Nucleic Acid Staining. Fluorophores & Applica6ons
|
|
|
- Augustine Owen
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nucleic Acid Staining Fluorophores & Applica6ons
2 Types of Nucleic Acid Stains Intercala)ng dyes- - ethidium bromide and propidium iodide Minor- groove binders- - DAPI and the Hoechst dyes Miscellaneous- - nucleic acid stains, including acridine orange, 7- AAD, LDS 751 and hydroxys6lbamidine, with special proper6es.
3 Cell- Impermeant Ethidium Bromide and Propidium Iodide Ethidium bromide and PI are structurally similar phenanthridinium intercalators. PI is more soluble in water and less membrane- permeant than EtBr, although both dyes are generally excluded from viable cells.
4 Ethidium Bromide (EtBr) and Propidium Iodide (PI) EtBr and PI are cell- impermeant; they are excluded from living cells. These dyes intercalate in between the base pairs of the DNA molecule. They bind with limle or no sequence preference at a stoichiometry of one dye per 4 5 base pairs of DNA. Both EtBr and PI also bind to RNA, requiring treatment with nucleases to dis6nguish between RNA and DNA PI is commonly used as a nuclear or chromosome counterstain and as a stain for dead cells.
5 DNA- Selec)ve Hoechst Dyes The Hoechst dyes 33258, and 34580, are cell membrane permeant, minor groove binding DNA stains that are excited by UV light and fluoresce bright blue upon binding to DNA. Hoechst dyes exhibit rela6vely large Stokes shi[s (excita6on/ emission maxima ~350/460 nm), making them suitable for mul6color labeling experiments. They are used in many cellular applica6ons, including cell- cycle and apoptosis studies and they are common nuclear counterstains.
6 AT- Selec)ve DAPI DAPI (4',6- diamidino- 2- phenylindole) shows blue fluorescence upon binding DNA and can be also be excited by UV. The blue- fluorescent DAPI stain apparently associates with the minor groove of dsdna, preferen6ally binding to AT clusters. DAPI is an excellent nuclear counterstain, showing a dis6nct banding pamern in chromosomes. Also useful for cell- cycle studies and mycoplasma detec6on.
7 Acridine Orange: A Dual- Fluorescence Nucleic Acid Stain Acridine orange is a dye that interacts with DNA and RNA by intercala6on or electrosta6c amrac6ons. This dye has green fluorescence with an emission maximum at 525 nm when bound to DNA. Upon associa6on with RNA, its emission is shi[ed to ~650 nm (red fluorescence). Useful for RNA/DNA discrimina6on measurements Lysosome labeling Flow cytometry Cell- cycle studies.
8 7- aminoac6nomycin D 7 AAD is a fluorescent intercalator that undergoes a spectral shi[ upon associa6on with DNA. Weakly permeant. GC- selec6ve. Useful for flow cytometry and chromosome banding.
9 Cell Fixa6on Preserving the cellular structures
10 CELL FIXATION The living cell is fluid or in a semi- fluid state, whereas fixa6on produces coagula6on of 6ssue proteins and cons6tuents, a necessary event to prevent their loss or diffusion during cell processing and/or staining. The objec6ve of fixa6on is to preserve cells and 6ssue cons6tuents in as close a life- like state as possible. Fixa6on arrests autolysis, and stabilizes the cellular cons6tuents so that they can withstand the subsequent stages of processing/staining. Fixa6on should also provide for the preserva6on of cell substances and proteins.
11 General Classes of Fixa6ves Aldehydes, such as formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde. Oxidizing agents: metallic ions and complexes, such as osmium tetroxide, chromic acid. Protein- denaturing agents, such as ace6c acid, methyl alcohol (methanol), ethyl alcohol (ethanol).
12 METHYL AND ETHYL ALCOHOL Protein- denaturing agents These fixa6ves can alter the structure of proteins, primarily due to the disrup6on of the hydrophobic bonds which contribute the ter6ary structure of proteins. However, hydrogen bonds appear to be more stable in methanol and ethanol than in water so that while affec6ng the ter6ary structure of proteins, these alcohols may preserve their secondary structure. These alcohols are both closely related in structure to water and can compete almost as effec6vely as the lamer for hydrogen bonds. Both replace water molecules in the 6ssues, unbound as well as bound, during fixa6on. While absolute ethanol preserves glycogen, it can cause distor6on of the nucleus and shrinkage of cytoplasm. If fixa6on is prolonged, the alcohols remove histones from the nuclei and later extract RNA and DNA.
13 ALDEHYDES Cross- linking fixa6ves The aldehydes form cross- links between proteins, crea6ng a gel, thus retaining cellular components in a life- like state. Soluble proteins are fixed to structural proteins and rendered insoluble, giving some mechanical strength to the en6re structure which enables it to withstand subsequent processing. With the aldehydes, cross- links are formed between protein molecules, the reac6on being mostly with basic amino acid lysine. A disadvantage may be the extent of protein denatura6on produced by this type of fixa6on. This can be cri6cal in the detec6on of an6gens both by immunofluorescence and immunoenzyme techniques.
14 OXIDIZING AGENTS Metallic ions and complexes The most commonly used metallic ion in fixa6on is osmium tetroxide which was ini6ally a 6ssue fixa6ve used in cytology, but poor penetra6on limited its applica6on in light microscopy. Recent studies show that the reac6on of osmium tetroxide is largely with lipid rather than protein. Osmium tetroxide is used for preserva6on of fine structures in electron microscopy and is effec6ve for small (2-3 mm 3 ) specimens.
