SERUM PROTEIN ELECTROPHORESIS
|
|
|
- Lynn Newton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SERUM PROTEIN ELECTROPHORESIS ABD-ALLA BSC - OMDURMAN AHLIA HIGH DOPLOMA DGREE - ELZAEM EL-AZHARY FORMER HEAD OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD BANK MINISTRY OF HEALTH LABORATORY ADMINISTRATION KHARTOUM STATE MARKETING MANAGER-LAB EQP DIVISION ALGAM COMPANY FOR DRUGS & CHEMICAL LTD 1
2 Learning Objective *1- To see the electrophoresis development. *2-To know the fraction of protein component. *3-To know the function of different protein fraction. *4- To know the purpose of serum protein electrophoresis. *5- Understanding the questions can be answered with a serum protein electrophoresis. 2
3 Learning Objective *6- Know the pathological conditions on serum protein electrophoresis. *7- Know the monoclonal Gammopathies on serum protein electrophoresis. *8- To know position of a monoclonal immunoglobuline in serum protein electrophoresis. *9- To know the Oligoclonal pattern. 3
4 Zone Electrophoresis *The technique of zone electrophoresis has been known since 1930 by Tiselius. Initially base on the use of liquid medium, then it mature into application on solid media (zone electrophoresis) :filter paper and then cellulose acetate membrane were use to stabilize the buffer. *The electrical current flow cause the various protein particles to migrate from their point of application, into zones varying with the proteins mobility and directly related to its electrical charge. 4
5 Zone Electrophoresis *In the middle of 80s.zone electrophoresis was considerably improved by the successive introduction of agar and agarose gel. *The interest Of agarose lies above all in the initial transiency of the gel which enables to detect very faint band (e.g. early monoclonal bands)and is essential for an efficient quantitative estimate by densitometry. 5
6 Zone Electrophoresis *Most technique available in the market employ 0.5 or 1% agarose gel, that is very close to ideal liquid-medium electrophoresis system. *Low agarose concentration leads to a large pore gel which enable free migration with minimum distortion especially for high molecular weight protein and lipid molecules. 6
7 Zone Electrophoresis *There are other methods which use gels with a high resolution like polyacrylamide gels which also separate by molecular filtration according to electrical charge. *Serum protein electrophoresis remain very commonly used analytical method in the field of clinical chemistry its performed on: 7
8 Zone Electrophoresis *1- cellulose acetate medium and followed by a staining procedure in ponceau red solution. *2- increasingly on standard agarose medium or some time in high resolution agarose gel followed by staining procedure in amidoblack solution which is more sensitive than ponceau red stain and is ideal for the detection of low concentration Gammopathies. 8
9 PROTEIN ELECTROPHORESIS INTERPRETATION *The electrophoretic separation of human serum,routinely perform in alkaline solution, result in 5 to 6 clearly defined fraction, depending on the medium used: *The albumin fraction showing biochemical homogeneity is the most important among the serum proteins. *Four group of migrating globulins,(α1,α2,β and γ globulins)which group together several protein having very different function and whose quantitative variation provide invaluable information for investigation for various organ specific diseases. 9
10 PROTEIN ELECTROPHORESIS INTERPRETATION * Liver synthesizing :the protein migrating in α1,α2 and β zone, * Lymphoid tissue: synthesizing immunity protein which essentially migrate in the γ globulins zone. *The interpretation of any protein electrophoresis presuppose the knowledge of the physiopathological variation in serum specific protein and shall be necessarily complemented by quantification of serum total protein. 10
11 THE FRACTION OF PROTEIN COMPONANT *1-The albumin *2-α1 globulins: orosomucoid, α1 antitrypsin, α1 antichymotrypsin. *3- α2 globulins: haptoglobin, α2 macroglobulin, ceruleoplasmin,cg globulin, α lipoprotein. *4-β1 β2 globulins: transferrin,hemopexin,c3 complement, β lipoprotein. *5- γ globulins :IgG,IgA,IgM,(IgD, IgE) 11
12 FUNCTION OF ALBUMIN *1- Maintain the oncotic pressure. *2- transports thyroid hormones. *3- transport other hormones,in particulate ones that are fat-soluble. *4-transport fatty acids. *5- transport unconjugated bilirubin. *6- transport many drugs. *7- competitively bind calcium ions. *8- serum albumin as a negative a cute-phase protein, is down regulated in inflammatory state. *9- prevent photo degradation of folic acid. 12
13 Orosomucoid (α1type ) *OROSOMUCOID (ORM) or alpha-1- acid glycoprotein : *acute phase protein. *has normal plasma concentration between mg/ml. *plasma level are effected by pregnancy,burns, certain drugs and certain disease particularly HIV. *IT IS function is to act as a carrier of basic and neutrally charge lipophilic compound. *In medicine it is known as the primary carried of basic (positively charged). 13
14 *ALPHA 1 ANTITRIPSIN (A1AT) *ALPHA -1- ANTICHYMOTRYPSIN * ALPHA 1 ANTITRIPSIN (A1AT): *IT IS inhibit wide variety of proteases. * protect tissues from enzymes of inflammatory cell especially neutrophil elastase. *It is from g/l. *alpha -1- ANTICHYMOTRYPSIN: *act as acute phase protein that induced during inflammation. inhibit the activity of certain enzyme called protease such as : A)cathepsin G that found in neutrophil. B)chymases found in mast cell 14
15 *ALPHA-2-HAPTOGLOBIN *ALPHA-2-MACROGLOULIN *Haptoglobin function is to : *bind free plasma hemoglobin,which allow degradative enzyme to gain access to the hemoglobin. *preventing loss of iron through the kidneys * protecting the kidney from damage by hemoglobin. *Alpha 2 macroglobulin : *act as an antiprotease and is able to inactivate an enormous variety of proteinasea. *It inhibitor of fibrinolysis by inhibiting plasmin and kallikrein, it is function as an inhibitor of coagulation by inhibiting thrombin. *Act as carrier protein it can bind to numerous growth factor and cytokines. 15
16 *CERULEOPLASMIN *GC GLOBULIN *LIPOPROTEIN(α2Type ) *ceruleoplasmin : *enzyme carries more than 95% of total copper in healthy human plasma the rest is accounted for macroglobulin. *It is inhibits copper-dependant oxidase activity, which associated with possible oxidation of Fe2+,which assisting in it is transport in the plasma in association with transferrin. *GC-globulin(Vitamin D binding protein) *It is a multifunctional protein found on the surface of many cell type. * bind to vitamin D and it is plasma metabolites and transports them to the target tissue *LIPOPROTEIN: is a biochemical assembly that contains both proteins and lipids bound to protein,which allow fats to move through the water inside and outside of the cell. *the proteins serve to emulsify, transports, structural protein,antigens, adhesions and toxins are lipoproteins 16
17 TRANSFERRIN, HEMOPEXIN, C3 COMPLEMENT(β1 β2 globulins) *Transferrin: an iron-binding blood plasma glycoprotein that control the level of free iron in the biological fluids. *Hemopexin: it bind the heme with the highest affinity of any known proteins its function is scavenging the heme release or lost by the turnover of heme proteins such as hemoglobin and protects the body from the oxidative damage that free heme can cause. *C3 Complement: plays a central role in the activation of complement system. its activation is required for both classical and alternative complement activation pathway.people with C3 deficiency are susceptible to bacterial infection. 17
18 THE PATHOLOGICAL VARIATION IN SERUM TOTAL PROTEIN *The reference range for total protein is 6.5 to 8.0 g/dl in healthy adult,this value is increased by around 0.3 g/dl in plasma as it contain fibrinogen and the coagulation proteins. The total protein at birth does not exceed 4.0 to 6.0 g/dl but albumin to globulin ratio (usually between 1.2 and 1.8) is equal in children and adult. *Variation in proteinemia will result from: *1-Fluctuations in the blood volume. *2- Protein synthesis abnormality. 18
19 HYPERPROTEINEMIA *HYPERPROTEINEMIA : characterize by, The increase of the total circulating protein volume: *polyclonal or monoclonal hyper γ globulinemia. The decrease in vascular water: hemoconcentration, *Nutritional supply deficiency *Liquid loss(heat stroke,diarrhea,vomiting) 19
20 HYPOPROTEINEMIA Characterized by: * The decrease in total circulating protein volume. -Nutritional supply deficiency(malnutrition) -Absorption defect. -Protein deficiency (coetaneous,renal,intestinal). -Lack of protein synthesis in liver. *An increase in vascular water hemodilution -Water over loading. *As a general rule, any serum total protein of less than 6.0 g/dl or greater than 8.0 g/dl should be complemented by a serum electrophoresis 20
21 What s the purpose of serum protein electrophoresis? *To detect abnormalities in serum proteins: *Quantitative: increased or decreased of some fractions *Qualitative: presence of abnormal fraction(s) 21
22 Several questions can be answered with a serum protein electrophoresis confirm a pathological diagnosis in association with other parameters: inflammation, hepatitis, cirrhotic or nephrotic profile Identify the presence of a monoclonal immunoglobulin when a myeloma is suspected with clinical signs Allow an early detection of asymptomatic myeloma To monitor the evolution of malignant disease or follow the efficiency of immunosuppressive treatment 22
23 Normal serum Gaussian aspect in gamma & No increase or additional deformation/peak in gamma, beta 1, beta 2 and alpha 2 Alb α1 α2 β1 β2 γ 23
24 Quantitative changes in serum protein electrophoresis Flags allow to easily detect quantitative abnormalities 24
25 Pathological conditions on serum protein electrophoresis 25
26 Multiple Pathologies screening TP, g/dl Alb α-1 α-2 β Split β β-γ bridge γ Acute inflammatory pattern and Hyper-estrogenism pattern Chronic inflammatory disorders Hypergammaglobulinemia + Liver disease/cirrhosis Nephrotic syndrome Protein-losing pattern/malnutrition Autoimmune reactions Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency Hypogammaglobulinemia Hemolytic anemias/congenital hemoglobin defects Total protein, Albumin, alpha 1 & 2 zones, beta zone, gamma zone (gammaglobulins ) 26
