Answers. Unit 1 Cell biology Chapter 1 Cells. Activity 1.1. Activity 1.2
|
|
|
- Georgia Casey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CELLS Answers Unit 1 Cell biology Chapter 1 Cells Activity Structure Cell membrane Type of cell Animal Plant Yeast Bacterial Cytoplasm Nucleus Cell wall Vacuole Chloroplast Plasmid 2. Answers will vary depending on the choice of materials available. 3. Answers will vary but are likely to include the key features of the different cell types. 4. Answers will vary but are likely to include the functions of the key features identified in Question Answers will vary but should include clean and careful diagrams, appropriately labelled. 6. Answers will vary but are likely to include structures and functions identified previously in this activity. 7. Answers will vary but key points to mention include: a title, a source and an opinion. Activity (a) 50 units (b) 125 units 1
2 CELL BIOLOGY Activity Answers will vary depending on the choice of cell, but key points to mention include: a title, labels and a description of the specialist function of the cell. 2. Type of cell Function Description Nerve cell Carries electrical messages Long insulated fibres Root hair cell Absorbs water and minerals Large surface area Red blood cell Transports oxygen Large surface area and no nucleus Sperm cell Swims towards an egg Tiny cell with a tail Palisade cell Photosynthesis Leaf cells which contain many chloroplasts Activity Answers will vary but are likely to include the following: genetic engineering, stem-cell therapy, clinical tests of drugs and medical research. 1. (a) A cell membrane; B cytoplasm; C nucleus 3 (b) 1 C; 2 A; 3 B 2 [1 out of 3 correct = 1 mark; all correct = 2] (c) Chloroplast and cell wall 2 2. (a) Yeast baking bread or brewing beer (alcohol) bacteria cheese or yoghurt 2 (b) 100 units 1 Total 10 2
3 CELL DIVISION Chapter 2 Cell division 1. Activity 2.1 Species Chromosome number in their cells African lion 38 Red kangaroo 16 Oak tree 24 Cabbage plant Key points to mention include: growth and repair. 3. Key points to mention include: production of new unspecialised cells by cell division followed by specialisation and organisation of these cells to replace lost tissues. 4. Models will vary but should include parent and daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes. 5. Key points to mention include: the growth of bacterial colonies from single bacterial cells by cell division. Activity (a) 64 (b) The graph points should be plotted accurately and joined by straight lines, with labelled and evenly scaled axes and labelled origin. Activity Cancer is caused by uncontrolled cell division which can produce a mass of cells called a tumour. Cancer cells can break off from the mass of cells and travel to other parts of the body in the bloodstream. 2. Answers will vary depending on the disease chosen but should mention at least three lifestyle choices. 3
4 CELL BIOLOGY 1. (a) Chromosome 1 (b) (i) identical to 1 (ii) identical to 1 2. Cancer cells 1 4. Growth repair replacement regeneration named example 1 Total 6 Chapter 3 DNA function and profiling Activity The human body is made up of cells. Each cell has a nucleus containing genetic information. The genetic information is made of DNA. Some sections of DNA are called genes. Each gene carries instructions for making a protein. 2. Protein group Example Job done by the protein Proteins which make up the body structure Proteins which control body function Bone protein Muscle protein Enzymes Antibodies Makes bones flexible Helps the body move Speed up chemical reactions in cells Help fight infections 3. Student s own answer but should include: title, source, be words long, and express an opinion about trustworthiness. Activity Washing powder. Answers will vary but are likely to include the following: washing powders may contain various enzymes to break down different types of stain, such as proteins, fats and starches. Washing powders containing enzymes work best at moderate temperatures and neutral ph. Enzymes are generally harvested from microorganisms. Apple juice. Answers will vary but are likely to include the following: enzymes are used to break down cell walls, making it easier to squeeze out the juice by mechanical means, and are used to reduce cloudiness. 2. Your plan should include a fully labelled diagram of any apparatus and a brief description of the measurements you will need to take. Think about how you can make your experiment fair you will need to control the amount of blackcurrant juice in each stain, the temperature and agitation of any washes. 4
5 DNA FUNCTION AND PROFILING Activity (a) Each individual has a unique combination of genes. (b) In forensics, DNA samples can be obtained from blood, saliva and skin. This information can be useful in helping the police to solve crimes. (c) Paternity tests can be carried out to confirm a child s biological father. (d) The food industry uses DNA profiling to check that the food labelled on the packet has not been replaced by something else, for example, using horse meat instead of beef to make burgers. (e) Genetic screening can be carried out to assess health risks such as cancer. (f) In archaeology, DNA profiling can be used to identify unknown remains. 2. (a) 1 and 3 (b) Child 2 is only biologically related to the mother. 3. Y 4. Answers will vary but are likely to include the following: an account of what you did and a labelled drawing of the boiling tube containing the extraction fluid, ethanol and fruit DNA. 5. The hair of suspect 2 and the owner was found at the scene/in the shop. The results only show that the suspect may have been in the shop. He may have shopped there or someone could have left a sample of his hair in the shop. Although the DNA evidence is useful, other evidence would also be required. Activity Answers will vary but should include both arguments for and against the question. 2. Answers will vary depending on each student s individual point of view. Students should be able to defend their assessment of each statement being an argument in favour or an argument against. 1. DNA carries the code/instructions for making proteins passes on inherited information/characteristics/genetic information Any one named example, e.g. enzymes, hormones, antibodies, muscle, hair, bones, nails The proteins are enzymes that break down and remove biological stains Any one of: forensics paternity testing assessing health risks food industry. 1 Plus one appropriate benefit such as: to identify a person who may have committed a crime to show the identity of the biological father to assess the chances of developing a certain disease or medical condition such as 5
6 CELL BIOLOGY cancer, diabetes, Alzheimer s to check if meat, fish and other food contents are as labelled Answers will vary but may include one of the following: privacy risks in medical genetic screening there are issues surrounding whether information should be shared with other family members public concerns that the information could be used by employers or insurance companies. 1 Total 6 Chapter 4 DNA, genes and chromosomes Activity (a) The nucleus is the region of a cell where the genetic code is stored. (b) Chromosomes are made of DNA. (c) A gene is a section of DNA that carries the code to make a protein. 2. A 4 B 2 C 5 D 3 E 1 Activity (a) DNA contains the instructions for making proteins. (b) Gene (c) From digested protein in its diet (d) Genes carry the coded instructions for making particular proteins. 2. In the course of this activity, students should realise that DNA has four coding letters (coloured beads in the model) and that each sequence of three code for one amino acid. Activity (a) Any three of: different genders, ages, skin colours, hair colours, or any other sensible difference. (b) They have inherited some of the same DNA from their parents, so they are quite alike but each also has unique DNA which makes them different. (c) Genetic information that is passed on from parents to offspring. 2. Answers will vary depending on the disease chosen but should include rarity, symptoms and treatments. 6
7 THERAPEUTIC USE OF CELLS 1. B 1 2. (a) X gene; Y protein 2 (b) As a code sequence of chemical letters 1 3. (a) Offspring inherit their DNA from their parents. 1 (b) The DNA of a human is unique to the individual. 1 Total 6 Chapter 5 Therapeutic use of cells Activity insulin gene obtained from human cell human insulin gene added to bacterial cell modified bacterial cells culture(d) human insulin extracted and purified 2. (a) 40 Approximate percentage of each age group with diabetes in < Age range (years) (b) As age increases, the percentage of individuals in the population with diabetes increases. (c) Increased level of obesity longer exposure to a high-sugar diet decreased level of exercise in later life increases the risk of developing diabetes. 7
8 CELL BIOLOGY Activity Stem cells are unspecialised cells found in embryos and in adult tissue. They can divide to produce more stem cells which can then become specialised to carry out different functions. 2. (b) Description of organ Examples Flat sheet Tube shaped Hollow sac Solid Skin, cornea Blood vessel, windpipe Bladder, stomach Liver, lung 3. Both therapies use a donor to give cells to a patient. Only bone marrow transplant relies on stem cells. Both therapies use a donor to give cells to a patient. In blood transfusions the donated cells are already specialised, but in bone marrow transplants the donated cells are unspecialised. 4. Answers will vary but are likely to include the following: must be licensed by HFEA (Human Fertilisation and Embryo Authority) must be considered absolutely necessary for research purposes embryos must have been created in vitro/for fertility treatment must have been donated with full consent of parents embryos must be no older than 14 days. 5. Answers will vary but, may include: Cornea transplant the cornea is the clear outer layer at the front of the eyeball; it acts as a window to the eye the cornea helps to focus light rays on to the retina at the back of the eye when damaged, it can become less transparent or change shape and affect vision stem cells from the patient s other (healthy) eye can be isolated they can be cultured in the laboratory and transplanted into the affected eye to repair the damaged cornea this can recover the person s sight Bone marrow transplant used to treat conditions affecting the blood cells such as leukaemia stem cells in transplant are special cells produced by bone marrow that can turn into different types of blood cells 8
