PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
|
|
|
- Stuart Dixon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SEMMELWEIS UIVERSITY PETER PAZMAY ATLI UIVERSITY Development of omplex urricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** onsortium leader PETER PAZMAY ATLI UIVERSITY onsortium members SEMMELWEIS UIVERSITY, DIALG AMPUS PUBLISER The Project has been realised with the support of the European Union and has been co-financed by the European Social Fund *** **Molekuláris bionika és Infobionika Szakok tananyagának komplex fejlesztése konzorciumi keretben ***A projekt az Európai Unió támogatásával, az Európai Szociális Alap társfinanszírozásával valósul meg.. TÁMP /2/A/KMR
2 Semmelweis University BIEMISTRY Metabolism of nucleotides (ukleotidok metabolizmusa) Raymund Machovich. TÁMP /2/A/KMR
3 Lecture objectives To learn: 1) Importance of nucleotide synthesis 2) Synthesis of purine ring, formation of AMP and GMP 3) Significance of phosphoribosyl-pyrophosphate synthetase 4) Regulation of ATPand GTP synthesis 5) Salvage ways of purine nucleotide synthesis 6) Pyrimidine synthesis 7) Synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides and its control 8) rigins of deoxythymidilate: Thymidylate synthase, thymidine kinase 9) Some anticancer drugs 10) Degradation of purine bases urate formation and its importance TÁMP /2/A/KMR
4 ucleotide structures 2 Syn - - P Anti ester bond -glicoside bond ucleotide: Adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP, adenylate, adenyl acid) ucleoside: ribose (R) -base (B) R Base: (purine-pyrimidine) B B Adenosine Adenine DS RS ATP camp AD UDP-galactose TÁMP /2/A/KMR
5 ucleotide metabolism Diet ucleotides Resynthesis Biosynthetic Intermediers: UDP-glucose DP-diacilglicerol Redox systems oenzymes oa, AD, FAD Regulation Adenosine ADP camp cgmp Energy ATP Informations: RA DA Various cells TÁMP /2/A/KMR
6 Diet: DS, RS Mono-(oligo-)nucleotides Ribose (R) Deoxyribose (dr)- nucleases Phosphatases ucleosides* Pi ucleosidases B (d)r Purine- Pyrimidinebases R dr Reuse * Thymidine 14 Uridine 3 for DA and RA synthesis TÁMP /2/A/KMR
7 Synthesis of purine ring 10 Formyl- TF Asp Gly Formyl-TF 4 1 Gln TÁMP /2/A/KMR
8 P R ATP AMP P R PP atalytic subunit Regulator subunit IMP AMP GMP PRPP-synthetase Regulator subunit breakdown TÁMP /2/A/KMR
9 Purine ring is synthesized on ribose-phosphate = 5 - P Ribose- 5 - phosphate ATP PRPP - synthetase AMP GMP IMP AMP = α - P 2 P P 5 Phosphoribosyl 1 pyrophosphate (PRPP) TÁMP /2/A/KMR
10 Glu Gln Gln-PRPP-amidotransferase - P 2 2 β 5 Phosphoribosyl 1 amine PPi Azaszerin (tumor chemotherapy) (Gln analog) TÁMP /2/A/KMR
11 2 Gly Pi ATP ADP 2 2 Ribose - P Phosphoribosyl glycinamide synthetase Ribose - P Glycinamide ribonucleotide 10 Formyl TF Phosphoribozyl glycinamide transferase TF Formylglycinamide ribonucleotide TÁMP /2/A/KMR
12 2 ADP ATP 2 2 Ribose P Formylglycin amidine ribonucleotide ATP Glu Gln synthetase 2 Ribose - P Formylglycinamide ribonucleotide Aminoimidazole TÁMP /2/A/KMR
13 synthetase ADP 2 2 carboxylase 2 Ribose- P 5 Aminoimidazole 4 carboxy ribonucleotide R ibose- P 5 aminoimidazole ribonucleotide Asp ATP synthetase ADP Succinylocarboxamide ribonucleotide TÁMP /2/A/KMR
14 ADP 5 Aminoimidazole 4 succinylcarboxamide ribonucleotide 2 2 Adenylosuccinate lyase R ibose- P Aminoimidasole carboxamide TÁMP /2/A/KMR
15 Fumarate 10 Formyl TF TF 2 2 Ribóz- P Transferase 2 Ribose- P 5 Aminoimidazole 4 carboxamide ribonucleotide 5 Formylaminoimidazole 2 carboxamide ribonucleotide IMP synthase TÁMP /2/A/KMR
16 IMP synthase PRPP kinase }Purine ring ypoxantine Ribose- P Inozinate (IMP) AMP GMP TÁMP /2/A/KMR
17 AMP and GMP synthesis IMP Adenylosuccinate synthetase AMP GDP GTP Pi Adenylosuccinate Asp R - P 2 AD AD IMP dehydrogenase GMP Xanthylate TÁMP /2/A/KMR
18 2 R - P R - P Adenylosuccinate Xanthylate TÁMP /2/A/KMR
19 ATP Gln 2 Fumarate Adenylosucccinate lyase AMP PPi GMP synthetase Glu 2 = R - P ATP GTP 2 = R - P Gln analogous Adenylate AMP Guanylate GMP TÁMP /2/A/KMR
20 Ribose 5 -P PRPP Transferase Synthetase Feedback controls of biosynthesis of purine nucleotides PR-amine ATP ATP ATP ATP IMP Synthetase Dehydrogenase Adenylo GTP succinate Xanthylate ATP ATP AMP GMP GTP TÁMP /2/A/KMR
21 = - -P 2 - = P P Purine nucleotides can be re-used ( Salvage ways ) Ө 2 PRPP Adenosine-phosphoribosyl transferase Adenine Adenylate (AMP) PPi R - P TÁMP /2/A/KMR
22 ypoxantine + PRPP ypoxantine-guaninephosphoribosyl transferase PPi Guanine + PRPP PPi IMP AMP, GMP, IMP inhibit their own syntheses 2 R - P R - P GMP TÁMP /2/A/KMR
23 A R (G R) + Adenosine kinase ATP ADP AMP (GMP) A: adenine G: guanine R: ribose TÁMP /2/A/KMR
24 arbamoyl phosphate 2 - P - Pyrimidine syntheses Asp Glu 2ADP arbamoyl-phosphate synthetase (kda 240) Different carbamoylphosphate synthetases. For pyrimidine: Gln in cytosol For urea: + 4 in mitochondria Gln - 3 2ATP UMP TÁMP /2/A/KMR
25 2 -P - - arbamoyl - P Aspartate transcarbamylase arbamoyl-phosphate synthase Mr AD Dihydroorotase Aspartate - transcarbamoylase Pi 2 2 carbamoyl-aspartate 2 2 Asp Dihydroorotase 2 Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase 2 Dihydroorotate AD AD rotate TÁMP /2/A/KMR
