ASSESSMENT OF THE DRAINAGE WATER REUSE IN THE IRRIGATION IMPROVEMENT AREAS, KAFR EL SHEIKH GOVERNORATE OF EGYPT
|
|
|
- Melina Singleton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ASSESSMENT OF THE DRAINAGE WATER REUSE IN THE IRRIGATION IMPROVEMENT AREAS, KAFR EL SHEIKH GOVERNORATE OF EGYPT A.El-Ganzori 1,.T. Abdel Gawad 2, A.El-Sayed 1, Adel Hashim 3 ABSTRACT During the period between March 1998 to July 1999, a study has been carried out to investigate the possibility to reuse the drainage water within the Irrigation Improvement Project (IIP) areas at El-Wasat and El-Manaifa in Kafr El Sheikh Governorate (DRI, 2000). A monitoring program on branch drains and irrigation canals was established and routinely implemented for the water quantity and quality. The program comprised five locations at El- Manaifa area and three at El-Wasat area. A simulation desk study was also conducted to predict the impacts of the reuse of drainage water within the IIP areas on the soil salinity and crop production. The study succeeded in answering where and, if possible, how much drainage water can be reused. The water supply-demand at each proposed mixing location was identified to calculate the water deficit spatially and temporally. The compensation of drainage water was determined using the salinity parameter as a guiding factor. According to FAO guidelines for drainage water reuse for agricultural uses, the TDS, Cl and Na concentrations in the drainage water could have slight to moderate salinity and toxicity problems. At any rate, the concentration of common metals in drainage and irrigation water does not reach the value that could cause problems to soil and plant. The bacteria count level for most of the sites comply with quality criteria to irrigate the restricted crops according to WHO guidelines (1989). The SIWARE model was used for the simulation study using the data for year The relative evapotranspiration rate was used as an indicator of crop yield. The simulated strategies were concentrated on the increase of the irrigation water salinity in steps after implementing the mixing plans. The effects of an increase of irrigation water salinity have been examined for El-Wasat and El-Manaifa areas. SIWARE model simulations have shown that: Evapotranspiration and the crop yield are impeded by salts as indicated by the average simulated soil salinity; The maximum reduction in relative evapotranspiration is not higher than 12.5%; The maximum increase of the soil salinity is 139% (3800 ppm) whereas the maximum increase of irrigation water salinity is 316% (1040 ppm). It is recommended to implement such a strategy, while starting the Irrigation Improvement Programme (IIP) for El-Wasat and El-Manaifa areas. Meanwhile, the national plan for the treatment of domestic wastewater should have a priority. This intervention of wastewater treatment would allow for the cultivation of different types of unrestricted crops. In all cases, an economical analysis would determine the optimum alternative. 1 Researcher, Drainage Research Institute, National Water Research Center, Ministry of Water Resources and Irrigation, Egypt 2 Director, Drainage Research Institute, National Water Research Center, Ministry of Water Resources and Irrigation, Egypt 3 Under Secretary, Irrigation Improvement Department, Ministry of Water Resources and Irrigation, Egypt 333
2 1. INTRODUCTION Preliminary studies indicated that there is a water supply shortage for both IIP project areas of El-Wasat (75,000 feddan) and El-Manaifa (47,000 feddan) in Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate. It is proposed to substitute shortage in fresh water supply from the available drainage water within the project areas, which could be mixed with canal fresh water at proper locations. The mixture should be within pre-determined quality limits that takes into consideration the long-term effect on the soils and crops in both areas. The study aimed at monitoring and defining the available drainage water resources and its quality in both project areas. The negative impacts on agriculture due to drainage water reuse have to be kept minimum. As the available quantities and qualities of the drainage water are subject to changes in the future, an integrated reuse plan that includes the recommended mixing locations were identified. The use of simulation model helped in predicting these future changes. The study objectives were as follows: Identifying the appropriate mixing locations to substitute the shortage in fresh water supply. The mixed water should meet the sustainability requirements of the agricultural production in the project area. Estimating the monthly abstraction from the drains and lifting head at each mixing location. To achieve the goal of the study, the following activities have been carried out: Identifying sources of water supply to the study areas. Determining water demands for each of the study areas which include irrigation, municipal and industrial water. Designing and setting-up of a monitoring network locations. Field monitoring and data analysis. Simulation study. 2. WATER QUANTITY AND QUALITY MONITORING 2.1 Proposed Mixing Locations The suitability of a mixing location to blend fresh and drainage water is usually assessed according to the following criteria: Minimum distance between the drain and canal where mixing is to take place, Smallest possible lifting head for the pump station to be constructed to lift drainage water to the canal, Quantity and quality of the drainage water are enough and suitable to satisfy the shortage in canal water. After mixing, the canal water quality should be within the permissible standards to protect soils, crop yield and the environment, Mixing location should be downstream of the current and future drinking water intakes, Mixing location should also be upstream the outfall of point source pollution such as wastewater treatment plant or factory outlets, 334
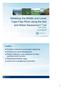
3 According to these criteria and in co-ordination with local IIP staff at Kafr El-Sheikh, locations in El-Wasat and El-Manaifa areas were proposed as mixing sites, Figure ARAB REPUBLIC OF EGYPT IRRIGATION IMPROVEMENT PROJECT PROJECT AREA BOUNDARIES MAIN CANALS SECONDARY CANALS SECONDARY DRAINS MAIN DRAINS PROPOSED REUSE PUMPING STATIONS CITIES EL ZINI Gadalia Canal MOHEET DRAIN ELSHARKI NO. 8 MOHEET DRAIN ELSHARKI NO. 7 N MM8F MM8D Manaifa 42,000 Feddan El Wasat 75,000 Feddan EL MANDORA MM7C MM7D MM7F MM5C MM5D MANAIFA SUB-PROJECT Faroun Drain El Shaba Canal MM6C MM6D MM6F Shaba No. 8 Lower Drain Sidi Salem No. 8 Drain MM2F MM2D Tida Shlma Canal Khawaled Canal Khawaled Drain MM3C MM3D Basis Canal Shalma Armona Canal MM1C MM1D Dakalt Canal EL WASAT SUB-PROJECT Hod El Hagey Drain Manaifa Canal El Shaba Canal Elasfal Drain MM9C MM4C MM4D 0 Kafr El Shiek 5 10 Kilometers 0 Approximate Scale 5 Miles M10C (1). ICEHM2000, Cairo University, Egypt, 2000, Volume 1, page Monitoring Program Actual field monitoring started early July, 1998 at the proposed mixing locations to assess the drainage and irrigation water quantity and quality and to determine the suitability of these locations for final selection of mixing sites and ratios. The correlation between the water level and flow discharge was obtained. Q-H relationship is considered acceptable when the correlation coefficient (R) is >= 0.50 to give a chance for more installed instruments to continuously measure the flow. Based on the findings of these measurements, significant Q-H relations were achieved at some measurement points. The final monitoring locations proposed for mixing and water quantity measurement methods in El-Wasat and El-Manaifa areas are shown in Table (1). Where 335
4 appropriate, Q-H relationships are also presented in the table. The land levelling is also determined, following the survey analysis, to obtain the lifting head for each location. Table (1) Final monitoring locations proposed for mixing and water quantity measurement methods in El-Wasat and Manaifa Areas. Name of the Canal or Drain Site Code Area served (fed.) Lifting head No of Measurements R Relationship El-Wasat Area El Melaha Canal MM1C Q = Hm ** 3 m Lower Drain No. 7 MM1D Q = Hm ** Shalma MM3C Q = Hm ** Lower Drain No. 8 MM3D 4 m Q = Hm Gad Allah MM2F Q = Hm * Nashert Drain MM2D 3 m Q = Hm ** Meet Yazied (El-Wasat MM9C 4 Q = Hm ** regulator) El-Manaifa Area El-Manaifa MM4C m Upper Drain No. 9 MM4D Q = Hm ** Abto MM5C Q = Hm ** Drain No. 9 MM5D 4 m El Shiekh Ibrahim MM6C El Shiekh Ibrahim MM6F 3 m Q = Hm ** Feeder Baher Nashert Drain MM6D Q = Hm ** El-Mostagada Company MM7C El-Mostagada Company MM7F 3 m Q = Hm * Feeder Drain No. 9 MM7D El-Gammalia MM8F Drain No. 9 MM8D 3 m Q = Hm El-Manaifa Intake M10C 6 Q = Hm R: Correlation Coefficient * Significant relationship ** Highly significant relationship Hm: Water surface depth from the reference point in m Q: Water Quantity in m Monitored Parameters, Measurement Methods and Frequency The ultimate goal of the proposed monitoring network is to obtain knowledge about the accurate values of the quantity and quality of irrigation and drainage water at the proposed locations in the study area. The data processing has started with field sheets and laboratory measurements and ended with the analysis tabulation that include all relevant details of chemical and hydrological data at each proposed mixing location presented on monthly basis. A number of steps were made to check the consistency of raw and processed data. In addition, graphs showing some important indicators were drawn. Table (2) presents the monitored parameters, measurement methods and frequency. For the sites with significant Q-H relationship, water quantities were estimated from water level data. For the other sites velocity measurements with the current meters were taken. Water salinity measurements were carried out during the process of measuring water quantity. Additionally, water samples were collected for laboratory analysis to determine the water quality parameters, which are: 336
