Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Summary for Policymakers
|
|
|
- Kelley Colin Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTERGOVERNMENTAL PANEL ON CLIMATE CHANGE Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis Summary for Policymakers Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change This Summary for Policymakers was formally approved at the 10th Session of Working Group I of the IPCC, Paris, February Note: Text, tables and figures given here are final but subject to copy-editing. Corrections made as of February 5th, 2007 Drafting Authors: Richard Alley, Terje Berntsen, Nathaniel L. Bindoff, Zhenlin Chen, Amnat Chidthaisong, Pierre Friedlingstein, Jonathan Gregory, Gabriele Hegerl, Martin Heimann, Bruce Hewitson, Brian Hoskins, Fortunat Joos, Jean Jouzel, Vladimir Kattsov, Ulrike Lohmann, Martin Manning, Taroh Matsuno, Mario Molina, Neville Nicholls, Jonathan Overpeck, Dahe Qin, Graciela Raga, Venkatachalam Ramaswamy, Jiawen Ren, Matilde Rusticucci, Susan Solomon, Richard Somerville, Thomas F. Stocker, Peter Stott, Ronald J. Stouffer, Penny Whetton, Richard A. Wood, David Wratt Draft Contributing Authors: Julie Arblaster, Guy Brasseur, Jens Hesselbjerg Christensen, Kenneth Denman, David W. Fahey, Piers Forster, Eystein Jansen, Philip D. Jones, Reto Knutti, Hervé Le Treut, Peter Lemke, Gerald Meehl, Philip Mote, David Randall, Dáithí A. Stone, Kevin E. Trenberth, Jürgen Willebrand, Francis Zwiers IPCC Secretariat, c/o WMO, 7bis, Avenue de la Paix, C.P. N 2300, 1211 Geneva 2, SWITZERLAND Phone: /8254/8284 Fax: / IPCC-Sec@wmo.int Website:
2 INTRODUCTION The Working Group I contribution to the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report describes progress in understanding of the human and natural drivers of climate change 1, observed climate change, climate processes and attribution, and estimates of projected future climate change. It builds upon past IPCC assessments and incorporates new findings from the past six years of research. Scientific progress since the TAR is based upon large amounts of new and more comprehensive data, more sophisticated analyses of data, improvements in understanding of processes and their simulation in models, and more extensive exploration of uncertainty ranges. The basis for substantive paragraphs in this Summary for Policymakers can be found in the chapter sections specified in curly brackets. HUMAN AND NATURAL DRIVERS OF CLIMATE CHANGE Changes in the atmospheric abundance of greenhouse gases and aerosols, in solar radiation and in land surface properties alter the energy balance of the climate system. These changes are expressed in terms of radiative forcing 2, which is used to compare how a range of human and natural factors drive warming or cooling influences on global climate. Since the Third Assessment Report (TAR), new observations and related modelling of greenhouse gases, solar activity, land surface properties and some aspects of aerosols have led to improvements in the quantitative estimates of radiative forcing. Global atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide have increased markedly as a result of human activities since 1750 and now far exceed pre-industrial values determined from ice cores spanning many thousands of years (see Figure SPM-1). The global increases in carbon dioxide concentration are due primarily to fossil fuel use and land-use change, while those of methane and nitrous oxide are primarily due to agriculture. {2.3, 6.4, 7.3} Carbon dioxide is the most important anthropogenic greenhouse gas (see Figure SPM-2). The global atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide has increased from a pre-industrial value of about 280 ppm to 379 ppm 3 in The atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide in 2005 exceeds by far the natural range over the last 650,000 years (180 to 300 ppm) as determined from ice cores. The annual carbon dioxide concentration growth-rate was larger during the last 10 years ( average: 1.9 ppm per year), than it has been since the beginning of continuous direct atmospheric measurements ( average: 1.4 ppm per year) although there is year-to-year variability in growth rates. {2.3, 7.3} The primary source of the increased atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide since the pre-industrial period results from fossil fuel use, with land use change providing another significant but smaller contribution. Annual fossil carbon dioxide emissions 4 increased from an average of 6.4 [6.0 to 6.8] 5 GtC 1 Climate change in IPCC usage refers to any change in climate over time, whether due to natural variability or as a result of human activity. This usage differs from that in the Framework Convention on Climate Change, where climate change refers to a change of climate that is attributed directly or indirectly to human activity that alters the composition of the global atmosphere and that is in addition to natural climate variability observed over comparable time periods. 2 Radiative forcing is a measure of the influence that a factor has in altering the balance of incoming and outgoing energy in the Earth-atmosphere system and is an index of the importance of the factor as a potential climate change mechanism. Positive forcing tends to warm the surface while negative forcing tends to cool it. In this report radiative forcing values are for 2005 relative to pre-industrial conditions defined at 1750 and are expressed in watts per square metre (W m -2 ). See Glossary and Section 2.2 for further details. 3 ppm (parts per million) or ppb (parts per billion, 1 billion = 1,000 million) is the ratio of the number of greenhouse gas molecules to the total number of molecules of dry air. For example: 300 ppm means 300 molecules of a greenhouse gas per million molecules of dry air. 4 Fossil carbon dioxide emissions include those from the production, distribution and consumption of fossil fuels and as a by-product from cement production. An emission of 1 GtC corresponds to 3.67 GtCO 2. 5 In general, uncertainty ranges for results given in this Summary for Policymakers are 90% uncertainty intervals unless stated otherwise, i.e., there is an estimated 5% likelihood that the value could be above the range given in square brackets and 5% likelihood that the value could be below that range. Best estimates are given where available. Assessed uncertainty intervals are not always symmetric about the corresponding best estimate. Note that a number of uncertainty ranges in the Working Group I TAR corresponded to 2-sigma (95%), often using expert judgement. Page 2 of 18
3 (23.5 [22.0 to 25.0] GtCO 2 ) per year in the 1990s, to 7.2 [6.9 to 7.5] GtC (26.4 [25.3 to 27.5] GtCO 2 ) per year in (2004 and 2005 data are interim estimates). Carbon dioxide emissions associated with land-use change are estimated to be 1.6 [0.5 to 2.7] GtC (5.9 [1.8 to 9.9] GtCO 2 ) per year over the 1990s, although these estimates have a large uncertainty. {7.3} FIGURE SPM-1. Atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide over the last 10,000 years (large panels) and since 1750 (inset panels). Measurements are shown from ice cores (symbols with different colours for different studies) and atmospheric samples (red lines). The corresponding radiative forcings are shown on the right hand axes of the large panels. {Figure 6.4} Page 3 of 18