9 THERAPEUTIC USE OF CELLS involves taking healthy stem cells from the bone marrow of one person ideally a close family member and transferring them to the patient best chance of getting a match is from a brother or sister if there are no matches in the family a search of the British Bone Marrow Registry can be carried out Skin grafting skin is removed from an unaffected area of the body and used to cover lost or damaged skin general anaesthetic or a local anaesthetic used, depending on the size and location of the affected area graft is held in place using stitches, staples, clips or special glue graft is covered with a sterile dressing until connected with the surrounding blood supply, about 5 7 days a dressing is placed over the area where the skin has been taken from to help protect it from infection it takes 1 2 years for the appearance of the skin to settle down completely 6. Answers will vary but are likely to include the following: argument for, the potential to treat serious conditions and save lives using cells that cannot be obtained in any other way; argument against, the idea that embryos have the same human rights as all people and should be protected. 1. (a) Approximate percentage Age range (years) [Two axes correctly scaled: 1 mark; two axes correctly labelled: 1 mark; bars accurately drawn: 1 mark] 3 (b) As the age of the population increases, the number of people (percentage of population) with diabetes increases B, C, A 1 3. Grafts transplants artificial organs 1 Total 6 9
10 CELL BIOLOGY Chapter 6 Enzymes and their use in industry Activity Enzyme: protein produced by living cells that acts as a biological catalyst Catalyst: a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction Substrate: the substance on which an enzyme works Product: substance made by an enzyme-catalysed reaction Specific: term used to describe an enzyme only being able to work on one particular substance 2. (a) Protein (b) They speed up chemical reactions in living cells. (c) Vital chemical reactions within the living cell would take place too slowly for the cell to survive. (d) They only work on one particular substance. (e) Substrate (f) Product (g) They remain unchanged (in the reactions that they speed up). (h) The breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase breakdown of starch into maltose by amylase. (i) Phosphorylase Activity (a) Starch has been produced. (b) Phosphorylase builds glucose into starch. (c) Row B shows that the phosphorylase did not contain any starch at the start. Row C shows that the glucose does not build up into starch on its own and that it is the phosphorylase which is active. 2. (a) (i) 10 minutes (ii) 21 minutes (iii) 30 minutes (b) The results shown in the graph suggest that starch breaks down to maltose. This is because, as the maltose level increases the starch level decreases. When all the starch has gone, no further maltose is made. 3. Plan should include: a labelled diagram of the apparatus, a method with a suitable control and the measurements to be taken, safety precautions, the variables that must be kept constant, any measures to increase the reliability of the results, and a results table with correct headings and units. 10
11 ENZYMES AND THEIR USE IN INDUSTRY 4. (f) (i) Only catalase can break down hydrogen peroxide catalase is specific to hydrogen peroxide enzymes are specific. (ii) Only one variable was altered important variables were controlled. (iii) Any two from: volume of hydrogen peroxide, volume/drops of detergent, volume of enzymes, time (iv) Any one from: temperature, concentration of solutions (v) Repeat the experiment (vi) Use different/more enzymes Activity (a) To allow a comparison with the volume of juice produced using pectinase to show the effect of using pectinase. (b) Any two from: type of apple, method of pulping apple, time, temperature, type of filter paper used (c) As the volume of pectinase increased, the volume of apple juice collected increased, then levelled off. (d) 2 times (e) 2 cm 3 is the lowest volume of pectinase needed to produce the maximum volume of juice. 2. Key points to mention include: the source of enzymes used in manufacture and their functions. 3. Plan should include: a list or labelled diagram of the apparatus, a method, a suitable control and the measurements to be taken, the variables that must be kept constant, any measures to increase the reliability of the results and a method of recording your results. 4. Answers will vary but should include both pros and cons of using each type of rennet, and a justification of the final choice. 1. They speed up chemical reactions in living organisms Without enzymes reactions would be too slow to maintain life/for survival X: substrate; Y: product 2 4. Break-down reactions give product molecules that are smaller than the substrate. 1 Whereas build-up reactions give product molecules that are larger than the substrate Any two from: production of leather, wine, cheese, yoghurt, soft-centred sweets, baking of bread, brewing of beer, treatment of sewage, tenderising meat, contact-lens cleaners, genetic engineering, treatment of blood clots and some types of tumour 2 Total 8 11
12 CELL BIOLOGY Chapter 7 Microorganisms Activity (a) Microorganisms are very small. (b) They are found almost everywhere. (c) The main examples of microorganisms are bacteria and fungi. (d) Microorganisms grow by producing new cells. (e) Some larger fungi grow by producing new cells to make fungal threads get longer. 2. Points to include in bacterial cell diagram: cell wall and cell membrane, no nucleus, circular DNA chromosomes and plasmids; points to include in fungal cell: separate nucleus, thicker cell wall. 3. Answers will vary but are likely to include references to microorganisms in nature, food, medicine and as the causes of diseases. 4. Answers will vary depending on the article selected for comment. Activity Microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi need suitable conditions to grow and reproduce. They need a food supply, water, warmth and a suitable ph. 2. Answers will vary depending on the surfaces selected for investigation, but should include a comment about the value of the control Petri dish. 3. Answers will vary but should include conclusions about how temperature (and then, in part (g), sugar concentration) affects the numbers of cells produced during the growth of yeast. 4. Method of preservation Examples of food preserved by this method Drying Freezing Pickling in vinegar Raisins, currants, sultanas, milk, lentils, rice, pasta, others Peas, sweetcorn, carrots, fish fingers, hamburgers, others Beetroot, onions, cabbage, gherkins, others 5. Antifungal: clotrimazole/others Antiseptic: alcohol/phenol/iodine/salt/tcp/others Antibiotic: penicillin/streptomycin/tetracycline/chloramphenicol/others 6. Student s own answer. 12
13 MICROGANISMS IN INDUSTRY 1. (a) A 1 (b) A nucleus is shown (a) 3 million 1 (b) 12 hours 1 (c) If the bacteria had been cultured at a lower temperature, the number of living cells present after 36 hours would have been less. 1 (d) Moisture level of acidity presence of chemicals/antibiotics/antiseptics level of oxygen present 1 Total 6 Chapter 8 Microorganisms in industry Activity Answers will vary but should include three properties of microorganisms that are useful in industry, such as ability to be cultured and some products that can be made. 2. Industrial activity The role of microorganisms in the process Brewing Baking Cheese production Sewage treatment Bioethanol production Produce alcohol Produce carbon dioxide, which makes dough rise Produce acids which thicken and flavour the products Break down human wastes to harmless substances Produce alcohol from plant material/sugar/ starch in crops 3. Answers will vary but should include a method, results, an explanation of the results and a comment about why a control is included in the experiment. 4. Answers will vary but should include a method, a graph of results and an explanation of the results. 5. Answers will vary but should include text, artwork and photos to illustrate the use of microorganisms in the production of biofuel, the treatment of sewage and in bioremediation. 13
14 CELL BIOLOGY 1. (a) They grow rapidly use a wide range of substances as food make a wide range of products. 1 (b) Microorganism Product 2 Bacteria Yoghurt or cheese Yeast Alcoholic drinks, e.g. beer and wine 2. (a) (i) Use an even scale from 0 and take label from table heading, including units. 1 (ii) Give an accurate plot of points and join points with straight lines. 1 (b) Yeast cells have enzymes which work best in warm conditions. 1 Total 6 Chapter 9 Photosynthesis Activity Answers will vary but should include the key words given: glucose, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll and light. 2. (a) Chloroplasts (b) Carbon dioxide and water (c) Chlorophyll (d) Glucose and oxygen (e) carbon dioxide + water glucose/sugar + oxygen Activity Answers will vary but should be roughly similar to Figure 9.2. Activity Results should be similar to those shown in the diagram illustrating positive and negative starch tests. 2. Cards should be ordered correctly according to the experimental steps described in Activity 9.3 Question 1. 14
