International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF, ISSN: , ISSN(Online): Vol.9, No.5, pp , 2016
|
|
|
- Oliver Matthews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF, ISSN: , ISSN(Online): Vol.9, No.5, pp , 2016 Nucleotide Sequences and Mutations in Katg Gene in Clinical Isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Isolates Resistant to Isoniazid in Papua-Indonesia Rosye H. R. Tanjung 1 and Yohanis Ngili 2 * 1 Department of Biology, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, University of Cenderawasih, Jayapura-Indonesia 2 Biochemistry Research Group, Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, University of Cenderawasih, Jayapura-Indonesia Abstract: Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Resistance to RIF is caused by mutations in the rpob gene encoding the β subunit of RNA polymerase, with the highest frequency at codon 526 and 531. While Isoniazid is a prodrug, must be activated by the enzyme catalase-peroxidase encoded by the gene katg of M. tuberculosis, this gene mutation resulting in INH resistant. The purpose of this research is to obtain information on the cause of the genotype level resistance to INH in clinical isolates of the MDR-TB. Stages of research conducted here is Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) allelespecific multiplex katg, agarose gel electrophoresis, determining the nucleotide sequence, and in silico analysis. Results PCR and agarose gel electrophoresis for all isolates showed two DNA bands measuring 0.4 kb and 0.3 kb. Homology analysis to compare the results of sequencing electropherogram 0.4 kb fragment katg gene of the isolates with the same fragment of M. tuberculosis strain H37Rv standard. PyMOL modeling results describe the position of each amino acid as a result of mutations in the DNA level in the three-dimensional structure of protein molecules M. tuberculosis catalase-peroxidase. Analysis of data obtained showed that the mutation G946T three isolates located at codon 316, GGC into TGC, resulting in the amino acid glycine is mutated to cysteine. Simulation of the spatial structure of catalase peroxidase with PyMOL program showed 316 amino acid residues near the active site binding INH. Catalase-peroxidase simulation with PyMOL program showed 290 amino acid residues located in the N terminus loop area and relatively far from the active site, the effect of these mutations and their relationship in the nature of resistance to INH unknown. Other isolates G795A mutated nucleotide located at codon 265, TTG into TTA, but did not cause amino acid changes that can be ascertained that the mutation is not the cause of the nature of the resistance. While isolate mutated at codon 315, which has been proven as a cause of INH resistance. The results of this study are expected to provide new information on the position of the mutation in the gene katg of M. tuberculosis that is resistant to INH therefore G946T mutation (Gly316Cys) and C896T (Ala290Val) to isolate not been previously reported. Keywords : Isoniazid, katg gene, MDR-TB, PCR, Isolate Papua. Introduction Tuberculosis (TB) is one health problem that has always been a concern of society and the government of Papua province, Indonesia. 1 TB is caused by an organism called Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and can spread
2 Yohanis Ngili et al /International Journal of PharmTech Research, 2016,9(5),pp from person to person through the air. TB disease usually occurs in the lungs, but can occur elsewhere in the body called Miliary TB if the tubercle bacillus enters the bloodstream and carried throughout the body, they grow and cause disease in many places. TB disease must be treated for at least 6 months, in some cases even longer. The initial treatment of TB disease include four drugs: isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. TB disease should be treated with at least two drugs which are prone basil. When using only one drug to treat TB, will lead to the growth of the population of TB bacilli resistant to the drug. Drug-resistant can also be caused if the patient does not take the medicine according to the recommended dosage. MDR TB is a condition in which TB bacteria are resistant to at least two drugs are rifampicin (RIF) and isoniazid (INH). MDR-TB is a disease that continues to grow and some studies suggest a link between the epidemic of HIV/AIDS by increasing the rate of TB. Therefore, when the attention is reduced then there will be the possibility of TB cases to rise again. Research into the causes of MDR-TB is very important in order to know how best prevention and treatment. 2 Research has been conducted on MDR-TB showed that RIF resistance occurs due to mutations in the gene rpob and resistance to INH is caused by mutations in several genes that katg, inha, kasa and ahpc. However, mutations that occur most often in the katg gene. KatG protein serves as a peroxidase enzyme catalase that degrades H 2 O 2 and organic peroxides, the only one who has the activity of catalase enzyme in M. tuberculosis. katg prodrug activating INH become reactive species to inhibit the formation of cell walls. In a previous study found that M. tuberculosis resistant to INH and RIF, it is known that there is a mutation in the gene rpob but no mutations in codon that usually occurs in the gene mutation katg315. This study aims to analyze the gene katg and determine whether there is a mutation at codon 315 in addition to contributing to the nature of resistance of M. tuberculosis to INH. Material and Methods Isolates were used obtained from this study that has been collecting clinical specimens such as sputum or lung fluid TB patients who come to the laboratory of Biochemistry, University of Cenderawasih, Jayapura, Indonesia. Test of genotype Tests conducted to determine the position of the mutation in the gene katg of the isolates were resistant to isoniazid and rifampin. The test is done using PCR methods, ie outside forward and reverse primer that will stick to the template DNA and primers specific to the wild-type allele. Outer primer pair will amplify band invariable. Primer in will stop at the end of 3' region of codon targets and a specific fragment of the wild-type allele. Changes bases are connected to the 3' end of the specific primer pairs causes the error between the DNA template and primer so that it will prevent the polymerase to extend the primer and no fragments are amplified. 1,3 katg315 gene multiplex PCR with primers in the reverse katg315 in the position 3' end of the pair with second base (G) of codon 315 wild-type allele (AGC). The absence of the mutation at position katg315, produce 0.29 kb fragment amplified with the outside primer KF and reverse primer in KR. If the mutation occurs, the results obtained are errors in pairs at the 3' primer in without any specific PCR products. Two outside primer KF and KR flanking the whole area katg315 and fragment 0.43 kb. PCR quality controlled by 0.43 kb fragments resulting from the amplification primer KF and KR. Primer sequences used are: (Table 1). Table 1. DNA primer used in this research Name of primer outside primer KF outside primer KR reverse inner primer 315katG The nucleotide sequences (5 3 ) GCA GAT GAT GGG GCT GAT CTA CG AAC GGG TCC GGG ATG GTG ATA CGA CCT CGA TGC CGC
