BBA Sixth Semester Total Quality Management
|
|
|
- Nathaniel Scot Henderson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter - II BBA Sixth Semester Total Quality Management -BIJAY LAL PRADHAN M Sc Statistics, FDPM(IIMA) PhD Scholar (TQM)
2 Syllabus Introduction to Quality and Quality management Conceptual Frameworks for Total Quality Management (TQM) TQM Tools Six Sigma Quality System Standards
3 Total Quality Management Chapter-2 Conceptual Framework for TQM
4 Conceptual Frameworks for Total Quality Management Early TQM Frameworks and Concepts: Deming s fourteen points, Juran s ten steps, Corsby s four absolute and fourteen steps to manage improvement, Feigenbaun s approach to total quality control, Concept on Kaizen s tools PDCA, 5s, 7 wastes, 7 old and new quality tools, 5 whys, value stream mapping,
5 Conceptual Frameworks for Total Quality Management Workstation improvement and success stories, Shigeo Shingo s approach Zero quality control, Just-In-Time(JIT), and Single Minute Exchange of Dies (SMED), Garvin s eight quality dimensions, Ishikawa (Fishbone) diagram, Taguchi s philosophy to quality, The common causes of TQM failures
6 Development of Quality Total Quality Managment Quality Assurance Quality Control Inspection
7 Characteristi cs Primary concern View of Quality Emphasis Methods Who is responsible Orientation and approach Inspection 1800S SQC 1930s Quality Assurance 1950s TQM Detection Control Coordination Management A Problem To be solved Proactive attack Product uniformity Gauging, measurement Inspection dept. Inspects quality Uniform product with less inspection Statistical quality tools Manufacturing and engineering departments Controls quality Designers role Programs and systems All Departments Builds in quality A competitive opportunity The market and consumer needs Strategic planning, goal setting Every (Team) one in the organization Manages in quality
8 Introduction Total Made up of the whole(or) Complete. Quality Degree of Excellence a product or service provides to the customer in present and future. Management Act, art, or manner of handling, controlling, directing, etc. TQM is the art of managing the whole to achieve excellence. 8
9 "TQM is a management approach for an organization, centered on quality, based on the participation of all its members and aiming at long-term success through customer satisfaction, and benefits to all members of the organization and to society." Definition TQM is composed of three paradigms: Total: Organization wide Quality: With its usual Definitions, with all its complexities (External Definition) Management: The system of managing with steps like Plan, Organise, Control, Lead, Staff, etc. 9
10 Definition Total Quality Management (TQM) is a management strategy aimed at embedding awareness of quality in all organizational processes. 10
11 Explanation TQM requires that the company maintain this quality standard in all aspects of its business. This requires ensuring that things are done right the first time and that defects and waste are eliminated from operations. 11
12 Guru s of TQM Walter.A.Shewhart -TQC W.Edwards Deming- 14 Points & PDCA Joseph.M.Juran-Juran s Trilogy and Ten steps A.Feiganbaum-Customer requirement, Employee Involvement, TQC. 12
13 TQM concept from Quality Gurus Edward Deming Father of Quality Management PhD in physics keen statistician US government in the department of Agriculture and the Bureau of Census 1950, Japan, Course on Quality Control Japanese embraced the notion of quality under Deming s inspiration.
14 Deming Deming believes in continuous improvement. He also believes that the consumer is the most important part of a production line. Meeting and exceeding the customers requirements is the task that everyone within the organization needs to accomplish with total commitment. Furthermore, Deming believes in the use of statistical process control (SPC) charts as major method for solving problems.
15 Deming s Fourteen Points 1. Create constancy of purpose to improve products and services 2. Adopt a new philosophy for the new economic age, with management learning what their responsibilities are and assuming leadership for change 3. Cease dependence on mass inspection to achieve quality, by building quality into the product
16 Deming s Fourteen Points 4. End the awarding of business on price; award business on total cost and move towards single suppliers 5. Improve constantly and forever the system of production and service 6. Institute training on the job 7. Institute leadership with the aim of supervising people to help them to do better job.
17 Deming s Fourteen Points 8. Drive out fear so that everyone can work effectively together for the organization 9. Break down barriers between departments. Encourage research, design, sales and production to work together to foresee difficulties belong to the whole system 10. Eliminate slogans, exhortations and numerical targets for the workforce since they are divisive, given that difficulties belong to the whole system
18 Deming s Fourteen Points 11. Eliminate quotas or work standards and management by objectives or numerical goals; leadership should be substituted instead 12. Remove barriers that rob people of their right to pride in their work 13. Encourage education and selfimprovement for everyone 14. Take action to accomplish the transformation
19 The first three principles clearly focus on the cultural aspects of the organization. The fourth principle focuses on the customer relationship The fifth principle is aimed for continuous improvement The sixth, seventh and eighth principles are related to human relationships and management style The ninth principle can be seen as linked to principle, a way for breaking down barriers.
20 The tenth principle, eliminate slogans, exhortation and numerical quotas. setting of targets and quotas is potentially meaningless and divisive unless accompanied by a specific action plan to improve the process. giving the work force a chance to work with pride. The idea of principle thirteen is continuously improve The final principle is to put everyone to work to achieve the transformation.
21 Deming Action Plan 1. Management must agree on the meaning of the quality programme, its implications and the direction to take 2. Top management must accept and adopt the new philosophy 3. Top management must communicate the plan and the necessity of it to the people in the organization 4. Every activity must be recognized as a step in a process and the customers of that process identified; the customers are responsible for the next stage of the process.
22 Deming Action Plan 5. Each stage must adopt the Deming or Shewart cycle -Plan, Do, Check, Action- as the basis of quality improvement 6. Team working must be engendered and encouraged to improve inputs and outputs, everyone must be enabled to contribute to this process 7. An organization for quality must be constructed with the support of knowledgeable statisticians
23 Joseph M. Juran 1924, Engineer Worked as civil servant, executive,, academic, arbitrator, director and management consultant. Quality Control Handbook 1950 Movement of Quality in Japan
24 Quality Trigology Quality Trilogy Definition Quality planning Quality control Quality improvement The activity of developing the products and processes required to meet customers needs. This process deals with execution of plans, conducting operations to meet the goals This process is the means of raising quality performance to unprecedented level.
25 Juran s Ten Steps 1. Build awareness of the need and opportunity for improvement. 2. Set goals for improvement. 3. Organize to reach the goals (establish a quality council, identify problems, select projects, appoint teams, designate facilitators). 4. Provide training. 5. Carry out projects to solve problems.
26 Juran s Ten Steps 6. Report progress. 7. Give recognition. 8. Communicate results. 9. Keep score 10. Maintain momentum by making annual improvement part of the regular systems and processes of the company.
27 Philip B. Crosby Graduate of the Western Reserve University After military service Quality control in manufacturing, Line inspector to quality director Philip Crosby Associates Incorporated and the Quality College based in Florida.
28 Four Absolute First Absolute : The definition of quality is conformance to requirements, not goodness. Second Absolute : The system for causing quality is preventive, not appraisal. Third Absolute Fourth Absolute : The performance standard must be zero defect, not that s close enough. The measurement of quality is the price of non conformance, not indexes
29 Crosby s Fourteen Steps Step 1 : Establish and ensure management commitment. It is vital that the whole management team participate in the programme. Step 2 : Form quality improvement teams (QITs) for quality improvement process planning and administration. The emphasis here is on multidisciplinary team effort. An initiative from the quality department will not be successful. It is essential to build team working across arbitrary; and often artificial, organizational boundaries.
30 Crosby s Fourteen Steps Step 3 : Establish quality measurements. These must apply to every activity throughout the company. A way must found to capture every aspect, design, manufacturing, delivery, and so on. These measurements provide a platform for the next step. Step 4 : Evaluate the cost of quality and explain its use as a management tool to measure waste. This evaluation must highlight, using the measures established in the previous step, where quality improvement will be profitable.
31 Crosby s Fourteen Steps Step 5 : Raise quality awareness among all employees. This is normally undertaken through the training of managers and supervisors, through communications such as videos and books, and by displays and posters. Step 6 : Take actions to correct problems identified through previous steps. This involves encouraging staff to identify and rectify defects, or pass them on to higher supervisory levels where they can be addressed.
32 Crosby s Fourteen Steps Step 7 : Establish a zero defects committee and programme. This is done by establishing a committee or working group to develop ways to initiate and implement a zero defects programme. Step 8 : Train supervisors and managers on their role and responsibilities in the quality improvement process. This step is focused on achieving understanding by all managers and supervisors of the steps in the quality improvement programme in order that they can explain these in turn.
