Continuous Monitoring of Pollution in the Nation s Precipitation
|
|
|
- Amie Howard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Continuous Monitoring of Pollution in the Nation s Precipitation Martin Risch and David A. Gay U.S. Geological Survey, Indiana Water Science Center, Indianapolis, IN, mrrisch@usgs.gov NADP Program Office, University of Illinois Urbana Champaign dgay@illinois.edu
2 Topics Brief overview: What wet and dry deposition NADP and how we operate Review of results Marty Risch/USGS will cover specific mercury topics in Indiana
3 How Do Pollutants Get into Rain?
4
5 Wet Deposition of Pollutants rainout washout
6 Dry Deposition of Pollutants Solids and gases fall out of the atmosphere Very difficult to measure But you can estimate the rate of deposition Flux = Conc X Deposition Velocity F = C x Vd
7 Other Mass Movement Processes Litterfall Litterfall Throughfall Throughfall
8 What Ecotoxics are in Precipitation? Chemicals Acids Bases (NH 3+ ) Oxidants (Cl -, Br -, O 3, OH - radicals) Metals (arsenic, vanadium, strontium, chromium, etc.) Organics (world of compounds) Other inorganics/industrialized compounds Radiological elements (alpha, beta, gamma)
9 What Ecotoxics are in Precipitation? Biological Elements Bacteria Viruses Spores fungi Physical Agents Solids/particulates Frozen water Radiation (from compounds)
10 What is the National Atmospheric Deposition Program?
11 A Cooperative Research Program (Un. Of Illinois) Measure wet deposition of pollutants We monitor the rate of pollution movement to the surface (dry deposition) North America US, Canada, and some in Mexico Also Taiwan, South America, Hawaii Owned and operated by our members Decisions made by our members Started in 1978, 35 th year acid rain network Over 450,000 precipitation samples
12 NADP is Five Networks measure wet deposition of pollutants 1. National Trends Network (NTN) 2. Atmospheric Integrated Research Monitoring Network (AIRMON) 3. Mercury Deposition Network (MDN) measure atmospheric concentrations (dry deposition) 4. Atmospheric Mercury Network (AMNet) 5. Ammonia Monitoring Network (AMoN)
13 NADP s Goal To monitor the chemistry of precipitation (rain and snow) and in the atmosphere, as consistently and as accurately as we can, for long periods to determine changes over time (trends).
14
15 Who is NADP?
16 Some of our Funders (100+ total agencies) Federal Agency Members Tribal Organizations Universities US States Other Organizations
17 What Does NADP Measure?
18 Network #1: National Trends Network (NTN) Collects one-week precipitation-only samples with NADP wet-dry collector Measures precipitation with gage Analyses Acids Nutrients Base Cations
19 Species Measured by the NADP acidic species free acidity (or ph), sulfate, nitrate, chloride nutrients nitrate, ammonium, orthophosphate earth crustal base cations calcium, magnesium, potassium salts sodium and chloride heavy metals mercury, trace metals (MDN)
20 National Trends Network (NTN)
21 NTN NV05 Great Basin National Park NTN IL11 Bondville, IL
22 AIRMoN PA15 Penn State Univ., PA MDN FL11 Everglades N.P., FL
23
24
25 Network #2: Atmospheric Integrated Research Monitoring Network (AIRMoN) Very similar to NTN, but collects daily when precipitation occurs Measures precipitation with NWS stick gage Measures same analytes as NTN Samples refrigerated from collection until analysis
26 Networks #3& 5: Mercury Deposition (MDN & AMNet)
27 Network #4: Ammonia Monitoring Network (AMoN) Measure atmospheric concentrations of ammonia Passive samplers Low cost, 2 week integrated sample
28
29 All of this information (including data) is on the web
30 So what are we finding?
31
32 ph Effects on Fish Population Source: HBRF, Acid Rain Revisited, 2001
33 Damage to Forests Mt. Mitchell, North Carolina
34
35 Acid Rain is still an issue.
36 Sulfate (SO 4= ) Deposition Animation Anion most associated with combustion and acid rain Deposition over time (kg per hectare per year)
37
38
39 Mercury Deposition
40 Bioaccumulation of Methyl Mercury Dry Deposition Wet Deposition Through Fall (wet+dry) Geologic Sources (soil, rock, base flow etc.) Litter Fall Hg Hg Hg Methylation Bacterial action (water and sediment) Zooplankton Small fish predatory fish Water Body/pore water
41
42 0.3 ppm, EPA FDA From E. Sutherland, USEPA
43 Many Sources of Atmospheric Mercury Coal combustion Incineration Medical Trash Cremation Industrial emissions (chlor-alkali) Cement production (Hg in lime) Mining Hg use in gold and silver mining (amalgam formation) Mining for Hg taconite Automobile Recycling Mercury in Landfills Fluorescent lamps dental amalgams (also in sewers) Thermometers Batteries Discarded electrical switches Others will surface Other carbon fossil fuels (gas/oil/diesel)? Volcanoes (St. Helens) Naturally enriched ores/soils Plate tectonic boundaries Cinnabar (HgS), taconite, others Soils and rocks (0.08 to 0.5 ppm in crust) Evaporation Soils Fresh water and Oceans Natural forest fires Tree bark (wood fire places) soils Volatilization from rocks? Wind Blown reintroduction Mine tailings Industrial contaminated soils Evolving Gases Mines, industrial areas Waste facilities (municipal in particular) Out of soil
44 Marty will be covering more here.
45 Ammonia Deposition
46 Ammonium (NH 4+ )
47 Why Measure? NH3 is very Reactive, Forms Particulates, Nitrogen Addition Ammonium sulfate Other compounds Ammonium chloride Ammonium nitrate
48 AMoN Network Sites 58 sites
49
50 2011 Annual Average Concentration
51 2011 Quarterly Average Concentration
52 Radiation Deposition
53 NADP Monitoring Observations During Fukushima Accident
54
55
56
57 Results in Context Detectable 131 I, 134 Cs, & 137 Cs 20% of sampled locations. Maximum 137 Cs deposition: ~ 3%-10% additional radioactivity to that present in a common m 2 of soil (5 cm deep). Maximum NADP-measured 137Cs (240 Bq/m 2 ) ~ 17% of the NYC and Birmingham deposition (1,400 Bq/m2) during atmospheric nuclear testing in 1963.