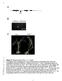
3 Yohanis Ngili et al /International Journal of PharmTech Research, 2016,9(5),pp PCR reactions were performed with PCR machine Perkin-Elmer GeneAmp PCR System 2700 on the conditions: initial denaturation 96 C for 3 min. Five cycles of 95 C 1 min, 62 C 1 min, 72 C 30 sec and, five cycles of 95 C 1 min, 60 C for 40 sec, and 72 C 30 sec. Twenty-two cycles of 94 C 1 min, 58 C for 40 sec, and 72 C 30 seconds. Final elongation 72 C for 3 min. A total of 5μL fragment amplification results in an agarose gel electrophoresis with a standard composition of 1.5%, using a marker puc and visualized under UV light. 4 Determination of nucleotide sequence and in silico analysis katg gene amplification along the 0.43 kb without using a primer in, with the same PCR conditions PCR. Results amplification is used to determine the nucleotide sequence (sequencing). While in silico analysis using the nucleotide sequence of DNAstar programs. To determine the positions of the mutated residues in the three-dimensional structure of proteins catalase-peroxidase using PyMOL program. Results and Discussion Several MDR-TB isolates were amplified by multiplex PCR method for determining the presence of mutations in nucleotides 944, codon 315, AGC became ACC. The mutation causes the inner-primer, K315 could not be able to stick to the second base codon 315 as a result there will be no amplification of nucleotides along 0.29 kb. 5 If there is no mutation there will be amplification of nucleotides along 0.43 kb and 0.29 kb. PCR results can be viewed by using agarose gel electrophoresis (Figure 1). 1.4 kb M + - P3 P2 P1 P4 P5 P6 0.5 kb 0.4 kb 0.2 kb 0.4 kb 0.3 kb 0.1 kb Fig 1. Agarose gel electrophoresis results of PCR multiplex. 315katG gene of the isolates MDR-TB from Papua, control (+): isolates normal strains H37Rv, control (-): water. Six isolates and controls (+) gives two bands at 0.4 kb and 0.3 kb. Pita 0.3 kb indicates that there is no mutation in the gene katg codon 315. In Fig 1 shows the results of multiplex PCR six isolates were MDR-TB is not mutated in katg315. Based on this test it is known that the six isolates that do not have mutations in katg315. Isolates DNA fragments are amplified along 0,43kb, and to confirm the results of PCR conducted to determine the nucleotide sequence by dideoxy method of Sanger. The results of the determination of the nucleotide sequence Determination of nucleotide sequence using the Sanger dideoxy method produces electropherogram and the nucleotide sequences of the isolates MDR-TB compared with normal strains H37Rv. The following are the nucleotide sequences of isolates Papua sequencing results. The nucleotide sequences of isolates Papua sequencing results: TTTTTAAGCC GGCGCTCGGA GTACGACTGC CTCCTTCGGA TTGGTCTTCG 50 GTCGCGAAAG CTGAATGGAA AGGCCCGCGT GCAAAAATCA GCCCCGTCTG 100 CAGGGGGTGT TCGTCCATCC GACCCCTATG CAGCTGGTGA TCGCGTCCTT 150 ACCGGTTCCG GTGCCATACG AGCTCTTCCA GCCCAAGCCC ATCTGCTCCA 200 GCGGAGCAGC CTCGGGTTCG GGGCCGACCA GATCGGCCGG GCCGGCGCCA 250
4 Yohanis Ngili et al /International Journal of PharmTech Research, 2016,9(5),pp TGGGTCTTAC CGAAAGTGTG ACCGCCGACG ATCAGCGCCG CTGTTTCGAC 300 GTCGTTCATG GCCATGCGCC GAAACGTCTC GCGAATGTCG ACCGCCGCGG 350 CCATGGGGTC CGGGTTGCCG TTCGGCCCCT CCGGGTTCAC GTAGCATCAG 400 CCCCATCTGC AAA 413 Analysis of homology Homology analysis using DNAstar Seqman program compares the six isolates with normal strains of M. tuberculosis H37Rv. katg gene of three isolates, which are shown only isolates P1, compared with natural strains H37Rv katg gene at nucleotide 944 and 946. In addition, compared also with P2 isolates that are MDR- TB but without the mutation at nucleotide 944 and 946; and with MDR-TB isolates P3 that have mutations in the two nucleotides. The results of homology analysis showed that three isolates (P4, P5, P6) had a mutation at nucleotide 946, changes the base G into T. (Figure 2) H37Rv Isolate 1 Isolate 2 Isolate 3 Fig 2. Homology analysis isolates Papua 2. Isolate 2 mutation in nucleotide 946, C to T, codon 316, GGC into TGC; and without the mutation at nucleotide 944, codon 315 AGC into ACC. Compared with H37Rv and other isolates of MDR-TB is not mutated in two positions. Benchmarking was also carried out with a 3 isolates had mutations at positions 946 and 944. The line amber indicates a base at codon 315, the green line shows the base at codon 316. The arrows indicate the nucleotides at positions 944 and 946 bases.
5 Yohanis Ngili et al /International Journal of PharmTech Research, 2016,9(5),pp Analysis of amino acid homology H37Rv compared with three other isolates: H37Rv: aag agc tcg tat ggc acc gga acc ggt aag gac gcg atc acc agc ggc atc gag gtc gta Lys Ser Ser Tyr Gly Thr Gly Thr Gly Lys Asp Ala Ile Thr Ser Gly Ile Glu Val Val K S S Y G T G T G K D A I T S G I E V V Isolat P1, P2, P3: aag agc tcg tat ggc acc gga acc ggt aag gac gcg atc acc agc tgc atc gag gtc gta Lys Ser Ser Tyr Gly Thr Gly Thr Gly Lys Asp Ala Ile Thr Ser Cys Ile Glu Val Val K S S Y G T G T G K D A I T S C I E V V Analysis of the data showed that the nucleotide 946 located at codon 316 first bases, GGC into TGC, resulting in the amino acid glycine is mutated to cysteine. This isolates all three did not have mutations in the gene katg codon 315. Previous studies have reported that mutations in the gene katg serin315threonin is the most frequent mutation. 7 Mutation at codon 315 resulting in reduced affinity peroxidase enzyme catalase to INH and can turn hydrogen bonds. 7-9 Effect of mutations in codon Gly316Cys against binding INH in the catalase peroxidase enzyme unknown but is thought to be the cause resistance properties of three isolates (P1, P2, and P3) to INH. Homology analysis of isolates P3 P3 isolates homology analysis showed that the katg gene mutation in its nucleotide 944, base G to C; and nucleotide 946 bases G into T. G944C mutation at codon 315 that converts the amino acid serine to threonine has been shown to cause resistance to INH. However, the results showed PCR amplification on 0.43 kb and 0.29 kb. This could happen because of the condition of PCR is so sensitive that there is an error in pairs on the inner-primer (Figure 3) H37Rv Isolate P3 Fig 3. Homology analysis isolates P3. P3 isolates have mutations at nucleotide 944, G to C, codon 315, AGC became ACC; and nucleotides 946, G to T, codon 316 GGC into TGC.
