Republican and Whig Ideologies Republicanism: A just society is one in which all citizens willingly subordinate their interests for the common good
|
|
|
- Dorothy Nicholson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Republican and Whig Ideologies Republicanism: A just society is one in which all citizens willingly subordinate their interests for the common good Govt serves the citizens Against hierarchy and aristocracy Whigism: The arbitrary power of monarchs and his ministers can pose a threat to liberty and corruption Together: Colonists are on alert against any threat to their liberties.
3 Mercantilism Colonies existed to supply raw materials and markets for English manufacturing. History of regulating the colonies for benefit of England: Navigation Acts of 1660 and 1663 are examples Colonists felt this system stifled their economy and gave England advantage But, most of these laws were loosely enforced There was a history of salutary neglect
4 French and Indian War Left England in major debt Also have to patrol the frontier against Native attacks Prime Minister George Grenville strictly enforces navigation acts Need sources of revenue.
5 Sugar Act (1764) Also called Revenue Act of 1764 Tax on sugar, molasses and other luxuries First attempt by Parliament to raise tax revenue on colonies for crown Actually lowered previous taxes, but more strictly enforced England set up admirality courts to enforce (no juries) Virtual representation
6 Currency Act (1764) Colonists could not issue paper money Colonies had issued paper money during economic downturn after war Tried to make up for amount of hard currency leaving the colonies to England (we bought more than we sold) It quickly depreciated which could have hurt colonial and English economies Colonists feel Parliament is overstepping its power
7 Stamp Act (1765) Already imposed in England English taxation rate 25 times higher than rate in colonies First direct tax on colonies Was to help pay for military in colonies Virginia House of Burgesses formally protests the tax Tried in Admiralty Courts
8 Sons (and Daughters) of Liberty Led protests in NY and Rhode Island to protest taxes Some violence (tar and feathering, raiding of homes, etc.) Stamp Act Congress: delegates from 9 colonies decide to protest tax collectively Boycott British goods Nonimportation agreements united American people Stamp Act repealed in 1766
9 More Taxes Declaratory Act (1766): Parliament has the power to enact laws as they see fit In response to American defiance to Stamp Act Townshend Acts (1767): Indirect duties (paid at American ports) on colonial imports, including tea, glass, paper, paint, etc. Specifically to pay for British officials in colonies More colonial boycotts (nonimportation) Increase in colonial smuggling Townshend Acts actually cost England money British troops sent to enforce the Acts and search for smuggled goods Repealed in 1770 (except tax on tea)--same day as Boston Massacre
10 The Boston Massacre (March 5,1770)
11 Committees of Correspondence Organized in Boston by Samuel Adams in 1772 Purpose à warn neighboring colonies about incidents with Britain à broaden the resistance movement. By 1773, each colony had a committee Virginia s committee was actually a standing committee in the House of Burgesses.
12 8 British East India Co.: Tea Act (1773) Monopoly on Br. tea imports in colonies to help it fend off bankruptcy. Many members of Parliament held shares. Permitted the Co. to sell tea directly to colonies without English middlemen (cheaper tea!) Britain would still get tax from Townshend duties Assumed colonists would choose cheaper tea.
13 Boston Tea Party Colonists refuse to allow ships on shore Governor Hutchinson refused to allow ships to return to Britain Colonists board ships and dump tea in Boston Harbor
14 Tar and Feathering
15 The Coercive or Intolerable Acts (1774) Lord North Closed harbor until tea paid for (Boston Port Act) Limits put on Town Meetings (Massachusetts Government Act) British troops immune to colonial law Changed power of local assemblies Quartering Act
16 The Quebec Act (1774)
17 First Continental Congress (1774) 55 delegates from 12 colonies (no GA) Agenda à How to respond to the Coercive Acts & the Quebec Act? 1 vote per colony represented.
18 Continental Congress Continued Said if Intolerable Acts were not repealed by end of 1774, English goods would be boycotted Created The Association : nonimportation, nonexportation, nonconsumption of British goods Parliament rejected Militias and illegal local governments formed Agreed to meet again in May, 1775 if colonial grievances were not redressed Bostonian movement spreads across the colonies
19 The Final Rupture Thomas Gage had 4000 Red Coats in Boston April 1775, he sent 700 troops to seize arms and munitions in Concord, Mass. Also arrest Sam Adams and John Hancock
20 The British Are Coming... Paul Revere & William Dawes make their midnight ride to warn the Minutemen of approaching British soldiers.
21 The Shot Heard Round the World! Lexington & Concord April 18,1775
Describe the colonists political heritage. Explain the colonists reaction to new taxes.
 Objectives Describe the colonists political heritage. Explain the colonists reaction to new taxes. Describe the methods the colonists used to protest British taxes. Understand the significance of the First
Objectives Describe the colonists political heritage. Explain the colonists reaction to new taxes. Describe the methods the colonists used to protest British taxes. Understand the significance of the First
STANDARD 1.2 EARLY GOVERNMENTS AND ROAD TO REVOLUTION
 STANDARD 1.2 EARLY GOVERNMENTS AND ROAD TO REVOLUTION REPRESENTATIVE GOVERNMENT A form of government in which elected officials would vote on the laws for the good of the society. The American model is
STANDARD 1.2 EARLY GOVERNMENTS AND ROAD TO REVOLUTION REPRESENTATIVE GOVERNMENT A form of government in which elected officials would vote on the laws for the good of the society. The American model is
Trouble Brewing. Colonies
 Trouble Brewing in the Colonies French and Indian War Aftermath Colonists began to become disenchanted with British rule after the French and Indian War Treatment of colonial militias during war Proclamation
Trouble Brewing in the Colonies French and Indian War Aftermath Colonists began to become disenchanted with British rule after the French and Indian War Treatment of colonial militias during war Proclamation
Birth of the Republic
 Birth of the Republic 1 2 The American Colonists Mainly of English descent Scotch-Irish / Germans --> Pennsylvania Black Africans --> the South Believed they were preserving the true traditions of English
Birth of the Republic 1 2 The American Colonists Mainly of English descent Scotch-Irish / Germans --> Pennsylvania Black Africans --> the South Believed they were preserving the true traditions of English
The French and Indian War
 The French and Indian War British/French Rivalry 1689: Glorious Revolution; England becomes a constitutional monarchy France ruled by Louis XIV; L état c est moi ; absolute monarchy France and England
The French and Indian War British/French Rivalry 1689: Glorious Revolution; England becomes a constitutional monarchy France ruled by Louis XIV; L état c est moi ; absolute monarchy France and England
Proclamation of /14/2010. Before 1763, the Navigation laws. Before 1763, the Navigation laws. The Proclamation of 1763 was issued mainly to
 Q: Why would 13 British colonies CHOOSE to leave the largest, richest, most power Empire in the world? When it comes to the Revolution, it could be said that the American colonists were 1. Eagar revolutionaries
Q: Why would 13 British colonies CHOOSE to leave the largest, richest, most power Empire in the world? When it comes to the Revolution, it could be said that the American colonists were 1. Eagar revolutionaries
THE ROAD TO REVOLUTION: ( )
 THE ROAD TO REVOLUTION: (1763-1775) Period 3 (1754-1800) Key Concept 3.1:II The desire of many colonists to assert ideals of self-government in the face of renewed British imperial efforts led to a colonial
THE ROAD TO REVOLUTION: (1763-1775) Period 3 (1754-1800) Key Concept 3.1:II The desire of many colonists to assert ideals of self-government in the face of renewed British imperial efforts led to a colonial
Chapter 6 Study Guide
 Chapter 6 Study Guide assembly boycott delegate independence Loyalist militia minutemen Patriot rebel repeal representation revolution self government Sons of Liberty traitor treason a law-making body
Chapter 6 Study Guide assembly boycott delegate independence Loyalist militia minutemen Patriot rebel repeal representation revolution self government Sons of Liberty traitor treason a law-making body
Analyze the ideological, military, social, and diplomatic aspects of the American Revolution.
 Analyze the ideological, military, social, and diplomatic aspects of the American Revolution. The Proclamation of 1763 When the French and Indian War ended, the French LEFT But the Indians remained And
Analyze the ideological, military, social, and diplomatic aspects of the American Revolution. The Proclamation of 1763 When the French and Indian War ended, the French LEFT But the Indians remained And
Breaking with Britain. Part I
 Breaking with Britain Part I Monday, February 6 th COMING SOON: Open Lab Test Review on Saturday, February 11 th from 10:00 am to 2:00 pm in 173A, 240, and 270 SWKT Midterm #1: February 14th 17th Tuesday,
Breaking with Britain Part I Monday, February 6 th COMING SOON: Open Lab Test Review on Saturday, February 11 th from 10:00 am to 2:00 pm in 173A, 240, and 270 SWKT Midterm #1: February 14th 17th Tuesday,
New British Measures & the Conservative Colonial Stance
 Topics of Consideration, 1763-1774 I. British North America in 1763 II. Stamp Act Debate, 1765-66 III. Townshend Debate, 1767-70 IV. Tea Act Debate, 1773-74 V. The Escalation of Tension I. British North
Topics of Consideration, 1763-1774 I. British North America in 1763 II. Stamp Act Debate, 1765-66 III. Townshend Debate, 1767-70 IV. Tea Act Debate, 1773-74 V. The Escalation of Tension I. British North
Economic History of the US
 Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #4 Peter Allen Econ 120 1 Mercantilism: Gold flows only to London Economic subordination Parliament did not allow colonies to bop surplus
Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #4 Peter Allen Econ 120 1 Mercantilism: Gold flows only to London Economic subordination Parliament did not allow colonies to bop surplus
Empires at War. Great Britain, France, and Spain. The First Three Wars. King William s ( ) Queen Anne s ( ) King George s ( )
 Essential Question In what ways did the French and Indian War alter the political, economic, and ideological relations between Britain and its American colonies? Empires at War Great Britain, France, and
Essential Question In what ways did the French and Indian War alter the political, economic, and ideological relations between Britain and its American colonies? Empires at War Great Britain, France, and
UNIT 1: PRINCIPLES of AMERICAN DEMOCRACY
 UNIT 1: PRINCIPLES of AMERICAN DEMOCRACY Types of Governments Authoritarian Governments: type where people have little to no power or rights. Monarchy: one person (king, queen, or ruling family) has control
UNIT 1: PRINCIPLES of AMERICAN DEMOCRACY Types of Governments Authoritarian Governments: type where people have little to no power or rights. Monarchy: one person (king, queen, or ruling family) has control
New British Measures & the Conservative Colonial Stance. New British Measures & the Conservative Colonial Stance. Topics of Consideration:
 Topics of Consideration: 1763-1774 IV. Tea Act Debate, 1773-74 V. The Escalation of Tension 1763 French and Indian War ends: Treaty of Paris New Situation for British New Situation for Colonials 1763 Pontiac
Topics of Consideration: 1763-1774 IV. Tea Act Debate, 1773-74 V. The Escalation of Tension 1763 French and Indian War ends: Treaty of Paris New Situation for British New Situation for Colonials 1763 Pontiac
Foundations of American Government
 Foundations of American Government Why Do We Need Government? Maintain social order Ensure domestic tranquility Establish justice Provide for the common defense Promote the general welfare Secure liberty
Foundations of American Government Why Do We Need Government? Maintain social order Ensure domestic tranquility Establish justice Provide for the common defense Promote the general welfare Secure liberty
Unit 1. The learner will investigate the foundations of the American political system and explore basic values and principles of American democracy.
 Unit 1 The learner will investigate the foundations of the American political system and explore basic values and principles of American democracy. 1.02 Which documents and people influenced the colonists
Unit 1 The learner will investigate the foundations of the American political system and explore basic values and principles of American democracy. 1.02 Which documents and people influenced the colonists
Life in the Colonies. Chapter 4, Section 1
 Life in the Colonies Chapter 4, Section 1 All English colonies shared a common English heritage, and that heritage included the idea that citizens had political rights. England also promoted the theory
Life in the Colonies Chapter 4, Section 1 All English colonies shared a common English heritage, and that heritage included the idea that citizens had political rights. England also promoted the theory
CHAPTER 2. Roots of American Democracy
 CHAPTER 2 Roots of American Democracy Section 1 Our English Heritage Influences from England s Early Government The English brought with them a history of LIMITED and REPRESENTATIVE government. England
CHAPTER 2 Roots of American Democracy Section 1 Our English Heritage Influences from England s Early Government The English brought with them a history of LIMITED and REPRESENTATIVE government. England
ENGLAND & THE COLONIES
 WARM UP 1 2 Create a triple Venn-Diagram that compares the New England, Middle and Southern colonies Include economic, political and social differences... ENGLAND & THE COLONIES Colonial Mercantilism Colonies
WARM UP 1 2 Create a triple Venn-Diagram that compares the New England, Middle and Southern colonies Include economic, political and social differences... ENGLAND & THE COLONIES Colonial Mercantilism Colonies
UNIT 1: PRINCIPLES of AMERICAN DEMOCRACY
 UNIT 1: PRINCIPLES of AMERICAN DEMOCRACY Principles of the Constitution Each of these concepts are important ideas that deal with limiting the power of government, and ensuring that the people retain power
UNIT 1: PRINCIPLES of AMERICAN DEMOCRACY Principles of the Constitution Each of these concepts are important ideas that deal with limiting the power of government, and ensuring that the people retain power
CHAPTER 3 SEC 1 England & Its Colonies US 1
 CHAPTER 3 SEC 1 England & Its Colonies US 1 Main Idea & Why It Matters England and its largely self-governing colonies prospered under a mutually beneficial trade relationship Why It Matters: The colonial
CHAPTER 3 SEC 1 England & Its Colonies US 1 Main Idea & Why It Matters England and its largely self-governing colonies prospered under a mutually beneficial trade relationship Why It Matters: The colonial
The American Revolution
 The American Revolution 1765-1783 http://www.history.com/topics/american-revolution/american-revolution-history/videos/american-revolution The American Revolution in relation to... the English Civil War
The American Revolution 1765-1783 http://www.history.com/topics/american-revolution/american-revolution-history/videos/american-revolution The American Revolution in relation to... the English Civil War
Roots of Representative Government
 2 Roots of Representative Government MAIN IDEA Colonists expected their government to preserve their basic rights as English subjects. WHY IT MATTERS NOW U.S. citizens expect these same rights, such as
2 Roots of Representative Government MAIN IDEA Colonists expected their government to preserve their basic rights as English subjects. WHY IT MATTERS NOW U.S. citizens expect these same rights, such as
Some Laws Are Intolerable W.M. Akers
 Some Laws Are Intolerable W.M. Akers Have you ever heard the expression about the straw that broke the camel's back? This is used to talk about a big negative consequence of a seemingly innocuous act.
Some Laws Are Intolerable W.M. Akers Have you ever heard the expression about the straw that broke the camel's back? This is used to talk about a big negative consequence of a seemingly innocuous act.
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 4 The American Revolution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Why do new ideas often spark change? How do new ways of thinking affect the way people respond to their surroundings? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary
Lesson 4 The American Revolution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Why do new ideas often spark change? How do new ways of thinking affect the way people respond to their surroundings? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary
Warm Up. Explain the economic concept of mercantilism:
 Warm Up 1 Explain the economic concept of mercantilism: 2 What laws did British Parliament pass to designed to enforce the economic concept of mercantilism 3 Explain the colonial reaction to the Navigation
Warm Up 1 Explain the economic concept of mercantilism: 2 What laws did British Parliament pass to designed to enforce the economic concept of mercantilism 3 Explain the colonial reaction to the Navigation
Sample file. THE ROAD TO INDEPENDENCE: United States History Workbook #3. Workbooks in This Series: Table of Contents:
 Page2 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Workbooks in This Series: 1. Early America 2. The Colonial Period 3. The Road to Independence 4. The Formation of a National Government 5. Westward
Page2 Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Workbooks in This Series: 1. Early America 2. The Colonial Period 3. The Road to Independence 4. The Formation of a National Government 5. Westward
CORRELATION GUIDE Level 1
 We the People The Citizen and the Constitution Published by the Center for Civic Education Funded by the U.S. Department of Education by act of Congress CORRELATION GUIDE Level 1 For Michigan Social Studies
We the People The Citizen and the Constitution Published by the Center for Civic Education Funded by the U.S. Department of Education by act of Congress CORRELATION GUIDE Level 1 For Michigan Social Studies
Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy
 Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy FOQ #1: Did the English Civil War help or hurt Democracy? Explain. FOQ #2: What were the causes of the American Revolutionary War? How did it end? FOQ #3: What were the
Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy FOQ #1: Did the English Civil War help or hurt Democracy? Explain. FOQ #2: What were the causes of the American Revolutionary War? How did it end? FOQ #3: What were the
Key areas to pay attention to for the CBA 2
 Sequencing Key areas to pay attention to for the CBA 2 There are four fundamental documents that are created in America and that lead to our system of government now. In sequential order they are Fundamental
Sequencing Key areas to pay attention to for the CBA 2 There are four fundamental documents that are created in America and that lead to our system of government now. In sequential order they are Fundamental
Chapter 2: THE EVOLUTION OF THE BRITISH EMPIRE
 Chapter 2: THE EVOLUTION OF THE BRITISH EMPIRE OBJECTIVES: We will study about the reorganization of the British colonies. We will see how the Glorious Revolution in Great Britain impacted the colonies.
Chapter 2: THE EVOLUTION OF THE BRITISH EMPIRE OBJECTIVES: We will study about the reorganization of the British colonies. We will see how the Glorious Revolution in Great Britain impacted the colonies.
THE STAMP ACT CRISIS CAUSES OF THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION. The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens CAUSES OF THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION THE STAMP ACT CRISIS Grade 5 United States History and Geography I. California Standards HISTORY-SOCIAL
The Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens CAUSES OF THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION THE STAMP ACT CRISIS Grade 5 United States History and Geography I. California Standards HISTORY-SOCIAL
Look up the Triangular Trade on pg. 95 of your textbook and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What was the triangular trade?
 Look up the Triangular Trade on pg. 95 of your textbook and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What was the triangular trade? 2. Which 3 regions were involved in the triangular trade?
Look up the Triangular Trade on pg. 95 of your textbook and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What was the triangular trade? 2. Which 3 regions were involved in the triangular trade?
Origins of American Government Chapter 2:1:
 Origins of American Government Chapter 2:1: Objectives: 2:1 Our Political Beginnings o Students will identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. o Students will explain
Origins of American Government Chapter 2:1: Objectives: 2:1 Our Political Beginnings o Students will identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. o Students will explain
The Origins of Early Government in the Colonies
 The Origins of Early Government in the Colonies Magna Carta, 1215 The Virginia House of Burgesses, 1619 The Mayflower Compact, 1620 General Court, 1629 Fundamental Orders of Connecticut, 1639 English Bill
The Origins of Early Government in the Colonies Magna Carta, 1215 The Virginia House of Burgesses, 1619 The Mayflower Compact, 1620 General Court, 1629 Fundamental Orders of Connecticut, 1639 English Bill
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #40 Aims: SWBAT identify the three geographic areas of the 13 colonies SWBAT identify and explain mercantilism DO NOW Directions:
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #40 Aims: SWBAT identify the three geographic areas of the 13 colonies SWBAT identify and explain mercantilism DO NOW Directions:
BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas
 BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas 1690 LOCKE S TWO TREATISES ON GOVERNMENT STATE: Man has three things in nature: Life, Liberty & Property which can never be taken away or given
BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas 1690 LOCKE S TWO TREATISES ON GOVERNMENT STATE: Man has three things in nature: Life, Liberty & Property which can never be taken away or given
Chapter 4. Anglo Saxon: A.D. mixed with the natives of the island Native Brits + Germans = rule the Island of England
 English History Chapter 4 Anglo Saxon: 450 1066 A.D. mixed with the natives of the island Native Brits + Germans = rule the Island of England 1066 A.D. Norman Conquest: William of Normandy France conquers
English History Chapter 4 Anglo Saxon: 450 1066 A.D. mixed with the natives of the island Native Brits + Germans = rule the Island of England 1066 A.D. Norman Conquest: William of Normandy France conquers
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution What is a government? A government is a person, or group, who has the power to provide law, order, services, and security within a country. Government gives organization and structure
Creating the Constitution What is a government? A government is a person, or group, who has the power to provide law, order, services, and security within a country. Government gives organization and structure
Makes civic virtue a necessity. Putting the common good (your country) before your own interests This is done through moral education
 Foundations of Government Greece (400 s BC): Democracy: rule by the people Rome (509-50 BC) Republic: Citizens govern, through elected representatives Focus on the common good Makes civic virtue a necessity
Foundations of Government Greece (400 s BC): Democracy: rule by the people Rome (509-50 BC) Republic: Citizens govern, through elected representatives Focus on the common good Makes civic virtue a necessity
APUSH. PowerPoint #2.1(Part1 of 4) Uni#1 Transformations of North America Unit #2 - British North America & the Atlantic World
 APUSH PowerPoint #2.1(Part1 of 4) Uni#1 Transformations of North America Unit #2 - British North America & the Atlantic World Chapters 1-3 BFW Textbook Topic 2.1 British North America English Background
APUSH PowerPoint #2.1(Part1 of 4) Uni#1 Transformations of North America Unit #2 - British North America & the Atlantic World Chapters 1-3 BFW Textbook Topic 2.1 British North America English Background
Scenario #1 The American Herald likes to go into depth on stories that are published by other newspapers from time to time. THE REIGN OF THE HEAVENS
 Scenario #1 The American Herald likes to go into depth on stories that are published by other newspapers from time to time. THE REIGN OF THE HEAVENS SOCIETY POST published an article entitled Perpetrators
Scenario #1 The American Herald likes to go into depth on stories that are published by other newspapers from time to time. THE REIGN OF THE HEAVENS SOCIETY POST published an article entitled Perpetrators
Cluster 2. Chapter 6 CONFEDERATION
 Cluster 2 Chapter 6 CONFEDERATION Page 2 of 10 Chapter 6 p. 172-186 Word Bank manifest destiny rep by pop railways Corn Laws Rupert s Land Ireland Orange Order majority British North America British North
Cluster 2 Chapter 6 CONFEDERATION Page 2 of 10 Chapter 6 p. 172-186 Word Bank manifest destiny rep by pop railways Corn Laws Rupert s Land Ireland Orange Order majority British North America British North
THE STRENGTH OF AMERICAN FEDERAL DEMOCRACY by Roger Myerson
 THE STRENGTH OF AMERICAN FEDERAL DEMOCRACY by Roger Myerson http://home.uchicago.edu/~rmyerson/research/amerfed.pdf The institutions received from England were admirably calculated to lay the foundation
THE STRENGTH OF AMERICAN FEDERAL DEMOCRACY by Roger Myerson http://home.uchicago.edu/~rmyerson/research/amerfed.pdf The institutions received from England were admirably calculated to lay the foundation
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 1 Government in Colonial America ESSENTIAL QUESTION What influenced the development of our government institutions? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary establish to create or set up levy to charge
Lesson 1 Government in Colonial America ESSENTIAL QUESTION What influenced the development of our government institutions? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary establish to create or set up levy to charge
Directions: Analyze each document and compose a fully-developed short answer to each question.
 Name: Mini DBQ - Moving Towards Revolution Directions: Analyze each document and compose a fully-developed short answer to each question. DOCUMENT A: Letters of Joseph Warren to Arthur Lee Joseph Warren,
Name: Mini DBQ - Moving Towards Revolution Directions: Analyze each document and compose a fully-developed short answer to each question. DOCUMENT A: Letters of Joseph Warren to Arthur Lee Joseph Warren,
Georgia Coffee County 6 th Grade Social Studies. Latin America CIVICS/GOVERNMENT UNDERSTANDINGS
 Georgia Coffee County 6 th Grade Social Studies Latin America CIVICS/GOVERNMENT UNDERSTANDINGS SS6CG1 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government
Georgia Coffee County 6 th Grade Social Studies Latin America CIVICS/GOVERNMENT UNDERSTANDINGS SS6CG1 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government
A Children s Book for the Declaration of Independence
 A Children s Book for the Declaration of Independence 1. Create a Children s Book to help explain the importance of the Declaration of Independence. 2. Your Children s Book will have 6 pages in total:
A Children s Book for the Declaration of Independence 1. Create a Children s Book to help explain the importance of the Declaration of Independence. 2. Your Children s Book will have 6 pages in total:
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1
 Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
WHEN THE U.S. WAS NEW
 WHEN THE U.S. WAS NEW When America was new, every state had its own rules. Money was not the same in all states. Each state had a leader. No one was the leader of all the people. This was not working!
WHEN THE U.S. WAS NEW When America was new, every state had its own rules. Money was not the same in all states. Each state had a leader. No one was the leader of all the people. This was not working!
YOUR KEY KNOWLEDGE THIS IS WHAT THE EXAMINER CAN TEST YOU ON
 YOUR KEY KNOWLEDGE THIS IS WHAT THE EXAMINER CAN TEST YOU ON CASE STUDY OCCUPY MELBOURNE On 15 October 2011, a group of protesters moved into Melbourne's City Square in Swanston Street. This action was
YOUR KEY KNOWLEDGE THIS IS WHAT THE EXAMINER CAN TEST YOU ON CASE STUDY OCCUPY MELBOURNE On 15 October 2011, a group of protesters moved into Melbourne's City Square in Swanston Street. This action was
A Children s Book for the Declaration of Independence
 A Children s Book for the Declaration of Independence 1. Create a Children s Book to help explain the importance of the Declaration of Independence. 2. Your Children s Book will have a 7 pages in total:
A Children s Book for the Declaration of Independence 1. Create a Children s Book to help explain the importance of the Declaration of Independence. 2. Your Children s Book will have a 7 pages in total:
Louis XIV ( ) -Arguably the most powerful absolute monarch of all time. Louis learned at a young age that he wanted to be an absolute monarch.
 Absolutism in seventeenth century Europe was tied to: the divine right of kings. The divine right of kings is a belief that rulers get their power to rule from God and were responsible to no one but God.
Absolutism in seventeenth century Europe was tied to: the divine right of kings. The divine right of kings is a belief that rulers get their power to rule from God and were responsible to no one but God.
The Sugar Act British Parliament 1764
 http://ahp.gatech.edu/sugar_act_bp_1764.html The Sugar Act British Parliament 1764 An act for granting certain duties in the British colonies and plantations in America,; for continuing, amending, and
http://ahp.gatech.edu/sugar_act_bp_1764.html The Sugar Act British Parliament 1764 An act for granting certain duties in the British colonies and plantations in America,; for continuing, amending, and
The Commercial Revolution Most of Europe remained agricultural. Fastest growing part of the economy was trade of goods. Those manufactured in Europe
 13. The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment People to Know 1. Henry VIII 2. Thomas Hobbes 3. Louis XIV 4. John Locke 5. William Blackstone 6. Sir Isaac Newton 7. Robert Boyle 8. Thomas Jefferson 9.
13. The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment People to Know 1. Henry VIII 2. Thomas Hobbes 3. Louis XIV 4. John Locke 5. William Blackstone 6. Sir Isaac Newton 7. Robert Boyle 8. Thomas Jefferson 9.
The French Revolution
 The French Revolution Using your notes, complete the following paragraph. The Enlightenment is also known as the. During this time, people began to reject the teachings of the and the and question traditional
The French Revolution Using your notes, complete the following paragraph. The Enlightenment is also known as the. During this time, people began to reject the teachings of the and the and question traditional
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1
 Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
EOC Test Preparation: British North America
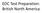 EOC Test Preparation: British North America English Colonies New England Colonies MA NH RI CT English Colonies Middle Colonies NY NJ PA DE British Colonies Southern Colonies MD VA NC SC GA Southern Colonies
EOC Test Preparation: British North America English Colonies New England Colonies MA NH RI CT English Colonies Middle Colonies NY NJ PA DE British Colonies Southern Colonies MD VA NC SC GA Southern Colonies
Quarter 1 CIVICS: What You Will Need to Know! WHAT is CIVICS? Civics The Growth of American Citizenship Citizenship
 WHAT is CIVICS? Civics the study of rights and duties of a citizen. Citizenship (SS.7.C.2.1) is the rights and duties of citizens, beginning in ancient Greece and Rome. In the 1700s, it became to mean
WHAT is CIVICS? Civics the study of rights and duties of a citizen. Citizenship (SS.7.C.2.1) is the rights and duties of citizens, beginning in ancient Greece and Rome. In the 1700s, it became to mean
British Legislation and Colonial Reactions Conflict in the Colonies. Colonial Reaction(s) General and or specific examples. Writs of Assistance, 1760
 BritishLegislation ProvisionoftheLegislation Whatdiditstateanddo? ColonialReaction(s) Generalandorspecific examples. WritsofAssistance, 1760 Basicallytheseweresearch warrants.theygavethebritish soldiersandofficialstherightto
BritishLegislation ProvisionoftheLegislation Whatdiditstateanddo? ColonialReaction(s) Generalandorspecific examples. WritsofAssistance, 1760 Basicallytheseweresearch warrants.theygavethebritish soldiersandofficialstherightto
Chapter 2.1 Our English Heritage P28-30
 Chapter 2.1 Our English Heritage P28-30 Influences from England s Early Government The English brought with them a history of limited and representative government. England was ruled by a monarch a king
Chapter 2.1 Our English Heritage P28-30 Influences from England s Early Government The English brought with them a history of limited and representative government. England was ruled by a monarch a king
Government. Date: Name:
 1207 Government 1207 Date: Name: American Government Social Studies 1207 TABLE OF CONTENTS Unit Objectives......2 Vocabulary.. 2 Character Trait... 3 Chapter 1 The Influence of History Settling the New
1207 Government 1207 Date: Name: American Government Social Studies 1207 TABLE OF CONTENTS Unit Objectives......2 Vocabulary.. 2 Character Trait... 3 Chapter 1 The Influence of History Settling the New
AP Exam Review. Chapter 3-4
 AP Exam Review Chapter 3-4 Chapter 3 The Constitution Colonies Declaration from the British (chapter 3) The British was imposing taxes on the colonies Boston Tea Party Video (schoolhouse rock boston tea
AP Exam Review Chapter 3-4 Chapter 3 The Constitution Colonies Declaration from the British (chapter 3) The British was imposing taxes on the colonies Boston Tea Party Video (schoolhouse rock boston tea
Unit One: Foundations of American Government
 Unit One: Foundations of American Government Intro Unit Lesson 1 1. Define demographics. Based on the pie charts below, compare the demographics of Durham to those of the United States as a whole. 2. We
Unit One: Foundations of American Government Intro Unit Lesson 1 1. Define demographics. Based on the pie charts below, compare the demographics of Durham to those of the United States as a whole. 2. We
PARLIAMENTARY POLICIES
 PARLIAMENTARY POLICIES Did Parliamentary policies toward the Thirteen Colonies after 1760 justify the American call for independence? Viewpoint: Yes. The colonial policies of Parliament violated Americans'
PARLIAMENTARY POLICIES Did Parliamentary policies toward the Thirteen Colonies after 1760 justify the American call for independence? Viewpoint: Yes. The colonial policies of Parliament violated Americans'
Primary Sources: Declaration of the Rights of Man
 Primary Sources: Declaration of the Rights of Man By Original document from the public domain, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.28.16 Word Count 886 This representation of the Declaration of the Rights of
Primary Sources: Declaration of the Rights of Man By Original document from the public domain, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.28.16 Word Count 886 This representation of the Declaration of the Rights of
Napoleon s Rise and Fall. AP Euro SAHS 2017
 Napoleon s Rise and Fall AP Euro SAHS 2017 Napoleon Gains Power Napoleon became a hero when he saved the National Assembly from the Royalist Napoleon was a fairly successful military leader He was able
Napoleon s Rise and Fall AP Euro SAHS 2017 Napoleon Gains Power Napoleon became a hero when he saved the National Assembly from the Royalist Napoleon was a fairly successful military leader He was able
We the People The Citizen and the Constitution. and the Arizona Social Studies Standards Level III
 We the People The Citizen and the Constitution STANDARD 2: CIVICS/GOVERNMENT and the Arizona Social Studies Standards Level III Students understand the ideals, rights, and responsibilities of citizenship,
We the People The Citizen and the Constitution STANDARD 2: CIVICS/GOVERNMENT and the Arizona Social Studies Standards Level III Students understand the ideals, rights, and responsibilities of citizenship,
Monarch. Appointed by the Crown/Monarch. Council All appointed by the
 GOVERNMENT SYSTEMS Vocabulary Suffrage: the right to vote in general elections Stipulation: requirement Allegiance: loyalty or commitment to a subordinate or superior Passion: very strong emotion Campaign:
GOVERNMENT SYSTEMS Vocabulary Suffrage: the right to vote in general elections Stipulation: requirement Allegiance: loyalty or commitment to a subordinate or superior Passion: very strong emotion Campaign:
Pangea to Early Colonists.notebook. October 19, 2015 PANGEA: Beginnings of a Nation
 PANGEA: (plate tectonics) A hypothetical continent including all the landmass of the earth prior to the Triassic period when all the land was connected as one. Continental drift Beginnings of a Nation
PANGEA: (plate tectonics) A hypothetical continent including all the landmass of the earth prior to the Triassic period when all the land was connected as one. Continental drift Beginnings of a Nation
The Canadian Constitution
 The Canadian Constitution Constitutions 2 What is a constitution? It is a list of rules which govern the actions of any organization. Nations have more complex constitutions but the the purpose is the
The Canadian Constitution Constitutions 2 What is a constitution? It is a list of rules which govern the actions of any organization. Nations have more complex constitutions but the the purpose is the
The British, recognizing that Newfoundland was no longer a collection of work camps, appointed a year-round governor in TOPIC 3.
 TOPIC 3.7 The first general election for representative government was held in 1832. How do you think candidates campaigned for the election? Why is representative government important? Introduction In
TOPIC 3.7 The first general election for representative government was held in 1832. How do you think candidates campaigned for the election? Why is representative government important? Introduction In
CIVICS & ECONOMICS EXAM STUDY GUIDE Name
 CIVICS & ECONOMICS EXAM STUDY GUIDE Name GOAL 1: Foundations of American Political System & Values & Principles of American Democracy Objective 1.01: How did geographic diversity influence the economic,
CIVICS & ECONOMICS EXAM STUDY GUIDE Name GOAL 1: Foundations of American Political System & Values & Principles of American Democracy Objective 1.01: How did geographic diversity influence the economic,
Foundations of Government. Section 1: Page 24
 Foundations of Government Section 1: Page 24 Types of governments: Govern means rule A government is any organization set up to make and enforce laws Every country in the world has their own form and system
Foundations of Government Section 1: Page 24 Types of governments: Govern means rule A government is any organization set up to make and enforce laws Every country in the world has their own form and system
Manitoba Becomes a Province1870
 141112111,1 Mao Manitoba Becomes a Province1870 The people from Ontario and the other English-speaking people who lived at the Red River wanted the colony to join Canada. Some Metis felt closer ties with
141112111,1 Mao Manitoba Becomes a Province1870 The people from Ontario and the other English-speaking people who lived at the Red River wanted the colony to join Canada. Some Metis felt closer ties with
Attributes of a good thesis: avoids
 A thesis statement declares what you believe and what you intend to prove. A well developed thesis statement summarizes the argument the writer will make. The thesis statement is typically located at the
A thesis statement declares what you believe and what you intend to prove. A well developed thesis statement summarizes the argument the writer will make. The thesis statement is typically located at the
The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England. Student Handouts, Inc.
 The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com James I James Stuart (James VI of Scotland) inherited the English throne from his cousin, Elizabeth I, in 1603
The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com James I James Stuart (James VI of Scotland) inherited the English throne from his cousin, Elizabeth I, in 1603
New England Colonies
 New England Colonies Connecticut Connecticut Founded: 1636 by Thomas Hooker Reason for Founding: believed government should be based on free consent Economy: small subsistence farms - growing enough to
New England Colonies Connecticut Connecticut Founded: 1636 by Thomas Hooker Reason for Founding: believed government should be based on free consent Economy: small subsistence farms - growing enough to
MODULE II CONSTITUTIONAL HISTORY
 MODULE II CONSTITUTIONAL HISTORY CIRCUMSTANCES PRIOR TO THE ACT THE INDIAN COUNCIL ACT, 1861 The events of the mutiny made Britishers realize the need to adopt the Indians in the legislature of the country
MODULE II CONSTITUTIONAL HISTORY CIRCUMSTANCES PRIOR TO THE ACT THE INDIAN COUNCIL ACT, 1861 The events of the mutiny made Britishers realize the need to adopt the Indians in the legislature of the country
The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England. Student Handouts, Inc.
 Slide 1 The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 James I James Stuart (James VI of Scotland) inherited the English throne from his cousin, Elizabeth
Slide 1 The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 James I James Stuart (James VI of Scotland) inherited the English throne from his cousin, Elizabeth
Section 5: Democratic Developments in England
 Chapter 1: Sources of the Democratic Tradition 2000 B.C.E. A.D. 1689 Section 5: Democratic Developments in England In medieval England, the Christian church, the nobility, and monarchy had all the power
Chapter 1: Sources of the Democratic Tradition 2000 B.C.E. A.D. 1689 Section 5: Democratic Developments in England In medieval England, the Christian church, the nobility, and monarchy had all the power
English Civil War, the Restoration, and the Glorious Revolution
 English Civil War, the Restoration, and the Glorious Revolution Vocabulary Parliament Legislative, or law-making, body in government representing the interests of the people. (ex. England) Magna Carta
English Civil War, the Restoration, and the Glorious Revolution Vocabulary Parliament Legislative, or law-making, body in government representing the interests of the people. (ex. England) Magna Carta
Section 3. Objectives
 Objectives Describe the Tudor monarchs relations with Parliament. Analyze how clashes between the Stuarts and Parliament ushered in a century of revolution. Understand how the English Civil War and the
Objectives Describe the Tudor monarchs relations with Parliament. Analyze how clashes between the Stuarts and Parliament ushered in a century of revolution. Understand how the English Civil War and the
The English Civil War and the Glorious Revolution
 The English Civil War and the Glorious Revolution Enduring Understanding: The relationship between citizens and their government is a fundamental component of political rule. To understand the role of
The English Civil War and the Glorious Revolution Enduring Understanding: The relationship between citizens and their government is a fundamental component of political rule. To understand the role of
Government Alive! Chapter 3:
 Government Alive! Chapter 3: 1. Introduction On July 4, 1976, Americans celebrated their nation's 200th birthday. Two centuries earlier, the United States of America had come into being with the signing
Government Alive! Chapter 3: 1. Introduction On July 4, 1976, Americans celebrated their nation's 200th birthday. Two centuries earlier, the United States of America had come into being with the signing
Lesson Confederation Conferences
 Lesson 3.4 - Confederation Conferences 1) Colony Perspectives Canada West (Ontario) Canada East (Québec) Newfoundland Prince Edward Island New Brunswick Nova Scotia 2) Conferences 1. 1864 The colonies
Lesson 3.4 - Confederation Conferences 1) Colony Perspectives Canada West (Ontario) Canada East (Québec) Newfoundland Prince Edward Island New Brunswick Nova Scotia 2) Conferences 1. 1864 The colonies
United States Government
 United States Government I. Early Governments (Intro) 100 years ago governments were led by rulers, who ruled by force Direct democracy- Greeks invented this government, government run by the people to
United States Government I. Early Governments (Intro) 100 years ago governments were led by rulers, who ruled by force Direct democracy- Greeks invented this government, government run by the people to
Liberty or Death! The Orations of Patrick Henry
 09/19/2017The Orations Original Document: of Patrick Henry SBC17-01 / 1 2017 Shreveport Bible Conference The Orations of Patrick Henry CONTENTS: East Ridge Bible Church 9400 Wallace Lake Road Shreveport,
09/19/2017The Orations Original Document: of Patrick Henry SBC17-01 / 1 2017 Shreveport Bible Conference The Orations of Patrick Henry CONTENTS: East Ridge Bible Church 9400 Wallace Lake Road Shreveport,
Spain s Empire Philip II - son of V - seized control of - empire of vast Defender of Spanish destroyed by Protestant England
 Module 11 Absolute Monarchs in Europe Absolutism A decline in feudalism led to a rise of strong national kingdoms with more authority Absolute rulers wanted to control every of society Believed in Right
Module 11 Absolute Monarchs in Europe Absolutism A decline in feudalism led to a rise of strong national kingdoms with more authority Absolute rulers wanted to control every of society Believed in Right
132. What type of government exists in Brazil? A. communist B. monarchy C. presidential democracy D. parliamentary democracy
 SS6CG2 The student will explain the structures of national governments in Latin America and the Caribbean. a. Compare the federal-republican systems of the Federative Republic of Brazil (Brazil) and the
SS6CG2 The student will explain the structures of national governments in Latin America and the Caribbean. a. Compare the federal-republican systems of the Federative Republic of Brazil (Brazil) and the
STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth,
 STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by c) assessing the impacts
STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by c) assessing the impacts
Follow this and additional works at: Part of the United States History Commons
 Salem State University Digital Commons at Salem State University Honors Theses Student Scholarship 2016-12-01 An Analysis Of The Motives Of The British Parliamentary Members, Edmund Burle, Isaac Barré,
Salem State University Digital Commons at Salem State University Honors Theses Student Scholarship 2016-12-01 An Analysis Of The Motives Of The British Parliamentary Members, Edmund Burle, Isaac Barré,
539 B.C The Spread of Human Rights
 539 B.C In 539 B.C., the armies of Cyrus the Great, the first king of ancient Persia, conquered the city of Babylon. But it was his next actions that marked a major advance for Man. He freed the slaves,
539 B.C In 539 B.C., the armies of Cyrus the Great, the first king of ancient Persia, conquered the city of Babylon. But it was his next actions that marked a major advance for Man. He freed the slaves,
Democratic Developments in England
 Democratic Developments in England England began developing democratic institutions that limited the power of the monarchy/king. Democratic traditions developed in England have influenced many countries,
Democratic Developments in England England began developing democratic institutions that limited the power of the monarchy/king. Democratic traditions developed in England have influenced many countries,
2. According to the principles included in the Declaration of. Independence, what is the main purpose of government?
 1. According to the principles included in the Declaration of Independence, what is the main purpose of government? To control dangerous people through harsh punishment. To ensure that everyone has enough
1. According to the principles included in the Declaration of Independence, what is the main purpose of government? To control dangerous people through harsh punishment. To ensure that everyone has enough
GRADE NINE CANADA S FEDERAL POLITICAL SYSTEM CANADA PASSPORT
 GRADE NINE CANADA S FEDERAL POLITICAL SYSTEM CANADA PASSPORT CHAPTER ONE How effectively does Canada s federal political system govern canada for all canadians? LEGISLATIVE BRANCH The Queen Canada is a
GRADE NINE CANADA S FEDERAL POLITICAL SYSTEM CANADA PASSPORT CHAPTER ONE How effectively does Canada s federal political system govern canada for all canadians? LEGISLATIVE BRANCH The Queen Canada is a
IASbaba ILP 2017: Sample Value Add: Polity
 Chapter 1: Historical Background Chapter priority: High (Important for both Prelims and Mains) Points to know: 1. British came to India in 1600 as traders (EIC had purely trading functions) 2. In 1765,
Chapter 1: Historical Background Chapter priority: High (Important for both Prelims and Mains) Points to know: 1. British came to India in 1600 as traders (EIC had purely trading functions) 2. In 1765,