58 Soybean Rust Deposition
59
60 All of this information (including data) is on the web
61 And NADP is open to all
62 Continuous Monitoring of Pollution in the Nation s Precipitation David A. Gay NADP Program Office, University of Illinois Urbana Champaign dgay@illinois.edu
Atmospheric Mercury Deposition And Impacts In The Pacific Northwest
 Atmospheric Mercury Deposition And Impacts In The Pacific Northwest Bob Brunette and David Gay National Atmospheric Deposition Program Mercury Deposition Network DGay@illinois.edu RobertBrunette@EurofinsUS.com
Atmospheric Mercury Deposition And Impacts In The Pacific Northwest Bob Brunette and David Gay National Atmospheric Deposition Program Mercury Deposition Network DGay@illinois.edu RobertBrunette@EurofinsUS.com
2011 Acid Deposition Summary
 2011 Acid Deposition Summary New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection NATURE AND SOURCES Atmospheric deposition is a process in which pollutants are deposited on land or water from the air. Deposition
2011 Acid Deposition Summary New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection NATURE AND SOURCES Atmospheric deposition is a process in which pollutants are deposited on land or water from the air. Deposition
Atmospheric Deposition in Pennsylvania: Monitoring Inputs and Ecosystem Effects
 Thanks to many collaborators Atmospheric Deposition in Pennsylvania: Monitoring Inputs and Ecosystem Effects Elizabeth W. Boyer Department of Ecosystem Science & Management, Pennsylvania State University
Thanks to many collaborators Atmospheric Deposition in Pennsylvania: Monitoring Inputs and Ecosystem Effects Elizabeth W. Boyer Department of Ecosystem Science & Management, Pennsylvania State University
National Atmospheric Deposition Program
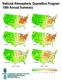 National Atmospheric Deposition Program Annual Summary Sulfate Sulfate Nitrate Nitrate Ammonium Ammonium - - Estimated Annual Deposition (millimoles/meter ) What Is NADP? In, scientists, students, educators,
National Atmospheric Deposition Program Annual Summary Sulfate Sulfate Nitrate Nitrate Ammonium Ammonium - - Estimated Annual Deposition (millimoles/meter ) What Is NADP? In, scientists, students, educators,
On the cover: The gradient maps represent (top) relative nitrogen (N) plus sulfur (S) wet deposition in 2011 as a percentage of the average annual
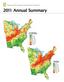 On the cover: The gradient maps represent (top) relative nitrogen (N) plus sulfur (S) wet deposition in as a percentage of the average annual wet deposition from to, and (bottom) total precipitation in
On the cover: The gradient maps represent (top) relative nitrogen (N) plus sulfur (S) wet deposition in as a percentage of the average annual wet deposition from to, and (bottom) total precipitation in
2017 Annual Summary. 40 Years of NADP
 2017 Annual Summary 40 Years of NADP 1978-2018 40 Years of NADP 1978-2018 On the cover: 2018 is the 40th Anniversary of NADP. The collage of maps and site photos represents the expansive history of what
2017 Annual Summary 40 Years of NADP 1978-2018 40 Years of NADP 1978-2018 On the cover: 2018 is the 40th Anniversary of NADP. The collage of maps and site photos represents the expansive history of what
2012 Annual Summary. Frequency of Bromide Detection (%) 25-50% > 50%
 Annual Summary Frequency of Bromide Detection (%) % - % - % > % Frequency of Bromide Detection (%) % - % - % > % On the cover: The proportional circle map represents the detection frequency of bromide
Annual Summary Frequency of Bromide Detection (%) % - % - % > % Frequency of Bromide Detection (%) % - % - % > % On the cover: The proportional circle map represents the detection frequency of bromide
Acid Deposition. Brief History Acids and Bases Chemical Processes and Sources Deposition Processes Acid Deposition Distribution Environmental Effects
 Acid Deposition 1 Acid Deposition Brief History Acids and Bases Chemical Processes and Sources Deposition Processes Acid Deposition Distribution Environmental Effects Health Effects Lakes and Forests Abatement
Acid Deposition 1 Acid Deposition Brief History Acids and Bases Chemical Processes and Sources Deposition Processes Acid Deposition Distribution Environmental Effects Health Effects Lakes and Forests Abatement
Acid Deposition. Acid Deposition. Early History of Acid Deposition
 Acid Deposition 1 Acid Deposition Brief History Acids and Bases Chemical Processes and Sources Deposition Processes Acid Deposition Distribution Environmental Effects Health Effects Lakes and Forests Abatement
Acid Deposition 1 Acid Deposition Brief History Acids and Bases Chemical Processes and Sources Deposition Processes Acid Deposition Distribution Environmental Effects Health Effects Lakes and Forests Abatement
Objectives. Aquatic Toxicology of Metals 4/20/11. Why are metals different than organic chemicals? Essential vs. Non-essential metals
 Aquatic Systems & Environmental Health Aquatic Toxicology of Metals David Barber barberd@vetmed.ufl.edu 392-2243 x.5540 Objectives Understand how metals differ from organic compounds including their source
Aquatic Systems & Environmental Health Aquatic Toxicology of Metals David Barber barberd@vetmed.ufl.edu 392-2243 x.5540 Objectives Understand how metals differ from organic compounds including their source
NADP Site Information Worksheet, Revised Version 1.6. NADP Site Information Worksheet
 NADP Site Information Worksheet Document Change History Version Description Effective Date 1.6 Clarify major sources to document Clarified Instrument 1 and Instrument 2 tables on pg 10 04/2016 1.5 Addition
NADP Site Information Worksheet Document Change History Version Description Effective Date 1.6 Clarify major sources to document Clarified Instrument 1 and Instrument 2 tables on pg 10 04/2016 1.5 Addition
How Ecosystems Work Section 2
 Objectives List the three stages of the carbon cycle. Describe where fossil fuels are located. Identify one way that humans are affecting the carbon cycle. List the tree stages of the nitrogen cycle. Describe
Objectives List the three stages of the carbon cycle. Describe where fossil fuels are located. Identify one way that humans are affecting the carbon cycle. List the tree stages of the nitrogen cycle. Describe
Pamela Padgett US Forest Service
 Pamela Padgett US Forest Service Pamela Padgett US Forest Service 1978 Ellis Cowling, 1 st Chair of Atmospheric Deposition Program Doug Whelpdale Canadian representative Jim Galloway Doug Fox Gary Stensland
Pamela Padgett US Forest Service Pamela Padgett US Forest Service 1978 Ellis Cowling, 1 st Chair of Atmospheric Deposition Program Doug Whelpdale Canadian representative Jim Galloway Doug Fox Gary Stensland
Aquatic Toxicology of Metals. David Barber ext
 Aquatic Toxicology of Metals David Barber barberd@vetmed.ufl.edu 352-392-2243 ext 1-5540 Why are metals different than organic chemicals? Some are essential micronutrients Natural parts of the earth s
Aquatic Toxicology of Metals David Barber barberd@vetmed.ufl.edu 352-392-2243 ext 1-5540 Why are metals different than organic chemicals? Some are essential micronutrients Natural parts of the earth s
Nutrient Cycles. Nutrient cycles involve flow of high quality energy from the sun through the environment & of elements.
