SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
|
|
|
- Gyles Perkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Table 1: RT-qPCR primer sequences. Sequences are shown from 5 to 3 direction; all primers are designed using mouse genome as reference. 36B4-F; TGAAGCAAAGGAAGAGTCGGAGGA LIPA-F; TGACTGACTAGCAAGCGTCCACAA 36B4-R; AAGCAGGCTGACTTGGTTGCTTTG L14Rik-F: TGGATACTGGTTTGAAGGGAGGCA L14Rik-R: AGCCTTTGTCCCAGCTAAAGTCCT ABCG8-F: TTGGACAACCTGTGGATAGTGCCT ABCG8-R: GGTGAAGTTGCCGATTTGTGTGGT ABO-F: ACAGACACTGAACCATCCTGGGTT ABO-R: AGACAAACACTGCGAAGGGAAGGA ADAMTS7-F; TCATGAACATGGTGGCTGGACTCT ADAMTS7-R; AGTCTCTTCGGCATGGTGTGTGAT ApoA1-F: TCACCCACACCCTTCAGGATGAAA ApoA1-R: ACACATAGTCTCTGCCGCTGTCTT APOA4-F: TTCTGACTCCGGGAAACATCCAGT APOA4-R: CTTGGCATTGTTGCTTAGCTGGGT APOA5-F: GCTTTGCAAACCCAGCTTCTGGTA APOA5-R: TTAACAGGAGCCCAACTCCAGGTT APOC3-F: TACAGGGCTACATGGAACAAGCCT APOC3-R: AGAATCCCAGAAGCCGGTGAACTT ATP5G1-F; ACGGGAATTCCAGACCAGTGTCAT ATP5G1-R; AGCTACCAAACACTGTGCCAATGC B2M-F; GCAGGTTCAAATGAATCTTCAGAGCATC B2M-R; TACGTAACACAGTTCCACCCGCCTC CD31-F; TGGAGTGGTCATCGCCACCTTAAT CD31-R; AACAGAAACCCGTGGAGATGTCCA CDKN2A-F: ACATCGTGCGATATTTGCGTTCCG CDKN2A-R: TTTAGCTCTGCTCTTGGGATTGGC CDKN2B-F: TGTTTGACATTTGGGTGGGTGCAG CDKN2B-R: ATTTCCTTGTCGAGCTGGAGGTGA CELSR2-F: ATGAGTGTGCTGGTGTCAGATGGT CELSR2-R: TGAATGAAGAGTCCCAGCAGTGGT CNNM2-F; GCCCACCGTGAAAGAAAGCAAGAT CNNM2-R; ATCTGGGATGGGCTAAACGCTTCT COL4A1-F; AGGATGCAACGGTACAAAGGGAGA COL4A1-R; TGGCCGAGAATTTCACCAGGATCT COL4A2-F: GCCAAACGCACTTCCTGGAATCAA COL4A2-R: CGGTGTTGCCCATGAATCCTTGTT CXCL12-F; TGCACGGCTGAAGAACAACAACAG LIPA-R; ATTACCTCCACACAAGGGCCAGAA MAPKAPK5-F; GCACCAAGCCAAAGGACGGTATTT MAPKAPK5-R; GAGCTTGCATTCGCGGTTGTACTT MIA3-F; TGAGTGCCATCGGGTTCAAGAAGA MIA3-R; TCGGCATGCGATTTACTCCACTCT MORF4L1-F; AATGGAGATGGTGGCAGTACCAGT MORF4L1-R; AATGGAGATGGTGGCAGTACCAGT MRAS-F: TCAGTGGGCCATCTTGGATGTTCT MRAS-R: TTGGGAATGACTCCCTGTCCTTGA MRPS6-F; TTGCTGCAGGAGGTAGAAACTGCT MRPS6-R; AGGCTTGCAAGACAACCAAGTGTG NT5C2-F: AAGTCAAAGAAACGGCAAGGGTGG NT5C2-R: TGCTGTCCAGGTGCTTGTAGAGTT PCSK9-F; ACAAGGACAGTCAACTCACAGCCA PCSK9-R; TGCAGCAGATGAGGACATCTGGAA PDGFD-F: ACTCCGCAGAGAGCATCCATCAAA PDGFD-R: GGCCATTGCTTGTCACCTGAATGT PEMT-F; TATGATGAGCCAGCCCAAGATGGA PEMT-R; GAAGCTGGACAGCACAAACACGAA PHACTR1-F; AAATCAAGAGGAGGCTGACTCGCA PHACTR1-R; TGCCACTTCCACGTAGTCACTGAA PIK3CG-F; TTTGTGGAAGCGAACATCCAGCAC PIK3CG-R; ATGCCAAACTCCAGCCACACATTC PPBP-F-F: TAACCTCCAGATCTTGCTGCTGCT PPBP-R-R: ACTCCTGGCCTGTACACATTCACA PSRC1-F; TCCTCAGCTAGCAACTCCCAATGT PSRC1-R; AGAATCTGGAGCTAGGGCACCTTT RASD1-F: AAGAGGTGCAAAGGCTCAAACAGC RASD1-R: TTTGTTACCGCAAATGACCAGCGG SH2B3-F: AGCCACTTTCTGCAGCTCTTCGAT SH2B3-R: AGTTCAGCTGCTGTTCATCTCCCA SLC22A3-F; ATCACCCGGAAGCAAGGAGAGAAA SLC22A3-R; GCGCTCGTGAACCAAGCAAACATA SLC5A3-F; TATTGTGGAGATGCAAGGAGGCCA SLC5A3-R; AAGAACAAAGCCTGCCATTCCACC SMG6-F; TATCGGGAGCAAGCCAACGATACA
2 CXCL12-R; TCACACCTCTCACATCTTGAGCCT CYP17A1-F: AAGCATATCCTTGTCACGGTGGGA CYP17A1-R: ACGGTGTTCGACTGAAGCCTACAT GALNT4-F; GATTGGTGGGTTTGACTGGCGTTT GALNT4-R; ATTCTTGACGTTCGCCTGTCCCTT GIP-F: TGGCTTTGAAGACCTGCTCTCTGT GIP-R: GGGCCAGCAAATTTAGCATGGGAT HHIPL1-F; AAGCTGGGTAAATCAGTCACCGGA HHIPL1-R; ACCTCGCTATACTTCCATTGGCCT HNF1A-F;TGTCTGCGGCCTTACACCAAGTAT HNF1A-R; AGGTAGCGAGGCCATGATAAGGTT ICAM1-F; AGATCACATTCACGGTGCTGGCTA ICAM1-R; AGCTTTGGGATGGTAGCTGGAAGA IL5-F: TCCCATGAGCACAGTGGTGAAAGA IL5-R : AGGAAGCCTCATCGTCTCATTGCT KCNE2-F: AGGGCTTACAGGTCTCAAGCTGAA KCNE2-R: ATTGGCTAATGTGGCCATGCTTCC KIAA1462-F;AGAATCGCGTCTTGGTGTTCCTGA KIAA1462-R; AGGGAAGACTGAGTGCAAAGCTGA KLHDC10-F; ACGGACTGGGTCGCTGTTTAAGAT KLHDC10-R; AACGCTCGATGAGTTCCTGTGTGA SMG6-R; AGGATAGGGTTGCTGGCTGCTAAA SNF8-F; AGAAGAAACTCGCAGAGGCCAAGT SNF8-R; TCTTCCGGATCTCTTGCTTGTGCT SORT1-F; ACCTGTTAGCTCTCAGCACCGAAA SORT1-R; CAGCTTTGCAGGAGCCATTCACAT SRR-F; AAGGAACAATTGCCCTGGAAGTGC SRR-R; ATTCCAGCAACCATTCCTCCTCCT TCF21-F; AGATCCCACCTCAAACCCAACACA TCF21-R; TGTTGGAGTCCACTTTCAGGGAGT TCTN1-F; TGCTGGTGCTCCTAAACTGCTACA TCTN1-R; TGGCCTTGGTGGAATTGAGATCCT TRIB1-F: CTTCAAGCAGATTGTTTCCGCCGT TRIB1-R: AGGCTTTCCAGTCTAAGCTGGGTT UBE2Z-F: AGTCTGTGACATGATGGAGGGCAA UBE2Z-R TTGCAGGCCACCTCATAGAAGTCA WDR12-F; AACGTTTGGCATCTGGAAGCACAG WDR12-R; AGAGACAGCGACACCAAAGAACCA ZC3HC1-F; AGTGAGTTCCTGGACCGGTTTCAA ZC3HC1-R; AATCAAGCTCATCCTCCAGCAGGT ZFP259-F; TGATGATCCCTCGGGAAACAGCTT ZFP259-R; TGCACTCTGGGCAGTTAGTGTTGA LDLR-F; CAACAATGGTGGCTGTTCCCACAT LDLR-R; ACTCACACTTGTAGCTGCCTTCCA
3 Supplementary Table 2: Fold-change values of GWAS CAD candidate genes exhibiting differential expression from healthy to diseased cell types.
