Alkaraji, un grand hydrologue iranien du IX e siècle
|
|
|
- Magdalen Johnson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Alkaraji, an Iranian Great Hydrologist in IXt h Century Alkaraji, un grand hydrologue iranien du IX e siècle Arash MALEKIAN Mohammad Javad POURAGHNIAEI Faculty of Natural Resources, University of Tehran PO Box , Karaj (Iran) arshmalek@yahoo.com m_pouraghniaei@yahoo.com Abstract The human civilization from beginning to this time include the name of great scientists that have had the major role in development and advancement of science, therefore our current knowledge is the collection of their efforts in different countries in centuries and years ago. Unfortunately some of these scientists that have had the advanced theories are unknown and their name aren t famous between current scientists. Iran, between the ancient civilized countries was the area of science exchange and dialogue of cultures. Iran was the origin of one of the oldest human cultures; because of it s major geopolitics conditions and it s location in the cross of east and west (in that time the most transport was by land travelling). Then Iranian and Muslims scientists have a great role in compliance of science, and in this paper we will introduce one of the greatest hydrologist in IX th century. Abol haseb-mohammad Alkaraji, the greatest Iranian Hydrologist, lived in IX th century. His advanced theories (which is valuable yet) are described in some books such as his ideas on hydrology and ground water in the book Exploitation of Hidden Waters but this scholar scientist isn t known in scientific communities of the world. He described most subjects related to hydrology and has some ideas on these matters. Most of his ideas are valid after hundred years. This paper describes Some of Alkaraji s ideas, including the reason of precipitation and closed cycle of water. Reason of water flow in the porosity media (hundred years before H. Darcy and Euler) on ground water and the genesis of springs and the effect of earth quick on its genesis, Geyser springs, different methods to finding aquifers and groundwater resources such as divining wells, study the vegetation cover, soil, geology and the study of physical and chemical properties of water, method of construction of Qanat, water refining and so on. 1
2 Alkaraji had had many trips to some of Islamic areas where were progressive in science on that time. His books are the collection and results of his experiences and enormous genius in many years ago. Note: Alkaraji s book isn t translated in English yet. The original book in Arabic language is in Paris museum. * * * 1. Introduction Iran, in its long history is the origin of many developed civilizations that have had deep effects on human and science history in the world. Because of considerable role and importance of Iran and Iranian scientists during history, it s impossible to ignore their efforts. One of the most important reasons for science development in ancient Iran was its special geographic and climatological condition. Mean rainfall in Iran is about on third of its average in the world and about two thirds of Iran has arid and semi-arid condition. There are some areas that don t receive a drop of rain in some years but a rainstorm cause suddenly big flood that destroys all things. These and other conditions such as hot days, cold nights, high evaporation and less biomass are the characteristics of most parts of Iran. For this reasons, water and its related science (hydrology) and study of the relationship between water and its environment and Iranian scientist has had major impression in development and evolution of hydrology, but many of these scientists and their theories are unknown up to this time. One of the greatest hydrologists is Abubakr-Mohammed-Ebn-Alhassan- Ashaseb-Alkaraji in IXt h Century. He borne in central part of Iran and traveled to many Islamic countries. He has written some books in natural sciences, but his the most famous book and also the emphasis of this paper is related to his book in hydrology entitled exploitation of hidden water. 2. Book Alkaraji, Iranian unknown genius scientist, as we know, has written twelve books in branches of science specially in math s and physics that some of them are as follow: Albadie fel Hesab (Introduction to Math), Alkafi fel Hesab (Compliance in Math) and Elal Hesab Eljabr (Reason of Algebra). Because of focus of the symposium Origin and History of Hydrology (OH 2 ), we will introduce his book in the field of hydrology and Ground water. In this book, Alkaraji has discussed and illustrated about some advanced theories in the 2
3 field of Water, Geology and vegetation cover study related to different parts of Hydrology in IXt h Century. 3. Alkaraji s theories 3.1. Gravity Force and spherical form of Earth Alkaraji before other scientists discussed about spherical form of Earth and he supposed the reason of water flows for this form of Earth. Also he defined the form of Earth as: Earth with it s mountains, plains, valleys and seas is spherical and all materials (solid, liquid) tend to center of Earth (Gravity force). Gravity force theory is related to Newton in 1727 but scientists and also Newton didn t know that Iranian scientist on thousand year before him discussed this theory clarify; any parts of things are polled to center of Earth. In other parts of his book wrote: The reason of destroying and damaging of building is their tendency to the center of Earth. We know exploration of gravity force is one of the important bases of the development of science. Karaji using this theory discussed and based to other theories and Newton using physical and math s proved it Equilibrium of forces in the Earth Alkaraji has written that because of mountain, valley and sea, the form of Earth is not absolute spheroid, because, if it was spherical, water covered all parts and there wasn t anywhere for living of people and animal. With tendency to center and Semi-spheroid theories he proved another theory named Equilibrium of Force and said: All forces that act on n material in Earth must be equilibrated in center of Earth Close cycle of Water and Environment and reason of precipitation Alkaraji has written: Sun absorbs the sweetest and lees denser parts of water and transforms it into air. Also : Transformation of air (vapor) to water in cold days and regions and retransformation of water to air (vapor) in warm days and regions cause a flow and is important in reclamation of lands, agriculture and irrigation. In the subject of precipitation he wrote: Water after saturation in land, comes to sea and origin of most water is from snow, rainfall and reaction of air (vapor) and water. 3
4 3.4. The reason of water flow He related this reason with gravity forces and surface differences and discussed its differences absolutely form center of Earth. But today, we suppose surface differences between two locations. H. Darcy in 1857 found the friction coefficient between liquid and bed of stream and discussed on water flows using physical and mathematical theories. Alkaraji, in IX th Century wrote: Water, as other materials tend to flow to the center of Earth form high to low elevation according to gravity force Generation of Ground Water Penetrated water Alkaraji wrote: There are reservoirs in Earth that water stores there and some parts of it comes up in the form of spring and water when reaches to an impervious layer and stops there. By using wells, it comes up according to its power and aquifer pressure Penetration of air into ground Humid vapor penetrates to the pores and transform to water after distillation. This theory named Distillation theory Updrawing of deep water In this theory, apart of precipitation infiltrate to the earth via pores and fill water resources in Earth. Acceptance of this theory is clear after precipitation with increasing of spring yield; Qanats and decreasing of water yield in drought periods Water finding By experimental Method In this case Alkaraji has been said: If an area has humidity, it has water in inner parts. He suggested an experiment in this subject. Also he said: In the morning if we see vapor or fog near Earth, that ground has water By divining Method Ancient Iranians are inventors of Qanat construction and using dowsing and measurement of water, they were able to find the amount and place of groundwater. They dug some wells in aquifer area and with harvesting samples, they estimated water yield. This method is one of the best methods for finding ground water By studying of vegetation cover In this case, Karaji explained some plants that are reasons of water presence in an area such as Sorrel, Celery, Nightshade, and PennyRoyal. 4
5 Today, the easiest method to finding ground water is the study of vegetation cover in area By study the soil and ground types Karaji s theories in the case of Hydrogeology are similar and up-to-date theories. He illustrates his idea on area of watershed, amount of snowy area, existence of pores and their role in infiltration. References 1. Behnia A.K. (1989): Make and Manage of Qanat Book. pp Bybordi M. (1974): Ghanat of Iran (drainage of Sloping Aquifer). J. of Irrigation and Drainage, 10785, pp Lightfoot (1996): Syrian Qanat Romani. J. of Arid Environment. 4. Kuros Gh. (1975): Water and Irrigation culture in ancient Iran. Ministry of Energy. 5. Pouraghniaei M.J. and al. (2000): Qanat as an ancient Iranian method for using groundwater. Int. Conference on groundwater, May 2000, Saitama, Japan. 5
Human impacts on groundwater resources in Iran
 Man's Influence on Freshwater Ecosystems and Water Use (Proceedings of a Boulder Symposium, July 1995). IAHS Publ. no. 230, 1995. 141 Human impacts on groundwater resources in Iran ALI VALI-KHODJEINI Irrigation
Man's Influence on Freshwater Ecosystems and Water Use (Proceedings of a Boulder Symposium, July 1995). IAHS Publ. no. 230, 1995. 141 Human impacts on groundwater resources in Iran ALI VALI-KHODJEINI Irrigation
How could we possibly change the Hydrologic Cycle on an Island as big as Vancouver Island?
