PRESS RELEASE. LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM August 4, 2013
|
|
|
- Dwight Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PRESS RELEASE LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM August 4, 2013 The 2014 area of low oxygen, commonly known as the Dead Zone, measured 13,080 square kilometers (= 5,052 square miles) as of Aug 1, 2014 at the end of the 30 th such cruise. Based on the May nitrogen load from the Mississippi River, the area was predicted by Gene Turner, Louisiana State University, to be 14,785 square kilometers (5,708 square miles). The size is proportional to the loading of nitrogen in the Mississippi River (in May), and the 2014 size fits well into the model prediction range. The July distribution of hypoxic waters is most often a single continuous zone along the Louisiana and adjacent Texas shelf, but this year was located in two separate areas. The largest area was off central to southeastern Louisiana between the deltas of the Mississippi and Atchafalaya rivers, and the smaller was off southwestern Louisiana.
2 The average size for the last five years is 14,352 square kilometers (= 5,543 square miles) and is three times larger than the environmental target (5,000 square kilometers; 1,991 square miles) approved by a federal/state task force in 2001 and maintained by the same task force in These areas are sometimes called Dead Zones because of the absence of commercial quantities of shrimp and fish in the bottom layer. The number of Dead Zones throughout the world has been increasing in the last several decades and currently totals over 550. The Dead Zone off the Louisiana coast is the second largest human-caused coastal hypoxic area in the global ocean and stretches from the mouth of the Mississippi River into Texas waters and less often, but increasingly more frequent, east of the Mississippi River. There is a series of coupled cause-and-effect relationships linking the amount of water emptying into the Gulf of Mexico and water quality in the Mississippi River to hypoxia. The fresher, warmer water in the upper layer is separated from the saltier, colder water in the lower layer, resulting in a barrier to the normal diffusion of oxygen from the surface to the bottom. The excess nutrients delivered by the river stimulate high phytoplankton biomass offshore, which fuels the coastal food web but also contributes to high carbon loading to the bottom layer. The decomposition of this carbon by bacteria leads to the low oxygen that is not resupplied from the surface waters. The amount of nutrient loading from the river increased considerably in the 1960s as a result of more intense agricultural activity in the watershed. The primary driver of the increased nutrient loading is agricultural land use, which is strongly influenced by farm policy. The nitrogen load has stabilized somewhat in the last two decades, but is still increasing. Additionally, the nitrate portion of the total nitrogen load is increasing. This is important, because the nitrate-n
3 concentration and load is proportional to the phytoplankton produced and the subsequent bottomwater hypoxia. Reducing the size of the hypoxic area requires, therefore, changes in land use. Pilot projects and recent development have demonstrated that this can be done for crops with benefits for farm communities, soil health, erosion reduction, and without compromising yields or profit. The long-term pattern in the hypoxic zone size shows that there is a greater sensitivity to nutrient loading that is carried over from one year to the next. These legacy effects can be explained as the result of incremental changes in organic matter accumulated in the sediments one year, and metabolized in later years, by changes in the nitrogen form, or long-term climate change Conditions The Mississippi River discharge was near the long-term average since 1935 along with a slightly lower nitrate concentration in the river at Baton Rouge, Louisiana. Immediately preceding the survey cruise, he river discharge was slightly above average, and the nitrate concentration increased well above average and reached a near-record high Flow of the Mississippi River at Tarbert Landing since 1935 with discharge for 2014 in red, compared to long-term conditions ( The horizontal black bar indicates the timing of the survey cruise.
4 The concentration of nitrite+nitrate (NO 2+3 ) at Baton Rouge, Louisiana, from 1997 through mid-july The data for 2012, 2013and 2014 are shown separately. The late burst of nutrient loading and freshwater discharge generated lush conditions for phytoplankton growth off the Mississippi and Atchafalaya Rivers. The winds and currents were pushing the Atchafalaya River to the east of its delta, so that much of the biological productivity was located between the two river deltas. The area to the west of the Atchafalaya delta was probably residual from earlier in the month, and larger in size than mapping done by the National Marine Fisheries Service as part of their SEAMAP cruises on the Oregon II, and a cruise undertaken by Texas A&M University, both in June and early July. The lowered salinity and high chlorophyll biomass are obvious in the distribution maps below. These areas were also supersaturated with dissolved oxygen with saturations well above 100% and one reading at 245% dissolved oxygen saturation. Distribution of the surface salinity along the Louisiana shelf, July 27 August 1, 2014.
5 Distribution of the surface water chlorophyll a biomass along the Louisiana shelf, July 27 August 1, 2014 The physical and biological conditions for the three weeks before the survey cruise are depicted in these time series from station C6C in 20-m water depth offshore of Terrebonne Bay. The bottom water oxygen at C6C was mostly below 2 mg/l but there was much mixing with the water column above rather than a constant value close to 0 mg/l as in most years. The signature of higher than average river discharge beginning in mid-july is seen in a decline of salinity in surface waters. Along with the lower salinity, the nitrate load of the Mississippi River was also higher during that period, which led to increases in chlorophyll in the surface waters. Surface water production lags after the delivery of river water to the Gulf.
6 The high chlorophyll biomass generated high amounts of dissolved oxygen in the process of photosynthesis, and oxygensupersaturated waters were prevalent in the high chlorophyll areas (see shelfwide map of chlorophyll). Wind conditions will mix the water column and force the currents. The mid-part of July was quite windy with speeds of 10 to 20 knots. These values are relevant to the increases in bottomwater oxygen above 2 mg/l at station C6C. The higher wave height in mid-july may have also been responsible for some mixing. This also helps explain the well-mixed upper water column to the west of the Atchafalaya River. The direction from which the wind blows also determines the foot print of the bottom-water hypoxic water mass. The winds were sustained from the west for much of mid-july and part of survey cruise time. This helps explain the movement of the water masses to the east. Data source: N. Rabalais, LUMCON, LSU WAVCIS,
7 The multiple inputs of data available to explain the distribution and nature of the hypoxic water mass are compelling. Hypoxia is a recurring environmental problem in Louisiana (and sometimes Texas and Mississippi) offshore waters. Long-term research and observations are the best ways to test and calibrate ecosystem models, to recognize the dynamic nature of our changing environment(s), and to improve the basis for sound management decisions. The annual measurement of the hypoxic area also provides a critical scientific record of the trend of hypoxia in the Gulf, to determine whether efforts to reduce nutrient loading upstream in the Mississippi River Basin are yielding results. Maintaining such a valuable ecological dataset can be difficult. However, without these continued observations and related research and modeling, the ability to predict changes in the ecosystem resulting from nutrient mitigation efforts in the Mississippi River watershed will be stymied. 30th Anniversary Cruise This year s shelfwide hypoxia cruise is the 30 th since Such an enduring effort and wealth of data are a priceless rarity in ecosystem research and education. The efforts of many collaborators over the years have resulted in outstanding improvements in our knowledge that have been communicated through a relentless effort in books, journal articles, data archives, teaching, educational outreach, public talks, as well as congressional briefings and legislation. But much remains to be learned as management and policy changes occur, climate fluctuates, global warming increases and the unknowns are revealed. For further information, contact: Dr. Nancy Rabalais, nrabalais@lumcon.edu, wk, c, or Dr. Gene Turner, euturne@lsu.edu, wk Visit the Gulf Hypoxia web site at for maps, figures, additional graphics and more information concerning this summer s research cruise, highlights of the 30 th anniversary, and previous cruises. Funding sources for this year s cruise come from: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research U.S. EPA Gulf of Mexico Program National Science Foundation.
