Reading the River, Summer Watersheds and Streams A unit for 8 th Grade Science. Arthur H. Shutt III. Bullitt Lick Middle School
|
|
|
- Martha Daniella Stevenson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reading the River, Summer 2001 Watersheds and Streams A unit for 8 th Grade Science Arthur H. Shutt III Bullitt Lick Middle School Bullitt County, Kentucky 1
2 Watersheds and Streams Grade Level: 8 Objectives In this lesson, Students will be able to: 1.) Identify components of what makes a watershed for a stream. 2.) Identify and diagram the area of the stream and its path to the Salt River. 3.) Develop a stream management plan that incorporates environmentally safe, best management practices. 4.) Conduct stream monitoring tests stream to assess environmental hazards. 5.) Design an educational plan to inform community members about the clean up and environmental maintenance of streams. 6.) Implement a plan of continuous watershed watch data collection for purposes of environmental stream safety. Program of Studies Scientific Inquiry Identify and refine questions that can be answered through scientific investigations combined with scientific information. Use appropriate equipment (e.g. water thermonator), tools (e.g. map), techniques (e.g. computer skills), technology (e.g. computer s), and mathematics in scientific investigations. Design and conduct different kinds of scientific investigations to answer different kinds of questions. Communicate (e.g. write, graph) designs, procedures, and results of scientific investigations. Review and analyze scientific investigations and explanations of other students. Conceptual Understanding Plan, demonstrate, relate, analyze, and recommend actions of discovery of stream watershed and environmental safety. Be able to solve problems using the scientific method. Be able to use scientific equipment appropriately. Apply knowledge of the relationship between humans, the environment, and the earth s resources. Be able to use modern technologies to sort and arrange data. 2
3 Be able to explain the changes in life and environmental conditions. Be able to demonstrate the role science plays in everyday life and explore different careers. Applications/Connections Investigate how science can be used to solve environmental quality problems. Examine the interaction between science and technology. Apply scientific theory and conceptual understandings to solve problems of technological design. Recognize that scientific knowledge comes from empirical standards, logical arguments and skepticism, and is subject to change, as new evidence becomes available. Core Content Investigate the structure of the Earth System (e.g. Water Cycle) SC-M Water, which covers the majority of the Earth s surface, circulates through the crust, oceans, and atmosphere, in what is known as the water cycle. Water dissolves minerals and gases and may carry them to the oceans. Investigate and analyze populations and ecosystems. SC-M A population consists of all individuals of a species that occur together at a given place and time. All populations living together and the physical factors with which they interact compose an ecosystem. SC-H Organisms both cooperate and compete in ecosystems. Often changes in one component of an ecosystem will have effects on the entire system that are difficult to predict. The interrelationships and interdependencies of these organisms may generate ecosystems that are stable for hundreds or thousands of years. SC-H Living organisms have the capacity to produce populations of infinite size. However, behaviors, environments, and resources influence the size of populations. Models (e.g., mathematical, physical, conceptual) can be used to make 3
4 predictions about changes in the size or rate of growth of a population. Materials 1.) Books handouts, electronic sources and other information on what makes a watershed and ecosystems. 2.) Pen, Paper, Pencil, clipboard, notebook and county map. 3.) Ecosystem and watershed survey checklists. 4.) Water monitoring kits and or equipment (temperature probes, ph probes, or kits, DO probes, or kits, Calculators, LabPros or CBL s, any other physical/chemical probes, kits as desired and available, depth gauge, tape measure, compass and protractor). Activity Procedures 1.) Discuss what makes a watershed, stream, river and an ecosystem. What makes a good Vs bad watershed stream, and clean vs. dirty environmental stream area. Also what do students expect to see at the stream watershed and its ecosystem? 2.) Have students work in pairs. 3.) Students will have previously researched resources, whether print or electronic, on watersheds and ecosystems. 4.) Field trip to follow classroom discussion. Have students take (notes, sketch, photograph, video) of stream area and start point of stream. 5.) Students will take trash bags to collect garbage at site(s) along the stream. Students will mark on maps the items that could not be picked up on the field trip to be able to report for pick-up by community. Definition and Explanation of Concepts Students need to understand the water cycle model and how it is important, even in an urban environment. With this understanding, the students can model stream flow and damage by any type of organism that does or does not belong in that stream watershed and the ecosystem of that area. Students have the need to understand that any action causes a reaction in the environment that can be both helpful and harmful. Ecosystems consist of all different species making up a population and physical factors that these species interact with. Those 4
5 organisms both compete and cooperate in ecosystems. What are the interrelationships and interdependencies that organisms generate for both helpful and harmful impacts? Can human beings and other organisms share the same stream watershed? Does Agriculture help or hurt a stream ecosystem? New housing areas and deforestation around the stream environment cause ripple effects that effect organisms that live downstream of the start point of the stream. Any behaviors, environment, and resources influence the living area of organisms. What models do we use to predict the changes and effects on the environment or stream life cycle? How can you, a student, make a difference to this stream? What about family, friends and others that live in your neighborhood? What about your state and country? Assessment Monitor what work the students are doing and ensuring that they understand the task laid out before them. Check what material the students are reading and researching and provide guidance or channel work to reach the desired goal of the class on this field trip. Write letters to family, neighbors and the community in which the student resides. Ensure that student includes finding of class from the field trip about the environment impact of the streams health. Have class vote, elect and respond by writing a letter to the editor of local newspaper, prepare a video informing of damage and clutter of stream watershed, or a presentation for the school or community on water issues impacting the community and relationship to the stream or watershed. Reference This lesson was adapted from Adopt a stream stream walk, found in: Splashing in Kentucky!: An Educator s guide to Nonpoint Source Water Pollution, by Neeley, Cathy L., Kentucky Waterways Alliance, 5
6 The Earth Mobile, Kentucky Division of Water, Nonpoint Source Section Rubric for Evaluating Model 1.) Was student able to identify all components making up a stream watershed? 2.) Did student accurately draw a map of stream area and its path to the Salt River? 3.) Did the plan of management for an environmentally safe stream incorporate best management practices? 4.) Did student demonstrate proper & accurate recording of monitoring results from the stream to the proper worksheet? 5.) Was a letter written to the editor of local newspaper or Community leaders? 6.) Did the implementation of the plan for the continuous stream watershed watch & safety incorporate best management practices? 60 points possible for this class field trip. Each Question is worth 10 points. 6
