Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
|
|
|
- Hilda Norman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector or Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages; class set) Worksheet (2 pages; class set) Learning Objectives. Students will be able to: Identify major forms of government (autocracy, monarchy, dictatorship, representative direct democracy, oligarchy, theocracy, anarchy) Compare contrast the major features of different forms of government Analyze examples of real-world governments STEP BY STEP ANTICIPATE DISTRIBUTE READ CHECK DISTRIBUTE COMPLETE by having students complete the Types of Governments & Leaders mind map. Make sure students feel free to add any ideas they think of, even if they might be wrong. Use students responses to create a collective mind map on the board. (If you have an interactive white board, try using the PowerPoint slide for this.) the Who Rules? reading to the class. the Who Rules? reading with the class. Ask students to be on the lookout for any types of government they came up with during the brainstorming activity. (Note: There is a PowerPoint version of the graphic organizer in the presentation.) for understing using the A/B Active Participation Activity. Either project the master uncover one question at a time, or use the PowerPoint version of the activity. Make sure the class answers as a chorus so you can check for understing all at once. the worksheet activities. Activity A (Identify That Government!) as a class by projecting a blank master or using the PowerPoint version of the activity. (Optional. You may also have students complete the activity on their own or in groups.) REVIEW answers to Activity A. ASSIGN REVIEW CLOSE students to complete Activities B C on the second worksheet page. (Note: There are also PowerPoint versions of these activities in the presentation.) answers if you wish. by returning to the mind map you created as a class on the board at the beginning of class. Ask students to look at the map think of at least one change that should be made. Call on students to come up make changes until the mind map reflects what they learned in the lesson. This lesson plan is part of the Foundations of Government series by icivics, Inc. a nonprofit organization dedicated to advancing civic education. Please visit for more resources to access the state stards aligned to this lesson plan. Provide feedback to feedback@icivics.org icivics, Inc. You may copy, distribute, or transmit this work for noncommercial purposes if you credit icivics. All other rights reserved.
2 Types of Governments. What kinds of governments exist? What kinds of leaders can be in charge of a country? Think about everything you ve ever heard of or learned add it to this mind map. Circle each idea you add draw a line to connect it to the main phrase (or to another idea you added). Keep brainstorming until you run out of room or time. Anticipation Activity Mind Map Who Rules? Types of Governments. What kinds of governments exist? What kinds of leaders can be in charge of a country? Think about everything you ve ever heard of or learned add it to this mind map. Circle each idea you add draw a line to connect it to the main phrase (or to another idea you added). Keep brainstorming until you run out of room or time. Anticipation Activity Mind Map
3 Someone s Got to Be In Charge If you compared all the governments in the world, you would find one thing in common: Someone is in charge. The question is, who? There are many different forms of government. Some have one leader who has all the control. Others give power to the people. Here are some forms of government that exist (or have existed) in the world: King Harald V of Norway with his wife, Queen Sonja. Norway is a constitutional monarchy. The king is the head of state has a mainly ceremonial role. The actual government is a democracy. Me, Myself, I An autocracy is a government in which one person has all the power. There are two main types of autocracy: a monarchy a dictatorship. In a monarchy, a king or queen rules the country. The king or queen is known as a monarch. Monarchs usually come to power through their family line: The current king or queen s oldest child becomes the next king or queen. In some monarchies, especially those in historical times, the monarch held all the power had the final say over the government. In modern times, monarchs usually share power with other parts of government. Often they are also subject to the country s constitution. A dictatorship is a form of government where one leader has absolute control over citizens lives. If there is a constitution, the dictator has control over that, too so it doesn t mean much. Although other parts of the government may exist, such as courts or a lawmaking body, these branches always do what the dictator wants them to do. They do not represent citizens. Power to the People! In a democracy, citizens hold the political power. There are two fundamental types of democracies: In a representative democracy, citizens elect leaders to represent their rights interests in government. The elected leaders, or representatives, do the day-to-day work of governing the country: They consider the issues, work to find solutions, pass laws, do all of the other things necessary to keep a country going. Citizens hold the ultimate power, though, because if they don t like what their representatives are doing, they can vote in new ones! In a direct democracy, there are no representatives. Citizens are directly involved in the day-to-day work of governing the country. Citizens might be required to participate in lawmaking or act as judges, for example. The best example of this was in the ancient Greek city-state called Athens. Most modern countries are too large for a direct democracy to work. A man votes in Peru. The Peruvian legislature Reading p.1