26 rotate rotate aciduria Transferase PRPP PPi rotate-phosphorybosyltransferase = - -P 2 - Decarboxylase ereditary breakdown or azauridine (anticancer) Th: uridine rotidylate rotidylate decarboxylase Uridylate (UMP) TÁMP /2/A/KMR
27 Ribose P UTP (uridine- triphosphate) ADP ATP ADP ATP UDP ucleoside UMPdiphosphate kinase kináse UMP rotidylate decarboxylase 2 ATP ADP 2 Gln 2 TP synthetase Glu TP (cytidine triphosphate) Ribose P Uridylate UMP Uridine monophosphate Ribose P P P TÁMP /2/A/KMR
28 Deoxyribonucleotide synthesis 5 P - P Base ADP 2 Ribonucleotide reductase: Its substrate: ribonucleotide diphosphate (BDP) ε ADP S S P - P 2 S enzime: BDP + ε S S Base dbdp + 2 TÁMP /2/A/KMR
29 Ribonucleotide reductase Regulation B1 B1 ATP datp B2 Fe Fe 3+ S S B2 Substrates: ADP DP UDP GDP TÁMP /2/A/KMR
30 ATP DP UDP Regulation of ribonucleotide reductase ddp dtp dudp dttp GDP dgdp dgtp ADP dadp datp TÁMP /2/A/KMR
31 = P dump dr Deoxythymidylate (dtmp) synthesis: Uridine-way methylene - TF Gly Thymidylate synthase Ser TF DF = P ADP Dihydrofolate reductase ADP 3 dr dtmp TÁMP /2/A/KMR
32 Deoxythimidylate (dtmp) synthesis: Thymidine-way 3 = 2 ATP Thymidine kinase ADP 3 = -P- 2 DA-degradation - cellular -diet dt (deoxythimidine) dtmp (Deoxythymidine-monophosphate) dt 3, 14 DA synthesis TÁMP /2/A/KMR
33 F - Uracil Incorporated into RA F- UDP, F - dudp Fluoro deoxyuridylate (F dump) - F P -dr Anticancer drugs UDP Ribonucleotide reductase dump dump Thymidilate - synthase Gly Ser, 5 10 Methylene TF DF TF analogues: ompatitive inhibitors (K i 10-9 M) Aminopterin Methotrexate ADP ADP Dihydrofolate reductase TF 2 - F dtmp ATP ATP TP dtdp dttp DA Pi Pi Polymerase S - enzym P -dr dt Thymidine kinase Kinases and phosphatases TÁMP /2/A/KMR
34 Pyrimidine and purine analogues 2 S 2 ytosine arabinose 6 mercaptopurine ( Immurán ) ypoxantine + PRPP S IMP DA synthesis is inhibited (dtp analogue) AMP GMP TÁMP /2/A/KMR
35 Degradation of purines PRPP Gln 2 Ribose - P AMP Adenylate deaminase 2-2 Asp GMP IMP Gln Phosphomono esterase Pi Ribose PRPP ypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase ypoxanthine Xanthine TÁMP /2/A/KMR
36 Guanine phosphoribsyl transferase IMP GMP ypoxanthine PRPP 2 Phosphomonoesterase Ribose Pi Guanine 2 Guanine deaminase Xanthine 2 Xanthine oxidase 2 2 atalase 2 Uric acid TÁMP /2/A/KMR
37 Degradation of purines: urate formation Xanthine 2 2 Xanthine oxidase 2 2 atalase 2 Uric acid (enol) Uric acid (keto) + Urate (low solubility) Gout, Kidney stone Allantoin urea TÁMP /2/A/KMR
38 igh level of urate results in deposition of sodium urate crystals AMP B or decreased A: IMP igh level of uricacid results in its deposition in kidney and joint (inflamed and painful) ypoxanthine ypoxanthine guaninephosphoribozyl transferase PRPP ATP Ribose 5 P B PRPPsynthetase (regulator subunit defect) Xanthine - oxidase Xanthineoxidase Xanthine Urate GMP A Guanine A Genetic lack: Lesch yhan syndrome Bizarre reactions: Self destructive tendencies (biting off their fingers, lip, toes), bad coordination, mental retardardation TÁMP /2/A/KMR
39 Treatment of gout Th: Allopurinol Xanthine oxidase Urate Xanthine oxidases are inhibited (xanthine and hypoxanthine are more soluble than uric acid) joints kidney ypoxanthine Allopurinol Urate is decreased, PRPP not TÁMP /2/A/KMR
40 igh urate level may be useful : Urate level of the human is 10-fold higher than in monkey a factor for the longer life time. Urate is an antioxaidant (like Vitamin E, bilirubin, etc). TÁMP /2/A/KMR
41 Adenosine-deaminase Its lack leads to a 100-fold increase in datp, which inhibits ribonucleotide reductase. The increase in datp, thus results in decrease of other deoxinucleotides necessary for DA synthesis in T and B lymphocytes. Its hereditary deficiency affects the immune system: SID-syndrome (sever combined immundeficiency). It is also called on IV AIDS, because of similar symptoms. TÁMP /2/A/KMR
42 Summary ucleotide metabolism is discussed from the viewpoint of their synthesis (because their amount is not enough in the diet) and they degradation (because they incorrect elimination causes pathological conditions)
43 Recommended literature Machovich R. A nucleotidok anyagcseréje rvosi Biokémia, Medicina kiadó, pp TÁMP /2/A/KMR
44 What is the role of nucleotides? 1) ydrolysis of PP bound of ATP to drive reactions that require an input of energy 2) Building blocks of DA and RA 3) omponenet of coenzymes 4) Second messengers 5) Allosteric effectors of metabolic procesess A: 1,2,5 B:3,4 : all D:2,4,5 E: 1,2
45 orrect answere for test question: TÁMP /2/A/KMR
46 Which of the compound(s) below is/are allosteric inhibitor(s) of PRPP amidotransferase? 1) ATP 2) IMP 3) PRPP 4) AD A: 1,2,3,4, B: 1,2,3 : 2 D: 2,3 E: 1 TÁMP /2/A/KMR
47 orrect answere for test question: TÁMP /2/A/KMR
Biosynthesis of nucleotides
 Biosynthesis of nucleotides De novo pathways De novo purine nucleotide synthesis Regulation of purine biosynthesis De novo pyrimidine nucleotides biosynthesis Salvage pathways Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Why
Biosynthesis of nucleotides De novo pathways De novo purine nucleotide synthesis Regulation of purine biosynthesis De novo pyrimidine nucleotides biosynthesis Salvage pathways Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Why
