Climate change and groundwater resources in China
|
|
|
- Leonard Gilmore
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Climate change and groundwater resources in China BAI Bing 1,3,4, CHENG Yan-pei 2, JIANG Zhong-cheng 1,3,4, ZHANG Cheng 1,3,4* 1 Institute of Karst Geology, CAGS, Guilin , China. 2 Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, Shijiazhuang , China. 3 Key Laboratory of Karst Dynamics, Ministry of Land and Resources, Guilin , China. 4 International Research Center on Karst under the Auspices of UNESCO, Guilin , China. Abstract: Water resources play an important role in supporting the economic and social development of China. The impact of climate change on water resources has become a bottleneck in this process, especially for major projects, with surface water and groundwater systems experiencing considerable impacts. The annual natural recharge of fresh groundwater is m 3, which accounts for approximately 31% of the water resources. Groundwater is the most significant water source for many cities and energy bases, and it is also the main source acting as a buffer against extreme climate events caused by climate change. However, most of the groundwater in China buried deeply and unevenly, which increases the difficulty of investigating and exploiting this resource.this paper illustrates the general conditions of China water resources and hydrogeological hazards, such as karst sinkholes, surface subsidence, and soil salinization, caused by climate change, El Nino, La Nina, other climate events and human activities and presents the regulatory measures enacted to mitigate these issues in China.The China Geological Survey (CGS) has organized professional teams to investigate and evaluate groundwater resources and the environment since Based on these investigations, the total quantity, expected exploitable quantity and current exploited quantity of groundwater in whole China have been evaluated. In addition, an evaluation of the groundwater pollution caused by climate change throughout China and key areas has been conducted. At present, the CGS is conducting national groundwater monitoring projects and establishing regional engineering and technical measures for water resource exploitation and utilization. Keywords: Groundwater; Water resource; Climate change; Hydrogeological hazard; Technical measure; China 1 Introduction 1.1 Status of groundwater in China Climate and water resources The general drainage system pattern in China is influenced by the following 3 main factors: Geographic position, monsoon area, and topography. China is mainly located in a temperate zone, and tropical monsoons from the Indian Ocean and Pacific Ocean are responsible for considerable precipitation in China. The precipitation in China differs according to the elevation and topography. The overall length of all rivers in * Corresponding author. chzhang@karst.ac.cn 44 China is approximately km, and the drainage area for rivers is larger than 100 km 2, and approximately of these drainage basins are over km 2. The annual mean average precipitation is 649 mm, which is varies annually. As shown in Fig. 1, from 1951 to 2002, the total precipitation decreased at an average of mm/yr because of the decreased rainfall in spring and autumn (WANG Ying et al. 2006). In the north, the precipitation level in a year with abundant rain could be 3 to 6 times higher than that of year with low rainfall. This variation in rainfall leads to changes in the runoff volume, which could differ by 10-fold in the same river. The distribution of rainfall at different spatial scales is also uneven. Greater rainfall occurs in the eastern and southern areas than in the western and
2 Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering Vol.5 Vol.4 No.1 No.2 Mar. Jun northern areas. Precipitation in summer accounts for 47% of the total for the whole year, although in the north, this value can reach 62%. The annual runoff depth is 280 mm (GUO Jing-hui, 1958; YOU Song-cai et al. 2002), and values of 666 mm have been observed in southeast areas, although the value decreases to 35 mm for certain rivers in northwest areas. Another outstanding feature of precipitation in China is the combination of rain and heat in the same period. Statistics of the People s Republic of China. Fig. 1 Annual precipitation of China from 1951 to 2002 In addition to precipitation, the other main factor that limits water resources is evaporation, which is affected by sunshine duration and intensity. The minimum evaporation value in China is estimated to be 500 mm/yr, and the maximum value is mm/yr (DU Chuan-li and LIU Xiao-dong, 2009). Compared with precipitation, evaporation is greater in western and northern areas, which exacerbates the differences in water resources in different areas. Moreover, increasing water vapor from land may lead to enhanced local convection and further changes in atmospheric circulation (Harding K J and Snyder P K, 2012; QIAN Y et al. 2013). The gross amount of China s water resources is 2.80 trillion m 3. With a population of 1.3 billion people, the average water resources amount per capita is approximately m 3, which is a quarter of the world s average level. The surface water amount is 2.68 trillion m 3, and the groundwater amount is 0.81 trillion m 3. Because of a lag in statistical data, a repeated amount of approximately 0.70 trillion m 3 is observed. Fig. 2 shows that the ratio of the population, area, arable land, GDP and socioeconomic elements are not consistent with the distribution of water resources in Northern and Southern China; these data were obtained from the China Statistical Yearbook in 2011, which was published by National Bureau of Fig. 2 Water resources and socioeconomic elements distribution in the north and south The water resources in China present five advantages and five disadvantages. The five advantages are as follows: 1) The total amount of water resources is abundant; 2) rain and heat occur in the same period, which is beneficial to agricultural production; 3) water yield in the mountainous area is large, which is beneficial to regulation and storage; 4) several large drainage systems contribute to the allocation of national water resources; and 5) groundwater storage conditions in the North China Plain are good. The five disadvantages are as follows: 1) Average water unit area per capita is small; 2) precipitation distribution is uneven annually and interannually; 3) precipitation distribution is uneven on a spatial scale; 4) water resources are inconsistent with socioeconomic elements, such as arable lands; and 5) water resources of the Yellow River drainage basin and southwest areas are difficult to exploit Groundwater The groundwater in China presents its own specific advantages and disadvantages. The advantages are as follows: Groundwater has a wide distribution that facilitates local utilization; groundwater is of high quality and is not easily polluted; thus, it is usually better than surface water; underground storage saves the space on the ground; and climate change has a relatively small influence on groundwater resources compared with surface water because groundwater has excellent regulation and storage capacities. However, the improper use of groundwater could cause serious environmental problems. For example, unreasonable irrigation practices cause soil salinization. Many environmental hazards are generated by 45
3 groundwater overexploitation, such as saline intrusion in coastal regions, water pollution and surface subsidence. For example, in Hebei Province, the shallow water table level has dropped by 5 m to a depth of 12 m from 1983 to 1999 over large areas (HAN Z, 2003). Groundwater also plays a key role in certain engineering projects, such as mining and landslide prevention. Groundwater is a freshwater resource that could be utilized; however, it requires a period of time to recover. Usually, the exploitation quantity of groundwater should not exceed the recharge amount. Otherwise, the ecological conditions will be worse and certain environmental hazards will occur, such as surface subsidence, drought, and rocky desertification. A comparison of the groundwater amount for with that for shows that the groundwater of China has decreased by 3.6%. In the last two decades, groundwater has accounted for approximately 18% of the total water supply on a national scale according to the Water Resources Bulletin by the Ministry of Water Resources of the People s Republic of China. China has focused on investigating, researching, exploiting and protecting groundwater resources. The China Geological Survey (CGS) has set up the Department of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology to organize scientists and technicians to conduct groundwater and environment investigations and research across China, and it has established a professional team of more than scientists and technicians from the Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology (IHEG) of Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (CAGS), the Institute of Karst Geology (IKG) of CAGS, and the International Research Center on Karst (IRCK) under the auspices of UNESCO, China Institute for Geo-Environmental Monitoring, Center for Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, China University of Geosciences as well as provincial hydrogeological teams and geo-environmental monitoring stations. The major fields for the related work include hydrogeological and environmental geological investigations, dynamical monitoring of groundwater and its environment; the relationship between groundwater and global climate change and human activities; international transboundary aquifer research; the exploitation, utilization and 46 protection of groundwater; and projects to address geohazards caused by groundwater. All of these related investigations and research have provided important support to the development, utilization and protection of groundwater in China and promoted international research on groundwater and associated environments. 1.2 Climate change Global climate changes in recent decades have influence on the global water cycle and led to water resources changes in China. Precipitation and evaporation controlled by monsoon climate are two significant factors affecting the spatial and temporal variability of water resources. In terms of ocean circulation, El Nino and La Nina are the results of global climate change directly affecting the water cycle. Climate changes become an obvious trend according to meteorological studies; therefore, the El Nino and La Nina phenomena have appeared more frequently in recent years. 2 Climate changes and groundwater sustainability 2.1 Climate changes and hydrologic variability In El Nino years, a larger amount of rainfall occurs in the rainy season in South China. In El Nino years, higher rainfall is usually accompanied by increased temperatures; consequently both precipitation and evaporation increase. La Nina years often follow El Nino years. La Nina is opposite to El Nino, and greater rainfall and higher temperatures appear in North China in summer (Wang C and Fiedler P C, 2006; GONG Dao-yi and WANG Shao-wu, 1999). Abnormal water cycle patterns cause unusual surface water conditions. The closed hydrological connection between surface water and groundwater recharge (YAO Hui and LI Dong-liang, 1992) as well as between runoff and discharge are also changed. The hydrological factors related to groundwater that are affected by climate change include the water table, groundwater amount and leakage among aquifers, which may increase the difficulty of exploiting and utilizing groundwater.
