Biosynthesis of nucleotides
|
|
|
- Collin Perkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biosynthesis of nucleotides De novo pathways De novo purine nucleotide synthesis Regulation of purine biosynthesis De novo pyrimidine nucleotides biosynthesis Salvage pathways Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
2 Why is the biosynthesis of nucleotides important? Nucleotides play a variety of important roles in all cells They are precursors of DNA and RNA. They are essential carriers of chemical energy a role primary of ATP and to some extent GTP. They are component of cofactors NAD, FAD, S-adenosylmethionine and coenzyme A, as well as of activated biosynthetic intermediates such as UDPglucose, and CDP-diacylglycerol Some such as camp, and cgmp, are also cellular second messengers. 2 types of pathways lead to nucleotides the de novo pathway and salvage pathway.
3 De novo pathways De novo synthesis of nucleotides begins with their metabolic precursors: amino acids, ribose 5-phosphate, CO 2 and NH 3. The de novo pathways for purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis appear to be nearly identical in all living organisms. The purine ring structure is built up one or a few atoms at atime, attached to ribose throughout the process. The pyrimidine ring is synthesized as orotate, attached to ribose phosphate, and then converted to the common pyrimidine nucleotides required in nucleic acid synthesis. Phosophoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) is important in both purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis
4 De novo purine nucleotide synthesis begins with PRPP 2 parent purine nucleotides AMP and GMP This pathway begins with PRPP. This pathway beside shows the origin of the carbon and nitrogen atom of the purine ring system. Glutamine Glycine Formyl H folate Aspartate And ATP 11 Steps to form inosinate(imp)
5 Biosynthesis of AMP and GMP from IMP Conversion of inosinate to adenylate requires the insertion of amino group derived from aspartate, this takes place in two reactions. A crucial difference is that GTP rather than ATP is source of the high-energy phosphate in synthesizing adenylosuccinate. Gluanylate is formed by the NAD + - requiring oxidation of inosinate at C-2. Followed by addition of an amino group derived from glutamine. ATP is cleaved to AMP and PP in the final step.
6 Regulation of purine biosynthesis 3 major feedback mechanism: 1) Inhibition of glutamine-prpp aminotransferase by IMP, AMP and GMP. AMP and GMP act synergistically. 2) Inhibition of IMP dehydrogenase by GMP. Inhibition of adenylosuccinate synthetase by AMP does not affecting the formation of GMP. 3) Inhibition of PRPP synthesis by ribose phosphate pyrophosphokinase. This enzyme is inhibited by ADP and GDP.
7 De novo pyrimidine nucleotides biosynthesis The common pyrimidine ribonucleotides are CMP (Cytidylate) and UMP (uridylate). De novo pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis proceeds in the some what different manner from purine. The pyrimidine is constructed from carbamoyl phosphate and aspartate. The ribose 5-phosphate is then added to completed pyrimidine by orotate phosphoribosyltransferase.
8 Thymidylate is derived from dcdp and dump DNA contain thymine rather than uracil, and de novo pathway to thymine involve only deoxyribonucleotides. The immediate precursor of thymidylate (dtmp) is dump. Ribonucleotide reductase. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase Deaminase dutp ase Thymidylate synthase
9 Salvage pathways Free purine and pyrimidine bases are constantly released in the cells during the metabolic degradation of nucleotides. Free purine are in large part salvaged and reused to make nucleotides, in a pathway much simpler than de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides. One of the primary salvage pathways consists of a single reaction catalyzed by adenosine phosphoribosyltransferase, in which free adenine react with PRPP to yield the corresponding adenine nucleotide: Adenine +PRPP AMP + PP i Free guanine and hypoxanthine are salvaged in the same way by hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. A similar salvage pathway exists for pyrimidine bases in microorganism, and possible in mammals. A genetic lack of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase activity, seen almost exclusively in male children, results in a bizarre set of syndrome called Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
10 Lesch-Nyhan syndrome A genetic lack of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase activity, Children with this genetic disorder, which become manifest by the age of 2 years. Are sometimes poorly coordinated and mentally retarded. In addition, they are extremely hostile and show compulsive self-destructive tendencies. They mutilate themselves by biting off their fingers, toes, and lips
Nucleotide Metabolism Biochemistry by Lippincott pp
 Nucleotide Metabolism Biochemistry by Lippincott pp 291-306 Metabolism: CONCEPT Ø Metabolism is the totality of an organism s chemical reactions. Ø A metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and
