MIAPE: Mass Spectrometry Quantification
|
|
|
- Leonard Anthony
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MIAPE: Mass Spectrometry Quantification Salvador Martínez-Bartolomé[1,12], Eric W. Deutsch[2], Pierre-Alain Binz[3], Andrew R. Jones[4], Martin Eisenacher[5], Gerhard Mayer[5], Alex Campos[6,12], Francesc Canals[7,12], Joan-Josep Bech-Serra[7,12], Montserrat Carrascal[8,12], Marina Gay[8,12], Alberto Paradela[1,12], Rosana Navajas[1,12], Miguel Marcilla[1,12], María Luisa Hernáez[9,12], María Dolores Gutiérrez-Blázquez[9,12], Luis Felipe Clemente Velarde[9,12], Kerman Aloria[10,12], Jabier Beaskoetxea[11,12], J. Alberto Medina-Aunon[1,12], Juan P. Albar[1,12] [1] Proteomics Facility, Centro Nacional de Biotecnología - CSIC, Madrid, Spain. [2] Institute for Systems Biology, 1441 N 34 th Street, Seattle, WA 98103, USA. [3] Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics, Rue Michel-Servet 1, CH-1211 Geneva 4, Switzerland. [4] Institute of Integrative Biology, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, UK. [5] Medizinisches Proteom-Center, Ruhr-Universitaet Bochum, Bochum, Germany. [6] Proteomics Platform, Barcelona Science Park, Barcelona, Spain. [7] Proteomics Laboratory, Vall d'hebron Institute of Oncology, Vall d'hebron University Hospital, Barcelona, Spain. [8] CSIC/UAB Proteomics Laboratory, Instituto de Investigaciones Biomédicas de Barcelona-Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas/Institut d'investigacions Biomèdiques August Pi i Sunyer (IIBB-CSIC/IDIBAPS), Bellaterra, Spain. [9] Proteomics Unit. Universidad Complutense de Madrid- Parque Científico de Madrid. Madrid, Spain. [10] Proteomics Core Facility-SGIKER, University of the Basque Country, UPV/EHU, Leioa Spain. [11] Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of the Basque Country, UPV/EHU, Leioa Spain. [12] ProteoRed Consortium, Spanish National Institute of Proteomics, Madrid, Spain. Author contact information: Salvador Martínez de Bartolomé Izquierdo Proteomics Facility, Centro Nacional de Biotecnología - CSIC, Madrid, Spain. ProteoRed Consortium, Spanish National Institute of Proteomics, Madrid, Spain. smartinez@proteored.org
2 MIAPE: Mass Spectrometry Quantification Version 1.0, 24 th October, 2012, Final. This module identifies the minimum information required to report the use of quantification techniques in a proteomics experiment, sufficient to support both the effective interpretation and assessment of the data and the potential recreation of the results of the data analysis. Introduction This document is one of a collection of technologyspecific modules that together constitute the Minimum Information about a Proteomics Experiment (MIAPE) reporting guidelines produced by the Proteomics Standards Initiative. MIAPE is structured around a parent document that lays out the principles to which the individual reporting guidelines adhere. In brief, a MIAPE module represents the minimum information that should be reported about a data set or an experimental process, to allow a reader to interpret and critically evaluate the conclusions reached, and to support their experimental corroboration. In practice a MIAPE module comprises a checklist of information that should be provided (for example about the protocols employed) when a data set is submitted to a public repository or when an experimental step is reported in a scientific publication (for instance in the materials and methods section). The MIAPE modules specify neither the format that information should be transferred in, nor the structure of the repository/text. However, PSI is not developing the MIAPE modules in isolation; several compatible data exchange standards are now well established and supported by public databases and data processing software in proteomics (for details see the PSI website Mass spectrometry is already a well-established protein identification tool and recent methodological and technological developments have also made possible the extraction of quantitative data of protein abundance in largescale studies. Several strategies for absolute and relative quantitative proteomics and the statistical assessment of quantifications are possible, each having specific measurements and therefore, different data analysis workflows. The guidelines for Mass Spectrometry Quantification allow the description of a wide range of quantitative approaches, including labelled and label-free techniques and also targeted approaches such as Selected Reaction Monitoring (SRM). These reporting guidelines cover the description of experimental design (as far as important for quantification) and samples, input data, quantification algorithm and resulting quantitative and statistical data. They do not explicitly cover sample preparation, but do require some minimal description for each sample and the labelling protocol (if applicable). They do not include any acquisition parameter or transition list (in case of SRM approaches), since these should be included in the corresponding MIAPE Mass Spectrometry module. Sections from earlier versions of other MIAPE modules dealing with quantification have been removed to avoid overlap (e.g. from MIAPE-MS and MIAPE-MSI). Reporting of quantification in gel experiments is still described in MIAPE-GI (gel informatics). Items falling outside the scope of this module may be captured in complementary modules, which can be obtained from the website ( Note that subsequent versions of this document may have altered scope, as will almost certainly be the case for all the MIAPE modules. The following section, detailing the reporting guidelines for the peptide and protein quantification analysis and their statistics, is subdivided as follows: 1. General features; the quantitative approach. 2. Experimental design and sample description; description of samples and assays (a run together with a labelling feature), group structure (resulting from experimental conditions and their values) and replicate structure.
3 3. Input data; description or reference to the dataset used for quantitative analysis. 4. Protocol; software and methods applied in the quantitative analysis (including transformation functions, aggregation functions, and statistical calculations). 5. Resulting data; actual resulting quantification values at the feature, peptide and/or protein level, plus units where appropriate. Reporting guidelines for the peptide and protein quantification analysis. 1. General features 1.1. Experiment identifier or name 1.2. Responsible person or role 1.3. Quantitative approach 2. Experimental design and sample description 2.1. Experimental design Groups Biological and technical replicates 2.2. Sample / Assay description Labelling protocol (if applicable) Sample description: Sample name Sample amount Sample labelling with assay definition, i.e. MS run / data set together with reporting ion mass, reagent or isotope labelled amino acid Replicates and/or groups Isotopic correction coefficients Internal references 3. Input data Description and reference of the dataset used for quantitative analysis (no actual values) Input data type 3.2. Input data format 3.3. Input data merging 3.4. Availability of the input data 4. Protocol Description of the software and methods applied in the quantitative analysis (including transformation functions, aggregation functions and statistical calculations) Quantification software name, version and manufacturer 4.2. Description of the selection and/or matching method of features, together with the description of the method of the primary extracted quantification values determination for each feature and/or peptide Confidence filter of features or peptides prior to quantification 4.4. Description of data calculation and transformation methods Missing values imputation and outliers removal Quantification values calculation and / or ratio determination from the primary extracted quantification values Replicate aggregation Normalization Inference protocol for calculating protein quantification values from peptide quantification values Protocol specific corrections 4.5. Description of methods for (statistical) estimation of correctness 4.6. Calibration curves of standards 5. Resulting data The actual quantification values resulting from your quantification software together with their estimated confidence 5.1. Quantification values at feature and/or at peptide level: Primary extracted quantification values for each feature, with their statistical estimation of correctness Quantification values for each peptide as a result of the aggregation of the values of the previous section (5.1.1), with their statistical estimation of correctness 5.2. Quantification values at protein level: Basic / raw quantification values with statistical estimation of correctness Transformed / aggregated / combined quantification values of the proteins at group level, with their statistical estimation of correctness Summary
4 The MIAPE: Mass Spectrometry Quantification minimum reporting guidelines for the peptide and protein quantification analysis specify that a significant number of details have to be captured for quantitative analysis, such as label-free, 18 O- labelling, AQUA, SILAC, itraq, TMT, ICAT, ICPL, 14 N/ 15 N or SRM approaches. However, it is clear that providing the information required by this document will enable the effective interpretation and assessment of quantitative data and potentially, support experimental corroboration. Much of the information required herein may already be stored in an electronic format, or exportable from the analysis software; we anticipate further automation of this process. These guidelines will evolve. To contribute, or to track the process to remain MIAPE-compliant, browse to the website at
5 Appendix One. The MIAPE: Mass Spectrometry Quantification glossary of required items Classification Definition 1. General features Global descriptors of the experiment 1.1 Experiment identifier or name 1.2 Responsible person or role 1.3 Quantitative approach Descriptive name and/or an identifier assigned to the experiment (may be assigned later by a public repository). Include keywords indicating which disease, model was studied. The (stable) primary contact person for this data set; this could be the experimenter, lab head, line manager etc. Where responsibility rests with an institutional role (e.g., one of a number of duty officers) rather than a person, give the official name of the role rather than any one person. In all cases give affiliation including address and stable contact information. Indicate the quantitative approach deployed in the experiment (e.g., itraq-4plex, SILAC, Label-free identity-based, feature- based, SRM, AQUA, 14 N/ 15 N). 2. Experimental design and sample description 2.1 Experimental design (to reference in section ) Groups Biological and technical replicates Description of the experimental sample grouping including group names (if appropriate). A group is a sample set that corresponds to a certain experimental condition with its value (i.e. condition gender with value female is group gender_female ). Description of the biological and/or technical replicate structure (if appropriate). This is also a group structure like above, but hierarchically ordered. In the case of technical replicates, describe the kind of technical replicates: e.g., cell lysis replicates: samples are replicated prior to cell lysis step, digestion replicates: samples are replicated prior to digestion step, LC-MS/MS replicates: samples are replicated prior to LC-MS/MS runs. 2. Experimental design and sample description 2.2 Sample / Assay description Labelling protocol (if applicable) Sample description In the case of label-based quantification methods, describe the labelling protocol, including the labelling level: if labelling occurs at the element, amino acid, peptide (terminus) or protein (terminus) level. For each sample, provide, if applicable, the information required in , , and : Sample name Unique name for the sample to be referred to elsewhere in the document.