 Nutrient Cycles Nutrient cycles (= biogeochemical cycles): natural processes that involve the flow of nutrients from the environment (air, water, soil, rock) to living organisms ( ) & back again. Nutrient
Nutrient Cycles Nutrient cycles (= biogeochemical cycles): natural processes that involve the flow of nutrients from the environment (air, water, soil, rock) to living organisms ( ) & back again. Nutrient
Section 2: The Cycling of Materials
 Section 2: The Cycling of Materials Preview Bellringer Objectives The Carbon Cycle How Humans Affect the Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle Decomposers and the Nitrogen Cycle The Phosphorus Cycle Section
Section 2: The Cycling of Materials Preview Bellringer Objectives The Carbon Cycle How Humans Affect the Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle Decomposers and the Nitrogen Cycle The Phosphorus Cycle Section
Introduction to Minnesota s plan to reduce mercury
 Introduction to Minnesota s plan to reduce mercury wq-iw4-02g2 Rebecca Place Mercury Program Coordinator September 26, 2017 Mercury in Minnesota Minnesota Department of Health Fish Consumption Advisories
Introduction to Minnesota s plan to reduce mercury wq-iw4-02g2 Rebecca Place Mercury Program Coordinator September 26, 2017 Mercury in Minnesota Minnesota Department of Health Fish Consumption Advisories
Just what is Acid Rain?
 Acid Rain Just what is Acid Rain? Acid Rain is the term used to describe the ways in which acid precipitates out of the atmosphere. Acid Rain is more accurately termed acid deposition. There are two types
Acid Rain Just what is Acid Rain? Acid Rain is the term used to describe the ways in which acid precipitates out of the atmosphere. Acid Rain is more accurately termed acid deposition. There are two types
NADP AMNet Standard Operating Procedure Site Report C - Laboratory: Quarterly Maintenance
 NADP AMNet Standard Operating Procedure Site Report C - Laboratory: Quarterly Maintenance For information about the National Atmospheric Deposition Program (NADP) contact: NADP Program Office Illinois
NADP AMNet Standard Operating Procedure Site Report C - Laboratory: Quarterly Maintenance For information about the National Atmospheric Deposition Program (NADP) contact: NADP Program Office Illinois
MANAGEMENT OF MERCURY AND MERCURY CONTAINING WASTES IN PAKISTAN
 MANAGEMENT OF MERCURY AND MERCURY CONTAINING WASTES IN PAKISTAN PRESENTATION BY ENGINEER MUMTAZ HUSSAIN ENVIRONMENT CONSULTANT & EDITOR, THE ENVIRON MONITOR LAHORE, 30 JULY 2009 OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION
MANAGEMENT OF MERCURY AND MERCURY CONTAINING WASTES IN PAKISTAN PRESENTATION BY ENGINEER MUMTAZ HUSSAIN ENVIRONMENT CONSULTANT & EDITOR, THE ENVIRON MONITOR LAHORE, 30 JULY 2009 OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION
State of Nevada Department of Conservation and Natural Resources Division of Environmental Protection Laboratory Scope of Accreditation
 Matrix: CWA (Non Potable Water) Discipline EPA 120.1 Chemistry Conductivity 8/1/2015 Aluminum 8/1/2015 Antimony 8/1/2015 Arsenic 8/1/2015 Barium 8/1/2015 Beryllium 8/1/2015 Boron 8/1/2015 Cadmium 8/1/2015
Matrix: CWA (Non Potable Water) Discipline EPA 120.1 Chemistry Conductivity 8/1/2015 Aluminum 8/1/2015 Antimony 8/1/2015 Arsenic 8/1/2015 Barium 8/1/2015 Beryllium 8/1/2015 Boron 8/1/2015 Cadmium 8/1/2015
13.5. Cycling of Matter. Water cycles through the environment.
 13.5 Cycling of Matter VOCABULARY hydrologic cycle biogeochemical cycle nitrogen fixation KEY CONCEPT Matter cycles in and out of an ecosystem. Main Ideas Water cycles through the environment. Elements
13.5 Cycling of Matter VOCABULARY hydrologic cycle biogeochemical cycle nitrogen fixation KEY CONCEPT Matter cycles in and out of an ecosystem. Main Ideas Water cycles through the environment. Elements
3 3 CYCLES OF MATTER
 3 3 CYCLES OF MATTER REVIEW: 1. What is an element? 2. What is a compound? 3. What are the 6 elements that are most important to living things? Matter = a substance that takes up space. BIOGEOCHEMICAL
3 3 CYCLES OF MATTER REVIEW: 1. What is an element? 2. What is a compound? 3. What are the 6 elements that are most important to living things? Matter = a substance that takes up space. BIOGEOCHEMICAL
Elements essential for life also cycle through ecosystems.
