14 th most abundant element in Earth s crust Sulfate is second most abundant anion in rivers (after bicarbonate) and in ocean after chloride
|
|
|
- Cynthia Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sulfur 14 th most abundant element in Earth s crust Sulfate is second most abundant anion in rivers (after bicarbonate) and in ocean after chloride Development of an oxygenated atmosphere facilitated this Aerosols (cloud condensation nuclei) Perturbed cycle Anthropogenic emissions of sulfur into the air are double natural emissions Acid rain, AMD Chemistry Variety of oxidation states II to +VI metal sulfides XS2 (-2) Hydrogen sulfide gas H2S (-2) FeS2 (-1) Sulfite SO2 3- (+5) Sulfate SO 4 2- (+6) Abundant so not limiting SO 4 2- is taken up by organisms and reduced to organic S Essential component of protein 1
2 60 61 Note may be as high as 120 dry deposition poorly understood WH by W.H. Schlesinger Schlesinger, / modified by S and B LOOK at table Active reservoirs (x g) Atmosphere Seawater 1280 Sedimentary rocks Evaporites 2470 Shales 4970 Land plants Soil organic Matter From S and B who took from Holser et al (1989) and Dobrovolsky (1994) 2
3 Atmosphere-short residence time Sources Biological (microbial) sources Volatile forms SO42- reduction Sulfate reduction can also lead to production of pyrite FeS2. Volcanic emissions SO2 Oceans Fossil fuel burning Dust and sea salt Microbial processes are important Wetland settings Chapter 7 Figure 7.10 and 7.18 Ocean setting Chapter pg 390 S&B Figure
4 Wetlands: brief introduction Wetland types 4
5 Hydric soils Mineral <20-35% organic Organic-primarily the remains of plants Histosols-muck and peat United States 53% lost in conterminous US from Agriculture Urban development 5
6 Control of nutrient cycles Redox Microbes Redox potential Measure of electron availability in a solution (negative more Used to quantify reduction Measured as Eh and is a quantitative measure of the soils ability to oxidize or reduce chemicals 6
7 From Mitsch and Gosselink, Wetlands (2000) 7
8 8
9 From Mitsch and Gosselink, From Mitsch and Gosselink, 9
10 From Mitsch and Gosselin k, Wetland s (2000) Oceans S species S and B Figure 9.29 Sources and sinks pg 390 Free ion SO 4 2- Second most abundant anion in the ocean Biological processes result in production of a variety of reduced forms 10
11 Microbes important in controlling forms In atmosphere most are reactive and have a short RT so deposited locally H2S Hydrogen sulfide-anaerobic setting-atmosphere CS2-Carbon disulfide precusor to OCS OCS-Carbonyl sulfide Table 13.3 (most abundant in atmosphere 5 yr RT) anoxic soils and industry and ocean (Source) plants and soils (Sink) Important source of stratosphere sulfate Organosulfides Methyl mercaptan CH3SH Dimethyl sulfide CH3SCH3 Dimethyl disulfide CH3SSCH3 Microbial processing Marine system sink- DMS to atmosphere Terrestrial and aquatic-h2s to atmosphere 11
12 OH radical important forms SO2 then SO42- that is deposited in precipitation DMSP (dimethylsulfoniopropionate) Produced within cells = Prymnesiophytes, Dinoflagellates Andreae 1990 Stress enhances release Species specific productionalso linked to nitrogen availability 12
13 Andreae paper Only certain organisms important Stress related release? Importance in cloud condensation nuclei Variation over glacial interglacial times S and B point to this also COS Carbonyl sulfide Most abundant sulfur species in the remote troposphere Not reactive long atmospheric residence time ~5 years In stratosphere important for maintaining sulfate aerosol Derived from abiotic photolysis of organic S compounds in seawater Oxidation of carbon disulfide-cs 2 emitted from anoxic soils and industry Table 13.3 Ocean is a sink Soils and vegetation are a sink 13
14 New work COS uptake through plant stomata may be a useful indicator of gross primary productivity COS due to long residence time-mixed to stratosphere Where, reactions with OH produce SO4 SO4 combines to produced aerosols Not increasing in atmosphere Coastal Marshes H2S, OCS, DMS, DMDS variable flux 14
15 Troposphere Residence time days SO4(2-) 1-2 days DMS Regional impacts Upper troposphere Aerosol S04 increasing over time Suggested due to aircraft. Dry deposition is poorly understood 15
16 16
Nutrient Cycling & Soils
 Nutrient Cycling & Soils tutorial by Paul Rich Outline 1. Nutrient Cycles What are nutrient cycles? major cycles 2. Water Cycle 3. Carbon Cycle 4. Nitrogen Cycle 5. Phosphorus Cycle 6. Sulfur Cycle 7.
Nutrient Cycling & Soils tutorial by Paul Rich Outline 1. Nutrient Cycles What are nutrient cycles? major cycles 2. Water Cycle 3. Carbon Cycle 4. Nitrogen Cycle 5. Phosphorus Cycle 6. Sulfur Cycle 7.
Nutrient Cycles. Nutrient cycles involve flow of high quality energy from the sun through the environment & of elements.
