SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Ralf Stafford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Structure and mechanism of a canonical poly(adp-ribose) glycohydrolase Mark S. Dunstan 1$, Eva Barkauskaite 2$, Pierre Lafite 3, Claire E. Knezevic 4, Amy Brassington 1, Marijan Ahel 5, Paul J. Hergenrother 4, David Leys 1 *, Ivan Ahel 2 * $ Equal contribution *Corresponding authors 1 Manchester Interdisciplinary Biocentre, Princess Street 131, M1 7DN, Manchester, UK 2 Cancer Research UK, Paterson Institute for Cancer Research, University of Manchester, Wilmslow Road, Manchester M20 4BX, UK 3 ICOA UMR CNRS 7311 Université d Orléans Rue de Chartres, F Orléans, France 4 University of Illinois, Department of Chemistry, Box 36-5, 261 Roger Adams Lab, 600 S. Mathews, Urbana, IL 61801, USA 5 Rudjer Boskovic Institute, Bijenicka 54, HR Zagreb, Croatia
2 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1 Structure-based sequence alignment of bactparg, the canonical TTPARG and the catalytic domain of human PARG. Mutations used in this study are boxed in green and starred. Residues, which completely or partially abolish TTPARG activity, are highlighted with a blue star. Residues conserved between all three proteins are in solid red boxes. Whereas, residues conserved only between TTPARG and hparg are in open red boxes. Arrows indicate N- terminal TTPARG truncations, Δ1-67 and Δ1-115, and corresponding N-terminal human PARG truncations, Δ1-569 and Δ1-619.
3 Protein Ligand Kd (nm) N Delta H (kcal/mol) Delta S (cal/mol K) WT ADP-Ribose 200 ± ± ± Supplementary Figure S2 Isothermal titration calorimetry with wild-type TTPARG. Top panel: raw ITC data illustrating TTPARG interaction with ADP-ribose at 298 K in 25 mm Tris ph 7.5. Bottom panel: integrated heat peaks fitted to a single binding site model (solid red line).
4 Supplementary Figure S3 Stereoview of the PARG catalytic loop (residues ) region. Atom coloured sticks with sigmaa weighted 2FoFc density are contoured at 1 sigma.
5 Supplementary Figure S4 The human PARG mutant protein lacking the RS/MTS motif and a large part of the N-terminal domain ( 1-619) retains significant PAR hydrolysis activity in vitro. Amounts of the wild type and mutant proteins in the assay were 1 pmol and 8 pmols respectively (right panel). Bottom panel represents the quantification graph. A unit of automodified PARP1 is described in materials and methods. Error bars represent s.d. (n=3). Purified PARG proteins are shown on the left.
6 Supplementary Figure S5 Purification of PARG proteins. Wild-type and mutant human and TTPARGs were purified as His6-tagged proteins by affinity chromatography.
7 Y296 E115/E256 W260/F398 E114/E255 S98/N240 F227/F371 Supplementary Figure S6 Comparison of TTPARG and bactparg active sites. The bactparg ADP-ribose complex structure is depicted in grey, with the TTPARG complex coloured as Figure 2 of the main text. Labels are given for the bactparg (black) and TTPARG (blue) structure. While several TTPARG residues have bactparg analogues, the TTPARG Y296 is located on a loop that has no structural counterpart in bactparg.
8 Supplementary Figure S7 IC50 curve of the inhibitor RBPI-3 against T. thermophila PARG (n=3). Error bars indicate standard deviation, representative TLC plate is shown at the bottom.
9 Supplementary Figure S8 Analysis of the reaction products of Tetrahymena thermophila PARG by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) coupled to time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOFMS). Extracted ion chromatograms using accurate mass of deprotonated ADP-ribose ( Da) in the samples resulting from the reaction by PARG on the poly(adp-ribosyl)ated PARP1 substrate (red) and the ADP-ribose standard solution of 0.6 ng/μl (black). The inserted figure shows mass spectrum of ADP-ribose peak. Oligomers of ADPribose with up to 5 ADP-ribose units, NAD, ADP, or AMP were not detected.
10 Supplementary Figure S9 Thermal shift analysis of ADP-ribose binding by TTPARG. All mutants that were designed to alter the proposed PAR n+1 ADPribose binding site retain ADP-ribose binding as indicated by a significant shift in thermal stability upon incubation with ADP-ribose.
