Characterization of cytoskeleton mechanical properties and 3D-actin structure in twisted adherent epithelial cells
|
|
|
- Tracy Berry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biorheology 40 (2003) IOS Press Characterization of cytoskeleton mechanical properties and 3D-actin structure in twisted adherent epithelial cells Redouane Fodil, Valérie Laurent, Emmanuelle Planus and Daniel Isabey INSERM U492, Faculté de Médecine, 8 rue du général Sarrail, Créteil, France Tel.: ; Fax: ; redouane.fodil@creteil.inserm.fr Abstract. Evaluation of the cytoskeleton mechanical properties requires specific micromanipulation techniques such as the magnetic twisting cytometry technique, in which microbeads are specifically linked to the cytoskeleton via transmembrane receptors. The aim of the study was to assess the structural relationship between the bead and the cytoskeleton structure. The spatial arrangement of the CSK network was therefore studied in fixed cells probed by beads and stained for F-actin by rhodamined phalloïdine. The spatial character of the actin CSK network, both in the bead neighborhood and at the cell scale, could then be studied for various degrees of fluorescent intensity from 3D-images of the actin structure, reconstructed from z-stack views obtained by confocal microscopy. Results show the feasibility of the staining/reconstruction technique which allows to reveal the three-dimensional organization of the cytoskeleton structure including an internal cytosolic structure with a high fluorescent F-actin intensity, and a sub-membranous cortical structure with a low fluorescent F-actin intensity. 1. Introduction Many questions in cell biology remain unanswered because of the lack of detailed knowledge about the three-dimensional organization of the complex cytoskeletal structure. Indeed, it is now largely admitted that the state of cellular deformation, which results from the spatial organization of the actin cytoskeleton, plays a crucial role in fundamental biological processes [2,3,9,10] as well as during cellular micromanipulations aiming at measure cell mechanical properties [12,13]. Since cellular mechanical properties have been shown to be strongly dependent on the CSK-specificity of the bead-cell linkage, one of the main problems is the structural assessment of the physical link between the bead and the cytoskeleton structure. We therefore considered F-actin structure of adherent epithelial cells in culture probed by ferromagnetic microbeads attached to the transmembrane mechanoreceptors. We performed systematic 3D-reconstructions of the F-actin structure stained by rhodamined phalloïdine in fixed cells. The spatial reconstruction of the F-actin structure was performed from z-stack images obtained by confocal microscopy as recently done by Blatter [1]. The proposed staining/reconstruction technique allows to reveal the three-dimensional organization of the cytoskeleton structure both in the bead vicinity and at the cell scale [4]. Noteworthy, reconstructions performed with double fluorescent intensity levels reveal an internal cytosolic structure with a high fluorescent F-actin intensity, and a sub-membranous cortical structure with a low fluorescent F-actin intensity which appear consistent with a double compartment model analysis of the mechanical cytoskeleton response [8,11] X/03/$ IOS Press. All rights reserved
2 242 R. Fodil et al. / Cytoskeleton mechanical properties and 3D-actin structure 2. Material and methods 2.1. Bead attachment Carboxyl ferromagnetic beads ( µm diameter, Spherotec Inc., IL, USA) were coated with arginine glycin aspartic acid (RGD) peptide following the company procedure (Telios Pharmaceutical Inc., CA, USA). Before used, coated-beads were incubated in serum free medium supplemented with 1% BSA for at least 30 minutes at 37 C to block non-specific binding. Beads were then added to the cells (40 µg per well) for 20 minutes at 37 Cin5%CO 2 95% air incubator. Unbound beads were washed away with serum free medium 1% BSA supplemented with 25 mm HEPES Staining of fixed cells We stained the F-actin structure of human alveolar epithelial cell monolayer (A549 cell line) with fluorescent phallotoxin. Small plastic wells were fixed with silicone on round glass coverslides which were placed in Petri dishes and the inside surface of the wells (0.5 cm 2 ) was coated with fibronectin at a concentration of 5 µg/cm 2. Cell monolayers with beads attached were rinsed twice with warm CSK-buffer (25 mm HEPES, 2 mm MgCl 2, 30 mm MES, 10 mm EGTA, 300 mm sucrose, ph 6.9) in order to maintain CSK integrity, as previously described. Cells were then fixed in 1% glutaraldehyde in CSK buffer for 15 minutes and incubated for 2 additional minutes with 0.5% Triton X100 and 0.25% glutaraldehyde in CSK-buffer at 37 C in order to permeabilized cells and then were rinsed twice with CSK-buffer. Rhodamined phalloïdin (0.76 µm) was dissolved in CSK-buffer and added to sample for 30 minutes in the dark and under humid chamber at room temperature. Cells were rinsed twice for 5 minutes with CSK-buffer, then a final rinse was performed with ddh 2 0. The coverslides were mounted with 100 µl of mounting medium on top of the cell monolayer to keep the cell thickness intact. Samples were stored overnight at 4 C before examination by laser confocal Confocal microscopy Stained cell monolayers were observed using the LSM 410 invert confocal microscope (Zeiss, Rueil- Malmaison, France). The latter has two internal helium-neon laser and one external argon ion laser. Image processing was performed using LSM 410 software. Fields of cells were randomly selected, brought into focus using a 63/1.4 numeric aperture Plan Neofluor objective. Epifluorescence was detected for a 543 nm excitation and 570 nm emission. A cross sectional image was recorded under confocal conditions and used to establish a plane of focus above the glass surface. Optical sections were recorded every 1 µm to reveal intracellular fluorescence. Apical localization of labelling was determined by obtaining vertical section D-reconstruction To undo the distortion due to the optical system of the confocal microscope, a 3D deconvolution process was performed on the stack of grey level images (8 bits) by the appropriate module of AxioVision software (Carl Zeiss, NY, USA). The deconvolution process uses a mathematical algorithm which takes into account the theoretical function PSF (Point Spread Function) calculated for each acquisition parameters. The fixed images data are implemented at the right scale in Amira 2.2 software (TGS
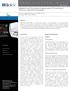
3 R. Fodil et al. / Cytoskeleton mechanical properties and 3D-actin structure 243 Fig. 1. Upper view (a) and vertical cross-section (b) views of three-dimensional reconstructions of fixed adherent epithelial cells probed by beads and stained for F-actin with rhodamine phalloïdine. The two fluorescent intensity levels used reveal an internal cytosolic structure with a high fluorescent F-actin intensity (dark grey), and an external cortical structure with a low fluorescent F-actin intensity (bright grey). Note that initial position of a given bead was spatially determined using spheres of appropriate sizes. Inc., CA, USA) which uses the threshold segmentation method to extract cell contours. Contours of external and internal sub-cellular structures corresponding to different levels of fluorescent intensity where defined using the curve of the logarithmic decrease in cumulated pixels of the stack images versus the gray level (0 to 255). The 3D-reconstruction was performed by a GMC module (Generalized Marching Cube algorithm) of Amira software which generates, using a triangulation method, an isosurface from segmented optical plans. Visualization of the 3D-reconstructed cells was performed using 3D-Studio Max v3.1 software (Kinetix, CA, USA), allowing calculation of volume from a surface, permitting by Boolean operations to generate vertical sections in the 3D-reconstructed cell. 3. Results and discussion Three-dimensional reconstruction of the cortical F-actin structure performed in fixed adherent epithelial cells probed by beads is presented in Fig. 1(a) (in bright grey). The threshold segmentation used for this reconstruction was about 5% of the full range of fluorescent intensity (0 255), a value which was given to represent the lowest F-actin density detectable. Although the F-actin was solely marked, it was possible to spatially determine the initial position of the beads using spheres whose sizes were precisely measured either under direct confocal microscopy or during post-acquisition from cell images stored in