Nucleotide Metabolism Biochemistry by Lippincott pp 291-306 Metabolism: CONCEPT Ø Metabolism is the totality of an organism s chemical reactions. Ø A metabolic pathway begins with a specific molecule and
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Diala
 number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala 1 P a g e Nucleotide metabolism In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala 1 P a g e Nucleotide metabolism In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala Nucleotide metabolism 1 P age In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala Nucleotide metabolism 1 P age In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
Lipid Metabolism. Lipid Metabolism. Lipid Metabolism
 Chem 352 - Lecture 10 Lipid, Amino Acid, and Nucleotide Metabolism Part III: Nucleotide Metabolism 1 Lipid Metabolism 2-1 Chem 352, Lecture 10, Part I: Lipid Metabolism 2 Lipid Metabolism 2-2 Question:
Chem 352 - Lecture 10 Lipid, Amino Acid, and Nucleotide Metabolism Part III: Nucleotide Metabolism 1 Lipid Metabolism 2-1 Chem 352, Lecture 10, Part I: Lipid Metabolism 2 Lipid Metabolism 2-2 Question:
I. NUCLEOTIDES. Nitrogenous bases are frequently represented by single letter abbreviations. The abbreviations for several bases are shown below:
 Biochemistry II Nucleotide Metabolism I. NUCLEOTIDES Nitrogenous bases are frequently represented by single letter abbreviations. The abbreviations for several bases are shown below: Common Nitrogenous
Biochemistry II Nucleotide Metabolism I. NUCLEOTIDES Nitrogenous bases are frequently represented by single letter abbreviations. The abbreviations for several bases are shown below: Common Nitrogenous
Nucleotide Metabolism
 Nucleotide Metabolism Nucleotide Synthesis De Novo Pathway Synthesize purine and pyrimidine nucleotides from low M.W. precursors Salvage Pathway synthesize nucleotides from nucleosides of nucleobases NB:
Nucleotide Metabolism Nucleotide Synthesis De Novo Pathway Synthesize purine and pyrimidine nucleotides from low M.W. precursors Salvage Pathway synthesize nucleotides from nucleosides of nucleobases NB:
Biochem for the Boards 2nd Edition
 Biochem for the Boards! Biochem for the Boards 2nd Edition Active Learning Workbook for the BDE 1, DDS, MA Bonus Chapter ucleotide Metabolism Socrates Publishing Co. ew York, Y Page 1 ucleotide Metabolism
Biochem for the Boards! Biochem for the Boards 2nd Edition Active Learning Workbook for the BDE 1, DDS, MA Bonus Chapter ucleotide Metabolism Socrates Publishing Co. ew York, Y Page 1 ucleotide Metabolism
GENERAL NUCLEIC ACID BIOCHEMISTRY 461, FALL A two (2) unit course for non-biochemistry majors only.
 GENERAL NUCLEIC ACID BIOCHEMISTRY 461, FALL 2010 A two (2) unit course for non-biochemistry majors only. PREREQUISITES: Biology 181 Organic Chemistry (Chem 241a,b) Concurrent/previous registration in Biochemistry
GENERAL NUCLEIC ACID BIOCHEMISTRY 461, FALL 2010 A two (2) unit course for non-biochemistry majors only. PREREQUISITES: Biology 181 Organic Chemistry (Chem 241a,b) Concurrent/previous registration in Biochemistry
Password: LECTURE 7: NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM
 http://smtom.lecture.ub.ac.id/ Password: LECTURE 7: NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM 51 All humans are 99,7% identical at DNA sequence level, and yet all of us carry a significant number of glitches in our genomes.
http://smtom.lecture.ub.ac.id/ Password: LECTURE 7: NUCLEOTIDE METABOLISM 51 All humans are 99,7% identical at DNA sequence level, and yet all of us carry a significant number of glitches in our genomes.
Nucleotide Metabolism
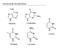 Nucleotide Metabolism Adenine Guanidine Uracil Thymine Cytosine Last Week Nucleotide Metabolism - Mostly, we think of nucleotides as being part of RNA/DNA, but now that we ve studied metabolism, we know
Nucleotide Metabolism Adenine Guanidine Uracil Thymine Cytosine Last Week Nucleotide Metabolism - Mostly, we think of nucleotides as being part of RNA/DNA, but now that we ve studied metabolism, we know
BIOC 312. Gehring Lecture 1 Jan 12
 Gehring Lecture 1 Jan 12 BIOC 312 Lecture Plan for Gehring (all lectures): 1) nomenclature, purine biosynthesis 2) pyrimidine biosynth, formation of tri-diphosphates, ribonucleotide reductase 3) Thymidylate
Gehring Lecture 1 Jan 12 BIOC 312 Lecture Plan for Gehring (all lectures): 1) nomenclature, purine biosynthesis 2) pyrimidine biosynth, formation of tri-diphosphates, ribonucleotide reductase 3) Thymidylate
Student Name Biochem. 461 Exam 1 Key, September 23, 2010
 Student Name Biochem. 461 Exam 1 Key, September 23, 2010 (100 POINTS TOTAL) ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED [10 pts] We will learn in Chapter 28 that ribonuclosides and deoxyribonucleosides
Student Name Biochem. 461 Exam 1 Key, September 23, 2010 (100 POINTS TOTAL) ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED [10 pts] We will learn in Chapter 28 that ribonuclosides and deoxyribonucleosides
Nucleotide Metabolism December 12-17, 2008 Dr. Robert Lyons. See: for supplementary course materials.
