Diffusion tensor (DT) imaging is an MR imaging technique
|
|
|
- David Pearson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
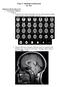
1 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Yamamoto Y. Miki S. Urayama Y. Fushimi T. Okada T. Hanakawa H. Fukuyama K. Togashi Diffusion Tensor Fiber Tractography of the Optic Radiation: Analysis with 6-, 12-, 40-, and 81- Directional Motion-Probing Gradients, a Preliminary Study BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Knowing the exact location of the optic radiation preoperatively is important for surgery of the temporal lobe. We hypothesized that a greater number of motion-probing gradients (MPGs) would provide better results of diffusion tensor (DT) fiber tractography of the optic radiation. To test this hypothesis, this study evaluated differences in DT fiber tractography of the optic radiation under different MPG settings. METHODS: DT images were obtained in 12 healthy volunteers (7 men, 5 women) with a mean age of 32 years (range, years) by using a 3T MR imaging scanner with single-shot echo-planar imaging with parallel acquisition (reduction factor 2). MPG was applied in 6, 12, 40, and 81 independent directions. The first region of interest (ROI) was placed in the occipital lobe, and the second ROI was placed in the lateral geniculate body. Fibers penetrating both ROIs were considered as the optic radiation. Anteroposterior distance between the tip of the Meyer loop and the lateral geniculate body on an axial section was defined as a loop index. Numbers of fibers and loop indices in both cerebral hemispheres were evaluated statistically. RESULTS: The optic radiation was well visualized in full length by DT fiber tractography in 20 of 24 hemispheres (83%). No significant differences were noted in number of fibers and loop indices among different MPG settings. CONCLUSION: DT fiber tractography can frequently depict almost the entire optic radiation. MPG number does not exert any significant effect on visualization of the optic radiation, and 6-directional MPG is thus sufficient for this purpose. Diffusion tensor (DT) imaging is an MR imaging technique that can be used to characterize the directional properties of the diffusion of water molecules. 1,2 Application of this technique to the human brain has been demonstrated to provide exceptional information regarding white matter architecture. 3,4 No other imaging techniques can provide equivalent information, so DT imaging is expected to become important for studying white matter anatomy and diagnosing various white matter abnormalities. Among the analyzing methods for DT imaging, DT fiber tractography has been reported as robust for visualizing and evaluating white matter fiber direction and connectivity in the brain. 5-7 DT fiber tractography requires calculation of various parameters of a DT ellipsoid. Among these parameters, direction of the largest eigenvector ( 1), which is the direction of greatest diffusivity and generally assumed to align with the direction of fiber bundles, is the most important and indispensable for DT ellipsoid-based fiber tractography reconstruction methods. 5,8 In DT ellipsoid-based fiber tractography, the path of a reconstructed fiber is determined by the direction of the Received January 19, 2006; accepted after revision April 10. From the Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine (A.Y., Y.M., Y.F., T.O., K.T.) and the Human Brain Research Center (S.i.U., T.H., H.F.), Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan. This work was supported in part by a Health and Labor Sciences Research Grant (H15-003) of Japan. Paper previously presented at: Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting of the Radiological Society of North America, November 22 December 2, 2005; Chicago, Ill. Please address correspondence to Yukio Miki, Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, Kyoto University, 54 Shogoin Kawahara-cho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto, , Japan; mikiy@kuhp.kyoto-u.ac.jp largest eigenvector ( 1) in each voxel. The number of motionprobing gradients (MPGs) has been reported as an important factor for calculating DT parameters. 9 However, to our knowledge, the MPG setting for optimal DT fiber tractography has not yet been determined. The optic radiation arches anteriorly and laterally from the lateral geniculate body before coursing posteriorly to the occipital cortex. This curved course represents a challenge for DT fiber tractography, because white matter tracts of the temporal stem intermingle with other fibers that course in various directions and are indistinguishable from surrounding white matter on MR imaging. 10 A recent article has reported that 3 layers of visual field trajectories were depicted by DT fiber tractography with a 32-MPG setting. 11 Knowing the exact location of the optic radiation preoperatively is important for surgery of the temporal lobe. 12 This information can be obtained exclusively by DT fiber tractography. However, to our knowledge, the appropriate number of MPGs for DT fiber tractography has not been decided. We hypothesized that a greater number of MPGs would improve visualization of the optic radiation. To test this hypothesis, the present study evaluated differences in DT fiber tractography of the optic radiation under different MPG settings. Methods Subjects Written informed consent was obtained from each volunteer, and all protocols for this prospective study were approved by the medical ethics committee of our institute. Data were obtained from 12 healthy 92 Yamamoto AJNR 28 Jan
2 volunteers (7 men, 5 women) with a mean age of 32 years (range, years) and no history of neurologic injury or psychiatric disease. Subjects did not have any medication, drug, or alcohol history. No subjects displayed any neurologic signs or symptoms. Data Acquisition DT images were obtained by using a 3T MR imaging scanner (Magnetom Trio, Syngo MR 2004A, Siemens, Erlangen, Germany) with an 8-channel phased-array head coil by using single-shot echo-planar imaging with parallel acquisition (generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions; reduction factor 2) in the axial plane. Imaging parameters were as follows: acquisition matrix, 96 96; FOV, 240 mm; section thickness, 2.5 mm; no intersection gap; 55 sections; TR, ms; TE, ms; b 0, 700 seconds/mm 2. Reconstruction matrix was the same as the acquisition matrix, and 2.5 mm 2.5 mm 2.5 mm isotropic voxel data were obtained. MPG was applied in 6, 12, 40, and 81 independent directions; the number of acquisitions was set at 13, 7, 2, and 1, respectively; the number of images was 5005, 5005, 4840, and 4950, respectively; and the acquisition time was 9 minutes 16 seconds, 9 minutes 25 seconds, 9 minutes 15 seconds, and 9 minutes 27 seconds, respectively. The number of signal intensity averages for b 0 images was 13, 7, 8, and 9, respectively. Repeated acquisition of the b 0 image is important for precise estimation of the tensor because variance of each of the elements of the tensor matrix should be minimized. 13 Data Processing DT imaging datasets were transferred to a workstation and processed by using DtiStudio, Version 2.3 software (H. Jiang, S. Mori; Johns Hopkins University, All diffusionweighted images were visually inspected by 2 authors for apparent artifacts due to subject motion and instrument malfunction, and no significant image deterioration was found. In our DT imaging dataset, there was low eddy-current related geometric distortion between images obtained in each MPG direction; thus, postprocessing distortion correction was not applied for this dataset. Fractional anisotropy (FA) and color map images 14 were calculated from diffusion-weighted images. DT fiber tractography was made by using the fiber assignment by continuous tracking method. 5,15 Fiber Tract Reconstruction Fiber tract reconstruction used a start and stop FA threshold of 0.25, 16 according to the FA threshold of for fiber tract reconstruction recommended by Mori et al 16 and Stieltjes et al. 17 We also used an inner product stop threshold of 0.34, prohibiting angles of 70 during tracking. 18 A relatively large angle threshold was used so that the optic radiation coursing in an acute angle at the Meyer loop could be reconstructed. To reconstruct tracts of the optic radiation, we used a multiple region-of-interest (ROI) approach to exploit existing anatomic knowledge of tract trajectories. 19 This method has low sensitivity to the ROI size and location and is highly beneficial for reproducible reconstruction of prominent white matter tracts with known trajectories. 19 When multiple ROIs were used for a tract reconstruction, we used 3 types of operations: AND, OR, and NOT. Choice of operations depended on the characteristic trajectory of the tract. 6 The first ROI was placed in the occipital lobe on a reconstructed coronal image with an OR operation, and after we placed the first ROI, the fibers penetrating this region were shown on axial, coronal, and sagittal images. The second ROI was manually placed in the lateral geniculate body on a reconstructed sagittal image with an AND operation. When we placed the second ROI, fibers penetrating the first ROI were already shown on a reconstructed sagittal image, so we could see a bundle of fibers penetrating the first ROI and the lateral geniculate body on a sagittal image. The second ROI could be placed on the lateral geniculate body with that fiber bundle as a landmark for the precise location. This 2-ROI method is relatively easy, and there is no variability that will bias the fiber tracking results. 19 Reconstructed fibers penetrating both ROIs were considered representative of the optic radiation. FA values in both ROIs were measured by a function of DtiStudio software and analyzed statistically if there was any difference in FA values among different MPG settings by using analysis of variance. If there was significant difference, a t test was used for each pair comparisons. For evaluating signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the diffusionweighted images, we used the following formula 20 : SNR (0.66 mean signal intensity) / (average of noise region standard deviations). A large ROI ( 2000 pixels) for signal intensity was placed in the brain tissue on an axial section containing the optic radiation. Four relatively small ROIs (144 pixels) for noise were placed in the background (air) at the 4 corners on the same section. This measurement was repeated throughout all the diffusion-weighted images, and we calculated the average value of SNR for each MPG setting. SNR differences among different MPG settings were evaluated statistically by using analysis of variance. Fiber Tractography Analysis For analyzing the course and location of the reconstructed optic radiation, we evaluated the Meyer loop because it is the most characteristic part of the optic radiation and its curved course was considered to be a challenge for diffusion tensor fiber tractography. 