 Nutrient Cycles Nutrient cycles (= biogeochemical cycles): natural processes that involve the flow of nutrients from the environment (air, water, soil, rock) to living organisms ( ) & back again. Nutrient
Nutrient Cycles Nutrient cycles (= biogeochemical cycles): natural processes that involve the flow of nutrients from the environment (air, water, soil, rock) to living organisms ( ) & back again. Nutrient
Ch. 5 - Nutrient Cycles and Soils
 Ch. 5 - Nutrient Cycles and Soils What are Nutrient (biogeochemical) Cycles? a process by which nutrients are recycled between living organisms and nonliving environment. The three general types of nutrient
Ch. 5 - Nutrient Cycles and Soils What are Nutrient (biogeochemical) Cycles? a process by which nutrients are recycled between living organisms and nonliving environment. The three general types of nutrient
Chemistry in the Environment
 Chemistry in the Environment Section 261 Earth s Atmosphere In your textbook, read about the terms used to describe the physical and chemical properties of Earth s atmosphere Complete each statement 1
Chemistry in the Environment Section 261 Earth s Atmosphere In your textbook, read about the terms used to describe the physical and chemical properties of Earth s atmosphere Complete each statement 1
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger,, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger,, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from soils
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from soils
5/6/2015. Matter is recycled within and between ecosystems.
 Biogeochemical Cycles/ Nutrient Cycles Biogeochemical Cycle Evaporation Water Cycle Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Runoff Vocabulary Seepage Root Uptake Carbon Cycle Phosphorus Cycle Nitrogen
Biogeochemical Cycles/ Nutrient Cycles Biogeochemical Cycle Evaporation Water Cycle Transpiration Condensation Precipitation Runoff Vocabulary Seepage Root Uptake Carbon Cycle Phosphorus Cycle Nitrogen
The Global Nitrogen Cycle
 OCN 401 The Global Nitrogen Cycle (11.30.10) Fig. 12.2. Units are 10 12 g N/yr (Tg) Role of N in Biogeochemistry Bioavailability of N (and/or P) can limit NPP on land/oceans; controls size of biomass N
OCN 401 The Global Nitrogen Cycle (11.30.10) Fig. 12.2. Units are 10 12 g N/yr (Tg) Role of N in Biogeochemistry Bioavailability of N (and/or P) can limit NPP on land/oceans; controls size of biomass N
NUTRIENT CYCLES REVIEW
 52 Name A.P. Environmental Science Date Mr. Romano NUTRIENT CYCLES REVIEW 1. Which of the following chain of events would occur as a result of land clearing/deforestation? (vocabulary check: efflux means
52 Name A.P. Environmental Science Date Mr. Romano NUTRIENT CYCLES REVIEW 1. Which of the following chain of events would occur as a result of land clearing/deforestation? (vocabulary check: efflux means
The Global Nitrogen Cycle, and Linkages Between C, N, and P Cycles
 OCN 401 The Global Nitrogen Cycle, and Linkages Between C, N, and P Cycles (12.1.11) The Contemporary N Cycle - Basic Facts - Reservoirs and Fluxes Global N and P Budgets - balance between N-fixation and
OCN 401 The Global Nitrogen Cycle, and Linkages Between C, N, and P Cycles (12.1.11) The Contemporary N Cycle - Basic Facts - Reservoirs and Fluxes Global N and P Budgets - balance between N-fixation and
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 18 September 2012 Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 18 September 2012 Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions
Geochemical Cycles, Aerosol
 Geochemical Cycles, Aerosol Geochemical cycles: Reservoirs and exchange Carbon Nitrogen Aerosol: What is an aerosol? Sources and sinks of aerosol particles Description of the atmospheric aerosol Literature
Geochemical Cycles, Aerosol Geochemical cycles: Reservoirs and exchange Carbon Nitrogen Aerosol: What is an aerosol? Sources and sinks of aerosol particles Description of the atmospheric aerosol Literature
CHAPTER 6: GEOCHEMICAL CYCLES Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017
 CHAPTER 6: GEOCHEMICAL CYCLES Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 THE EARTH: ASSEMBLAGE OF ATOMS OF THE 92 NATURAL ELEMENTS Most abundant elements: oxygen (in solid
CHAPTER 6: GEOCHEMICAL CYCLES Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 THE EARTH: ASSEMBLAGE OF ATOMS OF THE 92 NATURAL ELEMENTS Most abundant elements: oxygen (in solid
1) The Changing Carbon Cycle
 1) The Changing Carbon Cycle WG1 Chapter 6, figure 1 The numbers represent carbon reservoirs in Petagrams of Carbon (PgC; 10 15 gc) and the annual exchanges in PgC/year. The black numbers and arrows show
1) The Changing Carbon Cycle WG1 Chapter 6, figure 1 The numbers represent carbon reservoirs in Petagrams of Carbon (PgC; 10 15 gc) and the annual exchanges in PgC/year. The black numbers and arrows show
The Phosphorus Cycle
 Lecture Outline Introduction Global Cycle Overview Major Forms Anthropogenic Influences Terrestrial Processes Freshwater Processes Ocean Processes The Phosphorus Cycle No important gaseous form, present
Lecture Outline Introduction Global Cycle Overview Major Forms Anthropogenic Influences Terrestrial Processes Freshwater Processes Ocean Processes The Phosphorus Cycle No important gaseous form, present
Aerosol from biomass burning and mineral aerosols. 1. What are aerosols from biomass burning?