4 Supplementary Table 3: SNPs that had the most significant association in published GWAS studied were interrogated for their association with nearby gene expression in human aortic endothelial cells. Proxies for SNPs that were not genotyped were used to determine significant association. NA indicates no information was available for that SNP. GWAS SNP Chrom osome Proxy SNP Pairwise LD (r2) Distance from GWAS SNP (bp) Candidate gene(s) reported mouse homologs rs rs PPAP2B Ppap2b rs rs IL5 Il5 rs rs PIK3CG Pik3cg rs rs TRIB1 Trib1 rs rs ABO Abo rs rs PDGFD Pdgfd rs rs SH2B3 Sh2b3 rs rs ADAMTS7,MORF4L1 Adamts7, Morf4l1 rs rs RASD1, SMCR3, PEMT Rasd1, --, Pemt rs rs SMG6-SRR Smg6-Srr rs rs SLC5A3-MRPS6-KCNE2 Slc5a3-Mrps6-Kcne rs genotyped PCSK9 Pcsk9 rs genotyped MIA3 Mia3 rs genotyped SORT1-CELSR2-PSRC1 Sort1-Celsr2-Psrc1 rs genotyped MRAS Mras rs genotyped TCF21 Tcf21 rs genotyped PHACTR1 Phactr1 rs genotyped ANKS1A Anks1a rs genotyped ZC3HC1 Zc3hc1 rs genotyped ANRIL/CDKN2BAS Cdkn2a-Cdkn2b rs genotyped CYP17A1-NT5C2- CNNM2 rs genotyped LIPA Lipa rs genotyped CXCL12 Cxcl12 rs genotyped KIAA1462 Kiaa1462 Cyp17a1-Nt5c2- Cnnm2 rs genotyped ZNF259, APOA1-C3- A4-A5 Zfp259, ApoA1-C3- A4-A5 rs genotyped COL4A1-A2 Col4a1-Col4a2 rs genotyped UBE2Z-GIP-ATP5G1- SNF8 Ube2z-Gip-Atp5g1- Snf8 rs genotyped LDLR Ldlr rs NA LPA -- rs NA ABCG8 Abcg8 rs NA WDR12 Wdr12 rs NA C6orf L14Rik rs NA SLC22A3-LPAL2-LPA Slc22a3 rs NA HHIPL1 Hhipl1 rs NA APOE ApoE
5 Supplementary Table 4: Differential expression of genes at CAD GWAS loci with multiple candidate genes reported.
6 Supplementary Table 5: Differential expression of genes at CAD GWAS loci across all four cell types as determined by multivariate analysis comparing healthy to diseased state. Hotelling s T 2 test was performed for each gene using all samples; significance threshold is set at Gene Symbol Hotelling s T 2 test P-value Gene Symbol Hotelling s T 2 test P-value Col4a2 6.99E-03 Apoa1 1.00E+00 Cxcl E-03 Apoc3 1.00E+00 Nt5c2 2.60E-02 Cdkn2a 1.00E+00 Icam1 2.65E-02 Celsr2 1.00E+00 Mia3 2.67E-02 Cyp17a1 1.00E+00 Ppap2b 3.88E-02 Gip 1.00E+00 Pik3cg 4.41E-02 Hhipl1 1.00E+00 Mapkapk5 5.65E-02 Il5 1.00E+00 Smg6 5.80E-02 Klhdc E+00 Trib1 6.01E-02 Ldlr 1.00E+00 Adamts7 6.15E-02 Morf4l1 1.00E+00 Mrps6 1.08E-01 Pdgfd 1.00E+00 Cdkn2b 1.17E-01 Pemt 1.00E+00 Mras 1.22E-01 Phactr1 1.00E+00 Anks1a 1.33E-01 Rasd1 1.00E+00 Ube2z 1.37E-01 Slc22a3 1.00E+00 Snf8 1.43E-01 Slc5a3 1.00E+00 Srr 1.54E-01 Sort1 1.00E+00 Pcsk9 1.57E-01 Tcf E+00 KIAA E-01 Tctn1 1.00E+00 Col4a1 1.78E-01 Wdr E+00 Galnt4 1.94E-01 Zc3hc1 1.00E+00 Psrc1 2.63E-01 Zfp E+00 Cnnm2 2.87E-01 Abcg8 Not expressed Lipa 3.77E-01 Abo Not expressed Sh2b3 4.28E-01 Apoa4 Not expressed L14Rik 5.11E-01 Apoa5 Not expressed Atp5g1 6.28E-01 Kcne Not expressed
7 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: ApoE -/- BL6 mice at 4 weeks of age do not have the visible lipid deposits that are present in 24 week ApoE -/- BL6 mice, while 24 week wild-type BL6 mice do not develop atherosclerosis. Histology slides of sectioned aortic arch stained with oil red o, magnification 20x. A: 4 week, BL6 ApoE -/-; no lipid deposits observed B: 24 week BL6 ApoE -/-; intimal lesions visible C: 24 week BL6 wild-type; no lipid deposits observed
8 Supplementary Figure 2: Clustering of donors used in the study based on their genotypes with HapMap3 populations. HAEC: Human Aortic Endothelial Cell Donors; ASW: African ancestry in Southwest USA; CEU: Utah residents with Northern and Western European ancestry from the CEPH collection; CHB: Han Chinese in Beijing, China; CHD: Chinese in Metropolitan Denver, Colorado; GIH: Gujarati Indians in Houston, Texas; JPT: Japanese in Tokyo, Japan; LWK: Luhya in Webuye, Kenya; MXL: Mexican ancestry in Los Angeles, California; MKK: Maasai in Kinyawa, Kenya; TSI: Toscani in Italia; YRI: Yoruba in Ibadan, Nigeria.
9 Supplementary Figure 3. Genome-wide association of gene expression in HAECs under control and oxpapc conditions. The diagonal line with strong association depicts the local eqtls and each off-diagonal dot depicts the location of distant eqtls. Color of the dot is proportional to the association significance p-value. 1,502 and 1,504 genes had a significant cis association with nearby SNPs in control and oxpapc-treated cells, respectively. 1,239 of the transcripts overlapped between the two datasets. 185 and 164 genes showed evidence for trans associations in control and oxpapc-treated cells, respectively. 22 of the transcripts overlapped between two datasets
10 Supplementary Figure 4. Regional association plots of SNF8 transcript levels. Left panels show the regional association of SNF8 gene expression in (A) control and (B) oxpapc conditions. Association of the genotyped SNPs and the transcript expression as indicated by log 10 (P) values are plotted. The color of the SNPs indicates the strength of linkage disequilibrium with the peak SNP, which is in purple. Recombination rates are based on 1000 genomes European populations (1). Right panels show the expression level of SNF8 in individuals based on their SNP rs46522 genotypes.
11 Supplementary Figure 5. Regional association plots of SRR transcript levels. Left panels show the regional association of SRR gene expression in (A) control and (B) oxpapc conditions. Association of the genotyped SNPs and the transcript expression as indicated by log 10 (P) values are plotted. The color of the SNPs indicates the strength of linkage disequilibrium with the peak SNP, which is in purple. Recombination rates are based on 1000 genomes European populations (1). Right panels show the expression level of SRR in individuals based on their SNP rs (proxy for GWAS peak SNP rs216172, r 2 =1) genotypes.
12 Supplementary Figure 6. Regional association plots of MAPKAPK5 transcript levels. Left panels show the regional association of MAPKAPK5 gene expression in (A) control and (B) oxpapc conditions. Association of the genotyped SNPs and the transcript expression as indicated by log 10 (P) values are plotted. The color of the SNPs indicates the strength of linkage disequilibrium with the peak SNP, which is in purple. Recombination rates are based on 1000 genomes European populations (1). Right panels show the expression level of MAPKAPK5 in individuals based on their SNP rs (proxy for GWAS peak SNP rs , r 2 =0.873) genotypes.