4 The global atmospheric concentration of methane has increased from a pre-industrial value of about 715 ppb to 1732 ppb in the early 1990s, and is 1774 ppb in The atmospheric concentration of methane in 2005 exceeds by far the natural range of the last 650,000 years (320 to 790 ppb) as determined from ice cores. Growth rates have declined since the early 1990s, consistent with total emissions (sum of anthropogenic and natural sources) being nearly constant during this period. It is very likely 6 that the observed increase in methane concentration is due to anthropogenic activities, predominantly agriculture and fossil fuel use, but relative contributions from different source types are not well determined. {2.3, 7.4} The global atmospheric nitrous oxide concentration increased from a pre-industrial value of about 270 ppb to 319 ppb in The growth rate has been approximately constant since More than a third of all nitrous oxide emissions are anthropogenic and are primarily due to agriculture. {2.3, 7.4} FIGURE SPM-2. Global-average radiative forcing (RF) estimates and ranges in 2005 for anthropogenic carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and other important agents and mechanisms, together with the typical geographical extent (spatial scale) of the forcing and the assessed level of scientific understanding (LOSU). The net anthropogenic radiative forcing and its range are also shown. These require summing asymmetric uncertainty estimates from the component terms, and cannot be obtained by simple addition. Additional forcing factors not included here are considered to have a very low LOSU. Volcanic aerosols contribute an additional natural forcing but are not included in this figure due to their episodic nature. Range for linear contrails does not include other possible effects of aviation on cloudiness. {2.9, Figure 2.20} 6 In this Summary for Policymakers, the following terms have been used to indicate the assessed likelihood, using expert judgement, of an outcome or a result: Virtually certain > 99% probability of occurrence, Extremely likely > 95%, Very likely > 90%, Likely > 66%, More likely than not > 50%, Unlikely < 33%, Very unlikely < 10%, Extremely unlikely < 5%. (See Box TS.1.1 for more details). Page 4 of 18
5 The understanding of anthropogenic warming and cooling influences on climate has improved since the Third Assessment Report (TAR), leading to very high confidence 7 that the globally averaged net effect of human activities since 1750 has been one of warming, with a radiative forcing of +1.6 [+0.6 to +2.4] W m -2. (see Figure SPM-2). { , 2.9} The combined radiative forcing due to increases in carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide is [+2.07 to +2.53] W m -2, and its rate of increase during the industrial era is very likely to have been unprecedented in more than 10,000 years (see Figures SPM-1 and SPM-2). The carbon dioxide radiative forcing increased by 20% from 1995 to 2005, the largest change for any decade in at least the last 200 years. {2.3, 6.4} Anthropogenic contributions to aerosols (primarily sulphate, organic carbon, black carbon, nitrate and dust) together produce a cooling effect, with a total direct radiative forcing of -0.5 [-0.9 to -0.1] W m -2 and an indirect cloud albedo forcing of -0.7 [-1.8 to -0.3] W m -2. These forcings are now better understood than at the time of the TAR due to improved in situ, satellite and ground-based measurements and more comprehensive modelling, but remain the dominant uncertainty in radiative forcing. Aerosols also influence cloud lifetime and precipitation. {2.4, 2.9, 7.5} Significant anthropogenic contributions to radiative forcing come from several other sources. Tropospheric ozone changes due to emissions of ozone-forming chemicals (nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and hydrocarbons) contribute [+0.25 to +0.65] W m -2. The direct radiative forcing due to changes in halocarbons 8 is [+0.31 to +0.37] W m -2. Changes in surface albedo, due to land-cover changes and deposition of black carbon aerosols on snow, exert respective forcings of -0.2 [-0.4 to 0.0] and +0.1 [0.0 to +0.2] W m -2. Additional terms smaller than ±0.1 W m -2 are shown in Figure SPM-2. {2.3, 2.5, 7.2} Changes in solar irradiance since 1750 are estimated to cause a radiative forcing of [+0.06 to +0.30] W m -2, which is less than half the estimate given in the TAR. {2.7} DIRECT OBSERVATIONS OF RECENT CLIMATE CHANGE Since the TAR, progress in understanding how climate is changing in space and in time has been gained through improvements and extensions of numerous datasets and data analyses, broader geographical coverage, better understanding of uncertainties, and a wider variety of measurements. Increasingly comprehensive observations are available for glaciers and snow cover since the 1960s, and for sea level and ice sheets since about the past decade. However, data coverage remains limited in some regions. Warming of the climate system is unequivocal, as is now evident from observations of increases in global average air and ocean temperatures, widespread melting of snow and ice, and rising global average sea level (see Figure SPM-3). {3.2, 4.2, 5.5} Eleven of the last twelve years ( ) rank among the 12 warmest years in the instrumental record of global surface temperature 9 (since 1850). The updated 100-year linear trend ( ) of 0.74 [0.56 to 0.92] C is therefore larger than the corresponding trend for given in the TAR of 0.6 [0.4 to 0.8] C. The linear warming trend over the last 50 years (0.13 [0.10 to 0.16] C per decade) is nearly twice that for the last 100 years. The total temperature increase from to is 0.76 [0.57 to 0.95] C. Urban heat island effects are real but local, and have a negligible influence (less than C per decade over land and zero over the oceans) on these values. {3.2} 7 In this Summary for Policymakers the following levels of confidence have been used to express expert judgments on the correctness of the underlying science: very high confidence at least a 9 out of 10 chance of being correct; high confidence about an 8 out of 10 chance of being correct. (See Box TS.1.1) 8 Halocarbon radiative forcing has been recently assessed in detail in IPCC s Special Report on Safeguarding the Ozone Layer and the Global Climate System (2005). 9 The average of near surface air temperature over land, and sea surface temperature. Page 5 of 18
Summary for Policymakers Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis
 Summary for Policymakers Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis Robert Sausen DLR-Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen Guidance Notes for Lead Authors of the IPCC Fourth Assessment
Summary for Policymakers Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis Robert Sausen DLR-Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen Guidance Notes for Lead Authors of the IPCC Fourth Assessment
Summary for Policymakers
 A report of Working Group I of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Summary for Policymakers Drafting Authors: Richard B. Alley, Terje Berntsen, Nathaniel L. Bindoff, Zhenlin Chen, Amnat Chidthaisong,
A report of Working Group I of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Summary for Policymakers Drafting Authors: Richard B. Alley, Terje Berntsen, Nathaniel L. Bindoff, Zhenlin Chen, Amnat Chidthaisong,
Summary for Policymakers
 0 0 Working Group I Contribution to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report Climate Change 00: The Physical Science Basis Summary for Policymakers Draft Coordinating Lead
0 0 Working Group I Contribution to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report Climate Change 00: The Physical Science Basis Summary for Policymakers Draft Coordinating Lead
A report accepted by Working Group I of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change but not approved in detail
 A report accepted by Working Group I of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change but not approved in detail Acceptance of IPCC Reports at a Session of the Working Group or Panel signifies that the
A report accepted by Working Group I of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change but not approved in detail Acceptance of IPCC Reports at a Session of the Working Group or Panel signifies that the
What Do the Data Tell Us about Climate Change?
