What is ecology? Study of organisms and their interactions with each other and their environments
|
|
|
- Bertram Powell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 What is ecology? Study of organisms and their interactions with each other and their environments The interaction of biotic and abiotic factors Ecosystems
3 Why do we pursue the study of ecology? Preserve our natural resources Understand how human impacts affect: The survival of species The diversity of ecosystems The balance of global cycles Because we are curious about how nature works!
4 Ecosystems are made up of Communities Population Group of individuals of the same species residing in a defined habitat Community Groups of populations residing in a defined habitat, interacting with one another
5 Evolution and ecology are linked through natural selection Populations are larger than environment can support Not all individuals in the population will survive Those that do survive must have advantages (in their genes!) over those that don t The survivors pass on their genes to the next generation
6 How do organisms survive in their environments? Adaptations are inherited traits that improve the ability of individuals to survive in the environment They are advantageous characteristics that vary among individuals in a population They can be structural, behavioral, physiological Camouflage in frog fish Schooling behavior in fishes Salinity tolerance of mangrove plants
7 Biodiversity is important It is the number of different species and their abundance in a particular community Healthy communities have high biodiversity Lots of species High abundance of individual species
8 Which coral reef is healthier? Why?
9 How are coral reefs important to Hawaiian culture? They provide food Fish Invertebrates Algae (limu) They provide materials Coral for building Algae for medicine (limu kala) Shells for decoration and lure making Shark teeth for weaponry Whale bone/teeth worn by the Ali i
10
11 Hawaiians were excellent ecologists! They maintained healthy ecosystems because they knew there was a balance to nature They knew they were not separate from nature If you care for nature, nature will take care of you!
12
13 What is a reef building coral? Simple animal related to sea jellies and anemones Forms a symbiotic relationship with single celled alga called zooxanthellae Forms colonies Secretes calcium carbonate skeletons, the foundation of coral reef ecosystems
14 Where do reef building corals live? Shallow, clear, warm waters where their algal symbionts can photosynthesize
15 This is a coral colony, what do you notice?
16 WHAT IS A CORAL? A closer look reveals separate colonies of coral on the reef This is a typical Hawaiian reef Coral is an ANIMAL that has a plant (ALGAE) living inside it s cells, and together they form the calcium carbonate (MINERAL) reef structure that is the foundation of the coral reef ecosystem Each colony has many coral individuals, all of them identical clones within the colony Each individual coral animal is called a polyp, the brown/green specs inside the polyp tissue are actually the symbiotic algae or zooxanthellae
17 CORAL FACTS Corals have a simple body plan tentacles mouth stomach skeleton Reefs are living structures that can be seen from space! The algae/coral symbiosis allows these corals to grow massive reef structures, and is also why reefs are found in shallow (<300 feet), clear waters. The Great Barrier Reef in Australia ab out/biology/ Zooxanthellae live inside the cells of reef building coral and through photosynthesis provide 95% of the corals metabolic needs. g/m dr/bleac hed Coral.jpg ea.com.au/im ages/ GBR_NASA.jpg Coral bleaching is a stress response by both the coral and the algae that results in a breakdown of their symbiotic partnership. If the algae do not return to high enough densities within the coral cells soon after the bleaching episode, the coral will die.
18 Coral Colonies All polyps in one colony are genetically identical, which makes them clones.
19 Anatomy of coral polyp
20 The symbiosis Corals give up nutrients (waste) to the algae and the algae give food and Oxygen to corals
21 Benefits to the Coral Host Higher rates of calcification (skeleton deposition). Energy and materials for growth, repair, and reproduction. Removal of chemical wastes from animal metabolism (nutrient recycling). Receive chemicals that absorb damaging ultraviolet light.
22 Benefits to the Algal Symbiont Chemical wastes from animal metabolism are important inorganic nutrients for plants (nutrient recycling). Protection on the reef and from UV light. The zooxanthellae, non-motile single cells, get a place to live in the crowded reef environment.
23 Coral Feeding: some reef building corals eat occasionally Using nematocysts, which are stinging cells on their tentacles
24 Coral colonies make different forms
25
26 This is a Hawaiian reef community, what do you see?
27 How does a coral reef grow? Reef Growth is a balance between Construction and Erosion Construction Steps: Framework Building: corals Sediment Production: algae, shells, protists Cementation: encrusting coral and encrusting algae
28 Corals build the framework, sediment provides living space and food resources, and encrusting algae and corals cement the reef together
29 Encrusting coral also helps cement reef together J. Hoover J. Hoover
30 Erosion breaks down the reef Mechanical: storm events, waves, gravity Biological: animals that bore into or scrape the reef Chemical: with increasing acidity of ocean waters, the reefs could start to dissolve!
31 Mechanical erosion w Storms w Run off
32 Storm Wave Damage Before After
33 Storm Damage
34 Stream and River Runoff increases nutrients and sediments in the water
35 Freshwater from heavy rains can damage corals
36 Bioerosion: Browsers Those who rasp or scrape the surface to consume material growing on top of coral. Invertebrates: Sponges and Urchins Parrotfish
37 Bioerosion: Grazers Those who consume plant material down to, and often including, the coral Corallivorous Fishes Crown-of-Thorns Seastar (Acanthaster)
38 Chemical erosion Increasing ocean acidity can reduce the growth potential of reefs This can result in fragile reefs that more easily break during storm events Other calcifying organisms can sustain reduced growth and also be affected
39 Coral reef bleaching When corals loose their algal symbionts If they cannot regain their symbionts, the corals will die Stress causes bleaching, causes include: High temperatures Pollution Sedimentation Disease
40 Bleaching is when the algae leave the coral
41 Reef growth As long as construction outpaces erosion the reef will continue to grow What conditions promote optimal growth?
42 Factors Correlated with Healthy Coral Reef Growth wwater Temperature Range: C wnormal Seawater Salinity: wlow Inorganic Nutrient Concentration wclear, Transparent Water wlittle or No Sedimentation wvigorous Water Motion
43 Fringing Barrier Atolls
44 Fringing Reefs
45 Barrier Reef Lagoon Systems
46 Coral Atolls
47 Coral Atoll Formation: a sinking island surrounded by living coral
48
49
50 Ecological Role of Corals in Coral Reefs w Provide habitats for reef organisms w Porous framework w Solid substrate for attachment w Source of sand w Absorb wave energy w Provide food for corallivorous animals
51 Ecological Role of Corals in Coral Reefs w Absorb inorganic nutrients from the water w Feed on organic detritus and zooplankton w Compete with other organisms (and with each other) for space and light
52 Corals form the foundation of the coral reef ecosystem Coral reefs are much more than aggregations of coral
53 Herbivores w Some fish w Some snails and sea hares w Sea urchins w Green sea turtles w They eat the algae on the reef, keep it from overgrowing corals and other organisms that can t move (sessile). w Keep substrate clear for recruitment of sessile organisms.