 13.5 Cycling of Matter KEY CONCEPT Matter cycles in and out of an ecosystem. MAIN IDEAS Water cycles through the environment. Elements essential for life also cycle through ecosystems. VOCABULARY hydrologic
13.5 Cycling of Matter KEY CONCEPT Matter cycles in and out of an ecosystem. MAIN IDEAS Water cycles through the environment. Elements essential for life also cycle through ecosystems. VOCABULARY hydrologic
Lecture 1: Introduction
 Islamic University of Gaza Environmental Engineering Department Water Treatment EENV 4331 Lecture 1: Introduction Dr. Fahid Rabah 1 1.1 Water Cycle and Water Resources 2 1.2 Water Distribution on Earth
Islamic University of Gaza Environmental Engineering Department Water Treatment EENV 4331 Lecture 1: Introduction Dr. Fahid Rabah 1 1.1 Water Cycle and Water Resources 2 1.2 Water Distribution on Earth
Executive summary. Project objective. Report recommendations. ZMWG BAN Toxics! GAIA
 Reducing Global Emissions From Burning Mercury-added Products January 2009 ZMWG BAN Toxics! GAIA Page i Executive summary This assessment has been prepared for the Mercury Policy Project/Tides Center and
Reducing Global Emissions From Burning Mercury-added Products January 2009 ZMWG BAN Toxics! GAIA Page i Executive summary This assessment has been prepared for the Mercury Policy Project/Tides Center and
State of Nevada Department of Conservation and Natural Resources Division of Environmental Protection Laboratory Scope of Accreditation
 Matrix: CWA (Non Potable Water) Discipline: Chemistry ASTM D516-07 ASTM D6888-09 ASTM D7511-09e2 EPA 160.4 EPA 1631E EPA 1664A EPA 1664A (SGT-HEM) EPA 180.1 Sulfate 8/1/2018 Cyanide, Amenable 8/1/2018
Matrix: CWA (Non Potable Water) Discipline: Chemistry ASTM D516-07 ASTM D6888-09 ASTM D7511-09e2 EPA 160.4 EPA 1631E EPA 1664A EPA 1664A (SGT-HEM) EPA 180.1 Sulfate 8/1/2018 Cyanide, Amenable 8/1/2018
1. Energy to do work 2. Raw material to build/repair things (nutrients)
 1. Energy to do work 2. Raw material to build/repair things (nutrients) Living things are built from water Nutrients: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen 3. Essential nutrients are cycled through environment
1. Energy to do work 2. Raw material to build/repair things (nutrients) Living things are built from water Nutrients: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen 3. Essential nutrients are cycled through environment
Name Class Date. In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best matches the description.
 Skills Worksheet Concept Review MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best matches the description. 1. ground-level ozone 2. scrubber 3. radon gas 4. nitrogen oxides
Skills Worksheet Concept Review MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best matches the description. 1. ground-level ozone 2. scrubber 3. radon gas 4. nitrogen oxides
How Ecosystems Work Section 2. Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 2: Cycling of Materials DAY 1
 Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 2: Cycling of Materials DAY 1 The Carbon Cycle The carbon cycle is the movement of carbon from the nonliving environment into living things and back Carbon is the
Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 2: Cycling of Materials DAY 1 The Carbon Cycle The carbon cycle is the movement of carbon from the nonliving environment into living things and back Carbon is the
4/12. There is so much pollution in the air now that if it weren t for our lungs there d be no place to put it all. Robert Orben
 4/12 There is so much pollution in the air now that if it weren t for our lungs there d be no place to put it all. Robert Orben Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Air Pollution
4/12 There is so much pollution in the air now that if it weren t for our lungs there d be no place to put it all. Robert Orben Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Air Pollution
3.4 Cycles of Matter. Recycling in the Biosphere. Lesson Objectives. Lesson Summary
 3.4 Cycles of Matter Lesson Objectives Describe how matter cycles among the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem. Describe how water cycles through the biosphere. Explain why nutrients are important
3.4 Cycles of Matter Lesson Objectives Describe how matter cycles among the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem. Describe how water cycles through the biosphere. Explain why nutrients are important
Quality Assurance Report National Atmospheric Deposition Program 2010
 Quality Assurance Report National Atmospheric Deposition Program 2010 Laboratory Operations Central Analytical Laboratory Prepared by Tracy Dombek CAL Quality Assurance and Data Specialist National Atmospheric
Quality Assurance Report National Atmospheric Deposition Program 2010 Laboratory Operations Central Analytical Laboratory Prepared by Tracy Dombek CAL Quality Assurance and Data Specialist National Atmospheric
NADP Spring Meeting Notes. Joint session. May 3, Pensacola, FL
 Minutes from previous meeting approved. State of Networks - Gay NADP Spring Meeting Notes Joint session May 3, 2011 Pensacola, FL NT N cost increase from $91 to $93/sample, first increase since 2002. Total
Minutes from previous meeting approved. State of Networks - Gay NADP Spring Meeting Notes Joint session May 3, 2011 Pensacola, FL NT N cost increase from $91 to $93/sample, first increase since 2002. Total
Natural Ecosystem Change
 Environmental Science Set 3 of 9 Natural Ecosystem Change Presentation MEDIA Version 2 BIOZONE International 2009, 2013 Processes in Carbon Cycling Carbon cycles between the living (biotic) and non-living
Environmental Science Set 3 of 9 Natural Ecosystem Change Presentation MEDIA Version 2 BIOZONE International 2009, 2013 Processes in Carbon Cycling Carbon cycles between the living (biotic) and non-living
Ch. 5 - Nutrient Cycles and Soils
 Ch. 5 - Nutrient Cycles and Soils What are Nutrient (biogeochemical) Cycles? a process by which nutrients are recycled between living organisms and nonliving environment. The three general types of nutrient
Ch. 5 - Nutrient Cycles and Soils What are Nutrient (biogeochemical) Cycles? a process by which nutrients are recycled between living organisms and nonliving environment. The three general types of nutrient
Nutrient Cycling & Soils
 Nutrient Cycling & Soils tutorial by Paul Rich Outline 1. Nutrient Cycles What are nutrient cycles? major cycles 2. Water Cycle 3. Carbon Cycle 4. Nitrogen Cycle 5. Phosphorus Cycle 6. Sulfur Cycle 7.
Nutrient Cycling & Soils tutorial by Paul Rich Outline 1. Nutrient Cycles What are nutrient cycles? major cycles 2. Water Cycle 3. Carbon Cycle 4. Nitrogen Cycle 5. Phosphorus Cycle 6. Sulfur Cycle 7.
