von Willebrand factor: a hemostatic protein
|
|
|
- Asher Taylor
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 von Willebrand factor: a hemostatic protein!"#$%&'()*+',,-.'/01*+23'45'6*78+95' Cécile Denis INSERM U770 Le Kremlin-Bicêtre, France University of Ferrara October 19th, 2012!
2 Presentation schedule! Basic notions about hemostasis! Von Willebrand factor: introduction! Von Willebrand disease! Animal models of von Willebrand disease! The use of hydrodynamic injection to generate new murine models
3 Presentation schedule! Basic notions about hemostasis! Von Willebrand factor: introduction! Von Willebrand disease! Animal models of von Willebrand disease! The use of hydrodynamic injection to generate new murine models
4 Hemostasis The major goal of the hemostatic system is to keep the blood in its fluid state in the vascular compartment, while preventing excessive blood loss following vessel injury Four important steps can be distinguished: 1- Vasoconstriction of the damaged vessel reducing locally the blood flow and limiting the blood loss Vascular injury Platelet Red blood cell Endothelium
5 Hemostasis The major goal of the hemostatic system is to keep the blood in its fluid state in the vascular compartment, while preventing excessive blood loss following vessel injury Four important steps can be distinguished: 2- Primary hemostasis initiated by platelet adhesion to exposed subendothelial components and leading to platelet plug formation Collagen
6 Hemostasis The major goal of the hemostatic system is to keep the blood in its fluid state in the vascular compartment, while preventing excessive blood loss following vessel injury Four important steps can be distinguished: 3- Secondary hemostasis (or blood coagulation) achieving consolidation of the platelet plug by the formation of a fibrin network
7 Hemostasis The major goal of the hemostatic system is to keep the blood in its fluid state in the vascular compartment, while preventing excessive blood loss following vessel injury Four important steps can be distinguished: 4- Fibrinolysis inducing elimination of the clot during tissue reparation
8 Hemostasis The major goal of the hemostatic system is to keep the blood in its fluid state in the vascular compartment, while preventing excessive blood loss following vessel injury The hemostatic response must be quick, localized and carefully regulated. This process interconnects a series of physiological events involving vessels, blood cells, coagulation factors, coagulation inhibitors and fibrinolytic system.
9 Hemostasis and von Willebrand factor Von Willebrand factor (VWF): Key protein in primary hemostasis VWF GPIb-IX-V'
10 Presentation schedule! Basic notions about hemostasis! Von Willebrand factor: introduction! Von Willebrand disease! Animal models of von Willebrand disease! The use of hydrodynamic injection to generate new murine models
11 Life-cycle of von Willebrand factor (VWF) D1 D2 D D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B1-3 C1 C2 CK Biosynthesis Liver Clearance Storage and secretion in plasma FVIII Functions Formation of the platelet thrombus VWF Assembly of the VWF-FVIII complex Regulation of multimer size
12 Life-cycle of VWF D1 D2 D D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B1-3 C1 C2 CK Biosynthesis Liver Clearance Storage and secretion in plasma FVIII Functions Formation of the platelet thrombus VWF Assembly of the VWF-FVIII complex Regulation of multimer size
13 VWF biosynthesis Endothelial cells and megakaryocytes PS propeptide mature subunit D1 D2 D D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B1-3 C1 C2 CK N- -C -C Endoplasmic reticulum Peptide signal cleavage N-Glycosylations Dimerization Golgi O-Glycosylations Sulfatations Multimerization Trans Golgi network Sulfatations Multimerization Propeptide cleavage N C S S S S * * S 2.7x10 5 Da x10 6 Da S *
14 Multimeric structure of VWF D D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B1-3 C1 C2 CK Monomer 0.25 x 10 6 Da Dimer 0.5 x 10 6 Da Tetramer 1.0 x 10 6 Da Hexamer 1.5 x 10 6 Da 6 2 Multimer > 7.5 x 10 6 Da
15 Life-cycle of VWF D1 D2 D D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B1-3 C1 C2 CK Biosynthesis Liver Clearance Storage and secretion in plasma FVIII Functions Formation of the platelet thrombus VWF Assembly of the VWF-FVIII complex Regulation of multimer size
16 Storage and secretion of VWF! Constitutive secretion: plasma (5 à 10 µg/ml) and subendothelium! Regulated secretion: Platelet! granules and Weibel-Palade bodies of endothelial cells Anti-VWF-TRITC! Rod shaped granules measuring 100 nm in width and 1-5 µm in length! Presence of very high molecular weight multimers of VWF! VWF is required for Weibel-Palade body formation! Contain other proteins: P-selectin, angiopoietin-2, osteoprotegerin, IL-8! Exocytosis: thrombin, shear stress, histamin, PMA,!
17 Life-cycle of VWF D1 D2 D D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B1-3 C1 C2 CK Biosynthesis Liver Clearance Storage and secretion in plasma FVIII Functions Formation of the platelet thrombus VWF Assembly of the VWF-FVIII complex Regulation of multimer size
18 Regulation of VWF multimer size (1) Endothelial cells ADAMTS13 Endothelial VWF Plasma VWF ADAMTS13: A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease with ThromboSpondin type 1 Repeats, member 13.
19 Regulation of VWF multimer size (2) D D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B1-3 C1 C2 CK ADAMTS-13 cleaves VWF in its A2 domain between Tyr 1605 and Met 1606 ADAMTS-13 Platelet A2 domain VWF
20 VWF as an ADAMTS13 substrate VWF circulating in plasma: NO VWF bound to endothelial cells: YES VWF bound to platelets in a thrombus: YES VWF ATS13 PLAT collagen
21 Importance of ADAMTS13-mediated VWF cleavage ":9C23';?DE57+' ":9C23';?DE57+' 6*)4*)H';*+5I' ' ' $)4:+=53*23'7533;' $)4:+=53*23'7533;' 'C?3JC59;'L9:C'' A5*D53MK23245'D:4*5;'
22 Importance of ADAMTS13-mediated VWF cleavage ":9C23';?DE57+' N5O7*5)+'PNP&Q#RS'27JG*+<' K ;' #1:)+2)5:?;' '' C?3JC59;'!)+92G2;7?329' '+=9:CD:;*;'
23 Life-cycle of VWF D1 D2 D D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B1-3 C1 C2 CK Biosynthesis Liver Clearance Storage and secretion in plasma FVIII Functions Formation of the platelet thrombus VWF Assembly of the VWF-FVIII complex Regulation of multimer size
24 VWF role in platelet adhesion to the subendothelium at high shear rate!"#$%"&'' (&"")' *+,-)./01.#$'' (&"")'' Pictures taken by light microscopy of human platelets adhering to subendothelium from rabbit aorta (Tschopp et al, J Lab Clin Med 1974, 83, )
25 Platelet adhesion and aggregation at high shear rates (Jackson SP and Schoenwaelder SM, 2003)
26 Interaction VWF-Factor VIII (FVIII) FVIII/VWF complex A1 A2 B Me 2+ A3 C1 C2 VWF stabilizes FVIII hetero-dimeric structure VWF denies FVIII access to the factor X-activating complex VWF inhibits binding of FVIII to phospholipid-surface of activated platelets MØ VWF prevents cellular uptake by clearance receptors VWF protects FVIII from proteolysis by phospholipiddependent proteases (APC, factor Xa)
27 Reduced survival of FVIII in the absence of VWF 100' Residual FVIII' (Units/dL)' 10' 1' Hemophilia A Severe von Willebrand disease 0' 20' 40' 60' Time (h)'
28 VWF functional domains Adamts13 N- D1 D2 D D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B1-3 -C C1 C2 CK -C Factor VIII GPIb" Collagen VI Sulfatides Heparin Collagen I Collagen III GpIIbIIIa Interaction with FVIII Interaction with subendothelium Platelet translocation Firm adhesion and platelet aggregation
29 Regulation of VWF function There are many regulators of VWF function. One of them is related to its conformation Globular conformation (inactive)! Circulating VWF' A1 domain is inaccessible for platelet binding ADAMTS13 cleavage site in the A2 domain is unavailable! Stretched conformation (active)! VWF immobilized on a surface or submitted to high shear stress' A1 domain is accessible for platelet binding ADAMTS13 cleavage site in the A2 domain is available!
30 Life-cycle of VWF D1 D2 D D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B1-3 C1 C2 CK Biosynthesis Liver Clearance Storage and secretion in plasma FVIII Functions Formation of the platelet thrombus VWF Assembly of the VWF-FVIII complex Regulation of multimer size
31 Clearance of VWF! VWF and the FVIII/VWF complex are targeted to liver and spleen macrophages! VWF clearance is strongly influenced by its glycosylation profile! Endocytosis receptor(s) are only partially identified LRP1 (LDL receptor related protein) Ligands: FVIII, FIXa, FXa, Siglecs (Siglec-5) (sialic acid binding Ig-like lectins) (Pegon et al, Hematologica, 2012, In press)?? (Rastegarlari et al, Blood, 2012, 119: )??