 1 2 ucleotide Metabolism December 12-17, 2008 Dr. Robert Lyons See: http://seqcore.brcf.med.umich.edu/mcb500 for supplementary course materials. Medical relevance of nucleotide pathways Critical in cancer
1 2 ucleotide Metabolism December 12-17, 2008 Dr. Robert Lyons See: http://seqcore.brcf.med.umich.edu/mcb500 for supplementary course materials. Medical relevance of nucleotide pathways Critical in cancer
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Dr. Robert Lyons, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Dr. Robert Lyons, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Nucleic Acids. Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology 1
 Nucleic Acids Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology 1 Topics : 2 hrs - Nucleic acid ----------------------------- Nucleic acid structure
Nucleic Acids Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology 1 Topics : 2 hrs - Nucleic acid ----------------------------- Nucleic acid structure
Lecture 8. Chromosome. The Nuclei. Two Types of Nucleic Acids. Genes. Information Contained Within Each Cell
 Information Contained Within Each Cell Lecture 8 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Chapter 23: Section 1-5 Most higher organisms reproduce sexually! Sperm cell + Egg cell! Fertilized egg The wondrous
Information Contained Within Each Cell Lecture 8 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Chapter 23: Section 1-5 Most higher organisms reproduce sexually! Sperm cell + Egg cell! Fertilized egg The wondrous
Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids
 Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids E T Nyahangare Class Assignment 1. Write notes and outline the role of the following in protein biosynthesis a. DNA replication b. Transcription c. Genetic code
Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids E T Nyahangare Class Assignment 1. Write notes and outline the role of the following in protein biosynthesis a. DNA replication b. Transcription c. Genetic code
Nucleotide Metabolism
 Nucleotide Metabolism Dr. Chalermchai Mitrpant Outline Content Page Function of nucleotide 2 Nucleotide synthesis 3-6 Purine synthesis and its regulation 3-4 Pyrimidine synthesis and its regulation 5-6
Nucleotide Metabolism Dr. Chalermchai Mitrpant Outline Content Page Function of nucleotide 2 Nucleotide synthesis 3-6 Purine synthesis and its regulation 3-4 Pyrimidine synthesis and its regulation 5-6
36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L-
 36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L- 37. The essential fatty acids are A. palmitic acid B. linoleic acid C. linolenic
36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L- 37. The essential fatty acids are A. palmitic acid B. linoleic acid C. linolenic
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds
 Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License.
 Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License. Copyright 2007, Robert Lyons. The following information is intended
Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License. Copyright 2007, Robert Lyons. The following information is intended
Biosynthesis. Amino acids, N-containing molecules Nucleotides
 Biosynthesis Amino acids, N-containing molecules Nucleotides 1 Modified Fig 22-9 p. 827 Biosynthesis of A.A. Glucose All C derived from intermediates in Glycolysis 3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG) Phosphoenolpyruvate
Biosynthesis Amino acids, N-containing molecules Nucleotides 1 Modified Fig 22-9 p. 827 Biosynthesis of A.A. Glucose All C derived from intermediates in Glycolysis 3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG) Phosphoenolpyruvate
A. Incorrect! A sugar residue is only part of a nucleotide. Go back and review the structure of nucleotides.
 Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 24: ucleic Acids o. 1 of 10 1. What are the components of a nucleotide? (A) A sugar residue (B) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous base (C) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous
Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 24: ucleic Acids o. 1 of 10 1. What are the components of a nucleotide? (A) A sugar residue (B) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous base (C) A sugar residue + a nitrogenous
Figure S1: Time course of the energy charge in trehalose-grown wild-type and adk1 mutant cells after sudden increase of glucose concentration to 110
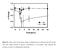 Figure S1: Time course of the energy charge in trehalose-grown wild-type and adk1 mutant cells after sudden increase of glucose concentration to 110 mmol/l. Data represent the average of at least two independent
Figure S1: Time course of the energy charge in trehalose-grown wild-type and adk1 mutant cells after sudden increase of glucose concentration to 110 mmol/l. Data represent the average of at least two independent
Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotide
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM. Omidiwura, B.R.O
 NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM Omidiwura, B.R.O Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid
NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM Omidiwura, B.R.O Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds. Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides
 Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
DNA and RNA Structure Guided Notes
 Nucleic acids, especially DNA, are considered as the key biomolecules that guarantee the continuity of life. DNA is the prime genetic molecule which carry all the hereditary information that's passed from
Nucleic acids, especially DNA, are considered as the key biomolecules that guarantee the continuity of life. DNA is the prime genetic molecule which carry all the hereditary information that's passed from
Nucleic Acids. By Sarah, Zach, Joanne, and Dean
 Nucleic Acids By Sarah, Zach, Joanne, and Dean Basic Functions Carry genetic information (DNA storing it) Protein synthesis Helps in cell division (DNA replicates itself) RNA- numerous functions during
Nucleic Acids By Sarah, Zach, Joanne, and Dean Basic Functions Carry genetic information (DNA storing it) Protein synthesis Helps in cell division (DNA replicates itself) RNA- numerous functions during
Nucleic acids -1 Purines
 Nucleic acids -1 Purines Purine metabolism Purine Biosynthesis: 5-Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide is carboxylated and this is followed by the addition of an aspartic acid to form 5-Aminoimidazole-
Nucleic acids -1 Purines Purine metabolism Purine Biosynthesis: 5-Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide is carboxylated and this is followed by the addition of an aspartic acid to form 5-Aminoimidazole-
1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1
 AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.5 Nucleic Acids and their functions Page 1 From the syllabus: 1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1 l. Nucleic
AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.5 Nucleic Acids and their functions Page 1 From the syllabus: 1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1 l. Nucleic
Chapter 17 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
 Chapter 17 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are the components that make up the genetic material DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). DNA is a macromolecule which contains all the
Chapter 17 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are the components that make up the genetic material DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). DNA is a macromolecule which contains all the
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I)
 Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I) Microbial Metabolism Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions that occur within a living organism. These chemical reactions are generally of two types: Catabolic:
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I) Microbial Metabolism Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions that occur within a living organism. These chemical reactions are generally of two types: Catabolic:
Enzymes, ATP and Bioenergetics
 Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College Enzymes, ATP and Bioenergetics Bioenergetics Bioenergetics can be defined as energy transfer mechanisms occurring within living organisms.
Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College Enzymes, ATP and Bioenergetics Bioenergetics Bioenergetics can be defined as energy transfer mechanisms occurring within living organisms.
Central Dogma. 1. Human genetic material is represented in the diagram below.
 Central Dogma 1. Human genetic material is represented in the diagram below. 4. If 15% of a DNA sample is made up of thymine, T, what percentage of the sample is made up of cytosine, C? A) 15% B) 35% C)
Central Dogma 1. Human genetic material is represented in the diagram below. 4. If 15% of a DNA sample is made up of thymine, T, what percentage of the sample is made up of cytosine, C? A) 15% B) 35% C)
8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids W. H. Freeman and Company
 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 1 Week 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 8.1 Some Basics 8.2 Nucleic Acid Structure 8.3 Nucleic Acid Chemistry 8.4 Other Functions of Nucleotides
8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 1 Week 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 8.1 Some Basics 8.2 Nucleic Acid Structure 8.3 Nucleic Acid Chemistry 8.4 Other Functions of Nucleotides
CHAPTER 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
 CHAPTER 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Key topics Biological function of nucleotides and nucleic acids Structures of common nucleotides Structure of double-stranded DNA Structures of ribonucleic acids
CHAPTER 8 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Key topics Biological function of nucleotides and nucleic acids Structures of common nucleotides Structure of double-stranded DNA Structures of ribonucleic acids
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 16 Monday 1 March
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 16 Monday 1 March Review Primary Structure of a portion of a polypeptide chain backbone of Polypeptide chain R-groups of amino acids Native conformation of a dimeric protein,
BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 16 Monday 1 March Review Primary Structure of a portion of a polypeptide chain backbone of Polypeptide chain R-groups of amino acids Native conformation of a dimeric protein,
Part IV => DNA and RNA. 4.1 Nucleotide Properties 4.1a Nucleotide Nomenclature 4.1b DNA Sequencing
 Part IV => DNA and RNA 4.1 Nucleotide Properties 4.1a Nucleotide Nomenclature 4.1b DNA Sequencing The Molecular Dogma of Life DNA carries genetic information in the form of its sequence of nucleotides
Part IV => DNA and RNA 4.1 Nucleotide Properties 4.1a Nucleotide Nomenclature 4.1b DNA Sequencing The Molecular Dogma of Life DNA carries genetic information in the form of its sequence of nucleotides
Paper : 03 Structure and Function of Biomolecules II Module: 02 Nucleosides, Nucleotides and type of Nucleic Acids
 Paper : 03 Structure and Function of Biomolecules II Module: 02 Nucleosides, Nucleotides and type of Nucleic Acids Principal Investigator Paper Coordinators Prof. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department
Paper : 03 Structure and Function of Biomolecules II Module: 02 Nucleosides, Nucleotides and type of Nucleic Acids Principal Investigator Paper Coordinators Prof. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department
DNA and RNA Structure. Unit 7 Lesson 1
 Unit 7 Lesson 1 Students will be able to: Explain the structure and function of the DNA and RNA. Illustrate the structure of nucleotide. Summarize the differences between DNA and RNA. Identify the different
Unit 7 Lesson 1 Students will be able to: Explain the structure and function of the DNA and RNA. Illustrate the structure of nucleotide. Summarize the differences between DNA and RNA. Identify the different
CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis General, rganic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis Learning bjectives: q Nucleosides & Nucleo@des:
CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis General, rganic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis Learning bjectives: q Nucleosides & Nucleo@des:
Biomolecules: nucleotides
 Biomolecules: nucleotides Nucleotides and nucleic acids Nucleic acids are linear hetero-polymers adapted to maintain and transmit the genetic information Depending on their sugar moiety they can be classified
Biomolecules: nucleotides Nucleotides and nucleic acids Nucleic acids are linear hetero-polymers adapted to maintain and transmit the genetic information Depending on their sugar moiety they can be classified
Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids. Central Dogma of Biology
 Roles: Energy currency (ATP, GTP) Chemical links in response of cells to hormones (camp) Involved in cofactors (NAD, FAD, CoA) Metabolic intermediates (acetyl CoA) Constituents of nucleic acids, DNA and