15 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Activity (a) The plant needs to be de-starched to make sure that all of its stores of starch are used up before the experiment is started. We can then be sure that the plant has made the starch detected under the conditions of the experiment. (b) A similar plant set up in exactly the same way but with no carbon dioxide absorbing chemical/soda lime/sodium hydroxide. (c) Less oxygen would have been produced/collected. Activity (a) Photosynthesis provides food/energy for all other organisms/animals/food chains/food webs and produces oxygen for respiration. (b) Any two food chains that include humans, e.g. grass cow humans wheat humans 2. Student s own answer. 1. Carbon dioxide and water 2 2. From light energy from the Sun 1 3. Sugar/glucose and oxygen 2 4. For food/energy or as producers of oxygen 1 5. (a) 50 kg 1 (b) Mass would increase 1 Total 8 15
16 CELL BIOLOGY Chapter 10 Limiting factors in photosynthesis Activity At point 1 on the graph, light intensity is a limiting factor. As the light intensity increases so does the rate of photosynthesis. At point 2 the light intensity has increased further but the rate of photosynthesis has remained the same. Therefore, at point 2 another factor must be in short supply and is limiting the rate of photosynthesis. 2. (a) Both axes correctly labelled with units. Plotted accurately and connected using a ruler. (b) There is no light energy for photosynthesis. (c) Light intensity is no longer a limiting factor. (d) Temperature carbon dioxide concentration (e) Repeat the experiment and calculate an average. Activity At point 1 on the graph, carbon dioxide concentration is increasing, as is the rate of photosynthesis. This tells us that carbon dioxide concentration is the limiting factor. At point 2 on the graph, the rate of photosynthesis stays the same despite the increasing carbon dioxide concentration. As the plant is being given more carbon dioxide, but the rate of photosynthesis is not increasing, carbon dioxide concentration cannot be the limiting factor. One of the other factors must be in short supply. Activity At point 1 on the graph, temperature is increasing, as is the rate of photosynthesis. This tells us that temperature is the limiting factor. At point 2 on the graph, the rate of photosynthesis is at a maximum or optimum. At point 3, the temperature continues to increase but the rate of photosynthesis decreases. This happens because the enzymes that control photosynthesis have an optimum temperature at which they work best. At temperatures above the optimum, the enzymes start to be denatured and the rate of photosynthesis slows down until it stops completely. 16
17 RESPIRATION Activity Answers will vary but should include the following key points: irrigation systems used to control the amount of water available; artificial lighting used so that the plants can continue growing at night or out of season; carbon dioxide added to the atmosphere around the plant by burning coal or oil stoves; artificial heating used to increase the temperature. 1. (a) 15 seconds 1 (b) Same size surface area thickness type of leaf 1 (c) Temperature light intensity carbon dioxide concentration 1 (d) Change the light intensity by moving the lamp different distances from the test tube (a) 240 kg 1 (b) Any two from: increased temperature, light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration 2 (c) Limiting factors 1 Total 8 Chapter 11 Respiration Activity (a) (i) The thermometers show a higher temperature in the experiment flask with the germinating peas. (ii) To stop heat getting into the peas from outside or to stop heat escaping to outside (b) Respiration releases energy in the form of heat. (c) The control shows that it must have been the respiration of the peas which released the heat energy. 2. Type of cell Oxygen used Product(s) All cells Yes Carbon dioxide and water High Yeast and plant cells No Carbon dioxide and alcohol Low Human muscle cells No Lactic acid Low Amount of energy released per molecule of glucose used (high or low) 17
18 CELL BIOLOGY 3. (a) glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy (b) glucose lactic acid + energy (c) glucose carbon dioxide + alcohol + energy 4. Successfully produce a model of glucose and appreciate that energy is contained in the bonds between the carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. 5. Answers will vary but should cover the difference between respiration in muscle cells using oxygen during moderate exercise and respiration in the absence of oxygen during intense exercise. Activity (a) Answers will vary but should include a sketch graph with title, labelled axes and correctly plotted points that shows respiration increasing as temperature increases over this temperature range. (b) Increasing temperature increases rate of respiration; at high temperatures respiration is slowed/stopped. (c) Respiration is controlled by enzymes, which are affected by temperature. (d) (i) 8 cm 3 CO 2 per hour (ii) 0 cm 3 CO 2 per hour respiration stops 2. Plan could include: (a) Method Set up three flasks each containing the same volume and concentration of yeast suspension. Add 1 g of sugar to one flask, 2 g to the second and 3 g to the third. Put a CO 2 sensor into each flask. Leave at the same temperature for the same length of time. Read CO 2 levels on the sensor. (b) Prediction The more sugar added, the higher the rate of respiration. 18
19 CONTROVERSIAL BIOLOGICAL PROCEDURES 1. Statement True False Correction In plant cells, respiration with oxygen produces carbon dioxide and alcohol. water In animal cells, respiration without oxygen produces lactic acid. Respiration with oxygen releases less energy than more respiration without oxygen (a) Flask C; has the best temperature for enzyme action. 2 (b) Mass of sugar ph oxygen availability 1 Total 6 Chapter 12 Controversial biological procedures Activity Answers will vary, but may include the following points: For: the procedure produces an exact genetic match for the material needed for treatment; it might save treatment costs. Against: the procedure does not recognise the human rights of the saviour sibling; the saviour sibling may feel valued only because of their potential to help their sibling and not as a person in their own right; the procedure may be stressful for the saviour sibling because of the emotional pressure and the potentially painful donation of tissue. Activity Answers will vary depending on the issue chosen. 19
20 CELL BIOLOGY 1. Answers may vary but could include one from the following sets of answers. (a) Saviour siblings 1 (b) Provides material for treatment of an ill sibling 1 (c) Breaches the human rights of the donor sibling and may cause emotional stress or pain to donor sibling 2 (a) Gene therapy 1 (b) Cures the genetic condition 1 (c) May damage health of patient/risk of cancer and offspring of patient may inherit the genes 2 (a) Pharming 1 (b) Inexpensive large quantities of product 1 (c) Welfare issues of pharmed organisms and safety of products for human use 2 (a) Transgenic organisms 1 (b) Increase crop yields/quality reduced pesticide application 1 (c) Health concerns of GM products and accidental release of GM genes 2 (a) Stem-cell technology 1 (b) Provide replacement tissues artificial organs 1 (c) Issues regarding embryonic stem cells and tumour formation in patients 2 (a) DNA profiling 1 (b) Allows identification of an individual from a small DNA sample in forensics paternity testing archaeology prediction of future health risks 1 (c) Use by insurance companies to deny cover and use by employers to deny work 2 Total 4 20
21 UNIT 1 PRACTICE ASSESSMENT Unit 1 Practice assessment National 3 1. (a) A: nucleus; B: cell membrane 2 (b) 2 Microorganism Use by humans Bacteria Yeast cells Making yoghurt Baking/bread-making or brewing/making beer or wine making 2. DNA carries the instructions to make proteins Forensics solving crimes; Archaeology identifying unknown remains 1 4. (a) Carbon dioxide 1 (b) (i) 4 (kg) 1 (ii) 8 (kg) mass increases by 2 (kg) 1 5. Bacteria and fungi/yeast 2 6. (a) 35 (g) 1 (b) Z 1 (c) If the temperature of the fermenter had been kept at 20 C, the mass of yeast cells present after 12 hours would be more. 1 Total 14 National 4 1. (a) 8 1 (b) Any one from: growth, repair, replacement cells, regeneration 1 2. Statement True False Correction 2 Genes are made of protein. DNA Genes are located on chromosomes. 3. Cell used therapeutically Product of the activity of these cells 2 Genetically engineered bacterial cells Insulin/factor VIII/HGH Stem cells Artificial organs 4. (a) Enzymes only act on one substrate type. 1 (b) Enzymes are unchanged by their reaction/can be used again and again. 1 21
22 CELL BIOLOGY 5. (a) Any one from: grow rapidly use diverse food sources make a wide range of products 1 (b) 5 1 (c) Any one from: dairy/cheese/yoghurt; bioremediation; sewage treatment; brewing; baking 1 6. (a) Temperature 1 (b) 30 ( C) 1 (c) Carbon dioxide concentration 1 7. (a) Alcohol/ethanol carbon dioxide 1 (b) (i) Increase 1 (ii) Cells produce heat energy during respiration Any one from the following sets of answers: (a) Saviour siblings 1 (b) Provides material for treatment of an ill sibling 1 (c) Thought to breach the human rights of the donor sibling may cause emotional stress or pain to donor sibling 1 (a) Gene therapy 1 (b) Cures the genetic condition 1 (c) May damage health of patient/risk of cancer offspring of patient may inherit the genes 1 (a) Pharming 1 (b) Inexpensive large quantities of product 1 (c) Welfare issues of pharmed organisms safety of products for human use 1 (a) Transgenic organisms 1 (b) Increase crop yields/quality reduced pesticide application 1 (c) Health concerns of GM products accidental release of GM genes 1 (a) Stem-cell technology 1 (b) Provide replacement tissues artificial organs 1 (c) Issues regarding use of embryonic stem cells tumour formation in patients 1 (a) DNA profiling 1 (b) Allows identification of an individual from a small DNA sample in forensics paternity testing archaeology prediction of future health risks 1 (c) Potential use by insurance companies to deny cover by employers to deny work 1 Total 20 22
National 5 Unit 1: Cell Biology Topic 1.1 Cell Structure. Which part of the cell is composed of cellulose? 1