4 244 R. Fodil et al. / Cytoskeleton mechanical properties and 3D-actin structure Interferential Contrast Nomarski. The degree of bead immersion in the cellular medium could also be determined by generating vertical sections with the reconstruction program (see Fig. 1(b)). Based on these 3D-reconstructions of external F-actin structure, the beads appear half immersed in the cellular medium. Indeed, degree of bead immersion is important to understand the twisting magnetic cytometry results as it happens to be a crucial parameter in the calculation of the elastic/viscous modulus [7]. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the internal F-actin structure is shown in Fig. 1(a) for the same cell. The threshold segmentation used for this reconstruction was about 36% of the full range of fluorescent intensity (0 255), an arbitrary value which was supposed to be sufficient to reveal the dense stress fiber structure. We present in Fig. 1(a), the 3D-reconstruction of the internal structure (in dark grey) which is embedded in the transparent external F-actin structure and which seems to determine the overall cell shape. It is also important to note that the dense structure concerns also the borders of the cell, meaning that the cell likely re-organizes its internal F-actin structure in addition to the local F-actin cortical structure surrounding the bead. This results reinforce the evidence of a mechanical continuum through the hierarchical CSK structure from the bead to low-density-f-actin then high-density-f-actin. In a recent study [8,11], it has been shown that the curve fitting analysis of the cellular response measured by twisting magnetic cytometry could be greatly improved by using a double compartment CSK model. The first compartment included a rapid (time constant <1 s), cortical CSK network embedding the bead, while the second compartment included a slow (time constant 30 s), cytosolic CSK, joining large regions of the cytoplasm, the behavior of each CSK compartments being represented by a simple Voigt model. Based on the double density CSK 3D-reconstruction study, we can postulate that the cortical CSK would represent the low F-actin density network while the cytosolic CSK would represent the denser F-actin network. Above all, the method presently proposed to reconstruct the CSK structure confirms early assumptions [5,6] about the physical linkage existing between coated beads and the cytoskeleton network and describes, through different levels of F-actin density, how this bead-csk linkage occurs, both structurally and mechanically. In conclusion, the present results demonstrate the feasibility of the 3D-reconstruction in fixed cells stained for F-actin using adapted commercially available software and provide a general tool to study and quantify the structural linkage and remodeling of CSK structures. References [1] L.A. Blatter, Cell volume measurements by fluorescence confocal microscopy: theoretical and practical aspects, Methods in Enzymology 307 (1999), [2] C.S. Chen, M. Mrksich, S. Huang, G.M. Whitesides and D.E. Ingber, Geometric control of cell life and death, Science 276(5317) (1997), [3] M.E. Chicurel, C.S. Chen and D.E. Ingber, Cellular control lies in the balance of forces, Current Opinion in Cell Biology 10(2) (1998), [4] R. Fodil, V. Laurent, S. Eddahibi, S. Wendling, E. Planus and D. Isabey, Parallel Assessment of the 3D-Actin Structure and Mechanical Properties of Cytoskeleton in Twisted Living Adherent Cells, Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry, Société de Biomécanique, Montreal, 108(1) (2000), 168. [5] D.E. Ingber, L. Dike, L. Hansen et al., Cellular tensegrity: exploring how mechanical changes in the cytoskeleton regulate cell growth, migration, and tissue pattern during morphogenesis, International Review of Cytology 150 (1994), [6] D.E. Ingber, The riddle of morphogenesis: a question of solution chemistry or molecular cell engineering?, Cell 75(7) (1993), [7] D. Isabey, V.M. Laurent, S. Hénon et al., Mechanical properties of adherent alveolar epithelial cells measured by bead micromanipulation: comparison of magnetic twisting cytometry vs optical tweezers, in: The FASEB Journal, Experimental Biology, Orlando, Florida, 15(4, Part I) (2001), A158.
5 R. Fodil et al. / Cytoskeleton mechanical properties and 3D-actin structure 245 [8] V.M. Laurent, E. Planus, R. Fodil and D. Isabey, Mechanical assessment by magnetocytometry of the cytosolic and cortical cytoskeletal compartments in adherent epithelial cells, in: Euromech. Colloqium no. 420: Mechanobiology of Cells and Tissues, Nancy (France), 2001, Biorheology 40 (2003), [9] A.J. Maniotis, C.S. Chen and D.E. Ingber, Demonstration of mechanical connections between integrins, cytoskeletal filaments, and nucleoplasm that stabilize nuclear structure, Proceedings of The National Academy of Sciences of The United States of America 94(3) (1997), [10] D.J. Mooney, R. Langer and D.E. Ingber, Cytoskeletal filament assembly and the control of cell spreading and function by extracellular matrix, J. Cell Sci. 108(Pt 6) (1995), [11] E. Planus, V.M. Laurent, R. Fodil, M.P. D Ortho, A. Harf and D. Isabey, A double-compartment model of the cytoskeletal mechanical response of locally twisted alveolar epithelial cells: the effect of modulating environmental conditions, in: The FASEB Journal, Experimental Biology 2001, Orlando, Florida, 15(4, Part I) (2001), A159. [12] N. Wang, J.P. Butler and D.E. Ingber, Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton, Science 260(5111) (1993), [13] N. Wang and D.E. Ingber, Control of cytoskeletal mechanics by extracellular matrix, cell shape, and mechanical tension, Biophys. J. 66(6) (1994),
Prestress and adhesion site dynamics control cell sensitivity to extracellular stiffness
 Author manuscript, published in "Biophysical Journal 2009;96(5):2009-22" DOI : 10.1016/j.bpj.2008.10.072 1 Prestress and adhesion site dynamics control cell sensitivity to extracellular stiffness S. Féréol
Author manuscript, published in "Biophysical Journal 2009;96(5):2009-22" DOI : 10.1016/j.bpj.2008.10.072 1 Prestress and adhesion site dynamics control cell sensitivity to extracellular stiffness S. Féréol
For labelling sub-cellular organelles in tissue sections, cell cultures and cell free experiments using our proprietary Red fluorescence probe
 ab112127 CytoPainter F-actin Staining Kit - Red Fluorescence Instructions for Use For labelling sub-cellular organelles in tissue sections, cell cultures and cell free experiments using our proprietary
ab112127 CytoPainter F-actin Staining Kit - Red Fluorescence Instructions for Use For labelling sub-cellular organelles in tissue sections, cell cultures and cell free experiments using our proprietary
Prestress and Adhesion Site Dynamics Control Cell Sensitivity to Extracellular Stiffness
 Biophysical Journal Volume 96 March 2009 2009 2022 2009 Prestress and Adhesion Site Dynamics Control Cell Sensitivity to Extracellular Stiffness S. Féréol, R. Fodil, V. M. Laurent, M. Balland, {k B. Louis,
Biophysical Journal Volume 96 March 2009 2009 2022 2009 Prestress and Adhesion Site Dynamics Control Cell Sensitivity to Extracellular Stiffness S. Féréol, R. Fodil, V. M. Laurent, M. Balland, {k B. Louis,
Combined fluorescence and AFM imaging of cells
 Combined fluorescence and AFM imaging of cells Introduction Combining optical and AFM imaging of cells opens up many possibilities for correlating structural information about the cell surface with functional
Combined fluorescence and AFM imaging of cells Introduction Combining optical and AFM imaging of cells opens up many possibilities for correlating structural information about the cell surface with functional
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2007
 Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2007 Fibronectin isolation and fluorescent labeling Human plasma Fn was isolated from fresh human plasma (Swiss
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2007 Fibronectin isolation and fluorescent labeling Human plasma Fn was isolated from fresh human plasma (Swiss
Supplemental material JCB. Pitaval et al., Cell shape and ciliogenesis Pitaval et al.
 Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Pitaval et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201004003/dc1 S1 Figure S1. Cell cycle exit analysis. (A) Experimental procedure. RPE1 cells were
Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Pitaval et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201004003/dc1 S1 Figure S1. Cell cycle exit analysis. (A) Experimental procedure. RPE1 cells were
Introduction. Figure 1. Oris Cell Migration Assay Principle
 Optimizing Performance of the Membrane-free, Oris Cell Migration Assay for High Throughput Screening using the BioTek Synergy HT Multi-Mode Microplate Reader Keren I. Hulkower, Renee L. Herber, and Scott
Optimizing Performance of the Membrane-free, Oris Cell Migration Assay for High Throughput Screening using the BioTek Synergy HT Multi-Mode Microplate Reader Keren I. Hulkower, Renee L. Herber, and Scott
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Matrigen Softwell Hydrogels Version 1.0 Contents General Questions... 3 Cell Culture and Experimental Questions... 6 Quality Control Technical Questions... 8 SoftTrac Products...
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Matrigen Softwell Hydrogels Version 1.0 Contents General Questions... 3 Cell Culture and Experimental Questions... 6 Quality Control Technical Questions... 8 SoftTrac Products...
Immunofluorescence Staining Protocol for 3 Well Chamber, removable
 Immunofluorescence Staining Protocol for 3 Well Chamber, removable This Application Note presents a simple protocol for the cultivation, fixation, and staining of cells using the 3 Well Chamber, removable.
Immunofluorescence Staining Protocol for 3 Well Chamber, removable This Application Note presents a simple protocol for the cultivation, fixation, and staining of cells using the 3 Well Chamber, removable.
Journal of Biological Engineering is an open access, peer-reviewed online journal that encompasses all aspects biological engineering.
 Journal of Biological Engineering is an open access, peer-reviewed online journal that encompasses all aspects biological engineering. The journal welcomes manuscripts on the following topics: synthetic
Journal of Biological Engineering is an open access, peer-reviewed online journal that encompasses all aspects biological engineering. The journal welcomes manuscripts on the following topics: synthetic
The BioFlux 200 System Using Well Plate Microfluidics for Live Cell Assays Product Overview and Tutorial
 The BioFlux 200 System Using Well Plate Microfluidics for Live Cell Assays Product Overview and Tutorial Introduction to the BioFlux System Enables live-cell assays with precisely-controlled shear flow
The BioFlux 200 System Using Well Plate Microfluidics for Live Cell Assays Product Overview and Tutorial Introduction to the BioFlux System Enables live-cell assays with precisely-controlled shear flow
PROTOCOL. Live Cell Imaging of 3D Cultures Grown on Alvetex Scaffold Using Confocal Microscopy. Introduction
 Page 1 Introduction Live cell imaging allows real time monitoring of cell shape and form during cell differentiation, proliferation and migration. Alvetex Scaffold offers a unique ability to study cell
Page 1 Introduction Live cell imaging allows real time monitoring of cell shape and form during cell differentiation, proliferation and migration. Alvetex Scaffold offers a unique ability to study cell
ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit: 2 color immunocytochemistry of cytochrome c and mitochondria.
 PROTOCOL ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSA07 Rev.1 DESCRIPTION ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit: 2 color immunocytochemistry
PROTOCOL ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSA07 Rev.1 DESCRIPTION ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit: 2 color immunocytochemistry
Fluorescence Light Microscopy for Cell Biology
 Fluorescence Light Microscopy for Cell Biology Why use light microscopy? Traditional questions that light microscopy has addressed: Structure within a cell Locations of specific molecules within a cell
Fluorescence Light Microscopy for Cell Biology Why use light microscopy? Traditional questions that light microscopy has addressed: Structure within a cell Locations of specific molecules within a cell
Immunofluorescence Confocal Microscopy of 3D Cultures Grown on Alvetex
 Immunofluorescence Confocal Microscopy of 3D Cultures Grown on Alvetex 1.0. Introduction Immunofluorescence uses the recognition of cellular targets by fluorescent dyes or antigen-specific antibodies coupled
Immunofluorescence Confocal Microscopy of 3D Cultures Grown on Alvetex 1.0. Introduction Immunofluorescence uses the recognition of cellular targets by fluorescent dyes or antigen-specific antibodies coupled
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION: 1. Supplemental methods 2. Supplemental figure legends 3. Supplemental figures
 Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2008 A microfluidics-based turning assay reveals complex growth cone responses to integrated gradients of substrate-bound
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2008 A microfluidics-based turning assay reveals complex growth cone responses to integrated gradients of substrate-bound
Cell-Environment Interactions. Chieh-Chun Chen
 Cell-Environment Interactions Chieh-Chun Chen Part 1: Soft Lithography in Biology and Biochemistry Chieh-Chun Chen Outlines Introduction Key features of soft lithography Applications In microscopic biochemical
Cell-Environment Interactions Chieh-Chun Chen Part 1: Soft Lithography in Biology and Biochemistry Chieh-Chun Chen Outlines Introduction Key features of soft lithography Applications In microscopic biochemical
The Product and Experiment Guide
 The Product and Experiment Guide Providing Solutions for Your Research p. 3 p. 10 p. 4 CELL CULTURE & MICROSCOPY IMMUNO- FLUORESCENCE LIVE CELL IMAGING p. 8 p. 7 p. 11 ANGIOGENESIS ASSAYS CHEMOTAXIS ASSAYS
The Product and Experiment Guide Providing Solutions for Your Research p. 3 p. 10 p. 4 CELL CULTURE & MICROSCOPY IMMUNO- FLUORESCENCE LIVE CELL IMAGING p. 8 p. 7 p. 11 ANGIOGENESIS ASSAYS CHEMOTAXIS ASSAYS
ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit
 ab110417 ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit Instructions for Use For the Immunocytochemistry analysis of cytochrome c and a mitochondrial marker (Complex Vα) in apoptotic cells and non-apoptotic
ab110417 ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit Instructions for Use For the Immunocytochemistry analysis of cytochrome c and a mitochondrial marker (Complex Vα) in apoptotic cells and non-apoptotic
lumox & x-well Technology
 lumox & x-well Technology lumox lumox dish & lumox multiwell lumox cell culture products are characterized by their ultra-thin, gas-permeable film base. Optimum gas exchange is guaranteed due to the gas
lumox & x-well Technology lumox lumox dish & lumox multiwell lumox cell culture products are characterized by their ultra-thin, gas-permeable film base. Optimum gas exchange is guaranteed due to the gas
Automated, Kinetic Imaging of Cell Migration and Invasion Assays using Corning FluoroBlok Permeable Supports
 A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Automated, Kinetic Imaging of Cell Migration and Invasion Assays using Corning FluoroBlok Permeable Supports Brad Larson, Principal Scientist, Applications Department, BioTek
A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Automated, Kinetic Imaging of Cell Migration and Invasion Assays using Corning FluoroBlok Permeable Supports Brad Larson, Principal Scientist, Applications Department, BioTek
Mapping of Mechanical Strains and Stresses around Quiescent Engineered Three-Dimensional Epithelial Tissues