13 Supplementary Figure 7. Regional association plots of TCTN1 transcript levels. Left panels show the regional association of TCTN1 gene expression in (A) control and (B) oxpapc conditions. Association of the genotyped SNPs and the transcript expression as indicated by log 10 (P) values are plotted. The color of the SNPs indicates the strength of linkage disequilibrium with the peak SNP, which is in purple. Recombination rates are based on 1000 genomes European populations (1). Right panels show the expression level of TCTN1 in individuals based on their SNP rs (proxy for GWAS peak SNP rs , r 2 =0.873) genotypes.
14 Supplementary Figure 8. Regional association plots of GALNT4 transcript levels. Left panels show the regional association of GALNT4 gene expression in (A) control and (B) oxpapc conditions. Association of the genotyped SNPs and the transcript expression as indicated by log 10 (P) values are plotted. The color of the SNPs indicates the strength of linkage disequilibrium with the peak SNP, which is in purple. Recombination rates are based on 1000 genomes European populations (1). Right panels show the expression level of GALNT4 in individuals based on their SNP rs genotypes.
15 Supplementary Figure 9. Regional association plots of PPAP2B transcript levels. Left panels show the regional association of PPAP2B gene expression in (A) control and (B) oxpapc conditions. Association of the genotyped SNPs and the transcript expression as indicated by log 10 (P) values are plotted. The color of the SNPs indicates the strength of linkage disequilibrium with the peak SNP, which is in purple. Recombination rates are based on 1000 genomes European populations (1). Right panels show the expression level of GALNT4 in individuals based on their SNP rs (proxy for GWAS peak SNP rs , r 2 =0.831) genotypes.
16 Supplementary Figure 10. Regional association plots of ICAM1 transcript levels. Left panels show the regional association of ICAM1 gene expression in (A) control and (B) oxpapc conditions. Association of the genotyped SNPs and the transcript expression as indicated by log 10 (P) values are plotted. The color of the SNPs indicates the strength of linkage disequilibrium with the peak SNP, which is in purple. Recombination rates are based on 1000 genomes European populations (1). Right panels show the expression level of ICAM1 in individuals based on their SNP rs genotypes. SUPPLEMENTARY REFERENCE 1. Pruim, R. J., R. P. Welch, S. Sanna, T. M. Teslovich, P. S. Chines, T. P. Gliedt, M. Boehnke, G. R. Abecasis, and C. J. Willer LocusZoom: regional visualization of genome-wide association scan results. Bioinformatics 26:
Genotyping Technology How to Analyze Your Own Genome Fall 2013
 Genotyping Technology 02-223 How to nalyze Your Own Genome Fall 2013 HapMap Project Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Samples & POP panels Genotyping centers Unique QC+ SNPs 269 samples (4 populations) HapMap International
Genotyping Technology 02-223 How to nalyze Your Own Genome Fall 2013 HapMap Project Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Samples & POP panels Genotyping centers Unique QC+ SNPs 269 samples (4 populations) HapMap International
S G. Design and Analysis of Genetic Association Studies. ection. tatistical. enetics
 S G ection ON tatistical enetics Design and Analysis of Genetic Association Studies Hemant K Tiwari, Ph.D. Professor & Head Section on Statistical Genetics Department of Biostatistics School of Public
S G ection ON tatistical enetics Design and Analysis of Genetic Association Studies Hemant K Tiwari, Ph.D. Professor & Head Section on Statistical Genetics Department of Biostatistics School of Public
Haplotypes, linkage disequilibrium, and the HapMap
 Haplotypes, linkage disequilibrium, and the HapMap Jeffrey Barrett Boulder, 2009 LD & HapMap Boulder, 2009 1 / 29 Outline 1 Haplotypes 2 Linkage disequilibrium 3 HapMap 4 Tag SNPs LD & HapMap Boulder,
Haplotypes, linkage disequilibrium, and the HapMap Jeffrey Barrett Boulder, 2009 LD & HapMap Boulder, 2009 1 / 29 Outline 1 Haplotypes 2 Linkage disequilibrium 3 HapMap 4 Tag SNPs LD & HapMap Boulder,
De novo human genome assemblies reveal spectrum of alternative haplotypes in diverse
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION De novo human genome assemblies reveal spectrum of alternative haplotypes in diverse populations Wong et al. The Supplementary Information contains 4 Supplementary Figures, 3
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION De novo human genome assemblies reveal spectrum of alternative haplotypes in diverse populations Wong et al. The Supplementary Information contains 4 Supplementary Figures, 3
Population description. 103 CHB Han Chinese in Beijing, China East Asian EAS. 104 JPT Japanese in Tokyo, Japan East Asian EAS
 1 Supplementary Table 1 Description of the 1000 Genomes Project Phase 3 representing 2504 individuals from 26 different global populations that are assigned to five super-populations Number of individuals
1 Supplementary Table 1 Description of the 1000 Genomes Project Phase 3 representing 2504 individuals from 26 different global populations that are assigned to five super-populations Number of individuals
Resources at HapMap.Org
 Resources at HapMap.Org HapMap Phase II Dataset Release #21a, January 2007 (NCBI build 35) 3.8 M genotyped SNPs => 1 SNP/700 bp # polymorphic SNPs/kb in consensus dataset International HapMap Consortium
Resources at HapMap.Org HapMap Phase II Dataset Release #21a, January 2007 (NCBI build 35) 3.8 M genotyped SNPs => 1 SNP/700 bp # polymorphic SNPs/kb in consensus dataset International HapMap Consortium
I/O Suite, VCF (1000 Genome) and HapMap
 I/O Suite, VCF (1000 Genome) and HapMap Hin-Tak Leung April 13, 2013 Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Ethnic Composition of 1000G vs HapMap........................ 2 2 1000 Genome vs HapMap YRI (Africans)
I/O Suite, VCF (1000 Genome) and HapMap Hin-Tak Leung April 13, 2013 Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Ethnic Composition of 1000G vs HapMap........................ 2 2 1000 Genome vs HapMap YRI (Africans)
Haplotypes Personalized Medicine: Understanding Your Own Genome Fall 2014
 Haplotypes 02-223 Personalized Medicine: Understanding Your Own Genome Fall 2014 Terminology Review llele: different forms of genecc variacons at a given gene or genecc locus Locus 1 has two alleles, and
Haplotypes 02-223 Personalized Medicine: Understanding Your Own Genome Fall 2014 Terminology Review llele: different forms of genecc variacons at a given gene or genecc locus Locus 1 has two alleles, and
Genome variation - part 1
 Genome variation - part 1 Dr Jason Wong Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW Day 2 Friday 21 th January 2016 Aims of the session Introduce major
Genome variation - part 1 Dr Jason Wong Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW Day 2 Friday 21 th January 2016 Aims of the session Introduce major
GENOME-WIDE data sets from worldwide panels of
 Copyright Ó 2010 by the Genetics Society of America DOI: 10.1534/genetics.110.116681 Population Structure With Localized Haplotype Clusters Sharon R. Browning*,1 and Bruce S. Weir *Department of Statistics,
Copyright Ó 2010 by the Genetics Society of America DOI: 10.1534/genetics.110.116681 Population Structure With Localized Haplotype Clusters Sharon R. Browning*,1 and Bruce S. Weir *Department of Statistics,
Human Populations: History and Structure
 Human Populations: History and Structure In the paper Novembre J, Johnson, Bryc K, Kutalik Z, Boyko AR, Auton A, Indap A, King KS, Bergmann A, Nelson MB, Stephens M, Bustamante CD. 2008. Genes mirror geography
Human Populations: History and Structure In the paper Novembre J, Johnson, Bryc K, Kutalik Z, Boyko AR, Auton A, Indap A, King KS, Bergmann A, Nelson MB, Stephens M, Bustamante CD. 2008. Genes mirror geography
The Whole Genome TagSNP Selection and Transferability Among HapMap Populations. Reedik Magi, Lauris Kaplinski, and Maido Remm
 The Whole Genome TagSNP Selection and Transferability Among HapMap Populations Reedik Magi, Lauris Kaplinski, and Maido Remm Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing 11:535-543(2006) THE WHOLE GENOME TAGSNP SELECTION
The Whole Genome TagSNP Selection and Transferability Among HapMap Populations Reedik Magi, Lauris Kaplinski, and Maido Remm Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing 11:535-543(2006) THE WHOLE GENOME TAGSNP SELECTION
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Large-scale association analysis identifies 13 new susceptibility loci for coronary artery disease 1. Overview A. Figures Supplementary Figure 1: GWA studies ask for large numbers.
Supplementary Information Large-scale association analysis identifies 13 new susceptibility loci for coronary artery disease 1. Overview A. Figures Supplementary Figure 1: GWA studies ask for large numbers.