33 Crosby s Fourteen Steps Step 9 : Hold a zero defects day to reaffirm management commitment. This can be achieved in a celebratory atmosphere. Step 10: Encourage individuals and groups to set improvement goals. Goals are of course of no value unless they are related to an appropriate timescale for their achievement. Step 11: Obstacle reporting (i.e., encourage employees to communicate to management any obstacles they take in attaining their improvement goals).
34 Crosby s Fourteen Steps Step 12: Recognize and appreciate all participants. Step 13: Establish quality councils to discuss quality matters on a regular basis. These are essentially forums composed of quality professionals and team leaders allowing them to communicate and determine action plans for further quality improvement. Step 14: Do it all over again to demonstrate that the improvement process never ends. Achievement of quality is an ongoing process. There is always further to go.
35 Armand V. Feigenbaum concept of Total Quality Control (TQC). His book Total Quality Control was first published in 1951 quality as a strategic business tool that requires involvement from everyone quality control as a measurement and evaluated tool. Quality begins with identification of customers requirements and ends with a product or service in the hands of a satisfied customer.
36 Ten attributes of Feigenbaum 1. Total Quality control must be a companywide process. It is a system for integrating quality development, maintenance and improvements efforts in an organization that will enable engineering, marketing, production and service to function at optimal economic levels while achieving customer satisfaction. 2. Quality is defined by the customer.
37 Ten attributes of Feigenbaum 3. Quality and cost is a sum, not a difference. Operating quality costs can be divided into four categories: prevention costs, appraisal costs, internal failure cost and external failure costs. 4. Quality requires both individual and team enthusiasm. 5. Quality is a way of managing. 6. Quality and innovation are interdependent.
38 Ten attributes of Feigenbaum 7. Quality is an ethic. 8. Enhanced quality demands continuous improvement. 9. Quality is the most cost-effective and least capital-intensive route to productivity. 10. Quality is implemented with a total system connected with customers and suppliers.
39 Concept of Kaizan tools Kaizen is ongoing improvement which involves everyone in the organization. Kaizen is a people-oriented approach to competitiveness continuous improvement will benefit the organisation and in turn will benefit the individual Continuous improvement focuses on the whole process (means and the ends) rather than the results only
40 PDCA Cycle Plan: Establish the objectives and processes necessary to deliver result in accordance to customer s requirements and organizations policies. Do: Implement the process. Check: Monitor and measure process and product against policies, objectives and requirement for the product and report result. Act: Take required actions to continually improve process performance.
41 5 S S.N Japanese English (5C) Meaning (5S) 1 Seiri Clear cut (organize) Determine what is necessary and unnecessary and dispose of the later 2 Seition Configuration Provide a convenient, safe and orderly (systematise) place for everything and keeping it there. 3 Seiso Clean and Monitor and restructure the condition check 4 Seiketsu Conform (standardisation) 5 Shitsuke Custom and Practice (Discpline) of working areas during cleaning Set standard, train and maintain. Develop the habit of routine maintenance and strive for further improvement.
42 Points for successful 5 S Participation by all people The program requires top management commitment The CEO should take leadership of the program The program should be supported by all 5S program should be self sustaining The CEO should take a periodic factory tour in person The program should generate sufficient impact at the initial stage Implementation of 5S should so hand in hand with other kaizen program.
43 Waste of Seven Meaning Wastages How to control? 1. Stock Stocking more than required 2. Waiting Wait of job to be performed 3. Over production Producing more than required 4. Transportation Un-necessary material Dispatch & transport to location 5. Processing All parts are processed at a time for production 6. Motion Motion for productivity & quality consistency (Automating waste) 7. Defective products More defective outputs making Reduce Lead Time Improve skill of worker JIT productions Balance and even loads to the equipments Flexible workers Fair prediction of demand Reducing set up times. Use of small specialized production rather than large. Efficient material handling system. Better location layout decision. Put into process what is required only. Suitable technology Improve the motion and then apply automation Group Technology Quality at source Technology improvement Skilled manpower
44 Tools for Quality Control Pareto Analysis Scatter Diagram Control Charts Flow Charts Cause and Effect, Fishbone, Ishikawa Diagram Histogram Check Sheets
45 Parato Analysis 80 : 20 Rule Detection of Vital few
46 Restaurant Complains Complaint Frequency Discourteous 12 server Slow service 42 Cold dinner 5 Cramped tables 20 Smoky air 10
47 Parato Chart
48 Scatter Diagram
49 Scatter Diagrams Scatter diagrams are used to represent and compare two sets of data Plot points of pairs of observations has the values(x 1,Y 1 ), (X 2,Y 2 ), (X 3,Y 3 ),.. (X n, Yn).
50 Control Chart
51 Flow Chart
52 Cause Effect Diagram
53 Histogram or Bar Graph
54 Check-Sheet
55 Seven New QC tools numerical data cannot always adequately express the facts The Seven New Q.C Tools are Affinity diagrams, Relation diagrams, Tree diagrams, Matrix diagrams, Priorities matrix, Arrow diagrams and Process decision program charts.
56 Affinity Diagram It is a technique to generate ideas and linkup with other ideas to form a common idea which facilitates breakthrough thinking and stimulate fresh ideas. The large number of ideas generated can be grouped according to their affinity or relationship to each other.
57 Affinity Diagram
58 Relation Diagram Relation diagram identifies and explores casual relationships among related concepts or ideas. It shows that every idea can be logically linked with more than one other idea Relation diagram is useful tools for finding appropriate strategies by relating different causes of a problem by identifying the root causes of the problem
59 Relation Diagram
60 Tree Diagram Tree Diagrams are drawn to develop a succession of strategies/ means for achieving an objective (target, goal or result) systematically and logically. Constructing this diagram yields specific guidelines for solving a problem. Tree Diagrams are also classified as strategy-development or component development diagrams.
61
62 Matrix Diagram Matrix diagram provides a picture of how well two sets of objects or issues are related and can identify missing pieces in the thought process. The visual depictions can help managers set priorities on plan and actions.
63 Matrix Diagram Actions Goals Improve work Environment Improve Manufacturing Technology Develop New Products Cost Effectivenes s High Quality Shareholder value
64 Priority Matrix This type of matrix is drawn when there are many tasks but there are not enough resources. So instead of just thinking which tasks are more important, the Priority Matrix is drawn. Matrix data analysis takes data and arranges them to display qualitative relationship among variables to make them more easily understood and analysed. It is based on the factor analysis of Statistical techniques.
65 Priority Matrix Requirement Important Weight Best Competition Evaluation Our Company Evaluation Difference Price Reliability Delivery Technical support
66 Arrow diagram This is also known as activity network diagram and is similar to Critical Path Method (CPM). It describes that who is going to do what and when?, what can be done in parallel and what can be done only in series, one after another. This diagram is mostly used by planning aid for construction projects and large manufacturing units.
67 Arrow Diagram
68 Process decision program charts (PDPC) Process decision program charts (PDPC) is a method for mapping out every conceivable event and contingency that can occur when moving from problem statement to possible solutions. PDPCs are used for planning the activities needed to solve problem when information is incomplete or the situation is fluid and hard to forecast.
69
70 5 w h y s Example: The problem is that client, Suraj Imp., is unhappy. Using the 5 Whys, you go through the following steps to get to the cause of the problem: 1. Why is our client, Suraj Imp., unhappy? Because we didn't deliver our services when we said we would. 2. Why were we unable to meet the agreed-upon timeline or schedule for delivery? The job took much longer than we thought it would. 3. Why did it take so much longer? Because we underestimated the complexity of the job. 4. Why did we underestimate the complexity of the job? Because we made a quick estimate of the time needed to complete it, and didn't list the individual stages needed to complete the project. 5. Why didn't we do this? Because we were running behind on other projects. We clearly need to review our time estimation and specification procedures.
71 Value Stream Mapping Value Stream Mapping (VSM) is the process of mapping the material and information flows required to coordinate the activities performed by manufacturers, suppliers and distributors to deliver products to customers. Not only the material flows but also information flows that signal and control the material flows.
72 VSM A typical VSM project involves the development of maps: (1) a Current State Map and (2) one or more Future State Maps that represent progressive improvements in the Current State Map.
73
74
75
76 Workstation Improvement A reasonable industrial workstation design affects not only the productivity but also the health of workers. In industrial workstation, the primary concern has usually been the improvement of the performance of the equipment and then the matching the abilities of the operator with the task requirement. Many industrial workstations are poorly designed, resulting in lower worker productivity and unnecessary injury at the workplace.