Structure and mechanism of a canonical poly(adp-ribose) glycohydrolase
 Received 3 Feb 2012 Accepted 4 May 2012 Published 6 Jun 2012 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms1889 Structure and mechanism of a canonical poly(adp-ribose) glycohydrolase Mark S. Dunstan 1, *, Eva Barkauskaite 2, *,
Received 3 Feb 2012 Accepted 4 May 2012 Published 6 Jun 2012 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms1889 Structure and mechanism of a canonical poly(adp-ribose) glycohydrolase Mark S. Dunstan 1, *, Eva Barkauskaite 2, *,
HEK293T. Fig. 1 in the
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Zinc uptake assay of hzip4 and hzip4-δecd transiently expressed in HEK293T cells. The results of one representative e experiment are shown in Fig. 1 in
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Zinc uptake assay of hzip4 and hzip4-δecd transiently expressed in HEK293T cells. The results of one representative e experiment are shown in Fig. 1 in
Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than. SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with
 Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with concentration of 800nM) were incubated with 1mM dgtp for the indicated
Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with concentration of 800nM) were incubated with 1mM dgtp for the indicated
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) and Mycobacterium smegmatis (Msmeg) contain two ε (dnaq) exonuclease homologs.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) and Mycobacterium smegmatis (Msmeg) contain two ε (dnaq) exonuclease homologs. (a) Sequence alignment of the ε-exonuclease homologs from four different
Supplementary Figure 1 Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) and Mycobacterium smegmatis (Msmeg) contain two ε (dnaq) exonuclease homologs. (a) Sequence alignment of the ε-exonuclease homologs from four different
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or
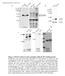 Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
Supplementatry Fig 1. Domain structure, biophysical characterisation and electron microscopy of a TD. (a) XTACC3/Maskin and XMAP215/chTOG domain
 Supplementatry Fig 1. Domain structure, biophysical characterisation and electron microscopy of a TD. (a) XTACC3/Maskin and XMAP215/chTOG domain architecture. Various C-terminal fragments were cloned and
Supplementatry Fig 1. Domain structure, biophysical characterisation and electron microscopy of a TD. (a) XTACC3/Maskin and XMAP215/chTOG domain architecture. Various C-terminal fragments were cloned and
Supplementary Figure 1 PZA inhibits root hair formation as well as cell elongation in the maturation zone of eto1-2 roots. (A) The PI staining of the
 Supplementary Figure 1 PZA inhibits root hair formation as well as cell elongation in the maturation zone of eto1-2 roots. (A) The PI staining of the roots of three-day-old etiolated seedlings of Col-0
Supplementary Figure 1 PZA inhibits root hair formation as well as cell elongation in the maturation zone of eto1-2 roots. (A) The PI staining of the roots of three-day-old etiolated seedlings of Col-0
human Cdc45 Figure 1c. (c)
 1 Details of the refined crystallographic model of human Cdc45 and comparison of its active-site region with that of bacterial RecJ. (a) Stereo view of a representative example of the final 2F o -F c electron
1 Details of the refined crystallographic model of human Cdc45 and comparison of its active-site region with that of bacterial RecJ. (a) Stereo view of a representative example of the final 2F o -F c electron
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2548
 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure of GltPhout. (a) Stereo view of a slice through a single GltPhout protomer shown in stick representation along with 2Fo-Fc and anomalous difference electron maps. The
Supplementary Figure 1. Structure of GltPhout. (a) Stereo view of a slice through a single GltPhout protomer shown in stick representation along with 2Fo-Fc and anomalous difference electron maps. The
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures 1-8
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figures 1-8 Supplementary Figure 1. TFAM residues contacting the DNA minor groove (A) TFAM contacts on nonspecific DNA. Leu58, Ile81, Asn163, Pro178, and Leu182
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figures 1-8 Supplementary Figure 1. TFAM residues contacting the DNA minor groove (A) TFAM contacts on nonspecific DNA. Leu58, Ile81, Asn163, Pro178, and Leu182
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
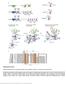 Supplementary Figure 1 Domain architecture and conformational states of the decapping complex, as revealed by structural studies. (a) Domain organization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp) and Saccharomyces
Supplementary Figure 1 Domain architecture and conformational states of the decapping complex, as revealed by structural studies. (a) Domain organization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp) and Saccharomyces
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/4/167/ra20/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Poly(ADP-Ribose) (PAR) Binding to Apoptosis-Inducing Factor Is Critical for PAR Polymerase-1 Dependent Cell Death (Parthanatos)
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/4/167/ra20/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Poly(ADP-Ribose) (PAR) Binding to Apoptosis-Inducing Factor Is Critical for PAR Polymerase-1 Dependent Cell Death (Parthanatos)
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL BIOCHEMICAL AND STRUCTURAL STUDIES ON THE M. TUBERCULOSIS O 6 -METHYLGUANINE METHYLTRANSFERASE AND MUTATED VARIANTS
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL BIOCHEMICAL AND STRUCTURAL STUDIES ON THE M. TUBERCULOSIS O 6 -METHYLGUANINE METHYLTRANSFERASE AND MUTATED VARIANTS Riccardo Miggiano 1, Valentina Casazza 1, Silvia Garavaglia 1,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL BIOCHEMICAL AND STRUCTURAL STUDIES ON THE M. TUBERCULOSIS O 6 -METHYLGUANINE METHYLTRANSFERASE AND MUTATED VARIANTS Riccardo Miggiano 1, Valentina Casazza 1, Silvia Garavaglia 1,
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3494
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Visualization of codon-dependent conformational rearrangements during translation termination
 Supplementary information for: Visualization of codon-dependent conformational rearrangements during translation termination Shan L. He 1 and Rachel Green 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department
Supplementary information for: Visualization of codon-dependent conformational rearrangements during translation termination Shan L. He 1 and Rachel Green 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department
Supplementary Table 1: List of CH3 domain interface residues in the first chain (A) and
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: List of CH3 domain interface residues in the first chain (A) and their side chain contacting residues in the second chain (B) a Interface Res. in Contacting
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: List of CH3 domain interface residues in the first chain (A) and their side chain contacting residues in the second chain (B) a Interface Res. in Contacting
Supplemental Figure 1. HepG2 cells were transfected with GLI luciferase reporter construct
 Supplemental Figure 1. HepG2 cells were transfected with GLI luciferase reporter construct (pgl38xgli), EWS-FLI1 luciferase reporter construct (NROB1-Luc) with or without GLI1, EWS- FLI1 and cdnas respectively.
Supplemental Figure 1. HepG2 cells were transfected with GLI luciferase reporter construct (pgl38xgli), EWS-FLI1 luciferase reporter construct (NROB1-Luc) with or without GLI1, EWS- FLI1 and cdnas respectively.
Supplementary Figure 1. α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.
 Supplementary Figure 1 α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. (a) Specificity of anti-n103 antibody. Anti-N103 antibody was coated on an ELISA plate and different concentrations of full-length
Supplementary Figure 1 α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. (a) Specificity of anti-n103 antibody. Anti-N103 antibody was coated on an ELISA plate and different concentrations of full-length
Supplementary Online Material. Structural mimicry in transcription regulation of human RNA polymerase II by the. DNA helicase RECQL5
 Supplementary Online Material Structural mimicry in transcription regulation of human RNA polymerase II by the DNA helicase RECQL5 Susanne A. Kassube, Martin Jinek, Jie Fang, Susan Tsutakawa and Eva Nogales
Supplementary Online Material Structural mimicry in transcription regulation of human RNA polymerase II by the DNA helicase RECQL5 Susanne A. Kassube, Martin Jinek, Jie Fang, Susan Tsutakawa and Eva Nogales
HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit. HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit
 Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit 96 Tests HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit Cat# 4690-096-K Cat# 4690-096-K Table
Instructions For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit 96 Tests HT F Homogeneous PARP Inhibition Assay Kit Cat# 4690-096-K Cat# 4690-096-K Table
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. The nucleotide binding dynamics of MSH2/MSH3 are lesion-dependent.