Supplementary Figure 1 a
 Supplementary Figure 1 a b GWAS second stage log 10 observed P 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 0 1 2 3 4 log 10 expected P rs3077 (P hetero =0.84) GWAS second stage (BBJ, Japan) First replication (BBJ, Japan) Second replication
Supplementary Figure 1 a b GWAS second stage log 10 observed P 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 0 1 2 3 4 log 10 expected P rs3077 (P hetero =0.84) GWAS second stage (BBJ, Japan) First replication (BBJ, Japan) Second replication
News. The International HapMap Project
 HapMap News A Publication of the Coriell Institute for Medical Research, V olume 1, 2004 The International HapMap Project Excitement is building as scientists begin to construct a resource called the haplotype
HapMap News A Publication of the Coriell Institute for Medical Research, V olume 1, 2004 The International HapMap Project Excitement is building as scientists begin to construct a resource called the haplotype
Human Population Differentiation Is Strongly Correlated with Local Recombination Rate
 Human Population Differentiation Is Strongly Correlated with Local Recombination Rate Alon Keinan 1,2,3 *, David Reich 1,2 1 Department of Genetics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, United
Human Population Differentiation Is Strongly Correlated with Local Recombination Rate Alon Keinan 1,2,3 *, David Reich 1,2 1 Department of Genetics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, United
Human Population Differentiation is Strongly Correlated With Local Recombination Rate
 Human Population Differentiation is Strongly Correlated With Local Recombination Rate The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Human Population Differentiation is Strongly Correlated With Local Recombination Rate The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Petar Pajic 1 *, Yen Lung Lin 1 *, Duo Xu 1, Omer Gokcumen 1 Department of Biological Sciences, University at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY.
 The psoriasis associated deletion of late cornified envelope genes LCE3B and LCE3C has been maintained under balancing selection since Human Denisovan divergence Petar Pajic 1 *, Yen Lung Lin 1 *, Duo
The psoriasis associated deletion of late cornified envelope genes LCE3B and LCE3C has been maintained under balancing selection since Human Denisovan divergence Petar Pajic 1 *, Yen Lung Lin 1 *, Duo
Browsing Genes and Genomes with Ensembl
 Browsing Genes and Genomes with Ensembl Victoria Newman Ensembl Outreach Officer EMBL-EBI Objectives What is Ensembl? What type of data can you get in Ensembl? How to navigate the Ensembl browser website.
Browsing Genes and Genomes with Ensembl Victoria Newman Ensembl Outreach Officer EMBL-EBI Objectives What is Ensembl? What type of data can you get in Ensembl? How to navigate the Ensembl browser website.
Sequence variation Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW
 Sequence variation Dr Jason Wong Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW Day 2 Friday 29 th January 2016 Aims of the session Introduce major human
Sequence variation Dr Jason Wong Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW Day 2 Friday 29 th January 2016 Aims of the session Introduce major human
Supplementary Figure 1. Study design of a multi-stage GWAS of gout.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Study design of a multi-stage GWAS of gout. Supplementary Figure 2. Plot of the first two principal components from the analysis of the genome-wide study (after QC) combined with
Supplementary Figure 1. Study design of a multi-stage GWAS of gout. Supplementary Figure 2. Plot of the first two principal components from the analysis of the genome-wide study (after QC) combined with
Supplementary Figure 1. Principle component analysis based on the GWAS subjects and the HapMap Phase 2 populations. (A) Distributions of all subjects
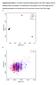 Supplementary Figure 1. Principle component analysis based on the GWAS subjects and the HapMap Phase 2 populations. (A) Distributions of all subjects in the GWAS stage and four HapMap populations; (B)
Supplementary Figure 1. Principle component analysis based on the GWAS subjects and the HapMap Phase 2 populations. (A) Distributions of all subjects in the GWAS stage and four HapMap populations; (B)
The HapMap Project and Haploview
 The HapMap Project and Haploview David Evans Ben Neale University of Oxford Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics Human Haplotype Map General Idea: Characterize the distribution of Linkage Disequilibrium
The HapMap Project and Haploview David Evans Ben Neale University of Oxford Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics Human Haplotype Map General Idea: Characterize the distribution of Linkage Disequilibrium
Genetic Variation and Genome- Wide Association Studies. Keyan Salari, MD/PhD Candidate Department of Genetics
 Genetic Variation and Genome- Wide Association Studies Keyan Salari, MD/PhD Candidate Department of Genetics How many of you did the readings before class? A. Yes, of course! B. Started, but didn t get
Genetic Variation and Genome- Wide Association Studies Keyan Salari, MD/PhD Candidate Department of Genetics How many of you did the readings before class? A. Yes, of course! B. Started, but didn t get
IL1B-CGTC haplotype is associated with colorectal cancer in. admixed individuals with increased African ancestry
 IL1B-CGTC haplotype is associated with colorectal cancer in admixed individuals with increased African ancestry María Carolina Sanabria-Salas 1, 2,*, Gustavo Hernández-Suárez 1, Adriana Umaña- Pérez 2,
IL1B-CGTC haplotype is associated with colorectal cancer in admixed individuals with increased African ancestry María Carolina Sanabria-Salas 1, 2,*, Gustavo Hernández-Suárez 1, Adriana Umaña- Pérez 2,
ARTICLE Population-Genetic Properties of Differentiated Human Copy-Number Polymorphisms
 ARTICLE Population-Genetic Properties of Differentiated Human Copy-Number Polymorphisms Catarina D. Campbell, 1 Nick Sampas, 2 Anya Tsalenko, 2 Peter H. Sudmant, 1 Jeffrey M. Kidd, 1,3 Maika Malig, 1 Tiffany
ARTICLE Population-Genetic Properties of Differentiated Human Copy-Number Polymorphisms Catarina D. Campbell, 1 Nick Sampas, 2 Anya Tsalenko, 2 Peter H. Sudmant, 1 Jeffrey M. Kidd, 1,3 Maika Malig, 1 Tiffany
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Genome-wide association study identifies 1p36.22 as a new susceptibility locus for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers Hongxing Zhang 1, Yun Zhai 1, Zhibin
Supplementary Materials Genome-wide association study identifies 1p36.22 as a new susceptibility locus for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers Hongxing Zhang 1, Yun Zhai 1, Zhibin
Genome-wide association study identifies a susceptibility locus for HCVinduced hepatocellular carcinoma. Supplementary Information
 Genome-wide association study identifies a susceptibility locus for HCVinduced hepatocellular carcinoma Vinod Kumar 1,2, Naoya Kato 3, Yuji Urabe 1, Atsushi Takahashi 2, Ryosuke Muroyama 3, Naoya Hosono
Genome-wide association study identifies a susceptibility locus for HCVinduced hepatocellular carcinoma Vinod Kumar 1,2, Naoya Kato 3, Yuji Urabe 1, Atsushi Takahashi 2, Ryosuke Muroyama 3, Naoya Hosono
Analysing Alu inserts detected from high-throughput sequencing data
 Analysing Alu inserts detected from high-throughput sequencing data Harun Mustafa Mentor: Matei David Supervisor: Michael Brudno July 3, 2013 Before we begin... Even though I'll only present the minimal
Analysing Alu inserts detected from high-throughput sequencing data Harun Mustafa Mentor: Matei David Supervisor: Michael Brudno July 3, 2013 Before we begin... Even though I'll only present the minimal
Update on the Genomics Data in the Health and Re4rement Study. Sharon Kardia Jennifer A. Smith University of Michigan April 2013
 Update on the Genomics Data in the Health and Re4rement Study Sharon Kardia Jennifer A. Smith University of Michigan April 2013 Genetic variation in SNPs (Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms) ATTGCAATCCGTGG...ATCGAGCCA.TACGATTGCACGCCG
Update on the Genomics Data in the Health and Re4rement Study Sharon Kardia Jennifer A. Smith University of Michigan April 2013 Genetic variation in SNPs (Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms) ATTGCAATCCGTGG...ATCGAGCCA.TACGATTGCACGCCG
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Lee JH, Cheng R, Barral S, Reitz C, Medrano M, Lantigua R, Jiménez-Velazquez IZ, Rogaeva E, St. George-Hyslop P, Mayeux R. Identification of novel loci for Alzheimer disease
Supplementary Online Content Lee JH, Cheng R, Barral S, Reitz C, Medrano M, Lantigua R, Jiménez-Velazquez IZ, Rogaeva E, St. George-Hyslop P, Mayeux R. Identification of novel loci for Alzheimer disease
Genotype quality control with plinkqc Hannah Meyer
 Genotype quality control with plinkqc Hannah Meyer 219-3-1 Contents Introduction 1 Per-individual quality control....................................... 2 Per-marker quality control.........................................