77 Workstation improvement The methods used in workstation improvement simplify the work or working methods and must go towards higher productivity. It is always desirable to perform the requisite the function with desired goal with minimum consumption of resources. Workstation is essentially concerned with finding better ways of doing things. It adds value and increases the efficiency by eliminating unnecessary operations, avoidable delays and other forms of waste.
78 Objective of WSI 1. To improve work methods and procedures. 2. To determine the best sequence of doing work. 3. To smoothen material flow with minimum of back tracking and to improve layout. 4. To improve the working conditions and hence to improve labour efficiency. 5. To reduce monotony in the work. 6. To improve plant and material utilisation. 7. Elimination of waste and unproductive operations. 8. To reduce the manufacturing costs through reducing cycle time of operations.
79
80 Shigeo Shingo s approach-zero QC Defects in production may be due to omitting processing (or operations), processing errors, equipment set-up errors, missing parts/component wrong parts/component and adjustment error A good process design prevents defects at all from occurring
81 ZQC consists of the following Source inspection: Checking for the factors that causes errors, not the resulting defect. 100 percent inspection: The operator inspects his or her own work 100 percent, or inexpensive Pokayoke (Poka means error and yokeru means prevent) devices inspect automatically for errors or defective operating condition Immediate action: Stopping operations instantly when a mistake is made and not resuming operations until the error is rectified. Feedback is provided through successive checks, in which the next person in the process immediately feedback information to the supplying operator to stop production and fix the error
82 Just In Time JIT is known as the Japanese philosophy for managing inventory. high volume of production by using minimum inventory of raw materials and work in progress JIT requires high level of quality at each stage of production process, strong vendor relations and fairly predictable demand for smooth flow of work.
83 JIT JIT provides for the cost efficient production in an organization and delivery of only the necessary parts in the right quantity at the right time and place with using the minimum of facilities. It integrated whole based on the principles of continuous improvements and elimination of all kinds of waste
84 (i) What is JIT? A management philosophy; A set of methods (ii) What it does? Reduce wastage Exposes bottle necks & problems Achieves streamline production. (iii) How is does? Employees participation Industrial engineering Continuing improvement. Total quality control ; Small lot size
85 JIT (iv) What it assumes? Stable environment Fairly predictable demand Strong vendor relation Efficient employees
86 Single Machine Exchange of Die If the set-up time is long (high cost), then more products should be produced in one batch in order to reduce set-up cost per unit. Operating like this has the effect of creating more inventories s Shigeo Shingo, of Toyota Motor Co. studied which ultimate objective was to change a machine tool in less than 10 minutes
87 SMED To effect SMED procedures, the logic is to establish the distinction between External set-up : Machine is running and Internal set-up : Machine is stopped In general, set-up times can be reduced by: Locating required inventory and machine tools closer to the operating area and Standardising the set-up functions of machines.
88 Gravin s Eight Quality Dimension Performance: measurable primary characteristics of a product or service Features: added characteristics that enhance the appeal of a product or service Conformance: meeting specifications or industry standards Reliability: consistency of performance over time Durability: useful life of a product or service Serviceability: resolution of problems and complaints Aesthetics: the sensory characteristics of a product or service Perceived quality: subjective assessment of quality based on cues related to the product
89 Taguchi Philosophy Taguchi's main objective is to identify the factors which are responsible for the product and the process variation and control their settings to optimal level. Japanese quality expert known for his work in the area of product design. the method is applied in a systematic and scientific way at a pre-production stage offline prior to the setting of the manufacturing process
90 Taguchi Philosophy Three steps in the engineering design cycle. System design: It is the basic prototype design that meets performance and tolerance specifications of the product. It includes section of materials, parts, components and system assembly. Parameter design: Given a system design, there are generally several parameters whose values need to be determined. One needs to find a functional relationship between the parameter and the measure of performance of the system to determine an optimal value of the parameter. Tolerance design: The purpose of this is to determine allowable ranges of the parameters whose values are optimized in parameter design stage. Achieving the optimal value of a parameter may be very expensive, whereas a sub-optimal value could give the desired quality at lower cost.
91 Common causes of TQM failure 1.Absence or lack of top management s commitment. 2. Inadequate knowledge or understanding of TQM principles and methodology. 3. Failure to accept TQM as a cultural revolution, i.e. a change in the organizational culture or the mind set of the employees: 4. Improper planning: Absence of long term vision, mission, and goals by the top management. Three components of successful TQM planning are (a) Obtaining company-wide commitment, (b) Communicating company vision, mission, and goals, and (c) Providing open communication about the company s new focus.
92 Common causes of TQM failure 5. Absence of continuous training and education 6. Inadequate use of empowerment and team work: 7. The Management related barriers are: (a) Fear of senior management losing control (b) Apprehension and doubts of the senior management, about the efficacy of the TQM methodology (c) Lack of leadership qualities (d) Failure in or faulty delegation of authority (e) Lack of motivation, at the senior level and (f) Managers do not support each other. 8. Incorrect or insufficient or incompatible organisational structure and isolated individuals and departments, autocratic organisational structure.
93 Common causes of TQM failure 9. Inefficient or ineffective measurement techniques and lack of access to data and results 10. The Customer related barriers may be listed as: (a) Inadequate attention to internal and external customers and the public. when a new product is launched (b) Lack of social responsiveness (c) Risks and benefits to the public are ignored or not evaluated. 11. Inability to build a learning organization that provides for continuous improvement.
Total Quality Management
 Seminar Series On Total Quality Management BIJAY LAL PRADHAN, Ph.D. Quality Assurance & Accreditation Centre, T.U. M Sc Statistics, FDPM(IIMA) Total Quality Management Course Title : Seminar on Total Quality
Seminar Series On Total Quality Management BIJAY LAL PRADHAN, Ph.D. Quality Assurance & Accreditation Centre, T.U. M Sc Statistics, FDPM(IIMA) Total Quality Management Course Title : Seminar on Total Quality
BBA Sixth Semester Total Quality Management. -BIJAY LAL PRADHAN M Sc Statistics, FDPM(IIMA) PhD Scholar (TQM)
 BBA Sixth Semester Total Quality Management -BIJAY LAL PRADHAN M Sc Statistics, FDPM(IIMA) PhD Scholar (TQM) Total Quality Management Course Title : Total Quality Management Code No. : MGT 163 Area of
BBA Sixth Semester Total Quality Management -BIJAY LAL PRADHAN M Sc Statistics, FDPM(IIMA) PhD Scholar (TQM) Total Quality Management Course Title : Total Quality Management Code No. : MGT 163 Area of
Chapter 2 Quality Theory
 Chapter 2 Quality Theory 2 1 Quality Gurus and Their Contributions to Quality Theory Edwards Deming Juseph M. Juran Kaoru Ishikawa Armand Feigenbaum Philip Crosby Genichi Taguchi . W. Edwards Deming Gained
Chapter 2 Quality Theory 2 1 Quality Gurus and Their Contributions to Quality Theory Edwards Deming Juseph M. Juran Kaoru Ishikawa Armand Feigenbaum Philip Crosby Genichi Taguchi . W. Edwards Deming Gained
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (KEY) UNIT- I
 SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (KEY) UNIT- I 1. Define quality. Quality is the totality of characteristics of an entity that bear on its ability to satisfy stated and implied needs. 2. What do you mean by quality
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (KEY) UNIT- I 1. Define quality. Quality is the totality of characteristics of an entity that bear on its ability to satisfy stated and implied needs. 2. What do you mean by quality
Introduction to Quality Management. BPF 2123 Quality Management System
 Introduction to Quality Management BPF 2123 Quality Management System 1 Chapter Outline Introduction Changes in the Business Culture Defining Quality Dimensions of Quality Gurus of Quality / TQM Historical
Introduction to Quality Management BPF 2123 Quality Management System 1 Chapter Outline Introduction Changes in the Business Culture Defining Quality Dimensions of Quality Gurus of Quality / TQM Historical
The Philosophy of TQM An Overview
 The Philosophy of TQM An Overview TQM = Customer-Driven Quality Management References for Lecture: Background Reference Material on Web: The Philosophy of TQM by Pat Hammett Customer Quality Measures Customers
The Philosophy of TQM An Overview TQM = Customer-Driven Quality Management References for Lecture: Background Reference Material on Web: The Philosophy of TQM by Pat Hammett Customer Quality Measures Customers
WHY QUALITY IS IMPORTANT? PRODUCT AND QUALITY COSTS OF POOR QUALITY COST OF ACHIEVING GOOD QUALITY. Prevention costs.