4 We, Ourselves, um Us In an oligarchy (OH-lih-gar-kee), a small group of people has all the power. Oligarchy is a Greek word that means rule by a few. Sometimes this means that only a certain group has political rights, such as members of one political party, one social class, or one race. For example, in some societies, only noble families who owned l could participate in politics. An oligarchy can also mean that a few people control the country. For example, a junta is a small group of people usually military officers who rule a country after taking it over by force. A junta often operates much like a dictatorship, except that several people share power. Crown of the Holy Roman Empire, which was tied to the Catholic church lasted from the 10th 19th century. Rule by None Religious Rule A theocracy is a government that recognizes God or a divine being as the ultimate authority. ( Theo is a Greek word that means god.) In a theocracy, religious law is used to settle disputes rule the people. A theocracy can also be a democracy, dictatorship, monarchy, or just about any other kind of government. For example, the Republic of Iran recognizes Islamic law, but Iran s citizens vote to elect their leaders. Modern theocracies are usually found in countries where the population is strongly religious. A In an anarchy, nobody is in control or everyone is, depending on how you look at it. Sometimes the word anarchy is used to refer to an out-ofcontrol mob. When it comes to government, anarchy would be one way to describe the human state of existence before any governments developed. It would be similar to the way animals live in the wild, with everyone looking out for themselves. Today, people who call themselves anarchists usually believe that people should be allowed to freely associate together without being subject to any nation or government. There are no countries that have anarchy as their form of government. From 1962 to 2011, Myanmar (also known as Burma) was ruled by a military junta that was condemned by the world for its human rights violations. An A inside a circle is the traditional symbol for anarchy. Where would you put theocracy on this chart? Reading p.2
5 A. Identify That Government! Identify the form(s) of government that each country has or had. Form of government: Form of government: Worksheet p.1
6 B. True or False? Use what you learned in the reading in Exercise A to fill in the chart below. C. Vocabulary. Solve the crossword puzzle using vocabulary from the reading Across 3. Type of democracy where citizens elect leaders to represent them in government 7. A small group that rules a country after taking it over by force 9. One person has all the power 10. Type of democracy where citizens are involved in day-to-day government Down 1. Recognizes God as the ultimate authority in government law 2. One leader has absolute control over citizens lives 4. Citizens hold the political power 5. A small group of people has all the power 6. People are not subject to any nation or government 8. A king or queen rules the country Worksheet p.2
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector or Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages;
Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector or Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages;
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages; class
Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages; class
Who Rules? Name: Anticipation Activity Mind Map
 Types of Governments. What kinds of governments exist? What kinds of leaders can be in charge of a country? Think about everything you ve ever heard of or learned add it to this mind map. Circle each idea
Types of Governments. What kinds of governments exist? What kinds of leaders can be in charge of a country? Think about everything you ve ever heard of or learned add it to this mind map. Circle each idea
Types of Governments
 Types of Governments Anarchy In an anarchy, nobody is in control or everyone is, depending on how you look at it. Sometimes the word anarchy is used to refer to an out-of control mob. When it comes to
Types of Governments Anarchy In an anarchy, nobody is in control or everyone is, depending on how you look at it. Sometimes the word anarchy is used to refer to an out-of control mob. When it comes to
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One Class Period Materials Needed: Student worksheets PowerPoint OR Transparency Copy Instructions: Student materials (double-sided, class set). Learning Objectives.
Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One Class Period Materials Needed: Student worksheets PowerPoint OR Transparency Copy Instructions: Student materials (double-sided, class set). Learning Objectives.
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Non-PowerPoint Option PowerPoint Option Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One Class Period Materials Needed: Student worksheets PowerPoint OR Transparency Copy Instructions: Student materials (double-sided,
Non-PowerPoint Option PowerPoint Option Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One Class Period Materials Needed: Student worksheets PowerPoint OR Transparency Copy Instructions: Student materials (double-sided,
Government: Definition, Forms, and Purpose.
 Government: Definition, Forms, and Purpose. SS6CG4 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and
Government: Definition, Forms, and Purpose. SS6CG4 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and
INTRODUCTION TO POLITICAL GEOGRAPHY Vocabulary Journal
 INTRODUCTION TO POLITICAL GEOGRAPHY Vocabulary Journal SET UP YOUR PAPER AS FOLLOWS: Get out notebook paper, OUT OF THE SPIRAL! From the left side, fold the paper vertically, to the center, or draw a line
INTRODUCTION TO POLITICAL GEOGRAPHY Vocabulary Journal SET UP YOUR PAPER AS FOLLOWS: Get out notebook paper, OUT OF THE SPIRAL! From the left side, fold the paper vertically, to the center, or draw a line
GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE
 TYPES OF GOVERNMENT GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE CITIZEN A LEGAL MEMBER OF A COUNTRY CONSTITUTION A WRITTEN PLAN
TYPES OF GOVERNMENT GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE CITIZEN A LEGAL MEMBER OF A COUNTRY CONSTITUTION A WRITTEN PLAN
Wednesday March 22, 2017
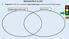 Wednesday March 22, 2017 1. Assignment 3. Open your workbook to page 8 (blank page), and draw the Venn Diagram below. dictatorship (autocracy) democracy What are you expected to do with these forms of
Wednesday March 22, 2017 1. Assignment 3. Open your workbook to page 8 (blank page), and draw the Venn Diagram below. dictatorship (autocracy) democracy What are you expected to do with these forms of
Thursday April 12,2018
 Thursday April 12,2018 1. Assignment 22. Please get the handout Who Rules? from the red basket and copy this Venn Diagram on the back. autocracy democracy Thursday April 12,2018 1. Assignment 22. Please
Thursday April 12,2018 1. Assignment 22. Please get the handout Who Rules? from the red basket and copy this Venn Diagram on the back. autocracy democracy Thursday April 12,2018 1. Assignment 22. Please
Title: (form of government) A. What is the big idea/definition for this form of government?
 Types/Forms of Government Notes Create this Outline/Chart on your own notebook paper. Make one for each of the following types of government: I. Autocracy, II. Communism, III. Direct Democracy, IV. Monarchy,
Types/Forms of Government Notes Create this Outline/Chart on your own notebook paper. Make one for each of the following types of government: I. Autocracy, II. Communism, III. Direct Democracy, IV. Monarchy,
Forms of Government. Who Rules?
