Warm-up. don t know you may use a dictionary or dictionary.com on your phones)
|
|
|
- Alice Jefferson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Warm-up 1. A state that conquers other lands and rules over them is known as an 2. What does republic mean? And where have you heard it used before? (If you don t know you may use a dictionary or dictionary.com on your phones) 3. What do you already know about Julius Caesar and the Roman Empire?
2 Most missed questions on test 1. Who was the father of history 2. Greek philosopher and tutor to Alexander the Great 3. Which of the following statements about Confucianism is true? a. It was widely practiced in India b. Confucius believed Chinese people should respect their mothers c. It is technically not considered a religion because it does not focus on worshipping a God or gods who created the Earth d. It is a religion devoted to achieving salvation through ones relationship with their ruler
3 Rome Most and missed Early Christianity questions on the Section test 1 1. Under Pericles reign, Greece went through a golden age. All of the following were goals of Pericles EXCEPT a. To make Sparta a colony of Athens b. Strengthen Athenian Democracy c. To hold and strengthen the empire d. To glorify Athens 2. Which statement most likely represents the view of a citizen of ancient Athens visiting Sparta? a. The government and society in Sparta are very strict. The people have little voince in government. b. I feel as though I have never left home. Everything is almost exactly the same as it is in Athens. c. This society allows for more freedom of expression that I have ever experienced in Athens. d. I have never heard of a society like Sparta that believes in only one God.
4 Roman Republic Chapter 6 section 1
5 Does this Empire look familiar? How does it compare to the one Alexander the Great created? How could Rome s geographic location help it to prosper?
6 Main Idea The Foundations of Rome From a small town on the banks of an Italian river, Rome grew to control the entire Mediterranean region. Reading Focus Where and how did Roman civilization develop? What led to Rome s becoming a republic? What were the major events in Rome s expansion?
7 Rome and Early Roman Christianity Civilization Develops Section 1 Italy s Geography Peninsula logical place for emergence of mighty empire Juts south from Europe far into Mediterranean Sea Lies almost halfway between eastern, western boundaries of the Mediterranean sea Protected by mountains, sea Rich soil, mild climate
8 The Mythical Founding of Rome Legend: Romulus and Remus, twin brothers raised by shewolf; founded city 753 BC Reality: Members of Indo- European tribe, Latins, reached Italy 1000s BC; built Rome City prospered partly from location on Tiber River Valuable trade routes, easy access to sea
9 The Rome Etruscan s and Early were Christianity the first group Section 1 of people to settle in Rome. They looked to the Ancient Greeks and Admired their style of Architecture and art.
10 Summarize What advantages did Rome s location give the city? Answer(s): protected by mountains; sea provided protection and transportation; had rich soil, pleasant climate; located on major trade routes; Tiber River provided easy access to the sea
11 Rome and A Early Bumpy Christianity Road to a Republic Section 1 Rome's era as a monarchy ended in 509 B.C. with the overthrow of its seventh king, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, whom ancient historians portrayed as cruel and tyrannical ruler, compared to his good and kind predecessors. A popular uprising was said to have arisen over the rape of a virtuous noblewoman, Lucretia, by the king's son. Whatever the cause, Rome turned from a monarchy into a republic, a word derived from res publica, or "property of the people."
12 Under a Republic A republic is a form of government in which power rests with citizens who have the right to vote for their leaders. In Rome, citizenship with voting rights was granted only to freeborn male citizens.
13 Patricians Rome Becomes a Republic Patricians were the wealthy landowners who held most of the power. The patricians inherited their power and social status. They claimed that their ancestry gave them the authority to make laws for Rome. Plebeians The other important group was the plebeians, the common farmers, artisans, and merchants who made up the majority of the population. The plebeians were citizens of Rome with the right to vote. However, they were barred by law from holding most important government positions. Invaders threatened 494 BC; plebeians refused to fight until changes made Patricians knew they would have no army, expanded plebian rights
14 Tribune Rome s leaders allowed the plebeians to form their own assembly and elect representatives called tribunes. Tribunes protected the rights of the plebeians from unfair acts of patrician officials. Government under the Republic Rome achieved a balanced government Their government had taken the best features of a monarchy (government by a king), an aristocracy (gov. by nobles), and a democracy (gov. by the people)
15 Twelve Tables An important victory for the plebeians was to force the creation of a written law code. With laws unwritten, patrician officials often interpreted the law to suit themselves. In 451 B.C., a group of ten officials began writing down Rome s laws. The laws were carved on twelve bronze tablets, or tables, and hung in the Forum. The Twelve Tables (Rome s first written law code) established the idea that all free citizens had a right to the protection of the law.
16 Republican Government New Offices and Institutions Elements of Government Rome had two officials called consuls. Like kings, they commanded the army and directed the government. The senate was the aristocratic (governed by nobles) branch of Rome s government. It had both legislative and administrative functions in the republic. At the end of their one-year term, Consuls entered the Senate of Rome, the highest legislative body of the government. Because the consuls and Senate both represented the interests of the patricians (aristocratic, wealthy classes), there was always tension between the wealthy classes and the plebeians, or common people. In times of crisis, the republic could appoint a dictator- a leader who had absolute power to make laws and command the army
17 Drawing Inferences Why did patricians want to prevent plebeians from holding important political positions?
18
19 For hundreds of years after the founding of the republic, Rome sought to expand its territories though trade and conquest. In order to do this what would a civilization need? Military Might The Republic Expands Successful expansion not possible without powerful army All Roman men between ages 17 and 46 with minimum amount of property required to serve in army during times of war TedEd Life of a Roman Teen
20 Forming an Opinion Do you think the Roman Republic owed its success more to its form of government or it s military? Why?