6 Sample amount Sample amount (including the appropriate units) Sample labelling with assay definition, i.e. MS run / data set together with reporting ion mass, reagent or isotope labelled amino acid Replicates and/or groups Isotopic correction coefficients Internal references In the case of label-based quantification methods, indicate which label is associated with which sample. If appropriate, provide the mass of the reporter ion (e.g. itraq 4-plex : 114), the reagent (e.g., ICPL- 12 C6) or the isotope labeled amino acid(s) used in this sample (e.g., 13 C6-Lysine and 13 C6- Arginine) or the isotope-labeled element (e.g. 15 N). Replicates and/or groups from sections and that the sample belongs to. One sample / assay is usually part of several replicates / groups, e.g. part of technical replicate X AND biological replicate Y, or part of gender_male AND age_ In case of itraq/tmt like labelling, provide the isotopic correction coefficients. In the case of other isotopic labels, percent enrichment, such as 98% 15 N. List of internal references used and their amount. Also state their specific purpose such as quantification, normalization or alignment. 3. Input data Description and reference of the dataset used for quantitative analysis: type, format and availability of the data. No actual values are requested here. 3.1 Input data type 3.2 Input data format 3.3 Input data merging 3.4 Availability of the input data Description of the type of the source data used for the quantitative analysis: Zoom scan, full MS scan, tandem MS, SRM chromatogram, etc Specify the input data format for the quantitation analysis, either post-processing formats such as mzidentml, protxml, pepxml, dat, or if needed provide the original format such as Thermo raw, AB Sciex wiff, mzdata, mzml, mzxml, mgf. For XML format data, provide the schema version number. In case of fractionation has been applied to the samples prior to the acquisition of MS data, specify which type of fractionation has been performed (e.g. chromatography-based, gel-based, etc.) and how many fractions/bands have been generated for each sample. State whether input data coming from each fractionation unit is merged in a single dataset prior to quantification analysis or not. In that case, describe the software or algorithm used for this purpose (name, manufacturer and version) or refer to the one described below in section 4.1. Specify the location of source data. Provide either a URI or the location of the files, or their availability.
7 4. Protocol Description of the software and methods applied in the quantitative analysis (including transformation functions, aggregation functions and statistical calculations). 4.1 Quantification software name, version and manufacturer 4.2 Description of the selection and/or matching method of features, together with the description of the method of the primary extracted quantification values determination for each feature and/or peptide 4.3 Confidence filter of features or peptides prior to quantification 4.4 Description of data calculation and transformation methods Missing values imputation and outliers removal Quantification values calculation and / or ratio determination from the primary extracted quantification values Replicate aggregation For each software (or library) used in the quantitative analysis, provide the trade name together with the version name or number according to the original code and functionality of the software. In case of in-house developed tools provide a brief description of it together with a reference if available. Brief description of the selected analysis pipeline if it is customizable from the software. Description of the methods together with its relevant parameters used in the selection and/or matching of features: e.g., feature detection (m/z and retention time windows, applied filters by charge state or by signal to noise, etc ), pairs finding, chromatogram alignment, the itraq reporter integration method (most confident centroid, most intense centroid, centroid sum over 20ppm window, etc ), or any other method performed to select and/or match features prior to their quantification. Also describe how the primary extracted quantification value for each feature and/or peptide is calculated (e.g., volume measurement, max peak intensity, etc ). Describe any filter threshold applied to the features (e.g. a threshold filter over the seed score in OpenMS software) or to the identification matches prior to quantification of features, such as FDR, FWER, score, probability thresholds, etc State if applicable in which level has been applied (PSM, peptide or protein level). This includes the description of how the threshold has been determined (e.g. arbitrary, decoy strategy, binomial distribution, etc ).Also state whether quantitation restricted to unique (i.e. non-shared) peptides or whether some features/peptides have been excluded from the quantification (e.g. containing a non-quantitative modification like oxidized methionine, etc ). If the later filter is described in a MIAPE Mass Spectrometry Informatics document, provide a reference to section 1.4 in which the reference is. Provide, if applicable, the information in to Also state at which level (feature, peptide and/or protein) the data calculation/transformation methods are performed and in which order (mathematical formulas are allowed). Describe the missing values imputation and outlier removal methods. Describe (if appropriate) what does a 0 value means, that is, whether it means absent or just below the level of detection, etc Describe how quantification values and / or ratios have been calculated from values described in section 4.2, e.g., aggregation of all features per peptide (average, geometric average, summing, ANOVA analysis), description of the enumerator and denominator of the ratio, etc Describe the calculation method aggregating / combining the values from peptide or experimental replicates and/or groups (e.g., average, geometric average, weighting, etc....), as well as any data transformation (e.g., logarithmization, multiplication, division, etc ).
8 4.4.4 Normalization Protein quantification values calculation and / or ratio determination from the peptide quantification values Description of any normalization procedure, e.g. 'median peptide ratio for all measurements forced to 1' or 'each sample spiked with equal amount of peptide X or protein Y, as per 2.2.4'. Describe how protein quantification values and / or ratios have been inferred from peptide quantification values (especially in case of shared peptides). Specify additional criteria like: take into account only proteins with at least two identified peptides used in order to filter PSMs before rolling up them into protein abundance Protocol specific corrections Describe any protocol specific corrections like: Arg-Pro conversion. 4.5 Description of methods for (statistical) estimation of correctness 4.6 Calibration curves of standards Describe how are calculated the values that describe the error potential of given / calculated quantification values (e.g., standard deviation, standard error, confidence interval, super-median of the experiment, standard error for the fit, standard error for the calculated ratio, coefficient of variation, p- value, FDR, FWER, etc ). Also describe any applied threshold or filter based in these statistical values (e.g., p-values <= 0.05). Also describe if any threshold value has been used to consider that a feature/peptide/protein is over-expressed, and why that value has been selected. If internal references are used (described in section 2.2.4), provide the resulting calibration curves. 5. Resulting data Provide the actual quantification values resulting from your quantification software together with their estimated confidence. Depending of the quantification technique or even of the quantification software, only some of the following items could be satisfied (e.g., for spectral counting, only quantification values at protein level can be provided) 5.1 Quantification values at peptide and/or feature level: Actual quantification values achieved for each peptide and/or, in case of feature-based quantification, for the corresponding features (mapped back from each peptide), together with their estimated confidence. Report each quantification value together with the appropriate information to identify the feature or peptide that is quantified (peptide sequence or peptide sequence plus the charge state, mass, retention time, etc ) Primary extracted quantification values for each feature (e.g. area, height, etc.), with their statistical estimation of correctness Quantification values for each peptide as a result of the aggregation of the values of the previous section (5.1.1), with their statistical estimation of correctness The calculated primary extracted quantification values for each feature and also values representing their confidence (see above 4.5). The values can be provided either by a URI or the location of the resulting data files. The transformed / aggregated / combined quantification values for each peptide, calculated from the quantification values from the previous section (5.1.1) (e.g. medians, averages, standard deviations, super-medians, fold changes, p-values etc ). Also provide the values representing their statistical estimation of confidence (see above 4.5). The values can be provided either by a URI or the location of the resulting data files, or their availability. 5.2 Quantification values at protein level: Actual quantification values achieved for each protein and for each protein ambiguity group, together with the confidence in the quantification value. Report each quantification value together with the appropriate information to identify the protein, such as the protein accessions.