PRESS RELEASE. LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM August 2, 2017 SUMMARY
 PRESS RELEASE LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM August 2, 2017 SUMMARY The 2017 area of low oxygen, commonly known as the Dead Zone, measured 22,720 square kilometers (= 8,776 square miles) is the
PRESS RELEASE LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM August 2, 2017 SUMMARY The 2017 area of low oxygen, commonly known as the Dead Zone, measured 22,720 square kilometers (= 8,776 square miles) is the
PRESS RELEASE. LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM July 28, Abstract
 PRESS RELEASE LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM July 28, 2013 Abstract The 2013 area of low oxygen, commonly known as the Dead Zone, measured 15,120 square kilometers (= 5,800 square miles) in this
PRESS RELEASE LOUISIANA UNIVERSITIES MARINE CONSORTIUM July 28, 2013 Abstract The 2013 area of low oxygen, commonly known as the Dead Zone, measured 15,120 square kilometers (= 5,800 square miles) in this
2010 DEAD ZONE ONE OF THE LARGEST EVER. 1 August 2010, from Cocodrie, Louisiana
 2010 DEAD ZONE ONE OF THE LARGEST EVER 1 August 2010, from Cocodrie, Louisiana The area of hypoxia, or low oxygen, in the northern Gulf of Mexico west of the Mississippi River delta covered 20,000 square
2010 DEAD ZONE ONE OF THE LARGEST EVER 1 August 2010, from Cocodrie, Louisiana The area of hypoxia, or low oxygen, in the northern Gulf of Mexico west of the Mississippi River delta covered 20,000 square
Science of the Causes of Hypoxia Nancy Rabalais et al.
 Science of the Causes of Hypoxia Nancy Rabalais et al. In support of overview of diversions and hypoxia, and context for refining science needs; July 14, 2014 Scientific Curiosity Hypothesis Testing Management
Science of the Causes of Hypoxia Nancy Rabalais et al. In support of overview of diversions and hypoxia, and context for refining science needs; July 14, 2014 Scientific Curiosity Hypothesis Testing Management
Intersection of Policy & Trends: Climate, Hypoxia, and Louisiana s Coast
 Intersection of Policy & Trends: Climate, Hypoxia, and Louisiana s Coast Doug Daigle Louisiana Hypoxia Working Group Louisiana Water Conference March 27, 2018 Louisiana State University Mississippi
Intersection of Policy & Trends: Climate, Hypoxia, and Louisiana s Coast Doug Daigle Louisiana Hypoxia Working Group Louisiana Water Conference March 27, 2018 Louisiana State University Mississippi
Causes of Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia
 Causes of Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Nancy N. Rabalais 1 R. Eugene Turner 2 1 Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium 2 Louisiana State University Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research, Coastal Ocean
Causes of Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Nancy N. Rabalais 1 R. Eugene Turner 2 1 Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium 2 Louisiana State University Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research, Coastal Ocean
Ocean Water Buoyancy and Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico. Definitions. Hypoxia in the Headlines. Joe Smith. ExxonMobil Upstream Research Company
 Ocean Water Buoyancy and Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico Joe Smith ExxonMobil Upstream Research Company Joe Smith 2004 Hypoxia NOAA Coastal Data Development Center Definitions Hypoxia is a term meaning low
Ocean Water Buoyancy and Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico Joe Smith ExxonMobil Upstream Research Company Joe Smith 2004 Hypoxia NOAA Coastal Data Development Center Definitions Hypoxia is a term meaning low
Overview of Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Policy in Doug Daigle Lower Mississippi River Sub-basin Committee
 Overview of Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Policy in 2017 Doug Daigle Lower Mississippi River Sub-basin Committee Mississippi Water Resources Conference April 12, 2017 Jackson, MS Nutrient Yields from the Mississippi
Overview of Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Policy in 2017 Doug Daigle Lower Mississippi River Sub-basin Committee Mississippi Water Resources Conference April 12, 2017 Jackson, MS Nutrient Yields from the Mississippi
Nancy Rabalais Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium
 Eutrophication, Coastal Hypoxia, Carbon & Climate Nancy Rabalais Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium nrabalais@lumcon.edu http://www.gulfhypoxia.net Charismatically stressed and dead benthic fauna
Eutrophication, Coastal Hypoxia, Carbon & Climate Nancy Rabalais Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium nrabalais@lumcon.edu http://www.gulfhypoxia.net Charismatically stressed and dead benthic fauna
Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico: Benefits and Challenges of Using Multiple Models to Inform Management Decisions
 Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico: Benefits and Challenges of Using Multiple Models to Inform Management Decisions Multiple Models for Management (M3.2) in the Chesapeake Bay February 25, 2013 Annapolis MD
Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico: Benefits and Challenges of Using Multiple Models to Inform Management Decisions Multiple Models for Management (M3.2) in the Chesapeake Bay February 25, 2013 Annapolis MD
2010 Forecast of the Summer Hypoxic Zone Size, Northern Gulf of Mexico
 2010 Forecast of the Summer Hypoxic Zone Size, Northern Gulf of Mexico Abstract As the environmental catastrophe from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill unfolds along the northern Gulf of Mexico, the persistent
2010 Forecast of the Summer Hypoxic Zone Size, Northern Gulf of Mexico Abstract As the environmental catastrophe from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill unfolds along the northern Gulf of Mexico, the persistent
The Role of Midwestern Agriculture in Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia. Peter Scharf Nutrient Management Specialist MU Agronomy Extension
 The Role of Midwestern Agriculture in Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Peter Scharf Nutrient Management Specialist MU Agronomy Extension What is hypoxia? Hyp = low Oxia = oxygen Hypoxia = low oxygen defined as less
The Role of Midwestern Agriculture in Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Peter Scharf Nutrient Management Specialist MU Agronomy Extension What is hypoxia? Hyp = low Oxia = oxygen Hypoxia = low oxygen defined as less