Roles: Energy currency (ATP, GTP) Chemical links in response of cells to hormones (camp) Involved in cofactors (NAD, FAD, CoA) Metabolic intermediates (acetyl CoA) Constituents of nucleic acids, DNA and
Paper 4: Biomolecules and Their Interactions Module 12: Bases, Sugars, Nucleosides and Nucleotides Introduction Nucleic acids are involved in storage
 Paper 4: Biomolecules and Their Interactions Module 12: Bases, Sugars, Nucleosides and Nucleotides Introduction Nucleic acids are involved in storage and transfer of genetic information. The double helical
Paper 4: Biomolecules and Their Interactions Module 12: Bases, Sugars, Nucleosides and Nucleotides Introduction Nucleic acids are involved in storage and transfer of genetic information. The double helical
Page 1. C) DNA molecules, only D) both DNA and RNA molecules. C) nitrogenous bases D) amino acids. C) starch and glycogen D) fats and oils
 Name: 1) Which molecules are composed of units known as nucleotides? A) messenger RNA molecules, only B) transfer RNA molecules, only 2) The individuality of an organism is determined by the organism's
Name: 1) Which molecules are composed of units known as nucleotides? A) messenger RNA molecules, only B) transfer RNA molecules, only 2) The individuality of an organism is determined by the organism's
Please contact us if any parts are missing or damaged. DNA Backbone
 DNA Starter Kit Contents 1-Group Set Contents 12 Red Foam Adenine Bases (DNASK-R-A) 12 Blue Foam Cytosine Bases (DNASK-R-C) 12 Green Foam Guanine Bases (DNASK-R-G) 12 Yellow Foam Thymine Bases (DNASK-R-T)
DNA Starter Kit Contents 1-Group Set Contents 12 Red Foam Adenine Bases (DNASK-R-A) 12 Blue Foam Cytosine Bases (DNASK-R-C) 12 Green Foam Guanine Bases (DNASK-R-G) 12 Yellow Foam Thymine Bases (DNASK-R-T)
ATP GTP UTP CTP
 Table S1. ATP (GTP) utilization for de novo synthesis of rtps ucleotide 5 phosphoribosyl ucleobase rmp rtp (total) pyrophosphate from glucose ATP 3 5 8 10 GTP 3 5 8 10 UTP 3 2 5 7 CTP 3 3 6 8 The numbers
Table S1. ATP (GTP) utilization for de novo synthesis of rtps ucleotide 5 phosphoribosyl ucleobase rmp rtp (total) pyrophosphate from glucose ATP 3 5 8 10 GTP 3 5 8 10 UTP 3 2 5 7 CTP 3 3 6 8 The numbers
Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Lecture - 16 Nucleic Acids - I
 Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture - 16 Nucleic Acids - I We start our discussion on Nucleic Acids and their components. Before we
Biochemistry Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Lecture - 16 Nucleic Acids - I We start our discussion on Nucleic Acids and their components. Before we
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 SEMMELWEIS UIVERSITY PETER PAZMAY ATLI UIVERSITY Development of omplex urricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** onsortium leader PETER PAZMAY ATLI UIVERSITY
SEMMELWEIS UIVERSITY PETER PAZMAY ATLI UIVERSITY Development of omplex urricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** onsortium leader PETER PAZMAY ATLI UIVERSITY
Biochemistry 694:301 Final Exam, Deis
 Biochemistry 694:301 Final Exam, Deis Mon., May 8, 2006 Name Row Letter Seat Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth two points. Answer the
Biochemistry 694:301 Final Exam, Deis Mon., May 8, 2006 Name Row Letter Seat Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth two points. Answer the
DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
 http://faculty.uca.edu/~johnc/mbi1440.htm DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis http://www.wappingersschools.org/rck/staff/teacherhp/johnson/visualvocab/mrna.gif DNA base pairs carry the genetic Section 12-1
http://faculty.uca.edu/~johnc/mbi1440.htm DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis http://www.wappingersschools.org/rck/staff/teacherhp/johnson/visualvocab/mrna.gif DNA base pairs carry the genetic Section 12-1
Syllabus for GUTS Lecture on DNA and Nucleotides
 Syllabus for GUTS Lecture on DNA and Nucleotides I. Introduction. DNA is the instruction manual for how to build a living organism here on earth. The instructions in DNA are propagated to future generations
Syllabus for GUTS Lecture on DNA and Nucleotides I. Introduction. DNA is the instruction manual for how to build a living organism here on earth. The instructions in DNA are propagated to future generations
NUCLEIC ACID. Subtitle
 NUCLEIC ACID Subtitle NUCLEIC ACID Building blocks of living organisms One of the four important biomolecule 1 st isolated from the nuclei of white blood cells by Friedrich Miescher (1860) Came from the
NUCLEIC ACID Subtitle NUCLEIC ACID Building blocks of living organisms One of the four important biomolecule 1 st isolated from the nuclei of white blood cells by Friedrich Miescher (1860) Came from the
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Amended by
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Amended by
* What are the nucleic acids?