Lipid Metabolism. Lipid Metabolism. Lipid Metabolism
 Chem 352 - Lecture 10 Lipid, Amino Acid, and Nucleotide Metabolism Part III: Nucleotide Metabolism 1 Lipid Metabolism 2-1 Chem 352, Lecture 10, Part I: Lipid Metabolism 2 Lipid Metabolism 2-2 Question:
Chem 352 - Lecture 10 Lipid, Amino Acid, and Nucleotide Metabolism Part III: Nucleotide Metabolism 1 Lipid Metabolism 2-1 Chem 352, Lecture 10, Part I: Lipid Metabolism 2 Lipid Metabolism 2-2 Question:
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala Nucleotide metabolism 1 P age In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala Nucleotide metabolism 1 P age In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
Nucleotide Metabolism
 Nucleotide Metabolism Nucleotide Synthesis De Novo Pathway Synthesize purine and pyrimidine nucleotides from low M.W. precursors Salvage Pathway synthesize nucleotides from nucleosides of nucleobases NB:
Nucleotide Metabolism Nucleotide Synthesis De Novo Pathway Synthesize purine and pyrimidine nucleotides from low M.W. precursors Salvage Pathway synthesize nucleotides from nucleosides of nucleobases NB:
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Diala
 number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala 1 P a g e Nucleotide metabolism In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala 1 P a g e Nucleotide metabolism In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
I. NUCLEOTIDES. Nitrogenous bases are frequently represented by single letter abbreviations. The abbreviations for several bases are shown below:
 Biochemistry II Nucleotide Metabolism I. NUCLEOTIDES Nitrogenous bases are frequently represented by single letter abbreviations. The abbreviations for several bases are shown below: Common Nitrogenous
Biochemistry II Nucleotide Metabolism I. NUCLEOTIDES Nitrogenous bases are frequently represented by single letter abbreviations. The abbreviations for several bases are shown below: Common Nitrogenous
Nucleotide Metabolism Biochemistry by Lippincott pp
 Nucleotide Metabolism Biochemistry by Lippincott pp 291-306 Metabolism: CONCEPT Ø Metabolism is the totality of an organism s chemical reactions. Ø A metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and
Nucleotide Metabolism Biochemistry by Lippincott pp 291-306 Metabolism: CONCEPT Ø Metabolism is the totality of an organism s chemical reactions. Ø A metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Dr. Robert Lyons, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Dr. Robert Lyons, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Biochem for the Boards 2nd Edition
 Biochem for the Boards! Biochem for the Boards 2nd Edition Active Learning Workbook for the BDE 1, DDS, MA Bonus Chapter ucleotide Metabolism Socrates Publishing Co. ew York, Y Page 1 ucleotide Metabolism
Biochem for the Boards! Biochem for the Boards 2nd Edition Active Learning Workbook for the BDE 1, DDS, MA Bonus Chapter ucleotide Metabolism Socrates Publishing Co. ew York, Y Page 1 ucleotide Metabolism
Password: LECTURE 7: NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM
 http://smtom.lecture.ub.ac.id/ Password: LECTURE 7: NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM 51 All humans are 99,7% identical at DNA sequence level, and yet all of us carry a significant number of glitches in our genomes.
http://smtom.lecture.ub.ac.id/ Password: LECTURE 7: NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM 51 All humans are 99,7% identical at DNA sequence level, and yet all of us carry a significant number of glitches in our genomes.
GENERAL NUCLEIC ACID BIOCHEMISTRY 461, FALL A two (2) unit course for non-biochemistry majors only.
 GENERAL NUCLEIC ACID BIOCHEMISTRY 461, FALL 2010 A two (2) unit course for non-biochemistry majors only. PREREQUISITES: Biology 181 Organic Chemistry (Chem 241a,b) Concurrent/previous registration in Biochemistry
GENERAL NUCLEIC ACID BIOCHEMISTRY 461, FALL 2010 A two (2) unit course for non-biochemistry majors only. PREREQUISITES: Biology 181 Organic Chemistry (Chem 241a,b) Concurrent/previous registration in Biochemistry
Nucleotide Metabolism December 12-17, 2008 Dr. Robert Lyons. See: for supplementary course materials.
 1 2 ucleotide Metabolism December 12-17, 2008 Dr. Robert Lyons See: http://seqcore.brcf.med.umich.edu/mcb500 for supplementary course materials. Medical relevance of nucleotide pathways Critical in cancer
1 2 ucleotide Metabolism December 12-17, 2008 Dr. Robert Lyons See: http://seqcore.brcf.med.umich.edu/mcb500 for supplementary course materials. Medical relevance of nucleotide pathways Critical in cancer
Biosynthesis. Amino acids, N-containing molecules Nucleotides
 Biosynthesis Amino acids, N-containing molecules Nucleotides 1 Modified Fig 22-9 p. 827 Biosynthesis of A.A. Glucose All C derived from intermediates in Glycolysis 3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG) Phosphoenolpyruvate
Biosynthesis Amino acids, N-containing molecules Nucleotides 1 Modified Fig 22-9 p. 827 Biosynthesis of A.A. Glucose All C derived from intermediates in Glycolysis 3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG) Phosphoenolpyruvate
Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License.
 Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License. Copyright 2007, Robert Lyons. The following information is intended
Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License. Copyright 2007, Robert Lyons. The following information is intended
BIOC 312. Gehring Lecture 1 Jan 12
 Gehring Lecture 1 Jan 12 BIOC 312 Lecture Plan for Gehring (all lectures): 1) nomenclature, purine biosynthesis 2) pyrimidine biosynth, formation of tri-diphosphates, ribonucleotide reductase 3) Thymidylate
Gehring Lecture 1 Jan 12 BIOC 312 Lecture Plan for Gehring (all lectures): 1) nomenclature, purine biosynthesis 2) pyrimidine biosynth, formation of tri-diphosphates, ribonucleotide reductase 3) Thymidylate
Nucleotide Metabolism
 Nucleotide Metabolism Adenine Guanidine Uracil Thymine Cytosine Last Week Nucleotide Metabolism - Mostly, we think of nucleotides as being part of RNA/DNA, but now that we ve studied metabolism, we know
Nucleotide Metabolism Adenine Guanidine Uracil Thymine Cytosine Last Week Nucleotide Metabolism - Mostly, we think of nucleotides as being part of RNA/DNA, but now that we ve studied metabolism, we know
Student Name Biochem. 461 Exam 1 Key, September 23, 2010
 Student Name Biochem. 461 Exam 1 Key, September 23, 2010 (100 POINTS TOTAL) ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED [10 pts] We will learn in Chapter 28 that ribonuclosides and deoxyribonucleosides
Student Name Biochem. 461 Exam 1 Key, September 23, 2010 (100 POINTS TOTAL) ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED [10 pts] We will learn in Chapter 28 that ribonuclosides and deoxyribonucleosides
Nucleotide Metabolism
 Nucleotide Metabolism Dr. Chalermchai Mitrpant Outline Content Page Function of nucleotide 2 Nucleotide synthesis 3-6 Purine synthesis and its regulation 3-4 Pyrimidine synthesis and its regulation 5-6
Nucleotide Metabolism Dr. Chalermchai Mitrpant Outline Content Page Function of nucleotide 2 Nucleotide synthesis 3-6 Purine synthesis and its regulation 3-4 Pyrimidine synthesis and its regulation 5-6
Chapters 7 & 19 - Nucleosides, Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
 hapters 7 & 19 - ucleosides, ucleotides and ucleic Acids ucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids function as vitamins and coenzymes, energy carriers, second messengers, catalysts, and as genetic information
hapters 7 & 19 - ucleosides, ucleotides and ucleic Acids ucleosides, nucleotides and nucleic acids function as vitamins and coenzymes, energy carriers, second messengers, catalysts, and as genetic information
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 16 Monday 1 March
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 16 Monday 1 March Review Primary Structure of a portion of a polypeptide chain backbone of Polypeptide chain R-groups of amino acids Native conformation of a dimeric protein,
BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 16 Monday 1 March Review Primary Structure of a portion of a polypeptide chain backbone of Polypeptide chain R-groups of amino acids Native conformation of a dimeric protein,
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
 ucleotides and ucleic Acids ucleotides: Composed of a sugar; a weak nitrogenous base; at least one phosphoryl group - - P - C 2 Base *ucleoside: sugar + base 2 Classes of ucleotides: Ribonucleotides and
ucleotides and ucleic Acids ucleotides: Composed of a sugar; a weak nitrogenous base; at least one phosphoryl group - - P - C 2 Base *ucleoside: sugar + base 2 Classes of ucleotides: Ribonucleotides and
36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L-
 36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L- 37. The essential fatty acids are A. palmitic acid B. linoleic acid C. linolenic
36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L- 37. The essential fatty acids are A. palmitic acid B. linoleic acid C. linolenic
Nucleic acids -1 Purines
 Nucleic acids -1 Purines Purine metabolism Purine Biosynthesis: 5-Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide is carboxylated and this is followed by the addition of an aspartic acid to form 5-Aminoimidazole-
Nucleic acids -1 Purines Purine metabolism Purine Biosynthesis: 5-Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide is carboxylated and this is followed by the addition of an aspartic acid to form 5-Aminoimidazole-
Case 16 Allosteric Regulation of ATCase
 Case 16 Allosteric Regulation of ATCase Focus concept An enzyme involved in nucleotide synthesis is subject to regulation by a variety of combinations of nucleotides. rerequisites roperties of allosteric
Case 16 Allosteric Regulation of ATCase Focus concept An enzyme involved in nucleotide synthesis is subject to regulation by a variety of combinations of nucleotides. rerequisites roperties of allosteric
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds. Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides
 Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Chapter 11. Nucleic Acids. Nucleotides. BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 11 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Chapter 11, page 1
 BC 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 11 Lecture otes 1 Chapter 11 ucleotides and ucleic Acids 2 ucleic Acids Two classes DA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) RA (Ribonucleic Acid) Polymers of nucleotides DA carries genetic
BC 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 11 Lecture otes 1 Chapter 11 ucleotides and ucleic Acids 2 ucleic Acids Two classes DA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) RA (Ribonucleic Acid) Polymers of nucleotides DA carries genetic
CHAPTER 31 NUCLEIC ACIDS AND HEREDITY SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS. ƒ H. Guanine H O. Uracil
 CAPTER 31 UCLEIC ACIDS AD EREDITY SLUTIS T REVIEW QUESTIS 1. The five nitrogen bases found in nucleotides: 3 C 2 Adenine Thymine Guanine Uracil 2 2 Cytosine 2. A nucleoside is a purine or pyrimidine base
CAPTER 31 UCLEIC ACIDS AD EREDITY SLUTIS T REVIEW QUESTIS 1. The five nitrogen bases found in nucleotides: 3 C 2 Adenine Thymine Guanine Uracil 2 2 Cytosine 2. A nucleoside is a purine or pyrimidine base
Super Models. Nucleic Acid Bases (nucleobases) Molecular Model Kit
 Super Models ucleic Acid Bases (nucleobases) Molecular Model Kit Copyright 2015 Ryler Enterprises, Inc. Recommended for ages 10 - adult! Caution: Atom centers and vinyl tubing are a choking hazard. Do
Super Models ucleic Acid Bases (nucleobases) Molecular Model Kit Copyright 2015 Ryler Enterprises, Inc. Recommended for ages 10 - adult! Caution: Atom centers and vinyl tubing are a choking hazard. Do
ATP GTP UTP CTP
 Table S1. ATP (GTP) utilization for de novo synthesis of rtps ucleotide 5 phosphoribosyl ucleobase rmp rtp (total) pyrophosphate from glucose ATP 3 5 8 10 GTP 3 5 8 10 UTP 3 2 5 7 CTP 3 3 6 8 The numbers
Table S1. ATP (GTP) utilization for de novo synthesis of rtps ucleotide 5 phosphoribosyl ucleobase rmp rtp (total) pyrophosphate from glucose ATP 3 5 8 10 GTP 3 5 8 10 UTP 3 2 5 7 CTP 3 3 6 8 The numbers
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds
 Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Chapter 24: Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids
 Chem 225 otes Page 138 I. Introduction Chapter 24: Carbohydrates and ucleic Acids A. Definitions and aming Conventions Carbohydrate: a sugar. A polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone with the molecular formula
Chem 225 otes Page 138 I. Introduction Chapter 24: Carbohydrates and ucleic Acids A. Definitions and aming Conventions Carbohydrate: a sugar. A polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone with the molecular formula