7 Lesson Context This is was adapted from several different sources of study on watershed and streams: What is a watershed? It s land that water flows across or under on its way to a stream, river, or lake. How do Watersheds work? The landscape is made up of many interconnected basins, or watersheds. Within each watershed, all water runs to the lowest point stream, river, or lake. On its way, water travels over the surface and across farm fields, forestland, suburban lawns, and city streets, or it seeps into the soil and travels as ground water. Large Watersheds, like the ones for the Mississippi River, Columbia River and Chesapeake Bay, are made up of many smaller watersheds across the several states. Are all watersheds the same? Not at all. Watersheds come in many different shapes and sizes and have many different features. Watersheds can have hills or mountains or be nearly flat. They can have farmland, rangeland, small towns, and big cities. Parts of your watershed can be so rough, rocky, or marshy that they re suited only for certain trees, plants and wildlife. Your Watershed community Everyone lives in a watershed. You and everyone in your watershed are part of the watershed community. The animals, birds, and fish are part of a watershed, too. You influence what happens in your watershed, good or bad, by how you treat the natural resources-the soil, water, air, plants, and animals. What happens in your small watershed also affects the larger watershed downstream. What is a Watershed, United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, Program aid #420, Slightly revised November
8 What is a Stream? What are its boundaries? Where does it begin? Where does it end? As it is described in Maine laws, a "stream" is a complex concept, modified by many qualifying terms that help in regulating abuses and uses of it, but an actual stream is even more complicated than its legal definition suggests. Watershed to stream bed Is the boundary of the stream the edge of the water, where you start to get your feet wet in soggy soil, the area that floods in heavy rains, or all the land that contributes surface runoff or groundwater to that stream? It is all of the above. The land area from which water drains into a body of water, either above or below ground, is called its watershed. The watershed may cover many square miles, extending far beyond the sounds of a brook or the smell of damp earth at the water's edge. Anything that affects the watershed will eventually impact the stream. A stream that winds through a wooded watershed, for example, will be a much different stream than one that flows through parking lots or golf courses. The borders of a stream are much broader than they appear to be at first sight. Clouds, rain and runoff Have you ever been in the woods during a storm and watched where the rain goes? Some falls directly onto a stream, but most of it falls on the land. There it collects in depressions and sinks slowly into the soil or evaporates into the air. In a hard rain, the water overflows into rivulets that race downhill to streams or pond. The water that percolates into the soil then becomes groundwater. It trickles through pore spaces in sand or gravel or between fractures in rocks to discharge into a spring or a stream. Plant roots absorb some of the groundwater, pull it up their stems and trunks to their leaves, and release it into the atmosphere. There it joins other water vapor evaporated from streams, lakes, or the ocean. Water droplets condense around microscopic particles of dust and salt to form clouds. When the clouds become saturated, the water falls back to earth as rain or snow and rejoins the stream's journey to the sea. In Maine, over 33,000 mapped miles of flowing water are part of this process that has been recycling water for billions of years. This process is called the hydrologic cycle. From its source to the sea Streams are like the capillaries and blood vessels that connect to the major arteries, the rivers. But unlike our body's circulation system, the smaller channels deliver most of the water and food to the bigger ones. Without feeder streams, our rivers would not exist. You could say a stream begins at its headwaters, often in the mountains, fed by an underground spring or the runoff from rain and snow melt. Rivulets of water flow downhill, merging together to become a stream which continues, mixing with other tributaries, until they all become a river flowing to the sea. Here in Maine the mouth of a river usually opens into the ocean in a broad bay where fresh water and salt water mix, called an estuary. The length of a stream may be only a few feet from where it emerges until it joins another stream, or it may traverse hundreds of miles, from the mountains to the sea. Some streams flow year-round, others only after a storm or when snow melts in the spring. What could be more dynamic than a stream? It is constantly changing its flow, its depth, even its bed, as anyone knows who has observed a stream in different seasons or at different places along its course. It scours, shifts channels, meanders, floods, erodes, carries and deposits silt. Squeeze a stream in one place, and like a water balloon, it bulges in another. Where it is restricted, the stream speeds up to compensate, eroding downstream banks or spreading out to flood adjacent property. 8
9 Many factors shape the character of a stream as it progresses from its headwaters to its mouth: the slope and current, the amount of water being transported, its temperature and water chemistry. These, in turn, influence the vegetation, the animals, the bottom sediments, and the shape of the channel at any point along the stream's journey. So just what is a stream? Its boundaries are as wide as its watershed, as long as the entire river system from source to sea, and as fluid as the water cycle itself. Work sited from web page, Ask Jeeves, What is a Stream? Resources: Ask Jeeves, What is a stream, Ask.com What is a Watershed, U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, Program aid #420, Revised Sept 1994, Slightly revised Nov Studying Watersheds: A confluence of Important Ideas, Haury, David L., Digest, SE ERIC EDO-SE Splashing in Kentucky: An Educator s Guide to Nonpoint Source Water Pollution, Neeley, Cathy L., Kentucky Waterways Alliance, The Earth Mobile, Kentucky Division of Water, Nonpoint Source Selection, 1998, pages
FACT FLASH. 5: Groundwater. What is groundwater? How does the ground store water? Fact Flash 5: Groundwater
 FACT FLASH 5: Groundwater What is groundwater? Groundwater is fresh water (from rain or melting ice and snow) that soaks into the soil and is stored in the tiny spaces (pores) between rocks and particles
FACT FLASH 5: Groundwater What is groundwater? Groundwater is fresh water (from rain or melting ice and snow) that soaks into the soil and is stored in the tiny spaces (pores) between rocks and particles
READING THE RIVER. All the water in the world SUMMER 2002 GRADES 9 10 INTEGRATED SCIENCES EARTH SCIENCE. RICHARD DUBé
 READING THE RIVER SUMMER 2002 All the water in the world GRADES 9 10 INTEGRATED SCIENCES EARTH SCIENCE RICHARD DUBé LLOYD MEMORIAL HIGH SCHOOL ERLANGER/ELSMERE SCHOOL DISTRICT KENTON COUNTY AUGUST 26,
READING THE RIVER SUMMER 2002 All the water in the world GRADES 9 10 INTEGRATED SCIENCES EARTH SCIENCE RICHARD DUBé LLOYD MEMORIAL HIGH SCHOOL ERLANGER/ELSMERE SCHOOL DISTRICT KENTON COUNTY AUGUST 26,
Science 8 Chapter 1 Section 1
 Science 8 Chapter 1 Section 1 Distribution of Water (pp. 8-13) How much fresh water do we have? The vast majority of water on Earth, about 97 percent, is salt water Two thirds of that fresh water supply
Science 8 Chapter 1 Section 1 Distribution of Water (pp. 8-13) How much fresh water do we have? The vast majority of water on Earth, about 97 percent, is salt water Two thirds of that fresh water supply
VI-1. The Water Cycle What is the water cycle? evaporate condenses surface runoff ground water
 Classroom Copy VI-1. The Water Cycle What is the water cycle? Did you know that the water we see all around us never gets destroyed, and new water never gets created? Instead, it constantly recycles and