4 Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering Vol.5 Vol.4 No.1 No.2 Mar. Jun Fig. 3 (a) Annual distribution of rainfall in Guangzhou, Nanning, Guiyang and Hong Kong for the period Fig. 3 (b) Annual runoff variations for the Pearl River and 3 major tributaries-west, North and East rivers Fig. 3 (c) Plot between the Pearl River annual surface runoff and South China annual rainfall. The correlation coefficient R2= indicates a strong positive correlation between the two variables (Lo P K P, 2014) 2.2 Impacts of climate change on groundwater Predicted sustainability of groundwater resource under climate change Groundwater is recharged via surface water infiltration and direct rainfall infiltration. Both of these processes are affected by precipitation and evaporation to a large extent. Rivers and lakes may have fissures and conduits to underground rivers. Less precipitation reduces the water in rivers and lakes and leads to insufficient recharge. Usually, water infiltrates to the subsurface through the soil layer. Climate change and variability are expected to have profound effects on soil water and temperature (Jasper K et al. 2006; Jungkunst H F et al. 2008). Precipitation must meet the soil capacity first before it reaches the aquifer. Sandström K (1995) showed that a 15% reduction in precipitation without changes in temperature resulted in a 40 50% reduction in groundwater recharge. Consequently, insufficient rainfall will reduce the infiltration recharge of groundwater. Less recharge causes less storage of groundwater. The amount of groundwater not only affects 47
5 exploitation and utilization but also influences the groundwater quality. If less recharge and storage persist for a long period, then the increasingly rigid demands for groundwater resources for national economic construction will lead to overexploitation and cause continuous decreases of the water table. JIANG Dong et al. (1999) showed that more than 100 cities had an obvious decrease of the water table and 56 relatively large regional funnels with a total area more than km 2 were formed. Over-exploitation of groundwater is serious in northern China, such as along the North China Plain, six basins of Shanxi Province, the Songnen Plain, and the inland basin of northwest China. In addition, excessive groundwater exploitation leads to declining terrestrial water storage, decreased stream flows, and weaker hydraulic connections between aquifers and rivers (Szilagyi J 1999, 2001; Kollet S J and Zlotnik V A, 2003; Biggs T W et al. 2008) Major threats to water resources and the environment because of the climate change An increasing trend of average temperature because of global climate change has led to melting sea ice and rising sea levels. In coastal areas, the risk of seawater intrusion increases with sea level rises. Because of its high salinity, seawater raises the total dissolved solubility (TDS) of groundwater and causes water quality deterioration. TDS also can rise with the groundwater shortages that threaten drinking and irrigation because of an insufficient inflow of fresh groundwater for dilution. In addition, strong evaporation can lead to soil salinization. High salinity soil will change the quality of infiltrated water and pollute the groundwater. In El Nino years, large amounts of rainfall in the rainy season lead to floods and water logging in South China and extreme droughts in North China when the rainy season ends. These two water resource problems are caused by climate change and threaten the socioeconomic development of China. La Nina years provide floods and water logging in North China during summer. In addition, abnormal sea water temperatures in the east Pacific increase the frequency of typhoons in La Nina years. Typhoons mainly influence the rainfall in East China, thus making the water cycle more complex (ZHANG Yue-cong and MENG 48 Xian-feng, 2005). Because of the shortage of water resources in the North China Plain, the shallow groundwater level of Hebei Province and Beijing decreased by m over the past 30 years. The deep groundwater of the North China Plain has already formed a regional cone of groundwater depressions crossing Hebei, Beijing, Tianjin, and Shandong. Up to km 2 of the area was covered by below-sea level groundwater, thus accounting for 55% of the entire area of the North China Plain. 2.3 Impact of climate change on groundwater dependent systems and sectors Water shortages and quality deterioration are the two major groundwater problems associated with climate change. These problems mainly emerge in the following three aspects: Human community, agriculture, and industry Human communities The six great basins of Shanxi Province suffer from groundwater shortages to different degrees. From 2001 to 2006, the overexploitation of groundwater in middle basins has reached to m 3 /yr. Because of decreasing water levels, groundwater could not easily be reached in Datong and Yuncheng. The shallow groundwater of the Changzhi Basin dried up, which reduced the ability of local residents to obtain drinking water. In the inclined region of the western Songnen Plain and the low region in the middle, the phreatic water level decreased by 3-5 m on average compared with that of the 1960s and may even decrease by 3-8 m in certain places. In the exploitation area of the concentrated water supply source in the high plain of eastern Songnen Plain, the water table declined by 5-25 m. Because the groundwater has been overexploited for a long time, the groundwater has changed from confined water to unconfined interlayer water, with the water level m lower than the aquifer roof and the yield of a single well declining by 30-50%. In the northwest areas, the groundwater level of the Shiyang River Drainage Basin has declined most dramatically. In the middle of the drainage basin, the water level decreased from m above the
6 Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering overflow zone of the springs to 1-5 m below the overflow zone, which decreased the springs flow rate, with some even drying up. Groundwater shortages not only cause decreases in the water table but also result in land subsidence and karst sinkholes. In the early 1990s, the land subsidence area was approximately km2 across 16 provinces (districts, cities), including Shanghai, Tianjin, Beijing, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Hebei. Until 2003, the land subsidence area reached km2, with a serious land subsidence region composed of the Yangtze Delta, North China Plain, Fen River and Wei River fault basin (YIN Yue-ping et al. 2005). The Yangtze Delta is the most serious land subsidence area in China. Shanghai has suffered from the earliest and most considerable land subsidence, which caused severe damage to the local society. In the 1920s, rapid urban construction along with increasing groundwater exploitation around the urban area caused immediate land subsidence. Thus far, the surface subsidence at over 200 mm in the Shanghai downtown area, Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou, and Jiaxing has covered an area of approximately km2, thus accounting for 1/3 of the total area, and this area is expected to be connected as a sheet. Although groundwater exploitation bans have been recently enacted and the water table in most areas is beginning to rebound, the subsidence rate is holding constant at mm/yr and even reaches mm/yr (Fig. 4). Vol.4 No.1 No.2 Mar. Jun Vol Cangzhou and northeast rural area of Beijing as the three centers. The land subsidence of Tianjin has occurred simultaneously with that of Shanghai since 1920s, and the deepest land subsidence is over 3.1 m, which is the deepest in China. The land subsidence of the North China Plain is connected with the west Hebei plains, which is consistent with the large cone of groundwater depression formed by groundwater exploitation. The Fen-Wei graben developed along the Wei River and six basins in Shanxi and spread obliquely. This area experiences strong tectonic movement, with the base structure lifting and falling dramatically. Because of groundwater exploitation, land subsidence and many ground fissures spread along tectonic lines. The Xi an area has experienced continuous subsidence at up to 2.6 m, with 13 ground fissures presenting a total length of 73 km. Taiyuan has experienced land subsidence up to 3 m, with the fissures presenting a total length of 15 km. Karst sinkholes are a special geohazard in karst areas, which are mainly distributed in South China, Central China, Southwest China and East China. The high-risk area for karst sinkholes is approximately km2, which encompasses more than 30 metropolises or medium cities, such as Guangzhou, Wuhan, Shenzhen, as well as 328 counties and small cities. Karst sinkholes have shown an increasing trend over time, changing from dozens of times per year before 1980 to several hundreds of times per year currently (Fig. 5). Spatially, karst sinkholes presented urbanized and industrialized trends. Fig. 4 Land Subsidence Model of Shanghai, China for ( Fig. 5 Changes in the frequency of karst sinkholes in China since 1960 As the largest land subsidence area in China, the area of the North China Plain experiencing subsidence is more than km2, with Tianjin, A majority of the karst sinkholes of China (81%) have been caused by human engineering. Groundwater overexploitation, dewatering mines, 49 49
