Supplementary Figure 1 Genetic relationship between local Tibetans and other East Asian populations.
|
|
|
- Mary Barnett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1 Genetic relationship between local Tibetans and other East Asian populations. 1
2 (A) Principal-components analysis. The first two principal components (PCs) are shown. Each individual is represented by one dot, and color corresponds to the population. The percentage of variance explained by each PC is shown on the axis. (b) Individual grouping inferred by ADMIXTURE. Results from k = 4 are shown. Each individual s genome is represented by a vertical bar composed of colored sections, where each section represents the proportion of an individual s ancestry derived from one of the k ancestral populations. Individuals are arrayed horizontally and grouped by population as indicated. JPT, Japanese; CHB, Chinese; Local Tibetan, Tibetans collected in this study. The two Local Tibetans who have the wild-type D4E variant (TU09 and TU12) are indicated in the plots. 2
3 Supplementary Figure 2 Analysis of purified wild-type PHD2 enzyme, the D4E and C127S single mutants, and the D4E and C127S double mutant. Recombinant enzymes were expressed in insect cells and were affinity purified exploiting their C- terminal Flag tags in anti-flag affinity gel columns. The near-to-homogeneity purified enzymes were analyzed by 10% SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie Blue staining. Molecular weight markers (kda) are shown on the left. 3
4 Fig. S3A Fig. S3B Supplementary Figure 3 Expression study of hypoxia and several HIF target genes. (a) Expression of hypoxia-regulated genes in granulocytes from Tibetan (n = 4) versus control (n = 6) subjects. (b) BFU-E expression of selected HIF target genes in Tibetan (n = 1) versus control (n = 2) erythroid progenitors grown at optimal EPO levels (3,000 mu). Two independent experiments (technical replicates) from BFU-Es were pooled together and utilized the statistical randomization test 4
5 using the Relative Expression Software Tool (REST, Qiagen). Error bars represent s.d. 5
6 Sample ID Race D4E C127S CA01 Filipino Wild-Type Heterozygous CA02 Japanese Wild-Type Heterozygous CA03 Japanese Wild-Type Wild-Type CA19 Japanese Wild-Type Wild-Type CA20 Japanese Wild-Type Wild-Type CA04 orean Wild-Ty e Heterozygous CA05 Korean Wild-Type Wild-Type CA06 Korean Wild-Type Heterozygous CA07 Korean Wild-Type Wild-Type CA08 Korean Wild-Type Wild-Type CA09 Korean Wild-Type Wild-Type CC01 European Wild-Type Heterozygous CC02 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CC03 European Wild-Type Heterozygous CC04 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CC05 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CC06 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CC07 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CC08 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CC09 European Wild-Type Heterozygous CC19 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CC20 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CC21 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CC22 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CC23 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CC24 European Wild-Type Heterozygous CC25 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CC26 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CC27 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CC28 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CM01 Mongolian Wild-Type Wild-Type CM02 Mongolian Heterozygous Heterozygous CM03 Mongolian Wild-Type Heterozygous CM04 Mongolian Wild-Type Heterozygous CM05 Mongolian Wild-Type Heterozygous CM06 Mongolian Wild-Type Wild-Type CM07 Mongolian Wild-Type Heterozygous CM08 Mongolian Wild-Type Heterozygous CM09 Mongolian Wild-Type Heterozygous CM10 Mongolian Wild-Type Wild-Type 1
7 CM11 Mongolian Wild-Type Wild-Type CA10 Japanese Wild-Type Wild-Type CA11 Japanese Heterozygous Heterozygous CA12 Japanese Wild-Type Heterozygous CA13 Japanese Wild-Type Wild-Type CA14 Korean Wild-Type Wild-Type CA15 Korean Wild-Type Heterozygous CA16 Korean Wild-Type Wild-Type CA17 Japanese Wild-Type Wild-Type CA18 Japanese Wild-Type Heterozygous CCH01 Han Chinese Wild-Type Heterozygous CCH02 Han Chinese Wild-Type Wild-Type CCH03 Han Chinese Wild-Type Wild-Type CCH05 Han Chinese Wild-Type Heterozygous CCH06 Han Chinese Wild-Type Homozygous CCH07 Han Chinese Wild-Type Heterozygous CCH13 Han Chinese Wild-Type Wild-Type CCH16 Han Chinese Wild-Type Heterozygous CCH17 Han Chinese Wild-Type Heterozygous CCH18 Han Chinese Wild-Type Heterozygous CCH20 Han Chinese Wild-Type Homozygous CCH21 Han Chinese Wild-Type Heterozygous CCH23 Han Chinese Wild-Type Heterozygous CHN35 Han Chinese Wild-Type Heterozygous CHN37 Han Chinese Wild-Type Wild-Type CHN43 Han Chinese Wild-Type Heterozygous CAU01 European Wild-Type Heterozygous CAU02 European Wild-Type Heterozygous CAU03 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CAU04 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CAU05 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CAU06 European Wild-Type Heterozygous CAU07 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CAU08 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CAU09 European Wild-Type Heterozygous CAU10 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CAU11 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CAU12 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CAU13 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CAU14 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CAU15 European Wild-Type Wild-Type 2
8 CAU16 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CAU17 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CAU18 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CAU19 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CAU20 European Wild-Type Heterozygous SCAU01 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU02 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU03 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU05 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU06 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU08 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU09 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU11 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU10 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU12 European Wild-Type Heterozygous SCAU13 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU14 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU15 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU16 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU17 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU18 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU19 European Wild-Type Wild-Type SCAU20 European Wild-Type Heterozygous CE28 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE36 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE30 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE31 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE32 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE34 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE35 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE37 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE38 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE42 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE43 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE33 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE39 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE44 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE51 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE52 European Wild-Type Wild-Type CE54 European Wild-Type Wild-Type 3