 WHY QUALITY IS IMPORTANT? Lecture 7: Quality management systems PRODUCT AND QUALITY Quality has direct impact on economic results in both ways Costs Incomes Quality assurance Poor quality costs Higher
WHY QUALITY IS IMPORTANT? Lecture 7: Quality management systems PRODUCT AND QUALITY Quality has direct impact on economic results in both ways Costs Incomes Quality assurance Poor quality costs Higher
Operations Management
 9-1 Management of Quality Operations Management William J. Stevenson 8 th edition 9-2 Management of Quality CHAPTER 9 Management of Quality McGraw-Hill/Irwin Operations Management, Eighth Edition, by William
9-1 Management of Quality Operations Management William J. Stevenson 8 th edition 9-2 Management of Quality CHAPTER 9 Management of Quality McGraw-Hill/Irwin Operations Management, Eighth Edition, by William
PMP Exam Preparation Workshop Project Quality Management
 PMP Exam Preparation Workshop Project Quality Management 1 Learning Objectives By the end of this session you will understand: The PM Quality Processes The PM Process Groups Project Quality Management
PMP Exam Preparation Workshop Project Quality Management 1 Learning Objectives By the end of this session you will understand: The PM Quality Processes The PM Process Groups Project Quality Management
Chapter 9 1. List and briefly explain the dimensions of product and service quality
 Chapter 9 1. List and briefly explain the dimensions of product and service quality Product Quality the dimensions of product quality include: 1. performance main characteristics or function of the product
Chapter 9 1. List and briefly explain the dimensions of product and service quality Product Quality the dimensions of product quality include: 1. performance main characteristics or function of the product
Managing Quality: Integrating the Supply Chain, 5e (Foster) Chapter 2 Quality Theory
 Managing Quality: Integrating the Supply Chain, 5e (Foster) Chapter 2 Quality Theory 1) A coherent group of general propositions used as principles of explanation for a class of phenomena is referred to
Managing Quality: Integrating the Supply Chain, 5e (Foster) Chapter 2 Quality Theory 1) A coherent group of general propositions used as principles of explanation for a class of phenomena is referred to
PMPA Tech Conference Do we have the Tools and Knowledge to weather the Storm?
 PMPA Tech Conference 2014 Do we have the Tools and Knowledge to weather the Storm? Quality Initiatives Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award ISO Standards (ISO 9001, ISO 14001, AS 9100, ETC ) Six Sigma
PMPA Tech Conference 2014 Do we have the Tools and Knowledge to weather the Storm? Quality Initiatives Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award ISO Standards (ISO 9001, ISO 14001, AS 9100, ETC ) Six Sigma
Chapter 1 Statistical Quality Control, 7th Edition by Douglas C. Montgomery. Copyright (c) 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 1 Learning Objectives 2 1.1 Definitions Meaning of Quality and Quality Improvement 1.1.1 The Eight Dimensions of Quality 1. Performance 2. Reliability 3. Durability 4. Serviceability 5. Aesthetics 6. Features
1 Learning Objectives 2 1.1 Definitions Meaning of Quality and Quality Improvement 1.1.1 The Eight Dimensions of Quality 1. Performance 2. Reliability 3. Durability 4. Serviceability 5. Aesthetics 6. Features
TQM and Reliability Engineering
 Total Quality Management & Reliability Engineering Dr V. Muralidharan Dept. of Mechatronics SRM University Introduction Total Quality Management TQM is an enhancement to the traditional way of doing business.
Total Quality Management & Reliability Engineering Dr V. Muralidharan Dept. of Mechatronics SRM University Introduction Total Quality Management TQM is an enhancement to the traditional way of doing business.
Project Quality Management. For the PMP Exam using PMBOK
 Project Quality Management For the PMP Exam using PMBOK Guide 5 th Edition PMI, PMP, PMBOK Guide are registered trade marks of Project Management Institute, Inc. Contacts Name: Khaled El-Nakib, PMP, PMI-RMP
Project Quality Management For the PMP Exam using PMBOK Guide 5 th Edition PMI, PMP, PMBOK Guide are registered trade marks of Project Management Institute, Inc. Contacts Name: Khaled El-Nakib, PMP, PMI-RMP
Dimensions of product and service quality
 Dimensions of product and service quality DIMENSIONS OF QUALITY Dimension Meaning and Example Performance Primary product characteristics, such as the brightness of the picture Features Secondary characteristics,
Dimensions of product and service quality DIMENSIONS OF QUALITY Dimension Meaning and Example Performance Primary product characteristics, such as the brightness of the picture Features Secondary characteristics,
Chapter Two: Literature Review
 Chapter Two: Literature Review 2.1 The Concept of Total Quality Management (TQM) TQM is only one of many approaches to getting work done and accomplishing goals. Several experiences have shown that by
Chapter Two: Literature Review 2.1 The Concept of Total Quality Management (TQM) TQM is only one of many approaches to getting work done and accomplishing goals. Several experiences have shown that by
PROJECT QUALITY MANAGEMENT. 1 Powered by POeT Solvers LImited
 PROJECT QUALITY MANAGEMENT 1 www.pmtutor.org Powered by POeT Solvers LImited WHAT S PROJECT QUALITY MANAGEMENT? WHAT S PROJECT QUALITY MANAGEMENT? Project Quality Management processes include all the activities
PROJECT QUALITY MANAGEMENT 1 www.pmtutor.org Powered by POeT Solvers LImited WHAT S PROJECT QUALITY MANAGEMENT? WHAT S PROJECT QUALITY MANAGEMENT? Project Quality Management processes include all the activities
TQM i.e. (Total Quality Management) Construction Projects
 TQM i.e. (Total Quality Management) In Construction Projects Concepts of i) KAIZEN i. e Continuous Improvement ii) ZERO DEFECTS i. e. Perfection in what ever we do Total quality management is a managerial
TQM i.e. (Total Quality Management) In Construction Projects Concepts of i) KAIZEN i. e Continuous Improvement ii) ZERO DEFECTS i. e. Perfection in what ever we do Total quality management is a managerial
Quality: Getting the Basics Right. Trevor Naidoo
 Quality: Getting the Basics Right Lecture outline What is quality? Evolution of quality management Focus of quality management customers Role of employees in quality improvement Quality in service companies
Quality: Getting the Basics Right Lecture outline What is quality? Evolution of quality management Focus of quality management customers Role of employees in quality improvement Quality in service companies
Historical Phases of Production
 Lean 101 Overview Lean Background Taiichi Ohno and Shigeo Shingo developed Lean Manufacturing at Toyota over a period of 20-30 years. Their intention was not to develop some sort of unified field theory
Lean 101 Overview Lean Background Taiichi Ohno and Shigeo Shingo developed Lean Manufacturing at Toyota over a period of 20-30 years. Their intention was not to develop some sort of unified field theory
Application of Continuous Improvement Process in Manufacturing Industry
 Application of Continuous Improvement Process in Manufacturing Industry Edwin Joy Pulikkottil 1, Sibinraj R 2 1,2PG Scholar, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, ECET Coimbatore, India ---------------------------------------------------------------------***---------------------------------------------------------------------
Application of Continuous Improvement Process in Manufacturing Industry Edwin Joy Pulikkottil 1, Sibinraj R 2 1,2PG Scholar, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, ECET Coimbatore, India ---------------------------------------------------------------------***---------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Quality Service. Unit 5
 Total Quality Service Unit 5 1 What is TQM? Total quality management (TQM) is an approach for continuously improving the quality of every aspect of business life.it is a never ending process of improvement
Total Quality Service Unit 5 1 What is TQM? Total quality management (TQM) is an approach for continuously improving the quality of every aspect of business life.it is a never ending process of improvement
Online International Interdisciplinary Research Journal, {Bi-Monthly}, Volume-II, Issue-II, Mar-Apr2012
 Software Development Process And The Total Quality Management Amit C. Joshi Department of Computer Management, Business Administration College, Buldana (M.S.), India. Abstract This paper discusses the
Software Development Process And The Total Quality Management Amit C. Joshi Department of Computer Management, Business Administration College, Buldana (M.S.), India. Abstract This paper discusses the
Total Quality Management Chapter 3 Quality Management Philosophies
 Total Quality Management Chapter 3 Quality Management Philosophies Chapter3 1 Quality Management Philosophies Dr. W. Edwards Deming: (1900-1993) is considered to be the Father of Modern Quality Dr. Deming
