Gene transfer by Agrobacterium tumefaciens to microspores and microspore-derived embryos of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.).
|
|
|
- Morris Harrell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gene transfer by Agrobacterium tumefaciens to microspores and microspore-derived embryos of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Teresa CEGIELSKA-TARAS, Tomasz PNIEWSKI, Laurencja SZALA, Katarzyna MIEDZINSKA Plant Breeding and Acclimatization Institute, Poznań, Strzeszyńska 26, Poland. Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, Poznań, Noskowskiego 12/14, Poland Abstract Embryogenic microspores and microspore-derived embryos of Brassica napus are very suitable materials for introduction of foreign genes. Both microspores and microsporederived embryos from winter oilseed rape homozygous line DH-O-120 and cultivar Bor were used in our study of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Those androgenic forms were cocultivated with strains EHA105 or LBA4404, each of them containing the binary plasmid pp35sgib with the GUS gene with intron under the 35SRNA CaMV promoter and the bar gene as a selective marker. To optimize the transformation system based on microspores and microspore-derived embryos, highly efficient and reproducible embryogenesis is essential. Recently, we have developed an efficient system for microspore embryogenesis and double-haploid production in winter oilseed rape. The transformation of microspores and microspore-derived embryos yields green plants without the complication of chimeras. Up to now all regenerated plants were haploids. PCR analysis was made to determine the presence of the pat gene in the regenerated plants and confirm that transformation was effective. Key-words: Agrobacterium tumefaciens, androgenesis, Brassica napus, microspore, microspore-derived embryos, transformation, winter oilseed rape. Introduction Microspores, haploid embryos, or cells derived from such embryos, are potentially useful as recipients of foreign genes, especially if the frequency of embryogenesis is high. A high frequency of plant regeneration is required for successful gene transfer and recovery of the transgenics. Microspore-derived embryos generally exhibit a high regeneration potential. Also, as a result of chromosome duplication, the introduced trait can be evaluated in the homozygote. To obtain fertile homozygous transgenic plants the technique of the Agrobacterium-mediated gene is used the most frequently (Huang 1992). One of the many attractive features of the microspore embryogenic system is the possibility of transformation
2 of individual cells. Because embryos are derived from individual cells, transformants can be recovered without the complication of chimeras. Because of the many variables (especially those related to plant materials, Agrobacterium strains, and gene constructs with limited access), it is difficult to reproduce published results exactly. The goal of this study was to develop an efficient method for delivery of foreign genes to winter oilseed rape microspores and microspore-derived embryos with the use of A. tumefaciens. Materials and methods Bacterial strains and plasmids Agrobacterium strains LBA4404 and EHA105, containing the binary plasmid pp35sgib with the GUS gene with intron under the 35SRNA CaMV promoter and the bar gene as a selectable marker were used. Plant material Microspores and microspore-derived embryos (MDEs)of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus) homozygous line DH-O120 and cultivar Bor were used. Microspores were isolated as in our earlier study (Cegielska-Taras et al. 1999), while microspore-derived embryos were prepared as in another study (Cegielska-Taras et al. 2001). Transformation of microspores Microspores of oilseed rape have thick walls, which make them difficult to inoculate with foreign DNA. Forty-eight hours after isolation, microspores were used for Agrobacteriummediated transformation. For this specific inoculation we used liquid NLN medium, ph 5.7, with 10 mg/l acetosyringone and 1M glucose for 20 min. After one day of cocultivation the bacteria were washed out with fresh NLN-medium containing 13% of sucrose and 100 mg/l timentin, and then incubated in the dark at 30 C for 7 days and then at 24 C. When the microspore-derived embryos became visible to the naked eye, they were placed on an illuminated rotary shaker at 24 C. When the embryos began to turn green, the medium was changed to NLN medium with 8% of sucrose and 100 mg/l timentin. Green embryos were cultured on solidified B 5 medium containing 0.1 mg/l GA 3, 300 mg/l timentin, 10 mg/l Basta and 2% of sucrose at 1 C for 2 weeks, to stimulate shoot development. Next, the petri dishes with green embryos were transferred to a growth chamber (24 C, photoperiod 16D/8N) for 2 weeks. Survived green explants were cultured on MS medium supplemented with 0.1 mm
3 kinetin, 300 mg/l timentin, 10 mg/l Basta and 2% of sucrose. The shoots that remained green on this medium were considered to be transformants and were transferred to root induction medium and then planted in the soil for further development. Transformation of microspore-derived embryos The 21-day-old microspore-derived embryos growing on B 5 medium with 0.1 mg/l GA 3 were exposed to low temperature for 2 weeks. Next, they were put for a few days in the growth chamber and used for transformation. Cotyledons and hypocotyls were punctured with a sawing needle dipped in A. tumefaciens suspension for 2 hours. After infection with A. tumefaciens, the explants were placed immediately in B 5 medium (basic) without antibiotics. The explants were cocultivated with A. tumefaciens for two days and transferred to B 5 medium with antibiotics (to inhibit bacterial growth) and 10 mg/l Basta for 4 weeks. After that period the still green explants were transferred to shoot induction media (MS medium containing 0.1 mm kinetin) with antibiotics and Basta. The explants were transferred to fresh medium every two weeks. Shoots that remained green on this medium were considered to be transformants and were placed in root induction medium. Plantlets were transferred to soil as above. All plants obtained were haploids, but chromosome doubling in these plants was quite easy. We used the method of colchicine treatment of secondary auxiliary shoots. The putative transgenic plants developed under greenhouse conditions to the fruiting stage and their seeds were collected. Confirmation of transformation: plant DNA isolation and PCR analysis Genomic DNA was isolated from leaf tissues by the modified CTAB method of McGarvey and Kaper (1991). The isolation procedure was modified by additional phenol and chloroform extraction of crude preparations before nucleic acid precipitation. DNA preparations were quantified with agarose gel electrophoresis by visual comparison of the samples with puc18 DNA digested with EcoR I as a quantity standard. Polymerase chain reactions (PCR) were performed in a volume of 20μl containing about 10ng of plant genomic DNA, 10mM Tris-HCl ph 8.8, 50mM KCl, 0.1% Triton X-100, 1.5mM MgCl 2, 0.2mM dntp, 50μM of each primer (primer F: 5 - TGA GCC CAG AAC GAC GCC-3 ; primer R: 5 -GGA CTT CAG CCT GCC GGT AC-3 ; internal primers of the pat gene were designed to amplify the 516bp DNA fragment) and 1 unit Taq DNA polymerase (Finnzymes). The PCR programme was set as follows: initial denaturation at 94ºC for 4 min,