54 Parrotfishes w They eat the algae on or zoox in corals w Important bioeroders: poop out crushed up coral skeleton
55 Surgeonfishes w Macroalgae eaters w Some form schools Hoover, J.P., 1993 Hoover, J.P., 1993 Hoover, J.P., 1993
56 Sea urchins w Importantmacroalgae eaters on the reef! w Can be seen in day but come out in the evening to graze Hoover, J.P., 1998
57 Green sea turtle w Also major grazer on the reef w Filamentous algae from shore to shallow reefs
58 Corallivores w Butterfly fishes w Many species feed on corals w Shape of mouth determines feeding style w Tearers: Threadfin w Pickers: Multiband w Biters: Ornate
59 Corallivores w Crown of thornes sea star w BIG sea star with toxic spines w Extrudes stomach onto coral head w Symbiotic crabs and shrimp can pinch it away w Triton s trumpet snail eats these guys Outbreaks can devastate reefs
60 Mucus feeders w Symbiotic crabs and shrimps: gall, trapezid crabs and alpheid shrimp w Protect coral from predators w In turn feed on coral mucus that is rich in high energy molecules w They receive protection from living in coral
61 Planktivores w Pickers selectively pick zooplankton from water column w Strainers are non selective feeders w sergeant major mam0
62 Piscivores Predators of fish Ambush predators Fish chasers Fish stalkers
63 Omnivores and scavengers w Omnivores: eat a variety of things: algae, fish, inverts etc w Filefish, pufferfish, trunkfish w Scavengers: Clean up the reef of dead or dying debris w Lobsters, shrimps, crabs, sharks, wrasses
64 Filter Feeders Passively feed on plankton in the water column
65 Detritivores w Sift through sand and sediments and clean it of decomposing organic material and nutrients
66 Symbioses on the reef w Obligate: one symbiont cannot live without the other w Corals and their symbiotic algae; Hawaiian cleaner wrasse
67 Symbioses on the reef w Facultative: usually found together in nature but can survive without one another
68 Coral Competition Corals compete for space and light They can grow over one another or shade one another They can attack neighbors with nemaotcysts
69 Overgrowth and Shading
70 dead zone Competing Corals
71 Coral reef ecosystems Are extremely diverse and dynamic ecosystems! They provide humans with: Food Income from tourism and fishing Coastal protection from storms Medicine potential from the diversity of organisms And much more!
72
73 Coral reef ecosystems are under threat! Over fishing Destructive fishing practices Climate change: increase temps and acidity Pollution Sedimentation Over exploitation Resource extraction
74
75
Coral Reefs: More than Beautiful. Jennifer Miselis University of South Carolina Program of Marine Science
 Coral Reefs: More than Beautiful Jennifer Miselis University of South Carolina Program of Marine Science Phylum: Classification of Corals Cnidaria Class(4): Anthozoa Hydrozoa Cubozoa Cubozoa Subclass(3):
Coral Reefs: More than Beautiful Jennifer Miselis University of South Carolina Program of Marine Science Phylum: Classification of Corals Cnidaria Class(4): Anthozoa Hydrozoa Cubozoa Cubozoa Subclass(3):
We didn t plan to talk about it, but since you asked... Here s some information on the health of the world s coral reefs.
 We didn t plan to talk about it, but since you asked... Here s some information on the health of the world s coral reefs. What is coral? What most people picture when the think of coral is actually just
We didn t plan to talk about it, but since you asked... Here s some information on the health of the world s coral reefs. What is coral? What most people picture when the think of coral is actually just
Chapter 2. Global and Local Impacts. Close-up of bleached fire coral after oiling during the Bahía las Minas spill in Panama (Arcadio Rodaniche)
 Chapter 2. Global and Local Impacts Close-up of bleached fire coral after oiling during the Bahía las Minas spill in Panama (Arcadio Rodaniche) 18 Oil Spills in Coral Reefs: Planning and Response Considerations
Chapter 2. Global and Local Impacts Close-up of bleached fire coral after oiling during the Bahía las Minas spill in Panama (Arcadio Rodaniche) 18 Oil Spills in Coral Reefs: Planning and Response Considerations
6 TH. Most of the Earth Is Covered with Water (2) Most Aquatic Species Live in Top, Middle, or Bottom Layers of Water (1)
 A Healthy Coral Reef in the Red Sea MILLER/SPOOLMAN ESSENTIALS OF ECOLOGY 6 TH Chapter 8 Aquatic Biodiversity Fig. 8 1, p. 168 Most of the Earth Is Covered with Water (2) Aquatic life zones Saltwater life
A Healthy Coral Reef in the Red Sea MILLER/SPOOLMAN ESSENTIALS OF ECOLOGY 6 TH Chapter 8 Aquatic Biodiversity Fig. 8 1, p. 168 Most of the Earth Is Covered with Water (2) Aquatic life zones Saltwater life
We didn t plan to talk about it, but since you asked... Here s some information on the health of the world s coral reefs.
 We didn t plan to talk about it, but since you asked... Here s some information on the health of the world s coral reefs. What is coral? What most people picture when the think of coral is actually just
We didn t plan to talk about it, but since you asked... Here s some information on the health of the world s coral reefs. What is coral? What most people picture when the think of coral is actually just
Climate Change and Coral Bleaching
 Rising ocean temperatures may push coral reefs to their limits. Climate Change and Coral Bleaching http://www.nova.org.au/coral-bleaching Essentials! Corals are animals that live in a mutually beneficial
Rising ocean temperatures may push coral reefs to their limits. Climate Change and Coral Bleaching http://www.nova.org.au/coral-bleaching Essentials! Corals are animals that live in a mutually beneficial
Coral Reefs- A Challenging Ecosystem for Human Societies* B. Salvat Originally published in Global Environmental Change, 1992, vol. 2, pp.
 Coral Reefs- A Challenging Ecosystem for Human Societies* B. Salvat Originally published in Global Environmental Change, 1992, vol. 2, pp. 12-18 18 Presented by: Amy Dewees & Melissa Parente What is coral?