9 Supplementary Table 1 List of the 121 controls of different ethnicity used in screening for EGLN1 mutation. 4
10 SampleID Origin PHD2- D4E PHD2- C127S MG03 India Heterozygous Heterozygous MG05 India Heterozygous Heterozygous MG07 India Heterozygous Homozygous MG08 India Heterozygous Wild- Type MG11 India Heterozygous Heterozygous MG12 India Heterozygous Heterozygous MG14 India Heterozygous Heterozygous MG15 India Homozygous Homozygous MG16 India Homozygous Homozygous MG17 India Heterozygous Heterozygous MG19 India Homozygous Homozygous MG20 India Heterozygous Heterozygous MG21 India Wild- Type Homozygous MG22 India Homozygous Homozygous MG24 India Heterozygous Heterozygous MG25 India Homozygous Homozygous MG27 India Heterozygous Heterozygous MG30 India Homozygous Homozygous MG32 India Homozygous Homozygous MG35 India Heterozygous Homozygous MG36 India Wild- Type Homozygous MG47 India Heterozygous Homozygous MG51 India Wild- Type Homozygous TCV5 India Heterozygous Homozygous TCV6 India Homozygous Homozygous TCV7 India Heterozygous Homozygous XT01 China Wild- Type Heterozygous XT02 China Wild- Type Wild- Type XT03 China Heterozygous Heterozygous XT04 China Homozygous Homozygous XT05 China Homozygous Homozygous XT06 China Homozygous Homozygous XT12 China Homozygous Homozygous XT13 China Wild- Type Homozygous XT16 China Homozygous Homozygous XT18 China Heterozygous Heterozygous XT20 China Heterozygous Heterozygous XT21 China Wild- Type Wild- Type 5
11 XT22 China Homozygous Homozygous ZT02 China Heterozygous Heterozygous ZT03 China Homozygous Homozygous ZT04 China Heterozygous Heterozygous ZT05 China Homozygous Homozygous ZT06 China Heterozygous Homozygous ZT07 China Homozygous Homozygous ZT11 China Heterozygous Homozygous ZT17 China Homozygous Homozygous ZT18 China Heterozygous Heterozygous ZT20 China Heterozygous Homozygous ZT23 China Heterozygous Heterozygous ZT24 China Heterozygous Heterozygous ZT26 China Heterozygous Heterozygous ZT27 China Heterozygous Heterozygous ZT29 China Homozygous Homozygous ZT30 China Homozygous Homozygous ZT31 China Homozygous Homozygous ZT32 China Heterozygous Homozygous ZT33 China Homozygous Homozygous ZT34 China Heterozygous Homozygous ZT36 China Homozygous Homozygous ZT37 China Heterozygous Homozygous ZT38 China Heterozygous Heterozygous ZT39 China Homozygous Homozygous ZT40 China Homozygous Homozygous ZT41 China Heterozygous Heterozygous Supplementary Table 2 List of the cohort Tibetan subjects (n=65) from India and China, screened for the EGLN1 variant. 6
12 EGLN1:c.12C>G EGLN1:c.380G>C Salt Lake & Virginia, USA (n=26) Mutation frequency 22 (85%) 26 (100%) Homozygous 20 (91%) 21 (81%) Heterozygous 2 (9%) 5 (19%) Allele frequency 42 / 52 (81%) 47 / 52 (90%) Himachal Pradesh, India (n=26) Mutation frequency 23 (89%) 25 (96%) Homozygous 8 (35%) 16 (64%) Heterozygous 15 (65%) 9 (36%) Allele frequency 31 / 52 (60%) 41 / 52 (79%) Qinghai province, China (n=39) Mutation frequency 35 (90%) 37 (95%) Homozygous 18 (51%) 24 (65%) Heterozygous 17 (49%) 13 (35%) Allele frequency 53 / 78 (68%) 61 / 78 (78%) Supplementary table 3 Tabulation of the mutation and allelic frequency from U.S. Tibetan and cohorts of Tibetans from India and China. 7
13 Observed number/proportion of recombinant chromosomes Number of PHD2 D4E chromosomes Recombinatio n rate (cm) Upstream SNPs Downstream SNPs Age (in generations) Age (in years, 25 year generation time) Log likelihood Maximum likelihood estimate % lower bound % upper bound SNPs* upstream of PHD2 D4E Chr. position (HG18) rs number Inferred ancestr al allele of EGLN1: c.12c>g Genetic distance to next SNP (in cm) Cumulative probability of observing a crossover (in cm) Cumulative proportion of EGLN1:c.12C>G Chr. without an observed crossover A A C A C C G A C G A G C G T A A C G C T T G
14 C T A C T G A G G C A G G A G G C G T G A G C A G C A A C T T T SNPs* downstream of PHD2 D4E Chr. position (HG18) rs number Inferred ancestral allele of EGLN1: c.12c>g Genetic distance to next SNP (in cm) Cumulative probability of observing a crossover (in cm) Cumulative proportion of EGLN1:c.12C>G Chr. without an observed crossover G G G C G A
15 T G C G A G T A C A C G A C G C C C C T T A C G C C C C Supplementary Table 4 Estimating the age of EGLN1:c.12C>G. *All SNPs were included within 0.25 cm of EGLN1:c.12C>G that had an allele frequency of the inferred ancestral allele of EGLN1:c.12C>G of less than 0.8 to ensure that only informative SNPs that could result observable recombination events were included in the analysis. 10
16 EGLN1/PHD2 primer set (NCBI Reference Sequence: NG_015865) Primers Sequence (5'- 3') Exon Tm ( O C) Expected size PHD2- X1F CCCCTATCTCTCTCCCCG bp PHD2- X1R CCTGTCCAGCACAAACCC 56.2 PHD2- X2F AACCTATCTTGTGTTCCCTA bp PHD2- X2R GAGAAAAAGACACCTGTAAG 46.3 PHD2_X3F TTTGGTTACTCCTGCTTACA bp PHD2_X3R CGTTTACTCTACAGATTCCC 49.1 PHD2- X4F AATACCACTTTTTCCCCGCA bp PHD2- X4R TTTCCTGAAAGCATCACCTG 56 PHD2- X5F TTGGAAGTACAAGCGTGAT bp PHD2- X5R TTCCTCCTGTAAGCAATCA 50.9 PPARA primer set (NCBI Reference Sequence: NG_012204) 5'- UTR Primers Sequence (5'- 3') Exo n Tm ( O C) Expected size PPARA X1F GAGGGGCGGTGCGTGTC bp PPARA X1R CCTCGCAAGAGTCCTCGGTG PPARA X2F TCCAGAGAACAACCGTAAT bp PPARA X2R GCATCACAAAGTAATAACCC PPARA v5x- F CAAAATACCGTAAACTGGG V bp PPARA v5x- R AGACACGATGCTCCTAAAC V Coding region Primers Sequence (5'- 3') Exo n Tm ( O C) Expected size PPARA X3F ATTGTTCCTCTTTCCTCCCA bp PPARA X3R GCACACTTACCCGTGATGAC PPARA X4F GCGAAATCACATCCTCATAG bp PPARA X4R TAAGTAGTTGATGGTGGCG PPARA X5F GAGCAACAAAAAAGGTGAG bp PPARA X5R AACTGAGGAACGAACTGG PPARA X6F ATGAAGGATGGGTCTGA bp PPARA X6R TTGCTTAACTGTGGGATA PPARA X7F TGGTGTCCTCCTTTGTAG bp PPARA X7R ACTGGATTTCCCATTGTC PPARA X8F AGCAGTTCTTGGGTGAT bp PPARA X8R AGGTTAAAGTGGTGGATAT v5 = PPARA variant 5 PPARA promoter region primer set 11