7 discharging, and underground engineering projects are the primary causes of karst sinkholes. For example, 97 karst sinkhole sites and 161 karst sinkholes occurred in Tailai Basin in Shandong Province. The karst sinkholes were mainly concentrated in the cone of a karst groundwater depression and the area under its influence, which are caused by the overexploitation of groundwater, which resulted in a decrease in the water table of over 10 m (WANG Yan-ling et al. 2015) Agriculture and Industry Although certain areas present a considerable amount of natural water resources, effectively detecting and exploiting groundwater is difficult because of the special geological conditions and geographic environment of groundwater; in addition, water conservancy projects have not developed the facilities for water storage. Engineering water shortages are common in every drainage area of China, especially in the karst mountainous areas of Southwest China, the watershed of the Yangtze River Drainage Area and the Pearl River Drainage Area. In Southwest China, the sub-tropical monsoon climate leads to considerable amounts of precipitation that are uneven annually. Karst fissures and conduits are well-developed underground, and rainfall transiently converges on the surface and disperses and infiltrates to recharge groundwater. Rainfall is discharged to deep-cut valleys through rapid runoff, which produces dramatic dynamical changes of the karst water table and fluxes. Therefore, it is quite difficult for karst aquifers to adjust groundwater effectively, which leads to extremely uneven spatial and temporal distributions of groundwater resources. In addition, because of the rough landforms of the karst mountainous region in Southwest China and the complicated karst aquifer structures, it is very difficult to explore and develop karst water resources, both technically and economically. This region is an entirely undeveloped economic area, and the engineering water shortages have not been solved effectively. 3 Adaptation to climate changes 50 Prior to this century, China had not investigated and evaluated groundwater pollution throughout the country. Formerly, investigations and research into groundwater mainly focused on assessing the formation conditions and the resource amounts, with less attention focused on water quality or pollution, which may have only been investigated locally. There was no systematical investigation of groundwater quality or pollution. From 2005 to 2016, the CGS of the Ministry of Land & Resources of China conducted national groundwater pollution investigations. The results showed that the overall groundwater quality was relatively good, although in certain regions, the groundwater was polluted severely. According to the investigation and monitoring results, the overall over-standard percentage of groundwater contamination in China is 15%, with nitrogen and metallic pollution the most serious. In addition, organic pollution is becoming more severe. Nitrogen contamination is the most serious pollution for groundwater, which is primarily from fertilizer overuse, dispersed breeding, landfills and sewage discharge. Heavy metal pollution, such as over-standard concentrations of Pb, Cr, and Hg, could also be found in certain places. These over-standard contaminants are distributed around urban areas, factories or mines. In addition, organic pollution could be detected in groundwater, including benzene serials of petrochemicals, organic chlorine solvents, and pesticides, especially in Eastern China in areas with a developed economy and inland cities with larger populations. Widespread agricultural pollution is an important cause of widespread shallow groundwater pollution. Key issues related to groundwater pollution in China can be organized according to the following three main aspects: First, large areas are suffering from groundwater pollution; second, regional detailed data on groundwater pollution are insufficient; and third, proper experience and technology are lacking to prevent and treat groundwater pollution. In Yunnan Province, the overall reservoir capacity only accounts for 2% of the interannual average runoff, with many existing dangerous reservoirs (WANG Yong-de, 2014). Since 2009, a number of provinces and cities, such as Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangxi, Sichuan and Chongqing, have
8 Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering Vol.5 Vol.4 No.1 No.2 Mar. Jun suffered from serious droughts continuously during winter and spring, which highlighted the predominant problems, such as a lack of water sources in this region, serious engineering water shortages and a lack of water conservation facilities (LI Wei and NAN Chun-hui, 2012). 4 Challenges and problems To address climate change, groundwater protection measures have been included in current laws and regulations; however, these measures are not sufficiently comprehensive and systematized, which produces large obstacles for implementation. Thus, these measures are not beneficial for groundwater monitoring and protection. This disadvantage is mainly reflected in the lack of comprehensive laws on groundwater resources. A comprehensive groundwater monitoring system is fundamental to hydrogeology, engineering geology and environmental geology. Because of insufficient funding, groundwater management and maintenance are lacking. Consequently, among the tens of thousands of monitoring stations, less than half are operational. There are only national monitoring stations that only cover 10.2% of the national territory. Areas with limited monitoring do not accurately convey the groundwater utilization in China. Supervisory departments are seriously inadequate at all levels; thus, sufficient and effective support is not provided for groundwater management. However, groundwater monitoring is a popular research topic in China, and most studies focus on 1) optimizing monitoring stations, 2) improving data reliability and 3) constructing groundwater monitoring models. Acknowledgements This study was supported by initial study on the relationship between groundwater-cave formation and evolution with the karst geological carbon sink, Basic Scientific Research Project of Institute of Karst Geology, CAGS (201501). References Biggs T W, Scott C A, et al Impacts of irrigation and anthropogenic aerosols on the water balance, heat fluxes, and surface temperature in a river basin. Water Resources Research, 44(12). DU Chuan-li, LIU Xiao-dong Analyses on land water resource in China based on simulation results of CLM 3. Meteorological Monthly, 35(8): GONG Dao-yi, WANG Shao-wu Influences on global land and Chinese precipitation from ENSO in centuries. Chinese Science Bulletin, 44(3): GUO Jing-hui The natural geographical factors of surface runoff formation in China. Acta Geographica Sinica, (2): Harding K J, Snyder P K Modeling the atmospheric response to irrigation in the Great Plains. Part I: General impacts on precipitation and the energy budget. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 13(6): Han Z Groundwater resources protection and aquifer recovery in China. Environmental Geology, 44(1): Jasper K, Calanca P, Fuhrer J Changes in summertime soil water patterns in complex terrain due to climatic change. Journal of Hydrology, 327(3): JIANG Dong, WANG Jian-hua, CHEN Pei-pei City environmental crisis and solutions to underwater over-deploit. Environmental Protection, (4): Jungkunst H F, Flessa H, et al Groundwater level controls CO 2, N 2 O and CH 4 fluxes of three different hydromorphic soil types of a temperate forest ecosystem. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 40(8): Kollet S J, Zlotnik V A Stream depletion predictions using pumping test data from a heterogeneous stream aquifer system (a case study from the Great Plains, USA). Journal of Hydrology, 281(1): LI Wei, NAN Chun-hui Consideration to solve the engineering water shortage in Southwest China. Haihe Water Resources, (4): 6-8. Lo P K P Quantifying the climatic impacts on rainfall in South China and water discharge in the pearl river (Zhujiang), China. Hong Kong: HKU Theses Online. QIAN Y, HUANG M, et al A modeling 51
9 study of irrigation effects on surface fluxes and land-air-cloud interactions in the Southern Great Plains. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 14(3): Sandström K Modeling the effects of rainfall variability on groundwater recharge in semi-arid Tanzania. Hydrology Research, 26(4-5): Szilagyi J Streamflow depletion investigations in the Republican River basin: Colorado, Nebraska, and Kansas. Journal of Environmental Systems, 27(3): Szilagyi J Identifying cause of declining flows in the Republican River. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 127(4): Wang C, Fiedler P C ENSO variability and the eastern tropical Pacific: A review. Progress in Oceanography, 69(2): WANG Yan-ling, CHEN Wei-qing, et al Development features and formation mechanisms of karst collapses in the Tailai Basin, Shandong Province. Carsologica Sinica. 34(5): WANG Ying, CAO Ming-Kui, et al The characteristics of spatio-temporal patterns in precipitation in China under the background of global climate change. Geographical Research, 25(6): WANG Yong-de The measurements and analysis of sustained droughts in Yunnan. China Water Resources, (15): YAO Hui, LI Dong-liang El Nino events, Chinese precipitation and historical floods and droughts. Quarterly Journal of Applied Meterology, (2): YIN Yue-ping, ZHANG Zuo-chen, ZHANG Kai-jun Land subsidence and countermeasures for its prevention in China. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 16(2): 1-8. YOU Song-cai, Kiyoshi Takahashi, Yuzuru Matsuoka Climate change impact on surface runoff in China. Quaternary Sciences, 22(2): ZHANG Yue-cong, MENG Xian-feng Causes of El Nino and La Nina Formation and their effects on Chinese climate. Journal of Chengde Teachers College for Nationalities, 25(2):
Issue paper: Aquifer Water Balance
 Issue paper: Aquifer Water Balance 1. Introduction And Background 1.1. Purpose and Scope The population in Kitsap County has grown rapidly in recent years and is expected to increase substantially in the
Issue paper: Aquifer Water Balance 1. Introduction And Background 1.1. Purpose and Scope The population in Kitsap County has grown rapidly in recent years and is expected to increase substantially in the
Sustainability of Groundwater Resources in the North China Plain
 Sustainability of Groundwater Resources in the North China Plain Jie Liu, Guoliang Cao, and Chunmiao Zheng Abstract The North China Plain (NCP) has one of the most depleted aquifers in the world due to
Sustainability of Groundwater Resources in the North China Plain Jie Liu, Guoliang Cao, and Chunmiao Zheng Abstract The North China Plain (NCP) has one of the most depleted aquifers in the world due to
Climate change and groundwater resources in Lao PDR
 Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering Vol.5 Vol.4 No.1 No.2 Mar. Jun. 2016 2017 Climate change and groundwater resources in Lao PDR Khongsab Somphone 1*, OunakoneKone Xayviliya 1 1 Division of
Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering Vol.5 Vol.4 No.1 No.2 Mar. Jun. 2016 2017 Climate change and groundwater resources in Lao PDR Khongsab Somphone 1*, OunakoneKone Xayviliya 1 1 Division of
Rationally Utilizing Water Resources to Control Soil Salinity in Irrigation Districts
 This paper was peer-reviewed for scientific content. Pages 1134-1138. In: D.E. Stott, R.H. Mohtar and G.C. Steinhardt (eds). 2001. Sustaining the Global Farm. Selected papers from the 10th International
This paper was peer-reviewed for scientific content. Pages 1134-1138. In: D.E. Stott, R.H. Mohtar and G.C. Steinhardt (eds). 2001. Sustaining the Global Farm. Selected papers from the 10th International