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The nucleotide binding dynamics of /MSH are lesion-dependent. Barbara A. L. Owen, Walter H. Lang, and Cynthia T. McMurray* mau 1 8 6 4 2 mau 8 6 4 2 mau 8 6 4 2 mau 8 7 6 5 4
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The nucleotide binding dynamics of /MSH are lesion-dependent. Barbara A. L. Owen, Walter H. Lang, and Cynthia T. McMurray* mau 1 8 6 4 2 mau 8 6 4 2 mau 8 6 4 2 mau 8 7 6 5 4
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Multiple sequence alignments of four Swi2/Snf2 subfamily proteins, ScChd1, SsoRad54 and the RNA helicase Vasa. The sequence alignments of the Swi2/Snf2 subfamily proteins, ScChd1
Supplementary Figure 1 Multiple sequence alignments of four Swi2/Snf2 subfamily proteins, ScChd1, SsoRad54 and the RNA helicase Vasa. The sequence alignments of the Swi2/Snf2 subfamily proteins, ScChd1
Supplementary Information. Small Molecule-Induced Domain Swapping as a Mechanism for Controlling Protein Function and Assembly
 Supplementary Information Small Molecule-Induced Domain Swapping as a Mechanism for Controlling Protein Function and Assembly Joshua M. Karchin, Jeung-Hoi Ha, Kevin E. Namitz, Michael S. Cosgrove, and
Supplementary Information Small Molecule-Induced Domain Swapping as a Mechanism for Controlling Protein Function and Assembly Joshua M. Karchin, Jeung-Hoi Ha, Kevin E. Namitz, Michael S. Cosgrove, and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS. Figure S1: Homology alignment of DDR2 amino acid sequence. Shown are
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1: Homology alignment of DDR2 amino acid sequence. Shown are the amino acid sequences of human DDR2, mouse DDR2 and the closest homologs in zebrafish and C. Elegans.
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1: Homology alignment of DDR2 amino acid sequence. Shown are the amino acid sequences of human DDR2, mouse DDR2 and the closest homologs in zebrafish and C. Elegans.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1. Crystallographic statistics CRM1-SNUPN complex Space group P6 4 22 a=b=250.4, c=190.4 Data collection statistics: CRM1-selenomethionine SNUPN MAD data Peak Inflection Remote Native
Supplementary Table 1. Crystallographic statistics CRM1-SNUPN complex Space group P6 4 22 a=b=250.4, c=190.4 Data collection statistics: CRM1-selenomethionine SNUPN MAD data Peak Inflection Remote Native
Supplementary Information: Chemical proteomics reveals ADP-ribosylation of small GTPases during oxidative stress
 Supplementary Information: Chemical proteomics reveals ADP-ribosylation of small GTPases during oxidative stress Nathan P. Westcott 1, Joseph P. Fernandez 2, Henrik Molina 2 and Howard C. Hang 1,* 1 Laboratory
Supplementary Information: Chemical proteomics reveals ADP-ribosylation of small GTPases during oxidative stress Nathan P. Westcott 1, Joseph P. Fernandez 2, Henrik Molina 2 and Howard C. Hang 1,* 1 Laboratory
15 June 2011 Supplementary material Bagriantsev et al.
 Supplementary Figure S1 Characterization of K 2P 2.1 (TREK-1) GOF mutants A, Distribution of the positions of mutated nucleotides, represented by a red x, from a pool of 18 unselected K 2P 2.1 (KCNK2)
Supplementary Figure S1 Characterization of K 2P 2.1 (TREK-1) GOF mutants A, Distribution of the positions of mutated nucleotides, represented by a red x, from a pool of 18 unselected K 2P 2.1 (KCNK2)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1: Suv39h1, but not Suv39h2, promotes HP1α sumoylation in vivo. In vivo HP1α sumoylation assay. Top: experimental scheme. Middle: we
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1: Suv39h1, but not Suv39h2, promotes HP1α sumoylation in vivo. In vivo HP1α sumoylation assay. Top: experimental scheme. Middle: we
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
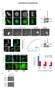 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1: Function of MICAL1 and dmical in cytokinesis (a) HeLa transfected with GFP- MICAL1 (green) were stained with Aurora B (red). Scale bars, 10 µm. (b) Western
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1: Function of MICAL1 and dmical in cytokinesis (a) HeLa transfected with GFP- MICAL1 (green) were stained with Aurora B (red). Scale bars, 10 µm. (b) Western
The molecular basis of lysine 48 ubiquitin chain synthesis by Ube2K
 Supplementary Information The molecular basis of lysine 48 ubiquitin chain synthesis by Adam J. Middleton, Catherine L. Day* Department of Biochemistry, Otago School of Medical Sciences, University of
Supplementary Information The molecular basis of lysine 48 ubiquitin chain synthesis by Adam J. Middleton, Catherine L. Day* Department of Biochemistry, Otago School of Medical Sciences, University of
Supporting information. Single-cell and subcellular pharmacokinetic imaging allows insight into drug action in vivo
 Supporting information Single-cell and subcellular pharmacokinetic imaging allows insight into drug action in vivo Greg Thurber 1, Katy Yang 1, Thomas Reiner 1, Rainer Kohler 1, Peter Sorger 2, Tim Mitchison
Supporting information Single-cell and subcellular pharmacokinetic imaging allows insight into drug action in vivo Greg Thurber 1, Katy Yang 1, Thomas Reiner 1, Rainer Kohler 1, Peter Sorger 2, Tim Mitchison
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany RNA ligands that distinguish metabolite-induced conformations in the TPP riboswitch Günter Mayer, Marie-Sophie L. Raddatz, Julia D. Grunwald,
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany RNA ligands that distinguish metabolite-induced conformations in the TPP riboswitch Günter Mayer, Marie-Sophie L. Raddatz, Julia D. Grunwald,
Supplementary Table 1. DNA sequence synthesized to express the Zika virus NS5 protein.