17 Primers Sequence (5'- 3') Exon Tm ( O C) Expected size PPRA_HNF4- REF TGCCAGGTAATGTCTTTGAG NA bp PPRA_HNF4- RER TCGGGAACGCAATGTG NA 53.6 EPAS1/HIF2A primer set (NCBI Reference Sequence: NG_016000) Primers Sequence (5'- 3') Exon Tm ( O C) Expected size HIF2A_gX1F GCGGGAGCTTTACACTCG bp HIF2A_gX1R GGAGAGAAGGGAACCCAAGT 57.1 HIF2A_gX2F AGGTATGATAGGCTGACAGTAAC bp HIF2A_gX2R GGATTCACGGTAAAGGTCA 52.8 HIF2A_gX3F GTCCCATCTGTTTTCACTCCA bp HIF2A_gX3R ACCTTCCACTCATTTCTACCC 55 HIF2A_gX4F AATCTGGAAGGTGGCTCA bp HIF2A_gX4R TCTCATCTCACAGGCTACATAC 51.9 HIF2A_gX5-6F CAATAGGCTGCCAAGAA bp HIF2A_gX5-6R TGGGAGACCACCAAATAC 50.1 HIF2A_gX7F TGTTTGATTTGCCTTCTG bp HIF2A_gX7R AGACTCAACCCACCCTC 48.2 HIF2A_gX8F CCTGGTCCTCACTGTCGT bp HIF2A_gX8R TCCCAACCCAGTATCCC 52.4 HIF2A_gX9F ATGCCTGGAGTCCTACC bp HIF2A_gX9R AGCAGATCCCTCACCTC 48.4 HIF2A_gX10F GTGAGCCCGATGGTTGTG bp HIF2A_gX10R GAACACTAAAAGGAAGAAAACAGC 57.1 HIF2A_gX11F GCTGAAGGGACATTTGG bp HIF2A_gX11R CACCAGACAGCAGGCAC 51.9 HIF2A_gX12F GGAATAGTGTTTGTGAGGTCGTA bp HIF2A_gX12R TAAATGGGGTATCAGATGGC 55 HIF2A_gX13F GCCAGGAAGCCCTAGCAT bp HIF2A_gX13R AGATGGAAAGGGGAAATGG 57.4 HIF2A_gX14-15F AGCCCATCCTGGTTCTTC bp HIF2A_gX14-15R CAGTATTCTAGCCTGAGTTTGAG 53.7 HIF2A_gX16F AGACACCACTGAAGGAGCA bp HIF2A_gX16R TTTGGCAACAACAATAACG 52.8 Sequence of primers used to generate baculoviruses coding for PHD2 D4E and C127S mutants Primers Forward Reverse PHD2:p.D4E GATCCATGGCCAATGAGAGCGGCG CGGGCCCGCCGCTCTCATTGGCCATGG 12
18 PHD2:p.C127S GGCCCGG CGGCCGCGTCGCCGTCTCGTGCGGC CGCC ATCC GCGGCCGCACGAGACGGCGACGCGGC CGC PHD2 primers for Real-Time Quantitative PCR Primers Sequence (5'- 3') Exon Tm ( O C) Expected size PHD2- qpcr- F TATCCGGGCAATGGAACGGGT TAT bp PHD2- qrcr- R GGTTCAATGTCAGCAAACTGG GCT PHD2- endogen- F TAAACCTTCAGATTCGGTCG bp PHD2- endogen- R CAGATTTGAAGTTGATCATGC A 3 - UTR 62.6 Hydrolysis probe use for expression assay Gene Probe GeneID Chr Name Cat# ALAS2 212 Xp11.21 aminolevulinate, delta-, synthase 2 Hs _m1 EGLN q42.1 egl nine homolog 1 (C. elegans) Hs _m1 EPAS p21- p16 endothelial PAS domain protein 1 / HIF2A Hs _m1 EPOR p13.3- p13.2 erythropoietin receptor Hs _m1 HIF1A q23.2 hypoxia inducible factor 1, alpha subunit Hs _m1 HK q22 hexokinase 1 Hs _m1 PDGFB q13.1 platelet- derived growth factor beta polypeptide Hs _m1 PDK q31.1 pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isozyme 1 Hs _m1 PPARA q13.31 peroxisome proliferator- activated receptor alpha Hs _m1 SLC2A p16.1 solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose Hs _m1 transporter) TFRC q29 transferrin receptor (p90, CD71) Hs _m1 TGFB q13.1 transforming growth factor, beta 1 Hs _m1 VEGFA p12 vascular endothelial growth factor A Hs _m1 VHL p25.3 von Hippel- Lindau tumor suppressor Hs _m1 13
19 Supplementary Table 5 List of sequence primers and hydrolysis probe sets use in the analysis. Supplementary Note USA Subjects of Tibetan ancestry residing in Utah and Virginia, USA were recruited and screened by FRL, TT, JP using IRB approved protocol. Each subject signed IRB approved Informed consent for blood donation. INDIA Subjects of Tibetan ancestry residing in Srinagar and Himachal Pradesh Indian provinces were recruited by our Indian collaborators, Dr. Parvaiz A. Koul (a co-author of this manuscript) from Jammu and Kashmir, and the Director of Tibetan Delek Hospital in Dharamshala Himachal Pradesh, Dr. Tsetan Dorji. One of us (TT) is a native Tibetan and he explained the project in Tibetan language and stressed again voluntary nature of our study. Each subject signed IRB approved Informed consent for blood donation. CHINA Subjects of Tibetan ancestry residing in Qinghai province were recruited by our Chinese collaborator Dr. Ge Ri-Li (a co-author of this manuscript). One of us (TT) is a native Tibetan and he explained the project in Tibetan language and stressed again voluntary nature of our study. Each subject signed IRB approved Informed consent for blood donation. 14
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3143
 Supplementary Figure 1 Quantile-quantile plot of the association P values obtained in the discovery sample collection. The two clear outlying SNPs indicated for follow-up assessment are rs6841458 and rs7765379.
Supplementary Figure 1 Quantile-quantile plot of the association P values obtained in the discovery sample collection. The two clear outlying SNPs indicated for follow-up assessment are rs6841458 and rs7765379.
Supplementary Figure 2.Quantile quantile plots (QQ) of the exome sequencing results Chi square was used to test the association between genetic
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1.Description of the study design The samples in the initial stage (China cohort, exome sequencing) including 216 AMD cases and 1,553 controls were from the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1.Description of the study design The samples in the initial stage (China cohort, exome sequencing) including 216 AMD cases and 1,553 controls were from the
monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal antibody was examined in
 Supplementary information Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1 Determination of the s pecificity of in-house anti-rhbdd1 mouse monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal
Supplementary information Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1 Determination of the s pecificity of in-house anti-rhbdd1 mouse monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Neighbor-joining tree of the 183 wild, cultivated, and weedy rice accessions.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Neighbor-joining tree of the 183 wild, cultivated, and weedy rice accessions. Relationships of cultivated and wild rice correspond to previously observed relationships 40. Wild rice
Supplementary Figure 1 Neighbor-joining tree of the 183 wild, cultivated, and weedy rice accessions. Relationships of cultivated and wild rice correspond to previously observed relationships 40. Wild rice
Supplementary Figure 1. Study design of a multi-stage GWAS of gout.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Study design of a multi-stage GWAS of gout. Supplementary Figure 2. Plot of the first two principal components from the analysis of the genome-wide study (after QC) combined with
Supplementary Figure 1. Study design of a multi-stage GWAS of gout. Supplementary Figure 2. Plot of the first two principal components from the analysis of the genome-wide study (after QC) combined with
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Xenopus model of missense mutations. A mutation equivalent to MCIDAS R381H/G355D was introduced in the Xenopus mcidas (R370H, G355D) by PCR, sequenced
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Xenopus model of missense mutations. A mutation equivalent to MCIDAS R381H/G355D was introduced in the Xenopus mcidas (R370H, G355D) by PCR, sequenced
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Supplementary Table 1. Idd13 candidate interval supporting human LTC-ICs.
 Supplementary Table 1. Idd13 candidate interval supporting human LTC-ICs. Chr Start position Genomic marker EnsEMBL gene ID Gene symbol Primer 1 (5 3 ) Primer 2 (5 3 ) 2 128675293 ENSMUSG00000027387 Zc3h8
Supplementary Table 1. Idd13 candidate interval supporting human LTC-ICs. Chr Start position Genomic marker EnsEMBL gene ID Gene symbol Primer 1 (5 3 ) Primer 2 (5 3 ) 2 128675293 ENSMUSG00000027387 Zc3h8
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table.
 Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
Supplementary Methods Illumina Genome-Wide Genotyping Single SNP and Microsatellite Genotyping. Supplementary Table 4a Supplementary Table 4b
 Supplementary Methods Illumina Genome-Wide Genotyping All Icelandic case- and control-samples were assayed with the Infinium HumanHap300 SNP chips (Illumina, SanDiego, CA, USA), containing 317,503 haplotype
Supplementary Methods Illumina Genome-Wide Genotyping All Icelandic case- and control-samples were assayed with the Infinium HumanHap300 SNP chips (Illumina, SanDiego, CA, USA), containing 317,503 haplotype
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
Enhancers mutations that make the original mutant phenotype more extreme. Suppressors mutations that make the original mutant phenotype less extreme
 Interactomics and Proteomics 1. Interactomics The field of interactomics is concerned with interactions between genes or proteins. They can be genetic interactions, in which two genes are involved in the
Interactomics and Proteomics 1. Interactomics The field of interactomics is concerned with interactions between genes or proteins. They can be genetic interactions, in which two genes are involved in the
Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental Data. Charron et al. Dynamic landscapes of four histone modifications during de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell (2009). 10.1105/tpc.109.066845 Supplemental Figure 1. Immunodetection
Supplemental Data. Charron et al. Dynamic landscapes of four histone modifications during de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell (2009). 10.1105/tpc.109.066845 Supplemental Figure 1. Immunodetection
Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity.
 Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity. (A) Amino acid alignment of HDA5, HDA15 and HDA18. The blue line
Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity. (A) Amino acid alignment of HDA5, HDA15 and HDA18. The blue line
Supplementary Figure 1 a
 Supplementary Figure 1 a b GWAS second stage log 10 observed P 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 0 1 2 3 4 log 10 expected P rs3077 (P hetero =0.84) GWAS second stage (BBJ, Japan) First replication (BBJ, Japan) Second replication
Supplementary Figure 1 a b GWAS second stage log 10 observed P 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 0 1 2 3 4 log 10 expected P rs3077 (P hetero =0.84) GWAS second stage (BBJ, Japan) First replication (BBJ, Japan) Second replication
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name integrin, alpha 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID ITGA1 Human This gene encodes the alpha 1 subunit of integrin
Gene Information Gene Name integrin, alpha 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID ITGA1 Human This gene encodes the alpha 1 subunit of integrin
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name transforming growth factor, beta 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID TGFB1 Human This gene encodes a member of the
Gene Information Gene Name transforming growth factor, beta 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID TGFB1 Human This gene encodes a member of the
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets. Gene structures are shown underneath each panel. Supplementary Figure 2 pref6::ref6-gfp complements
Supplementary Figure 1 ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets. Gene structures are shown underneath each panel. Supplementary Figure 2 pref6::ref6-gfp complements
Molecular Markers CRITFC Genetics Workshop December 9, 2014
 Molecular Markers CRITFC Genetics Workshop December 9, 2014 Molecular Markers Tools that allow us to collect information about an individual, a population, or a species Application in fisheries mating
Molecular Markers CRITFC Genetics Workshop December 9, 2014 Molecular Markers Tools that allow us to collect information about an individual, a population, or a species Application in fisheries mating
High-Resolution Melting Interactive Workshop AACC, July 25 th, 2006 Assay Description
 AACC, July 25 th, 2006 Assay Description List of Example Assays Page Technique Example assay 2 Unlabeled probe genotyping HR-1 Factor V Leiden mutation 6 Unlabeled probe genotyping - LightScanner Factor
AACC, July 25 th, 2006 Assay Description List of Example Assays Page Technique Example assay 2 Unlabeled probe genotyping HR-1 Factor V Leiden mutation 6 Unlabeled probe genotyping - LightScanner Factor
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4199
 Supplementary Figure 1 Base editing activities of engineered A3A-BE3 variants with mutations designed to disrupt non-specific interactions with substrate ssdna. Graphs illustrating the frequencies of C
Supplementary Figure 1 Base editing activities of engineered A3A-BE3 variants with mutations designed to disrupt non-specific interactions with substrate ssdna. Graphs illustrating the frequencies of C
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11326 Supplementary Figure 1: Histone exchange increases over the ORF in a set2 mutant. (a) Gene average analysis. Schematic representation of the bin distribution over the coding and
doi:10.1038/nature11326 Supplementary Figure 1: Histone exchange increases over the ORF in a set2 mutant. (a) Gene average analysis. Schematic representation of the bin distribution over the coding and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Secondary mutations as a mechanism of cisplatin resistance in BRCA2-mutated cancers Wataru Sakai, Elizabeth M. Swisher, Beth Y. Karlan, Mukesh K. Agarwal, Jake Higgins, Cynthia Friedman, Emily Villegas,
Secondary mutations as a mechanism of cisplatin resistance in BRCA2-mutated cancers Wataru Sakai, Elizabeth M. Swisher, Beth Y. Karlan, Mukesh K. Agarwal, Jake Higgins, Cynthia Friedman, Emily Villegas,
Candidate region (0.74 Mb) ATC TCT GGG ACT CAT GAG CAG GAG GCT AGC ATC TCT GGG ACT CAT TAG CAG GAG GCT AGC
 A idm-3 idm-3 B Physical distance (Mb) 4.6 4.86.6 8.4 C Chr.3 Recom. Rate (%) ATG 3.9.9.9 9.74 Candidate region (.74 Mb) n=4 TAA D idm-3 G3T(E4) G4A(W988) WT idm-3 ATC TCT GGG ACT CAT GAG CAG GAG GCT AGC
A idm-3 idm-3 B Physical distance (Mb) 4.6 4.86.6 8.4 C Chr.3 Recom. Rate (%) ATG 3.9.9.9 9.74 Candidate region (.74 Mb) n=4 TAA D idm-3 G3T(E4) G4A(W988) WT idm-3 ATC TCT GGG ACT CAT GAG CAG GAG GCT AGC
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms
 Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
GENOTYPING BY PCR PROTOCOL FORM MUTANT MOUSE REGIONAL RESOURCE CENTER North America, International
 Please provide the following information required for genetic analysis of your mutant mice. Please fill in form electronically by tabbing through the text fields. The first 2 pages are protected with gray
Please provide the following information required for genetic analysis of your mutant mice. Please fill in form electronically by tabbing through the text fields. The first 2 pages are protected with gray
TALEN mediated targeted editing of GM2/GD2-synthase gene modulates anchorage independent growth by reducing anoikis resistance in mouse tumor cells
 Supplementary Information for TALEN mediated targeted editing of GM2/GD2-synthase gene modulates anchorage independent growth by reducing anoikis resistance in mouse tumor cells Barun Mahata 1, Avisek
Supplementary Information for TALEN mediated targeted editing of GM2/GD2-synthase gene modulates anchorage independent growth by reducing anoikis resistance in mouse tumor cells Barun Mahata 1, Avisek
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. The pedigree information for American upland cotton breeding.
