Supplemental material JCB. Pitaval et al., Cell shape and ciliogenesis Pitaval et al.
|
|
|
- Camron Richard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Pitaval et al., S1
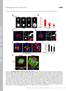
2 Figure S1. Cell cycle exit analysis. (A) Experimental procedure. RPE1 cells were synchronized at the G1/S transition and released with complete medium before being starved at various time points along the cell cycle in separated distinct experiments in a micropatterned 12-well plate. Cell behaviors were followed in time-lapse video microscopy. (B) Cells were plated on large, 500-µm-wide, fibronectin-coated discoidal micropatterns and monitored in time-lapse phase-contrast microscopy over 54 h to measure cell division time with respect to the time of starvation and to observe daughter cell fates. A few examples are highlighted. The blue cell divided once in the presence of serum. The daughters were starved in late G1 and gave rise to four daughters over the entire experiment. The red cell divided once in the presence of serum. The daughters were starved in early G1 and didn t divide any longer (Video 1). Bar, 100 µm. (C) Quantification of cell behavior upon serum starvation. The respective proportions of nondividing cells (red), cells dividing once (light blue), and cells dividing more than twice (dark blue) are shown on the histogram. The left bar shows cells that were not starved, and most cells divide several times (n = 16). In the middle bar, cells were starved in S phase, and in the right bar, cells were starved in G2 phase (n = 31 in both conditions). In these two cases, most cells divided once and then left the cell cycle. (D) Quantification of cell behavior upon serum starvation at various time points in G1. All cells divided once in the presence of serum and were starved in G1. The histogram shows the proportion of dividing cells (blue) and nondividing cells (red) depending on the duration between cell entry into G1 phase and the serum starvation time (n = 44, 46, 26, 46, 20, 36, and 28, respectively). We observed a progressive reduction of cells exiting the cell cycle all along G1. Plotted bars represent standard deviations. S2
3 Figure S2. Ezrin and myosin II localization and density. (A) RPE1 cells on small (750 µm2) and large (3,000 µm2) micropatterns were fixed and immunolabeled for phosphoezrin (top) and phosphomyosin II (bottom). Z acquisitions were performed and projected on a single image containing the maximal intensity of each pixel. Grayscales are identical for cells on small and large micropatterns. Ezrin staining reveals the presence of small microvilli only in confined cells. Myosin II staining decorates actin bundles in confined and spread cells, but these bundles are more conspicuous and numerous in spread cells. Bar, 5 µm. (B) RPE1 cells were plated on small or large micropatterns and treated or not treated with 10 µm Y27632 in the absence of serum for 24 h. Cells were fixed and stained for phosphoezrin and phosphomyosin II. The mean intensity per pixel (after background subtraction) was measured on individual images and compared between the two micropattern sizes. Ezrin staining was more intense in confined than in spread cells (top). Y27632 treatment slightly reduced phosphoezrin densities in confined but not in spread cells (middle). Phosphomyosin II staining appeared more dense in spread than in confined cells. Y27632 treatment strongly reduced phosphomyosin II densities in both confined and spread cells (bottom). a.u., arbitrary units. (C) Confocal Z stack optical sections showing dense phosphoezrin staining on top of confined cells (left) and dispersed staining on top of extended cells (right), in which the basal concentration of actin fibers is higher than on small cells. Bar, 5 µm. (D) RPE1 cells were plated on hard (polystyrene) and soft (polyacrylamide) substrates. They were starved for 24 h and stained for F-actin (left), phosphomyosin (middle), and acetylated tubulin (in white in the merge picture on the right). DNA is in blue. Actin bundles appeared thicker and straighter, and therefore probably more contracted, on hard than on soft substrate. *, P < 0.05 and ***, P < Horizontal bars represent mean values. Bars, 20 µm. S3
4 Figure S3. Labeling and quantification of centrosome position. RPE1 cells were plated on small (750 µm2) and large (3,000 µm2) micropatterns in the absence of serum for 24 h. (A) Micropatterned cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde. They were then immunolabeled for acetylated tubulin to reveal the primary cilium and/or cytoplasmic acetylated microtubules (green), immunolabeled for phosphomyosin II to detect the centrosome/basal body (red), and then stained with phalloidin to reveal actin filaments (blue) and Hoechst to reveal the nucleus (not depicted). The top row shows a primary cilium and the basal body on the dorsal surface of a cell confined on a small micropattern. The bottom row shows the acetylated microtubule network and the centrosome on the ventral surface of a cell spread on a large micropattern. Bars, 15 µm. Inset bars, 3 µm. (B) Micropatterned cells were fixed with cold methanol. They were then immunolabeled for -tubulin to reveal microtubules (red), immunolabeled for -tubulin to reveal centrosomes (green), and stained with Hoechst to reveal nucleus (blue). Z acquisitions were performed to detect the position of the centrosome (green arrows). It was either found above the nucleus, close to the dorsal cell surface (top), or below the nucleus, close to the ventral cell surface (bottom). Bars, 15 µm. The proportion of centrosome/basal body in the apical position close to the dorsal cell surface was quantified in cells plated on small (top, 750 µm2) and large (bottom, 3,000 µm2) micropatterns in the presence of culture medium without serum (control) and various cytoskeletal inhibitors (750 µm2: control, n = 84; cytochalasin D, n = 63; Y27632, n S4
5 Video 1. Monitoring of cell fate upon serum starvation. RPE1 cells were plated on large, 500-µm-wide, fibronectin-coated discoidal micropatterns and monitored in 10 time-lapse phase-contrast microscopy to measure cell division time with respect to the time of starvation and observe daughter cell fates. Time interval between two frames is 10 min. Colored dots are used as visual marks to follow individual cell fates. The blue cell s daughters were starved in late G1 and divided again. The red cell s daughters were starved in early G1 and didn t divide again. The green cell s daughters adopted asymmetric behaviors: one divided again and not the other. = 101; and 3,000 µm 2 : control, n = 49; cytochalasin D, n = 36; Y27632, n = 98). (C) Micropatterned cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde. They were then immunolabeled for acetylated tubulin (green), stained with phalloidin to reveal actin filaments (red), and stained with Hoechst to reveal nucleus (blue). Confocal Z stacks were performed and were either projected on the XY plane or sectioned along the XZ plane. Side views show the location of primary cilium on top of confined cells (left) and the presence of acetylated microtubules instead of a primary cilium in the cytoplasm of extended cells (right). X bars, 5 µm. Z bar, 2 µm. (D) The proportion of ciliated cells (Fig. 4) after different treatments is plotted against the proportion of cells having their centrosome in an apical position, close to the dorsal cell surface (see B). The two parameters could be linearly correlated with a correlation factor r 2 = Plotted bars represent standard deviations. S5