6 Yohanis Ngili et al /International Journal of PharmTech Research, 2016,9(5),pp Analysis of amino acid homology isolates P3 with natural strains H37Rv: H37Rv: aag agc tcg tat ggc acc gga acc ggt aag gac gcg atc acc agc ggc atc gag gtc gta Lys Ser Ser Tyr Gly Thr Gly Thr Gly Lys Asp Ala Ile Thr Ser Cys Ile Glu Val Val K S S Y G T G T G K D A I T S G I E V V Isolat P3: aag agc tcg tat ggc acc gga acc ggt aag gac gcg atc acc acc tgc atc gag gtc gta Lys Ser Ser Tyr Gly Thr Gly Thr Gly Lys Asp Ala Ile Thr Thr Cys Ile Glu Val Val K S S Y G T G T G K D A I T S G I E V V Other mutations in isolates P3 is at nucleotide 946, changing the base G to T, codon 316 GGC into TGC. Mutations in the same position with three other isolates. It is estimated that the mutation at codon 316 has become one of the causes of the nature of INH resistance in isolates P3, but the exact effect is not yet known. Another frequent mutation is at codon Arg463Leu, but this mutation has proven not associated with resistance to INH. Several mutations have been reported at codon Arg128Gln, Ala291Pro, and Thr275Pro. 10 His-108, which is one INH-binding residues have been reported mutated in INH resistant isolates, into acids glutamate and glutamine Mutations in the active site Asp-137 is an important role in binding INH has never been reported to have mutations, but mutations are the residues surrounding that N138S, A139P, S140N, or D142A. Mutants are given effect by changing the local conformation so that it can change the orientation of the side groups Asp-137 consequently can not bind INH Catalase-peroxidase protein visualization using the program PyMOL Previous research has crystallize M. tuberculosis catalase-peroxidase and have determined the threedimensional structure of the protein. This crystal structure data can be seen on public sites with names 1SJ2. 6 Position residues that have mutations in the gene katg 1SJ2 can be seen on structure by using PyMOL program. Catalase-peroxidase structure visualization space with PyMOL program showed amino acid residues 316 near the active site binding INH. The results of further analysis showed the change of surface residue 316 due to mutations glycine to cysteine. Glycine is an amino acid cysteine simplest whereas larger and can form a disulfide bond with another cysteine. But the effect of this glisin316sistein mutations in resistance to INH unknown. Previous research has shown that mutations at residue 315 lead to resistance to INH as result in changes in hydrogen bonds between heme and serin315. 1,6 Three isolates did not have mutations at residue 315 so that the mutation at residue 316 is strongly suspected to be the cause resistance properties. Residues 278 to 312 on catalase-peroxidase enzyme in M. tuberculosis is local loop, conformation is similar in two other peroxidase catalase structure that is at Haloarcula marismortui and Burkholderia pseudomallei. In Burkholderia pseudomallei catalase-peroxidase, loop area is estimated to be the substrate binding INH place to interact with enzymes. But another researchers stated that the M. tuberculosis catalaseperoxidase, the local loop is not the most important binding sites INH Mutations at amino acid residue 290 is located relatively far from the active site and its influence on the nature of INH resistance is unknown. Conclusion The analysis of six isolates were MDR-TB, which is mutated in a multiplex PCR rpob gene but this study did not have mutations in the gene katg codon 315. The analysis showed that the five isolates katg gene, by determining the nucleotide sequence, not mutated at codon position 315 and one strain mutated in these
7 Yohanis Ngili et al /International Journal of PharmTech Research, 2016,9(5),pp positions. Three of the five isolates above have the same type of mutation that is Gly316Cys. Two other isolates each have mutations in different positions, namely the position of mutations that alter amino acids Ala290Val and other positions do not change the amino acid. Simulation of the structure using PyMOL program shows that residue 316 is close to the active site binding INH, while residue 290 in the region of the loop ends of N relatively far from the active site. Mutations in the local loop is unknown influence in INH resistant properties. Three isolates did not have mutations in codon 315, which has been shown to cause resistance to INH, but occurs at codon 316. The mutation causes resistance to INH in three isolates were allegedly due to mutation at codon position 316. The flow of further research is needed to confirm whether these mutations are the only cause of resistance to INH in Papua isolates in other regions and compared to the eastern part of Indonesia. Acknowledgements The author would like to thank the Ministry of Research, Technology and Higher Education, Republic of Indonesia, which has provided a grant to fund this research. Appreciation to head of the Laboratory of Biochemistry, University of Cenderawasih which has provided laboratory equipment facility. In addition, it is thanks to some colleagues in the research group of Biochemistry, University of Cenderawasih, who have read and commented on this manuscript. References 1. Ubyaan, R., Maryuni, A.E., Sroyer, A., Palit, E.I.Y., Jukwati, Suaka, I.Y., and Ngili, Y. Moleculer analysis of Rifampin-Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain isolate from Papua-Indonesia. International Journal of PharmTech Research (4): Fang, Z., Doig, C., Rayner, A., Kenna, T., Watt, B., Forbes,K.J. (1999), Molecular evidence for heterogeneity of the multiple drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis population un Scotland (1990 to 1997). J Clin Microbiol., 37: Moukrousov, L., Otten, T., Filipenko, M., Vyazovaya, A., Chrapov, E., Limeschenko,E., Steklova, L., Vyshnevskiy, B., Narvskaya,O. (2003), Detection of isoniazid resistance Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains by a multiplex allele-specific PCR assay targeting katg codon 315 variation, J Clin Microbiol., 40: Parish, T., Smith, Debbie, A., Kendall, S., Casali, N., Bancroft, G.J., Stoker, N.G. (2003). Deletion of two component regulatory systems increases the virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Infect Immun., 71: Gillespies, S.H. (2002), Evolution of drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Clinical and molecular perspective, Antimicrob Agents Chemothers, 46: Bertrand, T., Eady, A.J.N., Jones, N,J., Jesmin, Nagy,M.J., Gregoire,J.N., Raven, L.E., Brown, A.K., (2004), Crystal Structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Catalase-Peroxidase, J. Biol. Chem., Vol 279, Issue 37, Werngren, J., Hoffner, S.E. (2003), Drug-susceptible Mycobacterium tuberculosis Beijing genotype does not develop mutation conferred resistance to rifampin at an elevated rate, J. Clin Microbiol., 41:1520: Cole,S.T., K.Eiglmeier, J.Parkhill, K.D.James, N.R.Thomson, P.R.Wheeler, N.Honore, T.Garnier, C.Churcher, D.Harris, K.Mungall, D.Basham, D.Brown, T.Chillingworth, R.Connor, R.M.Davies, K.Devlin, S.Duthoy, T.Feltwell, A.Fraser, N.Hamlin, S.Holroyd, T.Hornsby, K.Jagels, C.Lacroix, J.Maclean, M.S.L. Murphy, K.Oliver, J.Osborne, M.A.Quail, M.A.Rajandream, J.Rogers, S.Rutter, K.Seegar, J.Skelton, R.Squares, J.E.Sulston, K.Taylor, S.Whitehead, and B.G.Barrel. (1998), Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the complete genome sequence, Nature, 393: Brooks, G.F., Butel, J.S., Morse, S.A. (2004), Jwetz, Melnick, Adelberg s: Medical Microbiology. 23 rd eds. Intl ed. The McGraw-Hill companies. United states, Pym, A.S., Saint-Joanis, B., Cole, S.T. (2002). Effect of katg mutations on the virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the implication for transmission in humans, Infect Immun., 70: Rouse, D. A., Li, Z., Bai, G. H., and Morris, S. L. (1995), Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, 39,
8 Yohanis Ngili et al /International Journal of PharmTech Research, 2016,9(5),pp Rozwarski, D.A., Grant, G.A., Barton,D.H.R., Jacobs,W.R. & Sacchettini, J.C. (1998). Modification of the NaDH of the isoniazid target (InhA) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Science, 279, Rie, A.V., Warren, R., Mshanga, L., Jordaan, A.M., Spuy, G.D., Richardson, M., Simpson, J., Gie, R.P., Enarson, D.A., Beyers, N., Helden, P.D., Victor, T.C., (2001), Analysis for a limited number of genes codons can predict drug resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a high incidence community, J. Clin Microbiol., 39: Shoeb, H.A., Bowman, B.U., Ottolenghi, A.C. & Merola, A.J. (1985), Peroxidase-mediated oxidation of isoniazid, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 27, Soto, C.Y., Menendez, M.C., Perez, E., Samper, S., Gomez, A.B., Garcia, M.J., Martin,C. (2004), IS6110 mediates increased transcription of the phop virulence gene in a multidrug resistance clinical isolate responsible for tuberculosis outbreaks, J. Clin microbial, 42: Wei,C-J., Lei, B., Musser, J.M., Tu,S.C. (2003), Isoniazid activation defects in recombinant Mycobacterium tuberculosis catalase peroxidase (katg) mutants evident in InhA inhibitor production, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 47: Winder, F. (1960), Catalase and peroxidase in mycobacteria. A possible relationship to the mode of action of isoniazid, Am Rev Respir Dis., 81, Yue, J., Shi, W., Xie,J., Li,Y., Zeng,E., Wang,H. (2003), Mutation in the rpob gene of multidrug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from China. J. Clin Microbiol. 41: *****
Disease and selection in the human genome 3
 Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
G+C content. 1 Introduction. 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts. 3 Genome size. 4 Replichores and gene orientation. 5 Chirochores.