 Forms of Government Who Rules? What is a Government? A Government is an organized system that makes laws and decisions for the good of the country.» If you compare all the types of governments in the world,
Forms of Government Who Rules? What is a Government? A Government is an organized system that makes laws and decisions for the good of the country.» If you compare all the types of governments in the world,
Social Studies Content Area 2014 GED Assessment Targets. Types of modern and historical governments. (CG1.a)
 GED Preparation Lesson Plan Module: Social Studies Lesson Title: Systems and Forms of Government Standards: GED Preparation (Adult General Education) Social Studies Practices 2014 Assessment Targets High
GED Preparation Lesson Plan Module: Social Studies Lesson Title: Systems and Forms of Government Standards: GED Preparation (Adult General Education) Social Studies Practices 2014 Assessment Targets High
Power and Politics. Fill in the spaces with details to help you understand the different forms of government. How is power obtained?
 Power and Politics Fill in the spaces with details to help you understand the different forms of government. Type of Government Democracy Dictatorship Monarchy Who has the power? How is power obtained?
Power and Politics Fill in the spaces with details to help you understand the different forms of government. Type of Government Democracy Dictatorship Monarchy Who has the power? How is power obtained?
Political Systems (Forms of Government) Autocracy: Any form of government where one person (auto) holds all the power
 Name Political Systems (Forms of Government) Democracy: Any form of government where citizens control their government through voting in elections o Direct Democracy: All citizens have a chance to participate.
Name Political Systems (Forms of Government) Democracy: Any form of government where citizens control their government through voting in elections o Direct Democracy: All citizens have a chance to participate.
The Sovereign State STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide The Sovereign State Time Needed: Two class periods Materials Needed: Student Worksheets Power Point w/projector (optional) Colored pencils (optional) Copy Instructions: Anticipation & Closing
Teacher s Guide The Sovereign State Time Needed: Two class periods Materials Needed: Student Worksheets Power Point w/projector (optional) Colored pencils (optional) Copy Instructions: Anticipation & Closing
WHAT FORMS OF GOVERNMENT ARE OUT THERE? Exploring Governments Throughout the World
 WHAT FORMS OF GOVERNMENT ARE OUT THERE? Exploring Governments Throughout the World Should the people rule? Wing Station or Penn Station? Reflect How do you feel if you were outvoted? Is voting like this
WHAT FORMS OF GOVERNMENT ARE OUT THERE? Exploring Governments Throughout the World Should the people rule? Wing Station or Penn Station? Reflect How do you feel if you were outvoted? Is voting like this
Unit Three Word Cards. 1 civics. 2 political scientist. a social scientist who is trained to study government and citizenship
 1 civics the study the rights and duties of citizens and of how the government works Example: In order to preserve democracy for future generations, schools in the United States require courses in civics.
1 civics the study the rights and duties of citizens and of how the government works Example: In order to preserve democracy for future generations, schools in the United States require courses in civics.
Organization people set up to protect their community and enforce the rules
 ? Organization people set up to protect their community and enforce the rules Roles: Protect lives, liberties, and property of the community Provide services individuals cannot provide on their own Use
? Organization people set up to protect their community and enforce the rules Roles: Protect lives, liberties, and property of the community Provide services individuals cannot provide on their own Use
CH. 1: PRINCIPLES OF GOVERNMENT S E C T I O N 1 : G O V E R N M E N T A N D T H E S T A T E
 CH. 1: PRINCIPLES OF GOVERNMENT S E C T I O N 1 : G O V E R N M E N T A N D T H E S T A T E A. WHAT IS GOVERNMENT? is a system that we use to make and enforce public policies Public policies are anything
CH. 1: PRINCIPLES OF GOVERNMENT S E C T I O N 1 : G O V E R N M E N T A N D T H E S T A T E A. WHAT IS GOVERNMENT? is a system that we use to make and enforce public policies Public policies are anything
Government, you say? European governments
 Government, you say? European governments Why do we have governments? All countries require governments to function. Governments provide laws, structure, public services, and national defense. There are
Government, you say? European governments Why do we have governments? All countries require governments to function. Governments provide laws, structure, public services, and national defense. There are
Bell Ringer: August (30)31,
 Announcements: 1: Binders are STILL due 2: TEST NEXT WEEK Materials: 1: Binder 2: Cornell Notes 3: Types of Government Classwork Bell Ringer: August (30)31, 2018 1. Set up your Cornell notes 2. Across
Announcements: 1: Binders are STILL due 2: TEST NEXT WEEK Materials: 1: Binder 2: Cornell Notes 3: Types of Government Classwork Bell Ringer: August (30)31, 2018 1. Set up your Cornell notes 2. Across
Comparing Government Systems 1. Teachers Curriculum Institute
 P r e v i e w Work with your partner to read about six forms of government in today s world. Take turns reading each paragraph, using a low voice. As you read about each form of government, look for advantages
P r e v i e w Work with your partner to read about six forms of government in today s world. Take turns reading each paragraph, using a low voice. As you read about each form of government, look for advantages
Government Extra Study Practice
 Government Extra Study Practice Name: Period: What is Government? Government 1. I can explain the purpose of government 2. I can identify each of the following for dictatorship, monarchy, constitutional
Government Extra Study Practice Name: Period: What is Government? Government 1. I can explain the purpose of government 2. I can identify each of the following for dictatorship, monarchy, constitutional
Chapter 1 Foundations of Government. The purposes of Government Forms of Government Democracy in the United States
 Chapter 1 Foundations of Government The purposes of Government Forms of Government Democracy in the United States Definition of Government The formal institutions and processes through which decisions
Chapter 1 Foundations of Government The purposes of Government Forms of Government Democracy in the United States Definition of Government The formal institutions and processes through which decisions
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Basic Types of Government In a dictatorship, all powers are held by one person or group. In a democracy, authority lies with the people. The U.S. government
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Basic Types of Government In a dictatorship, all powers are held by one person or group. In a democracy, authority lies with the people. The U.S. government
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Define government and the basic powers every government holds. 2. Describe the four defining characteristics of a state. 3. Identify four theories
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Define government and the basic powers every government holds. 2. Describe the four defining characteristics of a state. 3. Identify four theories
Foundations of the American Political System
 Foundations of the American Political System Warm Up: Why does the government exist? What would the US be like if there were no government? How would your life be different if there were no government?
