Seeds are central to life on Earth:
|
|
|
- Jodie Hunt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Seeds Part 1 Seeds are central to life on Earth: 1. Establish a new plant (propagation) 2. Food for humans and animals 3. Genetic repository 4. Some things are not possible without seeds
2 Seeds Part 1 Seeds play a large part in the Rose Parade
3 Seeds Part 1 Imagine your world without seeds
4 Seeds Part 1 Imagine your world without seeds
5 Seeds Part 1 Imagine your world without seeds
6 Seeds Part 1 Imagine your world without seeds
7 Seeds are responsible for efficient and profitable agriculture
8
9 Perfect repository for genes
10 Seeds Part 1 Seeds are responsible for the success of angiosperms (seed-like structures ~ 360 million years bp, late Devonian period)
11 Seed plants began ~ 360 MYA exploded during Cenozoic era
12 Early land plants along the estuary margin, 400 million years ago Painting by J. Pennanen for the New Brunswick Museum
13 Club mosses lycopods Figure 21. Reconstruction of a tropical peat swamp of Middle Pennsylvanian age (about 300 million years ago). The taller plants were tree lycopsids (Lepidophloios), some of which grew to heights of 80 to 100 ft. Today, the lycopsids are represented by lowly club mosses. Other plants include cordaites (B), which were seed plants with strap-shaped leaves that are now extinct; tree ferns (C), which still live in warm, damp areas; calamites (D), which is a tree-size scouring rush; and pteridosperms (E), which were seed plants with fernlike leaves that are now extinct. The tree-like scouring rushes, which reached heights of 30 to 50 ft, are represented today by plants that grow in damp, but not necessarily warm, areas usually to only a few feet in height. From an illustration by Alice Pricket in GSA Today (Gastaldo et al., 1996); A. lycopsids; B. Cordaites; C. Tree ferns; D. Calamites; E. Pteridosperms
14 Seeds Part 1 Virtually all seeds are dormant at maturity The maintenance and release from dormancy is an unsolved biological mystery.
15 Vivipary is caused by a lack (or not enough) ABA Viviparous maize (McCarty et al 1989 Plant Cell)
16 Seeds of 17 tree species, all from the family Fabaceae, that cooccur in the Peruvian Amazon. Muller-Landau H C PNAS 2003;100: by National Academy of Sciences
17 Seeds Part 1 Botanically, a seed is a mature ovule. In most cases it results from fertilization (sperm nucleus + egg nucleus) Every seed consists of: Embryo Storage tissue (endosperm or cotyledon) Protective outer covering (seed coat, pericarp) Review Figure 4-1, morphological seed types to learn different parts of a seed. Corn seed (monocot)
18 Seeds Part 1 1. Seeds represent the successful result of sexual reproduction 2. Therefore, seeds represent genetic variability 3. Unless you buy an F1 hybrid 4. Meiosis is the process by which genetic recombination occurs (meiosis is different from mitosis see next slides) 5. Pollination occurs before fertilization
19 The cell cycle in a typical eukaryote (G 1 S G 2 M) (From Hartl and Jones 2002, Essential Genetics 3rd ed.)
20 Overview of Mitosis (From Hartl and Jones 2002, Essential Genetics 3 rd ed.) (From Hartl and Jones 2002, Essential Genetics 3rd ed.)
21 1. Production of haploid cells each containing complete genetic information. 2. Only in germ cells Meiosis 3. Reduction division followed by equational division 4. chromatids, centromere, homologues, 5. Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I Telophase I; Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II Telophase II; 6. Chiasma forms during prophase I
22 Seeds Part 1 Sexual reproduction (Figure 4-5) Pollination Pollen tube One tube nucleus Two generative nuclei Fertilization Embryo + one generative nucleus (zygote) 2n Double fertilization Two polar nuclei + one generative nucleus 3n endosperm Review Polygonum type embryo sac (Figure 4.5) Eight nuclei 3 antipodal 2 polar 1 egg 2 synergids
23 diploid diploid In most cases, three of the four megaspores degenerate haploid haploid Mitosis yields a two-celled structure One tube cell One generative cell In higher plants this structure differentiates into a pollen grain The remaining megaspore undergoes mitosis and asymmetric division Mitosis yields a seven-celled structure Figure 3.15 (Brooker 2007)
24 Double fertilization Provides storage material for the developing embryo Figure 2.2 (Brooker 2007) 3-66
25 Pollen grain = Po consisting of a Vegetative cell = VG and a Generative cell = GC, St = Stigma, St = Style, Pt = pollen tube, SC1 & SC2 = Sperm cell 1 and 2, O = ovule containing an embryo sac = ES (PRE = Before and POST = just after fertilization), E = egg cell, Sy = synergides, CC = Central cell, A = Antipodal cells, Zy = zygote, f CC = fertilized Central Cell (forms the endosperm)
26 a, In animals, a single fertilization event between maternal and paternal gametes forms the zygote (not shown). Initially, the animal embryo is under predominant control of the maternal genome, and the zygotic genome is only gradually activated over the course of embryogenesis. b, In plants, a double fertilization process generates the zygote and the endosperm tissue. Both the endosperm and the embryo are encased in maternal tissue that generates the seed coat. Chromosome symbols represent maternal (red) and paternal (blue) genomes. Nodine and Bartel 3 show that, in contrast to the case for animals, the plant zygotic genome is activated almost immediately after fertilization. Hale and Jacobsen 2012, Nature 482:42-44
27 Polygonum pattern of female gametophyte development. Polygonum pattern common to 70% of all angiosperms. Abbreviations: AC = antipodal cell AN = antipodal cell nucleus CC = central cell CV = cell vacuole DM = degenerative megaspore EC = egg cell EN = egg nucleus EV = egg vacuole II = inner integument M = megaspore N = nucleus OI = outer integument PN = polar nuclei SC = synergid cell SN = synergid nucleus SV = synergid vacuole Buchanan, Gruissem and Jones, Biochem & Mol Biol of Plants. 2000
28 Seeds Part 1 Seed Parts Embryo Radicle Cotyledon(s) Storage Tissue Endosperm Cotyledons Monocotyledonous plants (monocots) Dicotyledonous plants (dicots) Seed coat Testa Testa + Mucilaginous layer Woody Fibrous
29 Seeds Part 1 Mature embryo dicot
30 Seeds Part 1 Dicot seed & seedling structure
31 Seeds Part 1 Monocot seed structure
32 Capsicum annum From:
33
34
35
36
37 Le et al Plant Physiol., 144: Soybean life cycle
38 Soybean seed development a, Axis; c, cotyledon; ep, embryo proper; Le et al Plant Physiol., 144:
39 Transverse sections of soybean globular, heart, cotyledon and early maturation seed a, Axis; al, aleurone; c, cotyledon; cu, cuticle; ep, embryo proper; es, endosperm; hg, hourglass cells; ii, inner integument; oi, outer integument; pa, palisade layer; pl, plumule; py, parenchyma; rm, root meristem; s, suspensor; sc, seed coat; sm, shoot meristem; v, vascular tissues; vb, vascular bundle. Le et al Plant Physiol., 144:
40 Diversity of legume seed size Scale: bar = 1 cm Le et al Plant Physiol., 144:
41 Le et al Plant Physiol., 144: Diversity of legume embryo morphology
42
43 Seeds Part 1 Zea mays seed
44 Seeds Part 1 Seed Development 1. Three stages of seed development (Figure 4.8) a) I. Histodifferentiation b) II. Cell Expansion c) III. Maturation / drying i. Orthodox Seeds ii. Recalcitrant Seeds 2. Seed quality develops over time
45 Seeds Part 1 Stage I. Histodifferentiation 1. Dicot embryogenesis occurs in stages: a) Proembryo, globular, heart, torpedo, cotyledon Friml et al 2003, Nature;
46 Seeds Part 1 Stage I. Histodifferentiation 1. Dicot embryogenesis occurs in stages: a) Proembryo, globular, heart, torpedo, cotyledon globular torpedo cotyledon Nowack et al 2007, Nature;
47 Chlorophyll fluorescence at specific stages of Arabidopsis development A, B globular C, I heart E, P torpedo G, W walking-stick Tejos et al. 2010; Biol Res. 43:99-111
48 Seeds Part 1 Stage I. Histodifferentiation 1. Dicot embryogenesis occurs in stages: a) Proembryo, globular, heart, torpedo, cotyledon 2. Monocot embryogenesis: a) Proembryo, globular, scutellar, coleoptilar 3. Monocots have a scutellum, dicots have cotyledons) 4. Monocots have a plumule; dicots have a shoot 5. Monocots have a coleoptile to assist the plumule and a coleorhiza to protect the radicle during germination.