A. Incorrect! A sugar residue is only part of a nucleotide. Go back and review the structure of nucleotides.
 Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 24: ucleic Acids o. 1 of 10 1. What are the components of a nucleotide? (A) A sugar residue (B) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous base (C) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous
Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 24: ucleic Acids o. 1 of 10 1. What are the components of a nucleotide? (A) A sugar residue (B) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous base (C) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous
Human tissue information processing
 Human tissue information processing JELENKA SAVKOVICSTEVANOVIC Faulty of Technology and Metallury, Belgrade University,Karnegijeva 4, 11000 Belgrade SERBIA, savkovic@tmf.bg.ac.rs Abstract:In this paper
Human tissue information processing JELENKA SAVKOVICSTEVANOVIC Faulty of Technology and Metallury, Belgrade University,Karnegijeva 4, 11000 Belgrade SERBIA, savkovic@tmf.bg.ac.rs Abstract:In this paper
Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids
 Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids E T Nyahangare Class Assignment 1. Write notes and outline the role of the following in protein biosynthesis a. DNA replication b. Transcription c. Genetic code
Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids E T Nyahangare Class Assignment 1. Write notes and outline the role of the following in protein biosynthesis a. DNA replication b. Transcription c. Genetic code
Isolation of Nucleoside Metabolizing Enzymes from Alaska Pea Seeds (Pisum sativum L. cultivar Alaska)
 Isolation of ucleoside Metabolizing Enzymes from Alaska Pea Seeds (Pisum sativum L. cultivar Alaska) by Zahrah M. Altawil A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of the College of Graduate Studies at Middle
Isolation of ucleoside Metabolizing Enzymes from Alaska Pea Seeds (Pisum sativum L. cultivar Alaska) by Zahrah M. Altawil A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of the College of Graduate Studies at Middle
Nucleic Acids. Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology 1
 Nucleic Acids Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology 1 Topics : 2 hrs - Nucleic acid ----------------------------- Nucleic acid structure
Nucleic Acids Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology 1 Topics : 2 hrs - Nucleic acid ----------------------------- Nucleic acid structure
Paper : 03 Structure and Function of Biomolecules II Module: 02 Nucleosides, Nucleotides and type of Nucleic Acids
 Paper : 03 Structure and Function of Biomolecules II Module: 02 Nucleosides, Nucleotides and type of Nucleic Acids Principal Investigator Paper Coordinators Prof. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department
Paper : 03 Structure and Function of Biomolecules II Module: 02 Nucleosides, Nucleotides and type of Nucleic Acids Principal Investigator Paper Coordinators Prof. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department
* What are the nucleic acids?
 Nucleic Acids This lecture is meant to be a refreshment, it s a brief introduction to nucleic acids since we ll be given a full course about it next year in molecular biology. One last lecture and you
Nucleic Acids This lecture is meant to be a refreshment, it s a brief introduction to nucleic acids since we ll be given a full course about it next year in molecular biology. One last lecture and you
Figure S1: Time course of the energy charge in trehalose-grown wild-type and adk1 mutant cells after sudden increase of glucose concentration to 110
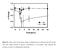 Figure S1: Time course of the energy charge in trehalose-grown wild-type and adk1 mutant cells after sudden increase of glucose concentration to 110 mmol/l. Data represent the average of at least two independent
Figure S1: Time course of the energy charge in trehalose-grown wild-type and adk1 mutant cells after sudden increase of glucose concentration to 110 mmol/l. Data represent the average of at least two independent
Metabolism of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides DNA replication
 Metabolism of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides DNA replication Biochemistry I Lecture 12 2008 (J.S.) 1 Purine and pyrimidine nucleotides are used in large quantities in the biosynthesis of nucleic acids.
Metabolism of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides DNA replication Biochemistry I Lecture 12 2008 (J.S.) 1 Purine and pyrimidine nucleotides are used in large quantities in the biosynthesis of nucleic acids.
Enzymes Part III: regulation I. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017
 Enzymes Part III: regulation I Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Mechanisms of regulation Expression of isoenzymes Regulation of enzymatic activity Inhibitors Conformational changes Allostery Modulators Reversible
Enzymes Part III: regulation I Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Mechanisms of regulation Expression of isoenzymes Regulation of enzymatic activity Inhibitors Conformational changes Allostery Modulators Reversible
Biomolecules: nucleotides
 Biomolecules: nucleotides Nucleotides and nucleic acids Nucleic acids are linear hetero-polymers adapted to maintain and transmit the genetic information Depending on their sugar moiety they can be classified
Biomolecules: nucleotides Nucleotides and nucleic acids Nucleic acids are linear hetero-polymers adapted to maintain and transmit the genetic information Depending on their sugar moiety they can be classified
Redacted for privacy
 AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF Richard K. Bestwick for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Biochemistry and Biophysics presented on July 23, 1982. Title: DNA Precursor Compartmentation in Mammalian Cells:
AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF Richard K. Bestwick for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Biochemistry and Biophysics presented on July 23, 1982. Title: DNA Precursor Compartmentation in Mammalian Cells:
CHARACTERIZATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM SOYBEAN. SEEDS (Glycine max L.) Lola S. JarAllah
 CHARACTERIZATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM SOYBEAN SEEDS (Glycine max L.) by Lola S. JarAllah A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science in Chemistry
CHARACTERIZATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM SOYBEAN SEEDS (Glycine max L.) by Lola S. JarAllah A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science in Chemistry
Paper 4: Biomolecules and Their Interactions Module 12: Bases, Sugars, Nucleosides and Nucleotides Introduction Nucleic acids are involved in storage
 Paper 4: Biomolecules and Their Interactions Module 12: Bases, Sugars, Nucleosides and Nucleotides Introduction Nucleic acids are involved in storage and transfer of genetic information. The double helical
Paper 4: Biomolecules and Their Interactions Module 12: Bases, Sugars, Nucleosides and Nucleotides Introduction Nucleic acids are involved in storage and transfer of genetic information. The double helical
IN-DEPTH CHARACTERIZATION OF THE PURIFICATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM ALASKA PEA SEEDS. Fiezah M. Alahmry
 IN-DEPTH CHARACTERIZATION OF THE PURIFICATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM ALASKA PEA SEEDS By Fiezah M. Alahmry A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master
IN-DEPTH CHARACTERIZATION OF THE PURIFICATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM ALASKA PEA SEEDS By Fiezah M. Alahmry A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master