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Rodríguez-Fraticelli et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203075/dc1 Figure S1. Cell spreading and lumen formation in confined
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Rodríguez-Fraticelli et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203075/dc1 Figure S1. Cell spreading and lumen formation in confined
Actin cap associated focal adhesions and their distinct role in cellular mechanosensing
 Actin cap associated focal adhesions and their distinct role in cellular mechanosensing Dong-Hwee Kim 1,2, Shyam B. Khatau 1,2, Yunfeng Feng 1,3, Sam Walcott 1,4, Sean X. Sun 1,2,4, Gregory D. Longmore
Actin cap associated focal adhesions and their distinct role in cellular mechanosensing Dong-Hwee Kim 1,2, Shyam B. Khatau 1,2, Yunfeng Feng 1,3, Sam Walcott 1,4, Sean X. Sun 1,2,4, Gregory D. Longmore
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Prashar et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201304095/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. FBT phagocytosis in cells expressing PM-GFP. (A) T-PC
Supplemental material Prashar et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201304095/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. FBT phagocytosis in cells expressing PM-GFP. (A) T-PC
Xu et al., Supplementary Figures 1-7
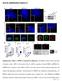 Xu et al., Supplementary Figures 1-7 Supplementary Figure 1. PIPKI is required for ciliogenesis. (a) PIPKI localizes at the basal body of primary cilium. RPE-1 cells treated with two sirnas targeting to
Xu et al., Supplementary Figures 1-7 Supplementary Figure 1. PIPKI is required for ciliogenesis. (a) PIPKI localizes at the basal body of primary cilium. RPE-1 cells treated with two sirnas targeting to
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Legends for Supplementary Tables. Supplementary Table 1. An excel file containing primary screen data. Worksheet 1, Normalized quantification data from a duplicated screen: valid
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Legends for Supplementary Tables. Supplementary Table 1. An excel file containing primary screen data. Worksheet 1, Normalized quantification data from a duplicated screen: valid
In most lineages, cell cycle exit is correlated with the
 Published October 18, 2010 This article has original data in the JCB Data Viewer http://jcb-dataviewer.rupress.org/jcb/browse/3211 JCB: Report Cell shape and contractility regulate ciliogenesis in cell
Published October 18, 2010 This article has original data in the JCB Data Viewer http://jcb-dataviewer.rupress.org/jcb/browse/3211 JCB: Report Cell shape and contractility regulate ciliogenesis in cell
Supplemental figures (1-9) Gu et al. ADF/Cofilin-Mediated Actin Dynamics Regulate AMPA Receptor Trafficking during Synaptic Plasticity
 Supplemental figures (1-9) Gu et al. ADF/Cofilin-Mediated Actin Dynamics Regulate AMPA Receptor Trafficking during Synaptic Plasticity Supplemental figure 1. The quantification method to determine the
Supplemental figures (1-9) Gu et al. ADF/Cofilin-Mediated Actin Dynamics Regulate AMPA Receptor Trafficking during Synaptic Plasticity Supplemental figure 1. The quantification method to determine the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a 14 12 Densitometry (AU) 1 8 6 4 2 t b 16 NMHC-IIA GAPDH NMHC-IIB Densitometry (AU) 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 1 nm 1 nm 1 nm 1 nm sirna 1 nm 1 nm Figure S1 S4 Quantification of protein levels. (a) The microtubule
a 14 12 Densitometry (AU) 1 8 6 4 2 t b 16 NMHC-IIA GAPDH NMHC-IIB Densitometry (AU) 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 1 nm 1 nm 1 nm 1 nm sirna 1 nm 1 nm Figure S1 S4 Quantification of protein levels. (a) The microtubule
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
JCB. Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY. Paul et al.,
 Supplemental material JCB Paul et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201502040/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Mutant p53-expressing cells display limited retrograde actin flow at
Supplemental material JCB Paul et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201502040/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Mutant p53-expressing cells display limited retrograde actin flow at
The Human Protein PRR14 Tethers Heterochromatin to the Nuclear Lamina During Interphase and Mitotic Exit
 Cell Reports, Volume 5 Supplemental Information The Human Protein PRR14 Tethers Heterochromatin to the Nuclear Lamina During Interphase and Mitotic Exit Andrey Poleshko, Katelyn M. Mansfield, Caroline
Cell Reports, Volume 5 Supplemental Information The Human Protein PRR14 Tethers Heterochromatin to the Nuclear Lamina During Interphase and Mitotic Exit Andrey Poleshko, Katelyn M. Mansfield, Caroline
Plutoni et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Plutoni et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201505105 /DC1 THE JOU RNAL OF CELL BIO LOGY Figure S1. Cell morphology during migration. (a) Protein extracts (20
Supplemental material JCB Plutoni et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201505105 /DC1 THE JOU RNAL OF CELL BIO LOGY Figure S1. Cell morphology during migration. (a) Protein extracts (20
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Table S1. Definition of quantitative cellular features
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Table S1. Definition of quantitative cellular features
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2271 Supplementary Figure a! WM266.4 mock WM266.4 #7 sirna WM266.4 #10 sirna SKMEL28 mock SKMEL28 #7 sirna SKMEL28 #10 sirna WM1361 mock WM1361 #7 sirna WM1361 #10 sirna 9 WM266. WM136
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2271 Supplementary Figure a! WM266.4 mock WM266.4 #7 sirna WM266.4 #10 sirna SKMEL28 mock SKMEL28 #7 sirna SKMEL28 #10 sirna WM1361 mock WM1361 #7 sirna WM1361 #10 sirna 9 WM266. WM136
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for Building Electromagnetic Hot Spots in Living Cells via Target-Triggered Nanoparticle Dimerization Wen Zhou, 1,2 Qiang Li, 1 Huiqiao Liu, 1 Jie Yang, 1 Dingbin Liu 1,2 * 1. College
