APPENDIX C CALCULATIONS
|
|
|
- Timothy Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Knowle Park, Cranleigh FRA APPENDIX C CALCULATIONS - Greenfield Runoff Estimation for Site - Calculations for Wallingford Procedure and Modified Rational Method Page 2
2 IH124 : Greenfield Peak Runoff Catchment Area AREA Standard average annual rainfall SAAR mm Soil Index (from FSR or Wallingford Procedure WRAP maps)* SOIL *SOIL is the SPR for the soil type, and for larger sites is a weighted sum of the individual soil classes for the site, where: SOIL = 0.1A SOIL A SOIL A SOIL A SOIL A SOIL5 AREA For smaller sites, use the SPR for the local soil type, as follows: SOIL TYPE AREA SOIL: SPR * The site area is less tn 50. Since the IoH124 methodology is QBAR 50 not calibrated for sites less tn 50 in area, the calculation should QBAR/ / be undertaken based on a 50 site area and proportionately adjusted QBAR site based on the ratio of the site size to Hydrological Area fig 4.2 Return Period Growth Factor (years) (table 4.3) Discrge rate Figures and table references from CIRIA C697 The SUDS Manual CIRIA 2007
3 FEH Method Knowle Park Catchment Area AREA Standard average annual rainfall SAAR mm BFIHOST FARL SPRHOST Qmed Conversion Qbar Hydrological Area fig 4.2 Return Period Growth Factor (years) (table 4.3) Discrge rate
4 Wallingford Procedure : Developed Peak Runoff Site Cracteristics Catchment Area AREA Approximate Longest Drainage Path L m 460 Difference in Ground Levels H m 3 Slope Slope (S) 1: 153 Permeable Surfaces (Rational Method runoff coefficient = 0.4) Impermeable Surfaces (Rational Method runoff coefficient = 0.95) 53% 47% Area Weighted Rational Method Runoff Coefficient 0.66 Site parameters from The Wallingford Procedure for Europe: Best Practice Guide to urban drainage modelling, HR Wallingford, July 2000 (CD) 60minute, 5 year return period rainfall M5-60 mm Ratio of M5-60 to 2day, 5 year return period rainfall r Time of Concentration Recommended Tc Method: Tc Method Choice: SCS: Sheet Flow SCS: Sheet Flow Surface Description Sheet Flow Paving or Brick Slope Sllow Roughness Coefficient (Manning's n) Flow Length, L m 460 M2-24hr mm Land Slope m/m Tc hr 0.64 Time of Concentration T c min Critical Storm Duration (minimum 5min) T crit min Critical Storm Rainfall and Runoff Z1 TC 0.80 M5-T crit 16.0 C 0.66 *Wallingford Procedure Figure 3.6 Discrge Rate Q = 2.78CiA Return Period Z2* Depth Intensity Discrge Rate (years) (mm) (mm/hr) *Wallingford Procedure Table 3.2
5 Modified Rational Method Storage Calculator Site Parameters Catchment Area AREA Approximate Longest Drainage Path L m 460 Difference in Ground Levels H m 3 Slope Slope (S) 1: 153 Permeable Surfaces (Rational Method runoff coefficient = 0.4) Impermeable Surfaces (Rational Method runoff coefficient = 0.95) 53% 47% Area Weighted Rational Method Runoff Coefficient 0.66 Site parameters from The Wallingford Procedure for Europe: Best Practice Guide to urban drainage modelling, HR Wallingford, July 2000 (CD) 60minute, 5 year return period rainfall M5-60 mm Ratio of M5-60 to 2day, 5 year return period rainfall r - Time of Concentration T c min Maximum Storm Runoff Storage Volume (modified rational method) T d 60.0 min Z1 TD 1.00 *Wallingford Procedure Figure 3.6 M5-T d 20.0 mm C 0.66 Z *Wallingford Procedure Table 3.2 M100-T d 40.6 mm Intensity 40.6 mm/hr Q d Q d,climate cnge Q limiting discrge Storage Volum Maximum storage required m Storage Volume (m 3 ) Storage Requirements Storm Duration (mins)
Drainage design tools
 Drainage design tools Richard Kellagher This presentation Designing drainage systems > Conveyance >Storage > Infiltration > Interception > Exceedence Assessing outline designs (planning) Checking detailed
Drainage design tools Richard Kellagher This presentation Designing drainage systems > Conveyance >Storage > Infiltration > Interception > Exceedence Assessing outline designs (planning) Checking detailed
SuDS design criteria for catchment flood protection Are current criteria appropriate?
 SuDS design criteria for catchment flood protection Are current criteria appropriate? Richard Kellagher SuDS Drainage design for catchment flood protection All countries of UK (roughly) in alignment, BUT
SuDS design criteria for catchment flood protection Are current criteria appropriate? Richard Kellagher SuDS Drainage design for catchment flood protection All countries of UK (roughly) in alignment, BUT
Appendix C. FSSR 14 Regional Growth Curves with Irish River Data. and. FSSR 16 (Greenfield) Rainfall Runoff Model Estimation
 Appendix C FSSR 14 Regional Growth Curves with Irish River Data and FSSR 16 (Greenfield) Rainfall Runoff Model Estimation Appendix C March 2005 C1 FSSR 14 Growth Curves with Irish River Data The Irish
Appendix C FSSR 14 Regional Growth Curves with Irish River Data and FSSR 16 (Greenfield) Rainfall Runoff Model Estimation Appendix C March 2005 C1 FSSR 14 Growth Curves with Irish River Data The Irish
Learning objectives. Upon successful completion of this lecture, the participants will be able to describe:
 Solomon Seyoum Learning objectives Upon successful completion of this lecture, the participants will be able to describe: The different approaches for estimating peak runoff for urban drainage network
Solomon Seyoum Learning objectives Upon successful completion of this lecture, the participants will be able to describe: The different approaches for estimating peak runoff for urban drainage network
Preliminary Rainfall Runoff Management for Developments EA/Defra Report Procedure W5-074/A Summary Guidance for Developers and Engineers
 Preliminary Rainfall Runoff Management for Developments EA/Defra Report Procedure W5-074/A Summary Guidance for Developers and Engineers 1. Objective of this guidance and Procedure W5-074/A is to assist
Preliminary Rainfall Runoff Management for Developments EA/Defra Report Procedure W5-074/A Summary Guidance for Developers and Engineers 1. Objective of this guidance and Procedure W5-074/A is to assist
Chapter 6. The Empirical version of the Rational Method
 Chapter 6 The Empirical version of the Rational Method The Empirical version is named because the parameters it uses (apart from rainfall data) are arbitrary and are generally based on experience or observation
Chapter 6 The Empirical version of the Rational Method The Empirical version is named because the parameters it uses (apart from rainfall data) are arbitrary and are generally based on experience or observation
MODULE 1 RUNOFF HYDROGRAPHS WORKSHEET 1. Precipitation
 Watershed MODULE 1 RUNOFF HYDROGRAPHS WORKSHEET 1 A watershed is an area of land thaaptures rainfall and other precipitation and funnels it to a lake or stream or wetland. The area within the watershed
Watershed MODULE 1 RUNOFF HYDROGRAPHS WORKSHEET 1 A watershed is an area of land thaaptures rainfall and other precipitation and funnels it to a lake or stream or wetland. The area within the watershed
Surface Water Guidance for Developers
 Surface Water Guidance for Developers Contents Overview of Sustainable Drainage Systems (SuDS)... 2 Information Required in a Flood Risk Assessment or Drainage Strategy... 3 Outline Planning Applications...
Surface Water Guidance for Developers Contents Overview of Sustainable Drainage Systems (SuDS)... 2 Information Required in a Flood Risk Assessment or Drainage Strategy... 3 Outline Planning Applications...
The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Sanitary Engineering- ECIV 4325 L5. Storm water Management
 The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Sanitary Engineering- ECIV 4325 L5. Storm water Management Husam Al-Najar Storm water management : Collection System Design principles The Objectives
The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Sanitary Engineering- ECIV 4325 L5. Storm water Management Husam Al-Najar Storm water management : Collection System Design principles The Objectives
Activity Calculating Property Drainage
 Page 1 of 5 Activity 2.3.11 Calculating Property Drainage Introduction When a property is developed, it is important to understand that changes to watershed characteristics (i.e., land use, slope, soil
Page 1 of 5 Activity 2.3.11 Calculating Property Drainage Introduction When a property is developed, it is important to understand that changes to watershed characteristics (i.e., land use, slope, soil
APPENDIX IV. APPROVED METHODS FOR QUANTIFYING HYDROLOGIC CONDITIONS OF CONCERN (NORTH ORANGE COUNTY)
 APPENDIX IV. APPROVED METHODS FOR QUANTIFYING HYDROLOGIC CONDITIONS OF CONCERN (NORTH ORANGE COUNTY) Hydromodification design criteria for the North Orange County permit area are based on the 2- yr, 24-hr
APPENDIX IV. APPROVED METHODS FOR QUANTIFYING HYDROLOGIC CONDITIONS OF CONCERN (NORTH ORANGE COUNTY) Hydromodification design criteria for the North Orange County permit area are based on the 2- yr, 24-hr
How Much Runoff? Coefficients for Urban land Use in South West WA and a comparison between Rational Method and volumetric runoff coefficients
 How Much Runoff? Coefficients for Urban land Use in South West WA and a comparison between Rational Method and volumetric runoff coefficients Written by: Jim Davies (PhD, FIEAust, Member IPWEA, SIA WA
How Much Runoff? Coefficients for Urban land Use in South West WA and a comparison between Rational Method and volumetric runoff coefficients Written by: Jim Davies (PhD, FIEAust, Member IPWEA, SIA WA
Rising Sun. Scaffold Hill. Flood Risk Assessment
 Rising Sun Scaffold Hill Flood Risk Assessment August 2010 Contents 1.0 Introduction... 4 2.0 Site Description... 5 3.0 Legislative Framework... 6 4.0 Flood Risk... 10 5.0 Surface Water Drainage... 11
Rising Sun Scaffold Hill Flood Risk Assessment August 2010 Contents 1.0 Introduction... 4 2.0 Site Description... 5 3.0 Legislative Framework... 6 4.0 Flood Risk... 10 5.0 Surface Water Drainage... 11
Developers Guide for Surface Water Management.
 Developers Guide for Surface Water Management www.southwark.gov.uk Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Requirements for Flood Risk Assessments and Drainage Strategies... 3 2.1 Planning Applications... 3 2.2
Developers Guide for Surface Water Management www.southwark.gov.uk Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Requirements for Flood Risk Assessments and Drainage Strategies... 3 2.1 Planning Applications... 3 2.2
Storm Sewer Design - Introduction
 Class 4 [1] Storm Sewer Design - Introduction As urban drainage can not be expected to accommodate all rainfall events, the first step in the design procedure is to select an appropriate design storm.
Class 4 [1] Storm Sewer Design - Introduction As urban drainage can not be expected to accommodate all rainfall events, the first step in the design procedure is to select an appropriate design storm.
Appendix 8.4. Site-wide Drainage Strategy
 Appendix 8.4 Site-wide Drainage Strategy Noble House, Capital Drive, Linford Wood, Milton Keynes MK14 6QP T +44 (0)1908 669898 F +44 (0)1908 669899 E harrisjt@rpsgroup.com W www.rpsgroup.com/design THE
Appendix 8.4 Site-wide Drainage Strategy Noble House, Capital Drive, Linford Wood, Milton Keynes MK14 6QP T +44 (0)1908 669898 F +44 (0)1908 669899 E harrisjt@rpsgroup.com W www.rpsgroup.com/design THE
ENGN.4010 ENGINEERING CAPSTONE DESIGN Watershed Analysis. CiA
 RATIONAL METHOD Q CiA Where: Q = Maximum Rate of Runoff (cfs) C = Runoff Coefficient i = Average Rainfall Intensity (in/hr) A = Drainage Area (in acres) RATIONAL METHOD Assumptions and Limitations: Watershed
RATIONAL METHOD Q CiA Where: Q = Maximum Rate of Runoff (cfs) C = Runoff Coefficient i = Average Rainfall Intensity (in/hr) A = Drainage Area (in acres) RATIONAL METHOD Assumptions and Limitations: Watershed
Rainfall, Runoff and Peak Flows: Calibration of Hydrologic Design Methods for the Kansas City Area
 Rainfall, Runoff and Peak Flows: Calibration of Hydrologic Design Methods for the Kansas City Area Bruce McEnroe, Bryan Young, Ricardo Gamarra and Ryan Pohl Department of Civil, Environmental, and Architectural
Rainfall, Runoff and Peak Flows: Calibration of Hydrologic Design Methods for the Kansas City Area Bruce McEnroe, Bryan Young, Ricardo Gamarra and Ryan Pohl Department of Civil, Environmental, and Architectural
Kildare County Council. Proposed Development of 77 no. Residential Units at College Wood Manor, Ballingappa Road, Clane, Co. Kildare.
 Job No. : 16027 SHB2-CLA-CS-MOR Date: Feb 2018 Kildare County Council Proposed Development of 77 no. Residential Units at College Wood Manor, Ballingappa Road, Clane, Co. Kildare. Engineering Report 2B
Job No. : 16027 SHB2-CLA-CS-MOR Date: Feb 2018 Kildare County Council Proposed Development of 77 no. Residential Units at College Wood Manor, Ballingappa Road, Clane, Co. Kildare. Engineering Report 2B
BEST PRACTICE FOR MODELLING SUSTAINABLE URBAN DRAINAGE SYSTEM STRUCTURES
 BEST PRACTICE FOR MODELLING SUSTAINABLE URBAN DRAINAGE SYSTEM STRUCTURES R. Kirkham, 1 C. Rayner 2 1 Clear Environmental Consultants Ltd, Rhona.Kirkham@clearltd.com 2 Claire.Rayner@wallingfordsoftware.com
BEST PRACTICE FOR MODELLING SUSTAINABLE URBAN DRAINAGE SYSTEM STRUCTURES R. Kirkham, 1 C. Rayner 2 1 Clear Environmental Consultants Ltd, Rhona.Kirkham@clearltd.com 2 Claire.Rayner@wallingfordsoftware.com
Rational Method Hydrological Calculations with Excel COURSE CONTENT
 Rational Method Hydrological Calculations with Excel Harlan H. Bengtson, PhD, P.E. COURSE CONTENT 1. Introduction Calculation of peak storm water runoff rate from a drainage area is often done with the
Rational Method Hydrological Calculations with Excel Harlan H. Bengtson, PhD, P.E. COURSE CONTENT 1. Introduction Calculation of peak storm water runoff rate from a drainage area is often done with the
A NEW RUNOFF VOLUME MODEL
 A NEW RUNOFF VOLUME MODEL WaPUG USER NOTE No 28 Martin P Osborne, Mouchel Group 1. INTRODUCTION A new runoff volume model was developed some years ago as an alternative to the existing Wallingford Procedure
A NEW RUNOFF VOLUME MODEL WaPUG USER NOTE No 28 Martin P Osborne, Mouchel Group 1. INTRODUCTION A new runoff volume model was developed some years ago as an alternative to the existing Wallingford Procedure
Runoff Calculations. Time of Concentration (T c or t c ) from one location to another within a watershed. Travel
 Runoff Calculations Bob Pitt University of Alabama and Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Time of Concentration and Travel Time (based on Chapter 3 of TR-55) Time of Concentration (T c ): time required
Runoff Calculations Bob Pitt University of Alabama and Shirley Clark Penn State Harrisburg Time of Concentration and Travel Time (based on Chapter 3 of TR-55) Time of Concentration (T c ): time required
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING. MSc CIVIL ENGINEERING SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATION 2017/2018 URBAN DRAINAGE SYSTEMS MODULE NO: BLT4022
 [ESS29] UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING MSc CIVIL ENGINEERING SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATION 2017/2018 URBAN DRAINAGE SYSTEMS MODULE NO: BLT4022 Date: Monday 21 st May 2018 Time: 10:00 13:00 INSTRUCTIONS
[ESS29] UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING MSc CIVIL ENGINEERING SEMESTER TWO EXAMINATION 2017/2018 URBAN DRAINAGE SYSTEMS MODULE NO: BLT4022 Date: Monday 21 st May 2018 Time: 10:00 13:00 INSTRUCTIONS
What is runoff? Runoff. Runoff is often defined as the portion of rainfall, that runs over and under the soil surface toward the stream
 What is runoff? Runoff Runoff is often defined as the portion of rainfall, that runs over and under the soil surface toward the stream 1 COMPONENTS OF Runoff or STREAM FLOW 2 Cont. The types of runoff
What is runoff? Runoff Runoff is often defined as the portion of rainfall, that runs over and under the soil surface toward the stream 1 COMPONENTS OF Runoff or STREAM FLOW 2 Cont. The types of runoff
Use of IDF Curves Design of a roof drainage system
 Use of IDF Curves Design of a roof drainage system Your engineering firm is currently planning the construction of a residential apartment building in Davos, Switzerland. Your task is to design the roof
Use of IDF Curves Design of a roof drainage system Your engineering firm is currently planning the construction of a residential apartment building in Davos, Switzerland. Your task is to design the roof
SECTION IV WATERSHED TECHNICAL ANALYSIS
 A. Watershed Modeling SECTION IV WATERSHED TECHNICAL ANALYSIS An initial step in the preparation of this stormwater management plan was the selection of a stormwater simulation model to be utilized. It
A. Watershed Modeling SECTION IV WATERSHED TECHNICAL ANALYSIS An initial step in the preparation of this stormwater management plan was the selection of a stormwater simulation model to be utilized. It
Photos - On site visit 23/08/2010 to 27/08/2010
 APPENDIX B: PHOTOS Photo No02 Photo No06 Photo No01 Photo No05 Photos - On site visit 23/08/2010 to 27/08/2010 Photo No07 Photo No03 Photo No08 Photo No04 Photo No10 Photo No14 Photo No09 Photo No13 Photos
APPENDIX B: PHOTOS Photo No02 Photo No06 Photo No01 Photo No05 Photos - On site visit 23/08/2010 to 27/08/2010 Photo No07 Photo No03 Photo No08 Photo No04 Photo No10 Photo No14 Photo No09 Photo No13 Photos
FAST WATER / SLOW WATER AN EVALUATION OF ESTIMATING TIME FOR STORMWATER RUNOFF
 FAST WATER / SLOW WATER AN EVALUATION OF ESTIMATING TIME FOR STORMWATER RUNOFF Factors Affecting Stormwater Runoff: Rainfall intensity % Impervious surfaces Watershed size Slope Soil type, soil compaction
FAST WATER / SLOW WATER AN EVALUATION OF ESTIMATING TIME FOR STORMWATER RUNOFF Factors Affecting Stormwater Runoff: Rainfall intensity % Impervious surfaces Watershed size Slope Soil type, soil compaction
Kildare County Council. Proposed Development of 74 no. Residential Units at Craddockstown Road, Cradockstown Demesne, Naas, Co. Kildare.
 Job No. : 16027 SHB1-CRA-CS-MOR Date: April 2017 Kildare County Council Proposed Development of 74 no. Residential Units at Craddockstown Road, Cradockstown Demesne, Naas, Co. Kildare. 2B Richview Office
Job No. : 16027 SHB1-CRA-CS-MOR Date: April 2017 Kildare County Council Proposed Development of 74 no. Residential Units at Craddockstown Road, Cradockstown Demesne, Naas, Co. Kildare. 2B Richview Office
Examination of PRZM5.0 Storm Rainfall Depth and Distribution Algorithms Compared to Current U.S. Storm Trends
 Examination of PRZM5.0 Storm Rainfall Depth and Distribution Algorithms Compared to Current U.S. Storm Trends August 24, 2016 Tammara L. Estes (Stone Environmental Inc.) Kevin L. Armbrust, Ph.D. (Louisiana
Examination of PRZM5.0 Storm Rainfall Depth and Distribution Algorithms Compared to Current U.S. Storm Trends August 24, 2016 Tammara L. Estes (Stone Environmental Inc.) Kevin L. Armbrust, Ph.D. (Louisiana
DRAINAGE OF IRRIGATED LANDS
 CVE 471 WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING DRAINAGE OF IRRIGATED LANDS Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ Civil Engineering Program Middle East Technical University Northern Cyprus Campus CVE 471 Water Resources
CVE 471 WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING DRAINAGE OF IRRIGATED LANDS Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ Civil Engineering Program Middle East Technical University Northern Cyprus Campus CVE 471 Water Resources
DRAINAGE & DESIGN OF DRAINAGE SYSTEM
 Drainage on Highways DRAINAGE & DESIGN OF DRAINAGE SYSTEM P. R.D. Fernando Chartered Engineer B.Sc.(Hons), M.Eng. C.Eng., MIE(SL) Drainage Requirement of Highway Drainage System Introduction Drainage means
Drainage on Highways DRAINAGE & DESIGN OF DRAINAGE SYSTEM P. R.D. Fernando Chartered Engineer B.Sc.(Hons), M.Eng. C.Eng., MIE(SL) Drainage Requirement of Highway Drainage System Introduction Drainage means
Storm Sewers, Page 2
 Storm Sewers storm sewer systems are dendritic systems used to collect and direct stormwater runoff storm sewer systems are integral components of any urban infrastructure curbs, gutters and storm inlets
Storm Sewers storm sewer systems are dendritic systems used to collect and direct stormwater runoff storm sewer systems are integral components of any urban infrastructure curbs, gutters and storm inlets
HYDROLOGIC AND HYDRAULIC TABLES AND CURVES
 APPENDIX C HYDROLOGIC AND HYDRAULIC TABLES AND CURVES PRECIPITATION TABLES Table C-1, page C-2, provides local data for use in designing drainage systems as discussed in Chapter 6. HYDROLOGIC SUPPLY CURVES
APPENDIX C HYDROLOGIC AND HYDRAULIC TABLES AND CURVES PRECIPITATION TABLES Table C-1, page C-2, provides local data for use in designing drainage systems as discussed in Chapter 6. HYDROLOGIC SUPPLY CURVES
APPENDIX E APPENDIX E ESTIMATING RUNOFF FOR SMALL WATERSHEDS
 APPENDIX E ESTIMATING RUNOFF FOR SMALL WATERSHEDS March 18, 2003 This page left blank intentionally. March 18, 2003 TABLES Table E.1 Table E.2 Return Frequencies for Roadway Drainage Design Rational Method
APPENDIX E ESTIMATING RUNOFF FOR SMALL WATERSHEDS March 18, 2003 This page left blank intentionally. March 18, 2003 TABLES Table E.1 Table E.2 Return Frequencies for Roadway Drainage Design Rational Method
Francis Sant. Proposed Free Range Poultry Unit, Pentrefelin, Llandeilo Flood Consequence Assessment. January 2018 Final Revision C SITE
 Francis Sant Proposed Free Range Poultry Unit, Pentrefelin, Llandeilo Flood Consequence Assessment SITE Final Revision C Project Document Status Revision Proposed Free Range Poultry Unit, Pentrefelin,
Francis Sant Proposed Free Range Poultry Unit, Pentrefelin, Llandeilo Flood Consequence Assessment SITE Final Revision C Project Document Status Revision Proposed Free Range Poultry Unit, Pentrefelin,
Flood Risk Assessment
 Flood Risk Assessment Low Whita Swaledale Morrison Utility Services Report Reference: CLE30080/05/01 Clear Environmental Consultants July 2015 QUALITY ASSURANCE Client: Morrison Utility Services Report
Flood Risk Assessment Low Whita Swaledale Morrison Utility Services Report Reference: CLE30080/05/01 Clear Environmental Consultants July 2015 QUALITY ASSURANCE Client: Morrison Utility Services Report
APPENDIX F RATIONAL METHOD
 7-F-1 APPENDIX F RATIONAL METHOD 1.0 Introduction One of the most commonly used procedures for calculating peak flows from small drainages less than 200 acres is the Rational Method. This method is most
7-F-1 APPENDIX F RATIONAL METHOD 1.0 Introduction One of the most commonly used procedures for calculating peak flows from small drainages less than 200 acres is the Rational Method. This method is most
Sustainability Criteria for the Design of Stormwater Drainage Systems for the 21 st Century
 Sustainability Criteria for the Design of Stormwater Drainage Systems for the 21 st Century R. Kellagher 1 and H. Udale-Clarke 1 * 1 HR Wallingford Ltd., Howbery Park, Wallingford. Oxfordshire, OX10 8BA,
Sustainability Criteria for the Design of Stormwater Drainage Systems for the 21 st Century R. Kellagher 1 and H. Udale-Clarke 1 * 1 HR Wallingford Ltd., Howbery Park, Wallingford. Oxfordshire, OX10 8BA,
Overview of NRCS (SCS) TR-20 By Dr. R.M. Ragan
 Overview of NRCS (SCS) TR-20 By Dr. R.M. Ragan TR-20 is a computer program for the simulation of runoff occurring from a single storm event. The program develops flood hydrographs from runoff and routes
Overview of NRCS (SCS) TR-20 By Dr. R.M. Ragan TR-20 is a computer program for the simulation of runoff occurring from a single storm event. The program develops flood hydrographs from runoff and routes
HIGHWAY DRAINAGE.
 Chapter VI HIGHWAY DRAINAGE Tewodros N. www.tnigatu.wordpress.com tedynihe@gmail.com I. INTRODUCTION Provision o of adequate drainage is an essential part of pavement design. Protection of pavement structure
Chapter VI HIGHWAY DRAINAGE Tewodros N. www.tnigatu.wordpress.com tedynihe@gmail.com I. INTRODUCTION Provision o of adequate drainage is an essential part of pavement design. Protection of pavement structure
Modelling Stormwater Contaminant Loads in Older Urban Catchments: Developing Targeted Management Options to Improve Water Quality
 Modelling Stormwater Contaminant Loads in Older Urban Catchments: Developing Targeted Management Options to Improve Water Quality Frances J. CHARTERS 1, Thomas A. COCHRANE 1, Aisling D. O SULLIVAN 1 1
Modelling Stormwater Contaminant Loads in Older Urban Catchments: Developing Targeted Management Options to Improve Water Quality Frances J. CHARTERS 1, Thomas A. COCHRANE 1, Aisling D. O SULLIVAN 1 1
Natural flood management within the Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act
 Natural flood management within the Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act Neil Nutt Halcrow CH2M Hill (SEPA secondment project) nuttn@halcrow.com 1 12/09/12 Acknowledgements Project Technical Advisory Group
Natural flood management within the Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act Neil Nutt Halcrow CH2M Hill (SEPA secondment project) nuttn@halcrow.com 1 12/09/12 Acknowledgements Project Technical Advisory Group
Foul Drainage Assessment and Surface Water Management Plan Land at Mill Lane Hawkinge CT18 7BY
 Foul Drainage Assessment and Surface Water Management Plan Land at Mill Lane Hawkinge CT18 7BY RMB Consultants (Civil Engineering) Ltd March 2015 RMB Consultants (Civil Engineering) Ltd 39 Cossington Road
Foul Drainage Assessment and Surface Water Management Plan Land at Mill Lane Hawkinge CT18 7BY RMB Consultants (Civil Engineering) Ltd March 2015 RMB Consultants (Civil Engineering) Ltd 39 Cossington Road
ASSESSMENT OF DRAINAGE CAPACITY OF CHAKTAI AND RAJAKHALI KHAL IN CHITTAGONG CITY AND INUNDATION ADJACENT OF URBAN AREAS
 Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), 9~11 February 2018, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN-978-984-34-3502-6) ASSESSMENT OF DRAINAGE
Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), 9~11 February 2018, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN-978-984-34-3502-6) ASSESSMENT OF DRAINAGE
Defra/Environment Agency Flood and Coastal Defence R&D Programme Preliminary rainfall runoff management for developments
 Defra/Environment Agency Flood and Coastal Defence R&D Programme Preliminary rainfall runoff management for developments R&D Technical Report W5-074/A/TR/1 Revision D DEFRA / Environment Agency Flood
Defra/Environment Agency Flood and Coastal Defence R&D Programme Preliminary rainfall runoff management for developments R&D Technical Report W5-074/A/TR/1 Revision D DEFRA / Environment Agency Flood
Copyright 2018 Pecivilexam.com all rights reserved- E-Book Water Resources and Environmental Depth Exam: 80 problems.
 PE Civil Exam 80- Water Resources and Environmental Questions & Answers (pdf Format) Depth Exam (Evening Session) PE Civil Depth Exam (Evening Session): This practice exam contains 80-questions and answers
PE Civil Exam 80- Water Resources and Environmental Questions & Answers (pdf Format) Depth Exam (Evening Session) PE Civil Depth Exam (Evening Session): This practice exam contains 80-questions and answers
APPENDIX E ESTIMATING RUNOFF FROM SMALL WATERSHEDS
 ESTIMATING RUNOFF FROM SMALL WATERSHEDS June 2011 THIS PAGE LEFT BLANK INTENTIONALLY. June 2011 TABLES Table E.1 Table E.2 Return Frequencies for Roadway Drainage Design Rational Method Values June 2011
ESTIMATING RUNOFF FROM SMALL WATERSHEDS June 2011 THIS PAGE LEFT BLANK INTENTIONALLY. June 2011 TABLES Table E.1 Table E.2 Return Frequencies for Roadway Drainage Design Rational Method Values June 2011
CIE4491 Lecture. Quantifying stormwater flow Rational method
 CIE4491 Lecture. Quantifying stormwater flow Rational method 27-5-2014 Marie-claire ten Veldhuis, Watermanagement Department Delft University of Technology Challenge the future Robust method stationary
CIE4491 Lecture. Quantifying stormwater flow Rational method 27-5-2014 Marie-claire ten Veldhuis, Watermanagement Department Delft University of Technology Challenge the future Robust method stationary
Runoff Routing Methods
 Runoff Routing Methods XPSWMM and XPStorm uses seven major types of Hydrograph Generation techniques available in Runoff. Back to: Help Documentation SWMM Runoff Non-linear Reservoir Method Subcatchments
Runoff Routing Methods XPSWMM and XPStorm uses seven major types of Hydrograph Generation techniques available in Runoff. Back to: Help Documentation SWMM Runoff Non-linear Reservoir Method Subcatchments
Designing for surface water runoff control: end-user requirements in Ireland
 Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 8, 635 640, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Designing for surface water runoff control:
Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 8, 635 640, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Designing for surface water runoff control:
What s so hard about Stormwater Modelling?
 What s so hard about Stormwater Modelling? A Pugh 1 1 Wallingford Software Pty Ltd, ann.pugh@wallingfordsoftware.com Abstract A common misconception of stormwater modelling is that it is simple. While
What s so hard about Stormwater Modelling? A Pugh 1 1 Wallingford Software Pty Ltd, ann.pugh@wallingfordsoftware.com Abstract A common misconception of stormwater modelling is that it is simple. While
Designing for surface water runoff control : end-user requirements in Ireland
 Provided by the author(s) and University College Dublin Library in accordance with publisher policies. Please cite the published version when available. Title Designing for surface water runoff control
Provided by the author(s) and University College Dublin Library in accordance with publisher policies. Please cite the published version when available. Title Designing for surface water runoff control
IBS Site Drainage: Senior Design Project
 IBS Site Drainage: Senior Design Project Len Wright, Ph.D., PE Lecturer, CEAE Wright.Len@gmail.com September 11, 2008 mwsw204i1.ppt/1 OUTLINE Motivation for Stormwater Management Quantity (both onsite,
IBS Site Drainage: Senior Design Project Len Wright, Ph.D., PE Lecturer, CEAE Wright.Len@gmail.com September 11, 2008 mwsw204i1.ppt/1 OUTLINE Motivation for Stormwater Management Quantity (both onsite,
Respond! Housing Association. Residential Development at Flinters Field, Athy, Co. Kildare. Engineering Report. Job No. : Date: April 2017
 Job No. : 16036 Date: April 2017 Respond! Housing Association Residential Development at Flinters Field, Athy, Co. Kildare Engineering Report 2B Richview Office Park Clonskeagh Dublin 14 Contents Amendment
Job No. : 16036 Date: April 2017 Respond! Housing Association Residential Development at Flinters Field, Athy, Co. Kildare Engineering Report 2B Richview Office Park Clonskeagh Dublin 14 Contents Amendment
Engineering Hydrology Class 3
 Engineering Hydrology Class 3 Topics and Goals: I.Develop s (estimate precipitation) II.Develop simple constant intensity design storm III.Develop SCS design storm Ocean s Why do we want to derive the?
Engineering Hydrology Class 3 Topics and Goals: I.Develop s (estimate precipitation) II.Develop simple constant intensity design storm III.Develop SCS design storm Ocean s Why do we want to derive the?
Landfill design General principles
 Landfill design General principles Average height of a landfill should be at least 15 m Each section (cell) should accommodate waste to be landfilled during 5 years period Sections/cells should be hydraulically
Landfill design General principles Average height of a landfill should be at least 15 m Each section (cell) should accommodate waste to be landfilled during 5 years period Sections/cells should be hydraulically
Modeling the Hydrologic Impacts of Control Structures Utilizing LiDAR, ICPR, and GIS Technologies
 Modeling the Hydrologic Impacts of Control Structures Utilizing LiDAR, ICPR, and GIS Technologies Keanan Bell NorthStar June 12, 2015 Project began in 2010 as a Hydrology Assessment and Conceptual Restoration
Modeling the Hydrologic Impacts of Control Structures Utilizing LiDAR, ICPR, and GIS Technologies Keanan Bell NorthStar June 12, 2015 Project began in 2010 as a Hydrology Assessment and Conceptual Restoration
HYDROLOGIC MODELING CONSISTENCY AND SENSITIVITY TO WATERSHED SIZE
 HYDROLOGIC MODELING CONSISTENCY AND SENSITIVITY TO WATERSHED SIZE by James C.Y. Guo. Professor, Civil Engineering, U. Of Colorado at Denver, James.Guo@cudenver.edu.. And Eric Hsu, Project Engineer, Parson
HYDROLOGIC MODELING CONSISTENCY AND SENSITIVITY TO WATERSHED SIZE by James C.Y. Guo. Professor, Civil Engineering, U. Of Colorado at Denver, James.Guo@cudenver.edu.. And Eric Hsu, Project Engineer, Parson
The SuDS Manual Frequently asked questions
 The SuDS Manual Frequently asked questions 1. Is source control still a requirement of the new SuDS Manual? Yes. Source control components are fundamental elements of a SuDS scheme. The benefits of source
The SuDS Manual Frequently asked questions 1. Is source control still a requirement of the new SuDS Manual? Yes. Source control components are fundamental elements of a SuDS scheme. The benefits of source
poga Engineering Planning Report Residential Scheme Earls Court Kill Co Kildare CONSULTING ENGINEERS STRUCTURAL & CIVIL
 poga Pat O Gorman & Associates CONSULTING ENGINEERS STRUCTURAL & CIVIL Engineering Planning Report Residential Scheme Earls Court Kill Co Kildare Ref: 1715-EPS(P)-R1 Date of Original Issue: July 2017 Date
poga Pat O Gorman & Associates CONSULTING ENGINEERS STRUCTURAL & CIVIL Engineering Planning Report Residential Scheme Earls Court Kill Co Kildare Ref: 1715-EPS(P)-R1 Date of Original Issue: July 2017 Date
Appendix E.2 Preliminary Hydrology Report
 Appendix E.2 Preliminary Hydrology Report PRELIMINARY HYDROLOGY STUDY HARVARD WESTLAKE SCHOOL PARKING STRUCTURE 3700 Coldwater Canyon North Hollywood, CA 91604 KPFF Job # 109046 August 12, 2013 CLIENT:
Appendix E.2 Preliminary Hydrology Report PRELIMINARY HYDROLOGY STUDY HARVARD WESTLAKE SCHOOL PARKING STRUCTURE 3700 Coldwater Canyon North Hollywood, CA 91604 KPFF Job # 109046 August 12, 2013 CLIENT:
Introduction. Keywords: Oil Palm, hydrology, HEC-HMS, HEC-RAS. a * b*
 The Effect of Land Changes Towards in Sg. Pandan Perwira Bin Khusairi Rahman 1,a* and Kamarul Azlan bin Mohd Nasir 1,b 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia a * wirakhusairirahman@gmail.com,
The Effect of Land Changes Towards in Sg. Pandan Perwira Bin Khusairi Rahman 1,a* and Kamarul Azlan bin Mohd Nasir 1,b 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia a * wirakhusairirahman@gmail.com,
FORT COLLINS STORMWATER CRITERIA MANUAL Hydrology Standards (Ch. 5) 1.0 Overview
 Chapter 5: Hydrology Standards Contents 1.0 Overview... 1 1.1 Storm Runoff Determination... 1 1.2 Design Storm Frequencies... 1 1.3 Water Quality Storm Provisions... 2 1.4 Design Storm Return Periods...
Chapter 5: Hydrology Standards Contents 1.0 Overview... 1 1.1 Storm Runoff Determination... 1 1.2 Design Storm Frequencies... 1 1.3 Water Quality Storm Provisions... 2 1.4 Design Storm Return Periods...
HOTEL KANATA 140 HEARST WAY KANATA, ONTARIO STORMWATER MANAGEMENT REPORT. Prepared for: David Johnston Architect. Prepared By:
 HOTEL KANATA 140 HEARST WAY KANATA, ONTARIO STORMWATER MANAGEMENT REPORT Prepared for: David Johnston Architect Prepared By: BaseTech Consulting Inc. 309 Roywood Crescent Newmarket, Ontario L3Y 1A6 BCI
HOTEL KANATA 140 HEARST WAY KANATA, ONTARIO STORMWATER MANAGEMENT REPORT Prepared for: David Johnston Architect Prepared By: BaseTech Consulting Inc. 309 Roywood Crescent Newmarket, Ontario L3Y 1A6 BCI
Rational Method vs OTTHYMO, Comparing Peak Discharge Rates By Alex Nichols, P.Eng.
 Rational Method vs OTTHYMO, Comparing Peak Discharge Rates By Alex Nichols, P.Eng. Urban stormwater management for small site is becoming more complex. All of the methods rely upon statistically derived
Rational Method vs OTTHYMO, Comparing Peak Discharge Rates By Alex Nichols, P.Eng. Urban stormwater management for small site is becoming more complex. All of the methods rely upon statistically derived
Study on Drainage Capacity by using Modified Rational Method and Storm Water Management Model
 Study on Drainage Capacity by using Modified Rational Method and Storm Water Management Model 1 Mi Pale Kyi, 2 Dr. Win Win Zin, 3 U Tin Maung 1 Ph.D Candidate, 2 Professor, 3 Visiting Professor 1, 2, 3
Study on Drainage Capacity by using Modified Rational Method and Storm Water Management Model 1 Mi Pale Kyi, 2 Dr. Win Win Zin, 3 U Tin Maung 1 Ph.D Candidate, 2 Professor, 3 Visiting Professor 1, 2, 3
Drainage Analysis. Appendix E
 Drainage Analysis Appendix E The existing and proposed storm drainage systems have been modeled with Bentley CivilStorm V8 computer modeling software. The peak stormwater discharge was determined for
Drainage Analysis Appendix E The existing and proposed storm drainage systems have been modeled with Bentley CivilStorm V8 computer modeling software. The peak stormwater discharge was determined for
DERIVATION AND CALIBRATION OF VOLUME-BASED RUNOFF COEFFICIENTS FOR DENVER AREA, COLORADO
 DERIVATION AND CALIBRATION OF VOLUME-BASED RUNOFF COEFFICIENTS FOR DENVER AREA, COLORADO Prepared by Dr. James C.Y. Guo, P.E., Professor and Director, Civil Engineering, U of Colorado Denver James.Guo@UCDenver.edu
DERIVATION AND CALIBRATION OF VOLUME-BASED RUNOFF COEFFICIENTS FOR DENVER AREA, COLORADO Prepared by Dr. James C.Y. Guo, P.E., Professor and Director, Civil Engineering, U of Colorado Denver James.Guo@UCDenver.edu
Risk-based assessment of climate change impact on storm drainage system
 Flood Recovery, Innovation and Response II 13 Risk-based assessment of climate change impact on storm drainage system Z. Alsaqqaf, H. Zhang & S. Mohamed Griffith School of Engineering, Griffith University,
Flood Recovery, Innovation and Response II 13 Risk-based assessment of climate change impact on storm drainage system Z. Alsaqqaf, H. Zhang & S. Mohamed Griffith School of Engineering, Griffith University,
1. Stream Network. The most common approach to quantitatively describing stream networks was postulated by Strahler (1952).
 1. Stream Network The most common approach to quantitatively describing stream networks was postulated by Strahler (1952). First Order Streams streams with no tributaries. Second Order Streams begin at
1. Stream Network The most common approach to quantitatively describing stream networks was postulated by Strahler (1952). First Order Streams streams with no tributaries. Second Order Streams begin at
Surface Water Drainage Pro-forma for major developments
 Surface Water Drainage Pro-forma for major developments We advise that developers complete this form and submit it to the Local Planning Authority with their planning application, referencing from where
Surface Water Drainage Pro-forma for major developments We advise that developers complete this form and submit it to the Local Planning Authority with their planning application, referencing from where
Presented by: Peter Spal, IBI Group. OECS Regional Engineering Workshop October 1, 2014
 Presented by: Peter Spal, IBI Group OECS Regional Engineering Workshop October 1, 2014 Presentation Topics Principles of Hydrology rational formula, unit hydrograph Modeling Methods SWMMHYMO Synthetic
Presented by: Peter Spal, IBI Group OECS Regional Engineering Workshop October 1, 2014 Presentation Topics Principles of Hydrology rational formula, unit hydrograph Modeling Methods SWMMHYMO Synthetic
International Journal of Advance Research in Engineering, Science & Technology
 Impact Factor (SJIF): 3.632 International Journal of Advance Research in Engineering, Science & Technology e-issn: 2393-9877, p-issn: 2394-2444 Volume 3, Issue 5, May-2016 ANALYSIS OF RAINFALL DATA AND
Impact Factor (SJIF): 3.632 International Journal of Advance Research in Engineering, Science & Technology e-issn: 2393-9877, p-issn: 2394-2444 Volume 3, Issue 5, May-2016 ANALYSIS OF RAINFALL DATA AND
The Effect of Surface Texture on Evaporation, Infiltration and Storage Properties of Paved Surfaces
 The Effect of Surface Texture on Evaporation, Infiltration and Storage Properties of Paved Surfaces M. Mansell* and F. Rollet School of Engineering and Science, University of the West of Scotland, Paisley
The Effect of Surface Texture on Evaporation, Infiltration and Storage Properties of Paved Surfaces M. Mansell* and F. Rollet School of Engineering and Science, University of the West of Scotland, Paisley
Hydraulic Design of Road- Edge Surface Water Channels
 Hydraulic Design of Road- Edge Surface Water Channels DN-DNG-03068 March 015 DN Design Standards TRANSPORT INFRASTRUCTURE IRELAND (TII) PUBLICATIONS About TII Transport Infrastructure Ireland (TII) is
Hydraulic Design of Road- Edge Surface Water Channels DN-DNG-03068 March 015 DN Design Standards TRANSPORT INFRASTRUCTURE IRELAND (TII) PUBLICATIONS About TII Transport Infrastructure Ireland (TII) is
Application of the UK Flood Estimation Handbook pooling group approach to the Munster Blackwater River
 Application of the UK Flood Estimation Handbook pooling group approach to the Munster Blackwater River By David Price Manuela Toth Alison Janes (Jacobs Babtie, 95 Bothwell St., Glasgow) Synopsis The paper
Application of the UK Flood Estimation Handbook pooling group approach to the Munster Blackwater River By David Price Manuela Toth Alison Janes (Jacobs Babtie, 95 Bothwell St., Glasgow) Synopsis The paper
Stormwater Management Report Bachman Terrace Residential Development
 Stormwater Management Report Bachman Terrace Residential Development Project # 160401069 Prepared for: Tega Developments Prepared by: Stantec Consulting Ltd. April 14, 2014 Sign-off Sheet This document
Stormwater Management Report Bachman Terrace Residential Development Project # 160401069 Prepared for: Tega Developments Prepared by: Stantec Consulting Ltd. April 14, 2014 Sign-off Sheet This document
16 th September 2016 BRIM Workshop Loughborough. Richard Allitt
 16 th September 2016 BRIM Workshop Loughborough Richard Allitt Contents Uncertainties in Flood Risk Modelling 4 components Catchment wetness Asset data Rainfall Modelling Regulatory regime AMP1 to AMP5
16 th September 2016 BRIM Workshop Loughborough Richard Allitt Contents Uncertainties in Flood Risk Modelling 4 components Catchment wetness Asset data Rainfall Modelling Regulatory regime AMP1 to AMP5
Peak discharge computation
 Ia/P 4 Peak Dischage Method Graphical Peak Discharge Method This chapter presents the Graphical Peak Discharge method for computing peak discharge from rural and urban areas. The Graphical method was developed
Ia/P 4 Peak Dischage Method Graphical Peak Discharge Method This chapter presents the Graphical Peak Discharge method for computing peak discharge from rural and urban areas. The Graphical method was developed
Site Location Plan E N. Cookson Way, Catterick DL9 4XG
 APPENDIX 1 Site Location Plan 421180E 498725N Cookson Way, Catterick DL9 4XG KEY SITE BOUNDARY (approx. 4.19ha) PERMEABLE AREA (approx. 1.03ha) N IMPERMEABLE AREA (approx. 3.16ha) PROPOSED HOUSING SITE
APPENDIX 1 Site Location Plan 421180E 498725N Cookson Way, Catterick DL9 4XG KEY SITE BOUNDARY (approx. 4.19ha) PERMEABLE AREA (approx. 1.03ha) N IMPERMEABLE AREA (approx. 3.16ha) PROPOSED HOUSING SITE
Section 1 - Introduction
 VERSION 1.0 Stormwater Solutions for Residential Sites Section 1 - Introduction Prepared for EcoWater Solutions A Department of Waitakere City Council 113 Central Park Drive Henderson WAITAKERE CITY November
VERSION 1.0 Stormwater Solutions for Residential Sites Section 1 - Introduction Prepared for EcoWater Solutions A Department of Waitakere City Council 113 Central Park Drive Henderson WAITAKERE CITY November
PRELIMINARY DRAINAGE REPORT FOR THE EDI MASTER PLAN
 PRELIMINARY DRAINAGE REPORT FOR THE EDI MASTER PLAN April 5, 2015 Wayne W. Chang, MS, PE 46548 Chang Civil Engineering Hydrology Hydraulics Sedimentation P.O. Box 9496 Rancho Santa Fe, CA 92067 (858) 692-0760
PRELIMINARY DRAINAGE REPORT FOR THE EDI MASTER PLAN April 5, 2015 Wayne W. Chang, MS, PE 46548 Chang Civil Engineering Hydrology Hydraulics Sedimentation P.O. Box 9496 Rancho Santa Fe, CA 92067 (858) 692-0760
INFLOW DESIGN FLOOD CONTROL SYSTEM PLAN PLANT GREENE COUNTY ASH POND ALABMA POWER COMPANY
 INFLOW DESIGN FLOOD CONTROL SYSTEM PLAN PLANT GREENE COUNTY ASH POND ALABMA POWER COMPANY Section 257.82 of EPA s regulations requires the owner or operator of an existing or new CCR surface impoundment
INFLOW DESIGN FLOOD CONTROL SYSTEM PLAN PLANT GREENE COUNTY ASH POND ALABMA POWER COMPANY Section 257.82 of EPA s regulations requires the owner or operator of an existing or new CCR surface impoundment
AED Design Requirements: Hydrology Studies (Provisional)
 US Army Corps of Engineers Afghanistan Engineer District AED Design Requirements: Hydrology Studies (Provisional) Various Locations, Afghanistan January 2010, Version 1.6 TABLE OF CONTENTS AED DESIGN REQUIREMENTS
US Army Corps of Engineers Afghanistan Engineer District AED Design Requirements: Hydrology Studies (Provisional) Various Locations, Afghanistan January 2010, Version 1.6 TABLE OF CONTENTS AED DESIGN REQUIREMENTS
DETENTION BASIN DESIGN USING RATIONAL HYDROGRAPHS
 DETENTION BASIN DESIGN USING RATIONAL HYDROGRAPHS By Thomas F. Smith, P.E., P.L.S. Bercek and Smith Engineering, Inc. www.bercekandsmith.com tfsmith2@bercekandsmith.com 1 Topics Covered: 2 1 Attributed
DETENTION BASIN DESIGN USING RATIONAL HYDROGRAPHS By Thomas F. Smith, P.E., P.L.S. Bercek and Smith Engineering, Inc. www.bercekandsmith.com tfsmith2@bercekandsmith.com 1 Topics Covered: 2 1 Attributed
RAIN WATER HARVESTING FOR URBAN FLOOD PEAK REDUCTION
 RAIN WATER HARVESTING FOR URBAN FLOOD PEAK REDUCTION Dr. A.K.Sarma, IIT Guwahati, India M. D. Baishya, Engineering Student, NERIST, India G. Giraud, Engineering Student, ENGEES, France 2005 INTRODUCTION
RAIN WATER HARVESTING FOR URBAN FLOOD PEAK REDUCTION Dr. A.K.Sarma, IIT Guwahati, India M. D. Baishya, Engineering Student, NERIST, India G. Giraud, Engineering Student, ENGEES, France 2005 INTRODUCTION
Heart of the Village (Cradley) Ltd. Flood Risk Assessment for a Commercial Development in. Cradley, Herefordshire. Report K0710/0.