4 next 35 cycles of denaturation at 94ºC for 1 min, annealing at 65ºC, elongation at 72ºC for 1 min, and a final extension at 72ºC for 5 min. Screening of plant genomic DNA samples for Agrobacterium DNA residual contamination was done by PCR analysis. Approximately 0.5 ng of Agrobacterium DNA was used in control reactions. Total bacterial DNA was extracted as follows: a sample of bacteria was suspended in 200μl of water, next boiled for 10 min and centrifuged. The supernatant was used as a PCR template. Amplification reactions were performed under similar conditions as above, except primers and PCR programme. Internal primers (primer F: 5 -TTG ACC TTG TTT CAG GTT TAC ACA-3 ; primer R: 5 -GAC GAG GAT AAT CAT CAT CGA AAC-3 ) of agrobacterial, chromosomal chva gene were designed to amplify the 777bp DNA fragment. The PCR programme has been performed as previously, except annealing at 62ºC. Polymerase chain reactions were performed in a PTC-200 MJ Research thermal cycler. The amplification products were analysed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Molecular weights were estimated with the use of 1kb ladder (Sigma) as a standard. Results and discussion Over the last 30 years a great deal of effort has gone into improving the quality of Brassica napus by both classical breeding and several tissue culture techniques, such as haploids and doubled haploids. Genetic engineering potentially can be used as a method for adding specific characteristics to existing varieties. Brassica microspore embryogenesis is a very desirable system for the introduction of foreign genes (Huang, 1992). The transformation of microspores directly yields green haploid embryos which can be recovered without the complication of chimeras. To optimize a microspore-based transformation system, highly efficient and reproducible embryogenesis is essential. Transformed embryos developed 1-2 weeks slower than controls conducted at the same time. Recently, we have developed a protocol for efficient microspore embryogenesis and doubled haploid production for winter oilseed rape (Cegielska-Taras et al. 1999, Cegielska-Taras et al. 2001). The most common herbicide resistance genes used for transformation of Brassica are bar and pat, which confer resistance to phosphinothricin, the active ingredient of the herbicide Basta. In experiments with microspores and the bar gene we regenerated more than 20 putative transformants. In a typical experiment with infection by Agrobacterium tumefaciens on the third day of microspore culture we can recover up to 30 embryos. The embryos on solid medium with the selective agent did not develop normally. Approximately five to ten embryos from each series survived in selective medium. Shoots were regenerated from
5 survived embryos through secondary embryogenesis (Cegielska-Taras, Szała 1997). After rooting, normal plants developed. All the plants were haploids. After chromosome doubling, seeds from each putative transformant were obtained. The results show that a high frequency of microspore embryogenesis is necessary for high transformation frequencies. Cocultivation of A. tumefaciens with microspore-derived embryos is a very convenient procedure because more than one hundred independent transformants have been produced thanks to the possibility of handling a great number of embryos in one experiment. The efficiency of the procedure was improved through using microspore-derived embryos after cold treatment. The cold treatment stimulates shoot regeneration very efficiently. Shoots developed readily from embryos that survived in the selective medium. The method is attractive also because of the high regenerative potential of the embryos. To detect the presence of the bar gene in the regenerated plants and confirm that transformation was effective, PCR analysis was made. In putative transgenic plants it indicated amplification of a 516bp fragment of the bar gene (Fig. 1). The first results of PCR analysis showed that 8.7% of plants regenerated from transformed microspores and about 30% of plants regenerated from transformed microspore-derived embryos were putative transformants. A. tumefaciens survives in plant tissue and occupies intercellular spaces for some time after transformation. This might falsify the results of molecular analysis (PCR). Screening of plant genomic DNA samples for Agrobacterium DNA residual contamination was done by PCR analysis. Agrobacterium DNA was used in control reactions. Amplification reactions were performed under similar conditions as above, except primers and PCR program. Internal primers of agrobacterial, chromosomal chva gene were designed to amplify the 777bp DNA fragment. For this reason PCR analysis was done with a starter specific to Agrobacterium gene chva, which is situated on the bacterial chromosome (Fig. 2). A further molecular analysis, i.e. Southern blotting and GUS expression of the putative transgenic plants, will be done soon as it can confirm the positive results of the process of transformation.
6 References Cegielska-Taras T., Szała L., Plant regeneration from microspore-derived embryos of Brassica napus L. Rośliny Oleiste [Oilseed Crops], XVIII, Cegielska-Taras T., Szała L., Nałęczyńska A., Kołodziej K., Ogrodowczyk M In vitro selection for high erucic acid content in microspore-derived embryos of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). J. Appl. Genet. 40, 4, Cegielska-Taras T., Tykarska T., Szała L., Kuraś L., Krzymański J Direct plant development from microspore-derived embryos of winter oilseed rape Brassica napus L. ssp. oleifera (DC.) Metzger. Euphytica, in press. Huang B Genetic manipulation of microspore and microspore-derived embryos. In Vitro Cell Devel. Biol. 28P: McGarvey P., Kaper J. M A simple and rapid method for screening transgenic plants using the PCR. BioFeedback, Vol. 11, No. 4, pp
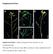
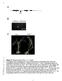
7 10000pz 6000pz 4000pz 3000pz 2000pz 1400pz 1000pz 750pz 500pz 400pz 300pz 516bp 10000pz 6000pz 4000pz 3000pz 2000pz 1400pz 1000pz 750pz 500pz 400pz 300pz 516bp Fig.1. PCR analysis of putative winter oilseed rape transgenic plants showing amplification of 516bp fragment of bar gene pz 6000pz 4000pz 3000pz 2000pz 1400pz 1000pz 750pz 500pz 400pz 300pz 777bp 10000pz 6000pz 4000pz 3000pz 2000pz 1400pz 1000pz 750pz 500pz 400pz 300pz 777bp Fig.2. Screening for Agrobacterium DNA traces in genomic DNA samples of putative transgenic winter oilseed rape plants. PCR analysis performed on plant and control DNA templates showing results of amplification of 777bp fragment of agrobacterial chromosomal chva gene
8 Lanes: M DNA size marker, wide range DNA marker (Sigma) 1-5 DH line O-120 plants, after MDE transformation using A. tumefaciens LBA cv. BOR plants, after MDE transformation using A. tumefaciens LBA DH line O-120 plants, after MDE transformation using A. tumefaciens EHA cv. BOR plants, after MDE transformation using A. tumefaciens EHA cv. BOR plants, after microspore transformation using A. tumefaciens LBA cv. BOR plants, after microspore transformation using A. tumefaciens EHA105 NC1 negative control 1 - untransformed DH line O-120 plant NC2 negative control 2 - untransformed cv. BOR plant W water PC positive control -pp35sgib plasmid PC1 positive control 1 DNA of A. tumefaciens LBA4404 PC2 positive control 2 DNA of A. tumefaciens EHA105 NC1/PC1 plant DNA of DH O-120 line mixed with DNA of A. tumefaciens LBA4404 NC2/PC2 plant DNA of cv. BOR mixed with DNA of A. tumefaciens EHA105
9
Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture
 Supplementary materials for Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture Article tile: Agrobacterium mediated Genetic Transformation of Miscanthus sinensis Authors: Ok-Jin Hwang 1, Mi-Ae Cho 1, Yun-Jeong Han 1,
Supplementary materials for Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture Article tile: Agrobacterium mediated Genetic Transformation of Miscanthus sinensis Authors: Ok-Jin Hwang 1, Mi-Ae Cho 1, Yun-Jeong Han 1,
The demonstration that wild-type T-DNA coding region can be replaced by any DNA sequence without any effect on its transfer from A.
