Biochemistry 674 Your Name: Nucleic Acids Prof. Jason Kahn Exam II (100 points total) November 17, 2005
|
|
|
- Susanna Hart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biochemistry 674 ucleic Acids Your ame: Prof. Jason Kahn Exam II (100 points total) ovember 17, 2005 You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded under any circumstances. Explanations should be concise and clear. I have given you more space than you should need, and there s extra space on the last page. You do not need a calculator for this exam, and no other study aids or materials are permitted. Generous partial credit will be given, i.e., if you don t know, guess. Honor Pledge: At the end of the exam time, please write out the following sentence below and sign it, or talk to me about it: I pledge on my honor that I have not given or received any unauthorized assistance on this examination. 1. Protein-ucleic Acid Recognition (35 pts): The modified nucleobase at the right is 2,6-diaminopurine (DAP). It is a useful probe for protein-nucleic acid interaction. (a; 4 pts) What feature of the DAP-T base pair increases the persistence length and thermal stability of DA that contains DAP? H H 2 H 2 dr
2 Biochemistry 674 Exam II, 11/17/05 2/7 (b; 11 pts) Today, your favorite protein (YFP) is a transcription factor that binds dsda. Its recognition site is: 5...ACAGGTATAACAGGT TGCCCATATTGTCCA...5 We would like to know which groove the protein recognizes. How could you use oligonucleotides with DAP substituted for A or G to probe this question? What are the expected results for a protein that binds in the minor vs. the major groove? (c; 8 pts) ow, suppose a crystal structure emerges that demonstrates that the experiment you did in (b) gave misleading answers. For example, suppose a position that you had identified as important is not contacted by YFP. How can you explain this result? What is the new most likely physical explanation of the origin of DAP s effect? [In science, there s nothing wrong with being wrong. It s only stupid or criminal behavior that is discouraged.] There s more space on the next page if you need it.
3 Biochemistry 674 Exam II, 11/17/05 3/7 (d; 6 pts) Do you think DAP substitution would lead to more stable/better rotationally positioned nucleosomes or not? Explain briefly. (e; 6 pts) ote that the recognition site for YFP is a direct repeat. What general kind of transcription factor have we mentioned that binds direct repeats? Why are transcription factors typically dimeric?
4 Biochemistry 674 Exam II, 11/17/05 4/7 2. Methods and miscellaneous (38 pts): The curve below shows a protein-da binding curve derived from EMSA data. ote the y-axis limits. (a; 4 pts) What is the equation for the YFP-DA Binding Curve fraction of DA bound as a function of 1.0 protein concentration for a simple protein- DA binding curve? Fraction Bound (b; 6 pts) On the graph, sketch the curve you would expect for YFP-DA binding with a K d of 20 nm. Indicate how you would determine K d from the graph [YFP] (nm) -- log scale (c; 12 pts) Give a possible physical explanation for the difference between expectation and reality. How can you modify the equation from (a) to account for the phenomenon? What do you think the true K d is for the YFP-DA interaction?
5 Biochemistry 674 Exam II, 11/17/05 5/7 (d; 9 pts) ChIP-on-a-chip reports on all of the binding sites for YFP. There are many sequences that match the consensus above but are not observed to have bound YFP in vivo. On the other hand, there are also many genes where the observed fold change in transcriptional activity +/- YFP is much larger than the observed change in occupancy. Briefly discuss a common explanation for these observations. (e; 7 pts) What is the chromatin modification commonly associated with transcriptional activation? How might you assess its role at the genomic level?
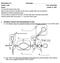
6 Biochemistry 674 Exam II, 11/17/05 6/7 3. DA Replication (27 pts): (a; 12 pts) Sketch the trombone model for the Pol III replication fork at the instant that the lagging strand polymerase is starting to extend an RA primer. Your diagram should include the core polymerases, the τ dimer, the clamp loader, SSB, β sliding clamps, primase, and helicase. (b; 6 pts) What is the advantage to the cell in having primer-template DA but not nicked DA stabilize the β-core interaction? How does this play out during the synthesis of an Okazaki fragment?