Foundations of the American Political System Warm Up: Why does the government exist? What would the US be like if there were no government? How would your life be different if there were no government?
AUTOCRACY. SS.7.C.3.1 Forms of Government
 AUTOCRACY An autocracy is a form of government where one person has unlimited power. One form of an autocracy is a dictatorship where a military leader secures power often through violent means. Another
AUTOCRACY An autocracy is a form of government where one person has unlimited power. One form of an autocracy is a dictatorship where a military leader secures power often through violent means. Another
UNITARY SYSTEM. (Levels of Government) If one central government runs the nation, the system is said to be a
 UNITARY SYSTEM (Levels of Government) If one central government runs the nation, the system is said to be a unitary system. The central government makes laws for the entire nation; local governments have
UNITARY SYSTEM (Levels of Government) If one central government runs the nation, the system is said to be a unitary system. The central government makes laws for the entire nation; local governments have
ROLES, PURPOSES AND TYPES OF GOVERNMENT
 ROLES, PURPOSES AND TYPES OF GOVERNMENT State versus Nation State: A politically organized union that has four essential features: - population (people) - territory - established governmt - sovereignty
ROLES, PURPOSES AND TYPES OF GOVERNMENT State versus Nation State: A politically organized union that has four essential features: - population (people) - territory - established governmt - sovereignty
Highlights: Comparing Forms of Government SS.7.C.3.1
 Highlights: Comparing Forms of Government SS.7.C.3.1 Compare different forms of government (direct democracy, representative democracy, socialism, communism, monarch, oligarchy, autocracy). Terri Susan
Highlights: Comparing Forms of Government SS.7.C.3.1 Compare different forms of government (direct democracy, representative democracy, socialism, communism, monarch, oligarchy, autocracy). Terri Susan
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 2
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 2 1 Objectives 1. Classify governments according to three sets of characteristics. 2. Define systems of government based on who can participate. 3. Identify
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 2 1 Objectives 1. Classify governments according to three sets of characteristics. 2. Define systems of government based on who can participate. 3. Identify
COUNTRY CARD VOCABULARY FLASH CARDS
 COUNTRY CARD VOCABULARY FLASH CARDS Learning Objective(s): The student will understand vocabulary by using flash cards. TEKS: 6.22A Social Studies Skills Materials Needed: Vocabulary Flash Cards Vocabulary:
COUNTRY CARD VOCABULARY FLASH CARDS Learning Objective(s): The student will understand vocabulary by using flash cards. TEKS: 6.22A Social Studies Skills Materials Needed: Vocabulary Flash Cards Vocabulary:
Chapter 1: Foundations of Government
 Chapter 1: Foundations of Government Section 1: The Purposes of Government Section 2: Forms of Government Section 3: Democracy in the United States Section 1 at a Glance The Purposes of Government Government
Chapter 1: Foundations of Government Section 1: The Purposes of Government Section 2: Forms of Government Section 3: Democracy in the United States Section 1 at a Glance The Purposes of Government Government
State Power: Got a Reservation? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One to two class periods Materials Needed: Student Worksheets Copy Instructions: Reading (2 pages; class set) Federal Power Cheat Sheet (1 page; class set) Strike-It Activity
Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One to two class periods Materials Needed: Student Worksheets Copy Instructions: Reading (2 pages; class set) Federal Power Cheat Sheet (1 page; class set) Strike-It Activity
How many countries are there in the world?