27 Inflammation Acute inflammation associated with : - increase of α1 and α2 globulins due to an increase of: orosomucoid, alpha-1 antitrypsin and haptoglobin - decrease of albumin Chronic inflammation associated with : - increase of alpha-1, alpha-2 globulins - polyclonal increase of gamma globulins - decrease of albumin 27
28 Acute Inflammation HPT A1AT ORO Alb α1 α2 β1 β2 γ Complementary immunofixation/immunotyping not AHMED MOHAMED required. Recheck thenazar electrophoresis in 3 months 28
29 Chronic Inflammation Increase of polyclonal Ig A in beta 2 and G in gamma Alb α1 α2 β1 β2 γ Complementary immunofixation/immunotyping not AHMED MOHAMED required. Recheck thenazar electrophoresis in 3 months 29
30 Nephrotic syndrome This disease is associated with : A decrease of albumin, alpha-1 globulins An increase of alpha-2 globulins (due to an increase of alpha-2 macroglobulin) On capillary systems: lipoproteins migrate inside albumin fraction no increase of beta globulins, but deformation of albumin fraction may occur Note: On gel: increase of alpha 2 and beta globulins (due to an increase of alpha-2 macroglobulin and alpha and beta lipoproteins in lipoid nephrosis) 30
31 Nephrotic syndrome Total protein concentration is decreased (under 60g/l or 6g/dl) Alpha 2 macroglobuline Alb α1 α2 β1 β2 γ Complementary immunofixation/ immunotyping not required ifnazar nephrotic syndrome is corroborated AHMED MOHAMED 31 by serum lipid results
32 Cirrhotic profile This disease is associated with : A polyclonal increase of beta2-gamma globulins (beta2-gamma bridge due to polyclonal increase of Ig A in beta) Hepatocellular insufficiency can also lead a decrease of albumin, alpha 1 and alpha 2 to 32
33 Beta 2 gamma bridge (Polyclonal increase of Ig A in beta 2 and Ig G in gamma) Immunotyping/Immunofixation is not required in case of known liver disease or positive liver function tests 33
34 Hypogammaglobulinemia Decrease of polyclonal immunoglobulins in gamma zone It is associated with : -Partial or total immunodeficiency - Immunosuppressive treatment - Free light chains disease or non secreting myeloma 34
35 Hypogammaglobulinemia If the clinical causes of This Hypogammaglobulinemia are unknown, it is NAZAR AHMED MOHAMED advisable to check 24h urine for Bence Jones protein. 35
36 Hypergammaglobulinemia Increase of polyclonal immunoglobulins in gamma zone It is associated with : - Inflammation - Cirrhosis - Sub acute and chronic infections 36
37 Congenital deficiency of A1AT in alpha 1 To follow this isoled alpha 1 decrease, a complementary A1AT quantification was performed. A1AT = 0.17g/L (normal ranges: g/l). Alb NAZAR α1ahmedα2 β1 β2 MOHAMED γ 37
38 Chronic inflammatory profile with underlying distortion in gamma Immunotyping/Immnofixation is required. NAZARwithin AHMED MOHAMED For repeat testing the next 3 to 6 months 38
39 Double albumin: a bisalbuminemia or something else? Possible causes : Congenital bisalbuminemia (genetic mutation) Bisalbuminemia due to acute pancreatitis: the release of pancreatic enzymes can lead to albumin splitting or Lipoproteins (check milky serum aspect) Biliary pigments (check icteric serum aspect) Due to a recent injection of X-ray contraste products in blood circulation. Ask a new sample within 4 days Some antibiotics: transitory bisalbuminemia due to drug interaction with albumin Complementary immunofixation/ immunotyping not required NAZAR AHMED MOHAMED 39
40 A Small additional fraction in albumine? Possible causes : Lipoproteins (check milky serum aspect) Biliary pigments (check icteric serum aspect) Due to a recent injection of X-ray contrast products in blood circulation. Ask a new sample within 4 days Some antibiotics: transitory bisalbuminemia due to drug interaction with albumin Capillary aging If the same phenomena is found on all analyses on the same capillary Complementary immunofixation/ NAZAR AHMED MOHAMED immunotyping not required 40
41 An additional fraction in albumin? Possible causes : Lipoproteins (check milky serum aspect) Biliary pigments (check icteric serum aspect) Due to a recent injection of X-ray contrast products in blood circulation. Ask a new sample within 4 days Some antibiotics: transitory bisalbuminemia due to drug interaction with albumin Complementary immunofixation/ NAZAR AHMED MOHAMED immunotyping not required 41
42 Lipoprotéines, biliary pigments 42
43 A Small additional fraction in alpha 1? Heterozygote phenotype of A1AT Alb α1 α2 β1 β2 γ Complementary immunofixation/ immunotyping not required 43
44 Hétérozygote phénotype of A1AT A1AT α1mohamedα2 Alb NAZAR AHMED β1 β2 γ 44
45 An additional fraction in alpha 2? Double peaks in alpha 2 in case of: - Hemolysed sample (haptoglobin-hemoglobin complex). Check the serum aspect and ask a new sample in case of hemolyzed sample - Specific phenotypes of Haptoglobin (genetic mutation) - Presence of a monoclonal immunoglobulin with anodic mobility 45
46 Hemolyzed sample Complex Hpt-Hb Alb α1 α2 β1 β2 Free Hb γ Sample not recommended by Sebia, ask a new sample 46
47 Haptoglobin phenotypes in alpha 2 zone Phenotype I - I Phenotype I - II Phenotype II - II 47
48 An additional fraction in alpha 2? If the patient is known for a gammopathy or indicates clinical signs for a gammopathy, perform an immunotyping If there is no information available for the patient, consider the alpha 2 value (in g/l or g/dl) and the context present on the electrophoretic profile If Patient alpha 2 value > Phoresis reference alpha 2 value without a context of inflammatory response, perform a immunotyping for a potential monoclonal immunoglobulin Patient alpha 2 value < Phoresis reference alpha 2 value without a context of inflammatory response, recheck the serum protein electrophoresis in 3 months If Patient alpha 2 value > Phoresis reference alpha 2 value with a context of inflammatory response, recheck the serum protein electrophoresis in 3 months 48
49 An additional fraction in alpha 2: monoclonal Ig? Patient alpha 2 value > Phoresis reference alpha 2 value (in g/l or g/dl) without a context of inflammatory response => Perform a immunotyping for a potential monoclonal immunoglobulin 49
50 An additional fraction in beta 2? Double peaks in beta 2 in case of: - Presence of fibrinogen (plasma/ serum with anti-clotting treatment). Plasma sample is not recommended, request a new sample. - Presence of a monoclonal immunoglobulin - Presence of C4 complement in case of inflammatory response - Presence of X-ray contrast products. Ask a new sample within 4 days 50
51 Fibrinogen in beta 2 (plasma or serum with anti-clotting treatment) Fibrinogen On gel electrophoresis: fibrinogen gives an extra band in the gamma fraction instead of beta 2 Alb α1 α2 β1 β2 γ IF/IT required: In both immunofixation or immunotyping, AHMED MOHAMED the antisera will not reactnazar with Fibrinogen 51
52 C4 complement in beta 2 on an acute inflammatory profile C4 Alb α1 α2 β1 β2 γ IF/IT required: In both immunofixation or immunotyping, the antisera will not react with C4 complement 52
53 C-Reactive Protein (CRP) in gamma on an acute inflammatory profile - Protidemia= 59 g/l CRP = 200mg/L IF/IT required: In both immunofixation or immunotyping, the antisera will not react with CRP 53
54 Monoclonal Gammopathies on serum protein electrophoresis 54
55 Immunoglobulin molecule Light chain (κ or λ) ~ 25 kda determine Ig type Heavy chain (γ, α, µ, δ or ε) ~ 55 kda determine Ig class (G, A, M, D or E) Disulfure bridge Each B lymphocyte, differentiated in a plasmocyte, produces an immunoglobulin (Ig) ~ 160 kda with 2 identical heavy chain and 2 identical light chain Igs are involved in the immune response against infections 55
56 Gammopathy and monoclonal immunoglobulin P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 Normal plasmocyte Secretion of a single immunoglobulin by plasmocyte at a similar rate Serum Polyclonal immunoglobulins Malignant transformation of a plasmocyte P1 P2 P3 P4 The proliferation of this malignant plasmocyte leads to an excess of his secreted immunoglobulin in the serum Serum Polyclonal immunoglobulins Monoclonal immunoglobulin 56
57 Serum protein electrophoresis and detection of monoclonal immunoglobulin Normal plasmocytes P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 Polyclonal immunoglobulins Malignant transformation of a plasmocyte Polyclonal Immunoglobulins Monoclonal immunoglobulin Qualitative and/or quantitative modifications of serum protein electrophoresis 57
58 Gammopathies characterized by the presence of a serum monoclonal immunoglobulin Symptomatic gammopathies: Multiple Myeloma (MM) Waldenström disease Non Hodgkins Lymphoma Chronic Lymphoïd Leukemia Heavy chain disease Amyloidosis Asymptomatic gammopathies: Smoldering myeloma (SM) Monoclonal Gammopathies of Undetermined Significance (MGUS) 58
59 Classification of monoclonal gammopathies MGUS Smoldering myeloma Multiple myeloma < 30 g/l > 30 g/l* No threshold Clonal bone marrow plasma cells < 10% > 10 %* > 10% End -organ damage** M-protein concentration At least one of these 2 criteria must be present ** End-organ damage: C Hyper Calcemia (Ca > 10,5mg/dL) R Renal insufficiency (Creatinine>2mg/dL) A Anemia (Hb <10g/dL) B Lytic Bone lesions Kyle & Rajkumar, 2009: Leukemia,23(1):3-9 59
60 Distribution of gammopathies for newly discovered monoclonal immunoglobulins Study Patients MGUS Multiple Myeloma Other LPS WM AL Malmö ( ) % 19% 6% 2% 1% Mayo clinic (2005) % 24% 4% 3% 11% Others 6% MGUS: Monoclonal gammopathies of undetermined significance WM: Waldenström macroglobulinemia Other LPS: Smoldering myeloma, Plasmocytoma Others: Chronic lymphoïd leucemia, non hodgkinien lymphoma.. Kyle & Rajkumar, 2006: Br J Haematol,134(6):
61 Position of a monoclonal immunoglobulin in serum protein electrophoresis Presence of a peak or distorsion in gamma Presence of an additional peak or an additional distorsion in beta 1 or beta 2 Beta 2 beta 1 without an inflammatory context or hepatic disease (increased alpha 1 and alpha 2 fractions, decreased albumin) Isolated increase or not of beta 1 (without a hemolyzed serum or an iron deficiency anemia) Patient alpha 2 value > reference alpha 2 value without an inflammatory context 61
62 Strong monoclonal immunoglobulin in the gamma zone Alb α1 α2 β1 β2 Complementary immunofixation/ Immunotyping required γ 62
