2. Which of the following molecules will NOT absorb in the infrared: a) CO 2 b) HCl c) O 2 d) O 3
|
|
|
- Suzan Martina Davis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name CHEM. 253 Spring, 2015 Exam 3 May 20, 2015 The energy emitted by a black body emitter = σt 4 where σ = 5.67 x 10-8 W m -2 K -4 Cross-sectional area = πr 2 and area of a sphere = 4πr 2 where r = radius. Short Answer and Multiple Choice Section. For multiple choice problems, select the best (only one) answer. 4 points per problem. 1. As a result of global warming, the poleward (northern in the northern hemisphere) edges of deserts are migrating poleward. This results in forests or shrublands being replaced by sparsely vegetated lands where albedo is higher. This is an example of: a) a positive feedback b) a negative feedback c) climate sensitivity d) the end of the world 2. Which of the following molecules will NT absorb in the infrared: a) C 2 b) H c) 2 d) 3 3. Which of the following is a so-called indirect effect of aerosols on climate? a) aerosol particles catalyze the reduction of C 2 to CH 4 increasing warming b) aerosol particles make clouds more reflective, increasing cooling c) aerosol particles absorb solar light, increasing warming d) aerosol particles catalyze ozone loss, decreasing warming 4. Both natural gas and coal contain fossil carbon and produce carbon dioxide on combusion. In terms of contributions to global warming, why is natural gas considered a better fuel? a) Natural gas provides more heat per mole of C 2 formed b) Coal contains more sulfur resulting in S 2 as well as C 2 c) Natural gas releases water when burned which results in cooling d) Natural gas burns cleaner producing almost no particulates 5. List one secondary advantage of using biofuels (besides the use of a renewable fuel to reduce overall carbon dioxide emissions). Secondary advantage: _oxygenates burn better, can use waste products to create, can improve fuel quality as additive, reduces air pollution 6. What is a green advantage of using polylactic acid over polyethylene for bottles? a) polylactic acid is easier to recycle b) polylactic acid is made from renewable resources c) polylactic acid is a more stable polymer d) polylactic acid is better for storing acidic drinks 7. Give one green advantage of using an ionic liquid in place of a traditional non-halogenated organic solvent? Green advantage: _less volatile, toxic, flammable_ 1
2 8. 2,4-D (see structure below), which is an herbicide is a weak acid (pk a = 2.73) that is weakly polar (K ow = 65). During oral exposure, most of the absorption through the GI tract will occur in: a) the mouth b) the throat c) the stomach d) the intestines H 9. Most toxic compounds have loss processes (tranformation or elimination) through one of two organs. List the organ and describe a loss process. organ: 1) liver 2) kidney loss process: 1) transformation 2) elimination Problem and Short Essay Question Section (be sure to show work if calculations are needed): 1. The solar constant (solar light flux) for Venus is 2620 W m -2 and its albedo is What is the expected surface temperature of Venus assuming it behaves as a blackbody emitter and has no greenhouse gases? The average surface temperature on Venus is 753 K. What can be concluded by this? See p. 1 for equations and constants. (12 pts) (1 A)F S πr 2 = 4πr 2 F V where A = albedo, F = flux (sun or venus), and r = radius and F V = σt 4 (blackbody emitter) This becomes: T 4 = (2620 W m -2 )(1 0.65)/(4σ) or T = 252 K Since T Measured > T Expected, there must be greenhouse gas warming on venus. 2. Chlorofluorocarbons were considered valuable fluids for refrigeration due to being inflammable and nontoxc. However, because of their potential to release into the stratosphere, they have largely been replaced by HCFCs or related compounds (e.g. CHF 2 CHF 2 ). Considerations as to replacements also need to 2
3 consider if replacement compounds act as greenhouse gases. Describe two factors that would be of interest to know to determine how strong replacement compounds are as greenhouse gases (8 pts). 1) If they absorb in window regions in the infrared 2) There lifetimes 3. An industrialist is interested in tapping methane clathrates at the bottom of oceans as a fuel source. The methane clathrate (CH 4 6H 2 ) is present as a solid under low temperatures and high pressures, but upon heating or reduction of pressure, CH 4 can be released as a gas. They are present at moderate concentrations at ocean bottoms. Assume the methane recovered is being used to generate electricity to replace coal combustion sources of electricity. Besides the economical cost to generate electricity, discuss whether this is likely to be beneficial for reduction in greenhouse gases. List one advantage and one potential disadvantage in this switch in resources for generating electricity with regards to greenhouse gas production. (8 pts) 1) Advantage: Switching from coal to CH 4 as a fuel is beneficial due to more energy per mole of carbon dioxide released 2) Potential Disadvantages: 1) getting fuel from the bottom of the ocean could require a lot of energy, 2) potential methane leaks as it is a strong greenhouse gas 4. Below is a scheme for the synthesis of setraline. Ti 4, and H 2 are reactants, while toluene, hexanes, THF, EtH, and EtAc are solvents, and Pd/C is a catalyst. (14 pts) 3
4 N NH Ti 4 Pd/C, H 2 + C H 3 NH 2 toluene hexanes THF a) Calculate the atom economy for synthesis of the product (don t worry about isomers for this part of the problem). See last page for a periodic table. product: C 17 H 17 N 2 MW = g/mol reactants: C 16 H CH 5 N + Ti 4 + H 2 MW = g/mol % = 306.2*100/514 = 59.6% b) Setraline is actually one of the cis isomers of the product shown above, and further workup requires isolation of the correct isomer. If only one of the diastereomers is useful, what does this say about the atom economy calculated in a). Could a synthesis yielding a single enantiomer be greener, even with poorer calculated atom economy? The atom economy is overstated because some of the product is waste (unless it can be re-racemized after separation). An enatiomeric synthesis could be greener even if its atom economy was a little lower. instead to make 1-butanol. The production of 1-butanol, like ethanol, is carried out using microorganisms in 5. The same glucose containing feedstocks (sugar, starch and cellulose) to produce ethanol, can be used water. fuel boiling point ( C) K(octanol water) melting point ( C) ethanol butanol a) Using the stoichiometry of the combustion reaction, determine whether 1-butanol or ethanol, if either, is a more energy dense fuel. (7 pts) reactions: ethanol: C 2 H 5 H C 2 + 3H 2 ratio 2 /C 2 = 3/2 butanol: C 4 H 9 H C 2 + 5H 2 ratio 2 /C 2 = 3/2 so energy density should be similar b) If using the same methods used for ethanol, will isolation of 1-butanol be easier or harder than for ethanol? Explain your answer. (5 pts) It will be harder for 1-butanol because it is less volatile so it will require more heat to distill it from water. 4
