Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and ERP 14. Outline
|
|
|
- Cordelia Holt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and ERP 14 1 Outline Global Company Profile: Wheeled Coach Dependent Demand Dependent Inventory Model Requirements MRP Structure MRP Management 2 1
2 Outline - Continued Lot-Sizing Techniques Extensions of MRP MRP In Services Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) 3 Learning Objectives When you complete this chapter you should be able to: 1. Develop a product structure 2. Build a gross requirements plan 3. Build a net requirements plan 4. Determine lot sizes for lot-for-lot, EOQ, and POQ 4 2
3 Learning Objectives When you complete this chapter you should be able to: 5. Describe MRP II 6. Describe closed-loop MRP 7. Describe ERP 5 MRP for Wheeled Coach Largest manufacturer of ambulances in the world International competitor 12 major ambulance designs 18,000 different inventory items 6,000 manufactured parts 12,000 purchased parts 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. 6 3
4 MRP for Wheeled Coach Four Key Tasks Material plan must meet both the requirements of the master schedule and the capabilities of the production facility Plan must be executed as designed Minimize inventory investment Maintain excellent record integrity 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. 7 Dependent Demand For any product for which a schedule can be established, dependent demand techniques should be used 8 4
5 Dependent Demand Benefits of MRP 1. Better response to customer orders 2. Faster response to market changes 3. Improved utilization of facilities and labor 4. Reduced inventory levels 9 Dependent Demand The demand for one item is related to the demand for another item Given a quantity for the end item, the demand for all parts and components can be calculated In general, used whenever a schedule can be established for an item MRP is the common technique 10 5
6 Dependent Inventory Model Requirements Effective use of dependent demand inventory models requires the following 1. Master production schedule 2. Specifications or bill of material 3. Inventory availability 4. Purchase orders outstanding 5. Lead times 11 Master Production Schedule (MPS) Specifies what is to be made and when Must be in accordance with the aggregate production plan Inputs from financial plans, customer demand, engineering, supplier performance As the process moves from planning to execution, each step must be tested for feasibility The MPS is the result of the production planning process 12 6
7 Master Production Schedule (MPS) MPS is established in terms of specific products Schedule must be followed for a reasonable length of time The MPS is quite often fixed or frozen in the near term part of the plan The MPS is a rolling schedule The MPS is a statement of what is to be produced, not a forecast of demand 13 The Planning Process 14 Figure
8 The Planning Process Production Capacity Inventory Marketing Customer demand Finance Cash flow Supply Chain Procurement Supplier performance Sales & Operations Planning Generates an aggregate plan Human Resources Staff planning Master production schedule 15 Figure 14.1 The Planning Process Master production schedule Material requirements plan Change master production schedule? Schedule and execute plan 16 Figure
9 Aggregate Production Plan Figure 14.2 Months January February Aggregate Plan 1,500 1,200 (Shows the total quantity of amplifiers) Weeks Master Production Schedule (Shows the specific type and quantity of amplifier to be produced 240-watt amplifier watt amplifier watt amplifier Master Production Schedule (MPS) Can be expressed in any of the following terms: 1. A customer order in a job shop (make-toorder) company 2. Modules in a repetitive (assemble-toorder or forecast) company 3. An end item in a continuous (stock-toforecast) company 18 9
10 MPS Example TABLE 14.1 Master Production Schedule for Chef John s Buffalo Chicken Mac & Cheese GROSS REQUIREMENTS FOR CHEF JOHN S BUFFALO MAC & CHEESE Day And so on Quantity Bills of Material List of components, ingredients, and materials needed to make product Provides product structure Items above given level are called parents Items below given level are called components or children 20 10
11 BOM Example Level 0 Product structure for Awesome (A) A 1 B (2) C (3) 2 E (2) E (2) F (2) 3 D (2) G (1) D (2) 21 BOM Example For an order of 50 Awesome speaker kits Level Part B: Product structure for Awesome (A) 2 x number of As = (2)(50) = 100 Part 0 C: 3 x number of As = A (3)(50) = 150 Part D: 2 x number of Bs 1 B (2) + 2 x number of Fs = (2)(100) + (2)(300) C (3) = 800 Part E: 2 x number of Bs + 2 x number of Cs = (2)(100) + (2)(150) = 500 Part 2 F: 2 x number E of Cs = (2)(150) (2) E = (2) F 300 (2) Part G: 1 x number of Fs = (1)(300) = D (2) G (1) D (2) 22 11
12 Modular Bills Bills of Material Modules are not final products but components that can be assembled into multiple end items Can significantly simplify planning and scheduling 23 Planning Bills Bills of Material Also called pseudo or super bills Created to assign an artificial parent to the BOM Used to group subassemblies to reduce the number of items planned and scheduled Used to create standard kits for production 24 12
13 Bills of Material Phantom Bills Describe subassemblies that exist only temporarily Are part of another assembly and never go into inventory Low-Level Coding Item is coded at the lowest level at which it occurs BOMs are processed one level at a time 25 Accurate Inventory Records Accurate inventory records are absolutely required for MRP (or any dependent demand system) to operate correctly Generally MRP systems require more than 99% accuracy 26 13
14 Purchase Orders Outstanding A by-product of well-managed purchasing and inventory control department Outstanding purchase orders must accurately reflect quantities and scheduled receipts 27 Lead Times for Components The time required to purchase, produce, or assemble an item For production the sum of the move, setup, and assembly or run times For purchased items the time between the recognition of a need and when its available for production TABLE 14.2 Lead Times for Awesome Speaker Kits (As) COMPONENT LEAD TIME A 1 week B 2 weeks C 1 week D 1 week E 2 week F 3 weeks G 2 weeks 28 14
15 Time-Phased Product Structure Start production of D 2 weeks 1 week G D 2 weeks 1 week 3 weeks 2 weeks Must have D and E completed here so production can begin on B Time in weeks 29 D E 2 weeks to produce E 1 week F B 1 week C A Figure 14.3 MRP Structure Figure 14.4 Data Files BOM Lead times (Item master file) Master production schedule Output Reports MRP by period report MRP by date report Planned order report Inventory data Purchasing data Material requirement planning programs (computer and software) Purchase advice Exception reports Order early or late or not needed Order quantity too small or too large 30 15
16 Determining Gross Requirements Starts with a production schedule for the end item 50 units of Item A in week 8 Using the lead time for the item, determine the week in which the order should be released a 1 week lead time means the order for 50 units should be released in week 7 This step is often called lead time offset or time phasing 31 Determining Gross Requirements From the BOM, every Item A requires 2 Item Bs 100 Item Bs are required in week 7 to satisfy the order release for Item A The lead time for the Item B is 2 weeks release an order for 100 units of Item B in week 5 The timing and quantity for component requirements are determined by the order release of the parent(s) 32 16
17 Determining Gross Requirements The process continues through the entire BOM one level at a time often called explosion By processing the BOM by level, items with multiple parents are only processed once, saving time and resources and reducing confusion Low-level coding ensures that each item appears at only one level in the BOM 33 Gross Requirements Plan TABLE 14.3 Gross Material Requirements Plan for 50 Awesome Speaker Kits (As) with Order Release Dates Also Shown WEEK A. Required date 50 Order release date 50 B. Required date 100 Order release date 100 C. Required date 150 Order release date 150 E. Required date Order release date F. Required date 300 Order release date 300 D. Required date Order release date G. Required date 300 Order release date 300 LEAD TIME 1 week 2 weeks 1 week 2 weeks 3 weeks 1 week 2 weeks 34 17
18 ITEM ON HAND ITEM ON HAND A 10 E 10 Net Requirements Plan B 15 F 5 C 20 G 0 D Net Requirements Plan 36 18