5 Chemical analysis to determine main ions, TDS, SAR and Adj SAR. Boron, nitrogen, and phosphorus BOD, COD, turbidity, grease, oil, total suspended solids and total volatile solids Bacteria Heavy metals (Cu, Fe, Zn, Pb) 337
6 Table (2) Monitored parameters, measurement methods and frequencies Parameter Measurement Method Frequency Water Quantity Q-H (Water Level Recorder) Hourly (daily average) Q-H (Staff Gauge) Twice a day (daily average) Velocity (Current Meter) Every other week Water Salinity Portable EC meter Every other week Chemical Parameters Sampling and in Situ Every other week Biological Parameters and Heavy Metals Sampling Monthly The samples were analysed at the DRI laboratory according to the established and wellknown Standard Operating Procedures. 2.4 Assessment of the Water Quality Parameters The following can be generally noticed from the in-situ measurements and laboratory analysis over the study period. Seasonal variation in the water quality is observed. It is noticed that the highest concentrations of the variable parameters occurred in winter and the lowest occurred mainly in summer. This is usually happened because all the head regulators of the irrigation canals are closed in alternative duration in winter for maintenance. Therefore the pollutants concentration increased in the wintertime. On the other hand, water discharge increases in the summer time due to high water requirement of the summer crops. These amounts of water increase the dilution rate of the pollutants. Summary of water quality variables is included in Table (3). 3. SIMULATION STUDY The SIWARE (Simulation of Irrigation Water management in the Arab Republic of Egypt) is a well-known model that was developed under the cooperation between the governments of Egypt and the Netherlands. The model has been successfully applied in Egypt as well as in Argentina, Pakistan and India after some modifications (Abdel- Gawad, S.T. et al., 1991), (Sijtsma, B.R. et al., 1995). 3.1 Model Application in Wasat and Manaifa Areas SIWARE is a regional scale model that cannot be run exclusively for El-Wasat and El- Manaifa areas in isolation of the rest of the Middle Delta region. Therefore, those two study areas were represented by a number of calculation units within model application over the Middle Delta region, using the parameters obtained from the calibration and validation of a previous study. The Middle Delta is about million feddans of cultivated land, and the supplied Nile irrigation water is about BCM/year. Year 1998 was selected to prepare the simulation-input data. 337
7 Table (3) Summary of the main water quality parameters at El-Wasat & El-Manaifa areas (1998 / 1999) Location Site Code BOD mg/l COD mg/l NH4 mg/l DO mg/l El- Wasat area stand 10 stand 15 Stand 45 stand 5 Min. Max. Av. Min. Max. Av. Min. Max. Av. Min. Max. Av. El- Melaha Canal MM1C Lower Drain No.7 MM1D Shalma Canal MM3C Lower Drain No.8 MM3D Gad Allah canal MM2F Nashart Drain MM2D El- Manaifa Area El-Manaifa Canal MM4C Upper Drain No.9 MM4D Abto canal MM5C Drain No.9 MM5D El-Shiekh Ibrahim MM6C canal Nashart Drain MM6D El Mostagada canal MM7C Drain No.9 MM7D El-Gammalia canal MM8F Drain No.9 MM8D
8 The Middle Delta region is characterized by arid climatic conditions. Low average annual rainfall varies from 180 mm/year along the Mediterranean to 25 mm/year at Cairo. High average daytime temperatures vary from 20 to 40 o C. Evaporation rates are accordingly high and reach values of 3,500 mm/year. The study region was subdivided into 116 calculation units. The size of the calculation units varied from a 3,500 feddans, up to a 38,000 feddans. The areas of interest in this study; namely El-Wasat and El-Manaifa area were represented by six and three calculation units, respectively. Figure (2) shows the boundaries of the calculation units of the study region of the Middle Delta as input to SIWARE, including the calculation units that comprise El-Wasat and El-Manaifa areas. The values of parameters for the initial condition input to the model were prepared using the model itself. The model was run for that region for a number of years, and the output of each year was used to prepare the initial conditions of the next year. To account for the reuse of drainage water to supplement the shortage in irrigation water, a number of model simulations were made using more saline irrigation water in the reuse areas. This is expected to represent the actual situation of mixing saline drainage water with fresh irrigation water in the reuse areas. 3.2 Input Data Processing Crop pattern As mentioned above, crop pattern within each calculation unit is simplified to average representative areas for each crop. This is done by summing all the areas cultivated with the same crop within the calculation unit. Moreover, only 11 crops have been considered in the model input. Minor crops that occupy small areas were added to the most similar one of the considered 11-crops. Crop pattern within each field agricultural district (called Markaz ) was used to prepare the crop pattern for the corresponding calculation unit in the model input. Table (4) shows the percentage of each area occupied by a major crop to the total cultivated area in the Middle Delta during the year Table (4) Cropping pattern and its relative area occupied by crops in the Middle Nile Delta (1998) Crop Name Area (feddan) Percentage (%) Long Berseem 5,354, Wheat 541, Winter Vegetables 32, Rice 454, Cotton 309, Maize 541, Summer vegetables 85, Perennials (trees) 101, Sugar beet 466, Short berseem 312, Nili vegetables 40, Winter fallow 37, Summer fallow 67,
9 Figure (2) The boundaries of the study area as defined in the SIWARE model schematization 340
10 3.2.2 Crop water requirement Crop water requirement is affected by the crop growth stage as a funct ion of time, and by the climatic conditions. Conveyance and operational losses of irrigation water depend on crop type, and they are included in the crop water requirement. Crop water requirement per unit area as a function of time has been calculated and tabulated for three zones in Egypt: Upper Egypt, Middle Egypt and Lower Egypt. These tables were prepared using field experiments and past experience. The entire Nile Delta, including the study areas of the Middle Delta, is located in the Lower Egypt zone. It is important to note that the actual water quantities supplied to the fields by the farmers may differ from the tabulated crop water requirement. The MWRI water requirement tables were used in preparing the crop pattern input to the model, as well as in calculating the crop water requirement. 3.3 Results of the simulation scenarios One of the main objectives for the analysis of the tested strategies is to determine the impacts of reusable drainage water for irrigation on the crop yield and soil salinity. The simulated strategies were concentrated on the increase of the irrigation water salinity after implementing the mixing plans. The salinity of irrigation water was increased in steps started from average value ~ 290 till ~1040 ppm for both areas. In addition, the analysis of the required mixing amounts of drainage water to compensate the shortage of fresh water, after monitoring the irrigation and drainage water, within the study area has shown the salinity level up to ~1000 ppm. Figure (3) shows the relation between the increase of irrigation water salinity and corresponding changes of the soil salinity and relative evapotranspiration for El-Manaifa area. El Manifa Area Relative ET (%) Soil Salinity (PPM) Soil Salinity Relative ET Irrigartion Water Salinity (PPM) Figure (3) Impacts of irrigation water salinity increase on the soil salinity and relative evapotranspiration for El-Manifa area The percent of increase of the irrigation water salinity and its effects on the percentage of decrease of the soil salinity and the relative evapotranspiration are summarised in table (5) for both areas. 341