7 Biochemistry 674 Exam II, 11/17/05 7/7 (c; 9 pts) How does kinetic partitioning allow the 3 5 exonuclease activity of a DA polymerase to make a large contribution to improved fidelity even though the exo activity itself is may not be particularly selective for mismatched DA? Give a possible reason for the lethality of an active mutant of the proofreading ε subunit of Pol III. Page Total Score
Biochemistry 674 Your Name: Nucleic Acids Prof. Jason Kahn Exam II (100 points total) November 13, 2006
 Biochemistry 674 Nucleic Acids Your Name: Prof. Jason Kahn Exam II (100 points total) November 13, 2006 You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded
Biochemistry 674 Nucleic Acids Your Name: Prof. Jason Kahn Exam II (100 points total) November 13, 2006 You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded
Biochemistry 674, Fall, 1995: Nucleic Acids Exam II: November 16, 1995 Your Name Here: PCR A C
 CHM 674 Exam II, 1995 1 iochemistry 674, Fall, 1995: Nucleic cids Prof. Jason Kahn Exam II: November 16, 1995 Your Name Here: This exam has five questions worth 20 points each. nswer all five. You do not
CHM 674 Exam II, 1995 1 iochemistry 674, Fall, 1995: Nucleic cids Prof. Jason Kahn Exam II: November 16, 1995 Your Name Here: This exam has five questions worth 20 points each. nswer all five. You do not
Biochemistry 661 Your Name: Nucleic Acids, Module I Prof. Jason Kahn Exam I (100 points total) September 23, 2010
 Biochemistry 661 Nucleic Acids, Module I Your Name: Prof. Jason Kahn Exam I (100 points total) September 23, 2010 You have 60 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be
Biochemistry 661 Nucleic Acids, Module I Your Name: Prof. Jason Kahn Exam I (100 points total) September 23, 2010 You have 60 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be
Biochemistry 674: Nucleic Acids Your Name:
 Biochemistry 674: Nucleic Acids Your Name: Exam II, November 18, 1997 Prof. Jason Kahn You do not need a calculator. Guess if you don t know. Give clear and concise answers. You have 85 minutes for this
Biochemistry 674: Nucleic Acids Your Name: Exam II, November 18, 1997 Prof. Jason Kahn You do not need a calculator. Guess if you don t know. Give clear and concise answers. You have 85 minutes for this
1. Transcription (40 pts):
 BCHM 674: Nucleic Acids Final Exam, Dec. 20, 2005 Your Name: Prof. Jason Kahn You have 120 minutes for this exam, which is worth 150 points. Thus you get about the same points per minute as for the 80
BCHM 674: Nucleic Acids Final Exam, Dec. 20, 2005 Your Name: Prof. Jason Kahn You have 120 minutes for this exam, which is worth 150 points. Thus you get about the same points per minute as for the 80
Biochemistry 674 Your Name: Nucleic Acids Prof. Jason Kahn Exam II (100 points total) November 13, 2006
 Biochemistry 674 Nucleic Acids Your Name: Prof. Jason Kahn Exam II (100 points total) November 13, 2006 You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded
Biochemistry 674 Nucleic Acids Your Name: Prof. Jason Kahn Exam II (100 points total) November 13, 2006 You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded
Biochemistry 465 Your Name: Biological Information Processing Prof. Jason Kahn Exam I (100 points total) March 2, 2006
 Biochemistry 465 Biological Information Processing Your Name: Prof. Jason Kahn Exam I (100 points total) March 2, 2006 You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not
Biochemistry 465 Biological Information Processing Your Name: Prof. Jason Kahn Exam I (100 points total) March 2, 2006 You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not
Biochemistry 674 Your Name: Nucleic Acids Prof. Jason Kahn Exam I October 11, Secondary Structure and Thermodynamics (25 pts):
 Biochemistry 674 Nucleic Acids Your Name: Prof. Jason Kahn Exam I October 11, 2001 You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded under any circumstances.
Biochemistry 674 Nucleic Acids Your Name: Prof. Jason Kahn Exam I October 11, 2001 You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded under any circumstances.
b. (4) In the space below, draw a reasonable G G base pair. c. (2) Indicate major and minor grooves and 5 and 3 ends on the duplex DNA at the right.
 Biochemistry 674: Nucleic cids Prof. Jason Kahn Exam I October 9, 1997 You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded under any circumstances. Explanations
Biochemistry 674: Nucleic cids Prof. Jason Kahn Exam I October 9, 1997 You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded under any circumstances. Explanations
Student name ID # Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores Total
 Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Total 1 1. Matching (7 pts). Each answer is used exactly once Helicase
Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Total 1 1. Matching (7 pts). Each answer is used exactly once Helicase
Fidelity of DNA polymerase
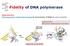 Fidelity of DNA polymerase Shape selectivity: DNA polymerase's conformational change for determination of fidelity for each nucleotide Induced fit: Structure determines function Matched nucleotide Fidelity
Fidelity of DNA polymerase Shape selectivity: DNA polymerase's conformational change for determination of fidelity for each nucleotide Induced fit: Structure determines function Matched nucleotide Fidelity
DNA replication. DNA replication. replication model. replication fork. chapter 6
 DN chapter 6 DN two complementary s bases joined by hydrogen bonds separation of s each - template determines order of nucleotides in duplicate parent DN s separate two identical daughter s model dispersive
DN chapter 6 DN two complementary s bases joined by hydrogen bonds separation of s each - template determines order of nucleotides in duplicate parent DN s separate two identical daughter s model dispersive
Prokaryotic Physiology. March 3, 2017
 1. (10 pts) Explain the replication of both strands of DNA in prokaryotes. At a minimum explain the direction of synthesis, synthesis of the leading and lagging strand, separation of the strands and the
1. (10 pts) Explain the replication of both strands of DNA in prokaryotes. At a minimum explain the direction of synthesis, synthesis of the leading and lagging strand, separation of the strands and the
DNA replication. DNA replication. replication model. replication fork. chapter 6
 DN chapter 6 DN two complementary s bases joined by hydrogen bonds separation of s each - template determines order of nucleotides in duplicate parent DN s separate two identical daughter s model dispersive
DN chapter 6 DN two complementary s bases joined by hydrogen bonds separation of s each - template determines order of nucleotides in duplicate parent DN s separate two identical daughter s model dispersive
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 11 DNA Replication
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 11 DNA Replication 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Are You Getting It?? Which characteristics will be part of semi-conservative replication? (multiple answers) a) The
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 11 DNA Replication 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Are You Getting It?? Which characteristics will be part of semi-conservative replication? (multiple answers) a) The
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 28, 2004
 DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 28, 2004 Conceptual model for proofreading based on kinetic considerations Fig. 24.44 stalling transient melting exonuclease site occupancy Following
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 28, 2004 Conceptual model for proofreading based on kinetic considerations Fig. 24.44 stalling transient melting exonuclease site occupancy Following
Welcome to Class 18! Lecture 18: Outline and Objectives. Replication is semiconservative! Replication: DNA DNA! Introductory Biochemistry!