63 Monoclonal immunoglobulin peak in gamma Complementary immunofixation/ Immunotyping required 63
64 Weak monoclonal immunoglobulin in the gamma zone Alb α1 α2 β1 β2 γ Complementary immunofixation/ Immunotyping required 64
65 Weak distortion in gamma (monoclonal immunoglobulin) Alb α1 α2 β1 β2 Complementary immunofixation/ Immunotyping required γ 65
66 Weak distortion in gamma (monoclonal immunoglobulin) Alb α1 α2 β1 β2 γ Complementary immunofixation/ Immunotyping required 66
67 Weak monoclonal immunoglobulin peak on hypogammaglobulinemia Alb α1 α2 β1 β2 γ Complementary immunofixation/ Immunotyping required 67
68 68
69 Monoclonal immunoglobulin distorsion in beta 1 Additional peak or isolated increase of Beta 1 without iron anemia Alb α1 α2 β1 β2 γ Complementary immunofixaton/ Immunotyping required 69
70 An additional fraction in alpha 2: monoclonal Ig? Patient alpha 2 value > Phoresis reference alpha 2 value (in g/l or g/dl) without a context of inflammatory response => Perform a immunotyping for a potential monoclonal immunoglobulin 70
71 Highly polymerized monoclonal immunoglobulin or something else? Warning: Migration is out of range indicates a delay of albumin migration. If the problem only appears on a sample out of the serie, the sample must be treated by BME/fluidil for a suspicion of highly polymerized monoclonal immunoglobulin 71
72 Treatment with Beta Mercaptoethanol (BME) to depolymerize a monoclonal Ig * Prepare a 1% BME reducing solution : 1) 90µL H2O + 10µL BME 2) 10µL 1/10 diluted BME + 90µL Fluidil (ref 4587) * 100µL of 1% BME reducing solution + 300µL serum * Incubate 10 mn at room temperature Analyze immediately the treated sample in Capillarys or Minicap without any delay To depolymerize Ig M, Ig A and free light chains 72
73 NAZAR centering AHMED MOHAMED «Migration out of range» 73
74 Before BME After BME After BME/Fluidil treatment for the same sample 74
75 Limit of sensitivity for monoclonal band detection Between g/l according to the mobility of the Mc and the polyclonal background Das Bildelement mit der Beziehungs-ID rid3 wurde in der Datei nicht gefunden g/l 75
76 Limit of sensitivity for monoclonal band detection Between g/l according to the mobility of the Mc and the polyclonal background 0.4 g/l 76
77 High resolution of Capillarys/Minicap to detect a weak monoclonal Ig Zoom + smoothing 0 77
78 High resolution of Capillarys/Minicap to detect a weak monoclonal Ig Zoom +smoothing 0 78
79 Quantification of a monoclonal immunoglobulin on serum protein electrophoresis The quantification is required for: Myeloma classification (MGUS, SM or symptomatic myeloma) Staging of symptomatic myeloma (stage I, II and III) To monitor an increase of malignant disease or the evolution from a non malignant state to a malignant state 79
80 Quantification of a monoclonal immunoglobulin on serum protein electrophoresis Peak quantitation on protein electrophoretic curve It is the most accurate quantitation: Requires: * accurate total protein measurement * accurate determination of the peak Nephelometric or turbidimetric measurement This measurement includes the concentration of the entire Ig class (monoclonal and polyclonal). This measurement may lead to significant discrepancies 80
81 Oligoclonal pattern *Oligoclonal: Refers to the presence of multiple, faint, narrow, and homogenous bands. *Hypergammaglobulinemia is due to an increase of several subclasses of immunoglobulins, that gives a picture of multiple "monoclonal" bands called "oligoclonal profile" or oligoclonal bands. 81
82 Oligoclonal pattern is observed in: autoimmune reactions associated with transplants In patients under immuno-suppressive treatment in case of autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, Gougerot-Sjögren syndrome, lupus erythematosus) infectious (viral, bacterial and parasitic) diseases (H.I.V., viral hepatitis, cytomegalovirus infection.) 82
83 Potential oligoclonal profile in gamma Complementary immunofixation/immunotyping required to distinguish an oligoclonal profile from a risk of polymerized monoclonal immunoglobulin 83
84 Do not report an oligoclonal profile in gamma, just because multiple distorsions are visible in gamma with an inflammatory profile! +BME No oligoclonal profile here but a polymerized Ig M 84
85 Potential oligoclonal profile with hypergamma Alb α1 α2 β1 β2 γ Prefer complementary Immunotyping to distinguish oligoclonal profile from high polyclonal background. In immunofixation oligoclonal profile may be hidden bynazar thisahmed highmohamed polyclonal background 85
86 Serum Electrophoresis interpretation 86
87 Faint distortion in gamma Complementary Immunotyping / Immunofixation is required NAZAR AHMED MOHAMED 87
88 Strong monoclonal peak in gamma Complementary Immunotyping / Immunofixation is required NAZAR AHMED MOHAMED 88
89 Chronic inflammatory profile Complementary Immunotyping / Immunofixation is not NAZAR AHMED required. Recheck the electrophoresis in 3MOHAMED months 89
90 Hypogammaglobulinemia If the clinical causes of this hypogammaglobulinemia are unknown, it is NAZAR AHMED MOHAMED advisable to check 24h urine for Bence Jones protein. 90
91 Acute Inflammatory Profile (Beta 2 = Beta 1 due to polyclonal increase of Ig A) Complementary Immunotyping / Immunofixation is NAZAR AHMED MOHAMED not required. Recheck the electrophoresis in 3 months 91
92 Beta 2 gamma bridge (Polyclonal increase of Ig A in beta 2 and Ig G in gamma) Immunotyping/Immunofixation is not required in case of known liver disease or positive liver function tests 92
93 Monoclonal peak in gamma Complementary Immunotyping / Immunofixation is required NAZAR AHMED MOHAMED 93
94 1. Acute inflammatory profile 2. Monoclonal peak in gamma and hypogammaglobulimemia Complementary Immunotyping / Immunofixation is required 94
95 Isolated increase of alpha 2 fraction Complementary Immunotyping / Immunofixation is required NAZAR AHMED MOHAMED 95
96 Monoclonal Peak in gamma Complementary Immunotyping / Immunofixation is required NAZAR AHMED MOHAMED 96
97 Beta 2-gamma bridge (Cirrhotic profile) Immunotyping is not required in case of known liver disease or positive liver function tests 97
98 Chronic inflammatory profile with underlying distortion in gamma Immunotyping/Immnofixation is required. NAZARwithin AHMED MOHAMED For repeat testing the next 3 to 6 months 98
99 Chronic inflammatory profile with a weak monoclonal peak Double aspect in alpha 2 could be due a HPT mutation Complementary Immunotyping / Immunofixation is NAZAR AHMED MOHAMED required. For repeat testing within the next 3 to 6 months 99
100 Potential oligoclonal profile in gamma Complementary Immunotyping / Immunofixation is required. For repeat testing within the next 3 to 6 months 100
101 Monoclonal Peak in gamma NAZAR AHMED MOHAMED Complementary Immunotyping / Immunofixation is required 101
102 Nephrotic profile Complementary Immunotyping / Immunofixation is not required if nephrotic syndrome is corroborated by serum lipid results 102
103 Inflammatory profile with potential oligoclonal profile in gamma Complementary immunotyping/immunofixation is required. For repeat testing within the next 3 to 6 months NAZAR AHMED MOHAMED 103
104 Monoclonal peak in beta 2 and hypogamma Complementary Immunotyping / Immunofixation is required 104
105 ANY QUESTION? 105
106 Learning Outcome *1- See the electrophoresis development. *2- Knowing the fraction of protein component. *3-See the function of different protein fraction. *4- Knowing the purpose of serum protein electrophoresis. *5- Knowing the questions can be answered with a serum protein electrophoresis. 106
107 Learning Outcome *6- Knowing the pathological conditions on serum protein electrophoresis. *7-Understanding Monoclonal Gammopathies on serum protein electrophoresis. *8- See the Position of a monoclonal immunoglobuline in serum protein electrophoresis. *9- Understanding the Oligoclonal pattern. 107
108 Summary *Serum protein electrophoresis is used to identify patients with multiple myeloma and other serum protein disorders. *Electrophoresis separates proteins based on their physical properties, and the subsets of these proteins are used in interpreting the results. *Plasma protein levels display reasonably predictable changes in response to acute inflammation, malignancy, trauma, necrosis, infarction, burns, and chemical injury. 108
109 THANK YOU FOR GOOD ATTENTION 109
+ Serum Protein Electrophoresis with Immunofixation
 + Serum Protein Electrophoresis with Immunofixation Dr.Ajay Phadke Centre Head SRL Diagnostics-Dr.Avinash Phadke s Lab + What is electrophoresis? Electrophoresis is a method of separating proteins based
+ Serum Protein Electrophoresis with Immunofixation Dr.Ajay Phadke Centre Head SRL Diagnostics-Dr.Avinash Phadke s Lab + What is electrophoresis? Electrophoresis is a method of separating proteins based
Typical bands found on serum gel electrophoresis:
 Gel Electrophoresis LD Recognise EPG patterns typical of other body fluids including urine and CSF Identify patterns of changes including - Paraproteins - Hypogamma - Acute phase - Circulating immune complexes
Gel Electrophoresis LD Recognise EPG patterns typical of other body fluids including urine and CSF Identify patterns of changes including - Paraproteins - Hypogamma - Acute phase - Circulating immune complexes
diag.of gammop Dr. A Sarrafnejad PhD Dep. Immunology School of public health TUMS
 laboratory diag.of gammop Dr. A Sarrafnejad PhD Dep. Immunology School of public health TUMS Sarrafnejad@tums.ac.ir Arne Wilhelm Kaurin Tiselius Nobel Prize for Chemistry (1948) Electrophoresis ٤ After
laboratory diag.of gammop Dr. A Sarrafnejad PhD Dep. Immunology School of public health TUMS Sarrafnejad@tums.ac.ir Arne Wilhelm Kaurin Tiselius Nobel Prize for Chemistry (1948) Electrophoresis ٤ After
بسم اهلل الرمحن الرحيم
 بسم اهلل الرمحن الرحيم Definition Multiple myeloma is a neoplastic plasma cell dyscrasia (PCD) that generally produced a monoclonal immunoglobulin protein, characterized by a clinical pentad: (a) anemia;
بسم اهلل الرمحن الرحيم Definition Multiple myeloma is a neoplastic plasma cell dyscrasia (PCD) that generally produced a monoclonal immunoglobulin protein, characterized by a clinical pentad: (a) anemia;