 National 5 Unit 1: Cell Biology Topic 1.1 Cell Structure 1. The diagram below shows parts of a plant cell. Which part of the cell is composed of cellulose? 1 2. Which structural feature is found in a plant
National 5 Unit 1: Cell Biology Topic 1.1 Cell Structure 1. The diagram below shows parts of a plant cell. Which part of the cell is composed of cellulose? 1 2. Which structural feature is found in a plant
Cell Biology Homework
 Cell Biology Homework NAME: CLASS: 1 1. The diagram below shows two cells. Cell Structure a) Complete the table below to give the name and functions of the parts labelled A, B and C. (2) Letter Part Function
Cell Biology Homework NAME: CLASS: 1 1. The diagram below shows two cells. Cell Structure a) Complete the table below to give the name and functions of the parts labelled A, B and C. (2) Letter Part Function
How well can you do this? 1. I can explain that cell division is used for growth and repair of damaged body parts (e.g. cuts and broken bones)
 I am confident that I understand this and I can apply this to problems 1.1 Cell division and its role in growth and repair 1. I can explain that cell division is used for growth and repair of damaged body
I am confident that I understand this and I can apply this to problems 1.1 Cell division and its role in growth and repair 1. I can explain that cell division is used for growth and repair of damaged body
National 4 Biology. Unit 1 Cell Biology. Summary Notes
 National 4 Biology Unit 1 Cell Biology Summary Notes 1. Cell division and it s role in growth and repair. Cell division The process of cell division is called mitosis. Each cell must divide to ensure the
National 4 Biology Unit 1 Cell Biology Summary Notes 1. Cell division and it s role in growth and repair. Cell division The process of cell division is called mitosis. Each cell must divide to ensure the
St Andrew s High School, Coatbridge Biology Department. National 5 Unit 1 Cell Biology Summary Notes
 St Andrew s High School, Coatbridge Biology Department National 5 Unit 1 Cell Biology Summary Notes Key area 1.1 : Cell Structure. Key area 1.2: Transport across Cell Membrane. Key area 1.3: DNA and the
St Andrew s High School, Coatbridge Biology Department National 5 Unit 1 Cell Biology Summary Notes Key area 1.1 : Cell Structure. Key area 1.2: Transport across Cell Membrane. Key area 1.3: DNA and the
Cells Reproduction and Inheritance
 S2 Biology 3 Cells Reproduction and Inheritance Cells Cells are the tiny building blocks that make up all living things. Living things can be unicellular or multicellular. Unicellular = organism made of
S2 Biology 3 Cells Reproduction and Inheritance Cells Cells are the tiny building blocks that make up all living things. Living things can be unicellular or multicellular. Unicellular = organism made of
Learning Intentions. I will practice taking measurements and calculating averages. I can describe the uses of enzymes in biological detergents.
 Learning Intentions I can name the cell structures and their functions. I can describe the process of diffusion. I can state the equation of aerobic respiration. I understand that food contains chemical
Learning Intentions I can name the cell structures and their functions. I can describe the process of diffusion. I can state the equation of aerobic respiration. I understand that food contains chemical
Animal and plant cells have several parts. Each part has a different function.
 (4) Q.Living organisms are made of cells. (a) Animal and plant cells have several parts. Each part has a different function. Draw one line from each cell part to the correct function of that part. (b)
(4) Q.Living organisms are made of cells. (a) Animal and plant cells have several parts. Each part has a different function. Draw one line from each cell part to the correct function of that part. (b)
The diagrams below show a human ovum (egg) and a human sperm. Which part does a sperm use to swim towards an egg?
 Year 9 Exam Biology Practice Questions Q. The diagrams below show a human ovum (egg) and a human sperm. What are eggs and sperm? Tick the correct box. animals cells organs Which part does a sperm use to
Year 9 Exam Biology Practice Questions Q. The diagrams below show a human ovum (egg) and a human sperm. What are eggs and sperm? Tick the correct box. animals cells organs Which part does a sperm use to
B2 Tuesday 12 th May (Additional Science)
 B2.1.1 Cells and cell structure State that all living things are made up of cells Identify, and describe the functions of, the following parts of human and animal cells: nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane,
B2.1.1 Cells and cell structure State that all living things are made up of cells Identify, and describe the functions of, the following parts of human and animal cells: nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane,
National 5 Biology. Unit 1 Homework. Cell Biology
 National 5 Biology Unit 1 Homework Cell Biology Sub-topic 1.1 Cell Structure 1. Identify the organelles labelled A - E in the following diagrams of an animal and a plant cell. 5 2. The following diagram
National 5 Biology Unit 1 Homework Cell Biology Sub-topic 1.1 Cell Structure 1. Identify the organelles labelled A - E in the following diagrams of an animal and a plant cell. 5 2. The following diagram
B1 Quick Revision Questions. B1 for AQA GCSE examination 2018 onwards
 B1 Quick Revision Questions Question 1... of 50 Name the 4 components that are found in an Animal Cell Answer 1... of 50 Nucleus, Mitochondria, Cell Membrane & Cytoplasm. Question 2... of 50 Name the other
B1 Quick Revision Questions Question 1... of 50 Name the 4 components that are found in an Animal Cell Answer 1... of 50 Nucleus, Mitochondria, Cell Membrane & Cytoplasm. Question 2... of 50 Name the other
Course Notes. Calderglen High School Biology Department. Cell Biology
 Calderglen High School Department Cell Course Notes 1 Cells All living organisms are made-up of cells. The detailed structure of these cells is too small to be seen with the naked eye. Biologists use a
Calderglen High School Department Cell Course Notes 1 Cells All living organisms are made-up of cells. The detailed structure of these cells is too small to be seen with the naked eye. Biologists use a
Passing on characteristics
 1 of 50 Boardworks Ltd 2006 2 of 50 Boardworks Ltd 2006 Passing on characteristics 3 of 50 Boardworks Ltd 2006 What makes this baby human? What determines its gender? In all living things, characteristics
1 of 50 Boardworks Ltd 2006 2 of 50 Boardworks Ltd 2006 Passing on characteristics 3 of 50 Boardworks Ltd 2006 What makes this baby human? What determines its gender? In all living things, characteristics
Perth Academy N5 Biology Cellular Biology Homework
 Perth Academy N5 Biology Cellular Biology Homework Homework 1 1. Euglena is a single celled organism. It is a specialised cell. The diagram below shows some of the structures within Euglena. (a) Euglena
Perth Academy N5 Biology Cellular Biology Homework Homework 1 1. Euglena is a single celled organism. It is a specialised cell. The diagram below shows some of the structures within Euglena. (a) Euglena
GraspIT AQA GCSE Cell Biology - ANSWERS
 A. Cell structure part 1 Eukaryotes, prokaryotes and animal and plant cells 1. Describe the similarities and differences between a typical plant and a typical animal cell. (4) Typical animal and plant
A. Cell structure part 1 Eukaryotes, prokaryotes and animal and plant cells 1. Describe the similarities and differences between a typical plant and a typical animal cell. (4) Typical animal and plant
Respiration. 2.2 Cell Metabolism Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able. to:
 Name: 2.2 Cell Metabolism Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able 2.2.5 1. Definition of the term: aerobic respiration. 2. Explain the role of aerobic respiration what does it
Name: 2.2 Cell Metabolism Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able 2.2.5 1. Definition of the term: aerobic respiration. 2. Explain the role of aerobic respiration what does it
St Ninian s High School
 St Ninian s High School National 5 Biology Cell Biology Revision Notes Name 1 Cell structure & function A cell is the basic unit of life and there are 4 main types of cells that you need to learn about
St Ninian s High School National 5 Biology Cell Biology Revision Notes Name 1 Cell structure & function A cell is the basic unit of life and there are 4 main types of cells that you need to learn about
Duncanrig Secondary School
 National 4 Biology Unit 1Topic 3: Therapeutic Uses of Cells, Duncanrig Secondary School Duncanrig Secondary School National 4 Biology Unit 1 Topic 3: Therapeutic Uses of Cells Pupils Activity Booklet National
National 4 Biology Unit 1Topic 3: Therapeutic Uses of Cells, Duncanrig Secondary School Duncanrig Secondary School National 4 Biology Unit 1 Topic 3: Therapeutic Uses of Cells Pupils Activity Booklet National
Cell Structure. Plant Cell. Animal Cell
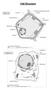 Cell Structure Plant Cell Animal Cell Fungal Cell (yeast) Bacterial Cell cytoplasm DNA plasmids capsule cell wall ribosomes cell membrane Structure Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast
Cell Structure Plant Cell Animal Cell Fungal Cell (yeast) Bacterial Cell cytoplasm DNA plasmids capsule cell wall ribosomes cell membrane Structure Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast
St Ninian s High School Biology Department. National 5 Biology. Cell Biology
 St Ninian s High School Biology Department National 5 Biology Cell Biology Revision Notes 1 Cell structure & function A cell is the basic unit of life and there are 4 main types of cells that you need
St Ninian s High School Biology Department National 5 Biology Cell Biology Revision Notes 1 Cell structure & function A cell is the basic unit of life and there are 4 main types of cells that you need
Instructions Answer all questions in the spaces provided. Do all rough work in this book. Cross through any work you do not want to be marked.