Genotype quality control with plinkqc Hannah Meyer 219-3-1 Contents Introduction 1 Per-individual quality control....................................... 2 Per-marker quality control.........................................
Supplementary Figure 2.Quantile quantile plots (QQ) of the exome sequencing results Chi square was used to test the association between genetic
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1.Description of the study design The samples in the initial stage (China cohort, exome sequencing) including 216 AMD cases and 1,553 controls were from the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1.Description of the study design The samples in the initial stage (China cohort, exome sequencing) including 216 AMD cases and 1,553 controls were from the
Alkes Price Harvard School of Public Health January 24 & January 26, 2017
 EPI 511, Advanced Population and Medical Genetics Week 1: Intro + HapMap / 1000 Genomes Linkage Disequilibrium Alkes Price Harvard School of Public Health January 24 & January 26, 2017 EPI 511: Course
EPI 511, Advanced Population and Medical Genetics Week 1: Intro + HapMap / 1000 Genomes Linkage Disequilibrium Alkes Price Harvard School of Public Health January 24 & January 26, 2017 EPI 511: Course
Identifying fenofibrate responsive CpG sites
 Cantor et al. BMC Proceedings 2018, 12(Suppl 9):43 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12919-018-0148-3 BMC Proceedings PROCEEDINGS Identifying fenofibrate responsive CpG sites Rita Cantor *, Linda Navarro and Calvin
Cantor et al. BMC Proceedings 2018, 12(Suppl 9):43 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12919-018-0148-3 BMC Proceedings PROCEEDINGS Identifying fenofibrate responsive CpG sites Rita Cantor *, Linda Navarro and Calvin
Supplementary Table 1. Idd13 candidate interval supporting human LTC-ICs.
 Supplementary Table 1. Idd13 candidate interval supporting human LTC-ICs. Chr Start position Genomic marker EnsEMBL gene ID Gene symbol Primer 1 (5 3 ) Primer 2 (5 3 ) 2 128675293 ENSMUSG00000027387 Zc3h8
Supplementary Table 1. Idd13 candidate interval supporting human LTC-ICs. Chr Start position Genomic marker EnsEMBL gene ID Gene symbol Primer 1 (5 3 ) Primer 2 (5 3 ) 2 128675293 ENSMUSG00000027387 Zc3h8
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. H3K27ac HiChIP enriches enhancer promoter-associated chromatin contacts.
 Supplementary Figure 1 H3K27ac HiChIP enriches enhancer promoter-associated chromatin contacts. (a) Schematic of chromatin contacts captured in H3K27ac HiChIP. (b) Loop call overlap for cohesin HiChIP
Supplementary Figure 1 H3K27ac HiChIP enriches enhancer promoter-associated chromatin contacts. (a) Schematic of chromatin contacts captured in H3K27ac HiChIP. (b) Loop call overlap for cohesin HiChIP
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Eigenvector plots for the three GWAS including subpopulations from the NCI scan.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Eigenvector plots for the three GWAS including subpopulations from the NCI scan. The NCI subpopulations are as follows: NITC, Nutrition Intervention Trial Cohort; SHNX, Shanxi Cancer
Supplementary Figure 1 Eigenvector plots for the three GWAS including subpopulations from the NCI scan. The NCI subpopulations are as follows: NITC, Nutrition Intervention Trial Cohort; SHNX, Shanxi Cancer
Practical consideration of genotype imputation: Sample size, window size, reference choice, and untyped rate
 Statistics and Its Interface Volume 4 (2011) 339 351 Practical consideration of genotype imputation: Sample size, window size, reference choice, and untyped rate Boshao Zhang, Degui Zhi, Kui Zhang, Guimin
Statistics and Its Interface Volume 4 (2011) 339 351 Practical consideration of genotype imputation: Sample size, window size, reference choice, and untyped rate Boshao Zhang, Degui Zhi, Kui Zhang, Guimin
Office Hours. We will try to find a time
 Office Hours We will try to find a time If you haven t done so yet, please mark times when you are available at: https://tinyurl.com/666-office-hours Thanks! Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium Biostatistics 666
Office Hours We will try to find a time If you haven t done so yet, please mark times when you are available at: https://tinyurl.com/666-office-hours Thanks! Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium Biostatistics 666
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3143
 Supplementary Figure 1 Quantile-quantile plot of the association P values obtained in the discovery sample collection. The two clear outlying SNPs indicated for follow-up assessment are rs6841458 and rs7765379.
Supplementary Figure 1 Quantile-quantile plot of the association P values obtained in the discovery sample collection. The two clear outlying SNPs indicated for follow-up assessment are rs6841458 and rs7765379.
Derrek Paul Hibar
 Derrek Paul Hibar derrek.hibar@ini.usc.edu Obtain the ADNI Genetic Data Quality Control Procedures Missingness Testing for relatedness Minor allele frequency (MAF) Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE) Testing
Derrek Paul Hibar derrek.hibar@ini.usc.edu Obtain the ADNI Genetic Data Quality Control Procedures Missingness Testing for relatedness Minor allele frequency (MAF) Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE) Testing
Evaluation of a multipoint method for imputing genotypes using HapMap III
 Mathematical Statistics Stockholm University Evaluation of a multipoint method for imputing genotypes using HapMap III Emil Rehnberg Examensarbete 2009:5 Postal address: Mathematical Statistics Dept. of
Mathematical Statistics Stockholm University Evaluation of a multipoint method for imputing genotypes using HapMap III Emil Rehnberg Examensarbete 2009:5 Postal address: Mathematical Statistics Dept. of
Population stratification. Background & PLINK practical
 Population stratification Background & PLINK practical Variation between, within populations Any two humans differ ~0.1% of their genome (1 in ~1000bp) ~8% of this variation is accounted for by the major
Population stratification Background & PLINK practical Variation between, within populations Any two humans differ ~0.1% of their genome (1 in ~1000bp) ~8% of this variation is accounted for by the major
The Human Genome. The raw data. The repeat content. Composition of the human genome bases. A s T s C s and G s and N s.
 3000000000 bases The Human Genome The raw data GATCTGATAAGTCCCAGGACTTCAGAAGagctgtgagaccttggccaagt cacttcctccttcaggaacattgcagtgggcctaagtgcctcctctcggg ACTGGTATGGGGACGGTCATGCAATCTGGACAACATTCACCTTTAAAAGT TTATTGATCTTTTGTGACATGCACGTGGGTTCCCAGTAGCAAGAAACTAA
3000000000 bases The Human Genome The raw data GATCTGATAAGTCCCAGGACTTCAGAAGagctgtgagaccttggccaagt cacttcctccttcaggaacattgcagtgggcctaagtgcctcctctcggg ACTGGTATGGGGACGGTCATGCAATCTGGACAACATTCACCTTTAAAAGT TTATTGATCTTTTGTGACATGCACGTGGGTTCCCAGTAGCAAGAAACTAA
Supplementary Figure 1. Linkage disequilibrium (LD) at the CDKN2A locus
 rs3731249 rs3731217 Supplementary Figure 1. Linkage disequilibrium (LD) at the CDKN2A locus. Minimal correlation was observed (r 2 =0.0007) in Hapmap CEU individuals between B ALL risk variants rs3731249
rs3731249 rs3731217 Supplementary Figure 1. Linkage disequilibrium (LD) at the CDKN2A locus. Minimal correlation was observed (r 2 =0.0007) in Hapmap CEU individuals between B ALL risk variants rs3731249
Bioinformatic Analysis of SNP Data for Genetic Association Studies EPI573
 Bioinformatic Analysis of SNP Data for Genetic Association Studies EPI573 Mark J. Rieder Department of Genome Sciences mrieder@u.washington washington.edu Epidemiology Studies Cohort Outcome Model to fit/explain
Bioinformatic Analysis of SNP Data for Genetic Association Studies EPI573 Mark J. Rieder Department of Genome Sciences mrieder@u.washington washington.edu Epidemiology Studies Cohort Outcome Model to fit/explain
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Genome-partitioning of genetic variation for complex traits using common SNPs Jian Yang, Teri A. Manolio, Louis R. Pasquale 3, Eric Boerwinkle 4, Neil Caporaso 5, Julie M. Cunningham
Supplementary Information Genome-partitioning of genetic variation for complex traits using common SNPs Jian Yang, Teri A. Manolio, Louis R. Pasquale 3, Eric Boerwinkle 4, Neil Caporaso 5, Julie M. Cunningham
Computational Workflows for Genome-Wide Association Study: I
 Computational Workflows for Genome-Wide Association Study: I Department of Computer Science Brown University, Providence sorin@cs.brown.edu October 16, 2014 Outline 1 Outline 2 3 Monogenic Mendelian Diseases
Computational Workflows for Genome-Wide Association Study: I Department of Computer Science Brown University, Providence sorin@cs.brown.edu October 16, 2014 Outline 1 Outline 2 3 Monogenic Mendelian Diseases
VEGAS2: Gene-based test software using 1000 Genomes reference sets. User Manual
 VEGAS2: Gene-based test software using 1000 Genomes reference sets. User Manual Version: 16:09:002 Date: 16 th September 2014 By Aniket Mishra, Stuart Macgregor Statistical Genetics Group QIMR Berghofer
VEGAS2: Gene-based test software using 1000 Genomes reference sets. User Manual Version: 16:09:002 Date: 16 th September 2014 By Aniket Mishra, Stuart Macgregor Statistical Genetics Group QIMR Berghofer
UKPMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Nature. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 April 1.
 UKPMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nature. 2010 October 28; 467(7319): 1061 1073. doi:10.1038/nature09534. A map of human genome variation from population scale sequencing
UKPMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nature. 2010 October 28; 467(7319): 1061 1073. doi:10.1038/nature09534. A map of human genome variation from population scale sequencing
Supplement: Systematic evaluation of coding variation identifies a candidate causal variant in TM6SF2 influencing total cholesterol
 Supplement: Systematic evaluation of coding variation identifies a candidate causal variant in TM6SF2 influencing total cholesterol Supplementary Tables SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE 1. Clinical characteristics
Supplement: Systematic evaluation of coding variation identifies a candidate causal variant in TM6SF2 influencing total cholesterol Supplementary Tables SUPPLEMENTARY TABLE 1. Clinical characteristics
Browsing Genes and Genomes with Ensembl
 Training materials - - - - Ensembl training materials are protected by a CC BY license http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ If you wish to re-use these materials, please credit Ensembl for their
Training materials - - - - Ensembl training materials are protected by a CC BY license http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ If you wish to re-use these materials, please credit Ensembl for their
Population differentiation analysis of 54,734 European Americans reveals independent evolution of ADH1B gene in Europe and East Asia
 Population differentiation analysis of 54,734 European Americans reveals independent evolution of ADH1B gene in Europe and East Asia Kevin Galinsky Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health American Society
Population differentiation analysis of 54,734 European Americans reveals independent evolution of ADH1B gene in Europe and East Asia Kevin Galinsky Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health American Society
PERSPECTIVES. A gene-centric approach to genome-wide association studies
 PERSPECTIVES O P I N I O N A gene-centric approach to genome-wide association studies Eric Jorgenson and John S. Witte Abstract Genic variants are more likely to alter gene function and affect disease
PERSPECTIVES O P I N I O N A gene-centric approach to genome-wide association studies Eric Jorgenson and John S. Witte Abstract Genic variants are more likely to alter gene function and affect disease
UK Biobank Axiom Array
 DATA SHEET Advancing human health studies with powerful genotyping technology Array highlights The Applied Biosystems UK Biobank Axiom Array is a powerful array for translational research. Designed using
DATA SHEET Advancing human health studies with powerful genotyping technology Array highlights The Applied Biosystems UK Biobank Axiom Array is a powerful array for translational research. Designed using
MEF-AOM MEF-DMH Symbol WT-AOM SKO-Mock SKO-AOM Symbol WT-DMH SKO-Mock SKO-DMH EG Rgs1 Ifit3 Ccl3 Usp18 Cxcl2 Rnf2 EG LOC Rgs1
 MEF-AOM Symol WT-AOM SKO-Mock SKO-AOM EG546166 2.097 2.571 2.850 Ifit3 2.064-2.984-3.111 Usp18 1.898-2.500-2.251 Rnf2 1.896 1.656 1.565 LOC667370 1.871-1.682-1.741 Ifit3 1.866-1.620-1.722 Usp18 1.860-8.756-6.861
MEF-AOM Symol WT-AOM SKO-Mock SKO-AOM EG546166 2.097 2.571 2.850 Ifit3 2.064-2.984-3.111 Usp18 1.898-2.500-2.251 Rnf2 1.896 1.656 1.565 LOC667370 1.871-1.682-1.741 Ifit3 1.866-1.620-1.722 Usp18 1.860-8.756-6.861
Supplementary Figure 1 Genetic relationship between local Tibetans and other East Asian populations.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Genetic relationship between local Tibetans and other East Asian populations. 1 (A) Principal-components analysis. The first two principal components (PCs) are shown. Each individual
Supplementary Figure 1 Genetic relationship between local Tibetans and other East Asian populations. 1 (A) Principal-components analysis. The first two principal components (PCs) are shown. Each individual
Genome-wide association study identifies five loci associated with susceptibility to pancreatic cancer in Chinese populations. Supplementary Materials
 Genome-wide association study identifies five loci associated with susceptibility to pancreatic cancer in Chinese populations Supplementary Materials Chen Wu 1, 22, Xiaoping Miao 2, 22, Liming Huang 1,
Genome-wide association study identifies five loci associated with susceptibility to pancreatic cancer in Chinese populations Supplementary Materials Chen Wu 1, 22, Xiaoping Miao 2, 22, Liming Huang 1,
Human Genetics and Gene Mapping of Complex Traits
 Human Genetics and Gene Mapping of Complex Traits Advanced Genetics, Spring 2015 Human Genetics Series Thursday 4/02/15 Nancy L. Saccone, nlims@genetics.wustl.edu ancestral chromosome present day chromosomes:
Human Genetics and Gene Mapping of Complex Traits Advanced Genetics, Spring 2015 Human Genetics Series Thursday 4/02/15 Nancy L. Saccone, nlims@genetics.wustl.edu ancestral chromosome present day chromosomes:
Amapofhumangenomevariationfrom population-scale sequencing
 doi:.38/nature9534 Amapofhumangenomevariationfrom population-scale sequencing The Genomes Project Consortium* The Genomes Project aims to provide a deep characterization of human genome sequence variation
doi:.38/nature9534 Amapofhumangenomevariationfrom population-scale sequencing The Genomes Project Consortium* The Genomes Project aims to provide a deep characterization of human genome sequence variation
The most recent meta-analysis of genome-wide association
 Clinical and Population Studies Prediction of Causal Candidate Genes in Coronary Artery Disease Loci Ingrid Brænne,* Mete Civelek,* Baiba Vilne,* Antonio Di Narzo, Andrew D. Johnson, Yuqi Zhao, Benedikt
Clinical and Population Studies Prediction of Causal Candidate Genes in Coronary Artery Disease Loci Ingrid Brænne,* Mete Civelek,* Baiba Vilne,* Antonio Di Narzo, Andrew D. Johnson, Yuqi Zhao, Benedikt
The most recent meta-analysis of genome-wide association
 Clinical and Population Studies Prediction of Causal Candidate Genes in Coronary Artery Disease Loci Ingrid Brænne,* Mete Civelek,* Baiba Vilne,* Antonio Di Narzo, Andrew D. Johnson, Yuqi Zhao, Benedikt
Clinical and Population Studies Prediction of Causal Candidate Genes in Coronary Artery Disease Loci Ingrid Brænne,* Mete Civelek,* Baiba Vilne,* Antonio Di Narzo, Andrew D. Johnson, Yuqi Zhao, Benedikt
Eric Green NHGRI Director
 Bringing Genomic Medicine into Focus Eric Green, M.D., Ph.D. Director, NHGRI The Relevance of Genomics Biomedical Researchers Healthcare Professionals Patients (and Friends & Relatives of Patients) Human
Bringing Genomic Medicine into Focus Eric Green, M.D., Ph.D. Director, NHGRI The Relevance of Genomics Biomedical Researchers Healthcare Professionals Patients (and Friends & Relatives of Patients) Human
Supplementary Fig. 1. Location of top two candidemia associated SNPs in CD58 gene
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1. Location of top two candidemia associated SNPs in CD58 gene locus. The region encompass CD58 and three long non-coding RNAs (RP4-655J12.4, RP5-1086K13.1 and
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1. Location of top two candidemia associated SNPs in CD58 gene locus. The region encompass CD58 and three long non-coding RNAs (RP4-655J12.4, RP5-1086K13.1 and
Source1 Source2 Target Std. Err. SNPs Samples Supplementary Table 1. Groups with significant evidence of East Asian admixture.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Source1 Source2 Target f 3 Std. Err. Z SNPs Samples Mala CHB BEB (Bengali) -0.004691 0.000195-24.029 412330 86 Mala CHB Thakur -0.008146 0.000349-23.311 385907 10 Mala CHB Hazara -0.005504
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Source1 Source2 Target f 3 Std. Err. Z SNPs Samples Mala CHB BEB (Bengali) -0.004691 0.000195-24.029 412330 86 Mala CHB Thakur -0.008146 0.000349-23.311 385907 10 Mala CHB Hazara -0.005504
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Loci associated with 2 hr glucose during pregnancy imputed to HAPMAP (a) and 1000 Genomes (b). Peak of association is in the first intron of HKDC1. Black bars
