Nucleotide Metabolism
|
|
|
- Claud Cunningham
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nucleotide Metabolism
2 Nucleotide Synthesis De Novo Pathway Synthesize purine and pyrimidine nucleotides from low M.W. precursors Salvage Pathway synthesize nucleotides from nucleosides of nucleobases NB: important targets for therapy of microbial or parasitic diseases
3
4 Nucleic Acid Degradation Intracellular Degradation Turnover of unstable RNA; cell death; ingested nucleic acids Extracellular Degradation Major route by which nucleosides or nucleobases become available in animals
5 Nucleic Acid Degradation endonucleases oligonucleotides phosphodiesterases mononucleotides nucleotidases ortho PO 4 ; nucleosides nucleoside phosphorylase base; ribose-1-p
6 Nucleoside Phosphorylase
7
8 PRPP is a Central Metabolite in De Novo and Salvage Pathways An intermediate in histidine and tryptophan biosynthesis Synthesis of nucleoside-5 -phosphate (nucleotide) from free bases
9
10 Low Molecular Weight Precursors to the Purine Ring Feedback regulation of early steps PRPP synthetase ( ) by AMP, ADP, GDP PRPP amidotransferase ( ) by AMP, GMP (synergistic inhibition)
11 Pathways from inosinic acid to GMP and AMP Energy drive is from GTP/ATP A way to control the proportion of IMP that go to adenine and guanine nucleotide synthesis (reciprocal substrate relation)
12 Conversion of Nucleoside Monophosphate to the Triphosphate Step 1- Specific ATP-Dependent Kinase Guanylate kinase Adenylate kinase Step 2 Non-Specific ATP-Dependent Nuceloside diphosphokinase
13 Control of Purine Biosynthesis
14 Primates uric acid Most mammals further oxidize the purine ring to allantoin and to allantoic acid or further to urea
15 Enzymatic abnormalities that lead to hyperuricemia and gout by elevating the rate of de novo purine nucleotide biosynthesis
16 Gout Excessive accumulation of uric acid 3/1000 suffer from HYPERURICEMIA Urate ppt. causes inflammation in the joints Painful arthritis Allopurinol inhibits xanthine oxidase Solubility: hypoxanthine/xanthine > uric acid
17
18 De Novo Synthesis of Pyrimidine Nucleotides Pyrimidine ring is assembled as a free base Unbranched pathway Aspartate transcarbamoylase ( ) by CTP (+) by ATP
19 Pyrimidine Ring
20 Control of Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
21 Catabolic Pathways in Pyrimidine Nucleotide Metabolism
22 Overview of Deoxyribonucleotide Biosynthesis
23 Overview of Deoxyribonucleotide Biosynthesis Close regulatory relationships between DNA synthesis and dntp metabolism Conversion of ribose to deoxyribose Conversion of uracil to thymine
24 Mechanism for Reduction of a Ribonucleoside Diphosphate by rndp Reductase Replacement of the 2 -hydroxyl moiety of the sugar by a hydride ion retention of configuration Ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase (rndp)
25 Reductive electron transport sequences in the action of ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase
26 Ribonucleoside Diphosphate Reductase Both activity and specificity being regulated To maintain balanced pools of DNA precursors (1) Activity Sites Low affinity binding of ATP or datp ATP binding (+) datp binding ( )
27 Ribonucleoside Diphosphate Reductase (2) Specificity Sites High affinity binding of ATP, datp, dgtp or dttp Modulates the activities of enzyme toward different substrates Maintain a balanced rate of production of dntps
28 Salvage and De Novo Synthetic Pathways to Thymine Nucleotides
29 Relationship between thymidylate synthase and enzymes of tetrahydrofolate metabolism
30 Thymidylate Synthesis: A Target Site for Cancer Chemotherapy Rapidly dividing cells (eg. cancer cells) require an abundant supply of deoxythymidylate for DNA synthesis Thymidylate synthase & Dihydrofolate reductase TARGET ENZYMES
31 Thymidylate Synthesis: A Target Site for Cancer Chemotherapy Fluorouracil fluorodeoxyuridylate (F-dUMP) suicide inhibition of thymidylate synthesis
32 Thymidylate Synthesis: A Target Site for Cancer Chemotherapy Aminopterin and methotrexate inhibit dihydrofolate reductase Acute leukemia Choriocarcinoma Rapidly growing tumors
Nucleotide Metabolism Biochemistry by Lippincott pp
 Nucleotide Metabolism Biochemistry by Lippincott pp 291-306 Metabolism: CONCEPT Ø Metabolism is the totality of an organism s chemical reactions. Ø A metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and
Nucleotide Metabolism Biochemistry by Lippincott pp 291-306 Metabolism: CONCEPT Ø Metabolism is the totality of an organism s chemical reactions. Ø A metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and
I. NUCLEOTIDES. Nitrogenous bases are frequently represented by single letter abbreviations. The abbreviations for several bases are shown below:
 Biochemistry II Nucleotide Metabolism I. NUCLEOTIDES Nitrogenous bases are frequently represented by single letter abbreviations. The abbreviations for several bases are shown below: Common Nitrogenous
Biochemistry II Nucleotide Metabolism I. NUCLEOTIDES Nitrogenous bases are frequently represented by single letter abbreviations. The abbreviations for several bases are shown below: Common Nitrogenous
Biosynthesis of nucleotides
 Biosynthesis of nucleotides De novo pathways De novo purine nucleotide synthesis Regulation of purine biosynthesis De novo pyrimidine nucleotides biosynthesis Salvage pathways Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Why
Biosynthesis of nucleotides De novo pathways De novo purine nucleotide synthesis Regulation of purine biosynthesis De novo pyrimidine nucleotides biosynthesis Salvage pathways Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Why
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Diala
 number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala 1 P a g e Nucleotide metabolism In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala 1 P a g e Nucleotide metabolism In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala Nucleotide metabolism 1 P age In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala Nucleotide metabolism 1 P age In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
GENERAL NUCLEIC ACID BIOCHEMISTRY 461, FALL A two (2) unit course for non-biochemistry majors only.