Supporting Information for Building Electromagnetic Hot Spots in Living Cells via Target-Triggered Nanoparticle Dimerization Wen Zhou, 1,2 Qiang Li, 1 Huiqiao Liu, 1 Jie Yang, 1 Dingbin Liu 1,2 * 1. College
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Signal mingle: Micropatterns of BMP-2 and fibronectin on soft biopolymeric films regulate myoblast shape and SMAD signaling. Vincent Fitzpatrick, Laure Fourel, Olivier Destaing,
Supporting Information Signal mingle: Micropatterns of BMP-2 and fibronectin on soft biopolymeric films regulate myoblast shape and SMAD signaling. Vincent Fitzpatrick, Laure Fourel, Olivier Destaing,
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material 1 Figure S1. Phylogenetic analysis of Cep72 and Lrrc36, comparative localization of Cep72 and Lrrc36 and Cep72 antibody characterization (A) Phylogenetic alignment of Cep72 and Lrrc36
Supplemental Material 1 Figure S1. Phylogenetic analysis of Cep72 and Lrrc36, comparative localization of Cep72 and Lrrc36 and Cep72 antibody characterization (A) Phylogenetic alignment of Cep72 and Lrrc36
Supplementary Information. Tau co-organizes dynamic microtubule and actin networks. and Isabelle Arnal 1,2,*
 Supplementary Information Tau co-organizes dynamic microtubule and actin networks Auréliane Elie 1,2, Elea Prezel 1,2, Christophe Guérin 3, Eric Denarier 1,2,4, Sacnicte Ramirez- Rios 1,2, Laurence Serre
Supplementary Information Tau co-organizes dynamic microtubule and actin networks Auréliane Elie 1,2, Elea Prezel 1,2, Christophe Guérin 3, Eric Denarier 1,2,4, Sacnicte Ramirez- Rios 1,2, Laurence Serre
THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY
 Supplemental Material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Toso et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200809055/dc1 Figure S1. Control experiments for sirna depletions used in Figs. 1 3. The phenotype
Supplemental Material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Toso et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200809055/dc1 Figure S1. Control experiments for sirna depletions used in Figs. 1 3. The phenotype
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Monteiro et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201306162/dc1 Figure S1. 3D deconvolution microscopy analysis of WASH and exocyst
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Monteiro et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201306162/dc1 Figure S1. 3D deconvolution microscopy analysis of WASH and exocyst
Supplementary Figure 1. Co-localization of GLUT1 and DNAL4 in BeWo cells cultured
 Supplementary Figure 1. Co-localization of GLUT1 and DNAL4 in BeWo cells cultured under static conditions. Cells were seeded in the chamber area of the device and cultured overnight without medium perfusion.
Supplementary Figure 1. Co-localization of GLUT1 and DNAL4 in BeWo cells cultured under static conditions. Cells were seeded in the chamber area of the device and cultured overnight without medium perfusion.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.18/ncb46 a Damage Fracture s s 7 5 16 1 9 26 5 µm 5 µm b Position of photo-damage site in cells 15 Counts 1 5-14 -12-1 -8-6 -4-2 Distance from damage site to tip (µm) Supplementary Figure 1 Effect
DOI: 1.18/ncb46 a Damage Fracture s s 7 5 16 1 9 26 5 µm 5 µm b Position of photo-damage site in cells 15 Counts 1 5-14 -12-1 -8-6 -4-2 Distance from damage site to tip (µm) Supplementary Figure 1 Effect
Supplementary Figure S1. Hoechst. cells/field. Myogenin. % of Myogenin+ cells. 0 h chase CONTROL. BrdU. 72 h chase. CONTROL BrdU CONTROL BrdU
 Hoechst Myogenin amyhc 24 h 48 h 72 h b cells/field 50 40 30 20 10 0 24h 48h 72h h after plating (4 days growth+ t) c e CONTROL 0 h chase % of Myogenin+ cells h after plating (4 days growth+ t) CONTROL
Hoechst Myogenin amyhc 24 h 48 h 72 h b cells/field 50 40 30 20 10 0 24h 48h 72h h after plating (4 days growth+ t) c e CONTROL 0 h chase % of Myogenin+ cells h after plating (4 days growth+ t) CONTROL
Supplemental Information. Dynamic Organization of Chromatin Domains. Revealed by Super-Resolution Live-Cell Imaging
 Molecular Cell, Volume 67 Supplemental Information Dynamic Organization of Chromatin Domains Revealed by Super-Resolution Live-Cell Imaging Tadasu Nozaki, Ryosuke Imai, Mai Tanbo, Ryosuke Nagashima, Sachiko
Molecular Cell, Volume 67 Supplemental Information Dynamic Organization of Chromatin Domains Revealed by Super-Resolution Live-Cell Imaging Tadasu Nozaki, Ryosuke Imai, Mai Tanbo, Ryosuke Nagashima, Sachiko
Fig. S1. Endocytosis of extracellular cargo does not depend on dia. (A) To visualize endocytosis, fluorescently labelled wheat germ agglutinin
 Fig. S1. Endocytosis of extracellular cargo does not depend on dia. (A) To visualize endocytosis, fluorescently labelled wheat germ agglutinin (WGA-Alexa555) was injected into the extracellular perivitteline
Fig. S1. Endocytosis of extracellular cargo does not depend on dia. (A) To visualize endocytosis, fluorescently labelled wheat germ agglutinin (WGA-Alexa555) was injected into the extracellular perivitteline
Immunofluorescence Confocal Microscopy of 3D Cultures Grown on Alvetex
 Immunofluorescence Confocal Microscopy of 3D Cultures Grown on Alvetex 1.0. Introduction Immunofluorescence uses the recognition of cellular targets by fluorescent dyes or antigen-specific antibodies coupled
Immunofluorescence Confocal Microscopy of 3D Cultures Grown on Alvetex 1.0. Introduction Immunofluorescence uses the recognition of cellular targets by fluorescent dyes or antigen-specific antibodies coupled
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Real-time deformability cytometry: contour detection and theoretical modeling.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Real-time deformability cytometry: contour detection and theoretical modeling. (a) Image of cell deformed in constriction; contour (red) according to image analysis algorithm. Scale
Supplementary Figure 1 Real-time deformability cytometry: contour detection and theoretical modeling. (a) Image of cell deformed in constriction; contour (red) according to image analysis algorithm. Scale
MT minus end catastrophe
 DOI: 1.138/ncb3241 MT minus end catastrophe frequency [s -1 ].2.15.1.5 control mgfp- TPX2 * * mgfp- TPX2 mini Supplementary Figure 1. TPX2 reduces catastrophes at the microtubule minus ends. Modified box-and-whiskers
DOI: 1.138/ncb3241 MT minus end catastrophe frequency [s -1 ].2.15.1.5 control mgfp- TPX2 * * mgfp- TPX2 mini Supplementary Figure 1. TPX2 reduces catastrophes at the microtubule minus ends. Modified box-and-whiskers
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of
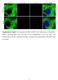 Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of LRRK1 bind to Grb2.