Apoptosis detection. Apoptosis assays for the Attune Acoustic Focusing Cytometer. APOPTOSIS DETECTION Attune Acoustic Focusing Cytometer
 POPTOSIS ETECTION ttune coustic Focusing Cytometer poptosis detection poptosis assays for the ttune coustic Focusing Cytometer poptosis is a carefully regulated process of cell death that occurs as a normal
POPTOSIS ETECTION ttune coustic Focusing Cytometer poptosis detection poptosis assays for the ttune coustic Focusing Cytometer poptosis is a carefully regulated process of cell death that occurs as a normal
Fundamentals and Applications of Biofilms Analysis, Structure and Physiology of Bacterial Biofilms Ching-Tsan Huang ( 黃慶璨 ) Office: Agronomy
 1 Fundamentals and Applications of Biofilms Analysis, Structure and Physiology of Bacterial Biofilms Ching-Tsan Huang ( 黃慶璨 ) Office: Agronomy Building, Room 111 Tel: (02) 33664454 E-mail: cthuang@ntu.edu.tw
1 Fundamentals and Applications of Biofilms Analysis, Structure and Physiology of Bacterial Biofilms Ching-Tsan Huang ( 黃慶璨 ) Office: Agronomy Building, Room 111 Tel: (02) 33664454 E-mail: cthuang@ntu.edu.tw
BIOLOGICAL SAMPLE PREPARATION FOR TEM OBSERVATION. TEM Seminar Nov 16, 2017 Astari Dwiranti, Ph.D
 BIOLOGICAL SAMPLE PREPARATION FOR TEM OBSERVATION TEM Seminar Nov 16, 2017 Astari Dwiranti, Ph.D Why do we need EM for biological samples? (O'Connor and Adams, 2010) Why do we need EM for biological samples?
BIOLOGICAL SAMPLE PREPARATION FOR TEM OBSERVATION TEM Seminar Nov 16, 2017 Astari Dwiranti, Ph.D Why do we need EM for biological samples? (O'Connor and Adams, 2010) Why do we need EM for biological samples?
Flow Cytometry for Ploidy and Genome Size analysis - 1. Functional principles
 Flow Cytometry for Ploidy and Genome Size analysis - 1. Functional principles The technique of plant ploidy and genome size analysis in a flow cytometer is based on the fluorescent labelling of the nuclear
Flow Cytometry for Ploidy and Genome Size analysis - 1. Functional principles The technique of plant ploidy and genome size analysis in a flow cytometer is based on the fluorescent labelling of the nuclear
PREPARATION OF HISTOLOGICAL SPECIMENS
 PREPARATION OF HISTOLOGICAL SPECIMENS Histo-techniques Preparation of tissue for microscopic examination Series of processes Ultimate aim to make tissue visible as it is Pathology Vs Anatomy Steps vary
PREPARATION OF HISTOLOGICAL SPECIMENS Histo-techniques Preparation of tissue for microscopic examination Series of processes Ultimate aim to make tissue visible as it is Pathology Vs Anatomy Steps vary
Lecture 13: Analysis of 2D gels
 Lecture 13: Analysis of 2D gels A complete proteomic analysis aims at collecting quantitative information about all protein in a sample. A normal 2 Dimensional gel electrophoresis results are analyzed
Lecture 13: Analysis of 2D gels A complete proteomic analysis aims at collecting quantitative information about all protein in a sample. A normal 2 Dimensional gel electrophoresis results are analyzed
Flow Cytometry. Marta Argenti, PhD student. Department of Biomedical Sciences Padua
 Flow Cytometry Marta Argenti, PhD student Department of Biomedical Sciences Padua 14.12.12 Flow ~ cells in motion Cyto ~ cell Metry ~ measure Physical properties: Flow Cytometry is the measurement of cells
Flow Cytometry Marta Argenti, PhD student Department of Biomedical Sciences Padua 14.12.12 Flow ~ cells in motion Cyto ~ cell Metry ~ measure Physical properties: Flow Cytometry is the measurement of cells
Technical Overview Cross-linking fixatives: What they are, what they do, and why we use them
 Technical Overview Cross-linking fixatives: What they are, what they do, and why we use them Focus on: Formaldehyde, Glutaraldehyde, and Osmium tetroxide M. Kuwajima/Kristen Harris Lab EM processing and
Technical Overview Cross-linking fixatives: What they are, what they do, and why we use them Focus on: Formaldehyde, Glutaraldehyde, and Osmium tetroxide M. Kuwajima/Kristen Harris Lab EM processing and
Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy
 Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy HL-6 and cells were cultured and cytospun onto glass slides. The cells were double immunofluorescence stained for Mt NPM1 and fibrillarin (nucleolar marker). Briefly,
Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy HL-6 and cells were cultured and cytospun onto glass slides. The cells were double immunofluorescence stained for Mt NPM1 and fibrillarin (nucleolar marker). Briefly,
CytoPainter Golgi Staining Kit Green Fluorescence
 ab139483 CytoPainter Golgi Staining Kit Green Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed for the detection of Golgi bodies by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139483 CytoPainter Golgi Staining Kit Green Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed for the detection of Golgi bodies by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids
 Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Living and Dead Cells Staining: -Cellstain- Double Staining Kit
 Introduction -Cellstain - Double Staining Kit combines Calcein-AM (used for fluorescent staining the living cells) and Propidium Iodide (used for a fluorescent staining of the dead cells) for simultaneous
Introduction -Cellstain - Double Staining Kit combines Calcein-AM (used for fluorescent staining the living cells) and Propidium Iodide (used for a fluorescent staining of the dead cells) for simultaneous
Cells and Tissues. Overview CELLS
 Cells and Tissues WIll The basic unit of structure and function in the human body is the cell. Each of a cell's parts, or organelles, as well as the entire cell, is organized to perform a specific function.
Cells and Tissues WIll The basic unit of structure and function in the human body is the cell. Each of a cell's parts, or organelles, as well as the entire cell, is organized to perform a specific function.