11 Table (5) The percentage of soil salinity increase and relative E t reduction due to the increase of irrigation water salinity within the study area. Percent of increase and decrease El Wasat El Manaifa Irrigation Water Salinity 87% 118% 174% 224% 106 % Relative Et -7% -10% -12% -12.5% % -9% -10% % Soil Salinity 102% 124% 139% 131% 68% 87% 102 % 97% 4. WATER DEFICIT The amounts of discharged irrigation water at the inlets of the study areas are summarised in table (6). The total amount of irrigation water to El-Wasat and El-Manaifa areas are 632 and 322 million cubic meters/year respectively. The salinity level is around 0.40 ms/cm for El-Wasat area and 0.39 ms/cm for El-Manaifa area. The increase of the salinity level could be described by the reuse of the drainage water practices upstream of the study areas. Based on the quantity of the irrigation water delivered to the areas and the cultivated area served, it can be concluded that the water duties are around 8000 and 7200 m 3 /fed for El-Wasat and El-Manaifa areas respectively. 152 % 237 % 316 % Table (6) Water delivery, El-Wasat and El-Manaifa areas (in million cubic meters) Month El Wasat (million m 3 ) EC (ms/cm) El Manaifa (million m 3 ) EC (ms/cm) Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb Mar Apr May June Table (7) summarises the deficit amounts and the calculated salinity levels after blending the required amounts of drainage water to replenish the shortage amounts of irrigation water. The data used through this analysis is the calculated crop water duty for each proposed mixing location and the measured quantity of the irrigation and drainage water. The table covered a period between July 1998 to June The following are some remarks of the operation of the monitored mixing locations: Some of the irrigation locations do not receive fresh water all the time. Due to lack of fresh water, these canals are supplied with drainage water directly because of the scattered feeders along the reach for each canal. 342
12 Table (7) Water deficit during the monitoring period at each mixing location and the calculated salinity after mixing with drainage water El-Wasat area El-Manaifa area Month MM1C MM1D MM2C MM2D MM3C MM3D MM6C MM6D MM4C MM4D MM5C MM5D MM7C MM7D MM8C MM8D Q F EC MIX. Q F EC MIX. Q F EC MIX. Q F EC MIX. Q F EC MIX. Q F EC MIX. Q F EC MIX. Q F EC MIX. m 3 /month PPM m 3 /month PPM x10 6 PPM m /month x10 6 PPM m /month x10 6 PPM m /month x10 6 PPM m /month x10 6 PPM m /month x10 6 PPM m /month x10 6 x10 6 Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Q c Fresh water canal discharge. EC ic Salinity of fresh canal irrigation water. SL c Salt load in fresh canal water. Q d Discharge of drain. EC d Salinity of drainage water. SL d Salt load in drainage water. Q R Required discharge of area served (calculated) Q F Water Quantity Deficit EC MIX. Salinity of mixing water 343
13 Several feeders are already existing within the boundaries of the areas and deliver drainage water to satisfy the shortage of irrigation water. The irrigation districts operate these feeders officially. However, these feeders are not operated continually since they depend on the level of the water at the drains. El-Wasat regulator and El-Manaifa intake represent the water delivered to both areas. These locations are monitored for the check and balance purposes. 5. Conclusions and Recommendations The previous analysis and discussion leads to the following main conclusions: All crops grown in the area suffer from the increase of the irrigation water salinity, although they already did so under the reference conditions; Evapotranspiration and the crop yield are also impeded by salts as indicated by the average simulated soil salinity; The maximum reduction in relative evapotranspiration is not higher than 12.5%; The maximum increase of the soil salinity is 139% whereas the maximum increase of irrigation water salinity is 316%. At any rate, the concentration of common metals in drainage and irrigation water does not reach the value that could cause problems to soil and plant. The BOD and COD concentrations in the monitored irrigation and drainage canals do not comply with the national standards. The following are recommended based on the water quality assessment: 1. A detailed study should be implemented to identify the sources of pollution to the areas and to define the appropriate pollution control measures. 2. There is a need to design and implement an environmental management plan to insure safe drainage water reuse after operation of the proposed mixing locations. 6. REFERENCES Abdel Gawad, S.T., Abdel Khalik, M.A., Boels, D., El Quosy, D.E., Roest, C.W.J., Rijtema, P.E., and M.F.R., Smit, 1991, Analysis of water management in the Eastern Nile Delta, Final Report, Reuse of Drainage Water Project, Report 30, DRI and WSC, Cairo, Egypt DRI, 2000, Assessment of the drainage water reuse in El-wasat & El-Manaifa areas, Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate, Final Report, Irrigation Improvement Project, March 2000, Cairo, Egypt. Sijtsma, B.R.; Boales D., VisserT.N.M, Roest C.W.J., Smit M.F.R., Siware User s Manual, 1995, Wageningen, Netherlands. 344
Simulation of water quality for the El-Salam canal in Egypt
 Water Pollution XII 27 Simulation of water quality for the El-Salam canal in Egypt W. M. A. Khalifa Department of Civil Engineering, Hail University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and Fayoum University, Egypt
Water Pollution XII 27 Simulation of water quality for the El-Salam canal in Egypt W. M. A. Khalifa Department of Civil Engineering, Hail University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and Fayoum University, Egypt
Non-Conventional Resources for Irrigation Water Demand in Egypt
 Non-Conventional Resources for Irrigation Water Demand in Egypt This presentation comprises four parts 1- Introduction 2- Egypt and Challenges 3- Water resources of Egypt 4- Conclusions and recommendations
Non-Conventional Resources for Irrigation Water Demand in Egypt This presentation comprises four parts 1- Introduction 2- Egypt and Challenges 3- Water resources of Egypt 4- Conclusions and recommendations
02/06/1437. Brackish Water Definition. Impact of Irrigation with Brackish Water on Soil and Plants. How can Salinity be expressed
 : Brackish Water Definition According to the Commonwealth of Australia (2011), brackish water is defined as the water that has more saline than fresh water, but not as much as seawater. It may result from
: Brackish Water Definition According to the Commonwealth of Australia (2011), brackish water is defined as the water that has more saline than fresh water, but not as much as seawater. It may result from
Case Study. BiOWiSH Aqua has Positive Long-Term Effects. Biological Help for the Human Race
 Case Study BiOWiSH Aqua has Positive Long-Term Effects After Two Years, Sustains Improved Effluent Quality in South Korean Slaughterhouse Executive Summary BiOWiSH Aqua was implemented in a South Korean
Case Study BiOWiSH Aqua has Positive Long-Term Effects After Two Years, Sustains Improved Effluent Quality in South Korean Slaughterhouse Executive Summary BiOWiSH Aqua was implemented in a South Korean
Quality of reclaimed water for turfgrass irrigation. Clinton Williams Lead Research Soil Scientist USDA-ARS ALARC
 Quality of reclaimed water for turfgrass irrigation Clinton Williams Lead Research Soil Scientist USDA-ARS ALARC Cost for Increasing Water Supply Option Cost (acre-ft) Desalination $1,400 Recycling for
Quality of reclaimed water for turfgrass irrigation Clinton Williams Lead Research Soil Scientist USDA-ARS ALARC Cost for Increasing Water Supply Option Cost (acre-ft) Desalination $1,400 Recycling for
Water resources management: case study of Sharkia governorate, Egypt
 Appl Water Sci (2012) 2:95 99 DOI 10.1007/s13201-012-0026-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Water resources management: case study of Sharkia governorate, Egypt Y. A. Mohamed M. Rashad Received: 31 January 2011 / Accepted:
Appl Water Sci (2012) 2:95 99 DOI 10.1007/s13201-012-0026-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Water resources management: case study of Sharkia governorate, Egypt Y. A. Mohamed M. Rashad Received: 31 January 2011 / Accepted:
Lecture 9A: Drainage Basins
 GEOG415 Lecture 9A: Drainage Basins 9-1 Drainage basin (watershed, catchment) -Drains surfacewater to a common outlet Drainage divide - how is it defined? Scale effects? - Represents a hydrologic cycle
GEOG415 Lecture 9A: Drainage Basins 9-1 Drainage basin (watershed, catchment) -Drains surfacewater to a common outlet Drainage divide - how is it defined? Scale effects? - Represents a hydrologic cycle
TRACE ELEMENTS STATUS IN THE SALINE SOILS LEACHED BY USING LOW QUALITY WATER
 Twelfth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC12 28 Alexandria, Egypt 1 TRACE ELEMENTS STATUS IN THE SALINE SOILS LEACHED BY USING LOW QUALITY WATER E. A. Abou Hussien * and Kh. A. Shaban ** *