32 Life-cycle of VWF D1 D2 D D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B1-3 C1 C2 CK Biosynthesis Liver Clearance VON WILLEBRAND DISEASE FVIII Functions Formation of the platelet thrombus Storage and secretion in plasma VWF Assembly of the VWF-FVIII complex Regulation of multimer size
33 Presentation schedule! Basic notions about hemostasis! Von Willebrand factor: introduction! Von Willebrand disease (VWD)! Animal models of von Willebrand disease! The use of hydrodynamic injection to generate new murine models
34 Classification of VWD Genetic bleeding disorder TYPE 1 (50-75% of cases)! Partial quantitative defects, accounting for 70% of the cases! Limited bleeding symptoms, normal activity of residual VWF! Dominant transmission TYPE 3 or severe (! 5% of cases)! Complete deficiency in VWF and strong reduction in FVIII! Combined defects in primary hemostasis and coagulation leading to severe bleeding symptoms! Recessive transmission TYPE 2 (20-45% of cases)! Qualitative defects! Four main subtypes (2A, 2B, 2M et 2N) according to the multimeric profile and affected function! Dominant or recessive transmission
35 VWD Type 2 Abnormal VWF interaction with its ligands With platelets and vessel wall or With FVIII Absence of high molecular weight VWF multimers Type 2A Abnormal VWF-platelets interaction Defective VWF-collagen Interaction Type 2M Defective VWF-FVIII interaction Type 2N Increased affinity Type 2B Loss of affinity Type 2M
36 VWD: Epidemiology! Prevalence in the general population # 1 p. 100 (Rodeguiero et al, Blood 1987)! Prevalence of symptomatic subjects # 1 p (Joint WHO/ISTH Meeting, London 1998)! Prevalence of severe form # 0.5 to 5 p In France (65 millions inhabitants): 7000 to 8000 symptomatic patients 50 to 100 patients with VWD type 3 ' Globally, there is a overrepresentation of women and of individuals with blood group O'
37 Hemorrhagic symptoms in VWD Symptoms' VWD (n=264)' NORMAL (n=500)' Epistaxis' Menorrhagia' Bleeding following tooth extraction' Gum bleeding' Post-surgical bleeding' 62.5%' 60.0%' 51.5%' 34.8%' 28.0%' 4.6%' 25.3%' 4.8%' 7.4%' 1.4%' Sylwer et al, Acta Paediatr Scand, 1973!
38 Presentation schedule! Basic notions about hemostasis! Von Willebrand factor: introduction! Von Willebrand disease! Animal models of von Willebrand disease! The use of hydrodynamic injection to generate new murine models
39 Animal models of VWD Canine type 1, 2, 3 VWD (1970) Various genetic defects Porcine type 3 VWD (1941) VWD models Reduced transcription Post-translational defects Murine type 1, 2 and 3 VWD (1990; 1998; 2008) Presence of gene modifiers (type 1 VWD) Genetically-induced (type 3 VWD) Hydrodynamic gene transfer (type 2 VWD)
40 Murine model of VWD VWF +/+ VWF -/- " Spontaneous hemorrhage at the abdominal level in 10% of the mutant neonates " Prolonged bleeding time VWF -/- mice represent a good model of human severe VWD (Denis et al, PNAS, 1998, 95: )
41 In vivo tests of VWF function!"##$%&'()*#+(,-%"(."%/(-00-1( # '&:?;5'2)5;+=5JT54' # 'F?+'S'CC':L'+=5'+2*3'5U+95C*+<'V*+='2';723153' # '!CC59;5'+2*3'*)'S,WF';23*)5' # '&52;?95'JC5'+:'R ;+ '2995;+':L'D3554*)H' # '#+:1'2X59'R-'C*)'*L'):';1:)+2)5:?;';+:1',234*540%0(*4$#"+(6#7" 8 9%&$:.#$(( %&;:31(%&(*#0#&<#3%.(=#00#"0( # '&:?;5'2)5;+=5JT54' # '!)E57+'9=:42C*)5'YZ'!@'+:'32D53' ;' # '$U+59*:9*T5'C5;5)+59*7'G5;;53;' # 'K?+'C:?;5'?)459'C*79:;7:15' # 'K3275'O3+59'12159';2+?92+54'V*+='V*+=',[\]'B5F3 S' ':)'G5;;53;'L:9'\'C*)'+:'*)4?75'G5;;53'*)E?9<'' # '&52;?95'JC5'+:'G5;;53':773?;*:)'
42 Presentation schedule! Basic notions about hemostasis! Von Willebrand factor: introduction! Von Willebrand disease! Animal models of von Willebrand disease! The use of hydrodynamic injection to generate new murine models
43 Aim of the study To develop murine models to study VWF structure-function relationships in vivo VWF-deficient mice Hydrodynamic injection
44 Hydrodynamic injection (1) In vivo transfection allowing transient expression of a transgene by the liver P'921*4'*)E57J:)':L'2'329H5'G:3?C5':L'' 132;C*4'N"P'G*2'+=5'+2*3'G5*)':L''C*75' $!"#$%&'(#!)(*+,%-!./0!(1!23%!!!!!!!4(567%8932!!!!!!!:8;%!<,*!1(=!>!</9!,(+?%@! $!"#$%&'(#!',%-!A!B!?%&!
45 Hydrodynamic injection (2) Mechanism Inferior vena cava Hepatic vein Liver " Exceeding the cardiac output " Development of high pressure " Back flow of the solution towards organs connected to the vena cava " The liver absorbs most of the injected solution " 10-40% of hepatocytes are transfected I.V. Injection Zhang et al, Human Gene Therapy, 1999, 10:1735; Liu et al, Gene Therapy, 1999, 6:1258
46 Hydrodynamic injection toxicity?! Very little, if any, deaths following injection! Animal growth is not affected in the days following hydrodynamic injection! Concentration of ions (Na+,K+, Cl-), total protein concentration, albumin and bilirubin concentrations are not affected! Concentration of liver specific enzymes such as alkaline phosphatase and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) remains unchanged! Concentration of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is increased 4-20 fold at 1 day post-injection but goes down to baseline within 3 days! Liver necrosis is apparent in 50% of the mice at 1 day post-injection and affects between 5-10% of hepatocytes! Platelet counts drop by 30% at 1 day post-injection
47 Expression in liver 'a*g59'*;:32j:)'bc/'2x59'*)e57j:)' ' WT VWF-/- VWF-/- + mvwf VWF expression is switched from endothelial cells in wild-type mice to hepatocytes in VWF knockout mice injected with mvwf cdna
48 VWF expression levels following hydrodynamic injection % Injection of 1-100µg of murine VWF cdna in VWF-/- mice % Blood collection 24h after injection % ELISA assay to measure VWF plasma levels *+,'2&3453'&.6.&4'789'' Y--' \--' c--' S--' b--' R--' &235;' B5C235;' )dcm\' -' R' b' \' R-' \-' R--' 20:;<=-5*+,'7µ>?5"@4.9'
49 Kinetic of expression of VWF after hydrodynamic injection % Injection of 50µg murine VWF cdna in VWF-/- mice % Blood collection at different time points after injection pcdna6 vector (CMV promoter) plive vector (albumin promoter) VWF plasma levels (%) n= Time (h)
50 VWF mutants expressed in vivo VWF Blood flow GPIb GPIIbIIIa VWF VWF-collagens GPIb-VWF GPIIbIIIa-VWF
51 Analysis of VWF carrying mutations in its main binding sites grsybp' NR,cbP' #R,fSP' /R,fYP' Nb\-eZ' '''Nh'''''''''''''NS''''''''''''PR''''''''''Pb''''''''''''''PS'''''''''Nc''''''''''''6RMS'''''''''''''FR'''''''''Fb'''''''''''''Fg' %ZN' ZK!D!' F:332H5)' ZK!!D!!!2' CDEFGF!,8&%! Murine cdna injected Tail bleeding FeCl 3 -induced thrombosis None Infinite Minimal Wild type Normal Normal GPIb!-binding mutant Infinite Minimal Collagen binding mutant Normal Reduced GPIIbIIIa-binding mutant Normal Reduced H>=I!%2!>*J!KLCMJ!<//NJ!<NJ!O.P!! H>=I!%2!>*J!M*((5J!<//NJ!..<J!.Q/O!!