Synthetic Biology for
 Synthetic Biology for Plasmids and DNA Digestion Plasmids Plasmids are small DNA molecules that are separate from chromosomal DNA They are most commonly found as double stranded, circular DNA Typical plasmids
Synthetic Biology for Plasmids and DNA Digestion Plasmids Plasmids are small DNA molecules that are separate from chromosomal DNA They are most commonly found as double stranded, circular DNA Typical plasmids
Partha Roy
 Fluorescence microscopy http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Partha Roy 1 Lecture Outline Definition of fluorescence Common fluorescent reagents Construction ti of a fluorescence microscope Optical
Fluorescence microscopy http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Partha Roy 1 Lecture Outline Definition of fluorescence Common fluorescent reagents Construction ti of a fluorescence microscope Optical
Purification of DNA from living cells
 Purification of DNA from living cells Total cell DNA & Plasmid DNA Grow and harvest bacterial culture Prepare cell extract Purify DNA from a cell extract Concentrate DNA samples Measure DNA concentration
Purification of DNA from living cells Total cell DNA & Plasmid DNA Grow and harvest bacterial culture Prepare cell extract Purify DNA from a cell extract Concentrate DNA samples Measure DNA concentration
Cellometer Vision CBA
 Features of the Vision CBA Image Cytometry System All-in-One System Basic cell counting, primary cell viability, and cellbased assays. See for Yourself Why the Top Ten Pharmaceutical Companies Trust Cellometer
Features of the Vision CBA Image Cytometry System All-in-One System Basic cell counting, primary cell viability, and cellbased assays. See for Yourself Why the Top Ten Pharmaceutical Companies Trust Cellometer
Purification: Step 1. Lecture 11 Protein and Peptide Chemistry. Cells: Break them open! Crude Extract
 Purification: Step 1 Lecture 11 Protein and Peptide Chemistry Cells: Break them open! Crude Extract Total contents of cell Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Big Problem: Crude extract is not the natural
Purification: Step 1 Lecture 11 Protein and Peptide Chemistry Cells: Break them open! Crude Extract Total contents of cell Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Big Problem: Crude extract is not the natural
Purification: Step 1. Protein and Peptide Chemistry. Lecture 11. Big Problem: Crude extract is not the natural environment. Cells: Break them open!
 Lecture 11 Protein and Peptide Chemistry Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Purification: Step 1 Cells: Break them open! Crude Extract Total contents of cell Big Problem: Crude extract is not the natural
Lecture 11 Protein and Peptide Chemistry Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Purification: Step 1 Cells: Break them open! Crude Extract Total contents of cell Big Problem: Crude extract is not the natural
LAB 6: Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of Restriction Digested Plasmid DNA
 LAB 6: Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of Restriction Digested Plasmid DNA I. Objectives The purpose of today s lab is to learn how to set up and run an agarose gel, separate DNA fragments on the gel, and
LAB 6: Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of Restriction Digested Plasmid DNA I. Objectives The purpose of today s lab is to learn how to set up and run an agarose gel, separate DNA fragments on the gel, and
Flow Cytometry Support Reagents
 Excite and inspire Flow Cytometry Support Reagents Introduction Miltenyi Biotec is a leading supplier of flow cytometry products, offering one of the broadest ranges of antibodies, kits, assays, and support
Excite and inspire Flow Cytometry Support Reagents Introduction Miltenyi Biotec is a leading supplier of flow cytometry products, offering one of the broadest ranges of antibodies, kits, assays, and support
Rapid Learning Center Presents. Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours
 Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/35 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/35 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1
 AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.5 Nucleic Acids and their functions Page 1 From the syllabus: 1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1 l. Nucleic
AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.5 Nucleic Acids and their functions Page 1 From the syllabus: 1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1 l. Nucleic
A Study of Potassium Permanganate 'Fixation' for Electron Microscopy
 241 A Study of Potassium Permanganate 'Fixation' for Electron Microscopy By S. BRADBURY AND G. A. MEEK (From the Department of Human Anatomy, South Parks Road, Oxford) With five plates (figs, i, 2, 4,
241 A Study of Potassium Permanganate 'Fixation' for Electron Microscopy By S. BRADBURY AND G. A. MEEK (From the Department of Human Anatomy, South Parks Road, Oxford) With five plates (figs, i, 2, 4,
Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes
 Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes DNA as the genetic material Heat-killed bacteria can transform living cells S Smooth R Rough Fred Griffith, 1920 DNA is the genetic material Oswald Avery Colin MacLeod Maclyn
Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes DNA as the genetic material Heat-killed bacteria can transform living cells S Smooth R Rough Fred Griffith, 1920 DNA is the genetic material Oswald Avery Colin MacLeod Maclyn
Introduction to Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
 Robert Driscoll, M.F.S. Heather Cunningham, M.S. Introduction to Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH) FISH is a cytogenetic technique used to detect the presence
Robert Driscoll, M.F.S. Heather Cunningham, M.S. Introduction to Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH) FISH is a cytogenetic technique used to detect the presence
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
DNA DNA Profiling 18. Discuss the stages involved in DNA profiling 19. Define the process of DNA profiling 20. Give two uses of DNA profiling
 Name: 2.5 Genetics Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 2.5.1 Heredity and Variation 1. Discuss the diversity of organisms 2. Define the term species 3. Distinguish between
Name: 2.5 Genetics Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 2.5.1 Heredity and Variation 1. Discuss the diversity of organisms 2. Define the term species 3. Distinguish between
DNA, Replication and RNA
 DNA, Replication and RNA The structure of DNA DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, is the blue prints for building all of life. DNA is a long molecule made up of units called NUCLEOTIDES. Each nucleotide is
DNA, Replication and RNA The structure of DNA DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, is the blue prints for building all of life. DNA is a long molecule made up of units called NUCLEOTIDES. Each nucleotide is
RNA Part I: Chemical Structure of RNA
 RA Part I: Chemical Structure of RA Structural differences between RA and DA Resistance of phosphate esters to basic hydrolysis The 2 - group of RA facilitates chemical cleavage in aqueous a by forming
RA Part I: Chemical Structure of RA Structural differences between RA and DA Resistance of phosphate esters to basic hydrolysis The 2 - group of RA facilitates chemical cleavage in aqueous a by forming
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Retention of RNA with LabelX.