49 Embryogenesis Goldberg et al. 1994, 266:
50
51 Seeds Part 1 Soybeans (Glycine max) (A) Late globular stage embryo (B) Heart stage embryo Abbreviations: A axis; CE chalazal end; C cotyledon; EP embryo proper; En endosperm; MPE micropylar end; S suspensor. Goldberg et al. 1994, 266:
52 Seeds Part 1 Capsella embryo
53 Seeds Part 1 Stage II. Cell Expansion 1. Stage II is marked by rapid expansion of cells 2. Cotyledons or endosperm accumulate CH 2 O, fats, oils, proteins. a) All seeds contain each component, but in characteristic amounts. 3. Dicots connection b/t mother plant and developing seed is through the funinculus. a) Assimilates reach the embryo via diffusion b) Excludes most viruses 4. Reserve accumulation is under genetic control: a) Plants have ~25,000 50,000 genes b) At least 50% are expressed during seed development
54 Seeds Part 1 Stage III. Maturation Drying 1. Two types of seeds: a) Orthodox seeds can be dried down to ~5-7% moisture b) Recalcitrant seeds remain viable > 20 % moisture content By comparison, humans can only withstand ~5% moisture loss c) Occurs when funiculus detaches from mother plant 2. Seeds develop ability to germinate before ability to withstand desiccation. 3. Maximum dry weight does not necessarily equate to physiological maturity. 4. Precocious germination (vivipary) is prevented by the plant hormone ABA, which accumulates during seed development. 5. Dry seeds can be stored a very long time, especially if kept very, very cold. 6. Maturation drying is under genetic control. a) Many different mrna transcripts are produced which aid in preparing the seed to withstand extreme desiccation
55 Anhydrobiosis life without water Tardigrades (water bears) inhabit temporary ponds and films of water in soil and on moist plants. They can lose up to 98% of its body water and survive for decades. Add water, and within moments the water bear will become active. From Campbell, 1996 Biology 4 th ed.
56
57 How long can seeds survive? Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. Ancient lake bed at Pulantien, Liaoning Province, China radiocarbon-dated to 1,350 ± 220 BCE Oldest confirmed germination Shin-Miller 1995, Am J Bot Photos from:
58 How long can seeds survive? Masada, an Herodian fortress overlooking the Dead Sea ~50 BCE to 70 CE date palm seed, Phoenix dactylifera L. Sallon et al., 2008, Science
59 Dead for 32,000 Years, an Arctic Plant Is Revived By NICHOLAS WADE Published: February 20, 2012 New York Times PNAS Narrow-leaf campion, Silene stenophylla
60 Fig. 4. Immature fruit of Silene stenophylla from burrow buried in permafrost more than 30,000 y ago. (A) Dissected fruit showing seeds and placenta (P). (B) Fragment of placenta with seeds at different developmental stages. (Scale bars, 1 mm.) Yashina et al PNAS doi/ /pnas
61 Observations of seed viability in relation to environment show that their longevity increases as the seed storage temperature and moisture decrease (19, 20). This same situation is seen for seed viability in the permafrost. First, at subzero temperatures the rates of biochemical reactions and biological processes become extremely slow and ensure preservation of the biological system. Second, in frozen ground, ice makes up 93 98% of total water volume (21); this frozen environment is effectively a biologically dry environment and favors conservation (22).
62 Seeds Part 1 Biotechnology of Seed Reserves 1. Modifying F.A. content (omega-3-fatty acids; novel cooking/industrial oils 2. Modifying amino acid content in maize (Brian Larkins work) 3. Adding to pathways (Golden rice)
63 Seeds Part 1 Ploidy levels in plants n = haploid number of chromosomes (germ cells) 2n = diploid number of chromosomes (somatic cells) 3n = triploid number of chromosomes (endosperm) Tetraploid species (e.g., potato) 2n=4x=48 (48 chromosomes in the tetraploid potato plant.
64 Scheme of carotenoid biosynthesis in relation to Golden Rice First committed step in carotenoid biosynthesis PSY and CrtI are targeted by G.E. Al-Babili, S. et al. J. Exp. Bot :
65 Golden Rice I. II. I. Different types of Golden Rice A. 1. Untransformed 2-4. single-transformant lines B. Co-transformant lines II. Carotenoid content of (A) control seeds, (B) single transformant; (C) z11b co-transformant (D) z4b co-transformant III. Structure of T-DNA region of pzpsc used in co-transformations. Abbreviations: LB-left border; RB-right border;! polyadenylation signal; p-promoters; psy phyotene synthase; ctrl-bacterial phytoene desaturase; lcy-lycopene B-cylcase; tp transit peptide. III. Ye et al Science 287:
66 The making of golden rice
67 Cross section of lily ovary.
68 Megaspore mother cell
69 Megaspore tetrads.
70 Embryo sac showing polar nuclei and egg nucleus.
71
72
Lecture Seeds. Topics. Fertilization
 Lecture 25-26. Seeds Topics Generalized seed structure Where the seed comes from Parts of the seed Kinds of seeds Dicots Monocots Fertilization The seed represents one of the most significant plant adaptations.
Lecture 25-26. Seeds Topics Generalized seed structure Where the seed comes from Parts of the seed Kinds of seeds Dicots Monocots Fertilization The seed represents one of the most significant plant adaptations.