System Dynamics Modeling for Sustainable Water Management of a Coastal Area in Shandong Province, China
 Journal of Earth Science and Engineering 4 (2016) 226-234 doi: 10.17265/2159-581X/2016.04.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING System Dynamics Modeling for Sustainable Water Management of a Coastal Area in Shandong
Journal of Earth Science and Engineering 4 (2016) 226-234 doi: 10.17265/2159-581X/2016.04.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING System Dynamics Modeling for Sustainable Water Management of a Coastal Area in Shandong
Economic Structure Transformation and Land Use Change of the Changjiang River Basin
 Chinese Geographical Science 2006 16(4) 289 293 DOI 10.1007/s11769-006-0289-6 www.springerlink.com Economic Structure Transformation and Land Use Change of the Changjiang River Basin WU Yingmei 1, 2, SU
Chinese Geographical Science 2006 16(4) 289 293 DOI 10.1007/s11769-006-0289-6 www.springerlink.com Economic Structure Transformation and Land Use Change of the Changjiang River Basin WU Yingmei 1, 2, SU
Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges
 Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges Components: Components and links Atmospheric water Surface water (including glacial water) Groundwater Links: Precipitation (atm(
Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges Components: Components and links Atmospheric water Surface water (including glacial water) Groundwater Links: Precipitation (atm(
Texas Water Resources Institute
 Texas Water Resources Institute April 1975 Volume 1 No. 5 Opportunities for Artificial Recharge By Jim Valliant, Research Engineer, Texas Agricultural Experiment Station Put "dirty" water back underground--i'd
Texas Water Resources Institute April 1975 Volume 1 No. 5 Opportunities for Artificial Recharge By Jim Valliant, Research Engineer, Texas Agricultural Experiment Station Put "dirty" water back underground--i'd
Climate change science, knowledge and impacts on water resources in South Asia
 Climate change science, knowledge and impacts on water resources in South Asia DIAGNOSTIC PAPER 1 GUILLAUME LACOMBE, PENNAN CHINNASAMY Regional Conference on Risks and Solutions: Adaptation Frameworks
Climate change science, knowledge and impacts on water resources in South Asia DIAGNOSTIC PAPER 1 GUILLAUME LACOMBE, PENNAN CHINNASAMY Regional Conference on Risks and Solutions: Adaptation Frameworks
Maintaining healthy rivers and lakes through water diversion from Yangtze River to Taihu Lake in Taihu Basin
 Water Science and Engineering, Sep. 2008, Vol. 1, No. 3, 36-43 ISSN 1674-2370, http://kkb.hhu.edu.cn, e-mail: wse@hhu.edu.cn Maintaining healthy rivers and lakes through water diversion from Yangtze River
Water Science and Engineering, Sep. 2008, Vol. 1, No. 3, 36-43 ISSN 1674-2370, http://kkb.hhu.edu.cn, e-mail: wse@hhu.edu.cn Maintaining healthy rivers and lakes through water diversion from Yangtze River
Susan P. Abano Engineer IV Policy and Program Division
 National Water Resources Board Integrated Water Resources Management Susan P. Abano Engineer IV Policy and Program Division National Water Resources Board Outline Philippines Water Resources Situationer
National Water Resources Board Integrated Water Resources Management Susan P. Abano Engineer IV Policy and Program Division National Water Resources Board Outline Philippines Water Resources Situationer
Rainwater Management. Dr. Iftikhar Ahmad. College of Earth and. University of The Punjab Lahore
 Rainwater Management in Major Cities of Punjab Dr. Iftikhar Ahmad College of Earth and Environmental Sciences. University of The Punjab Lahore Need For Rainfall Harvesting in Urban Areas of Punjab Groundwater
Rainwater Management in Major Cities of Punjab Dr. Iftikhar Ahmad College of Earth and Environmental Sciences. University of The Punjab Lahore Need For Rainfall Harvesting in Urban Areas of Punjab Groundwater
Issues include coverage gaps, delays, measurement continuity and consistency, data format and QC, political restrictions
 Satellite-based Estimates of Groundwater Depletion, Ph.D. Chief, Hydrological Sciences Laboratory NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt, MD Groundwater Monitoring Inadequacy of Surface Observations
Satellite-based Estimates of Groundwater Depletion, Ph.D. Chief, Hydrological Sciences Laboratory NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt, MD Groundwater Monitoring Inadequacy of Surface Observations
Urbanization and land subsidence in China.
 Urbanization and land subsidence in China. YUEPING YIN; KAIJUN ZHANG; XIAOCHUN LI China Geology Survey, Beijing, 100011, China. (e-mail:china. yyueping@mail.cgs.gov.cn) Abstract: Land subsidence due to
Urbanization and land subsidence in China. YUEPING YIN; KAIJUN ZHANG; XIAOCHUN LI China Geology Survey, Beijing, 100011, China. (e-mail:china. yyueping@mail.cgs.gov.cn) Abstract: Land subsidence due to
Seasonal and interannual variations of flow discharge from Pearl River into sea
 Water Science and Engineering, 2012, 5(4): 399-409 doi:10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2012.04.004 http://www.waterjournal.cn e-mail: wse2008@vip.163.com Seasonal and interannual variations of flow discharge
Water Science and Engineering, 2012, 5(4): 399-409 doi:10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2012.04.004 http://www.waterjournal.cn e-mail: wse2008@vip.163.com Seasonal and interannual variations of flow discharge
Tuo Shan Yan Dam and City Ningbo: Exploring the Historical Logic of Urban Water Management through a Big City of China
 Journal of Earth Science and Engineering 7 (2017) 127-135 doi: 10.17265/2159-581X/2017.03.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING Tuo Shan Yan Dam and City Ningbo: Exploring the Historical Logic of Urban Water Management
Journal of Earth Science and Engineering 7 (2017) 127-135 doi: 10.17265/2159-581X/2017.03.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING Tuo Shan Yan Dam and City Ningbo: Exploring the Historical Logic of Urban Water Management
East Maui Watershed Partnership Adapted from Utah State University and University of Wisconsin Ground Water Project Ages 7 th -Adult
 INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
Groundwater Crisis and Governance in China With Perspec,ves from the North China Plain
 Groundwater Crisis and Governance in China With Perspec,ves from the North China Plain Jie Liu 1, Chunmiao Zheng 1,2 1. Center for Water Research, Peking University 2. InternaConal Commission on Groundwater,
Groundwater Crisis and Governance in China With Perspec,ves from the North China Plain Jie Liu 1, Chunmiao Zheng 1,2 1. Center for Water Research, Peking University 2. InternaConal Commission on Groundwater,
U.S. Water Budget. Figure Source:Data from The Nation s Water Resources , Vol. 1, U.S. Water Resources Council.
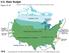 U.S. Water Budget Figure 10.18 10-9 Source:Data from The Nation s Water Resources 1975-2000, Vol. 1, U.S. Water Resources Council. Average U.S. Precipitation Figure 10.19 10-10 Source: U.S. Water Resources
U.S. Water Budget Figure 10.18 10-9 Source:Data from The Nation s Water Resources 1975-2000, Vol. 1, U.S. Water Resources Council. Average U.S. Precipitation Figure 10.19 10-10 Source: U.S. Water Resources
Nitrate contamination of groundwater in the alluvial fans of the Taihang Mts and Yanshan Mts
 (Proc. 6th International Groundwater Quality Conference held in Fremantle, Western Australia, 2 7 December 2007). IAHS Publ. 324, 2008. 79 Nitrate contamination of groundwater in the alluvial fans of the
(Proc. 6th International Groundwater Quality Conference held in Fremantle, Western Australia, 2 7 December 2007). IAHS Publ. 324, 2008. 79 Nitrate contamination of groundwater in the alluvial fans of the
Hydrology and Water Management. Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar
 Hydrology and Water Management Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar Course Outline Hydrologic Cycle and its Processes Water Balance Approach Estimation and Analysis of Precipitation Data Infiltration and Runoff
Hydrology and Water Management Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar Course Outline Hydrologic Cycle and its Processes Water Balance Approach Estimation and Analysis of Precipitation Data Infiltration and Runoff
Modeling the Managed Aquifer Recharge for Groundwater Salinity Management in the Sokh River Basin
 Modeling the Managed Aquifer Recharge for Groundwater Salinity Management in the Sokh River Basin A. Karimov, 1 I. Gracheva, 2 F. Miryusupov 2 1 International Water Management Institute (IWMI) Central
Modeling the Managed Aquifer Recharge for Groundwater Salinity Management in the Sokh River Basin A. Karimov, 1 I. Gracheva, 2 F. Miryusupov 2 1 International Water Management Institute (IWMI) Central
APRIL 2013 NATURE AGENCY MINISTRY OF THE ENVIRONMENT GROUNDWATER IN CHINA PART 1 - OCCURRENCE AND USE
 APRIL 2013 NATURE AGENCY MINISTRY OF THE ENVIRONMENT GROUNDWATER IN CHINA ADDRESS COWI Parallelvej 2 2800 Kongens Lyngby Denmark TEL +45 5640 2211 WWW COWI.COM APRIL 2013 NATURE AGENCY MINISTRY OF THE
APRIL 2013 NATURE AGENCY MINISTRY OF THE ENVIRONMENT GROUNDWATER IN CHINA ADDRESS COWI Parallelvej 2 2800 Kongens Lyngby Denmark TEL +45 5640 2211 WWW COWI.COM APRIL 2013 NATURE AGENCY MINISTRY OF THE
Effects of Paddy Field conversion to urban use on watershed hydrology in Southern China
 Effects of Paddy Field conversion to urban use on watershed hydrology in Southern China Di Fang, Mengsheng Qin, Hong Qian, Lei Sun, Lu Hao Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology Background
Effects of Paddy Field conversion to urban use on watershed hydrology in Southern China Di Fang, Mengsheng Qin, Hong Qian, Lei Sun, Lu Hao Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology Background
1.6 Influence of Human Activities and Land use Changes on Hydrologic Cycle
 1.6 Influence of Human Activities and Land use Changes on Hydrologic Cycle Watersheds are subjected to many types of changes, major or minor, for various reasons. Some of these are natural changes and
1.6 Influence of Human Activities and Land use Changes on Hydrologic Cycle Watersheds are subjected to many types of changes, major or minor, for various reasons. Some of these are natural changes and
WATERSHED. Maitland Valley. Report Card 201
 Maitland Valley WATERSHED Report Card 201 The Maitland Valley Conservation Authority has prepared this report card as a summary on the state of our forests, wetlands, surface water, and ground water resources.