 Lecture 18: Outline and Objectives Welcome to Class 18! Introductory Biochemistry! l DNA Replication! l DNA polymerase! l the enzymatic reaction! l proofreading and accuracy! l DNA synthesis! l origins
Lecture 18: Outline and Objectives Welcome to Class 18! Introductory Biochemistry! l DNA Replication! l DNA polymerase! l the enzymatic reaction! l proofreading and accuracy! l DNA synthesis! l origins
Biochemistry 674, Fall, 1996: Nucleic Acids Final Exam: December 16, 1996 Your Name Here:
 Biochemistry 674, Fall, 1996: Nucleic Acids Final Exam: December 16, 1996 Your Name Here: Prof. Jason Kahn This exam has six questions worth various numbers of points, for a total of 200. Answer all six.
Biochemistry 674, Fall, 1996: Nucleic Acids Final Exam: December 16, 1996 Your Name Here: Prof. Jason Kahn This exam has six questions worth various numbers of points, for a total of 200. Answer all six.
Enzymes used in DNA Replication
 Enzymes used in DNA Replication This document holds the enzymes used in DNA replication, their pictorial representation and functioning. DNA polymerase: DNA polymerase is the chief enzyme of DNA replication.
Enzymes used in DNA Replication This document holds the enzymes used in DNA replication, their pictorial representation and functioning. DNA polymerase: DNA polymerase is the chief enzyme of DNA replication.
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302. January 25, 2006
 DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 January 25, 2006 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 January 25, 2006 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
DNA Replication and Repair
 DN Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif DN Replication genetic information is passed on to the next generation semi-conservative Parent molecule with
DN Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif DN Replication genetic information is passed on to the next generation semi-conservative Parent molecule with
Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination
 Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination Copyright Copyright 2009 Pearson 2009 Pearson Education, Education, Inc. Inc. 11.1 DNA is reproduced by Semiconservative Replication The complementarity of
Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination Copyright Copyright 2009 Pearson 2009 Pearson Education, Education, Inc. Inc. 11.1 DNA is reproduced by Semiconservative Replication The complementarity of
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 26, 2005
 DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 26, 2005 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 26, 2005 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded under any circumstances.
 Biochemistry 465 Section I March 4, 1999 Exam #1 Prof. Jason D. Kahn Your Printed Name: Your SS#: Your Signature: You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be
Biochemistry 465 Section I March 4, 1999 Exam #1 Prof. Jason D. Kahn Your Printed Name: Your SS#: Your Signature: You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be
Molecular Biology (2)
 Molecular Biology (2) DNA replication Mamoun Ahram, PhD Second semester, 2018-2019 Resources This lecture Cooper, pp. 191-207 2 Some basic information The entire DNA content of the cell is known as genome.
Molecular Biology (2) DNA replication Mamoun Ahram, PhD Second semester, 2018-2019 Resources This lecture Cooper, pp. 191-207 2 Some basic information The entire DNA content of the cell is known as genome.
Biochemistry 302, February 11, 2004 Exam 1 (100 points) 1. What form of DNA is shown on this Nature Genetics cover? Z-DNA or left-handed DNA
 1 Biochemistry 302, February 11, 2004 Exam 1 (100 points) Name I. Structural recognition (very short answer, 2 points each) 1. What form of DNA is shown on this Nature Genetics cover? Z-DNA or left-handed
1 Biochemistry 302, February 11, 2004 Exam 1 (100 points) Name I. Structural recognition (very short answer, 2 points each) 1. What form of DNA is shown on this Nature Genetics cover? Z-DNA or left-handed
DNA Metabolism. I. DNA Replication. A. Template concept: 1. How can you make a copy of a molecule? 2. Complementary Hydrogen bonding
 DNA Metabolism I. DNA Replication A. Template concept: 1. How can you make a copy of a molecule? 2. Complementary Hydrogen bonding B. DNA replication follows a set of fundamental rules 1. Semiconservative
DNA Metabolism I. DNA Replication A. Template concept: 1. How can you make a copy of a molecule? 2. Complementary Hydrogen bonding B. DNA replication follows a set of fundamental rules 1. Semiconservative
Biochemistry 673 Your Name: Regulation of Metabolism Assoc. Prof. Jason Kahn Midterm Exam (100 points total) October 19, 2007
 Biochemistry 673 Your Name: Regulation of Metabolism Assoc. Prof. Jason Kahn Midterm Exam (100 points total) October 19, 2007 You have 50 minutes for this exam. Explanations should be concise and clear,
Biochemistry 673 Your Name: Regulation of Metabolism Assoc. Prof. Jason Kahn Midterm Exam (100 points total) October 19, 2007 You have 50 minutes for this exam. Explanations should be concise and clear,
BIOL 5304 Molecular Biology Fall 2018 Name. Homework #1 Due Monday, September 10 at 10:00 AM. 80 points - 1 -
 BIOL 5304 Molecular Biology Fall 2018 ame omework #1 Due Monday, September 10 at 10:00 AM 80 points - 1 - 1. (20 points-maximum) For each item at the left, find all the descriptions on the right that apply
BIOL 5304 Molecular Biology Fall 2018 ame omework #1 Due Monday, September 10 at 10:00 AM 80 points - 1 - 1. (20 points-maximum) For each item at the left, find all the descriptions on the right that apply
Please write your name or student ID number on every page.