NGOMEX: Effects of moderate hypoxia on benthic organisms in the Gulf of Mexico
 NGOMEX: Effects of moderate hypoxia on benthic organisms in the Gulf of Mexico Ed Buskey, Laura Ryckman, Wayne Gardner and Peter Thomas Marine Science Institute The University of Texas at Austin What is
NGOMEX: Effects of moderate hypoxia on benthic organisms in the Gulf of Mexico Ed Buskey, Laura Ryckman, Wayne Gardner and Peter Thomas Marine Science Institute The University of Texas at Austin What is
2014 Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Forecast Donald Scavia 1, Mary Anne Evans 2, Dan Obenour 1. June 17, 2014
 2014 Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Forecast Donald Scavia 1, Mary Anne Evans 2, Dan Obenour 1 1 University of Michgan 2 US Geological Survey Great Lakes Science Center June 17, 2014 The Gulf of Mexico annual
2014 Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Forecast Donald Scavia 1, Mary Anne Evans 2, Dan Obenour 1 1 University of Michgan 2 US Geological Survey Great Lakes Science Center June 17, 2014 The Gulf of Mexico annual
2013 Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Forecast Donald Scavia 1, Mary Anne Evans 2, Dan Obenour 1. June 17, 2013, observed area added January 2, 2014
 The 2013 Forecast 2013 Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Forecast Donald Scavia 1, Mary Anne Evans 2, Dan Obenour 1 1 University of Michgan 2 US Geological Survey Great Lakes Science Center June 17, 2013, observed
The 2013 Forecast 2013 Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Forecast Donald Scavia 1, Mary Anne Evans 2, Dan Obenour 1 1 University of Michgan 2 US Geological Survey Great Lakes Science Center June 17, 2013, observed
2016 Forecast: Summer Hypoxic Zone Size Northern Gulf of Mexico R. Eugene Turner 1 and Nancy N. Rabalais 2
 2016 Hypoxia Forecast 1 2016 Forecast: Summer Hypoxic Zone Size Northern Gulf of Mexico R. Eugene Turner 1 and Nancy N. Rabalais 2 Abstract Each year a hypoxic water mass with oxygen concentrations 2 mg
2016 Hypoxia Forecast 1 2016 Forecast: Summer Hypoxic Zone Size Northern Gulf of Mexico R. Eugene Turner 1 and Nancy N. Rabalais 2 Abstract Each year a hypoxic water mass with oxygen concentrations 2 mg
Global Warming leads to Underwater Deserts. SUHAS.E.P I Year.Dept of Mechanical engineering RVCE
 Global Warming leads to Underwater Deserts SUHAS.E.P I Year.Dept of Mechanical engineering RVCE Introduction Oxygen-poor waters occupy large volumes of the intermediate-depth eastern tropical oceans. Oxygen-poor
Global Warming leads to Underwater Deserts SUHAS.E.P I Year.Dept of Mechanical engineering RVCE Introduction Oxygen-poor waters occupy large volumes of the intermediate-depth eastern tropical oceans. Oxygen-poor
Nutrients, Algal Blooms and Red Tides in Hong Kong Waters. Paul J. Harrison and Jie XU
 Nutrients, Algal Blooms and Red Tides in Hong Kong Waters Paul J. Harrison and Jie XU Division of Environment, Hong Kong University of Science & Technology 1. Introduction The Pearl River is China's second
Nutrients, Algal Blooms and Red Tides in Hong Kong Waters Paul J. Harrison and Jie XU Division of Environment, Hong Kong University of Science & Technology 1. Introduction The Pearl River is China's second
The Dead Zone. Use the notes provided (attached to this sheet) to answer the following questions.
 The Dead Zone Use the notes provided (attached to this sheet) to answer the following questions. 1. Re-define Eutrophication: 2. What are the risks associated with an excess of Nitrogen? 3. What is a Dead
The Dead Zone Use the notes provided (attached to this sheet) to answer the following questions. 1. Re-define Eutrophication: 2. What are the risks associated with an excess of Nitrogen? 3. What is a Dead
Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Monitoring Implementation Plan. Alan Lewitus NOAA/NOS/NCCOS Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research
 Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Monitoring Implementation Plan Alan Lewitus NOAA/NOS/NCCOS Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research GCOOS Board of Directors Meeting 19 Aug 2008 Management Driver: Action Plans
Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Monitoring Implementation Plan Alan Lewitus NOAA/NOS/NCCOS Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research GCOOS Board of Directors Meeting 19 Aug 2008 Management Driver: Action Plans
Little Bay Water Quality Report Card Spring 2014
 Little Bay Water Quality Report Card Spring 2014 Little Bay is a small, semi-enclosed estuary located in the heart of Rockport, Texas. Estuaries, where freshwater from rivers and streams mixes with salt
Little Bay Water Quality Report Card Spring 2014 Little Bay is a small, semi-enclosed estuary located in the heart of Rockport, Texas. Estuaries, where freshwater from rivers and streams mixes with salt
GLOBAL WARMING LEADS TO UNDERWATER DESERTS" AND COASTAL DEAD ZONES
 GLOBAL WARMING LEADS TO UNDERWATER DESERTS" AND COASTAL DEAD ZONES Suhas E.P RVCE (VTU) No. 4/1 Golden Residency, Rmv 2 stage, Sanjaynagar, Bangalore SYNOPSIS Oxygen-poor waters occupy large volumes of
GLOBAL WARMING LEADS TO UNDERWATER DESERTS" AND COASTAL DEAD ZONES Suhas E.P RVCE (VTU) No. 4/1 Golden Residency, Rmv 2 stage, Sanjaynagar, Bangalore SYNOPSIS Oxygen-poor waters occupy large volumes of
HYPOXIA Definition: ~63 µm; 2 mg l -1 ; 1.4 ml l -1 ; 30 %
 HYPOXIA Definition: ~63 µm; 2 mg l -1 ; 1.4 ml l -1 ; 30 % Consequences of hypoxia Reduce habitat for living resources Change biogeochemical processes P released from sediments Denitrification reduced
HYPOXIA Definition: ~63 µm; 2 mg l -1 ; 1.4 ml l -1 ; 30 % Consequences of hypoxia Reduce habitat for living resources Change biogeochemical processes P released from sediments Denitrification reduced
Modeling Coastal Hypoxia: Lessons learned and perspectives for the future Part 1
 Modeling Coastal Hypoxia: Lessons learned and perspectives for the future Part 1 R. Eugene Turner 1 Dubravko Justi 1 and Nancy N. Rabalais 2 1 Louisiana State University, USA 2 Louisiana Universities Marine
Modeling Coastal Hypoxia: Lessons learned and perspectives for the future Part 1 R. Eugene Turner 1 Dubravko Justi 1 and Nancy N. Rabalais 2 1 Louisiana State University, USA 2 Louisiana Universities Marine
ONLINE SUPPORTING MATERIAL
 ONLINE SUPPORTING MATERIAL for the paper bg-22-78: Simulating the effects of phosphorus limitation in the Mississippi and Atchafalaya River plumes by A. Laurent, K. Fennel, J. Hu and R. Hetland. 5 Patterns