 AQA GCSE Biology F SET A Paper 1 Foundation Tier Author: Mike Smith Materials Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator. Instructions Answer all questions in the
AQA GCSE Biology F SET A Paper 1 Foundation Tier Author: Mike Smith Materials Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator. Instructions Answer all questions in the
New technology in biology
 New technology in biology Aims You have been asked to test a board game that can be used to revise the key concepts in this chapter. Work through the tasks below to show your understanding of these topics
New technology in biology Aims You have been asked to test a board game that can be used to revise the key concepts in this chapter. Work through the tasks below to show your understanding of these topics
National 5 Biology - Unit 1 Cell Biology
 1. Cell Structure National 5 Biology - Unit 1 Cell Biology Cells are the basic unit of life Stains can be used to make cell structures visible Organelles are present in cell cytoplasm and carry out a specialised
1. Cell Structure National 5 Biology - Unit 1 Cell Biology Cells are the basic unit of life Stains can be used to make cell structures visible Organelles are present in cell cytoplasm and carry out a specialised
test 7 3. What is the main function of a vacuole in a cell?
 test 7 Name: Date: 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a model cell setup. The locations of three different
test 7 Name: Date: 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a model cell setup. The locations of three different
B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport. B2.2 Tissues, organs and organ systems
 B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
Enzymes Anabolic Catabolic. Keywords
 Enzymes Enzymes Anabolic Catabolic Catalysts Substrate Product Catalase Denatured enzyme Hydrogen Peroxide Keywords Bioprocessing Sodium Alginate Active Site Bioreactor Immobolised enzyme Enzyme Substrate
Enzymes Enzymes Anabolic Catabolic Catalysts Substrate Product Catalase Denatured enzyme Hydrogen Peroxide Keywords Bioprocessing Sodium Alginate Active Site Bioreactor Immobolised enzyme Enzyme Substrate
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/2H London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 2H Higher Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4325/2H London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 2H Higher Tier Wednesday 11 May 2005 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for
B4 Life processes Q1 Question Label the animal cell. B4 Life processes. Question: Label the plant cell.
 Q1 Label the animal cell. Q2 : Label the plant cell. A cell membrane, B cytoplasm, C nucleus, D- mitochondria A cell wall, B vacuole, C chloroplast, D nucleus, E cell wall, F cytoplasm, G - mitochondria
Q1 Label the animal cell. Q2 : Label the plant cell. A cell membrane, B cytoplasm, C nucleus, D- mitochondria A cell wall, B vacuole, C chloroplast, D nucleus, E cell wall, F cytoplasm, G - mitochondria
Year 9 AQA GCSE Biology Revision Checklist
 Year 9 AQA GCSE Biology Revision Checklist Use this booklet to help you with your revision in preparation for your year 9 Biology exam and final examinations. This is the work that you will have covered
Year 9 AQA GCSE Biology Revision Checklist Use this booklet to help you with your revision in preparation for your year 9 Biology exam and final examinations. This is the work that you will have covered
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Friday 21 May 2010 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Nil
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Friday 21 May 2010 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Nil
Guided teaching hours: 4 hours
 Cell division Chapter overview Guided teaching hours: 4 hours In this chapter, students will learn about the process of cell division and after finishing the chapter should be able to describe the three
Cell division Chapter overview Guided teaching hours: 4 hours In this chapter, students will learn about the process of cell division and after finishing the chapter should be able to describe the three
Jeddah Knowledge International School
 Jeddah Knowledge International School Biochemistry Revision Pack 2015-2016 Quarter 2 Grade 9 Name: Section: Q2 G9 SCIENCE REVISION PACK 2015 2016 1 1 Q2 G9 Science Revision Pack Section A: Rates of Reaction
Jeddah Knowledge International School Biochemistry Revision Pack 2015-2016 Quarter 2 Grade 9 Name: Section: Q2 G9 SCIENCE REVISION PACK 2015 2016 1 1 Q2 G9 Science Revision Pack Section A: Rates of Reaction
Bacteria and Evolution Junior Science
 Bacteria and Evolution Junior Science Micro-organisms Micro-organisms (or microbes) are very small organisms, which are usually only visible with the aid of a microscope. Sometimes a colony of micro-organisms
Bacteria and Evolution Junior Science Micro-organisms Micro-organisms (or microbes) are very small organisms, which are usually only visible with the aid of a microscope. Sometimes a colony of micro-organisms
BIOLOGY HIGHER LEVEL
 *P14* PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2008 BIOLOGY HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS Section A. Answer any five questions from this section. Each question carries 20 marks. Write your answers in the spaces
*P14* PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2008 BIOLOGY HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS Section A. Answer any five questions from this section. Each question carries 20 marks. Write your answers in the spaces
Differentiation = Making specialized cells. Self-renewal = copying. What is a stem cell?
 Differentiation = Making specialized cells What is a stem cell? What the photo shows A lump of metal and lots of different kinds of screws that can be made from it. Things to think about What is a specialized
Differentiation = Making specialized cells What is a stem cell? What the photo shows A lump of metal and lots of different kinds of screws that can be made from it. Things to think about What is a specialized
Y10 Biology progression (9-1 AQA syllabus and Kerboodle)
 Y10 Biology progression (9-1 AQA syllabus and Kerboodle) Key: Separates only content Assessment: Y10 teaching specialist team to organise. All classes to do the same. Required practical: See Y10 folder
Y10 Biology progression (9-1 AQA syllabus and Kerboodle) Key: Separates only content Assessment: Y10 teaching specialist team to organise. All classes to do the same. Required practical: See Y10 folder
Revision Based on Chapter 15 Grade 10
 Revision Based on Chapter 15 Grade 10 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following has the disadvantage of possibly bringing
Revision Based on Chapter 15 Grade 10 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following has the disadvantage of possibly bringing
BIOLOGY 2b SUMMARY SHEET
 BIOLOGY 2b SUMMARY SHEET Information in italics is only needed at higher tier. B2.5.1 PROTEINS Protein molecules made up of long chains of amino acids. These long chains are folded to produce a specific
BIOLOGY 2b SUMMARY SHEET Information in italics is only needed at higher tier. B2.5.1 PROTEINS Protein molecules made up of long chains of amino acids. These long chains are folded to produce a specific
Curriculum for Excellence S2 Biology- Homework
 Name: Class: Teacher: Curriculum for Excellence S2 Biology- Homework HW 1,2 & 3 - Micro-Biology and Biotechnology HW 4, 5 & 6 Environmental Biology Homework Mark Comment Parent signature 1. Growth of microorganisms
Name: Class: Teacher: Curriculum for Excellence S2 Biology- Homework HW 1,2 & 3 - Micro-Biology and Biotechnology HW 4, 5 & 6 Environmental Biology Homework Mark Comment Parent signature 1. Growth of microorganisms
Page 3. 18) The diagram below illustrates some key steps of a procedure in one area of biotechnology.
 Name: 1117 1 Page 1 1) A small amount of DNA was taken from a fossil of a mammoth found frozen in glacial ice. Genetic technology can be used to produce a large quantity of identical DNA from this mammoth's
Name: 1117 1 Page 1 1) A small amount of DNA was taken from a fossil of a mammoth found frozen in glacial ice. Genetic technology can be used to produce a large quantity of identical DNA from this mammoth's
The genetic material is arranged differently in the cells of bacteria compared with animal and plant cells.