BIOLOGY. TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants)
 BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the ripe anther of a flower to the stigma of a flower. Pollination
BIOLOGY CLASS: VIII TOPIC: Life Processes: Growth, Reproduction & Development (plants) Pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the ripe anther of a flower to the stigma of a flower. Pollination
Sexual Reproduction of the Flowering Plant https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0uepq1w9c_e Prior learning
 Sexual Reproduction of the Flowering Plant https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0uepq1w9c_e Prior learning Working in Partnership draw a diagram of a flowering plant and write out the functions of the parts
Sexual Reproduction of the Flowering Plant https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0uepq1w9c_e Prior learning Working in Partnership draw a diagram of a flowering plant and write out the functions of the parts
DID YOU KNOW that the double coconut palm produces the largest
 Seed Germination Processes and Requirements DID YOU KNOW that the double coconut palm produces the largest seed in the world? It weighs about 50 pounds. The smallest seeds are like dust. Whatever the size
Seed Germination Processes and Requirements DID YOU KNOW that the double coconut palm produces the largest seed in the world? It weighs about 50 pounds. The smallest seeds are like dust. Whatever the size
Q1. Figure 1 shows a pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis. The letters represent alleles. Figure (1)
 Q1. Figure 1 shows a pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis. The letters represent alleles. Figure 1 (a) What is an allele? (b) Explain the appearance of one of the chromosomes in Figure 1. (c) The
Q1. Figure 1 shows a pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis. The letters represent alleles. Figure 1 (a) What is an allele? (b) Explain the appearance of one of the chromosomes in Figure 1. (c) The
Plant Reproduction and Multiplication. 1. Sexual Reproduction 2. Asexual Reproduction 3. Micropropagation
 Plant Reproduction and Multiplication 1. Sexual Reproduction 2. Asexual Reproduction 3. Micropropagation Sexual Versus Asexual Propagation Sexual propagation - plants are propagated from seeds - gives
Plant Reproduction and Multiplication 1. Sexual Reproduction 2. Asexual Reproduction 3. Micropropagation Sexual Versus Asexual Propagation Sexual propagation - plants are propagated from seeds - gives
DETERMINING THE GROWTH STAGES OF CORN
 DETERMINING THE GROWTH STAGES OF CORN Keith Glewen, Nebraska Extension Educator 1 Restrictions for Use of Adjuvants on Corn 2 3 3 Yield Protecting Factors Yield Building Factors WHY DETERMINE STAGES? 1.
DETERMINING THE GROWTH STAGES OF CORN Keith Glewen, Nebraska Extension Educator 1 Restrictions for Use of Adjuvants on Corn 2 3 3 Yield Protecting Factors Yield Building Factors WHY DETERMINE STAGES? 1.
DETERMINING THE GROWTH STAGES OF CORN AND SOYBEANS
 DETERMINING THE GROWTH STAGES OF CORN AND SOYBEANS Keith Glewen, UNL Extension Educator 3 HOW TO DETERMINE STAGES CORN Vegetative - Count Collars Reproductive - Kernel Characteristics SOYBEANS Vegetative
DETERMINING THE GROWTH STAGES OF CORN AND SOYBEANS Keith Glewen, UNL Extension Educator 3 HOW TO DETERMINE STAGES CORN Vegetative - Count Collars Reproductive - Kernel Characteristics SOYBEANS Vegetative
CHAPTER 14 Genetics and Propagation
 CHAPTER 14 Genetics and Propagation BASIC GENETIC CONCEPTS IN PLANT SCIENCE The plants we cultivate for our survival and pleasure all originated from wild plants. However, most of our domesticated plants
CHAPTER 14 Genetics and Propagation BASIC GENETIC CONCEPTS IN PLANT SCIENCE The plants we cultivate for our survival and pleasure all originated from wild plants. However, most of our domesticated plants
Soybean Seed Protein Genes Are Regulated Spatially during Embryogenesis
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 1, 1095-1 109, November 1989 O 1989 American Society of Plant Physiologists Soybean Seed Protein Genes Are Regulated Spatially during Embryogenesis Luis Perez-Grau and Robert B. Goldberg
The Plant Cell, Vol. 1, 1095-1 109, November 1989 O 1989 American Society of Plant Physiologists Soybean Seed Protein Genes Are Regulated Spatially during Embryogenesis Luis Perez-Grau and Robert B. Goldberg
Exam 1 PBG430/
 Exam 1 PBG430/530 2013 1. In the case of the Round Ready sugar beet in the Willamette Valley, the principal concern relates to which of the following: a. Possible health risks associated with excessive
Exam 1 PBG430/530 2013 1. In the case of the Round Ready sugar beet in the Willamette Valley, the principal concern relates to which of the following: a. Possible health risks associated with excessive
Gregor Mendel. Austrian Monk Worked with pea plants
 Gregor Mendel Austrian Monk Worked with pea plants A. True Breeding Pea Plants Self pollinate and produce new plants genetically identical to themselves Mendel decides to cross pollinate the plants Offspring
Gregor Mendel Austrian Monk Worked with pea plants A. True Breeding Pea Plants Self pollinate and produce new plants genetically identical to themselves Mendel decides to cross pollinate the plants Offspring
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only) I. Protein Synthesis: creation of new proteins a. Much of the cellular machinery is devoted to synthesizing
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only) I. Protein Synthesis: creation of new proteins a. Much of the cellular machinery is devoted to synthesizing
THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE EMBRYO=SAC AND EMBRYO OF AGROSTEMMA GITHAGO.*
 Feb., 1903.] Agrostemma githago. 365 THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE EMBRYO=SAC AND EMBRYO OF AGROSTEMMA GITHAGO.* MELVILLE THURSTON COOK. Agrostemma githago L,. was selected as a plant for comparison with Claytonia
Feb., 1903.] Agrostemma githago. 365 THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE EMBRYO=SAC AND EMBRYO OF AGROSTEMMA GITHAGO.* MELVILLE THURSTON COOK. Agrostemma githago L,. was selected as a plant for comparison with Claytonia
Ovule development in seeded and seedless grapes 1 )
 Vitis 9, 7-14 (197) N. Y. State Agricultural Experiment Station, Geneva, USA Ovule development in seeded and seedless grapes 1 ) by Introduction Descriptions of female gametophyte, endosperm and embryo
Vitis 9, 7-14 (197) N. Y. State Agricultural Experiment Station, Geneva, USA Ovule development in seeded and seedless grapes 1 ) by Introduction Descriptions of female gametophyte, endosperm and embryo
Exam Plant Genetics CSS/Hort 430/530
 Exam 1 2010 Plant Genetics CSS/Hort 430/530 Barley can produce seed which is hulled or hull-less. This trait is determined by one gene, hulled being the dominant phenotype and hull-less being the recessive.
Exam 1 2010 Plant Genetics CSS/Hort 430/530 Barley can produce seed which is hulled or hull-less. This trait is determined by one gene, hulled being the dominant phenotype and hull-less being the recessive.
Picture Keyword Table of Contents (LE)
 Picture Keyword Table of Contents (LE) First Letter Keyword Page Number Count a abiotic 1 2 absorption 2 1 acid rain 2 1 active transport 3 5 adaptation 5 11 amino acid chains 12 1 amino acid sequences
Picture Keyword Table of Contents (LE) First Letter Keyword Page Number Count a abiotic 1 2 absorption 2 1 acid rain 2 1 active transport 3 5 adaptation 5 11 amino acid chains 12 1 amino acid sequences
SEED GERMINATION. James C. Delouche 1
 SEED GERMINATION James C. Delouche 1 Germination is the crucial and final event in the life of a seed. It represents both the fulfillment and the completion of the basic function of seed - propagation.
SEED GERMINATION James C. Delouche 1 Germination is the crucial and final event in the life of a seed. It represents both the fulfillment and the completion of the basic function of seed - propagation.
BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 2 Making Use of Biology
 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2003 Advanced Subsidiary Examination BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 2 Making
Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2003 Advanced Subsidiary Examination BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 2 Making
Page 3. 18) The diagram below illustrates some key steps of a procedure in one area of biotechnology.