5 bonus) Is there a potentially less energy consuming method to transfer 1-butanol to fuel as an additive that is not available to ethanol. (3 pts) Yes. ne could do a direct extraction into fuel because 1-butanol is much less polar. 6. Given the following hypothetical toxin (below), write two possible reactions showing how the listed compound can be metabolized. Indicate if you expect that the product will be eliminated from the body more or less quickly than the original toxin. (10 pts) H Glc H C H 2 H 2 C faster removal H faster removal Glc C H 2 faster removal (Glc = glucose) 5
Green Chemistry Five ways in which the Chemical industry can become Greener Changing to renewable sources Use of alternatives to hazardous chemicals
 Green Chemistry Green Chemistry refers to the processes in the chemical industry that are being reinvented to make them more sustainable. The term sustain means to keep going. If we use resources faster
Green Chemistry Green Chemistry refers to the processes in the chemical industry that are being reinvented to make them more sustainable. The term sustain means to keep going. If we use resources faster
Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle
 Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle David Allen Gertz Regents Professor in Chemical Engineering, and Director, Center for Energy and Environmental Resources Concepts for today Greenhouse Effect
Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle David Allen Gertz Regents Professor in Chemical Engineering, and Director, Center for Energy and Environmental Resources Concepts for today Greenhouse Effect
GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB
 GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB A COMPUTER SIMULATION PROGRAM ON TEMPERATURE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISING After performing this computer simulation lab you will be able to: 1) understand the greenhouse effect
GLOBAL WARMING COMPUTER LAB A COMPUTER SIMULATION PROGRAM ON TEMPERATURE CHANGE AND SEA LEVEL RISING After performing this computer simulation lab you will be able to: 1) understand the greenhouse effect
Global Warming Science Solar Radiation
 SUN Ozone and Oxygen absorb 190-290 nm. Latent heat from the surface (evaporation/ condensation) Global Warming Science Solar Radiation Turbulent heat from the surface (convection) Some infrared radiation
SUN Ozone and Oxygen absorb 190-290 nm. Latent heat from the surface (evaporation/ condensation) Global Warming Science Solar Radiation Turbulent heat from the surface (convection) Some infrared radiation
T8-1 [166 marks] Which energy resource is renewable? A. Natural gas B. Uranium C. Biogas D. Coal
![T8-1 [166 marks] Which energy resource is renewable? A. Natural gas B. Uranium C. Biogas D. Coal T8-1 [166 marks] Which energy resource is renewable? A. Natural gas B. Uranium C. Biogas D. Coal](/thumbs/78/78599564.jpg) T8-1 [166 marks] 1. Which energy resource is renewable? A. Natural gas B. Uranium C. Biogas D. Coal 2. For a black-body at absolute temperature T the power emitted per unit area is P. What is the power
T8-1 [166 marks] 1. Which energy resource is renewable? A. Natural gas B. Uranium C. Biogas D. Coal 2. For a black-body at absolute temperature T the power emitted per unit area is P. What is the power
Name: Class: Date: 6. Most air pollution is produced by a. thermal inversions. c. ozone layer depletion. b. fuel burning. d. volcanic eruptions.
 Name: Class: Date: Air Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is often used to remove poisonous gases from industrial
Name: Class: Date: Air Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is often used to remove poisonous gases from industrial
Planetary Energy Balance
 Planetary Energy Balance Overview of Planetary Energy Balance Energy coming into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun is always in balance with the energy leaving Earth s atmosphere going back out into
Planetary Energy Balance Overview of Planetary Energy Balance Energy coming into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun is always in balance with the energy leaving Earth s atmosphere going back out into
read ALL of Chap. 21 Symbols to know: CO2 = carbon dioxide O2 = oxygen CH4 = methane (natural gas) Glucose = sugar
 read ALL of Chap. 21 Symbols to know: CO2 = carbon dioxide O2 = oxygen CH4 = methane (natural gas) Glucose = sugar Koppen Climate Zones / Factors Carbon Cycle / Ocean Acidification Greenhouse Effect /
read ALL of Chap. 21 Symbols to know: CO2 = carbon dioxide O2 = oxygen CH4 = methane (natural gas) Glucose = sugar Koppen Climate Zones / Factors Carbon Cycle / Ocean Acidification Greenhouse Effect /
read ALL of Chap. 21 Symbols to know: CO2 = carbon dioxide O2 = oxygen CH4 = methane (natural gas) Glucose = sugar
 read ALL of Chap. 21 Symbols to know: CO2 = carbon dioxide O2 = oxygen CH4 = methane (natural gas) Glucose = sugar Koppen Climate Zones / Factors Carbon Cycle / Ocean Acidification Greenhouse Effect /
read ALL of Chap. 21 Symbols to know: CO2 = carbon dioxide O2 = oxygen CH4 = methane (natural gas) Glucose = sugar Koppen Climate Zones / Factors Carbon Cycle / Ocean Acidification Greenhouse Effect /
Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate
 Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Required Reading: FP Chapter 14 (only sections that I cover) Suggested Introductory Reading: Jacob Chapter 7 Atmospheric Chemistry CHEM-5151 / ATOC-5151 Spring
Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Required Reading: FP Chapter 14 (only sections that I cover) Suggested Introductory Reading: Jacob Chapter 7 Atmospheric Chemistry CHEM-5151 / ATOC-5151 Spring
Chapter 11: Atmosphere
 To get you thinking This is our atmosphere. All life on Earth exists within this tiny protective blanket. Why is the atmosphere important to us? What do you think it does for us? Chapter 11: Atmosphere
To get you thinking This is our atmosphere. All life on Earth exists within this tiny protective blanket. Why is the atmosphere important to us? What do you think it does for us? Chapter 11: Atmosphere
The Chemistry of Climate Change. Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy
 The Chemistry of Climate Change Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy The Science of Global Climate There's a lot of differing data, but as far as I can gather, over the
The Chemistry of Climate Change Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy The Science of Global Climate There's a lot of differing data, but as far as I can gather, over the
Chapter 19 Global Change. Wednesday, April 18, 18
 Chapter 19 Global Change Module 62 Global Climate Change and the Greenhouse Effect After reading this module you should be able to distinguish among global change, global climate change, and global warming.