 Mapping of Mechanical Strains and Stresses around Quiescent Engineered Three-Dimensional Epithelial Tissues Nikolce Gjorevski and Celeste M. Nelson Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, and
Mapping of Mechanical Strains and Stresses around Quiescent Engineered Three-Dimensional Epithelial Tissues Nikolce Gjorevski and Celeste M. Nelson Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, and
Cellular Biomechanics. Linda Lowe-Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century October 17, 2011
 Cellular Biomechanics Linda Lowe-Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century October 17, 2011 Outline for today Tubes Vessel mechanics and disease Models Lung mechanics Technology integration Atherosclerosis
Cellular Biomechanics Linda Lowe-Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century October 17, 2011 Outline for today Tubes Vessel mechanics and disease Models Lung mechanics Technology integration Atherosclerosis
5 HARNESSING THE PURSE STRING FOR
 107 5 HARNESSING THE PURSE STRING FOR ACCELERATED WOUND CLOSURE Abstract Wound healing is essential in maintaining tissue integrity. Wounds can close via lamellipodial crawling, which involves the rapid
107 5 HARNESSING THE PURSE STRING FOR ACCELERATED WOUND CLOSURE Abstract Wound healing is essential in maintaining tissue integrity. Wounds can close via lamellipodial crawling, which involves the rapid
Analysis of cytoskeletal features in dried and living cells and slow dynamic experiments using Atomic Force Microscopy
 Analysis of cytoskeletal features in dried and living cells and slow dynamic experiments using Atomic Force Microscopy Author Watson, Gregory, Watson, Jolanta Published 008 Journal Title Journal of Physics:
Analysis of cytoskeletal features in dried and living cells and slow dynamic experiments using Atomic Force Microscopy Author Watson, Gregory, Watson, Jolanta Published 008 Journal Title Journal of Physics:
lumox & x-well Technology
 lumox & x-well Technology lumox lumox cell culture products are characterized by their ultra-thin, gas-permeable film base. Optimum gas exchange is guaranteed due to the gas permeability and the short
lumox & x-well Technology lumox lumox cell culture products are characterized by their ultra-thin, gas-permeable film base. Optimum gas exchange is guaranteed due to the gas permeability and the short
Cell culture NIH 3T3 fibroblasts were grown in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle Medium
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Cell culture NIH 3T3 fibroblasts were grown in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle Medium supplemented
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Cell culture NIH 3T3 fibroblasts were grown in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle Medium supplemented
B. ADM: C. D. Apoptosis: 1.68% 2.99% 1.31% Figure.S1,Li et al. number. invaded cells. HuH7 BxPC-3 DLD-1.
 A. - Figure.S1,Li et al. B. : - + - + - + E-cadherin CK19 α-sma vimentin β -actin C. D. Apoptosis: 1.68% 2.99% 1.31% - : - + - + - + Apoptosis: 48.33% 45.32% 44.59% E. invaded cells number 400 300 200
A. - Figure.S1,Li et al. B. : - + - + - + E-cadherin CK19 α-sma vimentin β -actin C. D. Apoptosis: 1.68% 2.99% 1.31% - : - + - + - + Apoptosis: 48.33% 45.32% 44.59% E. invaded cells number 400 300 200
ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody
 ab110417 ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Instructions for Use For the Immunocytochemistry analysis of cytochrome c and a mitochondrial marker (Complex Vα) in apoptotic cells and nonapoptotic
ab110417 ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Instructions for Use For the Immunocytochemistry analysis of cytochrome c and a mitochondrial marker (Complex Vα) in apoptotic cells and nonapoptotic
TractionsForAll. v1.0. September 1 st, Created by Aleksandar Marinković, Sc.D. & Daniel Tschumperlin, Ph.D.
 TractionsForAll v1.0 September 1 st, 2013 TractionsForAll v1.0 is freely distributed program that calculates tractions exerted by an adherent cell on the soft hydrogel substrate underneath. It is created
TractionsForAll v1.0 September 1 st, 2013 TractionsForAll v1.0 is freely distributed program that calculates tractions exerted by an adherent cell on the soft hydrogel substrate underneath. It is created
Visualizing mechanical tension across membrane receptors with a fluorescent sensor
 Nature Methods Visualizing mechanical tension across membrane receptors with a fluorescent sensor Daniel R. Stabley, Carol Jurchenko, Stephen S. Marshall, Khalid S. Salaita Supplementary Figure 1 Fabrication
Nature Methods Visualizing mechanical tension across membrane receptors with a fluorescent sensor Daniel R. Stabley, Carol Jurchenko, Stephen S. Marshall, Khalid S. Salaita Supplementary Figure 1 Fabrication
ab CytoPainter Phalloidin-iFluor 594
 Version 4 Last updated 23 May 2017 ab176757 CytoPainter Phalloidin-iFluor 594 Reagent For staining actin filaments (F-actin) in formaldehyde-fixed cells and tissues. This product is for research use only
Version 4 Last updated 23 May 2017 ab176757 CytoPainter Phalloidin-iFluor 594 Reagent For staining actin filaments (F-actin) in formaldehyde-fixed cells and tissues. This product is for research use only
Sample Preparation Manual for the 3D Cell Explorer. November 2016
 Sample Preparation Manual for the 3D Cell Explorer November 2016 Contents 1. IMPORTANT facts FOR THE SAMPLE PREPARATION 3 2. Specifications overview 4 3. Sample preparation 5 3.1 Cell confluency 5 3.2
Sample Preparation Manual for the 3D Cell Explorer November 2016 Contents 1. IMPORTANT facts FOR THE SAMPLE PREPARATION 3 2. Specifications overview 4 3. Sample preparation 5 3.1 Cell confluency 5 3.2
Farnesoid X Receptor and its ligands inhibit the function of platelets
 Farnesoid X Receptor and its ligands inhibit the function of platelets Article Accepted Version Figures and Legends Moraes, L. A., Unsworth, A. J., Vaiyapuri, S., Ali, M. S., Sasikumar, P., Sage, T., Flora,
Farnesoid X Receptor and its ligands inhibit the function of platelets Article Accepted Version Figures and Legends Moraes, L. A., Unsworth, A. J., Vaiyapuri, S., Ali, M. S., Sasikumar, P., Sage, T., Flora,
THE BASICS OF IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY
 THE BASICS OF IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY Introduction Immunohistochemistry (IHC) identifies specific tissue components by means of a specific antigen/antibody reaction tagged with a visible label. IHC makes
THE BASICS OF IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY Introduction Immunohistochemistry (IHC) identifies specific tissue components by means of a specific antigen/antibody reaction tagged with a visible label. IHC makes
The CQ1 Confocal Quantitative Image Cytometer and its Application to Biological Measurement
 The CQ1 Confocal Quantitative Image Cytometer and its Application to Biological Measurement Hirofumi Sakashita *1 Koji Ohashi *1 Kazuo Ozawa *2 ohei Tsubouchi *1 The CQ1 confocal quantitative image cytometer,
The CQ1 Confocal Quantitative Image Cytometer and its Application to Biological Measurement Hirofumi Sakashita *1 Koji Ohashi *1 Kazuo Ozawa *2 ohei Tsubouchi *1 The CQ1 confocal quantitative image cytometer,
ab CytoPainter ER Staining Kit Red Fluorescence
 ab139482 CytoPainter ER Staining Kit Red Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed to detect Human endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139482 CytoPainter ER Staining Kit Red Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed to detect Human endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Sample Preparation 3D Cell Explorer. Version 1.1 July 2015 Sabine Bautz
 Sample Preparation 3D Cell Explorer Version 1.1 July 2015 Sabine Bautz Contents 1. Important points to keep in mind for the sample preparation 3 2. Sample preparation specifications and data sheet 4 3.