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Loci associated with 2 hr glucose during pregnancy imputed to HAPMAP (a) and 1000 Genomes (b). Peak of association is in the first intron of HKDC1. Black bars
Original Article Polymorphisms of drug-metabolizing enzyme CYP2J2 in Wa population from Yunnan Province of China
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4260-4268 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0022448 Original Article Polymorphisms of drug-metabolizing enzyme CYP2J2 in Wa population from Yunnan Province of China Chan
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4260-4268 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0022448 Original Article Polymorphisms of drug-metabolizing enzyme CYP2J2 in Wa population from Yunnan Province of China Chan
administration of tamoxifen. Bars show mean ± s.e.m (n=10-11). P-value was determined by
 Supplementary Figure 1. Chimerism of CD45.2 + GFP + cells at 1 month post transplantation No significant changes were detected in chimerism of CD45.2 + GFP + cells between recipient mice repopulated with
Supplementary Figure 1. Chimerism of CD45.2 + GFP + cells at 1 month post transplantation No significant changes were detected in chimerism of CD45.2 + GFP + cells between recipient mice repopulated with
Efficient Association Study Design Via Power-Optimized Tag SNP Selection
 doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.2008.00469.x Efficient Association Study Design Via Power-Optimized Tag SNP Selection B. Han 1,H.M.Kang 1,M.S.Seo 2, N. Zaitlen 3 and E. Eskin 4, 1 Department of Computer Science
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.2008.00469.x Efficient Association Study Design Via Power-Optimized Tag SNP Selection B. Han 1,H.M.Kang 1,M.S.Seo 2, N. Zaitlen 3 and E. Eskin 4, 1 Department of Computer Science
Efficient Genomewide Selection of PCA-Correlated tsnps for Genotype Imputation
 Efficient Genomewide Selection of PCA-Correlated tsnps for Genotype Imputation Asif Javed 1,2, Petros Drineas 2, Michael W. Mahoney 3 and Peristera Paschou 4 1 Computational Biology Center, IBM T. J. Watson
Efficient Genomewide Selection of PCA-Correlated tsnps for Genotype Imputation Asif Javed 1,2, Petros Drineas 2, Michael W. Mahoney 3 and Peristera Paschou 4 1 Computational Biology Center, IBM T. J. Watson
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Analyses of present-day population differentiation. (A, B) Enrichment of strongly differentiated genic alleles for all present-day population comparisons
Supplementary Figures 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Analyses of present-day population differentiation. (A, B) Enrichment of strongly differentiated genic alleles for all present-day population comparisons
Mining GWAS Catalog & 1000 Genomes Dataset. Segun Fatumo
 Mining GWAS Catalog & 1000 Genomes Dataset Segun Fatumo What is GWAS Catalog NHGRI GWA Catalog www.genome.gov/gwastudies Citation How to cite the NHGRI GWAS Catalog: Hindorff LA, MacArthur J (European
Mining GWAS Catalog & 1000 Genomes Dataset Segun Fatumo What is GWAS Catalog NHGRI GWA Catalog www.genome.gov/gwastudies Citation How to cite the NHGRI GWAS Catalog: Hindorff LA, MacArthur J (European
Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS): Computational Them
 Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS): Computational Themes and Caveats October 14, 2014 Many issues in Genomewide Association Studies We show that even for the simplest analysis, there is little consensus
Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS): Computational Themes and Caveats October 14, 2014 Many issues in Genomewide Association Studies We show that even for the simplest analysis, there is little consensus
A genome-wide association study in Han Chinese identifies new susceptibility loci for. ankylosing spondylitis. Supplementary Materials
 A genome-wide association study in Han Chinese identifies new susceptibility loci for ankylosing spondylitis Supplementary Materials Zhiming Lin 1,24, Jin-Xin Bei 2,24, Meixin Shen 3, Qiuxia Li 1, Zetao
A genome-wide association study in Han Chinese identifies new susceptibility loci for ankylosing spondylitis Supplementary Materials Zhiming Lin 1,24, Jin-Xin Bei 2,24, Meixin Shen 3, Qiuxia Li 1, Zetao
Deep learning sequence-based ab initio prediction of variant effects on expression and disease risk
 Summer Review 7 Deep learning sequence-based ab initio prediction of variant effects on expression and disease risk Jian Zhou 1,2,3, Chandra L. Theesfeld 1, Kevin Yao 3, Kathleen M. Chen 3, Aaron K. Wong
Summer Review 7 Deep learning sequence-based ab initio prediction of variant effects on expression and disease risk Jian Zhou 1,2,3, Chandra L. Theesfeld 1, Kevin Yao 3, Kathleen M. Chen 3, Aaron K. Wong
Human Genetics and Gene Mapping of Complex Traits
 Human Genetics and Gene Mapping of Complex Traits Advanced Genetics, Spring 2017 Human Genetics Series Tuesday 4/10/17 Nancy L. Saccone, nlims@genetics.wustl.edu ancestral chromosome present day chromosomes:
Human Genetics and Gene Mapping of Complex Traits Advanced Genetics, Spring 2017 Human Genetics Series Tuesday 4/10/17 Nancy L. Saccone, nlims@genetics.wustl.edu ancestral chromosome present day chromosomes:
Summary. Introduction
 doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.2006.00305.x Variation of Estimates of SNP and Haplotype Diversity and Linkage Disequilibrium in Samples from the Same Population Due to Experimental and Evolutionary Sample Size
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.2006.00305.x Variation of Estimates of SNP and Haplotype Diversity and Linkage Disequilibrium in Samples from the Same Population Due to Experimental and Evolutionary Sample Size
A HapMap harvest of insights into the genetics of common disease
 Science in medicine A HapMap harvest of insights into the genetics of common disease Teri A. Manolio, Lisa D. Brooks, and Francis S. Collins National Human Genome Research Institute, Bethesda, Maryland,
Science in medicine A HapMap harvest of insights into the genetics of common disease Teri A. Manolio, Lisa D. Brooks, and Francis S. Collins National Human Genome Research Institute, Bethesda, Maryland,
ARTICLE Contrasting X-Linked and Autosomal Diversity across 14 Human Populations
 ARTICLE Contrasting X-Linked and Autosomal Diversity across 14 Human Populations Leonardo Arbiza, 1,2 Srikanth Gottipati, 1,2 Adam Siepel, 1 and Alon Keinan 1, * Contrasting the genetic diversity of the
ARTICLE Contrasting X-Linked and Autosomal Diversity across 14 Human Populations Leonardo Arbiza, 1,2 Srikanth Gottipati, 1,2 Adam Siepel, 1 and Alon Keinan 1, * Contrasting the genetic diversity of the
Weinian Rao, Yamin Ma, Li Ma, Jian Zhao, Qiling Li, Weikuan Gu, Kui Zhang, Vincent C.
 High resolution whole-genome haplotyping using limited seed data Weinian Rao, Yamin Ma, Li Ma, Jian Zhao, Qiling Li, Weikuan Gu, Kui Zhang, Vincent C. Bond, Qing Song. Supplementary Information 1. Supplementary
High resolution whole-genome haplotyping using limited seed data Weinian Rao, Yamin Ma, Li Ma, Jian Zhao, Qiling Li, Weikuan Gu, Kui Zhang, Vincent C. Bond, Qing Song. Supplementary Information 1. Supplementary
BTRY 7210: Topics in Quantitative Genomics and Genetics
 BTRY 7210: Topics in Quantitative Genomics and Genetics Jason Mezey Biological Statistics and Computational Biology (BSCB) Department of Genetic Medicine jgm45@cornell.edu January 29, 2015 Why you re here
BTRY 7210: Topics in Quantitative Genomics and Genetics Jason Mezey Biological Statistics and Computational Biology (BSCB) Department of Genetic Medicine jgm45@cornell.edu January 29, 2015 Why you re here
Balancing Selection on a Regulatory Region Exhibiting Ancient Variation That Predates Human Neandertal Divergence
 Balancing Selection on a Regulatory Region Exhibiting Ancient Variation That Predates Human Neandertal Divergence The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
Balancing Selection on a Regulatory Region Exhibiting Ancient Variation That Predates Human Neandertal Divergence The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Contents De novo assembly... 2 Assembly statistics for all 150 individuals... 2 HHV6b integration... 2 Comparison of assemblers... 4 Variant calling and genotyping... 4 Protein truncating variants (PTV)...