Classroom Copy VI-1. The Water Cycle What is the water cycle? Did you know that the water we see all around us never gets destroyed, and new water never gets created? Instead, it constantly recycles and
Water Resources. The Water Cycle. Section 1. Key Terms surface water river system watershed groundwater aquifer porosity permeability recharge zone
 Water Resources The next time you drink a glass of water, think about where the water came from. Did you know that some of the water in your glass may have been part of a rainstorm that pounded Earth long
Water Resources The next time you drink a glass of water, think about where the water came from. Did you know that some of the water in your glass may have been part of a rainstorm that pounded Earth long
There s a Watershed in My Backyard
 There s a Watershed in My Backyard www.ksagclassroom.org There s a Watershed in My Backyard Grade Level: 3-5,6-8 Academic Area(s): Science, Social Studies Topic(s): Earth Science, Geography Rev. August/2017
There s a Watershed in My Backyard www.ksagclassroom.org There s a Watershed in My Backyard Grade Level: 3-5,6-8 Academic Area(s): Science, Social Studies Topic(s): Earth Science, Geography Rev. August/2017
ECOSYSTEMS, WATERSHEDS AND POLLUTION CONTROL REVIEW
 ECOSYSTEMS, WATERSHEDS AND POLLUTION CONTROL REVIEW ECOSYSTEMS: (6 th grade content) How biotic and abiotic factors make an ecosystem: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdlwptkg-vi 1. A/An ecosystem is a
ECOSYSTEMS, WATERSHEDS AND POLLUTION CONTROL REVIEW ECOSYSTEMS: (6 th grade content) How biotic and abiotic factors make an ecosystem: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdlwptkg-vi 1. A/An ecosystem is a
Module 4.3. Energy in the Earth s Systems How do external and internal sources of energy affect the Earth s systems? CT Science Framework Topics
 Module 4.3 Energy in the Earth s Systems How do external and internal sources of energy affect the Earth s systems? Science Content Standard 4.3 CT Science Framework Topics 1. Water is continuously moving
Module 4.3 Energy in the Earth s Systems How do external and internal sources of energy affect the Earth s systems? Science Content Standard 4.3 CT Science Framework Topics 1. Water is continuously moving
When it Rains it Pours
 Lesson Summary: Students will understand how water is absorbed into the ground. They will also be able to explain the difference between pervious and impervious surfaces. Students will also learn about
Lesson Summary: Students will understand how water is absorbed into the ground. They will also be able to explain the difference between pervious and impervious surfaces. Students will also learn about
Journey of a Raindrop
 Journey of a Raindrop Grade Level Second to Fourth Duration Prep time: 15 minutes Activity time: 30 to 60 minutes Materials 10 different colored pony beads (from craft stores) 10 large pieces of paper
Journey of a Raindrop Grade Level Second to Fourth Duration Prep time: 15 minutes Activity time: 30 to 60 minutes Materials 10 different colored pony beads (from craft stores) 10 large pieces of paper
River Talk Patterns. Student Copy Page PART I (1 of 1) 3. Human nervous system. Waters and drainage patterns. Road system.
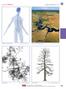 River Talk Patterns Student Copy Page PART I (1 of 1) 3 Human nervous system photo credit: Hemera Thinkstock Photos Waters and drainage patterns photo credit: Comstock Getty Images Road system photo credit:
River Talk Patterns Student Copy Page PART I (1 of 1) 3 Human nervous system photo credit: Hemera Thinkstock Photos Waters and drainage patterns photo credit: Comstock Getty Images Road system photo credit:
Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is the Water Cycle? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Water on the Move warm up 1 Water on the Move About three-fourths of Earth s surface is covered by water. Water on the Move Video!!! Water on the Move Water moves between Earth s surface and the atmosphere
Water on the Move warm up 1 Water on the Move About three-fourths of Earth s surface is covered by water. Water on the Move Video!!! Water on the Move Water moves between Earth s surface and the atmosphere
Read p.4 Activity. Class Discussion (The many ways people use water) P. 5. Read p.6 Read pp. 8-9
 Grade 8 Science Read p.4 Activity Class Discussion (The many ways people use water) P. 5 Read p.6 Read pp. 8-9 Water exists everywhere on Earth, and covers 70% of its surface. 97% of this water is found
Grade 8 Science Read p.4 Activity Class Discussion (The many ways people use water) P. 5 Read p.6 Read pp. 8-9 Water exists everywhere on Earth, and covers 70% of its surface. 97% of this water is found
Teacher Resources: Watersheds 1. Watershed Mini-Unit
 Teacher Resources: Watersheds 1 Watershed Mini-Unit Main Ideas: Accounts Main Ideas: Structure: The surface water system is connected to the atmospheric system and the groundwater system. Water can exist
Teacher Resources: Watersheds 1 Watershed Mini-Unit Main Ideas: Accounts Main Ideas: Structure: The surface water system is connected to the atmospheric system and the groundwater system. Water can exist
groundwater. Because watersheds are complex systems, each tends to respond differently to natural or human activities.
 The private development of Altos del María is located at an altitude between 550 and 1,000 meters above sea level in the environmentally sensitive Cordillera Central of Panama that separates the Pacific
The private development of Altos del María is located at an altitude between 550 and 1,000 meters above sea level in the environmentally sensitive Cordillera Central of Panama that separates the Pacific
The Spring Creek Stormwater Activity Book
 This booklet belongs to: The Spring Creek Stormwater Activity Book An activity booklet designed to teach children about water resources and stormwater pollution Created by the MS4 Partners College, Ferguson,
This booklet belongs to: The Spring Creek Stormwater Activity Book An activity booklet designed to teach children about water resources and stormwater pollution Created by the MS4 Partners College, Ferguson,
Pre-Event Activities. Blue River. Pre Field Trip Suggestions
 Blue River Have you heard we all live in a watershed? Well, it is true! This total body activity will allow students to demonstrate how water flows in a watershed while exploring how seasonal variations
Blue River Have you heard we all live in a watershed? Well, it is true! This total body activity will allow students to demonstrate how water flows in a watershed while exploring how seasonal variations
The Returning Raindrop
 Did you know that some of the water molecules we drink today may have been around when dinosaurs walked the Earth thousands of years ago? Water is continuously recycling in a process called the hydrologic
Did you know that some of the water molecules we drink today may have been around when dinosaurs walked the Earth thousands of years ago? Water is continuously recycling in a process called the hydrologic
Incredible Journey Water Cycle Game A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program
 Incredible Journey Water Cycle Game A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program OVERVIEW: Picture a class of students scurrying all over the room, pretending
Incredible Journey Water Cycle Game A lesson from the New Jersey Agricultural Society s Learning Through Gardening program OVERVIEW: Picture a class of students scurrying all over the room, pretending
What in the World is a Watershed? There s a Watershed in My Backyard - Activity 1
 Soil & Water What in the World is a Watershed? There s a Watershed in My Backyard - Activity 1 Science, Geography Materials Umbrella Spray bottle with water Large bath towel Supplemental watershed diagram
Soil & Water What in the World is a Watershed? There s a Watershed in My Backyard - Activity 1 Science, Geography Materials Umbrella Spray bottle with water Large bath towel Supplemental watershed diagram
Where does the water go?