 Supplementary Table 1. DNA sequence synthesized to express the Zika virus NS5 protein. MR766 NS5 sequence 1 ACAGAGAACAGATTGGTGGTGGAGGTGGGACGGGAGAGACTCTGGGAGAGAAGTGGAAAG 61 CTCGTCTGAATCAGATGTCGGCCCTGGAGTTCTACTCTTATAAAAAGTCAGGTATCACTG
Supplementary Table 1. DNA sequence synthesized to express the Zika virus NS5 protein. MR766 NS5 sequence 1 ACAGAGAACAGATTGGTGGTGGAGGTGGGACGGGAGAGACTCTGGGAGAGAAGTGGAAAG 61 CTCGTCTGAATCAGATGTCGGCCCTGGAGTTCTACTCTTATAAAAAGTCAGGTATCACTG
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3428
 Supplementary Figure 1 Biochemical characterization of the monou and oligou activity switch of TUT4(7). (a) Mouse TUT4 and human TUT7 were assayed for monou and Lin28-dependent oligou addition activities
Supplementary Figure 1 Biochemical characterization of the monou and oligou activity switch of TUT4(7). (a) Mouse TUT4 and human TUT7 were assayed for monou and Lin28-dependent oligou addition activities
Supplementary Figure S1 Purification of deubiquitinases HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated DUB-expressing plasmids.
 Supplementary Figure S1 Purification of deubiquitinases HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated DUB-expressing plasmids. The cells were harvested 72 h after transfection. FLAG-tagged deubiquitinases
Supplementary Figure S1 Purification of deubiquitinases HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated DUB-expressing plasmids. The cells were harvested 72 h after transfection. FLAG-tagged deubiquitinases
Supplementary Results Supplementary Table 1. P1 and P2 enrichment scores for wild-type subtiligase.
 Supplementary Results Supplementary Table 1. P1 and P2 enrichment scores for wild-type subtiligase. Supplementary Table 2. Masses of subtiligase mutants measured by LC-MS. Supplementary Table 2 (cont d).
Supplementary Results Supplementary Table 1. P1 and P2 enrichment scores for wild-type subtiligase. Supplementary Table 2. Masses of subtiligase mutants measured by LC-MS. Supplementary Table 2 (cont d).
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Results Construct purification and coupling. Two A1-GP1bα ReaLiSM constructs, with and without cysteine residues near the N and C-termini (Fig. S2a), were expressed and purified by Ni affinity chromatography
Results Construct purification and coupling. Two A1-GP1bα ReaLiSM constructs, with and without cysteine residues near the N and C-termini (Fig. S2a), were expressed and purified by Ni affinity chromatography
Oligonucleotides were purchased from Eurogentec, purified by denaturing gel electrophoresis
 SUPPLEMENRY INFORMION Purification of probes and Oligonucleotides sequence Oligonucleotides were purchased from Eurogentec, purified by denaturing gel electrophoresis and recovered by electroelution. Labelling
SUPPLEMENRY INFORMION Purification of probes and Oligonucleotides sequence Oligonucleotides were purchased from Eurogentec, purified by denaturing gel electrophoresis and recovered by electroelution. Labelling
DNA supercoiling, a critical signal regulating the basal expression of the lac operon in Escherichia coli
 Supplementary Information DNA supercoiling, a critical signal regulating the basal expression of the lac operon in Escherichia coli Geraldine Fulcrand 1,2, Samantha Dages 1,2, Xiaoduo Zhi 1,2, Prem Chapagain
Supplementary Information DNA supercoiling, a critical signal regulating the basal expression of the lac operon in Escherichia coli Geraldine Fulcrand 1,2, Samantha Dages 1,2, Xiaoduo Zhi 1,2, Prem Chapagain
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
SPHK1 Assay Kit. Catalog Number KA assays Version: 05. Intended for research use only.
 SPHK1 Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0906 400 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials Supplied...
SPHK1 Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0906 400 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials Supplied...
The structure and catalytic mechanism of a poly(adp-ribose) glycohydrolase
 Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nature. ; 477(7366): 616 620. doi:10.1038/nature10404. The structure and catalytic mechanism of a poly(adp-ribose) glycohydrolase
Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nature. ; 477(7366): 616 620. doi:10.1038/nature10404. The structure and catalytic mechanism of a poly(adp-ribose) glycohydrolase
Supplementary Note 1. Enzymatic properties of the purified Syn BVR
 Supplementary Note 1. Enzymatic properties of the purified Syn BVR The expression vector pet15b-syn bvr allowed us to routinely prepare 15 mg of electrophoretically homogenous Syn BVR from 2.5 L of TB-medium
Supplementary Note 1. Enzymatic properties of the purified Syn BVR The expression vector pet15b-syn bvr allowed us to routinely prepare 15 mg of electrophoretically homogenous Syn BVR from 2.5 L of TB-medium
Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 41
 Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 41 Molecular Mechanisms for the RNA-Dependent ATPase Activity of Upf1 and Its Regulation by Upf2 Sutapa Chakrabarti, Uma Jayachandran, Fabien Bonneau, Francesca
Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 41 Molecular Mechanisms for the RNA-Dependent ATPase Activity of Upf1 and Its Regulation by Upf2 Sutapa Chakrabarti, Uma Jayachandran, Fabien Bonneau, Francesca
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table.
 Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
1 24 C63 C β- β-
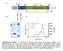 M40 Signal leaved RS1 Domain 59 110 142 Discoidin Domain 223 1 24 63 219 224 + - β- β- M M e e O O H H His 6 -Tag 250 150 100 75 50 37 * 25 20 Supplementary Figure 1 Purification of wild-type retinoschisin.
M40 Signal leaved RS1 Domain 59 110 142 Discoidin Domain 223 1 24 63 219 224 + - β- β- M M e e O O H H His 6 -Tag 250 150 100 75 50 37 * 25 20 Supplementary Figure 1 Purification of wild-type retinoschisin.