 GENERAL NUCLEIC ACID BIOCHEMISTRY 461, FALL 2010 A two (2) unit course for non-biochemistry majors only. PREREQUISITES: Biology 181 Organic Chemistry (Chem 241a,b) Concurrent/previous registration in Biochemistry
GENERAL NUCLEIC ACID BIOCHEMISTRY 461, FALL 2010 A two (2) unit course for non-biochemistry majors only. PREREQUISITES: Biology 181 Organic Chemistry (Chem 241a,b) Concurrent/previous registration in Biochemistry
Lipid Metabolism. Lipid Metabolism. Lipid Metabolism
 Chem 352 - Lecture 10 Lipid, Amino Acid, and Nucleotide Metabolism Part III: Nucleotide Metabolism 1 Lipid Metabolism 2-1 Chem 352, Lecture 10, Part I: Lipid Metabolism 2 Lipid Metabolism 2-2 Question:
Chem 352 - Lecture 10 Lipid, Amino Acid, and Nucleotide Metabolism Part III: Nucleotide Metabolism 1 Lipid Metabolism 2-1 Chem 352, Lecture 10, Part I: Lipid Metabolism 2 Lipid Metabolism 2-2 Question:
Student Name Biochem. 461 Exam 1 Key, September 23, 2010
 Student Name Biochem. 461 Exam 1 Key, September 23, 2010 (100 POINTS TOTAL) ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED [10 pts] We will learn in Chapter 28 that ribonuclosides and deoxyribonucleosides
Student Name Biochem. 461 Exam 1 Key, September 23, 2010 (100 POINTS TOTAL) ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED [10 pts] We will learn in Chapter 28 that ribonuclosides and deoxyribonucleosides
Biochem for the Boards 2nd Edition
 Biochem for the Boards! Biochem for the Boards 2nd Edition Active Learning Workbook for the BDE 1, DDS, MA Bonus Chapter ucleotide Metabolism Socrates Publishing Co. ew York, Y Page 1 ucleotide Metabolism
Biochem for the Boards! Biochem for the Boards 2nd Edition Active Learning Workbook for the BDE 1, DDS, MA Bonus Chapter ucleotide Metabolism Socrates Publishing Co. ew York, Y Page 1 ucleotide Metabolism
Nucleotide Metabolism
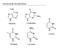 Nucleotide Metabolism Adenine Guanidine Uracil Thymine Cytosine Last Week Nucleotide Metabolism - Mostly, we think of nucleotides as being part of RNA/DNA, but now that we ve studied metabolism, we know
Nucleotide Metabolism Adenine Guanidine Uracil Thymine Cytosine Last Week Nucleotide Metabolism - Mostly, we think of nucleotides as being part of RNA/DNA, but now that we ve studied metabolism, we know
Password: LECTURE 7: NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM
 http://smtom.lecture.ub.ac.id/ Password: LECTURE 7: NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM 51 All humans are 99,7% identical at DNA sequence level, and yet all of us carry a significant number of glitches in our genomes.
http://smtom.lecture.ub.ac.id/ Password: LECTURE 7: NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM 51 All humans are 99,7% identical at DNA sequence level, and yet all of us carry a significant number of glitches in our genomes.
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Dr. Robert Lyons, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Dr. Robert Lyons, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Nucleotide Metabolism
 Nucleotide Metabolism Dr. Chalermchai Mitrpant Outline Content Page Function of nucleotide 2 Nucleotide synthesis 3-6 Purine synthesis and its regulation 3-4 Pyrimidine synthesis and its regulation 5-6
Nucleotide Metabolism Dr. Chalermchai Mitrpant Outline Content Page Function of nucleotide 2 Nucleotide synthesis 3-6 Purine synthesis and its regulation 3-4 Pyrimidine synthesis and its regulation 5-6
Nucleotide Metabolism December 12-17, 2008 Dr. Robert Lyons. See: for supplementary course materials.
 1 2 ucleotide Metabolism December 12-17, 2008 Dr. Robert Lyons See: http://seqcore.brcf.med.umich.edu/mcb500 for supplementary course materials. Medical relevance of nucleotide pathways Critical in cancer
1 2 ucleotide Metabolism December 12-17, 2008 Dr. Robert Lyons See: http://seqcore.brcf.med.umich.edu/mcb500 for supplementary course materials. Medical relevance of nucleotide pathways Critical in cancer
Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License.
 Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License. Copyright 2007, Robert Lyons. The following information is intended
Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License. Copyright 2007, Robert Lyons. The following information is intended
Biosynthesis. Amino acids, N-containing molecules Nucleotides
 Biosynthesis Amino acids, N-containing molecules Nucleotides 1 Modified Fig 22-9 p. 827 Biosynthesis of A.A. Glucose All C derived from intermediates in Glycolysis 3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG) Phosphoenolpyruvate
Biosynthesis Amino acids, N-containing molecules Nucleotides 1 Modified Fig 22-9 p. 827 Biosynthesis of A.A. Glucose All C derived from intermediates in Glycolysis 3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG) Phosphoenolpyruvate
BIOC 312. Gehring Lecture 1 Jan 12
 Gehring Lecture 1 Jan 12 BIOC 312 Lecture Plan for Gehring (all lectures): 1) nomenclature, purine biosynthesis 2) pyrimidine biosynth, formation of tri-diphosphates, ribonucleotide reductase 3) Thymidylate
Gehring Lecture 1 Jan 12 BIOC 312 Lecture Plan for Gehring (all lectures): 1) nomenclature, purine biosynthesis 2) pyrimidine biosynth, formation of tri-diphosphates, ribonucleotide reductase 3) Thymidylate
Central Dogma. 1. Human genetic material is represented in the diagram below.
 Central Dogma 1. Human genetic material is represented in the diagram below. 4. If 15% of a DNA sample is made up of thymine, T, what percentage of the sample is made up of cytosine, C? A) 15% B) 35% C)
Central Dogma 1. Human genetic material is represented in the diagram below. 4. If 15% of a DNA sample is made up of thymine, T, what percentage of the sample is made up of cytosine, C? A) 15% B) 35% C)
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 SEMMELWEIS UIVERSITY PETER PAZMAY ATLI UIVERSITY Development of omplex urricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** onsortium leader PETER PAZMAY ATLI UIVERSITY
SEMMELWEIS UIVERSITY PETER PAZMAY ATLI UIVERSITY Development of omplex urricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** onsortium leader PETER PAZMAY ATLI UIVERSITY
Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids
 Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids E T Nyahangare Class Assignment 1. Write notes and outline the role of the following in protein biosynthesis a. DNA replication b. Transcription c. Genetic code
Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids E T Nyahangare Class Assignment 1. Write notes and outline the role of the following in protein biosynthesis a. DNA replication b. Transcription c. Genetic code
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 16 Monday 1 March
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 16 Monday 1 March Review Primary Structure of a portion of a polypeptide chain backbone of Polypeptide chain R-groups of amino acids Native conformation of a dimeric protein,
BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 16 Monday 1 March Review Primary Structure of a portion of a polypeptide chain backbone of Polypeptide chain R-groups of amino acids Native conformation of a dimeric protein,
CHAPTER 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
 CHAPTER 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Key topics Biological function of nucleotides and nucleic acids Structures of common nucleotides Structure of double-stranded DNA Structures of ribonucleic acids
CHAPTER 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Key topics Biological function of nucleotides and nucleic acids Structures of common nucleotides Structure of double-stranded DNA Structures of ribonucleic acids
Feedback D. Incorrect! No, although this is a correct characteristic of RNA, this is not the best response to the questions.
 Biochemistry - Problem Drill 23: RNA No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements best describes the structural highlights of RNA? (A) RNA can be single or double stranded. (B) G-C pairs have 3 hydrogen
Biochemistry - Problem Drill 23: RNA No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements best describes the structural highlights of RNA? (A) RNA can be single or double stranded. (B) G-C pairs have 3 hydrogen
Please contact us if any parts are missing or damaged. DNA Backbone
 DNA Starter Kit Contents 1-Group Set Contents 12 Red Foam Adenine Bases (DNASK-R-A) 12 Blue Foam Cytosine Bases (DNASK-R-C) 12 Green Foam Guanine Bases (DNASK-R-G) 12 Yellow Foam Thymine Bases (DNASK-R-T)
DNA Starter Kit Contents 1-Group Set Contents 12 Red Foam Adenine Bases (DNASK-R-A) 12 Blue Foam Cytosine Bases (DNASK-R-C) 12 Green Foam Guanine Bases (DNASK-R-G) 12 Yellow Foam Thymine Bases (DNASK-R-T)
Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotide
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
A. Incorrect! A sugar residue is only part of a nucleotide. Go back and review the structure of nucleotides.
 Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 24: ucleic Acids o. 1 of 10 1. What are the components of a nucleotide? (A) A sugar residue (B) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous base (C) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous
Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 24: ucleic Acids o. 1 of 10 1. What are the components of a nucleotide? (A) A sugar residue (B) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous base (C) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous
Enzymes Part III: regulation I. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017
 Enzymes Part III: regulation I Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Mechanisms of regulation Expression of isoenzymes Regulation of enzymatic activity Inhibitors Conformational changes Allostery Modulators Reversible
Enzymes Part III: regulation I Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Mechanisms of regulation Expression of isoenzymes Regulation of enzymatic activity Inhibitors Conformational changes Allostery Modulators Reversible
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry. CHAPTER 10: Nucleic Acids
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 10: Nucleic Acids 2 o Nucleic
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 10: Nucleic Acids 2 o Nucleic
NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM. Omidiwura, B.R.O
 NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM Omidiwura, B.R.O Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid
NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM Omidiwura, B.R.O Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid
Nucleic Acids. By Sarah, Zach, Joanne, and Dean
 Nucleic Acids By Sarah, Zach, Joanne, and Dean Basic Functions Carry genetic information (DNA storing it) Protein synthesis Helps in cell division (DNA replicates itself) RNA- numerous functions during
Nucleic Acids By Sarah, Zach, Joanne, and Dean Basic Functions Carry genetic information (DNA storing it) Protein synthesis Helps in cell division (DNA replicates itself) RNA- numerous functions during
Human tissue information processing
 Human tissue information processing JELENKA SAVKOVICSTEVANOVIC Faulty of Technology and Metallury, Belgrade University,Karnegijeva 4, 11000 Belgrade SERBIA, savkovic@tmf.bg.ac.rs Abstract:In this paper
Human tissue information processing JELENKA SAVKOVICSTEVANOVIC Faulty of Technology and Metallury, Belgrade University,Karnegijeva 4, 11000 Belgrade SERBIA, savkovic@tmf.bg.ac.rs Abstract:In this paper
Nucleotides: structure and functions. Prof. Dalė Vieželienė Biochemistry department Room No
 Nucleotides: structure and functions Prof. Dalė Vieželienė Biochemistry department Room No. 229 Email: daleveze@med.kmu.lt Composition of Nucleic Acids Nucleotide structure Two types of nucleic acids:
Nucleotides: structure and functions Prof. Dalė Vieželienė Biochemistry department Room No. 229 Email: daleveze@med.kmu.lt Composition of Nucleic Acids Nucleotide structure Two types of nucleic acids:
DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
 http://faculty.uca.edu/~johnc/mbi1440.htm DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis http://www.wappingersschools.org/rck/staff/teacherhp/johnson/visualvocab/mrna.gif DNA base pairs carry the genetic Section 12-1
http://faculty.uca.edu/~johnc/mbi1440.htm DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis http://www.wappingersschools.org/rck/staff/teacherhp/johnson/visualvocab/mrna.gif DNA base pairs carry the genetic Section 12-1
Nucleic Acids. Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology 1
 Nucleic Acids Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology 1 Topics : 2 hrs - Nucleic acid ----------------------------- Nucleic acid structure
Nucleic Acids Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology 1 Topics : 2 hrs - Nucleic acid ----------------------------- Nucleic acid structure
Super Models. Nucleic Acid Bases (nucleobases) Molecular Model Kit
 Super Models ucleic Acid Bases (nucleobases) Molecular Model Kit Copyright 2015 Ryler Enterprises, Inc. Recommended for ages 10 - adult! Caution: Atom centers and vinyl tubing are a choking hazard. Do
Super Models ucleic Acid Bases (nucleobases) Molecular Model Kit Copyright 2015 Ryler Enterprises, Inc. Recommended for ages 10 - adult! Caution: Atom centers and vinyl tubing are a choking hazard. Do
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds
 Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Figure S1: Time course of the energy charge in trehalose-grown wild-type and adk1 mutant cells after sudden increase of glucose concentration to 110
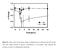 Figure S1: Time course of the energy charge in trehalose-grown wild-type and adk1 mutant cells after sudden increase of glucose concentration to 110 mmol/l. Data represent the average of at least two independent
Figure S1: Time course of the energy charge in trehalose-grown wild-type and adk1 mutant cells after sudden increase of glucose concentration to 110 mmol/l. Data represent the average of at least two independent
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds. Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides
 Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Syllabus for GUTS Lecture on DNA and Nucleotides
 Syllabus for GUTS Lecture on DNA and Nucleotides I. Introduction. DNA is the instruction manual for how to build a living organism here on earth. The instructions in DNA are propagated to future generations
Syllabus for GUTS Lecture on DNA and Nucleotides I. Introduction. DNA is the instruction manual for how to build a living organism here on earth. The instructions in DNA are propagated to future generations
Biomolecules: nucleotides
 Biomolecules: nucleotides Nucleotides and nucleic acids Nucleic acids are linear hetero-polymers adapted to maintain and transmit the genetic information Depending on their sugar moiety they can be classified
Biomolecules: nucleotides Nucleotides and nucleic acids Nucleic acids are linear hetero-polymers adapted to maintain and transmit the genetic information Depending on their sugar moiety they can be classified
The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function
 Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
* What are the nucleic acids?