 Name: 1117 1 Page 1 1) A small amount of DNA was taken from a fossil of a mammoth found frozen in glacial ice. Genetic technology can be used to produce a large quantity of identical DNA from this mammoth's
Name: 1117 1 Page 1 1) A small amount of DNA was taken from a fossil of a mammoth found frozen in glacial ice. Genetic technology can be used to produce a large quantity of identical DNA from this mammoth's
Tree Seed Components. Fdc
 Tree Seed Components A conifer seed has three main components: the seed coat, embryo, and megagametophyte. These components are shown dissected from a longitudinal section of a Douglas-fir seed in Figure
Tree Seed Components A conifer seed has three main components: the seed coat, embryo, and megagametophyte. These components are shown dissected from a longitudinal section of a Douglas-fir seed in Figure
Seed Germination and Stand Establishment. Thomas G Chastain CROP 200 Crop Ecology and Morphology
 Seed Germination and Stand Establishment Thomas G Chastain CROP 200 Crop Ecology and Morphology Seed Germination and Stand Establishment Seed Germination Seed Germination is defined as the following: A
Seed Germination and Stand Establishment Thomas G Chastain CROP 200 Crop Ecology and Morphology Seed Germination and Stand Establishment Seed Germination Seed Germination is defined as the following: A
Assessment Schedule 2010 Scholarship Biology (93101) Question One. Evidence Statement. Processes (P) that have led to NZ s two species of pohutukawa
 Scholarship Biology (93101) 2010 page 1 of 8 Assessment Schedule 2010 Scholarship Biology (93101) Statement Question One Processes (P) that have led to NZ s two species of pohutukawa PA Allopatric speciation
Scholarship Biology (93101) 2010 page 1 of 8 Assessment Schedule 2010 Scholarship Biology (93101) Statement Question One Processes (P) that have led to NZ s two species of pohutukawa PA Allopatric speciation
M P BHOJ (OPEN) UNIVERSITY, BHOPAL ASSIGNMENT QUESTION PAPER
 PAPER : I Plant Development and Reproduction Q.1 Explain use of mutants in understanding seeding development? OR Short note on :- (i) Tropisms (ii) Mobilization of food reserves Q.2 Describe the organization
PAPER : I Plant Development and Reproduction Q.1 Explain use of mutants in understanding seeding development? OR Short note on :- (i) Tropisms (ii) Mobilization of food reserves Q.2 Describe the organization
Biology BY5. D = Urethra (correct spelling required) 1. E = Epididymis 1. F = Seminiferous tubule 1
 Biology BY5 (a) A = Seminal vesicle B = Vas deferens (not: sperm duct) C = Prostate (gland) (not: Prostrate) D = Urethra (correct spelling required) E = Epididymis F = Seminiferous tubule (b) Seminiferous
Biology BY5 (a) A = Seminal vesicle B = Vas deferens (not: sperm duct) C = Prostate (gland) (not: Prostrate) D = Urethra (correct spelling required) E = Epididymis F = Seminiferous tubule (b) Seminiferous
Frequency of Keyword Totals - (All LE Regents Exams)
 Frequency of Keyword Totals - (All LE Regents Exams) KEYWORD COUNT KEYWORD COUNT ecosystem 58 DNA 48 energy pyramid 19 graph 19 scientific method 19 photosynthesis 43 decomposer 18 human impact 42 clone
Frequency of Keyword Totals - (All LE Regents Exams) KEYWORD COUNT KEYWORD COUNT ecosystem 58 DNA 48 energy pyramid 19 graph 19 scientific method 19 photosynthesis 43 decomposer 18 human impact 42 clone
DNA Technology. B. Using Bacteria to Clone Genes: Overview:
 DNA Technology A. Basic Vocabulary: is DNA from 2 different sources that is combined. is the direct manipulation of genes for practical purposes. literally means or in a test tube or flask. is the manipulation
DNA Technology A. Basic Vocabulary: is DNA from 2 different sources that is combined. is the direct manipulation of genes for practical purposes. literally means or in a test tube or flask. is the manipulation
Inheritance (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Inheritance (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Key definitions Chromosome Allele Gene Haploid nucleus Diploid nucleus Genotype Phenotype Homozygous Heterozygous Dominant Recessive A thread of DNA, made
Inheritance (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Key definitions Chromosome Allele Gene Haploid nucleus Diploid nucleus Genotype Phenotype Homozygous Heterozygous Dominant Recessive A thread of DNA, made
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer GCE Biology (6BI02) Paper: 01R. Unit 2: Development, Plants and the Environment
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2013 GCE Biology (6BI02) Paper: 01R Unit 2: Development, Plants and the Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2013 GCE Biology (6BI02) Paper: 01R Unit 2: Development, Plants and the Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world
Keyword Worksheet - (ALL LE Regents Exams)
 Keyword Worksheet - (ALL LE Regents Exams) Copyright 2013 by Roger B. Strout BS, MS - All Rights Reserved 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26.
Keyword Worksheet - (ALL LE Regents Exams) Copyright 2013 by Roger B. Strout BS, MS - All Rights Reserved 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26.
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1. Questions & Answers
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 1.1 In a DNA double helix each type of base forms a stable base pair with only one type of base. When
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 1.1 In a DNA double helix each type of base forms a stable base pair with only one type of base. When
CELLULAR PROCESSES; REPRODUCTION. Unit 5
 CELLULAR PROCESSES; REPRODUCTION Unit 5 Cell Cycle Chromosomes and their make up Crossover Cytokines Diploid (haploid diploid and karyotypes) Mitosis Meiosis What is Cancer? Somatic Cells THE CELL CYCLE
CELLULAR PROCESSES; REPRODUCTION Unit 5 Cell Cycle Chromosomes and their make up Crossover Cytokines Diploid (haploid diploid and karyotypes) Mitosis Meiosis What is Cancer? Somatic Cells THE CELL CYCLE
Genetic variation and change the short version
 Part 1: Biodiversity and variation Genetic variation and change the short version Define biodiversity and describe its advantages. Why is variation important to a species? What is DNA? A chromosome? A
Part 1: Biodiversity and variation Genetic variation and change the short version Define biodiversity and describe its advantages. Why is variation important to a species? What is DNA? A chromosome? A
Genetics 1 Star Test
 Name: ate: 1. The accompanying data table summarizes the results of an investigation in which seeds from the same plant were grown under different conditions of temperature and relative humidity. 2. The
Name: ate: 1. The accompanying data table summarizes the results of an investigation in which seeds from the same plant were grown under different conditions of temperature and relative humidity. 2. The
Adenine % Guanine % Thymine % Cytosine %
 1. Explain each of the following statements in terms of your knowledge of the structure and function of DNA. (i) In all living organisms the ratio species to another. A C T G is constant but the ratio
1. Explain each of the following statements in terms of your knowledge of the structure and function of DNA. (i) In all living organisms the ratio species to another. A C T G is constant but the ratio
TIME : 2 ½ hours permitted CAPE BIOLOGY RESOURCES 12/16/2011
 ADVANCED BIOLOGY RESOURCES FOR CARIBBEAN STUDENTS UNIT 1 BIOLOGY WORKSHEET ONE TIME : 2 ½ hours permitted CAPE BIOLOGY RESOURCES 12/16/2011 - 2 - SECTION A Answer ALL questions. You must write your answers
ADVANCED BIOLOGY RESOURCES FOR CARIBBEAN STUDENTS UNIT 1 BIOLOGY WORKSHEET ONE TIME : 2 ½ hours permitted CAPE BIOLOGY RESOURCES 12/16/2011 - 2 - SECTION A Answer ALL questions. You must write your answers
PUBLISHED BY. The Biological Club of the Ohio State University. TABLE OF CONTENTS THE EMBRYO-SAC AND EMBRYO OF NELUMBO.* HARLAN H. YORK.