 1 Introduction 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts 3 Genome size 4 Replichores and gene orientation 5 Chirochores 6 7 Codon usage 121 marc.bailly-bechet@univ-lyon1.fr Bacterial genome structures Introduction
1 Introduction 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts 3 Genome size 4 Replichores and gene orientation 5 Chirochores 6 7 Codon usage 121 marc.bailly-bechet@univ-lyon1.fr Bacterial genome structures Introduction
Lecture 11: Gene Prediction
 Lecture 11: Gene Prediction Study Chapter 6.11-6.14 1 Gene: A sequence of nucleotides coding for protein Gene Prediction Problem: Determine the beginning and end positions of genes in a genome Where are
Lecture 11: Gene Prediction Study Chapter 6.11-6.14 1 Gene: A sequence of nucleotides coding for protein Gene Prediction Problem: Determine the beginning and end positions of genes in a genome Where are
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular
![strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular](/thumbs/72/66361212.jpg) Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC
 Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures)
 Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures) Strain number Relevant genotype Source or reference 1045 AB1157 Graham Walker (Donnelly and Walker, 1989) 2458 3084 (MG1655)
Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures) Strain number Relevant genotype Source or reference 1045 AB1157 Graham Walker (Donnelly and Walker, 1989) 2458 3084 (MG1655)
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Xie YL, Chakravorty S, Armstrong DT, et al. Evaluation of a
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Xie YL, Chakravorty S, Armstrong DT, et al. Evaluation of a
Supporting Information. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2006
 Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
 www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Gene Mutations WS Summary: Students will learn about frame shift mutations and base substitution mutations. Goals & Objectives: Students will be able to demonstrate how mutations
www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Gene Mutations WS Summary: Students will learn about frame shift mutations and base substitution mutations. Goals & Objectives: Students will be able to demonstrate how mutations
Characterization of katg and rpob gene mutations in Multi Drug Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 9 (2014) pp. 1072-1080 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Characterization of katg and rpob gene mutations in Multi Drug Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 9 (2014) pp. 1072-1080 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Characterization of katg and rpob gene mutations in Multi Drug Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Supplemental Data. mir156-regulated SPL Transcription. Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering. Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana
 Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Codon Bias with PRISM. 2IM24/25, Fall 2007
 Codon Bias with PRISM 2IM24/25, Fall 2007 from RNA to protein mrna vs. trna aminoacid trna anticodon mrna codon codon-anticodon matching Watson-Crick base pairing A U and C G binding first two nucleotide
Codon Bias with PRISM 2IM24/25, Fall 2007 from RNA to protein mrna vs. trna aminoacid trna anticodon mrna codon codon-anticodon matching Watson-Crick base pairing A U and C G binding first two nucleotide
Lezione 10. Bioinformatica. Mauro Ceccanti e Alberto Paoluzzi
 Lezione 10 Bioinformatica Mauro Ceccanti e Alberto Paoluzzi Dip. Informatica e Automazione Università Roma Tre Dip. Medicina Clinica Università La Sapienza Lezione 10: Sintesi proteica Synthesis of proteins
Lezione 10 Bioinformatica Mauro Ceccanti e Alberto Paoluzzi Dip. Informatica e Automazione Università Roma Tre Dip. Medicina Clinica Università La Sapienza Lezione 10: Sintesi proteica Synthesis of proteins
Supporting Online Information
 Supporting Online Information Isolation of Human Genomic DNA Sequences with Expanded Nucleobase Selectivity Preeti Rathi, Sara Maurer, Grzegorz Kubik and Daniel Summerer* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
Supporting Online Information Isolation of Human Genomic DNA Sequences with Expanded Nucleobase Selectivity Preeti Rathi, Sara Maurer, Grzegorz Kubik and Daniel Summerer* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
Thr Gly Tyr. Gly Lys Asn
 Your unique body characteristics (traits), such as hair color or blood type, are determined by the proteins your body produces. Proteins are the building blocks of life - in fact, about 45% of the human
Your unique body characteristics (traits), such as hair color or blood type, are determined by the proteins your body produces. Proteins are the building blocks of life - in fact, about 45% of the human
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/494/eaan6284/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Activation of master virulence regulator PhoP in acidic ph requires the Salmonella-specific protein UgtL Jeongjoon
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/494/eaan6284/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Activation of master virulence regulator PhoP in acidic ph requires the Salmonella-specific protein UgtL Jeongjoon
Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
FROM DNA TO GENETIC GENEALOGY Stephen P. Morse
 1. GENES, CHROMOSOMES, AND DNA Chromosomes FROM DNA TO GENETIC GENEALOGY Stephen P. Morse (steve@stevemorse.org) Every human cell = 46 chromosomes (1 to 22 in pairs, 2 sex chromosomes) Male: sex chromosomes
1. GENES, CHROMOSOMES, AND DNA Chromosomes FROM DNA TO GENETIC GENEALOGY Stephen P. Morse (steve@stevemorse.org) Every human cell = 46 chromosomes (1 to 22 in pairs, 2 sex chromosomes) Male: sex chromosomes
Protein Synthesis. Application Based Questions
 Protein Synthesis Application Based Questions MRNA Triplet Codons Note: Logic behind the single letter abbreviations can be found at: http://www.biology.arizona.edu/biochemistry/problem_sets/aa/dayhoff.html
Protein Synthesis Application Based Questions MRNA Triplet Codons Note: Logic behind the single letter abbreviations can be found at: http://www.biology.arizona.edu/biochemistry/problem_sets/aa/dayhoff.html
Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH).
 Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
(a) Which enzyme(s) make 5' - 3' phosphodiester bonds? (c) Which enzyme(s) make single-strand breaks in DNA backbones?