 Photo from sdherps.org. Post Visit Activity Grade Five Where does the water go? Summary Students will explore where water goes around our earth and atmosphere while learning how the sun s energy affects
Photo from sdherps.org. Post Visit Activity Grade Five Where does the water go? Summary Students will explore where water goes around our earth and atmosphere while learning how the sun s energy affects
Water is a solid, liquid, & gas. 71% of earth s surface is water. Our body is two-thirds water. Fresh water water that is not salty and has little or
 Water is a solid, liquid, & gas. 71% of earth s surface is water. Our body is two-thirds water. Fresh water water that is not salty and has little or no taste, color, or smell. Salt water water that contains
Water is a solid, liquid, & gas. 71% of earth s surface is water. Our body is two-thirds water. Fresh water water that is not salty and has little or no taste, color, or smell. Salt water water that contains
Arizona Project WET University of Arizona Cooperative Extension, Maricopa County 4341 East Broadway Road Phoenix, AZ 85040
 ARIZONA WATER FESTIVAL STUDENT QUESTIONNAIRE Dear Teachers, The purpose of this student questionnaire is to assess student learning due to their participation in the water festival unit (the pre and post
ARIZONA WATER FESTIVAL STUDENT QUESTIONNAIRE Dear Teachers, The purpose of this student questionnaire is to assess student learning due to their participation in the water festival unit (the pre and post
Watershed Walk An exploration of urban watersheds
 Watershed Walk An exploration of urban watersheds Objectives: Students will be able to: describe what happens to water when it hits the ground. recognize that bodies of water are the end product of drainage
Watershed Walk An exploration of urban watersheds Objectives: Students will be able to: describe what happens to water when it hits the ground. recognize that bodies of water are the end product of drainage
The Hydrologic (Water) Cycle
 Ever since the Volcanic outgassing of water vapor 4 billion years ago, Earth has been recycling its water supply. gained lost Earth s has not or water since The Water Cycle - the model used to illustrate
Ever since the Volcanic outgassing of water vapor 4 billion years ago, Earth has been recycling its water supply. gained lost Earth s has not or water since The Water Cycle - the model used to illustrate
The Hydrological Cycle
 Hydrological Cycle The Hydrological Cycle What is the Hydrological Cycle? Hydrological cycle = The Water cycle What is precipitation, evaporation and condensation? Evaporation = Liquid to Gas (gains energy)
Hydrological Cycle The Hydrological Cycle What is the Hydrological Cycle? Hydrological cycle = The Water cycle What is precipitation, evaporation and condensation? Evaporation = Liquid to Gas (gains energy)
Watershed Activity 1
 Watershed Activity 1 Region: Eastern Coastlines Grade Level(s): 5-8 Time Required: One 45-minute class period Learning Objectives: The students will be able to understand that all water that falls on a
Watershed Activity 1 Region: Eastern Coastlines Grade Level(s): 5-8 Time Required: One 45-minute class period Learning Objectives: The students will be able to understand that all water that falls on a
Module 8: Weathering, Erosion, and Groundwater Topic 5 Content: The Water Cycle Presentation Notes. The Water Cycle
 The Water Cycle 1 Imagine taking a trip around the water cycle as a single drop of water. This cycle has no beginning or ending point, so it does not matter where the trip starts. Since over 70% of the
The Water Cycle 1 Imagine taking a trip around the water cycle as a single drop of water. This cycle has no beginning or ending point, so it does not matter where the trip starts. Since over 70% of the
IS IT SAFE TO GO INTO THE WATER? A 7 th Grade Science Unit
 IS IT SAFE TO GO INTO THE WATER? A 7 th Grade Science Unit READING THE RIVER Summer 2004 Lisa Klette Dayton Middle School Dayton Independent Schools Dayton, Kentucky Campbell County Summary This unit serves
IS IT SAFE TO GO INTO THE WATER? A 7 th Grade Science Unit READING THE RIVER Summer 2004 Lisa Klette Dayton Middle School Dayton Independent Schools Dayton, Kentucky Campbell County Summary This unit serves
7-4 Soil. By Cyndee Crawford September 2014
 7-4 Soil By Cyndee Crawford September 2014 Soil Table of Contents 28.Chemical Weathering Lab 29.What is a Watershed? / Watershed Demo 30.Groundwater Layers Book 31.Groundwater Notes 32.What is an aquifer?
7-4 Soil By Cyndee Crawford September 2014 Soil Table of Contents 28.Chemical Weathering Lab 29.What is a Watershed? / Watershed Demo 30.Groundwater Layers Book 31.Groundwater Notes 32.What is an aquifer?
Hydrosphere: Water Distribution
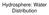 Hydrosphere: Water Distribution 1.Think About It Why is it that the water in your bottle could have been drunk by George Washington? 2. The Hydrosphere: An Overview The hydrosphere is ALL the water on/in/over
Hydrosphere: Water Distribution 1.Think About It Why is it that the water in your bottle could have been drunk by George Washington? 2. The Hydrosphere: An Overview The hydrosphere is ALL the water on/in/over
Introduction. Welcome to the Belgium Study Abroad Program. Courses:
 Introduction Welcome to the Belgium Study Abroad Program Courses: AGSM 335: Soil and Water Management BAEN 460: Principals of Environmental Hydrology BAEN 460 / AGSM 335 Combined lecture and HW sessions
Introduction Welcome to the Belgium Study Abroad Program Courses: AGSM 335: Soil and Water Management BAEN 460: Principals of Environmental Hydrology BAEN 460 / AGSM 335 Combined lecture and HW sessions
From My Backyard to Our Bay It s the 911 for the Chesapeake Bay
 From My Backyard to Our Bay Reporting Problems on Our Bay, Rivers, and Streams We can all be the eyes and ears of our local waterways. Maryland has established the Chesapeake Bay Safety and Environmental
From My Backyard to Our Bay Reporting Problems on Our Bay, Rivers, and Streams We can all be the eyes and ears of our local waterways. Maryland has established the Chesapeake Bay Safety and Environmental
What is a Watershed? Summary. Background. Chicago River Classroom Activity
 Chicago River Classroom Activity Summary Students will create models of a landscape. They will then make and test their predictions about the location of rivers and watershed boundaries. Students will
Chicago River Classroom Activity Summary Students will create models of a landscape. They will then make and test their predictions about the location of rivers and watershed boundaries. Students will
Shower Curtain Watershed
 Topic Watersheds Shower Curtain Watershed Grades 3-5 Sites Outdoors, Indoors Duration 30 minutes Materials Watershed pictures Labels or index cards Clear plastic shower curtain Spray bottles with water
Topic Watersheds Shower Curtain Watershed Grades 3-5 Sites Outdoors, Indoors Duration 30 minutes Materials Watershed pictures Labels or index cards Clear plastic shower curtain Spray bottles with water
2018 NACD POSTER CONTEST Sponsored By: 2018 Theme - Watersheds: Our Water, Our Home. Fact Sheet for Parents and Educators
 Fact Sheet for Parents and Educators What is a Watershed? A watershed is land that sheds water. Water from rain or snow can flow over the land it falls on. The water can flow to a river, lake, stream or
Fact Sheet for Parents and Educators What is a Watershed? A watershed is land that sheds water. Water from rain or snow can flow over the land it falls on. The water can flow to a river, lake, stream or
Nueces River Watershed
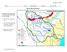 Name period Date assigned date due date returned Directions: You will color parts of the on the next page: 1. Trace the rivers and lakes in blue 2. Trace the outside edge of the watershed in red (it s
Name period Date assigned date due date returned Directions: You will color parts of the on the next page: 1. Trace the rivers and lakes in blue 2. Trace the outside edge of the watershed in red (it s
General Groundwater Concepts
 General Groundwater Concepts Hydrologic Cycle All water on the surface of the earth and underground are part of the hydrologic cycle (Figure 1), driven by natural processes that constantly transform water
General Groundwater Concepts Hydrologic Cycle All water on the surface of the earth and underground are part of the hydrologic cycle (Figure 1), driven by natural processes that constantly transform water
INVESTIGATING YOUR STREAM S DRAINAGE BASIN
 IT S OUR WATER INVESTIGATING YOUR STREAM S STREAM ACTIVITY SUMMARY Using maps, students will determine land uses in the drainage basin of their stream and calculate the approximate percentage of impervious
IT S OUR WATER INVESTIGATING YOUR STREAM S STREAM ACTIVITY SUMMARY Using maps, students will determine land uses in the drainage basin of their stream and calculate the approximate percentage of impervious
Air & Water Lesson 2. Chapter 6 Conserving Our Resources
 Air & Water Lesson 2 Chapter 6 Conserving Our Resources Objectives Summarize the importance of air. Describe the water cycle. Main Idea Living things use air and water to carry out their life processes.