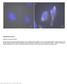 Supplementary Figure 1 Retention of RNA with LabelX. (a) Epi-fluorescence image of single molecule FISH (smfish) against GAPDH on HeLa cells expanded without LabelX treatment. (b) Epi-fluorescence image
Supplementary Figure 1 Retention of RNA with LabelX. (a) Epi-fluorescence image of single molecule FISH (smfish) against GAPDH on HeLa cells expanded without LabelX treatment. (b) Epi-fluorescence image
Pre-Lab: Molecular Biology
 Pre-Lab: Molecular Biology Name 1. What are the three chemical parts of a nucleotide. Draw a simple sketch to show how the three parts are arranged. 2. What are the rules of base pairing? 3. In double
Pre-Lab: Molecular Biology Name 1. What are the three chemical parts of a nucleotide. Draw a simple sketch to show how the three parts are arranged. 2. What are the rules of base pairing? 3. In double
SYTOX Green Dead Cell Stain
 SYTOX Green Dead Cell Stain *for flow cytometry* Catalog no. S34860 Table 1 Contents and storage Material Amount Concentration Storage* Stability SYTOX Green dead cell stain 1,000 µl 30 µm in DMSO 20 C
SYTOX Green Dead Cell Stain *for flow cytometry* Catalog no. S34860 Table 1 Contents and storage Material Amount Concentration Storage* Stability SYTOX Green dead cell stain 1,000 µl 30 µm in DMSO 20 C
Notes to accompany the slidecast on theory of SDS PAGE and Western blotting
 S317 Biological science: from genes to species Notes to accompany the slidecast on theory of SDS PAGE and Western blotting SDS PAGE SDS PAGE is a standard technique for determining the molecular size of
S317 Biological science: from genes to species Notes to accompany the slidecast on theory of SDS PAGE and Western blotting SDS PAGE SDS PAGE is a standard technique for determining the molecular size of
Different types of PCR and principles of Real Time PCR. Prof. Dr. Hamdy M. El-Aref Assiut University, Faculty of Agriculture Genetics Department
 Different types of PC and principles of eal Time PC. Prof. Dr. Hamdy M. El-Aref Assiut University, Faculty of Agriculture Genetics Department I N T O D U C T I O N PC Cycle (round) I N T O D U C T I O
Different types of PC and principles of eal Time PC. Prof. Dr. Hamdy M. El-Aref Assiut University, Faculty of Agriculture Genetics Department I N T O D U C T I O N PC Cycle (round) I N T O D U C T I O
Product Information. Before you begin. Component A 1 vial of 30 ul vial of 300 ul each Glycerol. Tris
 Glowing Products for Science Mix-n-Stain Antibody Labeling Kits Size: 1 labeling per kit Storage: -20 o C Stability: Stable for at least 1 year from date of receipt when stored as recommended. Components:
Glowing Products for Science Mix-n-Stain Antibody Labeling Kits Size: 1 labeling per kit Storage: -20 o C Stability: Stable for at least 1 year from date of receipt when stored as recommended. Components:
The preparation of native chromatin from cultured human cells.
 Native chromatin immunoprecipitation protocol The preparation of native chromatin from cultured human cells. All solutions need to be ice cold. Sucrose containing solutions must be made up fresh on the
Native chromatin immunoprecipitation protocol The preparation of native chromatin from cultured human cells. All solutions need to be ice cold. Sucrose containing solutions must be made up fresh on the
Introduction to Fluorescence Jablonski Diagram
 ntroduction to Fluorescence Jablonski Diagram Excited Singlet Manifold S1 internal conversion S2 k -isc k isc Excited riplet Manifold 1 S0 k nr k k' f nr fluorescence k p phosphorescence Singlet round
ntroduction to Fluorescence Jablonski Diagram Excited Singlet Manifold S1 internal conversion S2 k -isc k isc Excited riplet Manifold 1 S0 k nr k k' f nr fluorescence k p phosphorescence Singlet round
Analysis of Nucleic Acids using Flow Cytometry.
 Analysis of Nucleic Acids using Flow Cytometry. I) Introduction. Huw S. Kruger Gray, Ph.D. I.i) What is Flow Cytometry? Flow Cytometry (FCM) can be defined as: the measurement of physical and/or chemical
Analysis of Nucleic Acids using Flow Cytometry. I) Introduction. Huw S. Kruger Gray, Ph.D. I.i) What is Flow Cytometry? Flow Cytometry (FCM) can be defined as: the measurement of physical and/or chemical
GeNei TM Gel Extraction Teaching Kit Manual
 Teaching Kit Manual Cat No. New Cat No. KT43 106279 KT43A 106300 KT43B 106301 Revision No.: 00280507 CONTENTS Page No. Objective 3 Principle 3 Kit Description 5 Materials Provided 7 Procedure 8 Observation
Teaching Kit Manual Cat No. New Cat No. KT43 106279 KT43A 106300 KT43B 106301 Revision No.: 00280507 CONTENTS Page No. Objective 3 Principle 3 Kit Description 5 Materials Provided 7 Procedure 8 Observation
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) DNA and RNA Structure
 Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) DNA and RNA Structure Importance of DNA/RNA 3D Structure Nucleic acids are essential materials found in all living organisms. Their main function is to maintain and transmit
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) DNA and RNA Structure Importance of DNA/RNA 3D Structure Nucleic acids are essential materials found in all living organisms. Their main function is to maintain and transmit
Innovations To Meet Your Needs
 Innovations To Meet Your Needs Cooled CCD Camera 1340 x 1037 pixel resolution for greatest image quality 12-bit precision provides 3 orders of linear dynamic range Windows and Power Macintosh Software
Innovations To Meet Your Needs Cooled CCD Camera 1340 x 1037 pixel resolution for greatest image quality 12-bit precision provides 3 orders of linear dynamic range Windows and Power Macintosh Software
ab Apoptosis/Necrosis Detection Kit (blue, red, green)
 ab176750 Apoptosis/Necrosis Detection Kit (blue, red, green) Instructions for use: For detection of apoptosis and necrosis in adherent or suspension cells. This product is for research use only and is
ab176750 Apoptosis/Necrosis Detection Kit (blue, red, green) Instructions for use: For detection of apoptosis and necrosis in adherent or suspension cells. This product is for research use only and is
Immunostaining Protocols
 Immunostaining Protocols Lula L. Hilenski, Ph.D. Director Microscopy in Medicine Core Emory University Variables in standard immunostaining protocol 2-step or indirect immunofluorescence 1. Substrate on
Immunostaining Protocols Lula L. Hilenski, Ph.D. Director Microscopy in Medicine Core Emory University Variables in standard immunostaining protocol 2-step or indirect immunofluorescence 1. Substrate on
Multiplex Fluorescence Assays for Adherence Cells without Trypsinization
 Multiplex Fluorescence Assays for Adherence Cells without Trypsinization The combination of a bright field and three fluorescent channels allows the Celigo to perform many multiplexed assays. A gating
Multiplex Fluorescence Assays for Adherence Cells without Trypsinization The combination of a bright field and three fluorescent channels allows the Celigo to perform many multiplexed assays. A gating
Flow Cytometry - The Essentials
 Flow Cytometry - The Essentials Pocket Guide to Flow Cytometry: 1. Know your Cytometer 2. Understanding Fluorescence and Fluorophores 3. Gating Process 4. Controls 5. Optimization 6. Panel Building 7.