 How many countries are there in the world? Forms of Government There are (approximately) 196 countries in the world today. It depends on who you re asking and whether or not they consider territories,
How many countries are there in the world? Forms of Government There are (approximately) 196 countries in the world today. It depends on who you re asking and whether or not they consider territories,
The Rise of Democracy
 The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 1 The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 2 26.1 Last chapter we talked about the fact that mountains and seas isolated Greek communities. As a result Greek communities developed
The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 1 The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 2 26.1 Last chapter we talked about the fact that mountains and seas isolated Greek communities. As a result Greek communities developed
SS7 Civics: Ch 1.4. The Forms of Government
 SS7 Civics: Ch 1.4 The Forms of Government The Importance of Government Importance of Government A. A government is the ruling authority for a community. Importance of Government B. There are three primary
SS7 Civics: Ch 1.4 The Forms of Government The Importance of Government Importance of Government A. A government is the ruling authority for a community. Importance of Government B. There are three primary
Unit Portfolio: Interpreting Visual Images
 Unit Portfolio: Interpreting Visual Images 1. What can you tell about this man based only on what you see in this picture? Make up a brief biography based on your perception of this photo. Use complete
Unit Portfolio: Interpreting Visual Images 1. What can you tell about this man based only on what you see in this picture? Make up a brief biography based on your perception of this photo. Use complete
Unit 7: Civics, Government, and Global Politics (Lessons 1-3)
 Unit 7: Civics, Government, and Global Politics (Lessons 1-3) The will of the people is the source and the happiness of the people the end of all legitimate government upon Earth. --- John Quincy Adams
Unit 7: Civics, Government, and Global Politics (Lessons 1-3) The will of the people is the source and the happiness of the people the end of all legitimate government upon Earth. --- John Quincy Adams
Unit 7: Civics, Government, and Global Politics (Lessons 1-3)
 Unit 7: Civics, Government, and Global Politics (Lessons 1-3) The will of the people is the source and the happiness of the people the end of all legitimate government upon Earth. --- John Quincy Adams
Unit 7: Civics, Government, and Global Politics (Lessons 1-3) The will of the people is the source and the happiness of the people the end of all legitimate government upon Earth. --- John Quincy Adams
TABLE OF CONTENTS. SS.7.C.3.1 Updated 8/17 1
 COMPARING FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SS.7.C.3.1 Compare different forms of government (direct democracy, representative democracy, socialism, communism, monarchy, oligarchy, autocracy). TABLE OF CONTENTS Lesson
COMPARING FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SS.7.C.3.1 Compare different forms of government (direct democracy, representative democracy, socialism, communism, monarchy, oligarchy, autocracy). TABLE OF CONTENTS Lesson
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 2
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 2 Objectives 1. Classify governments according to three sets of characteristics. 2. Define systems of government based on who can participate. 3. Identify different
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 2 Objectives 1. Classify governments according to three sets of characteristics. 2. Define systems of government based on who can participate. 3. Identify different
What is Citizenship? A citizen is one who has specific rights and obligations within a political unit such as being a citizen of a country or a state.
 What is Citizenship? A citizen is one who has specific rights and obligations within a political unit such as being a citizen of a country or a state. All countries have their own definitions and expectations
What is Citizenship? A citizen is one who has specific rights and obligations within a political unit such as being a citizen of a country or a state. All countries have their own definitions and expectations
Further Exploration of Forms of Government. Unit 7, Lesson 3
 Further Exploration of Forms of Government Unit 7, Lesson 3 Forms of Government Who holds the power? Who is sovereign? One Person A Select Group of People The People Forms of Government Who holds the power?
Further Exploration of Forms of Government Unit 7, Lesson 3 Forms of Government Who holds the power? Who is sovereign? One Person A Select Group of People The People Forms of Government Who holds the power?
United States Government
 United States Government I. Early Governments (Intro) 100 years ago governments were led by rulers, who ruled by force Direct democracy- Greeks invented this government, government run by the people to
United States Government I. Early Governments (Intro) 100 years ago governments were led by rulers, who ruled by force Direct democracy- Greeks invented this government, government run by the people to
Forms of Government. Comparing Different. Benchmarks
 Forms of Government Comparing Different Forms of Government Benchmarks SS.7.C.3.1 Compare different forms of government (direct democracy, representative democracy, socialism, communism, monarchy, oligarchy,
Forms of Government Comparing Different Forms of Government Benchmarks SS.7.C.3.1 Compare different forms of government (direct democracy, representative democracy, socialism, communism, monarchy, oligarchy,
Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 1
 Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the ancient foundations of the state in Athens, in Rome, and in the feudal system. 2. Analyze the rise of sovereign states. 3.
Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the ancient foundations of the state in Athens, in Rome, and in the feudal system. 2. Analyze the rise of sovereign states. 3.
4. Which noun below can also be used. 5. What is the meaning of the phrase
 Name: Date: WEEK 35 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. What kinds of rights do you think people should have? For example, you probably think that people have the right to be safe from burglars.
Name: Date: WEEK 35 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. What kinds of rights do you think people should have? For example, you probably think that people have the right to be safe from burglars.
FORMS OF GOVERNMENT. Unit 2
 FORMS OF GOVERNMENT Unit 2 Forms of Government Type: Direct Democracy Def: government in which all citizens have equal power in decision making Pros: 1.) Every Citizen has equal power. 2.) Everyone is
FORMS OF GOVERNMENT Unit 2 Forms of Government Type: Direct Democracy Def: government in which all citizens have equal power in decision making Pros: 1.) Every Citizen has equal power. 2.) Everyone is
[ 1.1 ] Principles of Government
![[ 1.1 ] Principles of Government [ 1.1 ] Principles of Government](/thumbs/83/88387654.jpg) [ 1.1 ] Principles of Government [ 1.1 ] Principles of Government Key Terms - Use your book to define these in your notebook. government public policies legislative power executive power dictatorship democracy
[ 1.1 ] Principles of Government [ 1.1 ] Principles of Government Key Terms - Use your book to define these in your notebook. government public policies legislative power executive power dictatorship democracy
On the Level STEP BY STEP. through the reading pages together as a class. the graphic notes together as a class.
 Teacher s Guide On the Level Time Needed: One Class Period Materials Needed: Student Readings & Worksheets Copy Instructions: Double-side reading p. 1-2 Transparency of Venn diagram Single-side powers
Teacher s Guide On the Level Time Needed: One Class Period Materials Needed: Student Readings & Worksheets Copy Instructions: Double-side reading p. 1-2 Transparency of Venn diagram Single-side powers
3 rd Quarter ISN Table of Contents
 Students will be able to describe the development and impact of government as well as citizenship; the scientific and cultural advancements; and the roles and contributions of individuals in Ancient Greece.
Students will be able to describe the development and impact of government as well as citizenship; the scientific and cultural advancements; and the roles and contributions of individuals in Ancient Greece.
