhisa
Supplementary Information for Structure of human tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase-2 reveals the mechanism of protein tyrosine sulfation reaction Takamasa Teramoto, Yukari Fujikawa, Yoshirou Kawaguchi, Katsuhisa