2. Relay characteristics of proteins and protein electrophoresis / fractionation.
 UNIT: Proteins 15prot_elec.wpd Task Electrophoresis Objectives Upon completion of this exercise, the student will be able to: 1. Review electrophoresis information as presented in class. 2. Relay characteristics
UNIT: Proteins 15prot_elec.wpd Task Electrophoresis Objectives Upon completion of this exercise, the student will be able to: 1. Review electrophoresis information as presented in class. 2. Relay characteristics
Electrophoresis. Assays... INTERLAB ASSAYS. Instrument. Software Easy data management thanks to innovative Elfolab software. General Characteristic
 Software Easy data management thanks to innovative Elfolab software. Instrument Complete walk-away automation. Initial 52 results available within 50 minutes. Impressive 208 Serum Proteins samples per
Software Easy data management thanks to innovative Elfolab software. Instrument Complete walk-away automation. Initial 52 results available within 50 minutes. Impressive 208 Serum Proteins samples per
Multiple myeloma (MM) & related disorders
 Multiple myeloma (MM) & related disorders Plasma cell neoplasms Six major variants: (1) Multiple myeloma (2) Solitary plasmacytoma (3) Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma They secrete a single complete or partial
Multiple myeloma (MM) & related disorders Plasma cell neoplasms Six major variants: (1) Multiple myeloma (2) Solitary plasmacytoma (3) Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma They secrete a single complete or partial
Laboratory Persistence and Clinical Progression of Small Monoclonal Abnormalities
 Immunopathology / Persistence of IFE MGUS Laboratory Persistence and Clinical Progression of Small Monoclonal Abnormalities David L. Murray, MD, PhD, 1 Justin L. Seningen, MD, 1 Angela Dispenzieri, MD,
Immunopathology / Persistence of IFE MGUS Laboratory Persistence and Clinical Progression of Small Monoclonal Abnormalities David L. Murray, MD, PhD, 1 Justin L. Seningen, MD, 1 Angela Dispenzieri, MD,
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines. Diagnosis and Management of Myeloma
 Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Diagnosis and Management of Myeloma When to screen for Myeloma and related disorders Not recommended to screen the normal population Clinical Symptoms,
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Diagnosis and Management of Myeloma When to screen for Myeloma and related disorders Not recommended to screen the normal population Clinical Symptoms,
What do you do, with an M protein?
 What do you do, with an M protein? Cancer Day for Primary Care Emily Rimmer MD FRCPC January 31, 2014 emily.rimmer@cancercare.mb.ca Disclosure of Potential for Conflict of Interest Name of presenter: Emily
What do you do, with an M protein? Cancer Day for Primary Care Emily Rimmer MD FRCPC January 31, 2014 emily.rimmer@cancercare.mb.ca Disclosure of Potential for Conflict of Interest Name of presenter: Emily
Elevated Immunoglobulins and Paraproteins
 Elevated Immunoglobulins and Paraproteins NWL Pathology GP Study Afternoon Thursday 19 th October 2017 Dr Aristeidis Chaidos Consultant Haematologist and Honorary Senior Clinical Lecturer Hammersmith Hospital,
Elevated Immunoglobulins and Paraproteins NWL Pathology GP Study Afternoon Thursday 19 th October 2017 Dr Aristeidis Chaidos Consultant Haematologist and Honorary Senior Clinical Lecturer Hammersmith Hospital,
Serum Free Light Chain (FLC) Measurement Can Aid Capillary Zone Electrophoresis in Detecting Subtle FLC-Producing M Proteins
 Immunopathology / DETECTING SUBTLE FLC-PRODUCING M PROTEINS Serum Free Light Chain (FLC) Measurement Can Aid Capillary Zone Electrophoresis in Detecting Subtle FLC-Producing M Proteins Nasir A, Bakshi,
Immunopathology / DETECTING SUBTLE FLC-PRODUCING M PROTEINS Serum Free Light Chain (FLC) Measurement Can Aid Capillary Zone Electrophoresis in Detecting Subtle FLC-Producing M Proteins Nasir A, Bakshi,
chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated 14 September 1999 Transformed Pre- Ig Surface Surface Secreted B- ALL Macroglobulinemia Myeloma
 Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated Pre- B-cell B-cell Transformed B-cell Plasma cell Ig Surface Surface Secreted Major malignant counterpart
Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated Pre- B-cell B-cell Transformed B-cell Plasma cell Ig Surface Surface Secreted Major malignant counterpart
Urine Protein Electrophoresis and Immunoelectrophoresis Using Unconcentrated or Minimally Concentrated Urine Samples
 Immunopathology / Electrophoresis of Unconcentrated Urine Samples Urine Protein Electrophoresis and Immunoelectrophoresis Using Unconcentrated or Minimally Concentrated Urine Samples Anja C. Roden, MD,
Immunopathology / Electrophoresis of Unconcentrated Urine Samples Urine Protein Electrophoresis and Immunoelectrophoresis Using Unconcentrated or Minimally Concentrated Urine Samples Anja C. Roden, MD,
WG-ICQA Harmonisation of Interpretive Commenting EQA
 WG-ICQA Harmonisation of Interpretive Commenting EQA WG-ICQA Subgroup: Harmonisation of reporting of protein electrophoresis and serum FLC, and quantification of small monoclonal proteins Improved patient
WG-ICQA Harmonisation of Interpretive Commenting EQA WG-ICQA Subgroup: Harmonisation of reporting of protein electrophoresis and serum FLC, and quantification of small monoclonal proteins Improved patient
Assessment of Serum Free Light Chain Assays for Plasma Cell Disorder Screening in a Veterans Affairs Population
 Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol 36, no. 2, 2006 157 Assessment of Serum Free Light Chain Assays for Plasma Cell Disorder Screening in a Veterans Affairs
Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol 36, no. 2, 2006 157 Assessment of Serum Free Light Chain Assays for Plasma Cell Disorder Screening in a Veterans Affairs
Relatively Restricted Migration of Polyclonal IgG4 May Mimic a Monoclonal Gammopathy in IgG4-Related Disease
 Relatively Restricted Migration of Polyclonal 4 May Mimic a Monoclonal Gammopathy in 4-Related Disease Joannes F. M. Jacobs, MD, PhD, 1,2 Renate G. van der Molen, PhD, 1 and David F. Keren, MD, PhD 3 From
Relatively Restricted Migration of Polyclonal 4 May Mimic a Monoclonal Gammopathy in 4-Related Disease Joannes F. M. Jacobs, MD, PhD, 1,2 Renate G. van der Molen, PhD, 1 and David F. Keren, MD, PhD 3 From
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY LABORATORY EVALUATION OF IMMUNOPROLIFERATIVE DISORDERS
 Commentary provided by: Louann W. Lawrence, Dr.PH, MLS (ASCP) Professor Emeritus, Retired Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center New Orleans, LA EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY LABORATORY EVALUATION
Commentary provided by: Louann W. Lawrence, Dr.PH, MLS (ASCP) Professor Emeritus, Retired Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center New Orleans, LA EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY LABORATORY EVALUATION
SIGNIFICANCE OF GAMMA GLOBULINS IN MULTIPLE MYELOMA THROUGH SERUM ELECTROPHORETIC PATTERN
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Kumar et al. SJIF Impact Factor 6.647 Volume 6, Issue 7, 1211-1218 Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 SIGNIFICANCE OF GAMMA GLOBULINS IN MULTIPLE MYELOMA
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Kumar et al. SJIF Impact Factor 6.647 Volume 6, Issue 7, 1211-1218 Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 SIGNIFICANCE OF GAMMA GLOBULINS IN MULTIPLE MYELOMA
DIAGNOSIS OF MYELOMA BASED ON THE 2014 INTERNATIONAL MYELOMA WORKING GROUP
 INDONESIAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY AND MEDICAL LABORATORY Majalah Patologi Klinik Indonesia dan Laboratorium Medik Page 196 2018 March; 24(2): 196-200 p-issn 0854-4263 e-issn 2477-4685 Available
INDONESIAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY AND MEDICAL LABORATORY Majalah Patologi Klinik Indonesia dan Laboratorium Medik Page 196 2018 March; 24(2): 196-200 p-issn 0854-4263 e-issn 2477-4685 Available
Guidelines for the diagnosis of Multiple Myeloma Ass.lec.: Dr. Karam T. Agha M.Sc.Pathology
