Nutrients in Chesapeake Bay: The Nutrient Diet is Working!
|
|
|
- Sherilyn Chastity Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nutrients in Chesapeake Bay: The Nutrient Diet is Working! SERC 2017 Bay Optimism Lecture Series June, :1 Large Drainage Basin Only 0.2 acres per person for dilution of wastes Walt Boynton and Many Colleagues Center for Environmental Science, Univ MD
2 Key Bay Features Watershed huge compared to estuary (14:1) Bay is closely connected to the land (11,000 miles shoreline; 9 major rivers) Channel is stratified, isolating deep water Very shallow (mean depth = 27 feet) Most of its surface area is in tributaries & sounds Slow flushing (4-6 months) 0.15 acres of water per person.very dense from this perspective!
3 A Famous Chesapeake Bay Painting Clearly, Bay fish important Multiple fishing techniques and signs of large fish Emphasis on shallow waters Clear water and seagrasses From T. De Bry in Hariot 1588
4 A John Smith Diet Traded with natives for corn, venison, fish, oysters, nuts, beans, pumpkins traded swords for turkeys (a 1 for 1 deal probably not a good deal for the English) Tobacco it purges the superfluous phlegm and other gross humours and openeth all the pores and passages of the body from Harriot who died of a nasal tumor in 1621 the tobacco wars started early Jamestowners preferred a seaman s diet of pork, beef, fish, wheat and barley (even with the everpresent worms) Sturgeon (dried and pounded) The Starving Time (winter ) cats, dogs, horses and people this was a very tough life indeed! Hoobler 2006
5 And this had an important buffering effect between the land and the Bay All agree that the watershed was largely mature forests of one sort or another and wetter than it is now Photo: Virginia State Parks
6 Paleoecologists tell us Beavers were a key species regulating water and nutrients Credit: Bert Drake Pre-colonial landscape had MANY WETLANDS BEAVERS were important for cleaning the water One to 5 million of these busy rodents in pre-colonial watershed (~1940 human population) Restore the pre-colonial wet and marshy condition mimic the beavers with more conventional approaches From Brush 2008
7 Storm Water Management: Wet Pond Example Pollutant Removal Efficiencies: TSS: 46% TP: 46% TN: 32% There have been many of these constructed in the watershed We need to keep improving the efficiency of these beaverlike systems Credit: Michael J./Flickr
8 Patuxent River Estuary Circa 1832 Water Quality and Habitat Conditions can be much improved not to the 1832 condition and that may not be the optimal status So transparent are its waters that far out from shore you may see, in the openings of the seaweed forest, on its bottom the flashing sides of the finny tribe as they glide over the pearly sands. The Old Plantation by Hungerford (1859)
9 Costanza et al. 2000
10 Historical and Current Nitrogen Loads to the Patuxent River Estuary 8000 Nitrogen Loads, Kg N/day Before John Smith arrived Before intensive development Current Condition Time Periods Boynton et al., 1995
11 Credit: Lyntha Scott Eiler/US National Archives Credit: U.S. Department of Energy Credit: Chuck Gallegos/SERC, aerial support from LightHawk Credit: Chuck Gallegos/SERC, aerial support from LightHawk Agriculture Major Nutrient Sources Urban/Suburban Run-off Power generation, auto exhaust Point Sources (factories, sewage treatment plants) Summary All have increased during last 50 yrs Importance varies widely with location Most reductions with point sources
12 Figure by Walter Boynton
13 Figure by Walter Boynton
14 Nutrient Enrichment Effects: Estuarine Ecosystems Source: Global Warming and the Free State: Comprehensive Assessment of Climate Change Impacts in Maryland (p. 60)
15 Declining Nitrate (NO 3 ) and Ammonia (NH 3 ) deposition concentrations across the Bay watershed
16 Trends in Nutrient Loads from Long-Term Monitoring Sites in Chesapeake Bay 9 major rivers monitored for inputs to the Bay About 82% of entire watershed monitored by these sites Monitoring record includes last 3 decades more in some cases US-EPA Chesapeake Bay Program
17 Dissolved Phosphorus Dissolved Nitrogen Zhang et al., JAWRA, 2015
18 Testa et al. unpubl.
19 US-EPA Chesapeake Bay Program Boynton, et al Point Source N and P Loads are Decreasing Blue Plains TN Load: Huge decline in both TN and TP loads to the Potomac River from Blue Plains Back River (Baltimore, MD) TN loads reduced by ~ 50% Back River TN Load: In January, 2017 Back River loads will again be reduced by a further 50% Most P loads were reduced before N loads were reduced
20 Restoration of Mattawoman Creek: Potomac River estuary tributary strongly impacted by nutrients from 1970 mid-1990s large and persistent algal blooms, sea grasses rare Nutrient diet stimulated restoration Photo from Elena Gilroy
21 ALGAL BIOMASS DECREASED WITH SUBSTANTIAL LAG TIME Drought Year More Algae No clear response for about 4 years followed by sharp decline in algae 10 0 After 2005 low levels of algae became normal Major Nutrient load reduction completed Boynton, et al. 2012
22 Clearer Water WATER CLARITY INCREASED ALSO WITH A LAG TIME Drought Year More Algae No clear increase for about 8 years followed by sharp increase in clarity Water clarity and algae highly correlated in shallow Chesapeake Bay systems Major Nutrient WWTP load load reduction reduction completed Boynton, et al. 2012
23 More SAV Clearer Water SAV INCREASED SHORTER LAG WITH THRESHOLD RESPONSE Drought Year More Algae Very low levels of SAV were present prior to nutrient load reductions ha SAV Major Nutrient load reduction completed Major expansion of SAV in 2002, a severe drought year SAV relatively stable after 2002; lag in SAV relatively short Boynton, et al. 2012
24 Water Clarity: Hints of clearer water Secchi Depth measure the light available for SAV but it is also an index of nutrient and sediment loading problems Testa et al. unpubl.