Chapter 19 Global Change Module 62 Global Climate Change and the Greenhouse Effect After reading this module you should be able to distinguish among global change, global climate change, and global warming.
Global Climate Change. The sky is falling! The sky is falling!
 Global Climate Change The sky is falling! The sky is falling! 1 Global Climate Change Radiative Equilibrium, Solar and Earth Radiation Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Global Climate Change
Global Climate Change The sky is falling! The sky is falling! 1 Global Climate Change Radiative Equilibrium, Solar and Earth Radiation Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Global Climate Change
Crude Oil National 4
 Fuels National 4 A fuel is a chemical which burns to give out energy. When a fuel burns the chemical reaction is known as combustion. When combustion takes place the fuel is reacting with oxygen from the
Fuels National 4 A fuel is a chemical which burns to give out energy. When a fuel burns the chemical reaction is known as combustion. When combustion takes place the fuel is reacting with oxygen from the
Carbon dioxide is formed during the complete combustion of octane. + 12½O 2 8CO 2... [1] Why does incomplete combustion sometimes take place?
![Carbon dioxide is formed during the complete combustion of octane. + 12½O 2 8CO 2... [1] Why does incomplete combustion sometimes take place? Carbon dioxide is formed during the complete combustion of octane. + 12½O 2 8CO 2... [1] Why does incomplete combustion sometimes take place?](/thumbs/81/82825046.jpg) 1 Crude oil is a source of hydrocarbons which can be used as fuels or for processing into petrochemicals. Octane, C 8 18, is one of the alkanes present in petrol. Carbon dioxide is formed during the complete
1 Crude oil is a source of hydrocarbons which can be used as fuels or for processing into petrochemicals. Octane, C 8 18, is one of the alkanes present in petrol. Carbon dioxide is formed during the complete
ASTRONOMY 161. Introduction to Solar System Astronomy. Class 16
 ASTRONOMY 161 Introduction to Solar System Astronomy Class 16 Earth s Atmosphere Monday, February 19 Earth s Atmosphere: Key Concepts (1) The Earth s atmosphere consists mainly of nitrogen (N 2 ) and
ASTRONOMY 161 Introduction to Solar System Astronomy Class 16 Earth s Atmosphere Monday, February 19 Earth s Atmosphere: Key Concepts (1) The Earth s atmosphere consists mainly of nitrogen (N 2 ) and
Physics 100 Lecture 17. The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming April 2, 2018
 1 Physics 100 Lecture 17 The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming April 2, 2018 2 Class Quiz Ch. 7: Suppose your car burned bituminous coal instead of gasoline. How much coal would provide the same energy
1 Physics 100 Lecture 17 The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming April 2, 2018 2 Class Quiz Ch. 7: Suppose your car burned bituminous coal instead of gasoline. How much coal would provide the same energy
Chemistry 471/671. Global Climate Change
 Chemistry 471/671 Global Climate Change The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming These are NOT the same thing! To begin with, let s make the distinction 2 Earth Average temperature 15 C Average pressure:
Chemistry 471/671 Global Climate Change The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming These are NOT the same thing! To begin with, let s make the distinction 2 Earth Average temperature 15 C Average pressure:
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 7: 10-16-13 Outline of This Topic Climate forcings Things that directly
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 7: 10-16-13 Outline of This Topic Climate forcings Things that directly
Fig Figure 4.1a on Page 138. Heat Energy. Definition of Energy. Energy, Chemistry, and Society
 Energy, Chemistry, and Society Fig. 4.12 Figure 4.1a on Page 138 Practice Problems: 1, 3, 5-8, 10a, 12a, 13, 20, 22, 26, 27, 36, 46, 47, 48 Definition of Energy Energy is defined as the capacity to do
Energy, Chemistry, and Society Fig. 4.12 Figure 4.1a on Page 138 Practice Problems: 1, 3, 5-8, 10a, 12a, 13, 20, 22, 26, 27, 36, 46, 47, 48 Definition of Energy Energy is defined as the capacity to do
Session 14 Unit VI CLIMATIC CHANGE AND GLOBAL WARMING
 Session 14 Unit VI CLIMATIC CHANGE AND GLOBAL WARMING Dr. H.S. Ramesh Professor of Environmental Engineering S.J. College of Engineering, Mysore 570 006 Carbon di-oxide is a natural constituent of atmosphere,
Session 14 Unit VI CLIMATIC CHANGE AND GLOBAL WARMING Dr. H.S. Ramesh Professor of Environmental Engineering S.J. College of Engineering, Mysore 570 006 Carbon di-oxide is a natural constituent of atmosphere,
Chapter 13 The Earths Atmosphere
 Chapter 3 The Earths Atmosphere Name: Class: Date: Time: 79 minutes Marks: 79 marks Comments: Page of 28 The bar chart shows some of the gases in the atmospheres of Earth today and Mars today. (b) Complete
Chapter 3 The Earths Atmosphere Name: Class: Date: Time: 79 minutes Marks: 79 marks Comments: Page of 28 The bar chart shows some of the gases in the atmospheres of Earth today and Mars today. (b) Complete
TROPICS: insolation high year round, high sun angle and ~ constant duration
 GE 101, February 6, 14 Finish insolation variation Global environmental issues associated with insolation TRPICS: insolation high year round, high sun angle and ~ constant duration MID-LATITUDES: insolation
GE 101, February 6, 14 Finish insolation variation Global environmental issues associated with insolation TRPICS: insolation high year round, high sun angle and ~ constant duration MID-LATITUDES: insolation
Lecture 11: Global Warming. Human Acticities. Natural Climate Changes. Global Warming: Natural or Man-Made CO 2 CH 4
 Lecture 11: Global Warming Human Acticities CO 2 CH 4 The initial appearance of human species: last 100,000 to 200,000 years Development of the first civilization: the last 10,000 years What is the sensitivity
Lecture 11: Global Warming Human Acticities CO 2 CH 4 The initial appearance of human species: last 100,000 to 200,000 years Development of the first civilization: the last 10,000 years What is the sensitivity
Some resources (more websites later)
 Some resources (more websites later) Intergovernmental Panel Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis at http://www.ipcc.ch/pub/reports.htm John Houghton Global Warming - the complete briefing Cambridge
Some resources (more websites later) Intergovernmental Panel Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis at http://www.ipcc.ch/pub/reports.htm John Houghton Global Warming - the complete briefing Cambridge
Arctic shipping activities and possible consequences for the regional climate
 Arctic shipping activities and possible consequences for the regional climate Andreas Massling, Department of Environmental Science, Aarhus University, Roskilde, Denmark Jesper Christensen, Department
Arctic shipping activities and possible consequences for the regional climate Andreas Massling, Department of Environmental Science, Aarhus University, Roskilde, Denmark Jesper Christensen, Department
Sulfur oxides (SO x ) - particularly sulfur dioxide, a chemical compound with the formula SO 2. SO 2 is produced by volcanoes and in various
 AIR CANCER Sulfur oxides (SO x ) - particularly sulfur dioxide, a chemical compound with the formula SO 2. SO 2 is produced by volcanoes and in various industrial processes. Coal and petroleum often
AIR CANCER Sulfur oxides (SO x ) - particularly sulfur dioxide, a chemical compound with the formula SO 2. SO 2 is produced by volcanoes and in various industrial processes. Coal and petroleum often
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007
 ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
Hydrocarbons contain the elements... and... only. (1) H 6. Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence.
 Q. Alkanes are hydrocarbons found in crude oil. (a) (i) Complete the sentence. Hydrocarbons contain the elements... and... only. () Ethane is an alkane with the formula C H 6 Draw a ring around the correct
Q. Alkanes are hydrocarbons found in crude oil. (a) (i) Complete the sentence. Hydrocarbons contain the elements... and... only. () Ethane is an alkane with the formula C H 6 Draw a ring around the correct
crude oil is evaporated/vaporised (by heating) 1 the vapours are condensed (by cooling) 1
 M. (a) allow answers referring specifically to the naphtha fraction crude oil is evaporated/vaporised (by heating) the vapours are condensed (by cooling) (fractions condense) / boil at different temperatures
M. (a) allow answers referring specifically to the naphtha fraction crude oil is evaporated/vaporised (by heating) the vapours are condensed (by cooling) (fractions condense) / boil at different temperatures
GEOG 401: Week 2 Earth s Energy Balance
 GEOG 401: Week 2 Earth s Energy Balance Dr. John Abatzoglou Spring 2011 Lecture Goals (1) Understand the global balance of energy and associated fluxes of energy and energy types (2) Qualita@ve and quan@ta@ve
GEOG 401: Week 2 Earth s Energy Balance Dr. John Abatzoglou Spring 2011 Lecture Goals (1) Understand the global balance of energy and associated fluxes of energy and energy types (2) Qualita@ve and quan@ta@ve
Atmospheric Chemistry
 Atmospheric Chemistry Research Dr. Husam T. Majeed Department of Atmospheric Sciences 2nd Year Class First Semester 2018-2019 Course Syllabus 1. Introduction & Review Atmospheric Chemistry Box Models and
Atmospheric Chemistry Research Dr. Husam T. Majeed Department of Atmospheric Sciences 2nd Year Class First Semester 2018-2019 Course Syllabus 1. Introduction & Review Atmospheric Chemistry Box Models and
Renewable Energy Alternatives
 Renewable Energy Alternatives Reasons for Alternative Energy Fossil fuels won t last forever Renewable unlikely to run out Decrease air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions Less dependent on other nations
Renewable Energy Alternatives Reasons for Alternative Energy Fossil fuels won t last forever Renewable unlikely to run out Decrease air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions Less dependent on other nations
Errata to Global Warming: Understanding the Forecast 2nd Printing, 2008
 Errata to Global Warming: Understanding the Forecast 2nd Printing, 28 Chapter 3 Page 22. Formula 3.1, the fourth root is written incorrectly as the square root (there should be a little number 4 in superscript
Errata to Global Warming: Understanding the Forecast 2nd Printing, 28 Chapter 3 Page 22. Formula 3.1, the fourth root is written incorrectly as the square root (there should be a little number 4 in superscript
National 4 Chemistry. Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry Summary Notes
 National 4 Chemistry Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry Summary Notes Success Criteria I am confident that I understand this and I can apply this to problems? I have some understanding but I need to revise this
National 4 Chemistry Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry Summary Notes Success Criteria I am confident that I understand this and I can apply this to problems? I have some understanding but I need to revise this
Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases. Course Goals
 PCC 588 - January 6 and 8 2009 Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases T,Th 12:00-1:20 pm OSB 25 Course Goals The course focuses on factors controlling the global cycle
PCC 588 - January 6 and 8 2009 Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases T,Th 12:00-1:20 pm OSB 25 Course Goals The course focuses on factors controlling the global cycle
Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium
 Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium review session CCIU April 30, 2016 High-school standard HS-ESS2-4 focuses on the role energy flows play in Earth s climate HS-ESS2-4 Use a model to describe how variations
Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium review session CCIU April 30, 2016 High-school standard HS-ESS2-4 focuses on the role energy flows play in Earth s climate HS-ESS2-4 Use a model to describe how variations
OVERVIEW AND INTRO TO CLIMATE SCIENCE MIT SUMMER HSSP, 2016 WEEK 1
 OVERVIEW AND INTRO TO CLIMATE SCIENCE MIT SUMMER HSSP, 2016 WEEK 1 COURSE OVERVIEW THIS IS GOING TO BE FUN (I HOPE ) JOSH S BACKGROUND MIT: 2 nd Year Ph.D. Student Researching Atmospheric Chemistry U.C.
OVERVIEW AND INTRO TO CLIMATE SCIENCE MIT SUMMER HSSP, 2016 WEEK 1 COURSE OVERVIEW THIS IS GOING TO BE FUN (I HOPE ) JOSH S BACKGROUND MIT: 2 nd Year Ph.D. Student Researching Atmospheric Chemistry U.C.
Possible Exam Questions for Other Topics in Chemistry 10
 Climate Change (first exam) Possible Exam Questions for Other Topics in Chemistry 10 1. Convert between the following terms and definitions Anthracite = the highest rank of coal harder, glossy black coal
Climate Change (first exam) Possible Exam Questions for Other Topics in Chemistry 10 1. Convert between the following terms and definitions Anthracite = the highest rank of coal harder, glossy black coal
Global Climatic Change. GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 22 Ahrens: Chapter 16
 Global Climatic Change GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 22 Ahrens: Chapter 16 Global Climatic Change! Review: Radiation balance! Enhanced greenhouse effect! human-induced change! Climate feedbacks Climatic change!
Global Climatic Change GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 22 Ahrens: Chapter 16 Global Climatic Change! Review: Radiation balance! Enhanced greenhouse effect! human-induced change! Climate feedbacks Climatic change!
Climate Change and Ozone Loss
 Climate Change and Ozone Loss During the past 900,000 years, the earth has undergone a series of cold glacial periods followed by warmer interglacial periods. The past 10,000 years has been an interglacial
Climate Change and Ozone Loss During the past 900,000 years, the earth has undergone a series of cold glacial periods followed by warmer interglacial periods. The past 10,000 years has been an interglacial
Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Volcanic Eruptions and Global Temperature
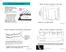 Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Radiative forcing of climate change
 Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
succeeding in the vce, 2017
 Unit 3 Chemistry succeeding in the vce, 2017 extract from the master class teaching materials Our Master Classes form a component of a highly specialised weekly program, which is designed to ensure that
Unit 3 Chemistry succeeding in the vce, 2017 extract from the master class teaching materials Our Master Classes form a component of a highly specialised weekly program, which is designed to ensure that
SUCCEEDING IN THE VCE 2017 UNIT 3 CHEMISTRY STUDENT SOLUTIONS
 SUCCEEDING IN THE VCE 017 UNIT CHEMISTRY STUDENT SOLUTIONS FOR ERRORS AND UPDATES, PLEASE VISIT WWW.TSFX.COM.AU/VCE-UPDATES QUESTION 1 The word "released" takes the negative sign into consideration. Answer
SUCCEEDING IN THE VCE 017 UNIT CHEMISTRY STUDENT SOLUTIONS FOR ERRORS AND UPDATES, PLEASE VISIT WWW.TSFX.COM.AU/VCE-UPDATES QUESTION 1 The word "released" takes the negative sign into consideration. Answer
Earth's Atmosphere. Atmospheric Layers. Atmospheric Layers
 Earth's Atmosphere Today we will talk about the part of Earth that is most important to our survival - the atmosphere Earth's atmosphere is unique in the Solar System and has changed greatly over time
Earth's Atmosphere Today we will talk about the part of Earth that is most important to our survival - the atmosphere Earth's atmosphere is unique in the Solar System and has changed greatly over time
The Greenhouse Effect
 Name: Date: The Greenhouse Effect This document provides an overview of the earth's atmospheric "greenhouse effect" by briefly exploring the atmospheres of nearby planets and discussing our atmosphere's
Name: Date: The Greenhouse Effect This document provides an overview of the earth's atmospheric "greenhouse effect" by briefly exploring the atmospheres of nearby planets and discussing our atmosphere's
Welcome to ATMS 111 Global Warming.
 Welcome to ATMS 111 Global Warming http://www.atmos.washington.edu/2010q1/111 Censored Spotted by Jennifer Le Today Review and Finish up The Greenhouse Effect - RG p 21-30 A rogues gallery of greenhouse
Welcome to ATMS 111 Global Warming http://www.atmos.washington.edu/2010q1/111 Censored Spotted by Jennifer Le Today Review and Finish up The Greenhouse Effect - RG p 21-30 A rogues gallery of greenhouse
Climate Change and Air Quality
 Climate Change and Air Quality SW PA Air Quality Action June 6, 2007 Peter J. Adams Associate Professor Civil and Environmental Engineering Engineering and Public Policy Outline Climate Change Primer What
Climate Change and Air Quality SW PA Air Quality Action June 6, 2007 Peter J. Adams Associate Professor Civil and Environmental Engineering Engineering and Public Policy Outline Climate Change Primer What
Climate Change Questions, Condensed
 Climate Change Questions, Condensed Chapter 8: Earth s Climate System and Natural Change Climate and Weather - Weather is the atmospheric conditions such as temperature, precipitation, wind, and humidity
Climate Change Questions, Condensed Chapter 8: Earth s Climate System and Natural Change Climate and Weather - Weather is the atmospheric conditions such as temperature, precipitation, wind, and humidity
Figure 1 - Global Temperatures - A plot from the EarthScience Centre at
 GLOBAL WARMING Global warming is evidenced by a steady rise in average global temperatures, changing climate, the fact that snow cover has decreased 10% over the past half-century and that glaciers have
GLOBAL WARMING Global warming is evidenced by a steady rise in average global temperatures, changing climate, the fact that snow cover has decreased 10% over the past half-century and that glaciers have
Lecture 2: Greenhouse Gases - Basic Background on Atmosphere - GHG Emission and Concentration Rise - California Regulation (AB32)
 Lecture 2: Greenhouse Gases - Basic Background on Atmosphere - GHG Emission and Concentration Rise - California Regulation (AB32) METR 113/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 February 15, 2011 Suggested Reading
Lecture 2: Greenhouse Gases - Basic Background on Atmosphere - GHG Emission and Concentration Rise - California Regulation (AB32) METR 113/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 February 15, 2011 Suggested Reading
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change MODULE 11: GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE UNIT 1: BIODIVERSITY Objectives Define terms. Understand global climate change. Describe the basic predictions of the global climate models. Understand
Global Climate Change MODULE 11: GLOBAL CLIMATE CHANGE UNIT 1: BIODIVERSITY Objectives Define terms. Understand global climate change. Describe the basic predictions of the global climate models. Understand
Human impact on the environment
 1 of 36 Boardworks Ltd 2006 2 of 36 Boardworks Ltd 2006 Human impact on the environment 3 of 36 Boardworks Ltd 2006 How does human activity affect the environment? Population growth 4 of 36 Boardworks
1 of 36 Boardworks Ltd 2006 2 of 36 Boardworks Ltd 2006 Human impact on the environment 3 of 36 Boardworks Ltd 2006 How does human activity affect the environment? Population growth 4 of 36 Boardworks
Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
 Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Air Pollution Air pollution- the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough
Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Air Pollution Air pollution- the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough
08 Energy, Power and climate change review answers
 08 Energy, Power and climate change review answers Power generation 1. Copy and complete: Thermal energy may be completely converted into work in a single process such as the adiabatic expansion of a gas
08 Energy, Power and climate change review answers Power generation 1. Copy and complete: Thermal energy may be completely converted into work in a single process such as the adiabatic expansion of a gas
Interesting points from presentations
 Interesting points from presentations The topics can be broken down, roughly, into the following categories Emissions of NOx, CO, VOCs, and other gases that influence ozone (and, thus, OH) Electric Vehicles
Interesting points from presentations The topics can be broken down, roughly, into the following categories Emissions of NOx, CO, VOCs, and other gases that influence ozone (and, thus, OH) Electric Vehicles
Figure 1 CO2 Levels vs. Volcanic Activity
 Figure 1 CO2 Levels vs. Volcanic Activity Note: Stratospheric Optical Thickness is the measure of aerosols (e.g., urban haze, smoke particles, desert dust, sea salt) distributed within a column of air
Figure 1 CO2 Levels vs. Volcanic Activity Note: Stratospheric Optical Thickness is the measure of aerosols (e.g., urban haze, smoke particles, desert dust, sea salt) distributed within a column of air
complex systems many different variables many alternative theories 1
 M.(a) any one from: complex systems many different variables many alternative theories (b) carbon dioxide allows short wavelength radiation to pass through allow greenhouse gas(es) for carbon dioxide the
M.(a) any one from: complex systems many different variables many alternative theories (b) carbon dioxide allows short wavelength radiation to pass through allow greenhouse gas(es) for carbon dioxide the
The Earth s Atmosphere-I. GEOL 1350: Introduction To Meteorology
 The Earth s Atmosphere-I GEOL 1350: Introduction To Meteorology 1 Overview What is the composition of Atmosphere? How did the atmosphere arrive at its current state? 2 Earth s Atmosphere Earth s atmosphere
The Earth s Atmosphere-I GEOL 1350: Introduction To Meteorology 1 Overview What is the composition of Atmosphere? How did the atmosphere arrive at its current state? 2 Earth s Atmosphere Earth s atmosphere
Global Warming & Climate Change Review Learning Target 1
 Learning Target 1 Click and drag the word to fit the proper description. Word Ice Off Dates Ice Core Samples Description 1.Scientist can check the gases in the bubbles and provide a good estimate of the
Learning Target 1 Click and drag the word to fit the proper description. Word Ice Off Dates Ice Core Samples Description 1.Scientist can check the gases in the bubbles and provide a good estimate of the
How can hydrocarbons be broken down into smaller molecules? What is an alkane? Give an example and draw it
 How can hydrocarbons be broken down into smaller molecules? What is an alkane? Give an example and draw it What kind of reaction happens when large hydrocarbons are broken down? What is the general formula
How can hydrocarbons be broken down into smaller molecules? What is an alkane? Give an example and draw it What kind of reaction happens when large hydrocarbons are broken down? What is the general formula
Biomass and Biofuels
 Biomass and Biofuels PHYS 4400, Principles and Varieties of Solar Energy Instructor: Randy J. Ellingson The University of Toledo February 11, 2014 What is bioenergy? Photosynthesis: the primary energy
Biomass and Biofuels PHYS 4400, Principles and Varieties of Solar Energy Instructor: Randy J. Ellingson The University of Toledo February 11, 2014 What is bioenergy? Photosynthesis: the primary energy
The Production of Electricity Power from Natural Gas. Image Source: Mscalora
 The Production of Electricity Power from Natural Gas Image Source: Mscalora How does it work? Natural Gas can be converted to Electricity using a Gas Turbine Power Plant While gas turbines can power up
The Production of Electricity Power from Natural Gas Image Source: Mscalora How does it work? Natural Gas can be converted to Electricity using a Gas Turbine Power Plant While gas turbines can power up
C1 The Essential Questions
 C1 The Essential Questions Name... Fundamental ideas (12 marks) ALWAYS ON THE EXAM 1. Complete the sentences: (i) The atomic number of an atom is the number of... (ii) The mass number of an atom is the
C1 The Essential Questions Name... Fundamental ideas (12 marks) ALWAYS ON THE EXAM 1. Complete the sentences: (i) The atomic number of an atom is the number of... (ii) The mass number of an atom is the
Global Warming and the Hydrological Cycle
 Global Warming and the Hydrological Cycle Climate Change Projections Wet regions will become wetter Dry regions will become drier Precipitation will occur less frequently Precipitation will be more intense
Global Warming and the Hydrological Cycle Climate Change Projections Wet regions will become wetter Dry regions will become drier Precipitation will occur less frequently Precipitation will be more intense
Greenhouse Effect. How we stay warm
 Greenhouse Effect How we stay warm The Sun s energy reaches Earth through Radiation (heat traveling through Space) How much solar radiation reaches Earth? The Earth s surface only absorbs 51% of incoming
Greenhouse Effect How we stay warm The Sun s energy reaches Earth through Radiation (heat traveling through Space) How much solar radiation reaches Earth? The Earth s surface only absorbs 51% of incoming
Climate Change Vocabulary Global Challenges for the 21 st Century Tony Del Vecchio, M.Ed. Atmosphere
 Atmosphere The mixture of gases surrounding the Earth. The Earth's atmosphere consists of about 79.1% nitrogen (by volume), 20.9% oxygen, 0.036% carbon dioxide and trace amounts of other gases. The atmosphere
Atmosphere The mixture of gases surrounding the Earth. The Earth's atmosphere consists of about 79.1% nitrogen (by volume), 20.9% oxygen, 0.036% carbon dioxide and trace amounts of other gases. The atmosphere
Normal equatorial flow. Climate Variability. El Niño-Southern Oscillation Human-caused climate change Alternative Energy sources
 Normal equatorial flow Climate Variability El Niño-Southern Oscillation Human-caused climate change Alternative Energy sources Vertical normal flow ENSO disruption of flow Vertical ENSO flow Normal vs.
Normal equatorial flow Climate Variability El Niño-Southern Oscillation Human-caused climate change Alternative Energy sources Vertical normal flow ENSO disruption of flow Vertical ENSO flow Normal vs.
1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 CHAPTER 22 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are the layers of Earth s atmosphere? How has Earth s atmosphere
CHAPTER 22 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are the layers of Earth s atmosphere? How has Earth s atmosphere
Climate Change, Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols
 Climate Change, Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols J Srinivasan J Srinivasan is a Professor at the Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences at Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. He was a lead author
Climate Change, Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols J Srinivasan J Srinivasan is a Professor at the Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences at Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. He was a lead author
Alternative Fuels, How to improve air quality
 Alternative Fuels, How to improve air quality 1 1 1 1 1 1 Introduction Nearly one-fifth of pollution in the USA is caused by cars and trucks. Fossil fuel-powered transportation is the primary contributor
Alternative Fuels, How to improve air quality 1 1 1 1 1 1 Introduction Nearly one-fifth of pollution in the USA is caused by cars and trucks. Fossil fuel-powered transportation is the primary contributor
ENVIS- IITM NEWSLETTER The Air Quality: A Global Challenge
 ENVIS- IITM NEWSLETTER The Air Quality: A Global Challenge GLOBAL WARMING Editorial Prof. B.N. Goswami (Director, IITM, Pune) Dr. G. Beig (ENVIS Co-ordinetor) Ms. Neha S. Parkhi (Program Officer) Mr. Rajnikant
ENVIS- IITM NEWSLETTER The Air Quality: A Global Challenge GLOBAL WARMING Editorial Prof. B.N. Goswami (Director, IITM, Pune) Dr. G. Beig (ENVIS Co-ordinetor) Ms. Neha S. Parkhi (Program Officer) Mr. Rajnikant
Have We Had an Impact? Global Warming. 3 Forms of Heat Transfer. Thickness of Earth s Atmosphere. The Impact on Engineering
 Have We Had an Impact? Global Warming The Impact on Engineering Have We Had an Impact? Have We Had an Impact? Thickness of Earth s Atmosphere 3 Forms of Heat Transfer The Earth s atmosphere is very thin.
Have We Had an Impact? Global Warming The Impact on Engineering Have We Had an Impact? Have We Had an Impact? Thickness of Earth s Atmosphere 3 Forms of Heat Transfer The Earth s atmosphere is very thin.
Fuels. N4 & N5 Homework Questions
 St Peter the Apostle High school Chemistry Department Fuels N4 & N5 Homework Questions Answer questions as directed by your teacher. National 4 level questions are first followed by National 5 level questions.
St Peter the Apostle High school Chemistry Department Fuels N4 & N5 Homework Questions Answer questions as directed by your teacher. National 4 level questions are first followed by National 5 level questions.
Aerosols (sources and processes)
 Aerosols (sources and processes) Soot is composed of aggregates of small particles (asbestos) rainout (wet deposition) Number Aerosol number is dominated by fine and ultrafine particles; aerosol mass
Aerosols (sources and processes) Soot is composed of aggregates of small particles (asbestos) rainout (wet deposition) Number Aerosol number is dominated by fine and ultrafine particles; aerosol mass
Q1.Scientists study the atmosphere on planets and moons in the Solar System to understand how the Earth s atmosphere has changed.
 Q1.Scientists study the atmosphere on planets and moons in the Solar System to understand how the Earth s atmosphere has changed. (a) Millions of years ago the Earth s atmosphere was probably just like
Q1.Scientists study the atmosphere on planets and moons in the Solar System to understand how the Earth s atmosphere has changed. (a) Millions of years ago the Earth s atmosphere was probably just like
Topic 6 National Chemistry Summary Notes. Fuels. Fuels and Combustion
 Topic 6 National Chemistry Summary Notes Fuels LI 1 Fuels and Combustion Coal, oil, gas and wood can all be used as fuels. These fuels have energy-rich chemical bonds which were created using the energy
Topic 6 National Chemistry Summary Notes Fuels LI 1 Fuels and Combustion Coal, oil, gas and wood can all be used as fuels. These fuels have energy-rich chemical bonds which were created using the energy
Atmospheric Chemistry (Option 1B)
 Atmospheric Chemistry (Option 1B) Introduction Option 1B consists of the following subsections: 1B.1 Oxygen 1B.2 Nitrogen 1B.3 Carbon Dioxide 1B.4 Atmospheric Pollution 1B.5 The Ozone Layer Some chemistry
Atmospheric Chemistry (Option 1B) Introduction Option 1B consists of the following subsections: 1B.1 Oxygen 1B.2 Nitrogen 1B.3 Carbon Dioxide 1B.4 Atmospheric Pollution 1B.5 The Ozone Layer Some chemistry
THE BIG ISLAND of Hawaii
 THE BIG ISLAND of Hawaii WHAT S AHEAD 18.1 EARTH S ATMOSPHERE 18.2 HUMAN ACTIVITYES AND EARTH S ATMOSPHERE 18.3 EARTH S WATER 18.4 HUMAN ACTIVITYES AND EARTH S WATER 18.5 GREEN CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 18.1 EARTH
THE BIG ISLAND of Hawaii WHAT S AHEAD 18.1 EARTH S ATMOSPHERE 18.2 HUMAN ACTIVITYES AND EARTH S ATMOSPHERE 18.3 EARTH S WATER 18.4 HUMAN ACTIVITYES AND EARTH S WATER 18.5 GREEN CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 18.1 EARTH
Aerosols. Liquid or solid particles suspended in the air. Some occur naturally, originating from volcanoes, dust storms, forest and grassland fires,
 Aerosols. Liquid or solid particles suspended in the air. Some occur naturally, originating from volcanoes, dust storms, forest and grassland fires, living vegetation, and sea spray.. Some are anthropogenic:
Aerosols. Liquid or solid particles suspended in the air. Some occur naturally, originating from volcanoes, dust storms, forest and grassland fires, living vegetation, and sea spray.. Some are anthropogenic:
Period 26 Solutions: Using Energy Wisely
 Period 26 Solutions: Using Energy Wisely Activity 26.1: Comparison of Energy Sources for Generating Electricity 1) Comparison of energy sources a) Fill in the table below to describe the advantages and
Period 26 Solutions: Using Energy Wisely Activity 26.1: Comparison of Energy Sources for Generating Electricity 1) Comparison of energy sources a) Fill in the table below to describe the advantages and
GREENHOUSE GASES 3/14/2016. Water Vapor, CO 2, CFCs, Methane and NO x all absorb radiation Water vapor and CO 2 are the primary greenhouse gases
 GREENHOUSE EFFECT The earth is like a greenhouse The atmosphere acts like the glass which lets the sun s rays pass through. The earth absorbs this as heat energy and keeps it in, only letting a little
GREENHOUSE EFFECT The earth is like a greenhouse The atmosphere acts like the glass which lets the sun s rays pass through. The earth absorbs this as heat energy and keeps it in, only letting a little
Topic # 7 Part II ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
 Topic # 7 Part II ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION All about the GASES IN THE ATMOSPHERE, esp. GREENHOUSE GASES! Class Notes pp 37-41 REVIEW: ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE The changes in temperature
Topic # 7 Part II ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION All about the GASES IN THE ATMOSPHERE, esp. GREENHOUSE GASES! Class Notes pp 37-41 REVIEW: ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE The changes in temperature
Higher temperatures will lead to... Animal extinctions
 what will you do? 1 Humans have been found guilty of damaging the system that maintains life on Earth. World News Why does climate change matter? Polar ice caps melting In the past, we were not sure why
what will you do? 1 Humans have been found guilty of damaging the system that maintains life on Earth. World News Why does climate change matter? Polar ice caps melting In the past, we were not sure why
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Climate Climate is characterized by the statistical properties of the weather over a period of time, including averages of local variables such as temperature, winds, humidity, pressure,
Global Climate Change Climate Climate is characterized by the statistical properties of the weather over a period of time, including averages of local variables such as temperature, winds, humidity, pressure,
ANSWERS: Combustion. 2C3H8(g) + 7O2(g) 6CO(g) + 8H2O(g)
 ANSWERS: Combustion organic molecule methane equation for complete combustion CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) equation for incomplete combustion 4CH4(g) + 5O2(g) 2CO(g) + 2C(s) + 8H2O(g) methanol 2CH3OH(l)
ANSWERS: Combustion organic molecule methane equation for complete combustion CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) equation for incomplete combustion 4CH4(g) + 5O2(g) 2CO(g) + 2C(s) + 8H2O(g) methanol 2CH3OH(l)
Radiative Forcing Components
 Radiative Forcing Components Content Definition of Radiative Forcing Radiation Balance Climate sensitivity Solar forcing Forcing due to atmospheric gas Definition of Radiative Forcing In climate science,
Radiative Forcing Components Content Definition of Radiative Forcing Radiation Balance Climate sensitivity Solar forcing Forcing due to atmospheric gas Definition of Radiative Forcing In climate science,
Greenhouse Effect Teacher Notes
 Before our present atmosphere was formed, radiant heat from the Sun was directly reflected from Earth s surface to be lost out into space. The original atmosphere was made up of hydrogen, water vapour,
Before our present atmosphere was formed, radiant heat from the Sun was directly reflected from Earth s surface to be lost out into space. The original atmosphere was made up of hydrogen, water vapour,
1 st find water. Search for Life
 1 st find water Search for Life Phoenix landed Phoenix Sunday found water 25 May in 2008 2008 Search for life 2 nd look for organic molecules Definition of organic molecules contains C and H Examples sugars,
1 st find water Search for Life Phoenix landed Phoenix Sunday found water 25 May in 2008 2008 Search for life 2 nd look for organic molecules Definition of organic molecules contains C and H Examples sugars,
You are almost done! TESTS 1 RQ: RQ-9. 1 Test: Test #4 & the Final Exam. After this week... here s what s left:
 Where are we now? You are almost done! After this week... here s what s left: TESTS 1 RQ: RQ-9 1 Test: Test #4 & the Final Exam A few wrap-up questions to start.... CLICKER TIME!! FLIP BACK TO p 56 in
Where are we now? You are almost done! After this week... here s what s left: TESTS 1 RQ: RQ-9 1 Test: Test #4 & the Final Exam A few wrap-up questions to start.... CLICKER TIME!! FLIP BACK TO p 56 in
Topic 8: Energy, power and climate change
 Topic 8: Energy, power and climate change 8.1 Energy degradation and power generation 8.1.1 State that thermal energy may be completely converted to work in a single process, but that continuous conversion
Topic 8: Energy, power and climate change 8.1 Energy degradation and power generation 8.1.1 State that thermal energy may be completely converted to work in a single process, but that continuous conversion
Air Pollution Types of air pollutants
 Air Pollution Types of air pollutants 1.Carbon compounds (e.g., CO2,CO) 2.Sulphur compounds (e.g., SO2, H2S and H2SO4) 3.Nitrogen oxides (e.g., NO, NO2 and HNO3 ) 4.Ozone (e.g., O3) 5.Fluorocarbons 6.Hydrocarbons
Air Pollution Types of air pollutants 1.Carbon compounds (e.g., CO2,CO) 2.Sulphur compounds (e.g., SO2, H2S and H2SO4) 3.Nitrogen oxides (e.g., NO, NO2 and HNO3 ) 4.Ozone (e.g., O3) 5.Fluorocarbons 6.Hydrocarbons
Global Warming. By William K. Tong. Adjunct Faculty, Earth Science Oakton Community College
 Global Warming By William K. Tong Adjunct Faculty, Earth Science Oakton Community College What Is Global Warming? According to the National Academy of Sciences, the Earth's surface temperature has risen
Global Warming By William K. Tong Adjunct Faculty, Earth Science Oakton Community College What Is Global Warming? According to the National Academy of Sciences, the Earth's surface temperature has risen
The September Equinox is today: Sep 23rd! It s considered the traditional end of Summer and the beginning of Fall
 More coming up in Topic #11 (class notes p 61) The September Equinox is today: Sep 23rd! It s considered the traditional end of Summer and the beginning of Fall The Sun s rays have greatest intensity right
More coming up in Topic #11 (class notes p 61) The September Equinox is today: Sep 23rd! It s considered the traditional end of Summer and the beginning of Fall The Sun s rays have greatest intensity right
Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011
 Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011 Reading Henson Rough Guide Chapter 1 Pages 75 127; 215; 227-244 Other pages
Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011 Reading Henson Rough Guide Chapter 1 Pages 75 127; 215; 227-244 Other pages
UNDERSTANDING HUMAN IMPACT ON EARTH SYSTEMS
 UNDERSTANDING HUMAN IMPACT ON EARTH SYSTEMS EVIDENCE OF BASIC KNOWLEDGE Science concepts and processes that help us have a more global understanding of our earth and the role human activity has on it.
UNDERSTANDING HUMAN IMPACT ON EARTH SYSTEMS EVIDENCE OF BASIC KNOWLEDGE Science concepts and processes that help us have a more global understanding of our earth and the role human activity has on it.
Topic # 7 ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
 Topic # 7 ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION All about the GASES IN THE ATMOSPHERE, esp. GREENHOUSE GASES! Class Notes pp 37-41 OBJECTIVES: To understand: -- the VERTICALSTRUCTURE of the atmosphere
Topic # 7 ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION All about the GASES IN THE ATMOSPHERE, esp. GREENHOUSE GASES! Class Notes pp 37-41 OBJECTIVES: To understand: -- the VERTICALSTRUCTURE of the atmosphere