 Supplementary Figure 1 The pedigree information for American upland cotton breeding. The integrated figure was modified from Fig. 1 to 10 in Calhoun, Bowman & May (1994). The accessions with blue color
Supplementary Figure 1 The pedigree information for American upland cotton breeding. The integrated figure was modified from Fig. 1 to 10 in Calhoun, Bowman & May (1994). The accessions with blue color
466 Asn (N) to Ala (A) Generate beta dimer Interface
 Table S1: Amino acid changes to the HexA α-subunit to convert the dimer interface from α to β and to introduce the putative GM2A binding surface from β- onto the α- subunit Residue position (α-numbering)
Table S1: Amino acid changes to the HexA α-subunit to convert the dimer interface from α to β and to introduce the putative GM2A binding surface from β- onto the α- subunit Residue position (α-numbering)
High-Resolution Melting analysis as a tool for rapid and sensitive detection of genotypes in cattle population
 Research and Development Station for Bovine, Arad, Romania High-Resolution Melting analysis as a tool for rapid and sensitive detection of genotypes in cattle population Daniela Elena Ilie, Ada Cean, Ioan
Research and Development Station for Bovine, Arad, Romania High-Resolution Melting analysis as a tool for rapid and sensitive detection of genotypes in cattle population Daniela Elena Ilie, Ada Cean, Ioan
Haplotypes, linkage disequilibrium, and the HapMap
 Haplotypes, linkage disequilibrium, and the HapMap Jeffrey Barrett Boulder, 2009 LD & HapMap Boulder, 2009 1 / 29 Outline 1 Haplotypes 2 Linkage disequilibrium 3 HapMap 4 Tag SNPs LD & HapMap Boulder,
Haplotypes, linkage disequilibrium, and the HapMap Jeffrey Barrett Boulder, 2009 LD & HapMap Boulder, 2009 1 / 29 Outline 1 Haplotypes 2 Linkage disequilibrium 3 HapMap 4 Tag SNPs LD & HapMap Boulder,
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name laminin, beta 3 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID LAMB3 Human The product encoded by this gene is a laminin that
Gene Information Gene Name laminin, beta 3 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID LAMB3 Human The product encoded by this gene is a laminin that
Genetic Variation and Genome- Wide Association Studies. Keyan Salari, MD/PhD Candidate Department of Genetics
 Genetic Variation and Genome- Wide Association Studies Keyan Salari, MD/PhD Candidate Department of Genetics How many of you did the readings before class? A. Yes, of course! B. Started, but didn t get
Genetic Variation and Genome- Wide Association Studies Keyan Salari, MD/PhD Candidate Department of Genetics How many of you did the readings before class? A. Yes, of course! B. Started, but didn t get
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Ihh interacts preferentially with its upstream neighboring gene Nhej1. Genes are indicated by gray lines, and Ihh and Nhej1 are highlighted in blue. 4C seq performed in E14.5 limbs
Supplementary Figure 1 Ihh interacts preferentially with its upstream neighboring gene Nhej1. Genes are indicated by gray lines, and Ihh and Nhej1 are highlighted in blue. 4C seq performed in E14.5 limbs
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Study participants We collected bone marrow and blood from patients with various myeloid malignancies after obtaining informed consent; this study abided by the principles laid out
Supplementary Methods Study participants We collected bone marrow and blood from patients with various myeloid malignancies after obtaining informed consent; this study abided by the principles laid out
CHAPTER 4 Cloning, expression, purification and preparation of site-directed mutants of NDUFS3 and NDUFS7
 CHAPTER 4 Cloning, expression, purification and preparation of site-directed mutants of NDUFS3 and NDUFS7 subunits of human mitochondrial Complex-I Q module N DUFS2, 3, 7 and 8 form the core subunits of
CHAPTER 4 Cloning, expression, purification and preparation of site-directed mutants of NDUFS3 and NDUFS7 subunits of human mitochondrial Complex-I Q module N DUFS2, 3, 7 and 8 form the core subunits of
Map-Based Cloning of Qualitative Plant Genes
 Map-Based Cloning of Qualitative Plant Genes Map-based cloning using the genetic relationship between a gene and a marker as the basis for beginning a search for a gene Chromosome walking moving toward
Map-Based Cloning of Qualitative Plant Genes Map-based cloning using the genetic relationship between a gene and a marker as the basis for beginning a search for a gene Chromosome walking moving toward
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Negative selection analysis of sgrnas targeting all Brd4 exons comparing day 2 to day 10 time points. Systematic evaluation of 64 Brd4 sgrnas in negative selection experiments, targeting
Supplementary Figure 1 Negative selection analysis of sgrnas targeting all Brd4 exons comparing day 2 to day 10 time points. Systematic evaluation of 64 Brd4 sgrnas in negative selection experiments, targeting
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID coagulation factor XIII, A1 polypeptide F13A1 Human This gene encodes the coagulation
Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID coagulation factor XIII, A1 polypeptide F13A1 Human This gene encodes the coagulation
Statistical Tools for Predicting Ancestry from Genetic Data
 Statistical Tools for Predicting Ancestry from Genetic Data Timothy Thornton Department of Biostatistics University of Washington March 1, 2015 1 / 33 Basic Genetic Terminology A gene is the most fundamental
Statistical Tools for Predicting Ancestry from Genetic Data Timothy Thornton Department of Biostatistics University of Washington March 1, 2015 1 / 33 Basic Genetic Terminology A gene is the most fundamental
S156AT168AY175A (AAA) were purified as GST-fusion proteins and incubated with GSTfused
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Supplemental Materials Supplemental Figure S1 (a) Phenotype of the wild type and grik1-2 grik2-1 plants after 8 days in darkness.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Supplemental Materials Supplemental Figure S1 (a) Phenotype of the wild type and grik1-2 grik2-1 plants after 8 days in darkness.
The RRPA knock-in allele was generated by homologous recombination in TC1 ES cells.
 Supplemental Materials Materials & Methods Generation of RRPA and RAPA Knock-in Mice The RRPA knock-in allele was generated by homologous recombination in TC1 ES cells. Targeted ES clones in which the
Supplemental Materials Materials & Methods Generation of RRPA and RAPA Knock-in Mice The RRPA knock-in allele was generated by homologous recombination in TC1 ES cells. Targeted ES clones in which the
Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
B) You can conclude that A 1 is identical by descent. Notice that A2 had to come from the father (and therefore, A1 is maternal in both cases).
 Homework questions. Please provide your answers on a separate sheet. Examine the following pedigree. A 1,2 B 1,2 A 1,3 B 1,3 A 1,2 B 1,2 A 1,2 B 1,3 1. (1 point) The A 1 alleles in the two brothers are
Homework questions. Please provide your answers on a separate sheet. Examine the following pedigree. A 1,2 B 1,2 A 1,3 B 1,3 A 1,2 B 1,2 A 1,2 B 1,3 1. (1 point) The A 1 alleles in the two brothers are
Fig. S1. Effect of p120-catenin overexpression on the interaction of SCUBE2 with E-cadherin. The expression plasmid encoding FLAG.