Please contact us if any parts are missing or damaged. DNA Backbone
 DNA Starter Kit Contents 1-Group Set Contents 12 Red Foam Adenine Bases (DNASK-R-A) 12 Blue Foam Cytosine Bases (DNASK-R-C) 12 Green Foam Guanine Bases (DNASK-R-G) 12 Yellow Foam Thymine Bases (DNASK-R-T)
DNA Starter Kit Contents 1-Group Set Contents 12 Red Foam Adenine Bases (DNASK-R-A) 12 Blue Foam Cytosine Bases (DNASK-R-C) 12 Green Foam Guanine Bases (DNASK-R-G) 12 Yellow Foam Thymine Bases (DNASK-R-T)
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds. Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides
 Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds. Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds. Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Lecture 8. Chromosome. The Nuclei. Two Types of Nucleic Acids. Genes. Information Contained Within Each Cell
 Information Contained Within Each Cell Lecture 8 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Chapter 23: Section 1-5 Most higher organisms reproduce sexually! Sperm cell + Egg cell! Fertilized egg The wondrous
Information Contained Within Each Cell Lecture 8 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Chapter 23: Section 1-5 Most higher organisms reproduce sexually! Sperm cell + Egg cell! Fertilized egg The wondrous
CHARACTERIZATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM ALASKA PEA SEEDS. Abdullah K. Shamsuddin
 CHARACTERIZATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM ALASKA PEA SEEDS by Abdullah K. Shamsuddin A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of the College of Graduate Studies at Middle Tennessee State University in Partial
CHARACTERIZATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM ALASKA PEA SEEDS by Abdullah K. Shamsuddin A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of the College of Graduate Studies at Middle Tennessee State University in Partial
Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotide
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids W. H. Freeman and Company
 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 1 Week 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 8.1 Some Basics 8.2 Nucleic Acid Structure 8.3 Nucleic Acid Chemistry 8.4 Other Functions of Nucleotides
8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 1 Week 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 8.1 Some Basics 8.2 Nucleic Acid Structure 8.3 Nucleic Acid Chemistry 8.4 Other Functions of Nucleotides
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I)
 Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I) Microbial Metabolism Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions that occur within a living organism. These chemical reactions are generally of two types: Catabolic:
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I) Microbial Metabolism Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions that occur within a living organism. These chemical reactions are generally of two types: Catabolic:
NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM. Omidiwura, B.R.O
 NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM Omidiwura, B.R.O Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid
NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM Omidiwura, B.R.O Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid
Part IV => DNA and RNA. 4.1 Nucleotide Properties 4.1a Nucleotide Nomenclature 4.1b DNA Sequencing
 Part IV => DNA and RNA 4.1 Nucleotide Properties 4.1a Nucleotide Nomenclature 4.1b DNA Sequencing The Molecular Dogma of Life DNA carries genetic information in the form of its sequence of nucleotides
Part IV => DNA and RNA 4.1 Nucleotide Properties 4.1a Nucleotide Nomenclature 4.1b DNA Sequencing The Molecular Dogma of Life DNA carries genetic information in the form of its sequence of nucleotides
The nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
 Nucleic acids are macromolecules composed of chains of mononucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds. The nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Nucleic acids are universal
Nucleic acids are macromolecules composed of chains of mononucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds. The nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Nucleic acids are universal
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Nucleic Acids Related Compounds ON HPLC COLUMNS
 ucleic Acids Related Compounds LC CLUMS o.ti88e Column performance in an aqueous elution Revolutionary um technology... more theoretical plates with Unison 6 8 6 8 6 8 6 6 7 8 9 6 7 8 9 6 7 8 9 6 7 8 9
ucleic Acids Related Compounds LC CLUMS o.ti88e Column performance in an aqueous elution Revolutionary um technology... more theoretical plates with Unison 6 8 6 8 6 8 6 6 7 8 9 6 7 8 9 6 7 8 9 6 7 8 9
Enzymes, ATP and Bioenergetics
 Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College Enzymes, ATP and Bioenergetics Bioenergetics Bioenergetics can be defined as energy transfer mechanisms occurring within living organisms.
Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College Enzymes, ATP and Bioenergetics Bioenergetics Bioenergetics can be defined as energy transfer mechanisms occurring within living organisms.
Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids
 eading: Ch8; 310-312, 279-285 Ch24; 957-961 Problems: Ch8 (text); 1,2,22 Ch8 (study-guide: facts); 1,2,4,5,7,8,9 emember Today at 5:30 in CAS-522 is the last MB workshop EXT eading: Ch8; 285-290 Ch24;
eading: Ch8; 310-312, 279-285 Ch24; 957-961 Problems: Ch8 (text); 1,2,22 Ch8 (study-guide: facts); 1,2,4,5,7,8,9 emember Today at 5:30 in CAS-522 is the last MB workshop EXT eading: Ch8; 285-290 Ch24;
Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Lecture - 16 Nucleic Acids - I
 Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture - 16 Nucleic Acids - I We start our discussion on Nucleic Acids and their components. Before we
Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture - 16 Nucleic Acids - I We start our discussion on Nucleic Acids and their components. Before we
Nucleic Acids: Structure and Function
 ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ydrolysis of nucleotides gives phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar,
ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ydrolysis of nucleotides gives phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar,
CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis General, rganic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis Learning bjectives: q Nucleosides & Nucleo@des:
CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis General, rganic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis Learning bjectives: q Nucleosides & Nucleo@des:
Chemical organization of cells
 The most frequent chemical elements of living cells are H, C, N, O, P, S that represent 99% of cell mass. This elements form the organic molecules: nucleic s, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Organic
The most frequent chemical elements of living cells are H, C, N, O, P, S that represent 99% of cell mass. This elements form the organic molecules: nucleic s, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Organic
Control of Metabolic Processes
 Control of Metabolic Processes Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College As described earlier, the metabolic processes occurring within living organisms (glycolysis, respiration,
Control of Metabolic Processes Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College As described earlier, the metabolic processes occurring within living organisms (glycolysis, respiration,