 EXAMPLE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 1. Topoisomerase does which one of the following? (a) Makes new DNA strands. (b) Unties knots in DNA molecules. (c) Joins the ends of double-stranded DNA molecules. (d) Is
EXAMPLE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 1. Topoisomerase does which one of the following? (a) Makes new DNA strands. (b) Unties knots in DNA molecules. (c) Joins the ends of double-stranded DNA molecules. (d) Is
DNA Begins the Process
 Biology I D N A DNA contains genes, sequences of nucleotide bases These Genes code for polypeptides (proteins) Proteins are used to build cells and do much of the work inside cells DNA Begins the Process
Biology I D N A DNA contains genes, sequences of nucleotide bases These Genes code for polypeptides (proteins) Proteins are used to build cells and do much of the work inside cells DNA Begins the Process
Page 2. Explain how the structure of DNA is related to its functions (Extra space)
 Q1.(a) Explain how the structure of DNA is related to its functions. (Extra space)... (6) Scientists investigated three genes, C, D and E, involved in controlling cell division. Page 2 They studied the
Q1.(a) Explain how the structure of DNA is related to its functions. (Extra space)... (6) Scientists investigated three genes, C, D and E, involved in controlling cell division. Page 2 They studied the
1. DNA, RNA structure. 2. DNA replication. 3. Transcription, translation
 1. DNA, RNA structure 2. DNA replication 3. Transcription, translation DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides DNA is a nucleic acid, made of long chains of nucleotides Nucleotide Phosphate group Nitrogenous
1. DNA, RNA structure 2. DNA replication 3. Transcription, translation DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides DNA is a nucleic acid, made of long chains of nucleotides Nucleotide Phosphate group Nitrogenous
Maria Lina Rosilawati 1 and Andi Yasmon 2
 DETECTION OF MULTIDRUG-RESISTANT MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS DIRECTLY FROM SPUTUM SAMPLES OF PATIENTS FROM JAKARTA, INDONESIA BY RADIOISOTOPE-BASED PCR-DOT BLOT HYBRIDIZATION Maria Lina Rosilawati 1 and
DETECTION OF MULTIDRUG-RESISTANT MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS DIRECTLY FROM SPUTUM SAMPLES OF PATIENTS FROM JAKARTA, INDONESIA BY RADIOISOTOPE-BASED PCR-DOT BLOT HYBRIDIZATION Maria Lina Rosilawati 1 and
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes
 Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Study Guide
 PART A. Read the following: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Study Guide Protein synthesis is the process used by the body to make proteins. The first step of protein synthesis is called Transcription. It occurs in the
PART A. Read the following: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Study Guide Protein synthesis is the process used by the body to make proteins. The first step of protein synthesis is called Transcription. It occurs in the
SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer
 TEACHER S GUIDE SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer SYNOPSIS This activity uses the metaphor of decoding a secret message for the Protein Synthesis process. Students teach themselves
TEACHER S GUIDE SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer SYNOPSIS This activity uses the metaphor of decoding a secret message for the Protein Synthesis process. Students teach themselves
Degenerate Code. Translation. trna. The Code is Degenerate trna / Proofreading Ribosomes Translation Mechanism
 Translation The Code is Degenerate trna / Proofreading Ribosomes Translation Mechanism Degenerate Code There are 64 possible codon triplets There are 20 naturally-encoding amino acids Several codons specify
Translation The Code is Degenerate trna / Proofreading Ribosomes Translation Mechanism Degenerate Code There are 64 possible codon triplets There are 20 naturally-encoding amino acids Several codons specify
INTRODUCTION TO THE MOLECULAR GENETICS OF THE COLOR MUTATIONS IN ROCK POCKET MICE
 The Making of the The Fittest: Making of the Fittest Natural Selection Natural and Adaptation Selection and Adaptation Educator Materials TEACHER MATERIALS INTRODUCTION TO THE MOLECULAR GENETICS OF THE
The Making of the The Fittest: Making of the Fittest Natural Selection Natural and Adaptation Selection and Adaptation Educator Materials TEACHER MATERIALS INTRODUCTION TO THE MOLECULAR GENETICS OF THE
Biomolecules: lecture 6
 Biomolecules: lecture 6 - to learn the basics on how DNA serves to make RNA = transcription - to learn how the genetic code instructs protein synthesis - to learn the basics on how proteins are synthesized
Biomolecules: lecture 6 - to learn the basics on how DNA serves to make RNA = transcription - to learn how the genetic code instructs protein synthesis - to learn the basics on how proteins are synthesized
Supplementary Information. Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins
 Supplementary Information Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins Chuhan Zong 1, Mikhail O. Maksimov 2, A. James Link 2,3 * Departments of 1 Chemistry, 2 Chemical and Biological Engineering, and
Supplementary Information Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins Chuhan Zong 1, Mikhail O. Maksimov 2, A. James Link 2,3 * Departments of 1 Chemistry, 2 Chemical and Biological Engineering, and
Landscape and Language of Molecular Diagnostics for TB Drug Resistance
 Landscape and Language of Molecular Diagnostics for TB Drug Resistance Purpose This module will provide: A brief overview of basic principles of molecular biology An introduction to mutations and their
Landscape and Language of Molecular Diagnostics for TB Drug Resistance Purpose This module will provide: A brief overview of basic principles of molecular biology An introduction to mutations and their
Search for and Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and Establishment of SNP Markers
 DNA Research 9, 163 171 (2002) Search for and Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and Establishment of SNP Markers Shinobu Nasu, Junko Suzuki, Rieko
DNA Research 9, 163 171 (2002) Search for and Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and Establishment of SNP Markers Shinobu Nasu, Junko Suzuki, Rieko
Level 2 Biology, 2017
 91159 911590 2SUPERVISOR S Level 2 Biology, 2017 91159 Demonstrate understanding of gene expression 2.00 p.m. Wednesday 22 November 2017 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with
91159 911590 2SUPERVISOR S Level 2 Biology, 2017 91159 Demonstrate understanding of gene expression 2.00 p.m. Wednesday 22 November 2017 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with
II 0.95 DM2 (RPP1) DM3 (At3g61540) b
 Table S2. F 2 Segregation Ratios at 16 C, Related to Figure 2 Cross n c Phenotype Model e 2 Locus A Locus B Normal F 1 -like Enhanced d Uk-1/Uk-3 149 64 36 49 DM2 (RPP1) DM1 (SSI4) a Bla-1/Hh-0 F 3 111
Table S2. F 2 Segregation Ratios at 16 C, Related to Figure 2 Cross n c Phenotype Model e 2 Locus A Locus B Normal F 1 -like Enhanced d Uk-1/Uk-3 149 64 36 49 DM2 (RPP1) DM1 (SSI4) a Bla-1/Hh-0 F 3 111
Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR
 Supplemental Dataset Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. DNA sequence Amino acid sequence WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR Allele 1 CCTGTC------------------GATAGC
Supplemental Dataset Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. DNA sequence Amino acid sequence WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR Allele 1 CCTGTC------------------GATAGC
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Chapter 17 Genes to Proteins Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The following questions refer to Figure 17.1, a simple metabolic
Exam Chapter 17 Genes to Proteins Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The following questions refer to Figure 17.1, a simple metabolic
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information CLOSTRIDIOLYSIN S: A POST-TRANSLATIONALLY MODIFIED BIOTOXIN FROM CLOSTRIDIUM BOTULINUM David J. Gonzalez 1, Shaun W. Lee 9, Mary E. Hensler 6, Andrew L. Markley 1, Samira Dahesh
Supporting Information CLOSTRIDIOLYSIN S: A POST-TRANSLATIONALLY MODIFIED BIOTOXIN FROM CLOSTRIDIUM BOTULINUM David J. Gonzalez 1, Shaun W. Lee 9, Mary E. Hensler 6, Andrew L. Markley 1, Samira Dahesh
Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis. Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010
 Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010 1 1- What is quick change site directed mutagenesis? 2- An overview of the kit contents. 3- A brief information
Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010 1 1- What is quick change site directed mutagenesis? 2- An overview of the kit contents. 3- A brief information
A Zero-Knowledge Based Introduction to Biology
 A Zero-Knowledge Based Introduction to Biology Konstantinos (Gus) Katsiapis 25 Sep 2009 Thanks to Cory McLean and George Asimenos Cells: Building Blocks of Life cell, membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondrion
A Zero-Knowledge Based Introduction to Biology Konstantinos (Gus) Katsiapis 25 Sep 2009 Thanks to Cory McLean and George Asimenos Cells: Building Blocks of Life cell, membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondrion
Supporting Information. Trifluoroacetophenone-Linked Nucleotides and DNA for Studying of DNA-protein Interactions by 19 F NMR Spectroscopy
 Supporting Information Trifluoroacetophenone-Linked Nucleotides and DNA for Studying of DNA-protein Interactions by 19 F NMR Spectroscopy Agata Olszewska, Radek Pohl and Michal Hocek # * Institute of Organic
Supporting Information Trifluoroacetophenone-Linked Nucleotides and DNA for Studying of DNA-protein Interactions by 19 F NMR Spectroscopy Agata Olszewska, Radek Pohl and Michal Hocek # * Institute of Organic
The B1 Protein Guides the Biosynthesis of a Lasso Peptide
 The B1 Protein Guides the Biosynthesis of a Lasso Peptide Shaozhou Zhu 1,2, Christopher D. Fage 1, Julian D. Hegemann 1, Andreas Mielcarek 1, Dushan Yan 1, Uwe Linne 1 & Mohamed A. Marahiel*,1 1 Department
The B1 Protein Guides the Biosynthesis of a Lasso Peptide Shaozhou Zhu 1,2, Christopher D. Fage 1, Julian D. Hegemann 1, Andreas Mielcarek 1, Dushan Yan 1, Uwe Linne 1 & Mohamed A. Marahiel*,1 1 Department
Gene mutation and DNA polymorphism
 Gene mutation and DNA polymorphism Outline of this chapter Gene Mutation DNA Polymorphism Gene Mutation Definition Major Types Definition A gene mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence that composes
Gene mutation and DNA polymorphism Outline of this chapter Gene Mutation DNA Polymorphism Gene Mutation Definition Major Types Definition A gene mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence that composes
MCB421 FALL2005 EXAM#3 ANSWERS Page 1 of 12. ANSWER: Both transposon types form small duplications of adjacent host DNA sequences.