Conformation of the Mineralocorticoid Receptor N- terminal Domain: Evidence for Induced and Stable Structure
 ME-10-0005 Conformation of the Mineralocorticoid Receptor N- terminal Domain: Evidence for Induced and Stable Structure Katharina Fischer 1, Sharon M. Kelly 2, Kate Watt 1, Nicholas C. Price 2 and Iain
ME-10-0005 Conformation of the Mineralocorticoid Receptor N- terminal Domain: Evidence for Induced and Stable Structure Katharina Fischer 1, Sharon M. Kelly 2, Kate Watt 1, Nicholas C. Price 2 and Iain
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chan et al. 10.1073/pnas.0903849106 SI Text Protein Purification. PCSK9 proteins were expressed either transiently in 2936E cells (1), or stably in HepG2 cells. Conditioned culture
Supporting Information Chan et al. 10.1073/pnas.0903849106 SI Text Protein Purification. PCSK9 proteins were expressed either transiently in 2936E cells (1), or stably in HepG2 cells. Conditioned culture
Family-wide analysis of poly(adp-ribose) polymerase activity
 Family-wide analysis of poly(adp-ribose) polymerase activity The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published
Family-wide analysis of poly(adp-ribose) polymerase activity The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 AS-NMD modulates FLM-dependent thermosensory flowering response in Arabidopsis NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Genomic sequence of FLM along with the splice sites. Sequencing
AS-NMD modulates FLM-dependent thermosensory flowering response in Arabidopsis NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Genomic sequence of FLM along with the splice sites. Sequencing
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3018
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of genetic complementation assay in Bmal1 / Per2 Luc fibroblasts. (a) Only Bmal1, not Bmal2, rescues circadian rhythms from cells. Cells expressing various Bmal constructs
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of genetic complementation assay in Bmal1 / Per2 Luc fibroblasts. (a) Only Bmal1, not Bmal2, rescues circadian rhythms from cells. Cells expressing various Bmal constructs
BurrH: a new modular DNA binding protein for genome engineering
 Supplementary information for: BurrH: a new modular protein for genome engineering Alexandre Juillerat, Claudia Bertonati, Gwendoline Dubois, Valérie Guyot, Séverine Thomas, Julien Valton, Marine Beurdeley,
Supplementary information for: BurrH: a new modular protein for genome engineering Alexandre Juillerat, Claudia Bertonati, Gwendoline Dubois, Valérie Guyot, Séverine Thomas, Julien Valton, Marine Beurdeley,
5.36 Biochemistry Laboratory Spring 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.36 Biochemistry Laboratory Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Laboratory Manual for URIECA
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.36 Biochemistry Laboratory Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Laboratory Manual for URIECA
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Peroxiredoxin-2 and STAT3 form a redox relay for H 2 O 2 signaling Mirko C. Sobotta 1, Willy Liou 1, Sarah Stöcker 1, Deepti Talwar 1, Michael Oehler 1, Thomas Ruppert 2, Annette
Supplementary Information Peroxiredoxin-2 and STAT3 form a redox relay for H 2 O 2 signaling Mirko C. Sobotta 1, Willy Liou 1, Sarah Stöcker 1, Deepti Talwar 1, Michael Oehler 1, Thomas Ruppert 2, Annette
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Design and Characterization of Bivalent BET Inhibitors
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Design and Characterization of Bivalent BET Inhibitors Minoru Tanaka 1,2,#, Justin M. Roberts 1,#, Hyuk-Soo Seo 3, Amanda Souza 1, Joshiawa Paulk 1, Thomas G. Scott 1, Stephen
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Design and Characterization of Bivalent BET Inhibitors Minoru Tanaka 1,2,#, Justin M. Roberts 1,#, Hyuk-Soo Seo 3, Amanda Souza 1, Joshiawa Paulk 1, Thomas G. Scott 1, Stephen
A quantitative investigation of linker histone interactions with nucleosomes and chromatin
 White et al Supplementary figures and figure legends A quantitative investigation of linker histone interactions with nucleosomes and chromatin 1 Alison E. White, Aaron R. Hieb, and 1 Karolin Luger 1 White
White et al Supplementary figures and figure legends A quantitative investigation of linker histone interactions with nucleosomes and chromatin 1 Alison E. White, Aaron R. Hieb, and 1 Karolin Luger 1 White
Supplementary Figure 1 Structural modeling and purification of V. cholerae ABH. (a) The migration of the purified rabh and catalytically inactive
 Supplementary Figure 1 Structural modeling and purification of V. cholerae ABH. (a) The migration of the purified rabh and catalytically inactive variants rabhs, rabhd, and rabhh are shown on 12% SDS-PAGE
Supplementary Figure 1 Structural modeling and purification of V. cholerae ABH. (a) The migration of the purified rabh and catalytically inactive variants rabhs, rabhd, and rabhh are shown on 12% SDS-PAGE
Second Generation PARP1 Pharmacodynamic Assay
 Second Generation PARP1 Pharmacodynamic Assay 1 What is a Pharmacodynamic Assay? Pharmacodynamic Assays: Provide evidence of drug action on molecular target. Guide drug development process. Base line values
Second Generation PARP1 Pharmacodynamic Assay 1 What is a Pharmacodynamic Assay? Pharmacodynamic Assays: Provide evidence of drug action on molecular target. Guide drug development process. Base line values
Kinetics Review. Tonight at 7 PM Phys 204 We will do two problems on the board (additional ones than in the problem sets)
 Quiz 1 Kinetics Review Tonight at 7 PM Phys 204 We will do two problems on the board (additional ones than in the problem sets) I will post the problems with solutions on Toolkit for those that can t make
Quiz 1 Kinetics Review Tonight at 7 PM Phys 204 We will do two problems on the board (additional ones than in the problem sets) I will post the problems with solutions on Toolkit for those that can t make
Molecular basis for H3K36me3 recognition by the Tudor domain of PHF1
 Supplementary information Molecular basis for H3K36me3 recognition by the Tudor domain of PHF1 Catherine A. Musselman 1, Nikita Avvakumov 2, Reiko Watanabe 3, Christopher G. Abraham 4, Marie-Eve Lalonde
Supplementary information Molecular basis for H3K36me3 recognition by the Tudor domain of PHF1 Catherine A. Musselman 1, Nikita Avvakumov 2, Reiko Watanabe 3, Christopher G. Abraham 4, Marie-Eve Lalonde
Supplementary Figure 1. Electron microscopy of gb-698glyco/1g2 Fab complex. a)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Electron microscopy of gb-698glyco/1g2 Fab complex. a) Representative images of 2D class averages of gb-698glyc bound to 1G2 Fab. Top views of the complex were underrepresented
Supplementary Figure 1. Electron microscopy of gb-698glyco/1g2 Fab complex. a) Representative images of 2D class averages of gb-698glyc bound to 1G2 Fab. Top views of the complex were underrepresented