10/18/2010 THINK ABOUT IT CHAPTER 3 THE BIOSHPERE RECYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE RECYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE
 THINK ABOUT IT CHAPTER 3 THE BIOSHPERE 3.4 Mrs. Michaelsen A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them
THINK ABOUT IT CHAPTER 3 THE BIOSHPERE 3.4 Mrs. Michaelsen A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them
EML 4930/EML 5930 Sustainable Energy Conversion Systems II Notes prepared by: Prof. Anjaneyulu Krothapalli
 EML 4930/EML 5930 Sustainable Energy Conversion Systems II Notes prepared by: Prof. Anjaneyulu Krothapalli Course Objectives This course is aimed at providing the necessary knowledge to design power systems
EML 4930/EML 5930 Sustainable Energy Conversion Systems II Notes prepared by: Prof. Anjaneyulu Krothapalli Course Objectives This course is aimed at providing the necessary knowledge to design power systems
5) Geological and anthropogenic sources of metals. Instructor: Martin Stillman ChB064
 Metals in Life or The Inorganic Chemistry of Life Chemistry 2211a 5) Geological and anthropogenic sources of metals Instructor: Martin Stillman ChB064 Martin.stillman@uwo.ca 1. Geological origins of metals
Metals in Life or The Inorganic Chemistry of Life Chemistry 2211a 5) Geological and anthropogenic sources of metals Instructor: Martin Stillman ChB064 Martin.stillman@uwo.ca 1. Geological origins of metals
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Tuesday, September 19, 17
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
National Atmospheric Deposition Program National Trends Network (NADP NTN) in North Carolina
 National Atmospheric Deposition Program National Trends Network (NADP NTN) in North Carolina Stakeholders Meeting 19 March 2014 Cari Furiness North Carolina State University Agenda Background (15 min)
National Atmospheric Deposition Program National Trends Network (NADP NTN) in North Carolina Stakeholders Meeting 19 March 2014 Cari Furiness North Carolina State University Agenda Background (15 min)
Analyses for geochemical investigations traditionally report concentrations as weight per volume of the measured ions (mg/l of NO 3 , NO 2
 Nitrate-Nitrogen 55 Nutrients The nutrients nitrogen and phosphorus occur naturally and also may be introduced to groundwater systems from urban and agricultural fertilizer applications, livestock or human
Nitrate-Nitrogen 55 Nutrients The nutrients nitrogen and phosphorus occur naturally and also may be introduced to groundwater systems from urban and agricultural fertilizer applications, livestock or human
by Dean Schmelter - Water Specialists Technologies
 Featured Article - Low Level Mercury Removal Understanding the new air quality rules, transport cycle, related health issues and clean air removal applications for this highly toxic substance. by Dean
Featured Article - Low Level Mercury Removal Understanding the new air quality rules, transport cycle, related health issues and clean air removal applications for this highly toxic substance. by Dean
Appendix C1: Batch Kinetics Tests
 Appendix C1: Batch Kinetics Tests This appendix contains the entire data set for the batch kinetics tests for the potential biofilter components. These tests were performed to provide estimates of optimal
Appendix C1: Batch Kinetics Tests This appendix contains the entire data set for the batch kinetics tests for the potential biofilter components. These tests were performed to provide estimates of optimal
Land Application of Biosolids Rules, Regulations and Benefits EPA regulations, under Title 40 Code of Federal Regulations Part 503 (40 CFR 503) -
 Land Application of Biosolids Rules, Regulations and Benefits Biosolids are frequently used for land application on cropland, pastures or timberland, where they decompose and furnish N-nitrogen, P- phosphorus
Land Application of Biosolids Rules, Regulations and Benefits Biosolids are frequently used for land application on cropland, pastures or timberland, where they decompose and furnish N-nitrogen, P- phosphorus
LESSON 3 OTHER LAND RESOURCES C H A P T E R 6, C O N S E R V I N G O U R R E S O U R C E S
 LESSON 3 OTHER LAND RESOURCES C H A P T E R 6, C O N S E R V I N G O U R R E S O U R C E S OBJECTIVES Compare renewable and nonrenewable resources. Describe how human activities affect the environment.
LESSON 3 OTHER LAND RESOURCES C H A P T E R 6, C O N S E R V I N G O U R R E S O U R C E S OBJECTIVES Compare renewable and nonrenewable resources. Describe how human activities affect the environment.
MLA Header: coal oil natural gas burning of fossil fuels volcanoes photosynthesis respiration ocean sugar greenhouse decayed
 MLA Header: s worksheet Please answer the following using the words in the text box. Carbon coal oil natural gas burning of fossil fuels volcanoes photosynthesis respiration ocean sugar greenhouse decayed
MLA Header: s worksheet Please answer the following using the words in the text box. Carbon coal oil natural gas burning of fossil fuels volcanoes photosynthesis respiration ocean sugar greenhouse decayed
Nutrient Cycling in an Aquatic Ecosystem
 Nutrient Cycling in an Aquatic Ecosystem 2.1 Productivity 2.2 Oxygen 2.3 Salinity 2.4 Carbon 2.5 Nitrogen 2.6 Phosphorous 2.7 Iron 2.8 Sulphur 2.9 Silica 2.3 Salinity of Inland Waters The salinity of freshwaters
Nutrient Cycling in an Aquatic Ecosystem 2.1 Productivity 2.2 Oxygen 2.3 Salinity 2.4 Carbon 2.5 Nitrogen 2.6 Phosphorous 2.7 Iron 2.8 Sulphur 2.9 Silica 2.3 Salinity of Inland Waters The salinity of freshwaters
3 3 Cycles of Matter. EOC Review
 EOC Review A freshwater plant is placed in a salt marsh. Predict the direction in which water will move across the plant s cell wall, and the effect of that movement on the plant. a. Water would move out
EOC Review A freshwater plant is placed in a salt marsh. Predict the direction in which water will move across the plant s cell wall, and the effect of that movement on the plant. a. Water would move out
Quality Assurance Report National Atmospheric Deposition Program 2013
 Quality Assurance Report National Atmospheric Deposition Program 2013 Laboratory Operations Central Analytical Laboratory Prepared by Nina Gartman CAL Quality Assurance Lab Project Specialist National
Quality Assurance Report National Atmospheric Deposition Program 2013 Laboratory Operations Central Analytical Laboratory Prepared by Nina Gartman CAL Quality Assurance Lab Project Specialist National
13.1 Ecologists Study Relationships. KEY CONCEPT Ecology is the study of the relationships among organisms and their environment.
 KEY CONCEPT Ecology is the study of the relationships among organisms and their environment. Ecologists study environments at different levels of organization. Ecology is the study of the interactions
KEY CONCEPT Ecology is the study of the relationships among organisms and their environment. Ecologists study environments at different levels of organization. Ecology is the study of the interactions
IMPROVE s Evolution. Data Tools Publications Special Studies Education Activities.