21 Crash Course
22 Twelve Tables Activity
23 The Conquest of Italy 265 BC, Romans had defeated Etruscans and Greek cities in Southern Italy Romans imposed two strict conditions on subject people subjects had to provide troops for Roman army, abandon any dealings with foreign nations Other than those conditions, Rome rarely interfered with domestic affairs of people it conquered Sicily Once in control of Italy, Rome turned attention to Sicily, large island to south of Italian Peninsula In Sicily, Rome came into conflict with Carthage, powerful North African trading city Conflict grew into series of three wars referred to as Punic Wars between B.C. Punic Wars raged for nearly 80 years
24 The Punic Wars Violence between Rome and Carthage broke out in 264 BC. Because the First Punic War was fought mostly at sea, Carthage s powerful navy dominated the early fighting. Soon, however, the Romans built a navy of their own and were able to defeat Carthage. Hannibal Brilliant Carthaginian military strategist 218 BC, he sought to surprise the Romans. He led his army across Pyrenees, Alps to invade Italy Hannibal ravaged Italy, defeated every army he faced Scipio Romans decided to take war to Africa General Publius Cornelius Scipio sailed to Africa, besieged Carthage Forced Hannibal to sail home Scipio defeated Hannibal, took Carthage, won Second Punic War The Romans had defeated Carthage, but it did not destroy the city as many citizens had wanted.
25 Horrible Histories Hannibal
26 Carthage Falls Huge losses of Second Punic War remained in memories of many Romans 149 BC Rome decided to destroy old enemy once and for all Declared war on Carthage for third time After siege of three years, Carthage fell Romans enslaved entire population, completely destroyed city They banned any people from living there
27 Building an Empire Rome s victories in the Punic Wars gave it dominance over the western Mediterranean. The Romans then went on to conquer the eastern half. By about 70 B.C., Rome s Mediterranean empire stretched from Anatolia in the east to Spain in the west.
The Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome
 Prologue 1 The Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Essential Question: How did Greece and Rome contribute to the development of democracy in the United States? Athens Builds a Limited Democracy Changes In
Prologue 1 The Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Essential Question: How did Greece and Rome contribute to the development of democracy in the United States? Athens Builds a Limited Democracy Changes In
Social Studies Review. Geography & Early Man
 Geography & Early Man Word Bank: Barter Latitude Basic needs Fresh water Culture Primary source Peninsula Good soil (fertile land) Longitude Directions: Fill in the blanks using the word bank above. 1.
Geography & Early Man Word Bank: Barter Latitude Basic needs Fresh water Culture Primary source Peninsula Good soil (fertile land) Longitude Directions: Fill in the blanks using the word bank above. 1.
Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 1
 Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the ancient foundations of the state in Athens, in Rome, and in the feudal system. 2. Analyze the rise of sovereign states. 3.
Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the ancient foundations of the state in Athens, in Rome, and in the feudal system. 2. Analyze the rise of sovereign states. 3.
Legacy of Ancient Greece & Rome. World History Dr. Robbins
 Legacy of Ancient Greece & Rome World History Dr. Robbins Athens Builds a Limited Democracy First large democracy in ancient Greece democracy = rule of the people City-state was basic political unit Earliest
Legacy of Ancient Greece & Rome World History Dr. Robbins Athens Builds a Limited Democracy First large democracy in ancient Greece democracy = rule of the people City-state was basic political unit Earliest
Enrichment Essay Ancient Greece and Rome and Their Influence on Modern Western Civilization (HA)
 Enrichment Essay Ancient Greece and Rome and Their Influence on Modern Western Civilization (HA) This essay examines the political, economic, and social structures of ancient Greece and Rome and explores
Enrichment Essay Ancient Greece and Rome and Their Influence on Modern Western Civilization (HA) This essay examines the political, economic, and social structures of ancient Greece and Rome and explores
M O T D onarchy ligarchy yranny emocracy
 In a monarchy, the power to rule rests in the hands of a single person, historically either a king or a queen. The word monarch comes directly from two Greek words monos and archon. In English, monos is
In a monarchy, the power to rule rests in the hands of a single person, historically either a king or a queen. The word monarch comes directly from two Greek words monos and archon. In English, monos is
The French Revolution
 The French Revolution Using your notes, complete the following paragraph. The Enlightenment is also known as the. During this time, people began to reject the teachings of the and the and question traditional
The French Revolution Using your notes, complete the following paragraph. The Enlightenment is also known as the. During this time, people began to reject the teachings of the and the and question traditional
Government in Athens
 SECTION 2 Government in Athens What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. Aristocrats and tyrants ruled early Athens. 2. Athens created the world s first democracy. 3. Ancient democracy was different than modern
SECTION 2 Government in Athens What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. Aristocrats and tyrants ruled early Athens. 2. Athens created the world s first democracy. 3. Ancient democracy was different than modern
AUTOCRACY. SS.7.C.3.1 Forms of Government
 AUTOCRACY An autocracy is a form of government where one person has unlimited power. One form of an autocracy is a dictatorship where a military leader secures power often through violent means. Another
AUTOCRACY An autocracy is a form of government where one person has unlimited power. One form of an autocracy is a dictatorship where a military leader secures power often through violent means. Another
MODELS OF GOVERNANCE: PALEOLITHIC ANCIENT ERA
 Students should explain how and why models of governance evolved between the Paleolithic and Ancient eras Section Overview: What is Government? : a system for controlling society Throughout history people
Students should explain how and why models of governance evolved between the Paleolithic and Ancient eras Section Overview: What is Government? : a system for controlling society Throughout history people
Standard 7-3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of independence movements that occurred throughout the world from 1770 through 1900.