 Fig. S1. Effect of p120-catenin overexpression on the interaction of SCUBE2 with E-cadherin. The expression plasmid encoding FLAG.SCUBE2, E-cadherin.Myc, or HA.p120-catenin was transfected in a combination
Fig. S1. Effect of p120-catenin overexpression on the interaction of SCUBE2 with E-cadherin. The expression plasmid encoding FLAG.SCUBE2, E-cadherin.Myc, or HA.p120-catenin was transfected in a combination
Association Mapping in Plants PLSC 731 Plant Molecular Genetics Phil McClean April, 2010
 Association Mapping in Plants PLSC 731 Plant Molecular Genetics Phil McClean April, 2010 Traditional QTL approach Uses standard bi-parental mapping populations o F2 or RI These have a limited number of
Association Mapping in Plants PLSC 731 Plant Molecular Genetics Phil McClean April, 2010 Traditional QTL approach Uses standard bi-parental mapping populations o F2 or RI These have a limited number of
Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Figure S2. Verification of ihog and boi
 Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Extracts from S2R+ cells, embryos, and adults were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with anti-ihog antibody. The Ihog
Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Extracts from S2R+ cells, embryos, and adults were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with anti-ihog antibody. The Ihog
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1.
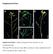 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section B and ONE question from Section C.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIO-2B02 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIO-2B02 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID HLA-DRB1 Human HLA-DRB1 belongs
Gene Information Gene Name major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID HLA-DRB1 Human HLA-DRB1 belongs
Supplemental Figure 1. Transcript profiles of Arabidopsis IPMS1 and IPMS2 in different tissues and developmental stages.
 Transcript level (intensity) Supplemental Data. Xing et al. Plant Cell (2017) 10.1105/tpc.17.00186 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 IPMS1 IPMS2 Supplemental Figure 1. Transcript profiles of Arabidopsis
Transcript level (intensity) Supplemental Data. Xing et al. Plant Cell (2017) 10.1105/tpc.17.00186 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 IPMS1 IPMS2 Supplemental Figure 1. Transcript profiles of Arabidopsis
Data Sources and Biobanks in the Asia-Pacific Region. Wei Zhou, MD, Ph.D. Department of Epidemiology, Merck Research Laboratories October 23, 2014
 Data Sources and Biobanks in the Asia-Pacific Region Wei Zhou, MD, Ph.D. Department of Epidemiology, Merck Research Laboratories October 23, 2014 1 Disclosures Wei Zhou is currently an employee of Merck
Data Sources and Biobanks in the Asia-Pacific Region Wei Zhou, MD, Ph.D. Department of Epidemiology, Merck Research Laboratories October 23, 2014 1 Disclosures Wei Zhou is currently an employee of Merck
A novel tool for monitoring endogenous alpha-synuclein transcription by NanoLuciferase
 A novel tool for monitoring endogenous alpha-synuclein transcription by NanoLuciferase tag insertion at the 3 end using CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technique Sambuddha Basu 1, 3, Levi Adams 1, 3, Subhrangshu
A novel tool for monitoring endogenous alpha-synuclein transcription by NanoLuciferase tag insertion at the 3 end using CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technique Sambuddha Basu 1, 3, Levi Adams 1, 3, Subhrangshu
amplify the conditional allele (2-lox) and recombined allele (1-lox) following tamoxifen
 Supplementary data Supplementary Table 1. Real-time PCR primer sequences Supplementary Fig. 1. (A) Genomic map of the Vhl (2-lox) conditional allele. Numbered boxes represent exon 1, which is targeted
Supplementary data Supplementary Table 1. Real-time PCR primer sequences Supplementary Fig. 1. (A) Genomic map of the Vhl (2-lox) conditional allele. Numbered boxes represent exon 1, which is targeted
Supplementary Figure 1. Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings.
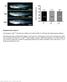 Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
AD BD TOC1. Supplementary Figure 1: Yeast two-hybrid assays showing the interaction between
 AD X BD TOC1 AD BD X PIFΔAD PIF TOC1 TOC1 PIFΔAD PIF N TOC1 TOC1 C1 PIFΔAD PIF C1 TOC1 TOC1 C PIFΔAD PIF C TOC1 Supplementary Figure 1: Yeast two-hybrid assays showing the interaction between PIF and TOC1
AD X BD TOC1 AD BD X PIFΔAD PIF TOC1 TOC1 PIFΔAD PIF N TOC1 TOC1 C1 PIFΔAD PIF C1 TOC1 TOC1 C PIFΔAD PIF C TOC1 Supplementary Figure 1: Yeast two-hybrid assays showing the interaction between PIF and TOC1
B6 FVB AKR. Percent survival 75 * C3Ou *** *** Days post-infection
 Percent survival 100 75 * B6 FVB AKR 50 C3Ou 25 *** *** 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Days post-infection Supplementary Figure S1: Survival of inbred mice strains following infection with Citrobacter rodentium.
Percent survival 100 75 * B6 FVB AKR 50 C3Ou 25 *** *** 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Days post-infection Supplementary Figure S1: Survival of inbred mice strains following infection with Citrobacter rodentium.
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID protein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent, 1A PPM1A Human The protein encoded by
Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID protein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent, 1A PPM1A Human The protein encoded by
Rapid Cycle PCR, Real Time Analysis, and Hi-Res Melting
 Rapid Cycle PCR, Real Time Analysis, and Hi-Res Melting Carl Wittwer Department of Pathology University of Utah ARUP Idaho Technology AMP, Oct. 31, 2008 Impatient, Lazy, and Cheap Rapid Cycle PCR Fast
Rapid Cycle PCR, Real Time Analysis, and Hi-Res Melting Carl Wittwer Department of Pathology University of Utah ARUP Idaho Technology AMP, Oct. 31, 2008 Impatient, Lazy, and Cheap Rapid Cycle PCR Fast
Prioritization: from vcf to finding the causative gene
 Prioritization: from vcf to finding the causative gene vcf file making sense A vcf file from an exome sequencing project may easily contain 40-50 thousand variants. In order to optimize the search for
Prioritization: from vcf to finding the causative gene vcf file making sense A vcf file from an exome sequencing project may easily contain 40-50 thousand variants. In order to optimize the search for
Supplemental Data. Hu et al. Plant Cell (2017) /tpc
 1 2 3 4 Supplemental Figure 1. DNA gel blot analysis of homozygous transgenic plants. (Supports Figure 1.) 5 6 7 8 Rice genomic DNA was digested with the restriction enzymes EcoRⅠ and BamHⅠ. Lanes in the
1 2 3 4 Supplemental Figure 1. DNA gel blot analysis of homozygous transgenic plants. (Supports Figure 1.) 5 6 7 8 Rice genomic DNA was digested with the restriction enzymes EcoRⅠ and BamHⅠ. Lanes in the
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Number and length distributions of the inferred fosmids.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Number and length distributions of the inferred fosmids. Fosmid were inferred by mapping each pool s sequence reads to hg19. We retained only those reads that mapped to within a
Supplementary Figure 1 Number and length distributions of the inferred fosmids. Fosmid were inferred by mapping each pool s sequence reads to hg19. We retained only those reads that mapped to within a
2. (So) get (fragments with gene) R / required gene. Accept: allele for gene / same gene 2
 M.(a). Cut (DNA) at same (base) sequence / (recognition) sequence; Accept: cut DNA at same place. (So) get (fragments with gene) R / required gene. Accept: allele for gene / same gene (b). Each has / they