Coleman et al., Supplementary Figure 1
 Coleman et al., Supplementary Figure 1 BrdU Merge G1 Early S Mid S Supplementary Figure 1. Sequential destruction of CRL4 Cdt2 targets during the G1/S transition. HCT116 cells were synchronized by sequential
Coleman et al., Supplementary Figure 1 BrdU Merge G1 Early S Mid S Supplementary Figure 1. Sequential destruction of CRL4 Cdt2 targets during the G1/S transition. HCT116 cells were synchronized by sequential
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Synthetic annealed poly(ra):poly(dt) hybrid induces type I interferon response. a) Bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) were transfected with or without
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Synthetic annealed poly(ra):poly(dt) hybrid induces type I interferon response. a) Bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) were transfected with or without
Molecular design principles underlying β-strand swapping. in the adhesive dimerization of cadherins
 Supplementary information for: Molecular design principles underlying β-strand swapping in the adhesive dimerization of cadherins Jeremie Vendome 1,2,3,5, Shoshana Posy 1,2,3,5,6, Xiangshu Jin, 1,3 Fabiana
Supplementary information for: Molecular design principles underlying β-strand swapping in the adhesive dimerization of cadherins Jeremie Vendome 1,2,3,5, Shoshana Posy 1,2,3,5,6, Xiangshu Jin, 1,3 Fabiana
Fig. S1. CrgA intracellular levels in M. tuberculosis. Ten and twenty micrograms of
 Supplementary data Fig. S1. CrgA intracellular levels in M. tuberculosis. Ten and twenty micrograms of cell free protein lysates from WT M. tuberculosis (Rv) together with various known concentrations
Supplementary data Fig. S1. CrgA intracellular levels in M. tuberculosis. Ten and twenty micrograms of cell free protein lysates from WT M. tuberculosis (Rv) together with various known concentrations
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 This supplementary information is an extension of the letter with the same title and includes further discussion on the comparison of our designed Fe B Mb (computer model and crystal structure) with the
This supplementary information is an extension of the letter with the same title and includes further discussion on the comparison of our designed Fe B Mb (computer model and crystal structure) with the
Supplementary information. for the paper:
 Supplementary information for the paper: Screening for protein-protein interactions using Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) Anca Margineanu 1*,
Supplementary information for the paper: Screening for protein-protein interactions using Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) Anca Margineanu 1*,
Supporting Information: A GPCR dimerization interface in human cone opsins
 Supporting Information: A GPCR dimerization interface in human cone opsins Beata Jastrzebska *, William D. Comar *, Megan J. Kaliszewski, Kevin C. Skinner, Morgan H. Torcasio, Anthony S. Esway, Hui Jin,
Supporting Information: A GPCR dimerization interface in human cone opsins Beata Jastrzebska *, William D. Comar *, Megan J. Kaliszewski, Kevin C. Skinner, Morgan H. Torcasio, Anthony S. Esway, Hui Jin,
Structural basis of a novel PD-L1 nanobody for immune checkpoint blockade
 Structural basis of a novel PD-L1 nanobody for immune checkpoint blockade Supplementary Materials Supplementary methods Table S1-S Figure S1-S 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 Supplementary Methods Competitive
Structural basis of a novel PD-L1 nanobody for immune checkpoint blockade Supplementary Materials Supplementary methods Table S1-S Figure S1-S 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 Supplementary Methods Competitive
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information The DMSP Lyase and Lyase-Like Cupin family consists of bona fide DMSP lyases as well as other enzymes with unknown functions Lei Lei, Kesava Phaneendra Cherukuri, Uria Alcolombri,
Supporting Information The DMSP Lyase and Lyase-Like Cupin family consists of bona fide DMSP lyases as well as other enzymes with unknown functions Lei Lei, Kesava Phaneendra Cherukuri, Uria Alcolombri,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Materials and Methods Circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. Far ultraviolet (UV) CD spectra of apo- and holo- CaM and the CaM mutants were recorded on a Jasco J-715 spectropolarimeter
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Materials and Methods Circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. Far ultraviolet (UV) CD spectra of apo- and holo- CaM and the CaM mutants were recorded on a Jasco J-715 spectropolarimeter
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Linkage preference of USP30 and USP domain architecture.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Linkage preference of USP30 and USP domain architecture. a, Catalytic efficiencies determined from Coomassie-stained gel-based kinetics for all eight diub linkages (see Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1 Linkage preference of USP30 and USP domain architecture. a, Catalytic efficiencies determined from Coomassie-stained gel-based kinetics for all eight diub linkages (see Supplementary
Supplementary information Bi-specific Aptamers mediating Tumour Cell Lysis
 Supplementary information Bi-specific Aptamers mediating Tumour Cell Lysis Figure S1 SELEX scheme of different CD16 DNA selection approaches. Nine rounds of filter SELEX were conducted in parallel, only
Supplementary information Bi-specific Aptamers mediating Tumour Cell Lysis Figure S1 SELEX scheme of different CD16 DNA selection approaches. Nine rounds of filter SELEX were conducted in parallel, only
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
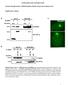 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Dynamic Phosphorylation of HP1 Regulates Mitotic Progression in Human Cells Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NDR1 interacts with HP1. (a) Immunoprecipitation using
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Dynamic Phosphorylation of HP1 Regulates Mitotic Progression in Human Cells Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NDR1 interacts with HP1. (a) Immunoprecipitation using
Masayoshi Honda, Jeehae Park, Robert A. Pugh, Taekjip Ha, and Maria Spies
 Molecular Cell, Volume 35 Supplemental Data Single-Molecule Analysis Reveals Differential Effect of ssdna-binding Proteins on DNA Translocation by XPD Helicase Masayoshi Honda, Jeehae Park, Robert A. Pugh,
Molecular Cell, Volume 35 Supplemental Data Single-Molecule Analysis Reveals Differential Effect of ssdna-binding Proteins on DNA Translocation by XPD Helicase Masayoshi Honda, Jeehae Park, Robert A. Pugh,
Supplementary Figure 1 Sequence alignment of representative CbbQ sequences.