 Nucleic Acids This lecture is meant to be a refreshment, it s a brief introduction to nucleic acids since we ll be given a full course about it next year in molecular biology. One last lecture and you
Nucleic Acids This lecture is meant to be a refreshment, it s a brief introduction to nucleic acids since we ll be given a full course about it next year in molecular biology. One last lecture and you
Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Lecture - 16 Nucleic Acids - I
 Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture - 16 Nucleic Acids - I We start our discussion on Nucleic Acids and their components. Before we
Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture - 16 Nucleic Acids - I We start our discussion on Nucleic Acids and their components. Before we
Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material. The Nature of Genetic Material. Chemical Nature of Nucleic Acids. Chromosomes - DNA and protein
 Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material The Nature of Genetic Material Chromosomes - DNA and protein Genes are subunits DNA = 4 similar nucleotides C(ytosine) A(denine) T(hymine) G(uanine) Proteins = 20 different
Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material The Nature of Genetic Material Chromosomes - DNA and protein Genes are subunits DNA = 4 similar nucleotides C(ytosine) A(denine) T(hymine) G(uanine) Proteins = 20 different
Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis General, rganic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis Learning bjectives: q Nucleosides & Nucleo@des:
CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis General, rganic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis Learning bjectives: q Nucleosides & Nucleo@des:
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 1953 article in Nature Directionality of DNA You need to number the carbons! u it matters! u 3 refers to the 3 carbon on the sugar u 5 refers to the 5 carbon
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 1953 article in Nature Directionality of DNA You need to number the carbons! u it matters! u 3 refers to the 3 carbon on the sugar u 5 refers to the 5 carbon
Nucleic acids. How DNA works. DNA RNA Protein. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) RNA (ribonucleic acid) Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
 Nucleic acid chemistry and basic molecular theory Nucleic acids DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) RNA (ribonucleic acid) Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Cell cycle DNA RNA Protein Transcription Translation
Nucleic acid chemistry and basic molecular theory Nucleic acids DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) RNA (ribonucleic acid) Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Cell cycle DNA RNA Protein Transcription Translation
Nucleic Acids: How Structure Conveys Information 1. What Is the Structure of DNA? 2. What Are the Levels of Structure in Nucleic Acids? 3.
 Fig. 9-CO, p.215 Nucleic Acids: How Structure Conveys Information 1. What Is the Structure of DNA? 2. What Are the Levels of Structure in Nucleic Acids? 3. What Is the Covalent Structure of Polynucleotides?
Fig. 9-CO, p.215 Nucleic Acids: How Structure Conveys Information 1. What Is the Structure of DNA? 2. What Are the Levels of Structure in Nucleic Acids? 3. What Is the Covalent Structure of Polynucleotides?
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible
DNA and RNA: Structure and Function. 阮雪芬 May 14, 2004
 DNA and RNA: Structure and Function 阮雪芬 May 14, 2004 Two Fundamental types of nucleic acids participate as genetic molecules DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid Found in the chromosome form in the cell s nucleus
DNA and RNA: Structure and Function 阮雪芬 May 14, 2004 Two Fundamental types of nucleic acids participate as genetic molecules DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid Found in the chromosome form in the cell s nucleus
What Are the Chemical Structures and Functions of Nucleic Acids?
 THE NUCLEIC ACIDS What Are the Chemical Structures and Functions of Nucleic Acids? Nucleic acids are polymers specialized for the storage, transmission, and use of genetic information. DNA = deoxyribonucleic
THE NUCLEIC ACIDS What Are the Chemical Structures and Functions of Nucleic Acids? Nucleic acids are polymers specialized for the storage, transmission, and use of genetic information. DNA = deoxyribonucleic
Chapter 17 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
 Chapter 17 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are the components that make up the genetic material DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). DNA is a macromolecule which contains all the
Chapter 17 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are the components that make up the genetic material DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). DNA is a macromolecule which contains all the
Nucleic acids -1 Purines
 Nucleic acids -1 Purines Purine metabolism Purine Biosynthesis: 5-Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide is carboxylated and this is followed by the addition of an aspartic acid to form 5-Aminoimidazole-
Nucleic acids -1 Purines Purine metabolism Purine Biosynthesis: 5-Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide is carboxylated and this is followed by the addition of an aspartic acid to form 5-Aminoimidazole-
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds. Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides
 Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds. Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds. Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1
 AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.5 Nucleic Acids and their functions Page 1 From the syllabus: 1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1 l. Nucleic
AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.5 Nucleic Acids and their functions Page 1 From the syllabus: 1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1 l. Nucleic
Paper 4: Biomolecules and Their Interactions Module 12: Bases, Sugars, Nucleosides and Nucleotides Introduction Nucleic acids are involved in storage
 Paper 4: Biomolecules and Their Interactions Module 12: Bases, Sugars, Nucleosides and Nucleotides Introduction Nucleic acids are involved in storage and transfer of genetic information. The double helical
Paper 4: Biomolecules and Their Interactions Module 12: Bases, Sugars, Nucleosides and Nucleotides Introduction Nucleic acids are involved in storage and transfer of genetic information. The double helical
Part IV => DNA and RNA. 4.1 Nucleotide Properties 4.1a Nucleotide Nomenclature 4.1b DNA Sequencing
 Part IV => DNA and RNA 4.1 Nucleotide Properties 4.1a Nucleotide Nomenclature 4.1b DNA Sequencing The Molecular Dogma of Life DNA carries genetic information in the form of its sequence of nucleotides
Part IV => DNA and RNA 4.1 Nucleotide Properties 4.1a Nucleotide Nomenclature 4.1b DNA Sequencing The Molecular Dogma of Life DNA carries genetic information in the form of its sequence of nucleotides
Lecture 8. Chromosome. The Nuclei. Two Types of Nucleic Acids. Genes. Information Contained Within Each Cell