 Lectures 40-41. Global change due to anthropogenic aerosols: Aerosol from biomass burning and mineral aerosols. Objectives: 1. What are aerosols from biomass burning? 2. What is mineral aerosol? 3. Direct
Lectures 40-41. Global change due to anthropogenic aerosols: Aerosol from biomass burning and mineral aerosols. Objectives: 1. What are aerosols from biomass burning? 2. What is mineral aerosol? 3. Direct
Main Natural Sources of Greenhouse Gases
 Main Natural Sources of Greenhouse Gases Content Atmospheric Composition Composition of the Earth s Atmosphere Greenhouse Gases The Radiative Forcing bar chart: AR5 version Natural Greenhouse Gases Water
Main Natural Sources of Greenhouse Gases Content Atmospheric Composition Composition of the Earth s Atmosphere Greenhouse Gases The Radiative Forcing bar chart: AR5 version Natural Greenhouse Gases Water
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 24 September 2013 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 24 September 2013 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification
Ecosystems and Nutrient Cycles Chapters 3
 Ecosystems and Nutrient Cycles Chapters 3 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells Figure 3-2 Prokaryotic cells: Have organelles. Bacteria and Archaea are composed of prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells: cells,
Ecosystems and Nutrient Cycles Chapters 3 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells Figure 3-2 Prokaryotic cells: Have organelles. Bacteria and Archaea are composed of prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells: cells,
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 20 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2016 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 20 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2016 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES. GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 10 Turco: Chapter 10; Dearden and Mitchell: Chapter 4
 GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 10 Turco: Chapter 10; Dearden and Mitchell: Chapter 4 Assignment 4 1. Suppose that a layer of air 1000 m thick has conditional stability. A rising parcel
GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 10 Turco: Chapter 10; Dearden and Mitchell: Chapter 4 Assignment 4 1. Suppose that a layer of air 1000 m thick has conditional stability. A rising parcel
Ecosystems: Nutrient Cycles
 Ecosystems: Nutrient Cycles Greeks, Native Peoples, Buddhism, Hinduism use(d) Earth, Air, Fire, and Water as the main elements of their faith/culture Cycling in Ecosystems the Hydrologic Cycle What are
Ecosystems: Nutrient Cycles Greeks, Native Peoples, Buddhism, Hinduism use(d) Earth, Air, Fire, and Water as the main elements of their faith/culture Cycling in Ecosystems the Hydrologic Cycle What are
Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake
 Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake Fig. 6.6 Recall: Current ocean is gaining Carbon.. OCEAN Reservoir size: 38000 Flux in: 90 Flux out: 88+0.2=88.2 90-88.2 = 1.8 Pg/yr OCEAN is gaining 1.8 Pg/yr Sum of the
Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake Fig. 6.6 Recall: Current ocean is gaining Carbon.. OCEAN Reservoir size: 38000 Flux in: 90 Flux out: 88+0.2=88.2 90-88.2 = 1.8 Pg/yr OCEAN is gaining 1.8 Pg/yr Sum of the
The next 2 weeks. Reading: IPCC (2007), Chap 7 (sections 7.4 and 7.5)
 PCC 588 Jan 15 The next 2 weeks Th. Jan 15: non-co 2 greenhouse gases CH 4 and N 2 O Tu. Jan 20: non-co 2 greenhouse gases: ozone, halocarbons Th. Jan 22: Aerosols and Climate Tu. Jan 27: Paper discussion
PCC 588 Jan 15 The next 2 weeks Th. Jan 15: non-co 2 greenhouse gases CH 4 and N 2 O Tu. Jan 20: non-co 2 greenhouse gases: ozone, halocarbons Th. Jan 22: Aerosols and Climate Tu. Jan 27: Paper discussion
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 23 September 2014 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2014 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 23 September 2014 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2014 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Nutrients elements required for the development, maintenance, and reproduction of organisms.
 Nutrient Cycles Energy flows through ecosystems (one way trip). Unlike energy, however, nutrients (P, N, C, K, S ) cycle within ecosystems. Nutrients are important in controlling NPP in ecosystems. Bottom-up
Nutrient Cycles Energy flows through ecosystems (one way trip). Unlike energy, however, nutrients (P, N, C, K, S ) cycle within ecosystems. Nutrients are important in controlling NPP in ecosystems. Bottom-up
Chapter 5 Questions Due for Homework Points: # 4, 9, 18, 23, 30, 31, 35, 36 and on notebook paper, not directly on these handouts
 Study Outline: Chapters 5, 6, & 9 Environmental Science AP Instructor: Ben Smith Biogeochemical Cycles: Global Recycling Program Ch. 5 Chapter 5 Questions Due for Homework Points: # 4, 9, 18, 23, 30, 31,
Study Outline: Chapters 5, 6, & 9 Environmental Science AP Instructor: Ben Smith Biogeochemical Cycles: Global Recycling Program Ch. 5 Chapter 5 Questions Due for Homework Points: # 4, 9, 18, 23, 30, 31,
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 19 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2017 Frank Sansone Outline 1. Nitrogen cycle
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 19 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2017 Frank Sansone Outline 1. Nitrogen cycle
Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65)
 Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65) 2.2 Biogeochemical Cycles (pages 42 52) In order to survive and grow, organisms must obtain nutrients that serve as sources of energy or chemical building blocks,
Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65) 2.2 Biogeochemical Cycles (pages 42 52) In order to survive and grow, organisms must obtain nutrients that serve as sources of energy or chemical building blocks,
Atmospheric Chemistry
 Atmospheric Chemistry Research Dr. Husam T. Majeed Department of Atmospheric Sciences 2nd Year Class First Semester 2018-2019 Course Syllabus 1. Introduction & Review Atmospheric Chemistry Box Models and
Atmospheric Chemistry Research Dr. Husam T. Majeed Department of Atmospheric Sciences 2nd Year Class First Semester 2018-2019 Course Syllabus 1. Introduction & Review Atmospheric Chemistry Box Models and
Lecture 21: Soil Redox; Hydric Soils; Wetlands
 Lecture 21: Soil Redox; Hydric Soils; Wetlands Soil Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Many Elements Exist in Multiple Oxidation States in Soils Oxygen: O 2 (0), H 2 O (-2) Carbon: CH 4 (-4), Organic C (-3 to
Lecture 21: Soil Redox; Hydric Soils; Wetlands Soil Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Many Elements Exist in Multiple Oxidation States in Soils Oxygen: O 2 (0), H 2 O (-2) Carbon: CH 4 (-4), Organic C (-3 to