 Nucleic Acids This lecture is meant to be a refreshment, it s a brief introduction to nucleic acids since we ll be given a full course about it next year in molecular biology. One last lecture and you
Nucleic Acids This lecture is meant to be a refreshment, it s a brief introduction to nucleic acids since we ll be given a full course about it next year in molecular biology. One last lecture and you
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds. Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides
 Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds. Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds Porphyrins Purines and pyrimidines Nucleosides and nucleotides Introduction to Heterocyclic Compounds. Cyclic compounds with one or more other elements along with carbon
Human tissue information processing
 Human tissue information processing JELENKA SAVKOVICSTEVANOVIC Faulty of Technology and Metallury, Belgrade University,Karnegijeva 4, 11000 Belgrade SERBIA, savkovic@tmf.bg.ac.rs Abstract:In this paper
Human tissue information processing JELENKA SAVKOVICSTEVANOVIC Faulty of Technology and Metallury, Belgrade University,Karnegijeva 4, 11000 Belgrade SERBIA, savkovic@tmf.bg.ac.rs Abstract:In this paper
RNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
 RNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA & RNA Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins within the cell. The first step in decoding these genetic messages is to copy part of the nucleotide
RNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA & RNA Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins within the cell. The first step in decoding these genetic messages is to copy part of the nucleotide
Which diagram represents a DNA nucleotide? A) B) C) D)
 3594-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) What is a definition of the term "gene"? A) a transfer-rna nucleotide sequence specific for a particular amino acid B) three messenger-rna nucleotides coded for a specific amino
3594-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) What is a definition of the term "gene"? A) a transfer-rna nucleotide sequence specific for a particular amino acid B) three messenger-rna nucleotides coded for a specific amino
Biochemistry study of the molecular basis of life
 Biochemistry : An Introduction Biochemistry study of the molecular basis of life n Study of the chemistry of living organisms Studies organic molecules & organic reactions in living organisms n Living
Biochemistry : An Introduction Biochemistry study of the molecular basis of life n Study of the chemistry of living organisms Studies organic molecules & organic reactions in living organisms n Living
CHAPTER 31 NUCLEIC ACIDS AND HEREDITY SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS. ƒ H. Guanine H O. Uracil
 CAPTER 31 UCLEIC ACIDS AD EREDITY SLUTIS T REVIEW QUESTIS 1. The five nitrogen bases found in nucleotides: 3 C 2 Adenine Thymine Guanine Uracil 2 2 Cytosine 2. A nucleoside is a purine or pyrimidine base
CAPTER 31 UCLEIC ACIDS AD EREDITY SLUTIS T REVIEW QUESTIS 1. The five nitrogen bases found in nucleotides: 3 C 2 Adenine Thymine Guanine Uracil 2 2 Cytosine 2. A nucleoside is a purine or pyrimidine base
DNA Structure, Function, and Engineering Page /14/2018 Dr. Amjid Iqbal 1
 DNA Structure, Function, and Engineering Page 40-51 2/14/2018 Dr. Amjid Iqbal 1 Background Organisms exhibit striking similarity at the molecular level. The structures and metabolic activities of all cells
DNA Structure, Function, and Engineering Page 40-51 2/14/2018 Dr. Amjid Iqbal 1 Background Organisms exhibit striking similarity at the molecular level. The structures and metabolic activities of all cells
Control of Metabolic Processes
 Control of Metabolic Processes Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College As described earlier, the metabolic processes occurring within living organisms (glycolysis, respiration,
Control of Metabolic Processes Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College As described earlier, the metabolic processes occurring within living organisms (glycolysis, respiration,
Proteins Amides from Amino Acids
 Chapter 26 and Chapter 28 Proteins Amides from Amino Acids Amino acids contain a basic amino group and an acidic carboxyl group Joined as amides between the ¾NH 2 of one amino acid and the ¾CO 2 H to the
Chapter 26 and Chapter 28 Proteins Amides from Amino Acids Amino acids contain a basic amino group and an acidic carboxyl group Joined as amides between the ¾NH 2 of one amino acid and the ¾CO 2 H to the
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA
 RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function
 Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
Chapter 11. Nucleic Acids. Nucleotides. BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 11 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Chapter 11, page 1
 BC 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 11 Lecture otes 1 Chapter 11 ucleotides and ucleic Acids 2 ucleic Acids Two classes DA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) RA (Ribonucleic Acid) Polymers of nucleotides DA carries genetic
BC 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 11 Lecture otes 1 Chapter 11 ucleotides and ucleic Acids 2 ucleic Acids Two classes DA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) RA (Ribonucleic Acid) Polymers of nucleotides DA carries genetic
Nucleic acids. The building blocks. Phosphates
 Nucleic acids Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleic acids found in the nuclei of living cells. They are the vehicles of genetic inheritance. Nucleic acids are condensation
Nucleic acids Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleic acids found in the nuclei of living cells. They are the vehicles of genetic inheritance. Nucleic acids are condensation
Lecture Overview. Overview of the Genetic Information. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Protein Synthesis Lecture 6
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Protein Synthesis Lecture 6 Lecture Overview The Genetic Information Structure of DNA/RNA DNA Replication Overview of protein synthesis
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Protein Synthesis Lecture 6 Lecture Overview The Genetic Information Structure of DNA/RNA DNA Replication Overview of protein synthesis
Take-Home Quiz II. Spring 2005 Semester
 Take-Home Quiz II General Instructions and Information: Obtain an answer sheet from the instructor and legibly write your name in the appropriate space. After placing your name and quiz version on the
Take-Home Quiz II General Instructions and Information: Obtain an answer sheet from the instructor and legibly write your name in the appropriate space. After placing your name and quiz version on the
REVISION: DNA, RNA & MEIOSIS 13 MARCH 2013
 REVISION: DNA, RNA & MEIOSIS 13 MARCH 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we revise The structure and functions of DNA The structure of RNA and its role in protein synthesis The process of cell division
REVISION: DNA, RNA & MEIOSIS 13 MARCH 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we revise The structure and functions of DNA The structure of RNA and its role in protein synthesis The process of cell division
Concept 5.5: Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary information
 Concept 5.5: Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary information The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide is programmed by a unit of inheritance called a gene Genes are made of DNA, a nucleic acid
Concept 5.5: Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary information The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide is programmed by a unit of inheritance called a gene Genes are made of DNA, a nucleic acid
UNIT 3 GENETICS LESSON #41: Transcription
 UNIT 3 GENETICS LESSON #41: Transcription Objective: Explain how transcription converts a gene into a singlestranded RNA molecule. Suppose you want to play a game but you need tokens and you only have
UNIT 3 GENETICS LESSON #41: Transcription Objective: Explain how transcription converts a gene into a singlestranded RNA molecule. Suppose you want to play a game but you need tokens and you only have
DNA Structure Review. 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below of a DNA molecule and on your knowledge of biology.