Total Quality Management Chapter 3 Quality Management Philosophies Chapter3 1 Quality Management Philosophies Dr. W. Edwards Deming: (1900-1993) is considered to be the Father of Modern Quality Dr. Deming
International Journal on Textile Engineering and Processes, ISSN: , Vol 1, Issue 1, Jan2015
 Total Quality Management in Terry Fabric Manufacturing Pranjali Chandurkar, CTF Abstract The challenge that companies face as the 21st Century gets underway, is to succeed in global economy where competition
Total Quality Management in Terry Fabric Manufacturing Pranjali Chandurkar, CTF Abstract The challenge that companies face as the 21st Century gets underway, is to succeed in global economy where competition
Quality Engineering (ME522)
 Quality Engineering (ME522) Dr. Monoj Bardalai Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Tezpur University 13-02-2019 2 Introduction: Total Quality Management (TQM) 6 Basic concepts 1. Involvement
Quality Engineering (ME522) Dr. Monoj Bardalai Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Tezpur University 13-02-2019 2 Introduction: Total Quality Management (TQM) 6 Basic concepts 1. Involvement
Quality Management Chapter 14
 Quality Management Chapter 14 1 Objectives What is Quality? Total Quality Management TQM in Service Cost of Quality Quality Improvements Quality Awards and Certifications 2 What is Quality? The Meaning
Quality Management Chapter 14 1 Objectives What is Quality? Total Quality Management TQM in Service Cost of Quality Quality Improvements Quality Awards and Certifications 2 What is Quality? The Meaning
Learning Objectives. Defining Quality. Defining Quality 5 Ways. Manufacturing Quality vs. Service Quality. Cost of Quality. Chapter 5 Managing Quality
 Chapter 5 Managing Quality Operations Management by R. Dan Reid & Nada R. Sanders 4th Edition Wiley 2010 Learning Objectives Explain the meaning of TQM Identify the costs of Quality Identify Quality leaders
Chapter 5 Managing Quality Operations Management by R. Dan Reid & Nada R. Sanders 4th Edition Wiley 2010 Learning Objectives Explain the meaning of TQM Identify the costs of Quality Identify Quality leaders
Applications of The Deming s 14 Principles. Who was Dr. W. Edwards Deming? Deming s Principles 10/14/13. W. Edwards Deming s 14 Points
 Applications of The Deming s 14 Principles Who was Dr. W. Edwards Deming? Dr. W. E. Deming was one of the world s leaders of Quality management. PRESENTED BY SACHIN KHANDELWAL 21 MEHUL LUDBE 22 SANDEEP
Applications of The Deming s 14 Principles Who was Dr. W. Edwards Deming? Dr. W. E. Deming was one of the world s leaders of Quality management. PRESENTED BY SACHIN KHANDELWAL 21 MEHUL LUDBE 22 SANDEEP
UNIT-4 ====================================================================== UNIVERSITY SYLLABUS
 UNIT-4 ====================================================================== UNIVERSITY SYLLABUS Quality Control: Meaning, process control, SQC control charts, single, double and sequential sampling,
UNIT-4 ====================================================================== UNIVERSITY SYLLABUS Quality Control: Meaning, process control, SQC control charts, single, double and sequential sampling,
Lean Gold Certification Blueprint
 The Lean Certification Blueprint provides additional useful information beyond the Body of Knowledge. The Body of Knowledge specifies the competencies, topics, and subtopics required by different types
The Lean Certification Blueprint provides additional useful information beyond the Body of Knowledge. The Body of Knowledge specifies the competencies, topics, and subtopics required by different types
Involve your team in continuous improvement: Content guide
 Involve your team in continuous improvement: Content guide Contents Involve your team in continuous improvement: Content guide 1 Overview 2 Key terms 2 Identifying opportunities for improvement 4 Total
Involve your team in continuous improvement: Content guide Contents Involve your team in continuous improvement: Content guide 1 Overview 2 Key terms 2 Identifying opportunities for improvement 4 Total
Implementation of Total Quality Management in Construction Company
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Implementation of Total Quality Management in Construction Company Syed Md. Shahwaz Mechanical Engineer(QA/QC and NDT) Anwesha Engineering
International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Implementation of Total Quality Management in Construction Company Syed Md. Shahwaz Mechanical Engineer(QA/QC and NDT) Anwesha Engineering
Total Quality Management
 Total Quality Management The way of managing organization to achieve excellence Total everything Quality degree of excellence Management art, act or way of organizing, controlling, planning, directing
Total Quality Management The way of managing organization to achieve excellence Total everything Quality degree of excellence Management art, act or way of organizing, controlling, planning, directing
Ch 26 Just-In-Time and Lean Production. What is Lean Production? Structure of Lean Production System. Activities in Manufacturing.
 Ch 26 Just-In-Time and Lean Production Sections: 1. Lean Production and Waste in Manufacturing 2. Just-in-time Production Systems 3. Autonomation 4. Worker Involvement What is Lean Production? Lean production
Ch 26 Just-In-Time and Lean Production Sections: 1. Lean Production and Waste in Manufacturing 2. Just-in-time Production Systems 3. Autonomation 4. Worker Involvement What is Lean Production? Lean production
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES QUESTION BANK UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES QUESTION BANK IV/VII Subject Code/Name: MG1401/Total Quality Management Year/Sem : UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION PART A( 2 marks) 1 Define quality. 2
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES QUESTION BANK IV/VII Subject Code/Name: MG1401/Total Quality Management Year/Sem : UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION PART A( 2 marks) 1 Define quality. 2
Quality management in construction projects
 Quality management in construction projects MSc, PMP, CQE ASQ. Introduction The quality as a concept has a deep root in the history, anyway the quality profession greatly evolved after World War II when
Quality management in construction projects MSc, PMP, CQE ASQ. Introduction The quality as a concept has a deep root in the history, anyway the quality profession greatly evolved after World War II when
Methods Engineering. Methods Engineering
 Methods Engineering 1 Methods Engineering Part II Chapters: 8. Introduction to Methods Engineering and Operations Analysis 9. Charting Techniques 10.Motion Study and Work Design 2 1 Chapter 8 Introduction
Methods Engineering 1 Methods Engineering Part II Chapters: 8. Introduction to Methods Engineering and Operations Analysis 9. Charting Techniques 10.Motion Study and Work Design 2 1 Chapter 8 Introduction
MODULE 3 Introduction to Quality and Quality Improvement in Health) Unit 3.3 The Theoretical Framework for Modern Quality Improvement
 MODULE 3 Introduction to Quality and Quality Improvement in Health) Unit 3.3 The Theoretical Framework for Modern Quality Improvement Unit 3.3: Objectives Discuss Deming s theory of profound knowledge
MODULE 3 Introduction to Quality and Quality Improvement in Health) Unit 3.3 The Theoretical Framework for Modern Quality Improvement Unit 3.3: Objectives Discuss Deming s theory of profound knowledge
Enhancing Audit Program Using Dr. Deming s 14 points. Naren Patel ASQ Fellow October 12-13, 2017
 Enhancing Audit Program Using Dr. Deming s 14 points Naren Patel ASQ Fellow October 12-13, 2017 1 Dr. Deming, the Father of Quality W. Edward Deming is famous for the insightful views, ideas and commentary
Enhancing Audit Program Using Dr. Deming s 14 points Naren Patel ASQ Fellow October 12-13, 2017 1 Dr. Deming, the Father of Quality W. Edward Deming is famous for the insightful views, ideas and commentary
Lean Manufacturing. Introduction & Background to Lean
 Lean Manufacturing Introduction & Background to Lean Professor Trevor Spedding P160 t.spedding@gre.ac.uk 01634 883425 Grahame Baker P237 g.baker@gre.ac.uk 01634 883302 Sam Berkhauer P345 BS983@gre.ac.uk
Lean Manufacturing Introduction & Background to Lean Professor Trevor Spedding P160 t.spedding@gre.ac.uk 01634 883425 Grahame Baker P237 g.baker@gre.ac.uk 01634 883302 Sam Berkhauer P345 BS983@gre.ac.uk
Process Performance and Quality Chapter 6
 Process Performance and Quality Chapter 6 How Process Performance and Quality fits the Operations Management Philosophy Operations As a Competitive Weapon Operations Strategy Project Management Process
Process Performance and Quality Chapter 6 How Process Performance and Quality fits the Operations Management Philosophy Operations As a Competitive Weapon Operations Strategy Project Management Process
Process Performance and Quality
 Process Performance and Quality How Process Performance and Quality fits the Operations Management Philosophy Chapter 6 Operations As a Competitive Weapon Operations Strategy Project Management Process
Process Performance and Quality How Process Performance and Quality fits the Operations Management Philosophy Chapter 6 Operations As a Competitive Weapon Operations Strategy Project Management Process
CSU Project Management Certificate Program
 CSU Project Management Certificate Program Project Quality Management Instructor: Ric Rothschild, PMP Contact Info: ric.rothschild@comcast.net 303-664-1117 1 Project Quality Management Agenda Introduction
CSU Project Management Certificate Program Project Quality Management Instructor: Ric Rothschild, PMP Contact Info: ric.rothschild@comcast.net 303-664-1117 1 Project Quality Management Agenda Introduction
Total Quality Management
 Total Quality Management James R. Evans Total Quality Management Contents About This Course How to Take This Course ix xi 1 Quality in Manufacturing and Service 1 A Brief History Modern Developments
Total Quality Management James R. Evans Total Quality Management Contents About This Course How to Take This Course ix xi 1 Quality in Manufacturing and Service 1 A Brief History Modern Developments
Workshop 5. Managing Quality. Kate Hughes & John Whiteley
 Workshop 5 Managing Quality Kate Hughes & John Whiteley 8-2 The various definitions of quality The transcendent approach views quality as synonymous with innate excellence. The manufacturing-based approach
Workshop 5 Managing Quality Kate Hughes & John Whiteley 8-2 The various definitions of quality The transcendent approach views quality as synonymous with innate excellence. The manufacturing-based approach
JICA Project Briefing Paper
 JICA Project Briefing Paper TQM IN JAPAN Deming, Juran and Ishikawa Dennis S. Tachiki Faculty of Business Administration Tamagawa University tachiki@bus.tamagawa.ac.jp If Japan can achieve high quality
JICA Project Briefing Paper TQM IN JAPAN Deming, Juran and Ishikawa Dennis S. Tachiki Faculty of Business Administration Tamagawa University tachiki@bus.tamagawa.ac.jp If Japan can achieve high quality
Principles of Operations Management: Concepts and Applications Topic Outline Principles of managing Operations (PMO)
 Principles of Operations Management: Concepts and Applications Topic Outline Principles of managing Operations (PMO) Session 1: Operations Management Foundations Define the science and practice of operations
Principles of Operations Management: Concepts and Applications Topic Outline Principles of managing Operations (PMO) Session 1: Operations Management Foundations Define the science and practice of operations
MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI KUALA LUMPUR
 STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR FIFTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION MGT2063 TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT DMGW-E-F-1/13, DMGQ-E-F-1/13, DMGA-E-F-1/13,
STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR FIFTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION MGT2063 TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT DMGW-E-F-1/13, DMGQ-E-F-1/13, DMGA-E-F-1/13,
northeastern pennsylvania industrial resource center Principles of Operational Excellence a brief overview of the initial assessment
 northeastern pennsylvania industrial resource center Principles of Operational Excellence a brief overview of the initial assessment Shingo Transformational Process Principle Based Architecture A culture
northeastern pennsylvania industrial resource center Principles of Operational Excellence a brief overview of the initial assessment Shingo Transformational Process Principle Based Architecture A culture
The JURAN Quality Program
 The JURAN Quality Program Revolutionized by Dr. Joseph M. Juran-- The Father of Quality Commerce 399 Group Project Presented by Group A4: Claire, Dan, Grace, Roy, Xinna June 30th 2005 "My job of contributing
The JURAN Quality Program Revolutionized by Dr. Joseph M. Juran-- The Father of Quality Commerce 399 Group Project Presented by Group A4: Claire, Dan, Grace, Roy, Xinna June 30th 2005 "My job of contributing
Analysis of Software Quality Tools Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Recall Case
 Analysis of Software Quality Tools Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Recall Case Aishwary Borkar, Aishwarya Auti, Robinson Ingle Symbiosis Institute of Computer Studies and Research SI(D)U Pune, India Symbiosis Institute
Analysis of Software Quality Tools Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Recall Case Aishwary Borkar, Aishwarya Auti, Robinson Ingle Symbiosis Institute of Computer Studies and Research SI(D)U Pune, India Symbiosis Institute
CHAPTER 3 PROJECT MANAGEMENT AND QUALITY. Dr. Abdul Aziz A. Bubshait. CEM 515 Construction Quality Assurance
 CHAPTER 3 PROJECT MANAGEMENT AND QUALITY Dr. Abdul Aziz A. Bubshait CEM 515 Construction Quality Assurance ١ Introduction Many excellent organizations seek to define the customers' project requirements
CHAPTER 3 PROJECT MANAGEMENT AND QUALITY Dr. Abdul Aziz A. Bubshait CEM 515 Construction Quality Assurance ١ Introduction Many excellent organizations seek to define the customers' project requirements
LEAN PRODUCTION SYSTEM
 LEAN PRODUCTION SYSTEM Introduction Lean Overview Process Control Tools 1. Flow Chart / Diagram 2. Check Sheet 3. Histogram 4. Pareto Chart / Diagram 5. Cause-and-Effect Diagram 6. Why-Why Diagram 7. Scatter
LEAN PRODUCTION SYSTEM Introduction Lean Overview Process Control Tools 1. Flow Chart / Diagram 2. Check Sheet 3. Histogram 4. Pareto Chart / Diagram 5. Cause-and-Effect Diagram 6. Why-Why Diagram 7. Scatter
Intelligent Solutions, Inc. Copyright 2008 Intelligent Solutions, Inc., All Rights Reserved. Geiger - 1
 Geiger - 1 It is important to note that data quality while critically important to business intelligence is also critical to the operations of the enterprise. Data Quality Management covers all operational
Geiger - 1 It is important to note that data quality while critically important to business intelligence is also critical to the operations of the enterprise. Data Quality Management covers all operational
DIRECTORATE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION DIPLOMA IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. M SCHEME onwards III YEAR V SEMESTER CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT CENTRE
 DIRECTORATE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION DIPLOMA IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING M SCHEME 2015-2016 onwards III YEAR V SEMESTER ELECTIVE THEORY 32071 TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT CENTRE Curriculum
DIRECTORATE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION DIPLOMA IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING M SCHEME 2015-2016 onwards III YEAR V SEMESTER ELECTIVE THEORY 32071 TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT CENTRE Curriculum
Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Wisconsin - Platteville 3. Statistical Process Control
 Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Wisconsin - Platteville 3. Statistical Process Control Yan Shi SE 3730 / CS 5730 Lecture Notes Outline About Deming and Statistical Process Control
Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Wisconsin - Platteville 3. Statistical Process Control Yan Shi SE 3730 / CS 5730 Lecture Notes Outline About Deming and Statistical Process Control
4. Which of the following are generally easy to detect using statistical methods, and it is usually economical to remove them?
 1. In total quality perspective, quality planning, and strategic business planning are treated as which of the following? a. Different b. *Consistent c. Indistinguishable d. Dissimilar 2. The marketing
1. In total quality perspective, quality planning, and strategic business planning are treated as which of the following? a. Different b. *Consistent c. Indistinguishable d. Dissimilar 2. The marketing
Managing the Lean Transformation
 Managing the Lean Transformation 22-23 February & 18-19 April 2016 Description: This four-day course will introduce operations managers to the system of philosophies and methods that are necessary for
Managing the Lean Transformation 22-23 February & 18-19 April 2016 Description: This four-day course will introduce operations managers to the system of philosophies and methods that are necessary for
APICS PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT TOPIC OUTLINE CONCEPTS AND APPLICATIONS
 APICS PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT TOPIC OUTLINE CONCEPTS AND APPLICATIONS About this Topic Outline This outline details the concepts and applications coved in all five of the APICS Principles of
APICS PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT TOPIC OUTLINE CONCEPTS AND APPLICATIONS About this Topic Outline This outline details the concepts and applications coved in all five of the APICS Principles of
Citation for published version (APA): Zhang, Z. (1997). Developing a TQM quality management method model. s.n.
 University of Groningen Developing a TQM quality management method model Zhang, Zhihai IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen Developing a TQM quality management method model Zhang, Zhihai IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
Lab Quality Confab LEAN Principles. 4 Fundamental LEAN Tools to Transform your Laboratory. Rita D Angelo, Bonnie Messinger, Bill Krzisnik
 Lab Quality Confab 2018 LEAN Principles 4 Fundamental LEAN Tools to Transform your Laboratory Rita D Angelo, Bonnie Messinger, Bill Krzisnik Learning Objectives The Learner will be able to: 1. Understand
Lab Quality Confab 2018 LEAN Principles 4 Fundamental LEAN Tools to Transform your Laboratory Rita D Angelo, Bonnie Messinger, Bill Krzisnik Learning Objectives The Learner will be able to: 1. Understand
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE WORKS OF W. EDWARDS DEMING
 Total Quality Management AN INTRODUCTION TO THE WORKS OF W. EDWARDS DEMING D E M I N G Dr. W. Edwards Deming (1900-1993) B.S. Electrical Engineering M.S./Ph.D. Mathematics / Physics Asked by Gen MacArthur
Total Quality Management AN INTRODUCTION TO THE WORKS OF W. EDWARDS DEMING D E M I N G Dr. W. Edwards Deming (1900-1993) B.S. Electrical Engineering M.S./Ph.D. Mathematics / Physics Asked by Gen MacArthur
14 Ways to Destroy Your Organization - And 14 Ways to Develop It!
 14 Ways to Destroy Your Organization - And 14 Ways to Develop It! CQI Presenta,on Dennis Sergent, January 26, 2076 Our Program This program provides examples to show how managers can o5en destroy their
14 Ways to Destroy Your Organization - And 14 Ways to Develop It! CQI Presenta,on Dennis Sergent, January 26, 2076 Our Program This program provides examples to show how managers can o5en destroy their
Global Operations and Supply Chain Management Final Exam Notes
 Global Operations and Supply Chain Management Final Exam Notes Lecture One Operations Management: the process that effectively produce, transform and deliver a product or service. Inputs -> transformation
Global Operations and Supply Chain Management Final Exam Notes Lecture One Operations Management: the process that effectively produce, transform and deliver a product or service. Inputs -> transformation
Quality Management EOE-072. It costs a lot to produce a bad product. Norman Augustine
 Quality Management EOE-072 It costs a lot to produce a bad product. Norman Augustine 1 Unit-1 Quality Concept 2 Meaning of Quality Meaning of Quality Producer s Perspective Co su er s Perspective Quality
Quality Management EOE-072 It costs a lot to produce a bad product. Norman Augustine 1 Unit-1 Quality Concept 2 Meaning of Quality Meaning of Quality Producer s Perspective Co su er s Perspective Quality
Information Technology Project Management Fifth Edition
 Information Technology Project Management Fifth Edition By Jack T. Marchewka Northern Illinois University 9-1 Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Managing Project Quality Chapter 9 9-2 Copyright 2015
Information Technology Project Management Fifth Edition By Jack T. Marchewka Northern Illinois University 9-1 Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Managing Project Quality Chapter 9 9-2 Copyright 2015
LEAN CERTIFICATION BODY OF KNOWLEDGE RUBRIC VERSION 3.0
 MODULE 1 LEAN CERTIFICATION BODY OF KNOWLEDGE RUBRIC VERSION 3.0 1. Cultural Enablers 15% 20% 25% 1.1. Principles of Cultural Enablers 3% 4% 5% 1.1.1. Respect for the individual 1.1.2. Humility 1.2. Processes
MODULE 1 LEAN CERTIFICATION BODY OF KNOWLEDGE RUBRIC VERSION 3.0 1. Cultural Enablers 15% 20% 25% 1.1. Principles of Cultural Enablers 3% 4% 5% 1.1.1. Respect for the individual 1.1.2. Humility 1.2. Processes
Removing the Barriers to Efficient Manufacturing
 Removing the Barriers to Efficient Manufacturing Daniel L. Ferguson /O\ \Cf*" ^ *^^S CRC Press I Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group,
Removing the Barriers to Efficient Manufacturing Daniel L. Ferguson /O\ \Cf*" ^ *^^S CRC Press I Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group,
Total Quality Management (TQM): A Strategy for Competitive Advantage
 Available online at : http://euroasiapub.org Vol. 6, Issue 9, September - 2016, pp. 51~55 Thomson Reuters ID: L-5236-2015 Total Quality Management (TQM): A Strategy for Competitive Advantage Dr Mahesh.
Available online at : http://euroasiapub.org Vol. 6, Issue 9, September - 2016, pp. 51~55 Thomson Reuters ID: L-5236-2015 Total Quality Management (TQM): A Strategy for Competitive Advantage Dr Mahesh.
UNIT I - INTRODUCTION
 SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2000 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2000 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
How the Ideas of a 1950s Statistician Taught me more about Management than Business School. Amy Shropshire, CASK Communications
 How the Ideas of a 1950s Statistician Taught me more about Management than Business School Amy Shropshire, CASK Communications Scrobbesbyrigscīr......but you can call me Amy W. Edwards Demming image Eighty-five
How the Ideas of a 1950s Statistician Taught me more about Management than Business School Amy Shropshire, CASK Communications Scrobbesbyrigscīr......but you can call me Amy W. Edwards Demming image Eighty-five
Quality Improvement in the Modular Housing Industry
 Quality Improvement in the Modular Housing Industry Ahmad K. Elshennawy, Ph.D. Michael A. Mullens, Ph.D., PE Isabelina Nahmens Department of Industrial Engineering & Management Systems University of Central
Quality Improvement in the Modular Housing Industry Ahmad K. Elshennawy, Ph.D. Michael A. Mullens, Ph.D., PE Isabelina Nahmens Department of Industrial Engineering & Management Systems University of Central
Understanding the Functions and Roles of Management. Managerial Functions. The Roles of Management. Organizing. Planning. Leading.
 Understanding the Functions and Roles of Management Prentice Hall, 2004 Business In Action 2e Chapter 6-1 Managerial Functions Planning Organizing Leading Controlling Prentice Hall, 2004 Business In Action
Understanding the Functions and Roles of Management Prentice Hall, 2004 Business In Action 2e Chapter 6-1 Managerial Functions Planning Organizing Leading Controlling Prentice Hall, 2004 Business In Action
Full file at
 WHAT IS THEORY? CHAPTER 2 QUALITY THEORY MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A coherent group of general propositions used as principles of explanation for a class of phenomena is referred to as a: A. postulate
WHAT IS THEORY? CHAPTER 2 QUALITY THEORY MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A coherent group of general propositions used as principles of explanation for a class of phenomena is referred to as a: A. postulate
UNIT I - INTRODUCTION
 UNIT I - INTRODUCTION Definition of Quality, Dimensions of Quality, Quality Planning, Quality costs Analysis Techniques for Quality Costs, Basic concepts of Total Quality Management, Historical Review,
UNIT I - INTRODUCTION Definition of Quality, Dimensions of Quality, Quality Planning, Quality costs Analysis Techniques for Quality Costs, Basic concepts of Total Quality Management, Historical Review,
Engaging All Employees to Eliminate the Eight Wastes
 Engaging All Employees to Eliminate the Eight Wastes Abstract Charles Aubrey Vice President, Anderson Pharmaceutical Packaging, USA Kaizen means continuous improvement in Japanese. It has become closely
Engaging All Employees to Eliminate the Eight Wastes Abstract Charles Aubrey Vice President, Anderson Pharmaceutical Packaging, USA Kaizen means continuous improvement in Japanese. It has become closely
UNIT 2 QUALITY PHILOSOPHY
 UNIT 2 QUALITY PHILOSOPHY 1 Quality What is quality? It is a relative word It lies in the eyes of the perceiver According to ISO 9000:2000, it is defined as the degree to which a set of inherent characteristics
UNIT 2 QUALITY PHILOSOPHY 1 Quality What is quality? It is a relative word It lies in the eyes of the perceiver According to ISO 9000:2000, it is defined as the degree to which a set of inherent characteristics
Malay (Rumi, Roman script)
 Hai Malay (Rumi, Roman script) Project Management Process Groups Project Integration Management Initiating Planning Executing Scope Monitoring & Controlling Closing Knowledge Areas Time Cost Quality Human
Hai Malay (Rumi, Roman script) Project Management Process Groups Project Integration Management Initiating Planning Executing Scope Monitoring & Controlling Closing Knowledge Areas Time Cost Quality Human
For the PMP Exam using PMBOK. PMI, PMP, PMBOK Guide are registered trade marks of Project Management Institute, Inc.