 MCB 110 First Exam A TOTAL OF SIX PAGES NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 36 II 35 III 27 IV 28 V 24 150 Please write your name or student ID number on every page. This exam
MCB 110 First Exam A TOTAL OF SIX PAGES NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 36 II 35 III 27 IV 28 V 24 150 Please write your name or student ID number on every page. This exam
 The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
DNA Replication I Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 24, 2005
 DNA Replication I Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 24, 2005 Watson Crick prediction: Each stand of parent DNA serves as a template for synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand Fig. 4.12 Proof
DNA Replication I Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 24, 2005 Watson Crick prediction: Each stand of parent DNA serves as a template for synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand Fig. 4.12 Proof
7.05 Recitation Schedule
 7.05 Spring 004 February 13, 004 7.05 Recitation Schedule Contact Information TA: Victor Sai Recitation: Friday, 3-4pm, -13 E-mail: sai@mit.edu ffice ours: Friday, 4-5pm, -13 Spring 004 Calendar Sun Monday
7.05 Spring 004 February 13, 004 7.05 Recitation Schedule Contact Information TA: Victor Sai Recitation: Friday, 3-4pm, -13 E-mail: sai@mit.edu ffice ours: Friday, 4-5pm, -13 Spring 004 Calendar Sun Monday
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 34 Friday 23 Apr.
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 34 Friday 23 Apr. Summary of DNA Replication in Prokaryotes origin of replication initial double helix origin of replication new growing polynucleotide chains Circular molecule
BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 34 Friday 23 Apr. Summary of DNA Replication in Prokaryotes origin of replication initial double helix origin of replication new growing polynucleotide chains Circular molecule
Cyclin- Dependent Protein Kinase. Function
 Complex Cyclin Cyclin- Dependent rotein Kinase Function promotes passage through restriction G1-CDK Complex Cyclin D CDK4 or CDK6 point in late G1 G1/S-CDK Complex Cyclin E CDK2 commits the cell to DA
Complex Cyclin Cyclin- Dependent rotein Kinase Function promotes passage through restriction G1-CDK Complex Cyclin D CDK4 or CDK6 point in late G1 G1/S-CDK Complex Cyclin E CDK2 commits the cell to DA
Chapter 3: Duplicating the DNA- Replication
 3. Basic Genetics Plant Molecular Biology Chapter 3: Duplicating the DNA- Replication Double helix separation New strand synthesis Plant Biotechnology Lecture 2 1 I've missed more than 9000 shots in my
3. Basic Genetics Plant Molecular Biology Chapter 3: Duplicating the DNA- Replication Double helix separation New strand synthesis Plant Biotechnology Lecture 2 1 I've missed more than 9000 shots in my
Molecular Biology: General Theory
 Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory
 Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes. Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes?
 Midterm Q Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes? G T 3 A 4 C 5 U 00% Midterm Q Which of the following
Midterm Q Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes? G T 3 A 4 C 5 U 00% Midterm Q Which of the following
Fundamental Process. Unit Map. Unit
 Unit 3 Unit Map 3.A DNA replication, repair and recombination 120 3.B RNA synthesis and processing 137 3.C Protein synthesis and processing 151 3.D Control of gene expression at transcription and translation
Unit 3 Unit Map 3.A DNA replication, repair and recombination 120 3.B RNA synthesis and processing 137 3.C Protein synthesis and processing 151 3.D Control of gene expression at transcription and translation
COURSE UNIT DESCRIPTION - MOLECULAR BIOLOGY I
 P stage) 4P P semester, COURSE UNIT DESCRIPTION - MOLECULAR BIOLOGY I MOLECULAR BIOLOGY I Course unit title Code Lecturer(s) Coordinator: Prof. Edita SUŽIEDĖLIENĖ Oer(s): Dr. Julija Armalytė Lect. dr.
P stage) 4P P semester, COURSE UNIT DESCRIPTION - MOLECULAR BIOLOGY I MOLECULAR BIOLOGY I Course unit title Code Lecturer(s) Coordinator: Prof. Edita SUŽIEDĖLIENĖ Oer(s): Dr. Julija Armalytė Lect. dr.