 DNA Structure Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below of a DNA molecule and on your knowledge of biology. Which activity occurs in the process of replication? A) Structure
DNA Structure Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below of a DNA molecule and on your knowledge of biology. Which activity occurs in the process of replication? A) Structure
Chapter 10. Chapter 10 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids. Nobel Prize Reginald H. Garrett Charles M. Grisham
 Reginald H. Garrett Charles M. Grisham Chapter 10 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Chapter 10 We have discovered the secret of life. Francis Crick, to patrons of The Eagle, a pub in Cambridge, England (1953)
Reginald H. Garrett Charles M. Grisham Chapter 10 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Chapter 10 We have discovered the secret of life. Francis Crick, to patrons of The Eagle, a pub in Cambridge, England (1953)
STRUCTURE OF RNA. Long unbranched,single stranded polymer of ribonucleotide units. A ribonucleotide unit has: 5-Carbon ribose sugar.
 STRUCTURE OF RNA & REPLICATION BY:HIMANSHU LATAWA BIOLOGY LECTURER G.G.S.S.SIRHIND MANDI anshu223@gmail.com 9815543311 STRUCTURE OF RNA Long unbranched,single stranded polymer of ribonucleotide units.
STRUCTURE OF RNA & REPLICATION BY:HIMANSHU LATAWA BIOLOGY LECTURER G.G.S.S.SIRHIND MANDI anshu223@gmail.com 9815543311 STRUCTURE OF RNA Long unbranched,single stranded polymer of ribonucleotide units.
Case 16 Allosteric Regulation of ATCase
 Case 16 Allosteric Regulation of ATCase Focus concept An enzyme involved in nucleotide synthesis is subject to regulation by a variety of combinations of nucleotides. rerequisites roperties of allosteric
Case 16 Allosteric Regulation of ATCase Focus concept An enzyme involved in nucleotide synthesis is subject to regulation by a variety of combinations of nucleotides. rerequisites roperties of allosteric
Molecular Genetics. The flow of genetic information from DNA. DNA Replication. Two kinds of nucleic acids in cells: DNA and RNA.
 Molecular Genetics DNA Replication Two kinds of nucleic acids in cells: DNA and RNA. DNA function 1: DNA transmits genetic information from parents to offspring. DNA function 2: DNA controls the functions
Molecular Genetics DNA Replication Two kinds of nucleic acids in cells: DNA and RNA. DNA function 1: DNA transmits genetic information from parents to offspring. DNA function 2: DNA controls the functions
BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 13
 BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 13 General topics for week 7 Session 13: Types of nucleic acids, DNA replication Useful links: 1. Visit this website and use its menu to locate information and practice
BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 13 General topics for week 7 Session 13: Types of nucleic acids, DNA replication Useful links: 1. Visit this website and use its menu to locate information and practice
Chapter 4: How Cells Work
 Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: l l l l l Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription:
Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: l l l l l Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription:
Chapter 4: How Cells Work
 Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription: Sending the
Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription: Sending the
IN-DEPTH CHARACTERIZATION OF THE PURIFICATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM ALASKA PEA SEEDS. Fiezah M. Alahmry
 IN-DEPTH CHARACTERIZATION OF THE PURIFICATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM ALASKA PEA SEEDS By Fiezah M. Alahmry A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master
IN-DEPTH CHARACTERIZATION OF THE PURIFICATION OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOSIDASE FROM ALASKA PEA SEEDS By Fiezah M. Alahmry A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master
Nucleic Acids. OpenStax College. 1 DNA and RNA
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44403 1 Nucleic Acids OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be
OpenStax-CNX module: m44403 1 Nucleic Acids OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 3 v Nucleic acids Ø Polymers specialized for the storage transmission and use of genetic information Ø Two types DNA
 AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 3 v Nucleic acids Ø Polymers specialized for the storage transmission and use of genetic information Ø Two types DNA Encodes hereditary information Used to specify the amino
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 3 v Nucleic acids Ø Polymers specialized for the storage transmission and use of genetic information Ø Two types DNA Encodes hereditary information Used to specify the amino
The nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
 Nucleic acids are macromolecules composed of chains of mononucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds. The nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Nucleic acids are universal
Nucleic acids are macromolecules composed of chains of mononucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds. The nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Nucleic acids are universal
Nucleic Acid Structure:
 Nucleic Acid Structure: Purine and Pyrimidine nucleotides can be combined to form nucleic acids: 1. Deoxyribonucliec acid (DNA) is composed of deoxyribonucleosides of! Adenine! Guanine! Cytosine! Thymine
Nucleic Acid Structure: Purine and Pyrimidine nucleotides can be combined to form nucleic acids: 1. Deoxyribonucliec acid (DNA) is composed of deoxyribonucleosides of! Adenine! Guanine! Cytosine! Thymine