Contents De novo assembly... 2 Assembly statistics for all 150 individuals... 2 HHV6b integration... 2 Comparison of assemblers... 4 Variant calling and genotyping... 4 Protein truncating variants (PTV)...
Human Genetic Studies: Challenges and Opportunities. Goncalo Abecasis Ann Arbor, MI
 Human Genetic Studies: Challenges and Opportunities Goncalo Abecasis Ann Arbor, MI Goal of Human Genetic Studies Find biological processes that, when changed, alter disease course Understand Disease: Enable
Human Genetic Studies: Challenges and Opportunities Goncalo Abecasis Ann Arbor, MI Goal of Human Genetic Studies Find biological processes that, when changed, alter disease course Understand Disease: Enable
By the end of this lecture you should be able to explain: Some of the principles underlying the statistical analysis of QTLs
 (3) QTL and GWAS methods By the end of this lecture you should be able to explain: Some of the principles underlying the statistical analysis of QTLs Under what conditions particular methods are suitable
(3) QTL and GWAS methods By the end of this lecture you should be able to explain: Some of the principles underlying the statistical analysis of QTLs Under what conditions particular methods are suitable
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)
 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Sequence variations Single nucleotide polymorphisms Insertions/deletions Copy number variations (large: >1kb) Variable (short) number tandem repeats Single Nucleotide
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Sequence variations Single nucleotide polymorphisms Insertions/deletions Copy number variations (large: >1kb) Variable (short) number tandem repeats Single Nucleotide
IN recent years there has been considerable interest in
 Copyright Ó 2010 by the Genetics Society of America DOI: 10.1534/genetics.110.113977 Natural Selection and the Distribution of Identity-by-Descent in the Human Genome Anders Albrechtsen,*,1,2 Ida Moltke,1
Copyright Ó 2010 by the Genetics Society of America DOI: 10.1534/genetics.110.113977 Natural Selection and the Distribution of Identity-by-Descent in the Human Genome Anders Albrechtsen,*,1,2 Ida Moltke,1
Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental Data. Charron et al. Dynamic landscapes of four histone modifications during de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell (2009). 10.1105/tpc.109.066845 Supplemental Figure 1. Immunodetection
Supplemental Data. Charron et al. Dynamic landscapes of four histone modifications during de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell (2009). 10.1105/tpc.109.066845 Supplemental Figure 1. Immunodetection
Axiom mydesign Custom Array design guide for human genotyping applications
 TECHNICAL NOTE Axiom mydesign Custom Genotyping Arrays Axiom mydesign Custom Array design guide for human genotyping applications Overview In the past, custom genotyping arrays were expensive, required
TECHNICAL NOTE Axiom mydesign Custom Genotyping Arrays Axiom mydesign Custom Array design guide for human genotyping applications Overview In the past, custom genotyping arrays were expensive, required
A review of intelligence GWAS hits: their relationship to country IQ and the issue of spatial autocorrelation.
 A review of intelligence GWAS hits: their relationship to country IQ and the issue of spatial autocorrelation. Davide Piffer email: pifferdavide@gmail.com Abstract A review of published intelligence GWA
A review of intelligence GWAS hits: their relationship to country IQ and the issue of spatial autocorrelation. Davide Piffer email: pifferdavide@gmail.com Abstract A review of published intelligence GWA
Popula'on Gene'cs I: Gene'c Polymorphisms, Haplotype Inference, Recombina'on Computa.onal Genomics Seyoung Kim
 Popula'on Gene'cs I: Gene'c Polymorphisms, Haplotype Inference, Recombina'on 02-710 Computa.onal Genomics Seyoung Kim Overview Two fundamental forces that shape genome sequences Recombina.on Muta.on, gene.c
Popula'on Gene'cs I: Gene'c Polymorphisms, Haplotype Inference, Recombina'on 02-710 Computa.onal Genomics Seyoung Kim Overview Two fundamental forces that shape genome sequences Recombina.on Muta.on, gene.c
More Introduction to Positive Selection
 More Introduction to Positive Selection Ryan Hernandez Tim O Connor ryan.hernandez@ucsf.edu 1 Genome-wide scans The EHH approach does not lend itself to a genomewide scan. Voight, et al. (2006) create
More Introduction to Positive Selection Ryan Hernandez Tim O Connor ryan.hernandez@ucsf.edu 1 Genome-wide scans The EHH approach does not lend itself to a genomewide scan. Voight, et al. (2006) create
Linking Genetic Variation to Important Phenotypes: SNPs, CNVs, GWAS, and eqtls
 Linking Genetic Variation to Important Phenotypes: SNPs, CNVs, GWAS, and eqtls BMI/CS 776 www.biostat.wisc.edu/bmi776/ Colin Dewey cdewey@biostat.wisc.edu Spring 2012 1. Understanding Human Genetic Variation
Linking Genetic Variation to Important Phenotypes: SNPs, CNVs, GWAS, and eqtls BMI/CS 776 www.biostat.wisc.edu/bmi776/ Colin Dewey cdewey@biostat.wisc.edu Spring 2012 1. Understanding Human Genetic Variation
ABSTRACT. In recent years population-based association studies have been advocated as the most
 ABSTRACT DICKSON, SAMUEL PRICE. Improving Discovery of Causal Variants in Genetic Association Studies. (Under the direction of committee, Dr. Greg Gibson and Dr. Marie Davidian). In recent years population-based
ABSTRACT DICKSON, SAMUEL PRICE. Improving Discovery of Causal Variants in Genetic Association Studies. (Under the direction of committee, Dr. Greg Gibson and Dr. Marie Davidian). In recent years population-based
Human Genetic Studies: Challenges and Opportunities. Goncalo Abecasis Ann Arbor, MI
 Human Genetic Studies: Challenges and Opportunities Goncalo Abecasis Ann Arbor, MI Goal of Human Genetic Studies Find biological processes that, when changed, alter disease course Understand Disease: Enable
Human Genetic Studies: Challenges and Opportunities Goncalo Abecasis Ann Arbor, MI Goal of Human Genetic Studies Find biological processes that, when changed, alter disease course Understand Disease: Enable
Quantitative Genomics and Genetics BTRY 4830/6830; PBSB
 Quantitative Genomics and Genetics BTRY 4830/6830; PBSB.5201.01 Lecture20: Haplotype testing and Minimum GWAS analysis steps Jason Mezey jgm45@cornell.edu April 17, 2017 (T) 8:40-9:55 Announcements Project
Quantitative Genomics and Genetics BTRY 4830/6830; PBSB.5201.01 Lecture20: Haplotype testing and Minimum GWAS analysis steps Jason Mezey jgm45@cornell.edu April 17, 2017 (T) 8:40-9:55 Announcements Project
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. The pedigree information for American upland cotton breeding.
 Supplementary Figure 1 The pedigree information for American upland cotton breeding. The integrated figure was modified from Fig. 1 to 10 in Calhoun, Bowman & May (1994). The accessions with blue color
Supplementary Figure 1 The pedigree information for American upland cotton breeding. The integrated figure was modified from Fig. 1 to 10 in Calhoun, Bowman & May (1994). The accessions with blue color
ORDERING HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONAL. Nilesh Dharajiya, M.D Nexus Center Drive San Diego, CA US. Cardiovascular Health
 Test Results Reviewed & Approved by: Laboratory Director, Nilesh Dharajiya, M.D. CARDIAC DNA INSIGHT PERSONAL DETAILS DOB Jan 1, 19XX ETHNICITY Caucasian ORDERING HEALTHCARE PROESSIONAL Nilesh Dharajiya,
Test Results Reviewed & Approved by: Laboratory Director, Nilesh Dharajiya, M.D. CARDIAC DNA INSIGHT PERSONAL DETAILS DOB Jan 1, 19XX ETHNICITY Caucasian ORDERING HEALTHCARE PROESSIONAL Nilesh Dharajiya,
Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 47, 598 606 (2015) Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C Borbala Mifsud, Filipe Tavares-Cadete, Alice N Young, Robert Sugar,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 47, 598 606 (2015) Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C Borbala Mifsud, Filipe Tavares-Cadete, Alice N Young, Robert Sugar,