DNA Model Building and Replica3on
 DNA Model Building and Replica3on DNA Replication S phase Origins of replication in E. coli and eukaryotes (a) Origin of replication in an E. coli cell Origin of replication Bacterial chromosome Doublestranded
DNA Model Building and Replica3on DNA Replication S phase Origins of replication in E. coli and eukaryotes (a) Origin of replication in an E. coli cell Origin of replication Bacterial chromosome Doublestranded
Questions from chapters in the textbook that are relevant for the final exam
 Questions from chapters in the textbook that are relevant for the final exam Chapter 9 Replication of DNA Question 1. Name the two substrates for DNA synthesis. Explain why each is necessary for DNA synthesis.
Questions from chapters in the textbook that are relevant for the final exam Chapter 9 Replication of DNA Question 1. Name the two substrates for DNA synthesis. Explain why each is necessary for DNA synthesis.
The replication forks Summarising what we know:
 When does replication occur? MBLG1001 lecture 10 Replication the once in a lifetime event! Full blown replication only occurs once, just before cell division BUT the DNA template is constantly being repaired.
When does replication occur? MBLG1001 lecture 10 Replication the once in a lifetime event! Full blown replication only occurs once, just before cell division BUT the DNA template is constantly being repaired.
DNApol then (4) adds deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates to the 3'-end of the primer until the molecules are completely replicated.
 Biochemistry II DNA Synthesis p-p-p-n-oh ssna is a nucleotide (of any particular base, as represented by the N) with a 5' triphosphate and a 3' hydroxide. This module is on DNA so the nucleotide is dntp
Biochemistry II DNA Synthesis p-p-p-n-oh ssna is a nucleotide (of any particular base, as represented by the N) with a 5' triphosphate and a 3' hydroxide. This module is on DNA so the nucleotide is dntp
Chapter Twelve: DNA Replication and Recombination
 This is a document I found online that is based off of the fourth version of your book. Not everything will apply to the upcoming exam so you ll have to pick out what you thing is important and applicable.
This is a document I found online that is based off of the fourth version of your book. Not everything will apply to the upcoming exam so you ll have to pick out what you thing is important and applicable.
DNA ORGANIZATION AND REPLICATION
 DNA ORGANIZATION AND REPLICATION THE CENTRAL DOGMA DNA Replication Transcription Translation STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF DNA DNA is present in the nucleus as CHROMATIN. The basic unit of chromatin is NUCLEOSOME
DNA ORGANIZATION AND REPLICATION THE CENTRAL DOGMA DNA Replication Transcription Translation STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF DNA DNA is present in the nucleus as CHROMATIN. The basic unit of chromatin is NUCLEOSOME
MCB 110 SP 2005 Second Midterm
 MCB110 SP 2005 Midterm II Page 1 ANSWER KEY MCB 110 SP 2005 Second Midterm Question Maximum Points Your Points I 40 II 40 III 36 IV 34 150 NOTE: This is my answer key (KC). The graders were given disgression
MCB110 SP 2005 Midterm II Page 1 ANSWER KEY MCB 110 SP 2005 Second Midterm Question Maximum Points Your Points I 40 II 40 III 36 IV 34 150 NOTE: This is my answer key (KC). The graders were given disgression
Fig. 16-7a. 5 end Hydrogen bond 3 end. 1 nm. 3.4 nm nm
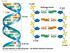 Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Requirements for the Genetic Material
 Requirements for the Genetic Material 1. Replication Reproduced and transmitted faithfully from cell to cell-generation to generation. 2. Information Storage Biologically useful information in a stable
Requirements for the Genetic Material 1. Replication Reproduced and transmitted faithfully from cell to cell-generation to generation. 2. Information Storage Biologically useful information in a stable
III. Detailed Examination of the Mechanism of Replication A. Initiation B. Priming C. Elongation D. Proofreading and Termination
 Outline for Replication I. General Features of Replication A. Semi-Conservative B. Starts at Origin C. Bidirectional D. Semi-Discontinuous II. Proteins and Enzymes of Replication III. Detailed Examination
Outline for Replication I. General Features of Replication A. Semi-Conservative B. Starts at Origin C. Bidirectional D. Semi-Discontinuous II. Proteins and Enzymes of Replication III. Detailed Examination
Quiz Submissions Quiz 4
 Quiz Submissions Quiz 4 Attempt 1 Written: Nov 1, 2015 17:35 Nov 1, 2015 22:19 Submission View Released: Nov 4, 2015 20:24 Question 1 0 / 1 point Three RNA polymerases synthesize most of the RNA present
Quiz Submissions Quiz 4 Attempt 1 Written: Nov 1, 2015 17:35 Nov 1, 2015 22:19 Submission View Released: Nov 4, 2015 20:24 Question 1 0 / 1 point Three RNA polymerases synthesize most of the RNA present
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 4: E. coli DNA Replicase Structure & Function. Gary Peter
 Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 4: E. coli DNA Replicase Structure & Function Gary Peter Learning Objectives 1. List and explain the mechanisms by which E. coli DNA is replicated 2. Describe
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 4: E. coli DNA Replicase Structure & Function Gary Peter Learning Objectives 1. List and explain the mechanisms by which E. coli DNA is replicated 2. Describe
BS GENOMES. DNA replication and repair
 BS2009 - GENOMES DNA replication and repair REPLICATION GENERAL PRINCIPLES START Must be ready Must know where to start FINISH Must all finish Must ensure that each piece of DNA is replicated only once
BS2009 - GENOMES DNA replication and repair REPLICATION GENERAL PRINCIPLES START Must be ready Must know where to start FINISH Must all finish Must ensure that each piece of DNA is replicated only once
You Should Be Able To
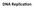 DNA Replica,on You Should Be Able To 1. Describe the func9on of: DNA POL1, DNA POL3, Sliding Clamp, SSBPs, Ligase, Topoisomerase, Helicase, Primase 2. Describe DNA synthesis on the leading and lagging