 Standard 7-3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of independence movements that occurred throughout the world from 1770 through 1900. 7-3.2 Analyze the effects of the Napoleonic Wars on the
Standard 7-3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of independence movements that occurred throughout the world from 1770 through 1900. 7-3.2 Analyze the effects of the Napoleonic Wars on the
What is nationalism? What impact can it have?
 What is nationalism? What impact can it have? Nation - a group of people who share a common history, culture, or language and who live in the same area Nationalism- strong feelings of support for one s
What is nationalism? What impact can it have? Nation - a group of people who share a common history, culture, or language and who live in the same area Nationalism- strong feelings of support for one s
A tyranny is a form of government in which the ruling power is in the hands of an individual who has seized control, often by illegal means.
 A monarchy is a form of government in which the ruling power is in the hands of a single person. Most monarchies have been ruled by kings, usually with the help of a council of advisors. The word monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which the ruling power is in the hands of a single person. Most monarchies have been ruled by kings, usually with the help of a council of advisors. The word monarchy
The French Revolution CH
 The French Revolution CH. 7.2-5 The Assembly Reforms France National Assembly, declared: 1. All citizens (men) of France EQUAL. 2. Declaration of the Rights of Man Copied from US Dec. of Ind. *Protect
The French Revolution CH. 7.2-5 The Assembly Reforms France National Assembly, declared: 1. All citizens (men) of France EQUAL. 2. Declaration of the Rights of Man Copied from US Dec. of Ind. *Protect
The cradle of democracy.
 The cradle of democracy. Democracy derives from the ancient Greek, demokratia. : Demos = The people Kratien = To rule Quick Notes - The stuff you should write down. Greek word - Democracy Demos = The people
The cradle of democracy. Democracy derives from the ancient Greek, demokratia. : Demos = The people Kratien = To rule Quick Notes - The stuff you should write down. Greek word - Democracy Demos = The people
Government in Athens
 Government in Athens Aristocrats Democracy was born in Ancient Greece in the city of Athens. Democracy is a form of a government in which people rule themselves. However, Athens was ruled first by kings,
Government in Athens Aristocrats Democracy was born in Ancient Greece in the city of Athens. Democracy is a form of a government in which people rule themselves. However, Athens was ruled first by kings,
In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to
 In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to control the governed; and in the next place oblige it to
In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to control the governed; and in the next place oblige it to
America: Republic vs. Democracy
 America: Republic vs. Democracy By Frank Li, Ph.D. Founder & President, West-East International, Inc. January 11, 2013 In my book Saving America, Chinese Style, I fundamentally questioned democracy as
America: Republic vs. Democracy By Frank Li, Ph.D. Founder & President, West-East International, Inc. January 11, 2013 In my book Saving America, Chinese Style, I fundamentally questioned democracy as
The Athenian Constitution (Document A)
 The Athenian Constitution (Document A) Source: The following excerpt comes from The Athenian Constitution, written by the Greek philosopher Aristotle between 330 and 322 BC. Aristotle was the leading Greek
The Athenian Constitution (Document A) Source: The following excerpt comes from The Athenian Constitution, written by the Greek philosopher Aristotle between 330 and 322 BC. Aristotle was the leading Greek
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution What is a government? A government is a person, or group, who has the power to provide law, order, services, and security within a country. Government gives organization and structure
Creating the Constitution What is a government? A government is a person, or group, who has the power to provide law, order, services, and security within a country. Government gives organization and structure
Watch the Preview for the lesson. Then write down examples of images that support the following statements or answer the questions below.
 P r e v i e w Watch the Preview for the lesson. Then write down examples of images that support the following statements or answer the questions below. 1. We live in a democracy. 2. We participate in our
P r e v i e w Watch the Preview for the lesson. Then write down examples of images that support the following statements or answer the questions below. 1. We live in a democracy. 2. We participate in our
The Rise of Democracy
 The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 1 The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 2 26.1 Last chapter we talked about the fact that mountains and seas isolated Greek communities. As a result Greek communities developed
The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 1 The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 2 26.1 Last chapter we talked about the fact that mountains and seas isolated Greek communities. As a result Greek communities developed
Department of Humanities and Social Science
 Barry Stocker Barry.Stocker@itu.edu.tr https://barrystockerac.wordpress.com Department of Humanities and Social Science Faculty of Science and Letters POLITICAL THEORY. ITB 227E NOTES WEEK TWO NICCOLÒ
Barry Stocker Barry.Stocker@itu.edu.tr https://barrystockerac.wordpress.com Department of Humanities and Social Science Faculty of Science and Letters POLITICAL THEORY. ITB 227E NOTES WEEK TWO NICCOLÒ
Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy
 Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy FOQ #1: Did the English Civil War help or hurt Democracy? Explain. FOQ #2: What were the causes of the American Revolutionary War? How did it end? FOQ #3: What were the
Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy FOQ #1: Did the English Civil War help or hurt Democracy? Explain. FOQ #2: What were the causes of the American Revolutionary War? How did it end? FOQ #3: What were the
Impossible demands made of government, which, if granted, would mean its end. Unsuccessful gov t attempts to suppress the revolutionaries
 Stages of Crane Brinton Impossible demands made of government, which, if granted, would mean its end Unsuccessful gov t attempts to suppress the revolutionaries Revolutions gain power and seem united.
Stages of Crane Brinton Impossible demands made of government, which, if granted, would mean its end Unsuccessful gov t attempts to suppress the revolutionaries Revolutions gain power and seem united.
SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government.
 SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government. 1a. Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution of power, particularly unitary, confederal, and federal types of government. Unitary
SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government. 1a. Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution of power, particularly unitary, confederal, and federal types of government. Unitary
German Unification. Nationalism in Europe Section 2. Preview
 Preview German Unification Main Idea / Reading Focus Steps Toward Unification Bismarck s Plan for Germany Quick Facts: Steps to Unification in Germany Faces of History: Otto von Bismarck Unification and
Preview German Unification Main Idea / Reading Focus Steps Toward Unification Bismarck s Plan for Germany Quick Facts: Steps to Unification in Germany Faces of History: Otto von Bismarck Unification and
English Civil War, the Restoration, and the Glorious Revolution
 English Civil War, the Restoration, and the Glorious Revolution Vocabulary Parliament Legislative, or law-making, body in government representing the interests of the people. (ex. England) Magna Carta
English Civil War, the Restoration, and the Glorious Revolution Vocabulary Parliament Legislative, or law-making, body in government representing the interests of the people. (ex. England) Magna Carta
Georgia Milestones Grade 6 EOG Study/Resource Guide for Students and Parents Page 201 of 218
 Unit 8: Canada Today In this unit, you will examine our neighbor to the north, Canada. You will learn about its forms of government, including presidential, unitary, monarchy, and parliamentary systems
Unit 8: Canada Today In this unit, you will examine our neighbor to the north, Canada. You will learn about its forms of government, including presidential, unitary, monarchy, and parliamentary systems
Nationalism, the Franco-Prussian
 Nationalism, the Franco-Prussian War, and the Origins of WWI The Unification of German, and the idea of a German Fatherland, 1869-1914 Spring 2012 Revised European Nationalism The Congress of Vienna was
Nationalism, the Franco-Prussian War, and the Origins of WWI The Unification of German, and the idea of a German Fatherland, 1869-1914 Spring 2012 Revised European Nationalism The Congress of Vienna was
LL Copy the chart below. Fill it in as we watch Types of Government game show.
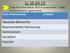 LL 10-24-13 Copy the chart below. Fill it in as we watch Types of Government game show. Form of Government 5 Details Absolute Monarchy Representative Democracy Communism Socialism Fascism The directions
LL 10-24-13 Copy the chart below. Fill it in as we watch Types of Government game show. Form of Government 5 Details Absolute Monarchy Representative Democracy Communism Socialism Fascism The directions
Lesson 3: Classical Greece
 Getting Started Lesson 3: Classical Greece In this lesson, you'll explore the Classical period in ancient Greek history, compare the city-states of Athens and Sparta, and learn about the Peloponnesian
Getting Started Lesson 3: Classical Greece In this lesson, you'll explore the Classical period in ancient Greek history, compare the city-states of Athens and Sparta, and learn about the Peloponnesian
The Unification of Italy
 The Unification of Italy The beginning of Italian Independence starts with the French Revolution and the Napoleonic Era Prior to this time period the Italian peninsula did not wish to be unified Elimination
The Unification of Italy The beginning of Italian Independence starts with the French Revolution and the Napoleonic Era Prior to this time period the Italian peninsula did not wish to be unified Elimination
The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England. Student Handouts, Inc.
 Slide 1 The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 James I James Stuart (James VI of Scotland) inherited the English throne from his cousin, Elizabeth
Slide 1 The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 James I James Stuart (James VI of Scotland) inherited the English throne from his cousin, Elizabeth
Ch. 2 Ancient Middle East and Egypt Test
 Name: Date: 1. The Fertile Cresent that lies between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers has had a significant impact on the Middle East because this area was the site of the A. establishment of the first
Name: Date: 1. The Fertile Cresent that lies between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers has had a significant impact on the Middle East because this area was the site of the A. establishment of the first
GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE
 TYPES OF GOVERNMENT GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE CITIZEN A LEGAL MEMBER OF A COUNTRY CONSTITUTION A WRITTEN PLAN
TYPES OF GOVERNMENT GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE CITIZEN A LEGAL MEMBER OF A COUNTRY CONSTITUTION A WRITTEN PLAN
Life in the Colonies. Chapter 4, Section 1
 Life in the Colonies Chapter 4, Section 1 All English colonies shared a common English heritage, and that heritage included the idea that citizens had political rights. England also promoted the theory
Life in the Colonies Chapter 4, Section 1 All English colonies shared a common English heritage, and that heritage included the idea that citizens had political rights. England also promoted the theory
Chapter 8: African Civilizations, 1500 B.C. A.D. 700
 Name Chapter 8: African Civilizations, 1500 B.C. A.D. 700 Period African Civilizations Diverse Societies in Africa Terms and Names Sahara Large desert in Africa savanna Grassy plain Sahel Land at the
Name Chapter 8: African Civilizations, 1500 B.C. A.D. 700 Period African Civilizations Diverse Societies in Africa Terms and Names Sahara Large desert in Africa savanna Grassy plain Sahel Land at the
Louis XIV Absolutism and Wars
 Louis XIV Absolutism and Wars Key Concept 2.1 Different models of political sovereignty affected the relationship among states and between states and individuals. Key Concept 2.1.I In much of Europe, absolute
Louis XIV Absolutism and Wars Key Concept 2.1 Different models of political sovereignty affected the relationship among states and between states and individuals. Key Concept 2.1.I In much of Europe, absolute
Map of North and South America
 PASS Social Studies Grade 7 Test 1 Map of North and South America (drawn around the year 1700) SC07SS070101 1. Judging from the above map, it is clear that Europeans in the year 1700 knew the least about
PASS Social Studies Grade 7 Test 1 Map of North and South America (drawn around the year 1700) SC07SS070101 1. Judging from the above map, it is clear that Europeans in the year 1700 knew the least about
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. France Under Louis XIV
 France Under Louis XIV Objectives Understand how Henry IV rebuilt France after the wars of religion. Explain how Louis XIV became an absolute monarch. Describe how Versailles was a symbol of royal power.