9 5.2.1 Basic / raw quantification values with statistical estimation of correctness Transformed / aggregated / combined quantification values of the proteins at group level, with their statistical estimation of correctness The calculated quantification value for each protein and for each protein ambiguity group and also values representing their confidence (see above 4.5). The values can be provided either by a URI or the location of the resulting data files. The transformed / aggregated / combined quantification values for each protein, calculated from the quantification values above (e.g. medians, averages, standard deviations, super-medians, fold changes, p-values etc ), at group level. Also provide the values representing their statistical estimation of confidence (see above 4.5). The values can be provided either by a URI or the location of the resulting data files, or their availability. Term glossary Feature: Any primary extracted quantification measurement. SRM: Selected Reaction Monitoring. Replicates: experiment to be reproduced or repeated in order to test the variability of observed values. Technical replicates: Replicates that share the same sample; i.e. the measurements are repeated. The technical variability is tested. Biological replicates: Replicate where different samples are used for testing the biological variability between the selected samples. Transformation functions: Any mathematical transformation of the data, such as logarithmizations, multiplications, divisions, etc Aggregation functions: Any mathematical operation applied to values from different replicates in order to obtain a single representative value. They can be averages, geometric averages, weighting, etc FDR: False Discovery Rate: the expected proportion of incorrect assignments among the accepted assignments. FWER: Family-wise Error Rate: probability of making one or more false discoveries, or type I errors among all the hypotheses when performing multiple pairwise tests. MIAPE Quant examples MIAPE Quant examples files are available in the HUPO-psi web page at: The following table shows which quantification technique is represented by each example: File name Quantification technique Institution where the example comes from MIAPE_Quant_v1.0_ICPL_CNB.docx ICPL CNB MIAPE_Quant_v1.0_ICPL_VH.doc ICPL HUVH MIAPE_Quant_v1.0_iTRAQ UCM-PCM.doc itraq UCM-PCM MIAPE_Quant_v1.0_iTRAQ_LPCSICUAB.doc itraq LP-CSIC/UAB
10 MIAPE_Quant_v1.0_LabelFree_PCB.doc Accurate Mass and Time Label-free PCB MIAPE_Quant_v1.0_SILAC_CNB.doc SILAC CNB MIAPE_Quant_v1.0_SILAC_MLHS.doc SILAC UCM-PCM MIAPE_Quant_v1.0_SILAC_VH.doc SILAC HUVH MIAPE_Quant_v1.0_SRM_LPCSICUAB.doc SRM LP-CSIC/UAB MIAPE_Quant_v1.0_spectralCount_MPC.xls Label-free spectral counting MPC Institutions CNB: National Center for Biotechnology, ProteoRed, Madrid, Spain HUVH: Vall d Hebron University Hospital, Barcelona, ProteoRed, Spain UCM-PCM: Universidad Complutense de Madrid- Parque Científico de Madrid, Madrid, ProteoRed, Spain LP-CSIC/UAB: Proteomics Laboratory, Instituto de Investigaciones Biomédicas de Barcelona - Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Barcelona, ProteoRed, Spain PCB: Proteomics Platform, Barcelona Science Park, Barcelona, ProteoRed, Spain MPC: Medizinisches Proteom-Center, Ruhr-Universitaet Bochum, Bochum, Germany
MIAPE: Mass Spectrometry Informatics
 MIAPE: Mass Spectrometry Informatics Pierre-Alain Binz[1,2]*, Robert Barkovich[3], Ronald C. Beavis[4], David Creasy[5], David M. Horn[6], Randall K. Julian Jr.[7], Sean L. Seymour[8], Chris F. Taylor[9],
MIAPE: Mass Spectrometry Informatics Pierre-Alain Binz[1,2]*, Robert Barkovich[3], Ronald C. Beavis[4], David Creasy[5], David M. Horn[6], Randall K. Julian Jr.[7], Sean L. Seymour[8], Chris F. Taylor[9],
Quantitative mass spec based proteomics
 Quantitative mass spec based proteomics Tuula Nyman Institute of Biotechnology tuula.nyman@helsinki.fi THE PROTEOME The complete protein complement expressed by a genome or by a cell or a tissue type (M.
Quantitative mass spec based proteomics Tuula Nyman Institute of Biotechnology tuula.nyman@helsinki.fi THE PROTEOME The complete protein complement expressed by a genome or by a cell or a tissue type (M.
Mass spectrometry Proteomics and MIAPE
 Mass spectrometry Proteomics and MIAPE Florian Breitwieser - Research Center of Molecular Medicine, Vienna, Austria Nov 18, 2010 Outline BioC-devel meeting Europe 17.-18. 11. 2010 MS-MS Proteomics Standard
Mass spectrometry Proteomics and MIAPE Florian Breitwieser - Research Center of Molecular Medicine, Vienna, Austria Nov 18, 2010 Outline BioC-devel meeting Europe 17.-18. 11. 2010 MS-MS Proteomics Standard
Current state of proteomics standardization and (C-)HPP data quality guidelines
 9/6/2016 3 Department of Pharmacy Analytical Biochemistry Current state of proteomics standardization and (C-)HPP data quality guidelines DTL focus meeting on data integration, standards and fair principles
9/6/2016 3 Department of Pharmacy Analytical Biochemistry Current state of proteomics standardization and (C-)HPP data quality guidelines DTL focus meeting on data integration, standards and fair principles
Quantitative Analysis on the Public Protein Prospector Web Site. Introduction
 Quantitative Analysis on the Public Protein Prospector Web Site Peter R. Baker 1, Nicholas J. Agard 2, Alma L. Burlingame 1 and Robert J. Chalkley 1 1 Mass Spectrometry Facility, Dept. of Pharmaceutical
Quantitative Analysis on the Public Protein Prospector Web Site Peter R. Baker 1, Nicholas J. Agard 2, Alma L. Burlingame 1 and Robert J. Chalkley 1 1 Mass Spectrometry Facility, Dept. of Pharmaceutical
New Approaches to Quantitative Proteomics Analysis
 New Approaches to Quantitative Proteomics Analysis Chris Hodgkins, Market Development Manager, SCIEX ANZ 2 nd November, 2017 Who is SCIEX? Founded by Dr. Barry French & others: University of Toronto Introduced
New Approaches to Quantitative Proteomics Analysis Chris Hodgkins, Market Development Manager, SCIEX ANZ 2 nd November, 2017 Who is SCIEX? Founded by Dr. Barry French & others: University of Toronto Introduced
MIAPE: Column Chromatography
 MIAPE: Column Chromatography Andrew R Jones 1,, Kathleen Carroll 2, David Knight 3, Kirsty MacLellan 4, Paula J Domann 5, Cristina Legido-Quigley 6, Lihua Huang 7, Lance Smallshaw 8 and Norman W Paton
MIAPE: Column Chromatography Andrew R Jones 1,, Kathleen Carroll 2, David Knight 3, Kirsty MacLellan 4, Paula J Domann 5, Cristina Legido-Quigley 6, Lihua Huang 7, Lance Smallshaw 8 and Norman W Paton
Estoril Education Day
 Estoril Education Day -Experimental design in Proteomics October 23rd, 2010 Peter James Note Taking All the Powerpoint slides from the Talks are available for download from: http://www.immun.lth.se/education/
Estoril Education Day -Experimental design in Proteomics October 23rd, 2010 Peter James Note Taking All the Powerpoint slides from the Talks are available for download from: http://www.immun.lth.se/education/
Enabling Systems Biology Driven Proteome Wide Quantitation of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
 Enabling Systems Biology Driven Proteome Wide Quantitation of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis SWATH Acquisition on the TripleTOF 5600+ System Samuel L. Bader, Robert L. Moritz Institute of Systems Biology,
Enabling Systems Biology Driven Proteome Wide Quantitation of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis SWATH Acquisition on the TripleTOF 5600+ System Samuel L. Bader, Robert L. Moritz Institute of Systems Biology,
Proteomics: A Challenge for Technology and Information Science. What is proteomics?
 Proteomics: A Challenge for Technology and Information Science CBCB Seminar, November 21, 2005 Tim Griffin Dept. Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Biophysics tgriffin@umn.edu What is proteomics? Proteomics
Proteomics: A Challenge for Technology and Information Science CBCB Seminar, November 21, 2005 Tim Griffin Dept. Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Biophysics tgriffin@umn.edu What is proteomics? Proteomics
Spectrum Mill MS Proteomics Workbench. Comprehensive tools for MS proteomics
 Spectrum Mill MS Proteomics Workbench Comprehensive tools for MS proteomics Meeting the challenge of proteomics data analysis Mass spectrometry is a core technology for proteomics research, but large-scale
Spectrum Mill MS Proteomics Workbench Comprehensive tools for MS proteomics Meeting the challenge of proteomics data analysis Mass spectrometry is a core technology for proteomics research, but large-scale
Proteomics software at MSI. Pratik Jagtap Minnesota Supercomputing institute
 Proteomics software at MSI. Pratik Jagtap Minnesota Supercomputing institute http://www.mass.msi.umn.edu/ Proteomics software at MSI. proteomics : emerging technology proteomics workflow search algorithms
Proteomics software at MSI. Pratik Jagtap Minnesota Supercomputing institute http://www.mass.msi.umn.edu/ Proteomics software at MSI. proteomics : emerging technology proteomics workflow search algorithms
Highly Confident Peptide Mapping of Protein Digests Using Agilent LC/Q TOFs
 Technical Overview Highly Confident Peptide Mapping of Protein Digests Using Agilent LC/Q TOFs Authors Stephen Madden, Crystal Cody, and Jungkap Park Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara, California,
Technical Overview Highly Confident Peptide Mapping of Protein Digests Using Agilent LC/Q TOFs Authors Stephen Madden, Crystal Cody, and Jungkap Park Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara, California,
Využití cílené proteomiky pro kontrolu falšování potravin: identifikace peptidových markerů v mase pomocí LC- Q Exactive MS/MS
 Využití cílené proteomiky pro kontrolu falšování potravin: identifikace peptidových markerů v mase pomocí LC- Q Exactive MS/MS Michal Godula Ph.D. Thermo Fisher Scientific The world leader in serving science
Využití cílené proteomiky pro kontrolu falšování potravin: identifikace peptidových markerů v mase pomocí LC- Q Exactive MS/MS Michal Godula Ph.D. Thermo Fisher Scientific The world leader in serving science
N- The rank of the specified protein relative to all other proteins in the list of detected proteins.