 The Ohio Naturalist PUBLISHED BY The Biological Club of the Ohio State University. Volume IV. JUNE, 1904. No. 8. TABLE OF CONTENTS YORK The Embryo-sac and Embryo of Nelumbo 167 OSBOKN Formal Opening of
The Ohio Naturalist PUBLISHED BY The Biological Club of the Ohio State University. Volume IV. JUNE, 1904. No. 8. TABLE OF CONTENTS YORK The Embryo-sac and Embryo of Nelumbo 167 OSBOKN Formal Opening of
Iowa State FFA Biotechnology CDE Comprehensive Knowledge Test
 Iowa State FFA Biotechnology CDE Comprehensive Knowledge Test - 2017 - Name Chapter 1. What is the name of the technique that allows geneticists to observe DNA fragments from a DNA sample and compare them
Iowa State FFA Biotechnology CDE Comprehensive Knowledge Test - 2017 - Name Chapter 1. What is the name of the technique that allows geneticists to observe DNA fragments from a DNA sample and compare them
CBA #4 Practice Exam Genetics. 1) (TEKS 5A) Which of the diagrams below shows the process of transcription:
 CBA #4 Practice Exam Genetics 1) (TEKS 5A) Which of the diagrams below shows the process of transcription: 2) (TEKS 5C) All of the following are true statements about cell differentiation EXCEPT A. Cell
CBA #4 Practice Exam Genetics 1) (TEKS 5A) Which of the diagrams below shows the process of transcription: 2) (TEKS 5C) All of the following are true statements about cell differentiation EXCEPT A. Cell
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOS) - Advanced Cell Biology
 Course objectives The main objective is to develop the ability to critically analyse and interpret the results of the scientific literature and to be able to apply this knowledge to afford new scientific
Course objectives The main objective is to develop the ability to critically analyse and interpret the results of the scientific literature and to be able to apply this knowledge to afford new scientific
Chapter 9 WHAT IS DNA?
 Notes DNA Chapter 9 WHAT IS DNA? DNA= Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA s job is to hold the entire genetic code for the organism. Human, tree, bacteria, mushroom, paramecium, etc! ALL HAVE DNA! DNA is held on
Notes DNA Chapter 9 WHAT IS DNA? DNA= Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA s job is to hold the entire genetic code for the organism. Human, tree, bacteria, mushroom, paramecium, etc! ALL HAVE DNA! DNA is held on
If you had 3 clones, what would you get them to do?! Aim high: How would you clone yourself?!
 If you had 3 clones, what would you get them to do?! Aim high: How would you clone yourself?! Genetic engineering Genetic and environmental differences B1.6 Variation Inheritance Types of reproduction
If you had 3 clones, what would you get them to do?! Aim high: How would you clone yourself?! Genetic engineering Genetic and environmental differences B1.6 Variation Inheritance Types of reproduction
DNA and DNA Replication
 Name Period PreAP Biology QCA 2 Review Your EOS exam is approximately 70 MC questions. This review, coupled with your QCA 1 review you received in October should lead you back through the important concepts
Name Period PreAP Biology QCA 2 Review Your EOS exam is approximately 70 MC questions. This review, coupled with your QCA 1 review you received in October should lead you back through the important concepts
Hartmann and Kester s Principles and Practices of Plant Propagation: A
 Hartmann and Kester s Principles and Practices of Plant Propagation: A Sneak Preview of the 9 th Edition Sandra B. Wilson 1, Fred T. Davies, Jr 2 and Robert L. Geneve 3 1 University of Florida, Department
Hartmann and Kester s Principles and Practices of Plant Propagation: A Sneak Preview of the 9 th Edition Sandra B. Wilson 1, Fred T. Davies, Jr 2 and Robert L. Geneve 3 1 University of Florida, Department
Physical Anthropology 1 Milner-Rose
 Physical Anthropology 1 Milner-Rose Chapter 3 Genetics: Reproducing Life and Producing Variation Our Origins By Clark Spencer Larsen Natural Selection operates on the levels of the 1. living, behaving
Physical Anthropology 1 Milner-Rose Chapter 3 Genetics: Reproducing Life and Producing Variation Our Origins By Clark Spencer Larsen Natural Selection operates on the levels of the 1. living, behaving
Supplemental Fig. 1. Transient expression of dynamic reporters of DNA methylation (DYNAMETs) in plants. (A) Schematic representation of potential
 Supplemental Fig. 1. Transient expression of dynamic reporters of DNA methylation (DYNAMETs) in plants. (A) Schematic representation of potential dynamic reporter of DNA methylation (DYNAMET). A DYNAMET
Supplemental Fig. 1. Transient expression of dynamic reporters of DNA methylation (DYNAMETs) in plants. (A) Schematic representation of potential dynamic reporter of DNA methylation (DYNAMET). A DYNAMET
B5 Growth and development. B5 Growth and development. Question How many different bases are found in DNA?
 Q1 How many different bases are found in DNA? Q2 Which DNA bases always pair together? 4 A with T G with C Q3 What is a gene? Q4 What are proteins made of? A gene is a short section of DNA that contains
Q1 How many different bases are found in DNA? Q2 Which DNA bases always pair together? 4 A with T G with C Q3 What is a gene? Q4 What are proteins made of? A gene is a short section of DNA that contains
Ag Science 1 (CP) or Instructor s Approval
 COURSE TITLE Description of Target Group Agriculture Science 2 is a one-year, laboratory science course designed as the second phase of the agriculture sequence. It is for the college-bound student with
COURSE TITLE Description of Target Group Agriculture Science 2 is a one-year, laboratory science course designed as the second phase of the agriculture sequence. It is for the college-bound student with
DNA and Chromosomes. 2. What molecules make up the rungs of the ladder? 3. What keeps the two sides of the ladder paired?
 DNA and Chromosomes Objectives: At the end of this lab you should be able to: 1. Describe the structure and function of DNA. 2. Know which bases in DNA pair with each other. 3. Define the terms chromatid,
DNA and Chromosomes Objectives: At the end of this lab you should be able to: 1. Describe the structure and function of DNA. 2. Know which bases in DNA pair with each other. 3. Define the terms chromatid,
four chromosomes ` four chromosomes correct markers (sister chromatids identical!)