France Under Louis XIV Objectives Understand how Henry IV rebuilt France after the wars of religion. Explain how Louis XIV became an absolute monarch. Describe how Versailles was a symbol of royal power.
Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire
 Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire Learning Goals: Analyze and Explain the impact of nationalism in Austro-Hungarian Empire and Ottoman Empire. Explain how Nationalism leads to WWI. Nationalism in
Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire Learning Goals: Analyze and Explain the impact of nationalism in Austro-Hungarian Empire and Ottoman Empire. Explain how Nationalism leads to WWI. Nationalism in
Nationalism in Europe Section 3
 Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire Learning Goals: Analyze and Explain the impact of nationalism in the Austro-Hungarian Empire and Ottoman Empire. Explain how Nationalism leads to WWI. Nationalism
Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire Learning Goals: Analyze and Explain the impact of nationalism in the Austro-Hungarian Empire and Ottoman Empire. Explain how Nationalism leads to WWI. Nationalism
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 4 The American Revolution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Why do new ideas often spark change? How do new ways of thinking affect the way people respond to their surroundings? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary
Lesson 4 The American Revolution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Why do new ideas often spark change? How do new ways of thinking affect the way people respond to their surroundings? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary
Department of Humanities and Social Science
 Barry Stocker Barry.Stocker@itu.edu.tr https://barrystockerac.wordpress.com Department of Humanities and Social Science Faculty of Science and Letters POLITICAL THEORY. ITB 227E NOTES WEEK ONE NICCOLÒ
Barry Stocker Barry.Stocker@itu.edu.tr https://barrystockerac.wordpress.com Department of Humanities and Social Science Faculty of Science and Letters POLITICAL THEORY. ITB 227E NOTES WEEK ONE NICCOLÒ
The History of Government The Origins of Government Ancient Civilizations The First Set of Laws
 The History of Government The Origins of Government Government is one of humanity's oldest and most important institutions. From earliest times, some kind of government has been a vital part of every society.
The History of Government The Origins of Government Government is one of humanity's oldest and most important institutions. From earliest times, some kind of government has been a vital part of every society.
Section 2. Objectives
 Objectives Understand how Henry IV rebuilt France after the wars of religion. Explain how Louis XIV became an absolute monarch. Describe how Versailles was a symbol of royal power. Identify Louis XIV s
Objectives Understand how Henry IV rebuilt France after the wars of religion. Explain how Louis XIV became an absolute monarch. Describe how Versailles was a symbol of royal power. Identify Louis XIV s
Document A: Pericles (Modified)
 Document A: Pericles (Modified) The following excerpt is from a speech known as The Funeral Oration, delivered by the Athenian general and politician Pericles in 431 BCE. Pericles was widely seen as the
Document A: Pericles (Modified) The following excerpt is from a speech known as The Funeral Oration, delivered by the Athenian general and politician Pericles in 431 BCE. Pericles was widely seen as the
The Age of Absolutism. World History
 The Age of Absolutism World History The Rise of Spain Spain had very profitable colonies in the Americas. Philip II uses this money to solidify his power and Spanish influence around the globe. He reigned
The Age of Absolutism World History The Rise of Spain Spain had very profitable colonies in the Americas. Philip II uses this money to solidify his power and Spanish influence around the globe. He reigned
Suppose you are on a sports team that is one play away from winning a game. Which is the best way to choose the final play of the game?
 Warm Up: Suppose you are on a sports team that is one play away from winning a game. Which is the best way to choose the final play of the game? A. Have the coach or the assistant coach choose. B. Have
Warm Up: Suppose you are on a sports team that is one play away from winning a game. Which is the best way to choose the final play of the game? A. Have the coach or the assistant coach choose. B. Have
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One Class Period Materials Needed: Student worksheets PowerPoint OR Transparency Copy Instructions: Student materials (double-sided, class set). Learning Objectives.
Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One Class Period Materials Needed: Student worksheets PowerPoint OR Transparency Copy Instructions: Student materials (double-sided, class set). Learning Objectives.
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Non-PowerPoint Option PowerPoint Option Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One Class Period Materials Needed: Student worksheets PowerPoint OR Transparency Copy Instructions: Student materials (double-sided,
Non-PowerPoint Option PowerPoint Option Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One Class Period Materials Needed: Student worksheets PowerPoint OR Transparency Copy Instructions: Student materials (double-sided,
THE STRENGTH OF AMERICAN FEDERAL DEMOCRACY by Roger Myerson
 THE STRENGTH OF AMERICAN FEDERAL DEMOCRACY by Roger Myerson http://home.uchicago.edu/~rmyerson/research/amerfed.pdf The institutions received from England were admirably calculated to lay the foundation
THE STRENGTH OF AMERICAN FEDERAL DEMOCRACY by Roger Myerson http://home.uchicago.edu/~rmyerson/research/amerfed.pdf The institutions received from England were admirably calculated to lay the foundation
Section 1 Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome
 Prologue Section 1 Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Main Idea The Greeks developed democracy, and the Romans added representative government. Why It Matters Now Representation and citizen participation
Prologue Section 1 Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Main Idea The Greeks developed democracy, and the Romans added representative government. Why It Matters Now Representation and citizen participation
Background. The background of Athenian Democracy. The definition of the term democracy. The three branches of Athenian government
 Name Period Page # Athenian Democracy Document Based Question: Was ancient Athens truly democratic? Background DIRECTIONS: As you view the PowerPoint presentation, take notes on The background of Athenian
Name Period Page # Athenian Democracy Document Based Question: Was ancient Athens truly democratic? Background DIRECTIONS: As you view the PowerPoint presentation, take notes on The background of Athenian
Document A: Pericles (Modified)
 Document A: Pericles (Modified) The following excerpt is from a speech known as The Funeral Oration, delivered by the Athenian general and politician Pericles in 431 BCE. Pericles was widely seen as the
Document A: Pericles (Modified) The following excerpt is from a speech known as The Funeral Oration, delivered by the Athenian general and politician Pericles in 431 BCE. Pericles was widely seen as the
Main Idea: The Ottomans established a Muslim empire that combined many cultures and lasted for more than 600 years.