 IMPROVE s Evolution Data Tools Publications Special Studies Education Activities http://vista.cira.colostate.edu/improve VIEWS VIEWS To be Archived Datasets to be included IMPROVE aerosol data Forest
IMPROVE s Evolution Data Tools Publications Special Studies Education Activities http://vista.cira.colostate.edu/improve VIEWS VIEWS To be Archived Datasets to be included IMPROVE aerosol data Forest
A.M. WEDNESDAY, 17 June minutes
 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE 236/01 SCIENCE FOUNDATION TIER CHEMISTRY 1 A.M. WEDNESDAY, 17 June 2009 45 minutes Question For Examiner s use Maximum Mark 1. 5 2. 7 3. 7 4. 7 5. 4
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE 236/01 SCIENCE FOUNDATION TIER CHEMISTRY 1 A.M. WEDNESDAY, 17 June 2009 45 minutes Question For Examiner s use Maximum Mark 1. 5 2. 7 3. 7 4. 7 5. 4
The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface
 Nitrogen and carbon cycles Water cycle The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface It is driven by radiation, convection and advection. It includes solid,
Nitrogen and carbon cycles Water cycle The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface It is driven by radiation, convection and advection. It includes solid,
3 3 Cycles of Matter
 3 3 Cycles of Matter Recycling in the Biosphere Energy - one way flow matter - recycled within and between ecosystems. biogeochemical cycles matter Elements, chemical compounds, and other forms passed
3 3 Cycles of Matter Recycling in the Biosphere Energy - one way flow matter - recycled within and between ecosystems. biogeochemical cycles matter Elements, chemical compounds, and other forms passed
N Goalby chemrevise.org
 4.10 Using Resources Humans use the Earth s resources to provide warmth, shelter, food and transport. Natural resources, supplemented by agriculture, provide food, timber, clothing and fuels. Finite resources
4.10 Using Resources Humans use the Earth s resources to provide warmth, shelter, food and transport. Natural resources, supplemented by agriculture, provide food, timber, clothing and fuels. Finite resources
ATMOSPHERIC DEPOSITION OF NUTRIENTS AND CONTAMINANTS
 ATMOSPHERIC DEPOSITION OF NUTRIENTS AND CONTAMINANTS Curtis D. Pollman 2008 Greater Everglades Ecosystem Restoration Conference, July 28 August 1 Naples, FL Objectives Provide an overview of the importance
ATMOSPHERIC DEPOSITION OF NUTRIENTS AND CONTAMINANTS Curtis D. Pollman 2008 Greater Everglades Ecosystem Restoration Conference, July 28 August 1 Naples, FL Objectives Provide an overview of the importance
5/6/2015. Matter is recycled within and between ecosystems.
 Biogeochemical Cycles/ Nutrient Cycles Biogeochemical Cycle Evaporation Water Cycle Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Runoff Vocabulary Seepage Root Uptake Carbon Cycle Phosphorus Cycle Nitrogen
Biogeochemical Cycles/ Nutrient Cycles Biogeochemical Cycle Evaporation Water Cycle Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Runoff Vocabulary Seepage Root Uptake Carbon Cycle Phosphorus Cycle Nitrogen
4.3 Water, Air, and Land Resources
 4.3 Water, Air, and Land Resources Water 1. Water covers nearly 71% of Earth s surface (mostly salt water) 2. Oceans are important a)currents regulate and moderate Earth s Climate (weather) b)water cycle
4.3 Water, Air, and Land Resources Water 1. Water covers nearly 71% of Earth s surface (mostly salt water) 2. Oceans are important a)currents regulate and moderate Earth s Climate (weather) b)water cycle
Angel International School - Manipay 3 rd Term Examination July, 2015
 Grade 08 Angel International School - Manipay 3 rd Term Examination July, 2015 Chemistry Duration: 2 Hours Index No:- Part I Choose the correct answer and underline it. 1. Which of the following correctly
Grade 08 Angel International School - Manipay 3 rd Term Examination July, 2015 Chemistry Duration: 2 Hours Index No:- Part I Choose the correct answer and underline it. 1. Which of the following correctly
1 st find water. Search for Life
 1 st find water Search for Life Phoenix landed Phoenix Sunday found water 25 May in 2008 2008 Search for life 2 nd look for organic molecules Definition of organic molecules contains C and H Examples sugars,
1 st find water Search for Life Phoenix landed Phoenix Sunday found water 25 May in 2008 2008 Search for life 2 nd look for organic molecules Definition of organic molecules contains C and H Examples sugars,
3 3 Cycles of Matter Slide 1 of 33
 1 of 33 Recycling in the Biosphere Recycling in the Biosphere Energy and matter move through the biosphere very differently. Unlike the one-way flow of energy, matter is recycled within and between ecosystems.
1 of 33 Recycling in the Biosphere Recycling in the Biosphere Energy and matter move through the biosphere very differently. Unlike the one-way flow of energy, matter is recycled within and between ecosystems.
Monitoring Sources of Mercury in the Atmosphere
 Proceedings of the Annual International Conference on Soils, Sediments, Water and Energy Volume 17 Article 4 2012 Monitoring Sources of Mercury in the Atmosphere James Metcalf George Mason University Douglas
Proceedings of the Annual International Conference on Soils, Sediments, Water and Energy Volume 17 Article 4 2012 Monitoring Sources of Mercury in the Atmosphere James Metcalf George Mason University Douglas
10/17/ Cycles of Matter. Recycling in the Biosphere. How does matter move among the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem?