RULES AND GOVERNMENT 6 STUDENT VOTE ACTIVITY RESOURCE
 RULES AND GOVERNMENT Governance is the system of practices and processes that a community or group uses to organize themselves and make decisions. Governance models determine who has authority or a voice
RULES AND GOVERNMENT Governance is the system of practices and processes that a community or group uses to organize themselves and make decisions. Governance models determine who has authority or a voice
In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to
 In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to control the governed; and in the next place oblige it to
In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to control the governed; and in the next place oblige it to
Who Rules? Do You Know Your Forms of Government?
 Who Rules? Do You Know Your Forms of Government? 1. One person is in charge. bsolute Democracy Monarchy 2. Citizens often have no rights. Democracy Dictatorship 3. Government where all citizens take part
Who Rules? Do You Know Your Forms of Government? 1. One person is in charge. bsolute Democracy Monarchy 2. Citizens often have no rights. Democracy Dictatorship 3. Government where all citizens take part
SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government.
 SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government. 1a. Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution of power, particularly unitary, confederal, and federal types of government. Unitary
SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government. 1a. Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution of power, particularly unitary, confederal, and federal types of government. Unitary
Chp. 2 Comparing Forms of Government
 Chp. 2 Comparing Forms of Government Objectives p. 002 In this chapter, the students will classify various political systems analyze the advantages and disadvantages of various political systems and compare
Chp. 2 Comparing Forms of Government Objectives p. 002 In this chapter, the students will classify various political systems analyze the advantages and disadvantages of various political systems and compare
Different Democracies. EQ: How is a parliamentary democracy different from a presidential democracy?
 Different Democracies EQ: How is a parliamentary democracy different from a presidential democracy? What does the Legislative Branch do with law? They MAKE the laws! What does the Executive Branch do with
Different Democracies EQ: How is a parliamentary democracy different from a presidential democracy? What does the Legislative Branch do with law? They MAKE the laws! What does the Executive Branch do with
GOVERNMENT & CITIZENSHIP CORE CONCEPT PART 8
 GOVERNMENT & CITIZENSHIP CORE CONCEPT PART 8 FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT Government = a group of people who have the power to make and enforce laws for a country or area. Purpose of Government 1. Protect
GOVERNMENT & CITIZENSHIP CORE CONCEPT PART 8 FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT Government = a group of people who have the power to make and enforce laws for a country or area. Purpose of Government 1. Protect
A. Unitary B. Parliamentary Democracy C. Democracy D. Federal E. Confederation F. Presidential Democracy G. Oligarchy I. Autocracy
 Name: Class Period: 2 3 Governments: Anticipation Guide Directions: You will make predictions about the answers to the following questions BEFORE learning about this unit. Write the letter of the vocabulary
Name: Class Period: 2 3 Governments: Anticipation Guide Directions: You will make predictions about the answers to the following questions BEFORE learning about this unit. Write the letter of the vocabulary
Three Levels of Power Distribution Ø Unitary Ø Ø
 SS6CG4 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and federal. b. Explain how governments determine
SS6CG4 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and federal. b. Explain how governments determine
LL Copy the chart below. Fill it in as we watch Types of Government game show.
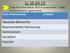 LL 10-24-13 Copy the chart below. Fill it in as we watch Types of Government game show. Form of Government 5 Details Absolute Monarchy Representative Democracy Communism Socialism Fascism The directions
LL 10-24-13 Copy the chart below. Fill it in as we watch Types of Government game show. Form of Government 5 Details Absolute Monarchy Representative Democracy Communism Socialism Fascism The directions
Rat in the Bucket review game Unit 1. World Governments
 Rat in the Bucket review game Unit 1 World Governments Question 1 A. Absolute Monarchy B. Constitutional A government in which the ruler and his army force people to obey. Monarchy C. Direct Democracy
Rat in the Bucket review game Unit 1 World Governments Question 1 A. Absolute Monarchy B. Constitutional A government in which the ruler and his army force people to obey. Monarchy C. Direct Democracy
Rat in the Bucket review game Unit 2. World Governments
 Rat in the Bucket review game Unit 2 World Governments Question 1 A. Absolute Monarchy B. Constitutional A government in which the ruler and his army force people to obey. Monarchy C. Direct Democracy
Rat in the Bucket review game Unit 2 World Governments Question 1 A. Absolute Monarchy B. Constitutional A government in which the ruler and his army force people to obey. Monarchy C. Direct Democracy
American Civics. Three Objectives: 1. What is Government?
 Syllabus Highlights 1. No Seating chart (avoid the back) 2. Don t ask to go to the bathroom Just take the pass! (do not go to the bathroom at the beginning of the hour) 3. All tests are curved against
Syllabus Highlights 1. No Seating chart (avoid the back) 2. Don t ask to go to the bathroom Just take the pass! (do not go to the bathroom at the beginning of the hour) 3. All tests are curved against
CHAPTER 1: FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: THE PURPOSE OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 2: FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 3: DEMOCRACY IN THE UNITED STATES
 CHAPTER 1: FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: THE PURPOSE OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 2: FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 3: DEMOCRACY IN THE UNITED STATES SECTION 1: THE PURPOSES OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: FOCUS
CHAPTER 1: FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: THE PURPOSE OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 2: FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 3: DEMOCRACY IN THE UNITED STATES SECTION 1: THE PURPOSES OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: FOCUS
SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship
 SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Define citizenship as stated in the 14 th Amendment Describe the process of becoming a naturalized citizen Evaluate
SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Define citizenship as stated in the 14 th Amendment Describe the process of becoming a naturalized citizen Evaluate
Foundations of Government. Section 1: Page 24
 Foundations of Government Section 1: Page 24 Types of governments: Govern means rule A government is any organization set up to make and enforce laws Every country in the world has their own form and system
Foundations of Government Section 1: Page 24 Types of governments: Govern means rule A government is any organization set up to make and enforce laws Every country in the world has their own form and system
Where is this in my book? It s in there, how about using the Index? But that s hard!