Sample Preparation 3D Cell Explorer Version 1.1 July 2015 Sabine Bautz Contents 1. Important points to keep in mind for the sample preparation 3 2. Sample preparation specifications and data sheet 4 3.
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion
 Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
Supplementary Information. Quantifying cell-generated mechanical forces within living embryonic tissues
 Supplementary Information Quantifying cell-generated mechanical forces within living embryonic tissues Otger Campàs, Tadanori Mammoto, Sean Hasso, Ralph A. Sperling, Daniel O Connell, Ashley G. Bischof,
Supplementary Information Quantifying cell-generated mechanical forces within living embryonic tissues Otger Campàs, Tadanori Mammoto, Sean Hasso, Ralph A. Sperling, Daniel O Connell, Ashley G. Bischof,
ab CytoPainter Mitochondrial Staining Kit NIR Fluorescence
 ab176747 CytoPainter Mitochondrial Staining Kit NIR Fluorescence Instructions for Use For staining Mitochondria in live cells with our proprietary NIR probe. This product is for research use only and is
ab176747 CytoPainter Mitochondrial Staining Kit NIR Fluorescence Instructions for Use For staining Mitochondria in live cells with our proprietary NIR probe. This product is for research use only and is
Live and Dead Cell Assay
 ab115347 Live and Dead Cell Assay Instructions for Use Differential fluorescent labeling of live and dead cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Last Updated
ab115347 Live and Dead Cell Assay Instructions for Use Differential fluorescent labeling of live and dead cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Last Updated
Supplementary Figure 1 Pfn1, but not other Pfn isoforms are expressed in
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pfn1, but not other Pfn isoforms are expressed in platelets. (a) RT-PCR of Pfn isoforms in control mouse platelets, Pfn1 -/- platelets and control heart. Expected band size for Pfn1
Supplementary Figure 1 Pfn1, but not other Pfn isoforms are expressed in platelets. (a) RT-PCR of Pfn isoforms in control mouse platelets, Pfn1 -/- platelets and control heart. Expected band size for Pfn1
Axol Guide to Performing Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Application Protocol Version 2.0
 Axol Guide to Performing Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Application Protocol Version 2.0 Table of Contents General ICC Protocol 3 Synaptic Marker ICC Protocol 5 Recommended Markers 6 Technical Support 7 2 General
Axol Guide to Performing Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Application Protocol Version 2.0 Table of Contents General ICC Protocol 3 Synaptic Marker ICC Protocol 5 Recommended Markers 6 Technical Support 7 2 General
In vivo recording, forepaw denervation, and isolation of slices: Methods for mapping the forepaw/lower jaw border in anesthetized adult rat primary
 Supplementary Methods In vivo recording, forepaw denervation, and isolation of slices: Methods for mapping the forepaw/lower jaw border in anesthetized adult rat primary somatosensory cortex (S1), forepaw
Supplementary Methods In vivo recording, forepaw denervation, and isolation of slices: Methods for mapping the forepaw/lower jaw border in anesthetized adult rat primary somatosensory cortex (S1), forepaw
Propidium Iodide. Catalog Number: Structure: Molecular Formula: C 27H 34I 2N 4. Molecular Weight: CAS #
 Catalog Number: 195458 Propidium Iodide Structure: Molecular Formula: C 27H 34I 2N 4 Molecular Weight: 668.45 CAS # 25535-16-4 Physical Description: Dark red crystals Description: Reagent used for the
Catalog Number: 195458 Propidium Iodide Structure: Molecular Formula: C 27H 34I 2N 4 Molecular Weight: 668.45 CAS # 25535-16-4 Physical Description: Dark red crystals Description: Reagent used for the
Application Microfluidic Cell Analysis Devices (I) Date: 2013/05/24. Dr. Yi-Chung Tung
 Application Microfluidic Cell Analysis Devices (I) Date: 2013/05/24 Dr. Yi-Chung Tung Mechanotransduction and the Study of Cellular Forces Mechanical forces play a critical role in nearly all aspects of
Application Microfluidic Cell Analysis Devices (I) Date: 2013/05/24 Dr. Yi-Chung Tung Mechanotransduction and the Study of Cellular Forces Mechanical forces play a critical role in nearly all aspects of
Supplementary Information. Tau co-organizes dynamic microtubule and actin networks. and Isabelle Arnal 1,2,*
 Supplementary Information Tau co-organizes dynamic microtubule and actin networks Auréliane Elie 1,2, Elea Prezel 1,2, Christophe Guérin 3, Eric Denarier 1,2,4, Sacnicte Ramirez- Rios 1,2, Laurence Serre
Supplementary Information Tau co-organizes dynamic microtubule and actin networks Auréliane Elie 1,2, Elea Prezel 1,2, Christophe Guérin 3, Eric Denarier 1,2,4, Sacnicte Ramirez- Rios 1,2, Laurence Serre
Confocal Microscopy Analyzes Cells
 Choosing Filters for Fluorescence A Laurin Publication Photonic Solutions for Biotechnology and Medicine November 2002 Confocal Microscopy Analyzes Cells Reprinted from the November 2002 issue of Biophotonics
Choosing Filters for Fluorescence A Laurin Publication Photonic Solutions for Biotechnology and Medicine November 2002 Confocal Microscopy Analyzes Cells Reprinted from the November 2002 issue of Biophotonics
Brightfield and Fluorescence Imaging using 3D PrimeSurface Ultra-Low Attachment Microplates
 A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Brightfield and Fluorescence Imaging using 3D PrimeSurface Ultra-Low Attachment Microplates Brad Larson, BioTek Instruments, Inc., Winooski, VT USA Anju Dang, S-BIO, Hudson,
A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Brightfield and Fluorescence Imaging using 3D PrimeSurface Ultra-Low Attachment Microplates Brad Larson, BioTek Instruments, Inc., Winooski, VT USA Anju Dang, S-BIO, Hudson,
JCB. Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY. Hong et al.,
 Supplemental material JCB Hong et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201412127/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Analysis of purified proteins by SDS-PAGE and pull-down assays. (A) Coomassie-stained
Supplemental material JCB Hong et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201412127/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Analysis of purified proteins by SDS-PAGE and pull-down assays. (A) Coomassie-stained
ab CytoPainter ER Staining Kit Red Fluorescence
 ab139482 CytoPainter ER Staining Kit Red Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed to detect Human endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139482 CytoPainter ER Staining Kit Red Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed to detect Human endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Immunofluorescence and phalloidin labeling of mammalian cells