 The demonstration that wild-type T-DNA coding region can be replaced by any DNA sequence without any effect on its transfer from A. tumefaciens to the plant inspired the promise that A. tumefaciens might
The demonstration that wild-type T-DNA coding region can be replaced by any DNA sequence without any effect on its transfer from A. tumefaciens to the plant inspired the promise that A. tumefaciens might
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH).
 Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis. Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010
 Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010 1 1- What is quick change site directed mutagenesis? 2- An overview of the kit contents. 3- A brief information
Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010 1 1- What is quick change site directed mutagenesis? 2- An overview of the kit contents. 3- A brief information
strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular
![strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular](/thumbs/72/66361212.jpg) Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
PCR Laboratory Exercise
 PCR Laboratory Exercise Advance Protocol (updated 1/2018) Introduction Detection of TPA-25 Alu by PCR A Human DNA Fingerprinting Lab Protocol 1994 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory DNA Learning Center In this
PCR Laboratory Exercise Advance Protocol (updated 1/2018) Introduction Detection of TPA-25 Alu by PCR A Human DNA Fingerprinting Lab Protocol 1994 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory DNA Learning Center In this
Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit
 1. Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit For fast and sensitive one-step RT-PCR www.tiangen.com/en RT121221 Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit Kit Contents Cat. no. KR113 Contents Hotmaster Taq Polymerase (2.5 U/μl) Quant
1. Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit For fast and sensitive one-step RT-PCR www.tiangen.com/en RT121221 Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit Kit Contents Cat. no. KR113 Contents Hotmaster Taq Polymerase (2.5 U/μl) Quant
CSS451 Spring 2010 Polymerase Chain Reaction Laboratory
 CSS451 Spring 2010 Polymerase Chain Reaction Laboratory The purpose of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is to amplify specific segments of DNA. If one knows the DNA sequence of regions of DNA that flank
CSS451 Spring 2010 Polymerase Chain Reaction Laboratory The purpose of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is to amplify specific segments of DNA. If one knows the DNA sequence of regions of DNA that flank
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
 Laboratory for Environmental Pathogens Research Department of Environmental Sciences University of Toledo Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Background information The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an
Laboratory for Environmental Pathogens Research Department of Environmental Sciences University of Toledo Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Background information The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an
2x PCR LongNova-RED PCR Master Mix
 2x PCR LongNova-RED Components RP85L 100 reactions (50 μl) RP85L-10 1000 reactions (50 μl) 2x PCR LongNova-RED 2 x 1.25 ml 20 x 1.25 ml PCR grade water 2 x 1.5 ml 20 x 1.5 ml Storage & Shiing Storage conditions
2x PCR LongNova-RED Components RP85L 100 reactions (50 μl) RP85L-10 1000 reactions (50 μl) 2x PCR LongNova-RED 2 x 1.25 ml 20 x 1.25 ml PCR grade water 2 x 1.5 ml 20 x 1.5 ml Storage & Shiing Storage conditions
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids
 Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC
 Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
High Pure PCR Template Preparation Kit for preparation of 100 nucleic acid samples Cat. No
 for preparation of 100 nucleic acid samples Cat. No. 1 796 88 Principle Cells are lysed during a short incubation with Proteinase K in the presence of a chaotropic salt (guanidine HCl), which immediately
for preparation of 100 nucleic acid samples Cat. No. 1 796 88 Principle Cells are lysed during a short incubation with Proteinase K in the presence of a chaotropic salt (guanidine HCl), which immediately
Supplemental Data. mir156-regulated SPL Transcription. Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering. Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana
 Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Hammer blot-mediated RNA extraction: an inexpensive, labor-saving method to extract RNA for plant virus detection
 Hammer blot-mediated RNA extraction: an inexpensive, labor-saving method to extract RNA for plant virus detection Md. Shamim Akhter et al. Online Supplementary Materials Supplementary methods Preparation
Hammer blot-mediated RNA extraction: an inexpensive, labor-saving method to extract RNA for plant virus detection Md. Shamim Akhter et al. Online Supplementary Materials Supplementary methods Preparation
PCR-based Markers and Cut Flower Longevity in Carnation
 PCRbased Markers and Cut Flower Longevity in Carnation Laura De Benedetti, Luca Braglia, Simona Bruna, Gianluca Burchi *, Antonio Mercuri and Tito Schiva Istituto Sperimentale per la Floricoltura, Corso
PCRbased Markers and Cut Flower Longevity in Carnation Laura De Benedetti, Luca Braglia, Simona Bruna, Gianluca Burchi *, Antonio Mercuri and Tito Schiva Istituto Sperimentale per la Floricoltura, Corso
Table of Contents. Description Kit Components Reagents not supplied in the kit Equipment required Storage...
 Table of Contents Description... 2 Kit Components... 2 Reagents not supplied in the kit... 2 Equipment required... 2 Storage... 2 References... 2 Principle... 3 Protocol... 4 Identification of HPV types...
Table of Contents Description... 2 Kit Components... 2 Reagents not supplied in the kit... 2 Equipment required... 2 Storage... 2 References... 2 Principle... 3 Protocol... 4 Identification of HPV types...
High Pure Technology and Silica Adsorption High Pure PCR Product Purification Kit
 for purification of DNA from PCR reactions Cat. No. 1 73 668 (50 purifications) Cat. No. 1 73 676 (50 purifications) Principle In the presence of chaotropic salt, product DNA binds selectively to glass
for purification of DNA from PCR reactions Cat. No. 1 73 668 (50 purifications) Cat. No. 1 73 676 (50 purifications) Principle In the presence of chaotropic salt, product DNA binds selectively to glass
FMF NIRCA PROTOCOL STEP 1.