Coral Reefs- A Challenging Ecosystem for Human Societies* B. Salvat Originally published in Global Environmental Change, 1992, vol. 2, pp. 12-18 18 Presented by: Amy Dewees & Melissa Parente What is coral?
Chapter 6. Aquatic Biodiversity. Chapter Overview Questions
 Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
Background. Tropical Communities. Worldwide distributions. Main Players. Coralline Algae
 1 Tropical Communities 2 Background Occupy less than 0.2% of planet, yet Have upwards of 5% of all species Use 50% of CaCO 3 and with it, CO 2 to build reefs; around 700 billion kg/year Very productive
1 Tropical Communities 2 Background Occupy less than 0.2% of planet, yet Have upwards of 5% of all species Use 50% of CaCO 3 and with it, CO 2 to build reefs; around 700 billion kg/year Very productive
Coral Reefs and Climate Change
 and Populations oral Reefs and limate hange 1 There are many different types of environments on the planet, and often many ecosystems within each environment. Ecosystems all contain a balance of abiotic
and Populations oral Reefs and limate hange 1 There are many different types of environments on the planet, and often many ecosystems within each environment. Ecosystems all contain a balance of abiotic
Student Exploration: Coral Reefs 1 Abiotic Factors
 Name: Date: Per. Student Exploration: Coral Reefs 1 Abiotic Factors Vocabulary: consumer, coral, coral bleaching, coral reef, filter feeder, food chain, food web, grazer, nutrients, ocean acidification,
Name: Date: Per. Student Exploration: Coral Reefs 1 Abiotic Factors Vocabulary: consumer, coral, coral bleaching, coral reef, filter feeder, food chain, food web, grazer, nutrients, ocean acidification,
Freshwater ecosystems
 Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
Marine lifestyles and relationships
 Marine lifestyles and relationships Marine Lifestyles and Enviros. Benthic organisms (benthos) live on or buried in the ocean floor (sediment) Can be sessile (attached) or mobile (moving) Pelagic organisms
Marine lifestyles and relationships Marine Lifestyles and Enviros. Benthic organisms (benthos) live on or buried in the ocean floor (sediment) Can be sessile (attached) or mobile (moving) Pelagic organisms
Gas Guzzlers. Biological Pump
 Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
AP Environmental Science
 AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
Coral Reef Communities. College of Marine Sciences, Shanghai Ocean University
 Coral Reef Communities Coral Reef Animal, vegetable or mineral? It s an animal which may live with a plant and makes a mineralbased skeleton. Illustration by Geoff Kelley in JEN Veron (2000) Corals of
Coral Reef Communities Coral Reef Animal, vegetable or mineral? It s an animal which may live with a plant and makes a mineralbased skeleton. Illustration by Geoff Kelley in JEN Veron (2000) Corals of
COMMUNITY ECOLOGY. Interspecific Interactions. Ecosystems unit
 COMMUNITY ECOLOGY Ecosystems unit Today s Big Ideas: An organism s biotic environment includes Other individuals in its own population Populations of other species living in the same area An assemblage
COMMUNITY ECOLOGY Ecosystems unit Today s Big Ideas: An organism s biotic environment includes Other individuals in its own population Populations of other species living in the same area An assemblage
Coral reefs. Coral reef ecosystems. Why are reefs important? Coastal ecosystems and ecosystem services
 Coral reef ecosystems Coral reefs What are corals, what are reefs? Ecology Human stresses History of climate and human stresses Why are reefs important? Biodiversity Shoreline protection Nurse juvenile
Coral reef ecosystems Coral reefs What are corals, what are reefs? Ecology Human stresses History of climate and human stresses Why are reefs important? Biodiversity Shoreline protection Nurse juvenile
Inquiry into Australia s biodiversity in a changing climate. 1. Terrestrial, marine and freshwater biodiversity in Australia and its territories
 Inquiry into Australia s biodiversity in a changing climate Submission from the Australian Coral Reef Society 1. Terrestrial, marine and freshwater biodiversity in Australia and its territories Reefs and
Inquiry into Australia s biodiversity in a changing climate Submission from the Australian Coral Reef Society 1. Terrestrial, marine and freshwater biodiversity in Australia and its territories Reefs and
Ocean Acidification Threatens Marine Ecosystems and Livelihood Security in Bangladesh
 Ocean Acidification Threatens Marine Ecosystems and Livelihood Security in Bangladesh M. Shahadat Hossain, S. M. Sharifuzzaman, Sayedur R Chowdhury, Subrata Sarker and Shah Nawaz Chowdhury Institute of
Ocean Acidification Threatens Marine Ecosystems and Livelihood Security in Bangladesh M. Shahadat Hossain, S. M. Sharifuzzaman, Sayedur R Chowdhury, Subrata Sarker and Shah Nawaz Chowdhury Institute of
Chapter 36: Population Growth
 Chapter 36: Population Growth Population: Population Concepts interbreeding group of same species Carrying Capacity: maximum population size an ecosystem can sustainably support Critical Number: minimum
Chapter 36: Population Growth Population: Population Concepts interbreeding group of same species Carrying Capacity: maximum population size an ecosystem can sustainably support Critical Number: minimum
Ecology. Limiting factors. Introduction to Marine Ecology. Ecological communities and ecosystems
 Introduction to Marine Ecology Physical limiting factors light, temperature, salinity, nutrients, gases variation within the ocean: depth and geography Marine habitats: where to make a living Marine feeding
Introduction to Marine Ecology Physical limiting factors light, temperature, salinity, nutrients, gases variation within the ocean: depth and geography Marine habitats: where to make a living Marine feeding
Coral Reefs. 1 of 5. An Ocean of Trouble
 This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Article Coral Reefs An Ocean of
This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Article Coral Reefs An Ocean of
Chapter 2 Interactions in Ecosystems
 Chapter 2 Interactions in Ecosystems Key Ideas Living things are connected to each other in complex interrelationships. Biotic and abiotic factors are responsible for shaping a community of living things.
Chapter 2 Interactions in Ecosystems Key Ideas Living things are connected to each other in complex interrelationships. Biotic and abiotic factors are responsible for shaping a community of living things.