Flow Cytometry - The Essentials Pocket Guide to Flow Cytometry: 1. Know your Cytometer 2. Understanding Fluorescence and Fluorophores 3. Gating Process 4. Controls 5. Optimization 6. Panel Building 7.
Chapter 15 DNA and RNA
 Chapter 15 DNA and RNA www.mrcbiology.com 1 Variation Variation means that individuals in a species have different characteristics to one another. Acquired Variation are not inherited. e.g learnt during
Chapter 15 DNA and RNA www.mrcbiology.com 1 Variation Variation means that individuals in a species have different characteristics to one another. Acquired Variation are not inherited. e.g learnt during
Application Note. Yeast Analysis with a life - dead staining kit (Yeast control - viability)
 Application Note Yeast Analysis with a life - dead staining kit (Yeast control - viability) (CyFlow Cube 8 and CyFlow Cube 6 with CyView TM version 1.5 CyFlow Space) Introduction The Partec Yeast control
Application Note Yeast Analysis with a life - dead staining kit (Yeast control - viability) (CyFlow Cube 8 and CyFlow Cube 6 with CyView TM version 1.5 CyFlow Space) Introduction The Partec Yeast control
Resolution of Microscopes Visible light is nm Dry lens(0.5na), green(530nm light)=0.65µm=650nm for oil lens (1.4NA) UV light (300nm) = 0.13µm f
 Microscopes and Microscopy MCB 380 Good information sources: Alberts-Molecular Biology of the Cell http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/ http://www.microscopyu.com/ Approaches to Problems in Cell Biology
Microscopes and Microscopy MCB 380 Good information sources: Alberts-Molecular Biology of the Cell http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/ http://www.microscopyu.com/ Approaches to Problems in Cell Biology
Methodology. Protocol for plant genome size estimation by flow cytometry (2) GSAD: a genome size in the Asteraceae database
 Methodology Isolation of plant nuclei We recommend (unless specified otherwise) working under cold conditions (i.e. keep all solutions, buffers and prepared samples for analysis on ice, and do the chopping
Methodology Isolation of plant nuclei We recommend (unless specified otherwise) working under cold conditions (i.e. keep all solutions, buffers and prepared samples for analysis on ice, and do the chopping
Tali Viability Kit Dead Cell Green
 Tali Viability Kit Dead Cell Green *for use with Tali Assays: Green, Green + Red* Catalog no. A10787 Table 1 Contents and storage Material Amount Concentration Storage* Stability Tali Dead Cell Green (SYTOX
Tali Viability Kit Dead Cell Green *for use with Tali Assays: Green, Green + Red* Catalog no. A10787 Table 1 Contents and storage Material Amount Concentration Storage* Stability Tali Dead Cell Green (SYTOX
Cell Imaging. Localization: Robust protein labeling of live or fixed cells
 F eat u r es & B e n efits ptions Cell Imaging with the alotag platform Localization: Robust protein labeling of live or fixed cells Trafficking & Turnover: Directly observe proteins with one or two colors
F eat u r es & B e n efits ptions Cell Imaging with the alotag platform Localization: Robust protein labeling of live or fixed cells Trafficking & Turnover: Directly observe proteins with one or two colors
Technical Review. Real time PCR
 Technical Review Real time PCR Normal PCR: Analyze with agarose gel Normal PCR vs Real time PCR Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) or kinetic PCR Key feature: Used to amplify and simultaneously
Technical Review Real time PCR Normal PCR: Analyze with agarose gel Normal PCR vs Real time PCR Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) or kinetic PCR Key feature: Used to amplify and simultaneously
Isolation of Nucleic Acids
 Isolation of Nucleic Acids Goals: removal of proteins DNA vs RNA isolate specific type of nucleic acid Types of Methods: differential solubility adsorption methods density gradient centrifugation Types
Isolation of Nucleic Acids Goals: removal of proteins DNA vs RNA isolate specific type of nucleic acid Types of Methods: differential solubility adsorption methods density gradient centrifugation Types
Fluorescence Lifetime-Based Discrimination and Quantification of Cellular DNA and RNA With Phase-Sensitive Flow Cytometry
 Published 2003 Wiley-Liss, Inc. Cytometry Part A 52A:46 55 (2003) Fluorescence Lifetime-Based Discrimination and Quantification of Cellular DNA and RNA With Phase-Sensitive Flow Cytometry H. Helen Cui,
Published 2003 Wiley-Liss, Inc. Cytometry Part A 52A:46 55 (2003) Fluorescence Lifetime-Based Discrimination and Quantification of Cellular DNA and RNA With Phase-Sensitive Flow Cytometry H. Helen Cui,
Reinforcement. Cells and Life CHAPTER 1 LESSON 1
 Reinforcement Cells and Life LESSON 1 Directions: In numbers 1 through 4 below, a code letter has been substituted for each letter of the alphabet. To find out what the sentence says, use the following
Reinforcement Cells and Life LESSON 1 Directions: In numbers 1 through 4 below, a code letter has been substituted for each letter of the alphabet. To find out what the sentence says, use the following
Investigation of cellular uptake mechanisms by correlative TEM and SIM
 Collaborative Research Center (SFB 1278) Investigation of cellular uptake mechanisms by correlative TEM and SIM Rainer Heintzmann, Fengjiao Ma, Institute of Physical Chemistry Stephanie Höppener, Martin
Collaborative Research Center (SFB 1278) Investigation of cellular uptake mechanisms by correlative TEM and SIM Rainer Heintzmann, Fengjiao Ma, Institute of Physical Chemistry Stephanie Höppener, Martin
Nucleic Acids and the RNA World. Pages Chapter 4
 Nucleic Acids and the RNA World Pages 74-89 Chapter 4 RNA vs. Protein Chemical Evolution stated that life evolved from a polymer called a protein. HOWEVER, now many scientists question this. There is currently
Nucleic Acids and the RNA World Pages 74-89 Chapter 4 RNA vs. Protein Chemical Evolution stated that life evolved from a polymer called a protein. HOWEVER, now many scientists question this. There is currently
AGAROSE GEL ELECTROPHORESIS. Assiut University
 AGAROSE GEL ELECTROPHORESIS By Prof. Dr. Asmaa Hussein Prof. of Zoonoses & Director of the MBRU Assiut University The standard method used to separate, identify electrophoresis and purify DNA fragments
AGAROSE GEL ELECTROPHORESIS By Prof. Dr. Asmaa Hussein Prof. of Zoonoses & Director of the MBRU Assiut University The standard method used to separate, identify electrophoresis and purify DNA fragments
Nucleic acids. What important polymer is located in the nucleus? is the instructions for making a cell's.
 Nucleic acids DNA - The Double Helix Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including
Nucleic acids DNA - The Double Helix Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including
DNA - The Double Helix
 DNA - The Double Helix Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including cell reproduction,
DNA - The Double Helix Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of the cell including cell reproduction,
Chapter 10 Analytical Biotechnology and the Human Genome
 Chapter 10 Analytical Biotechnology and the Human Genome Chapter Outline Enzyme tests and biosensors DNA-based tests DNA analysis technologies Human genome and genome-based analytical methods 1 Enzyme-based
Chapter 10 Analytical Biotechnology and the Human Genome Chapter Outline Enzyme tests and biosensors DNA-based tests DNA analysis technologies Human genome and genome-based analytical methods 1 Enzyme-based
Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10
 Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10 1. Which of the following is NOT needed for DNA replication? A. nucleotides B. ribosomes C. Enzymes (like polymerases) D. DNA E. all of the above are needed 2 The information
Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10 1. Which of the following is NOT needed for DNA replication? A. nucleotides B. ribosomes C. Enzymes (like polymerases) D. DNA E. all of the above are needed 2 The information
Name: Date: Pd: Nucleic acids
 Name: Date: Pd: DNA - The Double Helix Nucleic acids Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of
Name: Date: Pd: DNA - The Double Helix Nucleic acids Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. It is often called the "control center" because it controls all the activities of
What is DNA??? DNA = Deoxyribonucleic acid IT is a molecule that contains the code for an organism s growth and function
 Review DNA and RNA 1) DNA and RNA are important organic compounds found in cells, called nucleic acids 2) Both DNA and RNA molecules contain the following chemical elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
Review DNA and RNA 1) DNA and RNA are important organic compounds found in cells, called nucleic acids 2) Both DNA and RNA molecules contain the following chemical elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 10
 DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 10 DNA as the Genetic Material DNA was first extracted from nuclei in 1870 named nuclein after their source. Chemical analysis determined that DNA was a weak acid rich
DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 10 DNA as the Genetic Material DNA was first extracted from nuclei in 1870 named nuclein after their source. Chemical analysis determined that DNA was a weak acid rich
Midori Green DNA Stain Safety Test Reports
 Midori Green DNA Stain Safety Test Reports IDENTIFICATION OF THE PRODUCT AND OF THE COMPANY Product name Catalog number Supplier Information in case of emergency Midori Green DNA Stain MG01 MG02 Nippon
Midori Green DNA Stain Safety Test Reports IDENTIFICATION OF THE PRODUCT AND OF THE COMPANY Product name Catalog number Supplier Information in case of emergency Midori Green DNA Stain MG01 MG02 Nippon
The following general information is from: "Biochemical Techniques Theory and Practice" by J.F. Robyt and B.J. White, Waveland Press Inc., 1987.
 Biochemistry Laboratory DNA I (REVISED 4/02 KRD) Purpose: Isolation of DNA from Gambusia liver. The following general information is from: "Biochemical Techniques Theory and Practice" by J.F. Robyt and
Biochemistry Laboratory DNA I (REVISED 4/02 KRD) Purpose: Isolation of DNA from Gambusia liver. The following general information is from: "Biochemical Techniques Theory and Practice" by J.F. Robyt and
Types of chromatography
 Chromatography Physical separation method based on the differential migration of analytes in a mobile phase as they move along a stationary phase. Mechanisms of Separation: Partitioning Adsorption Exclusion
Chromatography Physical separation method based on the differential migration of analytes in a mobile phase as they move along a stationary phase. Mechanisms of Separation: Partitioning Adsorption Exclusion
Genes - DNA - Chromosome. Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology
 Genes - DNA - Chromosome Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology DNA Cellular DNA contains genes and intragenic regions both of which may
Genes - DNA - Chromosome Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology DNA Cellular DNA contains genes and intragenic regions both of which may
How antimicrobial agents work
 Physical and Chemical Control of Microbes Physical Agents heat or radiation Chemical Agents disinfectants or antiseptics Important Terms 1. Sterilization process of killing all viable microbes 2. Bactericide
Physical and Chemical Control of Microbes Physical Agents heat or radiation Chemical Agents disinfectants or antiseptics Important Terms 1. Sterilization process of killing all viable microbes 2. Bactericide
Supplementary material to Alterations in the properties of the cell membrane due to glycosphingolipid accumulation in a model of Gaucher disease
 Supplementary material to Alterations in the properties of the cell membrane due to glycosphingolipid accumulation in a model of Gaucher disease Gyula Batta, Lilla Soltész, Tamás Kovács, Tamás Bozó, Zoltán
Supplementary material to Alterations in the properties of the cell membrane due to glycosphingolipid accumulation in a model of Gaucher disease Gyula Batta, Lilla Soltész, Tamás Kovács, Tamás Bozó, Zoltán
8/21/2014. From Gene to Protein
 From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
An evaluation of volatile suspended solids as a true measure of. metabolic activity in activated sludge
 Presented at the WISA 2000 Biennial Conference, Sun City, South Africa, 28 May - 1 June 2000 An evaluation of volatile suspended solids as a true measure of metabolic activity in activated sludge AP Degenaar,
Presented at the WISA 2000 Biennial Conference, Sun City, South Africa, 28 May - 1 June 2000 An evaluation of volatile suspended solids as a true measure of metabolic activity in activated sludge AP Degenaar,
The Production of a Recombinant Biotechnology Product. Chapter 8
 The Production of a Recombinant Biotechnology Product Chapter 8 Objectives Give a basic overview of genetic engineering. Describe the processes involved in isolating a piece DNA of interest Mass producing
The Production of a Recombinant Biotechnology Product Chapter 8 Objectives Give a basic overview of genetic engineering. Describe the processes involved in isolating a piece DNA of interest Mass producing
green B 1 ) into a single unit to model the substrate in this reaction. enzyme
 Teacher Key Objectives You will use the model pieces in the kit to: Simulate enzymatic actions. Explain enzymatic specificity. Investigate two types of enzyme inhibitors used in regulating enzymatic activity.
Teacher Key Objectives You will use the model pieces in the kit to: Simulate enzymatic actions. Explain enzymatic specificity. Investigate two types of enzyme inhibitors used in regulating enzymatic activity.
Measuring Physiological and Metabolic Characteristics of Yeast Health for Beer Fermentation Samples using the Cellometer Vision
 Measuring Physiological and Metabolic Characteristics of Yeast Health for Beer Fermentation Samples using the Cellometer Vision Nexcelom Bioscience LLC. 360 Merrimack Street, Building 9 Lawrence, MA 01843
Measuring Physiological and Metabolic Characteristics of Yeast Health for Beer Fermentation Samples using the Cellometer Vision Nexcelom Bioscience LLC. 360 Merrimack Street, Building 9 Lawrence, MA 01843
CRITICAL ASPECTS OF STAINING FOR FLOW CYTOMETRY
 CRITICAL ASPECTS OF STAINING FOR FLOW CYTOMETRY From Givan, A.L. (2000), chapter in In Living Color: Protocols in Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting (R. Diamond and S. DeMaggio, eds). Springer, Berlin, pp
CRITICAL ASPECTS OF STAINING FOR FLOW CYTOMETRY From Givan, A.L. (2000), chapter in In Living Color: Protocols in Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting (R. Diamond and S. DeMaggio, eds). Springer, Berlin, pp
Fluorescent in-situ Hybridization
 Fluorescent in-situ Hybridization Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 Definition In situ hybridization is the method of localizing/ detecting specific nucleotide sequences in morphologically preserved
Fluorescent in-situ Hybridization Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 Definition In situ hybridization is the method of localizing/ detecting specific nucleotide sequences in morphologically preserved
Stretching DNA as a template for molecular construction
 title Workshop " DNA-Based Molecular Electronics" Jena, May 13-15, 2004 Stretching DNA as a template for molecular construction Masao Washizu 1, Yuji Kimura 1, Takuya Kobayashi 1, Osamu Kurosawa 1,2 Sayoko
title Workshop " DNA-Based Molecular Electronics" Jena, May 13-15, 2004 Stretching DNA as a template for molecular construction Masao Washizu 1, Yuji Kimura 1, Takuya Kobayashi 1, Osamu Kurosawa 1,2 Sayoko
Protein Techniques 1 APPENDIX TO CHAPTER 5
 Protein Techniques 1 APPENDIX T CHAPTER 5 Dialysis and Ultrafiltration If a solution of protein is separated from a bathing solution by a semipermeable membrane, small molecules and ions can pass through
Protein Techniques 1 APPENDIX T CHAPTER 5 Dialysis and Ultrafiltration If a solution of protein is separated from a bathing solution by a semipermeable membrane, small molecules and ions can pass through
Bundle 5 Test Review
 Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
Chapter 9 Controlling Microbial Growth in the Environment. 10/1/ MDufilho
 Chapter 9 Controlling Microbial Growth in the Environment 10/1/2017 1 MDufilho Table 91 Terminology of Microbial Control 10/1/2017 MDufilho 2 Number of living microbes Figure 91 A plot of microbial death
Chapter 9 Controlling Microbial Growth in the Environment 10/1/2017 1 MDufilho Table 91 Terminology of Microbial Control 10/1/2017 MDufilho 2 Number of living microbes Figure 91 A plot of microbial death
American Society of Cytopathology Core Curriculum in Molecular Biology
 American Society of Cytopathology Core Curriculum in Molecular Biology American Society of Cytopathology Core Curriculum in Molecular Biology Chapter 3 Molecular Techniques Separation and Detection, Part
American Society of Cytopathology Core Curriculum in Molecular Biology American Society of Cytopathology Core Curriculum in Molecular Biology Chapter 3 Molecular Techniques Separation and Detection, Part
6- Important Molecules of Living Systems. Proteins Nucleic Acids Taft College Human Physiology
 6- Important Molecules of Living Systems Proteins Nucleic Acids Taft College Human Physiology Proteins Proteins- made from: C, H, O, N, and S. Proteins are very large molecules composed of long chains
6- Important Molecules of Living Systems Proteins Nucleic Acids Taft College Human Physiology Proteins Proteins- made from: C, H, O, N, and S. Proteins are very large molecules composed of long chains
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses)
 NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
EZ-Vision DNA Dye as Loading Buffer
 EZ-Vision DNA Dye as Loading Buffer Code Description Size N472-SAMPLE EZ-VIsion One, DNA Dye as Loading Buffer, 6X 0.3 ml N650-SAMPLE EZ-Vision Two, DNA Dye as Loading Buffer, 6X 0.3 ml N313-SAMPLE EZ-Vision
EZ-Vision DNA Dye as Loading Buffer Code Description Size N472-SAMPLE EZ-VIsion One, DNA Dye as Loading Buffer, 6X 0.3 ml N650-SAMPLE EZ-Vision Two, DNA Dye as Loading Buffer, 6X 0.3 ml N313-SAMPLE EZ-Vision
Nuclear Condensation Assay Kit Green Fluorescence
 ab139479 Nuclear Condensation Assay Kit Green Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed to assay chromatin condensation in live cells using an intercalating dye which is excitable with a standard 488nm
ab139479 Nuclear Condensation Assay Kit Green Fluorescence Instructions for Use Designed to assay chromatin condensation in live cells using an intercalating dye which is excitable with a standard 488nm
DNA vs. RNA B-4.1. Compare DNA and RNA in terms of structure, nucleotides and base pairs.
 DNA vs. RNA B-4.1 Compare DNA and RNA in terms of structure, nucleotides and base pairs. Key Concepts l Nucleic Acids: l deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) l ribonucleic acid (RNA) l Nucleotides: l nitrogen base,
DNA vs. RNA B-4.1 Compare DNA and RNA in terms of structure, nucleotides and base pairs. Key Concepts l Nucleic Acids: l deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) l ribonucleic acid (RNA) l Nucleotides: l nitrogen base,
NUCLEUS. Fig. 2. Various stages in the condensation of chromatin
 NUCLEUS Animal cells contain DNA in nucleus (contains ~ 98% of cell DNA) and mitochondrion. Both compartments are surrounded by an envelope (double membrane). Nuclear DNA represents some linear molecules
NUCLEUS Animal cells contain DNA in nucleus (contains ~ 98% of cell DNA) and mitochondrion. Both compartments are surrounded by an envelope (double membrane). Nuclear DNA represents some linear molecules
DNA, Genes and their Regula4on. Me#e Voldby Larsen PhD, Assistant Professor
 DNA, Genes and their Regula4on Me#e Voldby Larsen PhD, Assistant Professor Learning Objecer this talk, you should be able to Account for the structure of DNA and RNA including their similari
DNA, Genes and their Regula4on Me#e Voldby Larsen PhD, Assistant Professor Learning Objecer this talk, you should be able to Account for the structure of DNA and RNA including their similari
Module 7: The Central Dogma. CSE590: Molecular programming and neural computation. All slides by Eric Klavins.
 Module 7: The Central Dogma CSE590: Molecular programming and neural computation. All slides by Eric Klavins. 1 The Central Dogma RNA Polymerase The Ribosome m Note: We will look mainly at prokaryo=c (e.g.
Module 7: The Central Dogma CSE590: Molecular programming and neural computation. All slides by Eric Klavins. 1 The Central Dogma RNA Polymerase The Ribosome m Note: We will look mainly at prokaryo=c (e.g.
Xfect Protein Transfection Reagent
 Xfect Protein Transfection Reagent Mammalian Expression Systems Rapid, high-efficiency, low-toxicity protein transfection Transfect a large amount of active protein Virtually no cytotoxicity, unlike lipofection
Xfect Protein Transfection Reagent Mammalian Expression Systems Rapid, high-efficiency, low-toxicity protein transfection Transfect a large amount of active protein Virtually no cytotoxicity, unlike lipofection
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 3 3/6/15
 Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 3 3/6/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided; circle the correct answer or answers for each multiple choice question and circle either
Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 3 3/6/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided; circle the correct answer or answers for each multiple choice question and circle either
USDA RiceCAP DNA extraction using DNeasy Plant Mini Kit.
 DNA extraction using DNeasy Plant Mini Kit. Preparatory work: 1. If using the kit for the first time, add ethanol to buffer AW and buffer AP3/E to obtain the working solutions. 2. Preheat a water bath
DNA extraction using DNeasy Plant Mini Kit. Preparatory work: 1. If using the kit for the first time, add ethanol to buffer AW and buffer AP3/E to obtain the working solutions. 2. Preheat a water bath
DNA Labeling in Living Cells
 q 2005 International Society for Analytical Cytology Cytometry Part A 67A:45 52 (2005) DNA Labeling in Living Cells Robert M. Martin, 1 Heinrich Leonhardt, 1,2 and M. Cristina Cardoso 1 * 1 Max Delbr uck
q 2005 International Society for Analytical Cytology Cytometry Part A 67A:45 52 (2005) DNA Labeling in Living Cells Robert M. Martin, 1 Heinrich Leonhardt, 1,2 and M. Cristina Cardoso 1 * 1 Max Delbr uck
Advanced fluorescence microscopy techniques
 Practice-oriented, student-friendly modernization of the biomedical education for strengthening the international competitiveness of the rural Hungarian universities TÁMOP-4.1.1.C-13/1/KONV-2014-0001 Advanced
Practice-oriented, student-friendly modernization of the biomedical education for strengthening the international competitiveness of the rural Hungarian universities TÁMOP-4.1.1.C-13/1/KONV-2014-0001 Advanced
translation The building blocks of proteins are? amino acids nitrogen containing bases like A, G, T, C, and U Complementary base pairing links
 The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? translation The building blocks of proteins are? Complementary base pairing links Define and name the Purines amino acids nitrogen
The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? translation The building blocks of proteins are? Complementary base pairing links Define and name the Purines amino acids nitrogen
Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype. CBS520 Eric Nabity
 Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype CBS520 Eric Nabity DNA is Just the Beginning DNA was determined to be the genetic material, and the structure was identified as a (double stranded) double helix.
Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype CBS520 Eric Nabity DNA is Just the Beginning DNA was determined to be the genetic material, and the structure was identified as a (double stranded) double helix.