Air & Water Lesson 2 Chapter 6 Conserving Our Resources Objectives Summarize the importance of air. Describe the water cycle. Main Idea Living things use air and water to carry out their life processes.
City of Texarkana, Arkansas. Storm Water Pollution
 City of Texarkana, Arkansas Storm Water Pollution STORM WATER GUIDE What is Storm Water Pollution? Stormwater can provide a toxic discharge which can enter into a lake, river or coastal water system. As
City of Texarkana, Arkansas Storm Water Pollution STORM WATER GUIDE What is Storm Water Pollution? Stormwater can provide a toxic discharge which can enter into a lake, river or coastal water system. As
Water Travels Grade 5
 TEACHING LEARNING COLLABORATIVE (TLC) EARTH SCIENCE Water Travels Grade 5 Created by: Shane Lee (Pomo Elementary School); Nola Montgomery (Clearlake Community School); Lori Kincaid (Lower Lake Elementary
TEACHING LEARNING COLLABORATIVE (TLC) EARTH SCIENCE Water Travels Grade 5 Created by: Shane Lee (Pomo Elementary School); Nola Montgomery (Clearlake Community School); Lori Kincaid (Lower Lake Elementary
Movement and Storage of Groundwater The Hydrosphere
 Movement and Storage of Groundwater The Hydrosphere The water on and in Earth s crust makes up the hydrosphere. About 97 percent of the hydrosphere is contained in the oceans. The water contained by landmasses
Movement and Storage of Groundwater The Hydrosphere The water on and in Earth s crust makes up the hydrosphere. About 97 percent of the hydrosphere is contained in the oceans. The water contained by landmasses
The Hydrosphere. Introduction To Surface Water. What Do You Think?
 Introduction To Surface Water Unit Essential Questions: How does the Earth cycle its water through its major reservoirs? How does society s use of resources affect water quality? Presentation Objectives:
Introduction To Surface Water Unit Essential Questions: How does the Earth cycle its water through its major reservoirs? How does society s use of resources affect water quality? Presentation Objectives:
Freshwater. 260 Points Total
 9 SURFACE WATER SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. (13 points) 1. An excessive amount of water
9 SURFACE WATER SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. (13 points) 1. An excessive amount of water
Properties of Water. Their shapes change when they are in different containers. Their volumes stay the same in any container.
 Name: Date: 1. Which statement correctly describes both gases and liquids? Their shapes stay the same in any container. Their shapes change when they are in different containers. Their volumes stay the
Name: Date: 1. Which statement correctly describes both gases and liquids? Their shapes stay the same in any container. Their shapes change when they are in different containers. Their volumes stay the
The rest of this article describes four biogeochemical cycles: the water cycle, carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and phosphorous cycle.
 BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES The chemical elements and water that are needed by living things keep recycling over and over on Earth. These cycles are called biogeochemical cycles. They pass back and forth through
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES The chemical elements and water that are needed by living things keep recycling over and over on Earth. These cycles are called biogeochemical cycles. They pass back and forth through
Neighborhood Watershed Walk An exploration of urban watersheds
 Neighborhood Watershed Walk An exploration of urban watersheds Objectives: Students will be able to: describe what happens to water when it hits the ground. identify how different kinds of urban infrastructure
Neighborhood Watershed Walk An exploration of urban watersheds Objectives: Students will be able to: describe what happens to water when it hits the ground. identify how different kinds of urban infrastructure
Healthy Natural Environments
 Photo Arseniy Krasnevsky Shutterstock Age Level: Ages 8 and older Subject Areas: Geography, Earth Science, Environmental Science, Mathematics Duration: Warm Up: 10 minutes Activity: 30 minutes Wrap Up:
Photo Arseniy Krasnevsky Shutterstock Age Level: Ages 8 and older Subject Areas: Geography, Earth Science, Environmental Science, Mathematics Duration: Warm Up: 10 minutes Activity: 30 minutes Wrap Up:
Water Distribution Rivers
 Water Distribution Rivers Question 1 One of the main issues concerning fresh water is that most of it is found where? A. Glaciers and Icecaps B. Aquifers C. Underground D. Oceans Question 2 How does water
Water Distribution Rivers Question 1 One of the main issues concerning fresh water is that most of it is found where? A. Glaciers and Icecaps B. Aquifers C. Underground D. Oceans Question 2 How does water
SALT LAKE COUNTY WATER QUALITY FAIR. Activity Book
 SALT LAKE COUNTY WATER QUALITY FAIR Activity Book Salt Lake County Water Quality Fair Activity Book An Activity Guide for Water Quality Education and Awareness May 2018 Funded by The Salt Lake County
SALT LAKE COUNTY WATER QUALITY FAIR Activity Book Salt Lake County Water Quality Fair Activity Book An Activity Guide for Water Quality Education and Awareness May 2018 Funded by The Salt Lake County
Watershed: an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas. It is the interdependent web of living
 Watershed: an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas. It is the interdependent web of living organisms that inhabit a geographic area and depend on it
Watershed: an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas. It is the interdependent web of living organisms that inhabit a geographic area and depend on it
Shower Curtain Watershed
 Shower Curtain Watershed Overview: What is a watershed and how do humans affect its health? What is a watershed? How do our actions affect the health of a watershed? Students explore these questions by
Shower Curtain Watershed Overview: What is a watershed and how do humans affect its health? What is a watershed? How do our actions affect the health of a watershed? Students explore these questions by
Maitland Valley WATERSHED
 Maitland Valley WATERSHED Report Card 2018 Maitland Conservation has prepared this report card as a summary of the state of your forests, wetlands, and water resources. WHERE ARE WE? We are one of 36 Conservation
Maitland Valley WATERSHED Report Card 2018 Maitland Conservation has prepared this report card as a summary of the state of your forests, wetlands, and water resources. WHERE ARE WE? We are one of 36 Conservation
Name Class Date. Section: Renewable Energy Today Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow.