52 Summary analysis of mutants Collagen and GPIIbIIIa binding mutants! Delayed vessel occlusion! Complete correction of bleeding time VWF interactions with collagens type I and III and with GPIIbIIIa are more important in the pathological thrombotic process than in the physiological process of hemostasis Interesting targets for anti-thrombotic therapy
53 Anti-thrombotic potential of mabs to VWF To test anti-thrombotic properties in mice of tools targeting VWF binding to collagens or to GPIIbIIIa mab 203 mab 505 mab 9 D D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B1-3 C1 C2 CK GPIb Collagen RGD GPIIbIIIa These mabs are directed against human VWF and do not crossreact with murine VWF Hydrodynamic injection of human VWF cdna in VWF -/- mice : Human VWF D D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B1-3 C1 C2 CK Murine GPIb!" Human VWF needs to be modified to interact with murine platelets
54 Can human VWF be modified to bind murine GPIb?! Mutagenesis of single residues potentially involved in the interaction between human VWF and murine GPIb or substitution of larger murine sequences into the A1 domain of human VWF! Hydrodynamic injection of the Vwf cdna variants to VWF -/- mice! One day later bleeding time test @ABM`M'
55 In vivo function of VWF chimeras (bleeding time) Only a chimera containing the entire murine A1 domain was able to correct the bleeding phenotype of VWF -/- mice
56 Functionality of huvwf/mu-a1 chimera in FeCl 3 - induced thrombosis model Hu-VWF/mu-A1 \'C*)' R-'C*)' b-'c*)' mu VWF \'C*)' R-'C*)' b-'c*)' Hu-VWF/mu-A1 chimera was able to restore thrombus formation in VWF KO mice
57 Recognition of huvwf/mu-a1 chimera by mabs to human VWF GPIb Collagen GPIIbIIIa D D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B1-3 C1 C2 CK mab 203 mab 505 mab 9 Hu VWF mu A1 Hu VWF mu VWF Hu VWF mu A1 Hu VWF mu VWF Hu VWF mu A1 Hu VWF mu VWF
58 Antibodies efficacy in a thrombosis model! Hydrodynamic injection of hu-vwf/mu-a1 cdna to VWF KO mice! 4 days later: IV injection of 100!g of mabs 9, 203, 505 or control isotype! Platelets labeling by retro-orbital injection of rhodamine 6G! Induction of vascular injury in mesenteric vessels by application of FeCl 3
59 Results Mabs efficacy in a thrombosis model Antibody Number of mice reaching venous occlusion Number of mice reaching arterial occlusion Control isotype ' 8 out of 8 tested 8 out of 8 tested mab 203 ^2)J'@ABM7:332H5)_' mab 505 ^2)J'@ABM7:332H5)_' mab 9 ^2)J'@ABMZK!!D!!!2_' 5 out of 8 tested 1 out of 8 tested 4 out of 8 tested 3 out of 8 tested 6 out of 8 tested 3 out of 8 tested Effect of the mabs anti VWF was stronger on thrombus formation in arteries than in veins when used preventively
60 Thrombus growth in arteries of mice pre-treated with anti-vwf mabs CPD'F:)+9:3'*;:+<15' P9+59*5;':773?;*:)k'' f':?+':l'f' 'c*75' A'51#' B'51#' CD'51#' EA'51#' A'51#' B'51#' G'51#' G'51#' HA'51#' P9+59*5;':773?;*:)k'' S':?+':L'f' 'C*75' A'51#' I'51#' C='51#' ED'51#' HA'51#' P9+59*5;':773?;*:)k'' R':?+':L'f' 'C*75' A'51#' I'51#' CG'51#' EH'51#' HA'51#' P9+59*5;':773?;*:)k'' S':?+':L'f' 'C*75'
61 Summary antibodies study! A model has been developed allowing to test therapeutic agents targeting human VWF in mouse! All the antibodies tested inhibiting the interactions of VWF with fibrillar collagen and platelet GPIIbIIIa were able to prevent thrombus formation in mesenteric arteries without affecting the bleeding phenotype of the treated animal.! Effect of the anti VWF mabs was stronger on thrombus formation in arteries than in veins.! Inhibition of the VWF-collagen and VWF-GPIIbIIIa axes is a promising strategy that deserves further investigations (other thrombosis models, other inhibiting agents!). (Navarrete et al, Blood, 2012, 120, )
62 Type 2B VWD! Characterized by increased VWF-GPIb! binding due to gain of function mutations! Leads to fluctuating thrombocytopenia and loss of high molecular weight VWF multimers! Different mutations lead to variable phenotype R1306Q V1316M D D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B1-3 C1 C2 CK Human type 2B patient RGD GPIb! Collagen GPIIbIIIa Federici et al, Blood, 2009, 113, 526
63 Generation of new models of VWD Comparison of two type 2B mutations: R1306Q and V1316M on 7299<*)H'+<15'b6'C?+2J:);' K32l?5m5;'^R- e`a_' AQ' N2<;'2X59'*)E57J:)'
64 Comparison of two type 2B mutations: R1306Q and V1316M: Effect on VWF multimer profile! 'a:;;':l'=*h='c:357?329'v5*h=+'c?3jc59;'*;'' ''''2;;:7*2+54'V*+='+<15'b6'C?+2J:);'*)'2D:?+'' ''''\-]':L'+=5'C*75'! 'Q=5'3:;;':L'=*H='C:357?329'V5*H=+'C?3JC59;'
65 Comparison of two type 2B mutations: R1306Q and V1316M: Effect on platelet aggregates +J-5*+,' KCDA=L' *CDC=M' R!5>6?!S(?2F8#$%&'(#! Q!5>6?!S(?2F8#$%&'(#!
66 Type 2B mice resemble the human phenotype: Impaired hemostasis Q2*3M73*1'D3554*)H' B5F3SM+=9:CD:;*;'C:453' wt V1316M Mesenteric venules - thombi >50 µm 7/7 1/5 - occlusion 6/7 0/5 Mesenteric arterioles - thombi >50 µm 7/7 0/5 - occlusion 6/7 0/5
67 ADAMTS13 deficiency worsens type 2B phenotype AQ' Q<15'b6'
68 Summary murine models of VWD! Hydrodynamic injection of mutant VWF allows reproduction of human VWD phenotypes! The technique is sensitive enough to reproduce phenotype subtleties associated with the expression of different mutations! Quick method to assess causative effect of mutations in the expression of the disease
The Coagulation Workup In The Office Setting
 CAA Conference alm Springs 2012 The Coagulation Workup In The Office Setting CAA Conference alm Springs, October 2012 Robert Miller, A-C Henoch-Schoenlein urpura 1 CAA Conference alm Springs 2012 2 CAA
CAA Conference alm Springs 2012 The Coagulation Workup In The Office Setting CAA Conference alm Springs, October 2012 Robert Miller, A-C Henoch-Schoenlein urpura 1 CAA Conference alm Springs 2012 2 CAA
Hemostasis and Thrombosis
 Hemostasis Hemostasis and Thrombosis Normal hemostasis is a consequence of tightly regulated processes that maintain blood in a fluid state in normal vessels, yet also permit the rapid formation of a hemostatic
Hemostasis Hemostasis and Thrombosis Normal hemostasis is a consequence of tightly regulated processes that maintain blood in a fluid state in normal vessels, yet also permit the rapid formation of a hemostatic
Hemostasis. by Mohie-Aldien Elsayed
 Hemostasis by Mohie-Aldien Elsayed Hemostasis Hemostasis is defined as the process that maintains the flowing blood in a fluid state and confined to the circulatory system Coagulation prevents excess blood
Hemostasis by Mohie-Aldien Elsayed Hemostasis Hemostasis is defined as the process that maintains the flowing blood in a fluid state and confined to the circulatory system Coagulation prevents excess blood
Common Inherited Bleeding Disorders
 CAA 2015 Annual Conference Common Inherited Bleeding Disorders Bob Miller, A October 8, 2015 VWF has two jobs Loosely bound to protect FVIII and tether to site of injury All other coagulation factors also
CAA 2015 Annual Conference Common Inherited Bleeding Disorders Bob Miller, A October 8, 2015 VWF has two jobs Loosely bound to protect FVIII and tether to site of injury All other coagulation factors also
International Society Laboratory Hematology Milan, May Current and Emerging Approaches for Assessing von Willebrand disease (VWD) in 2016
 International Society Laboratory Hematology Milan, 12-14 May 2016 Current and Emerging Approaches for Assessing von Willebrand disease (VWD) in 2016 Augusto B. FEDERICI Hematology and Transfusion Medicine
International Society Laboratory Hematology Milan, 12-14 May 2016 Current and Emerging Approaches for Assessing von Willebrand disease (VWD) in 2016 Augusto B. FEDERICI Hematology and Transfusion Medicine
Platelet type bleeding: (vwd) - Petechiae, purpura, ecchymoses, bruising - Menorrhagia, hematuria, occult GI bleed - Gingival bleeding, epistaxis
 1 Nadanotes.com 2 Nadanotes.com 3 Nadanotes.com Platelet type bleeding: (vwd) - Petechiae, purpura, ecchymoses, bruising - Menorrhagia, hematuria, occult GI bleed - Gingival bleeding, epistaxis Clotting
1 Nadanotes.com 2 Nadanotes.com 3 Nadanotes.com Platelet type bleeding: (vwd) - Petechiae, purpura, ecchymoses, bruising - Menorrhagia, hematuria, occult GI bleed - Gingival bleeding, epistaxis Clotting
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Factor XI as target for antithrombotic therapy van Montfoort, M.L. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Factor XI as target for antithrombotic therapy van Montfoort, M.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Montfoort, M. L. (2014). Factor XI
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Factor XI as target for antithrombotic therapy van Montfoort, M.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Montfoort, M. L. (2014). Factor XI
LABORATORY APPROACH TO BLEEDING DISORDERS DR NISHANTH PG 1 ST YEAR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY
 LABORATORY APPROACH TO BLEEDING DISORDERS DR NISHANTH PG 1 ST YEAR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY 1 WHEN IS THE LAB REQUIRED TO INVESTIGATE FOR A POSSIBLE BLEEDING DISORDER? Clinically suspected bleeding tendency
LABORATORY APPROACH TO BLEEDING DISORDERS DR NISHANTH PG 1 ST YEAR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY 1 WHEN IS THE LAB REQUIRED TO INVESTIGATE FOR A POSSIBLE BLEEDING DISORDER? Clinically suspected bleeding tendency
These handouts are only meant as a guide while you follow the presentation on the screen. Sometimes the speaker will change some of the slides.