 PROTEIN SUMMARY file N- The rank of the specified protein relative to all other proteins in the list of detected proteins. Unused (ProtScore) - A measure of the protein confidence for a detected protein,
PROTEIN SUMMARY file N- The rank of the specified protein relative to all other proteins in the list of detected proteins. Unused (ProtScore) - A measure of the protein confidence for a detected protein,
How to view Results with. Proteomics Shared Resource
 How to view Results with Scaffold 3.0 Proteomics Shared Resource An overview This document is intended to walk you through Scaffold version 3.0. This is an introductory guide that goes over the basics
How to view Results with Scaffold 3.0 Proteomics Shared Resource An overview This document is intended to walk you through Scaffold version 3.0. This is an introductory guide that goes over the basics
PEAKS 8 User Manual. PEAKS Team
 PEAKS 8 User Manual PEAKS Team PEAKS 8 User Manual PEAKS Team Publication date 2016 Table of Contents 1. Overview... 1 1. How to Use This Manual... 1 2. What Is PEAKS?... 1 3. What Is New in PEAKS 8?...
PEAKS 8 User Manual PEAKS Team PEAKS 8 User Manual PEAKS Team Publication date 2016 Table of Contents 1. Overview... 1 1. How to Use This Manual... 1 2. What Is PEAKS?... 1 3. What Is New in PEAKS 8?...
A highly sensitive and robust 150 µm column to enable high-throughput proteomics
 APPLICATION NOTE 21744 Robust LC Separation Optimized MS Acquisition Comprehensive Data Informatics A highly sensitive and robust 15 µm column to enable high-throughput proteomics Authors Xin Zhang, 1
APPLICATION NOTE 21744 Robust LC Separation Optimized MS Acquisition Comprehensive Data Informatics A highly sensitive and robust 15 µm column to enable high-throughput proteomics Authors Xin Zhang, 1
MetaboScape 2.0. Innovation with Integrity. Quickly Discover Metabolite Biomarkers and Use Pathway Mapping to Set them in a Biological Context
 M MetaboScape 2.0 Quickly Discover Metabolite Biomarkers and Use Pathway Mapping to Set them in a Biological Context Innovation with Integrity Metabolomics Providing a New Layer of Insight to Metabolomics
M MetaboScape 2.0 Quickly Discover Metabolite Biomarkers and Use Pathway Mapping to Set them in a Biological Context Innovation with Integrity Metabolomics Providing a New Layer of Insight to Metabolomics
LC/MS/MS Solutions for Biomarker Discovery QSTAR. Elite Hybrid LC/MS/MS System. More performance, more reliability, more answers
 LC/MS/MS Solutions for Biomarker Discovery QSTAR Elite Hybrid LC/MS/MS System More performance, more reliability, more answers More is better and the QSTAR Elite LC/MS/MS system has more to offer. More
LC/MS/MS Solutions for Biomarker Discovery QSTAR Elite Hybrid LC/MS/MS System More performance, more reliability, more answers More is better and the QSTAR Elite LC/MS/MS system has more to offer. More
PTM Identification and Localization from MS Proteomics Data
 05.10.17 PTM Identification and Localization from MS Proteomics Data Marc Vaudel Center for Medical Genetics and Molecular Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital, Bergen, Norway KG Jebsen Center for Diabetes
05.10.17 PTM Identification and Localization from MS Proteomics Data Marc Vaudel Center for Medical Genetics and Molecular Medicine, Haukeland University Hospital, Bergen, Norway KG Jebsen Center for Diabetes
A comprehensive evaluation of popular proteomics software workflows for label-free proteome quantification and imputation
 Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2017, 1 12 doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx054 Paper A comprehensive evaluation of popular proteomics software workflows for label-free proteome quantification and imputation Tommi V alikangas,
Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2017, 1 12 doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx054 Paper A comprehensive evaluation of popular proteomics software workflows for label-free proteome quantification and imputation Tommi V alikangas,
RockerBox. Filtering massive Mascot search results at the.dat level
 RockerBox Filtering massive Mascot search results at the.dat level Challenges Big experiments High amount of data Large raw and.dat files (> 2GB) How to handle our results?? The 2.2 peptide summary could
RockerBox Filtering massive Mascot search results at the.dat level Challenges Big experiments High amount of data Large raw and.dat files (> 2GB) How to handle our results?? The 2.2 peptide summary could
QUANLYNX APPLICATION MANAGER
 QUANLYNX APPLICATION MANAGER OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION QuanLynx, an Application Manager included with Waters MassLynx Software, is designed for quantitative analysis. Simply acquiring mass spectrometry data
QUANLYNX APPLICATION MANAGER OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION QuanLynx, an Application Manager included with Waters MassLynx Software, is designed for quantitative analysis. Simply acquiring mass spectrometry data
Advanced QA/QC characterization MS in QC : Multi Attribute Method
 Advanced QA/QC characterization MS in QC : Multi Attribute Method Global BioPharma Summit The world leader in serving science A Complex Problem: Drug Safety and Quality Safety Is the product safe to use?
Advanced QA/QC characterization MS in QC : Multi Attribute Method Global BioPharma Summit The world leader in serving science A Complex Problem: Drug Safety and Quality Safety Is the product safe to use?
The Waters strategy for the quantification of proteins
 Protein quantification workshop Barcelona, 13 th November 2012 The Waters strategy for the quantification of proteins Robert Tonge Ph.D. Principal Scientist, European Omics Waters Corporation MS Technology
Protein quantification workshop Barcelona, 13 th November 2012 The Waters strategy for the quantification of proteins Robert Tonge Ph.D. Principal Scientist, European Omics Waters Corporation MS Technology
Liver Mitochondria Proteomics Employing High-Resolution MS Technology
 Liver Mitochondria Proteomics Employing High-Resolution MS Technology Jenny Ho, 1 Loïc Dayon, 2 John Corthésy, 2 Umberto De Marchi, 2 Antonio Núñez, 2 Andreas Wiederkehr, 2 Rosa Viner, 3 Michael Blank,
Liver Mitochondria Proteomics Employing High-Resolution MS Technology Jenny Ho, 1 Loïc Dayon, 2 John Corthésy, 2 Umberto De Marchi, 2 Antonio Núñez, 2 Andreas Wiederkehr, 2 Rosa Viner, 3 Michael Blank,
Skyline & Panorama: Key Tools for Establishing a Targeted LC/MS Workflow
 Skyline & Panorama: Key Tools for Establishing a Targeted LC/MS Workflow Kristin Wildsmith Scientist, Biomarker Development LabKey User Conference October 6, 2016 Biomarkers enable drug development Drug
Skyline & Panorama: Key Tools for Establishing a Targeted LC/MS Workflow Kristin Wildsmith Scientist, Biomarker Development LabKey User Conference October 6, 2016 Biomarkers enable drug development Drug
How to view Results with Scaffold. Proteomics Shared Resource
 How to view Results with Scaffold Proteomics Shared Resource Starting out Download Scaffold from http://www.proteomes oftware.com/proteom e_software_prod_sca ffold_download.html Follow installation instructions
How to view Results with Scaffold Proteomics Shared Resource Starting out Download Scaffold from http://www.proteomes oftware.com/proteom e_software_prod_sca ffold_download.html Follow installation instructions
LTQ Orbitrap XL Hybrid FT Mass Spectrometer Unrivaled Performance and Flexibility
 m a s s s p e c t r o m e t r y LTQ Orbitrap XL Hybrid FT Mass Spectrometer Unrivaled Performance and Flexibility Part of Thermo Fisher Scientific LTQ Orbitrap XL OFFERING OUTSTANDING MASS ACCURACY, RESOLVING
m a s s s p e c t r o m e t r y LTQ Orbitrap XL Hybrid FT Mass Spectrometer Unrivaled Performance and Flexibility Part of Thermo Fisher Scientific LTQ Orbitrap XL OFFERING OUTSTANDING MASS ACCURACY, RESOLVING
Application Note. Authors. Abstract
 Automated, High Precision Tryptic Digestion and SISCAPA-MS Quantification of Human Plasma Proteins Using the Agilent Bravo Automated Liquid Handling Platform Application Note Authors Morteza Razavi, N.