13.5. Cycling of Matter. Water cycles through the environment.
 13.5 Cycling of Matter VOCABULARY hydrologic cycle biogeochemical cycle nitrogen fixation KEY CONCEPT Matter cycles in and out of an ecosystem. Main Ideas Water cycles through the environment. Elements
13.5 Cycling of Matter VOCABULARY hydrologic cycle biogeochemical cycle nitrogen fixation KEY CONCEPT Matter cycles in and out of an ecosystem. Main Ideas Water cycles through the environment. Elements
7.014 Lecture 20: Biogeochemical Cycles April 1, 2007
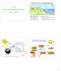 Global Nutrient Cycling - Biogeochemical Cycles 7.14 Lecture 2: Biogeochemical Cycles April 1, 27 Uptake Bioelements in Solution Weathering Precipitation Terrestrial Biomass Decomposition Volatile Elements
Global Nutrient Cycling - Biogeochemical Cycles 7.14 Lecture 2: Biogeochemical Cycles April 1, 27 Uptake Bioelements in Solution Weathering Precipitation Terrestrial Biomass Decomposition Volatile Elements
Biogeochemical cycles
 Biogeochemical cycles MATTER CYCLING IN ECOSYSTEMS Nutrient Cycles: Global Recycling Global Cycles recycle nutrients through the earth s air, land, water, and living organisms. Nutrients are the elements
Biogeochemical cycles MATTER CYCLING IN ECOSYSTEMS Nutrient Cycles: Global Recycling Global Cycles recycle nutrients through the earth s air, land, water, and living organisms. Nutrients are the elements
3 3 CYCLES OF MATTER
 3 3 CYCLES OF MATTER REVIEW: 1. What is an element? 2. What is a compound? 3. What are the 6 elements that are most important to living things? Matter = a substance that takes up space. BIOGEOCHEMICAL
3 3 CYCLES OF MATTER REVIEW: 1. What is an element? 2. What is a compound? 3. What are the 6 elements that are most important to living things? Matter = a substance that takes up space. BIOGEOCHEMICAL
Elements essential for life also cycle through ecosystems.
 13.5 Cycling of Matter KEY CONCEPT Matter cycles in and out of an ecosystem. MAIN IDEAS Water cycles through the environment. Elements essential for life also cycle through ecosystems. VOCABULARY hydrologic
13.5 Cycling of Matter KEY CONCEPT Matter cycles in and out of an ecosystem. MAIN IDEAS Water cycles through the environment. Elements essential for life also cycle through ecosystems. VOCABULARY hydrologic
Yakın Doğu Üniversitesi Mimarlık Fakültesi Peyzaj Mimarlığı Bölümü. PM 317 Human and Environment Assoc. Prof. Dr. Salih GÜCEL
 Yakın Doğu Üniversitesi Mimarlık Fakültesi Peyzaj Mimarlığı Bölümü PM 317 Human and Environment Assoc. Prof. Dr. Salih GÜCEL Composition of Living Organisms All organisms are composed of matter, and although
Yakın Doğu Üniversitesi Mimarlık Fakültesi Peyzaj Mimarlığı Bölümü PM 317 Human and Environment Assoc. Prof. Dr. Salih GÜCEL Composition of Living Organisms All organisms are composed of matter, and although
How Ecosystems Work Section 2. Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 2: Cycling of Materials DAY 1
 Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 2: Cycling of Materials DAY 1 The Carbon Cycle The carbon cycle is the movement of carbon from the nonliving environment into living things and back Carbon is the
Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 2: Cycling of Materials DAY 1 The Carbon Cycle The carbon cycle is the movement of carbon from the nonliving environment into living things and back Carbon is the
Chapter 3 Reading/Homework Quiz
 Name Chapter 3 Reading/Homework Quiz Date APES 1. Scientists estimate that tropical rain forests contain up to half of the earth s land plants and animal species. What percentage of the world s land surface
Name Chapter 3 Reading/Homework Quiz Date APES 1. Scientists estimate that tropical rain forests contain up to half of the earth s land plants and animal species. What percentage of the world s land surface
Aerosols. Liquid or solid particles suspended in the air. Some occur naturally, originating from volcanoes, dust storms, forest and grassland fires,
 Aerosols. Liquid or solid particles suspended in the air. Some occur naturally, originating from volcanoes, dust storms, forest and grassland fires, living vegetation, and sea spray.. Some are anthropogenic:
Aerosols. Liquid or solid particles suspended in the air. Some occur naturally, originating from volcanoes, dust storms, forest and grassland fires, living vegetation, and sea spray.. Some are anthropogenic:
How Ecosystems Work Section 2
 Objectives List the three stages of the carbon cycle. Describe where fossil fuels are located. Identify one way that humans are affecting the carbon cycle. List the tree stages of the nitrogen cycle. Describe
Objectives List the three stages of the carbon cycle. Describe where fossil fuels are located. Identify one way that humans are affecting the carbon cycle. List the tree stages of the nitrogen cycle. Describe
Aerosols (sources and processes)
 Aerosols (sources and processes) Soot is composed of aggregates of small particles (asbestos) rainout (wet deposition) Number Aerosol number is dominated by fine and ultrafine particles; aerosol mass
Aerosols (sources and processes) Soot is composed of aggregates of small particles (asbestos) rainout (wet deposition) Number Aerosol number is dominated by fine and ultrafine particles; aerosol mass
Table 4.1 Linnaean Classification System of Organisms.