 ACTIVITY What Do the Data Tell Us about Climate Change? LEARNING GOAL a To develop your analytical skills in reading and summarizing graphical data, trends, and scientific confidence INTRODUCTION The United
ACTIVITY What Do the Data Tell Us about Climate Change? LEARNING GOAL a To develop your analytical skills in reading and summarizing graphical data, trends, and scientific confidence INTRODUCTION The United
Radiative forcing of climate change
 Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change
 The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change Martin Manning Director, IPCC Working Group I Support Unit 1. Observed climate change 2. Drivers of climate change 3. Attribution of cause
The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change Martin Manning Director, IPCC Working Group I Support Unit 1. Observed climate change 2. Drivers of climate change 3. Attribution of cause
FOLLOW: Green House on Twitter
 Jan 31, 2012 Recommend 773 208 By Wendy Koch, USA TODAY Updated 1d 13h ago CAPTION By William Fernando Martinez, AP A new NASA study tries to lay to rest the skepticism about climate change, especially
Jan 31, 2012 Recommend 773 208 By Wendy Koch, USA TODAY Updated 1d 13h ago CAPTION By William Fernando Martinez, AP A new NASA study tries to lay to rest the skepticism about climate change, especially
FORTY-SIXTH SESSION OF THE IPCC Montreal, Canada, 6 10 September 2017 SHORT-LIVED CLIMATE FORCERS
 FORTY-SIXTH SESSION OF THE IPCC Montreal, Canada, 6 10 September 2017 IPCC-XLVI/Doc. 7 (4.VIII.2017) Agenda Item: 11 ENGLISH ONLY SHORT-LIVED CLIMATE FORCERS (Prepared by the Co-Chairs of the Bureau of
FORTY-SIXTH SESSION OF THE IPCC Montreal, Canada, 6 10 September 2017 IPCC-XLVI/Doc. 7 (4.VIII.2017) Agenda Item: 11 ENGLISH ONLY SHORT-LIVED CLIMATE FORCERS (Prepared by the Co-Chairs of the Bureau of
IPCC 5 th Assessment Report
 The WGI Contribution to the IPCC 5 th Assessment Report Thomas Stocker & Qin Dahe 259 Authors from 39 Countries WGI Technical Support Unit Team Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Key SPM Messages 19 Headlines
The WGI Contribution to the IPCC 5 th Assessment Report Thomas Stocker & Qin Dahe 259 Authors from 39 Countries WGI Technical Support Unit Team Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Key SPM Messages 19 Headlines
Understanding and attributing recent climate change
 Understanding and attributing recent climate change Peter Stott, Nathan Bindoff, John Church, Peter Clark, Greg Flato, Piers Forster, Nathan Gillett, Gabi Hegerl, Reto Knutti, Jochem Marotzke, Rowan Sutton,
Understanding and attributing recent climate change Peter Stott, Nathan Bindoff, John Church, Peter Clark, Greg Flato, Piers Forster, Nathan Gillett, Gabi Hegerl, Reto Knutti, Jochem Marotzke, Rowan Sutton,
Radiative Forcing and
 Radiative Forcing and Feedbacks in Climate Change Júlio C. S. Chagas Entrenamiento en Modelado Numérico de Escenarios de Cambios Climáticos Cachoeira Paulista, 30 de Agosto 4 de Septiembre de 2009. Definitions
Radiative Forcing and Feedbacks in Climate Change Júlio C. S. Chagas Entrenamiento en Modelado Numérico de Escenarios de Cambios Climáticos Cachoeira Paulista, 30 de Agosto 4 de Septiembre de 2009. Definitions
The Fifth Assessment: A Discussion of the IPCC Working Group 1 AR5 Report
 The Fifth Assessment: A Discussion of the IPCC Working Group 1 AR5 Report Prof. Chris E. Forest The Pennsylvania State University (ceforest@psu.edu) Lead Author - Chapter 9 - Evaluation of Climate Models!
The Fifth Assessment: A Discussion of the IPCC Working Group 1 AR5 Report Prof. Chris E. Forest The Pennsylvania State University (ceforest@psu.edu) Lead Author - Chapter 9 - Evaluation of Climate Models!
SPM1. Summary for Policymakers
 1 Summary for Policymakers Drafting Authors: Lisa V. Alexander (Australia), Simon K. Allen (Switzerland/New Zealand), Nathaniel L. Bindoff (Australia), François-Marie Bréon (France), John A. Church (Australia),
1 Summary for Policymakers Drafting Authors: Lisa V. Alexander (Australia), Simon K. Allen (Switzerland/New Zealand), Nathaniel L. Bindoff (Australia), François-Marie Bréon (France), John A. Church (Australia),
Scientific Foundation of Climate Change. Human Responsibility for Climate Change
 Scientific Foundation of Climate Change EOH 468 CSU Northridge Spring 2010 Peter Bellin, CIH, Ph.D. 1 Human Responsibility for Climate Change The IPCC finds that it is very likely that emissions of heat-trapping
Scientific Foundation of Climate Change EOH 468 CSU Northridge Spring 2010 Peter Bellin, CIH, Ph.D. 1 Human Responsibility for Climate Change The IPCC finds that it is very likely that emissions of heat-trapping
Local and Global Impacts of Climate Change: Predictions of the 5th IPCC Report
 Local and Global Impacts of Climate Change: Predictions of the 5th IPCC Report Peter Schlosser Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences and Department of Earth and Environmental Engineering The Earth
Local and Global Impacts of Climate Change: Predictions of the 5th IPCC Report Peter Schlosser Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences and Department of Earth and Environmental Engineering The Earth
PHY392S Physics of Climate. Lecture 1. Introduction
 PHY392S Physics of Climate Lecture 1 Introduction Slides based on material from Prof. K. Strong PHY392S - Physics of Climate Lecture 1, Page 1 Some Definitions Weather the fluctuating state of the atmosphere
PHY392S Physics of Climate Lecture 1 Introduction Slides based on material from Prof. K. Strong PHY392S - Physics of Climate Lecture 1, Page 1 Some Definitions Weather the fluctuating state of the atmosphere
15.023J / J / ESD.128J Global Climate Change: Economics, Science, and Policy Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.023J / 12.848J / ESD.128J Global Climate Change: Economics, Science, and Policy Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.023J / 12.848J / ESD.128J Global Climate Change: Economics, Science, and Policy Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:
IWRM as a Tool for Adaptation to Climate Change. Drivers and Impacts of Climate Change
 IWRM as a Tool for Adaptation to Climate Change Drivers and Impacts of Climate Change Outline presentation This session will address: The drivers/physical science basis of climate change The observed and
IWRM as a Tool for Adaptation to Climate Change Drivers and Impacts of Climate Change Outline presentation This session will address: The drivers/physical science basis of climate change The observed and
Scientific Facts on. Climate Change Assessment
 page 1/8 Scientific Facts on Climate Change 2001 Assessment Source document: IPCC (2001) Summary & Details: GreenFacts Context - The Earth's climate has changed over the last century and by 2001 there
page 1/8 Scientific Facts on Climate Change 2001 Assessment Source document: IPCC (2001) Summary & Details: GreenFacts Context - The Earth's climate has changed over the last century and by 2001 there
2. Climate Change: Projections of Climate Change: 2100 and beyond
 Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties An overview of the basic science An overview of the basic science 1. A Brief History of Global
Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties An overview of the basic science An overview of the basic science 1. A Brief History of Global
CLIMATE CHANGE 2013 The Physical Science Basis
 CLIMATE CHANGE 2013 The Physical Science Basis Headline Statements from the Summary for Policymakers Warming of the climate system is unequivocal, and since the 1950s, many of the observed changes are
CLIMATE CHANGE 2013 The Physical Science Basis Headline Statements from the Summary for Policymakers Warming of the climate system is unequivocal, and since the 1950s, many of the observed changes are
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Devizes & District U3A, 24 th November 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Why does Earth s climate change? Earth s Climate has always been changing
Global Climate Change Devizes & District U3A, 24 th November 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Why does Earth s climate change? Earth s Climate has always been changing
Understanding the Causes of Global Climate Change
 FACT SHEET I: Attribution Environment Understanding the Causes of Global Climate Change Average air temperatures at the Earth s surface have increased by approximately 0.6 o C (1 o F) over the 20 th century.