10 Anteroposterior distance between the anterior tip of the Meyer loop and the posterior end of the lateral geniculate body on an axial section was defined as a loop index (Fig 1). The loop index was considered to represent the course and location of the Meyer loop. Difference in the loop index among different MPG numbers was evaluated statistically by using analysis of variance. In addition to analyzing its shape, we counted the number of fibers in the optic radiation for both cerebral hemispheres by a function of DtiStudio software, and any difference due to MPG number was evaluated statistically by using a generalized linear mixed model, which is an extension of analysis of variance and regression analysis and has also been widely used in life science. 21 For the all statistical evaluations, values of P.05 were considered significant. Results FA value in the first ROI in the occipital lobe showed in 6 MPG, in 12 MPG, in 40 MPG, and in 81 MPG (values are mean values of 24 hemispheres SD). The FA value in the first ROI placed at the 6-MPG setting was significantly higher than that at other 3 MPG settings (P.0007). The FA value in the second ROI placed in the lateral geniculate body showed at 6 MPG, at 12 MPG, at 40 MPG, and at 81 MPG. The FA value in the second ROI at the 6-MPG setting was significantly higher than that at 12- and 40-MPG settings, and the FA value in the second ROI at the 81-MPG setting was significantly higher than that at the 40-MPG setting (P.002). BRAIN ORIGINAL RESEARCH AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:92 96 Jan
3 Fig 1. The anteroposterior distance between the tip of the Meyer loop and the lateral geniculate body on an axial section was defined as a loop index. Examples of loop index (A and B) are shown. Fig 2. Reconstructed diffusion tensor fiber tractography of the optic radiation by using 6-MPG (A), 12-MPG (B), 40-MPG (C), and 81-MPG (D) settings. SNR for each MPG setting showed at 6 MPG, at 12 MPG, at 40 MPG, and at 81 MPG. There was no significant difference in SNR value among different MPG settings (P.708). The loop index (anteroposterior distance between the anterior tip of the Meyer loop and the posterior end of the lateral geniculate body) was at 6 MPG, at 12 MPG, at 40 MPG, and at 81 MPG. There was no significant difference in loop index among different MPG settings (P.13). The optic radiation was well visualized along the full length by DT fiber tractography in 20 of 24 hemispheres (83%). No significant differences in number of fibers were noted among 6-, 12-, 40-, and 81-MPG settings (Fig 2) (P.53; 6 MPG, ; 12 MPG, ; 40 MPG, ; 81 MPG, ). Discussion In this study, the optic radiation was well visualized along the full length by DT fiber tractography in 20 of 24 hemispheres (83%). Contrary to our hypothesis, MPG number did not exert any significant effect on visualization of the optic radiation. This study is the first to analyze the relationship between DT fiber tractography of the optic radiation and MPG number. The largest eigenvector ( 1), indicating the direction of greatest diffusivity, is generally assumed to align with the direction of fiber bundles and thus represents an indispensable parameter for DT ellipsoid-based fiber tractography. 5,8 In an estimation of DT parameters, 30 independent directional MPGs have been reported as desirable for analysis of diffusivity, and 20 independent directional MPGs have been reported as desirable for analysis of anisotropy. 9 For calculation of DT parameters, particularly eigenvector, a smaller MPG number may introduce directional biases and reduced directional precision, whereas a larger MPG number can introduce more robust tensor ellipsoid estimation. 9,22-24 The minimal mathematic requirement for DT calculation is 6 independent directional MPG settings, and this may allow relatively short imaging time. Conversely, settings like 40 or 81 independent MPGs may involve relatively longer imaging times. However, the amount of imaging time is limited in most clinical situations. 94 Yamamoto AJNR 28 Jan
4 Choice of MPG settings thus involves a trade-off between minimizing directional bias and minimizing scanning time. As many unique directional MPGs as time will allow should reportedly be used for fiber tractography according to a Monte Carlo simulation approach. 9 However, in this actual human brain study, differences due to MPG number in DT fiber tractography of the optic radiation were not particularly prominent. Various reasons might underlie this finding. First, the issue of SNR is important in DT fiber tractography 19 and may not be negligible. In the present study, SNR values did not show any significant difference among different MPG settings, so SNR effect of different MPG settings on the results of fiber tractography in the present study can be considered negligible. Second, the multiple ROI approach was used in the present study, and this method has been reported to be robust for studying prominent tracts with known trajectories and low sensitivity to the ROI size and location. 19 The 2 ROI approach is a very strong analyzing method and it can make the difference of the fiber tractography obscure among the different MPG numbers. Third, we evaluated the optic radiation only and did not evaluate other fiber tracts such as the corticospinal tract. Anatomic features of the optic radiation fibers may have had some effect on the results of DT fiber tractography in this study and may have cancelled any positive effect of larger MPG numbers. Factors affecting SNR in DT imaging include the number of signal intensity averaging, MPG number, and encoding levels. 25 In the present study, b 0 images were obtained repeatedly for precise estimation of the tensor because variance of each of the elements of the tensor matrix should be minimized. 13 Low SNR may result in variance of each of the tensor elements and, finally, in overestimating FA value 26 ; thus, it will change DT parameters for fiber tractography. With the issue of SNR for DT parameter calculation, number of signal-intensity averaging and number of MPGs should be considered differently. A previous article reported that an increasing MPG number decreases error in DT parameter calculation more than the number of signal intensity averaging does. 27 In this study, FA values of ROIs for fiber reconstruction were significantly higher in the 6-MPG setting than those of other MPG settings. This higher FA value may partly reflect an error of DT parameter calculation because of the smaller MPG number as shown in previous reports. 13,27 Although there might have been an FA value calculation error in the smaller MPG setting, the results of fiber tractography showed no significant difference in the present study. We thus assume that the MPG number may be significant for DT parameter calculation; however, the effect of the MPG number for visualization of the optic radiation was insignificant in the present study. The optic radiation arches anteriorly and laterally from the lateral geniculate body before coursing posteriorly to the occipital cortex. This curved course represents a challenge for DT fiber tractography, because white matter tracts of the temporal stem intermingle with other fibers that course in various directions and are indistinguishable from the surrounding white matter on MR imaging studies. 10,11 Knowing the exact location of the optic radiation preoperatively is important for surgery of the temporal lobe. 12 In this study, DT fiber tractography depicted the optic radiation along almost the entire length in 83% of cases, irrespective of MPG number. DT imaging is noninvasive and is the only known method for gaining directional information on white matter of the brain. 3,4 This imaging method may contribute to preoperative planning and intraoperative evaluation for temporal and occipital lobe surgery. DT imaging may be feasible for surgical therapy of temporal lobe epilepsy, brain tumors, and other lesions in the brain near the optic radiation. 28 Multidirectional MPG settings have been used as an efficient evaluation method for determining intravoxel white matter fiber heterogeneity, such as Q-ball imaging for analysis of intravoxel fiber crossing In addition to these analyses, for the probabilistic DT fiber reconstruction approach, as large an MPG number as time will allow has been reported as necessary. 9 In these analytic methods, larger MPG numbers may have merit and be indispensable for effective analysis. This study has several limitations. First, only a limited number of subjects were enrolled into this preliminary study. A larger number should be enrolled in a future study. Second, only the optic radiation was evaluated. Other neuronal fiber bundles such as the corticospinal tract or superior longitudinal fascicles could be evaluated in future studies. Third, we evaluated the optic radiation only by the DT ellipsoid-based fiber tractography method with 1 threshold value setting. Further study is needed for evaluation of other fiber-reconstruction approaches such as the probabilistic approach 32 and for the effects of changing threshold values in the DT ellipsoidbased fiber tractography method. Fourth, we did not evaluate differences in various MPG spatial-distribution schemes. Further study is needed for evaluation of other MPG schemes. Conclusion In conclusion, DT fiber tractography can frequently depict the optic radiation along almost the entire length. MPG number does not exert a significant difference for visualization of the optic radiation in the equal SNR setting, and 6-directional MPG is sufficient for visualization of this structure. Acknowledgments We thank Susumu Mori, PhD, for his advice and Mitsunori Kanagaki, MD, PhD; Nobuyuki Mori, MD; and Eri Kitamura, MD for their vigorous support. References 1. Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LeBihan D. MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophys J 1994;66: Beaulieu C. The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system: a technical review. NMR Biomed 2002;15: Moseley ME, Cohen Y, Kucharczyk J, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of anisotropic water diffusion in cat central nervous system. Radiology 1990;176: Pierpaoli C, Jezzard P, Basser PJ, et al. Diffusion tensor MR imaging of the human brain. Radiology 1996;201: Mori S, Crain BJ, Chacko VP, et al. Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 1999;45: Wakana S, Jiang H, Nagae-Poetscher LM, et al. Fiber tract-based atlas of human white matter anatomy. Radiology 2004;230: Lee SK, Kim DI, Kim J, et al. Diffusion-tensor MR imaging and fiber tractography: a new method of describing aberrant fiber connections in developmental CNS anomalies. RadioGraphics 2005;25: Masutani Y, Aoki S, Abe O, et al. MR diffusion tensor imaging: recent advance and new techniques for diffusion tensor visualization. Eur J Radiol 2003;46: Jones DK. The effect of gradient sampling schemes on measures derived from diffusion tensor MRI: a Monte Carlo study. Magn Reson Med 2004;51: AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:92 96 Jan