ONLINE SUPPORTING MATERIAL for the paper bg-22-78: Simulating the effects of phosphorus limitation in the Mississippi and Atchafalaya River plumes by A. Laurent, K. Fennel, J. Hu and R. Hetland. 5 Patterns
Mississippi River Water Quality: Policy, Landscapes and Hypoxia
 Mississippi River Water Quality: Policy, Landscapes and Hypoxia Dennis Keeney Distinguished Lecture R. Eugene Turner Dept. Oceanography and Coastal Studies Louisiana State University (euturne@lsu.edu)
Mississippi River Water Quality: Policy, Landscapes and Hypoxia Dennis Keeney Distinguished Lecture R. Eugene Turner Dept. Oceanography and Coastal Studies Louisiana State University (euturne@lsu.edu)
Water Quality Monitoring Stations
 Water Quality Monitoring Stations Eastern Basin Race Narrows Western Basin Central Basin The CT Department of Environmental Protection (CT DEP) conducts a water quality CT DEP monitoring program for the
Water Quality Monitoring Stations Eastern Basin Race Narrows Western Basin Central Basin The CT Department of Environmental Protection (CT DEP) conducts a water quality CT DEP monitoring program for the
2017 Hypoxic Zone Conditions: Monitoring and Modeling Results
 2017 Hypoxic Zone Conditions: Monitoring and Modeling Results Alan Lewitus, Trevor Meckley, and David Scheurer NOAA National Ocean Service National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science Hypoxia Task Force
2017 Hypoxic Zone Conditions: Monitoring and Modeling Results Alan Lewitus, Trevor Meckley, and David Scheurer NOAA National Ocean Service National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science Hypoxia Task Force
The Hypoxic Zone in the Gulf of Mexico
 The Hypoxic Zone in the Gulf of Mexico References Council Committee on Environmental and Natural Resources. 2003. An Assessment of Coastal Hypoxia and Eutrophication in U.S. Water. National Science and
The Hypoxic Zone in the Gulf of Mexico References Council Committee on Environmental and Natural Resources. 2003. An Assessment of Coastal Hypoxia and Eutrophication in U.S. Water. National Science and
Gulf Coast Ecosystem Restoration Task Force
 Gulf Coast Ecosystem Restoration Task Force The Gulf of Mexico Regional Ecosystem Restoration Strategy The Consortium for Ocean Leadership Public Policy Forum The Capitol March 7, 2012 1 An Unprecedented
Gulf Coast Ecosystem Restoration Task Force The Gulf of Mexico Regional Ecosystem Restoration Strategy The Consortium for Ocean Leadership Public Policy Forum The Capitol March 7, 2012 1 An Unprecedented
SECTION 1 FRESHWATER SYSTEMS UNIT 4: AQUATIC ECOLOGY
 SECTION 1 FRESHWATER SYSTEMS UNIT 4: AQUATIC ECOLOGY CENTRAL CASE STUDY: STARVING THE LOUISIANA COAST OF SEDIMENT LOUISIANA IS LOSING 25MI2 OF COASTAL WETLANDS ANNUALLY WETLANDS SUPPORT A DIVERSITY OF
SECTION 1 FRESHWATER SYSTEMS UNIT 4: AQUATIC ECOLOGY CENTRAL CASE STUDY: STARVING THE LOUISIANA COAST OF SEDIMENT LOUISIANA IS LOSING 25MI2 OF COASTAL WETLANDS ANNUALLY WETLANDS SUPPORT A DIVERSITY OF
Building a Cooperative Monitoring Program for Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia and Interrelated Issues
 Building a Cooperative Monitoring Program for Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia and Interrelated Issues A proceedings paper by the Steering Committee of the: 6 th Annual NOAA/NGI Hypoxia Research Coordination Workshop:
Building a Cooperative Monitoring Program for Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia and Interrelated Issues A proceedings paper by the Steering Committee of the: 6 th Annual NOAA/NGI Hypoxia Research Coordination Workshop:
THE CHALLENGE OF NUTRIENT CONTROL IN LARGE SCALE WATERSHEDS: EFFORTS IN THE U.S.
 THE CHALLENGE OF NUTRIENT CONTROL IN LARGE SCALE WATERSHEDS: EFFORTS IN THE U.S. NAE Convocation of the Professional Engineering Societies David Dzombak Carnegie Mellon University May 16, 2011 OUTLINE
THE CHALLENGE OF NUTRIENT CONTROL IN LARGE SCALE WATERSHEDS: EFFORTS IN THE U.S. NAE Convocation of the Professional Engineering Societies David Dzombak Carnegie Mellon University May 16, 2011 OUTLINE
Science to Improve Management of the Gulf of Mexico Hypoxic Zone: A Collaborative Approach
 Science to Improve Management of the Gulf of Mexico Hypoxic Zone: A Collaborative Approach Alan Lewitus, David Kidwell, and Libby Jewett Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research National Oceanic and
Science to Improve Management of the Gulf of Mexico Hypoxic Zone: A Collaborative Approach Alan Lewitus, David Kidwell, and Libby Jewett Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research National Oceanic and
Reducing Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico: Advice from Three Models
 Estuaries Vol. 27, No. 3, p. 419 425 June 2004 Reducing Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico: Advice from Three Models DONALD SCAVIA 1,, *, DUBRAVKO JUSTIĆ 2, and VICTOR J. BIERMAN, JR. 3 1 National Oceanic and
Estuaries Vol. 27, No. 3, p. 419 425 June 2004 Reducing Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico: Advice from Three Models DONALD SCAVIA 1,, *, DUBRAVKO JUSTIĆ 2, and VICTOR J. BIERMAN, JR. 3 1 National Oceanic and
Water Quality in Chandeleur Sound in 2008 and 2010
 Water Quality in Chandeleur Sound in 2008 and 2010 John Lopez, Ph.D., Andy Baker, M.Sc. Ezra Boyd, M.A. Lake Pontchartrain Basin Foundation October 10, 2010 Introduction Chandeleur Sound is the shallow-water
Water Quality in Chandeleur Sound in 2008 and 2010 John Lopez, Ph.D., Andy Baker, M.Sc. Ezra Boyd, M.A. Lake Pontchartrain Basin Foundation October 10, 2010 Introduction Chandeleur Sound is the shallow-water
Dead Zones for Dinner
 STUDENT READING DEAD ZONES AND EUTROPHICATION: HOW FOOD WE EAT IS CONNECTED TO WATER POLLUTION Introduction Imagine scuba diving in an aquatic environment where life abounds--a place whose biological diversity
STUDENT READING DEAD ZONES AND EUTROPHICATION: HOW FOOD WE EAT IS CONNECTED TO WATER POLLUTION Introduction Imagine scuba diving in an aquatic environment where life abounds--a place whose biological diversity
Concepts of Coastal Deltaic Floodplain as Newly Emergent Ecosystems
 Concepts of Coastal Deltaic Floodplain as Newly Emergent Ecosystems Robert R. Twilley Department of Oceanography and Coastal Sciences Director of Louisiana Sea Grant College Program LSU Ecosystems of Coastal
Concepts of Coastal Deltaic Floodplain as Newly Emergent Ecosystems Robert R. Twilley Department of Oceanography and Coastal Sciences Director of Louisiana Sea Grant College Program LSU Ecosystems of Coastal
Mississippi River/Gulf of Mexico Watershed Nutrient Task Force Timeline for Reassessment Revised 9/5/06. Revised 9/5/06. Symposia.
 Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico Extent of Hypoxia in the Gulf Reassessment of the Science & Revision of the Action Plan Frequency of Occurrence 1985-1999 Rabalais, et al. Summer Hypoxia Dissolved Oxygen
Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico Extent of Hypoxia in the Gulf Reassessment of the Science & Revision of the Action Plan Frequency of Occurrence 1985-1999 Rabalais, et al. Summer Hypoxia Dissolved Oxygen
HYPOXIA ACTION PLAN: WHAT CAN MIDWEST AGRICULTURE DO? Dennis McKenna Illinois Department of Agriculture
 HYPOXIA ACTION PLAN: WHAT CAN MIDWEST AGRICULTURE DO? Dennis McKenna Illinois Department of Agriculture The hypoxic zone is an area in the northern Gulf of Mexico where dissolved oxygen concentrations
HYPOXIA ACTION PLAN: WHAT CAN MIDWEST AGRICULTURE DO? Dennis McKenna Illinois Department of Agriculture The hypoxic zone is an area in the northern Gulf of Mexico where dissolved oxygen concentrations
Characterization of Hypoxia
 NOAA COASTAL OCEAN PROGRAM Decision Analysis Series No. 15 Science for Solutions Characterization of Hypoxia Topic 1 Report for the Integrated Assessment on Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico Nancy N. Rabalais,
NOAA COASTAL OCEAN PROGRAM Decision Analysis Series No. 15 Science for Solutions Characterization of Hypoxia Topic 1 Report for the Integrated Assessment on Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico Nancy N. Rabalais,
Corn Acreage, Fertilizer Use, & Spring Nutrient Discharge in the Mississippi River Basin: Relationships & Impact on Hypoxia
 Corn Acreage, Fertilizer Use, & Spring Nutrient Discharge in the Mississippi River Basin: Relationships & Impact on Hypoxia C.S. Snyder, PhD, CCA Nitrogen Program Director Northern Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia:
Corn Acreage, Fertilizer Use, & Spring Nutrient Discharge in the Mississippi River Basin: Relationships & Impact on Hypoxia C.S. Snyder, PhD, CCA Nitrogen Program Director Northern Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia:
SCIENCE GRADES 5-8 JANIECE MISTICH LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
 HYPOXIA AND THE DEAD ZONE IN THE GULF OF MEXICO: IS IT THE MISSISSIPPI RIVER S FAULT? TIME ALLOTMENT: Introductory Activity: 20 minutes Learning Activity: Two 50 minute periods Culminating Activity #1:
HYPOXIA AND THE DEAD ZONE IN THE GULF OF MEXICO: IS IT THE MISSISSIPPI RIVER S FAULT? TIME ALLOTMENT: Introductory Activity: 20 minutes Learning Activity: Two 50 minute periods Culminating Activity #1:
Characterization of Hypoxia
 NOAA COASTAL OCEAN PROGRAM Decision Analysis Series No. 15 Science for Solutions Characterization of Hypoxia Topic 1 Report for the Integrated Assessment on Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico Nancy N. Rabalais,
NOAA COASTAL OCEAN PROGRAM Decision Analysis Series No. 15 Science for Solutions Characterization of Hypoxia Topic 1 Report for the Integrated Assessment on Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico Nancy N. Rabalais,
Ecology Chapter 11: Marine
 Ecology Chapter 11: Marine 1 I. Oceans made up of all waters between continents The World Ocean because waters are interconnected can be thought of as one large biome with many different ecosystems and
Ecology Chapter 11: Marine 1 I. Oceans made up of all waters between continents The World Ocean because waters are interconnected can be thought of as one large biome with many different ecosystems and
Impacts of ocean acidification on marine life in Long Island Sound. Christopher J. Gobler, PhD
 Impacts of ocean acidification on marine life in Long Island Sound Christopher J. Gobler, PhD Ocean acidification Lower ph, acidification Calcifying shellfish potentially vulnerable to ocean acidification
Impacts of ocean acidification on marine life in Long Island Sound Christopher J. Gobler, PhD Ocean acidification Lower ph, acidification Calcifying shellfish potentially vulnerable to ocean acidification
Wetland Policy In Vermont and Louisiana. Litsey Corona and Emily Karwat
 Wetland Policy In Vermont and Louisiana Litsey Corona and Emily Karwat What is a wetland? An area inundated by surface or groundwater with a frequency sufficient to support plants and animals that depend
Wetland Policy In Vermont and Louisiana Litsey Corona and Emily Karwat What is a wetland? An area inundated by surface or groundwater with a frequency sufficient to support plants and animals that depend
Seagrass Health in Texas
 Seagrass Health in Texas A Comprehensive Monitoring Program Florida Museum of Natural History Harte Institute Florida Museum of Natural History Prepared by Susan E. Linn Marine Science Department University
Seagrass Health in Texas A Comprehensive Monitoring Program Florida Museum of Natural History Harte Institute Florida Museum of Natural History Prepared by Susan E. Linn Marine Science Department University
Columbia River Plume correlation with Oregon/Washington dead zones
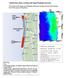 Columbia River Plume correlation with Oregon/Washington dead zones The location of the Oregon and Washington dead zones strongly correlate with Columbia River Plum summer flow patterns. OSU map OSU Map
Columbia River Plume correlation with Oregon/Washington dead zones The location of the Oregon and Washington dead zones strongly correlate with Columbia River Plum summer flow patterns. OSU map OSU Map
Time-series and Underway Assessments of Ocean Acidification and Carbon System Properties in Coastal Waters
 NGI Annual Meeting 2012 Time-series and Underway Assessments of Ocean Acidification and Carbon System Properties in Coastal Waters Wei-Jun Cai, Xinping Hu, Scott Noakes, Joe Salisbury, Doug Vandemark,
NGI Annual Meeting 2012 Time-series and Underway Assessments of Ocean Acidification and Carbon System Properties in Coastal Waters Wei-Jun Cai, Xinping Hu, Scott Noakes, Joe Salisbury, Doug Vandemark,
Coastal Restoration in Louisiana
 Coastal Restoration in Louisiana Presentation Topics Wetland Loss & the Importance of Coastal Louisiana The Coastal Restoration Effort The Louisiana Coastal Area Plan Development Components Status How
Coastal Restoration in Louisiana Presentation Topics Wetland Loss & the Importance of Coastal Louisiana The Coastal Restoration Effort The Louisiana Coastal Area Plan Development Components Status How
Hypoxia in the Northern Gulf of Mexico: Does the Science Support the Plan to Reduce, Mitigate, and Control Hypoxia?
 Estuaries and Coasts Vol. 30, No. 5, p. 753 772 October 2007 Hypoxia in the Northern Gulf of Mexico: Does the Science Support the Plan to Reduce, Mitigate, and Control Hypoxia? N. N. RABALAIS 1, *, R.
Estuaries and Coasts Vol. 30, No. 5, p. 753 772 October 2007 Hypoxia in the Northern Gulf of Mexico: Does the Science Support the Plan to Reduce, Mitigate, and Control Hypoxia? N. N. RABALAIS 1, *, R.