 These handouts are only meant as a guide while you follow the presentation on the screen. Sometimes the speaker will change some of the slides. If you would like the 1 slide per page handouts, please ask
These handouts are only meant as a guide while you follow the presentation on the screen. Sometimes the speaker will change some of the slides. If you would like the 1 slide per page handouts, please ask
Mutagenesis and Expression of Mammalian Clotting Factor IX. Mark McCleland The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia and Lycoming College
 Mutagenesis and Expression of Mammalian Clotting Factor IX Mark McCleland The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia and Lycoming College Hemophilia B X-linked blood clotting disorder characterized by a deficiency
Mutagenesis and Expression of Mammalian Clotting Factor IX Mark McCleland The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia and Lycoming College Hemophilia B X-linked blood clotting disorder characterized by a deficiency
Common Inherited Coagulation Disorders. Inherited Coagulation Disorders. All coagulation factors and platelets in circulation (unactivated)
 Common Inherited Coagulation Disorders Bob Miller, A 2017 Inherited Coagulation Disorders Brief review of coagulation Disorders related to platelet dysfunction (not the acquired thrombocytopenias) Disorders
Common Inherited Coagulation Disorders Bob Miller, A 2017 Inherited Coagulation Disorders Brief review of coagulation Disorders related to platelet dysfunction (not the acquired thrombocytopenias) Disorders
EMSA Mutant SOX10 proteins interfere with the DNA binding of wild type SOX10
 18-05-2010 SOX10 IL FENOTIPO MENO GRAVE È DOVUTO A DOWNREGULATION DA NMD Intron Minigene approach: * * Mutazione introdotta come controllo Northern blotting * mrna levels Inoue et al., Nature Genetics
18-05-2010 SOX10 IL FENOTIPO MENO GRAVE È DOVUTO A DOWNREGULATION DA NMD Intron Minigene approach: * * Mutazione introdotta come controllo Northern blotting * mrna levels Inoue et al., Nature Genetics
Session 1 Topics. Vascular Phase of Hemostasis. Coagulation Pathway. Action of Unfractionated Heparin. Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy
 ~~Marshfield Labs Presents~~ Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy Session 1 of 4 Session 1 Topics Review of coagulation and the vascular phase of hemostasis Unfractionated heparin Low molecular
~~Marshfield Labs Presents~~ Laboratory Monitoring of Anticoagulant Therapy Session 1 of 4 Session 1 Topics Review of coagulation and the vascular phase of hemostasis Unfractionated heparin Low molecular
De l'utilisation de la microscopie intravitale pour étudier la thrombose in vivo et tester de nouveaux médicaments antithrombotiques- 1er partie
 De l'utilisation de la microscopie intravitale pour étudier la thrombose in vivo et tester de nouveaux médicaments antithrombotiques- 1er partie Christophe Dubois INSERM UMR-S-1076, Faculté de Pharmacie,
De l'utilisation de la microscopie intravitale pour étudier la thrombose in vivo et tester de nouveaux médicaments antithrombotiques- 1er partie Christophe Dubois INSERM UMR-S-1076, Faculté de Pharmacie,
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly -
 BLOOD PHYSIOLOGY PART 2 ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 231 11 TH JULY 2011 Dr Karen Hayes Royal Devon & Exeter Correspondence to: kmhayes@hotmail.co.uk QUESTIONS Before continuing, try to answer the
BLOOD PHYSIOLOGY PART 2 ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 231 11 TH JULY 2011 Dr Karen Hayes Royal Devon & Exeter Correspondence to: kmhayes@hotmail.co.uk QUESTIONS Before continuing, try to answer the
Coagulation Mechanisms Dr. Nervana Bayoumy
 Coagulation Mechanisms Dr. Nervana Bayoumy Associate Professor Department of Physiology Objectives At the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Recognize the different clotting factors 2. Understand
Coagulation Mechanisms Dr. Nervana Bayoumy Associate Professor Department of Physiology Objectives At the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Recognize the different clotting factors 2. Understand
Using TEG in the ED, OR, and ICU. Don H. Van Boerum, MD, FACS
 Using TEG in the ED, OR, and ICU Don H. Van Boerum, MD, FACS Trauma Surgeon, Director of Surgical Critical Care, Co-Director of Shock Trauma ICU, Intermountain Medical Center, Intermountain Healthcare
Using TEG in the ED, OR, and ICU Don H. Van Boerum, MD, FACS Trauma Surgeon, Director of Surgical Critical Care, Co-Director of Shock Trauma ICU, Intermountain Medical Center, Intermountain Healthcare
BLOOD COAGULATION. 1. The initial phase of the process is vascular constriction. This limits the flow of blood to the area of injury.
 BLOOD COAGULATION The ability of the body to control the flow of blood following vascular injury is paramount to continued survival. The process of blood clotting and then the subsequent dissolution of
BLOOD COAGULATION The ability of the body to control the flow of blood following vascular injury is paramount to continued survival. The process of blood clotting and then the subsequent dissolution of
Physiology Unit 3 HEMATOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 3 HEMATOLOGY In Physiology Today Hematocrit Percentage of blood volume that is erythrocytes 45% in men 42% in women Average blood volume in is 5 L Plasma Large amounts of organic/inorganic
Physiology Unit 3 HEMATOLOGY In Physiology Today Hematocrit Percentage of blood volume that is erythrocytes 45% in men 42% in women Average blood volume in is 5 L Plasma Large amounts of organic/inorganic
General Principles of. Hemostasis. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 General Principles of Hemostasis Kristine Krafts, M.D. Hemostasis is a balancing act! pro-ting plugs up holes in blood vessels anti-ting keeps ting under control Pro-Clotting Pro-Clotting vessels platelets
General Principles of Hemostasis Kristine Krafts, M.D. Hemostasis is a balancing act! pro-ting plugs up holes in blood vessels anti-ting keeps ting under control Pro-Clotting Pro-Clotting vessels platelets
Local vasoconstriction. is due to local spasm of the smooth muscle (symp. reflex) can be maintained by platelet vasoconstrictors
 Hemostasis Hemostasis ( hemo =blood; sta= remain ) is the stoppage of bleeding, which is vitally important when blood vessels are damaged. Following an injury to blood vessels several actions may help
Hemostasis Hemostasis ( hemo =blood; sta= remain ) is the stoppage of bleeding, which is vitally important when blood vessels are damaged. Following an injury to blood vessels several actions may help
ISCT Paris April 25. Ex vivo platelet production Dominique Baruch INSERM UMR-S1140, Paris
 ISCT Paris April 25 Ex vivo platelet production Dominique Baruch INSERM UMR-S1140, Paris Platelet functions: to stop bleeding and beyond Adhesion Aggregation Clot retraction Secretion Procoagulant activity
ISCT Paris April 25 Ex vivo platelet production Dominique Baruch INSERM UMR-S1140, Paris Platelet functions: to stop bleeding and beyond Adhesion Aggregation Clot retraction Secretion Procoagulant activity
ZEBRAFISH VON WILLEBRAND FACTOR. Maira M. Carrillo, B.S. Dissertation Prepared for the Degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS
 ZEBRAFISH VON WILLEBRAND FACTOR Maira M. Carrillo, B.S. Dissertation Prepared for the Degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS August 2012 APPROVED: Pudur Jagadeeswaran, Major Professor
ZEBRAFISH VON WILLEBRAND FACTOR Maira M. Carrillo, B.S. Dissertation Prepared for the Degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS August 2012 APPROVED: Pudur Jagadeeswaran, Major Professor
Introduction Hemostasis: Tourniquet Test & Bleeding Time. Hematology-Immunology System Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran LOGO
 Introduction Hemostasis: Tourniquet Test & Bleeding Time Hematology-Immunology System Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran LOGO Hemostasis A series of reactions that function to stop bleeding, maintaining
Introduction Hemostasis: Tourniquet Test & Bleeding Time Hematology-Immunology System Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran LOGO Hemostasis A series of reactions that function to stop bleeding, maintaining
Primary hemostasis. Vascular endothelium Vasoconstriction : local tissue factor, nervous system
 Primary hemostasis Vascular endothelium Vasoconstriction : local tissue factor, nervous system Platelet Plug Platelet Adhesion Platelet Activation Platelet Aggregation Platelet Plug Formation Secondary
Primary hemostasis Vascular endothelium Vasoconstriction : local tissue factor, nervous system Platelet Plug Platelet Adhesion Platelet Activation Platelet Aggregation Platelet Plug Formation Secondary
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF BLEEDING DISORDERS
 LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF BLEEDING DISORDERS Primary & Secondary Hemostasis Disorders http://.columbia.edu/itc/hs/medical/selective/advclinicalpathology/2004/lecture/lab%20diagnosis%20of%20bleeding%20disorders.ppt
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF BLEEDING DISORDERS Primary & Secondary Hemostasis Disorders http://.columbia.edu/itc/hs/medical/selective/advclinicalpathology/2004/lecture/lab%20diagnosis%20of%20bleeding%20disorders.ppt
Mouse von Willebrand Factor (vwf) ELISA Kit
 Mouse von Willebrand Factor (vwf) ELISA Kit Catalog No. CSB-E08439m (96T) This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of mouse vwf concentrations in cell culture supernates,
Mouse von Willebrand Factor (vwf) ELISA Kit Catalog No. CSB-E08439m (96T) This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of mouse vwf concentrations in cell culture supernates,
Chapter Six. A murine model to study von Willebrand factor structure-function relationship in vivo. Submitted
 Chapter Six Chapter Six A murine model to study von Willebrand factor structure-function relationship in vivo Isabelle Marx Peter J. Lenting Thure Adler Ronan Pendu Olivier D. Christophe Cécile V. Denis
Chapter Six Chapter Six A murine model to study von Willebrand factor structure-function relationship in vivo Isabelle Marx Peter J. Lenting Thure Adler Ronan Pendu Olivier D. Christophe Cécile V. Denis
Ch 13: Blood. What does blood do? Transport: Regulation: Protection:
 Ch 13: Blood What does blood do? Transport: Regulation: Protection: SLOs Describe the composition of plasma and list the major functions of plasma proteins. Map hematopoiesis, starting from a pluripotent
Ch 13: Blood What does blood do? Transport: Regulation: Protection: SLOs Describe the composition of plasma and list the major functions of plasma proteins. Map hematopoiesis, starting from a pluripotent
Interaction of blood cells with the vessel wall in thrombosis
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2014 Interaction of blood cells with the vessel wall in thrombosis Jessica Kay Hansen University of Iowa Copyright 2014 Jessica Kay
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2014 Interaction of blood cells with the vessel wall in thrombosis Jessica Kay Hansen University of Iowa Copyright 2014 Jessica Kay