Twelfth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC12 28 Alexandria, Egypt 1 TRACE ELEMENTS STATUS IN THE SALINE SOILS LEACHED BY USING LOW QUALITY WATER E. A. Abou Hussien * and Kh. A. Shaban ** *
Salinity TMDL Development and Modeling in the Otter Creek Watershed. Erik Makus DEQ Hydrologist June 6, 2013
 Salinity TMDL Development and Modeling in the Otter Creek Watershed 1 Erik Makus DEQ Hydrologist June 6, 2013 Outline for Today: Otter Creek and the Tongue River Previous salinity modeling efforts Existing
Salinity TMDL Development and Modeling in the Otter Creek Watershed 1 Erik Makus DEQ Hydrologist June 6, 2013 Outline for Today: Otter Creek and the Tongue River Previous salinity modeling efforts Existing
Egypt. Water Management Strategies and Impacts on Livelihoods in. 5 th Regional Coordination Meeting Amman Jordan, 2013
 5 th Regional Coordination Meeting Amman Jordan, 2013 Water Management Strategies and Impacts on Livelihoods in Egypt INSERT COUNTRY MAP SHOWING LOCATION OF BENCHMARK SITE WLI Goal and Intended Outputs
5 th Regional Coordination Meeting Amman Jordan, 2013 Water Management Strategies and Impacts on Livelihoods in Egypt INSERT COUNTRY MAP SHOWING LOCATION OF BENCHMARK SITE WLI Goal and Intended Outputs
NBI strategic water resources analysis Phase I findings
 NBI strategic water resources analysis Phase I findings Abdulkarim H Seid NBI Secretariat The NBI Strategic Water Resources Analysis Key question: how to meet demands for water, food and energy upstream
NBI strategic water resources analysis Phase I findings Abdulkarim H Seid NBI Secretariat The NBI Strategic Water Resources Analysis Key question: how to meet demands for water, food and energy upstream
Lecture 1: Importance of Irrigation and Drainage
 The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Irrigation and Drainage- ECIV 5327 Lecture 1: Importance of Irrigation and Drainage Prepared by Husam Al-Najar 1 Irrigation and Drainage- course
The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Irrigation and Drainage- ECIV 5327 Lecture 1: Importance of Irrigation and Drainage Prepared by Husam Al-Najar 1 Irrigation and Drainage- course
Hydrological And Water Quality Modeling For Alternative Scenarios In A Semi-arid Catchment
 Hydrological And Water Quality Modeling For Alternative Scenarios In A Semi-arid Catchment AZIZ ABOUABDILLAH, ANTONIO LO PORTO METIER Final Conference: Brussels, Belgium-4-6 November 2009 Outline Problem
Hydrological And Water Quality Modeling For Alternative Scenarios In A Semi-arid Catchment AZIZ ABOUABDILLAH, ANTONIO LO PORTO METIER Final Conference: Brussels, Belgium-4-6 November 2009 Outline Problem
Lecture 8: Irrigation Water Quality
 The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Irrigation and Drainage- ECIV 5327 Lecture 8: Irrigation Water Quality Prepared by Husam Al-Najar Physical Parameters used in the evaluation
The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Irrigation and Drainage- ECIV 5327 Lecture 8: Irrigation Water Quality Prepared by Husam Al-Najar Physical Parameters used in the evaluation
Estimating annual irrigation water requirements
 Estimating annual irrigation water requirements Findings from the Sustainable dairy farm systems for profit project M5 Project Information Series - Studies on Mutdapilly Research Station and subtropical
Estimating annual irrigation water requirements Findings from the Sustainable dairy farm systems for profit project M5 Project Information Series - Studies on Mutdapilly Research Station and subtropical
5.5 Improving Water Use Efficiency of Irrigated Crops in the North China Plain Measurements and Modelling
 183 5.5 Improving Water Use Efficiency of Irrigated Crops in the North China Plain Measurements and Modelling H.X. Wang, L. Zhang, W.R. Dawes, C.M. Liu Abstract High crop productivity in the North China
183 5.5 Improving Water Use Efficiency of Irrigated Crops in the North China Plain Measurements and Modelling H.X. Wang, L. Zhang, W.R. Dawes, C.M. Liu Abstract High crop productivity in the North China
Stormwater Reuse Through Aquifer Storage & Recovery
 Stormwater Reuse Through Aquifer Storage & Recovery CITY OF NAPLES, FLORIDA PRESENTED BY: GREGG R. STRAKALUSE, P.E. DIRECTOR-STREETS & STORMWATER DEPT. DECEMBER 12, 2014 FLORIDA STORMWATER ASSOCIATION
Stormwater Reuse Through Aquifer Storage & Recovery CITY OF NAPLES, FLORIDA PRESENTED BY: GREGG R. STRAKALUSE, P.E. DIRECTOR-STREETS & STORMWATER DEPT. DECEMBER 12, 2014 FLORIDA STORMWATER ASSOCIATION
Voting Card on A Final Project
 Jordan Institution for Standards and Metrology Standardization Directorate Voting Card on A Final Project Project s No.: 893 / 2002 Project s Name: Water Reclaimed Wastewater Secretary of the Committee:
Jordan Institution for Standards and Metrology Standardization Directorate Voting Card on A Final Project Project s No.: 893 / 2002 Project s Name: Water Reclaimed Wastewater Secretary of the Committee:
Water Resources Director: Chris Graybeal
 Water Resources Director: Chris Graybeal Our Mission To promote and protect the environment, preserve natural resources, and ensure the health and safety of our customers. Granite Falls Wastewater Treatment
Water Resources Director: Chris Graybeal Our Mission To promote and protect the environment, preserve natural resources, and ensure the health and safety of our customers. Granite Falls Wastewater Treatment
MANAGEMENT OF SMALL-SCALE WATER LOGGING THROUGH SURFACE DRAIN MAINTENANCE
 Sarhad J. Agric. Vol. 23, No. 2, 2007 MANAGEMENT OF SMALL-SCALE WATER LOGGING THROUGH SURFACE DRAIN MAINTENANCE Tahir Sarwar, S. M. Bilal, Naveedullah, M. Jamal Khan and Javaid Tariq ABSTRACT The present
Sarhad J. Agric. Vol. 23, No. 2, 2007 MANAGEMENT OF SMALL-SCALE WATER LOGGING THROUGH SURFACE DRAIN MAINTENANCE Tahir Sarwar, S. M. Bilal, Naveedullah, M. Jamal Khan and Javaid Tariq ABSTRACT The present
Estimation of Irrigation Water Requirement of Maize (Zea-mays) using Pan Evaporation Method in Maiduguri, Northeastern Nigeria
 Estimation of Irrigation Water Requirement of Maize (Zea-mays) using Pan Evaporation Method in Maiduguri, Northeastern Nigeria *I. J. Tekwa 1 and E. K. Bwade 2 *johntekwa@gmail.com 07035134544; 07032340369.
Estimation of Irrigation Water Requirement of Maize (Zea-mays) using Pan Evaporation Method in Maiduguri, Northeastern Nigeria *I. J. Tekwa 1 and E. K. Bwade 2 *johntekwa@gmail.com 07035134544; 07032340369.
WATER QUALITY MODELING FOR THE SOUTHERN PART OF ASWAN HIGH DAM RESERVOIR, LAKE NUBIA
 WATER QUALITY MODELING FOR THE SOUTHERN PART OF ASWAN HIGH DAM RESERVOIR, LAKE NUBIA M. Elshemy 1, T.T. H. Le 1, G. Meon 1, and M. Heikal 1 Leichtweiss-Institute for Hydraulics and Water Resources, University
WATER QUALITY MODELING FOR THE SOUTHERN PART OF ASWAN HIGH DAM RESERVOIR, LAKE NUBIA M. Elshemy 1, T.T. H. Le 1, G. Meon 1, and M. Heikal 1 Leichtweiss-Institute for Hydraulics and Water Resources, University
Environmental Protection Licence 2688
 Perilya Environmental Protection Licence 2688 Licensee Perilya Broken Hill Limited (PBHL) Address Wentworth Rd, Broken Hill, NSW, 2880. Environmental Protection Licence 2688 (Southern Operations) Link
Perilya Environmental Protection Licence 2688 Licensee Perilya Broken Hill Limited (PBHL) Address Wentworth Rd, Broken Hill, NSW, 2880. Environmental Protection Licence 2688 (Southern Operations) Link
Rainwater Management. Dr. Iftikhar Ahmad. College of Earth and. University of The Punjab Lahore
 Rainwater Management in Major Cities of Punjab Dr. Iftikhar Ahmad College of Earth and Environmental Sciences. University of The Punjab Lahore Need For Rainfall Harvesting in Urban Areas of Punjab Groundwater
Rainwater Management in Major Cities of Punjab Dr. Iftikhar Ahmad College of Earth and Environmental Sciences. University of The Punjab Lahore Need For Rainfall Harvesting in Urban Areas of Punjab Groundwater
Afternoon Lecture Outline
 Afternoon Lecture Outline 1. Northern Prairies watershed hydrology 2. Solute mass balance in lakes and ponds 3. Simple mass balance simulation using MS Excel 4. Effects of sediment-water exchange on lake
Afternoon Lecture Outline 1. Northern Prairies watershed hydrology 2. Solute mass balance in lakes and ponds 3. Simple mass balance simulation using MS Excel 4. Effects of sediment-water exchange on lake
South African Milk Processors Organisation
 South African Milk Processors Organisation The voluntary organisation of milk processors for the promotion of the development of the secondary dairy industry to the benefit of the dairy industry, the consumer
South African Milk Processors Organisation The voluntary organisation of milk processors for the promotion of the development of the secondary dairy industry to the benefit of the dairy industry, the consumer
Estimation of irrigation water requirement of maize (Zea-mays) using pan evaporation method in maiduguri, Northeastern Nigeria
 March, 2011 Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at http://www.cigrjournal.org Vol. 13, No.1 1 Estimation of irrigation water requirement of maize (Zea-mays) using pan evaporation method in maiduguri,