5 10. Kier EL, Staib LH, Davis LM, et al. MR imaging of the temporal stem: anatomic dissection tractography of the uncinate fasciculus, inferior occipitofrontal fasciculus, and Meyer s loop of the optic radiation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2004;25: Yamamoto T, Yamada K, Nishimura T, et al. Tractography to depict three layers of visual field trajectories to the calcarine gyri. Am J Ophthalmol 2005; 140: Powell HW, Parker GJ, Alexander DC, et al. MR tractography predicts visual field defects following temporal lobe resection. Neurology 2005;65: Jones DK, Horsfield MA, Simmons A. Optimal strategies for measuring diffusion in anisotropic systems by magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 1999;42: Pajevic S, Pierpaoli C. Color schemes to represent the orientation of anisotropic tissues from diffusion tensor data: application to white matter fiber tract mapping in the human brain. Magn Reson Med 1999;42: Mori S, van Zijl PC. Fiber tracking: principles and strategies a technical review. NMR Biomed 2002;15: Mori S, Kaufmann WE, Davatzikos C, et al. Imaging cortical association tracts in the human brain using diffusion-tensor-based axonal tracking. Magn Reson Med 2002;47: Stieltjes B, Kaufmann WE, van Zijl PC, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging and axonal tracking in the human brainstem. Neuroimage 2001;14: Concha L, Gross DW, Beaulieu C. Diffusion tensor tractography of the limbic system. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2005;26: Huang H, Zhang J, van Zijl PC, et al. Analysis of noise effects on DTI-based tractography using the brute-force and multi-roi approach. Magn Reson Med 2004;52: McRobbie DW, Moore EA, Graves MJ, et al. MRI from Picture to Proton. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 2003: Grafen A, Hails R. Modern Statistics for the Life Sciences. New York: Oxford University Press; 2002: Papadakis NG, Xing D, Huang CL, et al. A comparative study of acquisition schemes for diffusion tensor imaging using MRI. J Magn Reson 1999;137: Papadakis NG, Murrills CD, Hall LD, et al. Minimal gradient encoding for robust estimation of diffusion anisotropy. Magn Reson Imaging 2000;18: Hasan KM, Parker DL, Alexander AL. Comparison of gradient encoding schemes for diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 2001;13: Chen B, Hsu EW. Noise removal in magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Med 2005;54: Anderson AW. Theoretical analysis of the effects of noise on diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Med 2001;46: Poonawalla AH, Zhou XJ. Analytical error propagation in diffusion anisotropy calculations. J Magn Reson Imaging 2004;19: Taoka T, Sakamoto M, Iwasaki S, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging in cases with visual field defect after anterior temporal lobectomy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2005;26: Wiegell MR, Larsson HB, Wedeen VJ. Fiber crossing in human brain depicted with diffusion tensor MR imaging. Radiology 2000;217: Tuch DS, Reese TG, Wiegell MR, et al. High angular resolution diffusion imaging reveals intravoxel white matter fiber heterogeneity. Magn Reson Med 2002;48: Tuch DS. Q-ball imaging. Magn Reson Med 2004;52: Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Jenkinson M, et al. Characterization and propagation of uncertainty in diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Magn Reson Med 2003; 50: Yamamoto AJNR 28 Jan
Artifacts Caused by Eddy Current in Diffusion MRI
 Artifacts Caused by Eddy Current in Diffusion MRI Xi Tan ABSTRACT Magnetic resonance diffusion imaging is potentially an important tool for the noninvasive characterization of normal and pathological tissue.
Artifacts Caused by Eddy Current in Diffusion MRI Xi Tan ABSTRACT Magnetic resonance diffusion imaging is potentially an important tool for the noninvasive characterization of normal and pathological tissue.
Pre-clinical and postmortem diffusion MRI
 manisha.aggarwal@jhu.edu Pre-clinical and postmortem diffusion MRI Manisha Aggarwal, Ph.D. Department of Radiology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Diffusion and tissue microstructure? signal
manisha.aggarwal@jhu.edu Pre-clinical and postmortem diffusion MRI Manisha Aggarwal, Ph.D. Department of Radiology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Diffusion and tissue microstructure? signal
Principles of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Its Applications to Basic Neuroscience Research
 Neuron 51, 527 539, September 7, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.08.012 Principles of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Its Applications to Basic Neuroscience Research Primer Susumu Mori
Neuron 51, 527 539, September 7, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.08.012 Principles of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Its Applications to Basic Neuroscience Research Primer Susumu Mori
Automated detection of white matter fiber bundles
 Automated detection of white matter fiber bundles Ralph Suarez, Olivier Commowick, Xavier Tomas-Fernandez, Sanjay Prabhu, Simon K. Warfield To cite this version: Ralph Suarez, Olivier Commowick, Xavier
Automated detection of white matter fiber bundles Ralph Suarez, Olivier Commowick, Xavier Tomas-Fernandez, Sanjay Prabhu, Simon K. Warfield To cite this version: Ralph Suarez, Olivier Commowick, Xavier
Supplementary Material Cohort Description
 Supplementary Material Cohort Description The following longitudinal twin cohorts were included: BrainSCALE: Brain Structure and Cognition: an Adolescent Longitudinal Twin Study into genetic etiology University
Supplementary Material Cohort Description The following longitudinal twin cohorts were included: BrainSCALE: Brain Structure and Cognition: an Adolescent Longitudinal Twin Study into genetic etiology University
Tissue-Based Affine Registration of Brain Images to form a Vascular Density Atlas
 Tissue-Based Affine Registration of Brain Images to form a Vascular Density Atlas Derek Cool, Dini Chillet, Jisung Kim, Jean-Phillipe Guyon, Mark Foskey, and Stephen Aylward Computer Aided Display and
Tissue-Based Affine Registration of Brain Images to form a Vascular Density Atlas Derek Cool, Dini Chillet, Jisung Kim, Jean-Phillipe Guyon, Mark Foskey, and Stephen Aylward Computer Aided Display and
Scan-rescan reproducibility of neurite microstructure estimates using NODDI
 TARIQ et al.: SCAN-RESCAN REPRODUCIBILITY OF NODDI 1 Scan-rescan reproducibility of neurite microstructure estimates using NODDI Maira Tariq 1 maira.tariq.11@ucl.ac.uk Torben Schneider 2 t.schneider@ucl.ac.uk
TARIQ et al.: SCAN-RESCAN REPRODUCIBILITY OF NODDI 1 Scan-rescan reproducibility of neurite microstructure estimates using NODDI Maira Tariq 1 maira.tariq.11@ucl.ac.uk Torben Schneider 2 t.schneider@ucl.ac.uk
Balancing versatility and value Introducing Optima MR T
 GE Healthcare Balancing versatility and value Introducing Optima MR360 1.5T Optima MR360 1.5T Providing an innovative balance in MR You know what you need from an MR scanner. The new Optima MR360 is engineered
GE Healthcare Balancing versatility and value Introducing Optima MR360 1.5T Optima MR360 1.5T Providing an innovative balance in MR You know what you need from an MR scanner. The new Optima MR360 is engineered
Visual Pathway Study Using In Vivo Diffusion Tensor Imaging Tractography to Complement Classic Anatomy
 Visual Pathway Study Using In Vivo Diffusion Tensor Imaging Tractography to Complement Classic Anatomy The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Visual Pathway Study Using In Vivo Diffusion Tensor Imaging Tractography to Complement Classic Anatomy The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
High-Speed 3T MR Spectroscopic Imaging of Prostate With Flyback Echo-Planar Encoding
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 25:1288 1292 (2007) Clinical Note High-Speed 3T MR Spectroscopic Imaging of Prostate With Flyback Echo-Planar Encoding Albert P. Chen, PhD, 1,2 Charles H. Cunningham,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 25:1288 1292 (2007) Clinical Note High-Speed 3T MR Spectroscopic Imaging of Prostate With Flyback Echo-Planar Encoding Albert P. Chen, PhD, 1,2 Charles H. Cunningham,
Background. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) non invasively measures metabolite concentrations
 Applying FID navigators to high field MRS in the body AAPM North Central Chapter Spring Meeting April 7th, 2017 Ryan M. Kalmoe Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Minnesota Advisor: Dr. Gregory
Applying FID navigators to high field MRS in the body AAPM North Central Chapter Spring Meeting April 7th, 2017 Ryan M. Kalmoe Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Minnesota Advisor: Dr. Gregory
DTI of White Matter in Brain Diseases; Potentials and Pitfalls
 DTI of White Matter in Brain Diseases; Potentials and Pitfalls Rick M. Dijkhuizen, PhD Biomedical MR Imaging and Spectroscopy Group Center for Image Sciences University Medical Center Utrecht Utrecht,
DTI of White Matter in Brain Diseases; Potentials and Pitfalls Rick M. Dijkhuizen, PhD Biomedical MR Imaging and Spectroscopy Group Center for Image Sciences University Medical Center Utrecht Utrecht,
Accelerating Clinical MRI in the 21 st Century
 Accelerating Clinical MRI in the 21 st Century Val M. Runge, MD Universitätsinstitut für Diagnostische, Interventionelle und Pädiatrische Radiologie University Hospital Bern Editor-in-Chief, Investigative
Accelerating Clinical MRI in the 21 st Century Val M. Runge, MD Universitätsinstitut für Diagnostische, Interventionelle und Pädiatrische Radiologie University Hospital Bern Editor-in-Chief, Investigative
Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 7T in Glasgow. A unique opportunity!