 Information Contained Within Each Cell Lecture 8 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Chapter 23: Section 1-5 Most higher organisms reproduce sexually! Sperm cell + Egg cell! Fertilized egg The wondrous
Information Contained Within Each Cell Lecture 8 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Chapter 23: Section 1-5 Most higher organisms reproduce sexually! Sperm cell + Egg cell! Fertilized egg The wondrous
translation The building blocks of proteins are? amino acids nitrogen containing bases like A, G, T, C, and U Complementary base pairing links
 The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? translation The building blocks of proteins are? Complementary base pairing links Define and name the Purines amino acids nitrogen
The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? translation The building blocks of proteins are? Complementary base pairing links Define and name the Purines amino acids nitrogen
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry. CHAPTER 10: Nucleic Acids
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 10: Nucleic Acids 2 o Nucleic
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 10: Nucleic Acids 2 o Nucleic
Paper : 03 Structure and Function of Biomolecules II Module: 02 Nucleosides, Nucleotides and type of Nucleic Acids
 Paper : 03 Structure and Function of Biomolecules II Module: 02 Nucleosides, Nucleotides and type of Nucleic Acids Principal Investigator Paper Coordinators Prof. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department
Paper : 03 Structure and Function of Biomolecules II Module: 02 Nucleosides, Nucleotides and type of Nucleic Acids Principal Investigator Paper Coordinators Prof. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department
Biochemistry study of the molecular basis of life
 Biochemistry : An Introduction Biochemistry study of the molecular basis of life n Study of the chemistry of living organisms Studies organic molecules & organic reactions in living organisms n Living
Biochemistry : An Introduction Biochemistry study of the molecular basis of life n Study of the chemistry of living organisms Studies organic molecules & organic reactions in living organisms n Living
The nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
 Nucleic acids are macromolecules composed of chains of mononucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds. The nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Nucleic acids are universal
Nucleic acids are macromolecules composed of chains of mononucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds. The nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Nucleic acids are universal
Chapter 4: How Cells Work
 Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: l l l l l Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription:
Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: l l l l l Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription:
Chapter 4: How Cells Work
 Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription: Sending the
Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription: Sending the
DNA and RNA Structure Guided Notes
 Nucleic acids, especially DNA, are considered as the key biomolecules that guarantee the continuity of life. DNA is the prime genetic molecule which carry all the hereditary information that's passed from
Nucleic acids, especially DNA, are considered as the key biomolecules that guarantee the continuity of life. DNA is the prime genetic molecule which carry all the hereditary information that's passed from
Division Ave. High School Ms. Foglia AP Biology. Nucleic acids. AP Biology Nucleic Acids. Information storage
 Nucleic acids 2006-2007 Nucleic Acids Information storage 2006-2007 1 DNA Nucleic Acids Function: u genetic material stores information w genes w blueprint for building proteins n DNA RNA proteins transfers
Nucleic acids 2006-2007 Nucleic Acids Information storage 2006-2007 1 DNA Nucleic Acids Function: u genetic material stores information w genes w blueprint for building proteins n DNA RNA proteins transfers
Page 1. C) DNA molecules, only D) both DNA and RNA molecules. C) nitrogenous bases D) amino acids. C) starch and glycogen D) fats and oils
 Name: 1) Which molecules are composed of units known as nucleotides? A) messenger RNA molecules, only B) transfer RNA molecules, only 2) The individuality of an organism is determined by the organism's
Name: 1) Which molecules are composed of units known as nucleotides? A) messenger RNA molecules, only B) transfer RNA molecules, only 2) The individuality of an organism is determined by the organism's
Metabolism of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides DNA replication
 Metabolism of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides DNA replication Biochemistry I Lecture 12 2008 (J.S.) 1 Purine and pyrimidine nucleotides are used in large quantities in the biosynthesis of nucleic acids.
Metabolism of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides DNA replication Biochemistry I Lecture 12 2008 (J.S.) 1 Purine and pyrimidine nucleotides are used in large quantities in the biosynthesis of nucleic acids.
Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA
 Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA Living organisms are complex systems. Hundreds of thousands of proteins exist inside each one of us to help carry out our daily functions. These proteins are produced locally,
Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA Living organisms are complex systems. Hundreds of thousands of proteins exist inside each one of us to help carry out our daily functions. These proteins are produced locally,
36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L-
 36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L- 37. The essential fatty acids are A. palmitic acid B. linoleic acid C. linolenic
36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L- 37. The essential fatty acids are A. palmitic acid B. linoleic acid C. linolenic
Double helix structure of DNA
 Replication Double helix structure of It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material. Watson & Crick
Replication Double helix structure of It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material. Watson & Crick
Case 16 Allosteric Regulation of ATCase
 Case 16 Allosteric Regulation of ATCase Focus concept An enzyme involved in nucleotide synthesis is subject to regulation by a variety of combinations of nucleotides. rerequisites roperties of allosteric
Case 16 Allosteric Regulation of ATCase Focus concept An enzyme involved in nucleotide synthesis is subject to regulation by a variety of combinations of nucleotides. rerequisites roperties of allosteric
Concept 5.5: Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary information
 Concept 5.5: Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary information The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide is programmed by a unit of inheritance called a gene Genes are made of DNA, a nucleic acid
Concept 5.5: Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary information The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide is programmed by a unit of inheritance called a gene Genes are made of DNA, a nucleic acid