 FMF NIRCA PROTOCOL STEP 1. After you have isolated patient s DNA and DNA from a healthy donor (wild type), you perform a nested PCR. The primers used to amplify exon 2 and exon 10 of the mefv gene are
FMF NIRCA PROTOCOL STEP 1. After you have isolated patient s DNA and DNA from a healthy donor (wild type), you perform a nested PCR. The primers used to amplify exon 2 and exon 10 of the mefv gene are
Preparing Samples for Analysis of Small RNA
 Preparing Samples for Analysis of Small RNA Topics 3 Introduction 4 Kit Contents and Equipment Checklist 6 Isolate Small RNA by Denaturing PAGE Gel 9 Ligate 5' RNA Adapters 12 Ligate 3' RNA Adapters 15
Preparing Samples for Analysis of Small RNA Topics 3 Introduction 4 Kit Contents and Equipment Checklist 6 Isolate Small RNA by Denaturing PAGE Gel 9 Ligate 5' RNA Adapters 12 Ligate 3' RNA Adapters 15
2054, Chap. 14, page 1
 2054, Chap. 14, page 1 I. Recombinant DNA technology (Chapter 14) A. recombinant DNA technology = collection of methods used to perform genetic engineering 1. genetic engineering = deliberate modification
2054, Chap. 14, page 1 I. Recombinant DNA technology (Chapter 14) A. recombinant DNA technology = collection of methods used to perform genetic engineering 1. genetic engineering = deliberate modification
Chapter 9 Genetic Engineering
 Chapter 9 Genetic Engineering Biotechnology: use of microbes to make a protein product Recombinant DNA Technology: Insertion or modification of genes to produce desired proteins Genetic engineering: manipulation
Chapter 9 Genetic Engineering Biotechnology: use of microbes to make a protein product Recombinant DNA Technology: Insertion or modification of genes to produce desired proteins Genetic engineering: manipulation
Gateway Cloning Protocol (Clough Lab Edition) This document is a modification of the Gateway cloning protocol developed by Manju in Chris Taylor's lab
 Gateway Cloning Protocol (Clough Lab Edition) This document is a modification of the Gateway cloning protocol developed by Manju in Chris Taylor's lab With the Gateway cloning system, a PCR fragment is
Gateway Cloning Protocol (Clough Lab Edition) This document is a modification of the Gateway cloning protocol developed by Manju in Chris Taylor's lab With the Gateway cloning system, a PCR fragment is
Pinpoint Slide DNA Isolation System Catalog No. D3001
 INSTRUCTIONS Pinpoint Slide DNA Isolation System Catalog No. D3001 Highlights Easily isolates genomic DNA in any targeted microscopic tissue area on a slide. The simple procedure combines Pinpoint tissue
INSTRUCTIONS Pinpoint Slide DNA Isolation System Catalog No. D3001 Highlights Easily isolates genomic DNA in any targeted microscopic tissue area on a slide. The simple procedure combines Pinpoint tissue
MightyAmp DNA Polymerase Ver.3
 Cat. # R076A For Research Use MightyAmp DNA Polymerase Ver.3 Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 3 IV. General PCR Reaction Mix... 3 V. Primer Design...
Cat. # R076A For Research Use MightyAmp DNA Polymerase Ver.3 Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 3 IV. General PCR Reaction Mix... 3 V. Primer Design...
Pasteurella multocida
 BACTOTYPE PCR Amplification Kit Pasteurella multocida Labor Diagnostik Leipzig Manual Technology The product group BACTOTYPE PCR Amplification Kit comprises optimised systems for the identification of
BACTOTYPE PCR Amplification Kit Pasteurella multocida Labor Diagnostik Leipzig Manual Technology The product group BACTOTYPE PCR Amplification Kit comprises optimised systems for the identification of
Low cost and non-toxic genomic DNA extraction for use in molecular marker studies.
 Low cost and non-toxic genomic DNA extraction for use in molecular marker studies. Version 1.4, February 28 th, 2013. Prepared by Bernhard Hofinger, Owen Huynh and Brad Till. 1. OBJECTIVE To develop and
Low cost and non-toxic genomic DNA extraction for use in molecular marker studies. Version 1.4, February 28 th, 2013. Prepared by Bernhard Hofinger, Owen Huynh and Brad Till. 1. OBJECTIVE To develop and
Amplicon Sequencing Template Preparation
 Amplicon Sequencing Template Preparation The DNA sample preparation procedure for Amplicon Sequencing consists of a simple PCR amplification reaction, but uses special Fusion Primers (Figure 1-1). The
Amplicon Sequencing Template Preparation The DNA sample preparation procedure for Amplicon Sequencing consists of a simple PCR amplification reaction, but uses special Fusion Primers (Figure 1-1). The
 PRODUCT INFORMATION Long PCR Enzyme Mix #K0182 500 u Lot Exp. 00.0000 Store at -20 C. CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS Long PCR Enzyme Mix is functionally tested in PCR amplification of 47.4 kb fragment from lambda
PRODUCT INFORMATION Long PCR Enzyme Mix #K0182 500 u Lot Exp. 00.0000 Store at -20 C. CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS Long PCR Enzyme Mix is functionally tested in PCR amplification of 47.4 kb fragment from lambda
Designing and creating your gene knockout Background The rada gene was identified as a gene, that when mutated, caused cells to become hypersensitive
 Designing and creating your gene knockout Background The rada gene was identified as a gene, that when mutated, caused cells to become hypersensitive to ionizing radiation. However, why these mutants are
Designing and creating your gene knockout Background The rada gene was identified as a gene, that when mutated, caused cells to become hypersensitive to ionizing radiation. However, why these mutants are
Sexing Bovine Preimplantation Embryos by PCR
 Sexing Bovine Preimplantation Embryos by PCR Katherine E.M. Hendricks 1, Leydson F. Martins 2, Justin M. Fear 1 and Peter J. Hansen 1 1 Dept. of Animal Sciences, University of Florida and Department of
Sexing Bovine Preimplantation Embryos by PCR Katherine E.M. Hendricks 1, Leydson F. Martins 2, Justin M. Fear 1 and Peter J. Hansen 1 1 Dept. of Animal Sciences, University of Florida and Department of
CONCEPTS AND METHODS INSTRUCTOR PLANNING. The following table will help you to plan and integrate the four parts of the experiment.
 CONCEPTS AND METHODS This laboratory can help students understand several important concepts of modern biology: The relationship between genotype and phenotype. Forensic identification of genes. Methods
CONCEPTS AND METHODS This laboratory can help students understand several important concepts of modern biology: The relationship between genotype and phenotype. Forensic identification of genes. Methods
TIANgel Mini DNA Purification Kit
 TIANgel Mini DNA Purification Kit For DNA purification from agarose and polyacrylamide gels www.tiangen.com/en DP130419 TIANgel Mini DNA Purification Kit Kit Contents (Spin column) Cat. no. DP208 Contents
TIANgel Mini DNA Purification Kit For DNA purification from agarose and polyacrylamide gels www.tiangen.com/en DP130419 TIANgel Mini DNA Purification Kit Kit Contents (Spin column) Cat. no. DP208 Contents
1. COMPONENTS. PyroStart Fast PCR Master Mix (2X) (#K0211 for 250 reactions of 20µl) 2. STORAGE 3. DESCRIPTION
 1 2 1 PyroStart Fast PCR Master Mix (2X) (#K0211 for 250 reactions of 20µl) TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. COMPONENTS... 2 2. STORAGE... 2 3. DESCRIPTION... 2 4. PROTOCOL FOR FAST PCR... 3 4.1. General Considerations...
1 2 1 PyroStart Fast PCR Master Mix (2X) (#K0211 for 250 reactions of 20µl) TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. COMPONENTS... 2 2. STORAGE... 2 3. DESCRIPTION... 2 4. PROTOCOL FOR FAST PCR... 3 4.1. General Considerations...