 2 of 33 3-3 Cycles of Matter How does matter move among the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem? 3 of 33 Recycling in the Biosphere Recycling in the Biosphere Energy and matter move through the
2 of 33 3-3 Cycles of Matter How does matter move among the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem? 3 of 33 Recycling in the Biosphere Recycling in the Biosphere Energy and matter move through the
Nutrient Cycles. I. Biogeochemical Cycles
 Nutrient Cycles Chapter 3: The Biosphere I. Biogeochemical Cycles a. a.k.a. nutrient cycles b. Nature does not throw anything away c. Cycle the path from nonliving environments to living organisms and
Nutrient Cycles Chapter 3: The Biosphere I. Biogeochemical Cycles a. a.k.a. nutrient cycles b. Nature does not throw anything away c. Cycle the path from nonliving environments to living organisms and
Locked Cycle Leaching Test and Yellowcake Precipitation
 Locked Cycle Leaching Test and Yellowcake Precipitation In 2013, the Saskatchewan Research Council ( SRC ) in Saskatoon, SK, Canada commenced locked cycle alkaline leach testing on drill core samples from
Locked Cycle Leaching Test and Yellowcake Precipitation In 2013, the Saskatchewan Research Council ( SRC ) in Saskatoon, SK, Canada commenced locked cycle alkaline leach testing on drill core samples from
Lesson Overview. Cycles of Matter. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so where do essential
Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so where do essential
GROUP II PAPER I Chemistry 1. One example of a chemical used in toothpaste is (a) chlorine(b) sulphur (c) carbon dioxide(d) calcium carbonate
 GROUP II PAPER I Chemistry 1. One example of a chemical used in toothpaste is (a) chlorine(b) sulphur (c) carbon dioxide(d) calcium carbonate 2. When a part of the body is injured, substances called are
GROUP II PAPER I Chemistry 1. One example of a chemical used in toothpaste is (a) chlorine(b) sulphur (c) carbon dioxide(d) calcium carbonate 2. When a part of the body is injured, substances called are
Chapter 3 - ATMOSPHERIC TRANSPORT AND MERCURY DEPOSITION
 Chapter 3 - ATMOSPHERIC TRANSPORT AND MERCURY DEPOSITION A. Introduction Mercury is an especially dynamic pollutant because of its unique physical, chemical, and bioaccumulative properties. The volatility
Chapter 3 - ATMOSPHERIC TRANSPORT AND MERCURY DEPOSITION A. Introduction Mercury is an especially dynamic pollutant because of its unique physical, chemical, and bioaccumulative properties. The volatility
1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods?
 Use with textbook pages 68 87. Nutrient cycles Answer the questions below. Comprehension 1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods? 2. Name a biotic process and an abiotic
Use with textbook pages 68 87. Nutrient cycles Answer the questions below. Comprehension 1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods? 2. Name a biotic process and an abiotic
Cycles of Ma,er. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Ecology Part 2. Living Environment
 Ecology Part 2 Living Environment Recycling in the Biosphere Matter is recycled within and between ecosystems Elements, chemical compounds, and other forms of matter are passed from one organism to another
Ecology Part 2 Living Environment Recycling in the Biosphere Matter is recycled within and between ecosystems Elements, chemical compounds, and other forms of matter are passed from one organism to another
6-2 Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources Slide 1 of 42
 6-2 Renewable and Nonrenewable 1 of 42 Classifying Classifying Environmental goods and services may be classified as either renewable or nonrenewable. Renewable resources can regenerate if they are alive,
6-2 Renewable and Nonrenewable 1 of 42 Classifying Classifying Environmental goods and services may be classified as either renewable or nonrenewable. Renewable resources can regenerate if they are alive,
Nutrient Cycles. Why? Model 1 The Water Cycle. How are nutrients recycled through ecosystems?
 Why? Nutrient Cycles How are nutrients recycled through ecosystems? We have learned the importance of recycling our trash. It allows us to use something again for another purpose and prevents the loss
Why? Nutrient Cycles How are nutrients recycled through ecosystems? We have learned the importance of recycling our trash. It allows us to use something again for another purpose and prevents the loss
Uniform Sanitary and Epidemiological and Hygienic Requirements for Goods Subject to Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision (Control) Chapter II
 1267 Uniform Sanitary and Epidemiological and Hygienic Requirements for Goods Subject to Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision (Control) Chapter II Section 21. Requirements for Mineral Waters 1268 Requirements
1267 Uniform Sanitary and Epidemiological and Hygienic Requirements for Goods Subject to Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision (Control) Chapter II Section 21. Requirements for Mineral Waters 1268 Requirements
14 th most abundant element in Earth s crust Sulfate is second most abundant anion in rivers (after bicarbonate) and in ocean after chloride
 Sulfur 14 th most abundant element in Earth s crust Sulfate is second most abundant anion in rivers (after bicarbonate) and in ocean after chloride Development of an oxygenated atmosphere facilitated this
Sulfur 14 th most abundant element in Earth s crust Sulfate is second most abundant anion in rivers (after bicarbonate) and in ocean after chloride Development of an oxygenated atmosphere facilitated this
Biogeochemical Cycles. {Living World
 Biogeochemical Cycles {Living World What Sustains Life on Earth? Solar energy, the cycling of matter, and gravity sustain the earth s life. Earth's Spheres Atmosphere layer of air that surrounds the Earth
Biogeochemical Cycles {Living World What Sustains Life on Earth? Solar energy, the cycling of matter, and gravity sustain the earth s life. Earth's Spheres Atmosphere layer of air that surrounds the Earth
air pollution air pollution atmospheric pollution atmosphere unit 9
 air pollution unit 9 air pollution health effects WHO estimates that air pollution killed 7 million people in 2012 - more than double previous estimates indoor vs. outdoor (ambient) household pollution
air pollution unit 9 air pollution health effects WHO estimates that air pollution killed 7 million people in 2012 - more than double previous estimates indoor vs. outdoor (ambient) household pollution
Quality Assurance Report National Atmospheric Deposition Program 2011
 Quality Assurance Report National Atmospheric Deposition Program 2011 Laboratory Operations Central Analytical Laboratory Prepared by Tracy Dombek CAL Quality Assurance and Data Specialist National Atmospheric
Quality Assurance Report National Atmospheric Deposition Program 2011 Laboratory Operations Central Analytical Laboratory Prepared by Tracy Dombek CAL Quality Assurance and Data Specialist National Atmospheric
Mercury Deposition from Rain and Snow in Virginia
 Proceedings of the Annual International Conference on Soils, Sediments, Water and Energy Volume 15 Article 8 June 2010 Mercury Deposition from Rain and Snow in Virginia Douglas Mose George Mason University
Proceedings of the Annual International Conference on Soils, Sediments, Water and Energy Volume 15 Article 8 June 2010 Mercury Deposition from Rain and Snow in Virginia Douglas Mose George Mason University