 Guidelines for the diagnosis of Multiple Myeloma 2014 By:British Committee for Standards in Haematology (BCSH) Ass.lec.: Dr. Karam T. Agha M.Sc.Pathology Diagnosis, prognostic factors and disease monitoring
Guidelines for the diagnosis of Multiple Myeloma 2014 By:British Committee for Standards in Haematology (BCSH) Ass.lec.: Dr. Karam T. Agha M.Sc.Pathology Diagnosis, prognostic factors and disease monitoring
chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated 14 September 1999 Pr e- Transformed Ig Su rf ace Su rf ace Secre ted Myelom a
 Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated Pr e- B-ce ll B-ce ll Transformed B-ce ll Plasma cell Ig Su rf ace Su rf ace Secre ted Major malignant
Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated Pr e- B-ce ll B-ce ll Transformed B-ce ll Plasma cell Ig Su rf ace Su rf ace Secre ted Major malignant
acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma
 Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated t d Pre- B-cell B-cell Ig Surface Transformed B-cell Surface Plasma cell Secreted Major malignant counterpart
Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated t d Pre- B-cell B-cell Ig Surface Transformed B-cell Surface Plasma cell Secreted Major malignant counterpart
Immunoglobulins. Structure
 Immunoglobulins Structure Definitions Immunoglobulin is a generic term that refers to a diverse group of molecules found in the blood and tissue fluids They are soluble globulin molecules and they generally
Immunoglobulins Structure Definitions Immunoglobulin is a generic term that refers to a diverse group of molecules found in the blood and tissue fluids They are soluble globulin molecules and they generally
Quantitative Determination Of Serum Iron, Unsaturated Iron Binding Capacity (UIBC), And Total Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC)
 Quantitative Determination Of Serum Iron, Unsaturated Iron Binding Capacity (UIBC), And Total Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC) Objectives To Determine The Normal Level Of Serum Iron. To Determine The Use Of
Quantitative Determination Of Serum Iron, Unsaturated Iron Binding Capacity (UIBC), And Total Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC) Objectives To Determine The Normal Level Of Serum Iron. To Determine The Use Of
Diagnosis and Follow-up of Multiple Myeloma and Related Disorders: The role of the laboratory
 Diagnosis and Follow-up of Multiple Myeloma and Related Disorders: The role of the laboratory Anne L Sherwood, PhD Director of Scientific Affairs The Binding Site, Inc. Learning Objectives Compare traditional
Diagnosis and Follow-up of Multiple Myeloma and Related Disorders: The role of the laboratory Anne L Sherwood, PhD Director of Scientific Affairs The Binding Site, Inc. Learning Objectives Compare traditional
Electron Beam Sterilization of the Agarose Gel Used for Electrophoresis
 Electron Beam Sterilization of the Agarose Gel Used for Electrophoresis D. Ighigeanu 1, D. Martin 1, E. Manaila 1, D.E. Stan 2, I. V. Baciu 3, G. Craciun 1, C. Oproiu 1, N. Iacob 1 1 National Institute
Electron Beam Sterilization of the Agarose Gel Used for Electrophoresis D. Ighigeanu 1, D. Martin 1, E. Manaila 1, D.E. Stan 2, I. V. Baciu 3, G. Craciun 1, C. Oproiu 1, N. Iacob 1 1 National Institute
CHAPTER 3 ANTIBODY STRUCTURE I
 CHAPTER 3 ANTIBODY STRUCTURE I See APPENDIX: (3) OUCHTERLONY ANALYSIS; (6), EQUILIBRIUM DIALYSIS; (7) CROSS-REACTIVITY Electrophoretic separation of serum proteins identifies the GAMMA-GLOBULIN fraction
CHAPTER 3 ANTIBODY STRUCTURE I See APPENDIX: (3) OUCHTERLONY ANALYSIS; (6), EQUILIBRIUM DIALYSIS; (7) CROSS-REACTIVITY Electrophoretic separation of serum proteins identifies the GAMMA-GLOBULIN fraction
Test Name Results Units Bio. Ref. Interval. Packed Cell Volume (PCV) %
 Lab No Mr DUMMY-----Z289 LLT12448 Age 15 Years Gender 16/4/2018 22600M 16/4/2018 23529M 27/6/2018 73049M Ref By Test Results Units Bio Ref Interval ANEMIA ANEL 1 COMLETE BLOOD COUNT (CBC) (Electrical Impedance
Lab No Mr DUMMY-----Z289 LLT12448 Age 15 Years Gender 16/4/2018 22600M 16/4/2018 23529M 27/6/2018 73049M Ref By Test Results Units Bio Ref Interval ANEMIA ANEL 1 COMLETE BLOOD COUNT (CBC) (Electrical Impedance
Serum heavy-light chain analysis (Hevylite): clinical applications for multiple myeloma
 Serum heavy-light chain analysis (Hevylite): clinical applications for multiple myeloma Kelly Endean PhD Scientific Affairs Manager, The Binding Site Focus of this talk An introduction to heavy-light chain
Serum heavy-light chain analysis (Hevylite): clinical applications for multiple myeloma Kelly Endean PhD Scientific Affairs Manager, The Binding Site Focus of this talk An introduction to heavy-light chain
Physiology Unit 3 HEMATOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 3 HEMATOLOGY In Physiology Today Hematocrit Percentage of blood volume that is erythrocytes 45% in men 42% in women Average blood volume in is 5 L Plasma Large amounts of organic/inorganic
Physiology Unit 3 HEMATOLOGY In Physiology Today Hematocrit Percentage of blood volume that is erythrocytes 45% in men 42% in women Average blood volume in is 5 L Plasma Large amounts of organic/inorganic
IMMUNOCHEMICAL TECHNIQUES
 24 IMMUNOCHEMICAL TECHNIQUES 24.1 INTRODUCTION All vertebrates have advanced immune system. The more complex the organism the more advanced the immune system. The immune system of mammals has evolved over
24 IMMUNOCHEMICAL TECHNIQUES 24.1 INTRODUCTION All vertebrates have advanced immune system. The more complex the organism the more advanced the immune system. The immune system of mammals has evolved over
SAS-MX IFE-1 Kit Instructions for Use
 SAS-MX IFE-1 Kit Instructions for Use Queensway South, Team Valley Trading Estate, 100300 Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, NE11 0SD, United Kingdom Tel: +44 (0)191 482 8440 Fax: +44 (0)191 482 8442 Email: info@helena-biosciences.com
SAS-MX IFE-1 Kit Instructions for Use Queensway South, Team Valley Trading Estate, 100300 Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, NE11 0SD, United Kingdom Tel: +44 (0)191 482 8440 Fax: +44 (0)191 482 8442 Email: info@helena-biosciences.com
Report of Survey conducted by IFCC WG Harmonisation of Interpretive Commenting EQA (WG-ICQA) subgroup:
 Report of Survey conducted by IFCC WG Harmonisation of Interpretive Commenting EQA (WG-ICQA) subgroup: Results of an international survey of the reporting of protein electrophoresis and serum free light
Report of Survey conducted by IFCC WG Harmonisation of Interpretive Commenting EQA (WG-ICQA) subgroup: Results of an international survey of the reporting of protein electrophoresis and serum free light
Suppression of Polyclonal Immunoglobulin Production by M-proteins Shows Isotype Specificity
 274 Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 31, no. 3, 2001 Suppression of Polyclonal Immunoglobulin Production by M-proteins Shows Isotype Specificity Liang Wang and David C. Young Department of
274 Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 31, no. 3, 2001 Suppression of Polyclonal Immunoglobulin Production by M-proteins Shows Isotype Specificity Liang Wang and David C. Young Department of
IMMU 7630 Fall 2018 ANTIBODY STRUCTURE
 IMMU 7630 Fall 2018 ANTIBODY STRUCTURE ANTIBODY IS IMMUNOGLOBULIN. Almost 130 years ago it was observed that a new activity appeared in the blood plasma of animals or humans who had been immunized with
IMMU 7630 Fall 2018 ANTIBODY STRUCTURE ANTIBODY IS IMMUNOGLOBULIN. Almost 130 years ago it was observed that a new activity appeared in the blood plasma of animals or humans who had been immunized with
Nephelometry and turbidimetry are liquid based immunoassays based on the measurement of scattered or absorbed light.
 1 Nephelometry and turbidimetry are liquid based immunoassays based on the measurement of scattered or absorbed light. Light scattering is the physical phenomenon resulting from the interaction of light
1 Nephelometry and turbidimetry are liquid based immunoassays based on the measurement of scattered or absorbed light. Light scattering is the physical phenomenon resulting from the interaction of light
This Infosheet explains what Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS) is and how it is diagnosed and managed.