2013 Health Press Ltd.
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Bleeding Disorders Second edition David Green MD PhD Professor of Medicine Emeritus Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University Chicago, Illinois, USA Christopher A Ludlam
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Bleeding Disorders Second edition David Green MD PhD Professor of Medicine Emeritus Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University Chicago, Illinois, USA Christopher A Ludlam
Pharmacology Lecture 5. Anticoagulants
 Pharmacology Lecture 5 Anticoagulants General overview Anti-thrombotic Drugs Antiplatlets Anticoagulants Fibrinolytics Anticoagulants Indirect Thrombin Inhibitors Anti-thrombotic effect is exerted by interaction
Pharmacology Lecture 5 Anticoagulants General overview Anti-thrombotic Drugs Antiplatlets Anticoagulants Fibrinolytics Anticoagulants Indirect Thrombin Inhibitors Anti-thrombotic effect is exerted by interaction
(B) Comparable expression of major integrin subunits and glycoproteins on the surface of resting WT and Lnk -/- platelets.
 Supplemental Figure S1. Characteristics of Lnk -/- platelets. (A) Electron micrographs of resting platelets showing the normal intracellular structure of Lnk -/ platelets. Samples were fixed with 4% PFA
Supplemental Figure S1. Characteristics of Lnk -/- platelets. (A) Electron micrographs of resting platelets showing the normal intracellular structure of Lnk -/ platelets. Samples were fixed with 4% PFA
Adv Pathophysiology Unit 4 Page 1 of 10. Learning Objectives for this file:
 Adv Pathophysiology Unit 4 Page 1 of 10 Learning Objectives for this file: Topics include structure & function of: 1. Coagulation process platelets, clotting factors 2. Coagulation cascade formation of
Adv Pathophysiology Unit 4 Page 1 of 10 Learning Objectives for this file: Topics include structure & function of: 1. Coagulation process platelets, clotting factors 2. Coagulation cascade formation of
Hypercoagulation. CP Conference 11/14/2006
 Hypercoagulation CP Conference 11/14/2006 Overview Hypercoagulation: poorly understood phenomena No definite cause is identified in > 40% of cases Three major factors in thrombus formation (Rudolf Virchow,
Hypercoagulation CP Conference 11/14/2006 Overview Hypercoagulation: poorly understood phenomena No definite cause is identified in > 40% of cases Three major factors in thrombus formation (Rudolf Virchow,
COAGULATION: BASIC PRINCIPLES. Peyman Eshghi Prof. of Pediatric Hematology & Oncology
 COAGULATION: BASIC PRINCIPLES Peyman Eshghi Prof. of Pediatric Hematology & Oncology 1395 Haemostasis overview: BV Injury Neural Contact/ Tissue Factor Blood Vessel Constriction Reduced Blood flow Platelet
COAGULATION: BASIC PRINCIPLES Peyman Eshghi Prof. of Pediatric Hematology & Oncology 1395 Haemostasis overview: BV Injury Neural Contact/ Tissue Factor Blood Vessel Constriction Reduced Blood flow Platelet
POST-ISTH: Novità dal meeting di Toronto 2015 Piastrine: fisiopatologia. Erica De Candia Università Cattolica -Roma
 POST-ISTH: Novità dal meeting di Toronto 2015 Piastrine: fisiopatologia Erica De Candia Università Cattolica -Roma Novità ISTH 2015: Piastrine: Fisiopatologia i) Alternative platelet function throughout
POST-ISTH: Novità dal meeting di Toronto 2015 Piastrine: fisiopatologia Erica De Candia Università Cattolica -Roma Novità ISTH 2015: Piastrine: Fisiopatologia i) Alternative platelet function throughout
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES/TABLES:
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES/TABLES: Journal: Nature Biotechnology Article Title: Correction of the coagulation defect in hemophilia using a factor Xa variant with novel engineered protease function. Authors:
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES/TABLES: Journal: Nature Biotechnology Article Title: Correction of the coagulation defect in hemophilia using a factor Xa variant with novel engineered protease function. Authors:
Hematology Emergencies: Problems with Platelets
 Hematology Emergencies: Problems with Platelets Christian Cable, MD, FACP Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology & Oncology Texas A&M HSC College of Medicine Scott & White Healthcare Fundamentals
Hematology Emergencies: Problems with Platelets Christian Cable, MD, FACP Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology & Oncology Texas A&M HSC College of Medicine Scott & White Healthcare Fundamentals
Stago Newsletter. Volume 6 Issue 1 May 2016
 1 Stago Newsletter Volume 6 Issue 1 May 2016 Haemostasis Catalogue 2016 2 INSIDE THIS ISSUE: 2016 Haemostasis Catalogue 2 VWF Collagen Binding 3 Customer Corner 4 ihemostasis and Haemoscore 5 Continuing
1 Stago Newsletter Volume 6 Issue 1 May 2016 Haemostasis Catalogue 2016 2 INSIDE THIS ISSUE: 2016 Haemostasis Catalogue 2 VWF Collagen Binding 3 Customer Corner 4 ihemostasis and Haemoscore 5 Continuing
Coagulopathy Case-2. Andy Nguyen, M.D. 2009
 Coagulopathy Case-2 Andy Nguyen, M.D. 2009 CLINICAL HISTORY A 42 year-old man brought to the emergency room with severe burn. Patient was rescued by firemen in a serious fire. He had been found unconscious
Coagulopathy Case-2 Andy Nguyen, M.D. 2009 CLINICAL HISTORY A 42 year-old man brought to the emergency room with severe burn. Patient was rescued by firemen in a serious fire. He had been found unconscious
VWF (Human) ELISA Kit
 VWF (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0512 96 assays Version: 27 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General Information...
VWF (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0512 96 assays Version: 27 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General Information...