Presto Soil DNA Extraction Kit
 Instruction Manual Ver. 02.23.17 For Research Use Only Presto Soil DNA Extraction Kit Advantages SLD004 (4 Preparation Sample Kit) SLD050 (50 Preparation Kit) SLD100 (100 Preparation Kit) Sample: 250-500
Instruction Manual Ver. 02.23.17 For Research Use Only Presto Soil DNA Extraction Kit Advantages SLD004 (4 Preparation Sample Kit) SLD050 (50 Preparation Kit) SLD100 (100 Preparation Kit) Sample: 250-500
Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
Supporting Online Information
 Supporting Online Information Isolation of Human Genomic DNA Sequences with Expanded Nucleobase Selectivity Preeti Rathi, Sara Maurer, Grzegorz Kubik and Daniel Summerer* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
Supporting Online Information Isolation of Human Genomic DNA Sequences with Expanded Nucleobase Selectivity Preeti Rathi, Sara Maurer, Grzegorz Kubik and Daniel Summerer* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
Genetic Engineering & Recombinant DNA
 Genetic Engineering & Recombinant DNA Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc) Permission required for reproduction or display. Applications of Genetic Engineering Basic science vs. Applied
Genetic Engineering & Recombinant DNA Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc) Permission required for reproduction or display. Applications of Genetic Engineering Basic science vs. Applied
Presto Stool DNA Extraction Kit
 Instruction Manual Ver. 10.21.17 For Research Use Only Presto Stool DNA Extraction Kit Advantages STLD004 (4 Preparation Sample Kit) STLD050 (50 Preparation Kit) STLD100 (100 Preparation Kit) Sample: 180-200
Instruction Manual Ver. 10.21.17 For Research Use Only Presto Stool DNA Extraction Kit Advantages STLD004 (4 Preparation Sample Kit) STLD050 (50 Preparation Kit) STLD100 (100 Preparation Kit) Sample: 180-200
Russian population genetics study of jack mackerel in the South Pacific. D.A. Zelenina S.M. Rastorguev
 SWG-09-INF-07 Russian population genetics study of jack mackerel in the South Pacific. D.A. Zelenina S.M. Rastorguev Purpose: to study the genetic polymorphism of the South Pacific jack mackerel. Material
SWG-09-INF-07 Russian population genetics study of jack mackerel in the South Pacific. D.A. Zelenina S.M. Rastorguev Purpose: to study the genetic polymorphism of the South Pacific jack mackerel. Material
Fast and reliable purification of up to 100 µg of transfection-grade plasmid DNA using a spin-column.
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZymoPURE Plasmid Miniprep Kit Catalog Nos. D4209, D4210, D4211 & D4212 (Patent Pending) Highlights Fast and reliable purification of up to 100 µg of transfection-grade plasmid DNA using
INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZymoPURE Plasmid Miniprep Kit Catalog Nos. D4209, D4210, D4211 & D4212 (Patent Pending) Highlights Fast and reliable purification of up to 100 µg of transfection-grade plasmid DNA using
DETECTION OF GMOs (LMOs).
 ISO/9001:2000 Certified Organisation NABL Accredited (ISO 17025) ISO 14000 DETECTION OF GMOs (LMOs). LALITHA R. GOWDA DEPARTMENT OF PROTEIN CHEMISTRY AND TECHNOLOGY CENTRAL FOOD TECHNOLOGICAL RESEARCH
ISO/9001:2000 Certified Organisation NABL Accredited (ISO 17025) ISO 14000 DETECTION OF GMOs (LMOs). LALITHA R. GOWDA DEPARTMENT OF PROTEIN CHEMISTRY AND TECHNOLOGY CENTRAL FOOD TECHNOLOGICAL RESEARCH
Recombinant DNA Technology. The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology. yeast. Biotechnology. Recombinant DNA technology.
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 8 Recombinant DNA Technology The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology?
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 8 Recombinant DNA Technology The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology?
Cat # Box1 Box2. DH5a Competent E. coli cells CCK-20 (20 rxns) 40 µl 40 µl 50 µl x 20 tubes. Choo-Choo Cloning TM Enzyme Mix
 Molecular Cloning Laboratories User Manual Version 3.3 Product name: Choo-Choo Cloning Kits Cat #: CCK-10, CCK-20, CCK-096, CCK-384 Description: Choo-Choo Cloning is a highly efficient directional PCR
Molecular Cloning Laboratories User Manual Version 3.3 Product name: Choo-Choo Cloning Kits Cat #: CCK-10, CCK-20, CCK-096, CCK-384 Description: Choo-Choo Cloning is a highly efficient directional PCR
TaKaRa PCR Amplification Kit
 Cat. # R011 For Research Use TaKaRa PCR Amplification Kit Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 4 IV. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 V. Principle...
Cat. # R011 For Research Use TaKaRa PCR Amplification Kit Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 4 IV. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 V. Principle...
Search for and Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and Establishment of SNP Markers
 DNA Research 9, 163 171 (2002) Search for and Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and Establishment of SNP Markers Shinobu Nasu, Junko Suzuki, Rieko
DNA Research 9, 163 171 (2002) Search for and Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and Establishment of SNP Markers Shinobu Nasu, Junko Suzuki, Rieko
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes
 Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
Bacterial 16S rdna PCR Kit Fast (800)
 Cat. # RR182A For Research Use Bacterial 16S rdna PCR Kit Fast (800) Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 IV. Storage...
Cat. # RR182A For Research Use Bacterial 16S rdna PCR Kit Fast (800) Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 IV. Storage...
Fungal rdna (D1/D2) PCR Kit Fast
 Cat. # RR184A For Research Use Fungal rdna (D1/D2) PCR Kit Fast Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 IV. Storage... 4 V.
Cat. # RR184A For Research Use Fungal rdna (D1/D2) PCR Kit Fast Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 IV. Storage... 4 V.
Diagnosis Sanger. Interpreting and Troubleshooting Chromatograms. Volume 1: Help! No Data! GENEWIZ Technical Support
 Diagnosis Sanger Interpreting and Troubleshooting Chromatograms GENEWIZ Technical Support DNAseq@genewiz.com Troubleshooting This troubleshooting guide is based on common issues seen from samples within
Diagnosis Sanger Interpreting and Troubleshooting Chromatograms GENEWIZ Technical Support DNAseq@genewiz.com Troubleshooting This troubleshooting guide is based on common issues seen from samples within
Laboratory Exercise 4. Multiplex PCR of Short Tandem Repeats and Vertical Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis.