Dead-Zones and Coastal Eutrophication: Case- Study of Chesapeake Bay W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory Cambridge, MD
 Dead-Zones and Coastal Eutrophication: Case- Study of Chesapeake Bay W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory Cambridge, MD Presentation to COSEE Trends Orientation at UMCES HPL 4 August
Dead-Zones and Coastal Eutrophication: Case- Study of Chesapeake Bay W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory Cambridge, MD Presentation to COSEE Trends Orientation at UMCES HPL 4 August
of Hypoxia in the Northern Gulf of Mexico
 of Hypoxia in the Northern Gulf of Mexico hile information gaps still exist and several factors discussed below may contribute to hypoxia, the overwhelming scientific evidence indicates that excess nitrogen
of Hypoxia in the Northern Gulf of Mexico hile information gaps still exist and several factors discussed below may contribute to hypoxia, the overwhelming scientific evidence indicates that excess nitrogen
Water Quality Analysis of Lakewood Lakes
 Water Quality Analysis of Lakewood Lakes December 2016 Prepared by WEST Consultants, Inc. Bellevue, Washington With support from HDR, Inc., Olympia, Washington TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... V
Water Quality Analysis of Lakewood Lakes December 2016 Prepared by WEST Consultants, Inc. Bellevue, Washington With support from HDR, Inc., Olympia, Washington TABLE OF CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... V
Mississippi River/Gulf of Mexico Watershed Nutrient (Hypoxia) Task Force
 Mississippi River/Gulf of Mexico Watershed Nutrient (Hypoxia) Task Force History and New Direction: Tracking Progress Towards Our Goal NEMW Institute Congressional Briefing Katie Flahive, US EPA January
Mississippi River/Gulf of Mexico Watershed Nutrient (Hypoxia) Task Force History and New Direction: Tracking Progress Towards Our Goal NEMW Institute Congressional Briefing Katie Flahive, US EPA January
Water Monitoring in Spa Creek: A Summary
 Water Monitoring in Spa Creek: A Summary Written by: Alexis Jones & Blake Harden Edited by: Hannah Krauss Water monitoring is very important in order to determine the health of the Chesapeake Bay and its
Water Monitoring in Spa Creek: A Summary Written by: Alexis Jones & Blake Harden Edited by: Hannah Krauss Water monitoring is very important in order to determine the health of the Chesapeake Bay and its
The Complex Impacts of Rivers on Coastal and Continental Shelf Environments
 The Complex Impacts of Rivers on Coastal and Continental Shelf Environments L. Donelson Wright Professor Emeritus, Virginia Institute of Marine Science September 6, 2007 At the most basic level, river-ocean
The Complex Impacts of Rivers on Coastal and Continental Shelf Environments L. Donelson Wright Professor Emeritus, Virginia Institute of Marine Science September 6, 2007 At the most basic level, river-ocean
Younjoo Lee and Walter Boynton. Horn Point Laboratory and Chesapeake Biological Laboratory University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science
 Younjoo Lee and Walter Boynton Horn Point Laboratory and Chesapeake Biological Laboratory University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science 1 Data and Method Summer Hypoxia Dissolve Oxygen Patterns
Younjoo Lee and Walter Boynton Horn Point Laboratory and Chesapeake Biological Laboratory University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science 1 Data and Method Summer Hypoxia Dissolve Oxygen Patterns
Oxygen in the Columbia River Estuary: Distribution and Dynamics. Pat Welle
 1 Oxygen in the Columbia River Estuary: Distribution and Dynamics Observation Prediction Analysis Collaboration Pat Welle Additional Contributors: Antonio Baptista 1 Yvette Spitz 2 Jesse E. Lopez 1 G.
1 Oxygen in the Columbia River Estuary: Distribution and Dynamics Observation Prediction Analysis Collaboration Pat Welle Additional Contributors: Antonio Baptista 1 Yvette Spitz 2 Jesse E. Lopez 1 G.
NOAA NGOMEX Program Management Science Needs
 NOAA NGOMEX Program Management Science Needs Alan Lewitus and David Hilmer NOAA National Ocean Service National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science Hypoxia Effects on Fish and Fisheries Workshop/Gulf of
NOAA NGOMEX Program Management Science Needs Alan Lewitus and David Hilmer NOAA National Ocean Service National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science Hypoxia Effects on Fish and Fisheries Workshop/Gulf of
Freshwater ecosystems
 Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
NUTRIENT THE OHIO RIVER
 NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT FOR THE OHIO RIVER Why nutrient management is necessary Nutrients are necessary for a healthy aquatic community, but Excessive quantities of nutrients can have negative effects Negative
NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT FOR THE OHIO RIVER Why nutrient management is necessary Nutrients are necessary for a healthy aquatic community, but Excessive quantities of nutrients can have negative effects Negative
Effects of Winds on Hypoxia Formation in the Pearl River Estuarine Coastal Waters
 The 1th International Estuarine Biogeochemistry Symposium May 19-22, 28, Xiamen China Effects of Winds on Hypoxia Formation in the Pearl River Estuarine Coastal Waters Kedong YIN 1,2,3, Paul J. Harrison
The 1th International Estuarine Biogeochemistry Symposium May 19-22, 28, Xiamen China Effects of Winds on Hypoxia Formation in the Pearl River Estuarine Coastal Waters Kedong YIN 1,2,3, Paul J. Harrison
Predicting the response of Gulf of Mexico hypoxia to variations in Mississippi River nitrogen load
 May 2003 Volume 48 Number 3 Limnol. Oceanogr., 48(3), 2003, 951 956 2003, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Predicting the response of Gulf of Mexico hypoxia to variations in
May 2003 Volume 48 Number 3 Limnol. Oceanogr., 48(3), 2003, 951 956 2003, by the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography, Inc. Predicting the response of Gulf of Mexico hypoxia to variations in
A case study of nonpoint-source pollution and eutrophication
 Algal Blooms in the Gulf of Mexico: A case study of nonpoint-source pollution and eutrophication Introduction What cause the dead zone? The time course of eutrophication What can we do about it? What is
Algal Blooms in the Gulf of Mexico: A case study of nonpoint-source pollution and eutrophication Introduction What cause the dead zone? The time course of eutrophication What can we do about it? What is
Continued from Lecture 20a
 IV. Primary Production (p.p.) Continued from Lecture 20a C. Biomass & Productivity 1. Biomass = mass of organic matter (in grams) a. Gross primary production = total amount of organic material synthesized
IV. Primary Production (p.p.) Continued from Lecture 20a C. Biomass & Productivity 1. Biomass = mass of organic matter (in grams) a. Gross primary production = total amount of organic material synthesized
Sokvanny Pan ENVS 190A/Thesis
 Evaluating the Quantitative Amount of Nitrogen Release from Midwest s Corn Production and Identifying Management Strategies for the Gulf of Mexico s Dead Zone. Sokvanny Pan ENVS 190A/Thesis May 14, 2014
Evaluating the Quantitative Amount of Nitrogen Release from Midwest s Corn Production and Identifying Management Strategies for the Gulf of Mexico s Dead Zone. Sokvanny Pan ENVS 190A/Thesis May 14, 2014
Relationships of water age with chlorophyll a concentrations in the eutrophic Lower Alafia River estuary. Michael S. Flannery Xinjian Chen
 Relationships of water age with chlorophyll a concentrations in the eutrophic Lower Alafia River estuary Michael S. Flannery Xinjian Chen Chlorophyll a (µg/l) Kilometers from river mouth KM = 16.47-1.96(Ln
Relationships of water age with chlorophyll a concentrations in the eutrophic Lower Alafia River estuary Michael S. Flannery Xinjian Chen Chlorophyll a (µg/l) Kilometers from river mouth KM = 16.47-1.96(Ln
Today: Dinner Time! Yum Yum
 Today: Productivity in the marine world Food webs and trophic levels Chemotrophic communities Dinner Time! Yum Yum Oceans are brimming with life Not a lot of diversity But a great abundance of organisms
Today: Productivity in the marine world Food webs and trophic levels Chemotrophic communities Dinner Time! Yum Yum Oceans are brimming with life Not a lot of diversity But a great abundance of organisms
GULF OF MEXICO - SEGMENT 2501
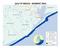 GULF OF MEXICO - SEGMENT 2501 GULF OF MEXICO - SEGMENT 2501 LAND COVER BACTERIA CHLOROPHYLL A Impairment Concern No Impairments or Concerns GULF OF MEXICO - SEGMENT 2501 OTHER IMPAIRMENTS Bays & Estuaries
GULF OF MEXICO - SEGMENT 2501 GULF OF MEXICO - SEGMENT 2501 LAND COVER BACTERIA CHLOROPHYLL A Impairment Concern No Impairments or Concerns GULF OF MEXICO - SEGMENT 2501 OTHER IMPAIRMENTS Bays & Estuaries
Nutrient Response to Sewage Abatement in Hong Kong
 Nutrient Response to Sewage Abatement in Hong Kong Prof. Paul J. Harrison Atmospheric, Marine & Coastal Environment Program Institute for the Environment HK University of Science & Technology Outline Background
Nutrient Response to Sewage Abatement in Hong Kong Prof. Paul J. Harrison Atmospheric, Marine & Coastal Environment Program Institute for the Environment HK University of Science & Technology Outline Background
Offshore petroleum platforms and dissolved oxygen in the northern Gulf of Mexico Key words Introduction
 Offshore petroleum platforms and dissolved oxygen in the northern Gulf of Mexico Derek G. Bolser Term Paper for Geographic Information Systems in Water Resources, Fall 2016 Key words: Gulf of Mexico, hypoxia,
Offshore petroleum platforms and dissolved oxygen in the northern Gulf of Mexico Derek G. Bolser Term Paper for Geographic Information Systems in Water Resources, Fall 2016 Key words: Gulf of Mexico, hypoxia,
Environmentalists Sue EPA Over Dead Zone in Gulf of Mexico
 SEARCH ENVIRONMENT Environmentalists Sue EPA Over Dead Zone in Gulf of Mexico The size of Connecticut and Rhode Island combined, the Gulf's dead zone is now the second largest in the world. By Dahr Jamail
SEARCH ENVIRONMENT Environmentalists Sue EPA Over Dead Zone in Gulf of Mexico The size of Connecticut and Rhode Island combined, the Gulf's dead zone is now the second largest in the world. By Dahr Jamail
Gas Guzzlers. Biological Pump
 Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
Implications of global climate change for estuarine & coastal ecosystems (Gulf of Mexico in particular)
 - The cumulative effects of global change, including climate change, increased population, & more intense industrialization & agribusiness, will likely continue & intensify the course of eutrophication
- The cumulative effects of global change, including climate change, increased population, & more intense industrialization & agribusiness, will likely continue & intensify the course of eutrophication
Advancing Ecological Modeling for Diversions and Hypoxia in the Northern Gulf of Mexico
 The 5th Annual NOAA/NGI Gulf Hypoxia Research Coordination Workshop: Advancing Ecological Modeling for Diversions and Hypoxia in the Northern Gulf of Mexico 14-16 July 2014 Mississippi State University
The 5th Annual NOAA/NGI Gulf Hypoxia Research Coordination Workshop: Advancing Ecological Modeling for Diversions and Hypoxia in the Northern Gulf of Mexico 14-16 July 2014 Mississippi State University
Protecting Utah s Water Resources. Nutrient Issues
 Protecting Utah s Water Resources Nutrient Issues Nutrient Issues Questions What are they? Why are they important? Nationally Locally What are the impact on my community Costs Timing What are Nutrients?
Protecting Utah s Water Resources Nutrient Issues Nutrient Issues Questions What are they? Why are they important? Nationally Locally What are the impact on my community Costs Timing What are Nutrients?
Nutrient Sources, Fate, Transport, and Effects Study of Galveston Bay, Texas Rachel Windham,
 Nutrient Sources, Fate, Transport, and Effects Study of Galveston Bay, Texas Rachel Windham, Department of Marine Biology Texas A&M University at Galveston 2 Acknowledgements: Dr. Antonietta Quigg Members
Nutrient Sources, Fate, Transport, and Effects Study of Galveston Bay, Texas Rachel Windham, Department of Marine Biology Texas A&M University at Galveston 2 Acknowledgements: Dr. Antonietta Quigg Members
Water Quality. Report for State of the Bay Casco Bay Water Quality Report for State of the Bay 2010 Friends of Casco Bay, 2009
 Water Quality Report for State of the Bay 2010 Casco Bay Water Quality Report for State of the Bay 2010 Friends of Casco Bay, 2009 Muskie School of Public Service University of Southern Maine www.cascobayestuary.org
Water Quality Report for State of the Bay 2010 Casco Bay Water Quality Report for State of the Bay 2010 Friends of Casco Bay, 2009 Muskie School of Public Service University of Southern Maine www.cascobayestuary.org
Student Data Sheet 1
 Student Data Sheet 1 Name Date Latitude (e.g. 75 o N) Longitude (e.g.18 o W) Recent weather conditions: Current weather (circle one) Clear Partly Cloudy Fog Overcast Rain Snow Air Temperature C or F Wind
Student Data Sheet 1 Name Date Latitude (e.g. 75 o N) Longitude (e.g.18 o W) Recent weather conditions: Current weather (circle one) Clear Partly Cloudy Fog Overcast Rain Snow Air Temperature C or F Wind
The Impact of Large Storm Events on Nutrient Loadings in Texas Rivers
 The Impact of Large Storm Events on Nutrient Loadings in Texas Rivers Paul Bireta Fall 2012 Nutrients can be damaging to natural water bodies, harming both human and ecological health. One of the primary
The Impact of Large Storm Events on Nutrient Loadings in Texas Rivers Paul Bireta Fall 2012 Nutrients can be damaging to natural water bodies, harming both human and ecological health. One of the primary
Rubisco is about 20% of the plant protein and is argued to be the most abundant protein on Earth (Sharkey, 1985). This Explain why N compounds