Maitland Valley WATERSHED Report Card 201 The Maitland Valley Conservation Authority has prepared this report card as a summary on the state of our forests, wetlands, surface water, and ground water resources.
Future groundwater extraction scenarios based on COMSOL multiphysics for the confined aquifer at Linfen basin, Shanxi Province, China
 CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING RESEARCH ARTICLE Future groundwater extraction scenarios based on COMSOL multiphysics for the confined aquifer at Linfen basin, Shanxi Province, China Received: 06 June
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING RESEARCH ARTICLE Future groundwater extraction scenarios based on COMSOL multiphysics for the confined aquifer at Linfen basin, Shanxi Province, China Received: 06 June
IPCC WG II Chapter 3 Freshwater Resources and Their Management
 IPCC WG II Chapter 3 Freshwater Resources and Their Management Impacts increasingly harmful & more costly to adapt as global temperature increases May imperil sustainable development goals Semi-arid /
IPCC WG II Chapter 3 Freshwater Resources and Their Management Impacts increasingly harmful & more costly to adapt as global temperature increases May imperil sustainable development goals Semi-arid /
The Accounting Methods of the Local Government Department Output by Factor Analysis
 Applied Economics and inance Vol., No. ; May 04 ISSN 33-794 E-ISSN 33-7308 Published by Redfame Publishing URL: http://aef.redfame.com The Accounting Methods of the Local Government Department Output by
Applied Economics and inance Vol., No. ; May 04 ISSN 33-794 E-ISSN 33-7308 Published by Redfame Publishing URL: http://aef.redfame.com The Accounting Methods of the Local Government Department Output by
Research on the Ability of Regional Industrial Sustainable Development
 American Journal of Operations Research, 2012, 2, 442-447 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajor.2012.23052 Published Online September 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajor) Research on the Ability of Regional
American Journal of Operations Research, 2012, 2, 442-447 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajor.2012.23052 Published Online September 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajor) Research on the Ability of Regional
Drought Situations and Management in Vietnam
 Drought Situations and Management in Vietnam Background: In Vietnam, drought is one of the most frequent natural disasters, only after flood and storm, and has been becoming more severe due to the impact
Drought Situations and Management in Vietnam Background: In Vietnam, drought is one of the most frequent natural disasters, only after flood and storm, and has been becoming more severe due to the impact
Climate Change Impact to the Water Resources of Eastern Caucasus (Kura Basin) Rivers and Ways of Its Mitigation
 Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 1 (2016) 32-37 doi: 10.17265/2332-8215/2016.01.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Climate Change Impact to the Water Resources of Eastern Caucasus (Kura Basin) Rivers and Ways of Its
Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 1 (2016) 32-37 doi: 10.17265/2332-8215/2016.01.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Climate Change Impact to the Water Resources of Eastern Caucasus (Kura Basin) Rivers and Ways of Its
Climate Change, Food and Water Security in Bangladesh
 12 29 March 2016 Climate Change, Food and Water Security in Bangladesh Haweya Ismail Research Analyst Global Food and Water Crises Research Programme Key Points Bangladesh s geographical location, poverty
12 29 March 2016 Climate Change, Food and Water Security in Bangladesh Haweya Ismail Research Analyst Global Food and Water Crises Research Programme Key Points Bangladesh s geographical location, poverty
Foundation Course. Semester 3 THREATS TO THE ENVIRONMENT
 Foundation Course Semester 3 THREATS TO THE ENVIRONMENT INTRODUCTION Atmosphere, water and soil are the most important components of environment in which we live. Atmospheric factors like rainfall, humidity,
Foundation Course Semester 3 THREATS TO THE ENVIRONMENT INTRODUCTION Atmosphere, water and soil are the most important components of environment in which we live. Atmospheric factors like rainfall, humidity,
Nitrate in Trout Brook
 Nitrate in Trout Brook Dakota County, Minnesota Prepared by Dakota County Soil and Water Conservation District, March 2014 Introduction Trout Brook is a trout stream in Dakota County, Minnesota. It is
Nitrate in Trout Brook Dakota County, Minnesota Prepared by Dakota County Soil and Water Conservation District, March 2014 Introduction Trout Brook is a trout stream in Dakota County, Minnesota. It is
Spatial and temporal change in the potential evapotranspiration sensitivity to meteorological factors in China ( )
 J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22(1): 3-14 DOI: 10.1007/s11442-012-0907-4 2012 Science Press Springer-Verlag Spatial and temporal change in the potential evapotranspiration sensitivity to meteorological factors
J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22(1): 3-14 DOI: 10.1007/s11442-012-0907-4 2012 Science Press Springer-Verlag Spatial and temporal change in the potential evapotranspiration sensitivity to meteorological factors
Analysis on Comparative Advantage in the Production of. Major Grain Varieties in Different Areas of China
 Analysis on Comparative Advantage in the Production of Major Grain Varieties in Different Areas of China Wang Xicheng 1 Qi Xiaoling 2 ( 1 West China Center for Economic Research of Southwestern University
Analysis on Comparative Advantage in the Production of Major Grain Varieties in Different Areas of China Wang Xicheng 1 Qi Xiaoling 2 ( 1 West China Center for Economic Research of Southwestern University
Description of the original design/recommendation or project/process
 Teng Wang (Alex) Eric Cook Peter Holleman Sonja Spray CHINA RIVER DIVERSION OUTLINE (TASK 1) Due April 4, 2007 Intro Brief summary of the situation/problem. The China River Diversion project, also known
Teng Wang (Alex) Eric Cook Peter Holleman Sonja Spray CHINA RIVER DIVERSION OUTLINE (TASK 1) Due April 4, 2007 Intro Brief summary of the situation/problem. The China River Diversion project, also known
Groundwater Resource Management an introduction to its scope and practice
 Sustainable Groundwater Management: Concepts and Tools Sustainable Groundwater Management Concepts & Tools Briefing Note Series Note 1 Groundwater Resource Management an introduction to its scope and practice
Sustainable Groundwater Management: Concepts and Tools Sustainable Groundwater Management Concepts & Tools Briefing Note Series Note 1 Groundwater Resource Management an introduction to its scope and practice
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 154 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 154 (2016 ) 326 333 12th International Conference on Hydroinformatics, HIC 2016 Water Resources Monitoring System Construction
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 154 (2016 ) 326 333 12th International Conference on Hydroinformatics, HIC 2016 Water Resources Monitoring System Construction
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF HYDROLOGY EDUCATIONAL CRITERIA
 AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF HYDROLOGY EDUCATIONAL CRITERIA AIH FORM011A Rev. 11/21/17 BASIC REQUIREMENTS Completion of a full course of study leading to a bachelor's or higher degree at an accredited college
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF HYDROLOGY EDUCATIONAL CRITERIA AIH FORM011A Rev. 11/21/17 BASIC REQUIREMENTS Completion of a full course of study leading to a bachelor's or higher degree at an accredited college
Freshwater. 260 Points Total
 9 SURFACE WATER SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. (13 points) 1. An excessive amount of water
9 SURFACE WATER SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. (13 points) 1. An excessive amount of water
System dynamics model of Suzhou water resources carrying capacity and its application
 Water Science and Engineering, 2010, 3(2): 144-155 doi:10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2010.02.003 http://www.waterjournal.cn e-mail: wse2008@vip.163.com System dynamics model of Suzhou water resources carrying
Water Science and Engineering, 2010, 3(2): 144-155 doi:10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2010.02.003 http://www.waterjournal.cn e-mail: wse2008@vip.163.com System dynamics model of Suzhou water resources carrying
Simulation and Contamination. Keywords: Petroleum hydrocarbon pollution; source apportionment; PCA-MLR; Karst fissure groundwater
 2017 2 nd International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environment Protection (ICSEEP 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-464-6 Source Apportionment of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Contamination in Karst Fissure Groundwater
2017 2 nd International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environment Protection (ICSEEP 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-464-6 Source Apportionment of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Contamination in Karst Fissure Groundwater