 Immunofluorescence and phalloidin labeling of mammalian cells 2 Contents Materials for immunofluorescence and phalloidin labeling of mammalian cells...1 Immunofluorescence-labelling on cultivated adherent
Immunofluorescence and phalloidin labeling of mammalian cells 2 Contents Materials for immunofluorescence and phalloidin labeling of mammalian cells...1 Immunofluorescence-labelling on cultivated adherent
Segments of the obstructed intestinal loops were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde
 Supplementary text Supplementary materials and methods Histopathological examination Segments of the obstructed intestinal loops were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) and embedded in paraffin wax with
Supplementary text Supplementary materials and methods Histopathological examination Segments of the obstructed intestinal loops were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) and embedded in paraffin wax with
ThiolTracker Violet (Glutathione Detection Reagent)
 ThiolTracker Violet (Glutathione Detection Reagent) Catalog nos. T10095, T10096 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Concentration Storage* Stability ThiolTracker Violet 180 assays
ThiolTracker Violet (Glutathione Detection Reagent) Catalog nos. T10095, T10096 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Concentration Storage* Stability ThiolTracker Violet 180 assays
Beta3 integrin promotes long-lasting activation and polarization of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 by immobilized ligand
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES Beta3 integrin promotes long-lasting activation and polarization of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 by immobilized ligand C. Ravelli et al. FIGURE S. I Figure S. I: Gremlin
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES Beta3 integrin promotes long-lasting activation and polarization of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 by immobilized ligand C. Ravelli et al. FIGURE S. I Figure S. I: Gremlin
RayBio Apoptosis Detection Kit, MitoCapture
 RayBio Apoptosis Detection Kit, MitoCapture User Manual Version 1.0 Mar 17, 2015 RayBio Apoptosis Detection Kit, MitroCapture Protocol (Cat#: 68MC-Apo-S100) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent
RayBio Apoptosis Detection Kit, MitoCapture User Manual Version 1.0 Mar 17, 2015 RayBio Apoptosis Detection Kit, MitroCapture Protocol (Cat#: 68MC-Apo-S100) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Real-time deformability cytometry: contour detection and theoretical modeling.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Real-time deformability cytometry: contour detection and theoretical modeling. (a) Image of cell deformed in constriction; contour (red) according to image analysis algorithm. Scale
Supplementary Figure 1 Real-time deformability cytometry: contour detection and theoretical modeling. (a) Image of cell deformed in constriction; contour (red) according to image analysis algorithm. Scale
Printing of biochemically-patterned slides with the InnoStamp40 for deterministic cell immobilization.
 Printing of biochemically-patterned slides with the InnoStamp40 for deterministic cell immobilization. Jean christophe CAU 1 1 Innopsys, Parc activestre, Carbonne France contact@innopsys.fr www.innopsys.com
Printing of biochemically-patterned slides with the InnoStamp40 for deterministic cell immobilization. Jean christophe CAU 1 1 Innopsys, Parc activestre, Carbonne France contact@innopsys.fr www.innopsys.com
to KLH (keyhole-limpet hemocyanin), corresponding to amino acid residues of
 1 EN-09-0410-REVISED VERSION 2 May 11 th 2009 3 Supplemental Data - Battista et al. 2009 4 Supplemental Materials and Methods 5 6 7 8 9 10 Seladin-1 antiserum In short, rabbits were immunized with the
1 EN-09-0410-REVISED VERSION 2 May 11 th 2009 3 Supplemental Data - Battista et al. 2009 4 Supplemental Materials and Methods 5 6 7 8 9 10 Seladin-1 antiserum In short, rabbits were immunized with the
Technical Manual No Version
 TUNEL Apoptosis Detection Kit Cat. No. L00301 (For Cryopreserved Tissue Sections, FITC-labled POD) Technical Manual No. 0269 Version 01132011 I Description. 1 II Key Features.... 1 III Kit Contents.. 1
TUNEL Apoptosis Detection Kit Cat. No. L00301 (For Cryopreserved Tissue Sections, FITC-labled POD) Technical Manual No. 0269 Version 01132011 I Description. 1 II Key Features.... 1 III Kit Contents.. 1
Supplementary Materials
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Toxicology Research. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Materials Confocal Microscopy and 3D Image Analysis Relative Quantitative
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Toxicology Research. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Materials Confocal Microscopy and 3D Image Analysis Relative Quantitative
The Nuclear Area Factor (NAF): a measure for cell apoptosis using microscopy and image analysis
 The Nuclear Area Factor (NAF): a measure for cell apoptosis using microscopy and image analysis Mark A. DeCoster Department of Biomedical Engineering and Institute for Micromanufacturing, Louisiana Tech
The Nuclear Area Factor (NAF): a measure for cell apoptosis using microscopy and image analysis Mark A. DeCoster Department of Biomedical Engineering and Institute for Micromanufacturing, Louisiana Tech
Zenon Goat IgG Labeling Kits
 Product Information Revised: 19 June 2007 Quick Facts Storage upon receipt: 2 6 C Protect from light Abs/Em: See Table 1 Unlabeled IgG antibody Zenon labeling reagent (labeled Fab fragment) Introduction
Product Information Revised: 19 June 2007 Quick Facts Storage upon receipt: 2 6 C Protect from light Abs/Em: See Table 1 Unlabeled IgG antibody Zenon labeling reagent (labeled Fab fragment) Introduction
ab CytoPainter Phalloidin-iFluor 488
 Version 3 Last updated 23 May 2017 ab176753 CytoPainter Phalloidin-iFluor 488 Reagent For staining actin filaments (F-actin) in formaldehyde-fixed cells and tissues. This product is for research use only
Version 3 Last updated 23 May 2017 ab176753 CytoPainter Phalloidin-iFluor 488 Reagent For staining actin filaments (F-actin) in formaldehyde-fixed cells and tissues. This product is for research use only
Tube Formation Assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis. 1. General Information. Application Note 19
 Tube Formation Assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis Contents 1. General Information... 1 2. Material... 2 3. Work Flow Overview... 3 4. Preparation of the Gel and the Slide... 4 4.1. Gel Application... 4 4.2.
Tube Formation Assays in µ-slide Angiogenesis Contents 1. General Information... 1 2. Material... 2 3. Work Flow Overview... 3 4. Preparation of the Gel and the Slide... 4 4.1. Gel Application... 4 4.2.