 1 Rubisco is about 20% of the plant protein and is argued to be the most abundant protein on Earth (Sharkey, 1985). This Explain why N compounds released when organic matter is combusted. 2 TRY database,
1 Rubisco is about 20% of the plant protein and is argued to be the most abundant protein on Earth (Sharkey, 1985). This Explain why N compounds released when organic matter is combusted. 2 TRY database,
Ch. 7 Aquatic Ecology
 Ch. 7 Aquatic Ecology 1.Coral Reefs: the aquatic equal to the tropical rain forests 2.The two major aquatic life zones A. saltwater or marine (estuaries, coastlines, coral reefs, coastal marshes, mangrove
Ch. 7 Aquatic Ecology 1.Coral Reefs: the aquatic equal to the tropical rain forests 2.The two major aquatic life zones A. saltwater or marine (estuaries, coastlines, coral reefs, coastal marshes, mangrove
GULF COAST LONG-TERM RESTORATION
 GULF COAST LONG-TERM RESTORATION Dr. Alyssa Dausman, USGS INTECOL 9: Large Scale Ecosystems June 6, 2012 Dawn Lavoie USGS & Shelby Walker NOAA FEDERAL Bureau of Ocean Energy Management National Aeronautics
GULF COAST LONG-TERM RESTORATION Dr. Alyssa Dausman, USGS INTECOL 9: Large Scale Ecosystems June 6, 2012 Dawn Lavoie USGS & Shelby Walker NOAA FEDERAL Bureau of Ocean Energy Management National Aeronautics
SYNERGISTIC PROJECT Using Linked Models to Predict the Impacts of Hypoxia on Gulf Coast Fisheries under Scenarios of Watershed and River Management
 SYNERGISTIC PROJECT Using Linked Models to Predict the Impacts of Hypoxia on Gulf Coast Fisheries under Scenarios of Watershed and River Management Kenneth Rose 1 LSU Workshop: Hypoxia effects on fish
SYNERGISTIC PROJECT Using Linked Models to Predict the Impacts of Hypoxia on Gulf Coast Fisheries under Scenarios of Watershed and River Management Kenneth Rose 1 LSU Workshop: Hypoxia effects on fish
Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary. Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP)
 Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP) Introduction: A key theme of the ongoing DCERP program is monitoring
Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP) Introduction: A key theme of the ongoing DCERP program is monitoring
ONSHORE HYDROGRAPHY OF TIMBALIER BAY, LOUISIANA
 ONSHORE HYDROGRAPHY OF TIMBALIER BAY, LOUISIANA by Keith C. Price ABSTRACT Synoptic measurements of salinity, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and transparency were made in Timbalier Bay, Louisiana,over
ONSHORE HYDROGRAPHY OF TIMBALIER BAY, LOUISIANA by Keith C. Price ABSTRACT Synoptic measurements of salinity, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and transparency were made in Timbalier Bay, Louisiana,over
COUPLED PHYSICAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL MODELS
 COUPLED PHYSICAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL MODELS Upwelling CONCEPTUAL MODEL OF EUTROPHICATION IN THE COASTAL OCEAN Nutrient/ Acid Deposition Local Emissions HABs! Phytoplankton Blooms Senesce and Settling Respiration:
COUPLED PHYSICAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL MODELS Upwelling CONCEPTUAL MODEL OF EUTROPHICATION IN THE COASTAL OCEAN Nutrient/ Acid Deposition Local Emissions HABs! Phytoplankton Blooms Senesce and Settling Respiration:
Today: Dinner Time! Yum Yum. Primary Producers = base of food web
 Today: Productivity in the marine world Food webs and trophic levels Chemotrophic communities Dinner Time! Yum Yum Oceans are brimming with life Not a lot of diversity But a great abundance of organisms
Today: Productivity in the marine world Food webs and trophic levels Chemotrophic communities Dinner Time! Yum Yum Oceans are brimming with life Not a lot of diversity But a great abundance of organisms
Hypoxia in the Gulf. Executive Summary
 Hypoxia in the Gulf Executive Summary Excess nutrients in freshwater from the Mississippi and Atchafalaya River Basin have been suggested as the primary cause of annual summer hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico
Hypoxia in the Gulf Executive Summary Excess nutrients in freshwater from the Mississippi and Atchafalaya River Basin have been suggested as the primary cause of annual summer hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico
STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems
 Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf
 Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf S.W.A. Naqvi, Hema Naik, A.K. Pratihary, M. Gauns, Witty D Souza, Gayatree Narvenkar, D.A. Jayakumar, M.S. Shailaja & P.V. Narvekar National Institute
Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf S.W.A. Naqvi, Hema Naik, A.K. Pratihary, M. Gauns, Witty D Souza, Gayatree Narvenkar, D.A. Jayakumar, M.S. Shailaja & P.V. Narvekar National Institute
Note: Slide numbers refer to the PowerPoint presentation which accompanies the lecture.
 LECTURE 13 - HYPOXIA Note: Slide numbers refer to the PowerPoint presentation which accompanies the lecture. Hypoxia, slide 1 here One of the more important chemicals parameters in natural waters is the
LECTURE 13 - HYPOXIA Note: Slide numbers refer to the PowerPoint presentation which accompanies the lecture. Hypoxia, slide 1 here One of the more important chemicals parameters in natural waters is the
eutrophication level indicators in Romanian seawater
 Journal of Environmental Protection and Ecology 10, No 3, 701 731 (2009) Recent data concerning evolution of the eutrophication level indicators in Romanian seawater A. Cociasu a, L. Varga b, L. Lazar
Journal of Environmental Protection and Ecology 10, No 3, 701 731 (2009) Recent data concerning evolution of the eutrophication level indicators in Romanian seawater A. Cociasu a, L. Varga b, L. Lazar
CBF Water Quality Interactive Map
 CBF Water Quality Interactive Map Student and adult groups that take part Often, they measure the water chemistry to evaluate the be doing it when you come out with us! By compiling these points on a map
CBF Water Quality Interactive Map Student and adult groups that take part Often, they measure the water chemistry to evaluate the be doing it when you come out with us! By compiling these points on a map
 Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition: An increasingly Important Source of new Nitrogen Supporting Coastal Eutrophication H Paerl 1, D. Whitall 2 and R. Dennis 3 1 UNC-CH CH Institute of Marine Sciences, Morehead
Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition: An increasingly Important Source of new Nitrogen Supporting Coastal Eutrophication H Paerl 1, D. Whitall 2 and R. Dennis 3 1 UNC-CH CH Institute of Marine Sciences, Morehead
RIVER SEDIMENTS AND COASTAL FISH PRODUCTION: WHAT ABOUT THE MEKONG?
 people Ÿ science Ÿ environment Ÿ partners! RIVER SEDIMENTS AND COASTAL FISH PRODUCTION: WHAT ABOUT THE MEKONG? Eric BARAN Eric GUERIN Project A Climate Resilient Mekong: Maintaining the Flows that Nourish
people Ÿ science Ÿ environment Ÿ partners! RIVER SEDIMENTS AND COASTAL FISH PRODUCTION: WHAT ABOUT THE MEKONG? Eric BARAN Eric GUERIN Project A Climate Resilient Mekong: Maintaining the Flows that Nourish