Impacts of Drought in the e Philippines
 Department of Science and Technology Department of Science and Technology Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration Impacts of Drought in the e Philippines by Rosalina
Department of Science and Technology Department of Science and Technology Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration Impacts of Drought in the e Philippines by Rosalina
Chinese River Basins Yellow River, Huai, Interior Basins. Preliminary results of the GCI II survey
 http://www.unmultimedia.org/photo/guidelines.jsp IISD GWSP Conference on the Water-Energy-Food Security Nexus May 1 5 2012 Chinese River Basins Yellow River, Huai, Interior Basins Preliminary results of
http://www.unmultimedia.org/photo/guidelines.jsp IISD GWSP Conference on the Water-Energy-Food Security Nexus May 1 5 2012 Chinese River Basins Yellow River, Huai, Interior Basins Preliminary results of
Robert W. Buddemeier*, Hillel Rubin**, and David P. Young *
 PROTECTING URBAN WATER SUPPLIES IN SOUTH-CENTRAL KANSAS BY INTEGRATED GROUNDWATER-SURFACE WATER MANAGEMENT TO MEET MUNICIPAL, AGRICULTURAL AND ECOSYSTEM WATER NEEDS Robert W. Buddemeier*, Hillel Rubin**,
PROTECTING URBAN WATER SUPPLIES IN SOUTH-CENTRAL KANSAS BY INTEGRATED GROUNDWATER-SURFACE WATER MANAGEMENT TO MEET MUNICIPAL, AGRICULTURAL AND ECOSYSTEM WATER NEEDS Robert W. Buddemeier*, Hillel Rubin**,
Application of SWAT Model in land-use. change in the Nile River Basin: A Review
 Application of SWAT Model in land-use change in the Nile River Basin: A Review By: Marwa Ali, Okke Batelaan and Willy Bauwens 15-6-2011 Application of SWAT Model in land-use 1 change in the Nile River
Application of SWAT Model in land-use change in the Nile River Basin: A Review By: Marwa Ali, Okke Batelaan and Willy Bauwens 15-6-2011 Application of SWAT Model in land-use 1 change in the Nile River
Groundwater resources in the Indo Gangetic Basin
 Groundwater resources in the Indo Gangetic Basin Resilience to climate change and abstraction Executive Summary Groundwater within the Indo Gangetic Basin (IGB) alluvial aquifer system forms one of the
Groundwater resources in the Indo Gangetic Basin Resilience to climate change and abstraction Executive Summary Groundwater within the Indo Gangetic Basin (IGB) alluvial aquifer system forms one of the
MEASUREMENT OF GROUNDWATER TEMPERATURE FOR UNDERGROUND THERMAL UTILIZATION
 MEASUREMENT OF GROUNDWATER TEMPERATURE FOR UNDERGROUND THERMAL UTILIZATION Kasumi YASUKAWA 1, Youhei UCHIDA 1, Norio TENMA 1, Somkid BUAPANG 2 and Hirofumi MURAOKA 1 1 GSJ/AIST, AIST Tsukuba Central 7,
MEASUREMENT OF GROUNDWATER TEMPERATURE FOR UNDERGROUND THERMAL UTILIZATION Kasumi YASUKAWA 1, Youhei UCHIDA 1, Norio TENMA 1, Somkid BUAPANG 2 and Hirofumi MURAOKA 1 1 GSJ/AIST, AIST Tsukuba Central 7,
The Springs and. Aquifer System of Florida. Debra Segal, M.S. Volunteer for the Howard T. Odum Florida Springs Institute. Rock Springs, Orange County
 The Springs and Rock Springs, Orange County Aquifer System of Florida Debra Segal, M.S. Volunteer for the Howard T. Odum Florida Springs Institute Who Has Visited a Spring in Florida? Photos by John Moran
The Springs and Rock Springs, Orange County Aquifer System of Florida Debra Segal, M.S. Volunteer for the Howard T. Odum Florida Springs Institute Who Has Visited a Spring in Florida? Photos by John Moran
Water Account, Mauritius 2013
 Republic of Mauritius Water Account, Mauritius 2013 Statistics Mauritius, Ministry of Finance and Economic Development June 15 Contents Foreword... III List of Symbols and Abbreviations... IV 1. Introduction...
Republic of Mauritius Water Account, Mauritius 2013 Statistics Mauritius, Ministry of Finance and Economic Development June 15 Contents Foreword... III List of Symbols and Abbreviations... IV 1. Introduction...
Evaluation of Sustainable Water Demand in a Coastal Environment using WEAP Model
 Proceedings of the Environmental Management Conference,, Nigeria, 2011 Evaluation of Sustainable Water Demand in a Coastal Environment using WEAP Model Ojekunle Z. O. 1*, Ojo K. O. 1, Idowu O. A. 1, Martins
Proceedings of the Environmental Management Conference,, Nigeria, 2011 Evaluation of Sustainable Water Demand in a Coastal Environment using WEAP Model Ojekunle Z. O. 1*, Ojo K. O. 1, Idowu O. A. 1, Martins
APES- Water Diversions Name: Brandon Tran
 APES- Water Diversions Name: Brandon Tran Purpose: Conduct research to analyze the effects of water diversions on surrounding ecosystems and human communities. Compare and contrast the problems and successes
APES- Water Diversions Name: Brandon Tran Purpose: Conduct research to analyze the effects of water diversions on surrounding ecosystems and human communities. Compare and contrast the problems and successes
Prospectives and Limits of Groundwater Use in Pakistan
 Prospectives and Limits of Groundwater Use in Pakistan International Waterlogging and Salinity Research Institute, Lahore, Pakistan Abstract Groundwater use in Pakistan has increased due to increased demand
Prospectives and Limits of Groundwater Use in Pakistan International Waterlogging and Salinity Research Institute, Lahore, Pakistan Abstract Groundwater use in Pakistan has increased due to increased demand
Analysis of air quality trends in 2017
 Analysis of air quality trends in 2017 This briefing was edited on 12 Jan 2018 to update province-level PM2.5 numbers in the industrial output chart on page 5. After the launch of China s war on pollution
Analysis of air quality trends in 2017 This briefing was edited on 12 Jan 2018 to update province-level PM2.5 numbers in the industrial output chart on page 5. After the launch of China s war on pollution
International Association of Hydrogeologists and China
 Journal of Groundwater Journal of Science Groundwater and Engineering Science and Vol.5 Engineering No.3 Jul. Vol.5 2017 No.3 Sept. 2017 International Association of Hydrogeologists and China HAN Zai-sheng
Journal of Groundwater Journal of Science Groundwater and Engineering Science and Vol.5 Engineering No.3 Jul. Vol.5 2017 No.3 Sept. 2017 International Association of Hydrogeologists and China HAN Zai-sheng
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT OF THE INFORMATION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY TO FARMER BASED ON GIS
 RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT OF THE INFORMATION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY TO FARMER BASED ON GIS Hao Zhang 1, Lei Xi 1, Xinming Ma 1,2,*, Zhongmin Lu 3, Yali Ji 1, Yanna Ren
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT OF THE INFORMATION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY TO FARMER BASED ON GIS Hao Zhang 1, Lei Xi 1, Xinming Ma 1,2,*, Zhongmin Lu 3, Yali Ji 1, Yanna Ren
Potential effects evaluation of dewatering an underground mine on surface water and groundwater located in a rural area
 Potential effects evaluation of dewatering an underground mine on surface water and groundwater located in a rural area ITRODUCTIO Michel Mailloux* Eng. M.Sc, Vincent Boisvert, M.Sc, Denis Millette, Eng.,
Potential effects evaluation of dewatering an underground mine on surface water and groundwater located in a rural area ITRODUCTIO Michel Mailloux* Eng. M.Sc, Vincent Boisvert, M.Sc, Denis Millette, Eng.,
The effect of Hilti / Salahi Recharge Dam in Batineh Area, Sultanate of Oman on the Quality of Groundwater Using GIS
 The effect of Hilti / Salahi Recharge Dam in Batineh Area, Sultanate of Oman on the Quality of Groundwater Using GIS William Bajjali University of Wisconsin Superior, Department of Biology & Earth Sciences,
The effect of Hilti / Salahi Recharge Dam in Batineh Area, Sultanate of Oman on the Quality of Groundwater Using GIS William Bajjali University of Wisconsin Superior, Department of Biology & Earth Sciences,
TEKS Lesson 7.8C: Effects of Human Activity on Surface Water and Groundwater
 Class ----- Date -------- TEKS Lesson 7.SC TEKS 7.8e Model the effects of human activity on groundwater surface water in a watershed. and TEKS Lesson 7.8C: Effects of Human Activity on Surface Water and
Class ----- Date -------- TEKS Lesson 7.SC TEKS 7.8e Model the effects of human activity on groundwater surface water in a watershed. and TEKS Lesson 7.8C: Effects of Human Activity on Surface Water and
The Hydrosphere: Lecture 8: Groundwater. Paul R. Houser,27 March 2012, Page 1
 The Hydrosphere: Lecture 8: Groundwater Paul R. Houser,27 March 2012, Page 1 Groundwater How is groundwater formed? What are the zones of subsurface water and their characteristics? What is a water table,
The Hydrosphere: Lecture 8: Groundwater Paul R. Houser,27 March 2012, Page 1 Groundwater How is groundwater formed? What are the zones of subsurface water and their characteristics? What is a water table,
Climate: describes the average condition, including temperature and precipitation, over long periods in a given area
 Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Effect of Urbanization on Climate Change in Nanjing
 , pp.255-260 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2013.31.55 Effect of Urbanization on Climate Change in Nanjing QIYingXiang 1, Yu Wenzheng *2, Chen Tianliang 2, Shao Li 2, Jin Wang 2 (1. School of Public Administration