FACT SHEET I: Attribution Environment Understanding the Causes of Global Climate Change Average air temperatures at the Earth s surface have increased by approximately 0.6 o C (1 o F) over the 20 th century.
Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium
 Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium review session CCIU April 30, 2016 High-school standard HS-ESS2-4 focuses on the role energy flows play in Earth s climate HS-ESS2-4 Use a model to describe how variations
Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium review session CCIU April 30, 2016 High-school standard HS-ESS2-4 focuses on the role energy flows play in Earth s climate HS-ESS2-4 Use a model to describe how variations
Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change
 Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change Earth s Climate has always been changing 1) Is climate changing now? Global Warming? Sea level rising IPCC 2007 Fig. 5.13 (p. 410) Recontructed
Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change Earth s Climate has always been changing 1) Is climate changing now? Global Warming? Sea level rising IPCC 2007 Fig. 5.13 (p. 410) Recontructed
Summary for Policymakers
 Twelfth Session of Working Group I Approved Summary for Policymakers Summary for Policymakers Drafting Authors: Lisa Alexander (Australia), Simon Allen (Switzerland/New Zealand), Nathaniel L. Bindoff (Australia),
Twelfth Session of Working Group I Approved Summary for Policymakers Summary for Policymakers Drafting Authors: Lisa Alexander (Australia), Simon Allen (Switzerland/New Zealand), Nathaniel L. Bindoff (Australia),
The use of non-co2 multipliers for the climate impact of aviation: The scientific basis
 Workshop on Aviation and Carbon Markets ICAO Headquarters Montreal, Quebec 18-19 June 2008 The use of non-co2 multipliers for the climate impact of aviation: The scientific basis by Dr. David W. Fahey
Workshop on Aviation and Carbon Markets ICAO Headquarters Montreal, Quebec 18-19 June 2008 The use of non-co2 multipliers for the climate impact of aviation: The scientific basis by Dr. David W. Fahey
SPM1. Summary for Policymakers
 1 Summary for Policymakers Drafting Authors: Lisa V. Alexander (Australia), Simon K. Allen (Switzerland/New Zealand), Nathaniel L. Bindoff (Australia), François-Marie Bréon (France), John A. Church (Australia),
1 Summary for Policymakers Drafting Authors: Lisa V. Alexander (Australia), Simon K. Allen (Switzerland/New Zealand), Nathaniel L. Bindoff (Australia), François-Marie Bréon (France), John A. Church (Australia),
Climate Change state of the science
 Climate Change state of the science Henley in Transition December 14 th 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s Climate has always been changing The planet is
Climate Change state of the science Henley in Transition December 14 th 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s Climate has always been changing The planet is
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 34. Global Warming Part I
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 34 Global Warming Part I Outline of three part global warming presentation What is the problem? How has the Earth s climate changed in recent years? Are these changes attributable
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 34 Global Warming Part I Outline of three part global warming presentation What is the problem? How has the Earth s climate changed in recent years? Are these changes attributable
Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011
 Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011 Reading Henson Rough Guide Chapter 1 Pages 75 127; 215; 227-244 Other pages
Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011 Reading Henson Rough Guide Chapter 1 Pages 75 127; 215; 227-244 Other pages
Changes to the Underlying Scientific-Technical Assessment to ensure consistency with the approved Summary for Policymakers
 THIRTY-SIXTH SESSION OF THE IPCC Stockholm, 26 September 2013 IPCC-XXXVI/Doc. 4 (27.IX.2013) Agenda Item: 3 ENGLISH ONLY ACCEPTANCE OF THE ACTIONS TAKEN AT THE TWELFTH SESSION OF WORKING GROUP I Working
THIRTY-SIXTH SESSION OF THE IPCC Stockholm, 26 September 2013 IPCC-XXXVI/Doc. 4 (27.IX.2013) Agenda Item: 3 ENGLISH ONLY ACCEPTANCE OF THE ACTIONS TAKEN AT THE TWELFTH SESSION OF WORKING GROUP I Working
Causes of past climate change and projections of future changes in climate. Peter Stott Met Office Hadley Centre, UK
 Causes of past climate change and projections of future changes in climate Peter Stott Met Office Hadley Centre, UK Overview 1.The causes of observed climate change 2.Global and regional climate projections
Causes of past climate change and projections of future changes in climate Peter Stott Met Office Hadley Centre, UK Overview 1.The causes of observed climate change 2.Global and regional climate projections
Climate Science from a Climate Scientist
 Climate Science from a Climate Scientist Professor Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading John Hall Venice Course, National Gallery, 25 th January 2017 Earth s Climate has always
Climate Science from a Climate Scientist Professor Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading John Hall Venice Course, National Gallery, 25 th January 2017 Earth s Climate has always
Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases. Course Goals
 PCC 588 - January 6 and 8 2009 Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases T,Th 12:00-1:20 pm OSB 25 Course Goals The course focuses on factors controlling the global cycle
PCC 588 - January 6 and 8 2009 Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases T,Th 12:00-1:20 pm OSB 25 Course Goals The course focuses on factors controlling the global cycle
Comments on Human and Natural Forcings. Climate changes (1900 to 2000) due to human activity. Climate Variability and Climate Change
 Comments on Human and Natural Forcings Human input of GH gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, CFCs ) has warmed the planet: net RF = +2.9 W/m 2 The largest single warming factor is increased
Comments on Human and Natural Forcings Human input of GH gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, CFCs ) has warmed the planet: net RF = +2.9 W/m 2 The largest single warming factor is increased
ALLEGED ERRORS IN THE SUMMARY FOR POLICYMAKERS OF THE WORKING GROUP III CONTRIBUTION TO THE FIFTH ASSESSMENT REPORT
 FORTIETH SESSION OF THE IPCC Copenhagen, Denmark, 27-31 October 2014 IPCC-XL/Doc. 18 (24.X.2014) Agenda Item: 13 ENGLISH ONLY ALLEGED ERRORS IN THE SUMMARY FOR POLICYMAKERS OF THE WORKING GROUP III CONTRIBUTION
FORTIETH SESSION OF THE IPCC Copenhagen, Denmark, 27-31 October 2014 IPCC-XL/Doc. 18 (24.X.2014) Agenda Item: 13 ENGLISH ONLY ALLEGED ERRORS IN THE SUMMARY FOR POLICYMAKERS OF THE WORKING GROUP III CONTRIBUTION
Greenhouse gases. A snow-covered surface refl ects massive amounts of sunlight and therefore has a cooling effect on the climate.