 Walker A Pore loop 1 Walker B Supplementary Figure 1 Sequence alignment of representative CbbQ sequences. Amino acid sequences of CbbQ1 and CbbQ2 proteins from selected chemoautotrophic bacteria were aligned
Walker A Pore loop 1 Walker B Supplementary Figure 1 Sequence alignment of representative CbbQ sequences. Amino acid sequences of CbbQ1 and CbbQ2 proteins from selected chemoautotrophic bacteria were aligned
Engineering splicing factors with designed specificities
 nature methods Engineering splicing factors with designed specificities Yang Wang, Cheom-Gil Cheong, Traci M Tanaka Hall & Zefeng Wang Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary
nature methods Engineering splicing factors with designed specificities Yang Wang, Cheom-Gil Cheong, Traci M Tanaka Hall & Zefeng Wang Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1 Collision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK2, PPK3 and PPK4 respectively.
 Supplementary Figure 1 lision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK, PPK3 and PPK respectively. % of nuclei with signal / field a 5 c ppif3:gus pppk1:gus 0 35 30 5 0 15 10
Supplementary Figure 1 lision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK, PPK3 and PPK respectively. % of nuclei with signal / field a 5 c ppif3:gus pppk1:gus 0 35 30 5 0 15 10
Supplementary Figure 1 PARP1 is involved in regulating the stability of mrnas from pro-inflammatory cytokine/chemokine mediators.
 Supplementary Figure 1 PARP1 is involved in regulating the stability of mrnas from pro-inflammatory cytokine/chemokine mediators. (a) A graphic depiction of the approach to determining the stability of
Supplementary Figure 1 PARP1 is involved in regulating the stability of mrnas from pro-inflammatory cytokine/chemokine mediators. (a) A graphic depiction of the approach to determining the stability of
Q22M, T44W, R81G, H83G, T84M, N130G, N172M, A234S, T236L, C9G, V48G, L50W, T78S, S101E, E237M, T265S, W267F 7, 11, , 239,
 111 Table 4-1. Summary of design calculations for Kemp elimination enzymes. The residues allowed for each required catalytic contact are indicated along with the actual catalytic residue chosen from the
111 Table 4-1. Summary of design calculations for Kemp elimination enzymes. The residues allowed for each required catalytic contact are indicated along with the actual catalytic residue chosen from the
The Need for a PARP Pharmacodynamic Assay
 The Need for a PARP Pharmacodynamic Assay Version 05/07/09 amsbiotechnology(europe)ltd info@amsbio.com www.amsbio.com (UK)+44(0)1235828200 (CH)+41(0)916045522 (DE)+49(0)69779099 DNA Repair Pathways Base
The Need for a PARP Pharmacodynamic Assay Version 05/07/09 amsbiotechnology(europe)ltd info@amsbio.com www.amsbio.com (UK)+44(0)1235828200 (CH)+41(0)916045522 (DE)+49(0)69779099 DNA Repair Pathways Base
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 2 Supplementary Figure 1: Sequence alignment of HsHSD17B8 and HsCBR4 of with KAR orthologs. The secondary structure elements as calculated by DSSP and residue numbers are displayed
Supplementary Figure 1 2 Supplementary Figure 1: Sequence alignment of HsHSD17B8 and HsCBR4 of with KAR orthologs. The secondary structure elements as calculated by DSSP and residue numbers are displayed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06721 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 The distribution of hatx-1[82q] in Cos7 cells. Cos7 cells are co-transfected with hatx-1[82q]-gfp (green)
doi: 10.1038/nature06721 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 The distribution of hatx-1[82q] in Cos7 cells. Cos7 cells are co-transfected with hatx-1[82q]-gfp (green)
PDIP46 (DNA polymerase δ interacting protein 46) is an activating factor for human DNA polymerase δ
 PDIP46 (DNA polymerase δ interacting protein 46) is an activating factor for human DNA polymerase δ Supplementary Material Figure S1. PDIP46 is associated with Pol isolated by immunoaffinity chromatography.
PDIP46 (DNA polymerase δ interacting protein 46) is an activating factor for human DNA polymerase δ Supplementary Material Figure S1. PDIP46 is associated with Pol isolated by immunoaffinity chromatography.