Case 1. Case 1. Case 2. Case 2. Review of Bleeding Disorders Case 1
 Review of Bleeding Disorders Case 1 Robert I. Handin, MD Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Hematology Division Brigham & Women s Hospital 20 year college student is home on spring break and
Review of Bleeding Disorders Case 1 Robert I. Handin, MD Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Hematology Division Brigham & Women s Hospital 20 year college student is home on spring break and
von Willebrand Factor (vwf) is a multimeric plasma
 Correction of Bleeding Symptoms in von Willebrand Factor Deficient Mice by Liver-Expressed von Willebrand Factor Mutants Isabelle Marx, Peter J. Lenting, Thure Adler, Ronan Pendu, Olivier D. Christophe,
Correction of Bleeding Symptoms in von Willebrand Factor Deficient Mice by Liver-Expressed von Willebrand Factor Mutants Isabelle Marx, Peter J. Lenting, Thure Adler, Ronan Pendu, Olivier D. Christophe,
von Willebrand Factor (vwf) is a multimeric plasma
 Correction of Bleeding Symptoms in von Willebrand Factor Deficient Mice by Liver-Expressed von Willebrand Factor Mutants Isabelle Marx, Peter J. Lenting, Thure Adler, Ronan Pendu, Olivier D. Christophe,
Correction of Bleeding Symptoms in von Willebrand Factor Deficient Mice by Liver-Expressed von Willebrand Factor Mutants Isabelle Marx, Peter J. Lenting, Thure Adler, Ronan Pendu, Olivier D. Christophe,
Platelet glycoprotein Ibα forms catch bonds with human WT vwf but not with type 2B von Willebrand disease vwf
 Related Commentary, page 3009 Research article Platelet glycoprotein Ibα forms catch bonds with human WT vwf but not with type 2B von Willebrand disease vwf Tadayuki Yago, 1 Jizhong Lou, 2,3 Tao Wu, 4
Related Commentary, page 3009 Research article Platelet glycoprotein Ibα forms catch bonds with human WT vwf but not with type 2B von Willebrand disease vwf Tadayuki Yago, 1 Jizhong Lou, 2,3 Tao Wu, 4
Platelets in mammals are anucleated cells that originate. Reviews. Adhesion Mechanisms in Platelet Function
 Reviews This Review is part of a thematic series on Mechanisms, Models, and In Vivo Imaging of Thrombus Formation, which includes the following articles: Activation of Platelet Function Through G Protein
Reviews This Review is part of a thematic series on Mechanisms, Models, and In Vivo Imaging of Thrombus Formation, which includes the following articles: Activation of Platelet Function Through G Protein
Personal history of excessive mucocutaneous bleeding. Family history of excessive bleeding. Laboratory tests of hemostasis consistent with VWD
 Diagnostic Approach Personal history of excessive mucocutaneous bleeding Family history of excessive bleeding Laboratory tests of hemostasis consistent with VWD Nose Bleeds Skin Bruising Gum Bleeding Menorrhagia
Diagnostic Approach Personal history of excessive mucocutaneous bleeding Family history of excessive bleeding Laboratory tests of hemostasis consistent with VWD Nose Bleeds Skin Bruising Gum Bleeding Menorrhagia
Profibrinolytic diabody targeting PAI-1 and TAFI for treatment of acute thrombotic disorders
 ProFiDIΛ Profibrinolytic diabody targeting PAI-1 and TAFI for treatment of acute thrombotic disorders THROMBOLYSIS WITH IMPROVED SAFETY A valorisation project of Unmet Medical Need = Safe Thrombolysis
ProFiDIΛ Profibrinolytic diabody targeting PAI-1 and TAFI for treatment of acute thrombotic disorders THROMBOLYSIS WITH IMPROVED SAFETY A valorisation project of Unmet Medical Need = Safe Thrombolysis
Characterization of antithrombin-specific RNA aptamers for use in anticoagulant therapy
 Characterization of antithrombin-specific RNA aptamers for use in anticoagulant therapy Yolanda M. Fortenberry, Ph.D. Hematology 2014 Conference Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine What are aptamers?
Characterization of antithrombin-specific RNA aptamers for use in anticoagulant therapy Yolanda M. Fortenberry, Ph.D. Hematology 2014 Conference Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine What are aptamers?
Membrane microvesicles: a circulating source for fibrinolysis, new antithrombotic
 Membrane microvesicles: a circulating source for fibrinolysis, new antithrombotic messengers 1 Laurent Plawinski, 2,3 Eduardo Anglés-Cano 1 CNRS UMR 5248 Imagerie Moléculaire et Nanobiotechnologie, Université
Membrane microvesicles: a circulating source for fibrinolysis, new antithrombotic messengers 1 Laurent Plawinski, 2,3 Eduardo Anglés-Cano 1 CNRS UMR 5248 Imagerie Moléculaire et Nanobiotechnologie, Université
Plasma fibronectin supports hemostasis and regulates thrombosis
 The Journal of Clinical Investigation Plasma fibronectin supports hemostasis and regulates thrombosis Yiming Wang, 1,2,3 Adili Reheman, 2 Christopher M. Spring, 2 Jalil Kalantari, 2,4 Alexandra H. Marshall,
The Journal of Clinical Investigation Plasma fibronectin supports hemostasis and regulates thrombosis Yiming Wang, 1,2,3 Adili Reheman, 2 Christopher M. Spring, 2 Jalil Kalantari, 2,4 Alexandra H. Marshall,
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Can Biomarkers Help to Guide Duration of Therapy After VTE? New Chest Guidelines 2016
 Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Can Biomarkers Help to Guide Duration of Therapy After VTE? Marlene Grenon, MD Associate Professor of Surgery University of California San Francisco UCSF Vascular Surgery Symposium
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) Can Biomarkers Help to Guide Duration of Therapy After VTE? Marlene Grenon, MD Associate Professor of Surgery University of California San Francisco UCSF Vascular Surgery Symposium
We are committed to translating ground-breaking science into genomic therapies that transform patients lives
 We are committed to translating ground-breaking science into genomic therapies that transform patients lives Liver-based expression of the human alpha-galactosidase A gene (GLA) in a murine Fabry model
We are committed to translating ground-breaking science into genomic therapies that transform patients lives Liver-based expression of the human alpha-galactosidase A gene (GLA) in a murine Fabry model
Special Coagulation - APC Resistance. DiaPharma Group, Inc. Customer Service: Technical Support:
 Special Coagulation - APC Resistance DiaPharma Group, Inc. Customer Service: 1.800.526.5224 Technical Support:1.800.447.3846 www.diapharma.com 1 Review of Hemostasis Overview Pathways of coagulation, anticoagulation,
Special Coagulation - APC Resistance DiaPharma Group, Inc. Customer Service: 1.800.526.5224 Technical Support:1.800.447.3846 www.diapharma.com 1 Review of Hemostasis Overview Pathways of coagulation, anticoagulation,
LABORATORY APPROCH TO THE BLEEDING PATIENT
 Anne Winkler, MD Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta Georgia Assistant Professor, Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Medical Director, Transfusion Service, Grady Health System Assistant Director,
Anne Winkler, MD Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta Georgia Assistant Professor, Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Medical Director, Transfusion Service, Grady Health System Assistant Director,
KILLING THROMBUS WITH
 KILLING THROMBUS WITH D. Dash Department of Biochemistry Institute of Medical Sciences Banaras Hindu University Thrombus has two components: (1) Protein Component composed of Insoluble Fibrin Clot (2)
KILLING THROMBUS WITH D. Dash Department of Biochemistry Institute of Medical Sciences Banaras Hindu University Thrombus has two components: (1) Protein Component composed of Insoluble Fibrin Clot (2)
Plasma Testing in the Clinical Coagulation Laboratory: New drugs, new problems.
 Test Plasma Testing in the Clinical Coagulation Laboratory: New drugs, new problems. Karen A. Moffat BEd, MSc, ART, FCSMLS(D) Technical Specialist, Coagulation, HRLMP Assistant Professor, Department of
Test Plasma Testing in the Clinical Coagulation Laboratory: New drugs, new problems. Karen A. Moffat BEd, MSc, ART, FCSMLS(D) Technical Specialist, Coagulation, HRLMP Assistant Professor, Department of
Acute Traumatic Coagulopathy
 Jean-Francois Pittet, M.D. Depts of Anesthesia and Surgery Cardiovascular Research Institute University of California San Francisco Acute Traumatic Coagulopathy Plan 1. Description of the coagulation system
Jean-Francois Pittet, M.D. Depts of Anesthesia and Surgery Cardiovascular Research Institute University of California San Francisco Acute Traumatic Coagulopathy Plan 1. Description of the coagulation system
Insights into thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura by monoclonal antibody-based analysis of the von Willebrand factor cleaving protease, ADAMTS-13
 Faculteit Wetenschappen Departement Chemie Afdeling Biochemie Laboratorium voor Trombose Onderzoek KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN CAMPUS KORTRIJK Insights into thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura by monoclonal
Faculteit Wetenschappen Departement Chemie Afdeling Biochemie Laboratorium voor Trombose Onderzoek KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN CAMPUS KORTRIJK Insights into thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura by monoclonal
Laboratory Testing Issues for Protein C, Protein S and Antithrombin Assays
 Laboratory Testing Issues for Protein C, Protein S and Antithrombin Assays Richard A. Marlar Ph.D. University of Oklahoma THSNA Meeting- Chicago, IL April 14-16, 2016 DISCLOSURE Richard A. Marlar, PhD
Laboratory Testing Issues for Protein C, Protein S and Antithrombin Assays Richard A. Marlar Ph.D. University of Oklahoma THSNA Meeting- Chicago, IL April 14-16, 2016 DISCLOSURE Richard A. Marlar, PhD
Farnesoid X Receptor and its ligands inhibit the function of platelets
 Farnesoid X Receptor and its ligands inhibit the function of platelets Article Accepted Version Figures and Legends Moraes, L. A., Unsworth, A. J., Vaiyapuri, S., Ali, M. S., Sasikumar, P., Sage, T., Flora,
Farnesoid X Receptor and its ligands inhibit the function of platelets Article Accepted Version Figures and Legends Moraes, L. A., Unsworth, A. J., Vaiyapuri, S., Ali, M. S., Sasikumar, P., Sage, T., Flora,
What Can We Learn from Animal Models of Coagulopathy and Bleeding (about plasma transfusion)?