American Samoa Coral Reefs
 American Samoa Coral Reefs Climate Change Vulnerability Assessment Summary An Important Note About this Document: This document represents an initial evaluation of vulnerability for coral reefs based on
American Samoa Coral Reefs Climate Change Vulnerability Assessment Summary An Important Note About this Document: This document represents an initial evaluation of vulnerability for coral reefs based on
2 Marine Ecosystems. Math Focus
 CHAPTER 3 2 Marine Ecosystems SECTION The Earth s Ecosystems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What abiotic factors affect marine ecosystems? What
CHAPTER 3 2 Marine Ecosystems SECTION The Earth s Ecosystems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What abiotic factors affect marine ecosystems? What
Ecology Chapter 11: Marine
 Ecology Chapter 11: Marine 1 I. Oceans made up of all waters between continents The World Ocean because waters are interconnected can be thought of as one large biome with many different ecosystems and
Ecology Chapter 11: Marine 1 I. Oceans made up of all waters between continents The World Ocean because waters are interconnected can be thought of as one large biome with many different ecosystems and
CORAL REEFS. Coral reefs are home to many organisms Provide habitat and shelter for 25 percent of all fish species in the deeper parts of the ocean.
 CORAL REEFS We have looked at the development of coral reefs starting with a volcanic island on which coral starts to appear. Coral is a kind of animal that needs to be in water. Being an animal, it also
CORAL REEFS We have looked at the development of coral reefs starting with a volcanic island on which coral starts to appear. Coral is a kind of animal that needs to be in water. Being an animal, it also
NOAA: The Heat is ON! Climate Change and Coral Reef Ecosystems
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP NOAA: The Heat is ON! Climate Change and Coral Reef Ecosystems Coral Bleaching Dr. Mark Eakin Thursday, April 30, 2009 Coral Bleaching 101 Presented by Mark Eakin
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP NOAA: The Heat is ON! Climate Change and Coral Reef Ecosystems Coral Bleaching Dr. Mark Eakin Thursday, April 30, 2009 Coral Bleaching 101 Presented by Mark Eakin
Food Chains, Food Webs, and the Transfer of Energy
 Food Chains, Food Webs, and the Transfer of Energy What is Ecology? Ecology is the scientific study of interactions between different organisms and between organisms and their environment or surroundings
Food Chains, Food Webs, and the Transfer of Energy What is Ecology? Ecology is the scientific study of interactions between different organisms and between organisms and their environment or surroundings
Unit 2 RELEVANCE OF ECOLOGY TO MARINE ECOTOURISM DEVELOPMENT
 Unit 2 RELEVANCE OF ECOLOGY TO MARINE ECOTOURISM DEVELOPMENT Objectives At the completion of this unit, you will be able to: Understand the fundamentals of coral reef ecology Identify threats to reef health
Unit 2 RELEVANCE OF ECOLOGY TO MARINE ECOTOURISM DEVELOPMENT Objectives At the completion of this unit, you will be able to: Understand the fundamentals of coral reef ecology Identify threats to reef health
Energy Flow & Nutrient Cycle 8/25/2015
 It involves understanding biotic and abiotic factors influencing the distribution and abundance of living things. Biotic Factors Competitors Disease Predators Food availability Habitat availability Symbiotic
It involves understanding biotic and abiotic factors influencing the distribution and abundance of living things. Biotic Factors Competitors Disease Predators Food availability Habitat availability Symbiotic
CHAPTER 2: PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY 11/29/16
 CHAPTER 2: PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY 11/29/16 Ecology The scientific discipline in which the relationship among living organisms and their interactions with their environments are studied. Scientist who study
CHAPTER 2: PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY 11/29/16 Ecology The scientific discipline in which the relationship among living organisms and their interactions with their environments are studied. Scientist who study
Chapter 12 & 13. Interactions of life The Nonliving Environment
 Chapter 12 & 13 Interactions of life The Nonliving Environment BIOSPHERE Biosphere - the part of the Earth that supports life. This includes the top portion of Earth s crust, all the waters that cover
Chapter 12 & 13 Interactions of life The Nonliving Environment BIOSPHERE Biosphere - the part of the Earth that supports life. This includes the top portion of Earth s crust, all the waters that cover
Bleaching Coral Reefs and Ocean Acidification. By Rachel Gallaher
 Bleaching Coral Reefs and Ocean Acidification By Rachel Gallaher Warming Oceans, Increasing Acidification About 25% of all CO2 released from anthropogenic sources enters the ocean where it then reacts
Bleaching Coral Reefs and Ocean Acidification By Rachel Gallaher Warming Oceans, Increasing Acidification About 25% of all CO2 released from anthropogenic sources enters the ocean where it then reacts
Ecology- The environment consists of 2 factors. vs. Energy in Ecosystems
 Ecology- Ecosystem- An area where living things interact Ex: Big= Ocean, desert Small- Puddle, rotten log Study of living things in their environment Community- Name: Habitat- Organisms in an ecosystem
Ecology- Ecosystem- An area where living things interact Ex: Big= Ocean, desert Small- Puddle, rotten log Study of living things in their environment Community- Name: Habitat- Organisms in an ecosystem
4/28/2013. Transmission of Light in Seawater. Color in the Ocean Color of ocean ranges from deep blue to yellow-green Factors Turbidity from runoff
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer Chapter summary in haiku form Primary produce Sunlight and phytoplankton Ocean is garden Chapter Overview Productivity
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer Chapter summary in haiku form Primary produce Sunlight and phytoplankton Ocean is garden Chapter Overview Productivity
Ecology Module B, Anchor 4
 Ecology Module B, Anchor 4 Key Concepts: - The biological influences on organisms are called biotic factors. The physical components of an ecosystem are called abiotic factors. - Primary producers are
Ecology Module B, Anchor 4 Key Concepts: - The biological influences on organisms are called biotic factors. The physical components of an ecosystem are called abiotic factors. - Primary producers are
Freshwater Ecosystems
 Aquatic Ecosystems Freshwater Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are mainly determined by the water s salinity. As a result, aquatic ecosystems are divided into freshwater and marine
Aquatic Ecosystems Freshwater Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are mainly determined by the water s salinity. As a result, aquatic ecosystems are divided into freshwater and marine