M.(a). Cut (DNA) at same (base) sequence / (recognition) sequence; Accept: cut DNA at same place. (So) get (fragments with gene) R / required gene. Accept: allele for gene / same gene (b). Each has / they
A Nucleus-Encoded Chloroplast Protein YL1 Is Involved in Chloroplast. Development and Efficient Biogenesis of Chloroplast ATP Synthase in Rice
 A Nucleus-Encoded Chloroplast Protein YL1 Is Involved in Chloroplast Development and Efficient Biogenesis of Chloroplast ATP Synthase in Rice Fei Chen 1,*, Guojun Dong 2,*, Limin Wu 1, Fang Wang 3, Xingzheng
A Nucleus-Encoded Chloroplast Protein YL1 Is Involved in Chloroplast Development and Efficient Biogenesis of Chloroplast ATP Synthase in Rice Fei Chen 1,*, Guojun Dong 2,*, Limin Wu 1, Fang Wang 3, Xingzheng
EPIB 668 Genetic association studies. Aurélie LABBE - Winter 2011
 EPIB 668 Genetic association studies Aurélie LABBE - Winter 2011 1 / 71 OUTLINE Linkage vs association Linkage disequilibrium Case control studies Family-based association 2 / 71 RECAP ON GENETIC VARIANTS
EPIB 668 Genetic association studies Aurélie LABBE - Winter 2011 1 / 71 OUTLINE Linkage vs association Linkage disequilibrium Case control studies Family-based association 2 / 71 RECAP ON GENETIC VARIANTS
Supplementary data. sienigma. F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM. a-p53
 Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information MicroRNA-212/132 family is required for epithelial stromal interactions necessary for mouse mammary gland development Ahmet Ucar, Vida Vafaizadeh, Hubertus Jarry, Jan Fiedler,
Supplementary Information MicroRNA-212/132 family is required for epithelial stromal interactions necessary for mouse mammary gland development Ahmet Ucar, Vida Vafaizadeh, Hubertus Jarry, Jan Fiedler,
Integrated Omics Study Delineates the Dynamics of Lipid Droplets in Rhodococcus Opacus PD630
 School of Natural Sciences and Mathematics 2013-10-22 Integrated Omics Study Delineates the Dynamics of Lipid Droplets in Rhodococcus Opacus PD630 UTD AUTHOR(S): Michael Qiwei Zhang 2013 The Authors This
School of Natural Sciences and Mathematics 2013-10-22 Integrated Omics Study Delineates the Dynamics of Lipid Droplets in Rhodococcus Opacus PD630 UTD AUTHOR(S): Michael Qiwei Zhang 2013 The Authors This
To investigate the heredity of the WFP gene, we selected plants that were homozygous
 Supplementary information Supplementary Note ST-12 WFP allele is semi-dominant To investigate the heredity of the WFP gene, we selected plants that were homozygous for chromosome 1 of Nipponbare and heterozygous
Supplementary information Supplementary Note ST-12 WFP allele is semi-dominant To investigate the heredity of the WFP gene, we selected plants that were homozygous for chromosome 1 of Nipponbare and heterozygous
Optimizing Cas9 and sgrna concentrations for increasing mutation efficiency. Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.3360
 Supplementary Figure 1 Optimizing Cas9 and sgrna concentrations for increasing mutation efficiency. (a) Wild-type, 2-dpf slc24a5 b1 embryos and a series of slc24a5 CRISPR-injected embryos; anterior is
Supplementary Figure 1 Optimizing Cas9 and sgrna concentrations for increasing mutation efficiency. (a) Wild-type, 2-dpf slc24a5 b1 embryos and a series of slc24a5 CRISPR-injected embryos; anterior is
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID FGFR1 Human The protein encoded by this gene
Gene Information Gene Name fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID FGFR1 Human The protein encoded by this gene
Zhang et al., RepID facilitates replication Initiation. Supplemental Information:
 Supplemental Information: a b 1 Supplementary Figure 1 (a) DNA sequence of all the oligonucleotides used in this study. Only one strand is shown. The unshaded nucleotide sequences show changes from the
Supplemental Information: a b 1 Supplementary Figure 1 (a) DNA sequence of all the oligonucleotides used in this study. Only one strand is shown. The unshaded nucleotide sequences show changes from the
Ramp1 EPD0843_4_B11. EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping
 EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
Usp14 EPD0582_2_G09. EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping
 EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
Supplementary Information. Werner Koch, Petra Hoppmann, Jakob C. Mueller, Albert Schömig & Adnan Kastrati
 Supplementary Information Werner Koch, Petra Hoppmann, Jakob C. Mueller, Albert Schömig & Adnan Kastrati The Supplementary Information has the following sections in order: 1. Supplementary Methods 2. Supplementary
Supplementary Information Werner Koch, Petra Hoppmann, Jakob C. Mueller, Albert Schömig & Adnan Kastrati The Supplementary Information has the following sections in order: 1. Supplementary Methods 2. Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
Amplicon size (bp) E ± SD
 Development of a probe-based qpcr assay for the detection of constitutional and somatic deletions in the NF1 gene. Application to genetic testing and tumor analysis. Terribas E, Garcia-Linares C, Lázaro
Development of a probe-based qpcr assay for the detection of constitutional and somatic deletions in the NF1 gene. Application to genetic testing and tumor analysis. Terribas E, Garcia-Linares C, Lázaro
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3494
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Supplementary Fig. 1. Location of top two candidemia associated SNPs in CD58 gene
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1. Location of top two candidemia associated SNPs in CD58 gene locus. The region encompass CD58 and three long non-coding RNAs (RP4-655J12.4, RP5-1086K13.1 and
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1. Location of top two candidemia associated SNPs in CD58 gene locus. The region encompass CD58 and three long non-coding RNAs (RP4-655J12.4, RP5-1086K13.1 and
Shaare Zedek Medical Center (SZMC) Gaucher Clinic. Peripheral blood samples were collected from each
 SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Sample collection and DNA extraction Pregnant Ashkenazi Jewish (AJ) couples, carrying mutation/s in the GBA gene, were recruited at the Shaare Zedek Medical Center (SZMC) Gaucher Clinic.
SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Sample collection and DNA extraction Pregnant Ashkenazi Jewish (AJ) couples, carrying mutation/s in the GBA gene, were recruited at the Shaare Zedek Medical Center (SZMC) Gaucher Clinic.
Fast, Accurate and Sensitive DNA Variant Detection from Sanger Sequencing:
 Fast, Accurate and Sensitive DNA Variant Detection from Sanger Sequencing: Patented, Anti-Correlation Technology Provides 99.5% Accuracy & Sensitivity to 5% Variant Knowledge Base and External Annotation
Fast, Accurate and Sensitive DNA Variant Detection from Sanger Sequencing: Patented, Anti-Correlation Technology Provides 99.5% Accuracy & Sensitivity to 5% Variant Knowledge Base and External Annotation
COVER PAGE SAMPLE DNA GENOTYPING FINAL REPORT. Date. Month XX, 20XX. Reviewed & approved by: Steve Granger, Ph.D, Chief Scientific Officer
 5962 La Place Court, Suite 275, Carlsbad, CA 92008 USA Tel 800.790.2258 Fax 760.448.5397 www.salimetrics.com COVER PAGE Project Name XXXXXXXXXXXXX Document Final Report Analysis Genotyping Researcher Name
5962 La Place Court, Suite 275, Carlsbad, CA 92008 USA Tel 800.790.2258 Fax 760.448.5397 www.salimetrics.com COVER PAGE Project Name XXXXXXXXXXXXX Document Final Report Analysis Genotyping Researcher Name
Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the prey clones identified in the yeast two hybrid screen.
Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the prey clones identified in the yeast two hybrid screen.
HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Using mutants to clone genes
 Using mutants to clone genes Objectives: 1. What is positional cloning? 2. What is insertional tagging? 3. How can one confirm that the gene cloned is the same one that is mutated to give the phenotype
Using mutants to clone genes Objectives: 1. What is positional cloning? 2. What is insertional tagging? 3. How can one confirm that the gene cloned is the same one that is mutated to give the phenotype
Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 47, 598 606 (2015) Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C Borbala Mifsud, Filipe Tavares-Cadete, Alice N Young, Robert Sugar,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 47, 598 606 (2015) Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C Borbala Mifsud, Filipe Tavares-Cadete, Alice N Young, Robert Sugar,
CMSC423: Bioinformatic Algorithms, Databases and Tools. Some Genetics
 CMSC423: Bioinformatic Algorithms, Databases and Tools Some Genetics CMSC423 Fall 2009 2 Chapter 13 Reading assignment CMSC423 Fall 2009 3 Gene association studies Goal: identify genes/markers associated
CMSC423: Bioinformatic Algorithms, Databases and Tools Some Genetics CMSC423 Fall 2009 2 Chapter 13 Reading assignment CMSC423 Fall 2009 3 Gene association studies Goal: identify genes/markers associated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12119 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND LEGENDS pre-let-7a- 1 +14U pre-let-7a- 1 Ddx3x Dhx30 Dis3l2 Elavl1 Ggt5 Hnrnph 2 Osbpl5 Puf60 Rnpc3 Rpl7 Sf3b3 Sf3b4 Tia1 Triobp U2af1 U2af2 1 6 2 4 3
doi:10.1038/nature12119 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND LEGENDS pre-let-7a- 1 +14U pre-let-7a- 1 Ddx3x Dhx30 Dis3l2 Elavl1 Ggt5 Hnrnph 2 Osbpl5 Puf60 Rnpc3 Rpl7 Sf3b3 Sf3b4 Tia1 Triobp U2af1 U2af2 1 6 2 4 3
Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3556 INTEGRATED SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE TEMPLATE. Supplementary Figure 1
 INTEGRATED SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE TEMPLATE Supplementary Figure 1 REF6 expression in transgenic lines. (a,b) Expression of REF6 in REF6-HA ref6 and REF6ΔZnF-HA ref6 plants detected by RT qpcr (a) and immunoblot
INTEGRATED SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE TEMPLATE Supplementary Figure 1 REF6 expression in transgenic lines. (a,b) Expression of REF6 in REF6-HA ref6 and REF6ΔZnF-HA ref6 plants detected by RT qpcr (a) and immunoblot
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Super-resolution imaging of fluorescently labeled, endogenous RNA Polymerase II in living cells with CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing Won-Ki Cho 1, Namrata Jayanth 1, Susan Mullen
Supplementary Information Super-resolution imaging of fluorescently labeled, endogenous RNA Polymerase II in living cells with CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing Won-Ki Cho 1, Namrata Jayanth 1, Susan Mullen
Petar Pajic 1 *, Yen Lung Lin 1 *, Duo Xu 1, Omer Gokcumen 1 Department of Biological Sciences, University at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY.
 The psoriasis associated deletion of late cornified envelope genes LCE3B and LCE3C has been maintained under balancing selection since Human Denisovan divergence Petar Pajic 1 *, Yen Lung Lin 1 *, Duo
The psoriasis associated deletion of late cornified envelope genes LCE3B and LCE3C has been maintained under balancing selection since Human Denisovan divergence Petar Pajic 1 *, Yen Lung Lin 1 *, Duo
A PCR Assay for the Anthocyaninless Mutation in Fast Plants and a Bridge Between Classical Genetics and Genomics
 Tested Studies for Laboratory Teaching Proceedings of the Association for Biology Laboratory Education Volume 39, Article 61, 2018 A PCR Assay for the Anthocyaninless Mutation in Fast Plants and a Bridge
Tested Studies for Laboratory Teaching Proceedings of the Association for Biology Laboratory Education Volume 39, Article 61, 2018 A PCR Assay for the Anthocyaninless Mutation in Fast Plants and a Bridge
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name minichromosome maintenance complex component 8 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID MCM8 Human The protein encoded by
Gene Information Gene Name minichromosome maintenance complex component 8 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID MCM8 Human The protein encoded by
Supplementary table 1: List of sequences of primers used in sequenom assay
 Supplementary table 1: List of sequences of primers used in sequenom assay SNP_ID 2nd-PCRP Sequence 1st-PCRP Sequence Allele specific (iplex) iplex primer primer Direction ROCK2 1 rs978906 ACGTTGGATGATAAAGCTCTCTCGGCAGTC
Supplementary table 1: List of sequences of primers used in sequenom assay SNP_ID 2nd-PCRP Sequence 1st-PCRP Sequence Allele specific (iplex) iplex primer primer Direction ROCK2 1 rs978906 ACGTTGGATGATAAAGCTCTCTCGGCAGTC
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Lee JH, Cheng R, Barral S, Reitz C, Medrano M, Lantigua R, Jiménez-Velazquez IZ, Rogaeva E, St. George-Hyslop P, Mayeux R. Identification of novel loci for Alzheimer disease
Supplementary Online Content Lee JH, Cheng R, Barral S, Reitz C, Medrano M, Lantigua R, Jiménez-Velazquez IZ, Rogaeva E, St. George-Hyslop P, Mayeux R. Identification of novel loci for Alzheimer disease
Erhard et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. c1-hbr allele structure. Diagram of the c1-hbr allele found in stocks segregating 1:1 for rpd1-1 and rpd1-2 homozygous mutants showing the presence of a 363 base pair (bp) Heartbreaker
Supplemental Figure 1. c1-hbr allele structure. Diagram of the c1-hbr allele found in stocks segregating 1:1 for rpd1-1 and rpd1-2 homozygous mutants showing the presence of a 363 base pair (bp) Heartbreaker
Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of LRRK1 bind to Grb2.
 Myc- HA-Grb2 Mr(K) 105 IP HA 75 25 105 1-1163 1-595 - + - + - + 1164-1989 Blot Myc HA total lysate 75 25 Myc HA Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of bind to Grb2. COS7 cells were cotransfected
Myc- HA-Grb2 Mr(K) 105 IP HA 75 25 105 1-1163 1-595 - + - + - + 1164-1989 Blot Myc HA total lysate 75 25 Myc HA Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of bind to Grb2. COS7 cells were cotransfected
Supplementary Data 1.
 Supplementary Data 1. Evaluation of the effects of number of F2 progeny to be bulked (n) and average sequencing coverage (depth) of the genome (G) on the levels of false positive SNPs (SNP index = 1).
Supplementary Data 1. Evaluation of the effects of number of F2 progeny to be bulked (n) and average sequencing coverage (depth) of the genome (G) on the levels of false positive SNPs (SNP index = 1).
Genotyping Technology How to Analyze Your Own Genome Fall 2013
 Genotyping Technology 02-223 How to nalyze Your Own Genome Fall 2013 HapMap Project Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Samples & POP panels Genotyping centers Unique QC+ SNPs 269 samples (4 populations) HapMap International
Genotyping Technology 02-223 How to nalyze Your Own Genome Fall 2013 HapMap Project Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Samples & POP panels Genotyping centers Unique QC+ SNPs 269 samples (4 populations) HapMap International