A hybrid structural approach to analyze ligand binding by the 5-HT4. receptor
 Supplement A hybrid structural approach to analyze ligand binding by the 5-HT4 receptor Pius S. Padayatti 1**, Liwen Wang 2**, Sayan Gupta 3, Tivadar Orban 4, Wenyu Sun 1, David Salom 1, Steve Jordan 5,
Supplement A hybrid structural approach to analyze ligand binding by the 5-HT4 receptor Pius S. Padayatti 1**, Liwen Wang 2**, Sayan Gupta 3, Tivadar Orban 4, Wenyu Sun 1, David Salom 1, Steve Jordan 5,
Supplementary Materials: A Toolbox of Genetically Encoded FRET-Based Biosensors for Rapid L-Lysine Analysis
 S1 of S9 Supplementary Materials: A Toolbox of Genetically Encoded FRET-Based Biosensors for Rapid L-Lysine Analysis Victoria Steffen, Julia Otten, Susann Engelmann, Andreas Radek, Michael Limberg, Bernd
S1 of S9 Supplementary Materials: A Toolbox of Genetically Encoded FRET-Based Biosensors for Rapid L-Lysine Analysis Victoria Steffen, Julia Otten, Susann Engelmann, Andreas Radek, Michael Limberg, Bernd
MIAPE: Column Chromatography
 MIAPE: Column Chromatography Andrew R Jones 1,, Kathleen Carroll 2, David Knight 3, Kirsty MacLellan 4, Paula J Domann 5, Cristina Legido-Quigley 6, Lihua Huang 7, Lance Smallshaw 8 and Norman W Paton
MIAPE: Column Chromatography Andrew R Jones 1,, Kathleen Carroll 2, David Knight 3, Kirsty MacLellan 4, Paula J Domann 5, Cristina Legido-Quigley 6, Lihua Huang 7, Lance Smallshaw 8 and Norman W Paton
Paul Bowyer. (Baker Lab, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine)
 Evaluation of selective inhibitors of the malarial cyclic GMP dependent protein kinase (PKG) Paul Bowyer (Baker Lab, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine) Talk summary An overview of the P. falciparum
Evaluation of selective inhibitors of the malarial cyclic GMP dependent protein kinase (PKG) Paul Bowyer (Baker Lab, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine) Talk summary An overview of the P. falciparum
Evaluation of Cu(I) Binding to the E2 Domain of the Amyloid. Precursor Protein A Lesson in Quantification of Metal Binding to
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Metallomics. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Evaluation of Cu(I) Binding to the E2 Domain of the Amyloid Precursor Protein A Lesson in Quantification
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Metallomics. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Evaluation of Cu(I) Binding to the E2 Domain of the Amyloid Precursor Protein A Lesson in Quantification
Supplementary Figure 1 a
 3 min PMA 45 min PMA AnnexinV-FITC Supplementary Figure 1 5 min PMA 15 min PMA a 9 min PMA 12 min PMA 5 min FGF7 15 min FGF7 3 min FGF7 6 min FGF7 9 min FGF7 12 min FGF7 5 min control 3 min control 6 min
3 min PMA 45 min PMA AnnexinV-FITC Supplementary Figure 1 5 min PMA 15 min PMA a 9 min PMA 12 min PMA 5 min FGF7 15 min FGF7 3 min FGF7 6 min FGF7 9 min FGF7 12 min FGF7 5 min control 3 min control 6 min
Suplementary Materials Epub: No 2016_1339 Vol. 63, Regular paper
 Suplementary Materials Epub: No 2016_1339 Vol. 63, 2016 https://doi.org/10.18388/abp.2016_1339 Regular paper How short RNAs impact the human ribonuclease Dicer activity: putative regulatory feedback-loops
Suplementary Materials Epub: No 2016_1339 Vol. 63, 2016 https://doi.org/10.18388/abp.2016_1339 Regular paper How short RNAs impact the human ribonuclease Dicer activity: putative regulatory feedback-loops
Crystal Structure of a Self-Splicing Group I Intron with Both Exons
 Supplementary Data for: Crystal Structure of a Self-Splicing Group I Intron with Both Exons Peter L. Adams, Mary R. Stahley, Anne B. Kosek, Jimin Wang and Scott A. Strobel The supplementary material includes
Supplementary Data for: Crystal Structure of a Self-Splicing Group I Intron with Both Exons Peter L. Adams, Mary R. Stahley, Anne B. Kosek, Jimin Wang and Scott A. Strobel The supplementary material includes
Modulating the Cascade architecture of a minimal Type I-F CRISPR-Cas system
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Modulating the Cascade architecture of a minimal Type I-F CRISPR-Cas system Daniel Gleditzsch 1, Hanna Müller-Esparza 1, Patrick Pausch 2,3, Kundan Sharma 4, Srivatsa Dwarakanath 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Modulating the Cascade architecture of a minimal Type I-F CRISPR-Cas system Daniel Gleditzsch 1, Hanna Müller-Esparza 1, Patrick Pausch 2,3, Kundan Sharma 4, Srivatsa Dwarakanath 1,
Supplemental Information. Natural RNA Polymerase Aptamers. Regulate Transcription in E. coli
 Molecular Cell, Volume 67 Supplemental Information Natural RNA Polymerase Aptamers Regulate Transcription in E. coli Nadezda Sedlyarova, Philipp Rescheneder, Andrés Magán, Niko Popitsch, Natascha Rziha,
Molecular Cell, Volume 67 Supplemental Information Natural RNA Polymerase Aptamers Regulate Transcription in E. coli Nadezda Sedlyarova, Philipp Rescheneder, Andrés Magán, Niko Popitsch, Natascha Rziha,
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information ATP-dependent unwinding of U4/U6 snrnas by the Brr2 helicase requires the C-terminus of Prp8 Corina Maeder 1,3, Alan K. Kutach 1,2,3, and Christine Guthrie 1 1 Department of Biochemistry
Supplemental Information ATP-dependent unwinding of U4/U6 snrnas by the Brr2 helicase requires the C-terminus of Prp8 Corina Maeder 1,3, Alan K. Kutach 1,2,3, and Christine Guthrie 1 1 Department of Biochemistry
Quantifying small numbers of antibodies with a near-universal protein-dna chimera
 Quantifying small numbers of antibodies with a near-universal protein-dna chimera Ian Burbulis, Kumiko Yamaguchi, Richard Yu, Orna Resnekov & Roger Brent Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary figure
Quantifying small numbers of antibodies with a near-universal protein-dna chimera Ian Burbulis, Kumiko Yamaguchi, Richard Yu, Orna Resnekov & Roger Brent Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary figure
Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Figure S2. Verification of ihog and boi
 Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Extracts from S2R+ cells, embryos, and adults were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with anti-ihog antibody. The Ihog
Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Extracts from S2R+ cells, embryos, and adults were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with anti-ihog antibody. The Ihog
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
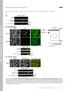 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Nakajima and Tanoue, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201104118/dc1 Figure S1. DLD-1 cells exhibit the characteristic morphology
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Nakajima and Tanoue, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201104118/dc1 Figure S1. DLD-1 cells exhibit the characteristic morphology
Supporting Information MANOTA: A PROMISING BIFUNCTIONAL CHELATING AGENT FOR COPPER-64 IMMUNOPET
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information MANOTA: A PROMISING BIFUNCTIONAL CHELATING AGENT FOR COPPER-64
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information MANOTA: A PROMISING BIFUNCTIONAL CHELATING AGENT FOR COPPER-64