 Some infections are caused by bacteria. The genetic material is arranged differently in the cells of bacteria compared with animal and plant cells. Describe two differences. Tuberculosis (TB) is an infection
Some infections are caused by bacteria. The genetic material is arranged differently in the cells of bacteria compared with animal and plant cells. Describe two differences. Tuberculosis (TB) is an infection
3.4 Unit 2 Biology 2. B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport. Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding to:
 3.4 Unit 2 Biology 2 B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. To get into or out of cells,
3.4 Unit 2 Biology 2 B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. To get into or out of cells,
GCSE (9 1) Combined Science (Biology) A (Gateway Science) J250/02 Paper 2, B4 B6 and CS7 (PAGs B1 B5)
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA GCSE (9 1) Combined Science (Biology) A (Gateway Science) Paper 2, B4 B6 and CS7 (PAGs B1 B5) (Foundation Tier) F Year 11 Test Time allowed: 1 hour 10 minutes You must have: a
Oxford Cambridge and RSA GCSE (9 1) Combined Science (Biology) A (Gateway Science) Paper 2, B4 B6 and CS7 (PAGs B1 B5) (Foundation Tier) F Year 11 Test Time allowed: 1 hour 10 minutes You must have: a
If you had 3 clones, what would you get them to do?! Aim high: How would you clone yourself?!
 If you had 3 clones, what would you get them to do?! Aim high: How would you clone yourself?! Genetic engineering Genetic and environmental differences B1.6 Variation Inheritance Types of reproduction
If you had 3 clones, what would you get them to do?! Aim high: How would you clone yourself?! Genetic engineering Genetic and environmental differences B1.6 Variation Inheritance Types of reproduction
Stem Cells. Part 1: What is a Stem Cell? STO Stem cells are unspecialized. What does this mean?
 STO-120 Stem Cells Part 1: What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells differ from other kinds of cells in the body. When a stem cell divides by mitosis, each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell
STO-120 Stem Cells Part 1: What is a Stem Cell? Stem cells differ from other kinds of cells in the body. When a stem cell divides by mitosis, each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4325/2H London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 2H Higher Tier Friday 21 May 2010 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4325/2H London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 2H Higher Tier Friday 21 May 2010 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference
Genetics 2 star. 1. Two different types of cells from an organism are shown. A. cause mutations to occur
 Name: Date: 1. Two different types of cells from an organism are shown. 3. Plants inherit genes that enable them to produce chlorophyll, but this pigment is not produced unless the plants are exposed to
Name: Date: 1. Two different types of cells from an organism are shown. 3. Plants inherit genes that enable them to produce chlorophyll, but this pigment is not produced unless the plants are exposed to
What information does the nucleus of a cell contain? Why is it so important? What is a donor animal? Why don t clones grow in the same way?
 CLONING- EXERCISES 1 ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS IN YOUR OWN WORDS AS FAR AS POSSIBLE! What information does the nucleus of a cell contain? Why is it so important? What is a donor animal? Why don t
CLONING- EXERCISES 1 ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS IN YOUR OWN WORDS AS FAR AS POSSIBLE! What information does the nucleus of a cell contain? Why is it so important? What is a donor animal? Why don t
Reinforcement. Cells and Life CHAPTER 1 LESSON 1
 Reinforcement Cells and Life LESSON 1 Directions: In numbers 1 through 4 below, a code letter has been substituted for each letter of the alphabet. To find out what the sentence says, use the following
Reinforcement Cells and Life LESSON 1 Directions: In numbers 1 through 4 below, a code letter has been substituted for each letter of the alphabet. To find out what the sentence says, use the following
Friday 10 June 2016 Morning
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA F Friday 10 June 2016 Morning GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A/ADDITIONAL SCIENCE A A162/01 Modules B4 B5 B6 (Foundation Tier) *5956111840* Candidates answer on the
Oxford Cambridge and RSA F Friday 10 June 2016 Morning GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A/ADDITIONAL SCIENCE A A162/01 Modules B4 B5 B6 (Foundation Tier) *5956111840* Candidates answer on the
Page 1. Name: UNIT: GENETICS TOPIC: DNA, GENES, CHROMOSOMES AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
 Name: 2705-1 - Page 1 UNIT: GENETICS TOPIC: DNA, GENES, CHROMOSOMES AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1) Which diagram best represents the relative locations of the structures in the key below? 1) 2) 3) 4) 2) Hereditary
Name: 2705-1 - Page 1 UNIT: GENETICS TOPIC: DNA, GENES, CHROMOSOMES AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1) Which diagram best represents the relative locations of the structures in the key below? 1) 2) 3) 4) 2) Hereditary
LEARNING OUTCOMES CCEA GCSE BIOLOGY: UNIT 1: Cells, Living Processes and Biodiversity
 Name 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES CCEA GCSE BIOLOGY: 1.1.1-1.1.10 UNIT 1: Cells, Living Processes and Biodiversity 1.1.1 1.1.2 1.1.3 LEARNING OUTCOMES PUPIL SELF-EVALUATION Requires Pupils should be able to: Good
Name 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES CCEA GCSE BIOLOGY: 1.1.1-1.1.10 UNIT 1: Cells, Living Processes and Biodiversity 1.1.1 1.1.2 1.1.3 LEARNING OUTCOMES PUPIL SELF-EVALUATION Requires Pupils should be able to: Good
Friday 10 June 2016 Morning
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA H Friday 10 June 2016 Morning GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A/ADDITIONAL SCIENCE A A162/02 Modules B4 B5 B6 (Higher Tier) *5956180306* Candidates answer on the Question
Oxford Cambridge and RSA H Friday 10 June 2016 Morning GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A/ADDITIONAL SCIENCE A A162/02 Modules B4 B5 B6 (Higher Tier) *5956180306* Candidates answer on the Question
Lesson 7A Specialized Cells, Stem Cells & Cellular Differentiation
 Lesson 7A Specialized Cells, Stem Cells & Cellular Differentiation Learning Goals I can explain the concept of cell differentiation and cell specialization. I can explain how the cell structure relates
Lesson 7A Specialized Cells, Stem Cells & Cellular Differentiation Learning Goals I can explain the concept of cell differentiation and cell specialization. I can explain how the cell structure relates
1 (a) Define the term genetic engineering [2]
![1 (a) Define the term genetic engineering [2] 1 (a) Define the term genetic engineering [2]](/thumbs/80/81552601.jpg) 1 (a) Define the term genetic engineering....[2] (b) Fig. 6.1 is a flow diagram that shows how insulin can be produced using genetic engineering. R Q L M N O P Fig. 6.1 Table 6.1 shows stages in the production
1 (a) Define the term genetic engineering....[2] (b) Fig. 6.1 is a flow diagram that shows how insulin can be produced using genetic engineering. R Q L M N O P Fig. 6.1 Table 6.1 shows stages in the production
Chapter 11: Applications of Biotechnology
 Chapter 11: Applications of Biotechnology Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 11-1 Why Biotechnology Works 11-2 Biotechnology
Chapter 11: Applications of Biotechnology Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 11-1 Why Biotechnology Works 11-2 Biotechnology
Introduction to Cells
 Introduction to Cells Key terms: Cell Microscopy Nucleus Organelle Micrograph Cytoplasm Define: Cell Microscopy Cell structure Today, all of biology is based on an understanding of what is going on within
Introduction to Cells Key terms: Cell Microscopy Nucleus Organelle Micrograph Cytoplasm Define: Cell Microscopy Cell structure Today, all of biology is based on an understanding of what is going on within
M08/4/BIOLO/SPM/ENG/TZ2/XX. Biology Standard level Paper 1. Wednesday 14 May 2008 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 M08/4/BIOLO/SPM/ENG/TZ2/XX 22086016 Biology Standard level Paper 1 Wednesday 14 May 2008 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUTIONS TO ANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer
M08/4/BIOLO/SPM/ENG/TZ2/XX 22086016 Biology Standard level Paper 1 Wednesday 14 May 2008 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUTIONS TO ANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer
Answers to Practice Exams
 -- Answers to Practice Exams Practice Exam A Section 1 Question Response Mark Top Tips 1. B 1 You must be able to identify cell structures from diagrams and know their functions. Find the number of cells
-- Answers to Practice Exams Practice Exam A Section 1 Question Response Mark Top Tips 1. B 1 You must be able to identify cell structures from diagrams and know their functions. Find the number of cells
plasma membrane Golgi apparatus cytoplasm lysosome endoplasmic reticulum nucleus nucleolus ribosome mitochondrion
 Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level 1 Achievement Standard 91156 Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level BIOLOGY 2.4 Externally assessed 4 credits
Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level 1 Achievement Standard 91156 Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level BIOLOGY 2.4 Externally assessed 4 credits
GCSE (9 1) Biology B (Twenty First Century Science) J257/04 Depth in biology (Higher Tier) Sample Question Paper SPECIMEN
 GCSE (9 1) Biology B (Twenty First Century Science) J257/04 Depth in biology (Higher Tier) Sample Question Paper H Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes You may use: a scientific or graphical
GCSE (9 1) Biology B (Twenty First Century Science) J257/04 Depth in biology (Higher Tier) Sample Question Paper H Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes You may use: a scientific or graphical
13-1 Changing the Living World
 13-1 Changing the Living World In the past, variation was limited to the variations already in nature or random variations that resulted from mutations. Now, scientists can change DNA and swap genes from
13-1 Changing the Living World In the past, variation was limited to the variations already in nature or random variations that resulted from mutations. Now, scientists can change DNA and swap genes from
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 4205-1 - Page 1 1) Which statement best describes the term "theory" as used in the gene-chromosome theory? A) A theory is never revised as new scientific evidence is presented. B) A theory is a hypothesis
Name: 4205-1 - Page 1 1) Which statement best describes the term "theory" as used in the gene-chromosome theory? A) A theory is never revised as new scientific evidence is presented. B) A theory is a hypothesis
BIOTECHNOLOGY. Understanding the Application
 BELLRINGER-5/4/15 1. What method would you guess forensic scientists use to identify criminals at crime scenes? 2. What do you think we mean by the term biotechnology? BIOTECHNOLOGY Understanding the Application
BELLRINGER-5/4/15 1. What method would you guess forensic scientists use to identify criminals at crime scenes? 2. What do you think we mean by the term biotechnology? BIOTECHNOLOGY Understanding the Application
9-1 GCSE Combined Science Knowledge Organiser. Biology- paper 1
 9-1 GCSE Combined Science Knowledge Organiser Biology- paper 1 Topic 1 Cell Biology pg 16-39 Topic 2- Organisation pg 40-75 Topic 3- Infection and Response pg 76-90 Topic 4 Bioenergetics pg 91-105 GCSE
9-1 GCSE Combined Science Knowledge Organiser Biology- paper 1 Topic 1 Cell Biology pg 16-39 Topic 2- Organisation pg 40-75 Topic 3- Infection and Response pg 76-90 Topic 4 Bioenergetics pg 91-105 GCSE
NATURE OF MICROBES WORKBOOK
 NATURE OF MICROBES WORKBOOK Name: Tutor Group: 1 Microbes and Mankind 4. NATURE OF MICROBES 1. OBJECTIVES: What are microbes and are there different types? How are they seen? How can they be grown? How
NATURE OF MICROBES WORKBOOK Name: Tutor Group: 1 Microbes and Mankind 4. NATURE OF MICROBES 1. OBJECTIVES: What are microbes and are there different types? How are they seen? How can they be grown? How
3. The arrows in the diagram below indicate the movement materials into and out of a single-celled organism.
 Part A Questions 1. In 1910, Thomas Morgan discovered a certain pattern of inheritance in fruit flies known as sex linkage. This discovery extended the ideas of inheritance that Gregor Mendel had discovered
Part A Questions 1. In 1910, Thomas Morgan discovered a certain pattern of inheritance in fruit flies known as sex linkage. This discovery extended the ideas of inheritance that Gregor Mendel had discovered
15.3 Applications of Genetic Engineering
 15.3 Applications of Genetic Engineering Agriculture and Industry Almost everything we eat and much of what we wear come from living organisms. Researchers have used genetic engineering to try to improve
15.3 Applications of Genetic Engineering Agriculture and Industry Almost everything we eat and much of what we wear come from living organisms. Researchers have used genetic engineering to try to improve
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission BIOLOGY ORDINARY LEVEL
 2013. M43 Write your Examination Number here Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2013 BIOLOGY ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 11 JUNE AFTERNOON, 2.00 5.00
2013. M43 Write your Examination Number here Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2013 BIOLOGY ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 11 JUNE AFTERNOON, 2.00 5.00
S3 science Biology Rota 1
 S3 science Biology Rota 1 Cells Name During Unit 1 I will learn about: Cell structure and function Diffusion and osmosis Enzymes Uses of microbes Respiration Homework Tasks For this topic you must complete
S3 science Biology Rota 1 Cells Name During Unit 1 I will learn about: Cell structure and function Diffusion and osmosis Enzymes Uses of microbes Respiration Homework Tasks For this topic you must complete
Cells, Tissues and Organs
 Cells, Tissues and Organs You have already learned the basic function of cells, but how do these cells work together to make you the truly amazing organism that you are? Some of the key words you will
Cells, Tissues and Organs You have already learned the basic function of cells, but how do these cells work together to make you the truly amazing organism that you are? Some of the key words you will
TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A TUESDAY 17 JUNE 2008 GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION A222/02. UNIT 2 Modules B4 B5 B6 (Higher Tier)
 H GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION A222/02 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A UNIT 2 Modules B4 B5 B6 (Higher Tier) TUESDAY 17 JUNE 2008 Morning Time: 40 minutes *CUP/T44358* Candidates answer
H GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION A222/02 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A UNIT 2 Modules B4 B5 B6 (Higher Tier) TUESDAY 17 JUNE 2008 Morning Time: 40 minutes *CUP/T44358* Candidates answer
Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Here s one thing genetic engineers do: Techniques for gene cloning enable scientists to prepare multiple identical copies of gene-sized pieces of DNA. Cloning means to make copies, in this case, copies
Here s one thing genetic engineers do: Techniques for gene cloning enable scientists to prepare multiple identical copies of gene-sized pieces of DNA. Cloning means to make copies, in this case, copies
thebiotutor.com 5D Cloning Time: 54 minutes Total marks available: 54 Total marks achieved: Andy Todd
 thebiotutor.com 5D Cloning Time: 54 minutes Total marks available: 54 Total marks achieved: Q1. The photograph shows a Siberian tiger. Siberian tigers are very rare and are in danger of becoming extinct.
thebiotutor.com 5D Cloning Time: 54 minutes Total marks available: 54 Total marks achieved: Q1. The photograph shows a Siberian tiger. Siberian tigers are very rare and are in danger of becoming extinct.
GATEWAY SCIENCE B632/01 BIOLOGY B Unit 2 Modules B4 B5 B6 (Foundation Tier)
 F GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION GATEWAY SCIENCE B632/01 BIOLOGY B Unit 2 Modules B4 B5 B6 (Foundation Tier) *CUP/T70845* Candidates answer on the question paper A calculator may be used for
F GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION GATEWAY SCIENCE B632/01 BIOLOGY B Unit 2 Modules B4 B5 B6 (Foundation Tier) *CUP/T70845* Candidates answer on the question paper A calculator may be used for
INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION BIOLOGY HANDOUT SELECTIVE BREEDING, GM & CLONING CLASS 9 AND 10
 INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL 2014 2015 ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION BIOLOGY HANDOUT SELECTIVE BREEDING, GM & CLONING CLASS 9 AND 10 Name :... Date:... Selective Breeding Selective breeding
INTERNATIONAL TURKISH HOPE SCHOOL 2014 2015 ACADEMIC YEAR CHITTAGONG SENIOR SECTION BIOLOGY HANDOUT SELECTIVE BREEDING, GM & CLONING CLASS 9 AND 10 Name :... Date:... Selective Breeding Selective breeding
Enzymes. 13. Explain the active site theory to examine enzyme function
 Name: 2.2 Cell Metabolism Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 2.2.1 Metabolism 1. Define the term: metabolism. 2.2.2 Sources of energy 2. State that solar energy is source
Name: 2.2 Cell Metabolism Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 2.2.1 Metabolism 1. Define the term: metabolism. 2.2.2 Sources of energy 2. State that solar energy is source
THE BENEFITS AND USES OF MICROBES
 MODULE 4 MICROBES AND MICROBIAL BIOTECHNOLOGY U N I T 2 THE BENEFITS AND USES OF MICROBES A. MICROBIAL BIOTECHNOLOGY 1 Read What is biotechnology? and decide which of the words below can be used instead
MODULE 4 MICROBES AND MICROBIAL BIOTECHNOLOGY U N I T 2 THE BENEFITS AND USES OF MICROBES A. MICROBIAL BIOTECHNOLOGY 1 Read What is biotechnology? and decide which of the words below can be used instead
Knowledge Booklet: Paper 1 Processes
 Knowledge Booklet: Paper Processes Big Questions and Vocabulary How do substances move in and out of cells? What is cell division? How do substances move around plants? How do we defend against disease?