 A k t u e l N a t u r v i d e n s k a b 2 0 0 9 G R E E N H O U S E G A S E S 13 Greenhouse gases - and their impact on the climate The greenhouse effect is the best understood and well mapped of the mechanisms
A k t u e l N a t u r v i d e n s k a b 2 0 0 9 G R E E N H O U S E G A S E S 13 Greenhouse gases - and their impact on the climate The greenhouse effect is the best understood and well mapped of the mechanisms
Transformational Climate Science. The future of climate change research following the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report
 Transformational Climate Science The future of climate change research following the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report www.exeter.ac.uk/climate2014 Working Group I The challenge of climate change #climate2014
Transformational Climate Science The future of climate change research following the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report www.exeter.ac.uk/climate2014 Working Group I The challenge of climate change #climate2014
Observed Changes and their Causes. Vicente Barros, Co-Chair WGII Gian-Kasper Plattner, Head WGI TSU for the SYR Core Writing Team
 Observed Changes and their Causes Vicente Barros, Co-Chair WGII Gian-Kasper Plattner, Head WGI TSU for the SYR Core Writing Team Human influence on the climate system is clear. Recent climate changes have
Observed Changes and their Causes Vicente Barros, Co-Chair WGII Gian-Kasper Plattner, Head WGI TSU for the SYR Core Writing Team Human influence on the climate system is clear. Recent climate changes have
CLIMATE CHANGE The Physical Science Basis WG I. IN TERGOV ERNMENTA L PA NEL ON climate
 IN TERGOV ERNMENTA L PA NEL ON climate change CLIMATE CHANGE 2013 The Physical Science Basis WG I WORKING GROUP I CONTRIBUTION TO THE FIFTH ASSESSMENT REPORT OF THE INTERGOVERNMENTAL PANEL ON CLIMATE CHANGE
IN TERGOV ERNMENTA L PA NEL ON climate change CLIMATE CHANGE 2013 The Physical Science Basis WG I WORKING GROUP I CONTRIBUTION TO THE FIFTH ASSESSMENT REPORT OF THE INTERGOVERNMENTAL PANEL ON CLIMATE CHANGE
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Fourth Assessment Report
 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Fourth Assessment Report Andrea J. Ray, Ph.D. NOAA Earth Systems Research Lab & NOAA-CIRES Western Water Assessment Boulder, CO Andrea.Ray@noaa.gov http:/www.cdc.noaa.gov
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Fourth Assessment Report Andrea J. Ray, Ph.D. NOAA Earth Systems Research Lab & NOAA-CIRES Western Water Assessment Boulder, CO Andrea.Ray@noaa.gov http:/www.cdc.noaa.gov
What does IPCC AR5 say? IPCC as a radical inside the closet
 What does IPCC AR5 say? IPCC as a radical inside the closet What does IPCC AR5 say? Plan: * What is IPCC? * The Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) - WR1: The physical basis - WR2: Impacts, adaptation and vulnerability
What does IPCC AR5 say? IPCC as a radical inside the closet What does IPCC AR5 say? Plan: * What is IPCC? * The Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) - WR1: The physical basis - WR2: Impacts, adaptation and vulnerability
Changing? What Is Climate and How Is It. You have probably seen or heard
 What Is Climate and How Is It Changing? Photo by Jesse Stanley Student Reading 1 Exit Glacier in Alaska has receded significantly in the last century. Photo by Jesse Stanley You have probably seen or heard
What Is Climate and How Is It Changing? Photo by Jesse Stanley Student Reading 1 Exit Glacier in Alaska has receded significantly in the last century. Photo by Jesse Stanley You have probably seen or heard
Climate Change, Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols
 Climate Change, Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols J Srinivasan J Srinivasan is a Professor at the Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences at Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. He was a lead author
Climate Change, Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols J Srinivasan J Srinivasan is a Professor at the Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences at Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. He was a lead author
LESSON 9: CONCEPTUALIZING MODULE II Factors Influencing Temperature
 LESSON 9: CONCEPTUALIZING MODULE II Factors Influencing Temperature PURPOSE/QUESTION To understand the need to compare data sets over different parameters thus increasing the strength for students climate
LESSON 9: CONCEPTUALIZING MODULE II Factors Influencing Temperature PURPOSE/QUESTION To understand the need to compare data sets over different parameters thus increasing the strength for students climate
Radiative Forcing Components
 Radiative Forcing Components Content Definition of Radiative Forcing Radiation Balance Climate sensitivity Solar forcing Forcing due to atmospheric gas Definition of Radiative Forcing In climate science,
Radiative Forcing Components Content Definition of Radiative Forcing Radiation Balance Climate sensitivity Solar forcing Forcing due to atmospheric gas Definition of Radiative Forcing In climate science,
Radiative forcing of gases, aerosols and, clouds.
 Lecture 23. Radiative forcing of gases, aerosols and, clouds. 1. Concepts of radiative forcing, climate sensitivity, and radiation feedbacks. 2. Radiative forcing of anthropogenic greenhouse gases. 3.
Lecture 23. Radiative forcing of gases, aerosols and, clouds. 1. Concepts of radiative forcing, climate sensitivity, and radiation feedbacks. 2. Radiative forcing of anthropogenic greenhouse gases. 3.
CLIMATE CHANGE The Physical Science Basis. Summary for Policymakers. climate change WG I INTERGOV ERNMENTA L PA NEL ON
 INTERGOV ERNMENTA L PA NEL ON climate change CLIMATE CHANGE 2013 The Physical Science Basis WG I WORKING GROUP I CONTRIBUTION TO THE FIFTH ASSESSMENT REPORT OF THE INTERGOVERNMENTAL PANEL ON CLIMATE CHANGE
INTERGOV ERNMENTA L PA NEL ON climate change CLIMATE CHANGE 2013 The Physical Science Basis WG I WORKING GROUP I CONTRIBUTION TO THE FIFTH ASSESSMENT REPORT OF THE INTERGOVERNMENTAL PANEL ON CLIMATE CHANGE
Lecture 29: Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes
 Lecture 29: Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes 1. The Meaning of Detection and Attribution The response to anthropogenic changes in climate forcing occurs against a backdrop of natural
Lecture 29: Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes 1. The Meaning of Detection and Attribution The response to anthropogenic changes in climate forcing occurs against a backdrop of natural
Earth s Climate from Space. Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Earth s Climate from Space Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s energy balance in space S πr 2 4πr 2 Outgoing Thermal Radiative Energy Absorbed Solar Radiative Energy
Earth s Climate from Space Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s energy balance in space S πr 2 4πr 2 Outgoing Thermal Radiative Energy Absorbed Solar Radiative Energy
Klimaänderung. Robert Sausen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen
 Klimaänderung Robert Sausen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen Vorlesung WS 2017/18 LMU München 8. Anthropogener und natürlicher Strahlungsantrieb
Klimaänderung Robert Sausen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen Vorlesung WS 2017/18 LMU München 8. Anthropogener und natürlicher Strahlungsantrieb
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report. Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report. Longer Report
 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report Longer Report NOTE: Un-edited copy prepared for COP-13. The entire report is subject to final copy-edit
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report Longer Report NOTE: Un-edited copy prepared for COP-13. The entire report is subject to final copy-edit
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report. Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report. Longer Report
 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report Longer Report NOTE: Un-edited copy prepared for COP-13. The entire report is subject to final copy-edit
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report Longer Report NOTE: Un-edited copy prepared for COP-13. The entire report is subject to final copy-edit
Greenhouse Effect. The Greenhouse Effect
 Greenhouse Effect The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases let short-wavelength radiation come into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun. However, they absorb and re-radiate Earth s long-wavelength radiation
Greenhouse Effect The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases let short-wavelength radiation come into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun. However, they absorb and re-radiate Earth s long-wavelength radiation
Climate Change: What do we know and what do we guess?
 What do we know and what do we guess? Manfred Grasserbauer * Vienna University of Technology * Director Institute for Environment and Sustainability, Joint Research Centre, European Commission (Ispra)
What do we know and what do we guess? Manfred Grasserbauer * Vienna University of Technology * Director Institute for Environment and Sustainability, Joint Research Centre, European Commission (Ispra)
8.1 Radiative Forcing
 Chapter Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing.1 Radiative Forcing There are a variety of ways to examine how various drivers contribute to climate change. In principle, observations of the climate
Chapter Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing.1 Radiative Forcing There are a variety of ways to examine how various drivers contribute to climate change. In principle, observations of the climate
The instrumental record goes back to about A few areas of the globe have not warmed in recent decades, mainly over some parts of the Southern
 The instrumental record goes back to about 1850. A few areas of the globe have not warmed in recent decades, mainly over some parts of the Southern Hemisphere oceans and parts of Antarctica. The rate of
The instrumental record goes back to about 1850. A few areas of the globe have not warmed in recent decades, mainly over some parts of the Southern Hemisphere oceans and parts of Antarctica. The rate of
Climate Change : Facts and Future Scenarios
 Climate Change : Facts and Future Scenarios Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research, Auckland, NZ FOA/MAF 6 th Annual Forest Biosecurity Workshop 8-9 th March 2007 Outline Facts
Climate Change : Facts and Future Scenarios Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research, Auckland, NZ FOA/MAF 6 th Annual Forest Biosecurity Workshop 8-9 th March 2007 Outline Facts
Summary for Policymakers
 Summary for Policymakers A Report of Working Group I of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Based on a draft prepared by: Daniel L. Albritton, Myles R. Allen, Alfons P. M. Baede, John A. Church,
Summary for Policymakers A Report of Working Group I of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Based on a draft prepared by: Daniel L. Albritton, Myles R. Allen, Alfons P. M. Baede, John A. Church,
Estimated Global Temperature and Growth Rate since Estimated global mean temperature
 1.1 Global Warming Estimated Global Temperature and Growth Rate since 1850 14.6 Estimated global mean temperature C 14.4 14.2 14.0 13.8 13.6 Period Years 25 50 100 150 Annual mean Smoothed series Growth
1.1 Global Warming Estimated Global Temperature and Growth Rate since 1850 14.6 Estimated global mean temperature C 14.4 14.2 14.0 13.8 13.6 Period Years 25 50 100 150 Annual mean Smoothed series Growth
Global Warming Potentials in AR4. V. Ramaswamy. NOAA/ Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, Princeton University
 Global Warming Potentials in AR4 V. Ramaswamy NOAA/ Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, Princeton University GWP Definition Defined as the ratio of the time-integrated radiative forcing from the instantaneous
Global Warming Potentials in AR4 V. Ramaswamy NOAA/ Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, Princeton University GWP Definition Defined as the ratio of the time-integrated radiative forcing from the instantaneous
A Climate Change Primer The IPCC Fourth Assessment Report
 A Climate Change Primer 2007 Nobel Peace Prize Richard McGehee Seminar on the Mathematics of Climate Change School of Mathematics October 31, 2007 http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/peace/laureates/2007/
A Climate Change Primer 2007 Nobel Peace Prize Richard McGehee Seminar on the Mathematics of Climate Change School of Mathematics October 31, 2007 http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/peace/laureates/2007/
Chapter 19 Global Change. Wednesday, April 18, 18
 Chapter 19 Global Change Module 62 Global Climate Change and the Greenhouse Effect After reading this module you should be able to distinguish among global change, global climate change, and global warming.
Chapter 19 Global Change Module 62 Global Climate Change and the Greenhouse Effect After reading this module you should be able to distinguish among global change, global climate change, and global warming.
Chapter outline. introduction. Reference. Chapter 6: Climate Change Projections EST 5103 Climate Change Science
 Chapter 6: Climate Change Projections EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of Science & Technology Chapter outline Future Forcing and Scenarios,
Chapter 6: Climate Change Projections EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of Science & Technology Chapter outline Future Forcing and Scenarios,
Introduction. Frequently Used Abbreviations and Acronyms
 This Appendix is based upon material provided by the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science. Frequently Used Abbreviations and Acronyms CO 2 : Carbon Dioxide IPCC: Intergovernmental Panel
This Appendix is based upon material provided by the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science. Frequently Used Abbreviations and Acronyms CO 2 : Carbon Dioxide IPCC: Intergovernmental Panel
The past, present and future climate of Peace District
 The past, present and future climate of Peace District Bill Taylor Pacific & Yukon The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) The work of the IPCC represents the consensus of the international
The past, present and future climate of Peace District Bill Taylor Pacific & Yukon The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) The work of the IPCC represents the consensus of the international
IPCC AR5 & UNFCCC COP21
 IPCC AR5 & UNFCCC COP21 28 th July 2015 平石尹彦 Taka Hiraishi IPCC organisation There is a small Secretariat in Geneva, and Technical Supports Units are in four host
IPCC AR5 & UNFCCC COP21 28 th July 2015 平石尹彦 Taka Hiraishi IPCC organisation There is a small Secretariat in Geneva, and Technical Supports Units are in four host
Maxwell Climate Change Workshop Background: The Nature of the Problem
 Maxwell Climate Change Workshop Background: The Nature of the Problem Peter J Wilcoxen Departments of Economics and Public Administration The Maxwell School of Syracuse University September 21, 2010 1
Maxwell Climate Change Workshop Background: The Nature of the Problem Peter J Wilcoxen Departments of Economics and Public Administration The Maxwell School of Syracuse University September 21, 2010 1
Announcements. Homework 7 - due today Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov.
 Tuesday, November 6th. Announcements. Homework 7 - due today Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov. 20 Lecture #17-1 For next week..homework
Tuesday, November 6th. Announcements. Homework 7 - due today Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov. 20 Lecture #17-1 For next week..homework
Climate change: recent changes in sea level and the ocean
 Climate change: recent changes in sea level and the ocean Prof. Ric Williams, Department of Earth and Ocean Sciences 1. Is climate change happening? 2. Why care about the ocean? Prof. Phil Woodworth, Proudman
Climate change: recent changes in sea level and the ocean Prof. Ric Williams, Department of Earth and Ocean Sciences 1. Is climate change happening? 2. Why care about the ocean? Prof. Phil Woodworth, Proudman
Drivers of Climate Change
 .3.3.1 Drivers of Climate Change Introduction Human activities have changed and continue to change the Earth s surface and atmospheric composition. Some of these changes have a direct or indirect impact
.3.3.1 Drivers of Climate Change Introduction Human activities have changed and continue to change the Earth s surface and atmospheric composition. Some of these changes have a direct or indirect impact
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Greenhouse Gases and Earth s Energy Balance 400 380 CO 2 in air 360 340 320 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 Year Global Climate Change 1 / 30 Outline of Topics 1 The Natural Earth System
Global Climate Change Greenhouse Gases and Earth s Energy Balance 400 380 CO 2 in air 360 340 320 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 Year Global Climate Change 1 / 30 Outline of Topics 1 The Natural Earth System
Climate Change and Air Quality
 Climate Change and Air Quality SW PA Air Quality Action June 6, 2007 Peter J. Adams Associate Professor Civil and Environmental Engineering Engineering and Public Policy Outline Climate Change Primer What
Climate Change and Air Quality SW PA Air Quality Action June 6, 2007 Peter J. Adams Associate Professor Civil and Environmental Engineering Engineering and Public Policy Outline Climate Change Primer What
Air Transportation: Emissions and Effects
 Air Transportation: Emissions and Effects Joyce E. Penner University of Michigan Report Co-ordinator: IPCC Special Report on Aviation and the Global Atmosphere Presentation to the First Regional Symposium
Air Transportation: Emissions and Effects Joyce E. Penner University of Michigan Report Co-ordinator: IPCC Special Report on Aviation and the Global Atmosphere Presentation to the First Regional Symposium
ENSC425/625 Climate Change and Global Warming
 ENSC425/625 Climate Change and Global Warming 1 Emission scenarios of greenhouse gases Projections of climate change Regional climate change (North America) Observed Changes and their Uncertainty 2 Figure
ENSC425/625 Climate Change and Global Warming 1 Emission scenarios of greenhouse gases Projections of climate change Regional climate change (North America) Observed Changes and their Uncertainty 2 Figure
8.5 Synthesis of Global Mean Radiative Forcing, Past and Future. Box 8.3 Volcanic Eruptions as Analogues
 Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing Chapter Box.3 Volcanic Eruptions as Analogues Volcanic eruptions provide a natural experiment of a stratospheric aerosol cloud that can serve to inform us of
Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing Chapter Box.3 Volcanic Eruptions as Analogues Volcanic eruptions provide a natural experiment of a stratospheric aerosol cloud that can serve to inform us of
Concerns about Climate Change and Global Warming
 1 Concerns about Climate Change and Global Warming 1.1 Introduction Climate is defined as the typical behavior of the atmosphere, the aggregation of the weather, and is generally expressed in terms of
1 Concerns about Climate Change and Global Warming 1.1 Introduction Climate is defined as the typical behavior of the atmosphere, the aggregation of the weather, and is generally expressed in terms of
IN SITU GEOTHERMAL ENERGY TECHNOLOGY: AN APPROACH FOR BUILDING CLEANER AND GREENER ENVIRONMENT
 Journal of Ecological Engineering Volume 17, Issue 1, Jan. 2016, pages 49 55 DOI: 10.12911/22998993/61189 Research Article IN SITU GEOTHERMAL ENERGY TECHNOLOGY: AN APPROACH FOR BUILDING CLEANER AND GREENER
Journal of Ecological Engineering Volume 17, Issue 1, Jan. 2016, pages 49 55 DOI: 10.12911/22998993/61189 Research Article IN SITU GEOTHERMAL ENERGY TECHNOLOGY: AN APPROACH FOR BUILDING CLEANER AND GREENER
Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Volcanic Eruptions and Global Temperature
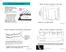 Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Model Documentation: Chalmers Climate Calculator (CCC)
 Model Documentation: Chalmers Climate Calculator (CCC) Model development: Christian Azar, Daniel Johansson Data collection: Christian Azar, Paulina Essunger, Daniel Johansson Web interface: Claes Andersson
Model Documentation: Chalmers Climate Calculator (CCC) Model development: Christian Azar, Daniel Johansson Data collection: Christian Azar, Paulina Essunger, Daniel Johansson Web interface: Claes Andersson
Key Points from the IPCC WGI Fifth Assessment Report. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis
 Key Points from the IPCC WGI Fifth Assessment Report. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis Produced by the Cambridge Centre for Climate Science for climate-related scientists within the University
Key Points from the IPCC WGI Fifth Assessment Report. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis Produced by the Cambridge Centre for Climate Science for climate-related scientists within the University
Understanding Global Warming
 Math 483 Spring Semester, 2013 California State University, Northridge Understanding Global Warming Global Warming is Real December 2012 is 334th consecutive Month with global temperatures above the 20th
Math 483 Spring Semester, 2013 California State University, Northridge Understanding Global Warming Global Warming is Real December 2012 is 334th consecutive Month with global temperatures above the 20th
Introduction to climate science : global climate variability and change, findings of IPCC AR5. Imad Khatib
 Environmental Quality Authority Introduction to climate science : global climate variability and change, findings of IPCC AR5 Imad Khatib Palestine National Training Seminar on Climate Change 26 28 January,
Environmental Quality Authority Introduction to climate science : global climate variability and change, findings of IPCC AR5 Imad Khatib Palestine National Training Seminar on Climate Change 26 28 January,
Draft Environmental Impact Statement
 The Safer Affordable Fuel-Efficient (SAFE) Vehicles Rule for Model Year 2021 2026 Passenger Cars and Light Trucks Draft Environmental Impact Statement July 2018 Docket No. NHTSA-2017-0069 Greenhouse Gas
The Safer Affordable Fuel-Efficient (SAFE) Vehicles Rule for Model Year 2021 2026 Passenger Cars and Light Trucks Draft Environmental Impact Statement July 2018 Docket No. NHTSA-2017-0069 Greenhouse Gas
Global Warming of 1.5 C
 Global Warming of 1.5 C Global Warming of 1.5 C An IPCC special report on the impacts of global warming of 1.5 C above preindustrial levels and related global greenhouse gas emission pathways, in the context
Global Warming of 1.5 C Global Warming of 1.5 C An IPCC special report on the impacts of global warming of 1.5 C above preindustrial levels and related global greenhouse gas emission pathways, in the context
Tuesday Dec 2nd TOPIC # 13 Global Warming Wrap Up TOPIC #14 IMPACTS & ISSUES
 Tuesday Dec 2nd TOPIC # 13 Global Warming Wrap Up TOPIC #14 IMPACTS & ISSUES SIT WITH YOUR GROUP TODAY ANNOUNCEMENTS: LINKING-TO-LIFE PROJECT PART A Your Ecological Footprint DUE in class TODAY! PART B
Tuesday Dec 2nd TOPIC # 13 Global Warming Wrap Up TOPIC #14 IMPACTS & ISSUES SIT WITH YOUR GROUP TODAY ANNOUNCEMENTS: LINKING-TO-LIFE PROJECT PART A Your Ecological Footprint DUE in class TODAY! PART B
Chapter 19 Global Change
 Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change Global change- any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global climate change-changes
Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change Global change- any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global climate change-changes
IPCC WG1 AR5 Report & its relevance to Southeast Asia region
 IPCC WG1 AR5 Report & its relevance to Southeast Asia region Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Fredolin Tangang IPCC WG1 Vice-Chair IPCC WG1 AR5 Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis The IPCC has
IPCC WG1 AR5 Report & its relevance to Southeast Asia region Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Fredolin Tangang IPCC WG1 Vice-Chair IPCC WG1 AR5 Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis The IPCC has
Training workshops on mainstreaming climate change in national development planning and budgeting HANDOUT FOR PARTICIPANTS
 Global Climate Change Alliance Support Facility Training workshops on mainstreaming climate change in national development planning and budgeting HANDOUT FOR PARTICIPANTS MODULE 3 Understanding the basics
Global Climate Change Alliance Support Facility Training workshops on mainstreaming climate change in national development planning and budgeting HANDOUT FOR PARTICIPANTS MODULE 3 Understanding the basics
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 7: 10-16-13 Outline of This Topic Climate forcings Things that directly
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 7: 10-16-13 Outline of This Topic Climate forcings Things that directly
Chapter 19 Global Change
 Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change change - any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global change - changes in the climate
Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change change - any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global change - changes in the climate
GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB
 GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB A COMPUTER SIMULATION PROGRAM ON TEMPERATURE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISING After performing this computer simulation lab you will be able to: 1) understand the greenhouse effect
GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB A COMPUTER SIMULATION PROGRAM ON TEMPERATURE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISING After performing this computer simulation lab you will be able to: 1) understand the greenhouse effect
Errata to Global Warming: Understanding the Forecast 2nd Printing, 2008
 Errata to Global Warming: Understanding the Forecast 2nd Printing, 28 Chapter 3 Page 22. Formula 3.1, the fourth root is written incorrectly as the square root (there should be a little number 4 in superscript
Errata to Global Warming: Understanding the Forecast 2nd Printing, 28 Chapter 3 Page 22. Formula 3.1, the fourth root is written incorrectly as the square root (there should be a little number 4 in superscript
Risk and Uncertainties in Anthropogenic. Control over Greenhouse Forcing in the TAR. with a focus on Atmospheric Chemistry
 FCCC, Bonn, 4-6 Apr 2002 SBSTA IPCC/TAR Michael Prather University of California at Irvine Risk and Uncertainties in Anthropogenic Control over Greenhouse Forcing in the TAR with a focus on Atmospheric
FCCC, Bonn, 4-6 Apr 2002 SBSTA IPCC/TAR Michael Prather University of California at Irvine Risk and Uncertainties in Anthropogenic Control over Greenhouse Forcing in the TAR with a focus on Atmospheric
THE ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON THE CLIMATE CHANGE IS CLEAR
 FROM IPCC AR5 WKG I: THE ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON THE CLIMATE CHANGE IS CLEAR Excerpts from IPCC AR5 by Toni Federico Scientific Committee of Sustainable Development Foundation SUMMARY Note from editor
FROM IPCC AR5 WKG I: THE ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON THE CLIMATE CHANGE IS CLEAR Excerpts from IPCC AR5 by Toni Federico Scientific Committee of Sustainable Development Foundation SUMMARY Note from editor
State of the global climate 2012 with reference to the past 20 years
 State of the global climate 2012 with reference to the past 20 years 2012 Further developed from the past 20 year UNEP report Keeping Track of Our Changing Environment From Rio to Rio+20 (1992-2012) UNEP
State of the global climate 2012 with reference to the past 20 years 2012 Further developed from the past 20 year UNEP report Keeping Track of Our Changing Environment From Rio to Rio+20 (1992-2012) UNEP
Global Climate Change 4
 Global Climate Change 4 Climate Change Consequences Climate Change Mitigation Climate Change Politics Tipping points GAT: we re heating up Hockey stick graph past 1000 years 2001 Data from thermometers
Global Climate Change 4 Climate Change Consequences Climate Change Mitigation Climate Change Politics Tipping points GAT: we re heating up Hockey stick graph past 1000 years 2001 Data from thermometers
Chapter 2. Climate Change: Scientific Basis
 a. The Greenhouse Effect Chapter 2 Climate Change: Scientific Basis Climate scientists have clearly established that: The Earth s atmosphere is like a greenhouse, reflecting some of the sun s harmful rays
a. The Greenhouse Effect Chapter 2 Climate Change: Scientific Basis Climate scientists have clearly established that: The Earth s atmosphere is like a greenhouse, reflecting some of the sun s harmful rays