 Prologue Where is this in my book? It s in there, how about using the Index? But that s hard! Section 1 Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Main Idea The Greeks developed democracy, and the Romans added
Prologue Where is this in my book? It s in there, how about using the Index? But that s hard! Section 1 Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Main Idea The Greeks developed democracy, and the Romans added
Suppose you are on a sports team that is one play away from winning a game. Which is the best way to choose the final play of the game?
 Warm Up: Suppose you are on a sports team that is one play away from winning a game. Which is the best way to choose the final play of the game? A. Have the coach or the assistant coach choose. B. Have
Warm Up: Suppose you are on a sports team that is one play away from winning a game. Which is the best way to choose the final play of the game? A. Have the coach or the assistant coach choose. B. Have
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 1 Principles of Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. S E C T I O N 1 Government and the State How is government defined? What are the basic
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 1 Principles of Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. S E C T I O N 1 Government and the State How is government defined? What are the basic
';: f ^ g & ^ # f f n s
 Z^cZ^^nt GOVERNMENT/CIVICS UNDERSTANDINGS ';: f ^ g & ^ # f f n s will compare and contrast various forms of government distnbute power: unitary, confederate, andfederat_ m a n f w
Z^cZ^^nt GOVERNMENT/CIVICS UNDERSTANDINGS ';: f ^ g & ^ # f f n s will compare and contrast various forms of government distnbute power: unitary, confederate, andfederat_ m a n f w
SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship
 SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Define citizenship as stated in the 14 th Amendment Describe the process of becoming a naturalized citizen Evaluate
SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Define citizenship as stated in the 14 th Amendment Describe the process of becoming a naturalized citizen Evaluate
Democracy and Its Doubles. Democracy
 Democracy and Its Doubles Woodruff 1 Democracy Definition: government by and for the people While capturing the idea of democracy, it is not much use What are the components of a democracy? 2 What Democracy
Democracy and Its Doubles Woodruff 1 Democracy Definition: government by and for the people While capturing the idea of democracy, it is not much use What are the components of a democracy? 2 What Democracy
State of Israel, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, & Islamic Republic of Iran
 State of Israel, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, & Islamic Republic of Iran Bell Ringer: Writing to Win Complete the following statement and add supporting details in your writing to win journal. You must have
State of Israel, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, & Islamic Republic of Iran Bell Ringer: Writing to Win Complete the following statement and add supporting details in your writing to win journal. You must have
132. What type of government exists in Brazil? A. communist B. monarchy C. presidential democracy D. parliamentary democracy
 SS6CG2 The student will explain the structures of national governments in Latin America and the Caribbean. a. Compare the federal-republican systems of the Federative Republic of Brazil (Brazil) and the
SS6CG2 The student will explain the structures of national governments in Latin America and the Caribbean. a. Compare the federal-republican systems of the Federative Republic of Brazil (Brazil) and the
A situation where there is no government. Anarchy. The provinces in Canada keep their power and the central government has limited power.
 Anarchy A situation where there is no government. Canada The provinces in Canada keep their power and the central government has limited power. Confederation a political system in which the central government
Anarchy A situation where there is no government. Canada The provinces in Canada keep their power and the central government has limited power. Confederation a political system in which the central government
Vocabulary. Unit 2 and Unit 3 Study Guide
 Confederacy: Vocabulary Province: Legislature/Congress/Parliament: Economics: Free Market: Laissez- Faire: Mixed- Market Economy: Bourgeoisie: Proletariat: I. Systems of Government A. Unitary System 1.
Confederacy: Vocabulary Province: Legislature/Congress/Parliament: Economics: Free Market: Laissez- Faire: Mixed- Market Economy: Bourgeoisie: Proletariat: I. Systems of Government A. Unitary System 1.
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1
 Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 2 Types of Government ESSENTIAL QUESTION What principles guide different types of government? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary institution establishment practice, or social organization assembly
Lesson 2 Types of Government ESSENTIAL QUESTION What principles guide different types of government? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary institution establishment practice, or social organization assembly
Principles of Government. Unit 1- Foundations of Government
 Principles of Government Unit 1- Foundations of Government Why learn about government? What are some things you could do if government did not exist? What are some things you could not do without the government?
Principles of Government Unit 1- Foundations of Government Why learn about government? What are some things you could do if government did not exist? What are some things you could not do without the government?