DNA Replica,on You Should Be Able To 1. Describe the func9on of: DNA POL1, DNA POL3, Sliding Clamp, SSBPs, Ligase, Topoisomerase, Helicase, Primase 2. Describe DNA synthesis on the leading and lagging
Molecular Biology, Lecture 3 DNA Replication
 Molecular Biology, Lecture 3 DNA Replication We will continue talking about DNA replication. We have previously t discussed the structure of DNA. DNA replication is the copying of the whole DNA content
Molecular Biology, Lecture 3 DNA Replication We will continue talking about DNA replication. We have previously t discussed the structure of DNA. DNA replication is the copying of the whole DNA content
Biochemistry. DNA Polymerase. Structure and Function of Biomolecules II. Principal Investigator
 Paper : 03 Module: 14 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry,
Paper : 03 Module: 14 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry,
Prokaryotic cells divide by pinching in two. Fig. 10-CO, p.240
 Prokaryotic cells divide by pinching in two Fig. 10-CO, p.240 Learning Objectives 1. What Is the Flow of Genetic Information in the Cell? 2. What Are the General Considerations in the Replication of DNA?
Prokaryotic cells divide by pinching in two Fig. 10-CO, p.240 Learning Objectives 1. What Is the Flow of Genetic Information in the Cell? 2. What Are the General Considerations in the Replication of DNA?
The Size and Packaging of Genomes
 DNA Replication The Size and Packaging of Genomes Vary greatly in size Ø Smallest viruses- 4 or 5 genes Ø Escherichia coli- 4,288 genes Ø Human cell- 20,000 to 25,000 genes E. coli 4 million base pairs
DNA Replication The Size and Packaging of Genomes Vary greatly in size Ø Smallest viruses- 4 or 5 genes Ø Escherichia coli- 4,288 genes Ø Human cell- 20,000 to 25,000 genes E. coli 4 million base pairs
DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA
 DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
Biological Sciences 50 Practice Exam 2
 NAME: Fall 2005 TF: Biological Sciences 50 Practice Exam 2 A. Be sure to write your name on the top of each of page of the examination. B. Write each answer only on the same page as the pertinent question.
NAME: Fall 2005 TF: Biological Sciences 50 Practice Exam 2 A. Be sure to write your name on the top of each of page of the examination. B. Write each answer only on the same page as the pertinent question.
Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section B and ONE question from Section C.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIO-2B02 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIO-2B02 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question
DNA REPLICATION. Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari»
 DNA REPLICATION Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari» Learning objectives 1. Understand the basic rules governing DNA replication 2. Understand the function of key proteins involved in a generalised replication
DNA REPLICATION Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari» Learning objectives 1. Understand the basic rules governing DNA replication 2. Understand the function of key proteins involved in a generalised replication
DNA Replication in Eukaryotes
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44517 1 DNA Replication in Eukaryotes OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m44517 1 DNA Replication in Eukaryotes OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
DNA REPLICATION. Third Stage. Lec. 12 DNA Replication. Lecture No.: 12. A. Watson & Crick (1952) C. Cairns (1963) autoradiographic experiment
 Lec. 12 DNA Replication A. Watson & Crick (1952) Proposed a model where hydrogen bonds break, the two strands separate, and DNA synthesis occurs semi-conservatively in the same net direction. While a straightforward
Lec. 12 DNA Replication A. Watson & Crick (1952) Proposed a model where hydrogen bonds break, the two strands separate, and DNA synthesis occurs semi-conservatively in the same net direction. While a straightforward
Bacterial DNA replication
 Bacterial DNA replication Summary: What problems do these proteins solve? Tyr OH attacks PO4 and forms a covalent intermediate Structural changes in the protein open the gap by 20 Å! 1 Summary: What problems
Bacterial DNA replication Summary: What problems do these proteins solve? Tyr OH attacks PO4 and forms a covalent intermediate Structural changes in the protein open the gap by 20 Å! 1 Summary: What problems
Principle 2. Overview of Central. 3. Nucleic Acid Structure 4. The Organization of
 Central dogma I and II the flow of genetic information 1. The Transforming Principle 2. Overview of Central Dogma 3. Nucleic Acid Structure 4. The Organization of DNA in Cells 5. DNA Replication 6. Gene
Central dogma I and II the flow of genetic information 1. The Transforming Principle 2. Overview of Central Dogma 3. Nucleic Acid Structure 4. The Organization of DNA in Cells 5. DNA Replication 6. Gene
DNA Replication III & DNA Damage/Modification Biochemistry 302. January 27, 2006
 DNA Replication III & DNA Damage/Modification Biochemistry 302 January 27, 2006 Bacterial replication organized into a membrane-bound replication factory Two replisomes do not travel away from one another
DNA Replication III & DNA Damage/Modification Biochemistry 302 January 27, 2006 Bacterial replication organized into a membrane-bound replication factory Two replisomes do not travel away from one another
Enter Legible BANNER ID: B 0 0
 INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY BIOL0280 Third Midterm Examination May 1, 2012 Enter Legible BANNER ID: B 0 0 Make sure that your Banner ID is on every page. This is the only way we have of matching you with
INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY BIOL0280 Third Midterm Examination May 1, 2012 Enter Legible BANNER ID: B 0 0 Make sure that your Banner ID is on every page. This is the only way we have of matching you with
ARUNAI ACADEMY FOR PG TRB-BOTANY DHARMAPURI REPLICATION - ENZYMES.