Principles and perspectives of gene therapy
 Principles and perspectives of gene therapy Prof. Józef Dulak, PhD, DSc Department of Medical Biotechnology Faculty of Biochemistry, Biophysics and Biotechnology Room 3.025/3.07 Phone 664-63-75 Email:
Principles and perspectives of gene therapy Prof. Józef Dulak, PhD, DSc Department of Medical Biotechnology Faculty of Biochemistry, Biophysics and Biotechnology Room 3.025/3.07 Phone 664-63-75 Email:
THESIS. for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE. Patricia C. Brock, B.S. Denton, Texas December, 1987
 A NEW LC COLUMN FOR THE SEPARATION AND THE QUANTITATION OF NUCLEOTIDES THESIS Presented to the Graduate Council of the North Texas State University in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
A NEW LC COLUMN FOR THE SEPARATION AND THE QUANTITATION OF NUCLEOTIDES THESIS Presented to the Graduate Council of the North Texas State University in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
CHAPTER 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
 CHAPTER 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Key topics Biological function of nucleotides and nucleic acids Structures of common nucleotides Structure of double-stranded DNA Structures of ribonucleic acids
CHAPTER 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Key topics Biological function of nucleotides and nucleic acids Structures of common nucleotides Structure of double-stranded DNA Structures of ribonucleic acids
Biochemistry 694:301 Final Exam, Deis
 Biochemistry 694:301 Final Exam, Deis Mon., May 8, 2006 Name Row Letter Seat Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth two points. Answer the
Biochemistry 694:301 Final Exam, Deis Mon., May 8, 2006 Name Row Letter Seat Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth two points. Answer the
Some He He e t ro r cy o clic Drugs Convenor: Dr. Dr Fa w Fa a w z a Aldabbagh
 Some eterocyclic Drugs Convenor: Dr. Fawaz Aldabbagh 1 Learning utcomes The student should be able to identify and write the structure of all nucleotides and nucleosides derived from DA and RA. Also know
Some eterocyclic Drugs Convenor: Dr. Fawaz Aldabbagh 1 Learning utcomes The student should be able to identify and write the structure of all nucleotides and nucleosides derived from DA and RA. Also know
NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER I EXAMINATION CBC922 Medicinal Chemistry. NOVEMBER TIME ALLOWED: 120 min
 AYAG TECLGICAL UIVERSITY SEMESTER I EXAMIATI 2006-2007 CBC922 Medicinal Chemistry VEMBER 2006 - TIME ALLWED 120 min ISTRUCTIS T CADIDATES 1. This examination paper contains TW (2) parts and comprises SIX
AYAG TECLGICAL UIVERSITY SEMESTER I EXAMIATI 2006-2007 CBC922 Medicinal Chemistry VEMBER 2006 - TIME ALLWED 120 min ISTRUCTIS T CADIDATES 1. This examination paper contains TW (2) parts and comprises SIX
Dina Al-Tamimi. Faisal Nimri. Ma amoun Ahram. 1 P a g e
 1 Dina Al-Tamimi Faisal Nimri Ma amoun Ahram 1 P a g e **Difference between Molecular Biology and Genetics: Molecular Biology: is a fancy term of biochemistry. It is the science that deals with DNA, RNA
1 Dina Al-Tamimi Faisal Nimri Ma amoun Ahram 1 P a g e **Difference between Molecular Biology and Genetics: Molecular Biology: is a fancy term of biochemistry. It is the science that deals with DNA, RNA
Central Dogma. 1. Human genetic material is represented in the diagram below.
 Central Dogma 1. Human genetic material is represented in the diagram below. 4. If 15% of a DNA sample is made up of thymine, T, what percentage of the sample is made up of cytosine, C? A) 15% B) 35% C)
Central Dogma 1. Human genetic material is represented in the diagram below. 4. If 15% of a DNA sample is made up of thymine, T, what percentage of the sample is made up of cytosine, C? A) 15% B) 35% C)
The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function
 Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
DNA and RNA Structure Guided Notes
 Nucleic acids, especially DNA, are considered as the key biomolecules that guarantee the continuity of life. DNA is the prime genetic molecule which carry all the hereditary information that's passed from
Nucleic acids, especially DNA, are considered as the key biomolecules that guarantee the continuity of life. DNA is the prime genetic molecule which carry all the hereditary information that's passed from
25.19: Coenzymes. Some reactions require additional organic molecules or metal ions. These are referred to as cofactors or coenzymes.
 25.19: oenzymes. Some reactions require additional organic molecules or metal ions. hese are referred to as cofactors or coenzymes. S Fe eme Biotin (vitamin B 7 ) 2 S + 2 hiamin Diphosphate (vitamin B
25.19: oenzymes. Some reactions require additional organic molecules or metal ions. hese are referred to as cofactors or coenzymes. S Fe eme Biotin (vitamin B 7 ) 2 S + 2 hiamin Diphosphate (vitamin B
Syllabus for GUTS Lecture on DNA and Nucleotides
 Syllabus for GUTS Lecture on DNA and Nucleotides I. Introduction. DNA is the instruction manual for how to build a living organism here on earth. The instructions in DNA are propagated to future generations
Syllabus for GUTS Lecture on DNA and Nucleotides I. Introduction. DNA is the instruction manual for how to build a living organism here on earth. The instructions in DNA are propagated to future generations
Nucleic Acids: Structure and Function
 ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ucleotides are made up of: phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar, and
ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ucleotides are made up of: phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar, and
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA
 RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
Page 1. C) DNA molecules, only D) both DNA and RNA molecules. C) nitrogenous bases D) amino acids. C) starch and glycogen D) fats and oils
 Name: 1) Which molecules are composed of units known as nucleotides? A) messenger RNA molecules, only B) transfer RNA molecules, only 2) The individuality of an organism is determined by the organism's
Name: 1) Which molecules are composed of units known as nucleotides? A) messenger RNA molecules, only B) transfer RNA molecules, only 2) The individuality of an organism is determined by the organism's
THE EFFECTS OF DERIVATIVES OF ADENOSINE 3',5'- MONOPHOSPHATE ON FLUID SECRETION BY THE SALIVARY GLANDS OF CALLIPHORA
 J. Exp. Biol. (1973), 59, S95-6o6 595 With 10 text-figures Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECTS OF DERIVATIVES OF ADENOSINE 3',5'- MONOPHOSPHATE ON FLUID SECRETION BY THE SALIVARY GLANDS OF CALLIPHORA
J. Exp. Biol. (1973), 59, S95-6o6 595 With 10 text-figures Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECTS OF DERIVATIVES OF ADENOSINE 3',5'- MONOPHOSPHATE ON FLUID SECRETION BY THE SALIVARY GLANDS OF CALLIPHORA
Super Models. Nucleotides Molecular Model Kit Copyright 2015 Ryler Enterprises, Inc. Recommended for ages 10 - adult
 Super Models! ucleotides Molecular Model Kit Copyright 015 Ryler Enterprises, Inc. Recommended for ages 10 - adult Caution: Atom centers and vinyl tubing are a choking hazard. Do not eat or chew model
Super Models! ucleotides Molecular Model Kit Copyright 015 Ryler Enterprises, Inc. Recommended for ages 10 - adult Caution: Atom centers and vinyl tubing are a choking hazard. Do not eat or chew model
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush I. Hierarchical structure of nucleic acids II. Structures of nucleotides A. Purines & pyrimidines B. Nucleosides & nucleotides
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush I. Hierarchical structure of nucleic acids II. Structures of nucleotides A. Purines & pyrimidines B. Nucleosides & nucleotides