 Heart of the Village (Cradley) Ltd Flood Risk Assessment for a Commercial Development in Cradley, Herefordshire Report K0710/0 March 2016 Prepared and submitted by LLP Old Grammar School Church Street,
Heart of the Village (Cradley) Ltd Flood Risk Assessment for a Commercial Development in Cradley, Herefordshire Report K0710/0 March 2016 Prepared and submitted by LLP Old Grammar School Church Street,
ENGINEERING INFRASTRUCTURE REPORT 32 & 34 TENNYSON AVE, TAKAPUNA ISSUED FOR RESOURCE CONSENT
 ENGINEERING INFRASTRUCTURE ENGINEERING INFRASTRUCTURE REPORT 32 & 34 TENNYSON AVE, TAKAPUNA ISSUED FOR RESOURCE CONSENT Job No 37240R#C Date May 17 Level 1, 12 14 Como Street, PO Box 33 426, Takapuna,
ENGINEERING INFRASTRUCTURE ENGINEERING INFRASTRUCTURE REPORT 32 & 34 TENNYSON AVE, TAKAPUNA ISSUED FOR RESOURCE CONSENT Job No 37240R#C Date May 17 Level 1, 12 14 Como Street, PO Box 33 426, Takapuna,
South Worcestershire Strategic Flood Risk Assessment Level 2 Update
 South Worcestershire Strategic Flood Risk Assessment Level 2 Update Worcester West Site Assessment Final Report February 2015 This page is intentionally left blank 2015s2316 Worcester West Site Assessment
South Worcestershire Strategic Flood Risk Assessment Level 2 Update Worcester West Site Assessment Final Report February 2015 This page is intentionally left blank 2015s2316 Worcester West Site Assessment
HYDROLOGIC CONSIDERATIONS. 22 nd Annual Nonpoint Source Pollution Conference Saratoga Springs, NY
 LOW IMPACT DEVELOPMENT HYDROLOGIC CONSIDERATIONS 22 nd Annual Nonpoint Source Pollution Conference Saratoga Springs, NY May 18, 2011 PRESENTATION AGENDA Introduction Definitions Discuss Impacts to Hydrologic
LOW IMPACT DEVELOPMENT HYDROLOGIC CONSIDERATIONS 22 nd Annual Nonpoint Source Pollution Conference Saratoga Springs, NY May 18, 2011 PRESENTATION AGENDA Introduction Definitions Discuss Impacts to Hydrologic
CONSISTENCY BETWEEN CUHP AND RATIONAL METHODS James C.Y. Guo, PhD, P.E., and Ben Urbonas, P.E., D.WRD 08/04/2008
 CONSISTENCY BETWEEN CUHP AND RATIONAL METHODS James C.Y. Guo, PhD, P.E., and Ben Urbonas, P.E., D.WRD 08/04/2008 When estimating runoff for a storm event it is assumed that the storm runoff occurs from
CONSISTENCY BETWEEN CUHP AND RATIONAL METHODS James C.Y. Guo, PhD, P.E., and Ben Urbonas, P.E., D.WRD 08/04/2008 When estimating runoff for a storm event it is assumed that the storm runoff occurs from
Design of Stormwater Wetlands
 Hydraulic & Hydrologic Stormwater Engineering Design of Stormwater Wetlands Jon Hathaway, EI Extension Associate NCSU Bio. And Ag. Engineering 6 Step Process 1. Watershed Analysis (Runoff Volume and Peak
Hydraulic & Hydrologic Stormwater Engineering Design of Stormwater Wetlands Jon Hathaway, EI Extension Associate NCSU Bio. And Ag. Engineering 6 Step Process 1. Watershed Analysis (Runoff Volume and Peak
Horton Landfill, Small Dole, West Sussex. Infill of geological SSSI. Surface Water Management Assessment. Current Approved Design
 Horton Landfill, Small Dole, West Sussex Infill of geological SSSI Surface Water Management Assessment Current Approved Design Planning Permission DC/814/07 (UB) Condition 21 (Surface Water Management)
Horton Landfill, Small Dole, West Sussex Infill of geological SSSI Surface Water Management Assessment Current Approved Design Planning Permission DC/814/07 (UB) Condition 21 (Surface Water Management)
STORM WATER MANAGEMENT USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS- A CASE STUDY OF SURAT CITY
 STORM WATER MANAGEMENT USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS- A CASE STUDY OF SURAT CITY 1 Ajay Gamit, 2 P. P. Lodha, 3 Indra Prakash and 4 Khalid Mehmood 1 ME (Final), 2 HOD, Civil Department, L. E. College, Morbi
STORM WATER MANAGEMENT USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS- A CASE STUDY OF SURAT CITY 1 Ajay Gamit, 2 P. P. Lodha, 3 Indra Prakash and 4 Khalid Mehmood 1 ME (Final), 2 HOD, Civil Department, L. E. College, Morbi
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. Synthetic Turf Athletic Field Drainage Design Assistance
 TECHNICAL BULLETIN Synthetic Turf Athletic Field Drainage Design Assistance The SportsEdge HQ geocomposite strip drain products are engineered specifically for use in synthetic turf athletic field base
TECHNICAL BULLETIN Synthetic Turf Athletic Field Drainage Design Assistance The SportsEdge HQ geocomposite strip drain products are engineered specifically for use in synthetic turf athletic field base
6 STOREY CONDOMINIUM 7480 DERRY ROAD WEST, MILTON
 6 STOREY CONDOMINIUM 7480 DERRY ROAD WEST, MILTON STORM WATER MANAGEMENT DESIGN BRIEF NEW DEVELOPMENT DRAINAGE SYSTEM REV 0 August 29, 2017 PREPARED BY: HALLEX PROJECT #170532 HALLEX NIAGARA HALLEX HAMILTON
6 STOREY CONDOMINIUM 7480 DERRY ROAD WEST, MILTON STORM WATER MANAGEMENT DESIGN BRIEF NEW DEVELOPMENT DRAINAGE SYSTEM REV 0 August 29, 2017 PREPARED BY: HALLEX PROJECT #170532 HALLEX NIAGARA HALLEX HAMILTON
Hydrology for Drainage Design. Design Considerations Use appropriate design tools for the job at hand:
 Hydrology for Drainage Design Robert Pitt Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Alabama Tuscaloosa, AL Objectives for Urban Drainage Systems are Varied Ensure personal safety
Hydrology for Drainage Design Robert Pitt Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Alabama Tuscaloosa, AL Objectives for Urban Drainage Systems are Varied Ensure personal safety
0.0. Pervious CN = 40. (Unconnected impervious) (Total impervious) Total impervious area (percent) Composite CN
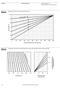 Figure 2-3 Composite CN with connected impervious area. 100 Composite CN 90 80 70 60 Pervious CN = 90 80 70 60 50 40 50 40 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Connected impervious area (percent) Figure 2-4
Figure 2-3 Composite CN with connected impervious area. 100 Composite CN 90 80 70 60 Pervious CN = 90 80 70 60 50 40 50 40 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Connected impervious area (percent) Figure 2-4