 Name Class Date Skills Worksheet Active Reading Section: Renewable Energy Today Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow. Solar cells, also called photovoltaic cells, convert the sun
Name Class Date Skills Worksheet Active Reading Section: Renewable Energy Today Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow. Solar cells, also called photovoltaic cells, convert the sun
East Maui Watershed Partnership Adapted from Utah State University and University of Wisconsin Ground Water Project Ages 7 th -Adult
 INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
The Drainage Basin System
 The Drainage Basin System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created in Flash. These
The Drainage Basin System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created in Flash. These
TODAY S GOALS. Intro to water and environmental issues
 TODAY S GOALS Intro to water and environmental issues Ecosystems Biomes Watershed Global water use and budgeting At the end of the class, we should be able to understand the complexity of water resources
TODAY S GOALS Intro to water and environmental issues Ecosystems Biomes Watershed Global water use and budgeting At the end of the class, we should be able to understand the complexity of water resources
PROTECT OUR WATER COLORING BOOK
 EM4855 Wally Otter Says: we really otter PROTECT OUR WATER COLORING BOOK By Marion E. Hay and Richard E. Hoover Adapted by Jerry A. Newman, Extension Youth Development Specialist and Edward B. Adams, Extension
EM4855 Wally Otter Says: we really otter PROTECT OUR WATER COLORING BOOK By Marion E. Hay and Richard E. Hoover Adapted by Jerry A. Newman, Extension Youth Development Specialist and Edward B. Adams, Extension
Why Care About Contaminants in Groundwater?
 Why Care About Contaminants in Groundwater? Subject/ target grade: Middle School (8 th grade) Earth Science Duration: Two 50 minute periods Setting: Classroom Materials and Equipment Needed: Per class
Why Care About Contaminants in Groundwater? Subject/ target grade: Middle School (8 th grade) Earth Science Duration: Two 50 minute periods Setting: Classroom Materials and Equipment Needed: Per class
13 Water: A Limited Resource
 13 Water: A Limited Resource Overview of Chapter 13 Importance of Water Water Use and Resource Problems Water Problems in U.S. and Canada Global Water Problems Water Management Water Conservation Water
13 Water: A Limited Resource Overview of Chapter 13 Importance of Water Water Use and Resource Problems Water Problems in U.S. and Canada Global Water Problems Water Management Water Conservation Water
THE WATER CYCLE IN GREATER VICTORIA
 THE WATER CYCLE IN GREATER VICTORIA KEY CONCEPTS THE GREATER VICTORIA DRINKING WATER SUPPLY SYSTEM IS DEPENDENT ON ANNUAL PRECIPITATION, WHICH FALLS MOSTLY AS RAIN. RESPONSIBILITY FOR WATER IS EVERYONE
THE WATER CYCLE IN GREATER VICTORIA KEY CONCEPTS THE GREATER VICTORIA DRINKING WATER SUPPLY SYSTEM IS DEPENDENT ON ANNUAL PRECIPITATION, WHICH FALLS MOSTLY AS RAIN. RESPONSIBILITY FOR WATER IS EVERYONE
Timing Key Narrative Snapshots a) 00:44 How does groundwater recharge occur? How do streams form?
 Module 4 Narration: Runoff and Recharge Timing Key Narrative Snapshots a) 00:44 How does groundwater recharge occur? How do streams form? These processes are closely linked. Lets first investigate how
Module 4 Narration: Runoff and Recharge Timing Key Narrative Snapshots a) 00:44 How does groundwater recharge occur? How do streams form? These processes are closely linked. Lets first investigate how
Arizona Project WET University of Arizona Cooperative Extension, Maricopa County 4341 East Broadway Road Phoenix, AZ 85040
 ARIZONA WATER FESTIVAL STUDENT QUESTIONNAIRE Dear Teachers, The purpose of this student questionnaire is to assess student learning due to their participation in the water festival unit (the pre and post
ARIZONA WATER FESTIVAL STUDENT QUESTIONNAIRE Dear Teachers, The purpose of this student questionnaire is to assess student learning due to their participation in the water festival unit (the pre and post
Flood Plain Functions
 Flood Plain Functions Lesson Abstract Summary: MO GLE: Subject Areas: Students will connect knowledge from previous watershed lessons to understand the functions of flood plains by participating in group
Flood Plain Functions Lesson Abstract Summary: MO GLE: Subject Areas: Students will connect knowledge from previous watershed lessons to understand the functions of flood plains by participating in group
The Spring Creek Stormwater Activity Book
 This booklet belongs to: The Spring Creek Stormwater Activity Book An activity booklet designed to teach children about water resources and stormwater pollution Created by the Penn State Office of Physical
This booklet belongs to: The Spring Creek Stormwater Activity Book An activity booklet designed to teach children about water resources and stormwater pollution Created by the Penn State Office of Physical
BUILDING A WATERSHED MODEL
 BUILDING A WATERSHED MODEL OBJECTIVES Define a watershed and describe how it functions Identify that students live in a watershed within the San Antonio River Basin TOPICS Watersheds Runoff TEKS ALIGNMENT
BUILDING A WATERSHED MODEL OBJECTIVES Define a watershed and describe how it functions Identify that students live in a watershed within the San Antonio River Basin TOPICS Watersheds Runoff TEKS ALIGNMENT
Your Place in the Watershed
 Your Place in the Watershed Subject Area: Natural Resources Unit Title: Colorado Watersheds Grade Level: 4th & 5th grade Objectives: To help students understand the concept of watersheds and the importance
Your Place in the Watershed Subject Area: Natural Resources Unit Title: Colorado Watersheds Grade Level: 4th & 5th grade Objectives: To help students understand the concept of watersheds and the importance
Groundwater Flow Demonstration Model Activities for grades 4-12
 Groundwater Flow Demonstration Model Activities for grades 4-12 NR/WQ/2012-5 SET-UP Please allow time to practice using the groundwater model before conducting demonstrations. 1. Remove the groundwater
Groundwater Flow Demonstration Model Activities for grades 4-12 NR/WQ/2012-5 SET-UP Please allow time to practice using the groundwater model before conducting demonstrations. 1. Remove the groundwater
Water exists everywhere on Earth, and covers 70% of its surface. 97% of this water is found in the oceans.