 Absolute Monarchs in the Middle East & Europe (1500 1800) Pondering the Entire Unit What might be a benefit as well as a drawback having one person with complete control (Absolutism) in charge of a country?
Absolute Monarchs in the Middle East & Europe (1500 1800) Pondering the Entire Unit What might be a benefit as well as a drawback having one person with complete control (Absolutism) in charge of a country?
Western Europe and Political Democracy
 Western Europe and Political Democracy Growing prosperity after 1850 contributed to the expansion of democracy in Western Europe. Western Europe and Political Democracy In the late 1800s, political democracy
Western Europe and Political Democracy Growing prosperity after 1850 contributed to the expansion of democracy in Western Europe. Western Europe and Political Democracy In the late 1800s, political democracy
HSC Modern History World War 1 Notes
 HSC Modern History Year 2016 Mark 90.00 Pages 44 Published Dec 28, 2016 HSC Modern History World War 1 Notes By Patrick (98.05 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Patrick. Patrick
HSC Modern History Year 2016 Mark 90.00 Pages 44 Published Dec 28, 2016 HSC Modern History World War 1 Notes By Patrick (98.05 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Patrick. Patrick
The Rise & Fall of Napoleon Ch. 22. Sections 3 & 4
 The Rise & Fall of Napoleon Ch. 22 Sections 3 & 4 Napoleon s Background Born in Corsica in 1769 Military education Military hero Drove British forces from port of Toulon in 1793 Captured northern Italy
The Rise & Fall of Napoleon Ch. 22 Sections 3 & 4 Napoleon s Background Born in Corsica in 1769 Military education Military hero Drove British forces from port of Toulon in 1793 Captured northern Italy
Lesson Two. Aims. Context. In this lesson we are going to find out about: what impact the civil war had on families
 Lesson Two England and the civil wars Aims In this lesson we are going to find out about: what impact the civil war had on families how Parliament was able to win the war what happened after the execution
Lesson Two England and the civil wars Aims In this lesson we are going to find out about: what impact the civil war had on families how Parliament was able to win the war what happened after the execution
The Commercial Revolution Most of Europe remained agricultural. Fastest growing part of the economy was trade of goods. Those manufactured in Europe
 13. The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment People to Know 1. Henry VIII 2. Thomas Hobbes 3. Louis XIV 4. John Locke 5. William Blackstone 6. Sir Isaac Newton 7. Robert Boyle 8. Thomas Jefferson 9.
13. The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment People to Know 1. Henry VIII 2. Thomas Hobbes 3. Louis XIV 4. John Locke 5. William Blackstone 6. Sir Isaac Newton 7. Robert Boyle 8. Thomas Jefferson 9.
Versailles - A Flawed Peace
 Versailles - A Flawed Peace Final German Offensive Cause: Russian surrender When: Spring of 1918 What: Came within 35 miles of Paris Result: Defeated by Allies at Second Battle of the Marne in July 1918
Versailles - A Flawed Peace Final German Offensive Cause: Russian surrender When: Spring of 1918 What: Came within 35 miles of Paris Result: Defeated by Allies at Second Battle of the Marne in July 1918
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages; class
Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages; class
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Define government and the basic powers every government holds. 2. Describe the four defining characteristics of a state. 3. Identify four theories
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Define government and the basic powers every government holds. 2. Describe the four defining characteristics of a state. 3. Identify four theories
TABLE OF CONTENTS. SS.7.C.3.1 Updated 8/17 1
 COMPARING FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SS.7.C.3.1 Compare different forms of government (direct democracy, representative democracy, socialism, communism, monarchy, oligarchy, autocracy). TABLE OF CONTENTS Lesson
COMPARING FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SS.7.C.3.1 Compare different forms of government (direct democracy, representative democracy, socialism, communism, monarchy, oligarchy, autocracy). TABLE OF CONTENTS Lesson
Italian Unification
 Italian Unification 1858-1870 Since the time of the middle ages, Italy has been a collection of provinces, early to mid 1800s Italy was ruled by Austria and the Pope. Major Obstacles to Unification Austrian
Italian Unification 1858-1870 Since the time of the middle ages, Italy has been a collection of provinces, early to mid 1800s Italy was ruled by Austria and the Pope. Major Obstacles to Unification Austrian
Chapter 21. Absolute Monarchs in Europe,
 Chapter 21 Absolute Monarchs in Europe, 1500-1800 Section 1: Spain s Empire and European Absolutism During a time of religious and economic instability, Philip II rules Spain with a strong hand. A Powerful
Chapter 21 Absolute Monarchs in Europe, 1500-1800 Section 1: Spain s Empire and European Absolutism During a time of religious and economic instability, Philip II rules Spain with a strong hand. A Powerful
Writing the Constitution
 Writing the Constitution Backwards Planning Curriculum Units Michael Hutchison, Writer Dr. Aaron Willis, Project Coordinator Justin Coffey, Editor Kerry Gordonson, Editor Social Studies School Service
Writing the Constitution Backwards Planning Curriculum Units Michael Hutchison, Writer Dr. Aaron Willis, Project Coordinator Justin Coffey, Editor Kerry Gordonson, Editor Social Studies School Service
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector or Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages;
Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector or Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages;
netw rks Reading Essentials and Study Guide Industrialization and Nationalism Lesson 3 Nationalism, Unification, and Reform
 and Study Guide Lesson 3 Nationalism, Unification, and Reform ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can innovation affect ways of life? How does revolution bring about political and economic change? Reading HELPDESK
and Study Guide Lesson 3 Nationalism, Unification, and Reform ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can innovation affect ways of life? How does revolution bring about political and economic change? Reading HELPDESK
STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth,
 STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by c) assessing the impacts
STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by c) assessing the impacts
4. Which noun below can also be used. 5. What is the meaning of the phrase
 Name: Date: WEEK 35 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. What kinds of rights do you think people should have? For example, you probably think that people have the right to be safe from burglars.