March, 2011 Agric Eng Int: CIGR Journal Open access at http://www.cigrjournal.org Vol. 13, No.1 1 Estimation of irrigation water requirement of maize (Zea-mays) using pan evaporation method in maiduguri,
STUDY FOR INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER TREATMENT USING SOME COAGULANTS
 STUDY FOR INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER TREATMENT USING SOME COAGULANTS H. El Karamany Environmental Engineering Department, Zagazig University, El-Zagazig, Egypt E-mail: dr_elkaramany@link.net ABSTRACT The motivations
STUDY FOR INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER TREATMENT USING SOME COAGULANTS H. El Karamany Environmental Engineering Department, Zagazig University, El-Zagazig, Egypt E-mail: dr_elkaramany@link.net ABSTRACT The motivations
Embankment and cut slope monitoring and analysis
 Embankment and cut slope monitoring and analysis Dr Derek Clarke and Dr Joel Smethurst Introduction - to understand the behaviour of clay slopes (natural/engineered/stabilised) - failure and serviceability
Embankment and cut slope monitoring and analysis Dr Derek Clarke and Dr Joel Smethurst Introduction - to understand the behaviour of clay slopes (natural/engineered/stabilised) - failure and serviceability
DRAINFRAME FOR RIDING THE TRAIN OF INTEGRATED WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN EGYPT
 DRAINFRAME FOR RIDING THE TRAIN OF INTEGRATED WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN EGYPT Hussam Fahmy Drainage Research Institute National Water Research Center, EGYPT Session 29: Irrigation and Drainage in the
DRAINFRAME FOR RIDING THE TRAIN OF INTEGRATED WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN EGYPT Hussam Fahmy Drainage Research Institute National Water Research Center, EGYPT Session 29: Irrigation and Drainage in the
Afternoon Lecture Outline. Northern Prairie Hydrology
 Afternoon Lecture Outline 1. Northern Prairies watershed hydrology 2. Solute mass balance in lakes and ponds 3. Simple mass balance simulation using MS Excel 4. Effects of sediment-water exchange on lake
Afternoon Lecture Outline 1. Northern Prairies watershed hydrology 2. Solute mass balance in lakes and ponds 3. Simple mass balance simulation using MS Excel 4. Effects of sediment-water exchange on lake
Electric Forward Market Report
 Mar-01 Mar-02 Jun-02 Sep-02 Dec-02 Mar-03 Jun-03 Sep-03 Dec-03 Mar-04 Jun-04 Sep-04 Dec-04 Mar-05 May-05 Aug-05 Nov-05 Feb-06 Jun-06 Sep-06 Dec-06 Mar-07 Jun-07 Sep-07 Dec-07 Apr-08 Jun-08 Sep-08 Dec-08
Mar-01 Mar-02 Jun-02 Sep-02 Dec-02 Mar-03 Jun-03 Sep-03 Dec-03 Mar-04 Jun-04 Sep-04 Dec-04 Mar-05 May-05 Aug-05 Nov-05 Feb-06 Jun-06 Sep-06 Dec-06 Mar-07 Jun-07 Sep-07 Dec-07 Apr-08 Jun-08 Sep-08 Dec-08
Water Quality Study In the Streams of Flint Creek and Flint River Watersheds For TMDL Development
 Water Quality Study In the Streams of Flint Creek and Flint River Watersheds For TMDL Development Idris Abdi Doctoral Dissertation Presentation Major Advisor: Dr. Teferi Tsegaye April 18, 2005 Alabama
Water Quality Study In the Streams of Flint Creek and Flint River Watersheds For TMDL Development Idris Abdi Doctoral Dissertation Presentation Major Advisor: Dr. Teferi Tsegaye April 18, 2005 Alabama
November 28, Dear Mr. Bechtold:
 4000 Hollywood Boulevard Seventh Floor, North Tower Hollywood, Florida 33021 (954) 987-0066 Fax: (954) 987-2949 November 28, 2012 Wastewater Compliance and Enforcement Section FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL
4000 Hollywood Boulevard Seventh Floor, North Tower Hollywood, Florida 33021 (954) 987-0066 Fax: (954) 987-2949 November 28, 2012 Wastewater Compliance and Enforcement Section FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL
Determination of the Optimal Date for Sowing of Wheat in Canal Irrigated Areas using FAO CROPWAT Model
 Determination of the Optimal Date for Sowing of Wheat in Canal Irrigated Areas using FAO CROPWAT Model Dr.T.B.S. Rajput and Neelam Patel Water Technology Centre, IARI, New Delhi 110 012, India ABSTRACT
Determination of the Optimal Date for Sowing of Wheat in Canal Irrigated Areas using FAO CROPWAT Model Dr.T.B.S. Rajput and Neelam Patel Water Technology Centre, IARI, New Delhi 110 012, India ABSTRACT
Water Quality of Fayoum Surface Water, Fayoum Province, Egypt
 Deltas in Times of Climate Change II, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, 24-26 Sept. 2014 Water Quality of Fayoum Surface Water, Fayoum Province, Egypt Mahmoud S.M. Abdel Wahed a,b,*, Essam A. Mohamed b, Christian
Deltas in Times of Climate Change II, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, 24-26 Sept. 2014 Water Quality of Fayoum Surface Water, Fayoum Province, Egypt Mahmoud S.M. Abdel Wahed a,b,*, Essam A. Mohamed b, Christian
Leila Talebi and Robert Pitt. Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental Engineering, The University of Alabama, P.O. Box , Tuscaloosa
 Leila Talebi and Robert Pitt Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental Engineering, The University of Alabama, P.O. Box 870205, Tuscaloosa May 2012 Global consumption of water increases every
Leila Talebi and Robert Pitt Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental Engineering, The University of Alabama, P.O. Box 870205, Tuscaloosa May 2012 Global consumption of water increases every
global science solutions
 global science solutions Tim Martin: Riverside Technology, inc. Fort Collins, Colorado, USA 2.4: Water Security Information and Tools to Support Global Water Security International Symposium on Synergistic
global science solutions Tim Martin: Riverside Technology, inc. Fort Collins, Colorado, USA 2.4: Water Security Information and Tools to Support Global Water Security International Symposium on Synergistic
Statement. Innovative Method for Rice Irrigation with High Potential of Water Saving. Yousri Ibrahim Atta
 Statement Innovative Method for Rice Irrigation with High Potential of Water Saving Yousri Ibrahim Atta Water Management Research Institute, National Water Research Center, Egypt Introduction: One of the
Statement Innovative Method for Rice Irrigation with High Potential of Water Saving Yousri Ibrahim Atta Water Management Research Institute, National Water Research Center, Egypt Introduction: One of the
Otter Creek Watershed TMDL Project. Stakeholder Meeting June 6, 2013
 Otter Creek Watershed TMDL Project Stakeholder Meeting June 6, 2013 1 Meeting Purpose Meet with watershed & technical advisory group members and watershed landowners to provide basic Otter Creek TMDL project
Otter Creek Watershed TMDL Project Stakeholder Meeting June 6, 2013 1 Meeting Purpose Meet with watershed & technical advisory group members and watershed landowners to provide basic Otter Creek TMDL project
CITY OF LONDON ENVIRONMENTAL & ENGINEERING SERVICES DEPARTMENT WASTEWATER TREATMENT OPERATIONS GREENWAY POLLUTION CONTROL CENTRE 2013 ANNUAL REPORT
 CITY OF LONDON ENVIRONMENTAL & ENGINEERING SERVICES DEPARTMENT WASTEWATER TREATMENT OPERATIONS GREENWAY POLLUTION CONTROL CENTRE 2013 ANNUAL REPORT FEBRUARY 2014 SUMMARY This annual report is in response
CITY OF LONDON ENVIRONMENTAL & ENGINEERING SERVICES DEPARTMENT WASTEWATER TREATMENT OPERATIONS GREENWAY POLLUTION CONTROL CENTRE 2013 ANNUAL REPORT FEBRUARY 2014 SUMMARY This annual report is in response
Inside of forest (for example) Research Flow
 Study on Relationship between Watershed Hydrology and Lake Water Environment by the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) Shimane University Hiroaki SOMURA Watershed degradation + Global warming Background
Study on Relationship between Watershed Hydrology and Lake Water Environment by the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) Shimane University Hiroaki SOMURA Watershed degradation + Global warming Background
GEOGRAPHY. H.C.G. Paper 2 (Two hours)
 GEOGRAPHY H.C.G. Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
GEOGRAPHY H.C.G. Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
Water Requirements of Qat (Catha edulis) Cultivation in the Central Highlands of Yemen
 Available Online Publications J. Sci. Res. 4 (1), 77-82 (2012) JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH www.banglajol.info/index.php/jsr Water Requirements of Qat (Catha edulis) Cultivation in the Central Highlands
Available Online Publications J. Sci. Res. 4 (1), 77-82 (2012) JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH www.banglajol.info/index.php/jsr Water Requirements of Qat (Catha edulis) Cultivation in the Central Highlands
Optimizing the Cropping Pattern in Gezira Scheme, Sudan
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 7, Issue 2, February 2017 22 Optimizing the Cropping Pattern in Gezira Scheme, Sudan Babiker O. Mahgoub, Omima A. Mirghani, Sara A.E.
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 7, Issue 2, February 2017 22 Optimizing the Cropping Pattern in Gezira Scheme, Sudan Babiker O. Mahgoub, Omima A. Mirghani, Sara A.E.