 10.1 Distribution of Water Water exists everywhere on Earth, and covers 70% of its surface. 97% of this water is found in the oceans. w Another 2% is ice and snow, leaving only 1% as fresh water found
10.1 Distribution of Water Water exists everywhere on Earth, and covers 70% of its surface. 97% of this water is found in the oceans. w Another 2% is ice and snow, leaving only 1% as fresh water found
Where s the Water?: Acting Out Science Cycles
 Where s the Water?: Acting Out Science Cycles SEASONS: SUBJECTS: EXT. SUBJECT: X MATERIALS For each student: water cycle card, water cycle picture, pencil. For class: glass of water, Where Does the Water
Where s the Water?: Acting Out Science Cycles SEASONS: SUBJECTS: EXT. SUBJECT: X MATERIALS For each student: water cycle card, water cycle picture, pencil. For class: glass of water, Where Does the Water
W A T E R F O R L I F E
 Module 4 The Hydrological Cycle Disclaimer: The contents of this presentation include original content as well as items compiled from a variety of sources. Though the sources are not attributed individually,
Module 4 The Hydrological Cycle Disclaimer: The contents of this presentation include original content as well as items compiled from a variety of sources. Though the sources are not attributed individually,
Where does your water shed? National Association of Conservation Districts (NACD) Poster Contest Promotion 2013 Contest
 Slide 1 Where does your water shed? National Association of Conservation Districts (NACD) Poster Contest Promotion 2013 Contest 1 Slide 2 Where does your water shed? Share an activity to show how water
Slide 1 Where does your water shed? National Association of Conservation Districts (NACD) Poster Contest Promotion 2013 Contest 1 Slide 2 Where does your water shed? Share an activity to show how water
Lesson 1.2 Recycling Matter
 Lesson 1.2 Recycling Matter Lesson Objectives Define biogeochemical cycles. Describe the water cycle and its processes. Give an overview of the carbon cycle. Outline the steps of the nitrogen cycle. Lesson
Lesson 1.2 Recycling Matter Lesson Objectives Define biogeochemical cycles. Describe the water cycle and its processes. Give an overview of the carbon cycle. Outline the steps of the nitrogen cycle. Lesson
Investigating Ecosystems
 Grade 4 Life Science Module Investigating Ecosystems In a code such as 5.2.4.D.1, the 5 indicates the science standards, the 2 indicates the physical science standard within the set of science standards,
Grade 4 Life Science Module Investigating Ecosystems In a code such as 5.2.4.D.1, the 5 indicates the science standards, the 2 indicates the physical science standard within the set of science standards,
What We Are Hoping For: Learning Goals. Runoff Human Impact o A, B, C. Learning Goals:
 LESSON Exploring: Water in Our Lives Introduce how salt moves into waterways by looking at where our water comes from and how runoff impacts the environment. What We Are Hoping For: Learning Goals Runoff
LESSON Exploring: Water in Our Lives Introduce how salt moves into waterways by looking at where our water comes from and how runoff impacts the environment. What We Are Hoping For: Learning Goals Runoff
French Creek Outdoor School Riparian Creek Field Study
 Siskiyou County Office of Education Kermith R. Walters, County Superintendent 1 French Creek Outdoor School Riparian Creek Field Study Station Over-View: (Allow 1.5 hours for this Station) The Creek Study
Siskiyou County Office of Education Kermith R. Walters, County Superintendent 1 French Creek Outdoor School Riparian Creek Field Study Station Over-View: (Allow 1.5 hours for this Station) The Creek Study
Objective: Students learn the processes of the water cycle and how pollution moves through the water cycle. Differentiation: Process by readiness
 Objective: Students learn the processes of the water cycle and how pollution moves through the water cycle. Differentiation: Process by readiness Pre-assessment data determines placement of students in
Objective: Students learn the processes of the water cycle and how pollution moves through the water cycle. Differentiation: Process by readiness Pre-assessment data determines placement of students in
Unit 2: Weather Dynamics Chapter 1: Hydrological Cycle
 UNIT 2 Chapter 1: Inquiring about Weather Unit 2: Weather Dynamics Chapter 1: Hydrological Cycle Science 10 Mrs. Purba Importance of H 2 O From the beginning of time when water first appeared, it has been
UNIT 2 Chapter 1: Inquiring about Weather Unit 2: Weather Dynamics Chapter 1: Hydrological Cycle Science 10 Mrs. Purba Importance of H 2 O From the beginning of time when water first appeared, it has been
1. Students will become familiar with the sources of water pollution
 Educators, Please Note! WLSSD education staff is available to present the Water Drop program upon request, call Sarah at (218) 740-4784 to schedule an appointment. Lesson Plan: River Rangers Water Quality
Educators, Please Note! WLSSD education staff is available to present the Water Drop program upon request, call Sarah at (218) 740-4784 to schedule an appointment. Lesson Plan: River Rangers Water Quality
The Water Cycle. 1. The diagram below is a cross-sectional view of rain falling on a farm field and then moving to the water table.
 1. The diagram below is a cross-sectional view of rain falling on a farm field and then moving to the water table. Which word best describes the movement of the rainwater through zone A? A. runoff B. saturation
1. The diagram below is a cross-sectional view of rain falling on a farm field and then moving to the water table. Which word best describes the movement of the rainwater through zone A? A. runoff B. saturation
THE IMPORTANCE OF WATER
 THE IMPORTANCE OF WATER 2/3rds of the Earth s surface is covered in. water Earth s aquatic ecosystems contain biomass more (living mass) than its terrestrial ecosystems. Phytoplankton are microscopic producers
THE IMPORTANCE OF WATER 2/3rds of the Earth s surface is covered in. water Earth s aquatic ecosystems contain biomass more (living mass) than its terrestrial ecosystems. Phytoplankton are microscopic producers
Lecture 14. Water: A Limited Resource. Lecture 14
 Lecture 14 Water: A Limited Resource Lecture 14 1. Importance of Water 2. Water Use and Resource Problems 3. Water Problems in U.S. and Canada 4. Global Water Problems 5. Water Management 6. Water Conservation
Lecture 14 Water: A Limited Resource Lecture 14 1. Importance of Water 2. Water Use and Resource Problems 3. Water Problems in U.S. and Canada 4. Global Water Problems 5. Water Management 6. Water Conservation
Understanding Environmental Impacts of Horticulture
 Lesson A1 3 Understanding Environmental Impacts of Horticulture Unit A. Horticultural Science Problem Area 1. Exploring the Horticulture Industry Lesson 3. Understanding Environmental Impacts of Horticulture
Lesson A1 3 Understanding Environmental Impacts of Horticulture Unit A. Horticultural Science Problem Area 1. Exploring the Horticulture Industry Lesson 3. Understanding Environmental Impacts of Horticulture
Watersheds & Water Pollution
 Watersheds & Water Pollution Runoff What is runoff? Review: When rain or snow falls onto the earth, it just doesn't sit there, it starts moving according to the laws of gravity. A portion of the precipitation
Watersheds & Water Pollution Runoff What is runoff? Review: When rain or snow falls onto the earth, it just doesn't sit there, it starts moving according to the laws of gravity. A portion of the precipitation
TB pg Liquid. Ice. Vapour. Surface water Underground water. Poles Icebergs Permafrost. Atmosphere
 The Hydrosphere TB pg. 227 Liquid Surface water Underground water Ice Poles Icebergs Permafrost Vapour Atmosphere TB pg. 228 Living organisms depend on it. Bodily structure of living organisms (cells,
The Hydrosphere TB pg. 227 Liquid Surface water Underground water Ice Poles Icebergs Permafrost Vapour Atmosphere TB pg. 228 Living organisms depend on it. Bodily structure of living organisms (cells,
Review of Chapter 1. Taken from: Check Your Understanding sections p. 13, 21 and 33
 Review of Chapter 1 Taken from: Check Your Understanding sections p. 13, 21 and 33 In case you were curious: Henry Hudson The Last Voyage of Henry Hudson, 1611 Painted in 1880 by: John Collier Today Hudson
Review of Chapter 1 Taken from: Check Your Understanding sections p. 13, 21 and 33 In case you were curious: Henry Hudson The Last Voyage of Henry Hudson, 1611 Painted in 1880 by: John Collier Today Hudson
Where did the water you drank today come from? Summary With a roll of the dice, you can simulate the movement of water within the water cycle.