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 24 September 2013 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 24 September 2013 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification
Air Pollution. Air Pollution 3/11/2015. Our Atmosphere IS a Resource. March 10, 2015 Mr. Alvarez
 Air Pollution March 10, 2015 Mr. Alvarez Air Pollution Air Pollution- the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough to harm plants,
Air Pollution March 10, 2015 Mr. Alvarez Air Pollution Air Pollution- the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough to harm plants,
Lesson Overview. Cycles of Matter. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so..where do essential
Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so..where do essential
Measuring Environmental Impacts - Air
 BC Hydro Provincial Integrated Electricity Plan Committee Meeting #2 (Technical Working Sessions) Measuring Environmental Impacts - Air Tim Lesiuk Senior Environmental Coordinator Climate Change Management
BC Hydro Provincial Integrated Electricity Plan Committee Meeting #2 (Technical Working Sessions) Measuring Environmental Impacts - Air Tim Lesiuk Senior Environmental Coordinator Climate Change Management
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from soils
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from soils
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 24 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
AIR QUALITY MONITORING
 AIR QUALITY MONITORING in Protected Areas & Wilderness CSS 496 AIR QUALITY MONITORING Adapted from NPS UCBN Vital Signs Workshop March 9-10, 2004 presentation by: Elizabeth Waddell Air Resources Specialist
AIR QUALITY MONITORING in Protected Areas & Wilderness CSS 496 AIR QUALITY MONITORING Adapted from NPS UCBN Vital Signs Workshop March 9-10, 2004 presentation by: Elizabeth Waddell Air Resources Specialist
Water Quality and Soils
 Water Quality and Soils Fresh Water Fresh surface water, groundwater, soil water 0.8% total earth water What s in the Water? Dissolved organic and inorganic compounds Particulate organics and inorganics
Water Quality and Soils Fresh Water Fresh surface water, groundwater, soil water 0.8% total earth water What s in the Water? Dissolved organic and inorganic compounds Particulate organics and inorganics
Acid deposition accumulation of potential acid-forming particles on a surface acids can result from natural causes
 1 Air Quality Issues: Part 2 - Acid Deposition, Greenhouse Gases EVPP 111 Lecture Dr. Largen 2 Air Quality Issues Air Pollution Indoor Air Pollution Acid Deposition Greenhouse Gases & Global Warming 3
1 Air Quality Issues: Part 2 - Acid Deposition, Greenhouse Gases EVPP 111 Lecture Dr. Largen 2 Air Quality Issues Air Pollution Indoor Air Pollution Acid Deposition Greenhouse Gases & Global Warming 3
Water Chemistry. Water 101
 Water Chemistry Water 101 I. Introduction A. Water is not pure Many different kinds of chemicals dissolved in it Ions, organic chemicals, organic matter, particulate matter, and gases can all be in water
Water Chemistry Water 101 I. Introduction A. Water is not pure Many different kinds of chemicals dissolved in it Ions, organic chemicals, organic matter, particulate matter, and gases can all be in water
Understanding Your Test Results
 Understanding Your Test Results The following interpretation is based on public drinking water system standards. These standards only apply to public water systems but the health implications are the same
Understanding Your Test Results The following interpretation is based on public drinking water system standards. These standards only apply to public water systems but the health implications are the same
NADP Site Selection and Installation Manual
 NADP Site Selection and Installation Manual For information about the National Atmospheric Deposition Program (NADP) contact: NADP Program Office Illinois State Water Survey University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
NADP Site Selection and Installation Manual For information about the National Atmospheric Deposition Program (NADP) contact: NADP Program Office Illinois State Water Survey University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Nutrients elements required for the development, maintenance, and reproduction of organisms.
 Nutrient Cycles Energy flows through ecosystems (one way trip). Unlike energy, however, nutrients (P, N, C, K, S ) cycle within ecosystems. Nutrients are important in controlling NPP in ecosystems. Bottom-up
Nutrient Cycles Energy flows through ecosystems (one way trip). Unlike energy, however, nutrients (P, N, C, K, S ) cycle within ecosystems. Nutrients are important in controlling NPP in ecosystems. Bottom-up
SWANA 2017 Leachate Basics and Quality Changes with Organics Removal. Steve Johnson M.Eng., P.Eng.
 SWANA 2017 Leachate Basics and Quality Changes with Organics Removal Steve Johnson M.Eng., P.Eng. May 2017 2 Landfills that take over 10,000 tonnes per year? How many of you have leachate collection systems?
SWANA 2017 Leachate Basics and Quality Changes with Organics Removal Steve Johnson M.Eng., P.Eng. May 2017 2 Landfills that take over 10,000 tonnes per year? How many of you have leachate collection systems?
Biogeochemical Cycles
 Biogeochemical Cycles SB4b. Explain the flow of matter and energy through ecosystems by explaining the need for cycling of major nutrients (C, O, H, N, P). Biogeochemical Cycles describe the flow of essential
Biogeochemical Cycles SB4b. Explain the flow of matter and energy through ecosystems by explaining the need for cycling of major nutrients (C, O, H, N, P). Biogeochemical Cycles describe the flow of essential
1. Which of the given statements about the reaction below are incorrect?
 1. Which of the given statements about the reaction below are incorrect? 2PbO(s) + C(s) 2Pb(s) + CO 2 (g) a. Lead is getting reduced b. Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised c. Carbon is getting oxidised
1. Which of the given statements about the reaction below are incorrect? 2PbO(s) + C(s) 2Pb(s) + CO 2 (g) a. Lead is getting reduced b. Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised c. Carbon is getting oxidised
W12A Landfill Groundwater, Leachate, Water Well, Landfill Gas and Surface Water Quality Monitoring Program
 W12A Landfill Groundwater, Leachate, Water Well, Landfill Gas and Surface Water Quality Monitoring Program The groundwater, leachate, water well, landfill gas and surface water monitoring programs are
W12A Landfill Groundwater, Leachate, Water Well, Landfill Gas and Surface Water Quality Monitoring Program The groundwater, leachate, water well, landfill gas and surface water monitoring programs are
S1 Building Blocks Summary Notes
 S1 Building Blocks Summary Notes Atoms & Molecules 1 We are developing our understanding of atoms and molecules. Atoms are the simplest building blocks of every substance in the universe. There are just
S1 Building Blocks Summary Notes Atoms & Molecules 1 We are developing our understanding of atoms and molecules. Atoms are the simplest building blocks of every substance in the universe. There are just
NADP AIRMoN Operations Manual, Version 2.5. Atmospheric Integrated Research Monitoring Network Site Operations Manual
 Atmospheric Integrated Research Monitoring Network Site Operations Manual For information about the National Atmospheric Deposition Program (NADP) contact: NADP Program Office Illinois State Water Survey
Atmospheric Integrated Research Monitoring Network Site Operations Manual For information about the National Atmospheric Deposition Program (NADP) contact: NADP Program Office Illinois State Water Survey