 Myc- HA-Grb2 Mr(K) 105 IP HA 75 25 105 1-1163 1-595 - + - + - + 1164-1989 Blot Myc HA total lysate 75 25 Myc HA Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of bind to Grb2. COS7 cells were cotransfected
Myc- HA-Grb2 Mr(K) 105 IP HA 75 25 105 1-1163 1-595 - + - + - + 1164-1989 Blot Myc HA total lysate 75 25 Myc HA Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of bind to Grb2. COS7 cells were cotransfected
Lecture 13. Motor Proteins I
 Lecture 13 Motor Proteins I Introduction: The study of motor proteins has become a major focus in cell and molecular biology. Motor proteins are very interesting because they do what no man-made engines
Lecture 13 Motor Proteins I Introduction: The study of motor proteins has become a major focus in cell and molecular biology. Motor proteins are very interesting because they do what no man-made engines
JCB. Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY. Prospéri et al.,
 Supplemental material JCB Prospéri et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201501018/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Myo1b Tail interacts with YFP-EphB2 coated beads and genistein inhibits
Supplemental material JCB Prospéri et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201501018/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Myo1b Tail interacts with YFP-EphB2 coated beads and genistein inhibits
Panx2 expression modulates neuronal differentiation SUPPLEMENTAL DATA. Figure Legends
 Panx2 expression modulates neuronal differentiation SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Figure Legends Suppl. Fig. S1. Antigenic determinants of the Panx2 antibodies employed in this study. (A) Schematic of mouse Panx2
Panx2 expression modulates neuronal differentiation SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Figure Legends Suppl. Fig. S1. Antigenic determinants of the Panx2 antibodies employed in this study. (A) Schematic of mouse Panx2
Supplemental Information. Characterization of Proprioceptive System. Dynamics in Behaving Drosophila Larvae. Using High-Speed Volumetric Microscopy
 urrent Biology, Volume 29 Supplemental Information haracterization of roprioceptive System Dynamics in Behaving Drosophila Larvae Using High-Speed Volumetric Microscopy Rebecca D. Vaadia, Wenze Li, Venkatakaushik
urrent Biology, Volume 29 Supplemental Information haracterization of roprioceptive System Dynamics in Behaving Drosophila Larvae Using High-Speed Volumetric Microscopy Rebecca D. Vaadia, Wenze Li, Venkatakaushik
(B) Comparable expression of major integrin subunits and glycoproteins on the surface of resting WT and Lnk -/- platelets.
 Supplemental Figure S1. Characteristics of Lnk -/- platelets. (A) Electron micrographs of resting platelets showing the normal intracellular structure of Lnk -/ platelets. Samples were fixed with 4% PFA
Supplemental Figure S1. Characteristics of Lnk -/- platelets. (A) Electron micrographs of resting platelets showing the normal intracellular structure of Lnk -/ platelets. Samples were fixed with 4% PFA
Aoki et al.,
 JCB: SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Aoki et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200609017/dc1 Supplemental materials and methods Calculation of the raw number of translocated proteins First, the average
JCB: SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Aoki et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200609017/dc1 Supplemental materials and methods Calculation of the raw number of translocated proteins First, the average
Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 )
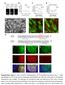 Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 ) homologous recombination arm (left) and of the right (3 )
Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 ) homologous recombination arm (left) and of the right (3 )
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured
 Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion
 Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
Visualizing Cells Molecular Biology of the Cell - Chapter 9
 Visualizing Cells Molecular Biology of the Cell - Chapter 9 Resolution, Detection Magnification Interaction of Light with matter: Absorbtion, Refraction, Reflection, Fluorescence Light Microscopy Absorbtion
Visualizing Cells Molecular Biology of the Cell - Chapter 9 Resolution, Detection Magnification Interaction of Light with matter: Absorbtion, Refraction, Reflection, Fluorescence Light Microscopy Absorbtion
Beta3 integrin promotes long-lasting activation and polarization of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 by immobilized ligand
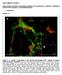 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES Beta3 integrin promotes long-lasting activation and polarization of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 by immobilized ligand C. Ravelli et al. FIGURE S. I Figure S. I: Gremlin
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES Beta3 integrin promotes long-lasting activation and polarization of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 by immobilized ligand C. Ravelli et al. FIGURE S. I Figure S. I: Gremlin
System of protein filaments in the cytoplasm of. eukaryotic cell that gives the cell shape and capacity for
 Cytoskeleton System of protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cell that gives the cell shape and capacity for directed movement. The protein filaments are responsible for the shaping, moving,
Cytoskeleton System of protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cell that gives the cell shape and capacity for directed movement. The protein filaments are responsible for the shaping, moving,
Supplemental Fig. 1: PEA-15 knockdown efficiency assessed by immunohistochemistry and qpcr
 Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Fig. 1: PEA-15 knockdown efficiency assessed by immunohistochemistry and qpcr A, LβT2 cells were transfected with either scrambled or PEA-15 sirna. Cells were then
Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Fig. 1: PEA-15 knockdown efficiency assessed by immunohistochemistry and qpcr A, LβT2 cells were transfected with either scrambled or PEA-15 sirna. Cells were then
No wash 2 Washes 2 Days ** ** IgG-bead phagocytosis (%)
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. No wash 2 Washes 2 Days Tat Control ** ** 2 4 6 8 IgG-bead phagocytosis (%) Supplementary Figure 1. Reversibility of phagocytosis inhibition by Tat. Human
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. No wash 2 Washes 2 Days Tat Control ** ** 2 4 6 8 IgG-bead phagocytosis (%) Supplementary Figure 1. Reversibility of phagocytosis inhibition by Tat. Human
ATX-LPA1 axis contributes to proliferation of chondrocytes by regulating fibronectin assembly leading to proper cartilage formation
 Scientific Reports Supplemental Information ATX-1 axis contributes to proliferation of chondrocytes by regulating fibronectin assembly leading to proper cartilage formation Tatsuji Nishioka, Naoaki Arima,
Scientific Reports Supplemental Information ATX-1 axis contributes to proliferation of chondrocytes by regulating fibronectin assembly leading to proper cartilage formation Tatsuji Nishioka, Naoaki Arima,
(phosphatase tensin) domain is shown in dark gray, the FH1 domain in black, and the
 Supplemental Figure 1. Predicted Domain Organization of the AFH14 Protein. (A) Schematic representation of the predicted domain organization of AFH14. The PTEN (phosphatase tensin) domain is shown in dark
Supplemental Figure 1. Predicted Domain Organization of the AFH14 Protein. (A) Schematic representation of the predicted domain organization of AFH14. The PTEN (phosphatase tensin) domain is shown in dark
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Antibodies For immunocytochemistry, the following antibodies were used: mouse anti-γ-h2ax (Upstate), rabbit anti-γ-h2ax (Abcam), rabbit anti-53bp1 (Novus), mouse anti-atm-phosphoserine1981
Supplementary Methods Antibodies For immunocytochemistry, the following antibodies were used: mouse anti-γ-h2ax (Upstate), rabbit anti-γ-h2ax (Abcam), rabbit anti-53bp1 (Novus), mouse anti-atm-phosphoserine1981
Histone Acetylation Controls the Inactive X Chromosome. Replication Dynamics
 Histone Acetylation Controls the Inactive X Chromosome Replication Dynamics Corella S. Casas-Delucchi 1,2,, Alessandro Brero 2,, Hans-Peter Rahn 2, Irina Solovei 3, Anton Wutz 4, Thomas Cremer 3, Heinrich
Histone Acetylation Controls the Inactive X Chromosome Replication Dynamics Corella S. Casas-Delucchi 1,2,, Alessandro Brero 2,, Hans-Peter Rahn 2, Irina Solovei 3, Anton Wutz 4, Thomas Cremer 3, Heinrich
Fluorescence Light Microscopy for Cell Biology
 Fluorescence Light Microscopy for Cell Biology Why use light microscopy? Traditional questions that light microscopy has addressed: Structure within a cell Locations of specific molecules within a cell
Fluorescence Light Microscopy for Cell Biology Why use light microscopy? Traditional questions that light microscopy has addressed: Structure within a cell Locations of specific molecules within a cell
Supplementary Figure 1. Related to Figure 1. Characterization of centrosome fragmentation in mitotically delayed RPE1 cells. (a) Cells transiently
 Supplementary Figure 1. Related to Figure 1. Characterization of centrosome fragmentation in mitotically delayed RPE1 cells. (a) Cells transiently transfected with EGFP centrin-2 (Green), synchronized
Supplementary Figure 1. Related to Figure 1. Characterization of centrosome fragmentation in mitotically delayed RPE1 cells. (a) Cells transiently transfected with EGFP centrin-2 (Green), synchronized
Visualizing mechanical tension across membrane receptors with a fluorescent sensor
 Nature Methods Visualizing mechanical tension across membrane receptors with a fluorescent sensor Daniel R. Stabley, Carol Jurchenko, Stephen S. Marshall, Khalid S. Salaita Supplementary Figure 1 Fabrication
Nature Methods Visualizing mechanical tension across membrane receptors with a fluorescent sensor Daniel R. Stabley, Carol Jurchenko, Stephen S. Marshall, Khalid S. Salaita Supplementary Figure 1 Fabrication
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2996
 Supplementary Figure 1 Negative-stain EM of native cytoplasmic dynein. (a) A representative micrograph of negatively stained dynein, with the flexible dimeric molecules circled in white. (b) Reference-free
Supplementary Figure 1 Negative-stain EM of native cytoplasmic dynein. (a) A representative micrograph of negatively stained dynein, with the flexible dimeric molecules circled in white. (b) Reference-free
Supplemental Information Control of apico-basal epithelial polarity by the microtubule minus-end binding protein CAMSAP3 and spectraplakin ACF7
 Supplemental Information Control of apico-basal epithelial polarity by the microtubule minus-end binding protein CAMSAP3 and spectraplakin ACF7 Ivar Noordstra, Qingyang Liu, Wilco Nijenhuis, Shasha Hua,
Supplemental Information Control of apico-basal epithelial polarity by the microtubule minus-end binding protein CAMSAP3 and spectraplakin ACF7 Ivar Noordstra, Qingyang Liu, Wilco Nijenhuis, Shasha Hua,
Supplementary Figure 1. Two activation pathways and four conformations of β 2 integrins. KIM127 (red) can specifically detect
 Supplementary Figure 1 Two activation pathways and four conformations of β 2 integrins. KIM127 (red) can specifically detect integrin extension (E + ) and mab24 (green) can specifically detect headpiece-opening
Supplementary Figure 1 Two activation pathways and four conformations of β 2 integrins. KIM127 (red) can specifically detect integrin extension (E + ) and mab24 (green) can specifically detect headpiece-opening
(A) Schematic illustration of sciatic nerve ligation. P, proximal; D, distal to the ligation site.
 SUPPLEMENTRY INFORMTION SUPPLEMENTL FIGURES Figure S1. () Schematic illustration of sciatic nerve ligation. P, proximal; D, distal to the ligation site. () Western blot of ligated and unligated sciatic
SUPPLEMENTRY INFORMTION SUPPLEMENTL FIGURES Figure S1. () Schematic illustration of sciatic nerve ligation. P, proximal; D, distal to the ligation site. () Western blot of ligated and unligated sciatic
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Inhibition kinetics of p53/hdm2 binding induced by Nutlin 3 on live cells. Reproducibility of the p53/hdm2 binding disruption kinetics induced by Nutlin 3
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Inhibition kinetics of p53/hdm2 binding induced by Nutlin 3 on live cells. Reproducibility of the p53/hdm2 binding disruption kinetics induced by Nutlin 3
 DOI: 0.038/ncb337 a RFP-Zyxin Actin b RFP Fluorescence 0 0 0 6 5 4 non-swirling CCW swirling, positive tilting of radial fibers c GFP-VASP Actin d GFP Fluorescence 0 0 0 6 5 4 non-swirling CCW swirling,
DOI: 0.038/ncb337 a RFP-Zyxin Actin b RFP Fluorescence 0 0 0 6 5 4 non-swirling CCW swirling, positive tilting of radial fibers c GFP-VASP Actin d GFP Fluorescence 0 0 0 6 5 4 non-swirling CCW swirling,
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
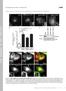 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Allison et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201211045/dc1 Figure S1. Spastin depletion causes increased endosomal tubulation.
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Allison et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201211045/dc1 Figure S1. Spastin depletion causes increased endosomal tubulation.
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2156 Figure S1 Depletion of p114rhogef with different sirnas. Caco-2 (a) and HCE (b) cells were transfected with individual sirnas, pools of the two sirnas or the On Target (OnT) sirna
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2156 Figure S1 Depletion of p114rhogef with different sirnas. Caco-2 (a) and HCE (b) cells were transfected with individual sirnas, pools of the two sirnas or the On Target (OnT) sirna
Supplementary Table, Figures and Videos
 Supplementary Table, Figures and Videos Table S1. Oligonucleotides used for different approaches. (A) RT-qPCR study. (B) qpcr study after ChIP assay. (C) Probes used for EMSA. Figure S1. Notch activation
Supplementary Table, Figures and Videos Table S1. Oligonucleotides used for different approaches. (A) RT-qPCR study. (B) qpcr study after ChIP assay. (C) Probes used for EMSA. Figure S1. Notch activation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2007
 Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2007 Fibronectin isolation and fluorescent labeling Human plasma Fn was isolated from fresh human plasma (Swiss
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2007 Fibronectin isolation and fluorescent labeling Human plasma Fn was isolated from fresh human plasma (Swiss
Supplementary Figure 1 Pfn1, but not other Pfn isoforms are expressed in
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pfn1, but not other Pfn isoforms are expressed in platelets. (a) RT-PCR of Pfn isoforms in control mouse platelets, Pfn1 -/- platelets and control heart. Expected band size for Pfn1
Supplementary Figure 1 Pfn1, but not other Pfn isoforms are expressed in platelets. (a) RT-PCR of Pfn isoforms in control mouse platelets, Pfn1 -/- platelets and control heart. Expected band size for Pfn1
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1245533/dc1 Supplementary Materials for A Mechanism for Reorientation of Cortical Microtubule Arrays Driven by Microtubule Severing Jelmer J. Lindeboom, Masayoshi
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1245533/dc1 Supplementary Materials for A Mechanism for Reorientation of Cortical Microtubule Arrays Driven by Microtubule Severing Jelmer J. Lindeboom, Masayoshi
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of truncated Borealin co-transfected with Borealin shrna.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of truncated Borealin co-transfected with Borealin shrna. HeLa M cells were transfected with empty psuper or a vector producing a shrna targetingg the 3 UTR (missing
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of truncated Borealin co-transfected with Borealin shrna. HeLa M cells were transfected with empty psuper or a vector producing a shrna targetingg the 3 UTR (missing
0.5% Triton X-100 for 5 min at room temperature. Fixed and permeabilized cells were
 1 Supplementary Methods Immunohistochemistry EBC-1 cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min at room temperature, followed by 0.5% Triton X-100 for 5 min at room temperature. Fixed and permeabilized
1 Supplementary Methods Immunohistochemistry EBC-1 cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min at room temperature, followed by 0.5% Triton X-100 for 5 min at room temperature. Fixed and permeabilized
The definitive version is available at www3.intersci. Supporting_Information.pdf (Supporting Information) Instructions for use
 Title Nonmuscle myosin II folds into a 10S form via two po Kiboku, Takayuki; Katoh, Tsuyoshi; Nakamura, Akio; K Author(s) Masayuki CitationGenes to Cells, 18(2): 90-109 Issue Date 2013-02 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/53054
Title Nonmuscle myosin II folds into a 10S form via two po Kiboku, Takayuki; Katoh, Tsuyoshi; Nakamura, Akio; K Author(s) Masayuki CitationGenes to Cells, 18(2): 90-109 Issue Date 2013-02 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/53054
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURECELLBIOLOGY 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURECELLBIOLOGY SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURECELLBIOLOGY 3 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURECELLBIOLOGY 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURECELLBIOLOGY SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURECELLBIOLOGY 3 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Live imaging reveals the dynamics and regulation of mitochondrial nucleoids during the cell cycle in Fucci2-HeLa cells Taeko Sasaki 1, Yoshikatsu Sato 2, Tetsuya Higashiyama 1,2,
Supplementary Information Live imaging reveals the dynamics and regulation of mitochondrial nucleoids during the cell cycle in Fucci2-HeLa cells Taeko Sasaki 1, Yoshikatsu Sato 2, Tetsuya Higashiyama 1,2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
Supplementary Figure 1 Structural modeling and purification of V. cholerae ABH. (a) The migration of the purified rabh and catalytically inactive
 Supplementary Figure 1 Structural modeling and purification of V. cholerae ABH. (a) The migration of the purified rabh and catalytically inactive variants rabhs, rabhd, and rabhh are shown on 12% SDS-PAGE
Supplementary Figure 1 Structural modeling and purification of V. cholerae ABH. (a) The migration of the purified rabh and catalytically inactive variants rabhs, rabhd, and rabhh are shown on 12% SDS-PAGE
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Shao et al. 10.1073/pnas.1504837112 SI Materials and Methods Immunofluorescence and Immunoblotting. For immunofluorescence, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and permeabilized
Supporting Information Shao et al. 10.1073/pnas.1504837112 SI Materials and Methods Immunofluorescence and Immunoblotting. For immunofluorescence, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and permeabilized
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Cell-mediated fibre recruitment drives extracellular matrix mechanosensing in engineered fibrillar microenvironments Brendon M. Baker 1,2,*+, Britta Trappmann 1,2,*, William Y. Wang 1, Mahmut S. Sakar
Cell-mediated fibre recruitment drives extracellular matrix mechanosensing in engineered fibrillar microenvironments Brendon M. Baker 1,2,*+, Britta Trappmann 1,2,*, William Y. Wang 1, Mahmut S. Sakar
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Rainero et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201109112/dc1 Figure S1. The expression of DGK- is reduced upon transfection
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Rainero et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201109112/dc1 Figure S1. The expression of DGK- is reduced upon transfection
SI8000 Live Cell Imaging System
 SI8000 Live Cell Imaging System Sony Biotechnology Inc. SI8000 Cell Motion Imaging System The Sony SI8000 Live Cell Imaging System detects and quantifies cellular motion using proprietary video processing
SI8000 Live Cell Imaging System Sony Biotechnology Inc. SI8000 Cell Motion Imaging System The Sony SI8000 Live Cell Imaging System detects and quantifies cellular motion using proprietary video processing
CHAPTER 16 THE CYTOSKELETON
 CHAPTER 16 THE CYTOSKELETON THE SELF-ASSEMBLY AND DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF CYTOSKELETAL FILAMENTS HOW CELLS REGULATE THEIR CYTOSKELETAL FILAMENTS MOLECULAR MOTORS THE CYTOSKELETON AND CELL BEHAVIOR THE SELF-ASSEMBLY
CHAPTER 16 THE CYTOSKELETON THE SELF-ASSEMBLY AND DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF CYTOSKELETAL FILAMENTS HOW CELLS REGULATE THEIR CYTOSKELETAL FILAMENTS MOLECULAR MOTORS THE CYTOSKELETON AND CELL BEHAVIOR THE SELF-ASSEMBLY
Journal of Biological Engineering is an open access, peer-reviewed online journal that encompasses all aspects biological engineering.