Automated, High Precision Tryptic Digestion and SISCAPA-MS Quantification of Human Plasma Proteins Using the Agilent Bravo Automated Liquid Handling Platform Application Note Authors Morteza Razavi, N.
Expand Your Research with Metabolomics and Proteomics. Christine Miller Omics Market Manager ASMS 2017
 Expand Your Research with Metabolomics and Proteomics Christine Miller Omics Market Manager ASMS 2017 New Additions to Agilent Omics Workflows Acquisition Ion Mobility Q-TOF IM All Ions MS/MS Find Features
Expand Your Research with Metabolomics and Proteomics Christine Miller Omics Market Manager ASMS 2017 New Additions to Agilent Omics Workflows Acquisition Ion Mobility Q-TOF IM All Ions MS/MS Find Features
Xevo G2-S QTof and TransOmics: A Multi-Omics System for the Differential LC/MS Analysis of Proteins, Metabolites, and Lipids
 Xevo G2-S QTof and TransOmics: A Multi-Omics System for the Differential LC/MS Analysis of Proteins, Metabolites, and Lipids Ian Edwards, Jayne Kirk, and Joanne Williams Waters Corporation, Manchester,
Xevo G2-S QTof and TransOmics: A Multi-Omics System for the Differential LC/MS Analysis of Proteins, Metabolites, and Lipids Ian Edwards, Jayne Kirk, and Joanne Williams Waters Corporation, Manchester,
Tony Mire-Sluis Vice President, Corporate, Product and Device Quality Amgen Inc
 The Regulatory Implications of the ever increasing power of Mass Spectrometry and its role in the Analysis of Biotechnology Products Where do we draw the line? Tony Mire-Sluis Vice President, Corporate,
The Regulatory Implications of the ever increasing power of Mass Spectrometry and its role in the Analysis of Biotechnology Products Where do we draw the line? Tony Mire-Sluis Vice President, Corporate,
Understanding life WITH NEXT GENERATION PROTEOMICS SOLUTIONS
 Innovative services and products for highly multiplexed protein discovery and quantification to help you understand the biological processes that shape life. Understanding life WITH NEXT GENERATION PROTEOMICS
Innovative services and products for highly multiplexed protein discovery and quantification to help you understand the biological processes that shape life. Understanding life WITH NEXT GENERATION PROTEOMICS
DISCOVERY AND VALIDATION OF TARGETS AND BIOMARKERS BY MASS SPECTROMETRY-BASED PROTEOMICS. September, 2011
 DISCOVERY AND VALIDATION OF TARGETS AND BIOMARKERS BY MASS SPECTROMETRY-BASED PROTEOMICS September, 2011 1 CAPRION PROTEOMICS Leading proteomics-based service provider - Biomarker and target discovery
DISCOVERY AND VALIDATION OF TARGETS AND BIOMARKERS BY MASS SPECTROMETRY-BASED PROTEOMICS September, 2011 1 CAPRION PROTEOMICS Leading proteomics-based service provider - Biomarker and target discovery
Faster, easier, flexible proteomics solutions
 Agilent HPLC-Chip LC/MS Faster, easier, flexible proteomics solutions Our measure is your success. products applications soft ware services Phospho- Anaysis Intact Glycan & Glycoprotein Agilent s HPLC-Chip
Agilent HPLC-Chip LC/MS Faster, easier, flexible proteomics solutions Our measure is your success. products applications soft ware services Phospho- Anaysis Intact Glycan & Glycoprotein Agilent s HPLC-Chip
Analysis of Large Scale MRM Studies Using Skyline
 Analysis of Large Scale MRM Studies Using Skyline Michael Schirm, PhD Associate Director, R&D Proteomics Skyline User Meeting June 04, 2017 Overview CRO providing mass spec based proteomics services since
Analysis of Large Scale MRM Studies Using Skyline Michael Schirm, PhD Associate Director, R&D Proteomics Skyline User Meeting June 04, 2017 Overview CRO providing mass spec based proteomics services since
Detecting Challenging Post Translational Modifications (PTMs) using CESI-MS
 Detecting Challenging Post Translational Modifications (PTMs) using CESI-MS Sensitive workflow for the detection of PTMs in biological samples from small sample volumes Klaus Faserl, 1 Bettina Sarg, 1
Detecting Challenging Post Translational Modifications (PTMs) using CESI-MS Sensitive workflow for the detection of PTMs in biological samples from small sample volumes Klaus Faserl, 1 Bettina Sarg, 1
Center for Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics Phone (612) (612)
 Outline Database search types Peptide Mass Fingerprint (PMF) Precursor mass-based Sequence tag Results comparison across programs Manual inspection of results Terminology Mass tolerance MS/MS search FASTA
Outline Database search types Peptide Mass Fingerprint (PMF) Precursor mass-based Sequence tag Results comparison across programs Manual inspection of results Terminology Mass tolerance MS/MS search FASTA
faster, confident more path to all the information in your samples. Agilent MassHunter Workstation Software Our measure is your success.
 Agilent MassHunter Workstation Software faster, A confident more path to all the information in your samples. Our measure is your success. products applications soft ware services MassHunter Workstation
Agilent MassHunter Workstation Software faster, A confident more path to all the information in your samples. Our measure is your success. products applications soft ware services MassHunter Workstation
Supplementary Figure 1. Utilization of publicly available antibodies in different applications.
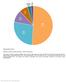 Supplementary Figure 1 Utilization of publicly available antibodies in different applications. The fraction of publicly available antibodies toward human protein targets is shown with data for the following
Supplementary Figure 1 Utilization of publicly available antibodies in different applications. The fraction of publicly available antibodies toward human protein targets is shown with data for the following
Improving coverage and consistency of MS-based proteomics. Limsoon Wong (Joint work with Wilson Wen Bin Goh)
 Improving coverage and consistency of MS-based proteomics Limsoon Wong (Joint work with Wilson Wen Bin Goh) 2 Proteomics vs transcriptomics Proteomic profile Which protein is found in the sample How abundant
Improving coverage and consistency of MS-based proteomics Limsoon Wong (Joint work with Wilson Wen Bin Goh) 2 Proteomics vs transcriptomics Proteomic profile Which protein is found in the sample How abundant
Informatics on MS-Based Proteomics
 Informatics on MS-Based Proteomics Yet-Ran Chen 陳逸然 Associate Research Fellow / Associate Professor Agricultural Biotech. Research Center / Institute of Biotechnology & Genomics and Systems Biology Academia
Informatics on MS-Based Proteomics Yet-Ran Chen 陳逸然 Associate Research Fellow / Associate Professor Agricultural Biotech. Research Center / Institute of Biotechnology & Genomics and Systems Biology Academia
PESTICIDE SCREENING APPLICATION SOLUTION
 PESTICIDE SCREENING APPLICATION SOLUTION The most innovative pesticide screening solution ever built for food, beverage, and water testing. As the global food trade continues to expand, so does the challenge
PESTICIDE SCREENING APPLICATION SOLUTION The most innovative pesticide screening solution ever built for food, beverage, and water testing. As the global food trade continues to expand, so does the challenge
MBios 478: Mass Spectrometry Applications [Dr. Wyrick] Slide #1. Lecture 25: Mass Spectrometry Applications
![MBios 478: Mass Spectrometry Applications [Dr. Wyrick] Slide #1. Lecture 25: Mass Spectrometry Applications MBios 478: Mass Spectrometry Applications [Dr. Wyrick] Slide #1. Lecture 25: Mass Spectrometry Applications](/thumbs/74/71368870.jpg) MBios 478: Mass Spectrometry Applications [Dr. Wyrick] Slide #1 Lecture 25: Mass Spectrometry Applications Measuring Protein Abundance o ICAT o DIGE Identifying Post-Translational Modifications Protein-protein
MBios 478: Mass Spectrometry Applications [Dr. Wyrick] Slide #1 Lecture 25: Mass Spectrometry Applications Measuring Protein Abundance o ICAT o DIGE Identifying Post-Translational Modifications Protein-protein
AB SCIEX TripleTOF 5600 SYSTEM. High-resolution quant and qual
 AB SCIEX TripleTOF 5600 SYSTEM High-resolution quant and qual AB SCIEX TripleTOF 5600 SYSTEM AB SCIEX is a global leader in the development of life science analytical technologies that help answer complex
AB SCIEX TripleTOF 5600 SYSTEM High-resolution quant and qual AB SCIEX TripleTOF 5600 SYSTEM AB SCIEX is a global leader in the development of life science analytical technologies that help answer complex
MIqPCR: Minimum Information about a Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction experiment Version 1.0, 4th April, 2008.