 Page 1 of 12 (10pts) 1. There are two mechanisms for transposition used by bacterial transposable elements: replicative (Tn3) and non-replicative (Tn5 and Tn10). Compare and contrast the two mechanisms
Page 1 of 12 (10pts) 1. There are two mechanisms for transposition used by bacterial transposable elements: replicative (Tn3) and non-replicative (Tn5 and Tn10). Compare and contrast the two mechanisms
Bioinformatics. ONE Introduction to Biology. Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Biology/CS 123A Fall 2012
 Bioinformatics ONE Introduction to Biology Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Biology/CS 123A Fall 2012 Biology Review DNA RNA Proteins Central Dogma Transcription Translation
Bioinformatics ONE Introduction to Biology Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Biology/CS 123A Fall 2012 Biology Review DNA RNA Proteins Central Dogma Transcription Translation
Describe the features of a gene which enable it to code for a particular protein.
 1. Answers should be written in continuous prose. Credit will be given for biological accuracy, the organisation and presentation of the information and the way in which the answer is expressed. Cancer
1. Answers should be written in continuous prose. Credit will be given for biological accuracy, the organisation and presentation of the information and the way in which the answer is expressed. Cancer
11 questions for a total of 120 points
 Your Name: BYS 201, Final Exam, May 3, 2010 11 questions for a total of 120 points 1. 25 points Take a close look at these tables of amino acids. Some of them are hydrophilic, some hydrophobic, some positive
Your Name: BYS 201, Final Exam, May 3, 2010 11 questions for a total of 120 points 1. 25 points Take a close look at these tables of amino acids. Some of them are hydrophilic, some hydrophobic, some positive
Quiz Submissions Quiz 4
 Quiz Submissions Quiz 4 Attempt 1 Written: Nov 1, 2015 17:35 Nov 1, 2015 22:19 Submission View Released: Nov 4, 2015 20:24 Question 1 0 / 1 point Three RNA polymerases synthesize most of the RNA present
Quiz Submissions Quiz 4 Attempt 1 Written: Nov 1, 2015 17:35 Nov 1, 2015 22:19 Submission View Released: Nov 4, 2015 20:24 Question 1 0 / 1 point Three RNA polymerases synthesize most of the RNA present
Just one nucleotide! Exploring the effects of random single nucleotide mutations
 Dr. Beatriz Gonzalez In-Class Worksheet Name: Learning Objectives: Just one nucleotide! Exploring the effects of random single nucleotide mutations Given a coding DNA sequence, determine the mrna Based
Dr. Beatriz Gonzalez In-Class Worksheet Name: Learning Objectives: Just one nucleotide! Exploring the effects of random single nucleotide mutations Given a coding DNA sequence, determine the mrna Based
DNA.notebook March 08, DNA Overview
 DNA Overview Deoxyribonucleic Acid, or DNA, must be able to do 2 things: 1) give instructions for building and maintaining cells. 2) be copied each time a cell divides. DNA is made of subunits called nucleotides
DNA Overview Deoxyribonucleic Acid, or DNA, must be able to do 2 things: 1) give instructions for building and maintaining cells. 2) be copied each time a cell divides. DNA is made of subunits called nucleotides
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 3 3/6/15
 Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 3 3/6/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided; circle the correct answer or answers for each multiple choice question and circle either
Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 3 3/6/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided; circle the correct answer or answers for each multiple choice question and circle either
 Problem: The GC base pairs are more stable than AT base pairs. Why? 5. Triple-stranded DNA was first observed in 1957. Scientists later discovered that the formation of triplestranded DNA involves a type
Problem: The GC base pairs are more stable than AT base pairs. Why? 5. Triple-stranded DNA was first observed in 1957. Scientists later discovered that the formation of triplestranded DNA involves a type
Problem Set Unit The base ratios in the DNA and RNA for an onion (Allium cepa) are given below.
 Problem Set Unit 3 Name 1. Which molecule is found in both DNA and RNA? A. Ribose B. Uracil C. Phosphate D. Amino acid 2. Which molecules form the nucleotide marked in the diagram? A. phosphate, deoxyribose
Problem Set Unit 3 Name 1. Which molecule is found in both DNA and RNA? A. Ribose B. Uracil C. Phosphate D. Amino acid 2. Which molecules form the nucleotide marked in the diagram? A. phosphate, deoxyribose
Chapter 3: Information Storage and Transfer in Life
 Chapter 3: Information Storage and Transfer in Life The trapped scientist examples are great for conceptual purposes, but they do not accurately model how information in life changes because they do not
Chapter 3: Information Storage and Transfer in Life The trapped scientist examples are great for conceptual purposes, but they do not accurately model how information in life changes because they do not
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation
 Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 17 Practice Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Garrod hypothesized that "inborn errors of metabolism" such as alkaptonuria
Ch 17 Practice Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Garrod hypothesized that "inborn errors of metabolism" such as alkaptonuria
Chapter 10. The Structure and Function of DNA. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 10 The Structure and Function of DNA PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey,
Chapter 10 The Structure and Function of DNA PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey,
Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription
 Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription Students must be positive that they understand standard PCR. There is a resource on the web for this purpose. Warn them before this class.
Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription Students must be positive that they understand standard PCR. There is a resource on the web for this purpose. Warn them before this class.
Stool GeneXpert MTB/Rif Assay
 Stool GeneXpert MTB/Rif Assay Standard Operating Procedure 1.0. Purpose The purpose of this standard operating procedure (SOP) is to detail the steps for correctly performing, interpreting, and documenting
Stool GeneXpert MTB/Rif Assay Standard Operating Procedure 1.0. Purpose The purpose of this standard operating procedure (SOP) is to detail the steps for correctly performing, interpreting, and documenting
Supplemental Data. Distinct Pathways for snorna and mrna Termination
 Molecular Cell, Volume 24 Supplemental Data Distinct Pathways for snorna and mrna Termination Minkyu Kim, Lidia Vasiljeva, Oliver J. Rando, Alexander Zhelkovsky, Claire Moore, and Stephen Buratowski A
Molecular Cell, Volume 24 Supplemental Data Distinct Pathways for snorna and mrna Termination Minkyu Kim, Lidia Vasiljeva, Oliver J. Rando, Alexander Zhelkovsky, Claire Moore, and Stephen Buratowski A
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
Codon bias and gene expression of mitochondrial ND2 gene in chordates
 www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 11(8) Codon bias and gene expression of mitochondrial ND2 gene in chordates Arif Uddin, Tarikul Huda Mazumder, Monisha Nath Choudhury & Supriyo Chakraborty* Department
www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 11(8) Codon bias and gene expression of mitochondrial ND2 gene in chordates Arif Uddin, Tarikul Huda Mazumder, Monisha Nath Choudhury & Supriyo Chakraborty* Department
Phenotypic response conferred by the Lr22a leaf rust resistance gene against ten Swiss P. triticina isolates.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypic response conferred by the leaf rust resistance gene against ten Swiss P. triticina isolates. The third leaf of Thatcher (left) and RL6044 (right) is shown ten days after
Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypic response conferred by the leaf rust resistance gene against ten Swiss P. triticina isolates. The third leaf of Thatcher (left) and RL6044 (right) is shown ten days after
BIOLOGY Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
 BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
1.) Draw the structure of guanine. Indicate where the hydrogen bonds form with cytosine. (4pts)
 Name Student ID# p 1.) Draw the structure of guanine. Indicate where the hydrogen bonds form with cytosine. (4pts) hydrogen bonds form at these sites O HN HN H N N R Microbial Genetics BIO 410/510 Fall
Name Student ID# p 1.) Draw the structure of guanine. Indicate where the hydrogen bonds form with cytosine. (4pts) hydrogen bonds form at these sites O HN HN H N N R Microbial Genetics BIO 410/510 Fall
Four different segments of a DNA molecule are represented below.
 Four different segments of a DNA molecule are represented below. There is an error in the DNA in which molecule? A. segment 1 only B. segment 3 only C. segment 2 and 3 D. segment 2 and 4 Explain the basic
Four different segments of a DNA molecule are represented below. There is an error in the DNA in which molecule? A. segment 1 only B. segment 3 only C. segment 2 and 3 D. segment 2 and 4 Explain the basic
Nucleic Acids Research
 Volume 10 Number 1 1982 VoLume 10 Number 11982 Nucleic Acids Research Nucleic Acids Research A convenient and adaptable package of DNA sequence analysis programs for microcomputers James Pustell and Fotis
Volume 10 Number 1 1982 VoLume 10 Number 11982 Nucleic Acids Research Nucleic Acids Research A convenient and adaptable package of DNA sequence analysis programs for microcomputers James Pustell and Fotis
DNA RNA Protein. THE DISCOVERY AND STRUCTURE OF DNA (SB2a) What is DNA? SCIENTISTS WHEN? IMPORTANT DISCOVERY
 DNA RNA Protein Notes THE DISCOVERY AND STRUCTURE OF DNA (SB2a) SCIENTISTS WHEN? IMPORTANT DISCOVERY Frederick Mieshcer Discovered in the white blood cells Phoebus Levene Oswald Avery Erwin Chargaff Alfred
DNA RNA Protein Notes THE DISCOVERY AND STRUCTURE OF DNA (SB2a) SCIENTISTS WHEN? IMPORTANT DISCOVERY Frederick Mieshcer Discovered in the white blood cells Phoebus Levene Oswald Avery Erwin Chargaff Alfred
Complexity of the Ruminococcus flavefaciens FD-1 cellulosome reflects an expansion of family-related protein-protein interactions
 Complexity of the Ruminococcus flavefaciens FD-1 cellulosome reflects an expansion of family-related protein-protein interactions Vered Israeli-Ruimy 1,*, Pedro Bule 2,*, Sadanari Jindou 3, Bareket Dassa
Complexity of the Ruminococcus flavefaciens FD-1 cellulosome reflects an expansion of family-related protein-protein interactions Vered Israeli-Ruimy 1,*, Pedro Bule 2,*, Sadanari Jindou 3, Bareket Dassa
Mycobacterium tuberculosis End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42100
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Mycobacterium tuberculosis End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42100
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Mycobacterium tuberculosis End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42100
Supplemental Information. Target-Mediated Protection of Endogenous. MicroRNAs in C. elegans. Inventory of Supplementary Information
 Developmental Cell, Volume 20 Supplemental Information Target-Mediated Protection of Endogenous MicroRNAs in C. elegans Saibal Chatterjee, Monika Fasler, Ingo Büssing, and Helge Großhans Inventory of Supplementary
Developmental Cell, Volume 20 Supplemental Information Target-Mediated Protection of Endogenous MicroRNAs in C. elegans Saibal Chatterjee, Monika Fasler, Ingo Büssing, and Helge Großhans Inventory of Supplementary
Worksheet: Mutations Practice
 Worksheet: Mutations Practice There are three ways that DNA can be altered when a mutation (change in DNA sequence) occurs. 1. Substitution one base-pairs is replaced by another: Example: G to C or A to
Worksheet: Mutations Practice There are three ways that DNA can be altered when a mutation (change in DNA sequence) occurs. 1. Substitution one base-pairs is replaced by another: Example: G to C or A to
DNA is normally found in pairs, held together by hydrogen bonds between the bases
 Bioinformatics Biology Review The genetic code is stored in DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA molecules are chains of four nucleotide bases Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine, Adenine DNA is normally found in pairs,
Bioinformatics Biology Review The genetic code is stored in DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA molecules are chains of four nucleotide bases Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine, Adenine DNA is normally found in pairs,
Folding simulation: self-organization of 4-helix bundle protein. yellow = helical turns
 Folding simulation: self-organization of 4-helix bundle protein yellow = helical turns Protein structure Protein: heteropolymer chain made of amino acid residues R + H 3 N - C - COO - H φ ψ Chain of amino
Folding simulation: self-organization of 4-helix bundle protein yellow = helical turns Protein structure Protein: heteropolymer chain made of amino acid residues R + H 3 N - C - COO - H φ ψ Chain of amino
Genetic Engineering & Recombinant DNA
 Genetic Engineering & Recombinant DNA Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc) Permission required for reproduction or display. Applications of Genetic Engineering Basic science vs. Applied
Genetic Engineering & Recombinant DNA Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc) Permission required for reproduction or display. Applications of Genetic Engineering Basic science vs. Applied
Some types of Mutagenesis
 Mutagenesis What Is a Mutation? Genetic information is encoded by the sequence of the nucleotide bases in DNA of the gene. The four nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine
Mutagenesis What Is a Mutation? Genetic information is encoded by the sequence of the nucleotide bases in DNA of the gene. The four nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine
Honors packet Instructions
 Honors packet Instructions The following are guidelines in order for you to receive FULL credit for this bio packet: 1. Read and take notes on the packet in full 2. Answer the multiple choice questions
Honors packet Instructions The following are guidelines in order for you to receive FULL credit for this bio packet: 1. Read and take notes on the packet in full 2. Answer the multiple choice questions
Chapter 2 - DNA MC [37 marks]
![Chapter 2 - DNA MC [37 marks] Chapter 2 - DNA MC [37 marks]](/thumbs/74/71041787.jpg) Chapter 2 - N MC [37 marks] 1. The image shows a N nucleotide. Which correctly identifies the parts labelled I and II? C 2. Which model represents transcription? 3. Which sequence represents the order
Chapter 2 - N MC [37 marks] 1. The image shows a N nucleotide. Which correctly identifies the parts labelled I and II? C 2. Which model represents transcription? 3. Which sequence represents the order
ENZYMES AND METABOLIC PATHWAYS
 ENZYMES AND METABOLIC PATHWAYS This document is licensed under the Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 Italy license, available at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/it/ 1. Enzymes build
ENZYMES AND METABOLIC PATHWAYS This document is licensed under the Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 Italy license, available at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/it/ 1. Enzymes build
Allele-Specific rpob PCR Assays for Detection of Rifampin-Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Sputum Smears
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, July 2003, p. 2231 2235 Vol. 47, No. 7 0066-4804/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.7.2231 2235.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, July 2003, p. 2231 2235 Vol. 47, No. 7 0066-4804/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.7.2231 2235.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Backtrack to a previous lecture: where do antibiotic resistance genes and alleles come from?