 How could we possibly change the Hydrologic Cycle on an Island as big as Vancouver Island? Do you think for a moment that humans altering the Hydrologic Cycle would also change the Weather? Precipitation
How could we possibly change the Hydrologic Cycle on an Island as big as Vancouver Island? Do you think for a moment that humans altering the Hydrologic Cycle would also change the Weather? Precipitation
Module 8: Weathering, Erosion, and Groundwater Topic 5 Content: The Water Cycle Presentation Notes. The Water Cycle
 The Water Cycle 1 Imagine taking a trip around the water cycle as a single drop of water. This cycle has no beginning or ending point, so it does not matter where the trip starts. Since over 70% of the
The Water Cycle 1 Imagine taking a trip around the water cycle as a single drop of water. This cycle has no beginning or ending point, so it does not matter where the trip starts. Since over 70% of the
Water is a solid, liquid, & gas. 71% of earth s surface is water. Our body is two-thirds water. Fresh water water that is not salty and has little or
 Water is a solid, liquid, & gas. 71% of earth s surface is water. Our body is two-thirds water. Fresh water water that is not salty and has little or no taste, color, or smell. Salt water water that contains
Water is a solid, liquid, & gas. 71% of earth s surface is water. Our body is two-thirds water. Fresh water water that is not salty and has little or no taste, color, or smell. Salt water water that contains
Water exists everywhere on Earth, and covers 70% of its surface. 97% of this water is found in the oceans.
 10.1 Distribution of Water Water exists everywhere on Earth, and covers 70% of its surface. 97% of this water is found in the oceans. w Another 2% is ice and snow, leaving only 1% as fresh water found
10.1 Distribution of Water Water exists everywhere on Earth, and covers 70% of its surface. 97% of this water is found in the oceans. w Another 2% is ice and snow, leaving only 1% as fresh water found
BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes
 BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes Assignment: HW#7 Next class lecture in AEPM 104 Today s topics SWAT exercise #2 The SWAT model review paper Hydrologic processes The Hydrologic Processes
BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes Assignment: HW#7 Next class lecture in AEPM 104 Today s topics SWAT exercise #2 The SWAT model review paper Hydrologic processes The Hydrologic Processes
RUNNING WATER AND GROUNDWATER
 NAME RUNNING WATER AND GROUNDWATER I. Introduction In this exercise we will investigate various features associated with streams and groundwater. Our drinking water ultimately comes from either streams
NAME RUNNING WATER AND GROUNDWATER I. Introduction In this exercise we will investigate various features associated with streams and groundwater. Our drinking water ultimately comes from either streams
UNIT HYDROGRAPH AND EFFECTIVE RAINFALL S INFLUENCE OVER THE STORM RUNOFF HYDROGRAPH
 UNIT HYDROGRAPH AND EFFECTIVE RAINFALL S INFLUENCE OVER THE STORM RUNOFF HYDROGRAPH INTRODUCTION Water is a common chemical substance essential for the existence of life and exhibits many notable and unique
UNIT HYDROGRAPH AND EFFECTIVE RAINFALL S INFLUENCE OVER THE STORM RUNOFF HYDROGRAPH INTRODUCTION Water is a common chemical substance essential for the existence of life and exhibits many notable and unique
WASA Quiz Review. Chapter 2
 WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
Analysis of the groundwater resource decline in an intramountain aquifer system in Central Iran
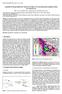 GEOLOGICA BELGICA (212) 15/3: 176-18 Analysis of the groundwater resource decline in an intramountain aquifer system in Central Iran Marc Van Camp 1, Mahdi Radfar2, Kristine Martens 1 and Kristine Walraevens
GEOLOGICA BELGICA (212) 15/3: 176-18 Analysis of the groundwater resource decline in an intramountain aquifer system in Central Iran Marc Van Camp 1, Mahdi Radfar2, Kristine Martens 1 and Kristine Walraevens
Hydrology and Water Management. Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar
 Hydrology and Water Management Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar Course Outline Hydrologic Cycle and its Processes Water Balance Approach Estimation and Analysis of Precipitation Data Infiltration and Runoff
Hydrology and Water Management Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar Course Outline Hydrologic Cycle and its Processes Water Balance Approach Estimation and Analysis of Precipitation Data Infiltration and Runoff
Hydrologic Cycle. Rain Shadow:
 Hydrologic Cycle The cyclical movement of water from the ocean to the atmosphere by evaporation, to the surface through precipitation, to streams through runoff and groundwater, and back to the ocean.
Hydrologic Cycle The cyclical movement of water from the ocean to the atmosphere by evaporation, to the surface through precipitation, to streams through runoff and groundwater, and back to the ocean.