biology Slide 1 of 39 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 biology 1 of 39 2 of 39 4-4 Aquatic Ecosystems Nearly three-fourths of the Earth s surface is covered with water. Almost all bodies of water contain a wide variety of communities governed by biotic and
biology 1 of 39 2 of 39 4-4 Aquatic Ecosystems Nearly three-fourths of the Earth s surface is covered with water. Almost all bodies of water contain a wide variety of communities governed by biotic and
4-4 Aquatic Ecosystems
 biology 1 of 39 2 of 39 Nearly three-fourths of the Earth s surface is covered with water. Almost all bodies of water contain a wide variety of communities governed by biotic and abiotic factors including
biology 1 of 39 2 of 39 Nearly three-fourths of the Earth s surface is covered with water. Almost all bodies of water contain a wide variety of communities governed by biotic and abiotic factors including
Ocean Acidification. Bibliography:
 When ecosystems undergo change it can have dramatic effects on the competition between species, food web dynamics and biodiversity. Ecosystems can undergo change by the addition of carbon dioxide into
When ecosystems undergo change it can have dramatic effects on the competition between species, food web dynamics and biodiversity. Ecosystems can undergo change by the addition of carbon dioxide into
Bio 112 Ecology: Final Practice Exam Multiple Choice
 Final Exam Topics: 1) Basic Ecological Principles a) Biomes, ecosystems, communities and populations i) Biomes: know the major ones and where they occur ii) Ecosystem: communities and physical environment
Final Exam Topics: 1) Basic Ecological Principles a) Biomes, ecosystems, communities and populations i) Biomes: know the major ones and where they occur ii) Ecosystem: communities and physical environment
3-1 What is Ecology?! The study of the. interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment
 Chapters 3,4 & 5 1 3-1 What is Ecology? The study of the interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment 2 Levels of Ecological Organization 3 3-2 Energy Flow main source of energy
Chapters 3,4 & 5 1 3-1 What is Ecology? The study of the interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment 2 Levels of Ecological Organization 3 3-2 Energy Flow main source of energy
1. All the interconnected feeding relationships in an ecosystem make up a food. a. Interaction b. Chain c. Network d. Web
 Ecology Unit Test DO NOT WRITE ON TEST!!! Take a deep breath, take your time, and make sure you understand exactly what the question is asking you. For true/false, fill in the correct bubble ( A for true
Ecology Unit Test DO NOT WRITE ON TEST!!! Take a deep breath, take your time, and make sure you understand exactly what the question is asking you. For true/false, fill in the correct bubble ( A for true
Freshwater Ecosystems
 Freshwater Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are mainly determined by the water s salinity. As a result, aquatic ecosystems are divided into freshwater and marine ecosystems. Freshwater
Freshwater Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are mainly determined by the water s salinity. As a result, aquatic ecosystems are divided into freshwater and marine ecosystems. Freshwater
Unit One Hydrodynamics. Adapted Animals
 Adapted Animals Lesson Objectives: Students will be able to do the following: Describe two food gathering mechanisms of animals in seagrass beds Compare and contrast features of sessile and motile organisms
Adapted Animals Lesson Objectives: Students will be able to do the following: Describe two food gathering mechanisms of animals in seagrass beds Compare and contrast features of sessile and motile organisms
STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems
 Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
SY 2018/ st Final Term Revision. Student s Name: Grade: 10A/B. Subject: Biology
 SY 2018/2019 1 st Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 10A/B Subject: Biology Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to
SY 2018/2019 1 st Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 10A/B Subject: Biology Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to
Unit 2: Ecology. Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology
 Unit 2: Ecology Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology Ecology Probe: Answer the questions and turn it in! This is a standard aquarium with a population of fish. There is no filter in this aquarium and no one
Unit 2: Ecology Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology Ecology Probe: Answer the questions and turn it in! This is a standard aquarium with a population of fish. There is no filter in this aquarium and no one
1. Understand the causes of permanent, seasonal and daily thermoclines in seas and oceans, and their ecological consequences.
 1 Ecosystems & Ecophysiology Lecture 7 Shallow seas Objectives 1. Understand the causes of permanent, seasonal and daily thermoclines in seas and oceans, and their ecological consequences. 2. Describe
1 Ecosystems & Ecophysiology Lecture 7 Shallow seas Objectives 1. Understand the causes of permanent, seasonal and daily thermoclines in seas and oceans, and their ecological consequences. 2. Describe
CORAL REEF CONSERVATION LESSON PLAN A Reef of Your Own
 Coral Reef Conservation CORAL REEF CONSERVATION LESSON PLAN A Reef of Your Own Theme Coral Reef Biology Links to Overview Essays and Resources Needed for Student Research http://oceanservice.noaa.gov/topics/ocean/coralreefs
Coral Reef Conservation CORAL REEF CONSERVATION LESSON PLAN A Reef of Your Own Theme Coral Reef Biology Links to Overview Essays and Resources Needed for Student Research http://oceanservice.noaa.gov/topics/ocean/coralreefs
What is Ecology? Includes land, air, and water as well as life. Living organisms are NOT distributed uniformly throughout the biosphere.
 Ecology What is Ecology? Ecology is the study of the interactions of organisms with one another and with their physical environment. Biosphere - part of the Earth in which life exists. Includes land, air,
Ecology What is Ecology? Ecology is the study of the interactions of organisms with one another and with their physical environment. Biosphere - part of the Earth in which life exists. Includes land, air,
Part IV Living World
 Part IV Living World Definition: a community of living organisms interacting with one another and with the nonliving components in their habitat. Population Community Individual Ecosystem Food Definition:
Part IV Living World Definition: a community of living organisms interacting with one another and with the nonliving components in their habitat. Population Community Individual Ecosystem Food Definition:
Climate change and the ocean
 Climate change and the ocean Hurricane intensification Sea level rise, loss of coral reefs Global conveyor belt Could less sea ice formation + melting Greenland ice sheet stop thermohaline circulation?
Climate change and the ocean Hurricane intensification Sea level rise, loss of coral reefs Global conveyor belt Could less sea ice formation + melting Greenland ice sheet stop thermohaline circulation?