Graphene oxide-enhanced cytoskeleton imaging and mitosis tracking
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary information for Graphene oxide-enhanced cytoskeleton imaging and mitosis tracking
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary information for Graphene oxide-enhanced cytoskeleton imaging and mitosis tracking
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Cell-mediated fibre recruitment drives extracellular matrix mechanosensing in engineered fibrillar microenvironments Brendon M. Baker 1,2,*+, Britta Trappmann 1,2,*, William Y. Wang 1, Mahmut S. Sakar
Cell-mediated fibre recruitment drives extracellular matrix mechanosensing in engineered fibrillar microenvironments Brendon M. Baker 1,2,*+, Britta Trappmann 1,2,*, William Y. Wang 1, Mahmut S. Sakar
No wash 2 Washes 2 Days ** ** IgG-bead phagocytosis (%)
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. No wash 2 Washes 2 Days Tat Control ** ** 2 4 6 8 IgG-bead phagocytosis (%) Supplementary Figure 1. Reversibility of phagocytosis inhibition by Tat. Human
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. No wash 2 Washes 2 Days Tat Control ** ** 2 4 6 8 IgG-bead phagocytosis (%) Supplementary Figure 1. Reversibility of phagocytosis inhibition by Tat. Human
Labware compatibility report. Directly order at:
 Labware compatibility report Directly order at: https://ibidi.com/12-labware Contents 1. Introduction 3 2. Compatible Labware 4 A. 35 mm dishes - high borders 4 µ-dish 35 mm, high 4 µ-dish 35mm, high Glass
Labware compatibility report Directly order at: https://ibidi.com/12-labware Contents 1. Introduction 3 2. Compatible Labware 4 A. 35 mm dishes - high borders 4 µ-dish 35 mm, high 4 µ-dish 35mm, high Glass
Lab module 6b Receptor-mediated endocytosis
 Goal for the module Lab module 6b Receptor-mediated endocytosis To follow the movement of a degraded ligand, LDL, and a recycled ligand, transferrin, as they undergo endocytic processing. Pre-lab homework
Goal for the module Lab module 6b Receptor-mediated endocytosis To follow the movement of a degraded ligand, LDL, and a recycled ligand, transferrin, as they undergo endocytic processing. Pre-lab homework
TUNEL Universal Apoptosis Detection Kit (FITC-labeled)
 TUNEL Universal Apoptosis Detection Kit (FITC-labeled) Cat. No. L00427 Technical Manual No. TM0623 Version 03102011 I Description. 1 II Key Features.... 1 III Kit Contents.. 1 IV Storage.. 2 V Protocol..
TUNEL Universal Apoptosis Detection Kit (FITC-labeled) Cat. No. L00427 Technical Manual No. TM0623 Version 03102011 I Description. 1 II Key Features.... 1 III Kit Contents.. 1 IV Storage.. 2 V Protocol..
Low Background D-A-D Type Fluorescent Probe for Imaging of Biothiols
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Low Background D-A-D Type Fluorescent
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Low Background D-A-D Type Fluorescent
Introduction to histology and its methods of study
 Introduction to histology and its methods of study Li shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology 1 What is histology Definition Cell: smallest units functions in the human body Tissue
Introduction to histology and its methods of study Li shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology 1 What is histology Definition Cell: smallest units functions in the human body Tissue
Introduction to N-STORM
 Introduction to N-STORM Dan Metcalf Advanced Imaging Manager Outline Introduction Principles of STORM Applications N-STORM overview Biological Scale Mitochondrion Microtubule Amino Acid 1Å Kinesin 1nm
Introduction to N-STORM Dan Metcalf Advanced Imaging Manager Outline Introduction Principles of STORM Applications N-STORM overview Biological Scale Mitochondrion Microtubule Amino Acid 1Å Kinesin 1nm
Sample Preparation 3D Cell Explorer. Version 1.1 July 2015 Sabine Bautz
 Sample Preparation 3D Cell Explorer Version 1.1 July 2015 Sabine Bautz Contents 1. Important points to keep in mind for the sample preparation 3 2. Sample preparation specifications and data sheet 4 3.
Sample Preparation 3D Cell Explorer Version 1.1 July 2015 Sabine Bautz Contents 1. Important points to keep in mind for the sample preparation 3 2. Sample preparation specifications and data sheet 4 3.
Paper presentation PNAS October 20, 2009 vol. 106 no
 Paper presentation Continuous imaging of plasmon rulers in live cells reveals early-stage caspase-3 activation at the single-molecule level Young-wook Jun a, Sassan Sheikholeslami a,1, Daniel R. Hostetter
Paper presentation Continuous imaging of plasmon rulers in live cells reveals early-stage caspase-3 activation at the single-molecule level Young-wook Jun a, Sassan Sheikholeslami a,1, Daniel R. Hostetter
Technical Note. Tissue Section Imaging. Published August The most recent version of this Technical Note is posted at licor.com/bio/support.
 Technical Note Tissue Section Imaging Published August 2017. The most recent version of this Technical Note is posted at licor.com/bio/support. Page 2 - Tissue Section Imaging Table of Contents Page I.
Technical Note Tissue Section Imaging Published August 2017. The most recent version of this Technical Note is posted at licor.com/bio/support. Page 2 - Tissue Section Imaging Table of Contents Page I.
Use of Phase Contrast Imaging to Track Morphological Cellular Changes due to Apoptotic Activity
 A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Use of Phase Contrast Imaging to Track Morphological Cellular Changes due to Apoptotic Activity Brad Larson and Peter Banks, Applications Department, BioTek Instruments, Inc.,
A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Use of Phase Contrast Imaging to Track Morphological Cellular Changes due to Apoptotic Activity Brad Larson and Peter Banks, Applications Department, BioTek Instruments, Inc.,
Force Measurement Software Module
 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss Force Measurement Software Module Optical tweezers are used to manipulate microscopic particles such as cells or sub-cellular structures. The Force Measurement (FM) module expands
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss Force Measurement Software Module Optical tweezers are used to manipulate microscopic particles such as cells or sub-cellular structures. The Force Measurement (FM) module expands
Ac(n cytoskeleton 12/7/11. The Cytoskeleton. Func0ons of the Cytoskeleton. B Visegrady. Elements of the Cytoskeleton
 The Cytoskeleton Ac(n cytoskeleton B Visegrady The cytoskeleton is an intricate network of protein filaments that extends throughout the cytoplasm. A skin cell (fibroblast) stained with Coomassie blue.
The Cytoskeleton Ac(n cytoskeleton B Visegrady The cytoskeleton is an intricate network of protein filaments that extends throughout the cytoplasm. A skin cell (fibroblast) stained with Coomassie blue.