B.sc. III Chemistry Paper b. Submited by :- Dr. Sangeeta Mehtani Associate Professor Deptt. Of Chemistry PGGCG, sec11 Chd
 B.sc. III Chemistry Paper b Submited by :- Dr. Sangeeta Mehtani Associate Professor Deptt. f Chemistry PGGCG, sec11 Chd Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins,ucleic Acids Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins,ucleic
B.sc. III Chemistry Paper b Submited by :- Dr. Sangeeta Mehtani Associate Professor Deptt. f Chemistry PGGCG, sec11 Chd Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins,ucleic Acids Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins,ucleic
Nucleic acids. The building blocks. Phosphates
 Nucleic acids Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleic acids found in the nuclei of living cells. They are the vehicles of genetic inheritance. Nucleic acids are condensation
Nucleic acids Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleic acids found in the nuclei of living cells. They are the vehicles of genetic inheritance. Nucleic acids are condensation
CHEM-E8130 Medicinal Chemistry
 CEM-E8130 Medicinal Chemistry Lecture 9: RA/DA Mimicry & Interference Jan Deska Laboratory of rganic Chemistry 01.12.2016 DA & RA structurally rather low level of diversity o o o four nucleobases (compared
CEM-E8130 Medicinal Chemistry Lecture 9: RA/DA Mimicry & Interference Jan Deska Laboratory of rganic Chemistry 01.12.2016 DA & RA structurally rather low level of diversity o o o four nucleobases (compared
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology
 Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Lecture Overview. Overview of the Genetic Information. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Protein Synthesis Lecture 6
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Protein Synthesis Lecture 6 Lecture Overview The Genetic Information Structure of DNA/RNA DNA Replication Overview of protein synthesis
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Protein Synthesis Lecture 6 Lecture Overview The Genetic Information Structure of DNA/RNA DNA Replication Overview of protein synthesis
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush I. Hierarchical structure of nucleic acids II. Structures of nucleotides A. Purines & pyrimidines B. Nucleosides & nucleotides
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush I. Hierarchical structure of nucleic acids II. Structures of nucleotides A. Purines & pyrimidines B. Nucleosides & nucleotides
6 Enzymes II W. H. Freeman and Company
 6 Enzymes II 2017 W. H. Freeman and Company The role of an enzyme in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is to: A. bind a transition state intermediate, such that it cannot be converted back to substrate. B.
6 Enzymes II 2017 W. H. Freeman and Company The role of an enzyme in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is to: A. bind a transition state intermediate, such that it cannot be converted back to substrate. B.
IB BIO I Macromolecule Test Van Roekel. Name Date Period. 1. Which of the following reactions occurs when a dipeptide is formed from amino acids?
 IB BI I Macromolecule Test Van Roekel ame Date Period 1. Which of the following reactions occurs when a dipeptide is formed from amino acids? ydrolysis Denaturation. ondensation xidation. Which structure
IB BI I Macromolecule Test Van Roekel ame Date Period 1. Which of the following reactions occurs when a dipeptide is formed from amino acids? ydrolysis Denaturation. ondensation xidation. Which structure
Molecular biology WID Masters of Science in Tropical and Infectious Diseases-Transcription Lecture Series RNA I. Introduction and Background:
 Molecular biology WID 602 - Masters of Science in Tropical and Infectious Diseases-Transcription Lecture Series RNA I. Introduction and Background: DNA and RNA each consists of only four different nucleotides.
Molecular biology WID 602 - Masters of Science in Tropical and Infectious Diseases-Transcription Lecture Series RNA I. Introduction and Background: DNA and RNA each consists of only four different nucleotides.
Four levels of protein Structure
 Proteins (polypeptides) Four levels of protein Structure Primary Structure (1 structure): Secondary Structure (2 structure): Tertiary Structure (3 structure): Quaternary Structure (4 structure): Proteins
Proteins (polypeptides) Four levels of protein Structure Primary Structure (1 structure): Secondary Structure (2 structure): Tertiary Structure (3 structure): Quaternary Structure (4 structure): Proteins
have the same enzyme as eukaryotes. The enzyme FGAR amidotransferase catalyzes the fourth step
 NOTICE: The copyright law of the United States (Title 17, United States Code) governs the making of reproductions of copyrighted material. One specified condition is that the reproduction is not to be
NOTICE: The copyright law of the United States (Title 17, United States Code) governs the making of reproductions of copyrighted material. One specified condition is that the reproduction is not to be
Effect of Histidine on Purine Nucleotide Synthesis and Utilization in Neurospora crassa
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Oct. 1975, p. 78-85 Copyright 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 124, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Histidine on Purine Nucleotide Synthesis and Utilization in Neurospora
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, Oct. 1975, p. 78-85 Copyright 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 124, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Histidine on Purine Nucleotide Synthesis and Utilization in Neurospora
DNA Structure, Function, and Engineering Page /14/2018 Dr. Amjid Iqbal 1
 DNA Structure, Function, and Engineering Page 40-51 2/14/2018 Dr. Amjid Iqbal 1 Background Organisms exhibit striking similarity at the molecular level. The structures and metabolic activities of all cells
DNA Structure, Function, and Engineering Page 40-51 2/14/2018 Dr. Amjid Iqbal 1 Background Organisms exhibit striking similarity at the molecular level. The structures and metabolic activities of all cells
STRUCTURE OF RNA. Long unbranched,single stranded polymer of ribonucleotide units. A ribonucleotide unit has: 5-Carbon ribose sugar.
 STRUCTURE OF RNA & REPLICATION BY:HIMANSHU LATAWA BIOLOGY LECTURER G.G.S.S.SIRHIND MANDI anshu223@gmail.com 9815543311 STRUCTURE OF RNA Long unbranched,single stranded polymer of ribonucleotide units.
STRUCTURE OF RNA & REPLICATION BY:HIMANSHU LATAWA BIOLOGY LECTURER G.G.S.S.SIRHIND MANDI anshu223@gmail.com 9815543311 STRUCTURE OF RNA Long unbranched,single stranded polymer of ribonucleotide units.
Chapter 10. Chapter 10 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids. Nobel Prize Reginald H. Garrett Charles M. Grisham
 Reginald H. Garrett Charles M. Grisham Chapter 10 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Chapter 10 We have discovered the secret of life. Francis Crick, to patrons of The Eagle, a pub in Cambridge, England (1953)
Reginald H. Garrett Charles M. Grisham Chapter 10 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Chapter 10 We have discovered the secret of life. Francis Crick, to patrons of The Eagle, a pub in Cambridge, England (1953)
1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1
 AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.5 Nucleic Acids and their functions Page 1 From the syllabus: 1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1 l. Nucleic
AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.5 Nucleic Acids and their functions Page 1 From the syllabus: 1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1 l. Nucleic