Writing the Constitution
 Writing the Constitution Backwards Planning Curriculum Units Michael Hutchison, Writer Dr. Aaron Willis, Project Coordinator Justin Coffey, Editor Kerry Gordonson, Editor Social Studies School Service
Writing the Constitution Backwards Planning Curriculum Units Michael Hutchison, Writer Dr. Aaron Willis, Project Coordinator Justin Coffey, Editor Kerry Gordonson, Editor Social Studies School Service
Political & Economic Systems Quiz
 World Geography Mr. Prindiville September 24, 2014 Quiz Form: A * Do not make any marks on this quiz sheet. * Be sure to copy the quiz form letter onto the back of your quizlet. Multiple Choice Identify
World Geography Mr. Prindiville September 24, 2014 Quiz Form: A * Do not make any marks on this quiz sheet. * Be sure to copy the quiz form letter onto the back of your quizlet. Multiple Choice Identify
Ancient Greece: Democracy is born
 Ancient Greece: Democracy is born By USHistory.org, adapted by Newsela staff on 04.05.17 Word Count 560 Level MAX This painting by Philipp von Foltz shows the Athenian politician Pericles delivering a
Ancient Greece: Democracy is born By USHistory.org, adapted by Newsela staff on 04.05.17 Word Count 560 Level MAX This painting by Philipp von Foltz shows the Athenian politician Pericles delivering a
Lesson 3: Classical Greece
 Getting Started Lesson 3: Classical Greece In this lesson, you'll explore the Classical period in ancient Greek history, compare the city-states of Athens and Sparta, and learn about the Peloponnesian
Getting Started Lesson 3: Classical Greece In this lesson, you'll explore the Classical period in ancient Greek history, compare the city-states of Athens and Sparta, and learn about the Peloponnesian
The History of Government. Mr. Cline Civics Marshall High School Marshall, IL Unit One: Presentation One
 The History of Government Mr. Cline Civics Marshall High School Marshall, IL Unit One: Presentation One * Reconciling What Government Should Be With What It Is Throughout the history of government, however,
The History of Government Mr. Cline Civics Marshall High School Marshall, IL Unit One: Presentation One * Reconciling What Government Should Be With What It Is Throughout the history of government, however,
Georgia Coffee County 6 th Grade Social Studies. Latin America CIVICS/GOVERNMENT UNDERSTANDINGS
 Georgia Coffee County 6 th Grade Social Studies Latin America CIVICS/GOVERNMENT UNDERSTANDINGS SS6CG1 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government
Georgia Coffee County 6 th Grade Social Studies Latin America CIVICS/GOVERNMENT UNDERSTANDINGS SS6CG1 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government
Question. What do you notice about the number of free vs. not free countries around the world?
 What is Government? Question 1) What do you notice about the number of free vs. not free countries around the world? 2) Where do you see most of the unfree countries in the world? I) What is Government?
What is Government? Question 1) What do you notice about the number of free vs. not free countries around the world? 2) Where do you see most of the unfree countries in the world? I) What is Government?
CHAPTER ONE. The Most Prevailing Constitutional Systems
 CHAPTER ONE The Most Prevailing Constitutional Systems THREE MODELS OF POLITICAL ORGANIZATION OF POWER MONOCRACY OLIGARCHY DEMOCRACY MONOCRACY It is the form of government in which power belongs to one
CHAPTER ONE The Most Prevailing Constitutional Systems THREE MODELS OF POLITICAL ORGANIZATION OF POWER MONOCRACY OLIGARCHY DEMOCRACY MONOCRACY It is the form of government in which power belongs to one
What is Government? Chapter 3
 Chapter 3 What is Government? You must have heard the word 'government' mentioned several times. In this chapter you will learn about what a government is and the important role it plays in our lives.
Chapter 3 What is Government? You must have heard the word 'government' mentioned several times. In this chapter you will learn about what a government is and the important role it plays in our lives.
# OF DAYS NEEDED FOR MASTERY DATES TAUGHT DATE ASSESSED. End of Week 9. Week 6. Week 7
 .1.1.a.1.1.b Identify describe different forms of government via the study of early current civilizs (ex. tribal, monarchy, democracy, republic, theocracy, oligarchy) Describe the structure roles of government
.1.1.a.1.1.b Identify describe different forms of government via the study of early current civilizs (ex. tribal, monarchy, democracy, republic, theocracy, oligarchy) Describe the structure roles of government
Grade 6 World Geography
 Grade 6 World Geography Civics 6.1 Foundations of Government 6.1. G.1 Compare and contrast various forms of governments found throughout the world (E.g. communism, socialism, democracy, autocracy, dictatorship)
Grade 6 World Geography Civics 6.1 Foundations of Government 6.1. G.1 Compare and contrast various forms of governments found throughout the world (E.g. communism, socialism, democracy, autocracy, dictatorship)
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1
 Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
City-States. Athens Vs. Sparta
 City-States Athens Vs. Sparta 9/20 Bell-Ringer 1. Define Democracy 2. What makes the United States a democracy? 3. In what ways is the United States not a democracy? Greek Polis Essential Question How
City-States Athens Vs. Sparta 9/20 Bell-Ringer 1. Define Democracy 2. What makes the United States a democracy? 3. In what ways is the United States not a democracy? Greek Polis Essential Question How
Foundations of American Government
 Foundations of American Government Why Do We Need Government? Maintain social order Ensure domestic tranquility Establish justice Provide for the common defense Promote the general welfare Secure liberty
Foundations of American Government Why Do We Need Government? Maintain social order Ensure domestic tranquility Establish justice Provide for the common defense Promote the general welfare Secure liberty
STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth,
 STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by c) assessing the impacts
STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by c) assessing the impacts
Watch the Preview for the lesson. Then write down examples of images that support the following statements or answer the questions below.
 P r e v i e w Watch the Preview for the lesson. Then write down examples of images that support the following statements or answer the questions below. 1. We live in a democracy. 2. We participate in our
P r e v i e w Watch the Preview for the lesson. Then write down examples of images that support the following statements or answer the questions below. 1. We live in a democracy. 2. We participate in our