1. An alteration of genetic information is shown below. 5. Part of a molecule found in cells is represented below.
 1. An alteration of genetic information is shown below. 5. Part of a molecule found in cells is represented below. A-G-T-A-C-C-G-A-T A-G-T-G-A-T This type of alteration of the genetic information is an
1. An alteration of genetic information is shown below. 5. Part of a molecule found in cells is represented below. A-G-T-A-C-C-G-A-T A-G-T-G-A-T This type of alteration of the genetic information is an
Proofreading, post-replication modification of DNA. Mitesh Shrestha
 Proofreading, post-replication modification of DNA Mitesh Shrestha Proofreading During DNA replication (copying), most DNA polymerases can check their work with each base that they add. This process is
Proofreading, post-replication modification of DNA Mitesh Shrestha Proofreading During DNA replication (copying), most DNA polymerases can check their work with each base that they add. This process is
The Biochemistry Of The Nucleic Acids
 The Biochemistry Of The Nucleic Acids 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Biochemistry Of The Nucleic Introduction. Nucleotides are found primarily as the monomeric units comprising the major nucleic acids of the cell,
The Biochemistry Of The Nucleic Acids 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Biochemistry Of The Nucleic Introduction. Nucleotides are found primarily as the monomeric units comprising the major nucleic acids of the cell,
Feedback D. Incorrect! No, although this is a correct characteristic of RNA, this is not the best response to the questions.
 Biochemistry - Problem Drill 23: RNA No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements best describes the structural highlights of RNA? (A) RNA can be single or double stranded. (B) G-C pairs have 3 hydrogen
Biochemistry - Problem Drill 23: RNA No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements best describes the structural highlights of RNA? (A) RNA can be single or double stranded. (B) G-C pairs have 3 hydrogen
The Structure and Func.on of Macromolecules Nucleic Acids
 The Structure and Func.on of Macromolecules Nucleic Acids The FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: Carbohydrates Lipids Protein
The Structure and Func.on of Macromolecules Nucleic Acids The FOUR Classes of Large Biomolecules All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: Carbohydrates Lipids Protein
Division Ave. High School Ms. Foglia AP Biology. Nucleic acids. AP Biology Nucleic Acids. Information storage
 Nucleic acids 2006-2007 Nucleic Acids Information storage 2006-2007 1 DNA Nucleic Acids Function: u genetic material stores information w genes w blueprint for building proteins n DNA RNA proteins transfers
Nucleic acids 2006-2007 Nucleic Acids Information storage 2006-2007 1 DNA Nucleic Acids Function: u genetic material stores information w genes w blueprint for building proteins n DNA RNA proteins transfers
Lecture Overview. Overview of the Genetic Information. Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Lecture 6
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Lecture 6 Lecture Overview What is the cell s genetic information? How/where is the genetic information stored in eukaryotic
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Lecture 6 Lecture Overview What is the cell s genetic information? How/where is the genetic information stored in eukaryotic
Nucleic acids. How DNA works. DNA RNA Protein. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) RNA (ribonucleic acid) Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
 Nucleic acid chemistry and basic molecular theory Nucleic acids DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) RNA (ribonucleic acid) Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Cell cycle DNA RNA Protein Transcription Translation
Nucleic acid chemistry and basic molecular theory Nucleic acids DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) RNA (ribonucleic acid) Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Cell cycle DNA RNA Protein Transcription Translation
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 1953 article in Nature Directionality of DNA You need to number the carbons! u it matters! u 3 refers to the 3 carbon on the sugar u 5 refers to the 5 carbon
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 1953 article in Nature Directionality of DNA You need to number the carbons! u it matters! u 3 refers to the 3 carbon on the sugar u 5 refers to the 5 carbon
Chapter 5: Nucleic Acids, etc.
 Chapter 5: Nucleic Acids, etc. Voet & Voet: Sections 1 & 3 Pages 82-84 & 88-93 Any introductory Biochemistry textbook will have an introductory chapter on nucleic acids Slide 1 Nucleotides and Derivatives
Chapter 5: Nucleic Acids, etc. Voet & Voet: Sections 1 & 3 Pages 82-84 & 88-93 Any introductory Biochemistry textbook will have an introductory chapter on nucleic acids Slide 1 Nucleotides and Derivatives
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
DNA. translation. base pairing rules for DNA Replication. thymine. cytosine. amino acids. The building blocks of proteins are?
 2 strands, has the 5-carbon sugar deoxyribose, and has the nitrogen base Thymine. The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? DNA translation Adenine pairs with Thymine, Thymine
2 strands, has the 5-carbon sugar deoxyribose, and has the nitrogen base Thymine. The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? DNA translation Adenine pairs with Thymine, Thymine
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible