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 7T in Glasgow A unique opportunity! An NHS MR Physicist's perspective... What is different about 7T scanners? What has already been achieved? Imaging Centre of Excellence
Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 7T in Glasgow A unique opportunity! An NHS MR Physicist's perspective... What is different about 7T scanners? What has already been achieved? Imaging Centre of Excellence
Comparison of In Vivo and Ex Vivo Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Rhesus Macaques at Short and Long Diffusion Times
 172 The Open Neuroimaging Journal, 2011, 5, (Suppl 2-M5) 172-178 Open Access Comparison of In Vivo and Ex Vivo Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Rhesus Macaques at Short and Long Diffusion Times Swati Rane 2
172 The Open Neuroimaging Journal, 2011, 5, (Suppl 2-M5) 172-178 Open Access Comparison of In Vivo and Ex Vivo Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Rhesus Macaques at Short and Long Diffusion Times Swati Rane 2
CQIE MRI PROCEDURES. American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center. Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence LEARNING MODULE
 Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence LEARNING MODULE CQIE MRI PROCEDURES American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center Imaging Core Laboratory v.2 Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence
Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence LEARNING MODULE CQIE MRI PROCEDURES American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center Imaging Core Laboratory v.2 Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence
Precision in Quantitative Imaging: Trial Development and Quality Assurance
 Precision in Quantitative Imaging: Trial Development and Quality Assurance Susanna I Lee MD, PhD Thanks to: Mitchell Schnall, Mark Rosen. Dan Sullivan, Patrick Bossuyt Imaging Chain: Patient Data Raw data
Precision in Quantitative Imaging: Trial Development and Quality Assurance Susanna I Lee MD, PhD Thanks to: Mitchell Schnall, Mark Rosen. Dan Sullivan, Patrick Bossuyt Imaging Chain: Patient Data Raw data
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF IN VIVO FLOW PHENOMENA
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF IN VIVO FLOW PHENOMENA So far we have seen that magnetic resonance can Locate the positions of spins (mainly water) with the aid of one or multiple field gradient: MRI Characterize
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF IN VIVO FLOW PHENOMENA So far we have seen that magnetic resonance can Locate the positions of spins (mainly water) with the aid of one or multiple field gradient: MRI Characterize
ClinScan. think forward. Small Animal MRI Solution for Molecular Imaging and Translational Research. Preclinical MRI
 ClinScan Small Animal MRI Solution for Molecular Imaging and Translational Research think forward Preclinical MRI Be Clinical from the Very Beginning With ClinScan you enter the field of translational
ClinScan Small Animal MRI Solution for Molecular Imaging and Translational Research think forward Preclinical MRI Be Clinical from the Very Beginning With ClinScan you enter the field of translational
Press Presse Press Presse
 Press Presse Press Presse Healthcare Sector Imaging & IT Division Erlangen, November 30, 2009 Siemens Introduces its New Power Couple at RSNA 2009 Tim and Dot* redefine productivity in MRI up to 30 percent
Press Presse Press Presse Healthcare Sector Imaging & IT Division Erlangen, November 30, 2009 Siemens Introduces its New Power Couple at RSNA 2009 Tim and Dot* redefine productivity in MRI up to 30 percent
American Journal of Neuroradiology
 Cervical spinal cord DTI is improved by reduced-fov with specific balance between numbers of diffusion gradient directions and numbers of averages. Journal: American Journal of Neuroradiology Manuscript
Cervical spinal cord DTI is improved by reduced-fov with specific balance between numbers of diffusion gradient directions and numbers of averages. Journal: American Journal of Neuroradiology Manuscript
Design and Preliminary Clinical Studies of an MRI-Guided Transrectal Prostate Intervention System
 Design and Preliminary Clinical Studies of an MRI-Guided Transrectal Prostate Intervention System Axel Krieger 1, Peter Guion 2, Csaba Csoma 1, Iulian Iordachita 1, Anurag K. Singh 2,3, Aradhana Kaushal
Design and Preliminary Clinical Studies of an MRI-Guided Transrectal Prostate Intervention System Axel Krieger 1, Peter Guion 2, Csaba Csoma 1, Iulian Iordachita 1, Anurag K. Singh 2,3, Aradhana Kaushal
FFGWAS. Fast Functional Genome Wide Association AnalysiS of Surface-based Imaging Genetic Data
 FFGWAS Fast Functional Genome Wide Association AnalysiS of Surface-based Imaging Genetic Data Chao Huang Department of Biostatistics Biomedical Research Imaging Center The University of North Carolina
FFGWAS Fast Functional Genome Wide Association AnalysiS of Surface-based Imaging Genetic Data Chao Huang Department of Biostatistics Biomedical Research Imaging Center The University of North Carolina
The first images of water diffusion
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Reviews and Commentary
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Reviews and Commentary
I-class. All together a better way to work. MAGNETOM Avanto.
 I-class. All together a better way to work. MAGNETOM Avanto www.siemens.com/medical Introducing I-class Innovative applications. Innovative workflow. Welcome to the next generation of MRI. Powered by innovative
I-class. All together a better way to work. MAGNETOM Avanto www.siemens.com/medical Introducing I-class Innovative applications. Innovative workflow. Welcome to the next generation of MRI. Powered by innovative
Implementation of fast macromolecular proton fraction mapping on 1.5 and 3 Tesla clinical MRI scanners: preliminary experience
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Implementation of fast macromolecular proton fraction mapping on 1.5 and 3 Tesla clinical MRI scanners: preliminary experience To cite this article:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Implementation of fast macromolecular proton fraction mapping on 1.5 and 3 Tesla clinical MRI scanners: preliminary experience To cite this article:
GE Healthcare. Introducing Brivo MR T. Bringing high-field MR. within reach
 GE Healthcare Introducing Brivo MR355 1.5T Bringing high-field MR within reach If 1.5T MR technology has been just out of reach for your practice, the Brivo MR355 will be a welcome advancement. The Brivo
GE Healthcare Introducing Brivo MR355 1.5T Bringing high-field MR within reach If 1.5T MR technology has been just out of reach for your practice, the Brivo MR355 will be a welcome advancement. The Brivo
Delivering the most exciting equation in MRI. MAGNETOM Verio. Answers for life.
 Delivering the most exciting equation in MRI. MAGNETOM Verio Answers for life. We know, we re excited too! Siemens has set a new benchmark in MRI again. As a proven innovator Siemens is bringing 3T field
Delivering the most exciting equation in MRI. MAGNETOM Verio Answers for life. We know, we re excited too! Siemens has set a new benchmark in MRI again. As a proven innovator Siemens is bringing 3T field
First Experiences with the World s First MAGNETOM Vida
 8 Clinical Whole-body Imaging First Experiences with the World s First MAGNETOM Vida Mike Notohamiprodjo, M.D. Associate Chair and Section Chief MRI, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology,
8 Clinical Whole-body Imaging First Experiences with the World s First MAGNETOM Vida Mike Notohamiprodjo, M.D. Associate Chair and Section Chief MRI, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology,
EXPERT REVIEW Connectome imaging for mapping human brain pathways
 Molecular Psychiatry (2017) 22, 1230 1240 www.nature.com/mp OPEN EXPERT REVIEW for mapping human brain pathways With the fast advance of connectome imaging techniques, we have the opportunity of mapping
Molecular Psychiatry (2017) 22, 1230 1240 www.nature.com/mp OPEN EXPERT REVIEW for mapping human brain pathways With the fast advance of connectome imaging techniques, we have the opportunity of mapping
Power-class. Expect more performance. MAGNETOM Symphony.
 Power-class. Expect more performance. MAGNETOM Symphony www.siemens.com/healthcare MAGNETOM Symphony with Power-class: Our MRI does more to boost your ROI. It s already one of the world s most in-demand
Power-class. Expect more performance. MAGNETOM Symphony www.siemens.com/healthcare MAGNETOM Symphony with Power-class: Our MRI does more to boost your ROI. It s already one of the world s most in-demand
RADIATION ONCOLOGY RESIDENCY PROGRAM Competency Evaluation of Resident
 Resident s Name: RADIATION ONCOLOGY RESIDENCY PROGRAM Competency Evaluation of Resident Rotation: PHYS 705: Clinical Rotation 3 Inclusive dates of rotation: Aug. 25, 2015 Feb. 25, 2016 Director or Associate
Resident s Name: RADIATION ONCOLOGY RESIDENCY PROGRAM Competency Evaluation of Resident Rotation: PHYS 705: Clinical Rotation 3 Inclusive dates of rotation: Aug. 25, 2015 Feb. 25, 2016 Director or Associate
Purpose. Methods and Materials
 MR cholangiopancreatography: Comparison between 3D fast recovery fast spin echo and 2D single shot fast spin echo sequences in the evaluation of choledocholithiasis. Poster No.: C-1193 Congress: ECR 2012
MR cholangiopancreatography: Comparison between 3D fast recovery fast spin echo and 2D single shot fast spin echo sequences in the evaluation of choledocholithiasis. Poster No.: C-1193 Congress: ECR 2012
MEDICAL PHYSICS (MED PHYS)
 Medical Physics (MED PHYS) 1 MEDICAL PHYSICS (MED PHYS) MED PHYS/PHYSICS 265 INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL PHYSICS Primarily for premeds and other students in the medical and biological sciences. Applications
Medical Physics (MED PHYS) 1 MEDICAL PHYSICS (MED PHYS) MED PHYS/PHYSICS 265 INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL PHYSICS Primarily for premeds and other students in the medical and biological sciences. Applications
NeuroImage 64 (2013) Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. NeuroImage. journal homepage:
 NeuroImage 64 (2013) 229 239 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect NeuroImage journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ynimg In vivo detection of microscopic anisotropy using quadruple pulsed-field
NeuroImage 64 (2013) 229 239 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect NeuroImage journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ynimg In vivo detection of microscopic anisotropy using quadruple pulsed-field
Computer Assisted Surgery Basics of medical imaging
 Computer Assisted Surgery Basics of medical imaging Prof. Leo Joskowicz School of Engineering and Computer Science The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, ISRAEL Medical Image Processing Basics of medical
Computer Assisted Surgery Basics of medical imaging Prof. Leo Joskowicz School of Engineering and Computer Science The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, ISRAEL Medical Image Processing Basics of medical
BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING (BME)
 Biomedical Engineering (BME) 1 BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING (BME) BME 500 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering Introduction to the concepts and research in biomedical engineering. Provides an overview of current
Biomedical Engineering (BME) 1 BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING (BME) BME 500 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering Introduction to the concepts and research in biomedical engineering. Provides an overview of current
Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) of the human. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping of Human Brain at 3T: A Multisite Reproducibility Study
 Published October 22, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4137 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping of Human Brain at 3T: A Multisite Reproducibility Study P.-Y. Lin, T.-C. Chao, and M.-L. Wu
Published October 22, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4137 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping of Human Brain at 3T: A Multisite Reproducibility Study P.-Y. Lin, T.-C. Chao, and M.-L. Wu
Reduced Field-of-View MRI Using Outer Volume Suppression for Spinal Cord Diffusion Imaging
 Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 57:625 630 (2007) Reduced Field-of-View MRI Using Outer Volume Suppression for Spinal Cord Diffusion Imaging B.J. Wilm, 1,2 * J. Svensson, 1,3 A. Henning, 2 K.P. Pruessmann,
Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 57:625 630 (2007) Reduced Field-of-View MRI Using Outer Volume Suppression for Spinal Cord Diffusion Imaging B.J. Wilm, 1,2 * J. Svensson, 1,3 A. Henning, 2 K.P. Pruessmann,
Preclinical MRI. Solutions for Small Animal Imaging. Molecular Imaging
 Preclinical MRI Solutions for Small Animal Imaging Molecular Imaging The Power of Imaging Applications Resolution Typical resolution in MRI is less than 200μm, to more than 20μm with 2D slices or full
Preclinical MRI Solutions for Small Animal Imaging Molecular Imaging The Power of Imaging Applications Resolution Typical resolution in MRI is less than 200μm, to more than 20μm with 2D slices or full
Clinical Applications. ImagingRite. Neuro Intervention. 1 ImagingRite
 Clinical Applications ImagingRite Neuro Intervention 1 ImagingRite ImagingRite, a comprehensive suite of imaging tools offered with Infinix -i angiographic systems, was designed to assist clinicians in
Clinical Applications ImagingRite Neuro Intervention 1 ImagingRite ImagingRite, a comprehensive suite of imaging tools offered with Infinix -i angiographic systems, was designed to assist clinicians in
PRINCIPLES OF CT AND MR IMAGING Marc-André d Anjou, DMV, DACVR Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Montreal Saint-Hyacinthe, Quebec, Canada
 PRINCIPLES OF CT AND MR IMAGING Marc-André d Anjou, DMV, DACVR Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Montreal Saint-Hyacinthe, Quebec, Canada CT and MR imaging offer superior diagnostic possibilities
PRINCIPLES OF CT AND MR IMAGING Marc-André d Anjou, DMV, DACVR Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Montreal Saint-Hyacinthe, Quebec, Canada CT and MR imaging offer superior diagnostic possibilities
An ultrasonic volumetric scanner for image-guided surgery
 International Congress Series 1230 (2001) 190 196 An ultrasonic volumetric scanner for image-guided surgery Jeremy Johnson a,b, *,Ömer Oralkan b, Kambiz Kaviani b, Utkan Demirci b, Mustafa Karaman b, Pierre
International Congress Series 1230 (2001) 190 196 An ultrasonic volumetric scanner for image-guided surgery Jeremy Johnson a,b, *,Ömer Oralkan b, Kambiz Kaviani b, Utkan Demirci b, Mustafa Karaman b, Pierre
Computer-Aided Surgical Navigation Coding Guide Neurosurgery. May 1, 2009
 Computer-Aided Surgical Navigation Coding Guide Neurosurgery May 1, 2009 Please direct any questions to: Kim Brew Manager, Reimbursement and Therapy Access Medtronic Surgical Technologies (904) 279-7569
Computer-Aided Surgical Navigation Coding Guide Neurosurgery May 1, 2009 Please direct any questions to: Kim Brew Manager, Reimbursement and Therapy Access Medtronic Surgical Technologies (904) 279-7569
High quality and fast scanning with Compressed SENSE at KCH
 FieldStrength MRI articles High quality and fast scanning with at KCH FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - November 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength At Kurashiki Central Hospital, use of resulted
FieldStrength MRI articles High quality and fast scanning with at KCH FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - November 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength At Kurashiki Central Hospital, use of resulted
Ingenia MR-OR. MR Systems. Confident decision making with intraoperative insights
 Ingenia MR-OR MR Systems Confident decision making with intraoperative insights Confident decision making with intraoperative insights Ingenia MR-OR intraoperative MRI delivers high-quality images during
Ingenia MR-OR MR Systems Confident decision making with intraoperative insights Confident decision making with intraoperative insights Ingenia MR-OR intraoperative MRI delivers high-quality images during
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Maryland, Baltimore Baltimore, MD 21201
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0098 TITLE: Evaluation of Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging in Traumatic Brain Injury PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Rao P Gullapalli CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Maryland, Baltimore
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0098 TITLE: Evaluation of Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging in Traumatic Brain Injury PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Rao P Gullapalli CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Maryland, Baltimore
better images mean better results
 better images mean better results Welcome to a better way for YOU and YOUR patient brought to you by is your complete advanced neuro solution for streamlining workflow and providing exceptional clinical
better images mean better results Welcome to a better way for YOU and YOUR patient brought to you by is your complete advanced neuro solution for streamlining workflow and providing exceptional clinical
Clarity CT Technology
 Clarity CT Technology WHITE PAPER January 2013 Using state of the art algorithms Sapheneia Clarity CT allows physicians to lower radiation dose when acquiring CT data while maintaining image quality. The
Clarity CT Technology WHITE PAPER January 2013 Using state of the art algorithms Sapheneia Clarity CT allows physicians to lower radiation dose when acquiring CT data while maintaining image quality. The
Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL)
 Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Imaging Seminars Series Stony Brook University, Health Science Center Stony Brook, NY - December 11 th, 2012 Francesca Zanderigo, PhD Layout BASIC PRINCIPLES ACQUISITION SEQUENCES
Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Imaging Seminars Series Stony Brook University, Health Science Center Stony Brook, NY - December 11 th, 2012 Francesca Zanderigo, PhD Layout BASIC PRINCIPLES ACQUISITION SEQUENCES
Assignment of the Water Slow-Diffusing Component in the Central Nervous System Using q-space Diffusion MRS: Implications for Fiber Tract Imaging
 FULL PAPERS Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 43:191 199 (2000) Assignment of the Water Slow-Diffusing Component in the Central Nervous System Using q-space Diffusion MRS: Implications for Fiber Tract Imaging
FULL PAPERS Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 43:191 199 (2000) Assignment of the Water Slow-Diffusing Component in the Central Nervous System Using q-space Diffusion MRS: Implications for Fiber Tract Imaging
Clinical Translation of Tumor Acidosis Measurements with AcidoCEST MRI
 Electronic Supplementary Material Clinical Translation of Tumor Acidosis Measurements with AcidoCEST MRI Journal: Molecular Imaging and Biology Kyle M. Jones, B.S., 1 Edward A. Randtke, Ph.D., 2 Eriko
Electronic Supplementary Material Clinical Translation of Tumor Acidosis Measurements with AcidoCEST MRI Journal: Molecular Imaging and Biology Kyle M. Jones, B.S., 1 Edward A. Randtke, Ph.D., 2 Eriko
Introduction: what do we mean by Quantitative MRI?