Supporting Information. An Aptazyme-Gold Nanoparticle Sensor for Amplified. Molecular Probing in Living Cells
 Supporting Information n ptazyme-gold Nanoparticle Sensor for mplified Molecular Probing in Living Cells Yanjing Yang, Jin Huang*, Xiaohai Yang, Ke Quan, He Wang, Le Ying, Nuli Xie, Min Ou, Kemin Wang*
Supporting Information n ptazyme-gold Nanoparticle Sensor for mplified Molecular Probing in Living Cells Yanjing Yang, Jin Huang*, Xiaohai Yang, Ke Quan, He Wang, Le Ying, Nuli Xie, Min Ou, Kemin Wang*
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Supplementary Method Sample preparation and image data acquisition Osteoclast - bone data Femoral bones were excised, fixed with 4%(v/v) paraformaldehyde buffered with 0.1 M phosphate
Supplementary Material Supplementary Method Sample preparation and image data acquisition Osteoclast - bone data Femoral bones were excised, fixed with 4%(v/v) paraformaldehyde buffered with 0.1 M phosphate
Samples of fluorescent and non-fluorescent specimens of Montastraea cavernosa were
 Online Materials and Methods Sample collection Samples of fluorescent and non-fluorescent specimens of Montastraea cavernosa were collected at depths ranging from 15 to 30 meters in the waters around Lee
Online Materials and Methods Sample collection Samples of fluorescent and non-fluorescent specimens of Montastraea cavernosa were collected at depths ranging from 15 to 30 meters in the waters around Lee
µ Slide Membrane ibipore Flow
 The ibidi product family is comprised of a variety of µ Slides and µ Dishes, which have all been designed for high end microscopic analysis of fixed or living cells. The high optical quality of the material
The ibidi product family is comprised of a variety of µ Slides and µ Dishes, which have all been designed for high end microscopic analysis of fixed or living cells. The high optical quality of the material
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Table S1. Definition of quantitative cellular features
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Table S1. Definition of quantitative cellular features
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Stavru et al. 0.073/pnas.357840 SI Materials and Methods Immunofluorescence. For immunofluorescence, cells were fixed for 0 min in 4% (wt/vol) paraformaldehyde (Electron Microscopy
Supporting Information Stavru et al. 0.073/pnas.357840 SI Materials and Methods Immunofluorescence. For immunofluorescence, cells were fixed for 0 min in 4% (wt/vol) paraformaldehyde (Electron Microscopy
The preparation of both fixed and living material is a new and equally demanding art.
 W hen viewed using a microscope, all parts of the human body - from chromosomes to sperm can be visually arresting. My work is inspired by scientific images of cells from organisms as diverse as algae
W hen viewed using a microscope, all parts of the human body - from chromosomes to sperm can be visually arresting. My work is inspired by scientific images of cells from organisms as diverse as algae
Visualizing Cells Molecular Biology of the Cell - Chapter 9
 Visualizing Cells Molecular Biology of the Cell - Chapter 9 Resolution, Detection Magnification Interaction of Light with matter: Absorbtion, Refraction, Reflection, Fluorescence Light Microscopy Absorbtion
Visualizing Cells Molecular Biology of the Cell - Chapter 9 Resolution, Detection Magnification Interaction of Light with matter: Absorbtion, Refraction, Reflection, Fluorescence Light Microscopy Absorbtion
Multiplexed 3D FRET imaging in deep tissue of live embryos Ming Zhao, Xiaoyang Wan, Yu Li, Weibin Zhou and Leilei Peng
 Scientific Reports Multiplexed 3D FRET imaging in deep tissue of live embryos Ming Zhao, Xiaoyang Wan, Yu Li, Weibin Zhou and Leilei Peng 1 Supplementary figures and notes Supplementary Figure S1 Volumetric
Scientific Reports Multiplexed 3D FRET imaging in deep tissue of live embryos Ming Zhao, Xiaoyang Wan, Yu Li, Weibin Zhou and Leilei Peng 1 Supplementary figures and notes Supplementary Figure S1 Volumetric
Supporting Information Corresponding Author
 Supporting Information In Vitro Multitissue Interface Model Supports Rapid Vasculogenesis and Mechanistic Study of Vascularization across Tissue Compartments Kevin P. Buno, 1 Xuemei Chen, 2,3 Justin A.
Supporting Information In Vitro Multitissue Interface Model Supports Rapid Vasculogenesis and Mechanistic Study of Vascularization across Tissue Compartments Kevin P. Buno, 1 Xuemei Chen, 2,3 Justin A.
Characterizing Phenotypes of Bacteria by Staining Method
 Experiment 3 Laboratory to Biology III Diversity of Microorganisms / Wintersemester / page 1 Experiment 3 Characterizing Phenotypes of Bacteria by Staining Method Advisor NN Reading Chapters in BBOM 9
Experiment 3 Laboratory to Biology III Diversity of Microorganisms / Wintersemester / page 1 Experiment 3 Characterizing Phenotypes of Bacteria by Staining Method Advisor NN Reading Chapters in BBOM 9
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Rodríguez-Fraticelli et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203075/dc1 Figure S1. Cell spreading and lumen formation in confined
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Rodríguez-Fraticelli et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203075/dc1 Figure S1. Cell spreading and lumen formation in confined
λ N -GFP: an RNA reporter system for live-cell imaging
 λ N -GFP: an RNA reporter system for live-cell imaging Nathalie Daigle & Jan Ellenberg Supplementary Figures and Text: Supplementary Figure 1 localization in the cytoplasm. 4 λ N22-3 megfp-m9 serves as
λ N -GFP: an RNA reporter system for live-cell imaging Nathalie Daigle & Jan Ellenberg Supplementary Figures and Text: Supplementary Figure 1 localization in the cytoplasm. 4 λ N22-3 megfp-m9 serves as
MitoTracker and MitoFluor Mitochondrion-Selective Probes
 MitoTracker and MitoFluor Mitochondrion-Selective Probes Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Storage Stability MitoTracker probes 20 vials each containing 50 µg lyophilized solid
MitoTracker and MitoFluor Mitochondrion-Selective Probes Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Storage Stability MitoTracker probes 20 vials each containing 50 µg lyophilized solid
Leaf-inspired Artificial Microvascular Networks (LIAMN) for Threedimensional
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Leaf-inspired Artificial Microvascular Networks (LIAMN) for Threedimensional
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Leaf-inspired Artificial Microvascular Networks (LIAMN) for Threedimensional
Characterizing Phenotypes of Bacteria by Staining Method
 Experiment 3 Laboratory to Biology III Diversity of Microorganisms / Wintersemester / page 1 Experiment Characterizing Phenotypes of Bacteria by Staining Method Advisor Reading NN Chapters 3.1, 3.7, 3.8,
Experiment 3 Laboratory to Biology III Diversity of Microorganisms / Wintersemester / page 1 Experiment Characterizing Phenotypes of Bacteria by Staining Method Advisor Reading NN Chapters 3.1, 3.7, 3.8,
STORM/PALM. Super Resolution Microscopy 10/31/2011. Looking into microscopic world of life
 Super Resolution Microscopy STORM/PALM Bo Huang Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, UCSF CSHL Quantitative Microscopy, 1/31/211 Looking into microscopic world of life 1 µm 1 µm 1 nm 1 nm 1 nm 1 Å Naked
Super Resolution Microscopy STORM/PALM Bo Huang Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, UCSF CSHL Quantitative Microscopy, 1/31/211 Looking into microscopic world of life 1 µm 1 µm 1 nm 1 nm 1 nm 1 Å Naked
Image-iT FX Kits with Alexa Fluor Secondary Detection Conjugates
 Image-iT FX Kits with Alexa Fluor Secondary Detection Conjugates Table 1. Contents and Storage Information. Material Amount Concentration Storage Stability Alexa Fluor IgG conjugates Alexa Fluor streptavidin
Image-iT FX Kits with Alexa Fluor Secondary Detection Conjugates Table 1. Contents and Storage Information. Material Amount Concentration Storage Stability Alexa Fluor IgG conjugates Alexa Fluor streptavidin