25 SAV off Poplar Island in late summer 2015 Photo: Peter McGowan/U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service
26 Area (hectares) Baywide SAV Pattern: Slow increases with strong inter-annual variability. Note strong increases during drought and posttropical storm Lee (2011). Drought Post-Lee US-EPA Chesapeake Bay Program
27 Area (hectares) The WHERE of SAV Recovery or not Note likely response to tropical storm Lee in freshwater and Oligohaline (low salinity) areas of the Bay Negative trend in Polyhaline (salty) portions of Bay likely related to temperature stress Orth et al., in review
28 Susquehanna Flats SAV at the Head of the Bay An unexpected piece of very good news A clear example of why long-term monitoring is so valuable for both trends and explanations This example also reminds us that once these habitats start to get better strong positive feedbacks can accelerate the restoration process Adapted from Gurbisz and Kemp 2014
29 Now this is a SAV bed! Huge expanse ~ 20 square miles (13,000 acres) Clear water Resilient to major storms; recovery from major storm = several years (not decades!) C. Gurbisz, UMCES
30 SAV in the Upper Chesapeake Bay: Drought response and storm resilience LOW FLOW LOW FLOW LOW FLOW LOW FLOW HIGH FLOW HIGH FLOW Figure from Cassie Gubisz Data: Orth/VIMS
31 Late Summer Anoxia Declining in Mainstem Bay Anoxia ( no oxygen ) occurs in the deepest Bay water No multicellular organisms in CB can tolerate these conditions Size of anoxic zone varies from year to year Source: eake_bay_dissolved_oxygen_forecast/
32 MD Bay Anoxia: September Data (0-0.2 mg/l) 1600 Anoxic Volume, 10 6 m Average Maryland late September anoxic 0 Year Source: Maryland Department of Natural Resources
33 Late Summer Anoxia Declining in Mainstem Bay Long-term decline in late summer anoxia ( no oxygen ) This decline larger than expected from modest declines in load Explanation likely related to nutrient diet kickin in Testa et al. in review
34 Ecosystem Degradation Tipping Points: Points where a system shifts from one stable state to another Some ecosystems recover from eutrophication in the same way as they degraded Delaware River, NY Harbor Other respond positively to load reductions, but the response only occurs upon reaching a threshold reduction Recovery may also follow a similar trajectory as degradation, but only after a delay a lag time Mattawoman Creek, Susquehanna Flats, Gunston Cove
35 Tipping Points: Oxygen Interactions with Nitrogen Lower oxygen (hypoxic) can cause higher ammonium (NH 4 ) Anammox Denitrification Algae Algae X X H 2 S Nitrification Source: Testa, et al. in review
36 Long-Term Bay Trends for O 2, NH 4, & NO 3 in Late Summer Significant trends over 3 decades Late-summer mean values Increasing dissolved oxygen Decreasing ammonium Increasing nitrate Hypoxic region of Bay is becoming less hypoxic an important sign of recovery Testa et al. in prep
37 Changing Land Uses in Maryland More hardened surfaces = more runoff Population increases continue to put pressure on natural buffers Over 100 years of forest re-growth reversed in late 1980s
38 So, that s a very brief story of the watershed and estuary There have been a heap of changes in the Bay since John Smith arrived in 1608 The Bay suffers from too much of a good thing too much nutrient and sediment input among other stressors This Bay can be fixed by doing enough of the right things reduce nutrient and sediment inputs, and prudently manage habitats and fisheries Evidence says we are making real progress we need to finish the job!
Thresholds in Recovery of Eutrophic Bay Sub-Systems: Five Case-Studies
 Thresholds in Recovery of Eutrophic Bay Sub-Systems: Five Case-Studies W. Michael Kemp, Walter Boynton, and Denise Breitburg University of Maryland CES & SERC (Collaborators: J. Testa, Y. Lee, J. Hagy,
Thresholds in Recovery of Eutrophic Bay Sub-Systems: Five Case-Studies W. Michael Kemp, Walter Boynton, and Denise Breitburg University of Maryland CES & SERC (Collaborators: J. Testa, Y. Lee, J. Hagy,
Dead-Zones and Coastal Eutrophication: Case- Study of Chesapeake Bay W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory Cambridge, MD
 Dead-Zones and Coastal Eutrophication: Case- Study of Chesapeake Bay W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory Cambridge, MD Presentation to COSEE Trends Orientation at UMCES HPL 4 August
Dead-Zones and Coastal Eutrophication: Case- Study of Chesapeake Bay W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory Cambridge, MD Presentation to COSEE Trends Orientation at UMCES HPL 4 August
Eutrophication. A Synthesis for Scientific Understanding and Management Applications. W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory
 Eutrophication in Chesapeake Bay: A Synthesis for Scientific Understanding and Management Applications W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory Cambridge, MD Work supported by UMCES,
Eutrophication in Chesapeake Bay: A Synthesis for Scientific Understanding and Management Applications W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory Cambridge, MD Work supported by UMCES,
Chesapeake Bay Nitrogen Assessments
 Chesapeake Bay Nitrogen Assessments May 20, 2010 Workshop on Nitrogen Assessment Science in the USA Thomas E. Jordan Chesapeake Bay Watershed Area=167,000 km 2 Spans 6 states + DC 6 physiographic provinces
Chesapeake Bay Nitrogen Assessments May 20, 2010 Workshop on Nitrogen Assessment Science in the USA Thomas E. Jordan Chesapeake Bay Watershed Area=167,000 km 2 Spans 6 states + DC 6 physiographic provinces
Chesapeake Bay Water Quality Restoration:
 Chesapeake Bay Water Quality Restoration: The Transition to a Regulatory Approach Building on Decades of Cooperative Partnership Rich Batiuk Assoc. Director for Science Chesapeake Bay Program Office U.S.
Chesapeake Bay Water Quality Restoration: The Transition to a Regulatory Approach Building on Decades of Cooperative Partnership Rich Batiuk Assoc. Director for Science Chesapeake Bay Program Office U.S.
STATE OF THE BAY IN 2012
 9 10 11 STATE OF THE BAY IN 2012 Nitrogen &!Phosphorus Bay-wide nitrogen loads were similar to 2010, but phosphorus loads decreased. These loads are highly elated to river flows and stormwater runoff that
9 10 11 STATE OF THE BAY IN 2012 Nitrogen &!Phosphorus Bay-wide nitrogen loads were similar to 2010, but phosphorus loads decreased. These loads are highly elated to river flows and stormwater runoff that
Restoring the Water-Quality Conditions in the Chesapeake Bay: What is working and what still needs to be done
 Restoring the Water-Quality Conditions in the Chesapeake Bay: What is working and what still needs to be done Scott Phillips, USGS Water-Quality Goal Team January 12, 2015 Many Contributors Authors: Christina
Restoring the Water-Quality Conditions in the Chesapeake Bay: What is working and what still needs to be done Scott Phillips, USGS Water-Quality Goal Team January 12, 2015 Many Contributors Authors: Christina
Chapter Seven: Factors Affecting the Impact of Nutrient Enrichment on the Lower Estuary
 Chapter Seven: Factors Affecting the Impact of Nutrient Enrichment on the Lower Estuary As presented in Chapter Six, the water quality data for the upper stations of the tidal freshwater Potomac Estuary
Chapter Seven: Factors Affecting the Impact of Nutrient Enrichment on the Lower Estuary As presented in Chapter Six, the water quality data for the upper stations of the tidal freshwater Potomac Estuary
Integrating Air and Water Environmental Management in the Chesapeake Bay Program: An Encouraging Tale
 Integrating Air and Water Environmental Management in the Chesapeake Bay Program: An Encouraging Tale SERC Lecture Series August 15, 2017 Lewis C. Linker 1, Gary W. Shenk 1, Jesse Bash, & Ping Wang 3 1U.S.
Integrating Air and Water Environmental Management in the Chesapeake Bay Program: An Encouraging Tale SERC Lecture Series August 15, 2017 Lewis C. Linker 1, Gary W. Shenk 1, Jesse Bash, & Ping Wang 3 1U.S.
Fact Sheet. Pennsylvania s Chesapeake Bay Tributary Strategy Goals for Nutrient and Sediment Reduction and Habitat Restoration
 Fact Sheet Commonwealth of Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection Pennsylvania s Chesapeake Bay Tributary Strategy Goals for Nutrient and Sediment Reduction and Habitat Restoration Why were
Fact Sheet Commonwealth of Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection Pennsylvania s Chesapeake Bay Tributary Strategy Goals for Nutrient and Sediment Reduction and Habitat Restoration Why were
Incorporating monitoring, modeling and trends analyses into management decisions: a Choptank River example
 Incorporating monitoring, modeling and trends analyses into management decisions: a Choptank River example Emily Trentacoste, PhD EPA Chesapeake Bay Program WQGIT Meeting 7/10/2017 DRAFT. DO NOT CITE OR
Incorporating monitoring, modeling and trends analyses into management decisions: a Choptank River example Emily Trentacoste, PhD EPA Chesapeake Bay Program WQGIT Meeting 7/10/2017 DRAFT. DO NOT CITE OR
The Chesapeake Bay Blueprint:
 PHASE II The Chesapeake Bay Blueprint: THE BEST HOPE FOR RESTORING CLEAN WATER THIS NATION HAS EVER SEEN Peter McGowan/U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Strategic Plan 2016-2020 The Chesapeake Bay Foundation
PHASE II The Chesapeake Bay Blueprint: THE BEST HOPE FOR RESTORING CLEAN WATER THIS NATION HAS EVER SEEN Peter McGowan/U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Strategic Plan 2016-2020 The Chesapeake Bay Foundation
Reducing Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sediment Pollution Progress Update. Jeff Corbin, Senior Advisor to the EPA Administrator
 Reducing Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sediment Pollution Progress Update Jeff Corbin, Senior Advisor to the EPA Administrator Reducing Pollution Briefing Package Overview 1. 29-11 Milestones 2. 211 Progress
Reducing Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sediment Pollution Progress Update Jeff Corbin, Senior Advisor to the EPA Administrator Reducing Pollution Briefing Package Overview 1. 29-11 Milestones 2. 211 Progress
Qian Zhang (UMCES / CBPO) Joel Blomquist (USGS / ITAT)
 CBP STAC Water Clarity Workshop Solomons, MD, 02/06/2017 Long-term Riverine Inputs from Major Tributaries to Chesapeake Bay Relevant to Water Clarity Qian Zhang (UMCES / CBPO) Joel Blomquist (USGS / ITAT)
CBP STAC Water Clarity Workshop Solomons, MD, 02/06/2017 Long-term Riverine Inputs from Major Tributaries to Chesapeake Bay Relevant to Water Clarity Qian Zhang (UMCES / CBPO) Joel Blomquist (USGS / ITAT)
Lake & Watershed Resource Management Associates P O Box 65; Turner, ME
 Lake & Watershed Resource Management Associates P O Box 65; Turner, ME 207-336-2980 LWRMA@megalink.net 2008 Baseline Water Quality Monitoring and Assessment of Pemaquid and Biscay Ponds At the request
Lake & Watershed Resource Management Associates P O Box 65; Turner, ME 207-336-2980 LWRMA@megalink.net 2008 Baseline Water Quality Monitoring and Assessment of Pemaquid and Biscay Ponds At the request
Recap of Day 1 and Linking Biogeochemical Trends Across Spatio-Temporal Scales in Estuarine Environments
 Recap of Day 1 and Linking Biogeochemical Trends Across Spatio-Temporal Scales in Estuarine Environments Jeremy Testa Walter Boynton Lora Harris Casey Hodgkins Ben Henry Key Questions/Objectives Does management
Recap of Day 1 and Linking Biogeochemical Trends Across Spatio-Temporal Scales in Estuarine Environments Jeremy Testa Walter Boynton Lora Harris Casey Hodgkins Ben Henry Key Questions/Objectives Does management
Eutrophication: Tracing Nutrient Pollution Back to Penns Creek
 Eutrophication: Tracing Nutrient Pollution Back to Penns Creek Nutrients are substances that life depends on for growth and reproduction. However, when these nutrients enter our planets waterways in excess,
Eutrophication: Tracing Nutrient Pollution Back to Penns Creek Nutrients are substances that life depends on for growth and reproduction. However, when these nutrients enter our planets waterways in excess,
Water Monitoring in Spa Creek: A Summary
 Water Monitoring in Spa Creek: A Summary Written by: Alexis Jones & Blake Harden Edited by: Hannah Krauss Water monitoring is very important in order to determine the health of the Chesapeake Bay and its
Water Monitoring in Spa Creek: A Summary Written by: Alexis Jones & Blake Harden Edited by: Hannah Krauss Water monitoring is very important in order to determine the health of the Chesapeake Bay and its
Restoring a National Treasure: Chesapeake Bay. Presented by Dan Nees, Director Environmental Finance Center University of Maryland April 27, 2007
 Restoring a National Treasure: Chesapeake Bay Presented by Dan Nees, Director Environmental Finance Center University of Maryland April 27, 2007 Agenda Introduction to the Chesapeake Bay Restoration challenges
Restoring a National Treasure: Chesapeake Bay Presented by Dan Nees, Director Environmental Finance Center University of Maryland April 27, 2007 Agenda Introduction to the Chesapeake Bay Restoration challenges
CHAPTER 15 WATER POLLUTION. INTO THE GULF Researchers try to pin down what s choking the Gulf of Mexico
 CHAPTER 15 WATER POLLUTION INTO THE GULF Researchers try to pin down what s choking the Gulf of Mexico SAVING THE BAY Teams of researchers try to pin down what s choking the Chesapeake Water pollution
CHAPTER 15 WATER POLLUTION INTO THE GULF Researchers try to pin down what s choking the Gulf of Mexico SAVING THE BAY Teams of researchers try to pin down what s choking the Chesapeake Water pollution
Factoring in the Influence of the Conowingo Reservoir on State Allocations
 Factoring in the Influence of the Conowingo Reservoir on State Allocations Presented to the Chesapeake Bay Commission on behalf of the Modeling Workgroup September 9, 2016 Lee Currey Director, Science
Factoring in the Influence of the Conowingo Reservoir on State Allocations Presented to the Chesapeake Bay Commission on behalf of the Modeling Workgroup September 9, 2016 Lee Currey Director, Science
Protecting & Restoring Local Waters and the Chesapeake Bay
 Protecting & Restoring Local Waters and the Chesapeake Bay Restore America s Estuaries National Conference Gregory Barranco Chesapeake Bay Program Office November 2010 The Chesapeake Bay and Watershed
Protecting & Restoring Local Waters and the Chesapeake Bay Restore America s Estuaries National Conference Gregory Barranco Chesapeake Bay Program Office November 2010 The Chesapeake Bay and Watershed
Evaluation of the Effectiveness of SAV Restoration Approaches in the Chesapeake Bay
 Evaluation of the Effectiveness of SAV Restoration Approaches in the Chesapeake Bay Response to a program review requested of STAC by the SAV Workgroup Lee Karrh 3/27/2012 Brief Background On Review Baywide
Evaluation of the Effectiveness of SAV Restoration Approaches in the Chesapeake Bay Response to a program review requested of STAC by the SAV Workgroup Lee Karrh 3/27/2012 Brief Background On Review Baywide
Chesapeake Bay Restora/on Effort
 Chesapeake Bay Restora/on Effort Dave Nemazie Associate VP for External Affairs 15 April 2015 Leadership Maryland A Shallow Bay with a Large Watershed Watershed: 64,000 m 2 Ave Depth: 6 m Max Depth: 50
Chesapeake Bay Restora/on Effort Dave Nemazie Associate VP for External Affairs 15 April 2015 Leadership Maryland A Shallow Bay with a Large Watershed Watershed: 64,000 m 2 Ave Depth: 6 m Max Depth: 50
Chesapeake Bay Program in Pennsylvania. Karl G. Brown Executive Secretary PA State Conservation Commission
 Chesapeake Bay Program in Pennsylvania Karl G. Brown Executive Secretary PA State Conservation Commission 1 PA s Chesapeake Basin Over 50 percent of the land in PA drains to the Chesapeake Bay The Susquehanna
Chesapeake Bay Program in Pennsylvania Karl G. Brown Executive Secretary PA State Conservation Commission 1 PA s Chesapeake Basin Over 50 percent of the land in PA drains to the Chesapeake Bay The Susquehanna
Lake & Watershed Resource Management Associates P O Box 65; Turner, ME
 Lake & Watershed Resource Management Associates P O Box 65; Turner, ME 207-336-2980 LWRMA @megalink.net 2009 Baseline Water Quality Monitoring and Assessment of McCurdy Pond At the request of the Pemaquid
Lake & Watershed Resource Management Associates P O Box 65; Turner, ME 207-336-2980 LWRMA @megalink.net 2009 Baseline Water Quality Monitoring and Assessment of McCurdy Pond At the request of the Pemaquid
Finalizing the Chesapeake Bay Health Index (BHI)
 Finalizing the Chesapeake Bay Health Index (BHI) Part 1: Water Quality Index Part 2: Biotic Index Bill Dennison Ben Longstaff, Michael Williams, Claire Buchanan, Roberto Llansó, and Peter Bergstrom On
Finalizing the Chesapeake Bay Health Index (BHI) Part 1: Water Quality Index Part 2: Biotic Index Bill Dennison Ben Longstaff, Michael Williams, Claire Buchanan, Roberto Llansó, and Peter Bergstrom On
CHESAPEAKE BAY COMPREHENSIVE WATER RESOURCES AND RESTORATION PLAN - UPDATE. Update to Chesapeake Bay Program STAR January 25, 2018
 CHESAPEAKE BAY COMPREHENSIVE WATER RESOURCES AND RESTORATION 255 255 255 237 237 237 0 0 0 217 217 217 163 163 163 200 200 200 PLAN - UPDATE 131 132 122 239 65 53 80 119 27 110 135 120 252 174.59 112 92
CHESAPEAKE BAY COMPREHENSIVE WATER RESOURCES AND RESTORATION 255 255 255 237 237 237 0 0 0 217 217 217 163 163 163 200 200 200 PLAN - UPDATE 131 132 122 239 65 53 80 119 27 110 135 120 252 174.59 112 92
BAY BAROMETER. Health and Restoration. in the Chesapeake Watershed
 BAY BAROMETER 212-213 Health and Restoration in the Chesapeake Watershed AT A GLANCE 212-13 BAY HEALTH RESTORATION Water Quality Wetlands 29 percent of the Bay and its tidal rivers met overall conditions
BAY BAROMETER 212-213 Health and Restoration in the Chesapeake Watershed AT A GLANCE 212-13 BAY HEALTH RESTORATION Water Quality Wetlands 29 percent of the Bay and its tidal rivers met overall conditions
CLMP+ Report on Grass Lake (Anoka County) Lake ID# CLMP+ Data Summary
 CLMP+ Report on Grass Lake (Anoka County) Lake ID# 02-0113-00 2012-2013 CLMP+ Data Summary October 2014 Authors Shannon Martin, MPCA Editing and graphic design Public Information Office Staff The (MPCA)
CLMP+ Report on Grass Lake (Anoka County) Lake ID# 02-0113-00 2012-2013 CLMP+ Data Summary October 2014 Authors Shannon Martin, MPCA Editing and graphic design Public Information Office Staff The (MPCA)
DRAFT. Tidal Trends in Water Quality: Potomac River 2017 Tributary Summary
 DRAFT Tidal Trends in Water Quality: Potomac River 2017 Tributary Summary Sept 26, 2018 1 Contents 1. Location... 3 1.1 Watershed Physiography... 3 1.2 Tidal Waters and Stations... 4 2. Tidal Water Quality
DRAFT Tidal Trends in Water Quality: Potomac River 2017 Tributary Summary Sept 26, 2018 1 Contents 1. Location... 3 1.1 Watershed Physiography... 3 1.2 Tidal Waters and Stations... 4 2. Tidal Water Quality
Fact Sheet. Chesapeake Bay Water Quality
 Fact Sheet Chesapeake Bay Water Quality Water quality is a critical measure of the Chesapeake Bay s health. For the Bay to be healthy and productive, the water must be safe for people and must support
Fact Sheet Chesapeake Bay Water Quality Water quality is a critical measure of the Chesapeake Bay s health. For the Bay to be healthy and productive, the water must be safe for people and must support
Cultural accelerated by anthropogenic activities
 EUTROPHICATION IMPLICATIONS OF N & P Intent of this lecture? Link our discussions of terrestrial N & P dynamics with its influences on receiving water bodies How the relative amounts of N & P can influence
EUTROPHICATION IMPLICATIONS OF N & P Intent of this lecture? Link our discussions of terrestrial N & P dynamics with its influences on receiving water bodies How the relative amounts of N & P can influence
Assessment of Chesapeake Assimilation Capacity Application to Phase III Draft Targets
 Assessment of Chesapeake Assimilation Capacity Application to Phase III Draft Targets Water Quality Goal Implementation Team January 22, 2018 Lew Linker, EPA-CBPO, Gary Shenk, USGS and Richard Tian, UMCES
Assessment of Chesapeake Assimilation Capacity Application to Phase III Draft Targets Water Quality Goal Implementation Team January 22, 2018 Lew Linker, EPA-CBPO, Gary Shenk, USGS and Richard Tian, UMCES
Factoring in the Influence of the Conowingo Reservoir on State Allocations
 Factoring in the Influence of the Conowingo Reservoir on State Allocations Presented to the Water Quality GIT September 26, 2016 Lee Currey and Dave Monatali Director, Science Services Administration Maryland
Factoring in the Influence of the Conowingo Reservoir on State Allocations Presented to the Water Quality GIT September 26, 2016 Lee Currey and Dave Monatali Director, Science Services Administration Maryland
Climate Change and Chesapeake Bay Habitats
 Climate Change and Chesapeake Bay Habitats Donna Marie Bilkovic Sustainable Fisheries GIT Meeting 4 June 2014 Virginia Institute of Marine Science www.ccrm.vims.edu http://www.chesapeake.org/stac/ Existing
Climate Change and Chesapeake Bay Habitats Donna Marie Bilkovic Sustainable Fisheries GIT Meeting 4 June 2014 Virginia Institute of Marine Science www.ccrm.vims.edu http://www.chesapeake.org/stac/ Existing
CLMP+ Report on Fleming Lake (Aitkin County)
 CLMP+ Report on Fleming Lake (Aitkin County) Lake ID# -5-5-6 CLMP+ Data Summary July 7 Authors Shannon Martin Contributors/acknowledgements Terry Dahlberg Sandy Dahlberg Pam Anderson For questions regarding
CLMP+ Report on Fleming Lake (Aitkin County) Lake ID# -5-5-6 CLMP+ Data Summary July 7 Authors Shannon Martin Contributors/acknowledgements Terry Dahlberg Sandy Dahlberg Pam Anderson For questions regarding
Climate Change and Chesapeake Bay Habitats
 Climate Change and Chesapeake Bay Habitats Donna Marie Bilkovic STAC Chesapeake Bay Forage Base Workshop 12 November 2014 http://www.chesapeake.org/stac/ Virginia Institute of Marine Science www.ccrm.vims.edu
Climate Change and Chesapeake Bay Habitats Donna Marie Bilkovic STAC Chesapeake Bay Forage Base Workshop 12 November 2014 http://www.chesapeake.org/stac/ Virginia Institute of Marine Science www.ccrm.vims.edu
Baltimore City Department of Public Works
 Baltimore City Department of Public Works Back River WWTP Process and Construction Overview Michael F. Gallagher, Chief Wastewater Facilities Division Wastewater Treatment Chesapeake Bay Restoration Water
Baltimore City Department of Public Works Back River WWTP Process and Construction Overview Michael F. Gallagher, Chief Wastewater Facilities Division Wastewater Treatment Chesapeake Bay Restoration Water
Sustainable Fisheries GIT: Fish Habitat
 Quarterly Progress Meeting - May 2017 Chesapeake Bay Program Science. Restoration Partnership. Sustainable Fisheries GIT: Fish Habitat Bruce Vogt, NOAA and Sustainable Fisheries GIT Coordinator Gina Hunt,
Quarterly Progress Meeting - May 2017 Chesapeake Bay Program Science. Restoration Partnership. Sustainable Fisheries GIT: Fish Habitat Bruce Vogt, NOAA and Sustainable Fisheries GIT Coordinator Gina Hunt,
Climate Change & the Chesapeake TS3 workgroup chapter. European MedSeA
 Climate Change & the Chesapeake TS3 workgroup chapter European MedSeA 21 ST CENTURY CLIMATE CHANGE AND SUBMERGED AQUATIC VEGETATION IN THE CHESAPEAKE BAY The 20 th century story: nutrient pollution, eutrophication,
Climate Change & the Chesapeake TS3 workgroup chapter European MedSeA 21 ST CENTURY CLIMATE CHANGE AND SUBMERGED AQUATIC VEGETATION IN THE CHESAPEAKE BAY The 20 th century story: nutrient pollution, eutrophication,
Restoring the Chesapeake Bay Challenges & Opportunities
 Restoring the Chesapeake Bay Challenges & Opportunities Jeff Corbin Senior Advisor for Chesapeake Bay U.S. EPA May 29, 2014 A few things to talk about History of Bay Restoration How are we doing? What
Restoring the Chesapeake Bay Challenges & Opportunities Jeff Corbin Senior Advisor for Chesapeake Bay U.S. EPA May 29, 2014 A few things to talk about History of Bay Restoration How are we doing? What
Fish Habitat Management Strategy Outline
 Fish Habitat Management Strategy Outline Executive Summary 1. CBP Communications team will draft after the other sections are complete. Outcome and Baselines Fish Habitat Outcome: Continually improve effectiveness
Fish Habitat Management Strategy Outline Executive Summary 1. CBP Communications team will draft after the other sections are complete. Outcome and Baselines Fish Habitat Outcome: Continually improve effectiveness
Integrating Water Quality and Natural Filters into Maryland s Marine Spatial Planning Efforts
 Integrating Water Quality and Natural Filters into Maryland s Marine Spatial Planning Efforts Nicole Carlozo NOAA Coastal Management Fellow July 31, 2014 Watershed-scale restoration targeting helps direct
Integrating Water Quality and Natural Filters into Maryland s Marine Spatial Planning Efforts Nicole Carlozo NOAA Coastal Management Fellow July 31, 2014 Watershed-scale restoration targeting helps direct
Osher Course. What Lies Beneath the Inland Bays?
 Osher Course What Lies Beneath the Inland Bays? Objectives for Course Describe the Delaware Inland Bays and their tributaries Illustrate the ecology and importance of estuaries Demonstrate the threats
Osher Course What Lies Beneath the Inland Bays? Objectives for Course Describe the Delaware Inland Bays and their tributaries Illustrate the ecology and importance of estuaries Demonstrate the threats
Triblet Characteristics & Responses
 Triblet Characteristics & Responses K.G. Sellner 1, W.R. Boynton 2, J. Testa 2, T. Rosen 3, R.J. Orth 4, D. Dauer 5, and J. Uphoff 6 1 Center for Coastal & Watershed Studies, Hood College 2 UMCES-CBL 3
Triblet Characteristics & Responses K.G. Sellner 1, W.R. Boynton 2, J. Testa 2, T. Rosen 3, R.J. Orth 4, D. Dauer 5, and J. Uphoff 6 1 Center for Coastal & Watershed Studies, Hood College 2 UMCES-CBL 3
Long Island s. Environmental Issues. Environmental Issues. Environmental Setting. Environmental Setting. Suburbia and the Environment
 Environmental Issues Long Island s Environmental Issues Copyright 2011 AFG 1 agricultural land air pollution aquifers automobile barrier islands biozones fisheries groundwater recharge invasive species
Environmental Issues Long Island s Environmental Issues Copyright 2011 AFG 1 agricultural land air pollution aquifers automobile barrier islands biozones fisheries groundwater recharge invasive species
Riparian Buffers and Stream Restoration
 Riparian Buffers and Stream Restoration Why focus on riparian areas? Link land and water on any given site and link landscapes together in a watershed Riparian corridors protect the circulatory system
Riparian Buffers and Stream Restoration Why focus on riparian areas? Link land and water on any given site and link landscapes together in a watershed Riparian corridors protect the circulatory system
Water for Virginia Master Naturalists. What are the types What is important to know about: Functions Values Issues
 Water for Virginia Master Naturalists What are the types What is important to know about: Functions Values Issues Francis J. Reilly, Jr. http://advancedmastergardener.org/water.htm Frank@TheReillyGroup.net
Water for Virginia Master Naturalists What are the types What is important to know about: Functions Values Issues Francis J. Reilly, Jr. http://advancedmastergardener.org/water.htm Frank@TheReillyGroup.net
Estuary Adventures. Background. Objective
 Estuary Adventures Objective Students will work in groups to understand the concept of estuaries, their importance, and the role that density plays in the mixing of fresh and salt water. Students will
Estuary Adventures Objective Students will work in groups to understand the concept of estuaries, their importance, and the role that density plays in the mixing of fresh and salt water. Students will
Eutrophication and the Saltwater Hudson River
 Eutrophication and the Saltwater Hudson River Part 1: Primary Production and Eutrophication in the Hudson Since the Industrial Revolution, the Hudson River has had problems with pollution, yet the challenges
Eutrophication and the Saltwater Hudson River Part 1: Primary Production and Eutrophication in the Hudson Since the Industrial Revolution, the Hudson River has had problems with pollution, yet the challenges
2016 Summit Lake Water Quality Report Prepared by Thurston County Environmental Health Division
 ! 216 Summit Lake Water Quality Report Prepared by Thurston County Environmental Health Division PART OF TOTTEN INLET WATERSHED LENGTH OF LAKE: 2.2 miles SHORELINE LENGTH: 5.6 miles LAKE SIZE: 53 acres
! 216 Summit Lake Water Quality Report Prepared by Thurston County Environmental Health Division PART OF TOTTEN INLET WATERSHED LENGTH OF LAKE: 2.2 miles SHORELINE LENGTH: 5.6 miles LAKE SIZE: 53 acres
Modeling Quarterly Review Meeting January 14, Bruce Michael Maryland Department of Natural Resources
 Ongoing Conowingo Dam / Lower Susquehanna River Studies Modeling Quarterly Review Meeting January 14, 2015 Bruce Michael Maryland Department of Natural Resources Draft Lower Susquehanna River Watershed
Ongoing Conowingo Dam / Lower Susquehanna River Studies Modeling Quarterly Review Meeting January 14, 2015 Bruce Michael Maryland Department of Natural Resources Draft Lower Susquehanna River Watershed
Citizen Science and the Chesapeake Bay Program s Water Quality Monitoring Program
 Citizen Science and the Chesapeake Bay Program s Water Quality Monitoring Program Peter Tango USGS @ CBPO Mid-Atlantic Volunteer Monitoring Conference August 7, 2015 Nick DiPasquale Director Chesapeake
Citizen Science and the Chesapeake Bay Program s Water Quality Monitoring Program Peter Tango USGS @ CBPO Mid-Atlantic Volunteer Monitoring Conference August 7, 2015 Nick DiPasquale Director Chesapeake
Phosphorus Goal Setting Process Questions and Answers 2010
 Lake Winnipesaukee Watershed Management Plan Phase I: Meredith, Paugus, Saunders Bays 1. What is phosphorus? Phosphorus (P) is a naturally occurring element and a major nutrient required for biological
Lake Winnipesaukee Watershed Management Plan Phase I: Meredith, Paugus, Saunders Bays 1. What is phosphorus? Phosphorus (P) is a naturally occurring element and a major nutrient required for biological
Urban Geology Spring 2011
 Urban Geology Spring 2011 Gowanus Canal Historical use New York City Water pollution Sewage treatment plants Eutrophication Combined sewage outflows (CSO) Remediation Sustainability Gowanus Canal today
Urban Geology Spring 2011 Gowanus Canal Historical use New York City Water pollution Sewage treatment plants Eutrophication Combined sewage outflows (CSO) Remediation Sustainability Gowanus Canal today
Chesapeake Bay Foundation 101. Robert Jennings
 Chesapeake Bay Foundation 101 Robert Jennings About the Bay Chesapeake Bay Watershed 64,000 square miles 19 major rivers 400 smaller creeks 3,000 species of plants and animals 17 million people How s the
Chesapeake Bay Foundation 101 Robert Jennings About the Bay Chesapeake Bay Watershed 64,000 square miles 19 major rivers 400 smaller creeks 3,000 species of plants and animals 17 million people How s the
Water Quality Monitoring Stations
 Water Quality Monitoring Stations Eastern Basin Race Narrows Western Basin Central Basin The CT Department of Environmental Protection (CT DEP) conducts a water quality CT DEP monitoring program for the
Water Quality Monitoring Stations Eastern Basin Race Narrows Western Basin Central Basin The CT Department of Environmental Protection (CT DEP) conducts a water quality CT DEP monitoring program for the
Guiding the Restoration of the Chesapeake Bay: The EPA Chesapeake Bay Program Partnership. Keely Clifford U.S. Embassy Paris
 Guiding the Restoration of the Chesapeake Bay: The EPA Chesapeake Bay Program Partnership Keely Clifford U.S. Embassy Paris PISCES Workshop June 14, 2011 1 Chesapeake Bay Watershed About 17 million people
Guiding the Restoration of the Chesapeake Bay: The EPA Chesapeake Bay Program Partnership Keely Clifford U.S. Embassy Paris PISCES Workshop June 14, 2011 1 Chesapeake Bay Watershed About 17 million people
The Continued Evolution of Our Chesapeake Bay and Basin Long-term Water Quality Monitoring Program: Growing with Partnerships
 The Continued Evolution of Our Chesapeake Bay and Basin Long-term Water Quality Monitoring Program: Growing with Partnerships Peter J. Tango Chesapeake Bay Monitoring Coordinator USGS@CBPO Chesapeake Bay
The Continued Evolution of Our Chesapeake Bay and Basin Long-term Water Quality Monitoring Program: Growing with Partnerships Peter J. Tango Chesapeake Bay Monitoring Coordinator USGS@CBPO Chesapeake Bay
A restoration goal for Chesapeake Bay phytoplankton communities. Executive Summary
 A restoration goal for Chesapeake Bay phytoplankton communities Executive Summary A Phytoplankton Index of Biotic Integrity (PIBI) has been developed for Chesapeake Bay. 1 It is currently used to analyze
A restoration goal for Chesapeake Bay phytoplankton communities Executive Summary A Phytoplankton Index of Biotic Integrity (PIBI) has been developed for Chesapeake Bay. 1 It is currently used to analyze
Chesapeake Bay. report card
 Chesapeake Bay report card 2010 C- C Healthy water quality provides better habitat conditions for crabs, fish, and other aquatic species. issolved oxygen is essential to the survival of all these organisms;
Chesapeake Bay report card 2010 C- C Healthy water quality provides better habitat conditions for crabs, fish, and other aquatic species. issolved oxygen is essential to the survival of all these organisms;
Chesapeake Bay Program Partnership s Investment in the Chesapeake Monitoring Cooperative: What s Different This Time Around
 Chesapeake Bay Program Partnership s Investment in the Chesapeake Monitoring Cooperative: What s Different This Time Around Rich Batiuk Associate Director for Science, Analysis and Implementation Chesapeake
Chesapeake Bay Program Partnership s Investment in the Chesapeake Monitoring Cooperative: What s Different This Time Around Rich Batiuk Associate Director for Science, Analysis and Implementation Chesapeake
Coastal Ecosystems: Saving Chesapeake Bay. Note the highest pigment concentrations (red) in coastal regions, especially estuaries
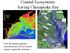 Coastal Ecosystems: Saving Chesapeake Bay Note the highest pigment concentrations (red) in coastal regions, especially estuaries Coastal Ecosystems: human impacts Humans severely impact the coastal zone
Coastal Ecosystems: Saving Chesapeake Bay Note the highest pigment concentrations (red) in coastal regions, especially estuaries Coastal Ecosystems: human impacts Humans severely impact the coastal zone
Hadlock Pond, Washington Co., Lake Hadlock Association, Inc.
 Hadlock Pond, Washington Co., Lake Hadlock Association, Inc. Lake Characteristics Watershed Characteristics Surface Area (ac/ha) Max Depth (ft/m) Mean Depth (ft/m) Retention Time (years) Water Class Dam
Hadlock Pond, Washington Co., Lake Hadlock Association, Inc. Lake Characteristics Watershed Characteristics Surface Area (ac/ha) Max Depth (ft/m) Mean Depth (ft/m) Retention Time (years) Water Class Dam
Chesapeake Bay Watershed Agreement Final draft January 29, 2014
 Chesapeake Bay Watershed Agreement Final draft January 29, 2014 Public comment invited through March 17, 2014. Visit: www.chesapeakebay.net/watershedagreement 1 Preamble The Chesapeake Bay watershed is
Chesapeake Bay Watershed Agreement Final draft January 29, 2014 Public comment invited through March 17, 2014. Visit: www.chesapeakebay.net/watershedagreement 1 Preamble The Chesapeake Bay watershed is
Innovative Agricultural Practices to Mitigate Groundwater Nutrient Contamination
 Innovative Agricultural Practices to Mitigate Groundwater Nutrient Contamination Maryland Groundwater Symposium Jason Keppler Maryland Department of Agriculture Ditch Drained Systems Flat, low-lying, poorly
Innovative Agricultural Practices to Mitigate Groundwater Nutrient Contamination Maryland Groundwater Symposium Jason Keppler Maryland Department of Agriculture Ditch Drained Systems Flat, low-lying, poorly
Program Title: Exploring Erosion Processes
 UNC Coastal Studies Institute On Site Programming 1 Program Title: Exploring Erosion Processes Figure 1 Wind driven waves lapping an estuarine shore. Program Abstract: The focus of this program is the
UNC Coastal Studies Institute On Site Programming 1 Program Title: Exploring Erosion Processes Figure 1 Wind driven waves lapping an estuarine shore. Program Abstract: The focus of this program is the
COG Region s Potomac Water Quality & Wastewater Treatment Fact Sheet (current draft, as of 7/28/09)
 COG Region s Potomac Water Quality & Wastewater Treatment Fact Sheet (current draft, as of 7/28/9) Background: Current Fact Sheet was prepared several years ago to summarize trends for certain water quality
COG Region s Potomac Water Quality & Wastewater Treatment Fact Sheet (current draft, as of 7/28/9) Background: Current Fact Sheet was prepared several years ago to summarize trends for certain water quality
Continuous Monitoring Network Strategy Continued Discussion. Peter Tango November 18, 2015 DIWG-INWG SERC
 Continuous Monitoring Network Strategy Continued Discussion Peter Tango USGS@CBPO November 18, 2015 DIWG-INWG meeting @ SERC Existing Chesapeake Bay Program Continuous Monitoring Programming Shallow water
Continuous Monitoring Network Strategy Continued Discussion Peter Tango USGS@CBPO November 18, 2015 DIWG-INWG meeting @ SERC Existing Chesapeake Bay Program Continuous Monitoring Programming Shallow water
Chesapeake Bay Report Card 2016
 hesapeake Bay Report ard 216 University of Maryland enter for Environmental Science Fun for you and your family Stewardship is defined as the responsible oversight and protection of something considered
hesapeake Bay Report ard 216 University of Maryland enter for Environmental Science Fun for you and your family Stewardship is defined as the responsible oversight and protection of something considered
Jeffrey Cornwell, Michael Owens, Lisa Kellogg Thanks to RIE Newell and K Paynter
 Jeffrey Cornwell, Michael Owens, Lisa Kellogg Thanks to RIE Newell and K Paynter Source: Tom Toles (2013) The Washington Post. 2014 Funding: Kellogg, M. L., J. C. Cornwell, M. S. Owens, and K. T. Paynter.
Jeffrey Cornwell, Michael Owens, Lisa Kellogg Thanks to RIE Newell and K Paynter Source: Tom Toles (2013) The Washington Post. 2014 Funding: Kellogg, M. L., J. C. Cornwell, M. S. Owens, and K. T. Paynter.
CHESAPEAKE BAY FOUNDATION Save the Bay
 CHESAPEAKE BAY FOUNDATION Save the Bay The Chesapeake Bay s Health Remains Stressed in 2000 We are frequently asked, How s the Chesapeake Bay doing? Unfortunately, our answer this year is that the Bay
CHESAPEAKE BAY FOUNDATION Save the Bay The Chesapeake Bay s Health Remains Stressed in 2000 We are frequently asked, How s the Chesapeake Bay doing? Unfortunately, our answer this year is that the Bay
Climate Change Impacts of Most Concern for CB Agreement Goal & Outcome Attainment
 Climate Change Impacts of Most Concern for CB Agreement Goal & Outcome Attainment Zoë P. Johnson, Climate Change Coordinator Chesapeake Bay Program STAC Workshop March 7-8, 2016 Climate Change: Real Consequences
Climate Change Impacts of Most Concern for CB Agreement Goal & Outcome Attainment Zoë P. Johnson, Climate Change Coordinator Chesapeake Bay Program STAC Workshop March 7-8, 2016 Climate Change: Real Consequences
Chapter 4.4. Development of a Water Quality Index for the Maryland Coastal Bays
 Chapter 4.4 Development of a Water Quality Index for the Maryland Coastal Bays Tim Carruthers 1 and Catherine Wazniak 2 1 Integration and Application Network, University of Maryland Center for Environmental
Chapter 4.4 Development of a Water Quality Index for the Maryland Coastal Bays Tim Carruthers 1 and Catherine Wazniak 2 1 Integration and Application Network, University of Maryland Center for Environmental
Chesapeake Bay Program Partnership s Scientific, Technical Assessment and Reporting (STAR) Team Briefing and Options Paper:
 Chesapeake Bay Program Partnership s Scientific, Technical Assessment and Reporting (STAR) Team Briefing and Options Paper: Addressing CBP Partnership s and Non-tidal Monitoring Network s 2013 Funding
Chesapeake Bay Program Partnership s Scientific, Technical Assessment and Reporting (STAR) Team Briefing and Options Paper: Addressing CBP Partnership s and Non-tidal Monitoring Network s 2013 Funding
The Hypoxic Zone in the Gulf of Mexico
 The Hypoxic Zone in the Gulf of Mexico References Council Committee on Environmental and Natural Resources. 2003. An Assessment of Coastal Hypoxia and Eutrophication in U.S. Water. National Science and
The Hypoxic Zone in the Gulf of Mexico References Council Committee on Environmental and Natural Resources. 2003. An Assessment of Coastal Hypoxia and Eutrophication in U.S. Water. National Science and
Chesapeake Bay Program Models:
 Chesapeake Bay Program Models: A Guide to Better Understanding Modeling and Decision Support Tool Forum Penn State Harrisburg August 1, 2011 1 Mark Dubin Agricultural Technical Coordinator University of
Chesapeake Bay Program Models: A Guide to Better Understanding Modeling and Decision Support Tool Forum Penn State Harrisburg August 1, 2011 1 Mark Dubin Agricultural Technical Coordinator University of
James River Alternatives Analysis June 23, 2005
 James River Alternatives Analysis June 23, 2005 Prepared by: Virginia Department of Environmental Quality in cooperation with the U.S. EPA Chesapeake Bay Program Office [ THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
James River Alternatives Analysis June 23, 2005 Prepared by: Virginia Department of Environmental Quality in cooperation with the U.S. EPA Chesapeake Bay Program Office [ THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
Mike Langland USGS PA Agricultural Advisory Board April 28, 2016
 Mike Langland USGS PA Agricultural Advisory Board April 28, 2016 Chesapeake Bay Nontidal Monitoring Network - Loads to the Bay (1) How are nitrogen, phosphorus, and suspendedsediment loads responding to
Mike Langland USGS PA Agricultural Advisory Board April 28, 2016 Chesapeake Bay Nontidal Monitoring Network - Loads to the Bay (1) How are nitrogen, phosphorus, and suspendedsediment loads responding to
Nutrients, Algal Blooms and Red Tides in Hong Kong Waters. Paul J. Harrison and Jie XU
 Nutrients, Algal Blooms and Red Tides in Hong Kong Waters Paul J. Harrison and Jie XU Division of Environment, Hong Kong University of Science & Technology 1. Introduction The Pearl River is China's second
Nutrients, Algal Blooms and Red Tides in Hong Kong Waters Paul J. Harrison and Jie XU Division of Environment, Hong Kong University of Science & Technology 1. Introduction The Pearl River is China's second
NUTRIENTS AND PARTICLES TAHOE.UCDAVIS.EDU 9
 NUTRIENTS AND PARTICLES 9 Sources of clarity-reducing and blueness-reducing pollutants In 2017 Research has quantified the primary sources of nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) and particulate material
NUTRIENTS AND PARTICLES 9 Sources of clarity-reducing and blueness-reducing pollutants In 2017 Research has quantified the primary sources of nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) and particulate material
The Chesapeake Bay TMDL
 The Chesapeake Bay TMDL December 29, 2010 EPA Update on Implementation Progress County Engineers Association of Maryland Fall Conference 2015 Jon M. Capacasa, Water Division Director US EPA Region III
The Chesapeake Bay TMDL December 29, 2010 EPA Update on Implementation Progress County Engineers Association of Maryland Fall Conference 2015 Jon M. Capacasa, Water Division Director US EPA Region III
What Characterizes the Taninim Estuary in Relation to Other Mediterranean Microestuaries in Israel and Implications for the River rehabilitation
 What Characterizes the Taninim Estuary in Relation to Other Mediterranean Microestuaries in Israel and Implications for the River rehabilitation Sarig Gafny (sarig@ruppin.ac.il) The RIME team: Gitai Yahel,
What Characterizes the Taninim Estuary in Relation to Other Mediterranean Microestuaries in Israel and Implications for the River rehabilitation Sarig Gafny (sarig@ruppin.ac.il) The RIME team: Gitai Yahel,
The Corsica River Project ~A Five Year Update~ Monitoring from the Field to the Estuary LID/NPS Conference Philadelphia
 The Corsica River Project ~A Five Year Update~ Monitoring from the Field to the Estuary 2011 LID/NPS Conference Philadelphia The Corsica River Watershed t Nutrient Loads by Land Use (MDE 2000) 809 Septic
The Corsica River Project ~A Five Year Update~ Monitoring from the Field to the Estuary 2011 LID/NPS Conference Philadelphia The Corsica River Watershed t Nutrient Loads by Land Use (MDE 2000) 809 Septic
Update on Straits Pond
 Update on Straits Pond Presented to the Board of Selectmen July 27, 2017 Issues of Concern raised by citizens along Straits Pond: Midges (?) Offensive odor Excessive Algae Background: Straits Pond is a