Knowledge Booklet: Paper Processes Big Questions and Vocabulary How do substances move in and out of cells? What is cell division? How do substances move around plants? How do we defend against disease?
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number. HIGHER TIER (Grades D-A*)
 GCSE in ADDITIONAL SCIENCE Specimen Assessment Materials 21 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE HIGHER TIER (Grades D-A*) BIOLOGY 2 Cells and metabolism, digestion and
GCSE in ADDITIONAL SCIENCE Specimen Assessment Materials 21 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE HIGHER TIER (Grades D-A*) BIOLOGY 2 Cells and metabolism, digestion and
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number UNIT 2: VARIATION, HOMEOSTASIS AND MICRO-ORGANISMS FOUNDATION TIER SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS
 GCSE BIOLOGY Sample Assessment Materials 75 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE BIOLOGY UNIT 2: VARIATION, HOMEOSTASIS AND MICRO-ORGANISMS FOUNDATION TIER SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS (1
GCSE BIOLOGY Sample Assessment Materials 75 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE BIOLOGY UNIT 2: VARIATION, HOMEOSTASIS AND MICRO-ORGANISMS FOUNDATION TIER SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS (1
Genetics review. 3. The chart below shows relationships between genes, the environment, and coloration of tomato plants.
 Name: Date: 1. When the bacterium Serratia marcescens is grown on a sterile culture medium in a petri dish at 30, the bacterial colonies are cream colored. When this same bacterium is cultured under identical
Name: Date: 1. When the bacterium Serratia marcescens is grown on a sterile culture medium in a petri dish at 30, the bacterial colonies are cream colored. When this same bacterium is cultured under identical
Cell Biology. Sub-Topic (1.5) Genetic Engineering. On completion of this subtopic I will be able to state that
 Cell Biology Sub-Topic (1.5) Genetic Engineering On completion of this subtopic I will be able to state that Genetic information can be transferred from one cell to another by genetic engineering. Bacteria
Cell Biology Sub-Topic (1.5) Genetic Engineering On completion of this subtopic I will be able to state that Genetic information can be transferred from one cell to another by genetic engineering. Bacteria
4. Base your answer to the following question on A product of genetic engineering technology is represented below.
 name 1. When humans first domesticated dogs, there was relatively little diversity in the species. Today, there are many variations such as the German shepherd and the dalmatian. This increase in diversity
name 1. When humans first domesticated dogs, there was relatively little diversity in the species. Today, there are many variations such as the German shepherd and the dalmatian. This increase in diversity
Frequency of Keyword Totals - (All LE Regents Exams)
 Frequency of Keyword Totals - (All LE Regents Exams) KEYWORD COUNT KEYWORD COUNT ecosystem 58 DNA 48 energy pyramid 19 graph 19 scientific method 19 photosynthesis 43 decomposer 18 human impact 42 clone
Frequency of Keyword Totals - (All LE Regents Exams) KEYWORD COUNT KEYWORD COUNT ecosystem 58 DNA 48 energy pyramid 19 graph 19 scientific method 19 photosynthesis 43 decomposer 18 human impact 42 clone
AS Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level. DNA Replication
 AS 91156 Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level. DNA Replication (2017:3) Mitosis The table below shows how mitosis occurs at different rates in different types of human cells.
AS 91156 Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level. DNA Replication (2017:3) Mitosis The table below shows how mitosis occurs at different rates in different types of human cells.
Introduction to Cells
 Introduction to Cells Key terms: Cell Microscopy Nucleus Organelle Micrograph Cytoplasm Define: Cell Microscopy Cell structure Today, all of biology is based on an understanding of what is going on within
Introduction to Cells Key terms: Cell Microscopy Nucleus Organelle Micrograph Cytoplasm Define: Cell Microscopy Cell structure Today, all of biology is based on an understanding of what is going on within
SPECIMEN. day June 20XX Morning/Afternoon MAXIMUM MARK 95 DRAFT PMT
 F day June 20XX Morning/Afternoon GCSE (9 1) Combined Science B (Twenty First Century Science) J260/01 Biology (Foundation tier) SAMPLE MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK 95 DRAFT Duration: 1 hour 45 minutes This
F day June 20XX Morning/Afternoon GCSE (9 1) Combined Science B (Twenty First Century Science) J260/01 Biology (Foundation tier) SAMPLE MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK 95 DRAFT Duration: 1 hour 45 minutes This
Perth Academy N5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Homework Booklet
 Perth Academy N5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Homework Booklet 1 HOMEWORK 1 1. (a) Multicellular organisms are composed of different types of cells which are specialised. Describe what this means and
Perth Academy N5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Homework Booklet 1 HOMEWORK 1 1. (a) Multicellular organisms are composed of different types of cells which are specialised. Describe what this means and
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 17 November 2010 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4325/1F London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 17 November 2010 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination
QUESTIONSHEET 1. The diagram shows a method of screening fungi for the production of an antibiotic. fungus A fungus B fungus C [2] ...
![QUESTIONSHEET 1. The diagram shows a method of screening fungi for the production of an antibiotic. fungus A fungus B fungus C [2] ... QUESTIONSHEET 1. The diagram shows a method of screening fungi for the production of an antibiotic. fungus A fungus B fungus C [2] ...](/thumbs/77/75444315.jpg) QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows a method of screening fungi for the production of an antibiotic. test fungus petri dish containing nutrient agar 1 2 3 4 5 6 streaks of different test bacteria The diagrams
QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows a method of screening fungi for the production of an antibiotic. test fungus petri dish containing nutrient agar 1 2 3 4 5 6 streaks of different test bacteria The diagrams
Unit 8.3: Biotechnology
 Unit 8.3: Biotechnology Lesson Objectives Describe gene cloning and the polymerase chain reaction. Explain how DNA technology is applied in medicine and agriculture. Identify some of the ethical, legal,
Unit 8.3: Biotechnology Lesson Objectives Describe gene cloning and the polymerase chain reaction. Explain how DNA technology is applied in medicine and agriculture. Identify some of the ethical, legal,
Protein shape and function is determined by the sequence of amino acids that make up the protein. Amino acids are held together by peptide bonds to
 Protein shape and function is determined by the sequence of amino acids that make up the protein. Amino acids are held together by peptide bonds to form peptides. Peptides are held together by hydrogen
Protein shape and function is determined by the sequence of amino acids that make up the protein. Amino acids are held together by peptide bonds to form peptides. Peptides are held together by hydrogen
What s s the Deal With DNA? Forensic Science
 What s s the Deal With DNA? Forensic Science Introduction The same stuff that makes your eyes green or your hair curly can pinpoint you as the perpetrator of a crime. DNA determines much of who you are
What s s the Deal With DNA? Forensic Science Introduction The same stuff that makes your eyes green or your hair curly can pinpoint you as the perpetrator of a crime. DNA determines much of who you are
2.2.3 Syllabus Objectives
 Enzymes 2.2.3 Syllabus Objectives Define the term: enzymes State the nature, folded shape & functions of enzymes. Explain the role of enzymes in plants and animals including role in metabolism Explain
Enzymes 2.2.3 Syllabus Objectives Define the term: enzymes State the nature, folded shape & functions of enzymes. Explain the role of enzymes in plants and animals including role in metabolism Explain
Higher Biology. Unit 2: Homework Booklet Metabolism and Survival
 Higher Biology Unit 2: Homework Booklet Metabolism and Survival 0 1 Sub Topic 2.1: Regulation of Metabolism 1. Membranes can form small compartments within cells. Small compartments have: A high surface
Higher Biology Unit 2: Homework Booklet Metabolism and Survival 0 1 Sub Topic 2.1: Regulation of Metabolism 1. Membranes can form small compartments within cells. Small compartments have: A high surface
BIOTECHNOLOGY. Understanding the Application
 BIOTECHNOLOGY Understanding the Application GENETIC ENGINEERING Genetic engineering refers to any process in which man alters an organism s DNA Examples: cloning, genetically modified organisms (GMO),
BIOTECHNOLOGY Understanding the Application GENETIC ENGINEERING Genetic engineering refers to any process in which man alters an organism s DNA Examples: cloning, genetically modified organisms (GMO),
REVIEW. What Do You Remember? UNIT
 UNIT B REVIEW The following icons indicate the Achievement Chart category addressed by each question. K/U Knowledge/Understanding T/I Thinking/Investigation C Communication A Application What Do You Remember?
UNIT B REVIEW The following icons indicate the Achievement Chart category addressed by each question. K/U Knowledge/Understanding T/I Thinking/Investigation C Communication A Application What Do You Remember?