 Laboratory Exercise 4 4 Multiplex PCR of Short Tandem Repeats and Vertical Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis B A C K G R O U N D The human genome contains over 3000 million base pairs, which are distributed
Laboratory Exercise 4 4 Multiplex PCR of Short Tandem Repeats and Vertical Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis B A C K G R O U N D The human genome contains over 3000 million base pairs, which are distributed
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
GM (Genetically Modified) Plants. Background
 1 GM (Genetically Modified) Plants Background Genetically modified crops (GM) have been used since 1996 in the U.S. GM crops contain foreign genetic material The DNA may be from another plant or from a
1 GM (Genetically Modified) Plants Background Genetically modified crops (GM) have been used since 1996 in the U.S. GM crops contain foreign genetic material The DNA may be from another plant or from a
Molecular Techniques Third-year Biology
 PLANNING Genetics Lab practices Molecular Techniques. Genetics Lab practices protocol. 2015-16 PCR-DIRECTED MUTAGENESIS, MOLECULAR CLONING AND RESTRICTION ANALYSIS Sessions 1 & 2 (2x3 hours): PCR-directed
PLANNING Genetics Lab practices Molecular Techniques. Genetics Lab practices protocol. 2015-16 PCR-DIRECTED MUTAGENESIS, MOLECULAR CLONING AND RESTRICTION ANALYSIS Sessions 1 & 2 (2x3 hours): PCR-directed
Recombinant DNA Technology
 History of recombinant DNA technology Recombinant DNA Technology (DNA cloning) Majid Mojarrad Recombinant DNA technology is one of the recent advances in biotechnology, which was developed by two scientists
History of recombinant DNA technology Recombinant DNA Technology (DNA cloning) Majid Mojarrad Recombinant DNA technology is one of the recent advances in biotechnology, which was developed by two scientists
Chapter 7 Agricultural Biotechnology
 Chapter 7 Agricultural Biotechnology Outline: 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Plant tissue culture 7.3 Genetically Modified Plant 7.4 Animal cloning 7.5 Genetically modified animal 2 Learning outcomes: Describe the
Chapter 7 Agricultural Biotechnology Outline: 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Plant tissue culture 7.3 Genetically Modified Plant 7.4 Animal cloning 7.5 Genetically modified animal 2 Learning outcomes: Describe the
HiPer Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Teaching Kit
 HiPer Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM031 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 3.5 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis:
HiPer Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM031 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 3.5 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis:
XactEdit Cas9 Nuclease with NLS User Manual
 XactEdit Cas9 Nuclease with NLS User Manual An RNA-guided recombinant endonuclease for efficient targeted DNA cleavage Catalog Numbers CE1000-50K, CE1000-50, CE1000-250, CE1001-250, CE1001-1000 Table of
XactEdit Cas9 Nuclease with NLS User Manual An RNA-guided recombinant endonuclease for efficient targeted DNA cleavage Catalog Numbers CE1000-50K, CE1000-50, CE1000-250, CE1001-250, CE1001-1000 Table of
Supporting Information. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2006
 Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
NOTES - CH 15 (and 14.3): DNA Technology ( Biotech )
 NOTES - CH 15 (and 14.3): DNA Technology ( Biotech ) Vocabulary Genetic Engineering Gene Recombinant DNA Transgenic Restriction Enzymes Vectors Plasmids Cloning Key Concepts What is genetic engineering?
NOTES - CH 15 (and 14.3): DNA Technology ( Biotech ) Vocabulary Genetic Engineering Gene Recombinant DNA Transgenic Restriction Enzymes Vectors Plasmids Cloning Key Concepts What is genetic engineering?
Genetics Lecture 21 Recombinant DNA
 Genetics Lecture 21 Recombinant DNA Recombinant DNA In 1971, a paper published by Kathleen Danna and Daniel Nathans marked the beginning of the recombinant DNA era. The paper described the isolation of
Genetics Lecture 21 Recombinant DNA Recombinant DNA In 1971, a paper published by Kathleen Danna and Daniel Nathans marked the beginning of the recombinant DNA era. The paper described the isolation of
Diagnosis and Quantification of Strawberry Vein Banding Virus Using Molecular Approaches
 Diagnosis and Quantification of Strawberry Vein Banding Virus Using Molecular Approaches Ali Mahmoudpour Department of Plant Pathology, University of California, Davis, CA, 95616, USA Current Address:
Diagnosis and Quantification of Strawberry Vein Banding Virus Using Molecular Approaches Ali Mahmoudpour Department of Plant Pathology, University of California, Davis, CA, 95616, USA Current Address:
Author. Abstract. Introduction. Agriculture
 Nested Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction for the Determination of DNA From Genetically Modified Corn and Soy Beans Using the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer Application Agriculture Author Mark Jensen Agilent
Nested Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction for the Determination of DNA From Genetically Modified Corn and Soy Beans Using the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer Application Agriculture Author Mark Jensen Agilent
Instructions for Use Life Science Kits & Assays
 Instructions for Use Life Science Kits & Assays Content Content 1 Product and order number... I 2 Storage conditions... I 3 Description... II 3.1 Quality data... II 3.2 Unit definition... II 4 Delivered
Instructions for Use Life Science Kits & Assays Content Content 1 Product and order number... I 2 Storage conditions... I 3 Description... II 3.1 Quality data... II 3.2 Unit definition... II 4 Delivered
User Manual. Catalog No.: DWSK-V101 (10 rxns), DWSK-V102 (25 rxns) For Research Use Only
 DNA Walking SpeedUp TM Kit SpeedUp Sequencing SpeedUp BAC Clone Sequencing SpeedUp Genome Walking SpeedUp Transgene Location Detection SpeedUp Deletion/ Insertion/ Isoform Detection User Manual Version
DNA Walking SpeedUp TM Kit SpeedUp Sequencing SpeedUp BAC Clone Sequencing SpeedUp Genome Walking SpeedUp Transgene Location Detection SpeedUp Deletion/ Insertion/ Isoform Detection User Manual Version
High-throughput cloning and expression in recalcitrant bacteria
 High-throughput cloning and expression in recalcitrant bacteria Eric R Geertsma & Bert Poolman Supplementary text and figures: Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of SfiI sites yielding identical 3 extensions
High-throughput cloning and expression in recalcitrant bacteria Eric R Geertsma & Bert Poolman Supplementary text and figures: Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of SfiI sites yielding identical 3 extensions
BIOLOGY Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
 BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
Amplifying the ALU intron for Hardy- Weinberg Analysis Part 1
 Bio 212 Lab Name: Amplifying the ALU intron for Hardy- Weinberg Analysis Part 1 OBJECTIVES: Review the following terms and concepts presented in Biology 211: enzymes, DNA structure and replication, role
Bio 212 Lab Name: Amplifying the ALU intron for Hardy- Weinberg Analysis Part 1 OBJECTIVES: Review the following terms and concepts presented in Biology 211: enzymes, DNA structure and replication, role
PCR based Testing of Living Modified Organisms (LMOs)
 PCR based Testing of Living Modified Organisms (LMOs) Gurinder Jit Randhawa Senior Scientist NRC on DNA Fingerprinting NBPGR New Delhi The first commercially available transgenic crop was the FLAVR-SAVR