Part I: Salish Sea Introduction. Review:
 Part I: Salish Sea Introduction Review: The Salish Sea The Salish Sea was formed about 20,000 years ago during the last ice age by the carving action of glaciers. There are 3 major parts of the Salish
Part I: Salish Sea Introduction Review: The Salish Sea The Salish Sea was formed about 20,000 years ago during the last ice age by the carving action of glaciers. There are 3 major parts of the Salish
4/13/2015. The Biosphere
 The Biosphere Ecology- the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment. The word ecology was first used in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel. Biosphere- contains the
The Biosphere Ecology- the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment. The word ecology was first used in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel. Biosphere- contains the
Intertidal Ecology. Key concepts: intertidal zones, nutrient upwelling, desiccation, holdfasts, water vascular systems, larval recruitment
 Intertidal Ecology Lesson Objectives: Students will be able to do the following: Describe the rocky intertidal zone Differentiate between the four intertidal zones Explain one way that physical processes
Intertidal Ecology Lesson Objectives: Students will be able to do the following: Describe the rocky intertidal zone Differentiate between the four intertidal zones Explain one way that physical processes
Ecology Energy Flow Ecosystem Structure Interactions Among Species Population Dynamics Reproductive Patterns
 Ecology Energy Flow Ecosystem Structure Interactions Among Species Population Dynamics Reproductive Patterns Ecology is a study of connections in nature. How organisms interact with one another and with
Ecology Energy Flow Ecosystem Structure Interactions Among Species Population Dynamics Reproductive Patterns Ecology is a study of connections in nature. How organisms interact with one another and with
In a community, each species cares about two things:
 Chapter 45 Communities are groups of populations that interact with each other Communities rely on two different things: Composition: the actual species in a community Diversity: the number of different
Chapter 45 Communities are groups of populations that interact with each other Communities rely on two different things: Composition: the actual species in a community Diversity: the number of different
Climate change and the ocean. Climate change and the ocean. Change in ocean currents. Change in ocean currents. Global conveyor belt
 Climate change and the ocean Climate change and the ocean Avg Pacific and Indian Hurricane intensification, loss of coral reefs Atlantic Ocean Mean concentration of anthropogenic carbon as of 1994 in μmol/kg
Climate change and the ocean Climate change and the ocean Avg Pacific and Indian Hurricane intensification, loss of coral reefs Atlantic Ocean Mean concentration of anthropogenic carbon as of 1994 in μmol/kg
The Biosphere Chapter 3. What Is Ecology? Section 3-1
 The Biosphere Chapter 3 What Is Ecology? Section 3-1 Interactions and Interdependence Ecology is the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings.
The Biosphere Chapter 3 What Is Ecology? Section 3-1 Interactions and Interdependence Ecology is the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings.
OCEANOGRAPHY Chapter 13
 OCEANOGRAPHY Chapter 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer part 3: Regional Productivity Energy and Nutrients in Marine Ecosystems, Fisheries Notes from the textbook, integrated with original
OCEANOGRAPHY Chapter 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer part 3: Regional Productivity Energy and Nutrients in Marine Ecosystems, Fisheries Notes from the textbook, integrated with original
A consumer that eats secondary consumers is a tertiary, or third level, consumer. Snakes and hawks are often the tertiary consumers in a food chain.
 Your muscles use energy to help you move, and your nervous system uses energy to help you understand the world around you. But how does your body obtain and use this energy? Animals, including humans,
Your muscles use energy to help you move, and your nervous system uses energy to help you understand the world around you. But how does your body obtain and use this energy? Animals, including humans,
Aquatic Biome. Book. Saltwater Marsh. Anthropogenic Influence. Examples. Producers Consumers Abiotic Factors
 Aquatic Biome Use the provided pieces to complete this book. Glue the appropriate pieces for each biome into the book. Use the internet to help you. Book Saltwater Marsh Freshwater Marsh Bog Lakes and
Aquatic Biome Use the provided pieces to complete this book. Glue the appropriate pieces for each biome into the book. Use the internet to help you. Book Saltwater Marsh Freshwater Marsh Bog Lakes and
ECOLOGY. Lesson 1 Biotic & Abiotic factors Levels of Organization Ecosystem Requirements
 ECOLOGY Lesson 1 Biotic & Abiotic factors Levels of Organization Ecosystem Requirements Living Non-Living Biotic Factors Abiotic Factors Circle of Life (clip from Lion King) Ecology the study of the relationships
ECOLOGY Lesson 1 Biotic & Abiotic factors Levels of Organization Ecosystem Requirements Living Non-Living Biotic Factors Abiotic Factors Circle of Life (clip from Lion King) Ecology the study of the relationships
Climate change in Hawaii and U.S. tropical islands
 Climate change in Hawaii and U.S. tropical islands By U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.31.17 Word Count 1,092 Level 1030L A sea turtle is seen swimming above a reef
Climate change in Hawaii and U.S. tropical islands By U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.31.17 Word Count 1,092 Level 1030L A sea turtle is seen swimming above a reef
Notes: Ocean Environments and Food Webs. Source: CMAPP
 Notes: Ocean Environments and Food Webs Source: CMAPP What lives in the ocean? 95% of ocean is unexplored! Known organisms are put into 3 groups: bottom dwellers live on the sea floor/bottom (seaweed,
Notes: Ocean Environments and Food Webs Source: CMAPP What lives in the ocean? 95% of ocean is unexplored! Known organisms are put into 3 groups: bottom dwellers live on the sea floor/bottom (seaweed,
We must protect aquatic life zones from the pollutants, water controls, and deterioration that we press upon them every day.
 Chapter 8 Aquatic Biodiversity Summary 1. The basic types of aquatic life zones are the surface, middle, and bottom layers. The life in aquatic life zones is influenced by temperature, access to sunlight
Chapter 8 Aquatic Biodiversity Summary 1. The basic types of aquatic life zones are the surface, middle, and bottom layers. The life in aquatic life zones is influenced by temperature, access to sunlight
How Ecosystems Work: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles
 How Ecosystems Work: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles Bubble in your ID and the answer to the 25 questions. You can look up the answers to these question on line. 1. The flow of solar energy through an
How Ecosystems Work: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles Bubble in your ID and the answer to the 25 questions. You can look up the answers to these question on line. 1. The flow of solar energy through an
Lesson Overview 4.5 Aquatic Ecosystems
 Lesson Overview 4.5 Conditions Underwater What factors affect life in aquatic ecosystems? Aquatic organisms are affected primarily by the water s depth, temperature, flow, and amount of dissolved nutrients.
Lesson Overview 4.5 Conditions Underwater What factors affect life in aquatic ecosystems? Aquatic organisms are affected primarily by the water s depth, temperature, flow, and amount of dissolved nutrients.
