Bio 10 Lecture Notes 9: Ecology SRJC
|
|
|
- Bryce Anderson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biomes A broad region characterized by vegetation types shaped by: Climate Average weather condition in a region Climate is affected by: amount of incoming solar radiation prevailing winds Topography- the elevation of land masses Rain Shadow Air rises on the windward side, loses moisture before passing over the mountain As you travel higher in elevation, conditions resemble those at higher latitudes (i.e. going up a mountain can seem like traveling toward the poles) Composition of regional soils. Terrestrial Biomes Deserts- Annual rainfall < 10 centimeters; high level of evaporation Form between 30 degrees north and south and in rain shadows Dry Shrublands and Woodlands Semiarid regions with cooler, wet winters and hot, dry summers Occur in western or southern coastal regions between latitudes 30 and 40 Plants adapted to dry conditions and fire (some rely on fire!) Dry Grasslands Shortgrass prarie Tallgrass prarie Desertification California Chaparral Conversion of large regions of natural grasslands to desert-like conditions Forest Biomes Tall trees form a continuous canopy Evergreen broadleaves in tropical latitudes Deciduous broadleaves in most temperate latitudes Evergreen conifers at high temperate elevations and at high latitudes Tropical Rainforests- lots of moisture, greatest diversity if life Tall Trees- competition for light Vines grow on tree trunks Large, dark green leaves adapted to living in shade of taller plants Epiphytes- plants growing on tree trunks, some can be parasitic Tropical forest canopies are layered, space is limiting factor Temperate Deciduous Forests- broad-leaf trees, drop leaves in winter Coniferous Forests- needle-shaped leaves conserve heat, keep them all year round A. Carranza Page 1 7/25/2015
2 Tundra- plants grow low to conserve heat Arctic Permafrost lies beneath surface Alpine Occurs at high latitudes The Water Provinces: Freshwater Biomes Lakes- Bodies of standing freshwater Eutrophic: shallow, nutrient-rich; has high primary productivity (green water) Oligotrophic: deep, nutrient-poor; has low primary productivity (clear water) Thermal Layering In temperate-zone lakes, water can form distinct layers during summer Seasonal Overturn In spring and fall, temperatures in the lake become more uniform Oxygen-rich surface waters mix with deeper oxygen-poor layers Nutrients that accumulated at bottom are brought to the surface Eutrophication Enrichment of a body of water with nutrients Can occur naturally over long time span Can be triggered by pollutants Rivers and Streams Water moves continuously in one direction. Water may become polluted as it travels to the sea. Estuary Partially enclosed area where saltwater and freshwater mix Dominated by salt-tolerant plants Chesapeake Bay, San Francisco Bay, salt marshes of New England Salt Marsh Mangrove Wetlands Tropical saltwater ecosystem Form in nutrient-rich tidal flats Dominant plants are salt-tolerant mangroves Florida, Southeast Asia Estuarine Food Webs Primary producers are phytoplankton and salt-tolerant plants Much primary production enters detrital food webs Detritus (decomposing organic material) feeds bacteria, nematodes, snails, crabs, fish A. Carranza Page 2 7/25/2015
3 Ocean Provinces (biomes) Intertidal-(Littoral zone)- within the mean high and low tides Intertidal Zones Upper littoral submerged during highest tides of cycle (low diversity) Midlittoral zone regularly submerged and exposed (moderate diversity) Lower littoral exposed only during lowest tides Benthic- attached to or living at the bottom Pelagic- swimming or drifting in the water column (open water) Sandy Coastlines Loose sediments, continually rearranged Few grazing food webs Detrital food webs from organic debris Interstitial Meiofauna Communities of microscopic animals living between sand grains Coral Reef Biomes Reef-building corals have photosynthetic, dinoflagellate symbionts Oceanic Biome (or Province) Photic Zone (Euphotic zone) depth to which light can reach photosynthetic organisms Marine Snow- form basis of food chain where light cannot reach Hydrothermal Vents Chemoautotrophic bacteria use mineral-rich hot water as energy source Upwelling Brings cold, nutrient-rich bottom waters to the surface Upwelling of cool water along western coasts Wind driven phenomenon A. Carranza Page 3 7/25/2015
4 Ecosystems A group of interacting populations and their physical environment. All interacting by a flow of energy and with their physical and chemical environments. Modes of Nutrition Photoautotrophs (photo= light, auto=self, trophos=nutrition) Capture sunlight or chemical energy Primary producers Heterotrophs (hetero= other, trophos= nutrition) Extract energy from other organisms or organic wastes Consumers, decomposers, detritivores (eat detritus) Role of Organisms Primary Producers Photoautotrophs Consumers Herbivore- primary consumers Carnivores-secondary consumers, can also be tertiary or further level, depending on who they eat. Omnivores- can be both primary and secondary depending on what they re eating Parasites- secondary or primary consumer,depending on who they parasitize Decomposers- can enter food chain at any trophic level depending on what they re eating Trophic Levels (Feeding relationships) All organisms at a trophic level are the same number of steps away from the energy input into the system Autotrophs are producers closest to energy input first trophic level Energy Flow One-way flow of energy: sun primary producers consumers Primary Productivity Gross primary productivity- total amount of photosynthate created Net primary productivity- amount available to primary consumers (stored by plants) Pyramids of biomass and energy- biomass and energy decrease as you go higher up the food chain Most energy is lost as heat or used to perform work (metabolic pathways) The Rule of Ten or 10% Law - only 10 percent of energy and biomass are present at each successive trophic level Biological magnification- contaminants accumulate in organisms at top of food chain Water Cycle Generally, water evaporates from ocean, falls as precipitation then flows back to ocean Plants Influence the Water Cycle A. Carranza Page 4 7/25/2015
5 Plants Protect Soil Deforestation leads to soil and nutrient erosion Carbon Cycle Reservoirs Atmosphere Oceans Trees and shells (clams etc) are carbon biomass holding stations Decomposers recycle and liberate carbon from the holding stations Decomposition Rates Higher rates in forests due to favorable conditions (moist and warm) Not much carbon accumulates Peat Bog Slow decomposition due anaerobic conditions, more C accumulates Source to Atmosphere Plant and animal respiration Burning of plants Fossil fuels Volcanic acitivity Carbon Cycle Carbon is assimilated by plants then passed on to consumers Consumers and decomposers release C back to atmosphere as CO2 Nitrogen Cycle Reservoir atmosphere Source to Plants Nitrogen-fixing bacteria Decomposition Plant Limiting Factor for Growth Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen fixing bacteria reduce atmospheric N2 to ammonia (NH3) Primary producers can assimilate NH3 and NO3 to make amino acids Consumers eat producers and acquire N in amino acid form Decomposer bacteria recycle N from organic material Ammonifying bacteria turn NO3 to NH3 Nitrifying bacteria turn NH3 to NO3 Another group of bacteria (denitrifying) turn NO3 to N2 Atmospheric N2 Nitrate (NO3) Ammonia (NH3) A. Carranza Page 5 7/25/2015