 MGUS This Infosheet explains what Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS) is and how it is diagnosed and managed. What is MGUS? Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, or
MGUS This Infosheet explains what Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS) is and how it is diagnosed and managed. What is MGUS? Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, or
ABC of laboratory techniques for diagnosis and follow-up of monoclonal gammopathies. An Hendrickx MSc. Scientific Advisor
 ABC of laboratory techniques for diagnosis and follow-up of monoclonal gammopathies An Hendrickx MSc. Scientific Advisor In this talk introduction biology of free light chains laboratorium investigation
ABC of laboratory techniques for diagnosis and follow-up of monoclonal gammopathies An Hendrickx MSc. Scientific Advisor In this talk introduction biology of free light chains laboratorium investigation
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Plasma Protein Fractions in Healthy Blood Donors Quantitated by an Automated Multicapillary Electrophoresis System
 Plasma Protein Fractions in Healthy Blood Donors Quantitated by an Automated Multicapillary Electrophoresis System Anders Larsson* and Lars-Olof Hansson Department of Medical Sciences, Clinical Chemistry,
Plasma Protein Fractions in Healthy Blood Donors Quantitated by an Automated Multicapillary Electrophoresis System Anders Larsson* and Lars-Olof Hansson Department of Medical Sciences, Clinical Chemistry,
June Laboratory Evaluation of Plasma Cell Neoplasms Stan McCormick, MD
 June 2011 Laboratory Evaluation of Plasma Cell Neoplasms Stan McCormick, MD In this issue we review the laboratory work up of patients suspected of having a plasma cell neoplasm. As the range in clinical
June 2011 Laboratory Evaluation of Plasma Cell Neoplasms Stan McCormick, MD In this issue we review the laboratory work up of patients suspected of having a plasma cell neoplasm. As the range in clinical
Analytically coherent
 ZO M OCTOBER 2017 N 7 sebia FLC Free light chain testing coherent with electrophoretic methods Analytically coherent SPE: 3.1 g/l FLC Nephelometry: 32.2 g/l FLC ELISA: 3.1 g/l Principle The sebia FLC Kappa
ZO M OCTOBER 2017 N 7 sebia FLC Free light chain testing coherent with electrophoretic methods Analytically coherent SPE: 3.1 g/l FLC Nephelometry: 32.2 g/l FLC ELISA: 3.1 g/l Principle The sebia FLC Kappa
Performance of the Sebia CAPILLARYS 2 for Detection and Immunotyping of Serum Monoclonal Paraproteins
 Immunopathology / SEBIA CAPILLARYS 2 PARAPROTEIN DETECTION Performance of the Sebia CAPILLARYS 2 for Detection and Immunotyping of Serum Monoclonal Paraproteins Zhaohai Yang, MD, PhD, Keith Harrison, MD,
Immunopathology / SEBIA CAPILLARYS 2 PARAPROTEIN DETECTION Performance of the Sebia CAPILLARYS 2 for Detection and Immunotyping of Serum Monoclonal Paraproteins Zhaohai Yang, MD, PhD, Keith Harrison, MD,
Diagnosis and Follow-up of Multiple Myeloma and Related Disorders: The role of the laboratory
 Diagnosis and Follow-up of Multiple Myeloma and Related Disorders: The role of the laboratory Anne L Sherwood, PhD Director of Scientific Affairs The Binding Site, Inc. Learning Objectives Compare traditional
Diagnosis and Follow-up of Multiple Myeloma and Related Disorders: The role of the laboratory Anne L Sherwood, PhD Director of Scientific Affairs The Binding Site, Inc. Learning Objectives Compare traditional
Jerry A. Katzmann, 1* Raynell J. Clark, 1 Roshini S. Abraham, 1 Sandra Bryant, 1 James F. Lymp, 1 Arthur R. Bradwell, 2 and Robert A. Kyle 1.
 Clinical Chemistry 48:9 1437 1444 (2002) Enzymes and Protein Markers Serum Reference Intervals and Diagnostic Ranges for Free and Free Immunoglobulin Light Chains: Relative Sensitivity for Detection of
Clinical Chemistry 48:9 1437 1444 (2002) Enzymes and Protein Markers Serum Reference Intervals and Diagnostic Ranges for Free and Free Immunoglobulin Light Chains: Relative Sensitivity for Detection of
So we can separate antigens into their components and allow them to react with their antibodies
 Ag-ab reactions As for single immunodiffusion, double immunodiffusion can be also combined with electrophoresis to speed up the reaction, and in this case the test is called immunoelectrophoresis. So electrophoresis
Ag-ab reactions As for single immunodiffusion, double immunodiffusion can be also combined with electrophoresis to speed up the reaction, and in this case the test is called immunoelectrophoresis. So electrophoresis
Immunoglobulins. Harper s biochemistry Chapter 49
 Immunoglobulins Harper s biochemistry Chapter 49 Immune system Detects and inactivates foreign molecules, viruses, bacteria and microorganisms Two components with 2 strategies B Lymphocytes (humoral immune
Immunoglobulins Harper s biochemistry Chapter 49 Immune system Detects and inactivates foreign molecules, viruses, bacteria and microorganisms Two components with 2 strategies B Lymphocytes (humoral immune
The monoclonal gammopathies constitute a group of
 Sequence of Testing for Monoclonal Gammopathies The first test for recognition of monoclonal gammopathies should be serum protein electrophoresis with highresolution agarose gel. Serum protein electrophoresis
Sequence of Testing for Monoclonal Gammopathies The first test for recognition of monoclonal gammopathies should be serum protein electrophoresis with highresolution agarose gel. Serum protein electrophoresis
The Incidence and Significance of Pseudoparaproteins in a Community Hospital
 Annals o f Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 30, no. 3, 2000 289 The Incidence and Significance of Pseudoparaproteins in a Community Hospital Stephen Lewis Strobel Department of Pathology, St. Vincent
Annals o f Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 30, no. 3, 2000 289 The Incidence and Significance of Pseudoparaproteins in a Community Hospital Stephen Lewis Strobel Department of Pathology, St. Vincent
Applicazioni della misura delle Free Light Chain nella pratica clinica. Maria Teresa Petrucci
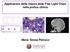 Applicazioni della misura delle Free Light Chain nella pratica clinica Maria Teresa Petrucci Serum free light chain immunoassay Heavy chain Kappa Light chain Hidden surface Lambda Exposed surface Serum
Applicazioni della misura delle Free Light Chain nella pratica clinica Maria Teresa Petrucci Serum free light chain immunoassay Heavy chain Kappa Light chain Hidden surface Lambda Exposed surface Serum
Coagulopathy Case-2. Andy Nguyen, M.D. 2009
 Coagulopathy Case-2 Andy Nguyen, M.D. 2009 CLINICAL HISTORY A 42 year-old man brought to the emergency room with severe burn. Patient was rescued by firemen in a serious fire. He had been found unconscious
Coagulopathy Case-2 Andy Nguyen, M.D. 2009 CLINICAL HISTORY A 42 year-old man brought to the emergency room with severe burn. Patient was rescued by firemen in a serious fire. He had been found unconscious
Electro refers to electron flow or current. Thus Electrophoresis is movement under electric current.
 ELECTROPHORESIS Electrophoresis Electro refers to electron flow or current. Phoresis refers to movement. Thus Electrophoresis is movement under electric current. This technique therefore can separate molecules
ELECTROPHORESIS Electrophoresis Electro refers to electron flow or current. Phoresis refers to movement. Thus Electrophoresis is movement under electric current. This technique therefore can separate molecules
Understanding MGUS and Smoldering Multiple Myeloma
 Multiple Myeloma Cancer of the Bone Marrow Understanding MGUS and Smoldering Multiple Myeloma u-mgus+smm_en_2017_i1 12650 Riverside Drive, Suite 206 North Hollywood, CA 91607 USA Telephone: 800-452-CURE
Multiple Myeloma Cancer of the Bone Marrow Understanding MGUS and Smoldering Multiple Myeloma u-mgus+smm_en_2017_i1 12650 Riverside Drive, Suite 206 North Hollywood, CA 91607 USA Telephone: 800-452-CURE
SWOG ONCOLOGY RESEARCH PROFESSIONAL (ORP) MANUAL GENERAL FORMS AND GUIDELINES MYELOMA FORMS CHAPTER 16D REVISED: SEPTEMBER 2016
 MYELOMA FORMS The guidelines and figures below are specific to Myeloma studies. The information in this manual does NOT represent a complete set of required forms for any myeloma study. Please refer to
MYELOMA FORMS The guidelines and figures below are specific to Myeloma studies. The information in this manual does NOT represent a complete set of required forms for any myeloma study. Please refer to
BIL 256 Cell and Molecular Biology Lab Spring, Development of the Immune System
 BIL 256 Cell and Molecular Biology Lab Spring, 2007 Development of the Immune System Background Information I. Serum Proteins Blood is a remarkable tissue containing cellular elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes
BIL 256 Cell and Molecular Biology Lab Spring, 2007 Development of the Immune System Background Information I. Serum Proteins Blood is a remarkable tissue containing cellular elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes
االستاذ المساعد الدكتور خالد ياسين الزاملي \مناعة \المرحلة الثانية \ التحليالت المرضية \ المعهد التقني كوت
 Types of Antigen Antibody Reactions Serological tests are widely used for detection of either serum antibodies or antigens for diagnosis of a wide variety of infectious diseases. These serological tests
Types of Antigen Antibody Reactions Serological tests are widely used for detection of either serum antibodies or antigens for diagnosis of a wide variety of infectious diseases. These serological tests
Index. Quinzanini, M. Departments of Rheumatology, Immunology & Allergology, Azienda Ospedaliera Spedali Civili, Brescia, Italy
 Poster from the Congress EUROMEDLAB Barcelona, 1-5 June 2003 15 th IFCC-FESCC European Congress of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine 22 nd National Congress of the Spanish Society of Clinical
Poster from the Congress EUROMEDLAB Barcelona, 1-5 June 2003 15 th IFCC-FESCC European Congress of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine 22 nd National Congress of the Spanish Society of Clinical
Measuring Myeloma in the LAB. BL Ferry Clinical Lead Sept 15 th 2014
 Measuring Myeloma in the LAB BL Ferry Clinical Lead Sept 15 th 2014 Oxford Immunology Laboratory Clinical Immunology Churchill WHAT DO WE MEASURE AND HOW? Clinical Immunology Churchill Serum proteins Proteins