, pp.255-260 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2013.31.55 Effect of Urbanization on Climate Change in Nanjing QIYingXiang 1, Yu Wenzheng *2, Chen Tianliang 2, Shao Li 2, Jin Wang 2 (1. School of Public Administration
SO 2, NO X and Acid Deposition Problems in China - Impact on Agriculture
 Phyton (Austria) Special issue: "Global change" Vol. 42 Fasc. 3 (255)-(264) 1.10.2002 SO 2, NO X and Acid Deposition Problems in China - Impact on Agriculture By L. YANG 1>2), I. STULEN 2), L. J. DE KOK
Phyton (Austria) Special issue: "Global change" Vol. 42 Fasc. 3 (255)-(264) 1.10.2002 SO 2, NO X and Acid Deposition Problems in China - Impact on Agriculture By L. YANG 1>2), I. STULEN 2), L. J. DE KOK
Hydrological sciences in perspective
 Hydrology 2000. IAHS Publ. no. 171, 1987. Hydrological sciences in perspective ZBIGNIEW W. KUNDZEWICZ, LARS GOTTSCHALK & BRUCE WEBB IITBODUCTIOI Hydrology is concerned with the study of water although
Hydrology 2000. IAHS Publ. no. 171, 1987. Hydrological sciences in perspective ZBIGNIEW W. KUNDZEWICZ, LARS GOTTSCHALK & BRUCE WEBB IITBODUCTIOI Hydrology is concerned with the study of water although
Introduction. Welcome to the Belgium Study Abroad Program. Courses:
 Introduction Welcome to the Belgium Study Abroad Program Courses: AGSM 335: Soil and Water Management BAEN 460: Principals of Environmental Hydrology BAEN 460 / AGSM 335 Combined lecture and HW sessions
Introduction Welcome to the Belgium Study Abroad Program Courses: AGSM 335: Soil and Water Management BAEN 460: Principals of Environmental Hydrology BAEN 460 / AGSM 335 Combined lecture and HW sessions
Numerical modeling of reducing total nitrogen through inflow from channels in Datong Lake, China
 Numerical modeling of reducing total nitrogen through inflow from channels in Datong Lake, China Q. ZHOU1, W.R. HUANG1*, N.Q. ZHOU1, F. TENG2, B.B. WANG2, X.Q. LIU2, S. XIE2, X.P. SHEN2 1 Department of
Numerical modeling of reducing total nitrogen through inflow from channels in Datong Lake, China Q. ZHOU1, W.R. HUANG1*, N.Q. ZHOU1, F. TENG2, B.B. WANG2, X.Q. LIU2, S. XIE2, X.P. SHEN2 1 Department of
Vulnerabilities to Climate Change Impacts and Strengthening Disaster Risk Management in East Asian Cities
 Hanoi, Vietnam 2008 Primer Reducing Vulnerabilities to Climate Change Impacts and Strengthening Disaster Risk Management in East Asian Cities I/ CITY DESCRIPTION A. Hanoi Topography and demography characteristics
Hanoi, Vietnam 2008 Primer Reducing Vulnerabilities to Climate Change Impacts and Strengthening Disaster Risk Management in East Asian Cities I/ CITY DESCRIPTION A. Hanoi Topography and demography characteristics
Watershed: an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas. It is the interdependent web of living
 Watershed: an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas. It is the interdependent web of living organisms that inhabit a geographic area and depend on it
Watershed: an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas. It is the interdependent web of living organisms that inhabit a geographic area and depend on it
The Water Cycle and Water Insecurity
 Edexcel Geography A-level The Water Cycle and Water Insecurity PMT Education Written by Jeevan Singh The Water Cycle and Water Insecurity Enquiry question 1: What are the processes operating within the
Edexcel Geography A-level The Water Cycle and Water Insecurity PMT Education Written by Jeevan Singh The Water Cycle and Water Insecurity Enquiry question 1: What are the processes operating within the
A Water Reuse System in Wetland Paddy Supports the Growing Industrial Water Needs
 A Water Reuse System in Wetland Paddy Supports the Growing Industrial Water Needs Yu-Chuan Chang, and Chen Shi-Kai Abstract A water reuse system in wetland paddy was simulated to supply water for industrial
A Water Reuse System in Wetland Paddy Supports the Growing Industrial Water Needs Yu-Chuan Chang, and Chen Shi-Kai Abstract A water reuse system in wetland paddy was simulated to supply water for industrial
Climate Change. Weather Patterns and Drinking Water Resources. WE CArE AbouT WATEr. IT s WHAT WE do.
 WE CArE AbouT WATEr. IT s WHAT WE do. Climate Change Weather Patterns and Drinking Water Resources Grade Level: 9-12 objective: Students will explore the potential impacts of climate change on drinking
WE CArE AbouT WATEr. IT s WHAT WE do. Climate Change Weather Patterns and Drinking Water Resources Grade Level: 9-12 objective: Students will explore the potential impacts of climate change on drinking
ESTIMATION OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACT ON WATER RESOURCES BY USING BILAN WATER BALANCE MODEL
 ESTIMATION OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACT ON WATER RESOURCES BY USING BILAN WATER BALANCE MODEL Stanislav Horacek, Ladislav Kasparek, Oldrich Novicky T. G. Masaryk Water Research Institute Prague, Czech Republic
ESTIMATION OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACT ON WATER RESOURCES BY USING BILAN WATER BALANCE MODEL Stanislav Horacek, Ladislav Kasparek, Oldrich Novicky T. G. Masaryk Water Research Institute Prague, Czech Republic
Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming Case Study
 Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming Case Study Key Concepts: Greenhouse Gas Carbon dioxide El Niño Global warming Greenhouse effect Greenhouse gas La Niña Land use Methane Nitrous oxide Radiative forcing
Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming Case Study Key Concepts: Greenhouse Gas Carbon dioxide El Niño Global warming Greenhouse effect Greenhouse gas La Niña Land use Methane Nitrous oxide Radiative forcing
MAJOR THEMES IN ARIZONA S WATER FUTURE
 Chapter 2 MAJOR THEMES IN ARIZONA S WATER FUTURE KATHY JACOBS AND MARSHALL A. WORDEN Seven major themes or overarching concerns regarding Arizona s water future are discussed in succeeding chapters. Information
Chapter 2 MAJOR THEMES IN ARIZONA S WATER FUTURE KATHY JACOBS AND MARSHALL A. WORDEN Seven major themes or overarching concerns regarding Arizona s water future are discussed in succeeding chapters. Information
FACTSHEET INTRODUCTION. help rebalance the water cycle, mitigate the effects of climate change and improve human health and livelihoods.
 1 FACTSHEET INTRODUCTION World Water Day, on 22 March every year, is about focusing attention on the importance of water. This year s theme, Nature for Water, explores nature-based solutions (NBS) to the
1 FACTSHEET INTRODUCTION World Water Day, on 22 March every year, is about focusing attention on the importance of water. This year s theme, Nature for Water, explores nature-based solutions (NBS) to the
Utilization of water resources and its effects on the hydrological environment of the Tarim River basin in Xinjiang, China
 Water Resources Systems Water Availability and Global Change (Proceedings of symposium HS02n held during IUGG2003 al Sapporo. July 2003). IAHS Publ. no. 280. 2003. 23 Utilization of water resources and
Water Resources Systems Water Availability and Global Change (Proceedings of symposium HS02n held during IUGG2003 al Sapporo. July 2003). IAHS Publ. no. 280. 2003. 23 Utilization of water resources and
Introduction of Chinese Cooperation Initiatives on Scientific Research under CEWP. Sun Yan Research Coordinator, MWR 20 June, 2013 Brussels
 Introduction of Chinese Cooperation Initiatives on Scientific Research under CEWP Sun Yan Research Coordinator, MWR 20 June, 2013 Brussels Contents Background Chinese Initiatives Summary of Chinese Initiatives
Introduction of Chinese Cooperation Initiatives on Scientific Research under CEWP Sun Yan Research Coordinator, MWR 20 June, 2013 Brussels Contents Background Chinese Initiatives Summary of Chinese Initiatives
Title Action Plan toward Effective Flood Hazard Mapping in My Country
 Title Action Plan toward Effective Flood Hazard Mapping in My Country JICA region focused training course on flood hazard mapping Sep 2006 LAI TUAN ANH Division of Geodesy Department of Planning and Management
Title Action Plan toward Effective Flood Hazard Mapping in My Country JICA region focused training course on flood hazard mapping Sep 2006 LAI TUAN ANH Division of Geodesy Department of Planning and Management
CLIMATE CHANGE AND FLOOD RISK IN THE MEKONG DELTA ADAPTATION AND COEXISTENCE IN FLOOD-PRONE RICE AREA
 CLIMATE CHANGE AND FLOOD RISK IN THE MEKONG DELTA ADAPTATION AND COEXISTENCE IN FLOOD-PRONE RICE AREA Hideto Fujii Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences 1-1 Ohwashi, Tsukuba, Ibaraki
CLIMATE CHANGE AND FLOOD RISK IN THE MEKONG DELTA ADAPTATION AND COEXISTENCE IN FLOOD-PRONE RICE AREA Hideto Fujii Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences 1-1 Ohwashi, Tsukuba, Ibaraki
Isotope hydrology and water resources management in Africa
 Isotope hydrology and water resources management in Africa Current status and challenges Cheikh B. Gaye International initiatives At the Millennium Summit in 2000 and during the 2002 World Summit on Sustainable
Isotope hydrology and water resources management in Africa Current status and challenges Cheikh B. Gaye International initiatives At the Millennium Summit in 2000 and during the 2002 World Summit on Sustainable
Bottled Water: What s the problem?