 MIqPCR: Minimum Information about a Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction experiment Version 1.0, 4th April, 2008. RDML-Consortium This module identifies the minimum information required to report the
MIqPCR: Minimum Information about a Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction experiment Version 1.0, 4th April, 2008. RDML-Consortium This module identifies the minimum information required to report the
Data processing for LCMS-based metabolomics
 IDEOM Data processing for LCMS-based metabolomics Dr Darren Creek Darren.creek@glasgow.ac.uk Intensity Metabolomics Data Processing Aim: To get meaningful metabolic information from LCMS raw data Retention
IDEOM Data processing for LCMS-based metabolomics Dr Darren Creek Darren.creek@glasgow.ac.uk Intensity Metabolomics Data Processing Aim: To get meaningful metabolic information from LCMS raw data Retention
[ VION IMS QTOF ] BEYOND RESOLUTION
![[ VION IMS QTOF ] BEYOND RESOLUTION [ VION IMS QTOF ] BEYOND RESOLUTION](/thumbs/78/77357165.jpg) [ VION IMS QTOF ] BEYOND RESOLUTION THE BENEFITS ARE CLEAR and routinely available, Complex samples give complex data with overlapping spectra and background interferences, making compound identification
[ VION IMS QTOF ] BEYOND RESOLUTION THE BENEFITS ARE CLEAR and routinely available, Complex samples give complex data with overlapping spectra and background interferences, making compound identification
Thermo Scientific Peptide Mapping Workflows. Upgrade Your Maps. Fast, confident and more reliable peptide mapping.
 Thermo Scientific Peptide Mapping Workflows Upgrade Your Maps Fast, confident and more reliable peptide mapping. Smarter Navigation... Peptide mapping is a core analytic in biotherapeutic development.
Thermo Scientific Peptide Mapping Workflows Upgrade Your Maps Fast, confident and more reliable peptide mapping. Smarter Navigation... Peptide mapping is a core analytic in biotherapeutic development.
Bioinformatic Tools. So you acquired data.. But you wanted knowledge. So Now What?
 Bioinformatic Tools So you acquired data.. But you wanted knowledge So Now What? We have a series of questions What the Heck is That Ion? How come my MW does not match? How do I make a DB to search against?
Bioinformatic Tools So you acquired data.. But you wanted knowledge So Now What? We have a series of questions What the Heck is That Ion? How come my MW does not match? How do I make a DB to search against?
Investigating Biological Variation of Liver Enzymes in Human Hepatocytes
 Investigating Biological Variation of Liver Enzymes in Human Hepatocytes SWATH Acquisition on the TripleTOF Systems Xu Wang 1, Hui Zhang 2, Christie Hunter 1 1 SCIEX, USA, 2 Pfizer, USA MS/MS ALL with
Investigating Biological Variation of Liver Enzymes in Human Hepatocytes SWATH Acquisition on the TripleTOF Systems Xu Wang 1, Hui Zhang 2, Christie Hunter 1 1 SCIEX, USA, 2 Pfizer, USA MS/MS ALL with
VICH Topic GL2 (Validation: Methodology) GUIDELINE ON VALIDATION OF ANALYTICAL PROCEDURES: METHODOLOGY
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit CVMP/VICH/591/98-FINAL London, 10 December 1998 VICH Topic GL2 (Validation: Methodology) Step 7 Consensus
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit CVMP/VICH/591/98-FINAL London, 10 December 1998 VICH Topic GL2 (Validation: Methodology) Step 7 Consensus
Progenesis QI for proteomics: a first-rate solution for relative and absolute quantitative workflows Richard R. Sprenger, PhD
 Progenesis QI for proteomics: a first-rate solution for relative and absolute quantitative workflows Richard R. Sprenger, PhD Lipid Research Group Institute for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology University
Progenesis QI for proteomics: a first-rate solution for relative and absolute quantitative workflows Richard R. Sprenger, PhD Lipid Research Group Institute for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology University
High Resolution Accurate Mass Peptide Quantitation on Thermo Scientific Q Exactive Mass Spectrometers. The world leader in serving science
 High Resolution Accurate Mass Peptide Quantitation on Thermo Scientific Q Exactive Mass Spectrometers The world leader in serving science Goals Explore the capabilities of High Resolution Accurate Mass
High Resolution Accurate Mass Peptide Quantitation on Thermo Scientific Q Exactive Mass Spectrometers The world leader in serving science Goals Explore the capabilities of High Resolution Accurate Mass
A Unique LC-MS Assay for Host Cell Proteins(HCPs) ) in Biologics
 A Unique LC-MS Assay for Host Cell Proteins(HCPs) ) in Biologics Catalin Doneanu,, Ph.D. Biopharmaceutical Sciences, Waters September 16, 2009 Mass Spec 2009 2009 Waters Corporation Host Cell Proteins
A Unique LC-MS Assay for Host Cell Proteins(HCPs) ) in Biologics Catalin Doneanu,, Ph.D. Biopharmaceutical Sciences, Waters September 16, 2009 Mass Spec 2009 2009 Waters Corporation Host Cell Proteins
MassHunter Profinder: Batch Processing Software for High Quality Feature Extraction of Mass Spectrometry Data
 MassHunter Profinder: Batch Processing Software for High Quality Feature Extraction of Mass Spectrometry Data Technical Overview Introduction LC/MS metabolomics workflows typically involve the following
MassHunter Profinder: Batch Processing Software for High Quality Feature Extraction of Mass Spectrometry Data Technical Overview Introduction LC/MS metabolomics workflows typically involve the following
Thermo Scientific Mass Spectrometric Immunoassay (MSIA) Pipette Tips. Next generation immunoaffinity. Robust quantitative platform
 Thermo Scientific Mass Spectrometric Immunoassay (MSIA) Pipette Tips Next generation immunoaffinity Robust quantitative platform Immunoaffinity sample preparation Thermo Scientific Mass Spectrometric Immunoassay
Thermo Scientific Mass Spectrometric Immunoassay (MSIA) Pipette Tips Next generation immunoaffinity Robust quantitative platform Immunoaffinity sample preparation Thermo Scientific Mass Spectrometric Immunoassay
Rapid Peptide Catabolite ID using the SCIEX Routine Biotransform Solution
 Rapid Peptide Catabolite ID using the SCIEX Routine Biotransform Solution Rapidly Identify Major Catabolites with the SCIEX X500R QTOF System and MetabolitePilot TM 2.0 Software Ian Moore and Jinal Patel
Rapid Peptide Catabolite ID using the SCIEX Routine Biotransform Solution Rapidly Identify Major Catabolites with the SCIEX X500R QTOF System and MetabolitePilot TM 2.0 Software Ian Moore and Jinal Patel
Utilizing novel technology for the analysis of therapeutic antibodies and host cell protein contamination
 Utilizing novel technology for the analysis of therapeutic antibodies and host cell protein contamination Kelli Jonakin, Ph.D. Senior Field Application Scientist, Seattle, WA Eric Johansen, Ph.D. Senior
Utilizing novel technology for the analysis of therapeutic antibodies and host cell protein contamination Kelli Jonakin, Ph.D. Senior Field Application Scientist, Seattle, WA Eric Johansen, Ph.D. Senior
Integrated analysis of shotgun proteomic data with PatternLab for proteomics 4.0
 Integrated analysis of shotgun proteomic data with PatternLab for proteomics 4.0 Paulo C Carvalho 1,2,7, Diogo B Lima 1,7, Felipe V Leprevost 1,3, Marlon D M Santos 1, Juliana S G Fischer 1, Priscila F
Integrated analysis of shotgun proteomic data with PatternLab for proteomics 4.0 Paulo C Carvalho 1,2,7, Diogo B Lima 1,7, Felipe V Leprevost 1,3, Marlon D M Santos 1, Juliana S G Fischer 1, Priscila F
Improve the performance of your Proteomics LC-MS facility with Quic
 APPLICATION NOTE Improve the performance of your Proteomics LC-MS facility with Quic FEATURES An active queue of per-run QC analyses that checking supports real-time folder monitoring A multitude of readouts
APPLICATION NOTE Improve the performance of your Proteomics LC-MS facility with Quic FEATURES An active queue of per-run QC analyses that checking supports real-time folder monitoring A multitude of readouts
Monoclonal Antibody Characterization on Q Exactive and Oribtrap Elite. Yi Zhang, Ph.D Senior Proteomic Marketing Specialist Oct.