C. Incorrect! Threonine is an amino acid, not a nucleotide base.
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 05: RNA and Protein Biosynthesis Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following bases are only found in RNA? Question #01 (A) Ribose. (B) Uracil. (C) Threonine. (D) Adenine.
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 05: RNA and Protein Biosynthesis Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following bases are only found in RNA? Question #01 (A) Ribose. (B) Uracil. (C) Threonine. (D) Adenine.
8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids W. H. Freeman and Company
 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 1 Week 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 8.1 Some Basics 8.2 Nucleic Acid Structure 8.3 Nucleic Acid Chemistry 8.4 Other Functions of Nucleotides
8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 1 Week 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 8.1 Some Basics 8.2 Nucleic Acid Structure 8.3 Nucleic Acid Chemistry 8.4 Other Functions of Nucleotides
1-Microbial Taxonomy: classification nomenclature identification
 Part 1 Basic Medical Microbiology 1-Microbial Taxonomy: Taxonomy is the area of biologic science comprising three distinct, but highly interrelated, disciplines that include classification, nomenclature,
Part 1 Basic Medical Microbiology 1-Microbial Taxonomy: Taxonomy is the area of biologic science comprising three distinct, but highly interrelated, disciplines that include classification, nomenclature,
Nucleic acids. The building blocks. Phosphates
 Nucleic acids Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleic acids found in the nuclei of living cells. They are the vehicles of genetic inheritance. Nucleic acids are condensation
Nucleic acids Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleic acids found in the nuclei of living cells. They are the vehicles of genetic inheritance. Nucleic acids are condensation
RNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
 RNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA & RNA Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins within the cell. The first step in decoding these genetic messages is to copy part of the nucleotide
RNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA & RNA Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins within the cell. The first step in decoding these genetic messages is to copy part of the nucleotide
Nucleic Acids. The Ribose Sugar
 Nucleic cids adenosine triphosphate (TP) a mononucleotide Nucleic acids consist of: a ribose (aldopentose) sugar; a heteroaromatic, glycosidic base; a phosphoester. ribonucleic acid (RN) a polynucleotide
Nucleic cids adenosine triphosphate (TP) a mononucleotide Nucleic acids consist of: a ribose (aldopentose) sugar; a heteroaromatic, glycosidic base; a phosphoester. ribonucleic acid (RN) a polynucleotide
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush I. Hierarchical structure of nucleic acids II. Structures of nucleotides A. Purines & pyrimidines B. Nucleosides & nucleotides
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush I. Hierarchical structure of nucleic acids II. Structures of nucleotides A. Purines & pyrimidines B. Nucleosides & nucleotides
The Biochemistry Of The Nucleic Acids
 The Biochemistry Of The Nucleic Acids 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Biochemistry Of The Nucleic Introduction. Nucleotides are found primarily as the monomeric units comprising the major nucleic acids of the cell,
The Biochemistry Of The Nucleic Acids 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Biochemistry Of The Nucleic Introduction. Nucleotides are found primarily as the monomeric units comprising the major nucleic acids of the cell,
Dina Al-Tamimi. Faisal Nimri. Ma amoun Ahram. 1 P a g e
 1 Dina Al-Tamimi Faisal Nimri Ma amoun Ahram 1 P a g e **Difference between Molecular Biology and Genetics: Molecular Biology: is a fancy term of biochemistry. It is the science that deals with DNA, RNA
1 Dina Al-Tamimi Faisal Nimri Ma amoun Ahram 1 P a g e **Difference between Molecular Biology and Genetics: Molecular Biology: is a fancy term of biochemistry. It is the science that deals with DNA, RNA
Watson & Crick. DNA Replication. Directionality of DNA. Double helix structure of DNA. The DNA backbone. Anti-parallel strands
 Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of Directionality of You need to number the carbons! it matters! P 4 nucleotide N base This will be IMPRTANT!! 4 ribose
Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of Directionality of You need to number the carbons! it matters! P 4 nucleotide N base This will be IMPRTANT!! 4 ribose
RNA is a single strand molecule composed of subunits called nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds.