 Name KEY total=107 pts 1. Genes G and H are on one chromosome; gene F is on another chromosome. Assume the organism is diploid and that there is no crossing over in this species. You are examining the
Name KEY total=107 pts 1. Genes G and H are on one chromosome; gene F is on another chromosome. Assume the organism is diploid and that there is no crossing over in this species. You are examining the
3. Protein(s)or polypeptide(s): a. are a chain of amino acids b. is a rare molecule in an organism
 2018 Iowa FFA Ag Biotechnology CDE General Knowledge Exam 1. A plant breeder makes a cross between two plants that are both the genotype Aa (Aa X Aa). How many different genotypes with respect to the A,a
2018 Iowa FFA Ag Biotechnology CDE General Knowledge Exam 1. A plant breeder makes a cross between two plants that are both the genotype Aa (Aa X Aa). How many different genotypes with respect to the A,a
Alfalfa. Seed Germination Seedling Growth Vegetative Development. North Dakota State University NDSU Extension Service
 North Dakota State University NDSU Extension Service Alfalfa Seed Germination Seedling Growth Vegetative Development R-648, (Revised), January 1999 Dwain Meyer, Professor of Plant Sciences, Agricultural
North Dakota State University NDSU Extension Service Alfalfa Seed Germination Seedling Growth Vegetative Development R-648, (Revised), January 1999 Dwain Meyer, Professor of Plant Sciences, Agricultural
PLT 302. Technology Innovations in Agriculture. David W. Still 8 February 2012
 PLT 302 Technology Innovations in Agriculture David W. Still dwstill@csupmomona.edu 8 February 2012 The most difficult subjects can be explained to the most slow- witted man if he has not formed any idea
PLT 302 Technology Innovations in Agriculture David W. Still dwstill@csupmomona.edu 8 February 2012 The most difficult subjects can be explained to the most slow- witted man if he has not formed any idea
DESIGNER GENES SAMPLE TOURNAMENT
 DESIGNER GENES SAMPLE TOURNAMENT PART ONE- GENETICS PROBLEMS In dogs, the inheritance of hair color involves a gene (B) for black hair and a gene (b) for brown hair. A dominant (C) is also involved. It
DESIGNER GENES SAMPLE TOURNAMENT PART ONE- GENETICS PROBLEMS In dogs, the inheritance of hair color involves a gene (B) for black hair and a gene (b) for brown hair. A dominant (C) is also involved. It
Lecture 4 04/12/2018
 Lecture 4 04/12/2018 Communicating cells may be close (local) or far (distant) Local signaling: a chemical signal which communicates between 2 nearby cells. Paracrine signaling: a cell secretes the signal
Lecture 4 04/12/2018 Communicating cells may be close (local) or far (distant) Local signaling: a chemical signal which communicates between 2 nearby cells. Paracrine signaling: a cell secretes the signal
Genetics Lecture Notes Lectures 6 9
 Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 6 9 Lecture 6 Until now our analysis of genes has focused on gene function as determined by phenotype differences brought about by different alleles or by a direct
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 6 9 Lecture 6 Until now our analysis of genes has focused on gene function as determined by phenotype differences brought about by different alleles or by a direct
1. (a) Define sex linkage... State one example of sex linkage... Key. 1st generation. Male. Female
 1. Define sex linkage. State one example of sex linkage. Draw a simple pedigree chart that clearly shows sex linkage in humans. Use conventional symbols. Start with an affected woman and an unaffected
1. Define sex linkage. State one example of sex linkage. Draw a simple pedigree chart that clearly shows sex linkage in humans. Use conventional symbols. Start with an affected woman and an unaffected
Regional Localization of Suspensor mrnas during Early Embryo Development
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 13, 2409 2425, November 2001, www.plantcell.org 2001 American Society of Plant Biologists Regional Localization of Suspensor mrnas during Early Embryo Development Koen Weterings, a,1,2
The Plant Cell, Vol. 13, 2409 2425, November 2001, www.plantcell.org 2001 American Society of Plant Biologists Regional Localization of Suspensor mrnas during Early Embryo Development Koen Weterings, a,1,2
For example: You are constantly loosing skin cells, in order to keep your skin healthy, your body needs to be constantly making new skin cells.
 Name: Cells and Reproduction A. The Cell Life Cycle The many cells in your body are constantly and. For example: You are constantly loosing skin cells, in order to keep your skin healthy, your body needs
Name: Cells and Reproduction A. The Cell Life Cycle The many cells in your body are constantly and. For example: You are constantly loosing skin cells, in order to keep your skin healthy, your body needs
amino acid nucleic acid nucleotide DNA/RNA enzymes lock and key model catalyst carbohydrate monosaccharide glucose
 Unit 1: Biomolecules I. Terms You Should Know lipid fatty acid & glycerol monomer biomolecule protein amino acid nucleic acid nucleotide DNA/RNA enzymes lock and key model catalyst carbohydrate monosaccharide
Unit 1: Biomolecules I. Terms You Should Know lipid fatty acid & glycerol monomer biomolecule protein amino acid nucleic acid nucleotide DNA/RNA enzymes lock and key model catalyst carbohydrate monosaccharide
CBSE QUESTION PAPER. BIOLOGY (Theory)
 CBSE QUESTION PAPER BIOLOGY (Theory) Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of four sections A, B, C and D. Section
CBSE QUESTION PAPER BIOLOGY (Theory) Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of four sections A, B, C and D. Section
Animal and plant cells have several parts. Each part has a different function.
 (4) Q.Living organisms are made of cells. (a) Animal and plant cells have several parts. Each part has a different function. Draw one line from each cell part to the correct function of that part. (b)
(4) Q.Living organisms are made of cells. (a) Animal and plant cells have several parts. Each part has a different function. Draw one line from each cell part to the correct function of that part. (b)
Genetically Modified Organisms
 Genetically Modified Organisms By Kendra Hogan For Dr. William R. Proulx, PhD, RD Associate Professor of Nutrition & Dietetics In partial fulfillment for the requirements of NUTR243 Food and Nutrition
Genetically Modified Organisms By Kendra Hogan For Dr. William R. Proulx, PhD, RD Associate Professor of Nutrition & Dietetics In partial fulfillment for the requirements of NUTR243 Food and Nutrition
Key Words: glyphosate-resistant corn; genetically engineered corn; corn pollen; pollen transport; corn seed purity, transgene.
 AgBioForum Volume 4, Number 2 2001 Pages 87-92 CROSS POLLINATION FROM GENETICALLY ENGINEERED CORN: WIND TRANSPORT AND SEED SOURCE John M. Jemison, Jr. & Michael E. Vayda 1 Pollen transport from genetically
AgBioForum Volume 4, Number 2 2001 Pages 87-92 CROSS POLLINATION FROM GENETICALLY ENGINEERED CORN: WIND TRANSPORT AND SEED SOURCE John M. Jemison, Jr. & Michael E. Vayda 1 Pollen transport from genetically
Wk Std Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 13 Obj./Essential question: ~DNA Structure ~DNA Replication
 Wk Std Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 13 NO SCHOOL What are the 4 nitrogenous bases of DNA? DNA & Ch 11.1 281-287 replication review questions When 2 daughter strands of dna are synthesized from
Wk Std Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 13 NO SCHOOL What are the 4 nitrogenous bases of DNA? DNA & Ch 11.1 281-287 replication review questions When 2 daughter strands of dna are synthesized from
Chromosomes. M.Sc. Biotechnology. Hawler Medical University, Iraq
 Chromosomes Bashdar Mahmud Hussen M.Sc. Biotechnology Hawler Medical University, Iraq bashdar@res.hmu.edu.iq bmhscience@yahoo.com History of Chromosome Karl Nagali (1842) E. Russow (1872) first description
Chromosomes Bashdar Mahmud Hussen M.Sc. Biotechnology Hawler Medical University, Iraq bashdar@res.hmu.edu.iq bmhscience@yahoo.com History of Chromosome Karl Nagali (1842) E. Russow (1872) first description
Page 1. Name: 1) Which letter indicates a cell structure that directly controls the movement of molecules into and out of the cell?