 Monoclonal Antibody Characterization on Q Exactive and Oribtrap Elite Yi Zhang, Ph.D Senior Proteomic Marketing Specialist Oct. 12, 211 Outline Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer in mab Characterization Intact
Monoclonal Antibody Characterization on Q Exactive and Oribtrap Elite Yi Zhang, Ph.D Senior Proteomic Marketing Specialist Oct. 12, 211 Outline Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer in mab Characterization Intact
ipep User s Guide Proteomics
 Proteomics ipep User s Guide ipep has been designed to aid in designing sample preparation techniques around the detection of specific sites or motifs in proteins and proteomes. The first application,
Proteomics ipep User s Guide ipep has been designed to aid in designing sample preparation techniques around the detection of specific sites or motifs in proteins and proteomes. The first application,
Optimization-Based Peptide Mass Fingerprinting for Protein Mixture Identification
 Optimization-Based Peptide Mass Fingerprinting for Protein Mixture Identification Weichuan Yu, Ph.D. Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
Optimization-Based Peptide Mass Fingerprinting for Protein Mixture Identification Weichuan Yu, Ph.D. Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
Key Words Q Exactive Focus, SIEVE Software, Biomarker, Discovery, Metabolomics
 Metabolomic Profiling in Drug Discovery: Understanding the Factors that Influence a Metabolomics Study and Strategies to Reduce Biochemical and Chemical Noise Mark Sanders 1, Serhiy Hnatyshyn 2, Don Robertson
Metabolomic Profiling in Drug Discovery: Understanding the Factors that Influence a Metabolomics Study and Strategies to Reduce Biochemical and Chemical Noise Mark Sanders 1, Serhiy Hnatyshyn 2, Don Robertson
INTEGRATED DATA MODELING IN HIGH-THROUGHPUT PROTEOMICES
 INTEGRATED DATA MODELING IN HIGH-THROUGHPUT PROTEOMICES By SHUANGSHUANG JIN A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of The requirements for the degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY IN COMPUTER SCIENCE
INTEGRATED DATA MODELING IN HIGH-THROUGHPUT PROTEOMICES By SHUANGSHUANG JIN A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of The requirements for the degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY IN COMPUTER SCIENCE
A High-Confidence Human Plasma Proteome Reference Set with Estimated Concentrations in PeptideAtlas
 MCP Papers in Press. Published on June 1, 2011 as Manuscript M110.006353 Plasma proteome reference set in PeptideAtlas A High-Confidence Human Plasma Proteome Reference Set with Estimated Concentrations
MCP Papers in Press. Published on June 1, 2011 as Manuscript M110.006353 Plasma proteome reference set in PeptideAtlas A High-Confidence Human Plasma Proteome Reference Set with Estimated Concentrations
Thermo Scientific TSQ Quantum Access MAX
 www.ietltd.com Proudly serving laboratories worldwide since 1979 CALL +847.913.0777 for Refurbished & Certified Lab Equipment Thermo Scientific TSQ Quantum Access MAX UNSURPASSED PRICE TO PERFORMANCE Superior
www.ietltd.com Proudly serving laboratories worldwide since 1979 CALL +847.913.0777 for Refurbished & Certified Lab Equipment Thermo Scientific TSQ Quantum Access MAX UNSURPASSED PRICE TO PERFORMANCE Superior
Thermo Scientific Proteomics & Metabolomics Seminar Tour
 Proteomics & Seminar Tour Ignite your workflows with our with Cutting Edge LC-MS Technology Stop by to learn the latest advances in mass spectrometry workflows, technologies launched at 2012 ASMS and talk
Proteomics & Seminar Tour Ignite your workflows with our with Cutting Edge LC-MS Technology Stop by to learn the latest advances in mass spectrometry workflows, technologies launched at 2012 ASMS and talk
Proteomics And Cancer Biomarker Discovery. Dr. Zahid Khan Institute of chemical Sciences (ICS) University of Peshawar. Overview. Cancer.
 Proteomics And Cancer Biomarker Discovery Dr. Zahid Khan Institute of chemical Sciences (ICS) University of Peshawar Overview Proteomics Cancer Aims Tools Data Base search Challenges Summary 1 Overview
Proteomics And Cancer Biomarker Discovery Dr. Zahid Khan Institute of chemical Sciences (ICS) University of Peshawar Overview Proteomics Cancer Aims Tools Data Base search Challenges Summary 1 Overview
rapiflex Innovation with Integrity Designed for Molecules that Matter. MALDI TOF/TOF
 rapiflex Designed for Molecules that Matter. Innovation with Integrity MALDI TOF/TOF rapiflex TM The first MALDI-TOF/TOF that adapts to your needs. The rapiflex is the most advanced MALDI TOF/TOF system
rapiflex Designed for Molecules that Matter. Innovation with Integrity MALDI TOF/TOF rapiflex TM The first MALDI-TOF/TOF that adapts to your needs. The rapiflex is the most advanced MALDI TOF/TOF system
MasterView Software. Turn data into answers reliable data processing made easy ONE TOUCH PRODUCTIVITY
 MasterView Software Turn data into answers reliable data processing made easy ONE TOUCH PRODUCTIVITY Mass spectrometers especially high-resolution, accurate mass instruments produce a significant amount
MasterView Software Turn data into answers reliable data processing made easy ONE TOUCH PRODUCTIVITY Mass spectrometers especially high-resolution, accurate mass instruments produce a significant amount
TurboMass GC/MS Software
 TurboMass GC/MS Software GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY / MASS SPECTROMETRY P R O D U C T N O T E Today s demanding laboratory requires software that is easy to learn yet offers sophisticated instrument control, robust
TurboMass GC/MS Software GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY / MASS SPECTROMETRY P R O D U C T N O T E Today s demanding laboratory requires software that is easy to learn yet offers sophisticated instrument control, robust
Revision of 30 April 2013 draft, 4 November 2013
 GUIDANCE DOCUMENT FOR SINGLE LABORATORY VALIDATION OF QUANTITATIVE ANALYTICAL METHODS USED IN SUPPORT OF PRE- AND POST-REGISTRATION DATA REQUIREMENTS FOR PLANT PROTECTION AND BIOCIDAL PRODUCTS INTRODUCTION
GUIDANCE DOCUMENT FOR SINGLE LABORATORY VALIDATION OF QUANTITATIVE ANALYTICAL METHODS USED IN SUPPORT OF PRE- AND POST-REGISTRATION DATA REQUIREMENTS FOR PLANT PROTECTION AND BIOCIDAL PRODUCTS INTRODUCTION
The clearly better choice
 Agilent Accurate-Mass 6500 Series Q-TOF and 600 Series TOF LC/MS Systems The clearly better choice in TOF and Q-TOF LC/MS Our measure is your success. products applications soft ware services The unmatched
Agilent Accurate-Mass 6500 Series Q-TOF and 600 Series TOF LC/MS Systems The clearly better choice in TOF and Q-TOF LC/MS Our measure is your success. products applications soft ware services The unmatched
SoftMax Pro 5 Software
 SoftMax Pro 5 Software THE INDUSTRy STANDARD IN MICROPLATE DATA ANALySIS > SIMPLE AND CUSTOMIZABLE ASSAy SETUP > flexible AND POWERfUL DATA ANALySIS > COMPLETE fda 21 CfR PART 11 COMPLIANCE TOOLS > INTEGRATION
SoftMax Pro 5 Software THE INDUSTRy STANDARD IN MICROPLATE DATA ANALySIS > SIMPLE AND CUSTOMIZABLE ASSAy SETUP > flexible AND POWERfUL DATA ANALySIS > COMPLETE fda 21 CfR PART 11 COMPLIANCE TOOLS > INTEGRATION
Modification Site Localization Scoring Integrated into a Search Engine
 Modification Site Localization Scoring Integrated into a Search Engine Peter R. Baker 1, Jonathan C. Trinidad 1, Katalin F. Medzihradszky 1, Alma L. Burlingame 1 and Robert J. Chalkley 1 1 Mass Spectrometry
Modification Site Localization Scoring Integrated into a Search Engine Peter R. Baker 1, Jonathan C. Trinidad 1, Katalin F. Medzihradszky 1, Alma L. Burlingame 1 and Robert J. Chalkley 1 1 Mass Spectrometry
Analysis of Illegal Dyes in Food Matrices Using Automated Online Sample Preparation with Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
 Analysis of Illegal Dyes in Food Matrices Using Automated Online Sample Preparation with Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Yang Shi, Catherine Lafontaine, and François A. Espourteille Thermo Fisher
Analysis of Illegal Dyes in Food Matrices Using Automated Online Sample Preparation with Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Yang Shi, Catherine Lafontaine, and François A. Espourteille Thermo Fisher
An Unbiased Approach to Increasing Proteome Coverage Using Ion Mobility with MS E
 An Unbiased Approach to Increasing Proteome Coverage Using Ion Mobility with MS E John Rontree 2011 Waters Corporation 1 Current Issues with Protein Identification in Complex Mixtures Poor reproducibility
An Unbiased Approach to Increasing Proteome Coverage Using Ion Mobility with MS E John Rontree 2011 Waters Corporation 1 Current Issues with Protein Identification in Complex Mixtures Poor reproducibility
Breakthrough ifunnel Technology
 Agilent 6550 ifunnel Q-TOF LC/MS System Breakthrough ifunnel Technology for CLEARLY BETTER sensitivity Agilent 6550 ifunnel Q-TOF LC/MS System Unmatched speed and analytical sensitivity for your most challenging
Agilent 6550 ifunnel Q-TOF LC/MS System Breakthrough ifunnel Technology for CLEARLY BETTER sensitivity Agilent 6550 ifunnel Q-TOF LC/MS System Unmatched speed and analytical sensitivity for your most challenging
ENCODE RBP Antibody Characterization Guidelines
 ENCODE RBP Antibody Characterization Guidelines Approved on November 18, 2016 Background An integral part of the ENCODE Project is to characterize the antibodies used in the experiments. This document
ENCODE RBP Antibody Characterization Guidelines Approved on November 18, 2016 Background An integral part of the ENCODE Project is to characterize the antibodies used in the experiments. This document
Version of This Document The current version of this document is: version 1.0, release candidate 5, 20 June 2014.