 The Versatility of RNA Primary structure of RNA RNA is a single strand molecule composed of subunits called nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds. Each nucleotide subunit is composed of a ribose sugar,
The Versatility of RNA Primary structure of RNA RNA is a single strand molecule composed of subunits called nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds. Each nucleotide subunit is composed of a ribose sugar,
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points
 Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the back of the
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the back of the
Nucleic acids AP Biology
 Nucleic acids 2006-2007 Nucleic Acids Information storage 2006-2007 Nucleic Acids Function: u genetic material DNA stores information w genes w blueprint for building proteins n DNA RNA proteins transfers
Nucleic acids 2006-2007 Nucleic Acids Information storage 2006-2007 Nucleic Acids Function: u genetic material DNA stores information w genes w blueprint for building proteins n DNA RNA proteins transfers
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 3 v Nucleic acids Ø Polymers specialized for the storage transmission and use of genetic information Ø Two types DNA
 AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 3 v Nucleic acids Ø Polymers specialized for the storage transmission and use of genetic information Ø Two types DNA Encodes hereditary information Used to specify the amino
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 3 v Nucleic acids Ø Polymers specialized for the storage transmission and use of genetic information Ø Two types DNA Encodes hereditary information Used to specify the amino
Chapter 12: Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Biology Textbook Notes Chapter 12: Molecular Biology of the Gene p. 214-219 The Genetic Material (12.1) - Genetic Material must: 1. Be able to store information that pertains to the development, structure,
Biology Textbook Notes Chapter 12: Molecular Biology of the Gene p. 214-219 The Genetic Material (12.1) - Genetic Material must: 1. Be able to store information that pertains to the development, structure,
BIOCHEMISTRY Nucleic Acids
 BIOCHEMISTRY Nucleic Acids BIOB111 CHEMISTRY & BIOCHEMISTRY Session 17 Session Plan Types of Nucleic Acids Nucleosides Nucleotides Primary Structure of Nucleic Acids DNA Double Helix DNA Replication Types
BIOCHEMISTRY Nucleic Acids BIOB111 CHEMISTRY & BIOCHEMISTRY Session 17 Session Plan Types of Nucleic Acids Nucleosides Nucleotides Primary Structure of Nucleic Acids DNA Double Helix DNA Replication Types
Chapter 11. Nucleic Acids. Nucleotides. BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 11 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Chapter 11, page 1
 BC 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 11 Lecture otes 1 Chapter 11 ucleotides and ucleic Acids 2 ucleic Acids Two classes DA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) RA (Ribonucleic Acid) Polymers of nucleotides DA carries genetic
BC 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 11 Lecture otes 1 Chapter 11 ucleotides and ucleic Acids 2 ucleic Acids Two classes DA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) RA (Ribonucleic Acid) Polymers of nucleotides DA carries genetic
PHYS 498 HW3 Solutions: 1. We have two equations: (1) (2)
 PHYS 498 HW3 Solutions: 1. We have two equations: (1) (2) Where Conc is the initial concentration of [B] or [SA] Since [B] = [SA], the second equation simplifies to: (3) Using equation (1) and (3), we
PHYS 498 HW3 Solutions: 1. We have two equations: (1) (2) Where Conc is the initial concentration of [B] or [SA] Since [B] = [SA], the second equation simplifies to: (3) Using equation (1) and (3), we
6 Enzymes II W. H. Freeman and Company
 6 Enzymes II 2017 W. H. Freeman and Company The role of an enzyme in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is to: A. bind a transition state intermediate, such that it cannot be converted back to substrate. B.
6 Enzymes II 2017 W. H. Freeman and Company The role of an enzyme in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is to: A. bind a transition state intermediate, such that it cannot be converted back to substrate. B.
Gene and DNA structure. Dr Saeb Aliwaini
 Gene and DNA structure Dr Saeb Aliwaini 2016 DNA during cell cycle Cell cycle for different cell types Molecular Biology - "Study of the synthesis, structure, and function of macromolecules (DNA, RNA,
Gene and DNA structure Dr Saeb Aliwaini 2016 DNA during cell cycle Cell cycle for different cell types Molecular Biology - "Study of the synthesis, structure, and function of macromolecules (DNA, RNA,
DNA Structure, Function, and Engineering Page /14/2018 Dr. Amjid Iqbal 1
 DNA Structure, Function, and Engineering Page 40-51 2/14/2018 Dr. Amjid Iqbal 1 Background Organisms exhibit striking similarity at the molecular level. The structures and metabolic activities of all cells
DNA Structure, Function, and Engineering Page 40-51 2/14/2018 Dr. Amjid Iqbal 1 Background Organisms exhibit striking similarity at the molecular level. The structures and metabolic activities of all cells
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Amended by
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Amended by
DNA and RNA Structure. Unit 7 Lesson 1
 Unit 7 Lesson 1 Students will be able to: Explain the structure and function of the DNA and RNA. Illustrate the structure of nucleotide. Summarize the differences between DNA and RNA. Identify the different
Unit 7 Lesson 1 Students will be able to: Explain the structure and function of the DNA and RNA. Illustrate the structure of nucleotide. Summarize the differences between DNA and RNA. Identify the different
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE. Lecture Presentation by Cindy S. Malone, PhD, California State University Northridge. FIFTH EDITION Freeman Quillin Allison
 BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE FIFTH EDITION Freeman Quillin Allison 4 Lecture Presentation by Cindy S. Malone, PhD, California State University Northridge In this chapter you will learn that Nucleic acids store the
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE FIFTH EDITION Freeman Quillin Allison 4 Lecture Presentation by Cindy S. Malone, PhD, California State University Northridge In this chapter you will learn that Nucleic acids store the