 Table.1 Linnaean Classification System of rganisms. Domain Kingdom Phylum Class rder Family Genus Species Table.2 Comparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Characteristic Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Cell
Table.1 Linnaean Classification System of rganisms. Domain Kingdom Phylum Class rder Family Genus Species Table.2 Comparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Characteristic Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Cell
Another cause of diversity may be the creation of different habitats within a region by periodic disturbance A community that forms if the land is
 Another cause of diversity may be the creation of different habitats within a region by periodic disturbance A community that forms if the land is undisturbed and that perpetuates itself for as long as
Another cause of diversity may be the creation of different habitats within a region by periodic disturbance A community that forms if the land is undisturbed and that perpetuates itself for as long as
Water cycles through ecosystems.
 Water cycles through ecosystems. Water is stored on Earth s surface in lakes, rivers, and oceans. Water is found underground, filling the spaces between soil particles and cracks in rocks. Large amounts
Water cycles through ecosystems. Water is stored on Earth s surface in lakes, rivers, and oceans. Water is found underground, filling the spaces between soil particles and cracks in rocks. Large amounts
10/18/2010 THINK ABOUT IT CHAPTER 3 THE BIOSHPERE RECYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE RECYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE
 THINK ABOUT IT CHAPTER 3 THE BIOSHPERE 3.4 Mrs. Michaelsen A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them
THINK ABOUT IT CHAPTER 3 THE BIOSHPERE 3.4 Mrs. Michaelsen A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES
 BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES A biogeochemical cycle or cycling of substances is a pathway by which a chemical element or molecule moves through both biotic and abiotic compartments of Earth.
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES A biogeochemical cycle or cycling of substances is a pathway by which a chemical element or molecule moves through both biotic and abiotic compartments of Earth.
Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Volcanic Eruptions and Global Temperature
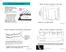 Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Section 2: The Cycling of Materials
 Section 2: The Cycling of Materials Preview Bellringer Objectives The Carbon Cycle How Humans Affect the Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle Decomposers and the Nitrogen Cycle The Phosphorus Cycle Section
Section 2: The Cycling of Materials Preview Bellringer Objectives The Carbon Cycle How Humans Affect the Carbon Cycle The Nitrogen Cycle Decomposers and the Nitrogen Cycle The Phosphorus Cycle Section
Lecture 17 Guest Lecturer this week. Prof. Greg Ravizza
 Lecture 17 Guest Lecturer this week. Prof. Greg Ravizza Migrating Reservoirs in the Hydrologic Cycle - Inorganic solubility examples from Rain and River chemistry Migrating Reservoirs in the Hydrologic
Lecture 17 Guest Lecturer this week. Prof. Greg Ravizza Migrating Reservoirs in the Hydrologic Cycle - Inorganic solubility examples from Rain and River chemistry Migrating Reservoirs in the Hydrologic
Prepare for Learning. A 4000 year old corpse preserved in ice. Why hasn t it decomposed?
 Prepare for Learning A 4000 year old corpse preserved in ice. Why hasn t it decomposed? Why is carbon important? Carbon is the main constituent of all living cells (biochemistry, organic chemistry) Component
Prepare for Learning A 4000 year old corpse preserved in ice. Why hasn t it decomposed? Why is carbon important? Carbon is the main constituent of all living cells (biochemistry, organic chemistry) Component
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Tuesday, September 19, 17
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
ChE 505 Chapter 1N revised 01/17/13
 ENVIRONMENTAL REACTION ENGINEERING 1.1 Introduction Chemical reactions play a key role in generation of pollutants (e.g. combustion of fossil fuels) as well as in pollution abatement (e.g. automobile exhaust
ENVIRONMENTAL REACTION ENGINEERING 1.1 Introduction Chemical reactions play a key role in generation of pollutants (e.g. combustion of fossil fuels) as well as in pollution abatement (e.g. automobile exhaust
3 3 Cycles of Matter
 3 3 Cycles of Matter Recycling in the Biosphere Energy - one way flow matter - recycled within and between ecosystems. biogeochemical cycles matter Elements, chemical compounds, and other forms passed
3 3 Cycles of Matter Recycling in the Biosphere Energy - one way flow matter - recycled within and between ecosystems. biogeochemical cycles matter Elements, chemical compounds, and other forms passed
Research Question What ecological and other services do coastal wetlands provide?
 Bringing Wetlands to Market Part 1 Introduction Blue, Green, and Bountiful: Wetlands and carbon Estuary Principle Principle 5: Humans, even those living far from the coast, rely on goods and services supplied
Bringing Wetlands to Market Part 1 Introduction Blue, Green, and Bountiful: Wetlands and carbon Estuary Principle Principle 5: Humans, even those living far from the coast, rely on goods and services supplied
Leif Backman HENVI Seminar February 19, 2009
 Methane Sources and Sinks Leif Backman HENVI Seminar February 19, 2009 Background Atmospheric methane Sources & Sinks Concentration variations & trends Objective & methods Objective & Goals Research plan
Methane Sources and Sinks Leif Backman HENVI Seminar February 19, 2009 Background Atmospheric methane Sources & Sinks Concentration variations & trends Objective & methods Objective & Goals Research plan
Biogeochemical Cycles. {Living World
 Biogeochemical Cycles {Living World What Sustains Life on Earth? Solar energy, the cycling of matter, and gravity sustain the earth s life. Earth's Spheres Atmosphere layer of air that surrounds the Earth
Biogeochemical Cycles {Living World What Sustains Life on Earth? Solar energy, the cycling of matter, and gravity sustain the earth s life. Earth's Spheres Atmosphere layer of air that surrounds the Earth
How Ecosystems Work Section 1. Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1
 Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1 Life Depends on the Sun Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1 Life Depends on the Sun Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Estuarine and Coastal Biogeochemistry
 Estuarine and Coastal Biogeochemistry OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 9 April 2013 Reading: Seitzinger & Mayorga (2008) 2013 Frank Sansone 1. Global coastal zone Outline 2. Nutrient loading in estuaries
Estuarine and Coastal Biogeochemistry OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 9 April 2013 Reading: Seitzinger & Mayorga (2008) 2013 Frank Sansone 1. Global coastal zone Outline 2. Nutrient loading in estuaries
Lesson Overview. Cycles of Matter. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so where do essential
Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so where do essential
Ecosystems. Trophic relationships determine the routes of energy flow and chemical cycling in ecosystems.