 PSI Recommendation PSI Proteomics Informatics Workgroup Version 1.0, release candidate 5 Johannes Griss, European Bioinformatics Institute Timo Sachsenberg, University of Tübingen Mathias Walzer, University
PSI Recommendation PSI Proteomics Informatics Workgroup Version 1.0, release candidate 5 Johannes Griss, European Bioinformatics Institute Timo Sachsenberg, University of Tübingen Mathias Walzer, University
Proudly serving laboratories worldwide since 1979 CALL for Refurbished & Certified Lab Equipment QTRAP 5500
 www.ietltd.com Proudly serving laboratories worldwide since 1979 CALL +847.913.0777 for Refurbished & Certified Lab Equipment QTRAP 5500 Powerful synergy results when the world s most sensitive triple
www.ietltd.com Proudly serving laboratories worldwide since 1979 CALL +847.913.0777 for Refurbished & Certified Lab Equipment QTRAP 5500 Powerful synergy results when the world s most sensitive triple
Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Soybean CV127 Using Real-time PCR. Validation Report
 Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Soybean CV127 Using Real-time PCR Validation Report 20 September 2011 Joint Research Centre Institute for Health and Consumer Protection Molecular Biology
Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Soybean CV127 Using Real-time PCR Validation Report 20 September 2011 Joint Research Centre Institute for Health and Consumer Protection Molecular Biology
A Complete Workflow Solution for Intact Monoclonal Antibody Characterization Using a New High-Performance Benchtop Quadrupole- Orbitrap LC-MS/MS
 A Complete Workflow Solution for Intact Monoclonal Antibody Characterization Using a New High-Performance Benchtop Quadrupole- Orbitrap LC-MS/MS Zhiqi Hao, 1 Yi Zhang, 1 David Horn, 1 Seema Sharma, 1 Shiaw-Lin
A Complete Workflow Solution for Intact Monoclonal Antibody Characterization Using a New High-Performance Benchtop Quadrupole- Orbitrap LC-MS/MS Zhiqi Hao, 1 Yi Zhang, 1 David Horn, 1 Seema Sharma, 1 Shiaw-Lin
Protein preparation and digestion. P. aeruginosa strains were grown in in AB minimal medium
 Supplementary data itraq-based Proteomics Analyses Protein preparation and digestion. P. aeruginosa strains were grown in in AB minimal medium supplemented with 5g L -1 glucose for 48 hours at 37 C with
Supplementary data itraq-based Proteomics Analyses Protein preparation and digestion. P. aeruginosa strains were grown in in AB minimal medium supplemented with 5g L -1 glucose for 48 hours at 37 C with
Maximizing Chromatographic Resolution of Peptide Maps using UPLC with Tandem Columns
 Maximizing Chromatographic Resolution of Peptide Maps using UPLC with Tandem Columns Hongwei Xie, Martin Gilar, and Jeff Mazzeo Waters Corporation, Milford, MA U.S. APPLICATION BENEFITS The ACQUITY UPLC
Maximizing Chromatographic Resolution of Peptide Maps using UPLC with Tandem Columns Hongwei Xie, Martin Gilar, and Jeff Mazzeo Waters Corporation, Milford, MA U.S. APPLICATION BENEFITS The ACQUITY UPLC
Hillary B. Hewitson, Thomas E. Wheat, Diane M. Diehl INTRODUCTION
 Enhanc em ent o f t h e U P L C Am ino Ac i d Ana lysis So lu t io n w it h F l e x ibl e Detector Options Hillary B. Hewitson, Thomas E. Wheat, Diane M. Diehl INTRODUCTION The measurement of amino acids
Enhanc em ent o f t h e U P L C Am ino Ac i d Ana lysis So lu t io n w it h F l e x ibl e Detector Options Hillary B. Hewitson, Thomas E. Wheat, Diane M. Diehl INTRODUCTION The measurement of amino acids
Personal Genomics Platform White Paper Last Updated November 15, Executive Summary
 Executive Summary Helix is a personal genomics platform company with a simple but powerful mission: to empower every person to improve their life through DNA. Our platform includes saliva sample collection,
Executive Summary Helix is a personal genomics platform company with a simple but powerful mission: to empower every person to improve their life through DNA. Our platform includes saliva sample collection,
User Bulletin. ABI PRISM 7000 Sequence Detection System DRAFT. SUBJECT: Software Upgrade from Version 1.0 to 1.1. Version 1.
 User Bulletin ABI PRISM 7000 Sequence Detection System 9/15/03 SUBJECT: Software Upgrade from Version 1.0 to 1.1 The ABI PRISM 7000 Sequence Detection System version 1.1 software is a free upgrade. Also
User Bulletin ABI PRISM 7000 Sequence Detection System 9/15/03 SUBJECT: Software Upgrade from Version 1.0 to 1.1 The ABI PRISM 7000 Sequence Detection System version 1.1 software is a free upgrade. Also
Quantitative LC-MS Analysis of 14 Benzodiazepines in Urine Using TraceFinder 1.1 Software and High Resolution Accurate Mass
 Application Note: 529 Quantitative LC-MS Analysis of 14 Benzodiazepines in Urine Using TraceFinder 1.1 Software and High Resolution Accurate Mass Xiang He, Marta Kozak; Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Jose,
Application Note: 529 Quantitative LC-MS Analysis of 14 Benzodiazepines in Urine Using TraceFinder 1.1 Software and High Resolution Accurate Mass Xiang He, Marta Kozak; Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Jose,
Generating Automated and Efficient LC/MS Peptide Mapping Results with the Biopharmaceutical Platform Solution with UNIFI
 with the Biopharmaceutical Platform Solution with UNIFI Vera B. Ivleva, Ying Qing Yu, Scott Berger, and Weibin Chen Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA A P P L I C AT ION B E N E F I T S The ability to
with the Biopharmaceutical Platform Solution with UNIFI Vera B. Ivleva, Ying Qing Yu, Scott Berger, and Weibin Chen Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA A P P L I C AT ION B E N E F I T S The ability to
Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Cotton Line MON Using Real-time PCR. Validation Report
 Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Cotton Line MON 15985 Using Real-time PCR Validation Report 19 June 2008 Joint Research Centre Institute for Health and Consumer Protection Biotechnology
Event-specific Method for the Quantification of Cotton Line MON 15985 Using Real-time PCR Validation Report 19 June 2008 Joint Research Centre Institute for Health and Consumer Protection Biotechnology
About OMICS Group Conferences
 About OMICS Group OMICS Group International is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of
About OMICS Group OMICS Group International is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of
Outline. Analysis of Microarray Data. Most important design question. General experimental issues
 Outline Analysis of Microarray Data Lecture 1: Experimental Design and Data Normalization Introduction to microarrays Experimental design Data normalization Other data transformation Exercises George Bell,
Outline Analysis of Microarray Data Lecture 1: Experimental Design and Data Normalization Introduction to microarrays Experimental design Data normalization Other data transformation Exercises George Bell,
ICP Expert software. Technical Overview. Introduction
 ICP Expert software Technical Overview Introduction The Agilent 5110 ICP-OES provides fast sample analysis, using less gas, without compromising on performance for tough samples. It has been designed for
ICP Expert software Technical Overview Introduction The Agilent 5110 ICP-OES provides fast sample analysis, using less gas, without compromising on performance for tough samples. It has been designed for
Proteomics. Proteomics is the study of all proteins within organism. Challenges
 Proteomics Proteomics is the study of all proteins within organism. Challenges 1. The proteome is larger than the genome due to alternative splicing and protein modification. As we have said before we
Proteomics Proteomics is the study of all proteins within organism. Challenges 1. The proteome is larger than the genome due to alternative splicing and protein modification. As we have said before we
Towards unbiased biomarker discovery
 Towards unbiased biomarker discovery High-throughput molecular profiling technologies are routinely applied for biomarker discovery to make the drug discovery process more efficient and enable personalised
Towards unbiased biomarker discovery High-throughput molecular profiling technologies are routinely applied for biomarker discovery to make the drug discovery process more efficient and enable personalised