Name: Date: WEEK 35 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. What kinds of rights do you think people should have? For example, you probably think that people have the right to be safe from burglars.
Chapter Introduction Section 1: The French Revolution Begins Section 2: Radical Revolution and Reaction Section 3: The Age of Napoleon Visual Summary
 Chapter Introduction Section 1: The French Revolution Begins Section 2: Radical Revolution and Reaction Section 3: The Age of Napoleon Visual Summary The BIG Idea Struggle for Rights Social inequality
Chapter Introduction Section 1: The French Revolution Begins Section 2: Radical Revolution and Reaction Section 3: The Age of Napoleon Visual Summary The BIG Idea Struggle for Rights Social inequality
Distribution of Power. Unitary Confederation Federal
 Governments of Asia SS7CG7 a. Compare and Contrast the federal republic of the Republic of India, the communist state of the People s Republic of China, and the constitutional monarchy of Japan, distinguishing
Governments of Asia SS7CG7 a. Compare and Contrast the federal republic of the Republic of India, the communist state of the People s Republic of China, and the constitutional monarchy of Japan, distinguishing
DRAFT SOCIAL SCIENCES STANDARDS: CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT
 DRAFT SOCIAL SCIENCES STANDARDS: CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT CORE STANDARDS Civics and Government 10. Examine the relationship between government and citizens to distinguish and evaluate the ways that civic
DRAFT SOCIAL SCIENCES STANDARDS: CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT CORE STANDARDS Civics and Government 10. Examine the relationship between government and citizens to distinguish and evaluate the ways that civic
Public affairs overseas
 Basic Public Affairs Specialist Course Public affairs overseas What do you think are the chances of you being stationed overseas at some point in your career, whether permanently assigned or deployed to
Basic Public Affairs Specialist Course Public affairs overseas What do you think are the chances of you being stationed overseas at some point in your career, whether permanently assigned or deployed to
What is Government? Chapter 3
 Chapter 3 What is Government? You must have heard the word 'government' mentioned several times. In this chapter you will learn about what a government is and the important role it plays in our lives.
Chapter 3 What is Government? You must have heard the word 'government' mentioned several times. In this chapter you will learn about what a government is and the important role it plays in our lives.
Hapsburg Absolute monarch Divine right
 Absolutism Spain Objective: Discuss and analyze the golden age and decline of Spain as a power. Key Terms and People: Hapsburg, absolute monarch, divine right, Charles V, Peace of Augsburg, Philip II,
Absolutism Spain Objective: Discuss and analyze the golden age and decline of Spain as a power. Key Terms and People: Hapsburg, absolute monarch, divine right, Charles V, Peace of Augsburg, Philip II,
UNIFICATION OF ITALY. Background. The Austrian Empire. Reactionary Rulers. Notes. 4 Nationalism in Europe
 2 UNIFICATION OF ITALY Nationalism and liberalism stimulated the revolutionary changes of 1848 throughout the Central Europe, especially in Italy, Germany and the whole of the Austrian Empire. The liberal
2 UNIFICATION OF ITALY Nationalism and liberalism stimulated the revolutionary changes of 1848 throughout the Central Europe, especially in Italy, Germany and the whole of the Austrian Empire. The liberal
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Basic Types of Government In a dictatorship, all powers are held by one person or group. In a democracy, authority lies with the people. The U.S. government
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Basic Types of Government In a dictatorship, all powers are held by one person or group. In a democracy, authority lies with the people. The U.S. government
Look up the Triangular Trade on pg. 95 of your textbook and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What was the triangular trade?
 Look up the Triangular Trade on pg. 95 of your textbook and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What was the triangular trade? 2. Which 3 regions were involved in the triangular trade?
Look up the Triangular Trade on pg. 95 of your textbook and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What was the triangular trade? 2. Which 3 regions were involved in the triangular trade?
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 4
 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 4 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1204 HISTORY OF GOVERNMENTS Unit 4 HISTORY OF GOVERNMENTS INTRODUCTION 3 1. ANCIENT GOVERNMENTS 5 A PRIMITIVE GOVERNMENT PRIMER 6
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 4 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1204 HISTORY OF GOVERNMENTS Unit 4 HISTORY OF GOVERNMENTS INTRODUCTION 3 1. ANCIENT GOVERNMENTS 5 A PRIMITIVE GOVERNMENT PRIMER 6
In the early 1800s, German speaking people lived in a number of small and medium-sized states as well and in Prussia and Austrian Hapsburg empire.
 German Unification In the early 1800s, German speaking people lived in a number of small and medium-sized states as well and in Prussia and Austrian Hapsburg empire. Between 1806 and 1812 Napoleon made
German Unification In the early 1800s, German speaking people lived in a number of small and medium-sized states as well and in Prussia and Austrian Hapsburg empire. Between 1806 and 1812 Napoleon made
Germanic Kingdoms Unite Under Charlemagne
 Germanic Kingdoms Unite Under Charlemagne Warmup Which group of people followed a code of chivalry? If you don t know, ask your neighbor Medieval Europe Middle Ages (also called The Dark Ages) 500-1500
Germanic Kingdoms Unite Under Charlemagne Warmup Which group of people followed a code of chivalry? If you don t know, ask your neighbor Medieval Europe Middle Ages (also called The Dark Ages) 500-1500
Analyze the ideological, military, social, and diplomatic aspects of the American Revolution.
 Analyze the ideological, military, social, and diplomatic aspects of the American Revolution. The Proclamation of 1763 When the French and Indian War ended, the French LEFT But the Indians remained And
Analyze the ideological, military, social, and diplomatic aspects of the American Revolution. The Proclamation of 1763 When the French and Indian War ended, the French LEFT But the Indians remained And
Prologue Section 3 Democracy Develops in England
 Prologue Section 3 Democracy Develops in England Edward the Confessor Dies (one of the last Anglo-Saxon Kings of England) Some sources say that Edward had promised the throne to his cousin William. The
Prologue Section 3 Democracy Develops in England Edward the Confessor Dies (one of the last Anglo-Saxon Kings of England) Some sources say that Edward had promised the throne to his cousin William. The
THE AGE OF EISENHOWER
 THE AGE OF EISENHOWER 1952-1960 1952 Election REP- Dwight D. Eisenhower DEM- Gov. Adlai Stevenson (IL) Issues: Ike pledged to end the Korea War Attacks Truman s handling of Korea, Communism, and corruption
THE AGE OF EISENHOWER 1952-1960 1952 Election REP- Dwight D. Eisenhower DEM- Gov. Adlai Stevenson (IL) Issues: Ike pledged to end the Korea War Attacks Truman s handling of Korea, Communism, and corruption
Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent
 Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent If YOU were there You are a farmer in Southwest Asia about 6,000 years ago. You live near a slow-moving river, with many shallow lakes and marshes. The river makes
Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent If YOU were there You are a farmer in Southwest Asia about 6,000 years ago. You live near a slow-moving river, with many shallow lakes and marshes. The river makes
Barbarians. Indo- European tribes. Barbarian and Romans. Romulus and Remus on the Tiber
 Barbarians Indo- European tribes Barbarian and Romans Romulus and Remus on the Tiber Romulus and Remus Romulus and Remus Down the river Tiber Reestablishing their rule Romulus Kills Remus Germanic Tribes
Barbarians Indo- European tribes Barbarian and Romans Romulus and Remus on the Tiber Romulus and Remus Romulus and Remus Down the river Tiber Reestablishing their rule Romulus Kills Remus Germanic Tribes
The English Civil War and the Glorious Revolution
 The English Civil War and the Glorious Revolution Enduring Understanding: The relationship between citizens and their government is a fundamental component of political rule. To understand the role of
The English Civil War and the Glorious Revolution Enduring Understanding: The relationship between citizens and their government is a fundamental component of political rule. To understand the role of
2/16/2015. Outcome: Absolutism & Absolute Monarchs. French Absolutism, Enlightenment, & Revolution
 Outcome: Absolutism & Absolute Monarchs French Absolutism, Enlightenment, & Revolution 1 Constructive Response Questions 1. Describe what an absolute monarch is and provide two examples: 2 What Will We
Outcome: Absolutism & Absolute Monarchs French Absolutism, Enlightenment, & Revolution 1 Constructive Response Questions 1. Describe what an absolute monarch is and provide two examples: 2 What Will We
DEMOCRACY DOWN UNDER. Student facts. How should a nation be ruled? 1. Absolute monarchy. 2. Direct democracy.
 Student facts How should a nation be ruled? Have you ever thought about how Australia is ruled? What about other countries around the world? Are they all ruled in the same way? Australia is a democracy,
Student facts How should a nation be ruled? Have you ever thought about how Australia is ruled? What about other countries around the world? Are they all ruled in the same way? Australia is a democracy,
We the People Lesson 1
 We the People Lesson 1 1. What is the purpose of government according to the natural rights philosophers? The main purpose of government should be to protect people s natural rights. 2. Where does government
We the People Lesson 1 1. What is the purpose of government according to the natural rights philosophers? The main purpose of government should be to protect people s natural rights. 2. Where does government
The Unification of Germany
 The Unification of Germany Steps in German Unification (1861-1871) 1861 William I becomes King of Prussia 1862 Bismarck appointed chief minister 1864 The Danish War 1866 The Austro- Prussian War (Seven
The Unification of Germany Steps in German Unification (1861-1871) 1861 William I becomes King of Prussia 1862 Bismarck appointed chief minister 1864 The Danish War 1866 The Austro- Prussian War (Seven
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 3 Absolutism in Europe ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does the exercise of absolute power affect a country? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary stability the state of being stable; strong enough to endure
Lesson 3 Absolutism in Europe ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does the exercise of absolute power affect a country? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary stability the state of being stable; strong enough to endure
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 2
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 2 Objectives 1. Classify governments according to three sets of characteristics. 2. Define systems of government based on who can participate. 3. Identify different
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 2 Objectives 1. Classify governments according to three sets of characteristics. 2. Define systems of government based on who can participate. 3. Identify different
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector or Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages;
Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector or Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages;
A situation where there is no government. Anarchy. The provinces in Canada keep their power and the central government has limited power.
 Anarchy A situation where there is no government. Canada The provinces in Canada keep their power and the central government has limited power. Confederation a political system in which the central government
Anarchy A situation where there is no government. Canada The provinces in Canada keep their power and the central government has limited power. Confederation a political system in which the central government