 AP BIOLOGY ECOLOGY ACTIVITY #5 Ecosystems NAME DATE HOUR An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community as well as all the abiotic factors with which they interact. The dynamics of an
AP BIOLOGY ECOLOGY ACTIVITY #5 Ecosystems NAME DATE HOUR An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community as well as all the abiotic factors with which they interact. The dynamics of an
Biogeochemical Cycles Comic Strips/Story. {Living World
 Biogeochemical Cycles Comic Strips/Story {Living World Introduction The Earth is a closed system for matter, except for small amounts of cosmic debris that enter the Earth s atmosphere. This means that
Biogeochemical Cycles Comic Strips/Story {Living World Introduction The Earth is a closed system for matter, except for small amounts of cosmic debris that enter the Earth s atmosphere. This means that
TABLE OF CONTENTS. 4, Environmental Chemistry 2, Biogeochemical cycle of carbon and nitrogen
 Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag CHE_P4_M2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2. Introduction 2.1. Bio-distribution of elements 2.2. Biogeochemical cycles 3. Carbon cycle 3.1.
Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag CHE_P4_M2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2. Introduction 2.1. Bio-distribution of elements 2.2. Biogeochemical cycles 3. Carbon cycle 3.1.
Cycles of Ma,er. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Lesson 1.2 Recycling Matter
 Lesson 1.2 Recycling Matter Lesson Objectives Define biogeochemical cycles. Describe the water cycle and its processes. Give an overview of the carbon cycle. Outline the steps of the nitrogen cycle. Lesson
Lesson 1.2 Recycling Matter Lesson Objectives Define biogeochemical cycles. Describe the water cycle and its processes. Give an overview of the carbon cycle. Outline the steps of the nitrogen cycle. Lesson
Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work? Chapter 3
 Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work? Chapter 3 Core Case Study: Tropical Rain Forests Are Disappearing Cover about 2% of the earth s land surface Contain about 50% of the world s known plant
Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work? Chapter 3 Core Case Study: Tropical Rain Forests Are Disappearing Cover about 2% of the earth s land surface Contain about 50% of the world s known plant
3 3 Cycles of Matter. EOC Review
 EOC Review A freshwater plant is placed in a salt marsh. Predict the direction in which water will move across the plant s cell wall, and the effect of that movement on the plant. a. Water would move out
EOC Review A freshwater plant is placed in a salt marsh. Predict the direction in which water will move across the plant s cell wall, and the effect of that movement on the plant. a. Water would move out
Human perturbations to the global Nitrogen cycle
 Human perturbations to the global Nitrogen cycle Lecture for Biogeochemistry and Global Change Edzo Veldkamp The pace of human caused global change has increased in modern history, but none so rapidly
Human perturbations to the global Nitrogen cycle Lecture for Biogeochemistry and Global Change Edzo Veldkamp The pace of human caused global change has increased in modern history, but none so rapidly
Radiative forcing of climate change
 Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
Inputs. Outputs. Component/store. Section of a system where material or energy is held. Something that enters the system (material or energy)
 .. Inputs Something that enters the system (material or energy) Outputs Something that leaves the system (material or energy) Component/store Section of a system where material or energy is held Transfer/flow
.. Inputs Something that enters the system (material or energy) Outputs Something that leaves the system (material or energy) Component/store Section of a system where material or energy is held Transfer/flow
pk g = 1.41 pk 1 = 6.35 pk 2 = ph of pure water? ph of rain
 Acid Rain Acid deposition consists of delivery of acid substances or precursors, principally sulfur and nitrogen oxides, acids, and salts, from the atmosphere to the earth surface (Schwartz 1989) Wet deposition-
Acid Rain Acid deposition consists of delivery of acid substances or precursors, principally sulfur and nitrogen oxides, acids, and salts, from the atmosphere to the earth surface (Schwartz 1989) Wet deposition-
Rubisco is about 20% of the plant protein and is argued to be the most abundant protein on Earth (Sharkey, 1985). This Explain why N compounds
 1 Rubisco is about 20% of the plant protein and is argued to be the most abundant protein on Earth (Sharkey, 1985). This Explain why N compounds released when organic matter is combusted. 2 TRY database,
1 Rubisco is about 20% of the plant protein and is argued to be the most abundant protein on Earth (Sharkey, 1985). This Explain why N compounds released when organic matter is combusted. 2 TRY database,
Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
 Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Friedland and Relyea Environmental Science for AP, second edition 2015 W.H. Freeman and Company/BFW AP is a trademark registered and/or owned
Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Friedland and Relyea Environmental Science for AP, second edition 2015 W.H. Freeman and Company/BFW AP is a trademark registered and/or owned
B.Sc Ist Year Environment and Water Management (Semester-I) Unit 1. Concept of Environment Environment; Concept importance and major components
 B.Sc Ist Year Environment and Water Management (Semester-I) Unit 1. Concept of Environment Environment; Concept importance and major components The term Environment can be broadly defined as one s surroundings.