MILLER/SPOOLMAN 17 TH LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT. Chapter 8 Aquatic Biodiversity
 MILLER/SPOOLMAN LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT 17 TH Chapter 8 Aquatic Biodiversity Core Case Study: Why Should We Care about Coral Reefs? (1) Biodiversity Formation Tiny animals (polyps) and algae have mutualistic
MILLER/SPOOLMAN LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT 17 TH Chapter 8 Aquatic Biodiversity Core Case Study: Why Should We Care about Coral Reefs? (1) Biodiversity Formation Tiny animals (polyps) and algae have mutualistic
Human Impact on Coral Reefs. Ice ages have come and gone. Coral reefs have persisted. Sylvia Earle
 Human Impact on Coral Reefs Ice ages have come and gone. Coral reefs have persisted. Sylvia Earle What is a Coral? Corals are ancient animals related to jellyfish and anemones. An individual coral is known
Human Impact on Coral Reefs Ice ages have come and gone. Coral reefs have persisted. Sylvia Earle What is a Coral? Corals are ancient animals related to jellyfish and anemones. An individual coral is known
II. Needs of Organisms. Biosphere A. All parts of the earth that contains and support life 1. Geosphere 2. Atmosphere 3.
 I. Earth s Spheres A. Hydrosphere: Water part of the planet B. Atmosphere: Gas part of the earth C. Biosphere: Life part of the earth D. Geosphere: Rock/Soil part of the earth E. Mr. Wright s famous saying,
I. Earth s Spheres A. Hydrosphere: Water part of the planet B. Atmosphere: Gas part of the earth C. Biosphere: Life part of the earth D. Geosphere: Rock/Soil part of the earth E. Mr. Wright s famous saying,
Energy. Raw materials to make building blocks of life. From sun or chemicals. From food
 Energy From sun or chemicals Raw materials to make building blocks of life From food Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth Autotrophs will use energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide
Energy From sun or chemicals Raw materials to make building blocks of life From food Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth Autotrophs will use energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide
Weekly summary of Tropic101x as posted by student Lucia_Agudelo. With minor grammatical and content edits by Tropic101x team
 Weekly summary of Tropic101x as posted by student Lucia_Agudelo With minor grammatical and content edits by Tropic101x team Summary of Week 3 NUTRIENT CYCLES LECTURE 3.1.1 Elements like carbon (C) and
Weekly summary of Tropic101x as posted by student Lucia_Agudelo With minor grammatical and content edits by Tropic101x team Summary of Week 3 NUTRIENT CYCLES LECTURE 3.1.1 Elements like carbon (C) and
Midway. Global Coral Reef Conservation Project
 Global Coral Reef Conservation Project Midway Midway Special Regional Characteristics Midway Atoll is located over 2,000 kilometers from the nearest inhabited island (Hawaii s Kauai) and is one of the
Global Coral Reef Conservation Project Midway Midway Special Regional Characteristics Midway Atoll is located over 2,000 kilometers from the nearest inhabited island (Hawaii s Kauai) and is one of the
Ecosystems. Trophic relationships determine the routes of energy flow and chemical cycling in ecosystems.
 AP BIOLOGY ECOLOGY ACTIVITY #5 Ecosystems NAME DATE HOUR An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community as well as all the abiotic factors with which they interact. The dynamics of an
AP BIOLOGY ECOLOGY ACTIVITY #5 Ecosystems NAME DATE HOUR An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community as well as all the abiotic factors with which they interact. The dynamics of an
What is Ecology? The study of the interactions between organisms and the living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) components of their environment.
 Chapter 18 What is Ecology? The study of the interactions between organisms and the living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) components of their environment. What is Biodiversity? Biodiversity is the sum
Chapter 18 What is Ecology? The study of the interactions between organisms and the living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) components of their environment. What is Biodiversity? Biodiversity is the sum
Studying organisms in their environment
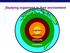 Studying organisms in their environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How do nutrients move in the ecosystem? How does
Studying organisms in their environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How do nutrients move in the ecosystem? How does
OGT Intervention. Ecology and Cellular Processes
 OGT Intervention Ecology and Cellular Processes Ecology The study of relationships between living organisms and their environment Ecosystem- All of the organisms in an area and the nonliving factors (abiotic)
OGT Intervention Ecology and Cellular Processes Ecology The study of relationships between living organisms and their environment Ecosystem- All of the organisms in an area and the nonliving factors (abiotic)
Classifying our Biotic Environment (Trophic Levels) Ecology. Ecology is study how things interact with other and else in the.
 Ecology Ecology is study how things interact with other and else in the. Ecologists focus their attention on in order to organize their studies. Ecosystems can be very large or very small. For example:
Ecology Ecology is study how things interact with other and else in the. Ecologists focus their attention on in order to organize their studies. Ecosystems can be very large or very small. For example:
Monitoring Coral Reef Ecosystems with Quadrats
 Monitoring Coral Reef Ecosystems with Quadrats Background & Key Concepts Coral reefs grow at rates ranging from 1 cm to 100 cm per year. Over long periods of time, they can form huge structures, making
Monitoring Coral Reef Ecosystems with Quadrats Background & Key Concepts Coral reefs grow at rates ranging from 1 cm to 100 cm per year. Over long periods of time, they can form huge structures, making
Marine Science 1 Study Guide Use/read your teacher support document and go online to study the following topics for test Monday/Tuesday.
 Marine Science 1 Study Guide Use/read your teacher support document and go online to study the following topics for test Monday/Tuesday. 1. Hurricanes a. A tropical cyclone (Figure 7.2) is a storm system,
Marine Science 1 Study Guide Use/read your teacher support document and go online to study the following topics for test Monday/Tuesday. 1. Hurricanes a. A tropical cyclone (Figure 7.2) is a storm system,
Ecology Greek "oikos" = house study of the interactions among living things, and between living things and their environment
 2.1 and 2.2 Organisms and Their Relationships Section 2.1 Ecology Greek "oikos" = house study of the interactions among living things, and between living things and their environment Research Methods observation
2.1 and 2.2 Organisms and Their Relationships Section 2.1 Ecology Greek "oikos" = house study of the interactions among living things, and between living things and their environment Research Methods observation
Another dimension of Biodiversity is how recognizable associations of organisms inhabit the same place as ecosystems
 ECOLOGY Another dimension of Biodiversity is how recognizable associations of organisms inhabit the same place as ecosystems Understanding these associations is the subject of Ecology For example, coral
ECOLOGY Another dimension of Biodiversity is how recognizable associations of organisms inhabit the same place as ecosystems Understanding these associations is the subject of Ecology For example, coral
Keystone Biology Remediation B4: Ecology
 Keystone Biology Remediation B4: Ecology Assessment Anchors: to describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e. organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere) (B.4.1.1) to describe
Keystone Biology Remediation B4: Ecology Assessment Anchors: to describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e. organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere) (B.4.1.1) to describe
13-14 LL Final Exam (Science) Biology B Assessment ID: dna.5702 ib LL Final Exam (Science) Biology B
 13-14 LL Final Exam (Science) Biology B Generated On March 26, 2014, 3:02 PM PDT 1 An ecosystem that has a wide VARIETY of species within it is said to have a large. A. population B. habitat C. niche D.