 Journal of Biological Engineering is an open access, peer-reviewed online journal that encompasses all aspects biological engineering. The journal welcomes manuscripts on the following topics: synthetic
Journal of Biological Engineering is an open access, peer-reviewed online journal that encompasses all aspects biological engineering. The journal welcomes manuscripts on the following topics: synthetic
Fast, three-dimensional super-resolution imaging of live cells
 Nature Methods Fast, three-dimensional super-resolution imaging of live cells Sara A Jones, Sang-Hee Shim, Jiang He & Xiaowei Zhuang Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure 3
Nature Methods Fast, three-dimensional super-resolution imaging of live cells Sara A Jones, Sang-Hee Shim, Jiang He & Xiaowei Zhuang Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure 3
Stable chromosomal units determine the spatial and temporal organization of DNA replication
 Research Article 5353 Stable chromosomal units determine the spatial and temporal organization of DNA replication Nicolas Sadoni 1, M. Cristina Cardoso 2, Ernst H. K. Stelzer 3, Heinrich Leonhardt 1,2
Research Article 5353 Stable chromosomal units determine the spatial and temporal organization of DNA replication Nicolas Sadoni 1, M. Cristina Cardoso 2, Ernst H. K. Stelzer 3, Heinrich Leonhardt 1,2
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION: 1. Supplemental methods 2. Supplemental figure legends 3. Supplemental figures
 Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2008 A microfluidics-based turning assay reveals complex growth cone responses to integrated gradients of substrate-bound
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2008 A microfluidics-based turning assay reveals complex growth cone responses to integrated gradients of substrate-bound
Automated Digital Microscopy
 A p p l i c a t i o n G u i d e Peter Banks, Ph.D. and Peter J. Brescia, Applications Department, BioTek Instruments, Inc., Winooski, VT Table of Contents Introduction ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A p p l i c a t i o n G u i d e Peter Banks, Ph.D. and Peter J. Brescia, Applications Department, BioTek Instruments, Inc., Winooski, VT Table of Contents Introduction ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
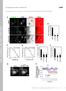 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Yamaguchi et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201009126/dc1 S1 Figure S2. The expression levels of GFP-Akt1-PH and localization
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Yamaguchi et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201009126/dc1 S1 Figure S2. The expression levels of GFP-Akt1-PH and localization
Ac(n cytoskeleton 12/7/11. The Cytoskeleton. Func0ons of the Cytoskeleton. B Visegrady. Elements of the Cytoskeleton
 The Cytoskeleton Ac(n cytoskeleton B Visegrady The cytoskeleton is an intricate network of protein filaments that extends throughout the cytoplasm. A skin cell (fibroblast) stained with Coomassie blue.