 Introduction: what do we mean by Quantitative MRI? Paul Tofts PhD formerly Chair in Imaging Physics Brighton and Sussex Medical School, UK ISMRM 2010 Quantitative MRI slide 1 Overview 1. Quantification:
Introduction: what do we mean by Quantitative MRI? Paul Tofts PhD formerly Chair in Imaging Physics Brighton and Sussex Medical School, UK ISMRM 2010 Quantitative MRI slide 1 Overview 1. Quantification:
Detecting Peripheral Nerves in the Elbow using Three-Dimensional Diffusion-Weighted PSIF Sequences: a Feasibility Pilot Study
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:81-87 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.2.81 Detecting Peripheral Nerves in the Elbow using Three-Dimensional Diffusion-Weighted PSIF Sequences: a Feasibility
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:81-87 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.2.81 Detecting Peripheral Nerves in the Elbow using Three-Dimensional Diffusion-Weighted PSIF Sequences: a Feasibility
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy from fundamental developments to improved noninvasive diagnosis and characterisation of children s brain tumours.
 Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy from fundamental developments to improved noninvasive diagnosis and characterisation of children s brain tumours. Martin Wilson IOP Medical Physics Group Scientific and
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy from fundamental developments to improved noninvasive diagnosis and characterisation of children s brain tumours. Martin Wilson IOP Medical Physics Group Scientific and
Computational methods in bioinformatics: Lecture 1
 Computational methods in bioinformatics: Lecture 1 Graham J.L. Kemp 2 November 2015 What is biology? Ecosystem Rain forest, desert, fresh water lake, digestive tract of an animal Community All species
Computational methods in bioinformatics: Lecture 1 Graham J.L. Kemp 2 November 2015 What is biology? Ecosystem Rain forest, desert, fresh water lake, digestive tract of an animal Community All species
Magnetic Resonance Brain Image Segmentation and Reconstruction Technique Based on Genetic Fuzzy Clustering Technique
 Magnetic Resonance Brain Image Segmentation and Reconstruction Technique Based on Genetic Fuzzy Clustering Technique Liu Tao 1, *,Liu Xiuzhen 2 1 Faculty of Biomedical Engineering, The Fourth Military
Magnetic Resonance Brain Image Segmentation and Reconstruction Technique Based on Genetic Fuzzy Clustering Technique Liu Tao 1, *,Liu Xiuzhen 2 1 Faculty of Biomedical Engineering, The Fourth Military
Considerations in applying 3D PRESS H-1 brain MRSI with an eight-channel phased-array coil at 3 T
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging 24 (2006) 1295 1302 Considerations in applying 3D PRESS H-1 brain MRSI with an eight-channel phased-array coil at 3 T Yan Li a,b, Joseph A. Osorio a,b, Esin Ozturk-Isik a,b,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging 24 (2006) 1295 1302 Considerations in applying 3D PRESS H-1 brain MRSI with an eight-channel phased-array coil at 3 T Yan Li a,b, Joseph A. Osorio a,b, Esin Ozturk-Isik a,b,
The Unique, New MRI Philips Ingenia 3 Tesla is now in Ayios Therissos! The first-ever digital broadband MR system has been installed in Ayios
 The Unique, New MRI Philips Ingenia 3 Tesla is now in Ayios Therissos! The first-ever digital broadband MR system has been installed in Ayios Therissos-Nicosia that delivers crystal clear images, remarkable
The Unique, New MRI Philips Ingenia 3 Tesla is now in Ayios Therissos! The first-ever digital broadband MR system has been installed in Ayios Therissos-Nicosia that delivers crystal clear images, remarkable
MAGNETOM Skyra: The Mannheim Perspective
 MAGNETOM Skyra: The Mannheim Perspective Henrik J. Michaely; Stefan O. Schoenberg Institute of Clinical Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, University Medical Center Mannheim, University of Heidelberg, Germany
MAGNETOM Skyra: The Mannheim Perspective Henrik J. Michaely; Stefan O. Schoenberg Institute of Clinical Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, University Medical Center Mannheim, University of Heidelberg, Germany
Intraobserver and Interobserver Variability in Schemes for Estimating Volume of Brain Lesions on MR Images in Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:239 244, February 1998 Intraobserver and Interobserver Variability in Schemes for Estimating Volume of Brain Lesions on MR Images in Multiple Sclerosis Massimo Filippi, Mark A.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:239 244, February 1998 Intraobserver and Interobserver Variability in Schemes for Estimating Volume of Brain Lesions on MR Images in Multiple Sclerosis Massimo Filippi, Mark A.
Study of Laser Ablation in the In Vivo Rabbit Brain With MR Thermometry
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 16:147 152 (2002) Original Research Study of Laser Ablation in the In Vivo Rabbit Brain With MR Thermometry Lili Chen, PhD, 1 Janaka P. Wansapura, PhD, 1 Gary Heit,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 16:147 152 (2002) Original Research Study of Laser Ablation in the In Vivo Rabbit Brain With MR Thermometry Lili Chen, PhD, 1 Janaka P. Wansapura, PhD, 1 Gary Heit,
BME101 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering Medical Imaging Özlem BİRGÜL Ankara University Department of Biomedical Engineering
 BME101 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering Medical Imaging Özlem BİRGÜL Ankara University Department of Biomedical Engineering Outline What is Medical Imaging? History of Medical Imaging X-Ray Imaging
BME101 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering Medical Imaging Özlem BİRGÜL Ankara University Department of Biomedical Engineering Outline What is Medical Imaging? History of Medical Imaging X-Ray Imaging
Physicists Quality Control for MR Equipment
 Physicists Quality Control for MR Equipment Geoffrey D. Clarke, Ph.D. University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio 1 Overview ABR and the role of the Qualified Medical Physicist/ MR Scientist
Physicists Quality Control for MR Equipment Geoffrey D. Clarke, Ph.D. University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio 1 Overview ABR and the role of the Qualified Medical Physicist/ MR Scientist
Changes of lesion load on yearly dual-echo brain MR images are used as a secondary end-point to monitor the effects of treatment on multiple scle-
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:133 137, January 1999 Interscanner Variation in Brain MR Lesion Load Measurements in Multiple Sclerosis Using Conventional Spin-Echo, Rapid Relaxation-Enhanced, and Fast-FLAIR
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:133 137, January 1999 Interscanner Variation in Brain MR Lesion Load Measurements in Multiple Sclerosis Using Conventional Spin-Echo, Rapid Relaxation-Enhanced, and Fast-FLAIR
Optimization of 31 P magnetic resonance spectroscopy in vivo
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Optimization of 31 P magnetic resonance spectroscopy in vivo To cite this article: A V Manzhurtsev et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 945 012005 View
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Optimization of 31 P magnetic resonance spectroscopy in vivo To cite this article: A V Manzhurtsev et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 945 012005 View
your standard Making high performance Powered by ostream Multiva 1.5T MR systems This material is not for distribution in the USA.