 Test What Can We Learn from Animal Models of Coagulopathy and Bleeding (about plasma transfusion)? William Sheffield Associate Director, Research CBS Centre for Innovation, and Professor, Pathology and
Test What Can We Learn from Animal Models of Coagulopathy and Bleeding (about plasma transfusion)? William Sheffield Associate Director, Research CBS Centre for Innovation, and Professor, Pathology and
Activation and specificity of Thrombin. Giulia Pavani
 Activation and specificity of Thrombin Giulia Pavani Summary Regulation of a Serine Protease: Thrombin Zymogen Enzyme Substrate Specificity Staphylocoagulase Bacteria know how a protease works (much more
Activation and specificity of Thrombin Giulia Pavani Summary Regulation of a Serine Protease: Thrombin Zymogen Enzyme Substrate Specificity Staphylocoagulase Bacteria know how a protease works (much more
Isolation of mouse monocytes: Mouse monocytes were isolated using a modified
 Supplemental Material Extended Methods Isolation of mouse monocytes: Mouse monocytes were isolated using a modified method described (1). Citrated mouse whole blood was mixed with equal volume of PBS,
Supplemental Material Extended Methods Isolation of mouse monocytes: Mouse monocytes were isolated using a modified method described (1). Citrated mouse whole blood was mixed with equal volume of PBS,
Current laboratory practices in the diagnosis and management of haemophilia
 Current laboratory practices in the diagnosis and management of haemophilia Marc Jacquemin University of Leuven BSTH 2013 Detection of severe haemophilia A Validation of the FVIII assay for the detection
Current laboratory practices in the diagnosis and management of haemophilia Marc Jacquemin University of Leuven BSTH 2013 Detection of severe haemophilia A Validation of the FVIII assay for the detection
Management of Bleeding in the Anticoagulated Patient Short Snappers CSIM 2015 Elizabeth Zed, MD, FRCPC October 17, 2015
 + Management of Bleeding in the Anticoagulated Patient Short Snappers CSIM 2015 Elizabeth Zed, MD, FRCPC October 17, 2015 + Disclosures Off label use of PCC and apcc will be discussed My centre participates
+ Management of Bleeding in the Anticoagulated Patient Short Snappers CSIM 2015 Elizabeth Zed, MD, FRCPC October 17, 2015 + Disclosures Off label use of PCC and apcc will be discussed My centre participates
If not heparin for bypass then what? Dr Tony Moriarty Consultant Cardiac Anaesthetist Birmingham United Kingdom
 If not heparin for bypass then what? Dr Tony Moriarty Consultant Cardiac Anaesthetist Birmingham United Kingdom Heparin Discovered 1916, commercial available 1935 Heparin Is there an alternative, not really
If not heparin for bypass then what? Dr Tony Moriarty Consultant Cardiac Anaesthetist Birmingham United Kingdom Heparin Discovered 1916, commercial available 1935 Heparin Is there an alternative, not really
Platelet deposition (%) Fibronectin
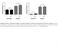 Platelet deposition (%) Platelet deposition (%) 60 p = 0.347 60 p = 1.000 40 p = 0.881 40 20 20 p = 0.114 0 Up Down Up Down 0 Up Down Up Down Fibrinogen Collagen I Fibronectin Collagen I Supplementary
Platelet deposition (%) Platelet deposition (%) 60 p = 0.347 60 p = 1.000 40 p = 0.881 40 20 20 p = 0.114 0 Up Down Up Down 0 Up Down Up Down Fibrinogen Collagen I Fibronectin Collagen I Supplementary
Structure of IgG and IgM
 Structure of IgG and IgM Fig. 5-1 A,B Crystal Structure of Secreted IgG Fig. 5-1 C Structure of an Ig Domain Fig. 5-2 Proteolytic Fragments of IgG (1) Fig. 5-3A Proteolytic Fragments of IgG (2) Fig. 5-3B
Structure of IgG and IgM Fig. 5-1 A,B Crystal Structure of Secreted IgG Fig. 5-1 C Structure of an Ig Domain Fig. 5-2 Proteolytic Fragments of IgG (1) Fig. 5-3A Proteolytic Fragments of IgG (2) Fig. 5-3B
A Microfluidic Approach For Investigating The Role Of Blood Flow In Thrombosis
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations 2018 A Microfluidic Approach For Investigating The Role Of Blood Flow In Thrombosis Bradley Andrew Herbig University of
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations 2018 A Microfluidic Approach For Investigating The Role Of Blood Flow In Thrombosis Bradley Andrew Herbig University of
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/9/eaat5401/dc1 Supplementary Materials for GLK-IKKβ signaling induces dimerization and translocation of the AhR-RORγt complex in IL-17A induction and autoimmune
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/9/eaat5401/dc1 Supplementary Materials for GLK-IKKβ signaling induces dimerization and translocation of the AhR-RORγt complex in IL-17A induction and autoimmune
The Combined Use of Bypassing Agents with Antithrombin Reduction in Plasma of Hemophilia A and B Patients with Inhibitors
 Venkat Living Venkat with Hemophilia Living with Hemophilia The Combined Use of Bypassing Agents with Antithrombin Reduction in Plasma of Hemophilia A and B Patients with Inhibitors Tami Livnat 1, Alfica
Venkat Living Venkat with Hemophilia Living with Hemophilia The Combined Use of Bypassing Agents with Antithrombin Reduction in Plasma of Hemophilia A and B Patients with Inhibitors Tami Livnat 1, Alfica
Hemostasis practice: state-of-the-art
 Perspective Page 1 of 6 Hemostasis practice: state-of-the-art Giuseppe Lippi 1, Emmanuel J. Favaloro 2 1 Section of Clinical Biochemistry, Department of Neurological, Biomedical and Movement Sciences,
Perspective Page 1 of 6 Hemostasis practice: state-of-the-art Giuseppe Lippi 1, Emmanuel J. Favaloro 2 1 Section of Clinical Biochemistry, Department of Neurological, Biomedical and Movement Sciences,
Index. Autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura (AITP), 100, 102, 105, 108, 187 Automated platelet counters, , 108
 A Accuracy, 6, 7, 15, 46, 52, 53, 61, 75, 100, 143, 144, 149, 166, 176, 178 Acquired coagulation disorders, 111 115 Acquired platelet disorders, 99 108 ACT. See Activated clotting time (ACT) Activated
A Accuracy, 6, 7, 15, 46, 52, 53, 61, 75, 100, 143, 144, 149, 166, 176, 178 Acquired coagulation disorders, 111 115 Acquired platelet disorders, 99 108 ACT. See Activated clotting time (ACT) Activated
Haemostasis. The function of haemostasis is: to prevent blood loss from injured vessels. to stop bleeding. to prevent thrombosis
 Haemostasis Haemostasis The function of haemostasis is: to prevent blood loss from injured vessels to stop bleeding to prevent thrombosis Haemostasis blood endothelium basement membrane subendothelium
Haemostasis Haemostasis The function of haemostasis is: to prevent blood loss from injured vessels to stop bleeding to prevent thrombosis Haemostasis blood endothelium basement membrane subendothelium
4/5/2017. Molecular Testing Applications in Coagulation. Disclosures. Objectives. Human Genome Chromosome Analysis.
 Disclosures Relevant Financial Relationship(s): NONE Molecular Testing Applications in Coagulation Off Label Usage: NONE Sara Lassila, MB(ASCP) CM Clinical Laboratory Scientists of Alaska April 6 th, 2017
Disclosures Relevant Financial Relationship(s): NONE Molecular Testing Applications in Coagulation Off Label Usage: NONE Sara Lassila, MB(ASCP) CM Clinical Laboratory Scientists of Alaska April 6 th, 2017
Manejo de la transfusión de plaquetas. Ileana López-Plaza, MD
 Manejo de la transfusión de plaquetas Ileana López-Plaza, MD Thrombocytopenia Common in ICU setting 25-38% with< 100,000/µL 2-3 % with < 10,000/µL Common etiologies Drug-induced: heparin, antibiotics,
Manejo de la transfusión de plaquetas Ileana López-Plaza, MD Thrombocytopenia Common in ICU setting 25-38% with< 100,000/µL 2-3 % with < 10,000/µL Common etiologies Drug-induced: heparin, antibiotics,
Immunoglobulins. Harper s biochemistry Chapter 49
 Immunoglobulins Harper s biochemistry Chapter 49 Immune system Detects and inactivates foreign molecules, viruses, bacteria and microorganisms Two components with 2 strategies B Lymphocytes (humoral immune
Immunoglobulins Harper s biochemistry Chapter 49 Immune system Detects and inactivates foreign molecules, viruses, bacteria and microorganisms Two components with 2 strategies B Lymphocytes (humoral immune
Chapter 3. Clonal selection
 Chapter 3. Clonal selection I have called this principle, by which each slight variation, if useful, is preserved, by the term of Natural Selection -Charles Darwin, On the Origin of Species, 1859 4 The
Chapter 3. Clonal selection I have called this principle, by which each slight variation, if useful, is preserved, by the term of Natural Selection -Charles Darwin, On the Origin of Species, 1859 4 The
Principles of Coagulation Testing. Andy Nguyen, MD 8/4/2010
 Principles of Coagulation Testing Andy Nguyen, MD 8/4/2010 FSP and D-Dimer FDP vs. D-DIMER Fibrin is formed as the end result of coagulation cascade activation Fibrinolysis causes cleavage of fibrinogen,
Principles of Coagulation Testing Andy Nguyen, MD 8/4/2010 FSP and D-Dimer FDP vs. D-DIMER Fibrin is formed as the end result of coagulation cascade activation Fibrinolysis causes cleavage of fibrinogen,
Basic coagulation applications and case studies
 Basic coagulation applications and case studies Jing Jin Clinical laboratory Scientist (MLS, ASCP) - Coagulation/Hematology Stanford University Hospital and Clinics 1 Agenda Overview about 3 major phases
Basic coagulation applications and case studies Jing Jin Clinical laboratory Scientist (MLS, ASCP) - Coagulation/Hematology Stanford University Hospital and Clinics 1 Agenda Overview about 3 major phases
Supplementary Figure 1 a
 3 min PMA 45 min PMA AnnexinV-FITC Supplementary Figure 1 5 min PMA 15 min PMA a 9 min PMA 12 min PMA 5 min FGF7 15 min FGF7 3 min FGF7 6 min FGF7 9 min FGF7 12 min FGF7 5 min control 3 min control 6 min
3 min PMA 45 min PMA AnnexinV-FITC Supplementary Figure 1 5 min PMA 15 min PMA a 9 min PMA 12 min PMA 5 min FGF7 15 min FGF7 3 min FGF7 6 min FGF7 9 min FGF7 12 min FGF7 5 min control 3 min control 6 min
Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human
 Supplementary Figure 1: Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human platelets in the absence of elevated shear and induces platelet agglutination as detected by flow cytometry.