 The Water Cycle Where did the water you drank today come from? Summary With a roll of the dice, you can simulate the movement of water within the water cycle. Objectives Students will learn the complex
The Water Cycle Where did the water you drank today come from? Summary With a roll of the dice, you can simulate the movement of water within the water cycle. Objectives Students will learn the complex
Elementary Lesson Plan #4
 Elementary Lesson Plan #4 GRADE(S): 3 rd, 4 th, 5 th TOPIC: Watershed TITLE: Watershed Model OVERVIEW: Everyone lives in a watershed and everything that is done in a watershed can affect the receiving
Elementary Lesson Plan #4 GRADE(S): 3 rd, 4 th, 5 th TOPIC: Watershed TITLE: Watershed Model OVERVIEW: Everyone lives in a watershed and everything that is done in a watershed can affect the receiving
OBJECTIVES BACKGROUND INFORMATION SUBJECTS: TIME: MATERIALS: The student will do the following: 1. Define groundwater.
 9-12 FROM GROUND TO WATER SUBJECTS: TIME: Language Arts, Science (Physical Science, Earth Science) 1 class period MATERIALS: Student Sheets: The Hidden Resource Groundwater. Keeping it Safe Keeping it
9-12 FROM GROUND TO WATER SUBJECTS: TIME: Language Arts, Science (Physical Science, Earth Science) 1 class period MATERIALS: Student Sheets: The Hidden Resource Groundwater. Keeping it Safe Keeping it
Reading the River Summer 2004 July 31, A Unit for Grade 8 Science An Adventure in Water. Karyl White Rowan County Middle School Rowan County
 Reading the River Summer 2004 July 31, 2004 A Unit for Grade 8 Science An Adventure in Water Karyl White Rowan County Middle School Rowan County Grade Level: 8 Create a Model Filtration System to Purify
Reading the River Summer 2004 July 31, 2004 A Unit for Grade 8 Science An Adventure in Water Karyl White Rowan County Middle School Rowan County Grade Level: 8 Create a Model Filtration System to Purify
9 Week Unit EARTH S SYSTEMS UNIT 3. Fifth Grade Rogers Public Schools
 9 Week Unit UNIT 3 EARTH S SYSTEMS Fifth Grade Rogers Public Schools : Earth s Systems 9 weeks In this unit, students develop an understanding of how the Earth s major systems (geosphere, biosphere, hydrosphere,
9 Week Unit UNIT 3 EARTH S SYSTEMS Fifth Grade Rogers Public Schools : Earth s Systems 9 weeks In this unit, students develop an understanding of how the Earth s major systems (geosphere, biosphere, hydrosphere,
Lesson Focus: watershed and non point source pollution
 From Brook to Ocean Lesson Focus: watershed and non point source pollution Lesson objectives: To create an understanding that everyone is part of a watershed and that humans can affect that watershed in
From Brook to Ocean Lesson Focus: watershed and non point source pollution Lesson objectives: To create an understanding that everyone is part of a watershed and that humans can affect that watershed in
Topic 3, Subtopic A of Review Handbook or Chapter 10 of Earth Science Book. 97% of Earth s water is found as saltwater in Earth s oceans.
 Topic 3, Subtopic A of Review Handbook or Chapter 10 of Earth Science Book Groundwater 97% of Earth s water is found as saltwater in Earth s oceans. That leaves only 3% for freshwater! But 90% of the freshwater
Topic 3, Subtopic A of Review Handbook or Chapter 10 of Earth Science Book Groundwater 97% of Earth s water is found as saltwater in Earth s oceans. That leaves only 3% for freshwater! But 90% of the freshwater
Water Quality indicators and How Human Activities Affect Water Quality
 Water Quality indicators and How Human Activities Affect Water Quality Name: Online Assignment: Period: Date: Purpose: to learn how to evaluate water quality and how pollution can make water unavailable
Water Quality indicators and How Human Activities Affect Water Quality Name: Online Assignment: Period: Date: Purpose: to learn how to evaluate water quality and how pollution can make water unavailable
CHARACTERISTICS & PROCESSES OF SCIENCE raindrops keep falling the water cycle
 CHARACTERISTICS & PROCESSES OF SCIENCE the water cycle Frameworks SCIENCE ESS 8.7.16 Conduct investigations demonstrating the water cycle. LS 4.6.2 Conduct simulations demonstrating competition for resources
CHARACTERISTICS & PROCESSES OF SCIENCE the water cycle Frameworks SCIENCE ESS 8.7.16 Conduct investigations demonstrating the water cycle. LS 4.6.2 Conduct simulations demonstrating competition for resources
Objectives: 1. Students. will be able 2. Students 3. Students pollution. 4. Students. Materials: Newspaper. you like. powder. students: Standards:
 Chicago River Classroom Activity Summary Students will create models of a landscape. They willl then make and test their predictions about the location of rivers and watershed boundaries. Students will
Chicago River Classroom Activity Summary Students will create models of a landscape. They willl then make and test their predictions about the location of rivers and watershed boundaries. Students will
Next Generation Science Standards* Correlation
 Next Generation Science Standards* Correlation Engineering Design Where You Will Find It Define a simple design problem reflecting a need or a want that includes specified criteria for success and constraints
Next Generation Science Standards* Correlation Engineering Design Where You Will Find It Define a simple design problem reflecting a need or a want that includes specified criteria for success and constraints
4.2 The Water Cycle. Recycling water. Sharing water with the dinosaurs. The Sun drives the water cycle. Wind and weather. Gravity
 4.2 The Water Cycle The Sun keeps water moving through the hydrosphere by providing energy. In this section, you will learn about the water cycle and where water goes so that it is available for people,
4.2 The Water Cycle The Sun keeps water moving through the hydrosphere by providing energy. In this section, you will learn about the water cycle and where water goes so that it is available for people,
Earth Science Chapter 6 Section 1 Review
 Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 6 Section 1 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What process is illustrated by the arrows labeled
Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 6 Section 1 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What process is illustrated by the arrows labeled