 Bottled Water: What s the problem? Where does your water come from? Groundwater Reservoir River What is groundwater? Aquifers and Groundwater Groundwater: any water that is found underground in cracks
Bottled Water: What s the problem? Where does your water come from? Groundwater Reservoir River What is groundwater? Aquifers and Groundwater Groundwater: any water that is found underground in cracks
Anthropogenic Influences and Their Impact on Global Climate
 Anthropogenic Influences and Their Impact on Global Climate By Ria Detmer GEO 387H Professor Yang November 18, 2008 Abstract Scientist has raised some concerns with the current rise of temperature throughout
Anthropogenic Influences and Their Impact on Global Climate By Ria Detmer GEO 387H Professor Yang November 18, 2008 Abstract Scientist has raised some concerns with the current rise of temperature throughout
Water, Salinity and Irrigation in Australia s Murray-Darling Basin & Hetao Irrigation District
 Water, Salinity and Irrigation in Australia s Murray-Darling Basin & Hetao Irrigation District Ian White Australian National University Ian White FTSE Research Major research area is water resources with
Water, Salinity and Irrigation in Australia s Murray-Darling Basin & Hetao Irrigation District Ian White Australian National University Ian White FTSE Research Major research area is water resources with
Energy-saving Potential Study on Telecommunication Base Station Free Cooling With a Thermosyphon Heat Exchanger in China
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International High Performance Buildings Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 Energy-saving Potential Study on Telecommunication Base Station Free Cooling With
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International High Performance Buildings Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 Energy-saving Potential Study on Telecommunication Base Station Free Cooling With
Climatic Change, in review, Dec 2002 THE EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON WATER RESOURCES IN THE WEST: INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW
 THE EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON WATER RESOURCES IN THE WEST: INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW Tim Barnett Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla, CA Robert Malone Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos,
THE EFFECTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON WATER RESOURCES IN THE WEST: INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW Tim Barnett Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla, CA Robert Malone Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos,
Fresh Water Treaty. International Setting and Issues in Water, Environment and Development
 Fresh Water Treaty Preamble International Setting and Issues in Water, Environment and Development 1. In recent years most countries have faced a grave economic crisis which generated a great decrease
Fresh Water Treaty Preamble International Setting and Issues in Water, Environment and Development 1. In recent years most countries have faced a grave economic crisis which generated a great decrease
Leila Talebi and Robert Pitt. Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental Engineering, The University of Alabama, P.O. Box , Tuscaloosa
 Leila Talebi and Robert Pitt Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental Engineering, The University of Alabama, P.O. Box 870205, Tuscaloosa May 2012 Global consumption of water increases every
Leila Talebi and Robert Pitt Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental Engineering, The University of Alabama, P.O. Box 870205, Tuscaloosa May 2012 Global consumption of water increases every
Environmental Geography
 Environmental Geography Lecture 13 Water Pollution Lecture 13: Water Pollution I. Water Pollution A. Groundwater B. Surface Water C. Regulation II. Water Use in California 1 I. Water Pollution Types of
Environmental Geography Lecture 13 Water Pollution Lecture 13: Water Pollution I. Water Pollution A. Groundwater B. Surface Water C. Regulation II. Water Use in California 1 I. Water Pollution Types of
Genetic Algorithm based Simulation Optimization Approach to Seawater Intrusion
 International Symposium on Genetic Algorithm based Simulation Optimization Approach to Seawater Intrusion 1313 Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM 2014) February 19 21, 2014, CWRDM, Kozhikode,
International Symposium on Genetic Algorithm based Simulation Optimization Approach to Seawater Intrusion 1313 Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM 2014) February 19 21, 2014, CWRDM, Kozhikode,
1. Introduction. Keywords Groundwater, Vulbnerability, Aquifer, Aquitard, Vadose zone. Alsharifa Hind Mohammad
 World Environment 2014, 4(1): 22-32 DOI: 10.5923/j.env.20140401.03 New Groundwater Vulnerability Index for the Main Aquifers in Central Catchment Area in Jordan and Validation of the Results Using NO 3
World Environment 2014, 4(1): 22-32 DOI: 10.5923/j.env.20140401.03 New Groundwater Vulnerability Index for the Main Aquifers in Central Catchment Area in Jordan and Validation of the Results Using NO 3
EFFECTS OF WATERSHED TOPOGRAPHY, SOILS, LAND USE, AND CLIMATE ON BASEFLOW HYDROLOGY IN HUMID REGIONS: A REVIEW
 PROGRESS IN PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY EFFECTS OF WATERSHED TOPOGRAPHY, SOILS, LAND USE, AND CLIMATE ON BASEFLOW HYDROLOGY IN HUMID REGIONS: A REVIEW KATIE PRICE 2011 Presented by: Jordan Martin Article Overview
PROGRESS IN PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY EFFECTS OF WATERSHED TOPOGRAPHY, SOILS, LAND USE, AND CLIMATE ON BASEFLOW HYDROLOGY IN HUMID REGIONS: A REVIEW KATIE PRICE 2011 Presented by: Jordan Martin Article Overview
2016 SWAT Conference Reporter: Chengchun Sun Co-worker: Shufeng Chen; Wenliang Wu
 Nitrate leaching characteristics in a typical high-yield production area under different irrigation and fertilization management practices in the North China Plain 2016 SWAT Conference Reporter: Chengchun
Nitrate leaching characteristics in a typical high-yield production area under different irrigation and fertilization management practices in the North China Plain 2016 SWAT Conference Reporter: Chengchun
UNIT HYDROGRAPH AND EFFECTIVE RAINFALL S INFLUENCE OVER THE STORM RUNOFF HYDROGRAPH
 UNIT HYDROGRAPH AND EFFECTIVE RAINFALL S INFLUENCE OVER THE STORM RUNOFF HYDROGRAPH INTRODUCTION Water is a common chemical substance essential for the existence of life and exhibits many notable and unique
UNIT HYDROGRAPH AND EFFECTIVE RAINFALL S INFLUENCE OVER THE STORM RUNOFF HYDROGRAPH INTRODUCTION Water is a common chemical substance essential for the existence of life and exhibits many notable and unique
Water Pollution and Environmental Governance of the Tai and Chao Lake Basins in China in an International Perspective
 Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 2015, 7, 830-842 Published Online July 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jwarp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2015.710067 Water Pollution and Environmental
Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 2015, 7, 830-842 Published Online July 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jwarp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2015.710067 Water Pollution and Environmental
CHAPTER FIVE Runoff. Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib. Overland flow interflow
 Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) CHAPTER FIVE Runoff Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib Overland flow interflow Base flow Saturated overland flow ١ ٢ 5.1 Introduction To Runoff Runoff
Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) CHAPTER FIVE Runoff Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib Overland flow interflow Base flow Saturated overland flow ١ ٢ 5.1 Introduction To Runoff Runoff
Flood risk management and land use planning in changing climate conditions Mikko Huokuna Finnish Environment Institute, SYKE
 10th International Drainage Workshop of ICID 06.-11. July 2008 Flood risk management and land use planning in changing climate conditions Mikko Huokuna Finnish Environment Institute, SYKE Background hydrological
10th International Drainage Workshop of ICID 06.-11. July 2008 Flood risk management and land use planning in changing climate conditions Mikko Huokuna Finnish Environment Institute, SYKE Background hydrological
Shallow groundwater dynamics in North China Plain
 J. Geogr. Sci. (2009) 19: 175-188 DOI: 10.1007/s11442-009-0175-0 2009 Science in China Press Springer-Verlag Shallow groundwater dynamics in North China Plain WANG Shiqin 1, * SONG Xianfang 1, WANG Qinxue
J. Geogr. Sci. (2009) 19: 175-188 DOI: 10.1007/s11442-009-0175-0 2009 Science in China Press Springer-Verlag Shallow groundwater dynamics in North China Plain WANG Shiqin 1, * SONG Xianfang 1, WANG Qinxue