SALTON SEA SOLAR PONDS PILOT PROJECT
 SALTON SEA SOLAR PONDS PILOT PROJECT Agrarian Research 162 East Line Street Suite E Bishop, CA 93514 Under contract to: Goal of Salinity Management Stabilize (or reduce slightly) the salinity of the Salton
SALTON SEA SOLAR PONDS PILOT PROJECT Agrarian Research 162 East Line Street Suite E Bishop, CA 93514 Under contract to: Goal of Salinity Management Stabilize (or reduce slightly) the salinity of the Salton
CROPPING STRUCTURES ADJUSTMENTS UNDER WATER LIMITATIONS IN THE EGYPTIAN AGRICULTURE. Amin I. Abdou. National Research Centre, Egypt
 CROPPING STRUCTURES ADJUSTMENTS UNDER WATER LIMITATIONS IN THE EGYPTIAN AGRICULTURE Amin I. Abdou National Research Centre, Egypt aminabdou3@yahoo.com Abstract Using programming methods, the two s of cropping
CROPPING STRUCTURES ADJUSTMENTS UNDER WATER LIMITATIONS IN THE EGYPTIAN AGRICULTURE Amin I. Abdou National Research Centre, Egypt aminabdou3@yahoo.com Abstract Using programming methods, the two s of cropping
Water Operations 101. Jerry Johns and John Leahigh Department of Water Resources BDCP Steering Committee 5/8/09
 Water Operations 101 Jerry Johns and John Leahigh Department of Water Resources BDCP Steering Committee 5/8/09 Water Operations Overview Where Does BDCP Fit Into California Planning Hydrologic Variability
Water Operations 101 Jerry Johns and John Leahigh Department of Water Resources BDCP Steering Committee 5/8/09 Water Operations Overview Where Does BDCP Fit Into California Planning Hydrologic Variability
The Impacts of Climate Change on Portland s Water Supply
 The Impacts of Climate Change on Portland s Water Supply Richard Palmer and Margaret Hahn University of Washington Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Joe Dvorak, Dennis Kessler, Azad Mohammadi
The Impacts of Climate Change on Portland s Water Supply Richard Palmer and Margaret Hahn University of Washington Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Joe Dvorak, Dennis Kessler, Azad Mohammadi
... Flood-Runoff Farming (FRF)
 WATER HARVESTING FOR DRYLAND FARMING.... Flood-Runoff Farming (FRF) Weldemichael A. Tesfuhuney, Sue Walker & PS. van Heerden Department of Soil, Crop & Climate Sciences February 11, 213 SANCID 212 Symposium
WATER HARVESTING FOR DRYLAND FARMING.... Flood-Runoff Farming (FRF) Weldemichael A. Tesfuhuney, Sue Walker & PS. van Heerden Department of Soil, Crop & Climate Sciences February 11, 213 SANCID 212 Symposium
This document can be made available in other accessible formats as soon as practicable and upon request. Staff Report. Infrastructure & Public Works
 This document can be made available in other accessible formats as soon as practicable and upon request Staff Report Infrastructure & Public Works Report To: Committee of the Whole Meeting Date: March
This document can be made available in other accessible formats as soon as practicable and upon request Staff Report Infrastructure & Public Works Report To: Committee of the Whole Meeting Date: March
I/I Analysis & Water Balance Modelling. Presented by Paul Edwards
 I/I Analysis & Water Balance Modelling Presented by Paul Edwards Contents Background Wet Weather Model Calibration Inflow / Infiltration Assessment Flow Containment Options Water Balance Model 20 Year
I/I Analysis & Water Balance Modelling Presented by Paul Edwards Contents Background Wet Weather Model Calibration Inflow / Infiltration Assessment Flow Containment Options Water Balance Model 20 Year
BOD/COD a Measure of Dairy Waste Treatment Efficiency- A Case Study
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 13, Issue 5 Ver. VIII (Sep. - Oct. 2016), PP 107-114 www.iosrjournals.org BOD/COD a Measure of Dairy
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 13, Issue 5 Ver. VIII (Sep. - Oct. 2016), PP 107-114 www.iosrjournals.org BOD/COD a Measure of Dairy
Chapter 9: Adoption and impact of supplemental irrigation in wheat-based systems in Syria
 Chapter 9: Adoption and impact of supplemental irrigation in wheat-based systems in Syria 131 132 Chapter 9: Adoption and impact of supplemental irrigation in wheat-based systems in Syria A. Bader, N.
Chapter 9: Adoption and impact of supplemental irrigation in wheat-based systems in Syria 131 132 Chapter 9: Adoption and impact of supplemental irrigation in wheat-based systems in Syria A. Bader, N.
Water quality deterioration of the Euphrates River before entering Iraqi lands
 Water Pollution XII 3 Water quality deterioration of the Euphrates River before entering Iraqi lands H. S. Al-Bahrani Faculty of Engineering, University of Kufa, Iraq Abstract Euphrates River passes through
Water Pollution XII 3 Water quality deterioration of the Euphrates River before entering Iraqi lands H. S. Al-Bahrani Faculty of Engineering, University of Kufa, Iraq Abstract Euphrates River passes through
IMPACT OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON WATER AVAILABILITY AND EXTREME FLOWS IN ADDIS ABABA
 IMPACT OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON WATER AVAILABILITY AND EXTREME FLOWS IN ADDIS ABABA Contents Background of climate change Climate Change Studies in and Around Addis Ababa Impact of climate change on Water
IMPACT OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON WATER AVAILABILITY AND EXTREME FLOWS IN ADDIS ABABA Contents Background of climate change Climate Change Studies in and Around Addis Ababa Impact of climate change on Water
Efficient reuse of irrigation drainage water in agriculture, Behera governorate, Egypt
 Efficient reuse of irrigation drainage water in agriculture, Behera governorate, Egypt Opportunities and challenges by Noha Mohsen Hanafy Mahmoud Supervisor Dr. Nadir Elagib, Prof. Dr. Ahmed Al-Salaymeh,
Efficient reuse of irrigation drainage water in agriculture, Behera governorate, Egypt Opportunities and challenges by Noha Mohsen Hanafy Mahmoud Supervisor Dr. Nadir Elagib, Prof. Dr. Ahmed Al-Salaymeh,
Initial Assessment of Climate Change in the Chesapeake Bay Watershed
 Initial Assessment of Climate Change in the Chesapeake Bay Watershed STAC Workshop on Adapting to Climate Change In the Chesapeake Bay March 15, 2011 Lewis Linker 1, Thomas Johnson 2, and Gary Shenk 1
Initial Assessment of Climate Change in the Chesapeake Bay Watershed STAC Workshop on Adapting to Climate Change In the Chesapeake Bay March 15, 2011 Lewis Linker 1, Thomas Johnson 2, and Gary Shenk 1
A Case Study For Evaluating Sustainable Saline Soil Management Un exemple d évaluation de la gestion d un sol salin en vue d une agriculture durable
 Scientific registration number: 2524 Symposium n : 29 Presentation: poster A Case Study For Evaluating Sustainable Saline Soil Management Un exemple d évaluation de la gestion d un sol salin en vue d une
Scientific registration number: 2524 Symposium n : 29 Presentation: poster A Case Study For Evaluating Sustainable Saline Soil Management Un exemple d évaluation de la gestion d un sol salin en vue d une
JEDDAH INDUSTRIAL CITY
 JEDDAH INDUSTRIAL CITY WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT A Presentation by : Engr. Mowafaq Al-Sugeir Managing Director ICDOC SAWEA 2007 WORKSHOP, AL-KHOBER 4 December 2007 Built & Being Operated by : on Build-Operate-Transfer
JEDDAH INDUSTRIAL CITY WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT A Presentation by : Engr. Mowafaq Al-Sugeir Managing Director ICDOC SAWEA 2007 WORKSHOP, AL-KHOBER 4 December 2007 Built & Being Operated by : on Build-Operate-Transfer
CHAPTER FIVE Runoff. Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib. Overland flow interflow
 Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) CHAPTER FIVE Runoff Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib Overland flow interflow Base flow Saturated overland flow ١ ٢ 5.1 Introduction To Runoff Runoff
Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) CHAPTER FIVE Runoff Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib Overland flow interflow Base flow Saturated overland flow ١ ٢ 5.1 Introduction To Runoff Runoff
Climate Change Challenges faced by Agriculture in Punjab
 Climate Change Challenges faced by Agriculture in Punjab Dr. M. Mohsin Iqbal and Dr. Arshad M. Khan Global Change Impact Studies Centre (GCISC), Islamabad Seminar on Impacts of Climate Change on Agriculture
Climate Change Challenges faced by Agriculture in Punjab Dr. M. Mohsin Iqbal and Dr. Arshad M. Khan Global Change Impact Studies Centre (GCISC), Islamabad Seminar on Impacts of Climate Change on Agriculture
Water Governance Benchmarking Criteria
 Water Governance Benchmarking Criteria Click on each red number in order to link to the corresponding paragraph. Click again on the red number in order to return to criteria page. Numbers found next to
Water Governance Benchmarking Criteria Click on each red number in order to link to the corresponding paragraph. Click again on the red number in order to return to criteria page. Numbers found next to
MODELING PHOSPHORUS LOADING TO THE CANNONSVILLE RESERVOIR USING SWAT