 Multiva 1.5T MR systems This material is not for distribution in the USA. 2015 Koninklijke Philips N.V. All rights reserved. Specifications are subject to change without notice. Trademarks are the property
Multiva 1.5T MR systems This material is not for distribution in the USA. 2015 Koninklijke Philips N.V. All rights reserved. Specifications are subject to change without notice. Trademarks are the property
Ingenia MR-RT. MR Systems. The comprehensive MR-sim solution to fit your planning
 Ingenia MR-RT MR Systems The comprehensive MR-sim solution to fit your planning Table of contents Experience the difference MRI makes 3 A comprehensive MR-sim solution 4 Position with precision 6 See clearly
Ingenia MR-RT MR Systems The comprehensive MR-sim solution to fit your planning Table of contents Experience the difference MRI makes 3 A comprehensive MR-sim solution 4 Position with precision 6 See clearly
AAPM Scientific Meeting Imaging Symposium. State of the Art in Quantitative Imaging CT, PET and MRI. Which Imaging Modality is the Most Quantitative
 AAPM Scientific Meeting Imaging Symposium State of the Art in Quantitative Imaging CT, PET and MRI Michael McNitt-Gray, PhD, FAAPM; UCLA Paul Kinahan, PhD, U. Washington Ed Jackson, PhD, FAAPM, UT-MD Anderson
AAPM Scientific Meeting Imaging Symposium State of the Art in Quantitative Imaging CT, PET and MRI Michael McNitt-Gray, PhD, FAAPM; UCLA Paul Kinahan, PhD, U. Washington Ed Jackson, PhD, FAAPM, UT-MD Anderson
Leksell. Vantage Stereotactic System. Advancing stereotactic neurosurgery
 Leksell Vantage Stereotactic System Advancing stereotactic neurosurgery Innovation built on strong foundations Since the founding of our company by Lars Leksell more than 45 years ago, Elekta has delivered
Leksell Vantage Stereotactic System Advancing stereotactic neurosurgery Innovation built on strong foundations Since the founding of our company by Lars Leksell more than 45 years ago, Elekta has delivered
Introduction to Quantitative Imaging as a Biomarker in Clinical Trials
 Quantitative Medical Imaging for Clinical Research and Practice Educational Session ACRIN 2009 Introduction to Quantitative Imaging as a Biomarker in Clinical Trials Katarzyna J. Macura, MD, PhD Johns
Quantitative Medical Imaging for Clinical Research and Practice Educational Session ACRIN 2009 Introduction to Quantitative Imaging as a Biomarker in Clinical Trials Katarzyna J. Macura, MD, PhD Johns
Image-Guided Thoracic Surgery using a Mobile C-Arm for CBCT: Image Quality, Dose, and First Experience in Imaging the Fully Deflated Lung
 Image-Guided Thoracic Surgery using a Mobile C-Arm for CBCT: Image Quality, Dose, and First Experience in Imaging the Fully Deflated Lung S Schafer, 1 A Uneri, 1 DJ Mirota, 1 S Nithiananthan, 1 JW Stayman,
Image-Guided Thoracic Surgery using a Mobile C-Arm for CBCT: Image Quality, Dose, and First Experience in Imaging the Fully Deflated Lung S Schafer, 1 A Uneri, 1 DJ Mirota, 1 S Nithiananthan, 1 JW Stayman,
2018 REVIEW CATEGORIES
 2018 REVIEW CATEGORIES 100 Neuro 101 Neuro: Acquisition 102 Neuro: Processing 103 Neuro: Neonatal & Pediatric - Normal Development 104 Neuro: Neonatal & Pediatric - Clinical Studies 105 Neuro: Normal Aging
2018 REVIEW CATEGORIES 100 Neuro 101 Neuro: Acquisition 102 Neuro: Processing 103 Neuro: Neonatal & Pediatric - Normal Development 104 Neuro: Neonatal & Pediatric - Clinical Studies 105 Neuro: Normal Aging
GE Healthcare. PET/CT + MR Trimodality Imaging
 Unlocking new possibilities with PET/CT + MR 1 PET/CT MR PET/CT + MR The exquisite soft-tissue-contrast of 3.0T MR. The exceptional metabolic insight of PET imaging. The precise anatomical reference of
Unlocking new possibilities with PET/CT + MR 1 PET/CT MR PET/CT + MR The exquisite soft-tissue-contrast of 3.0T MR. The exceptional metabolic insight of PET imaging. The precise anatomical reference of
MEDICAL magnetic resonance (MR) imaging during interventional
 3382 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL. 40, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER 2004 Permanent Conical Magnet for Interventional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Manlio G. Abele and Henry Rusinek Abstract We describe an open
3382 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL. 40, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER 2004 Permanent Conical Magnet for Interventional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Manlio G. Abele and Henry Rusinek Abstract We describe an open
Life Sciences Reporting Summary
 Life Sciences Reporting Summary Adams Waldorf, Rajagopal, Gale Initial submission Revised version Final submission Nature Research wishes to improve the reproducibility of the work that we publish. This
Life Sciences Reporting Summary Adams Waldorf, Rajagopal, Gale Initial submission Revised version Final submission Nature Research wishes to improve the reproducibility of the work that we publish. This
Comparison of the course and key points of the Optic Radiations using dissection and Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 Comparison of the course and key points of the Optic Radiations using dissection and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Naam student: Roland P. Nooij Studentnummer: 1816845 Facultair begeleider: E.W. Hoving Extern
Comparison of the course and key points of the Optic Radiations using dissection and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Naam student: Roland P. Nooij Studentnummer: 1816845 Facultair begeleider: E.W. Hoving Extern
Class 7: Methods in Research By: Ray
 Class 7: Methods in Research By: Ray Method in Brain Research 1. Non-Invasive (Human) o Imaging Computerized (Axial) Tomography (X-rays). Static pictures and high spatial resolution. Horizontal plane only.
Class 7: Methods in Research By: Ray Method in Brain Research 1. Non-Invasive (Human) o Imaging Computerized (Axial) Tomography (X-rays). Static pictures and high spatial resolution. Horizontal plane only.
Supplementary Figure 1 Sizing and Relaxometry of Derivatized Ferumoxytol. a, Dynamic light scattering shows no change in diameter between the
 Supplementary Figure 1 Sizing and Relaxometry of Derivatized Ferumoxytol. a, Dynamic light scattering shows no change in diameter between the clinical specimen (Ferumoxytol) after buffer exchange and the
Supplementary Figure 1 Sizing and Relaxometry of Derivatized Ferumoxytol. a, Dynamic light scattering shows no change in diameter between the clinical specimen (Ferumoxytol) after buffer exchange and the
Award Number: W81XWH TITLE: Magnetic Resonance Characterization of Axonal Response to Spinal Cord Injury
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0713 TITLE: Magnetic Resonance Characterization of Axonal Response to Spinal Cord Injury PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: David B Hackney CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Beth Israel Deaconess
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0713 TITLE: Magnetic Resonance Characterization of Axonal Response to Spinal Cord Injury PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: David B Hackney CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Beth Israel Deaconess
Vantage Titan 1.5T MR. The Intelligent Choice.
 Vantage Titan 1.5T MR. The Intelligent Choice. Scalable. M-Powered. Performance. Vantage Titan MR is designed to satisfy the demands of today s challenging clinical environment, addressing the requirements
Vantage Titan 1.5T MR. The Intelligent Choice. Scalable. M-Powered. Performance. Vantage Titan MR is designed to satisfy the demands of today s challenging clinical environment, addressing the requirements
The Reliability of Preoperative Simulation Surgery Planning for Distraction Osteogensis in Craniosynostosis Patients
 Original Article Journal of International Society for Simulation Surgery 2016;3(1):22-27 pissn 2383-5389 / eissn 2383-8116 http://dx.doi.org/10.18204/jissis.2016.3.1.022 ORCID Mohammed Ahmed Hussein: orcid.org/0000-0002-5807-6628
Original Article Journal of International Society for Simulation Surgery 2016;3(1):22-27 pissn 2383-5389 / eissn 2383-8116 http://dx.doi.org/10.18204/jissis.2016.3.1.022 ORCID Mohammed Ahmed Hussein: orcid.org/0000-0002-5807-6628
Quality Control Concerns for New Generations of CT, MRI, & PET
 Quality Control Concerns for New Generations of CT, MRI, & PET David W. Jordan, Ph.D. Sr. Medical Physicist, UH Case Medical Center Clinical Assistant Professor, CWRU Disclosures No financial disclosures
Quality Control Concerns for New Generations of CT, MRI, & PET David W. Jordan, Ph.D. Sr. Medical Physicist, UH Case Medical Center Clinical Assistant Professor, CWRU Disclosures No financial disclosures
Buy One, Get Two for Free: Simultaneous Knee T2 Mapping and Morphological Analysis On Synthetic Images Using GRAPPATINI
 Buy One, Get Two for Free: Simultaneous Knee T2 Mapping and Morphological Analysis On Synthetic Images Using GRAPPATINI Marion Roux, Tom Hilbert, Jean-Baptise Ledoux, Fabio Becce, Tobias Kober, Patrick
Buy One, Get Two for Free: Simultaneous Knee T2 Mapping and Morphological Analysis On Synthetic Images Using GRAPPATINI Marion Roux, Tom Hilbert, Jean-Baptise Ledoux, Fabio Becce, Tobias Kober, Patrick
MRI. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 MRI Magnetic Resonance Imaging Key Points MRI: The magnet is always on Know the essential components of an MRI system Know general idea of how MRI captures an image; three steps: Magnetic Alignment, Proton
MRI Magnetic Resonance Imaging Key Points MRI: The magnet is always on Know the essential components of an MRI system Know general idea of how MRI captures an image; three steps: Magnetic Alignment, Proton
Radiography Curriculum Analysis
 Program Number Program Name Date / /20 Radiography Curriculum Analysis DIRECTIONS: Determine the course(s) in which each of the following content area is covered and enter the course number(s) and/or title(s).