PCR based Testing of Living Modified Organisms (LMOs) Gurinder Jit Randhawa Senior Scientist NRC on DNA Fingerprinting NBPGR New Delhi The first commercially available transgenic crop was the FLAVR-SAVR
Sensitivity vs Specificity
 Viral Detection Animal Inoculation Culturing the Virus Definitive Length of time Serology Detecting antibodies to the infectious agent Detecting Viral Proteins Western Blot ELISA Detecting the Viral Genome
Viral Detection Animal Inoculation Culturing the Virus Definitive Length of time Serology Detecting antibodies to the infectious agent Detecting Viral Proteins Western Blot ELISA Detecting the Viral Genome
Guide-it sgrna In Vitro Transcription and Screening Systems User Manual
 Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Guide-it sgrna In Vitro Transcription and Screening Systems User Manual Cat. Nos. 631438, 631439 & 631440 (042114) Clontech Laboratories, Inc. A Takara Bio Company 1290 Terra
Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Guide-it sgrna In Vitro Transcription and Screening Systems User Manual Cat. Nos. 631438, 631439 & 631440 (042114) Clontech Laboratories, Inc. A Takara Bio Company 1290 Terra
Presto Mini Plasmid Kit
 Instruction Manual Ver. 03.06.17 For Research Use Only Presto Mini Plasmid Kit PDH004 (4 Preparation Sample Kit) PDH100 (100 Preparation Kit) PDH300 (300 Preparation Kit) Advantages Sample: 1-7 ml of cultured
Instruction Manual Ver. 03.06.17 For Research Use Only Presto Mini Plasmid Kit PDH004 (4 Preparation Sample Kit) PDH100 (100 Preparation Kit) PDH300 (300 Preparation Kit) Advantages Sample: 1-7 ml of cultured
Table of contents. I. Flowchart of blunt end cloning of PCR products...2. II. Description...3. III. Kit Components...3
 Table of contents I. Flowchart of blunt end cloning of PCR products...2 II. Description...3 III. Kit Components...3 IV. Reagents and Instruments Required...3 V. Storage...3 VI. About puc118 Hinc II/BAP...4
Table of contents I. Flowchart of blunt end cloning of PCR products...2 II. Description...3 III. Kit Components...3 IV. Reagents and Instruments Required...3 V. Storage...3 VI. About puc118 Hinc II/BAP...4
Chapter 8 Recombinant DNA Technology. 10/1/ MDufilho
 Chapter 8 Recombinant DNA Technology 10/1/2017 1 MDufilho The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology? Recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) technology Intentionally modifying
Chapter 8 Recombinant DNA Technology 10/1/2017 1 MDufilho The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology? Recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) technology Intentionally modifying
ABSTRACT: 25 DEVELOPMENT OF TRANSGENIC SOYBEAN PLANTS WITH SORGHUM C4-SPECIFIC PEPC GENE
 ABSTRACT: 25 DEVELOPMENT OF TRANSGENIC SOYBEAN PLANTS WITH SORGHUM C4-SPECIFIC PEPC GENE ZHANG Y 2, MAN W Q 1,*, NAN X R 2, LI Z R 2 & LIU X L 1 1 Soybean Research Institute, Heilongjiang Academy of Agricultural
ABSTRACT: 25 DEVELOPMENT OF TRANSGENIC SOYBEAN PLANTS WITH SORGHUM C4-SPECIFIC PEPC GENE ZHANG Y 2, MAN W Q 1,*, NAN X R 2, LI Z R 2 & LIU X L 1 1 Soybean Research Institute, Heilongjiang Academy of Agricultural
Plasmid Midiprep Plus Purification Kit. Cat. # : DP01MD-P10/ DP01MD-P50 Size : 10/50 Reactions Store at RT For research use only
 Plasmid Midiprep Plus Purification Kit Cat. # : DP01MD-P10/ DP01MD-P50 Size : 10/50 Reactions Store at RT For research use only 1 Description: The Plasmid Midiprep Plus Purification Kit provides simple
Plasmid Midiprep Plus Purification Kit Cat. # : DP01MD-P10/ DP01MD-P50 Size : 10/50 Reactions Store at RT For research use only 1 Description: The Plasmid Midiprep Plus Purification Kit provides simple
GenepHlow Gel Extraction Kit
 Instruction Manual Ver. 02.10.17 For Research Use Only GenepHlow Gel Extraction Kit DFG004 (4 Preparation Sample Kit) DFG100 (100 Preparation Kit) DFG300 (300 Preparation Kit) Advantages Convenient: includes
Instruction Manual Ver. 02.10.17 For Research Use Only GenepHlow Gel Extraction Kit DFG004 (4 Preparation Sample Kit) DFG100 (100 Preparation Kit) DFG300 (300 Preparation Kit) Advantages Convenient: includes
Supplemental Materials. DNA preparation. Dehalogenimonas lykanthroporepellens strain BL-DC-9 T (=ATCC
 Supplemental Materials DNA preparation. Dehalogenimonas lykanthroporepellens strain BL-DC-9 T (=ATCC BAA-1523 = JCM 15061) was grown in defined basal medium amended with 0.5 mm 1,1,2- trichloroethane (1,1,2-TCA)
Supplemental Materials DNA preparation. Dehalogenimonas lykanthroporepellens strain BL-DC-9 T (=ATCC BAA-1523 = JCM 15061) was grown in defined basal medium amended with 0.5 mm 1,1,2- trichloroethane (1,1,2-TCA)
Guide-it Indel Identification Kit User Manual
 Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Guide-it Indel Identification Kit User Manual Cat. No. 631444 (120114) Clontech Laboratories, Inc. A Takara Bio Company 1290 Terra Bella Avenue, Mountain View, CA 94043, USA
Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Guide-it Indel Identification Kit User Manual Cat. No. 631444 (120114) Clontech Laboratories, Inc. A Takara Bio Company 1290 Terra Bella Avenue, Mountain View, CA 94043, USA
ChIP-chip protocol adapted for the mod-encode project
 ChIP-chip protocol adapted for the mod-encode project Version 1.2 : August 2007 Nicolas Nègre, Xiaochun Ni, Sergey Lavrov, Giacomo Cavalli and Kevin P. White University of Chicago, Department of Human
ChIP-chip protocol adapted for the mod-encode project Version 1.2 : August 2007 Nicolas Nègre, Xiaochun Ni, Sergey Lavrov, Giacomo Cavalli and Kevin P. White University of Chicago, Department of Human
Amplification and Labeling of DNA for Microarray Hybridization, using the Round A/B/C Random DNA Amplification Protocol
 Amplification and Labeling of DNA for Microarray Hybridization, using the Round A/B/C Random DNA Amplification Protocol Goal: To amplify and label DNA prior to hybridization to a microarray, in a relatively
Amplification and Labeling of DNA for Microarray Hybridization, using the Round A/B/C Random DNA Amplification Protocol Goal: To amplify and label DNA prior to hybridization to a microarray, in a relatively
MOLECULAR CLONING AND SEQUENCING OF FISH MPR 46
 MOLECULAR CLONING AND SEQUENCING OF FISH MPR 46 INTRODUCTION The mammalian MPR 46 (human, mouse, bovine) sequences show extensive homologies. Among the non-mammalian vertebrates, only a partial sequence
MOLECULAR CLONING AND SEQUENCING OF FISH MPR 46 INTRODUCTION The mammalian MPR 46 (human, mouse, bovine) sequences show extensive homologies. Among the non-mammalian vertebrates, only a partial sequence
Genetics module. DNA Structure, Replication. The Genetic Code; Transcription and Translation. Principles of Heredity; Gene Mapping
 Genetics module Lectures DNA Structure, Replication The Genetic Code; Transcription and Translation Principles of Heredity; Gene Mapping Controlling Gene Expression Mutation and Cancer Textbook: Introduction
Genetics module Lectures DNA Structure, Replication The Genetic Code; Transcription and Translation Principles of Heredity; Gene Mapping Controlling Gene Expression Mutation and Cancer Textbook: Introduction
Laboratory #7 PCR PCR
 1 Laboratory #7 Polymerase chain reaction () is DNA replication in a test tube. In vitro enzymatic amplification of a specific segment of DNA. Many Applications. direct cloning from DNA or cdna. Mutagenesis
1 Laboratory #7 Polymerase chain reaction () is DNA replication in a test tube. In vitro enzymatic amplification of a specific segment of DNA. Many Applications. direct cloning from DNA or cdna. Mutagenesis
TRANSPOSON INSERTION SITE VERIFICATION
 TRANSPOSON INSERTION SITE VERIFICATION Transposon and T-DNA insertion in Arabidopsis genes can be identified using the Arabidopsis thaliana Insertion Database (ATIdb) (http://atidb.org/cgi-perl/gbrowse/atibrowse).
TRANSPOSON INSERTION SITE VERIFICATION Transposon and T-DNA insertion in Arabidopsis genes can be identified using the Arabidopsis thaliana Insertion Database (ATIdb) (http://atidb.org/cgi-perl/gbrowse/atibrowse).
Table of Contents. PrimeScript TM RT-PCR Kit. I. Kit Contents...2. Storage...3. Principle...4. Features...5. V. Notes...5. Protocol...
 Table of Contents I. Kit Contents...2 II. III. IV. Storage...3 Principle...4 Features...5 V. Notes...5 VI. Protocol...6 VII. PCR Condition...8 VIII. Application...8 IX. Preparation of RNA sample...10 X.
Table of Contents I. Kit Contents...2 II. III. IV. Storage...3 Principle...4 Features...5 V. Notes...5 VI. Protocol...6 VII. PCR Condition...8 VIII. Application...8 IX. Preparation of RNA sample...10 X.
Supplementary Fig. 1. Isolation and in vitro expansion of EpCAM + cholangiocytes. For collagenase perfusion, enzyme solution was injected from the
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Isolation and in vitro expansion of EpCAM + cholangiocytes. For collagenase perfusion, enzyme solution was injected from the portal vein for digesting adult livers, whereas it was
Supplementary Fig. 1. Isolation and in vitro expansion of EpCAM + cholangiocytes. For collagenase perfusion, enzyme solution was injected from the portal vein for digesting adult livers, whereas it was
YeaStar Genomic DNA Kit Catalog No. D2002
 Instructions YeaStar Genomic DNA Kit Catalog No. D2002 Table of Contents General Information...... 1 Package Contents Ordering Information General Description...... 2 Protocol I.......... 2 Protocol II.
Instructions YeaStar Genomic DNA Kit Catalog No. D2002 Table of Contents General Information...... 1 Package Contents Ordering Information General Description...... 2 Protocol I.......... 2 Protocol II.
Supplemental Information. Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids. Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites. to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination
 Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 42 Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination Konstantina Skourti-Stathaki, Nicholas
Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 42 Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination Konstantina Skourti-Stathaki, Nicholas
4/26/2015. Cut DNA either: Cut DNA either:
 Ch.20 Enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences (restriction sites) resulting in segments of DNA (restriction fragments) Typically 4-8 bp in length & often palindromic Isolated from bacteria (Hundreds
Ch.20 Enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences (restriction sites) resulting in segments of DNA (restriction fragments) Typically 4-8 bp in length & often palindromic Isolated from bacteria (Hundreds
Supporting Information. Trifluoroacetophenone-Linked Nucleotides and DNA for Studying of DNA-protein Interactions by 19 F NMR Spectroscopy
 Supporting Information Trifluoroacetophenone-Linked Nucleotides and DNA for Studying of DNA-protein Interactions by 19 F NMR Spectroscopy Agata Olszewska, Radek Pohl and Michal Hocek # * Institute of Organic
Supporting Information Trifluoroacetophenone-Linked Nucleotides and DNA for Studying of DNA-protein Interactions by 19 F NMR Spectroscopy Agata Olszewska, Radek Pohl and Michal Hocek # * Institute of Organic
Detection limits of the strip test and PCR for genetically modified corn in Brazil
 Detection limits of the strip test and PCR for genetically modified corn in Brazil V.E. Nascimento, É.V.R. Von Pinho, R.G. Von Pinho and A.D. do Nascimento Júnior Departamento Agricultura, Universidade
Detection limits of the strip test and PCR for genetically modified corn in Brazil V.E. Nascimento, É.V.R. Von Pinho, R.G. Von Pinho and A.D. do Nascimento Júnior Departamento Agricultura, Universidade
DNA Technology. B. Using Bacteria to Clone Genes: Overview:
 DNA Technology A. Basic Vocabulary: is DNA from 2 different sources that is combined. is the direct manipulation of genes for practical purposes. literally means or in a test tube or flask. is the manipulation
DNA Technology A. Basic Vocabulary: is DNA from 2 different sources that is combined. is the direct manipulation of genes for practical purposes. literally means or in a test tube or flask. is the manipulation
STUDY OF VNTR HUMAN POLYMORPHISMS BY PCR
 STUDY OF VNTR HUMAN POLYMORPHISMS BY PCR Ref. PCR1 1. OBJECTIVE OF THE EXPERIMENT The objective of this experiment is to introduce students to the principles and practice of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
STUDY OF VNTR HUMAN POLYMORPHISMS BY PCR Ref. PCR1 1. OBJECTIVE OF THE EXPERIMENT The objective of this experiment is to introduce students to the principles and practice of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Non-Organic-Based Isolation of Mammalian microrna using Norgen s microrna Purification Kit
 Application Note 13 RNA Sample Preparation Non-Organic-Based Isolation of Mammalian microrna using Norgen s microrna Purification Kit B. Lam, PhD 1, P. Roberts, MSc 1 Y. Haj-Ahmad, M.Sc., Ph.D 1,2 1 Norgen
Application Note 13 RNA Sample Preparation Non-Organic-Based Isolation of Mammalian microrna using Norgen s microrna Purification Kit B. Lam, PhD 1, P. Roberts, MSc 1 Y. Haj-Ahmad, M.Sc., Ph.D 1,2 1 Norgen
DNA Technology. Asilomar Singer, Zinder, Brenner, Berg
 DNA Technology Asilomar 1973. Singer, Zinder, Brenner, Berg DNA Technology The following are some of the most important molecular methods we will be using in this course. They will be used, among other
DNA Technology Asilomar 1973. Singer, Zinder, Brenner, Berg DNA Technology The following are some of the most important molecular methods we will be using in this course. They will be used, among other