19 Determining Net Requirements Starts with a production schedule for the end item 50 units of Item A in week 8 Because there are 10 Item As on hand, only 40 are actually required (net requirement) = (gross requirement on-hand inventory) The planned order receipt for Item A in week 8 is 40 units 40 = Determining Net Requirements Following the lead time offset procedure, the planned order release for Item A is now 40 units in week 7 The gross requirement for Item B is now 80 units in week 7 There are 15 units of Item B on hand, so the net requirement is 65 units in week 7 A planned order receipt of 65 units in week 7 generates a planned order release of 65 units in week
20 Determining Net Requirements A planned order receipt of 65 units in week 7 generates a planned order release of 65 units in week 5 The on-hand inventory record for Item B is updated to reflect the use of the 15 items in inventory and shows no on-hand inventory in week 8 This is referred to as the Gross-to-Net calculation and is the third basic function of the MRP process 39 Gross Requirements Schedule Figure 14.5 A S B C Lead time = 4 for A Master schedule for A B C Lead time = 6 for S Master schedule for S Master schedule for B sold directly Periods Periods Gross requirements: B 10 = =45 Therefore, these are the gross requirements for B 40 20
21 Net Requirements Plan The logic of net requirements Gross requirements + Allocations Total requirements On + Scheduled = hand receipts Net requirements Available inventory 41 MRP Planning Sheet Figure
22 Safety Stock BOMs, inventory records, purchase and production quantities may not be perfect Consideration of safety stock may be prudent Should be minimized and ultimately eliminated Typically built into projected on-hand inventory 43 MRP Management MRP dynamics Facilitates replanning when changes occur System nervousness can result from too many changes Time fences put limits on replanning Pegging links each item to its parent allowing effective analysis of changes 44 22
23 MRP Management MRP limitations MRP does not do detailed scheduling it plans Works best in product-focused, repetitive environments Requires fixed lead time and infinite size time buckets 45 Lot-Sizing Techniques Lot-for-lot techniques order just what is required for production based on net requirements May not always be feasible If setup costs are high, lot-for-lot can be expensive Economic order quantity (EOQ) EOQ expects a known constant demand and MRP systems often deal with unknown and variable demand 46 23
24 Lot-Sizing Techniques Periodic order quantity (POQ) orders quantity needed for a predetermined time period Interval = EOQ / average demand per period Order quantity set to cover the interval Order quantity calculated when order is released No extra inventory 47 Lot-Sizing Techniques Dynamic lot sizing techniques Balance lot size and setup costs Part period balancing (least total cost) Least unit cost Least period cost (Silver-Meal) Dynamic programming approach Wagner-Whitin 48 24
25 Lot-for-Lot Example WEEK Gross requirements Scheduled receipts Projected on hand Net requirements Planned order receipts Planned order releases Holding cost = $1/week; Setup cost = $100; Lead time = 1 week 49 Lot-for-Lot Example No on-hand inventory is carried through the system Total holding cost = $0 WEEK Gross There are seven 35setups for this 0 item in this 30 plan requirements Total ordering cost = 7 x $100 = $700 Scheduled receipts Projected on hand Net requirements Planned order receipts Planned order releases Holding cost = $1/week; Setup cost = $100; Lead time = 1 week 50 25
26 EOQ Lot Size Example WEEK Gross requirements Scheduled receipts Projected on hand Net requirements Planned order receipts Planned order releases Holding cost = $1/week; Setup cost = $100; Lead time = 1 week Average weekly gross requirements = 27; EOQ = 73 units 51 EOQ Lot Size Example Annual demand D = 1,404 Holding cost = 375 units x $1 (including 57 units on WEEK hand at end of week 10) Gross Ordering requirements cost = 4 x $100 = $400 Total Scheduled cost = $375 + $400 = $775 receipts Projected on hand Net requirements Planned order receipts Planned order releases Holding cost = $1/week; Setup cost = $100; Lead time = 1 week Average weekly gross requirements = 27; EOQ = 73 units 52 26
27 POQ Lot Size Example WEEK Gross requirements Scheduled receipts Projected on hand Net requirements Planned order receipts Planned order releases EOQ = 73 units; Average weekly gross requirements = 27; POQ interval = 73/27 3 weeks 53 POQ Lot Size Example Setups = 3 x $100 = $300 WEEK Holding cost = ( ) units x $1 = $ Gross requirements Total cost = $300 + $195 = $ Scheduled receipts Projected on hand Net requirements Planned order receipts Planned order releases EOQ = 73 units; Average weekly gross requirements = 27; POQ interval = 73/27 3 weeks 54 27
28 Lot-Sizing Summary For these three examples COSTS SETUP HOLDING TOTAL Lot-for-lot $700 $0 $700 EOQ $400 $375 $775 POQ $300 $195 $ Lot-Sizing Summary In theory, lot sizes should be recomputed whenever there is a lot size or order quantity change In practice, this results in system nervousness and instability Lot-for-lot should be used when low-cost setups can be achieved 56 28
29 Lot-Sizing Summary Lot sizes can be modified to allow for scrap, process constraints, and purchase lots Use lot-sizing with care as it can cause considerable distortion of requirements at lower levels of the BOM When setup costs are significant and demand is reasonably smooth, POQ or EOQ should give reasonable results 57 Extensions of MRP MRP II Closed-Loop MRP Capacity Planning 58 29
30 Material Requirements Planning II Requirement data can be enriched by other resources Generally called MRP II or Material Resource Planning Outputs can include scrap, packaging waste, effluent, carbon emissions Data used by purchasing, production scheduling, capacity planning, inventory, warehouse management 59 Material Resource Planning TABLE 14.4 Material Resource Planning (MRP II) Weeks LT Computer Labor Hrs:.2 each 20 Machine Hrs:.2 each 20 Scrap: 1 ounce fiberglass each 6.25 lb Payables: $0 each $0 PC Board (1 each) Labor Hrs:.15 each 15 Machine Hrs:.1 each 10 Scrap:.5 ounces copper each lb Payables: raw material at $5 each $500 Processors (5 each) Labor Hrs:.2 each 100 Machine Hrs:.2 each 100 Scrap:.01 ounces of acid waste each lb Payables: processors at $10 each $5,
31 Closed-Loop MRP System Figure 14.7 Aggregate Plan OK? NO Priority Management Capacity Management OK? NO Develop Master Production Schedule OK? YES Prepare Materials Requirements Pan Evaluate Resource Availability (Rough Cut) Determine Capacity Availability Planning OK? YES Detailed Production Activity Control (Shop Scheduling/Dispatching) Implement Input/Output Control Execution (in repetitive systems JIT techniques are used) 61 Capacity Planning Feedback from the MRP system Load reports show resource requirements for work centers Work can be moved between work centers to smooth the load or bring it within capacity 62 31
32 Smoothing Tactics 1. Overlapping Sends part of the work to following operations before the entire lot is complete Reduces lead time 2. Operations splitting Sends the lot to two different machines for the same operation Shorter throughput time but increased setup costs 3. Order or lot splitting Breaking up the order into smaller lots and running part earlier (or later) in the schedule 63 Order Splitting Develop a capacity plan for a work cell at Wiz Products There are 12 hours available each day Each order requires 1 hour Day Orders
33 Order Splitting CAPACITY REQUIRED (HOURS) CAPACITY AVAILABLE (HOURS) UTILIZATION: OVER/ (UNDER) (HOURS) PRODUCTION PLANNER S ACTION NEW PRODUCTION SCHEDULE UNITS DAY ORDERED (2) Split order: move 2 units to day Split order: move one unit to day 6 or request overtime (2) Split order: move 2 units to day Order Splitting Standard labor-hours Figure Capacity exceeded on days 2, 3, and Days (a) Available capacity Standard labor-hours orders moved to day 1 from day 2 (a day early) 1 order forced to overtime or to day 6 2 orders moved to day 4 (a day early) Days (b) 66 33
34 MRP in Services Some services or service items are directly linked to demand for other services These can be treated as dependent demand services or items Restaurants Hospitals Hotels 67 MRP in Services (a) PRODUCT STRUCTURE TREE Figure 14.9 Buffalo Chicken Mac & Cheese Garnish with Buffalo Chicken mix, Blue Cheese, Scallions Baked Buffalo Chicken Mac & Cheese Unbaked Buffalo Chicken Mac & Cheese Buffalo Chicken Mix Buffalo Sauce Smoked Pulled Chicken Blue Cheese Crumbles Cooked Elbow Macaroni Grated Pepper Jack Cheese Chopped Scallions Mac & Cheese Base Milk 68 34