B.Sc Ist Year Environment and Water Management (Semester-I) Unit 1. Concept of Environment Environment; Concept importance and major components The term Environment can be broadly defined as one s surroundings.
The amount of fixed nitrogen (N that has chemically combined with other
 Chapter 1: Introduction The cycle of N is unique in that it consists of a massive, well-mixed, and (to most organisms) wholly unavailable pool of nitrogen gas (N 2 ) in the atmosphere; a relatively small
Chapter 1: Introduction The cycle of N is unique in that it consists of a massive, well-mixed, and (to most organisms) wholly unavailable pool of nitrogen gas (N 2 ) in the atmosphere; a relatively small
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems. Review How energy flows What is the difference between a food chain, food web, and food pyramid?
 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Review How energy flows What is the difference between a food chain, food web, and food pyramid? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xhr1iebeops https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=alusi_6ol8m
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Review How energy flows What is the difference between a food chain, food web, and food pyramid? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xhr1iebeops https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=alusi_6ol8m
N-cycle: biogeochemistry. Biological flows of Nitrogen
 N-cycle: biogeochemistry SWES 410/510 April 4, 2014 I. N cycling A. simplest possible B. Global N budget C. Effects of N-cycling ( the Nitrogen Cascade ) II. Nitrous Oxide (N 2 O) budgets III. Data-Model
N-cycle: biogeochemistry SWES 410/510 April 4, 2014 I. N cycling A. simplest possible B. Global N budget C. Effects of N-cycling ( the Nitrogen Cascade ) II. Nitrous Oxide (N 2 O) budgets III. Data-Model
Ecology: Part 2. Biology Mrs. Bradbury
 Ecology: Part 2 Biology Mrs. Bradbury Model 1: Food Chains Food Chain simple model showing the movement of matter and energy through ecosystems. Autotrophs Heterotrophs Decomposers Arrows show energy transfer
Ecology: Part 2 Biology Mrs. Bradbury Model 1: Food Chains Food Chain simple model showing the movement of matter and energy through ecosystems. Autotrophs Heterotrophs Decomposers Arrows show energy transfer
Objectives: Define the term biogeochemical cycles. Compare and contrast how carbon, phosphorus, nitrogen, and water cycle through the environment.
 Objectives: Define the term biogeochemical cycles. Compare and contrast how carbon, phosphorus, nitrogen, and water cycle through the environment. Explain how human impact is affecting biogeochemical cycles
Objectives: Define the term biogeochemical cycles. Compare and contrast how carbon, phosphorus, nitrogen, and water cycle through the environment. Explain how human impact is affecting biogeochemical cycles
Chapter 2 9/15/2015. Chapter 2. Penny Boat. 2.1 The Role of Water in Cycles of Matter
 Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Cycles of Matter 2.1 The Role of Water in Cycles of Matter 2.2 Biogeochemical Cycles 2.3 the Balance of the Matter and Energy Exchange 2.1 The Role of Water in Cycles of Matter In this
Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Cycles of Matter 2.1 The Role of Water in Cycles of Matter 2.2 Biogeochemical Cycles 2.3 the Balance of the Matter and Energy Exchange 2.1 The Role of Water in Cycles of Matter In this
3 3 Cycles of Matter Slide 1 of 33
 1 of 33 Recycling in the Biosphere Recycling in the Biosphere Energy and matter move through the biosphere very differently. Unlike the one-way flow of energy, matter is recycled within and between ecosystems.
1 of 33 Recycling in the Biosphere Recycling in the Biosphere Energy and matter move through the biosphere very differently. Unlike the one-way flow of energy, matter is recycled within and between ecosystems.
CO 2 (g) + H 2 O = H 2 CO 3 log K H = HCO 3 log K 1 = HCO - 3 = H CO 3 log K 2 = -9.0
 Ocean 400 Chemical Oceanography Winter 2006 Your Name Final Exam Read all questions carefully before you begin to answer. Use the back of the pages if necessary. Points are assigned to each question in
Ocean 400 Chemical Oceanography Winter 2006 Your Name Final Exam Read all questions carefully before you begin to answer. Use the back of the pages if necessary. Points are assigned to each question in
Pennsylvania Senior Environment Corps. Table of Contents Part 2 Getting Started:. 21 Chemical Analysis... 22
 Table of Contents Part 2 Getting Started:. 21 Chemical Analysis.... 22 3 Chapter 2: Getting Started 21 Chemical Analysis of the Water Dependent on your area, you may measure for several parameters. In
Table of Contents Part 2 Getting Started:. 21 Chemical Analysis.... 22 3 Chapter 2: Getting Started 21 Chemical Analysis of the Water Dependent on your area, you may measure for several parameters. In
Environmental Science. Physics and Applications
 Environmental Science 1 Environmental Science. Physics and Applications. Carbon Cycle Picture from the IPCC report on the environment. 4. Carbon cycle 4.1 Carbon cycle, introduction 4.2 The oceans 4.3
Environmental Science 1 Environmental Science. Physics and Applications. Carbon Cycle Picture from the IPCC report on the environment. 4. Carbon cycle 4.1 Carbon cycle, introduction 4.2 The oceans 4.3
BIOGEOCHEMISTRY BIOGEOCHEMISTR Y OF N NREM
 BIOGEOCHEMISTRY OF N NREM 665 Dominant Pathways for N Cycling Plant Uptake: assimilation of NH + - 4 and NO 3 into biomass N Fixation: Conversion of gaseous N 2 to NH 3 Ammonia Volatilization: NH 4+ NH
BIOGEOCHEMISTRY OF N NREM 665 Dominant Pathways for N Cycling Plant Uptake: assimilation of NH + - 4 and NO 3 into biomass N Fixation: Conversion of gaseous N 2 to NH 3 Ammonia Volatilization: NH 4+ NH
10/17/ Cycles of Matter. Recycling in the Biosphere. How does matter move among the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem?