 MODELING PHOSPHORUS LOADING TO THE CANNONSVILLE RESERVOIR USING SWAT Bryan Tolson 1 & Christine Shoemaker 2 1. PhD Student, 2. Professor School of Civil & Environmental Engineering Cornell University PWT
MODELING PHOSPHORUS LOADING TO THE CANNONSVILLE RESERVOIR USING SWAT Bryan Tolson 1 & Christine Shoemaker 2 1. PhD Student, 2. Professor School of Civil & Environmental Engineering Cornell University PWT
Use of a distributed catchment model to assess hydrologic modifications in the Upper Ganges Basin
 River Basin Management VI 177 Use of a distributed catchment model to assess hydrologic modifications in the Upper Ganges Basin L. Bharati 1, V. Smakhtin 2, P. Jayakody 2, N. Kaushal 3 & P. Gurung 1 1
River Basin Management VI 177 Use of a distributed catchment model to assess hydrologic modifications in the Upper Ganges Basin L. Bharati 1, V. Smakhtin 2, P. Jayakody 2, N. Kaushal 3 & P. Gurung 1 1
Crop Water Requirement. Presented by: Felix Jaria:
 Crop Water Requirement Presented by: Felix Jaria: Presentation outline Crop water requirement Irrigation Water requirement Eto Penman Monteith Etcrop Kc factor Ks Factor Total Available water Readily available
Crop Water Requirement Presented by: Felix Jaria: Presentation outline Crop water requirement Irrigation Water requirement Eto Penman Monteith Etcrop Kc factor Ks Factor Total Available water Readily available
Modeling the Middle and Lower Cape Fear River using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool Sam Sarkar Civil Engineer
 Modeling the Middle and Lower Cape Fear River using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool Sam Sarkar Civil Engineer Outline Problem statement and project objectives Watershed model development Model calibration
Modeling the Middle and Lower Cape Fear River using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool Sam Sarkar Civil Engineer Outline Problem statement and project objectives Watershed model development Model calibration
The Confluence Model. Presentation to Modeling and Forecasting Working Group January 21, 2015
 The Confluence Model Presentation to Modeling and Forecasting Working Group January 21, 2015 Introductions Presenter: Gary Fiske Working Group Water Department staff Objective: Penetrate the Black Box
The Confluence Model Presentation to Modeling and Forecasting Working Group January 21, 2015 Introductions Presenter: Gary Fiske Working Group Water Department staff Objective: Penetrate the Black Box
Cokato Lake (86-263) Wright County. Hydrologic Investigation
 Cokato Lake (86-263) Wright County Hydrologic Investigation April 14, 2005 Cokato Lake (86-263) Wright County Hydrologic Investigation April 14, 2005 Problem Statement In recent years, heavy rainfall has
Cokato Lake (86-263) Wright County Hydrologic Investigation April 14, 2005 Cokato Lake (86-263) Wright County Hydrologic Investigation April 14, 2005 Problem Statement In recent years, heavy rainfall has
Overview of the Surface Hydrology of Hawai i Watersheds. Ali Fares Associate Professor of Hydrology NREM-CTAHR
 Overview of the Surface Hydrology of Hawai i Watersheds Ali Fares Associate Professor of Hydrology NREM-CTAHR 5/23/2008 Watershed Hydrology Lab 1 What is Hydrology? Hydrology is the water science that
Overview of the Surface Hydrology of Hawai i Watersheds Ali Fares Associate Professor of Hydrology NREM-CTAHR 5/23/2008 Watershed Hydrology Lab 1 What is Hydrology? Hydrology is the water science that
Arkansas Water Resources Center
 Arkansas Water Resources Center WATER SAMPLING, ANALYSIS AND ANNUAL LOAD DETERMINATIONS FOR TSS, NITROGEN AND PHOSPHORUS AT THE L ANGUILLE RIVER NEAR PALESTINE Submitted to the Arkansas Soil and Water
Arkansas Water Resources Center WATER SAMPLING, ANALYSIS AND ANNUAL LOAD DETERMINATIONS FOR TSS, NITROGEN AND PHOSPHORUS AT THE L ANGUILLE RIVER NEAR PALESTINE Submitted to the Arkansas Soil and Water
Application of a Basin Scale Hydrological Model for Characterizing flow and Drought Trend
 Application of a Basin Scale Hydrological Model for Characterizing flow and Drought Trend 20 July 2012 International SWAT conference, Delhi INDIA TIPAPORN HOMDEE 1 Ph.D candidate Prof. KOBKIAT PONGPUT
Application of a Basin Scale Hydrological Model for Characterizing flow and Drought Trend 20 July 2012 International SWAT conference, Delhi INDIA TIPAPORN HOMDEE 1 Ph.D candidate Prof. KOBKIAT PONGPUT
ANNUAL PLATTE RIVER SURFACE WATER FLOW SUMMARY
 ANNUAL PLATTE RIVER SURFACE WATER FLOW SUMMARY 4/3/213 Platte River Recovery Implementation Program 213 ANNUAL SURFACE WATER FLOW SUMMARY DRAFT Prepared by staff of the Platte River Recovery Implementation
ANNUAL PLATTE RIVER SURFACE WATER FLOW SUMMARY 4/3/213 Platte River Recovery Implementation Program 213 ANNUAL SURFACE WATER FLOW SUMMARY DRAFT Prepared by staff of the Platte River Recovery Implementation
Climate, soils and the advantages of North East Tasmania for irrigated agriculture
 Climate, soils and the advantages of North East Tasmania for irrigated agriculture October 2012 The information presented primarily concerns the area of the north east of Tasmania that will be serviced
Climate, soils and the advantages of North East Tasmania for irrigated agriculture October 2012 The information presented primarily concerns the area of the north east of Tasmania that will be serviced
Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Water Resources in the Beas Basin &
 Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Water Resources in the Beas Basin & Possible lessons for future management of the Ganga Adebayo Adeloye Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, UK MICCI: Overview of Beas
Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Water Resources in the Beas Basin & Possible lessons for future management of the Ganga Adebayo Adeloye Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, UK MICCI: Overview of Beas
ESTIMATING THE EFFECT OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON THE HYDROLOGY OF THE NILE RIVER IN THE 21 ST CENTURY
 ESTIMATING THE EFFECT OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON THE HYDROLOGY OF THE NILE RIVER IN THE 21 ST CENTURY International System Dynamics Conference Delft, Netherlands 24 July 2014 Bruce Keith, Radley Horton, Erica
ESTIMATING THE EFFECT OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON THE HYDROLOGY OF THE NILE RIVER IN THE 21 ST CENTURY International System Dynamics Conference Delft, Netherlands 24 July 2014 Bruce Keith, Radley Horton, Erica
Fresh Water Augmentation and Salinity Management in Kuttanad
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Fresh Water Augmentation and Salinity Management in Kuttanad Geeja K George**, Charles P Joseph*, Karthik C*, Nebu Thomas*, Vipin Jose* * (Civil Engineering VIII Semester Students,
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Fresh Water Augmentation and Salinity Management in Kuttanad Geeja K George**, Charles P Joseph*, Karthik C*, Nebu Thomas*, Vipin Jose* * (Civil Engineering VIII Semester Students,
Schedule 2 TECHNICAL INFORMATION
 Schedule 2 TECHNICAL INFORMATION This document is intended to provide context to the Haida Gwaii Request for Expressions of Interest (RFEOI) for the potential electricity supply opportunity for clean electricity
Schedule 2 TECHNICAL INFORMATION This document is intended to provide context to the Haida Gwaii Request for Expressions of Interest (RFEOI) for the potential electricity supply opportunity for clean electricity
Seventh International Water Technology Conference IWTC7 Egypt 1-3 April 2003 SECONDARY TREATMENT OF SULLAGE WASTEWATER
 SECONDARY TREATMENT OF SULLAGE WASTEWATER Abstract: USING ROUGH AND SLOW SAND FILTRATION A. El-Morsy Ahmed Water Engineering Dept., Faculty of Engineering, Tanta University, Tanta, Egypt Challenges of
SECONDARY TREATMENT OF SULLAGE WASTEWATER Abstract: USING ROUGH AND SLOW SAND FILTRATION A. El-Morsy Ahmed Water Engineering Dept., Faculty of Engineering, Tanta University, Tanta, Egypt Challenges of
28-31 August 2017 Bari, Italy
 Improved Agricultural water uses Workshop 28-31 August 2017 Bari, Italy Reduce vulnerability in Jordan in the context of water scarcity and increasing food /energy demand Al-Ghadeer Al-Abyad watershed
Improved Agricultural water uses Workshop 28-31 August 2017 Bari, Italy Reduce vulnerability in Jordan in the context of water scarcity and increasing food /energy demand Al-Ghadeer Al-Abyad watershed
Rational IPP Permitting
 Rational IPP Permitting Protect POTW/Environment and Promote Local Economy FISHBECK, THOMPSON, CARR, & HUBER INC. Jerald O. Thaler, PE MWEA IPP Seminar October 6, 2016 Rational IPP Permitting? Accurate/Up-to-Date
Rational IPP Permitting Protect POTW/Environment and Promote Local Economy FISHBECK, THOMPSON, CARR, & HUBER INC. Jerald O. Thaler, PE MWEA IPP Seminar October 6, 2016 Rational IPP Permitting? Accurate/Up-to-Date
Tracking Sources of excess nitrate discharge in Lake Victoria, Kenya for improved Nitrogen use efficiency in the catchment
 Tracking Sources of excess nitrate discharge in Lake Victoria, Kenya for improved Nitrogen use efficiency in the catchment B. Nyilitya, S. Mureithi, P. Boeckx 7th International Nitrogen Initiative 216