The Cytoskeleton Ac(n cytoskeleton B Visegrady The cytoskeleton is an intricate network of protein filaments that extends throughout the cytoplasm. A skin cell (fibroblast) stained with Coomassie blue.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure a.5 fold of increase.5 plaa plaa with LY plaa /piaa plaa /piaa with LY b 5 5 5 plaa plaa /piaa No LY with LY No LY with LY c 6X fluorescence plaa plaa with LY plaa /piaa plaa /piaa
Supplementary Figure a.5 fold of increase.5 plaa plaa with LY plaa /piaa plaa /piaa with LY b 5 5 5 plaa plaa /piaa No LY with LY No LY with LY c 6X fluorescence plaa plaa with LY plaa /piaa plaa /piaa
NOGO-A/RTN4A and NOGO-B/RTN4B are simultaneously expressed in. epithelial, fibroblast and neuronal cells and maintain ER morphology
 SREP-16-11884B Supplementary information NOGO-A/RTN4A and NOGO-B/RTN4B are simultaneously expressed in epithelial, fibroblast and neuronal cells and maintain ER morphology Olli Rämö a*, Darshan Kumar a*,
SREP-16-11884B Supplementary information NOGO-A/RTN4A and NOGO-B/RTN4B are simultaneously expressed in epithelial, fibroblast and neuronal cells and maintain ER morphology Olli Rämö a*, Darshan Kumar a*,
Graphene oxide-enhanced cytoskeleton imaging and mitosis tracking
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary information for Graphene oxide-enhanced cytoskeleton imaging and mitosis tracking
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary information for Graphene oxide-enhanced cytoskeleton imaging and mitosis tracking
Application Microfluidic Cell Analysis Devices (I) Date: 2013/05/24. Dr. Yi-Chung Tung
 Application Microfluidic Cell Analysis Devices (I) Date: 2013/05/24 Dr. Yi-Chung Tung Mechanotransduction and the Study of Cellular Forces Mechanical forces play a critical role in nearly all aspects of
Application Microfluidic Cell Analysis Devices (I) Date: 2013/05/24 Dr. Yi-Chung Tung Mechanotransduction and the Study of Cellular Forces Mechanical forces play a critical role in nearly all aspects of
λ N -GFP: an RNA reporter system for live-cell imaging
 λ N -GFP: an RNA reporter system for live-cell imaging Nathalie Daigle & Jan Ellenberg Supplementary Figures and Text: Supplementary Figure 1 localization in the cytoplasm. 4 λ N22-3 megfp-m9 serves as
λ N -GFP: an RNA reporter system for live-cell imaging Nathalie Daigle & Jan Ellenberg Supplementary Figures and Text: Supplementary Figure 1 localization in the cytoplasm. 4 λ N22-3 megfp-m9 serves as
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Self-Powered Electrical Stimulation for Enhancing Neural Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Graphene-Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) Hybrid Microfibers Weibo Guo, 1,2
Supporting Information Self-Powered Electrical Stimulation for Enhancing Neural Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Graphene-Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) Hybrid Microfibers Weibo Guo, 1,2
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Retention of RNA with LabelX.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Retention of RNA with LabelX. (a) Epi-fluorescence image of single molecule FISH (smfish) against GAPDH on HeLa cells expanded without LabelX treatment. (b) Epi-fluorescence image
Supplementary Figure 1 Retention of RNA with LabelX. (a) Epi-fluorescence image of single molecule FISH (smfish) against GAPDH on HeLa cells expanded without LabelX treatment. (b) Epi-fluorescence image
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Moutin et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110101/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Tagged Homer1a and Homer are functional and display different
Supplemental material Moutin et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110101/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Tagged Homer1a and Homer are functional and display different
Observation of Immuno-Labeled Cells at High Resolution Using. Soft X-Ray Microscopy
 Observation of Immuno-Labeled Cells at High Resolution Using Soft X-Ray Microscopy A. Yamamoto, Y. Fukui 1, Y. Yoshimura 1, K. Okuno 2, K. Takemoto 3, T. Okamoto 2, H. amba 1 and H. Kihara 3 Abstract The
Observation of Immuno-Labeled Cells at High Resolution Using Soft X-Ray Microscopy A. Yamamoto, Y. Fukui 1, Y. Yoshimura 1, K. Okuno 2, K. Takemoto 3, T. Okamoto 2, H. amba 1 and H. Kihara 3 Abstract The
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Transcriptional output transiently spikes upon mitotic exit
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Transcriptional output transiently spikes upon mitotic exit Viola Vaňková Hausnerová 1, 2, Christian Lanctôt 1* 1 BIOCEV and Department of Cell Biology, Faculty of Science, Charles
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Transcriptional output transiently spikes upon mitotic exit Viola Vaňková Hausnerová 1, 2, Christian Lanctôt 1* 1 BIOCEV and Department of Cell Biology, Faculty of Science, Charles
Chapter 15. Cytoskeletal Systems. Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Cytoskeletal Systems Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Table 15-1 - Microtubules Table 15-1 - Microfilaments Table 15-1 Intermediate Filaments Table 15-3 Microtubules
Chapter 15 Cytoskeletal Systems Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Table 15-1 - Microtubules Table 15-1 - Microfilaments Table 15-1 Intermediate Filaments Table 15-3 Microtubules
With the ibidi Culture-Insert 2 Well in a µ-dish 35 mm
 Wound Healing Assay With the ibidi Culture-Insert 2 Well in a µ-dish 35 mm 1. General information Cell migration plays a central role in many complex physiological and pathological processes. The wound
Wound Healing Assay With the ibidi Culture-Insert 2 Well in a µ-dish 35 mm 1. General information Cell migration plays a central role in many complex physiological and pathological processes. The wound
Supplementary Figure 1: Two modes of low concentration of BsSMC on a DNA (a) Protein staining (left) and fluorescent imaging of Cy3 (right) confirm
 Supplementary Figure 1: Two modes of low concentration of BsSMC on a DNA (a) Protein staining (left) and fluorescent imaging of Cy3 (right) confirm that BsSMC was labeled with Cy3 NHS-Ester. In each panel,
Supplementary Figure 1: Two modes of low concentration of BsSMC on a DNA (a) Protein staining (left) and fluorescent imaging of Cy3 (right) confirm that BsSMC was labeled with Cy3 NHS-Ester. In each panel,
JCB. Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY. Hong et al.,
 Supplemental material JCB Hong et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201412127/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Analysis of purified proteins by SDS-PAGE and pull-down assays. (A) Coomassie-stained
Supplemental material JCB Hong et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201412127/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Analysis of purified proteins by SDS-PAGE and pull-down assays. (A) Coomassie-stained
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 July 29.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging. 2011 June 9; 2011(March 30 2011-April 2 2011): 1330 1333. doi: 10.1109/ISBI.2011.5872646. AUTOMATED
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging. 2011 June 9; 2011(March 30 2011-April 2 2011): 1330 1333. doi: 10.1109/ISBI.2011.5872646. AUTOMATED
Characterization of cytoskeleton mechanical properties and 3D-actin structure in twisted adherent epithelial cells
 Biorheology 40 (2003) 241 245 241 IOS Press Characterization of cytoskeleton mechanical properties and 3D-actin structure in twisted adherent epithelial cells Redouane Fodil, Valérie Laurent, Emmanuelle
Biorheology 40 (2003) 241 245 241 IOS Press Characterization of cytoskeleton mechanical properties and 3D-actin structure in twisted adherent epithelial cells Redouane Fodil, Valérie Laurent, Emmanuelle
A legacy of innovation and discovery
 A legacy of innovation and discovery CellInsight CX7 LZR High Content Analysis Platform Quantifiably brilliant data Since the introduction of Thermo Scientific ArrayScan High Content Analysis (HCA) Readers
A legacy of innovation and discovery CellInsight CX7 LZR High Content Analysis Platform Quantifiably brilliant data Since the introduction of Thermo Scientific ArrayScan High Content Analysis (HCA) Readers