Measuring Myeloma in the LAB BL Ferry Clinical Lead Sept 15 th 2014 Oxford Immunology Laboratory Clinical Immunology Churchill WHAT DO WE MEASURE AND HOW? Clinical Immunology Churchill Serum proteins Proteins
Coagulation Mechanisms Dr. Nervana Bayoumy
 Coagulation Mechanisms Dr. Nervana Bayoumy Associate Professor Department of Physiology Objectives At the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Recognize the different clotting factors 2. Understand
Coagulation Mechanisms Dr. Nervana Bayoumy Associate Professor Department of Physiology Objectives At the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Recognize the different clotting factors 2. Understand
The Cardiovascular System: Blood
 The Cardiovascular System: Blood The Functions of Blood General Overview Provides a system for rapid transport within the body Nutrients Hormones Waste products Respiratory gases Cells & Blood Components
The Cardiovascular System: Blood The Functions of Blood General Overview Provides a system for rapid transport within the body Nutrients Hormones Waste products Respiratory gases Cells & Blood Components
Structure of IgG and IgM
 Structure of IgG and IgM Fig. 5-1 A,B Crystal Structure of Secreted IgG Fig. 5-1 C Structure of an Ig Domain Fig. 5-2 Proteolytic Fragments of IgG (1) Fig. 5-3A Proteolytic Fragments of IgG (2) Fig. 5-3B
Structure of IgG and IgM Fig. 5-1 A,B Crystal Structure of Secreted IgG Fig. 5-1 C Structure of an Ig Domain Fig. 5-2 Proteolytic Fragments of IgG (1) Fig. 5-3A Proteolytic Fragments of IgG (2) Fig. 5-3B
Laboratory Procedure Handout. IMMUNOGLOBULIN M IgM
 KING ABDUL AZIZ UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF APPLEID MEDICAL SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNOLOGY Laboratory Procedure Handout IMMUNOGLOBULIN M IgM Immunodiffusion single diffusion precipitation
KING ABDUL AZIZ UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF APPLEID MEDICAL SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNOLOGY Laboratory Procedure Handout IMMUNOGLOBULIN M IgM Immunodiffusion single diffusion precipitation
Laboratories and the New IMWG Myeloma Guidelines
 Laboratories and the New IMWG Myeloma Guidelines David F. Keren, M.D. Professor of Pathology Division Director, Clinical Pathology The University of Michigan dkeren@med.umich.edu Speaker Disclosure In
Laboratories and the New IMWG Myeloma Guidelines David F. Keren, M.D. Professor of Pathology Division Director, Clinical Pathology The University of Michigan dkeren@med.umich.edu Speaker Disclosure In
Freelite for Measurement of Urine-Free Light Chains in Monoclonal Gammopathies
 Freelite for Measurement of Urine-Free Light Chains in Monoclonal Gammopathies Montgomery Lobe, MD, and Donald Pasquale, MD Abstract Monoclonal gammopathies are characterized by production of monoclonal
Freelite for Measurement of Urine-Free Light Chains in Monoclonal Gammopathies Montgomery Lobe, MD, and Donald Pasquale, MD Abstract Monoclonal gammopathies are characterized by production of monoclonal
Paediatrica Indonesiana. Using iron profiles to identify anemia of chronic disease in anemic children with tuberculosis
 Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 51 July NUMBER 4 Original Article Using iron profiles to identify anemia of chronic disease in anemic children with tuberculosis Reni Wigati, Endang Windiastuti, Badriul
Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 51 July NUMBER 4 Original Article Using iron profiles to identify anemia of chronic disease in anemic children with tuberculosis Reni Wigati, Endang Windiastuti, Badriul
Blood is 55% Plasma (Liquid)
 Blood is 55% Plasma (Liquid) The plasma portion of blood is: 91% Water Maintains blood volume Transports molecules 7% Proteins (ie: clotting proteins, albumin, immunoglobulins ) 2 % Salts, gases (O 2,
Blood is 55% Plasma (Liquid) The plasma portion of blood is: 91% Water Maintains blood volume Transports molecules 7% Proteins (ie: clotting proteins, albumin, immunoglobulins ) 2 % Salts, gases (O 2,
Veins Valves prevent engorgement and backflow. Baroreceptor reflex. Veins returning blood
 Veins have large radii and low resistance. Walls are thin, not elastic Most blood volume is in veins Veins returning blood Veins Valves prevent engorgement and backflow Sympathetic NS constricts veins
Veins have large radii and low resistance. Walls are thin, not elastic Most blood volume is in veins Veins returning blood Veins Valves prevent engorgement and backflow Sympathetic NS constricts veins
Electron Beam Sterilization of the Agarose Gel Used for Electrophoresis
 Electron Beam Sterilization of the Agarose Gel Used for Electrophoresis D. Ighigeanu 1), D. Martin 1), E. Manaila 1), D.E. Stan 2), I. V. Baciu 3), G. Craciun 1), C. Oproiu 1), N. Iacob 1) 1) National
Electron Beam Sterilization of the Agarose Gel Used for Electrophoresis D. Ighigeanu 1), D. Martin 1), E. Manaila 1), D.E. Stan 2), I. V. Baciu 3), G. Craciun 1), C. Oproiu 1), N. Iacob 1) 1) National
Veins Valves prevent engorgement and backflow. Baroreceptor reflex. Veins returning blood
 Veins have large radii and low resistance. Walls are thin, not elastic Most blood volume is in veins Veins returning blood Veins Valves prevent engorgement and backflow Sympathetic NS constricts veins
Veins have large radii and low resistance. Walls are thin, not elastic Most blood volume is in veins Veins returning blood Veins Valves prevent engorgement and backflow Sympathetic NS constricts veins
International Foundations of Medicine Basic Science Exam Blueprint
 International Foundations of Medicine Basic Science Exam Blueprint General Principles 28% 30% Biochemistry and molecular biology gene expression: DNA structure, replication, and exchange gene expression:
International Foundations of Medicine Basic Science Exam Blueprint General Principles 28% 30% Biochemistry and molecular biology gene expression: DNA structure, replication, and exchange gene expression:
Blood Physiology. Blood Physiology. Dr. Rodolfo T. Rafael. Agglutination Hemolysis Immunology
 Blood Physiology Dr. Rodolfo T. Rafael 1 Blood Physiology Agglutination Hemolysis Immunology 2 1 Agglutination is an antigen- antibody reaction Blood clumping of red blood cells Blood Typing 3 BLOOD TYPING
Blood Physiology Dr. Rodolfo T. Rafael 1 Blood Physiology Agglutination Hemolysis Immunology 2 1 Agglutination is an antigen- antibody reaction Blood clumping of red blood cells Blood Typing 3 BLOOD TYPING
Part 1 examination. Clinical Biochemistry: First paper. Tuesday 26 September Candidates must answer FOUR questions only
 Tuesday 26 September 2017 Candidates must answer FOUR questions only Time allowed: three hours 1. Outline how pre-analytical factors can affect the results of clinical biochemistry tests and describe what
Tuesday 26 September 2017 Candidates must answer FOUR questions only Time allowed: three hours 1. Outline how pre-analytical factors can affect the results of clinical biochemistry tests and describe what
University Journal of Pre and Para Clinical Sciences
 ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 3 Issue 1 2017 A case report of false positive Bence Jones proteinuria. SIVA SRINIVASAN Department of Biochemistry, MADRAS MEDICAL COLLEGE AND GOVERNMENT GENERAL HOSPITAL Abstract
ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 3 Issue 1 2017 A case report of false positive Bence Jones proteinuria. SIVA SRINIVASAN Department of Biochemistry, MADRAS MEDICAL COLLEGE AND GOVERNMENT GENERAL HOSPITAL Abstract
The History of The Binding Site
 Systems ebook Contents 3. History 4. RID Reader 5. Software 7. Calibration methods 9. Technology 11. Complement Assays 13. Immunoglobulin Assays 15. Human Complement Functional Assays 15. Human Protein
Systems ebook Contents 3. History 4. RID Reader 5. Software 7. Calibration methods 9. Technology 11. Complement Assays 13. Immunoglobulin Assays 15. Human Complement Functional Assays 15. Human Protein
Capillary Zone Electrophoresis in the Evaluation of Serum Protein Abnormalities
 Capillary Zone Electrophoresis in the Evaluation of Serum Protein Abnormalities David F. Keren, MD Key Words: Capillary zone electrophoresis; M-protein; Serum protein electrophoresis; monoclonal gammopathy;
Capillary Zone Electrophoresis in the Evaluation of Serum Protein Abnormalities David F. Keren, MD Key Words: Capillary zone electrophoresis; M-protein; Serum protein electrophoresis; monoclonal gammopathy;
Immunology 2011 Lecture 9 Immunoglobulin Biosynthesis 3 October
 Immunology 2011 Lecture 9 Immunoglobulin Biosynthesis 3 October APC Antigen processing (dendritic cells, MΦ et al.) Antigen "presentation" Ag/Ab complexes Antigenspecific triggering B T ANTIGEN Proliferation
Immunology 2011 Lecture 9 Immunoglobulin Biosynthesis 3 October APC Antigen processing (dendritic cells, MΦ et al.) Antigen "presentation" Ag/Ab complexes Antigenspecific triggering B T ANTIGEN Proliferation
Accuracy of Serum IgM and IgA Monoclonal Protein Measurements by Densitometry
 160 Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 33, no. 2, 2003 Accuracy of Serum IgM and IgA Monoclonal Protein Measurements by Densitometry C. Howard Tseng, 1 Chin-Yung Chang, 2 Kevin S. Liu, 3 and
160 Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 33, no. 2, 2003 Accuracy of Serum IgM and IgA Monoclonal Protein Measurements by Densitometry C. Howard Tseng, 1 Chin-Yung Chang, 2 Kevin S. Liu, 3 and
The New England Journal of Medicine A LONG-TERM STUDY OF PROGNOSIS IN MONOCLONAL GAMMOPATHY OF UNDETERMINED SIGNIFICANCE. Patients
 A LONG-TERM STUDY OF PROGNOSIS IN MONOCLONAL GAMMOPATHY OF UNDETERMINED SIGNIFICANCE ROBERT A. KYLE, M.D., TERRY M. THERNEAU, PH.D., S. VINCENT RAJKUMAR, M.D., JANICE R. OFFORD, B.S., DIRK R. LARSON, M.S.,
A LONG-TERM STUDY OF PROGNOSIS IN MONOCLONAL GAMMOPATHY OF UNDETERMINED SIGNIFICANCE ROBERT A. KYLE, M.D., TERRY M. THERNEAU, PH.D., S. VINCENT RAJKUMAR, M.D., JANICE R. OFFORD, B.S., DIRK R. LARSON, M.S.,
Stem Cells and Multiple Myeloma
 Stem Cells and Multiple Myeloma What is Multiple Myeloma Multiple Myeloma is a cancer of your plasma cells, a type of white blood cell present in your bone marrow Plasma cells normally make proteins called
Stem Cells and Multiple Myeloma What is Multiple Myeloma Multiple Myeloma is a cancer of your plasma cells, a type of white blood cell present in your bone marrow Plasma cells normally make proteins called
BCH 462. Western Blot
 BCH 462 Western Blot Blotting Immunoassay: A test that uses antibody and antigen complexes [immuno-complexes] as a means of generating measurable results. Antigens [Ag]: A substance that when introduced
BCH 462 Western Blot Blotting Immunoassay: A test that uses antibody and antigen complexes [immuno-complexes] as a means of generating measurable results. Antigens [Ag]: A substance that when introduced
Antibodies (Immunoglobulins)
 Antibodies (Immunoglobulins) The immune system plays a major role in the body s defense mechanisms against pathogens and other foreign bodies. It protects organisms from infection with a layered defense
Antibodies (Immunoglobulins) The immune system plays a major role in the body s defense mechanisms against pathogens and other foreign bodies. It protects organisms from infection with a layered defense
ANEMIA OF CHRONIC DISEASE (ACD)
 ANEMIA OF CHRONIC DISEASE (ACD) seminar Martin Vokurka 2007 Unofficial study material 1 VERY COMMON!!! In hospitalized patients is the second most common after iron deficiency OFTEN NEGLECTED!! Unofficial
ANEMIA OF CHRONIC DISEASE (ACD) seminar Martin Vokurka 2007 Unofficial study material 1 VERY COMMON!!! In hospitalized patients is the second most common after iron deficiency OFTEN NEGLECTED!! Unofficial
FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM IN CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
 FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM IN CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY Department of Microbiology and Immunology Clinical Immunology Laboratory Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science 1/20/17 Fellowship Program in Clinical
FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM IN CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY Department of Microbiology and Immunology Clinical Immunology Laboratory Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science 1/20/17 Fellowship Program in Clinical
Case Report Transient Monoclonal Gammopathy Induced by Disseminated Staphylococcus aureus Infection
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 607104, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/607104 Case Report Transient Monoclonal Gammopathy Induced by Disseminated Staphylococcus aureus Infection Dimitrios Stoimenis,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 607104, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/607104 Case Report Transient Monoclonal Gammopathy Induced by Disseminated Staphylococcus aureus Infection Dimitrios Stoimenis,
Lecture 23: Clinical and Biomedical Applications of Proteomics; Proteomics Industry
 Lecture 23: Clinical and Biomedical Applications of Proteomics; Proteomics Industry Clinical proteomics is the application of proteomic approach to the field of medicine. Proteome of an organism changes
Lecture 23: Clinical and Biomedical Applications of Proteomics; Proteomics Industry Clinical proteomics is the application of proteomic approach to the field of medicine. Proteome of an organism changes
Serum Protein Electrophoretic Pattern as a Differential Diagnostic Tool
 Serum Protein Electrophoretic Pattern as a Differential Diagnostic Tool Dr. George Gborienemi Simeon (Corresponding Author) Department of Medical Laboratory, Niger Delta University, Bayelsa State, Nigeria.
Serum Protein Electrophoretic Pattern as a Differential Diagnostic Tool Dr. George Gborienemi Simeon (Corresponding Author) Department of Medical Laboratory, Niger Delta University, Bayelsa State, Nigeria.
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF PLASMA PROTEINS VOLUME 1
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF PLASMA PROTEINS VOLUME 1 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF PLASMA PROTEINS VOLUME 1 Edited by A. C. Allison Clinical Research Centre Watford Road Harrow Middlesex PLENUM PRESS LONDON
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF PLASMA PROTEINS VOLUME 1 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF PLASMA PROTEINS VOLUME 1 Edited by A. C. Allison Clinical Research Centre Watford Road Harrow Middlesex PLENUM PRESS LONDON
Local vasoconstriction. is due to local spasm of the smooth muscle (symp. reflex) can be maintained by platelet vasoconstrictors
 Hemostasis Hemostasis ( hemo =blood; sta= remain ) is the stoppage of bleeding, which is vitally important when blood vessels are damaged. Following an injury to blood vessels several actions may help
Hemostasis Hemostasis ( hemo =blood; sta= remain ) is the stoppage of bleeding, which is vitally important when blood vessels are damaged. Following an injury to blood vessels several actions may help
Humoral Immune Response. Dr. Iman Hussein Shehata Professor of Medical Microbiology and Immunology
 Humoral Immune Response Dr. Iman Hussein Shehata Professor of Medical Microbiology and Immunology Intended Learning Outcomes By the end of this lesson the student is expected to: 1-Decribe the sequence
Humoral Immune Response Dr. Iman Hussein Shehata Professor of Medical Microbiology and Immunology Intended Learning Outcomes By the end of this lesson the student is expected to: 1-Decribe the sequence
Anion Gap and Immunoglobulin Concentration
 Anion Gap and Immunoglobulin Concentration ALBERT A. KESHGEGIAN, M.D., PH.D. Keshgegian, Albert A.: Anion gap and immunoglobulin concentration. Am J Clin Pathol 74: 22-26,190. The serum anion gap is often
Anion Gap and Immunoglobulin Concentration ALBERT A. KESHGEGIAN, M.D., PH.D. Keshgegian, Albert A.: Anion gap and immunoglobulin concentration. Am J Clin Pathol 74: 22-26,190. The serum anion gap is often
Convenient and Effective Method for Removing Fibrinogen from Serum Specimens before Protein Electrophoresis
 Clinical Chemistry 49:6 868 872 (2003) Proteomics and Protein Markers Convenient and Effective Method for Removing Fibrinogen from Serum Specimens before Protein Electrophoresis Ling L. Qiu, 1 Stanley
Clinical Chemistry 49:6 868 872 (2003) Proteomics and Protein Markers Convenient and Effective Method for Removing Fibrinogen from Serum Specimens before Protein Electrophoresis Ling L. Qiu, 1 Stanley
Controls & Calibrators Immunology Control & Coagulation
 Controls & Calibrators Immunology Control & Coagulation Immunology Control & Coagulation Human Serum based controls designed to monitor the precision of proteins and other analyte test methods, including
Controls & Calibrators Immunology Control & Coagulation Immunology Control & Coagulation Human Serum based controls designed to monitor the precision of proteins and other analyte test methods, including
Serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation by a semiautomated electrophoresis system
 Clinical Chemistry 44:5 944 949 (1998) Enzymes and Protein Markers Serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation by a semiautomated electrophoresis system Xavier Bossuyt, * Ann Bogaerts, Gilberte Schiettekatte,
Clinical Chemistry 44:5 944 949 (1998) Enzymes and Protein Markers Serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation by a semiautomated electrophoresis system Xavier Bossuyt, * Ann Bogaerts, Gilberte Schiettekatte,
EXAM COVER SHEET. Course Code: CLS 432. Course Description: Clinical Biochemistry. Example Past Exam Modal Answer.
 EXAM COVER SHEET Course Code: CLS 432 Course Description: Clinical Biochemistry Example Past Exam Modal Answer Duration: 2 hour 1st semester 1432/1433 Part 1 Multiple choice questions Answer all the questions
EXAM COVER SHEET Course Code: CLS 432 Course Description: Clinical Biochemistry Example Past Exam Modal Answer Duration: 2 hour 1st semester 1432/1433 Part 1 Multiple choice questions Answer all the questions
BIMM18 Dec 20 th - Flow cytometry in clinical diagnostics
 BIMM18 Dec 20 th - Flow cytometry in clinical diagnostics I. B cell leukemia and lymphomas Immunophenotyping as part of the diagnostic work- up of hematologic malignancies offers a rapid and effective
BIMM18 Dec 20 th - Flow cytometry in clinical diagnostics I. B cell leukemia and lymphomas Immunophenotyping as part of the diagnostic work- up of hematologic malignancies offers a rapid and effective
BCH 462. Single Radial Immunodiffusion and Immuno-electrophoresis
 BCH 462 Single Radial Immunodiffusion and Immuno-electrophoresis Immunoassays tests include: 1. Precipitation. 2. Agglutination. 3. Immunofluorescence. 4. Radioimmunoassay (RIA). 5. Enzyme-Linked Immuno
BCH 462 Single Radial Immunodiffusion and Immuno-electrophoresis Immunoassays tests include: 1. Precipitation. 2. Agglutination. 3. Immunofluorescence. 4. Radioimmunoassay (RIA). 5. Enzyme-Linked Immuno
A Study of Serum Protein Electrophoresis in Patients with Multiple Myeloma
 MULTIPLE THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MYELOMA MEDICAL JOURNAL A Study of Serum Protein Electrophoresis in Patients with Multiple Myeloma Hind Shakir Ahmed ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: Multiple myeloma (MM) is caused
MULTIPLE THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MYELOMA MEDICAL JOURNAL A Study of Serum Protein Electrophoresis in Patients with Multiple Myeloma Hind Shakir Ahmed ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: Multiple myeloma (MM) is caused
CAPILLARYS PROTEIN(E) 6
 CAPILLARYS PROTEIN(E) 6 Ref. 2003 2017/04 INTENDED USE The CAPILLARYS PROTEIN(E) 6 kit is designed for the separation of human serum and urine proteins in alkaline buffer (ph 9.9) by capillary electrophoresis
CAPILLARYS PROTEIN(E) 6 Ref. 2003 2017/04 INTENDED USE The CAPILLARYS PROTEIN(E) 6 kit is designed for the separation of human serum and urine proteins in alkaline buffer (ph 9.9) by capillary electrophoresis
Ch 13: Blood. What does blood do? Transport: Regulation: Protection:
 Ch 13: Blood What does blood do? Transport: Regulation: Protection: SLOs Describe the composition of plasma and list the major functions of plasma proteins. Map hematopoiesis, starting from a pluripotent
Ch 13: Blood What does blood do? Transport: Regulation: Protection: SLOs Describe the composition of plasma and list the major functions of plasma proteins. Map hematopoiesis, starting from a pluripotent