13-14 LL Final Exam (Science) Biology B Generated On March 26, 2014, 3:02 PM PDT 1 An ecosystem that has a wide VARIETY of species within it is said to have a large. A. population B. habitat C. niche D.
HYDROSPHERE EOG REVIEW
 HYDROSPHERE EOG REVIEW 1 Why is fresh water in short supply on Earth? A. Most of it is frozen B. Most of it is polluted C. Most of it is in the atmosphere D. Most of it is trapped underground A. About
HYDROSPHERE EOG REVIEW 1 Why is fresh water in short supply on Earth? A. Most of it is frozen B. Most of it is polluted C. Most of it is in the atmosphere D. Most of it is trapped underground A. About
Kapolei Middle School Science Students Explore Plankton: Discover Intricate, Supportive Coral Reef with Scientists
 Kapolei Middle School Science Students Explore Plankton: Discover Intricate, Supportive Coral Reef with Scientists Continuing a collaboration spanning six years and involving more than one thousand students,
Kapolei Middle School Science Students Explore Plankton: Discover Intricate, Supportive Coral Reef with Scientists Continuing a collaboration spanning six years and involving more than one thousand students,
Chapter 3 The Biosphere. Essential Question: How are ecosystems organized for energy transfer?
 Chapter 3 The Biosphere Essential Question: How are ecosystems organized for energy transfer? Sec. 3-1 THE BIOSPHERE eco = house logy = the study of Ecology is the study of ecosystems and the interactions
Chapter 3 The Biosphere Essential Question: How are ecosystems organized for energy transfer? Sec. 3-1 THE BIOSPHERE eco = house logy = the study of Ecology is the study of ecosystems and the interactions
Overview of Chapter 3
 Overview of Chapter 3 What is Ecology? The Energy of Life Laws of Thermodynamics Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Flow of Energy Through Ecosystems Producers, Consumers and Decomposers Path of Energy
Overview of Chapter 3 What is Ecology? The Energy of Life Laws of Thermodynamics Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Flow of Energy Through Ecosystems Producers, Consumers and Decomposers Path of Energy
Chapter 5 AQUATIC BIOMES
 Chapter 5 AQUATIC BIOMES 1 OUTLINE Marine Ecosystems Coasts - Sandy, Rocky, Salt Marsh, Mangrove Coral Reefs Open Ocean Hydrothermal Vents Freshwater Ecosystems - Lakes, Rivers, Wetlands Human Disturbance
Chapter 5 AQUATIC BIOMES 1 OUTLINE Marine Ecosystems Coasts - Sandy, Rocky, Salt Marsh, Mangrove Coral Reefs Open Ocean Hydrothermal Vents Freshwater Ecosystems - Lakes, Rivers, Wetlands Human Disturbance
Let s Be Oral About Coral. much support has been placed on the preservation of polar bears, the fact that all animals are
 Let s Be Oral About Coral Allison Feng 1 Let s Be Oral About Coral When climate change is thought of in relation to animals, the archetypal image of a lone polar bear floating on a piece of melting ice
Let s Be Oral About Coral Allison Feng 1 Let s Be Oral About Coral When climate change is thought of in relation to animals, the archetypal image of a lone polar bear floating on a piece of melting ice
Marine Life. Communities
 Marine Life Communities Habitat, Population, Community, Niche Every marine organism lives in a unique set of physical conditions within a given region of ocean, termed its habitat. A group of marine organism
Marine Life Communities Habitat, Population, Community, Niche Every marine organism lives in a unique set of physical conditions within a given region of ocean, termed its habitat. A group of marine organism
Aquatic (Marine)Ecosystems
 Aquatic (Marine)Ecosystems 71% of the Earth s surface is water. The other 29% consists of continents and islands. To break the numbers down, 96.5% is salt water, 3.5% is freshwater lakes and frozen water
Aquatic (Marine)Ecosystems 71% of the Earth s surface is water. The other 29% consists of continents and islands. To break the numbers down, 96.5% is salt water, 3.5% is freshwater lakes and frozen water
Food for thought Coral Reef Food Web. Photo credit: George Stoyle
 Food for thought Coral Reef Food Web Photo credit: George Stoyle Notes for teachers: Food for thought is an interactive food webs game, designed to give pupils an appreciation for the fact that every organism
Food for thought Coral Reef Food Web Photo credit: George Stoyle Notes for teachers: Food for thought is an interactive food webs game, designed to give pupils an appreciation for the fact that every organism
Stephen Broadbelt President Cayman Islands Tourism Association
 WORKSHOP: The Sustainable Dive Market 10 th Sustainable Tourism Conference 29 th April 2008 Stephen Broadbelt President Cayman Islands Tourism Association S THE LETTER OF THE DAY IS GREEN PEOPLE? We CAN
WORKSHOP: The Sustainable Dive Market 10 th Sustainable Tourism Conference 29 th April 2008 Stephen Broadbelt President Cayman Islands Tourism Association S THE LETTER OF THE DAY IS GREEN PEOPLE? We CAN
Little Bay Water Quality Report Card Spring 2014
 Little Bay Water Quality Report Card Spring 2014 Little Bay is a small, semi-enclosed estuary located in the heart of Rockport, Texas. Estuaries, where freshwater from rivers and streams mixes with salt
Little Bay Water Quality Report Card Spring 2014 Little Bay is a small, semi-enclosed estuary located in the heart of Rockport, Texas. Estuaries, where freshwater from rivers and streams mixes with salt
Teacher s Answer Key
 Ocean on the edge Scavenger Hunt Teacher s Answer Key (STUDENT ANSWERS MAY VARY SLIGHTLY) Thank you for choosing the Aquarium of the Pacific as your field trip destination! We are excited to share the
Ocean on the edge Scavenger Hunt Teacher s Answer Key (STUDENT ANSWERS MAY VARY SLIGHTLY) Thank you for choosing the Aquarium of the Pacific as your field trip destination! We are excited to share the