6 Community Interactions Community A group of interacting populations Populations are affected by: Available living space (habitat) Resource Availability (niche) Species interactions Habitat an organism s mailing address; the type of place where the individuals normally live Niche an organism s profession (role) in the community Species Interactions Symbiosis Living together for at least some part of the life cycle Most interactions are neutral; they have no effect on either species Commensalism helps one species and has no effect on the other Mutualism helps both species Some are obligatory; partners depend upon each other (coevolution) Yucca plants and yucca moth Mycorrhizal fungi and plants Anemone fish and anemone Parasitism Parasites draw nutrients from hosts live on or in host body Vectors Convey a parasite from host to host Parasitoids Develop inside another species Consume and kill host Micro Parasites microscopic; bacteria, protozoa, etc Competition Interspecific: among different species Exploitative competition- get as much of resource before competitor Interference competition- behaviorally keeping competitor from a resource Intraspecific: between members of the same species Intraspecific competition is most intense Territoriality Allelopathy (sibling harming)- impeding, hurting or killing same species rivals Some species have eliminated ways of avoiding competition: Resource partitioning- developing a very specified niche and focus on resources not common to competitor May use resources in a different way or time Minimizes competition and allows coexistence A. Carranza Page 6 7/25/2015
7 Lions hunt big game, cheetahs go after smaller, faster prey Competitive Exclusion Principle When two species compete for identical resources, one will be more successful and will eventually eliminate the other Predators animals that feed on other living organisms free-living do not reside on their prey Carnivores and omnivores Predator-Prey Relationships Species are limited by the number of available prey In some cases predators limit a prey species Coevolution Two or more species exert selection pressure on each other Prey defenses evolve Prey Defenses Camouflage Warning coloration Mimicry Predator Responses Predators counter prey defenses with new adaptations stealth camouflage avoidance of chemical repellents Community Dynamics Factors affecting changes in community structure Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis Ecological Community stability is an uneasy balance Community Instability Disturbances can cause a community to change in ways that persist even if the change is reversed. In some cases these are considered alternate stable states Keystone Species A species that has a disproportionately large effect on community structure Removal of a keystone species can cause drastic changes in a community can increase or decrease diversity Species Introductions Exotic species A species moves out of its home range and takes up residence in a new place No natural enemies or controls Can outcompete native species Ecological Succession Over time, one array of species is replaced by another Types of Succession Primary succession: new environments Begins with foundation species A. Carranza Page 7 7/25/2015
8 Ends with climax community Secondary succession: communities destroyed or displaced May not have foundation species Also ends with climax community Climax Community Stable array of species that does not change over time The final community in ecological succession In a particular habitat, succession produces the same climax community Population Ecology Population All members of a species living in a defined area at the same time Ecological principles govern growth and sustainability of all populations Demographics Population size- Total number of individuals Population Age Structure Divides population into age categories Reproductive base pre-reproductive and reproductive age categories Population Density the number of individuals per unit area. Population Distribution Patterns of Population Distribution Random Dispersion- the position of each individual is independent of the others. Uniform Dispersion-when individuals are evenly spaced. Clumped Dispersion- when individuals aggregate in patches. Clumped is most common type * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Random Uniform Clumped Population Size and Exponential Growth + Births: add to population - Deaths: subtract from population + Immigration: add to population -Emigration: subtract from population r = Net reproduction per individual per unit time (r = b - d, assuming no migration) Variable combines per capita birth and death rates (assuming both constant) Can be used to calculate rate of growth of a population A. Carranza Page 8 7/25/2015
9 Birth Rate b = number of births / number of individuals Death Rate d = number of deaths / number of individuals Zero Population Growth Interval in which number of births is balanced by number of deaths Assume no change as a result of migration Population size remains stable Exponential Growth Equation G = rn G is population growth per unit time r is net reproduction per individual per unit time N is population size Exponential Growth Population size grows by increasing increments during successive intervals The larger the population, the more individuals reproduce Effect of Deaths Population grows exponentially as long as per capita death rates are lower than per capita birth rates Biotic Potential Maximum rate of increase per individual under ideal conditions Varies between species In nature, biotic potential is rarely reached Limiting Factors Any essential resource that is in short supply All limiting factors acting on a population dictate sustainable population size Carrying Capacity (K) Maximum number of individuals that can be sustained in a particular habitat Logistic growth occurs when population size is limited by carrying capacity Logistic Growth As size of the population increases, rate of reproduction decreases When the population reaches carrying capacity, population growth ceases Logistic Growth Equation G = rmax N (K-N/K) G = population growth per unit time A. Carranza Page 9 7/25/2015
10 rmax = maximum population growth rate per unit time N = number of individuals K = carrying capacity Overshooting Capacity Population may temporarily increase above carrying capacity Overshoot is usually followed by a crash; dramatic increase in deaths J (exponential) vs S (logistic) curves Density-Dependent Controls Logistic growth equation deals with density-dependent controls Limiting factors become more intense as population size increases Disease, competition, parasites, toxic effects of waste products Density-Independent Controls Factors unaffected by population density Natural disasters or climate changes affect large and small populations alike Survivorship Curves a plot of age-specific survival 3 types of survivorship curves Type I high survivorship until fairly late in life typical of species w/ low reproductive rates reproduce fewer young, spend time and energy nurturing and protecting young, larger, stronger, more developed offspring (more likely to survive in competitive env.) humans, elephants K-selected species Predictable Environments found late in succession, stable well-defined communities # AGE Type II fairly constant death rate at all ages lizards, small mammals, song birds Type III highest death rate early in life reproduce at a young age, produce large # of offspring, devote little care to offspring, may die after reproducing starfish, oysters r-selected species Unpredictable Environments A. Carranza Page 10 7/25/2015
11 Life History Patterns Patterns of timing of reproduction and survivorship Vary among species Life History Traits Age of first reproduction Number of offspring per reproduction event Body size at maturity Brood interval Human Population Growth Population exceeds 6 billion Rates of increase vary among countries Average annual increase is 1.3% Population continues to increase exponentially Increase in growth rate Expansion of habitat and new climatic zones Increased capacity in existing habitats Population has sidestepped limiting factors Technology better shelter, sewage disposal Medicine immunization, disease control, prenatal care, better hygiene Human population has grown almost exponentially for three centuries. The human population increased relatively slowly until about 1650 when the Plague took an untold number of lives. Now doubling time ~50yrs (at 1.2%). Inevitability, human populations will stop growing, but how or when we are not sure. A. Carranza Page 11 7/25/2015
Bio 112 Ecology: Final Practice Exam Multiple Choice
 Final Exam Topics: 1) Basic Ecological Principles a) Biomes, ecosystems, communities and populations i) Biomes: know the major ones and where they occur ii) Ecosystem: communities and physical environment
Final Exam Topics: 1) Basic Ecological Principles a) Biomes, ecosystems, communities and populations i) Biomes: know the major ones and where they occur ii) Ecosystem: communities and physical environment
Ecology Review. Name: Date: Period:
 Ecology Review Name: Date: Period: 1. Define the terms ecology and ecosystem. Ecology - The study of the interactions among organisms and their environment Ecosystem - collection of all the organisms that
Ecology Review Name: Date: Period: 1. Define the terms ecology and ecosystem. Ecology - The study of the interactions among organisms and their environment Ecosystem - collection of all the organisms that
Bio 112 Ecology: Final Study Guide
 Bio 112 Ecology: Final Study Guide Below is an outline of the topics and concepts covered on the final exam. This packet also includes a practice test, along with answers to questions 1-44. You may submit
Bio 112 Ecology: Final Study Guide Below is an outline of the topics and concepts covered on the final exam. This packet also includes a practice test, along with answers to questions 1-44. You may submit
What is Ecology? Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
 ECOLOGY What is Ecology? The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings Factors involved in ecology Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
ECOLOGY What is Ecology? The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings Factors involved in ecology Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
3-1 What is Ecology?! The study of the. interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment
 Chapters 3,4 & 5 1 3-1 What is Ecology? The study of the interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment 2 Levels of Ecological Organization 3 3-2 Energy Flow main source of energy
Chapters 3,4 & 5 1 3-1 What is Ecology? The study of the interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment 2 Levels of Ecological Organization 3 3-2 Energy Flow main source of energy
REVIEW 8: ECOLOGY UNIT. A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned:
 Period Date REVIEW 8: ECOLOGY UNIT A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Populations group of individuals of same species living in same area (size, density, distribution/dispersion)
Period Date REVIEW 8: ECOLOGY UNIT A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Populations group of individuals of same species living in same area (size, density, distribution/dispersion)
1. Global Climate. Latitude and Sunlight Intensity 12/4/2014. Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere. 1.
 Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere 1. Global Climate 2. Terrestrial Biomes 3. Aquatic Biomes 4. Factors Affecting Species Distribution 1. Global Climate Latitude and Sunlight Intensity
Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere 1. Global Climate 2. Terrestrial Biomes 3. Aquatic Biomes 4. Factors Affecting Species Distribution 1. Global Climate Latitude and Sunlight Intensity
Allegheny-Clarion Valley School District
 Allegheny-Clarion Valley School District Jr./Sr. High School Name of Course: Ecology Grade Level: 9-12 Persons Writing/Revising Curriculum: Joni Runyan Laura Jamison *** Created 2015-16 School Year Unit
Allegheny-Clarion Valley School District Jr./Sr. High School Name of Course: Ecology Grade Level: 9-12 Persons Writing/Revising Curriculum: Joni Runyan Laura Jamison *** Created 2015-16 School Year Unit
Ecology Module B, Anchor 4
 Ecology Module B, Anchor 4 Key Concepts: - The biological influences on organisms are called biotic factors. The physical components of an ecosystem are called abiotic factors. - Primary producers are
Ecology Module B, Anchor 4 Key Concepts: - The biological influences on organisms are called biotic factors. The physical components of an ecosystem are called abiotic factors. - Primary producers are
Theme 7 Review: Ecology
 Theme 7 Review: Ecology 7.1: All living systems require constant input of free energy. 7.2: All biological systems from cells and organisms to populations, communities and ecosystems are affected by complex
Theme 7 Review: Ecology 7.1: All living systems require constant input of free energy. 7.2: All biological systems from cells and organisms to populations, communities and ecosystems are affected by complex
Ecosystems. 6.L.2.2 Explain how plants respond to external stimuli (including dormancy and forms of tropism) to enhance survival in an environment.
 Ecosystems Date: 6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment. 6.L.2.1 Summarize how energy derived from
Ecosystems Date: 6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment. 6.L.2.1 Summarize how energy derived from
Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book)
 Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p.87-89 (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book) Term Definition Weather Day-to-day condition of earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p.87-89 (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book) Term Definition Weather Day-to-day condition of earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
OBJECTIVE. Describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e., organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere)
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e., organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere) Describe the characteristic biotic and abiotic components of aquatic
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e., organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere) Describe the characteristic biotic and abiotic components of aquatic
Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 34 THE BIOSPHERE: AN INTRODUCTION TO EARTH S DIVERSE ENVIRONMENTS
 Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 34 THE BIOSPHERE: AN INTRODUCTION TO EARTH S DIVERSE ENVIRONMENTS 1. aquatic biomes photic zone aphotic zone 2. 9 terrestrial (land) biomes tropical rain forest savannah (tropical
Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 34 THE BIOSPHERE: AN INTRODUCTION TO EARTH S DIVERSE ENVIRONMENTS 1. aquatic biomes photic zone aphotic zone 2. 9 terrestrial (land) biomes tropical rain forest savannah (tropical
extinction rates. (d) water availability and solar radiation levels are highest in the tropics. (e) high temperature causes rapid speciation.
 NOTE: Questions #57 100 that follow may have been based in part on material supplied by a textbook publisher. For that reason, the answers to them are provided free (as they were to the students that semester.
NOTE: Questions #57 100 that follow may have been based in part on material supplied by a textbook publisher. For that reason, the answers to them are provided free (as they were to the students that semester.
Ecology Review A: Top Ten
 Ecology Review A: Top Ten 1. Populations Group of individuals of same species living in the same area at the same time Habitat vs. niche Competition a. Survivorship curves Type 1 = most live long life
Ecology Review A: Top Ten 1. Populations Group of individuals of same species living in the same area at the same time Habitat vs. niche Competition a. Survivorship curves Type 1 = most live long life
Introduction to Ecology
 Introduction to Ecology Ecology The study of all components (abiotic and biotic) within a defined area. Basic organization: Biosphere Biomes Ecosystems Communities Populations Individuals Scales of Ecological
Introduction to Ecology Ecology The study of all components (abiotic and biotic) within a defined area. Basic organization: Biosphere Biomes Ecosystems Communities Populations Individuals Scales of Ecological
SY 2018/ st Final Term Revision. Student s Name: Grade: 10A/B. Subject: Biology
 SY 2018/2019 1 st Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 10A/B Subject: Biology Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to
SY 2018/2019 1 st Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 10A/B Subject: Biology Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to
What is Ecology? Includes land, air, and water as well as life. Living organisms are NOT distributed uniformly throughout the biosphere.
 Ecology What is Ecology? Ecology is the study of the interactions of organisms with one another and with their physical environment. Biosphere - part of the Earth in which life exists. Includes land, air,
Ecology What is Ecology? Ecology is the study of the interactions of organisms with one another and with their physical environment. Biosphere - part of the Earth in which life exists. Includes land, air,
Ecology: Chapters Worksheet
 Ecology: Chapters 34 36 Worksheet Name: Chapter 34: The Biosphere Concept 34.1 The biosphere is the global ecosystem. (pp. 744 749) The scientific study of the interactions among organisms and between
Ecology: Chapters 34 36 Worksheet Name: Chapter 34: The Biosphere Concept 34.1 The biosphere is the global ecosystem. (pp. 744 749) The scientific study of the interactions among organisms and between
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater
 Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
Introduction to Ecology
 Introduction to Ecology Ecology The study of all components (abiotic and biotic) within a defined area. Basic organization: Biosphere Biomes Ecosystems Communities Populations Individuals Scales of Ecological
Introduction to Ecology Ecology The study of all components (abiotic and biotic) within a defined area. Basic organization: Biosphere Biomes Ecosystems Communities Populations Individuals Scales of Ecological
BIOL 300 Foundations of Biology Summer 2017 Telleen Lecture Outline. Ecology and Ecosystems
 BIOL 300 Foundations of Biology Summer 2017 Telleen Lecture Outline Ecology and Ecosystems I. What is ecology? A. Derived from the Greek: 1. oikos house 2. logos study of 3. study of the house in which
BIOL 300 Foundations of Biology Summer 2017 Telleen Lecture Outline Ecology and Ecosystems I. What is ecology? A. Derived from the Greek: 1. oikos house 2. logos study of 3. study of the house in which
Ecosystems. Trophic relationships determine the routes of energy flow and chemical cycling in ecosystems.
 AP BIOLOGY ECOLOGY ACTIVITY #5 Ecosystems NAME DATE HOUR An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community as well as all the abiotic factors with which they interact. The dynamics of an
AP BIOLOGY ECOLOGY ACTIVITY #5 Ecosystems NAME DATE HOUR An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community as well as all the abiotic factors with which they interact. The dynamics of an
ECOSYSTEMS. Follow along in chapter 54. *Means less important
 ECOSYSTEMS Follow along in chapter 54 *Means less important How do ecosystems function? What is an ecosystem? All living things in an area and their abiotic environment Ecosystem function can be easily
ECOSYSTEMS Follow along in chapter 54 *Means less important How do ecosystems function? What is an ecosystem? All living things in an area and their abiotic environment Ecosystem function can be easily
Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems
 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Section 1: Community Ecology Section 2: Terrestrial Biomes Section 3: Aquatic Ecosystems Click on a lesson name to select. 3.1 Community Ecology Communities A biological
Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Section 1: Community Ecology Section 2: Terrestrial Biomes Section 3: Aquatic Ecosystems Click on a lesson name to select. 3.1 Community Ecology Communities A biological
Intro to Ecology. Chapter 18
 Intro to Ecology Chapter 18 Interdependence: A Key Theme in Ecology Ecology- study of the interactions of living organisms w/ one another and w/ their physical environment (soil, water,weather) Interdependence:
Intro to Ecology Chapter 18 Interdependence: A Key Theme in Ecology Ecology- study of the interactions of living organisms w/ one another and w/ their physical environment (soil, water,weather) Interdependence:
What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions.
 Ecology What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions. Biotic Factors Living things in the environment. Animals Plants Fungi Protists Bacteria Abiotic
Ecology What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions. Biotic Factors Living things in the environment. Animals Plants Fungi Protists Bacteria Abiotic
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Tuesday, September 19, 17
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Ecology the study of the interactions between organisms and the living and nonliving components of the environment
 Ecology the study of the interactions between organisms and the living and nonliving components of the environment 5/23/14 1 1. Levels of Ecological organization A. Biosphere- Earth, atmosphere and all
Ecology the study of the interactions between organisms and the living and nonliving components of the environment 5/23/14 1 1. Levels of Ecological organization A. Biosphere- Earth, atmosphere and all
What is Ecology? QGdH3QU
 Ecology What is Ecology? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tgr- QGdH3QU Ecology The study of the interactions of different organisms (living things) between each other and with their environment (surroundings).
Ecology What is Ecology? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tgr- QGdH3QU Ecology The study of the interactions of different organisms (living things) between each other and with their environment (surroundings).
6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment.
 Ecosystems 6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment. 6.L.2.1 Summarize how energy derived from the
Ecosystems 6.L.2 Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems and the responses of populations to the biotic and abiotic factors in their environment. 6.L.2.1 Summarize how energy derived from the
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes
 Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
3.2 Biomes and Aquatic Zones
 3.2 Biomes and Aquatic Zones Learning Goals: 1. Identify a biome based on its temperature, precipitation, and dominant plant species. 2. Identify a marine life zone based on its location and amounts of
3.2 Biomes and Aquatic Zones Learning Goals: 1. Identify a biome based on its temperature, precipitation, and dominant plant species. 2. Identify a marine life zone based on its location and amounts of
AP Bio Summer Assignment Mrs. Oswald
 AP Bio Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. Oswald Welcome to AP Biology! I look forward to a great year. Due to the large volume of content we have to cover, your summer assignment will be to read the Ecology
AP Bio Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. Oswald Welcome to AP Biology! I look forward to a great year. Due to the large volume of content we have to cover, your summer assignment will be to read the Ecology
8/7/18. UNIT 5: ECOLOGY Chapter 15: The Biosphere
 UNIT 5: ECOLOGY Chapter 15: The Biosphere I. Life in the Earth System (15.1) A. The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that is inhabited by life 1. Biosphere- part of Earth where life exists a. Includes
UNIT 5: ECOLOGY Chapter 15: The Biosphere I. Life in the Earth System (15.1) A. The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that is inhabited by life 1. Biosphere- part of Earth where life exists a. Includes
Chapter 4. Ecosystems and Communities
 Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Communities I. The Role of Climate 4-1 A. Weather = Day to day conditions of Earth s atmosphere in a particular place and time B. Climate = Average year after year conditions of
Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Communities I. The Role of Climate 4-1 A. Weather = Day to day conditions of Earth s atmosphere in a particular place and time B. Climate = Average year after year conditions of
9/23/2015 Question 1 Review Chapter 15 What biome do you live in? Biomes Answer 1 Question 2 Temperate Deciduous Forest Name the 6 Major biomes.
 Review Chapter 15 Biomes Question 1 What biome do you live in? Answer 1 Question 2 Temperate Deciduous Forest Name the 6 Major biomes. 1 Answer 2 Question 3 Fill in Tropical Rainforest Desert Temperate
Review Chapter 15 Biomes Question 1 What biome do you live in? Answer 1 Question 2 Temperate Deciduous Forest Name the 6 Major biomes. 1 Answer 2 Question 3 Fill in Tropical Rainforest Desert Temperate
Chapter 36: Population Growth
 Chapter 36: Population Growth Population: Population Concepts interbreeding group of same species Carrying Capacity: maximum population size an ecosystem can sustainably support Critical Number: minimum
Chapter 36: Population Growth Population: Population Concepts interbreeding group of same species Carrying Capacity: maximum population size an ecosystem can sustainably support Critical Number: minimum
Chapter 12 & 13. Interactions of life The Nonliving Environment
 Chapter 12 & 13 Interactions of life The Nonliving Environment BIOSPHERE Biosphere - the part of the Earth that supports life. This includes the top portion of Earth s crust, all the waters that cover
Chapter 12 & 13 Interactions of life The Nonliving Environment BIOSPHERE Biosphere - the part of the Earth that supports life. This includes the top portion of Earth s crust, all the waters that cover
LEARNING OUTCOME B1. Biomes. Biomes. Factors Creating Biomes 26/10/2011. Section Biomes. Factors Creating Biomes
 Section 1.1 - Biomes LEARNING OUTCOME B1 Key Terms abiotic adaptation biome biotic climate climatograph Science 10 Biology Biomes Biomes are the largest division of the largest division of the biosphere.
Section 1.1 - Biomes LEARNING OUTCOME B1 Key Terms abiotic adaptation biome biotic climate climatograph Science 10 Biology Biomes Biomes are the largest division of the largest division of the biosphere.
2018 ECOLOGY YEAR 2 (2018) PART ONE GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY
 2018 ECOLOGY YEAR 2 (2018) PART ONE GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY KAREN L. LANCOUR National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science DISCLAIMER - This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may
2018 ECOLOGY YEAR 2 (2018) PART ONE GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY KAREN L. LANCOUR National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science DISCLAIMER - This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may
Name: Class: Date: Ver: 2
 Indicate the answer choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The primary reason why southern sea otter recovery is ecologically important is because they. a. encourage tourism
Indicate the answer choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The primary reason why southern sea otter recovery is ecologically important is because they. a. encourage tourism
Chapter 55: Ecosystems
 Ch. 55 Warm-Up 1. Draw an energy pyramid and label the following trophic levels: Primary producer Primary consumer Secondary consumer Tertiary consumer 2. What is an example of an organism at each level
Ch. 55 Warm-Up 1. Draw an energy pyramid and label the following trophic levels: Primary producer Primary consumer Secondary consumer Tertiary consumer 2. What is an example of an organism at each level
Ecosystem consists of the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment.
 Ecosystem consists of the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment. An ecosystem can be terrestrial (on land) or aquatic (in water) An ecosystem
Ecosystem consists of the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment. An ecosystem can be terrestrial (on land) or aquatic (in water) An ecosystem
CHAPTER 2: PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY 11/29/16
 CHAPTER 2: PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY 11/29/16 Ecology The scientific discipline in which the relationship among living organisms and their interactions with their environments are studied. Scientist who study
CHAPTER 2: PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY 11/29/16 Ecology The scientific discipline in which the relationship among living organisms and their interactions with their environments are studied. Scientist who study
Chapter 55: Ecosystems
 Chapter 55: Ecosystems You Must Know: How energy flows through the ecosystem (food chains and food webs) The difference between gross primary productivity and net primary productivity. The carbon and nitrogen
Chapter 55: Ecosystems You Must Know: How energy flows through the ecosystem (food chains and food webs) The difference between gross primary productivity and net primary productivity. The carbon and nitrogen
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Ecology. Climate. Global Climate. Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere
 Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere Ecology oikos - home! logos - to study! Ecology - the study of interactions between organisms and the environment! Answer important questions:! Where
Chapter 52: Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere Ecology oikos - home! logos - to study! Ecology - the study of interactions between organisms and the environment! Answer important questions:! Where
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 21-1 Terrestrial Biomes
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 21-1 Terrestrial Biomes Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. The biome that is characterized by the presence of permafrost is called a. savanna
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 21-1 Terrestrial Biomes Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. The biome that is characterized by the presence of permafrost is called a. savanna
BIOMES. Living World
 BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
COMMUNITY ECOLOGY. Interspecific Interactions. Ecosystems unit
 COMMUNITY ECOLOGY Ecosystems unit Today s Big Ideas: An organism s biotic environment includes Other individuals in its own population Populations of other species living in the same area An assemblage
COMMUNITY ECOLOGY Ecosystems unit Today s Big Ideas: An organism s biotic environment includes Other individuals in its own population Populations of other species living in the same area An assemblage
Core Case Study: Southern Sea Otters: Are They Back from the Brink of Extinction?
 Core Case Study: Southern Sea Otters: Are They Back from the Brink of Extinction? Habitat Hunted: early 1900s Partial recovery Why care about sea otters? Ethics Keystone species Tourism dollars Just last
Core Case Study: Southern Sea Otters: Are They Back from the Brink of Extinction? Habitat Hunted: early 1900s Partial recovery Why care about sea otters? Ethics Keystone species Tourism dollars Just last
Climate: describes the average condition, including temperature and precipitation, over long periods in a given area
 Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
15.1 Life in the Earth System. KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems.
 15.1 Life in the Earth System KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is the portion of Earth that is inhabited by life. The
15.1 Life in the Earth System KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is the portion of Earth that is inhabited by life. The
CHAPTER 1, SECTION 1 CHAPTER 3, SECTION 4
 CHAPTER 1, SECTION 1 Define Sustainability and Sustainable Living in your own words. The ability for the earth and all living things on it to survive and adapt to changing environmental conditions. Take
CHAPTER 1, SECTION 1 Define Sustainability and Sustainable Living in your own words. The ability for the earth and all living things on it to survive and adapt to changing environmental conditions. Take
2.D.1-Environmental Influences
 2.D.1-Environmental Influences Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce, and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. EU 2A- Growth, reproduction and
2.D.1-Environmental Influences Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce, and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. EU 2A- Growth, reproduction and
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Welcome Back! The Final is Coming! 12/13/16
 Welcome Back! The Final is Coming! 12/13/16 1. The picture below depicts what level of organization? 2. What organelle assists plants with producing their own food? *Bonus: What are plants classified as
Welcome Back! The Final is Coming! 12/13/16 1. The picture below depicts what level of organization? 2. What organelle assists plants with producing their own food? *Bonus: What are plants classified as
Chapter 3: Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems
 Chapter 3: Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems How would you describe your Community? Did you include your family and friends? Did you include your school? Did you include plants and animals? A biological
Chapter 3: Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems How would you describe your Community? Did you include your family and friends? Did you include your school? Did you include plants and animals? A biological
Guide 34. Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles. p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/
 Guide 34 Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/ Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists
Guide 34 Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/ Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists
1. All organisms are made of cells. Cells are the smallest unit of life
 1. All organisms are made of cells Cells are the smallest unit of life 2. All organisms need energy Any living organism needs energy to live They take in and use energy. 3. All organisms respond to the
1. All organisms are made of cells Cells are the smallest unit of life 2. All organisms need energy Any living organism needs energy to live They take in and use energy. 3. All organisms respond to the
Ecosystems and the Biosphere Outline
 Ecosystems and the Biosphere Outline Ecosystems Processes in an ecosystem Production, respiration, decomposition How energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem Biosphere Biogeochemical Cycles Gaia
Ecosystems and the Biosphere Outline Ecosystems Processes in an ecosystem Production, respiration, decomposition How energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem Biosphere Biogeochemical Cycles Gaia
Warm Up Exercise. Based on your knowledge of the carbon cycle, what do you think might happen if vast areas of forest are cleared?
 Warm Up Exercise Based on your knowledge of the carbon cycle, what do you think might happen if vast areas of forest are cleared? The Role of Climate Weather- the day-to-day condition of Earth s atmosphere
Warm Up Exercise Based on your knowledge of the carbon cycle, what do you think might happen if vast areas of forest are cleared? The Role of Climate Weather- the day-to-day condition of Earth s atmosphere
79. Cone- bearing trees are characteristic of the a) taiga. b) tropical rain forest. c) temperate deciduous forest. d) savanna.
 73. The portion of a species resource (biological, chemical, and physical) which a particular species actually utilizes is known as the: a) Reserve niche b) Conservation niche c) Basic niche d) Fundamental
73. The portion of a species resource (biological, chemical, and physical) which a particular species actually utilizes is known as the: a) Reserve niche b) Conservation niche c) Basic niche d) Fundamental
Classifying our Biotic Environment (Trophic Levels) Ecology. Ecology is study how things interact with other and else in the.
 Ecology Ecology is study how things interact with other and else in the. Ecologists focus their attention on in order to organize their studies. Ecosystems can be very large or very small. For example:
Ecology Ecology is study how things interact with other and else in the. Ecologists focus their attention on in order to organize their studies. Ecosystems can be very large or very small. For example:
Biology Chapter Two. Principles of Ecology
 Biology Chapter Two Principles of Ecology 2.1 Organisms and Their Environment Objectives: 1. Distinguish between the biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. 2. Compare the different levels of biological
Biology Chapter Two Principles of Ecology 2.1 Organisms and Their Environment Objectives: 1. Distinguish between the biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. 2. Compare the different levels of biological
Global ecology. Landscape ecology. Ecosystem ecology
 Global ecology Landscape ecology Ecosystem ecology Community ecology Population ecology Organismal ecology 1 Atmosphere Low angle of incoming sunlight 90 N (North Pole) 23.5 N (Tropic of Cancer) Sun overhead
Global ecology Landscape ecology Ecosystem ecology Community ecology Population ecology Organismal ecology 1 Atmosphere Low angle of incoming sunlight 90 N (North Pole) 23.5 N (Tropic of Cancer) Sun overhead
AP Biology Summer Work
 AP Biology Summer Work 2017-2018 Mrs. Schreiber, kschreiber@mpsd.org Welcome to AP Biology! I look forward to working with you this year! Please read the information below regarding your summer assignment.
AP Biology Summer Work 2017-2018 Mrs. Schreiber, kschreiber@mpsd.org Welcome to AP Biology! I look forward to working with you this year! Please read the information below regarding your summer assignment.
Ecosystem = A group of interacting populations and their physical environment.
 Ecosystem = Ecosystem = A group of interacting populations and their physical environment. All interacting by a flow of energy and with their physical and chemical environments. Ecosystems can be Large
Ecosystem = Ecosystem = A group of interacting populations and their physical environment. All interacting by a flow of energy and with their physical and chemical environments. Ecosystems can be Large
Ecosystems and the Biosphere: Energy Flow Through the Ecosystem and the Recycling of Matter
 Name Ecosystems and the Biosphere: Energy Flow Through the Ecosystem and the Recycling of Matter Overview: An ecosystem is: All of the organisms living on Earth need to carry out life processes such as
Name Ecosystems and the Biosphere: Energy Flow Through the Ecosystem and the Recycling of Matter Overview: An ecosystem is: All of the organisms living on Earth need to carry out life processes such as
AP Central, run by the College Board, has a vast amount of information regarding all AP classes, not only biology. Go to this website:
 AP Biology Summer Packet, 2017 Mrs. House Welcome to AP Biology! In order to prepare you for the rigorous year ahead, I have put together a packet of information, assignments, and suggested reading to
AP Biology Summer Packet, 2017 Mrs. House Welcome to AP Biology! In order to prepare you for the rigorous year ahead, I have put together a packet of information, assignments, and suggested reading to
Science 1206 Unit 1 Test Please shade the letter of the best possible answer on the scan sheet provided.
 Science 1206 Unit 1 Test Part A: Multiple Choice. (60%) Name: Please shade the letter of the best possible answer on the scan sheet provided. 1. Which describes a system that meets the needs of both present
Science 1206 Unit 1 Test Part A: Multiple Choice. (60%) Name: Please shade the letter of the best possible answer on the scan sheet provided. 1. Which describes a system that meets the needs of both present
Freshwater ecosystems
 Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
The nitrogen cycle is an example of a. carbohydrate cycle c. hydrologic cycle b. atmospheric cycle d. sedimentary cycle
 Environmental Science Semester Exam Study Guide Chapter 4: Ecology 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Ecology is the study of how a. organisms interact with each other and their nonliving environment b.
Environmental Science Semester Exam Study Guide Chapter 4: Ecology 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Ecology is the study of how a. organisms interact with each other and their nonliving environment b.
Ecology Final Exam. 2. What is a pioneer species? What is the most common pioneer species? First species to move into an ecosystem - lichen
 1. What is extinction? All members of a species die off 2. What is a pioneer species? What is the most common pioneer species? First species to move into an ecosystem - lichen 3. Why would a 5 cubic meter
1. What is extinction? All members of a species die off 2. What is a pioneer species? What is the most common pioneer species? First species to move into an ecosystem - lichen 3. Why would a 5 cubic meter
THE EARTH S BIOSPHERE
 THE EARTH S BIOSPHERE l Energy Flows in Ecological Systems l Ecosystem Structure l Productivity and Biodiversity Energy Flows in Ecological Systems Producers and Consumers l Organisms with the ability
THE EARTH S BIOSPHERE l Energy Flows in Ecological Systems l Ecosystem Structure l Productivity and Biodiversity Energy Flows in Ecological Systems Producers and Consumers l Organisms with the ability
The Biosphere Chapter 3. What Is Ecology? Section 3-1
 The Biosphere Chapter 3 What Is Ecology? Section 3-1 Interactions and Interdependence Ecology is the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings.
The Biosphere Chapter 3 What Is Ecology? Section 3-1 Interactions and Interdependence Ecology is the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings.
AP Biology Summer Assignment Unit 7 Ecology Chps
 Name Period Date Chp. 40 Define: 1. Abiotic: AP Biology Summer Assignment Unit 7 Ecology Chps. 40-43 2. Biotic: 3. Biomes: 4. Demography: 5. Exponential population growth: 6. Logistic population growth:
Name Period Date Chp. 40 Define: 1. Abiotic: AP Biology Summer Assignment Unit 7 Ecology Chps. 40-43 2. Biotic: 3. Biomes: 4. Demography: 5. Exponential population growth: 6. Logistic population growth:
ANSWER KEY - Ecology Review Packet
 ANSWER KEY - Ecology Review Packet OBJECTIVE 1: Ecosystem Structure 1. What is the definition of an abiotic factor? Give one example. A nonliving part of an ecosystem. Example: water 2. What is the definition
ANSWER KEY - Ecology Review Packet OBJECTIVE 1: Ecosystem Structure 1. What is the definition of an abiotic factor? Give one example. A nonliving part of an ecosystem. Example: water 2. What is the definition
Ecology. The study of organisms and their interaction with the environment
 Ecology The study of organisms and their interaction with the environment Ecology Biosphere broadest, most inclusive level of organization - deepest part of the ocean to 6 miles above the earth - all organisms
Ecology The study of organisms and their interaction with the environment Ecology Biosphere broadest, most inclusive level of organization - deepest part of the ocean to 6 miles above the earth - all organisms
Ecology Unit Notes: b. = Individual of a single species in. c. = more than one living in the same area.
 Ecology Unit Notes: Name: Period: Daily Question: Explain an example of how something non-living affects the ecosystem. Then explain an example of how something living affects the ecosystem. Overview of
Ecology Unit Notes: Name: Period: Daily Question: Explain an example of how something non-living affects the ecosystem. Then explain an example of how something living affects the ecosystem. Overview of
Chapter 22: Energy in the Ecosystem
 Chapter 22: Energy in the Ecosystem What is ecology? Global human issues Physical limits Ecosystems Organisms Populations Species Interactions Communities Energy flows and nutrients cycle C, H 2 0, P,
Chapter 22: Energy in the Ecosystem What is ecology? Global human issues Physical limits Ecosystems Organisms Populations Species Interactions Communities Energy flows and nutrients cycle C, H 2 0, P,
Regents Living Environment Ecology and Human Impact on Ecosystems
 Regents Living Environment Ecology and Human Impact on Ecosystems Part I Ecology Ecology Vocabulary Pioneer Organisms Biosphere Ecosystem Community Population Succession Biotic Food web Autotroph Biomass
Regents Living Environment Ecology and Human Impact on Ecosystems Part I Ecology Ecology Vocabulary Pioneer Organisms Biosphere Ecosystem Community Population Succession Biotic Food web Autotroph Biomass
Climate and Biodiversity
 LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 7 Climate and Biodiversity Core Case Study: A Temperate Deciduous Forest Why do forests grow in some areas and not others? Climate Tropical
LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 7 Climate and Biodiversity Core Case Study: A Temperate Deciduous Forest Why do forests grow in some areas and not others? Climate Tropical
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 24 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
What is a producer? Plants and their relatives ie algae
 What is a producer? Plants and their relatives ie algae What is an autotroph? A producer/ plant or plant relative that can make its own food How do producers make their own food? photosynthesis What is
What is a producer? Plants and their relatives ie algae What is an autotroph? A producer/ plant or plant relative that can make its own food How do producers make their own food? photosynthesis What is
Slide 1. Earth Science. Chapter 11 Living Systems
 Slide 1 Earth Science Chapter 11 Living Systems Slide 2 Biomes A biome is a region with a certain climate and certain forms of vegetation. It is mostly the climate temperature and precipitation in an area
Slide 1 Earth Science Chapter 11 Living Systems Slide 2 Biomes A biome is a region with a certain climate and certain forms of vegetation. It is mostly the climate temperature and precipitation in an area
Producers. living systems need energy to function. autotrophs. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth.
 Producers living systems need energy to function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth. sources of energy sunlight inorganic chemical compounds. autotrophs. capture energy from sunlight
Producers living systems need energy to function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth. sources of energy sunlight inorganic chemical compounds. autotrophs. capture energy from sunlight
Keystone Biology Remediation B4: Ecology
 Keystone Biology Remediation B4: Ecology Assessment Anchors: to describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e. organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere) (B.4.1.1) to describe
Keystone Biology Remediation B4: Ecology Assessment Anchors: to describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e. organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere) (B.4.1.1) to describe
Chapter 4: Ecosystems & Communities
 Chapter 4: Ecosystems & Communities Section 4.1 The Role of Climate In Earth s atmosphere, temperature, precipitation, and other environmental factors combine to produce weather and climate. Weather is
Chapter 4: Ecosystems & Communities Section 4.1 The Role of Climate In Earth s atmosphere, temperature, precipitation, and other environmental factors combine to produce weather and climate. Weather is
Ecology. Mrs. Flannery
 Ecology Mrs. Flannery What is ECOLOGY?? Ecology is the scientific study of the interactions between organisms and their environments. Biotic factors = living components of the environment. Abiotic factors
Ecology Mrs. Flannery What is ECOLOGY?? Ecology is the scientific study of the interactions between organisms and their environments. Biotic factors = living components of the environment. Abiotic factors
Energy Movement. How Life Interacts. Food Chains. Trophic Levels. Levels. Pathway which shows how matter and energy is moved through an ecosystem
 Food Chains Energy Movement Pathway which shows how matter and energy is moved through an ecosystem Always starts with the SUN and ends with a DECOMPOSER Arrows indicate direction in which energy is transferred
Food Chains Energy Movement Pathway which shows how matter and energy is moved through an ecosystem Always starts with the SUN and ends with a DECOMPOSER Arrows indicate direction in which energy is transferred
Chapter : Ecology Notes
 Chapter 18 21 : Ecology Notes 1. Ecology: Scientific Study of Interaction between organisms and their environment (a branch of biological sciences); inter-relationship between living and nonliving parts
Chapter 18 21 : Ecology Notes 1. Ecology: Scientific Study of Interaction between organisms and their environment (a branch of biological sciences); inter-relationship between living and nonliving parts
Ecological Levels of Organization
 This occurs when soil is permanently frozen These biomes have very little precipitation We live in this biome example This consists of all living and nonliving factors This consists of all populations
This occurs when soil is permanently frozen These biomes have very little precipitation We live in this biome example This consists of all living and nonliving factors This consists of all populations
Questions 3-6 refer to the diagram of surface currents in the oceans. 3. A current responsible for moving heat away from the equator.
 1. Long term differences in which two variables are the primary determinants of climate? (A) Temperature and cloud cover (B) Precipitation and temperature (C) Precipitation and soil type (D) Temperature
1. Long term differences in which two variables are the primary determinants of climate? (A) Temperature and cloud cover (B) Precipitation and temperature (C) Precipitation and soil type (D) Temperature
Studying organisms in their environment
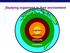 Studying organisms in their environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How do nutrients move in the ecosystem? How does
Studying organisms in their environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How do nutrients move in the ecosystem? How does
12. How could forest fire change populations in the ecosystem? Populations could be destroyed or have to relocate,
 Name: Ecology Review Sheet 15-16 Directions: This review should be completed by using your Interactive Notebook (IAN). This review is worth +5 points on your Ecology test, if it is completed and turned
Name: Ecology Review Sheet 15-16 Directions: This review should be completed by using your Interactive Notebook (IAN). This review is worth +5 points on your Ecology test, if it is completed and turned
Relationships in Ecosystems
 Unit 2 Relationships in Ecosystems WARM-UP Questions 1. What do you think the basic needs of life are? 2. What is the environment? 3. How do you define life what are 4 things all living organisms have
Unit 2 Relationships in Ecosystems WARM-UP Questions 1. What do you think the basic needs of life are? 2. What is the environment? 3. How do you define life what are 4 things all living organisms have
Chapter 54. Ecosystems. PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition. Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 54 Ecosystems PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community,
Chapter 54 Ecosystems PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community,