Program Number Program Name Date / /20 Radiography Curriculum Analysis DIRECTIONS: Determine the course(s) in which each of the following content area is covered and enter the course number(s) and/or title(s).
Determination of the Orientation of Collagen Fibers in Human Bone
 THE ANATOMICAL RECORD 266:103 107 (2002) DOI 10.1002/ar.10043 Determination of the Orientation of Collagen Fibers in Human Bone SHIGEYOSHI OSAKI, 1 *SETSUKO TOHNO, 2 YOSHIYUKI TOHNO, 2 KAZUO OHUCHI, 3
THE ANATOMICAL RECORD 266:103 107 (2002) DOI 10.1002/ar.10043 Determination of the Orientation of Collagen Fibers in Human Bone SHIGEYOSHI OSAKI, 1 *SETSUKO TOHNO, 2 YOSHIYUKI TOHNO, 2 KAZUO OHUCHI, 3
Meet your new business partner. MAGNETOM ESSENZA. Answers for life.
 Meet your new business partner. MAGNETOM ESSENZA Answers for life. The most affordable *, all-new 1.5T MRI MAGNETOM ESSENZA was developed from the ground up to be an affordable, reliable powerhouse that
Meet your new business partner. MAGNETOM ESSENZA Answers for life. The most affordable *, all-new 1.5T MRI MAGNETOM ESSENZA was developed from the ground up to be an affordable, reliable powerhouse that
LASER ULTRASONICS INSPECTIONS OF AERONAUTICAL COMPONENTS VALIDATED BY COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY
 7 th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace Mo.3.A.2 LASER ULTRASONICS INSPECTIONS OF AERONAUTICAL COMPONENTS VALIDATED BY COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Esmeralda CUEVAS AGUADO 1, Carlos GALLEGUILLOS 2, Covadonga
7 th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace Mo.3.A.2 LASER ULTRASONICS INSPECTIONS OF AERONAUTICAL COMPONENTS VALIDATED BY COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Esmeralda CUEVAS AGUADO 1, Carlos GALLEGUILLOS 2, Covadonga
Complex Treatments in Proton Therapy - Selected Topics. Martin Bues, PhD Proton Therapy M.D. Anderson Cancer Center
 Complex Treatments in Proton Therapy - Selected Topics Educational Workshop PTCOG 46, May 18-20, Wanjie, China Martin Bues, PhD Proton Therapy M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Outline Topic 1: Topic 2: Topic
Complex Treatments in Proton Therapy - Selected Topics Educational Workshop PTCOG 46, May 18-20, Wanjie, China Martin Bues, PhD Proton Therapy M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Outline Topic 1: Topic 2: Topic
QIBA Profile: Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DWI)
 QIBA Profile: Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DWI) Stage: A. Initial Draft Notation in this Template Template Element Appears as Instructions Boilerplate text Plain black text Don't change.
QIBA Profile: Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DWI) Stage: A. Initial Draft Notation in this Template Template Element Appears as Instructions Boilerplate text Plain black text Don't change.
CT Guided Electromagnetic Navigational Bronchoscopy
 CT Guided Electromagnetic Navigational Bronchoscopy Duke Thoracoscopic Lobectomy Workshop March 21, 2018 Thomas A. D Amico MD Gary Hock Professor of Surgery Chief Thoracic Surgery, Chief Medical Officer
CT Guided Electromagnetic Navigational Bronchoscopy Duke Thoracoscopic Lobectomy Workshop March 21, 2018 Thomas A. D Amico MD Gary Hock Professor of Surgery Chief Thoracic Surgery, Chief Medical Officer
Propel your imaging abilities into the future.
 GE Healthcare Propel your imaging abilities into the future. SIGNA CREATOR Imagine what MR can be. Leap ahead and create your future in imaging. Meet SIGNA Creator, named for its ability to help you create
GE Healthcare Propel your imaging abilities into the future. SIGNA CREATOR Imagine what MR can be. Leap ahead and create your future in imaging. Meet SIGNA Creator, named for its ability to help you create
Optimisation in CT. A case for shared approach. Stephen J. Golding University of Oxford
 Optimisation in CT A case for shared approach Stephen J. Golding University of Oxford Body CT 1979: 10 mm sections 20 second exposure 60 second reconstruction Body CT 2007 Submillimetre sections instant
Optimisation in CT A case for shared approach Stephen J. Golding University of Oxford Body CT 1979: 10 mm sections 20 second exposure 60 second reconstruction Body CT 2007 Submillimetre sections instant
Computed Tomography: Optimization of acquisition protocols & Justification of clinical referrals. Koos Geleijns, medical physicist
 Computed Tomography: Optimization of acquisition protocols & Justification of clinical referrals Koos Geleijns, medical physicist CT delivers excellent 3D image quality CT delivers excellent 3D image quality
Computed Tomography: Optimization of acquisition protocols & Justification of clinical referrals Koos Geleijns, medical physicist CT delivers excellent 3D image quality CT delivers excellent 3D image quality
QIBA Profile: Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DWI)
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 QIBA Profile: Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DWI) Stage: A. Initial Draft Notation in this Template Template Element Appears as Instructions Boilerplate
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 QIBA Profile: Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DWI) Stage: A. Initial Draft Notation in this Template Template Element Appears as Instructions Boilerplate
The Latest in Radiation Dose Reduction Techniques in CT
 The Latest in Radiation Dose Reduction Techniques in CT Cynthia H. McCollough, PhD, FAAPM, FACR Professor of Radiologic Physics Director, CT Clinical Innovation Center Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic,
The Latest in Radiation Dose Reduction Techniques in CT Cynthia H. McCollough, PhD, FAAPM, FACR Professor of Radiologic Physics Director, CT Clinical Innovation Center Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic,
DESIGN OF AN ANTHROPOMORPHIC INTENSITY MODULATED RADIATION THERAPY QUALITY ASSURANCE PHANTOM
 DESIGN OF AN ANTHROPOMORPHIC INTENSITY MODULATED RADIATION THERAPY QUALITY ASSURANCE PHANTOM Dee-Ann Radford, David S. Followill, Peter A. Balter, William F. Hanson Department of Radiation Physics The
DESIGN OF AN ANTHROPOMORPHIC INTENSITY MODULATED RADIATION THERAPY QUALITY ASSURANCE PHANTOM Dee-Ann Radford, David S. Followill, Peter A. Balter, William F. Hanson Department of Radiation Physics The
Geneva January 10 11, th Swiss Experimental. Surgery Symposium. MGY / 4thSESS /
 4th Swiss Experimental Surgery Symposium Geneva January 10 11, 2008 Source: Reflex issue 2, 2007 The 3 Rs Reduction Replacement Refinement NC3R http://www.nc3rs.org.uk/category.asp?catid =9 No specific
4th Swiss Experimental Surgery Symposium Geneva January 10 11, 2008 Source: Reflex issue 2, 2007 The 3 Rs Reduction Replacement Refinement NC3R http://www.nc3rs.org.uk/category.asp?catid =9 No specific
A Dynamic Data Driven Grid System for Intra-operative Image Guided Neurosurgery
 A Dynamic Data Driven Grid System for Intra-operative Image Guided Neurosurgery A Majumdar 1, A Birnbaum 1, D Choi 1, A Trivedi 2, S. K. Warfield 3, K. Baldridge 1, and Petr Krysl 2 1 S & 2 Structural
A Dynamic Data Driven Grid System for Intra-operative Image Guided Neurosurgery A Majumdar 1, A Birnbaum 1, D Choi 1, A Trivedi 2, S. K. Warfield 3, K. Baldridge 1, and Petr Krysl 2 1 S & 2 Structural