CHAPTER ONE : INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER ONE : INTRODUCTION WHAT IS THE HYDROLOGY? The Hydrology means the science of water. It is the science that deals with the occurrence, circulation and distribution of water of the earth and earth
CHAPTER ONE : INTRODUCTION WHAT IS THE HYDROLOGY? The Hydrology means the science of water. It is the science that deals with the occurrence, circulation and distribution of water of the earth and earth
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Grotzinger Jordan. Understanding Earth. Sixth Edition
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 17: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE AND GROUNDWATER 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 17 The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater 1 About the Hydrologic
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 17: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE AND GROUNDWATER 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 17 The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater 1 About the Hydrologic
Water Resources. The Water Cycle. Section 1. Key Terms surface water river system watershed groundwater aquifer porosity permeability recharge zone
 Water Resources The next time you drink a glass of water, think about where the water came from. Did you know that some of the water in your glass may have been part of a rainstorm that pounded Earth long
Water Resources The next time you drink a glass of water, think about where the water came from. Did you know that some of the water in your glass may have been part of a rainstorm that pounded Earth long
General Groundwater Concepts
 General Groundwater Concepts Hydrologic Cycle All water on the surface of the earth and underground are part of the hydrologic cycle (Figure 1), driven by natural processes that constantly transform water
General Groundwater Concepts Hydrologic Cycle All water on the surface of the earth and underground are part of the hydrologic cycle (Figure 1), driven by natural processes that constantly transform water
The Hydrological Cycle
 Hydrological Cycle The Hydrological Cycle What is the Hydrological Cycle? Hydrological cycle = The Water cycle What is precipitation, evaporation and condensation? Evaporation = Liquid to Gas (gains energy)
Hydrological Cycle The Hydrological Cycle What is the Hydrological Cycle? Hydrological cycle = The Water cycle What is precipitation, evaporation and condensation? Evaporation = Liquid to Gas (gains energy)
Read p.4 Activity. Class Discussion (The many ways people use water) P. 5. Read p.6 Read pp. 8-9
 Grade 8 Science Read p.4 Activity Class Discussion (The many ways people use water) P. 5 Read p.6 Read pp. 8-9 Water exists everywhere on Earth, and covers 70% of its surface. 97% of this water is found
Grade 8 Science Read p.4 Activity Class Discussion (The many ways people use water) P. 5 Read p.6 Read pp. 8-9 Water exists everywhere on Earth, and covers 70% of its surface. 97% of this water is found
Groundwater: the Big Picture
 Groundwater: the Big Picture 1 1.1 Introduction This book is about water in the pore spaces of the subsurface. Most of that water flows quite slowly and is usually hidden from view, but it occasionally
Groundwater: the Big Picture 1 1.1 Introduction This book is about water in the pore spaces of the subsurface. Most of that water flows quite slowly and is usually hidden from view, but it occasionally
CHAPTER 13 OUTLINE The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater. Hydrologic cycle. Hydrologic cycle cont.
 CHAPTER 13 OUTLINE The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Hydrologic cycle The hydrologic cycle is
CHAPTER 13 OUTLINE The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Hydrologic cycle The hydrologic cycle is
True False Click and Drag Artesian wells are naturally under pressure and require no additional pumps to get the water out of the ground.
 True False Click and Drag Artesian wells are naturally under pressure and require no additional pumps to get the water out of the ground. Groundwater recharge is the water from infiltration Groundwater
True False Click and Drag Artesian wells are naturally under pressure and require no additional pumps to get the water out of the ground. Groundwater recharge is the water from infiltration Groundwater
Science 8 Chapter 1 Section 1
 Science 8 Chapter 1 Section 1 Distribution of Water (pp. 8-13) How much fresh water do we have? The vast majority of water on Earth, about 97 percent, is salt water Two thirds of that fresh water supply
Science 8 Chapter 1 Section 1 Distribution of Water (pp. 8-13) How much fresh water do we have? The vast majority of water on Earth, about 97 percent, is salt water Two thirds of that fresh water supply
Lecture 11: Water Flow; Soils and the Hydrologic Cycle
 Lecture 11: Water Flow; Soils and the Hydrologic Cycle Water Flow in Soils Types of Water Flow in Soil Saturated flow: Soil pores completely filled with water; controlled by the hydrostatic potential After
Lecture 11: Water Flow; Soils and the Hydrologic Cycle Water Flow in Soils Types of Water Flow in Soil Saturated flow: Soil pores completely filled with water; controlled by the hydrostatic potential After
Introduction. Welcome to the Belgium Study Abroad Program. Courses:
 Introduction Welcome to the Belgium Study Abroad Program Courses: AGSM 335: Soil and Water Management BAEN 460: Principals of Environmental Hydrology BAEN 460 / AGSM 335 Combined lecture and HW sessions
Introduction Welcome to the Belgium Study Abroad Program Courses: AGSM 335: Soil and Water Management BAEN 460: Principals of Environmental Hydrology BAEN 460 / AGSM 335 Combined lecture and HW sessions
Air & Water Lesson 2. Chapter 6 Conserving Our Resources
 Air & Water Lesson 2 Chapter 6 Conserving Our Resources Objectives Summarize the importance of air. Describe the water cycle. Main Idea Living things use air and water to carry out their life processes.
Air & Water Lesson 2 Chapter 6 Conserving Our Resources Objectives Summarize the importance of air. Describe the water cycle. Main Idea Living things use air and water to carry out their life processes.
Drought conditions and management strategies in Iran
 Drought conditions and management strategies in Iran Parviz Garshasbi Deputy head of watershed management forest, range and watershed management organization, Jihad-agriculture ministry p.garsh@yahoo.com
Drought conditions and management strategies in Iran Parviz Garshasbi Deputy head of watershed management forest, range and watershed management organization, Jihad-agriculture ministry p.garsh@yahoo.com
Davood Nikkami (PhD)
 Country Report of The IR. Iran 28-30 Jan., 2009, Bangkok, Thailand Workshop on Improving Agricultural Productivity, Water Use Efficiency & Strengthening Rural Livelihoods Davood Nikkami (PhD) Soil Conservation
Country Report of The IR. Iran 28-30 Jan., 2009, Bangkok, Thailand Workshop on Improving Agricultural Productivity, Water Use Efficiency & Strengthening Rural Livelihoods Davood Nikkami (PhD) Soil Conservation
Kariz(Qanat); An Eternal Friendly System For Harvesting Groundwater
 Kariz(Qanat); An Eternal Friendly System For Harvesting Groundwater An evaluation of the sustainability of Qanats under changing socio economic and climatic conditions in Iran This article has been prepared
Kariz(Qanat); An Eternal Friendly System For Harvesting Groundwater An evaluation of the sustainability of Qanats under changing socio economic and climatic conditions in Iran This article has been prepared
DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY POST GRADUATE GOVT. COLLEGE FOR GIRLS.SECTOR-11 CHANDIGARH CLASS-B.A.II PAPER-A RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT: WORLD PATTERNS
 DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY POST GRADUATE GOVT. COLLEGE FOR GIRLS.SECTOR-11 CHANDIGARH CLASS-B.A.II PAPER-A RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT: WORLD PATTERNS Hydrological cycle The sun, which drives the water cycle,
DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY POST GRADUATE GOVT. COLLEGE FOR GIRLS.SECTOR-11 CHANDIGARH CLASS-B.A.II PAPER-A RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT: WORLD PATTERNS Hydrological cycle The sun, which drives the water cycle,
Afghanistan. A Countrywide Overview of Groundwater Resources and Challenges By: Vincent W. Uhl
 Afghanistan A Countrywide Overview of Groundwater Resources and Challenges By: Vincent W. Uhl Country Overview Area: 647,500 km 2 Population: +/- 30 Million Economy: Principally Agriculture ¾ of the country
Afghanistan A Countrywide Overview of Groundwater Resources and Challenges By: Vincent W. Uhl Country Overview Area: 647,500 km 2 Population: +/- 30 Million Economy: Principally Agriculture ¾ of the country
1. Apply knowledge of the controlling variables for groundwater flow. 2. Demonstrate groundwater flow direction based on hydraulic head observations.
 .9-12 HYDRAULIC HEAD SUBJECTS: TIME: Science (Physical Science, Physics), Math 1 class period MATERIALS: Copies of student sheets and background information OBJECTIVES The student will do the following:
.9-12 HYDRAULIC HEAD SUBJECTS: TIME: Science (Physical Science, Physics), Math 1 class period MATERIALS: Copies of student sheets and background information OBJECTIVES The student will do the following:
Topic 3, Subtopic A of Review Handbook or Chapter 10 of Earth Science Book. 97% of Earth s water is found as saltwater in Earth s oceans.
 Topic 3, Subtopic A of Review Handbook or Chapter 10 of Earth Science Book Groundwater 97% of Earth s water is found as saltwater in Earth s oceans. That leaves only 3% for freshwater! But 90% of the freshwater
Topic 3, Subtopic A of Review Handbook or Chapter 10 of Earth Science Book Groundwater 97% of Earth s water is found as saltwater in Earth s oceans. That leaves only 3% for freshwater! But 90% of the freshwater
FACT FLASH. 5: Groundwater. What is groundwater? How does the ground store water? Fact Flash 5: Groundwater
 FACT FLASH 5: Groundwater What is groundwater? Groundwater is fresh water (from rain or melting ice and snow) that soaks into the soil and is stored in the tiny spaces (pores) between rocks and particles
FACT FLASH 5: Groundwater What is groundwater? Groundwater is fresh water (from rain or melting ice and snow) that soaks into the soil and is stored in the tiny spaces (pores) between rocks and particles
The Hydrosphere. Introduction To Surface Water. What Do You Think?
 Introduction To Surface Water Unit Essential Questions: How does the Earth cycle its water through its major reservoirs? How does society s use of resources affect water quality? Presentation Objectives:
Introduction To Surface Water Unit Essential Questions: How does the Earth cycle its water through its major reservoirs? How does society s use of resources affect water quality? Presentation Objectives:
The Hydrologic Cycle. Floods 3 5. Flood Science LESSON PLAN 1. Key Terms and Concepts. Purposes. Objectives
 LESSON PLAN 1 The Hydrologic Cycle Floods It is important for children to understand the hydrologic cycle in preparation for learning the science behind floods and flash floods. Key Terms and Concepts
LESSON PLAN 1 The Hydrologic Cycle Floods It is important for children to understand the hydrologic cycle in preparation for learning the science behind floods and flash floods. Key Terms and Concepts
Groundwater basics. Groundwater and surface water: a single resource. Pore Spaces. Simplified View
 Groundwater and surface water: a single resource Santa Cruz River, Tucson Groundwater basics Groundwater is water found within the pore spaces of geologic material beneath the surface of the Earth. It
Groundwater and surface water: a single resource Santa Cruz River, Tucson Groundwater basics Groundwater is water found within the pore spaces of geologic material beneath the surface of the Earth. It
The Hydrologic (Water) Cycle
 Ever since the Volcanic outgassing of water vapor 4 billion years ago, Earth has been recycling its water supply. gained lost Earth s has not or water since The Water Cycle - the model used to illustrate
Ever since the Volcanic outgassing of water vapor 4 billion years ago, Earth has been recycling its water supply. gained lost Earth s has not or water since The Water Cycle - the model used to illustrate
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition
 Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 17: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE AND GROUNDWATER Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright 2007
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 17: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE AND GROUNDWATER Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright 2007
Introduction to Groundwater
 Introduction to Groundwater Unit Essential Questions: How does the Earth cycle its water through its major reservoirs? How does society s use of resources affect water quality? Presentation Objectives:
Introduction to Groundwater Unit Essential Questions: How does the Earth cycle its water through its major reservoirs? How does society s use of resources affect water quality? Presentation Objectives:
Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is the Water Cycle? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Water on the Move warm up 1 Water on the Move About three-fourths of Earth s surface is covered by water. Water on the Move Video!!! Water on the Move Water moves between Earth s surface and the atmosphere
Water on the Move warm up 1 Water on the Move About three-fourths of Earth s surface is covered by water. Water on the Move Video!!! Water on the Move Water moves between Earth s surface and the atmosphere
Groundwater and surface water: a single resource. Santa Cruz River, Tucson
 Groundwater and surface water: a single resource Santa Cruz River, Tucson 1942 1989 1 Groundwater basics Groundwater is water found within the pore spaces of geologic material beneath the surface of the
Groundwater and surface water: a single resource Santa Cruz River, Tucson 1942 1989 1 Groundwater basics Groundwater is water found within the pore spaces of geologic material beneath the surface of the
GY 111 Lecture Note Series Groundwater and Hydrogeology
 GY 111 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2008-09) 1 GY 111 Lecture Note Series Groundwater and Hydrogeology Lecture Goals A) The hydrologic cycle B) Groundwater dynamics C) Mapping groundwater (done in class not
GY 111 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2008-09) 1 GY 111 Lecture Note Series Groundwater and Hydrogeology Lecture Goals A) The hydrologic cycle B) Groundwater dynamics C) Mapping groundwater (done in class not
The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater
 CHAPTER 17 The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater Chapter Summary The hydrologic cycle is a flowchart or model for the distribution and movements of water on and below the surface of the Earth. The major
CHAPTER 17 The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater Chapter Summary The hydrologic cycle is a flowchart or model for the distribution and movements of water on and below the surface of the Earth. The major
Unit 2: Weather Dynamics Chapter 1: Hydrological Cycle
 UNIT 2 Chapter 1: Inquiring about Weather Unit 2: Weather Dynamics Chapter 1: Hydrological Cycle Science 10 Mrs. Purba Importance of H 2 O From the beginning of time when water first appeared, it has been
UNIT 2 Chapter 1: Inquiring about Weather Unit 2: Weather Dynamics Chapter 1: Hydrological Cycle Science 10 Mrs. Purba Importance of H 2 O From the beginning of time when water first appeared, it has been
The role of dams in securing the surface water in the northern and eastern parts of the United Arab Emirates (UAE)
 Changes in Water Resources Systems: Methodologies to Maintain Water Security and Ensure Integrated Management (Proceedings of Symposium HS at IUGG, Perugia, July ). IAHS Publ.,. The role of dams in securing
Changes in Water Resources Systems: Methodologies to Maintain Water Security and Ensure Integrated Management (Proceedings of Symposium HS at IUGG, Perugia, July ). IAHS Publ.,. The role of dams in securing
groundwater. Because watersheds are complex systems, each tends to respond differently to natural or human activities.
 The private development of Altos del María is located at an altitude between 550 and 1,000 meters above sea level in the environmentally sensitive Cordillera Central of Panama that separates the Pacific
The private development of Altos del María is located at an altitude between 550 and 1,000 meters above sea level in the environmentally sensitive Cordillera Central of Panama that separates the Pacific
Water Balance Methodology
 Water Balance Methodology Integrating the Site with the Watershed and the Stream March 2012 An initiative under the umbrella of the Water Sustainability Action Plan for British Columbia Water Balance Methodology
Water Balance Methodology Integrating the Site with the Watershed and the Stream March 2012 An initiative under the umbrella of the Water Sustainability Action Plan for British Columbia Water Balance Methodology
TD 603. Water Resources Milind Sohoni sohoni/ Lecture 2: Water cycle, stocks and flows. () July 28, / 30
 TD 603 Water Resources Milind Sohoni www.cse.iitb.ac.in/ sohoni/ Lecture 2: Water cycle, stocks and flows () July 28, 2013 1 / 30 The basic movement of water source: USGS. () July 28, 2013 2 / 30 The basic
TD 603 Water Resources Milind Sohoni www.cse.iitb.ac.in/ sohoni/ Lecture 2: Water cycle, stocks and flows () July 28, 2013 1 / 30 The basic movement of water source: USGS. () July 28, 2013 2 / 30 The basic
HYDROLOGY - BASIC CONCEPTS
 HYDROLOGY - BASIC CONCEPTS Hydrology Hydrology is the science of the waters of the earth and its atmosphere. It deals with occurrence, circulation, distribution and movements of these waters over the globe
HYDROLOGY - BASIC CONCEPTS Hydrology Hydrology is the science of the waters of the earth and its atmosphere. It deals with occurrence, circulation, distribution and movements of these waters over the globe
KARTIK SHARMA LECT. IN CIVIL ENGINEERING GGSGP CHEEKA
 The Hydrological Cycle KARTIK SHARMA LECT. IN CIVIL ENGINEERING GGSGP CHEEKA The Hydrological Cycle What you need to know: Be able to draw a diagram of the hydrological cycle. Describe its main elements.
The Hydrological Cycle KARTIK SHARMA LECT. IN CIVIL ENGINEERING GGSGP CHEEKA The Hydrological Cycle What you need to know: Be able to draw a diagram of the hydrological cycle. Describe its main elements.
Directed Reading. Section: The Water Cycle. what did they discover? question remained? MOVEMENT OF WATER ON EARTH.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Water Cycle 1. What question has puzzled people for centuries? 2. Once people were able to measure the amount of water that falls to Earth, what did they
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Water Cycle 1. What question has puzzled people for centuries? 2. Once people were able to measure the amount of water that falls to Earth, what did they
Movement and Storage of Groundwater The Hydrosphere
 Movement and Storage of Groundwater The Hydrosphere The water on and in Earth s crust makes up the hydrosphere. About 97 percent of the hydrosphere is contained in the oceans. The water contained by landmasses
Movement and Storage of Groundwater The Hydrosphere The water on and in Earth s crust makes up the hydrosphere. About 97 percent of the hydrosphere is contained in the oceans. The water contained by landmasses
The Texas A&M University and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Hydrologic Modeling Inventory (HMI) Questionnaire
 The Texas A&M University and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Hydrologic Modeling Inventory (HMI) Questionnaire May 4, 2010 Name of Model, Date, Version Number Dynamic Watershed Simulation Model (DWSM) 2002
The Texas A&M University and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Hydrologic Modeling Inventory (HMI) Questionnaire May 4, 2010 Name of Model, Date, Version Number Dynamic Watershed Simulation Model (DWSM) 2002
Topic 5. Water in the Atmosphere, Surface, and Subsurface. Unique Properties of Water Heat Properties 10/24/2017. Phase Changes
 Topic 5 Water in the Atmosphere, Surface, and Subsurface Properties of Water Omit Humidity and Atmospheric Moisture Distribution of Water The Hydrologic Cycle The Water Balance Concept Groundwater Characteristics
Topic 5 Water in the Atmosphere, Surface, and Subsurface Properties of Water Omit Humidity and Atmospheric Moisture Distribution of Water The Hydrologic Cycle The Water Balance Concept Groundwater Characteristics
Measuring and Valuing Ecosystem Services: InVEST and Modeling Approaches
 Measuring and Valuing Ecosystem Services: InVEST and Modeling Approaches Adrian L. Vogl Comparative Groundwater Law & Policy Workshop April 9, 2013 A Modeling Approach Simple conceptual reservoir models
Measuring and Valuing Ecosystem Services: InVEST and Modeling Approaches Adrian L. Vogl Comparative Groundwater Law & Policy Workshop April 9, 2013 A Modeling Approach Simple conceptual reservoir models
Climate Change Water Implications for Michigan Communities, Landsystems and Agriculture
 Climate Change Water Implications for Michigan Communities, Landsystems and Agriculture Distinguished Senior Research Specialist Department of Geography Institute of Water Research Climate Change Summary
Climate Change Water Implications for Michigan Communities, Landsystems and Agriculture Distinguished Senior Research Specialist Department of Geography Institute of Water Research Climate Change Summary
The natural environment Upper grade of Primary Education (10-12 years old)
 Slide 1 1 and 2 The climate in Anantapur The school with which we are having the exchange is located in the State of Andhra Pradesh, a wet and hot Indian region. As this State is quite big, we will focus
Slide 1 1 and 2 The climate in Anantapur The school with which we are having the exchange is located in the State of Andhra Pradesh, a wet and hot Indian region. As this State is quite big, we will focus
Hydrologic Cycle. Water Availabilty. Surface Water. Groundwater
 Hydrologic Cycle Hydrologic ydoogccyce cycle Surface Water Groundwater Water Availabilty 1 Hydrologic Cycle Constant movement of water above, on, and, below the earth s surface (Heath) Endless circulation
Hydrologic Cycle Hydrologic ydoogccyce cycle Surface Water Groundwater Water Availabilty 1 Hydrologic Cycle Constant movement of water above, on, and, below the earth s surface (Heath) Endless circulation
THE HYDROSPHERE PART 3
 THE HYDROSPHERE PART 3 Surface Freshwater: Rivers and Streams River is a large channel along which water is continually flowing down a slope; it is made of many streams that come together. Stream is a
THE HYDROSPHERE PART 3 Surface Freshwater: Rivers and Streams River is a large channel along which water is continually flowing down a slope; it is made of many streams that come together. Stream is a
The Water Cycle. 1. The diagram below is a cross-sectional view of rain falling on a farm field and then moving to the water table.
 1. The diagram below is a cross-sectional view of rain falling on a farm field and then moving to the water table. Which word best describes the movement of the rainwater through zone A? A. runoff B. saturation
1. The diagram below is a cross-sectional view of rain falling on a farm field and then moving to the water table. Which word best describes the movement of the rainwater through zone A? A. runoff B. saturation
Hydrology in Watershed
 Setting the Course for Improved Water Quality Hydrology in Watershed Systems Photo by Don Berger Minnesota Pollution Control Agency Session 5A: A TMDL training gprogram for local government leaders and
Setting the Course for Improved Water Quality Hydrology in Watershed Systems Photo by Don Berger Minnesota Pollution Control Agency Session 5A: A TMDL training gprogram for local government leaders and
Battle for the Biosphere
 Battle for the Biosphere Biome: A large community of plants and animals that occupies a distinct region e.g. the Tropical rainforest. Biosphere: The parts of the land, sea and atmosphere where organisms
Battle for the Biosphere Biome: A large community of plants and animals that occupies a distinct region e.g. the Tropical rainforest. Biosphere: The parts of the land, sea and atmosphere where organisms
1 Hydrologic Cycle. Chin - chapter 1. Dr. Luis E. Lesser
 1 Hydrologic Cycle Chin - chapter 1 Dr. Luis E. Lesser All Tables and Figures (except where noted) were kindly provided by Pearson, from the textbook by David A. Chin, 2013. Water Resources Engineering,
1 Hydrologic Cycle Chin - chapter 1 Dr. Luis E. Lesser All Tables and Figures (except where noted) were kindly provided by Pearson, from the textbook by David A. Chin, 2013. Water Resources Engineering,
UCS Mi-STAR Science 7 Semester 1 Midterm Exam Review Guide
 Name Date Hour 2018-2019 UCS Mi-STAR Science 7 Semester 1 Midterm Exam Review Guide Question How does cold air compare to warm air? Cold air weighs more than hot air. When a 9-centimeter balloon is filled
Name Date Hour 2018-2019 UCS Mi-STAR Science 7 Semester 1 Midterm Exam Review Guide Question How does cold air compare to warm air? Cold air weighs more than hot air. When a 9-centimeter balloon is filled
HYDROLOGY NOTES LLAMA, LLAMA AND WRITE YOU NAME AND PERIOD AT THE TOP
 HYDROLOGY NOTES LLAMA, LLAMA AND WRITE YOU NAME AND PERIOD AT THE TOP QUIZ TIME: WHAT IS HYDROLOGY GOING TO BE ABOUT? A. A NATIVE AMERICAN MYTH ABOUT HYDROL THE SPIRIT WHO CONTROLS THE RAIN. B. AN EARLY
HYDROLOGY NOTES LLAMA, LLAMA AND WRITE YOU NAME AND PERIOD AT THE TOP QUIZ TIME: WHAT IS HYDROLOGY GOING TO BE ABOUT? A. A NATIVE AMERICAN MYTH ABOUT HYDROL THE SPIRIT WHO CONTROLS THE RAIN. B. AN EARLY
TOPICAL RESPONSE 3: CLIMATE CHANGE AND ITS EFFECTS
 TOPICAL RESPONSE 3: CLIMATE CHANGE AND ITS EFFECTS Comments point to uncertainty in future conditions that may affect water supplies, such as declines in fish species in the Bay-Delta and climate change
TOPICAL RESPONSE 3: CLIMATE CHANGE AND ITS EFFECTS Comments point to uncertainty in future conditions that may affect water supplies, such as declines in fish species in the Bay-Delta and climate change
East Maui Watershed Partnership Adapted from Utah State University and University of Wisconsin Ground Water Project Ages 7 th -Adult
 INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
Agronomy 406 World Climates
 Agronomy 406 World Climates February 13, 2018 Hydrologic cycle. Team 4 Climate News presentation this Thursday. Review: METED module, Understanding the Hydrologic Cycle Active review session for the midterm
Agronomy 406 World Climates February 13, 2018 Hydrologic cycle. Team 4 Climate News presentation this Thursday. Review: METED module, Understanding the Hydrologic Cycle Active review session for the midterm
Term Info Picture. The process by which liquid water changes to gas. The process by which water vapor changes in to liquid water.
 Water Cycle S6E3. Obtain, evaluate and communicate information to recognize the significant role of water in Earth s processes. A. Ask questions to determine where water is located on Earth s surface (oceans,
Water Cycle S6E3. Obtain, evaluate and communicate information to recognize the significant role of water in Earth s processes. A. Ask questions to determine where water is located on Earth s surface (oceans,
Water Cycle. Are you really drinking the same water as the caveman?
 Water Cycle Are you really drinking the same water as the caveman? Water Cycle Water is always on the move. Rain falling where you live may have been water in the ocean just days before. And the water
Water Cycle Are you really drinking the same water as the caveman? Water Cycle Water is always on the move. Rain falling where you live may have been water in the ocean just days before. And the water
Water Distribution Rivers
 Water Distribution Rivers Question 1 One of the main issues concerning fresh water is that most of it is found where? A. Glaciers and Icecaps B. Aquifers C. Underground D. Oceans Question 2 How does water
Water Distribution Rivers Question 1 One of the main issues concerning fresh water is that most of it is found where? A. Glaciers and Icecaps B. Aquifers C. Underground D. Oceans Question 2 How does water
Unit 2: Geomorphologic and Hydrologic Characteristics of Watersheds. ENVS 435: Watershed Management INSTR.: Dr. R.M. Bajracharya
 Unit 2: Geomorphologic and Hydrologic Characteristics of Watersheds ENVS 435: Watershed Management INSTR.: Dr. R.M. Bajracharya Watersheds are hydro-geologic units Water flow and cycling are basic and
Unit 2: Geomorphologic and Hydrologic Characteristics of Watersheds ENVS 435: Watershed Management INSTR.: Dr. R.M. Bajracharya Watersheds are hydro-geologic units Water flow and cycling are basic and
Review of Chapter 1. Taken from: Check Your Understanding sections p. 13, 21 and 33
 Review of Chapter 1 Taken from: Check Your Understanding sections p. 13, 21 and 33 In case you were curious: Henry Hudson The Last Voyage of Henry Hudson, 1611 Painted in 1880 by: John Collier Today Hudson
Review of Chapter 1 Taken from: Check Your Understanding sections p. 13, 21 and 33 In case you were curious: Henry Hudson The Last Voyage of Henry Hudson, 1611 Painted in 1880 by: John Collier Today Hudson
The Spring Creek Stormwater Activity Book
 This booklet belongs to: The Spring Creek Stormwater Activity Book An activity booklet designed to teach children about water resources and stormwater pollution Created by the MS4 Partners College, Ferguson,
This booklet belongs to: The Spring Creek Stormwater Activity Book An activity booklet designed to teach children about water resources and stormwater pollution Created by the MS4 Partners College, Ferguson,
Water Resources Engineering. Prof. R. Srivastava. Department of Water Resources Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur.
 Water Resources Engineering Prof. R. Srivastava Department of Water Resources Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture # 13 Today we will continue to discuss some of the abstractions
Water Resources Engineering Prof. R. Srivastava Department of Water Resources Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture # 13 Today we will continue to discuss some of the abstractions
Water Resources Engineering
 Subject Code 10B11CE 513 Subject Name Course Structure (L -T) 3-1 Course Credit 4 Water Resources Engineering Course objective: In we are working in the field of irrigation Engg. we should know how much
Subject Code 10B11CE 513 Subject Name Course Structure (L -T) 3-1 Course Credit 4 Water Resources Engineering Course objective: In we are working in the field of irrigation Engg. we should know how much
River Talk Patterns. Student Copy Page PART I (1 of 1) 3. Human nervous system. Waters and drainage patterns. Road system.
 River Talk Patterns Student Copy Page PART I (1 of 1) 3 Human nervous system photo credit: Hemera Thinkstock Photos Waters and drainage patterns photo credit: Comstock Getty Images Road system photo credit:
River Talk Patterns Student Copy Page PART I (1 of 1) 3 Human nervous system photo credit: Hemera Thinkstock Photos Waters and drainage patterns photo credit: Comstock Getty Images Road system photo credit:
VI-1. The Water Cycle What is the water cycle? evaporate condenses surface runoff ground water
 Classroom Copy VI-1. The Water Cycle What is the water cycle? Did you know that the water we see all around us never gets destroyed, and new water never gets created? Instead, it constantly recycles and
Classroom Copy VI-1. The Water Cycle What is the water cycle? Did you know that the water we see all around us never gets destroyed, and new water never gets created? Instead, it constantly recycles and
Ground Water Chapter 11
 Ground Water Chapter 11 How does water get underground? How is water stored underground? How does water move? How do we find it? Why we need to protect it. Lake Powell. Water levels are decreasing every
Ground Water Chapter 11 How does water get underground? How is water stored underground? How does water move? How do we find it? Why we need to protect it. Lake Powell. Water levels are decreasing every
Agricultural Land and Water Regime Protection by Drainage Retention Capacity (DREC) of Surface Soil Layers (Region of Cerhovice Brook, Czech Republic)
 ISBN 978-93-84422-55-4 International Conference on Agriculture, Ecology and Biological Engineering (AEBE-15 Antalya (Turkey Sept. 7-8, 2015 pp. 1-7 Agricultural Land and Water Regime Protection by Drainage
ISBN 978-93-84422-55-4 International Conference on Agriculture, Ecology and Biological Engineering (AEBE-15 Antalya (Turkey Sept. 7-8, 2015 pp. 1-7 Agricultural Land and Water Regime Protection by Drainage
22 Tubewell Drainage Systems
 22 Tubewell Drainage Systems WK Boehmer' and J Boonstra2 221 Introduction ' Tubewell drainage is a technique of controlling the watertable and salinity in agricultural areas It consists of pumping, from
22 Tubewell Drainage Systems WK Boehmer' and J Boonstra2 221 Introduction ' Tubewell drainage is a technique of controlling the watertable and salinity in agricultural areas It consists of pumping, from
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
 STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE CONS 385 Hydrology and Hydrogeology Prepared By: Adrienne C. Rygel, Ph.D. CANINO SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY Department
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE CONS 385 Hydrology and Hydrogeology Prepared By: Adrienne C. Rygel, Ph.D. CANINO SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY Department
WATER AND THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE
 WATER AND THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE Summary Water is essential for the support of life and can be considered as a fundamental environmental good. Water is needed to support human habitation, grow crops and
WATER AND THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE Summary Water is essential for the support of life and can be considered as a fundamental environmental good. Water is needed to support human habitation, grow crops and
Weather has always been a hot topic of conversation. We talk about whether it is hot or cold, windy or calm, snowy or dry. We listen to the radio to
 Weather has always been a hot topic of conversation. We talk about whether it is hot or cold, windy or calm, snowy or dry. We listen to the radio to figure out if the weather will be different tomorrow.
Weather has always been a hot topic of conversation. We talk about whether it is hot or cold, windy or calm, snowy or dry. We listen to the radio to figure out if the weather will be different tomorrow.
Black River Watershed Management Plan Plan
 Black River Watershed Management Plan Plan Final Report Part II: Appendices May 2010 This watershed management plan was prepared for the New York State Department of State Division of Coastal Resources
Black River Watershed Management Plan Plan Final Report Part II: Appendices May 2010 This watershed management plan was prepared for the New York State Department of State Division of Coastal Resources
Simulation of Rainfall-Runoff Using WEAP Model (Case Study: Qaraso Basin)
 AGRICULTURAL COMMUNICATIONS, 2014, 2(4): 63-68. Simulation of Rainfall-Runoff Using WEAP Model (Case Study: Qaraso Basin) BEHROOZ YAGHOBI*, SAEID SHABANLOU AND FARIBORZ YOSEFVAND Department of Water Engineering,
AGRICULTURAL COMMUNICATIONS, 2014, 2(4): 63-68. Simulation of Rainfall-Runoff Using WEAP Model (Case Study: Qaraso Basin) BEHROOZ YAGHOBI*, SAEID SHABANLOU AND FARIBORZ YOSEFVAND Department of Water Engineering,
Are we water rich or water poor. Levente Ronczyk: The Challenge of Water Resources Management in Hungary
 Levente Ronczyk University of Pécs Faculty of Sciences Institute of Geography, Hungary hidrogen@gamma.ttk.pte.hu Are we water rich or water poor country? The Challenges of Water Resources Management in
Levente Ronczyk University of Pécs Faculty of Sciences Institute of Geography, Hungary hidrogen@gamma.ttk.pte.hu Are we water rich or water poor country? The Challenges of Water Resources Management in
Hydrology in a Dynamic Earth
 Hydrology in a Dynamic Earth By David R. Maidment Center for Research in Water Resources University of Texas at Austin November 6, 2005 A theme of hydrologic change implies that hydrologic processes are
Hydrology in a Dynamic Earth By David R. Maidment Center for Research in Water Resources University of Texas at Austin November 6, 2005 A theme of hydrologic change implies that hydrologic processes are
Suitable for grades 3-5. atmospheric composition. solar radiation. climate variability and change. volcanoes. clouds. carbon cycle.
 Color and Understand the Global Climate System atmospheric composition solar radiation climate variability and change H 2 0, CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O, O 3, etc. aerosols volcanoes clouds atmosphere-ice interaction
Color and Understand the Global Climate System atmospheric composition solar radiation climate variability and change H 2 0, CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O, O 3, etc. aerosols volcanoes clouds atmosphere-ice interaction
Runoff Volume: The Importance of Land Cover
 Runoff Volume: The Importance of Land Cover Grade Level: 9-12 Time: 1-2 class periods Learning Objectives: - Quantify the volume of water that runs off different land uses in a watershed. - Analyze the
Runoff Volume: The Importance of Land Cover Grade Level: 9-12 Time: 1-2 class periods Learning Objectives: - Quantify the volume of water that runs off different land uses in a watershed. - Analyze the
IPCC WG II Chapter 3 Freshwater Resources and Their Management
 IPCC WG II Chapter 3 Freshwater Resources and Their Management Impacts increasingly harmful & more costly to adapt as global temperature increases May imperil sustainable development goals Semi-arid /
IPCC WG II Chapter 3 Freshwater Resources and Their Management Impacts increasingly harmful & more costly to adapt as global temperature increases May imperil sustainable development goals Semi-arid /
CTB3300WCx Introduction to Water and Climate
 CTB3300WCx Introduction to Water and Climate GWC 1 Water cycle Welcome! My name is Hubert Savenije and I am a Hydrologist Hubert Savenije Hydrology is the science of water. It tries to describe and understand
CTB3300WCx Introduction to Water and Climate GWC 1 Water cycle Welcome! My name is Hubert Savenije and I am a Hydrologist Hubert Savenije Hydrology is the science of water. It tries to describe and understand
WELCOME TO PERIOD 24: WATER ENERGY. Homework #23 is due today.
 WELCOME TO PERIOD 24: WATER ENERGY Homework #23 is due today. PHYSICS 1104 PERIOD 24 What is the Earth s water cycle? How is water used to generate electricity? What effects will climate change have on
WELCOME TO PERIOD 24: WATER ENERGY Homework #23 is due today. PHYSICS 1104 PERIOD 24 What is the Earth s water cycle? How is water used to generate electricity? What effects will climate change have on
CHAPTER FIVE Runoff. Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib. Overland flow interflow
 Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) CHAPTER FIVE Runoff Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib Overland flow interflow Base flow Saturated overland flow ١ ٢ 5.1 Introduction To Runoff Runoff
Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) CHAPTER FIVE Runoff Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib Overland flow interflow Base flow Saturated overland flow ١ ٢ 5.1 Introduction To Runoff Runoff
Timing Key Narrative Snapshots a) 00:44 How does groundwater recharge occur? How do streams form?
 Module 4 Narration: Runoff and Recharge Timing Key Narrative Snapshots a) 00:44 How does groundwater recharge occur? How do streams form? These processes are closely linked. Lets first investigate how
Module 4 Narration: Runoff and Recharge Timing Key Narrative Snapshots a) 00:44 How does groundwater recharge occur? How do streams form? These processes are closely linked. Lets first investigate how
Harvesting in the Arab Region (
 Title Omani Experience in Flash Floods, D and Water Harvesting Author(s) Ahmed Said Al Barwani Proceedings of the Second Internati Citation Floods in Wadi Systems: Disaster Ri Harvesting in the Arab Region
Title Omani Experience in Flash Floods, D and Water Harvesting Author(s) Ahmed Said Al Barwani Proceedings of the Second Internati Citation Floods in Wadi Systems: Disaster Ri Harvesting in the Arab Region
In the name of God. Country Level Presentation Iran Country Report. Rome, Italy, December 15 th, 2015
 In the name of God Country Level Presentation Iran Country Report Rome, Italy, December 15 th, 2015 Area Population No of provinces Average Rainfall Neighboring Countries 1.648 million km 2 >78 million
In the name of God Country Level Presentation Iran Country Report Rome, Italy, December 15 th, 2015 Area Population No of provinces Average Rainfall Neighboring Countries 1.648 million km 2 >78 million
The Spring Creek Stormwater Activity Book
 This booklet belongs to: The Spring Creek Stormwater Activity Book An activity booklet designed to teach children about water resources and stormwater pollution Created by the Penn State Office of Physical
This booklet belongs to: The Spring Creek Stormwater Activity Book An activity booklet designed to teach children about water resources and stormwater pollution Created by the Penn State Office of Physical
SAMPLE CHAPTERS UNESCO EOLSS GROUNDWATER MONITORING. Masanori Ando Musashino University, Japan
 GROUNDWATER MONITORING Masanori Ando Musashino University, Japan Keywords: groundwater, monitoring, sampling, monitoring program, monitoring location, sampling programs, flow measurement, sampling techniques,
GROUNDWATER MONITORING Masanori Ando Musashino University, Japan Keywords: groundwater, monitoring, sampling, monitoring program, monitoring location, sampling programs, flow measurement, sampling techniques,
Groundwater. Say Thanks to the Authors Click (No sign in required)
 Groundwater Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org CK-12
Groundwater Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org CK-12