 Biology 322 Lecture Nov 15, 2010 Anouncements: see course web site Backtrack to a previous lecture: where do antibiotic resistance genes and alleles come from? Thinking about the nature of mutation & about
Biology 322 Lecture Nov 15, 2010 Anouncements: see course web site Backtrack to a previous lecture: where do antibiotic resistance genes and alleles come from? Thinking about the nature of mutation & about
The Expression of Recombinant Sheep Prion Protein (RecShPrPC) and its Detection Using Western Blot and Immuno-PCR
 The Expression of Recombinant Sheep Prion Protein (RecShPrPC) and its Detection Using Western Blot and Immuno-PCR S. Thomas, C. S. Fernando, J. Roach, U. DeSilva and C. A. Mireles DeWitt The objective
The Expression of Recombinant Sheep Prion Protein (RecShPrPC) and its Detection Using Western Blot and Immuno-PCR S. Thomas, C. S. Fernando, J. Roach, U. DeSilva and C. A. Mireles DeWitt The objective
Supporting Information. Table of Contents
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Spatial Regulation of a Common Precursor from Two Distinct Genes
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Spatial Regulation of a Common Precursor from Two Distinct Genes
Lecture for Wednesday. Dr. Prince BIOL 1408
 Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
 Review Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Protein synthesis requires two steps: transcription and translation. DNA contains codes Three bases in DNA code
Review Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Protein synthesis requires two steps: transcription and translation. DNA contains codes Three bases in DNA code
2.5. Equipment and materials supplied by user Template preparation by cloning into plexsy_invitro-2 vector 4. 6.
 Manual 15 Reactions LEXSY in vitro Translation Cell-free protein expression kit based on Leishmania tarentolae contains the vector plexsy_invitro-2 Cat. No. EGE-2002-15 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT INTENDED
Manual 15 Reactions LEXSY in vitro Translation Cell-free protein expression kit based on Leishmania tarentolae contains the vector plexsy_invitro-2 Cat. No. EGE-2002-15 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT INTENDED
Rapid Detection of rpob Gene Mutations in Rif-resistant M. tuberculosis Isolates by Oligonucleotide Microarray 1
 BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 22, 253-258 (2009) www.besjournal.com Rapid Detection of rpob Gene Mutations in Rif-resistant M. tuberculosis Isolates by Oligonucleotide Microarray 1 AI-HUA SUN *,
BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 22, 253-258 (2009) www.besjournal.com Rapid Detection of rpob Gene Mutations in Rif-resistant M. tuberculosis Isolates by Oligonucleotide Microarray 1 AI-HUA SUN *,
Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10
 Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10 1. Which of the following is NOT needed for DNA replication? A. nucleotides B. ribosomes C. Enzymes (like polymerases) D. DNA E. all of the above are needed 2 The information
Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10 1. Which of the following is NOT needed for DNA replication? A. nucleotides B. ribosomes C. Enzymes (like polymerases) D. DNA E. all of the above are needed 2 The information
CS 4491/CS 7990 SPECIAL TOPICS IN BIOINFORMATICS
 1 CS 4491/CS 7990 SPECIAL TOPICS IN BIOINFORMATICS * Some contents are adapted from Dr. Jean Gao at UT Arlington Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University 2 Genetics The discovery of
1 CS 4491/CS 7990 SPECIAL TOPICS IN BIOINFORMATICS * Some contents are adapted from Dr. Jean Gao at UT Arlington Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University 2 Genetics The discovery of
466 Asn (N) to Ala (A) Generate beta dimer Interface
 Table S1: Amino acid changes to the HexA α-subunit to convert the dimer interface from α to β and to introduce the putative GM2A binding surface from β- onto the α- subunit Residue position (α-numbering)
Table S1: Amino acid changes to the HexA α-subunit to convert the dimer interface from α to β and to introduce the putative GM2A binding surface from β- onto the α- subunit Residue position (α-numbering)
SELECTION OF MOLECULAR APTAMERS FOR
 SELECTION OF MOLECULAR APTAMERS FOR IDENTIFICATION OF LIVE CELLS OF RALSTONIA SOLANACEARUM: A NEW POTENTIAL METHOD IN PLANT PATHOLOGY Patrice Champoiseau, University of Florida 2009 APS ANNUAL MEETING
SELECTION OF MOLECULAR APTAMERS FOR IDENTIFICATION OF LIVE CELLS OF RALSTONIA SOLANACEARUM: A NEW POTENTIAL METHOD IN PLANT PATHOLOGY Patrice Champoiseau, University of Florida 2009 APS ANNUAL MEETING
From mechanism to medicne
 From mechanism to medicne a look at proteins and drug design Chem 342 δ δ δ+ M 2009 δ+ δ+ δ M Drug Design - an Iterative Approach @ DSU Structural Analysis of Receptor Structural Analysis of Ligand-Receptor
From mechanism to medicne a look at proteins and drug design Chem 342 δ δ δ+ M 2009 δ+ δ+ δ M Drug Design - an Iterative Approach @ DSU Structural Analysis of Receptor Structural Analysis of Ligand-Receptor
Daily Agenda. Warm Up: Review. Translation Notes Protein Synthesis Practice. Redos
 Daily Agenda Warm Up: Review Translation Notes Protein Synthesis Practice Redos 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place? 3. Replicate this strand of DNA into complimentary
Daily Agenda Warm Up: Review Translation Notes Protein Synthesis Practice Redos 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place? 3. Replicate this strand of DNA into complimentary
1. DNA replication. (a) Why is DNA replication an essential process?
 ame Section 7.014 Problem Set 3 Please print out this problem set and record your answers on the printed copy. Answers to this problem set are to be turned in to the box outside 68120 by 5:00pm on Friday
ame Section 7.014 Problem Set 3 Please print out this problem set and record your answers on the printed copy. Answers to this problem set are to be turned in to the box outside 68120 by 5:00pm on Friday
A netlike rolling circle nucleic acid amplification technique
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information A netlike rolling circle nucleic acid amplification technique Xiaoli Zhu,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information A netlike rolling circle nucleic acid amplification technique Xiaoli Zhu,
Alpha-helices, beta-sheets and U-turns within a protein are stabilized by (hint: two words).
 1 Quiz1 Q1 2011 Alpha-helices, beta-sheets and U-turns within a protein are stabilized by (hint: two words) Value Correct Answer 1 noncovalent interactions 100% Equals hydrogen bonds (100%) Equals H-bonds
1 Quiz1 Q1 2011 Alpha-helices, beta-sheets and U-turns within a protein are stabilized by (hint: two words) Value Correct Answer 1 noncovalent interactions 100% Equals hydrogen bonds (100%) Equals H-bonds