Update on Straits Pond Presented to the Board of Selectmen July 27, 2017 Issues of Concern raised by citizens along Straits Pond: Midges (?) Offensive odor Excessive Algae Background: Straits Pond is a
Coastal Bays. report card. Gold stars for partnerships
 partners, and visitors, the Maryland between citizens, business, the Program, the Maryland Department of atural Resources, and the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service has documented more than 113, spawning 212
partners, and visitors, the Maryland between citizens, business, the Program, the Maryland Department of atural Resources, and the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service has documented more than 113, spawning 212
How Nutrient Trading Can Help Restore the Chesapeake Bay
 WRI FACT SHEET How Nutrient Trading Can Help Restore the Chesapeake Bay Congress is considering proposals to revise and strengthen the Clean Water Act for the Chesapeake Bay region and improve the health
WRI FACT SHEET How Nutrient Trading Can Help Restore the Chesapeake Bay Congress is considering proposals to revise and strengthen the Clean Water Act for the Chesapeake Bay region and improve the health
Full Title of Priority: Enhanced Analysis and Explanation of Water-Quality Data for the TMDL Mid-Point Assessment
 MIDPOINT ASSESSMENT PRIORITY WORK PLAN: MEASURE AND EXPLAIN WATER-QUALITY CHANGES LEAD: SCIENTIFIC, TECHNICAL ANALYSIS, AND REPORT (STAR) TEAM 2016-17 EXPECTATIONS Full Title of Priority: Enhanced Analysis
MIDPOINT ASSESSMENT PRIORITY WORK PLAN: MEASURE AND EXPLAIN WATER-QUALITY CHANGES LEAD: SCIENTIFIC, TECHNICAL ANALYSIS, AND REPORT (STAR) TEAM 2016-17 EXPECTATIONS Full Title of Priority: Enhanced Analysis
Chesapeake Bay Report Card 2017
 University of Maryland enter for Environmental Science hesapeake Bay Report ard 217 Healthy fish populations in the Bay Health of Fisheries, 24 217 SORE (%) 1 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 ombined Fisheries Index
University of Maryland enter for Environmental Science hesapeake Bay Report ard 217 Healthy fish populations in the Bay Health of Fisheries, 24 217 SORE (%) 1 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 ombined Fisheries Index
The Snapshot CONODOGUINET CREEK WATERSHED SNAPSHOT
 CONODOGUINET CREEK WATERSHED SNAPSHOT ABOVE: CONODOGUINET CREEK AT RT 74 BRIDGE FACING DOWNSTREAM The Snapshot The Conodoguinet Watershed Snapshot was a collaborative effort to engage local citizens in
CONODOGUINET CREEK WATERSHED SNAPSHOT ABOVE: CONODOGUINET CREEK AT RT 74 BRIDGE FACING DOWNSTREAM The Snapshot The Conodoguinet Watershed Snapshot was a collaborative effort to engage local citizens in
Jerrit Askvig, Leah Bode, Nathan Cushing, Colin Mullery December 1, 2010
 Jerrit Askvig, Leah Bode, Nathan Cushing, Colin Mullery December 1, 2010 Agenda Context Stakeholder Analysis Problem Statement Scope Design Alternatives Method Analysis/Simulation Project Plan/Budget Risk
Jerrit Askvig, Leah Bode, Nathan Cushing, Colin Mullery December 1, 2010 Agenda Context Stakeholder Analysis Problem Statement Scope Design Alternatives Method Analysis/Simulation Project Plan/Budget Risk
CBP Climate Resiliency Workgroup. June 20, 2016
 2017 Midpoint Assessment Management Needs: Estimated Influence of 2025 and 2050 Sea Level Rise and Tidal Marsh Loss on Chesapeake Bay Water Quality Standards CBP Climate Resiliency Workgroup June 20, 2016
2017 Midpoint Assessment Management Needs: Estimated Influence of 2025 and 2050 Sea Level Rise and Tidal Marsh Loss on Chesapeake Bay Water Quality Standards CBP Climate Resiliency Workgroup June 20, 2016
Some Modeling Approaches and Issues for Nitrogen
 Some Modeling Approaches and Issues for Nitrogen Susquehanna River basin workshop June 23, 2004 Robert W. Howarth Department of Ecology & Evolutionary Biology Cornell University Two models: ReNuMa (based
Some Modeling Approaches and Issues for Nitrogen Susquehanna River basin workshop June 23, 2004 Robert W. Howarth Department of Ecology & Evolutionary Biology Cornell University Two models: ReNuMa (based
From My Backyard to Our Bay It s the 911 for the Chesapeake Bay
 From My Backyard to Our Bay Reporting Problems on Our Bay, Rivers, and Streams We can all be the eyes and ears of our local waterways. Maryland has established the Chesapeake Bay Safety and Environmental
From My Backyard to Our Bay Reporting Problems on Our Bay, Rivers, and Streams We can all be the eyes and ears of our local waterways. Maryland has established the Chesapeake Bay Safety and Environmental
Fishing and Boating: Past, Present, and Restoration Thoughts
 Fishing and Boating: Past, Present, and Restoration Thoughts West Branch Susquehanna River Douglas Austen Pennsylvania Fish and Boat Commission West Branch Basin Stream Resources Miles Category 1,249
Fishing and Boating: Past, Present, and Restoration Thoughts West Branch Susquehanna River Douglas Austen Pennsylvania Fish and Boat Commission West Branch Basin Stream Resources Miles Category 1,249
Seagrass Health in Texas
 Seagrass Health in Texas A Comprehensive Monitoring Program Florida Museum of Natural History Harte Institute Florida Museum of Natural History Prepared by Susan E. Linn Marine Science Department University
Seagrass Health in Texas A Comprehensive Monitoring Program Florida Museum of Natural History Harte Institute Florida Museum of Natural History Prepared by Susan E. Linn Marine Science Department University
Bay Barometer Spotlight on Health and Restoration in the. Chesapeake Bayand its Watershed
 Bay Barometer 211 212 Spotlight on Health and Restoration in the Chesapeake Bayand its Watershed From the Bay Program Director Resilience; the term is defined as the ability to recover quickly from setbacks.
Bay Barometer 211 212 Spotlight on Health and Restoration in the Chesapeake Bayand its Watershed From the Bay Program Director Resilience; the term is defined as the ability to recover quickly from setbacks.
North Dakota s Nutrient Reduction Strategy. Presented to the 2016 ND Water Quality Monitoring Conference March 4, 2016
 North Dakota s Nutrient Reduction Strategy Presented to the 2016 ND Water Quality Monitoring Conference March 4, 2016 Nutrients Nutrients, in appropriate amounts, are essential to the growth and health
North Dakota s Nutrient Reduction Strategy Presented to the 2016 ND Water Quality Monitoring Conference March 4, 2016 Nutrients Nutrients, in appropriate amounts, are essential to the growth and health
Owasco Lake Day
 Introductions Halfman apologizes for not presenting this talk himself. A family reunion took precedent. Owasco Lake Day 6-25--14 1 The beginnings Preliminary water quality comparison of the Finger Lakes
Introductions Halfman apologizes for not presenting this talk himself. A family reunion took precedent. Owasco Lake Day 6-25--14 1 The beginnings Preliminary water quality comparison of the Finger Lakes