 2 of 33 3-3 Cycles of Matter How does matter move among the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem? 3 of 33 Recycling in the Biosphere Recycling in the Biosphere Energy and matter move through the
2 of 33 3-3 Cycles of Matter How does matter move among the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem? 3 of 33 Recycling in the Biosphere Recycling in the Biosphere Energy and matter move through the
Transport & Transformation of chemicals in an ecosystem, involving numerous interrelated physical, chemical, & biological processes
 OPEN Wetland Ecology Lectures 14-15-16 Wetland Biogeochemistry What is biogeochemical cycling? Transport & Transformation of chemicals in an ecosystem, involving numerous interrelated physical, chemical,
OPEN Wetland Ecology Lectures 14-15-16 Wetland Biogeochemistry What is biogeochemical cycling? Transport & Transformation of chemicals in an ecosystem, involving numerous interrelated physical, chemical,
SEAWATER 101. Seawater s Amazing Physical and Chemical Properties. Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector - Instructor
 SEAWATER 101 Seawater s Amazing Physical and Chemical Properties Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector - Instructor The Nature of Water Topics To Be Covered Elements of Water Chemical Bonding The Water
SEAWATER 101 Seawater s Amazing Physical and Chemical Properties Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector - Instructor The Nature of Water Topics To Be Covered Elements of Water Chemical Bonding The Water
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems
 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems are chemicals required for growth and other life processes. Nutrients move through the biosphere in Nutrients often accumulate in areas called Without interference, generally
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems are chemicals required for growth and other life processes. Nutrients move through the biosphere in Nutrients often accumulate in areas called Without interference, generally
Guide 34. Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles. p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/
 Guide 34 Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/ Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists
Guide 34 Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/ Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists
Bell Ringer AP Practice
 Bell Ringer AP Practice 1) Reasons that the population size of an exotic species often grows rapidly when the species is introduced in a new environment include which of the following? i. The exotic species
Bell Ringer AP Practice 1) Reasons that the population size of an exotic species often grows rapidly when the species is introduced in a new environment include which of the following? i. The exotic species
Natural Ecosystem Change
 Environmental Science Set 3 of 9 Natural Ecosystem Change Presentation MEDIA Version 2 BIOZONE International 2009, 2013 Processes in Carbon Cycling Carbon cycles between the living (biotic) and non-living
Environmental Science Set 3 of 9 Natural Ecosystem Change Presentation MEDIA Version 2 BIOZONE International 2009, 2013 Processes in Carbon Cycling Carbon cycles between the living (biotic) and non-living
Introduction. OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography. 9 January TR 12:00 13:15 in MSB 315
 Introduction 9 January 2018 OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography TR 12:00 13:15 in MSB 315 Brian Glazer glazer@hawaii.edu Biogeochemistry & microbial geochemistry Chris Measures chrism@soest.hawaii.edu Chemistry
Introduction 9 January 2018 OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography TR 12:00 13:15 in MSB 315 Brian Glazer glazer@hawaii.edu Biogeochemistry & microbial geochemistry Chris Measures chrism@soest.hawaii.edu Chemistry
Radiative forcing of gases, aerosols and, clouds.
 Lecture 23. Radiative forcing of gases, aerosols and, clouds. 1. Concepts of radiative forcing, climate sensitivity, and radiation feedbacks. 2. Radiative forcing of anthropogenic greenhouse gases. 3.
Lecture 23. Radiative forcing of gases, aerosols and, clouds. 1. Concepts of radiative forcing, climate sensitivity, and radiation feedbacks. 2. Radiative forcing of anthropogenic greenhouse gases. 3.
Risk and Uncertainties in Anthropogenic. Control over Greenhouse Forcing in the TAR. with a focus on Atmospheric Chemistry
 FCCC, Bonn, 4-6 Apr 2002 SBSTA IPCC/TAR Michael Prather University of California at Irvine Risk and Uncertainties in Anthropogenic Control over Greenhouse Forcing in the TAR with a focus on Atmospheric
FCCC, Bonn, 4-6 Apr 2002 SBSTA IPCC/TAR Michael Prather University of California at Irvine Risk and Uncertainties in Anthropogenic Control over Greenhouse Forcing in the TAR with a focus on Atmospheric
Unit 11.2: Recycling Matter
 Unit 11.2: Recycling Matter Lesson Objectives Define biogeochemical cycles. Describe the water cycle and its processes. Give an overview of the carbon cycle. Outline the steps of the nitrogen cycle. Vocabulary
Unit 11.2: Recycling Matter Lesson Objectives Define biogeochemical cycles. Describe the water cycle and its processes. Give an overview of the carbon cycle. Outline the steps of the nitrogen cycle. Vocabulary
Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle
 Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle David Allen Gertz Regents Professor in Chemical Engineering, and Director, Center for Energy and Environmental Resources Concepts for today Greenhouse Effect
Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle David Allen Gertz Regents Professor in Chemical Engineering, and Director, Center for Energy and Environmental Resources Concepts for today Greenhouse Effect
How Ecosystems Work Section 1. Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1
 Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1 Life Depends on the Sun Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1 Life Depends on the Sun Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes
 Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
3.4 Cycles of Matter. Recycling in the Biosphere. Lesson Objectives. Lesson Summary
 3.4 Cycles of Matter Lesson Objectives Describe how matter cycles among the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem. Describe how water cycles through the biosphere. Explain why nutrients are important
3.4 Cycles of Matter Lesson Objectives Describe how matter cycles among the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem. Describe how water cycles through the biosphere. Explain why nutrients are important