Supplementary Figure 1: Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human platelets in the absence of elevated shear and induces platelet agglutination as detected by flow cytometry.
NEW INITIATIVES. Factor XIII, Fibrinolysis, Heparin. Piet Meijer. ECAT Foundation. Leiden The Netherlands
 NEW INITIATIVES Factor XIII, Fibrinolysis, Heparin Piet Meijer ECAT Foundation Leiden The Netherlands DISCLOSURE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None Pilot study on Fibrinolytic
NEW INITIATIVES Factor XIII, Fibrinolysis, Heparin Piet Meijer ECAT Foundation Leiden The Netherlands DISCLOSURE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None Pilot study on Fibrinolytic
CHROMOGENIC SUBSTRATE TECHNOLOGY. Giovanni Russi
 CHROMOGENIC SUBSTRATE TECHNOLOGY Giovanni Russi What is a chromogenic substrate? A peptide linked to a chromophore The peptide is formed by 3-5 residues The chromophore is p-nitroaniline (p-na) The residues
CHROMOGENIC SUBSTRATE TECHNOLOGY Giovanni Russi What is a chromogenic substrate? A peptide linked to a chromophore The peptide is formed by 3-5 residues The chromophore is p-nitroaniline (p-na) The residues
VWF (Human) ELISA Kit
 VWF (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0512 96 assays Version: 33 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General Information...
VWF (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0512 96 assays Version: 33 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General Information...
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplemental Methods:
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods: Immunoprecipitation- As we described but with some modifications [22]. As part of another ongoing project, lysate from human umbilical vein endothelial cells
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods: Immunoprecipitation- As we described but with some modifications [22]. As part of another ongoing project, lysate from human umbilical vein endothelial cells
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP)
 European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 29 July 2004 CPMP/BPWG/1089/00 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF PLASMA
European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 29 July 2004 CPMP/BPWG/1089/00 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF PLASMA
WFH 2014 World Congress Medical Free Paper 8 ALN AT3: An Investigational RNAi Therapeutic Targeting Antithrombin for the Treatment of Hemophilia
 WFH 214 World Congress Medical Free Paper 8 ALN AT3: An Investigational RNAi Therapeutic Targeting Antithrombin for the Treatment of Hemophilia May 15, 214 Akin Akinc, PhD Antithrombin and ALN-AT3 Program
WFH 214 World Congress Medical Free Paper 8 ALN AT3: An Investigational RNAi Therapeutic Targeting Antithrombin for the Treatment of Hemophilia May 15, 214 Akin Akinc, PhD Antithrombin and ALN-AT3 Program
Platelet Activation by Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Haemostasis and Thrombosis
 1358 Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2009, 15, 1358-1372 Platelet Activation by Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Haemostasis and Thrombosis Steve P. Watson * Centre for Cardiovascular Sciences, Institute
1358 Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2009, 15, 1358-1372 Platelet Activation by Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Haemostasis and Thrombosis Steve P. Watson * Centre for Cardiovascular Sciences, Institute
MCB 4211, Fall 2018, Practice Exam 1 Last, First name Student ID # Seat No. ***NOTE: Exam will have 40 multiple choice questions.
 MCB 4211, Fall 2018, Practice Exam 1 Last, First name Student ID # Seat No. ***NOTE: Exam 1 2018 will have 40 multiple choice questions. READ ALL THE CHOICES AND SELECT THE BEST 1. Which of the following
MCB 4211, Fall 2018, Practice Exam 1 Last, First name Student ID # Seat No. ***NOTE: Exam 1 2018 will have 40 multiple choice questions. READ ALL THE CHOICES AND SELECT THE BEST 1. Which of the following
a. Hypoxanthine was present in the media. MCB 4211, Fall 2018, Practice Exam 1 Last, First name Student ID # Seat No.
 MCB 4211, Fall 2018, Practice Exam 1 Last, First name Student ID # Seat No. ***NOTE: Exam 1 2018 will have 40 multiple choice questions. READ ALL THE CHOICES AND SELECT THE BEST 1. Which of the following
MCB 4211, Fall 2018, Practice Exam 1 Last, First name Student ID # Seat No. ***NOTE: Exam 1 2018 will have 40 multiple choice questions. READ ALL THE CHOICES AND SELECT THE BEST 1. Which of the following
Laboratory investigation in the Bleeding Patient. Dr Craig Taylor Consultant Haematologist May 2016
 Laboratory investigation in the Bleeding Patient Dr Craig Taylor Consultant Haematologist May 2016 Introduction Bleeding is common May consume significant resources Crossmatched blood Lab results may be
Laboratory investigation in the Bleeding Patient Dr Craig Taylor Consultant Haematologist May 2016 Introduction Bleeding is common May consume significant resources Crossmatched blood Lab results may be
Immune System. Branden & Tooze, Chapter 15 Protects complex multicellular organisms from pathogens, e.g. virus, bacteria, yeast, parasites, worms, etc
 Immune System Branden & Tooze, Chapter 15 Protects complex multicellular organisms from pathogens, e.g. virus, bacteria, yeast, parasites, worms, etc Innate immunity first line of defense past physical
Immune System Branden & Tooze, Chapter 15 Protects complex multicellular organisms from pathogens, e.g. virus, bacteria, yeast, parasites, worms, etc Innate immunity first line of defense past physical
HaematologY. Dr Tom Bate Again!
 HaematologY Dr Tom Bate Again! THE FRCA What you need to know Blood Groups ~30 blood group systems recognised (ISBT) ABO, Rhesus, Lewis, Kell, Duffy, Kidd MNS system, Kell system The ABO antigens are the
HaematologY Dr Tom Bate Again! THE FRCA What you need to know Blood Groups ~30 blood group systems recognised (ISBT) ABO, Rhesus, Lewis, Kell, Duffy, Kidd MNS system, Kell system The ABO antigens are the
Coagulation Cascade. TF-VIIa. Tissue Factor + VII. XIIa. Prothrombin. XIa. IXa. VIIIa. Thrombin. XL- Fibrin. XIII Monomer. Fibrinogen.
 Coagulation Cascade Intrinsic Pathway Extrinsic Pathway Contact Activation XIIa XI XIa Prekallikrein HMW Kininogen IX IXa Ca 2+ Anticoagulation proteins: Protein C, Protein S, Antithrombin III, TFPI TF
Coagulation Cascade Intrinsic Pathway Extrinsic Pathway Contact Activation XIIa XI XIa Prekallikrein HMW Kininogen IX IXa Ca 2+ Anticoagulation proteins: Protein C, Protein S, Antithrombin III, TFPI TF
Platelet-collagen interaction: is GPVI the central receptor?
 Review article Platelet-collagen interaction: is GPVI the central receptor? Bernhard Nieswandt and Steve P. Watson At sites of vascular injury, platelets come into contact with subendothelial collagen,
Review article Platelet-collagen interaction: is GPVI the central receptor? Bernhard Nieswandt and Steve P. Watson At sites of vascular injury, platelets come into contact with subendothelial collagen,
Coagulation in perspective: Blood management. Objectives
 Coagulation in perspective: Blood management Julie Wegner, PhD jawrbl@gmail.com Objectives To gain a basic understanding of the following: 1. Coagulation components and processes Why patients bleed. 2.
Coagulation in perspective: Blood management Julie Wegner, PhD jawrbl@gmail.com Objectives To gain a basic understanding of the following: 1. Coagulation components and processes Why patients bleed. 2.
OVERVIEW OF LABORATORY DIAGNOSTIC TESTING FOR PLATELET DISORDERS
 OVERVIEW OF LABORATORY DIAGNOSTIC TESTING FOR PLATELET DISORDERS Catherine P. M. Hayward, MD PhD, FRCP(C) Head, Coagulation, Hamilton Regional Laboratory Medicine Program Professor, Pathology and Molecular
OVERVIEW OF LABORATORY DIAGNOSTIC TESTING FOR PLATELET DISORDERS Catherine P. M. Hayward, MD PhD, FRCP(C) Head, Coagulation, Hamilton Regional Laboratory Medicine Program Professor, Pathology and Molecular