 Name: 1) Which letter indicates a cell structure that directly controls the movement of molecules into and out of the cell? A) A B) B C) C D) D 2) A single-celled organism is represented in the diagram
Name: 1) Which letter indicates a cell structure that directly controls the movement of molecules into and out of the cell? A) A B) B C) C D) D 2) A single-celled organism is represented in the diagram
Supplementary Information. c d e
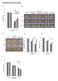 Supplementary Information a b c d e f Supplementary Figure 1. atabcg30, atabcg31, and atabcg40 mutant seeds germinate faster than the wild type on ½ MS medium supplemented with ABA (a and d-f) Germination
Supplementary Information a b c d e f Supplementary Figure 1. atabcg30, atabcg31, and atabcg40 mutant seeds germinate faster than the wild type on ½ MS medium supplemented with ABA (a and d-f) Germination
Biology 30 Work Plan
 Units / Topics Unit 1 Chemical Basis of Life Unit 2 Cell Structure and Function Time Major Learning Outcomes Frame 10 Hrs. Appreciate the basic principles of chemistry which are involved in life processes
Units / Topics Unit 1 Chemical Basis of Life Unit 2 Cell Structure and Function Time Major Learning Outcomes Frame 10 Hrs. Appreciate the basic principles of chemistry which are involved in life processes
Chapter 3. DNA Replication & The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 3 DNA Replication & The Cell Cycle DNA Replication and the Cell Cycle Before cells divide, they must duplicate their DNA // the genetic material DNA is organized into strands called chromosomes
Chapter 3 DNA Replication & The Cell Cycle DNA Replication and the Cell Cycle Before cells divide, they must duplicate their DNA // the genetic material DNA is organized into strands called chromosomes
Unit 5 - Genetics. Page 1
 Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Many years ago, a scientist grew pea plants that produced wrinkled peas. The peas from these plants produced new plants that also produced wrinkled
Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Many years ago, a scientist grew pea plants that produced wrinkled peas. The peas from these plants produced new plants that also produced wrinkled
Recommended Resources: The following resources may be useful in teaching this
 Unit B: Plant Anatomy Lesson 5: Understanding Seed Anatomy Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Identify the major parts
Unit B: Plant Anatomy Lesson 5: Understanding Seed Anatomy Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Identify the major parts
MUDRA LIFE SCIENCES VOLUME-07 PART B & C MODEL QUESTION BANK FOR THE TOPICS: *Mudra* Life Sciences For NET & SET Exams.
 MUDRA LIFE SCIENCES VOLUME-07 PART B & C MODEL QUESTION BANK FOR THE TOPICS: 12. APPLIED BIOLOGY UNIT-1 1 UNIT-2 17 13. METHODS IN BIOLOGY UNIT-1 39 UNIT-2 69 UNIT-3 93 0 12. APPLIED BIOLOGY UNIT - 1 1.
MUDRA LIFE SCIENCES VOLUME-07 PART B & C MODEL QUESTION BANK FOR THE TOPICS: 12. APPLIED BIOLOGY UNIT-1 1 UNIT-2 17 13. METHODS IN BIOLOGY UNIT-1 39 UNIT-2 69 UNIT-3 93 0 12. APPLIED BIOLOGY UNIT - 1 1.
Structure Function Role in protein production (not all may relate directly to this)
 Genetics 2014 Semester 1 Final Exam Review Sheet Unit 1: Cells Structure and Function. Review Questions: 1. What is the function of the following cell structures? Structure Function Role in protein production
Genetics 2014 Semester 1 Final Exam Review Sheet Unit 1: Cells Structure and Function. Review Questions: 1. What is the function of the following cell structures? Structure Function Role in protein production
Bio Study Guide. What is the structure of a DNA. A nitrogen base (ATCG/AUCG) connected to a sugar and a phosphate. nucleotide?
 What are nucleic acids? The largest organic molecules. Master organisms, they are in control of cell functions. They are found in all living organisms, and they are two types of them- DNA and RNA. They
What are nucleic acids? The largest organic molecules. Master organisms, they are in control of cell functions. They are found in all living organisms, and they are two types of them- DNA and RNA. They
Plant and Soil Science I
 PRECISION EXAMS Plant and Soil Science I EXAM INFORMATION Items 50 Points 50 Prerequisites NONE Grade Level 9-12 Course Length ONE YEAR DESCRIPTION Students will demonstrate knowledge and skills in a wide
PRECISION EXAMS Plant and Soil Science I EXAM INFORMATION Items 50 Points 50 Prerequisites NONE Grade Level 9-12 Course Length ONE YEAR DESCRIPTION Students will demonstrate knowledge and skills in a wide
Q. Importing better varieties of plants from outside and acclimatizing i them to local l environment is 1. Selection 2. Cloning 3. Introduction 4. Het
 CET BIOLOGY BIOTECHNOLOGY II Q. Importing better varieties of plants from outside and acclimatizing i them to local l environment is 1. Selection 2. Cloning 3. Introduction 4. Heterosis Q. Bagging is done
CET BIOLOGY BIOTECHNOLOGY II Q. Importing better varieties of plants from outside and acclimatizing i them to local l environment is 1. Selection 2. Cloning 3. Introduction 4. Heterosis Q. Bagging is done
Cell Division. embryo: an early stage of development in organisms
 Over the past several years, a debate has been brewing over the use of stem cells. Stem cells can be used to treat certain diseases and conditions such as spinal cord injuries, diabetes, arthritis, and
Over the past several years, a debate has been brewing over the use of stem cells. Stem cells can be used to treat certain diseases and conditions such as spinal cord injuries, diabetes, arthritis, and
REGENERATION IN MONOCOTYLEDONOUS SEEDLINGS 1
 REGENERATION IN MONOCOTYLEDONOUS SEEDLINGS 1 CARL D. LA RUE (Received for publication September 13, 1933) The experiments described in this paper were made for comparison with those conducted by the writer
REGENERATION IN MONOCOTYLEDONOUS SEEDLINGS 1 CARL D. LA RUE (Received for publication September 13, 1933) The experiments described in this paper were made for comparison with those conducted by the writer
Plant Propagation PLS 3223/5222
 Plant Propagation PLS 3223/5222 Dr. Sandra Wilson Dr. Mack Thetford Techniques of Seed Production and Handling Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Objectives are to Understand: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Different sources for seeds
Plant Propagation PLS 3223/5222 Dr. Sandra Wilson Dr. Mack Thetford Techniques of Seed Production and Handling Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Objectives are to Understand: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Different sources for seeds
Biology Semester Exam Study Guide--January 2016
 Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Standard B-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the molecular basis of heredity.