 ARUNAI ACADEMY FOR PG TRB-BOTANY DHARMAPURI.9500244679 REPLICATION - ENZYMES DNA HELICASE Sparation of two strands- DNA helicase enzyme functions Unwinds DNA. DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen
ARUNAI ACADEMY FOR PG TRB-BOTANY DHARMAPURI.9500244679 REPLICATION - ENZYMES DNA HELICASE Sparation of two strands- DNA helicase enzyme functions Unwinds DNA. DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen
RNA: Structure & Synthesis. Amr S. Moustafa, M.D.; Ph.D.
 RNA: Structure & Synthesis By Amr S. Moustafa, M.D.; Ph.D. Objectives The differences between DNA and RNA The structure and functions of RNAs RNA synthesis (Transcription) Post-transcriptional events (modifications)
RNA: Structure & Synthesis By Amr S. Moustafa, M.D.; Ph.D. Objectives The differences between DNA and RNA The structure and functions of RNAs RNA synthesis (Transcription) Post-transcriptional events (modifications)
The flow of Genetic information
 The flow of Genetic information http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter3/animation dna_replication quiz_1_.html 1 DNA Replication DNA is a double-helical molecule Watson and
The flow of Genetic information http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter3/animation dna_replication quiz_1_.html 1 DNA Replication DNA is a double-helical molecule Watson and
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points
 Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the back of the
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the back of the
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: I 32 II 33 III 24 IV 30 V
 MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 32 II 33 III 24 IV 30 V 31 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 32 II 33 III 24 IV 30 V 31 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses)
 NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
Lecture 1 Sunday, 4 March :24 pm
 Lecture 1 Sunday, 4 March 2018 10:24 pm Amino acid side chains can be Hydrophobic, hydrophilic Positive, negatively charged Movement of information OH removed from 2' carbon to make the end more stable
Lecture 1 Sunday, 4 March 2018 10:24 pm Amino acid side chains can be Hydrophobic, hydrophilic Positive, negatively charged Movement of information OH removed from 2' carbon to make the end more stable
7.014 Quiz II Handout
 7.014 Quiz II Handout Quiz II: Wednesday, March 17 12:05-12:55 54-100 **This will be a closed book exam** Quiz Review Session: Friday, March 12 7:00-9:00 pm room 54-100 Open Tutoring Session: Tuesday,
7.014 Quiz II Handout Quiz II: Wednesday, March 17 12:05-12:55 54-100 **This will be a closed book exam** Quiz Review Session: Friday, March 12 7:00-9:00 pm room 54-100 Open Tutoring Session: Tuesday,
Tutorial Week #9 Page 1 of 11
 Tutorial Week #9 Page 1 of 11 Tutorial Week #9 DNA Replication Before the tutorial: Read ECB Chapter 6 p195-207, and review your lecture notes Read this tutorial and create a table of definitions and functions
Tutorial Week #9 Page 1 of 11 Tutorial Week #9 DNA Replication Before the tutorial: Read ECB Chapter 6 p195-207, and review your lecture notes Read this tutorial and create a table of definitions and functions
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 13
 Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 13 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University February 11, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 13 February 11, 2013 1 / 26 Outline Questions and answers replication
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 13 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University February 11, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 13 February 11, 2013 1 / 26 Outline Questions and answers replication
Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang
 Today s Agenda: I. DNA Structure II. DNA Replication III. DNA Proofreading and Repair IV. The Central Dogma V. Transcription VI. Post-transcriptional Modifications Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11
Today s Agenda: I. DNA Structure II. DNA Replication III. DNA Proofreading and Repair IV. The Central Dogma V. Transcription VI. Post-transcriptional Modifications Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chromosomes and DNA Morgan s experiments with Drosophila were able to link hereditary factors to specific locations on chromosomes. The double-helical model
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chromosomes and DNA Morgan s experiments with Drosophila were able to link hereditary factors to specific locations on chromosomes. The double-helical model
Genetic Information: DNA replication
 Genetic Information: DNA replication Umut Fahrioglu, PhD MSc DNA Replication Replication of DNA is vital to the transmission of genomes and the genes they contain from one cell generation to the other.
Genetic Information: DNA replication Umut Fahrioglu, PhD MSc DNA Replication Replication of DNA is vital to the transmission of genomes and the genes they contain from one cell generation to the other.
SCBC203 Cell Division & DNA Synthesis. Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318
 SCBC203 Cell Division & DNA Synthesis Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318 Rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives 1. Explain the biological roles & significance
SCBC203 Cell Division & DNA Synthesis Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318 Rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives 1. Explain the biological roles & significance
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.8 DNA REPLICATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: SEMICONSERVATIVE REPLICATION Before replication was understood, there were three of how DNA is replicated Conservative replication states that after replication, there is
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: SEMICONSERVATIVE REPLICATION Before replication was understood, there were three of how DNA is replicated Conservative replication states that after replication, there is
Biology 30 DNA Review: Importance of Meiosis nucleus chromosomes Genes DNA
 Biology 30 DNA Review: Importance of Meiosis Every cell has a nucleus and every nucleus has chromosomes. The number of chromosomes depends on the species. o Examples: Chicken 78 Chimpanzee 48 Potato 48
Biology 30 DNA Review: Importance of Meiosis Every cell has a nucleus and every nucleus has chromosomes. The number of chromosomes depends on the species. o Examples: Chicken 78 Chimpanzee 48 Potato 48
DNA Replication and Repair
 DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
Hershey & Chase Avery, MacLeod, & McCarty DNA: The Genetic Material
 DA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 Griffith s experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae Live S strain cells killed the mice Live R strain cells did not kill the mice eat-killed S strain cells did not kill
DA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 Griffith s experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae Live S strain cells killed the mice Live R strain cells did not kill the mice eat-killed S strain cells did not kill
DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication Test Review
 DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication Test Review What does DNA stand for? Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA is what type of macromolecule? DNA is a nucleic acid The building blocks
DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication Test Review What does DNA stand for? Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA is what type of macromolecule? DNA is a nucleic acid The building blocks
DNA: Structure & Replication
 DNA Form & Function DNA: Structure & Replication Understanding DNA replication and the resulting transmission of genetic information from cell to cell, and generation to generation lays the groundwork
DNA Form & Function DNA: Structure & Replication Understanding DNA replication and the resulting transmission of genetic information from cell to cell, and generation to generation lays the groundwork
STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE
 STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE Consists of three parts: Deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Adenine (purine), Cytosine, Guanine (purine), Thymine Purine: 2 carbon rings of nitrogen-containing
STRUCTURE OF A NUCLEOTIDE Consists of three parts: Deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Adenine (purine), Cytosine, Guanine (purine), Thymine Purine: 2 carbon rings of nitrogen-containing
Gene Expression- Protein Synthesis
 Gene Expression- Protein Synthesis Protein synthesis is the key to expression of biological information - Structural Protein: bones, cartilage - Contractile Proteins: myosin, actin - Enzymes - Transport
Gene Expression- Protein Synthesis Protein synthesis is the key to expression of biological information - Structural Protein: bones, cartilage - Contractile Proteins: myosin, actin - Enzymes - Transport
Biology Summer 2013 MIDTERM EXAM
 Biology 105 - Summer 2013 MIDTERM EXAM Name: SCORE: 5 X 2 Point Questions 10 points 12 X 5 Point Questions 60 points 4 X 10 Point Questions 40 points Drop the lowest of the 10 point questions -10 points
Biology 105 - Summer 2013 MIDTERM EXAM Name: SCORE: 5 X 2 Point Questions 10 points 12 X 5 Point Questions 60 points 4 X 10 Point Questions 40 points Drop the lowest of the 10 point questions -10 points
DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid
 DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms DNA controls all the chemical changes which take place in cells DNA Structure
DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms DNA controls all the chemical changes which take place in cells DNA Structure
AP Biology Day 27. Wednesday, October 26, 2016
 AP Biology Day 27 Wednesday, October 26, 2016 Do-Now 1. Double check Is your unit log complete? Is your lab notebook up to date with scores? Did you write your Unit 4 log standards? Did you begin filling
AP Biology Day 27 Wednesday, October 26, 2016 Do-Now 1. Double check Is your unit log complete? Is your lab notebook up to date with scores? Did you write your Unit 4 log standards? Did you begin filling
Nucleic Acids: Structure and Function
 ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ucleotides are made up of: phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar, and
ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ucleotides are made up of: phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar, and
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number:
 MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 35 II 29 III 30 IV 32 V 24 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 35 II 29 III 30 IV 32 V 24 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
Polymerase chain reaction
 Core course BMS361N Genetic Engineering Polymerase chain reaction Prof. Narkunaraja Shanmugam Dept. Of Biomedical Science School of Basic Medical Sciences Bharathidasan University The polymerase chain
Core course BMS361N Genetic Engineering Polymerase chain reaction Prof. Narkunaraja Shanmugam Dept. Of Biomedical Science School of Basic Medical Sciences Bharathidasan University The polymerase chain
BCMB Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair
 BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
BCMB Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair
 BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
The Structure of DNA
 The Structure of DNA Questions to Ponder 1) How is the genetic info copied? 2) How does DNA store the genetic information? 3) How is the genetic info passed from generation to generation? The Structure
The Structure of DNA Questions to Ponder 1) How is the genetic info copied? 2) How does DNA store the genetic information? 3) How is the genetic info passed from generation to generation? The Structure