Tracking Sources of excess nitrate discharge in Lake Victoria, Kenya for improved Nitrogen use efficiency in the catchment B. Nyilitya, S. Mureithi, P. Boeckx 7th International Nitrogen Initiative 216
ISO Monitoring and Measurement Nonconformance and Corrective and Preventative Action
 ISO 14001 4.5.1 Monitoring and Measurement 4.5.2 Nonconformance and Corrective and Preventative Action 4.5.1 Monitoring and Measurement The organization shall establish and maintain documented procedures
ISO 14001 4.5.1 Monitoring and Measurement 4.5.2 Nonconformance and Corrective and Preventative Action 4.5.1 Monitoring and Measurement The organization shall establish and maintain documented procedures
AIACC Regional Study AS07: Southeast Asia Regional Vulnerability to Changing Water Resource and Extreme Hydrological Events due to Climate Change
 AIACC Regional Study AS07: Southeast Asia Regional Vulnerability to Changing Water Resource and Extreme Hydrological Events due to Climate Change Progress report: period mid-year 2003 Brief Summary: In
AIACC Regional Study AS07: Southeast Asia Regional Vulnerability to Changing Water Resource and Extreme Hydrological Events due to Climate Change Progress report: period mid-year 2003 Brief Summary: In
Unit 6. The current wastewater treatment systems in Gaza Strip
 The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Advanced Sanitary Engineering- ECIV 5325 Unit 6. The current wastewater treatment systems in Gaza Strip Prepared by Husam Al-Najar Existing
The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Advanced Sanitary Engineering- ECIV 5325 Unit 6. The current wastewater treatment systems in Gaza Strip Prepared by Husam Al-Najar Existing
WATER FROM THE CLOUDS
 WATER FROM THE CLOUDS 814 mm per year on land or 110 000 km 3 56% is evapotranspirated by forests and natural landscapes 5% is evapotranspirated by rainfed agriculture 39% available for human uses (irrigation,
WATER FROM THE CLOUDS 814 mm per year on land or 110 000 km 3 56% is evapotranspirated by forests and natural landscapes 5% is evapotranspirated by rainfed agriculture 39% available for human uses (irrigation,
Modified Blaney-Criddle for Excel
 Modified Blaney-Criddle for Excel This allocation program which calculates a maximum monthly supplemental crop requirement and an average annual supplemental requirement using the Modified Blaney-Criddle
Modified Blaney-Criddle for Excel This allocation program which calculates a maximum monthly supplemental crop requirement and an average annual supplemental requirement using the Modified Blaney-Criddle
A WASTE LOAD MODEL ANALYSIS FOR EL NOUBARIYA CANAL DRINKING WATER ABSTRACTION, EGYPT
 Fourteenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC 4, Cairo, Egypt A WASTE LOAD MODEL ANALYSIS FOR EL NOUBARIYA CANAL DRINKING WATER ABSTRACTION, EGYPT N. S. Donia and H. A. Farag Associate Professor,
Fourteenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC 4, Cairo, Egypt A WASTE LOAD MODEL ANALYSIS FOR EL NOUBARIYA CANAL DRINKING WATER ABSTRACTION, EGYPT N. S. Donia and H. A. Farag Associate Professor,
QUESTIONNAIRE FOR GENERAL WTP REQUESTED DATA FOR THE WATER TREATMENT PLANT (WTP) - Application : groundwater (well pit); urban wastewater;
 REQUESTED DATA FOR THE WATER TREATMENT PLANT (WTP) - Application : ENVIRONMENTAL DATA - Temperature min. : C - Temperature max. : C - Altitude (m.a.s.l) : m - Plant location (geographic area, seismic zone,
REQUESTED DATA FOR THE WATER TREATMENT PLANT (WTP) - Application : ENVIRONMENTAL DATA - Temperature min. : C - Temperature max. : C - Altitude (m.a.s.l) : m - Plant location (geographic area, seismic zone,
FAYOUM CITY SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT, DEVELOPMENT STAGES, CASE STUDY
 FAYOUM CITY SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT, DEVELOPMENT STAGES, CASE STUDY Ahmed El-Zayat, Environmental Engineering Group, Egypt Emaill: ahmed_el_zayat@yahoo.com Introduction This case study focuses on three
FAYOUM CITY SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT, DEVELOPMENT STAGES, CASE STUDY Ahmed El-Zayat, Environmental Engineering Group, Egypt Emaill: ahmed_el_zayat@yahoo.com Introduction This case study focuses on three
Irrigation Efficiency and the Nile Delta Water Balance
 Massive Irrigation Efficiency and the Nile Delta Water Balance François Molle, Ibrahim Gaafar, Doaa Ezzat El-Agha and Edwin Rap 2016 Water and salt management in the Nile Delta: Report No.9 2 Irrigation
Massive Irrigation Efficiency and the Nile Delta Water Balance François Molle, Ibrahim Gaafar, Doaa Ezzat El-Agha and Edwin Rap 2016 Water and salt management in the Nile Delta: Report No.9 2 Irrigation
2011 ANNUAL WATER REPORT
 2011 ANNUAL WATER REPORT June 2012 Engineering and Operations Department TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 2 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 3 2.0 PARKSVILLE WATER SYSTEM... 3 3.0 DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM... 6 4.0 SCADA... 9 5.0
2011 ANNUAL WATER REPORT June 2012 Engineering and Operations Department TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 2 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 3 2.0 PARKSVILLE WATER SYSTEM... 3 3.0 DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM... 6 4.0 SCADA... 9 5.0
ISPRS Archives XXXVIII-8/W3 Workshop Proceedings: Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture
 IMPACT ANALYSIS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON DIFFERENT CROPS IN GUJARAT, INDIA Vyas Pandey, H.R. Patel and B.I. Karande Department of Agricultural Meteorology, Anand Agricultural University, Anand-388 110, India
IMPACT ANALYSIS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON DIFFERENT CROPS IN GUJARAT, INDIA Vyas Pandey, H.R. Patel and B.I. Karande Department of Agricultural Meteorology, Anand Agricultural University, Anand-388 110, India
SUITABILITY OF AGRICULTURAL DRAINAGE WATERS FOR IRRIGATION ABSTRACT
 SUITABILITY OF AGRICULTURAL DRAINAGE WATERS FOR IRRIGATION Noha,A.M., Ibrahim.A.M., Matlob.M.N. and Ali.O.M. Soil Sci.Dep.Agric. Faculty, Suez Canal Univ. ABSTRACT The area under studying is bounded from
SUITABILITY OF AGRICULTURAL DRAINAGE WATERS FOR IRRIGATION Noha,A.M., Ibrahim.A.M., Matlob.M.N. and Ali.O.M. Soil Sci.Dep.Agric. Faculty, Suez Canal Univ. ABSTRACT The area under studying is bounded from
Myths and Facts about a Drought Year in the San Joaquin Valley
 Myths and Facts about a Drought Year in the San Joaquin Valley 2013 has been the driest year on record in California and Southern Oregon. In the San Joaquin Valley, Hanford, California, got only 1.99 inches
Myths and Facts about a Drought Year in the San Joaquin Valley 2013 has been the driest year on record in California and Southern Oregon. In the San Joaquin Valley, Hanford, California, got only 1.99 inches
CANADA BRITISH COLUMBIA WATER QUALITY MONITORING AGREEMENT
 CANADA BRITISH COLUMBIA WATER QUALITY MONITORING AGREEMENT WATER QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF SIMILKAMEEN RIVER AT US BORDER (1976 2) Prepared by: Burke Phippen BWP Consulting March, 22 Environment Canada Environnement
CANADA BRITISH COLUMBIA WATER QUALITY MONITORING AGREEMENT WATER QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF SIMILKAMEEN RIVER AT US BORDER (1976 2) Prepared by: Burke Phippen BWP Consulting March, 22 Environment Canada Environnement
Preserving Lake Kinneret (Sea of Galilee, Israel) as a strategic water resource in a changing climate
 Preserving Lake Kinneret (Sea of Galilee, Israel) as a strategic water resource in a changing climate Dr. Doron Markel Water Authority of Israel doronm10@water.gov.il Acknowledgment: Prof. Sharon Megdal
Preserving Lake Kinneret (Sea of Galilee, Israel) as a strategic water resource in a changing climate Dr. Doron Markel Water Authority of Israel doronm10@water.gov.il Acknowledgment: Prof. Sharon Megdal
ROSETTA BRANCH WASTE LOAD ALLOCATION MODEL
 Ninth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC9 25, Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt 277 ROSETTA BRANCH WASTE LOAD ALLOCATION MODEL Noha Donia Assistant Professor, Engineering Department, Ain Shams University
Ninth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC9 25, Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt 277 ROSETTA BRANCH WASTE LOAD ALLOCATION MODEL Noha Donia Assistant Professor, Engineering Department, Ain Shams University
Performance of the Groundwater Containment System at the Former Canada Creosote Site. Tom Jacklin, M.Eng., P.Eng.
 Performance of the Groundwater Containment System at the Former Canada Creosote Site Tom Jacklin, M.Eng., P.Eng. March 20, 2012 Presentation Overview 1. 1995 Remedial Actions and Containment 2. Evaluation
Performance of the Groundwater Containment System at the Former Canada Creosote Site Tom Jacklin, M.Eng., P.Eng. March 20, 2012 Presentation Overview 1. 1995 Remedial Actions and Containment 2. Evaluation