 B-4.1 Compare DNA and RNA in terms of structure, nucleotides, and base pairs. Taxonomy Level: 2.6-B Understand Conceptual Knowledge Key Concepts: Nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), ribonucleic
B-4.1 Compare DNA and RNA in terms of structure, nucleotides, and base pairs. Taxonomy Level: 2.6-B Understand Conceptual Knowledge Key Concepts: Nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), ribonucleic
C. Incorrect! Second Law: Law of Independent Assortment - Genes for different traits sort independently of one another in the formation of gametes.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 20: Chromosomes and Genetic Technology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed, (3) Pick
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 20: Chromosomes and Genetic Technology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed, (3) Pick
A Level. A Level Biology. Cells, Microscopes, Cell Cycle and Immunity Questions. AQA, OCR, Edexcel. Name: Total Marks: Page 1
 AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Cells, Microscopes, Cell Cycle and Immunity Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.The diagram shows a eukaryotic cell. (a) Complete the table by giving the letter
AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Cells, Microscopes, Cell Cycle and Immunity Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1.The diagram shows a eukaryotic cell. (a) Complete the table by giving the letter
Biology Monday 9 November 2015 Paper Two Question and response book
 2015 Senior External Examination Biology Monday 9 November 2015 Paper Two Question and response book 1 pm to 3:10 pm Time allowed Perusal time: 10 minutes Working time: 2 hours Examination materials provided
2015 Senior External Examination Biology Monday 9 November 2015 Paper Two Question and response book 1 pm to 3:10 pm Time allowed Perusal time: 10 minutes Working time: 2 hours Examination materials provided
B2 Tuesday 12 th May (Additional Science)
 B2.1.1 Cells and cell structure State that all living things are made up of cells Identify, and describe the functions of, the following parts of human and animal cells: nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane,
B2.1.1 Cells and cell structure State that all living things are made up of cells Identify, and describe the functions of, the following parts of human and animal cells: nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane,
GCE A level 1075/01 BIOLOGY/HUMAN BIOLOGY - BY5
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 2 Candidate Number GCE A level 1075/01 BIOLOGY/HUMAN BIOLOGY - BY5 A.M. FRIDAY, 22 June 2012 1¾ hours Question For s use Maximum Mark 1. 5 Mark Awarded 2. 8 3. 7 4. 6
Surname Other Names Centre Number 2 Candidate Number GCE A level 1075/01 BIOLOGY/HUMAN BIOLOGY - BY5 A.M. FRIDAY, 22 June 2012 1¾ hours Question For s use Maximum Mark 1. 5 Mark Awarded 2. 8 3. 7 4. 6
Amoeba Sisters: Cell Cycle & Cancer. Cell Cycle & Cancer Video
 Warm Up 1.) How are proteins made (relationship between DNA and a ribosome)? 2.) The Agrodiaetus Butterfly has 268 total chromosomes. How many chromosomes do their gametes have? 3.) What part of your body
Warm Up 1.) How are proteins made (relationship between DNA and a ribosome)? 2.) The Agrodiaetus Butterfly has 268 total chromosomes. How many chromosomes do their gametes have? 3.) What part of your body
12 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 12 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Locating Genes
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 12 The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Locating Genes
Assessment of mechanical damage in sweet corn seeds by image analysis
 UNIVERSITY OF SÃO PAULO Luiz de Queiroz College of Department of Crop Science Assessment of mechanical damage in sweet corn seeds by image analysis Francisco G GOMES-JUNIOR & Silvio M CICERO Introduction
UNIVERSITY OF SÃO PAULO Luiz de Queiroz College of Department of Crop Science Assessment of mechanical damage in sweet corn seeds by image analysis Francisco G GOMES-JUNIOR & Silvio M CICERO Introduction
DNA and GENETICS UNIT NOTES
 DNA and GENETICS UNIT NOTES NAME: DO NOT LOSE! DNA DNA - Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid Shape is called double helix DNA has the information for our cells to make proteins. DNA through transcription makes mrna
DNA and GENETICS UNIT NOTES NAME: DO NOT LOSE! DNA DNA - Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid Shape is called double helix DNA has the information for our cells to make proteins. DNA through transcription makes mrna
Philip W. Becraft Genetics, Development & Cell Biology Dept. Agronomy Dept. IOWA STATE UNIVERSITY
 Philip W. Becraft Genetics, Development & Cell Biology Dept. Agronomy Dept. IOWA STATE UNIVERSITY Genetic Approach to Studying Grain Formation opaque5 (o5) is a mutant gene o5 mutant kernels are very defective
Philip W. Becraft Genetics, Development & Cell Biology Dept. Agronomy Dept. IOWA STATE UNIVERSITY Genetic Approach to Studying Grain Formation opaque5 (o5) is a mutant gene o5 mutant kernels are very defective
Goal 3. Friday, May 10, 13
 Goal 3 Bio.3.1 Explain how traits are determined by the structure and function of DNA. Bio.3.2 Understand how the environment, and/or the interaction of alleles, influences the expression of genetic traits.
Goal 3 Bio.3.1 Explain how traits are determined by the structure and function of DNA. Bio.3.2 Understand how the environment, and/or the interaction of alleles, influences the expression of genetic traits.
AGRO/ANSC/BIO/GENE/HORT 305 Fall, 2016 Overview of Genetics Lecture outline (Chpt 1, Genetics by Brooker) #1
 AGRO/ANSC/BIO/GENE/HORT 305 Fall, 2016 Overview of Genetics Lecture outline (Chpt 1, Genetics by Brooker) #1 - Genetics: Progress from Mendel to DNA: Gregor Mendel, in the mid 19 th century provided the
AGRO/ANSC/BIO/GENE/HORT 305 Fall, 2016 Overview of Genetics Lecture outline (Chpt 1, Genetics by Brooker) #1 - Genetics: Progress from Mendel to DNA: Gregor Mendel, in the mid 19 th century provided the
Structure of DNA Introductory Videos:
 Structure of DNA Introductory Videos: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qy8dk5is1f0 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zghkhmoyc5i DNA is a macromolecule made of nucleotides. Each human cell carries a complete
Structure of DNA Introductory Videos: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qy8dk5is1f0 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zghkhmoyc5i DNA is a macromolecule made of nucleotides. Each human cell carries a complete
Optimising wheat grain shape and size for improved processing quality
 Optimising wheat grain shape and size for improved processing quality Crop Science Initiative funded - 4 year project RRes: JIC: SCRI: University of Bath: University of Oxford: University of Manchester:
Optimising wheat grain shape and size for improved processing quality Crop Science Initiative funded - 4 year project RRes: JIC: SCRI: University of Bath: University of Oxford: University of Manchester:
Tetrazolium test procedure for Sorghum bicolor x S. sudanense
 Tetrazolium test procedure for Sorghum bicolor x S. sudanense Topics: TZ Test according to ISTA Rules (2004) TZ Test according to ISTA Working Sheets on Tetrazolium Testing 2003 TZ Test according to Handbook
Tetrazolium test procedure for Sorghum bicolor x S. sudanense Topics: TZ Test according to ISTA Rules (2004) TZ Test according to ISTA Working Sheets on Tetrazolium Testing 2003 TZ Test according to Handbook
Name: Date: IF YOU GOT BELOW A 70% RETAKING THE TEST IS MANDATORY.
 IF YOU GOT BELOW A 70% RETAKING THE TEST IS MANDATORY. 1. What is a mutation? Any change in a DNA sequence 2. Name and describe the two categories types of gene mutations. Point: substitution, one nucleotide
IF YOU GOT BELOW A 70% RETAKING THE TEST IS MANDATORY. 1. What is a mutation? Any change in a DNA sequence 2. Name and describe the two categories types of gene mutations. Point: substitution, one nucleotide
The Seed of Cardiospermum halicacabum L. A Criticism. Abd El Rahman+Kadry. {received August 9th, 1959) to Guerin s observation (1901).
 m. ««i t 1 * Acta Botanica Neerlandica 9 (I960) 330-332 The Seed of Cardiospermum halicacabum L. A Criticism Abd El Rahman+Kadry (.Faculty of Agriculture, Ain Shams University, Quobbah Palace, Egypt) {received
m. ««i t 1 * Acta Botanica Neerlandica 9 (I960) 330-332 The Seed of Cardiospermum halicacabum L. A Criticism Abd El Rahman+Kadry (.Faculty of Agriculture, Ain Shams University, Quobbah Palace, Egypt) {received