35 (b) BILL OF MATERIALS Production Specifications MRP in Services Buffalo Chicken Mac & Cheese (6 portions) Ingredients Quantity Measure Unit Cost Total Cost Elbow Macaroni (large, uncooked) oz. $ 0.09 $ 1.80 Cheese-Pepper Jack (grated) oz Mac and Cheese Base (from oz refrigerator) Milk 4.00 oz Smoked Pulled Chicken 2.00 lb Buffalo Sauce 8.00 oz Blue Cheese Crumbles 4.00 oz Scallions 2.00 oz Labor Hrs. 0.2 hrs Distribution Resource Planning (DRP) Using dependent demand techniques through the supply chain Expected demand or sales forecasts become gross requirements All other levels are computed DRP pulls inventory through the system Small and frequent replenishments 70 35
36 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) An extension of the MRP system to tie in customers and suppliers 1. Allows automation and integration of many business processes 2. Shares common data bases and business practices 3. Produces information in real time Coordinates business from supplier evaluation to customer invoicing 71 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) ERP modules include Basic MRP Finance Human resources Supply chain management (SCM) Customer relationship management (CRM) Sustainability 72 36
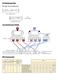
37 Figure ERP and MRP 73 Figure ERP and MRP Customer Relationship Management Invoicing Sales Order (order entry, product configuration, sales management) Shipping Distributors, retailers, and end users 74 37
38 Figure ERP and MRP Master Production Schedule Inventory Management Bills of Material MRP Work Orders Purchasing and Lead Times Table 13.6 Routings and Lead Times 75 Figure ERP and MRP Supply-Chain Management Vendor Communication (schedules, EDI, advanced shipping notice, e-commerce, etc.) 76 38
39 Figure Finance/ Accounting Accounts Receivable ERP and MRP General Ledger Accounts Payable Payroll Table Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) ERP systems have the potential to Reduce transaction costs Increase the speed and accuracy of information Facilitates a strategic emphasis on JIT systems and supply chain integration Can be expensive and time-consuming to install 78 39
40 SAP s ERP Modules Figure ERP in the Service Sector ERP systems have been developed for health care, government, retail stores, hotels, and financial services Also called efficient consumer response (ECR) systems Objective is to tie sales to buying, inventory, logistics, and production 80 40
Net Requirements Plan. The logic of net requirements. MRP Planning Sheet. Gross Requirements Schedule
 Net Requirements Plan The logic of net requirements Gross Requirements Schedule MRP Planning Sheet Safety Stock BOMs, inventory records, purchase and production quantities may not be perfect Consideration
Net Requirements Plan The logic of net requirements Gross Requirements Schedule MRP Planning Sheet Safety Stock BOMs, inventory records, purchase and production quantities may not be perfect Consideration
Manajemen Persediaan. MRP Lot For Lot. Modul ke: Fakultas FEB. Program Studi Manajemen
 Modul ke: 10 Manajemen Persediaan MRP Lot For Lot Fakultas FEB Program Studi Manajemen Learning Objectives Describe the conditions under which MRP is most appropriate. Describe the inputs, outputs, and
Modul ke: 10 Manajemen Persediaan MRP Lot For Lot Fakultas FEB Program Studi Manajemen Learning Objectives Describe the conditions under which MRP is most appropriate. Describe the inputs, outputs, and
7/14/2010. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall.
 15 Resource Planning PowerPoint Slides by Jeff Heyl For Operations Management, 9e by Krajewski/Ritzman/Malhotra 21 Pearson Education 15 1 Resource Planning At the heart of any organization Starts t with
15 Resource Planning PowerPoint Slides by Jeff Heyl For Operations Management, 9e by Krajewski/Ritzman/Malhotra 21 Pearson Education 15 1 Resource Planning At the heart of any organization Starts t with
Chapter 18. Materials Requirements Planning
 1 Chapter 18 Materials Requirements Planning Material Requirements Planning 2 Materials requirements planning (MRP) is a means for determining the number of parts, components, and materials needed to produce
1 Chapter 18 Materials Requirements Planning Material Requirements Planning 2 Materials requirements planning (MRP) is a means for determining the number of parts, components, and materials needed to produce
Chapter 12. Enterprise Resource Planning
 Chapter 12 Enterprise Resource Planning Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Organizes and manages a company s business processes by sharing information across functional areas Connects with supply-chain
Chapter 12 Enterprise Resource Planning Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Organizes and manages a company s business processes by sharing information across functional areas Connects with supply-chain
Chapter 6 RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEMS. Prepared by Mark A. Jacobs, PhD
 Chapter 6 RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEMS Prepared by Mark A. Jacobs, PhD LEARNING OBJECTIVES You should be able to: Describe the hierarchical operations planning process in terms of materials planning (APP,
Chapter 6 RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEMS Prepared by Mark A. Jacobs, PhD LEARNING OBJECTIVES You should be able to: Describe the hierarchical operations planning process in terms of materials planning (APP,
Material Resources Planning
 Operations and Supply Planning PGDM 2018-20 Material Resources Planning Vinay Kumar Kalakbandi Assistant Professor Operations Management 170 Introduction Computerised information system Aids in planning
Operations and Supply Planning PGDM 2018-20 Material Resources Planning Vinay Kumar Kalakbandi Assistant Professor Operations Management 170 Introduction Computerised information system Aids in planning
Enterprise Resource Planning
 Resource Planning Enterprise Resource Planning What Is ERP? Software designed for organizing and managing business processes Modules share information across all business functions Can share customer sales
Resource Planning Enterprise Resource Planning What Is ERP? Software designed for organizing and managing business processes Modules share information across all business functions Can share customer sales
Materials and Resource Requirements Planning
 CHAPTER FIFTEEN Materials and Resource Requirements Planning McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Where We Are Now Relationships Sustainability Globalization
CHAPTER FIFTEEN Materials and Resource Requirements Planning McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Where We Are Now Relationships Sustainability Globalization
Breakdown. Learn the implications of the breakdown field in Item Master Data
 Breakdown Learn the implications of the breakdown field in Item Master Data Boyum Solution IT A/S beas tutorial TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 2 2. Process... 2 2.1. Mode of procurement in beas...
Breakdown Learn the implications of the breakdown field in Item Master Data Boyum Solution IT A/S beas tutorial TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 2 2. Process... 2 2.1. Mode of procurement in beas...
What is ERP? Source: Wikipedia
 Brad Staats What is ERP? Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems integrate internal and external management information across an entire organization. The purpose of ERP is to facilitate the flow of
Brad Staats What is ERP? Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems integrate internal and external management information across an entire organization. The purpose of ERP is to facilitate the flow of
Operation Management QUESTION BANK
 1. Explain forecasting methods 2. Explain classification of inventory Operation Management QUESTION BANK 3. Calculate a and b constants for the given no of births in previous years and cycles so Year 1
1. Explain forecasting methods 2. Explain classification of inventory Operation Management QUESTION BANK 3. Calculate a and b constants for the given no of births in previous years and cycles so Year 1
MPR Sample Test. CPIM(Certified In Production & Inventory Management) - 1 -
 CPIM(Certified In Production & Inventory Management) MPR Sample Test. 1. Which of the following would NOT be a key operating objective? A. Inventory dollars. B. Shipment dollars. C. Factory location selection.
CPIM(Certified In Production & Inventory Management) MPR Sample Test. 1. Which of the following would NOT be a key operating objective? A. Inventory dollars. B. Shipment dollars. C. Factory location selection.
History IE 376 PRODUCTION INFORMATION SYSTEMS. Course Notes Lecture #2.A Material Requirements Planning
 IE PRODUCTION INFORMATION SYSTEMS Course Notes Lecture #.A Material Requirements Planning IE Bilkent University Manufacturing Planning and Control System Routing file Resource planning Bills of material
IE PRODUCTION INFORMATION SYSTEMS Course Notes Lecture #.A Material Requirements Planning IE Bilkent University Manufacturing Planning and Control System Routing file Resource planning Bills of material
Material Requirements Planning (MRP), chap 15
 Material Requirements Planning (MRP), chap 15 Chapter 15: Learning Outcomes When you complete this chapter you should be able to: 1. Develop a product structure 2. Build a gross requirements plan 3. Build
Material Requirements Planning (MRP), chap 15 Chapter 15: Learning Outcomes When you complete this chapter you should be able to: 1. Develop a product structure 2. Build a gross requirements plan 3. Build
Priority for MRP. Run MRP based on actual orders, forecasts or static requirements. Run MRP simulations until you re satisfied with the plans
 WHY CHOOSE PRIORITY? WORLD S MOST CONFIGURABLE ERP tailor fields, screens, menus, reports, stationery drag and drop workflows business rules, automated data entry, automated repetitive tasks Priority for
WHY CHOOSE PRIORITY? WORLD S MOST CONFIGURABLE ERP tailor fields, screens, menus, reports, stationery drag and drop workflows business rules, automated data entry, automated repetitive tasks Priority for
KEY ISSUES in Advanced Operations Management. Timo Seppälä
 KEY ISSUES in Advanced Operations Management Timo Seppälä Production as a value creation process Operations system forms the transformation process between the inputs and the outputs of a manufacturing
KEY ISSUES in Advanced Operations Management Timo Seppälä Production as a value creation process Operations system forms the transformation process between the inputs and the outputs of a manufacturing
Resources Planning. Introduction
 Operations Management - II PGDM 2017-19 Resources Planning Vinay Kumar Kalakbandi Assistant Professor Operations Management Survey No. 38, Cherlaguda Village, Shamshabad Mandal, RR District, Hyderabad-
Operations Management - II PGDM 2017-19 Resources Planning Vinay Kumar Kalakbandi Assistant Professor Operations Management Survey No. 38, Cherlaguda Village, Shamshabad Mandal, RR District, Hyderabad-
MANUFACTURING RESOURCE PLANNING AND ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEMS: AN OVERVIEW
 MANUFACTURING RESOURCE PLANNING AND ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEMS: AN OVERVIEW Al-Naimi Assistant Professor Industrial Engineering Branch Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy University
MANUFACTURING RESOURCE PLANNING AND ENTERPRISE RESOURCE PLANNING SYSTEMS: AN OVERVIEW Al-Naimi Assistant Professor Industrial Engineering Branch Department of Production Engineering and Metallurgy University
Chapter 6 Resource Planning Systems
 Chapter 6 Resource Planning Systems TRUE/FALSE 1. The resource and operations planning done by operations managers is intended to balance capacity and output. 2. MRP is the production planning system intended
Chapter 6 Resource Planning Systems TRUE/FALSE 1. The resource and operations planning done by operations managers is intended to balance capacity and output. 2. MRP is the production planning system intended
Subbu Ramakrishnan. Manufacturing Finance with SAP. ERP Financials. Bonn Boston
 Subbu Ramakrishnan Manufacturing Finance with SAP ERP Financials Bonn Boston Contents at a Glance 1 Overview of Manufacturing Scenarios Supported by SAP... 25 2 Overview of Finance Activities in a Make-to-Stock
Subbu Ramakrishnan Manufacturing Finance with SAP ERP Financials Bonn Boston Contents at a Glance 1 Overview of Manufacturing Scenarios Supported by SAP... 25 2 Overview of Finance Activities in a Make-to-Stock
Note 8: Materials Requirements Planning
 Note 8: Materials Requirements Planning In materials requirements planning (MRP), orders for component parts are timed to coincide with the production schedule of the products in which they are used. We
Note 8: Materials Requirements Planning In materials requirements planning (MRP), orders for component parts are timed to coincide with the production schedule of the products in which they are used. We
Introduction Manufacturing Data Management
 Introduction Data Data ERP LX Product Integration CAP Rough Cut CAP MRP Detail Finite Forward Scheduling Daily Work Center Available Daily Work Center Available Daily Work Center Available INV Inventory
Introduction Data Data ERP LX Product Integration CAP Rough Cut CAP MRP Detail Finite Forward Scheduling Daily Work Center Available Daily Work Center Available Daily Work Center Available INV Inventory
9. What are the activities within the scope of production planning? 1. Aggregate production planning
 UNIT-II PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL AND COMPUTERISED PROCESS PLANNING 1. Define Process Planning Process planning involves determining the sequence of processing and assembly steps that must be accomplished
UNIT-II PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL AND COMPUTERISED PROCESS PLANNING 1. Define Process Planning Process planning involves determining the sequence of processing and assembly steps that must be accomplished
WHITE PAPER. Control Manufacturing Costs with Odoo Open ERP
 WHITE PAPER Control Manufacturing Costs with Odoo Open ERP USA ODOO WHITE PAPER 1 The challenge of controlling costs looms large in many manufacturing sectors but clearing this hurdle is not insurmountable.
WHITE PAPER Control Manufacturing Costs with Odoo Open ERP USA ODOO WHITE PAPER 1 The challenge of controlling costs looms large in many manufacturing sectors but clearing this hurdle is not insurmountable.
Management Information Systems, Sixth Edition. Chapter 3: Business Functions and Supply Chains
 Management Information Systems, Sixth Edition Chapter 3: Business Functions and Supply Chains Objectives Identify various business functions and the role of ISs in these functions Explain how ISs in the
Management Information Systems, Sixth Edition Chapter 3: Business Functions and Supply Chains Objectives Identify various business functions and the role of ISs in these functions Explain how ISs in the
MASTER PRODUCTION SCHEDULE (MPS)
 MASTER PRODUCTION SCHEDULE (MPS) Anticipated build schedule for manufacturing end products (or product options) A statement of production, not a statement of market demand MPS takes into account capacity
MASTER PRODUCTION SCHEDULE (MPS) Anticipated build schedule for manufacturing end products (or product options) A statement of production, not a statement of market demand MPS takes into account capacity
What is MRP (I, II, III) 1. MRP-I
 What is MRP (I, II, III) 1. MRP-I Introduction: Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a software based production planning and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. Although
What is MRP (I, II, III) 1. MRP-I Introduction: Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a software based production planning and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. Although
UNIT II PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL AND COMPUTERISED PROCESS PLANNING
 UNIT II PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL AND COMPUTERISED PROCESS PLANNING 2 Process Planning Product design for each product has been developed in the design department. To convert the product design into
UNIT II PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL AND COMPUTERISED PROCESS PLANNING 2 Process Planning Product design for each product has been developed in the design department. To convert the product design into
 PRODUCTION PLANNING ANDCONTROL AND COMPUTER AIDED PRODUCTION PLANNING Production is a process whereby raw material is converted into semi-finished products and thereby adds to the value of utility of products,
PRODUCTION PLANNING ANDCONTROL AND COMPUTER AIDED PRODUCTION PLANNING Production is a process whereby raw material is converted into semi-finished products and thereby adds to the value of utility of products,
APICS PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT TOPIC OUTLINE CONCEPTS AND APPLICATIONS
 APICS PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT TOPIC OUTLINE CONCEPTS AND APPLICATIONS About this Topic Outline This outline details the concepts and applications coved in all five of the APICS Principles of
APICS PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT TOPIC OUTLINE CONCEPTS AND APPLICATIONS About this Topic Outline This outline details the concepts and applications coved in all five of the APICS Principles of
LOT SIZING IN MRP. Week Gross requirements Scheduled receipts Projected available balance Net Requirements
 LOT SIZING IN MRP The net data is subjected lot sizing Lot sizes developed can satisfy the net for one or more weeks The basic trade-off involves the elimination of one or more setups at the expense of
LOT SIZING IN MRP The net data is subjected lot sizing Lot sizes developed can satisfy the net for one or more weeks The basic trade-off involves the elimination of one or more setups at the expense of
CP-81 The best waze to get to destination MRP! Paul Whiteman Lexell Blue Susan Pucciano Lexell Blue
 CP-81 The best waze to get to destination MRP! Paul Whiteman Lexell Blue Susan Pucciano Lexell Blue Agenda Introductions Manufacturing Maturity and MRP Roadmap System Configuration and Master Data Setup
CP-81 The best waze to get to destination MRP! Paul Whiteman Lexell Blue Susan Pucciano Lexell Blue Agenda Introductions Manufacturing Maturity and MRP Roadmap System Configuration and Master Data Setup
One Software to manage your entire bakery business.
 One Software to manage your entire bakery business. Why choose ibake ERP : ibake ERP is an enterprise-class ERP solution for bakeries that manages POS, front office, manufacturing, warehouse, inventory
One Software to manage your entire bakery business. Why choose ibake ERP : ibake ERP is an enterprise-class ERP solution for bakeries that manages POS, front office, manufacturing, warehouse, inventory
Yuji Yamamoto PPU411. Today s topic. What is MPS and MRP Developing MPS How to make MRP Enterprise Resource Planning Kanban system
 Yuji Yamamoto PPU411 Today s topic What is MPS and MRP Developing MPS How to make MRP Enterprise Resource Planning Kanban system 1 Production planning and scheduling Demand Production planning 1,400pcs/m
Yuji Yamamoto PPU411 Today s topic What is MPS and MRP Developing MPS How to make MRP Enterprise Resource Planning Kanban system 1 Production planning and scheduling Demand Production planning 1,400pcs/m
Enterprise Information Systems
 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: Kerry Augustine Enterprise Information Systems Lecture Outline 6 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Learning Objectives 1. Explain how
ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: Kerry Augustine Enterprise Information Systems Lecture Outline 6 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Learning Objectives 1. Explain how
12/02/2018. Enterprise Information Systems. Learning Objectives. System Category Enterprise Systems. ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems
 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: Kerry Augustine Enterprise Information Systems Lecture Outline 6 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Learning Objectives 1. Explain how
ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: Kerry Augustine Enterprise Information Systems Lecture Outline 6 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Learning Objectives 1. Explain how
Enterprise Information Systems
 Instructor: Kevin Robertson Enterprise Information Systems Lecture Outline 6/7 Learning Objectives 1. Explain how organizations support business activities by using information technologies across the
Instructor: Kevin Robertson Enterprise Information Systems Lecture Outline 6/7 Learning Objectives 1. Explain how organizations support business activities by using information technologies across the
Infor ERP LN 6.1 Enterprise Planning. User's Guide for Order Planning
 Infor ERP LN 6.1 Enterprise Planning User's Guide for Order Planning Copyright 2008 Infor All rights reserved. The word and design marks set forth herein are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of
Infor ERP LN 6.1 Enterprise Planning User's Guide for Order Planning Copyright 2008 Infor All rights reserved. The word and design marks set forth herein are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of
CRC Press Taylor &. Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an Informa business
 Basics of Supply Chain Management Jayanta Kumar Bandyopadhyay CRC Press Taylor &. Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an Informa business Contents
Basics of Supply Chain Management Jayanta Kumar Bandyopadhyay CRC Press Taylor &. Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an Informa business Contents
Introduction to Production Planning
 Introduction to Production Planning Production Planning: what does it deal with? 2 The Production Manager question is: WHAT ( which product ), WHEN ( considered some time horizon ), HOW ( with which materials
Introduction to Production Planning Production Planning: what does it deal with? 2 The Production Manager question is: WHAT ( which product ), WHEN ( considered some time horizon ), HOW ( with which materials
GBI - Introductory Course 6/11/2015
 SAP University Alliances Version 2.11 Authors Bret Wagner Stefan Weidner Production Planning and Execution (PP) Product 6.0 EhP4 Global Bike Inc. Level Beginner Focus Cross-functional integration Production
SAP University Alliances Version 2.11 Authors Bret Wagner Stefan Weidner Production Planning and Execution (PP) Product 6.0 EhP4 Global Bike Inc. Level Beginner Focus Cross-functional integration Production
Hybrid Manufacturing Methods
 Hybrid Manufacturing Methods The following manufacturing execution and costing methods are supported in SyteLine. These methods can be combined in a single environment so that the optimal method is used
Hybrid Manufacturing Methods The following manufacturing execution and costing methods are supported in SyteLine. These methods can be combined in a single environment so that the optimal method is used
Materials Requirements Planning
 Materials Requirements Planning Independent and Dependent Demand Independent Demand A Dependent Demand B(4) C(2) D(2) E(1) D(3) F(2) Independent demand is uncertain. Dependent demand is certain. Dependent
Materials Requirements Planning Independent and Dependent Demand Independent Demand A Dependent Demand B(4) C(2) D(2) E(1) D(3) F(2) Independent demand is uncertain. Dependent demand is certain. Dependent
Which of the following are subareas of the People Integration subcomponent of SAP NetWeaver?
 SAP EDUCATION SAMPLE QUESTIONS: C_TERP10_60 SAP Certified Business Associate with SAP ERP 6.0 print view Disclaimer: These sample questions are for self-evaluation purposes only and do not appear on the
SAP EDUCATION SAMPLE QUESTIONS: C_TERP10_60 SAP Certified Business Associate with SAP ERP 6.0 print view Disclaimer: These sample questions are for self-evaluation purposes only and do not appear on the
Chapter 2 Enterprise Systems
 Chapter 2 Enterprise Systems TRUE/FALSE 1. One of the primary goals of implementing an ERP system is to standardize systems across multiple locations and multiple divisions. T 2. Submitting a purchase
Chapter 2 Enterprise Systems TRUE/FALSE 1. One of the primary goals of implementing an ERP system is to standardize systems across multiple locations and multiple divisions. T 2. Submitting a purchase
Planning. Planning Horizon. Stages of Planning. Dr. Richard Jerz
 Planning Dr. Richard Jerz 1 Planning Horizon Aggregate planning: Intermediate-range capacity planning, usually covering 2 to 12 months. Long range Short range Intermediate range Now 2 months 1 Year 2 Stages
Planning Dr. Richard Jerz 1 Planning Horizon Aggregate planning: Intermediate-range capacity planning, usually covering 2 to 12 months. Long range Short range Intermediate range Now 2 months 1 Year 2 Stages
What can Visual Planner do for you Rick Worley TriMin Systems April 2016
 What can Visual Planner do for you Rick Worley TriMin Systems April 2016 Infor Planning Tools MRP Traditional Materials Planning in Batch Mode Requires support from CRP Visual Planner Advanced Material
What can Visual Planner do for you Rick Worley TriMin Systems April 2016 Infor Planning Tools MRP Traditional Materials Planning in Batch Mode Requires support from CRP Visual Planner Advanced Material
DIGITAL INDUSTRY INNOVATION MAPS INDUSTRIAL MACHINERY & COMPONENTS. Digital Transformation Posters. Digital Industry Innovation Maps
 SAP LEONARDO INNOVATON SERVICE SHOWROOM DIGITAL INDUSTRY INNOVATION MAPS INDUSTRIAL MACHINERY & COMPONENTS Digital Transformation Posters Summarize your digital transformation with S/4HANA on one page
SAP LEONARDO INNOVATON SERVICE SHOWROOM DIGITAL INDUSTRY INNOVATION MAPS INDUSTRIAL MACHINERY & COMPONENTS Digital Transformation Posters Summarize your digital transformation with S/4HANA on one page
PLANNING FOR PRODUCTION
 PLANNING FOR PRODUCTION Forecasting Forecasting is the first major activity in the planning, involving careful study of past data and present scenario to estimate the occurence, timing or magnitude of
PLANNING FOR PRODUCTION Forecasting Forecasting is the first major activity in the planning, involving careful study of past data and present scenario to estimate the occurence, timing or magnitude of
Optimizing Reverse Logistics with SAP
 Srivathsan Narayanan Optimizing Reverse Logistics with SAP ERP Bonn Boston Contents Preface... 11 Introduction... 15 1 Reverse Logistics... 17 1.1 Definition of Reverse Logistics... 17 1.2 Business Processes
Srivathsan Narayanan Optimizing Reverse Logistics with SAP ERP Bonn Boston Contents Preface... 11 Introduction... 15 1 Reverse Logistics... 17 1.1 Definition of Reverse Logistics... 17 1.2 Business Processes
Infor LN Enterprise Planning User Guide for Order Planning
 Infor LN Enterprise Planning User Guide for Order Planning Copyright 2018 Infor Important Notices The material contained in this publication (including any supplementary information) constitutes and contains
Infor LN Enterprise Planning User Guide for Order Planning Copyright 2018 Infor Important Notices The material contained in this publication (including any supplementary information) constitutes and contains
Microsoft Business Solutions-Axapta Production enables you to flexibly manage your manufacturing processes for increased profitability.
 Microsoft Business Solutions Axapta Production gives you real-time insight into your manufacturing processes to help you increase production efficiency and reduce costs. Key Benefits: Minimize lead times
Microsoft Business Solutions Axapta Production gives you real-time insight into your manufacturing processes to help you increase production efficiency and reduce costs. Key Benefits: Minimize lead times
Planning. Dr. Richard Jerz rjerz.com
 Planning Dr. Richard Jerz 1 Planning Horizon Aggregate planning: Intermediate range capacity planning, usually covering 2 to 12 months. Long range Short range Intermediate range Now 2 months 1 Year 2 Stages
Planning Dr. Richard Jerz 1 Planning Horizon Aggregate planning: Intermediate range capacity planning, usually covering 2 to 12 months. Long range Short range Intermediate range Now 2 months 1 Year 2 Stages
Requirements Planning Implementation Guide Release 9.2
 [1]JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Applications Requirements Planning Implementation Guide Release 9.2 E63942-04 April 2018 Describes how to set up and use JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Requirements Planning to create
[1]JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Applications Requirements Planning Implementation Guide Release 9.2 E63942-04 April 2018 Describes how to set up and use JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Requirements Planning to create
Principles of Production & Inventory Management PPIM
 Principles of Production & Inventory Management PPIM PPIM course sessions. 1. Manufacturing Strategies & Resource Management 2. Product Development Cycle 3. Forecasting and Forecasting Techniques 4. Production
Principles of Production & Inventory Management PPIM PPIM course sessions. 1. Manufacturing Strategies & Resource Management 2. Product Development Cycle 3. Forecasting and Forecasting Techniques 4. Production
APACHE V4 is the ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) solution for industrial companies
 APACHE V4 is the ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) solution for industrial companies It's an integrated and modular software that provides management tools to the operational areas of a manufacturing
APACHE V4 is the ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) solution for industrial companies It's an integrated and modular software that provides management tools to the operational areas of a manufacturing
Planning. Planning Horizon. Stages of Planning. Dr. Richard Jerz
 Planning Dr. Richard Jerz 1 Planning Horizon Aggregate planning: Intermediate range capacity planning, usually covering 2 to 12 months. Long range Short range Intermediate range Now 2 months 1 Year 2 Stages
Planning Dr. Richard Jerz 1 Planning Horizon Aggregate planning: Intermediate range capacity planning, usually covering 2 to 12 months. Long range Short range Intermediate range Now 2 months 1 Year 2 Stages
Material available on web at
 Material available on web at http://gtumcain.wordpress.com Major topics Modules of ERP Human Resources Management Financial Management Inventory Management Quality Management Sales and Distribution (Murlidhar
Material available on web at http://gtumcain.wordpress.com Major topics Modules of ERP Human Resources Management Financial Management Inventory Management Quality Management Sales and Distribution (Murlidhar
Customizing Materials Management Processes in SAP. ERP Operations
 Akash Agrawal Customizing Materials Management Processes in SAP ERP Operations Bonn Boston Contents at a Glance 1 Introduction... 21 2 SAP Organizational Structure... 33 3 Master Data... 55 4 Procurement
Akash Agrawal Customizing Materials Management Processes in SAP ERP Operations Bonn Boston Contents at a Glance 1 Introduction... 21 2 SAP Organizational Structure... 33 3 Master Data... 55 4 Procurement
Operation Management (OM) Introduction
 Operation Management (OM) Introduction Ing.J.Skorkovský, CSc, Department of Corporate Economy FACULTY OF ECONOMICS AND ADMINISTRATION Masaryk University Brno Czech Republic What is going on? Use of Operations
Operation Management (OM) Introduction Ing.J.Skorkovský, CSc, Department of Corporate Economy FACULTY OF ECONOMICS AND ADMINISTRATION Masaryk University Brno Czech Republic What is going on? Use of Operations
Cost Accounting. Unbeaten Path. BPCS S Systems Logic for Calculating Routing Costs CST Unbeaten Path International Ltd.
 Cost Accounting BPCS S Systems Logic for Calculating Routing Costs Unbeaten Path CST.12 CST.13 ❶ ❷ ❸ ❹ ❺ ❻ ❼ For a given item, the system goes to the Routing file to determine the Workcenter number. At
Cost Accounting BPCS S Systems Logic for Calculating Routing Costs Unbeaten Path CST.12 CST.13 ❶ ❷ ❸ ❹ ❺ ❻ ❼ For a given item, the system goes to the Routing file to determine the Workcenter number. At
Introduction. Introduction. Introduction LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 Valua%on and pricing (November 5, 2013) LEARNING OBJECTIVES Lecture 9 Control 1. Understand the importance of inventory control and ABC analysis. 2. Use the economic order quantity (EOQ) to determine how
Valua%on and pricing (November 5, 2013) LEARNING OBJECTIVES Lecture 9 Control 1. Understand the importance of inventory control and ABC analysis. 2. Use the economic order quantity (EOQ) to determine how
QMRP Base System. Highlights:
 The QMRP Base System consists of the menu and security systems, inventory control, product structure processing, product costing, and manufacturing order processing. Additional functionality is provided
The QMRP Base System consists of the menu and security systems, inventory control, product structure processing, product costing, and manufacturing order processing. Additional functionality is provided
Test-king.C_TSCM42_65.80 Questions
 Test-king.C_TSCM42_65.80 Questions Number: C_TSCM42_65 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 4.9 http://www.gratisexam.com/ C_TSCM42_65 SAP Certified Application Associate - Production -
Test-king.C_TSCM42_65.80 Questions Number: C_TSCM42_65 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 4.9 http://www.gratisexam.com/ C_TSCM42_65 SAP Certified Application Associate - Production -
Production Management and Scheduling
 Production Management and Scheduling Meet Your Due Dates Your production process can be simple or complex, time consuming or quick, but one thing remains constant the drive to meet your customer s delivery
Production Management and Scheduling Meet Your Due Dates Your production process can be simple or complex, time consuming or quick, but one thing remains constant the drive to meet your customer s delivery
Chapter 9 ACHIEVING OPERATIONAL EXCELLENCE AND CUSTOMER INTIMACY: ENTERPRISE APPLICATIONS. 14-Dec-15. Enterprise Systems
 MANAGING THE DIGITAL FIRM, 12 TH EDITION Learning Objectives Chapter 9 ACHIEVING OPERATIONAL EXCELLENCE AND CUSTOMER INTIMACY: ENTERPRISE APPLICATIONS VIDEO CASES Case 1: Sinosteel Strengthens Business
MANAGING THE DIGITAL FIRM, 12 TH EDITION Learning Objectives Chapter 9 ACHIEVING OPERATIONAL EXCELLENCE AND CUSTOMER INTIMACY: ENTERPRISE APPLICATIONS VIDEO CASES Case 1: Sinosteel Strengthens Business
INFORMATION SYSTEMS IN THE ENTERPRISE
 Chapter 2 INFORMATION SYSTEMS IN THE ENTERPRISE 2.1 2003 by Prentice Hall OBJECTIVES What are the key system applications in a business? What role do they play? How do information systems support the major
Chapter 2 INFORMATION SYSTEMS IN THE ENTERPRISE 2.1 2003 by Prentice Hall OBJECTIVES What are the key system applications in a business? What role do they play? How do information systems support the major
Custom Manufacturing Guide DBA Software Inc.
 Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Why You Need Custom Manufacturing 5 3 Total Control Workflow 8 4 Custom Manufacturing Sequence of Events 10 5 Advance Setup - Standard Processes 12 6 Advance
Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Why You Need Custom Manufacturing 5 3 Total Control Workflow 8 4 Custom Manufacturing Sequence of Events 10 5 Advance Setup - Standard Processes 12 6 Advance
Exact Macola Distribution Pro. Transform your business into an automated, high-yield, efficient operation
 Exact Macola Distribution Pro Transform your business into an automated, high-yield, efficient operation Macola Distribution Pro makes it easy to get started and is cost effective to implement Macola Distribution
Exact Macola Distribution Pro Transform your business into an automated, high-yield, efficient operation Macola Distribution Pro makes it easy to get started and is cost effective to implement Macola Distribution
Index. Dell Computer Corporation, 247 direct sales model, 248 Internet, incorporation of, 247 Demand collaboration,
 I Index A Action plan and execution, 212 labor force, 212 monitoring, 212 project owner, appointment of, 212 purchase order placing, 212 selection of partners, 212 selection of sites, 212 staff, appointment
I Index A Action plan and execution, 212 labor force, 212 monitoring, 212 project owner, appointment of, 212 purchase order placing, 212 selection of partners, 212 selection of sites, 212 staff, appointment
Functional Area Systems Production / Operation Systems
 Functional Area Systems Production / Operation Systems Lecture Outline 5 Part 4 Instructor: Trevor Nadeau Examples: Functional Area Info Systems 2 Functional Area Information Systems 3 Computers in Manufacturing
Functional Area Systems Production / Operation Systems Lecture Outline 5 Part 4 Instructor: Trevor Nadeau Examples: Functional Area Info Systems 2 Functional Area Information Systems 3 Computers in Manufacturing
TU-E2020 ADVANCED OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT. Master Production Scheduling Material Requirements Planning
 TU-E2020 ADVANCED OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Master Production Scheduling Material Requirements Planning Schedule for classes 26.10 Introduction to the Course / TS 27.10 Different models of Planning for Production
TU-E2020 ADVANCED OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Master Production Scheduling Material Requirements Planning Schedule for classes 26.10 Introduction to the Course / TS 27.10 Different models of Planning for Production
2 Recently, there has been a decline in the interest in operations management.
 1 Historically in most manufacturing organizations, operations was viewed as an internal function that is buffered from the external environment. ) True ) False 2 Recently, there has been a decline in
1 Historically in most manufacturing organizations, operations was viewed as an internal function that is buffered from the external environment. ) True ) False 2 Recently, there has been a decline in
A typical manufacturing plant
 CHAPTER6: PRODUCTION PLANNING & CONTROL Production planning is concerned with the determination of production, inventory, and work force levels to meet fluctuating demand A typical manufacturing plant
CHAPTER6: PRODUCTION PLANNING & CONTROL Production planning is concerned with the determination of production, inventory, and work force levels to meet fluctuating demand A typical manufacturing plant
Oman College of Management and Technology
 Oman College of Management and Technology Course 803303 PIS Chapter 7 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) CS/MIS Department What is MRP? (Material Requirements Planning) Is a basic tool for performing
Oman College of Management and Technology Course 803303 PIS Chapter 7 Material Requirements Planning (MRP) CS/MIS Department What is MRP? (Material Requirements Planning) Is a basic tool for performing
Exact Macola Manufacturing Pro. Deliver continuous process improvement and increase profitability in every area of your business
 Exact Macola Manufacturing Pro Deliver continuous process improvement and increase profitability in every area of your business Macola Manufacturing Pro lowers the total cost of ownership for serious manufacturing
Exact Macola Manufacturing Pro Deliver continuous process improvement and increase profitability in every area of your business Macola Manufacturing Pro lowers the total cost of ownership for serious manufacturing
Lot-Sizing in MRP. Lot Sizing in MRP IE 376 PRODUCTION INFORMATION SYSTEMS. Course Notes Lecture #3 Lot sizing in MRP Systems
 PRODUCTION INFORMATION SYSTEMS Course Notes Lecture #3 Lot sizing in MRP Systems Bilkent University Lot-Sizing in MRP Lot-size is the quantity ordered/produced at one time Large lots are preferred because:
PRODUCTION INFORMATION SYSTEMS Course Notes Lecture #3 Lot sizing in MRP Systems Bilkent University Lot-Sizing in MRP Lot-size is the quantity ordered/produced at one time Large lots are preferred because:
AUTOSIMPLY. Manufacturing Order. Features. About AutoSimply
 AUTOSIMPLY Manufacturing Order About AutoSimply Autosimply is a Sage Developer Partner since 2004. Founded by a group of ACCPAC consultants with over 10 years project experience, we know and understand
AUTOSIMPLY Manufacturing Order About AutoSimply Autosimply is a Sage Developer Partner since 2004. Founded by a group of ACCPAC consultants with over 10 years project experience, we know and understand
02/10/2016. Functional Area Systems Production / Operation Systems. Examples: Functional Area Info Systems. Functional Area Information Systems
 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: Kerry Augustine Functional Area Systems Production / Operation Systems Lecture Outline 5, Part 4 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Examples:
ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: Kerry Augustine Functional Area Systems Production / Operation Systems Lecture Outline 5, Part 4 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Examples:
Notes for Production and Operations Management- I
 Notes for Production and Operations Management- I Factors affecting Process Design Decisions Nature of product/service demand Degree of vertical integration Production Flexibility Degree of automation
Notes for Production and Operations Management- I Factors affecting Process Design Decisions Nature of product/service demand Degree of vertical integration Production Flexibility Degree of automation
Supply Chain Systems II: Supply Chain Modules
 Supply Chain Systems II: Supply Chain Modules ctl.mit.edu Evolution of Supply Chain Tools 1960-1970 s IBM developed a Bill of Materials Processor (BOMP) Mainframe based database systems mainly to track
Supply Chain Systems II: Supply Chain Modules ctl.mit.edu Evolution of Supply Chain Tools 1960-1970 s IBM developed a Bill of Materials Processor (BOMP) Mainframe based database systems mainly to track
SAP Material Master A Practical Guide. Matthew Johnson
 SAP Material Master A Practical Guide Matthew Johnson TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents Preface 7 1 Introduction 11 2 Material Master Basics 17 2.1 Material master structure 17 2.2 Creating and accessing
SAP Material Master A Practical Guide Matthew Johnson TABLE OF CONTENTS Table of Contents Preface 7 1 Introduction 11 2 Material Master Basics 17 2.1 Material master structure 17 2.2 Creating and accessing
Progressus PSA: Capabilities That Drive Your People to Perform
 Progressus PSA: Capabilities That Drive Your People to Perform It s All About the People Progressus PSA is people-centric, cloud power for emerging professional services firms and project-based businesses
Progressus PSA: Capabilities That Drive Your People to Perform It s All About the People Progressus PSA is people-centric, cloud power for emerging professional services firms and project-based businesses
2. Define e-buisness. Explain with a neat sketch the transaction processing cycle in detail.
 1. With the help of neat figure, explain the enterprise application architecture illustrating the major cross functional enterprise application and their interrelationships. 2. Define e-buisness. Explain
1. With the help of neat figure, explain the enterprise application architecture illustrating the major cross functional enterprise application and their interrelationships. 2. Define e-buisness. Explain
" gain cost-effective control and flexibility.
 SSA enterprise resource planning > SSA PRMS " gain cost-effective control and flexibility. How can you prevail as a manufacturer? To prevail in today s tough economic environment, manufacturing companies
SSA enterprise resource planning > SSA PRMS " gain cost-effective control and flexibility. How can you prevail as a manufacturer? To prevail in today s tough economic environment, manufacturing companies
FEATURES IN TRIMIT FURNITURE BASED ON BUSINESS CENTRAL
 FEATURES IN TRIMIT FURNITURE BASED ON BUSINESS CENTRAL Date: 14-12-2018 This document provides an overview of the most important features available in TRIMIT Furniture based on Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business
FEATURES IN TRIMIT FURNITURE BASED ON BUSINESS CENTRAL Date: 14-12-2018 This document provides an overview of the most important features available in TRIMIT Furniture based on Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business
Supply Chain. Planning. Answer Essential Questions. For Your Business Quickly and Easily
 Maximum Per formance Answer Essential Questions For Your Business Quickly and Easily This module enhances Microsoft Dynamics SL with advanced replenishment methods focusing on planning the supply chain.
Maximum Per formance Answer Essential Questions For Your Business Quickly and Easily This module enhances Microsoft Dynamics SL with advanced replenishment methods focusing on planning the supply chain.
Contents Introduction to Logistics... 6
 CONTENTS Contents... 3 1. Introduction to Logistics... 6 1.1 Interfaces between Logistics Manufacturing....7 1.2 Logistics: Manufacturing issues in Customer Service...9 I.3 Production scheduling...10 1.4
CONTENTS Contents... 3 1. Introduction to Logistics... 6 1.1 Interfaces between Logistics Manufacturing....7 1.2 Logistics: Manufacturing issues in Customer Service...9 I.3 Production scheduling...10 1.4
FEATURES IN TRIMIT FURNITURE 2017
 FEATURES IN TRIMIT FURNITURE 2017 This document provides an overview of the most important features available in TRIMIT Furniture, as they are available in version 2017 of December 2016. The purpose of
FEATURES IN TRIMIT FURNITURE 2017 This document provides an overview of the most important features available in TRIMIT Furniture, as they are available in version 2017 of December 2016. The purpose of
Glossary for Sales and Operations Planning, Sales Forecasting and Master Scheduling
 Glossary for Sales and Operations Planning, Sales Forecasting and Master Scheduling Definitions are from books on these subjects by Tom Wallace and Bob Stahl ABC Classification The grouping of items based
Glossary for Sales and Operations Planning, Sales Forecasting and Master Scheduling Definitions are from books on these subjects by Tom Wallace and Bob Stahl ABC Classification The grouping of items based
Introduction to ERP. Shital H. More
 Introduction to ERP Introduction:- ERP is an abbreviation for Enterprise Resource Planning It is the techniques and concepts for integrated management resources to improve the efficiency of enterprise
Introduction to ERP Introduction:- ERP is an abbreviation for Enterprise Resource Planning It is the techniques and concepts for integrated management resources to improve the efficiency of enterprise
Outline. Push-Pull Systems Global Company Profile: Toyota Motor Corporation Just-in-Time, the Toyota Production System, and Lean Operations
 JIT and Lean Operations Outline Push-Pull Systems Global Company Profile: Toyota Motor Corporation Just-in-Time, the Toyota Production System, and Lean Operations Eliminate Waste Remove Variability Improve
JIT and Lean Operations Outline Push-Pull Systems Global Company Profile: Toyota Motor Corporation Just-in-Time, the Toyota Production System, and Lean Operations Eliminate Waste Remove Variability Improve
Best Practices in Demand and Inventory Planning
 W H I T E P A P E R Best Practices in Demand and Inventory Planning for Chemical Companies Executive Summary In support of its present and future customers, CDC Software sponsored this white paper to help
W H I T E P A P E R Best Practices in Demand and Inventory Planning for Chemical Companies Executive Summary In support of its present and future customers, CDC Software sponsored this white paper to help
Manufacturing Functionlity in Microsoft Dynamics GP. Gain complete control over your inventory, production and orders.
 Manufacturing Functionlity in Microsoft Dynamics GP Gain complete control over your inventory, production and orders. Control your Inventory Costing and Inventory Control Are you confident and in control
Manufacturing Functionlity in Microsoft Dynamics GP Gain complete control over your inventory, production and orders. Control your Inventory Costing and Inventory Control Are you confident and in control
What s New in PBS v12.04 by Module
 What s New in PBS v12.04 by Module System-wide Features Check Reconciliation Order Entry Manufacturing Accounts Payable General Ledger Purchase Order Data Import Manager Accounts Receivable Inventory Control
What s New in PBS v12.04 by Module System-wide Features Check Reconciliation Order Entry Manufacturing Accounts Payable General Ledger Purchase Order Data Import Manager Accounts Receivable Inventory Control
120 Eagle Rock Ave, Suite 330 East Hanover, NJ Phone: Fax:
 120 Eagle Rock Ave, Suite 330 East Hanover, NJ 07936 Phone: 866.627.2362 Fax: 973.758.6120 www.mapadoc.com Contents About MAPADOC... 3 Features... 5 Intuitive and Easy to Use... 5 Flexible and Customizable...
120 Eagle Rock Ave, Suite 330 East Hanover, NJ 07936 Phone: 866.627.2362 Fax: 973.758.6120 www.mapadoc.com Contents About MAPADOC... 3 Features... 5 Intuitive and Easy to Use... 5 Flexible and Customizable...
A Comparison between SAP B1 & Tally ERP
 A Comparison between SAP B1 & Tally ERP Functionalities SAP B1 Tally ERP Business Masters (Customers, Suppliers) with Multiple Bill To & Ship To Addresses Item Masters with Multiple UOM definition, UOM
A Comparison between SAP B1 & Tally ERP Functionalities SAP B1 Tally ERP Business Masters (Customers, Suppliers) with Multiple Bill To & Ship To Addresses Item Masters with Multiple UOM definition, UOM
Job Manager for Job Shops
 Job Manager for Job Shops What makes Job Shops unique? First, most orders are for a unique item or service. No two Jobs are alike. The Job is a one of a kind job, not a mass production type job. Mass Production
Job Manager for Job Shops What makes Job Shops unique? First, most orders are for a unique item or service. No two Jobs are alike. The Job is a one of a kind job, not a mass production type job. Mass Production
Financial Transfer Guide DBA Software Inc.
 Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Why You Need the Financial Transfer 6 3 Total Control Workflow 10 4 Financial Transfer Overview 12 5 Multiple Operating Entities Setup 15 6 General Ledger
Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Why You Need the Financial Transfer 6 3 Total Control Workflow 10 4 Financial Transfer Overview 12 5 Multiple Operating Entities Setup 15 6 General Ledger