 For the PMP Exam using PMBOK Guide 5 th Edition PMI, PMP, PMBOK Guide are registered trade marks of Project Management Institute, Inc. 1 Contacts Name: Khaled El-Nakib, MSc, PMP, PMI-RMP URL: http://www.khaledelnakib.com
For the PMP Exam using PMBOK Guide 5 th Edition PMI, PMP, PMBOK Guide are registered trade marks of Project Management Institute, Inc. 1 Contacts Name: Khaled El-Nakib, MSc, PMP, PMI-RMP URL: http://www.khaledelnakib.com
JUST IN TIME (JIT), LEAN, AND TOYOTA PRODUCTION SYSTEM (TPS)
 JUST IN TIME (JIT), LEAN, AND TOYOTA PRODUCTION SYSTEM (TPS) Dr. Mahmoud Abbas Mahmoud Al-Naimi Assistant Professor Industrial Engineering Branch Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy University
JUST IN TIME (JIT), LEAN, AND TOYOTA PRODUCTION SYSTEM (TPS) Dr. Mahmoud Abbas Mahmoud Al-Naimi Assistant Professor Industrial Engineering Branch Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy University
LEAN MANUFACTUING-CONCEPT, LIMITATION, APPLICATIONS: AN OVERVIEW
 LEAN MANUFACTUING-CONCEPT, LIMITATION, APPLICATIONS: AN OVERVIEW Submitted By Ms. PUNAM NIVRUTTI PATIL DPGD/OC13/1243 SPECIALIZATION: OPERATIONS WELINGKAR INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT DEVELOPMENT & RESEACH
LEAN MANUFACTUING-CONCEPT, LIMITATION, APPLICATIONS: AN OVERVIEW Submitted By Ms. PUNAM NIVRUTTI PATIL DPGD/OC13/1243 SPECIALIZATION: OPERATIONS WELINGKAR INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT DEVELOPMENT & RESEACH
Outline. Push-Pull Systems Global Company Profile: Toyota Motor Corporation Just-in-Time, the Toyota Production System, and Lean Operations
 JIT and Lean Operations Outline Push-Pull Systems Global Company Profile: Toyota Motor Corporation Just-in-Time, the Toyota Production System, and Lean Operations Eliminate Waste Remove Variability Improve
JIT and Lean Operations Outline Push-Pull Systems Global Company Profile: Toyota Motor Corporation Just-in-Time, the Toyota Production System, and Lean Operations Eliminate Waste Remove Variability Improve
Chapter 3: Employee Involvement
 Chapter 3: Employee Involvement Maslow s Hierarchy of needs: Motivation Self actualization Esteem Social Security Survival 26-09-2018 1 Herzberg s two factor theory Motivators- recognition, responsibility,
Chapter 3: Employee Involvement Maslow s Hierarchy of needs: Motivation Self actualization Esteem Social Security Survival 26-09-2018 1 Herzberg s two factor theory Motivators- recognition, responsibility,
Learning Objectives. 1. Explain how lean systems improve internal and supply chain operations
 CHAPTER EIGHT Lean Systems McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1. Explain how lean systems improve internal and supply chain operations
CHAPTER EIGHT Lean Systems McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1. Explain how lean systems improve internal and supply chain operations
STATISTICAL QUALITY CONTROL. Majid Rafiee Department of Industrial Engineering Sharif University of Technology
 STATISTICAL QUALITY CONTROL Majid Rafiee Department of Industrial Engineering Sharif University of Technology rafiee@sharif.ir Quality Improvement in Modern Business Environment Copyright Notice Parts
STATISTICAL QUALITY CONTROL Majid Rafiee Department of Industrial Engineering Sharif University of Technology rafiee@sharif.ir Quality Improvement in Modern Business Environment Copyright Notice Parts
SEMBODAI RUKMANI VARATHARAJAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 SEMBODAI RUKMANI VARATHARAJAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICSAND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub.Code :GE6757 Branch / Year / Sem : ECE/IV/VII Sub.Name :TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT
SEMBODAI RUKMANI VARATHARAJAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICSAND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub.Code :GE6757 Branch / Year / Sem : ECE/IV/VII Sub.Name :TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT
Quality Management in Construction Projects. Dr. Nabil El Sawalhi
 Quality Management in Construction Projects Dr. Nabil El Sawalhi 1 Quality Definition The American Society for Quality (ASQ) glossary defines quality as A subjective term for which, each person has his
Quality Management in Construction Projects Dr. Nabil El Sawalhi 1 Quality Definition The American Society for Quality (ASQ) glossary defines quality as A subjective term for which, each person has his
IE 362 Quality Control. Week1. (Quality and TQM) Lecture Outline
 IE 362 Quality Control Week1 Introduction to Quality Improvement. (Quality and TQM) Dr. Sun Olapiriyakul Lecture Outline Meaning of quality 8 dimensions of quality TQM Quality concepts and philosophies
IE 362 Quality Control Week1 Introduction to Quality Improvement. (Quality and TQM) Dr. Sun Olapiriyakul Lecture Outline Meaning of quality 8 dimensions of quality TQM Quality concepts and philosophies
Chapter 11. In-Time and Lean Production
 Chapter 11 Just-In In-Time and Lean Production What is JIT? Producing only what is needed, when it is needed A philosophy An integrated management system JIT s mandate: Eliminate all waste Basic Elements
Chapter 11 Just-In In-Time and Lean Production What is JIT? Producing only what is needed, when it is needed A philosophy An integrated management system JIT s mandate: Eliminate all waste Basic Elements
TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT AND LIBRARIES AND INFORMATION CENTERS
 TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT AND LIBRARIES AND INFORMATION CENTERS Mr. Sanjay Patel L. M. College of Pharmacy, Ahmedabad, India ABSTRACT In this paper I am discussing Objectives in libraries, Quality Control,
TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT AND LIBRARIES AND INFORMATION CENTERS Mr. Sanjay Patel L. M. College of Pharmacy, Ahmedabad, India ABSTRACT In this paper I am discussing Objectives in libraries, Quality Control,
CHAPTER 6 PROCESS IMPROVEMENT
 CHAPTER 6 PROCESS IMPROVEMENT Expected Outcomes Able to identify several different approaches towards continuous process improvement Understand method applied to continuous improvement in quality aspect
CHAPTER 6 PROCESS IMPROVEMENT Expected Outcomes Able to identify several different approaches towards continuous process improvement Understand method applied to continuous improvement in quality aspect
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Nowadays, manufacturing firms are in the position to redefine and redesign their manufacturing systems in order to meet the competitive demands raised by market challenges. The
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Nowadays, manufacturing firms are in the position to redefine and redesign their manufacturing systems in order to meet the competitive demands raised by market challenges. The
Information Technology Project Management
 Information Technology Project Management by Jack T. Marchewka Power Point Slides by Jack T. Marchewka, Northern Illinois University Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. all rights reserved. Reproduction
Information Technology Project Management by Jack T. Marchewka Power Point Slides by Jack T. Marchewka, Northern Illinois University Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. all rights reserved. Reproduction
Project Quality Management
 1 Project Quality Management Unit 8 Eng.elsaka09@gmail.com Project Quality Management Includes the processes and activities of the performing organization that determine quality policies, objectives, and
1 Project Quality Management Unit 8 Eng.elsaka09@gmail.com Project Quality Management Includes the processes and activities of the performing organization that determine quality policies, objectives, and
INTRODUCTION 1. When manufacturing processes of products being examine through customer s perspective, we will be able to identify 2 types of processe
 INTRODUCTION 1. When manufacturing processes of products being examine through customer s perspective, we will be able to identify 2 types of processes, the Value-Added and Non-Value Added. 2. The later
INTRODUCTION 1. When manufacturing processes of products being examine through customer s perspective, we will be able to identify 2 types of processes, the Value-Added and Non-Value Added. 2. The later
INTRODUCTION 1. When manufacturing processes of products being examine through customer s perspective, we will be able to identify 2 types of processe
 INTRODUCTION 1. When manufacturing processes of products being examine through customer s perspective, we will be able to identify 2 types of processes, the Value-Added and Non-Value Added. 2. The later
INTRODUCTION 1. When manufacturing processes of products being examine through customer s perspective, we will be able to identify 2 types of processes, the Value-Added and Non-Value Added. 2. The later
Glossary of Lean Terminology
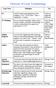 Glossary of Terminology Term Definition Use 5S: Used for Improving organization of the workplace: Sort > Set in order > Shine > Stardize > Sustain Create an organized work area A3 Thinking: Affinity Diagram:
Glossary of Terminology Term Definition Use 5S: Used for Improving organization of the workplace: Sort > Set in order > Shine > Stardize > Sustain Create an organized work area A3 Thinking: Affinity Diagram:
