Chapter 2 - Practice Test #1
|
|
|
- Michael Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2 - Practice Test #1 6. Chemical systems tend to move toward positions of A. minimum enthalpy and maximum entropy. B. maximum enthalpy and minimum entropy. C. minimum enthalpy and minimum entropy. D. maximum enthalpy and maximum entropy. 7. An equilibrium system shifts left when the A. rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. B. rate of the forward reaction is less than the rate of the reverse reaction. C. rate of the forward reaction is greater than the rate of the reverse reaction. D. rate of the forward reaction and the reverse reaction are constant. 8. A 1.00 L flask contains a gaseous equilibrium system. The addition of reactants to this flask results in a A. shift left and a decrease in the concentration of the products. B. shift left and a increase in the concentration of the products. C. shift right and a decrease in the concentration of the products. D. shift right and a increase in the concentration of the products. 9. Consider the following equilibrium: CH 4(g) + H 2 O (g) + heat CO (g) + 3H 2(g) In which of the following will both stresses shift the equilibrium to the right? A. a decrease in temperature and a decrease in volume B. a increase in temperature and a decrease in volume C. a decrease in temperature and a increase in volume D. a increase in temperature and a increase in volume 10. Consider the following equilibrium: 2SO 2(g) + O 2(g) 2SO 3(g) H = -198 kj There will be no shift in this equilibrium when A. more O 2 is added. C. the volume is increased. B. a catalyst is added. D. the temperature is increased. 11. Consider the following equilibrium: 2Fe (s) + 3H 2 O (g) Fe 2 O 3(s) + 3H 2(g) The equilibrium expression is A. Keq = [Fe 2 O 3 ][H 2 ] 3 B. Keq = [Fe 2 O 3 ][3H 2 ] [Fe] 2 [H 2 O] 3 [2Fe][3H 2 O] C. Keq = [H 2 ] 3 D. Keq = [ H 2 ] 3 [H 2 O] 3 1
2 12. Consider the following equilibrium: N 2 O 4(g) 2NO 2(g) Keq = At equilibrium, the [N 2 O 4 ] is equal to A B. [NO 2 ] [NO 2 ] C D. [NO 2 ] 2 [NO 2 ] Which of the following equilibrium systems most favours the products? A. Cl 2(g) 2Cl (g) Keq = 6.4 x B. Cl 2(g) + 2NO (g) 2NOCl (g) Keq = 3.7 x 10 8 C. Cl 2(g) + 2NO 2(g) 2NO 2 Cl (g) Keq = 1.8 D. 2HCl (g) H 2(g) + Cl 2(g) Keq = 2.0 x Consider the following equilibrium: 4KO 2(s) + 2H 2 O (g) 4KOH (s) + 3O 2(g) The equilibrium expression is A. Keq = [KOH] 4 [O 2 ] 3 B. Keq = [O 2 ] 3 [KO 2 ] 2 [H 2 O] 2 [ H 2 O] 2 C. Keq = [KO 2 ] 4 [H 2 O] 2 D. Keq = [ H 2 O] 2 [KOH] 4 [O 2 ] 3 [O 2 ] Consider the following equilibrium: N 2(g) + O 2(g) 2NO (g) H = +181 kj When the temperature is decreased, the equilibrium: A. shifts left and the Keq value increases B. shifts left and the Keq value decreases C. shifts right and the Keq value increases D. shifts right and the Keq value decreases 16. Consider the following equilibrium: CaCO 3(s) kj CaO + CO 2(g) The value of the equilibrium constant will increase when A. CO 2 is added. B. CO 2 is removed. C. the temperature is increased. D. the temperature is decreased. 17. Consider the following equilibrium: C (s) + H 2 O (g) CO (g) + H 2(g) The contents of a 1.00 L container at equilibrium were analyzed and found to contain 0.20 mole C, 0.20 mole H 2 O, 0.60 mole CO, and 0.60 mole H 2, The equilibrium constant is A B C. 1.8 D
3 18. Consider the following equilibrium: N 2 O 4(g) 2NO 2(g) Keq = 4.61 x 10-3 A 1.00 L container at equilibrium was analyzed and found to contain mole NO 2. At equilibrium, the concentration of N 2 O 4 is A M B M C M D M 19. Consider the following potential energy diagram: PE (kj) 225kJ 50kJ Progress of Reaction The forward reaction is A.exothermic and the H = -50 kj B. endothermic and the H = +50 kj C. exothermic and the H = -225 kj D. endothermic and the H = +225 kj 20. Consider the following equilibrium: H 2 O (g) + CO (g) H 2(g) + CO 2(g) A closed container is initially filled with H2O and CO. As the reaction proceeds to equilibrium the A. [CO] and [CO 2 ] both increase B. [CO] and [CO 2 ] both decrease C. [CO] increases and [CO 2 ] decreases D. [CO] decreases and [CO 2 ] increases 21. Consider the equilibrium: H 2(g) + I 2(g) 2HI (g) The pressure of the system is increased by reducing the volume. When comparing the new equilibrium with the original equilibrium, A. all concentrations remain constant B. the concentrations of all species have increased C. reactant concentrations have increased while products decreased D. reactant concentrations have decreased while products increased 22. Consider the following equilibrium: N 2 O 4(g) 2NO 2(g) A 1.00 L container is initially filled with moles of N 2 O 4. At equilibrium, moles NO 2 are present. What is the equilibrium concentration of N 2 O 4? A M B M C M D M 3
4 23. Equilibrium is dynamic process because the A. macroscopic properties are not changing B. mass of the reactants equals the mass of the products C. forward and reverse reactions continue to occur D. concentrations of reactants and products are constant 24. Consider the following equilibrium: C (s) + 2H 2(g) CH 4(g) The addition of H2 will cause the equilibrium to shift to the A. left and [CH 4 ] will increase B. left and [CH 4 ] will decrease C. right and [CH 4 ] will increase D. right and [CH 4 ] will decrease 25. Given the following system: 2CrO 4 2- (aq) + 2H + (aq) Cr 2 O 7 2- (aq) + H 2 O (l) Which of the following chemicals, when added to the above equilibrium, would result in a decrease in [CrO 4 2- ]? A. NaOH B. HNO 3 C. Na 2 CrO 4 D. Na 2 Cr 2 O Addition of a catalyst to an equilibrium system A. increases the value of the Keq. B. increases the yield of the products. C. has no effect on the rates of the reaction. D. increases the rate of formation of both reactants and products. 27. Consider the following reaction: 2B (s) + 3F 2(g) 2BF 3(g) The equilibrium expression is A. Keq = [2BF 3 ] [3F 2 ] B. Keq = [F 2 ] 3 [BF 3 ] C. Keq = [BF 3 ] 2 [F 2 ] 3 D. Keq = [BF 3 ] 2 [B][F 2 ] Consider the following equilibrium: 2NO (g) N 2(g) + O 2(g) Keq = 2.01 x The value of the equilibrium constant indicates that the A. [NO] 2 < [N 2 ][ O 2 ] C. [NO] = [N 2 ][ O 2 ] B. [NO] 2 > [N 2 ][ O 2 ] D. [NO] > [N 2 ][ O 2 ] 29. Consider the equilibrium: H 2(g) + I 2(g) 2HI (g) At equilibrium the [H 2 } = M, [I 2 ] = M, and [HI] = M. The value of the equilibrium constant is: A. 2.5 x 10-3 C. 6.4 x 10 1 B. 1.6 x 10-2 D. 4.0 x
5 30. Consider the equilibrium: H 2 O (g) + Cl 2 O (g) 2HOCl (g) Keq = 9.0 x 10-2 A 1.0 L flask contains a mixture of 1.8 x 10-1 mole H 2 O, 4.0 x 10-4 mole Cl 2 O, and 8.0 x 10-2 mole HOCl. To establish equilibrium, the system will proceed to the A. left because the trial Keq > Keq B. left because the trial Keq < Keq C. right because the trial Keq > Keq D. right because the trial Keq < Keq 31. Consider the following equilibrium: SO 2(g) + NO 2(g) SO 3(g) + NO + energy The equilibrium does not shift with a change in A. volume B. temperature C. concentration of products D. concentration of reactions 32. Consider the following equilibrium : SO 2 Cl 2(g) + energy SO 2(g) + Cl 2(g) When the temperature is decreased, the equilibrium shifts A. left and the [SO 2 Cl 2 ] increases B. left and the [SO 2 Cl 2 ] decreases C. right and the [SO 2 Cl 2 ] increases D. right and the [SO 2 Cl 2 ] decreases 33. Consider the following equilibrium: NH 3(g) + HCl (g) NH 4 Cl (s) + energy Which of the following will result in a decrease in the mass of NH 4 Cl? A. adding NH 3 B. removing HCl C. decreasing the volume D. decreasing the temperature 34. Consider the following equilibrium: PCl 3(g) + Cl 2(g) PCl 5(g) When 0.40 moles of PCl 3 and 0.40 moles of Cl 2 are placed in a 1.00 L container and allowed to reach equilibrium, mole of PCl 5 are present. From this information, the value of the Keq is A B C. 3.3 D. 10 5
6 Subjective 1. Concentrations of H 2, I 2, and HI in a mixture at equilibrium at 425 o C were found to be 1.52 x 10-2 M, 3.55 x 10-2 M, and 2.57 x 10-1 M respectively. Calculate the equilibrium constant. H 2(g) + I 2(g) 2HI (g) moles of PCl 5 are placed in a 2.00 L container and goes to equilibrium at 200 o C. If 0.60 moles of PCl 5 are present at equilibrium, calculate the equilibrium constant. PCl 5(g) PCl 3(g) + Cl 2(g) 3. An equilibrium system has a Keq = 50 at 0 o C and a Keq = 80 at 20 o C. a) As the temperature was increased, which direction did the reaction shift? b) Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? 4. If the initial [H 2 ] = M and [I 2 ] = M and the Keq = 55.6 at 20 o C, calculate the equilibrium concentration of all molecules. H 2(g) + I 2(g) 2HI (g) 5. Consider the following data obtained for the following equilibrium: Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN - (aq) FeSCN 2+ (aq)
7 moles CO, 1.60 moles H 2 O, 6.00 moles CO 2, and 6.00 moles H 2 are put in a 2.00 L container at 600 o C. CO(g) + H 2 O(g) CO 2(g) + H 2(g) Keq = 10.0 a) Show by calculation the reaction is not at equilibrium. b) Which way will the reaction shift in order to achieve equilibrium? c) Calculate the equilibrium concentration of CO 2.
8 1. Consider the following reaction mechanism: Step1: NO (g) + O 3(g) NO 2(g) + O 2(g) Step2: O (g) + NO 2(g) NO (g) + O 2(g) The catalyst is: A. O 2 B. O 3 C. NO D. NO 2 2. Consider the following reaction: 2NH 3(g) N 2(g) + 3H 2(g) A flask is initially filled with NH 3. As the system approaches equilibrium, the rate of the forward reaction A. increases as the rate of the reverse reaction decreases B. decreases as the rate of the reverse reaction increases C. increases as the rate of the reverse reaction increases D. decreases as the rate of the reverse reaction decreases 3. Consider the following reaction: Na 2 CO 3(s) + 2HCl (aq) 2NaCl (aq) + CO 2(g) + H 2 O (l) ΔH = -153 KJ In this reaction A. minimum enthalpy and maximum entropy both favour the products B. minimum enthalpy and maximum entropy both favour the reactants C. minimum enthalpy favours products and maximum entropy reactants D. minimum enthalpy favours reactants and maximum entropy products 4. In all systems at equilibrium, the A. concentration of reactants is less than the concentration of the products B. concentration of reactants and the concentration of the products are equal C. concentration of reactants is greater than the concentration of the products D. concentration of reactants and the products are constant 5. Consider the following mechanism: Step 1: N 2 O (g) N 2(g) + O (g) Step 2: N 2 O(g) + O (g) N 2(g) + O 2(g) A reactant in the overall equation is A. O B. O 2 C. N 2 D. N 2 O
9 6. Chemical systems tend to move toward positions of A. minimum enthalpy and maximum entropy. B. maximum enthalpy and minimum entropy. C. minimum enthalpy and minimum entropy. D. maximum enthalpy and maximum entropy. 7. An equilibrium system shifts left when the A. rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. B. rate of the forward reaction is less than the rate of the reverse reaction. C. rate of the forward reaction is greater than the rate of the reverse reaction. D. rate of the forward reaction and the reverse reaction are constant. 8. A 1.00 L flask contains a gaseous equilibrium system. The addition of reactants to this flask results in a A. shift left and a decrease in the concentration of the products. B. shift left and a increase in the concentration of the products. C. shift right and a decrease in the concentration of the products. D. shift right and a increase in the concentration of the products. 9. Consider the following equilibrium: CH 4(g) + H 2 O (g) + heat CO (g) + 3H 2(g) In which of the following will both stresses shift the equilibrium to the right? A. a decrease in temperature and a decrease in volume B. a increase in temperature and a decrease in volume C. a decrease in temperature and a increase in volume D. a increase in temperature and a increase in volume 10. Consider the following equilibrium: 2SO 2(g) + O 2(g) 2SO 3(g) H = -198 kj There will be no shift in this equilibrium when A. more O 2 is added. B. a catalyst is added. C. the volume is increased. D. the temperature is increased.
10 11. Consider the following equilibrium: 2Fe (s) + 3H 2 O (g) Fe 2 O 3(s) + 3H 2(g) The equilibrium expression is A. Keq = [Fe 2 O 3 ][H 2 ] 3 B. Keq = [Fe 2 O 3 ][3H 2 ] [Fe] 2 [H 2 O] 3 [2Fe][3H 2 O] C. Keq = [H 2 ] 3 D. Keq = [ H 2 ] 3 [H 2 O] Consider the following equilibrium: N 2 O 4(g) 2NO 2(g) Keq = At equilibrium, the [N 2 O 4 ] is equal to A B. [NO 2 ] [NO 2 ] C D. [NO 2 ] 2 [NO 2 ] Which of the following equilibrium systems most favours the products? A. Cl 2(g) 2Cl (g) Keq = 6.4 x B. Cl 2(g) + 2NO (g) 2NOCl (g) Keq = 3.7 x 10 8 C. Cl 2(g) + 2NO 2(g) 2NO 2 Cl (g) Keq = 1.8 D. 2HCl (g) H 2(g) + Cl 2(g) Keq = 2.0 x Consider the following equilibrium: 4KO 2(s) + 2H 2 O (g) 4KOH (s) + 3O 2(g) The equilibrium expression is A. Keq = [KOH] 4 [O 2 ] 3 B. Keq = [O 2 ] 3 [KO 2 ] 2 [H 2 O] 2 [ H 2 O] 2 C. Keq = [KO 2 ] 4 [H 2 O] 2 D. Keq = [ H 2 O] 2 [KOH] 4 [O 2 ] 3 [O 2 ] Consider the following equilibrium: N 2(g) + O 2(g) 2NO (g) H = +181 kj When the temperature is decreased, the equilibrium: A. shifts left and the Keq value increases B. shifts left and the Keq value decreases C. shifts right and the Keq value increases D. shifts right and the Keq value decreases
11 16. Consider the following equilibrium: CaCO 3(s) kj CaO + CO 2(g) The value of the equilibrium constant will increase when A. CO 2 is added. B. CO 2 is removed. C. the temperature is increased. D. the temperature is decreased. 17. Consider the following equilibrium: C (s) + H 2 O (g) CO (g) + H 2(g) The contents of a 1.00 L container at equilibrium were analyzed and found to contain 0.20 mole C, 0.20 mole H 2 O, 0.60 mole CO, and 0.60 mole H 2, The equilibrium constant is A B C. 1.8 D Consider the following equilibrium: N 2 O 4(g) 2NO 2(g) Keq = 4.61 x 10-3 A 1.00 L container at equilibrium was analyzed and found to contain mole NO 2. At equilibrium, the concentration of N 2 O 4 is A M B M C M D M 19. Consider the following potential energy diagram: PE (kj) 225kJ 50kJ Progress of Reaction The forward reaction is A. exothermic and the H = -50 kj B. endothermic and the H = +50 kj C. exothermic and the H = -225 kj D. endothermic and the H = +225 kj 20. Consider the following equilibrium: H 2 O (g) + CO (g) H 2(g) + CO 2(g) A closed container is initially filled with H2O and CO. As the reaction proceeds to equilibrium the A. [CO] and [CO 2 ] both increase B. [CO] and [CO 2 ] both decrease C. [CO] increases and [CO 2 ] decreases
12 A M B M C M D M 23. Equilibrium is dynamic process because the A. macroscopic properties are not changing B. mass of the reactants equals the mass of the products C. forward and reverse reactions continue to occur D. concentrations of reactants and products are constant 24. Consider the following equilibrium: C (s) + 2H 2(g) CH 4(g) The addition of H2 will cause the equilibrium to shift to the A. left and [CH 4 ] will increase B. left and [CH 4 ] will decrease C. right and [CH 4 ] will increase D. right and [CH 4 ] will decrease
13 25. Given the following system: 2CrO 4 2- (aq) + 2H + (aq) Cr 2 O 7 2- (aq) + H 2 O (l) Which of the following chemicals, when added to the above equilibrium, would result in a decrease in [CrO 4 2- ]? A. NaOH B. HNO 3 C. Na 2 CrO 4 D. Na 2 Cr 2 O Addition of a catalyst to an equilibrium system A. increases the value of the Keq. B. increases the yield of the products. C. has no effect on the rates of the reaction. D. increases the rate of formation of both reactants and products. 27. Consider the following reaction: 2B (s) + 3F 2(g) 2BF 3(g) The equilibrium expression is A. Keq = [2BF 3 ] [3F 2 ] B. Keq = [F 2 ] 3 [BF 3 ] C. Keq = [BF 3 ] 2 [F 2 ] 3 D. Keq = [BF 3 ] 2 [B][F 2 ] Consider the following equilibrium: 2NO (g) N 2(g) + O 2(g) Keq = 2.01 x The value of the equilibrium constant indicates that the A. [NO] 2 < [N 2 ][ O 2 ] B. [NO] 2 > [N 2 ][ O 2 ] C. [NO] = [N 2 ][ O 2 ] D. [NO] > [N 2 ][ O 2 ]
14 29. Consider the equilibrium: H 2(g) + I 2(g) 2HI (g) At equilibrium the [H 2 } = M, [I 2 ] = M, and [HI] = M. The value of the equilibrium constant is: A. 2.5 x 10-3 B. 1.6 x 10-2 C. 6.4 x 10 1 D. 4.0 x Consider the following equilibrium: H 2 O (g) + Cl 2 O (g) 2HOCl (g) Keq = 9.0 x 10-2 A 1.0 L flask contains a mixture of 1.8 x 10-1 mole H 2 O, 4.0 x 10-4 mole Cl 2 O, and 8.0 x 10-2 mole HOCl. To establish equilibrium, the system will proceed to the A. left because the trial Keq > Keq B. left because the trial Keq < Keq C. right because the trial Keq > Keq D. right because the trial Keq < Keq 31. Consider the following equilibrium: SO 2(g) + NO 2(g) SO 3(g) + NO + energy The equilibrium does not shift with a change in A. volume B. temperature C. concentration of products D. concentration of reactions 32. Consider the following equilibrium : SO 2 Cl 2(g) + energy SO 2(g) + Cl 2(g) When the temperature is decreased, the equilibrium shifts A. left and the [SO 2 Cl 2 ] increases B. left and the [SO 2 Cl 2 ] decreases C. right and the [SO 2 Cl 2 ] increases D. right and the [SO 2 Cl 2 ] decreases 33. Consider the following equilibrium: NH 3(g) + HCl (g) NH 4 Cl (s) + energy Which of the following will result in a decrease in the mass of NH 4 Cl? A. adding NH 3 B. removing HCl C. decreasing the volume D. decreasing the temperature
15 34. Consider the following equilibrium: PCl 3(g) + Cl 2(g) PCl 5(g) When 0.40 moles of PCl 3 and 0.40 moles of Cl 2 are placed in a 1.00 L container and allowed to reach equilibrium, mole of PCl 5 are present. From this information, the value of the Keq is Subjective A B C. 3.3 D Concentrations of H 2, I 2, and HI in a mixture at equilibrium at 425 o C were found to be 1.52 x 10-2 M, 3.55 x 10-2 M, and 2.57 x 10-1 M respectively. Calculate the equilibrium constant. H 2(g) + I 2(g) 2HI (g) Keq = (2.57 x 10-1 ) 2 = 122 ( 1.52 x 10-2 )(3.55 x 10-2 ) moles of PCl 5 are placed in a 2.00 L container and goes to equilibrium at 200 o C. If 0.60 moles of PCl 5 are present at equilibrium, calculate the equilibrium constant. PCl 5(g) PCl 3(g) + Cl 2(g) I C E Keq = (1.70) 2 = 9.6 (0.30)
16 3. An equilibrium system has a Keq = 50 at 0 o C and a Keq = 80 at 20 o C. a) As the temperature was increased, which direction did the reaction shift? Right b) Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? Endothermic 4. If the initial [H 2 ] = M and [I 2 ] = M and the Keq = 55.6 at 20 o C, calculate the equilibrium concentration of all molecules. H 2(g) + I 2(g) 2HI (g) I C x x 2x E x x 2x (2x) 2 = 55.6 (0.2 x) 2 2x = x x = M [HI] = M [H 2 ] = [I 2 ] = M 5. Consider the following data obtained for the following equilibrium: Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN - (aq) FeSCN 2+ (aq) [Fe 3+ ] [SCN - ] [FeSCN 2+ ] Experiment x 10-2 M 8.02 x 10-5 M 9.22 x 10-4 M Experiment x 10-3 M 3.65 x 10-4 M? Calculate [FeSCN 2+ ] in experiment 2. Keq = (9.22 x 10-4 ) = x 10 2 (3.91 x 10-2 )( 8.02 x 10-5 ) Keq = (x) = x 10 2 (6.27 x 10-3 M)(3.65 x 10-4 M) x = 6.73 x 10-4 M moles CO, 1.60 moles H 2 O, 6.00 moles CO 2, and 6.00 moles H 2 are put in a
17 c) Calculate the equilibrium concentration of CO 2. CO(g) + H 2 O(g) CO2(g) + H2(g) I C x x x x E x x 3.00 x x [ x] 2 = 10.0 [ x] 2 square both sides x = x 3.00 x = (0.8 + x) x = x = x x = x = [CO2] x = 2.88 M
EQUILIBRIUM PRACTICE TEST
 EQUILIBRIUM PRACTICE TEST 1. Consider the following reaction: 2NH 3(g) N 2(g) + 3H 2(g) A flask is initially filled with NH 3. As the system approaches equilibrium, the rate of the forward reaction A.
EQUILIBRIUM PRACTICE TEST 1. Consider the following reaction: 2NH 3(g) N 2(g) + 3H 2(g) A flask is initially filled with NH 3. As the system approaches equilibrium, the rate of the forward reaction A.
Name Practice Questions Date Equilibrium
 Name Practice Questions Date Equilibrium 1. CaCO3(s) «Ca 2+ (aq) + CO3 2 (aq) Which of the following reagents, when added to the above equilibrium system, would cause more CaCO3 to dissolve? KNO3(s) CaCO3(s)
Name Practice Questions Date Equilibrium 1. CaCO3(s) «Ca 2+ (aq) + CO3 2 (aq) Which of the following reagents, when added to the above equilibrium system, would cause more CaCO3 to dissolve? KNO3(s) CaCO3(s)
Review Package: Equilibrium Constant Keq & Calculations
 3. Consider the following equilibrium system: O2(g) + 2HF(g) OF2(g) H = +318 kj/mol If the temperature of the system is increased, A. Keq will decrease B. H will decrease C. Keq will increase D. H will
3. Consider the following equilibrium system: O2(g) + 2HF(g) OF2(g) H = +318 kj/mol If the temperature of the system is increased, A. Keq will decrease B. H will decrease C. Keq will increase D. H will
Chemistry 12 Tutorial 6-Questions & Self-Test Only
 Chemistry 12 Tutorial 6 Questions and Self-Test Only 1. The equilibrium equation for the formation of ammonia is: N 2(g) + 3H 2(g) 2NH 3(g) In an equilibrium mixture at 200 C, the concentrations were found
Chemistry 12 Tutorial 6 Questions and Self-Test Only 1. The equilibrium equation for the formation of ammonia is: N 2(g) + 3H 2(g) 2NH 3(g) In an equilibrium mixture at 200 C, the concentrations were found
The Equilibrium Constant (K eq)
 The Constant (K eq) 1. The Law: K eq is called the. Keq = [PRODUCTS] [REACTANTS] eg. aa + bb + xx + yy + where a, b, x, y are of the balanced equation. A,B,X & Y are the and in the equation Keq = [X] x
The Constant (K eq) 1. The Law: K eq is called the. Keq = [PRODUCTS] [REACTANTS] eg. aa + bb + xx + yy + where a, b, x, y are of the balanced equation. A,B,X & Y are the and in the equation Keq = [X] x
Unit 3 - Solubility Practice Test # 2
 1. onsider the following experiment: Unit 3 Solubility Practice Test # 2 1.0 ml 0.20 M g + + an unknown solution precipitate 1.0 ml 020 M Sr 2+ + an unknown solution no precipitate The unknown solution
1. onsider the following experiment: Unit 3 Solubility Practice Test # 2 1.0 ml 0.20 M g + + an unknown solution precipitate 1.0 ml 020 M Sr 2+ + an unknown solution no precipitate The unknown solution
14.1 Dynamic Equilibrium, Keq, and the Mass Action Expression
 14.1 Dynamic Equilibrium, Keq, and the Mass Action Expression The Equilibrium Process Dr. Fred Omega Garces Chemistry 201 Miramar College 1 Dynamic Equilibrium, Keq and the Mass Action Expression Extent
14.1 Dynamic Equilibrium, Keq, and the Mass Action Expression The Equilibrium Process Dr. Fred Omega Garces Chemistry 201 Miramar College 1 Dynamic Equilibrium, Keq and the Mass Action Expression Extent
Chapter 17 Solubility and Complex Ion Equilibria
 Chem 1046 General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 8th Edition Prof George W.J. Kenney, Jr Last Update: 27Nov2008 Chapter 17 Solubility and Complex Ion Equilibria These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text,
Chem 1046 General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 8th Edition Prof George W.J. Kenney, Jr Last Update: 27Nov2008 Chapter 17 Solubility and Complex Ion Equilibria These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text,
Topic Reacting masses Level GCSE Outcomes 1. To calculate reacting masses 2. To set out mole calculations in a grid format
 Topic Reacting masses Level GCSE Outcomes 1. To calculate reacting masses 2. To set out mole calculations in a grid format Problems on Reacting Masses of Solids Section 1 1. What is the mass of magnesium
Topic Reacting masses Level GCSE Outcomes 1. To calculate reacting masses 2. To set out mole calculations in a grid format Problems on Reacting Masses of Solids Section 1 1. What is the mass of magnesium
CHEMISTRY 112 EXAM 3 JUNE 17, 2011 FORM A
 CHEMISTRY 112 EXAM 3 JUNE 17, 2011 FORM A 1. Consider the following reaction: A + B C + D What are the signs of ΔH and ΔS for the reaction to always be spontaneous? ΔH ΔS A. + + B. C. + D. + 2. What is
CHEMISTRY 112 EXAM 3 JUNE 17, 2011 FORM A 1. Consider the following reaction: A + B C + D What are the signs of ΔH and ΔS for the reaction to always be spontaneous? ΔH ΔS A. + + B. C. + D. + 2. What is
1. Which of the given statements about the reaction below are incorrect?
 1. Which of the given statements about the reaction below are incorrect? 2PbO(s) + C(s) 2Pb(s) + CO 2 (g) a. Lead is getting reduced b. Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised c. Carbon is getting oxidised
1. Which of the given statements about the reaction below are incorrect? 2PbO(s) + C(s) 2Pb(s) + CO 2 (g) a. Lead is getting reduced b. Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised c. Carbon is getting oxidised
Exercise 6a. Balancing equations
 Exercise 6a Balancing equations Balance the following equations. To get you started _ indicates the first six questions where numbers need to be inserted to achieve the balance. In one or two difficult
Exercise 6a Balancing equations Balance the following equations. To get you started _ indicates the first six questions where numbers need to be inserted to achieve the balance. In one or two difficult
JSUNIL TUTORIAL, SAMASTIPUR
 Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Q 1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air? Ans. Before burning in air, the magnesium ribbon is cleaned by rubbing with a sandpaper.
Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Q 1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air? Ans. Before burning in air, the magnesium ribbon is cleaned by rubbing with a sandpaper.
Sn 2+ (aq) + 2 Ag + (aq) Sn 4+ (aq) + 2 Ag(s),
 1. Which change in oxidation number represents oxidation? A) Sn 2+ (aq) Sn 4+ (aq) B) Sn 2+ (aq) Sn(s) C) Sn 4+ (aq) Sn 2+ (aq) D) Sn 4+ (aq) Sn(s) E) Sn(s) Sn 2 (aq) 2. In the reaction Sn 2+ (aq) + 2
1. Which change in oxidation number represents oxidation? A) Sn 2+ (aq) Sn 4+ (aq) B) Sn 2+ (aq) Sn(s) C) Sn 4+ (aq) Sn 2+ (aq) D) Sn 4+ (aq) Sn(s) E) Sn(s) Sn 2 (aq) 2. In the reaction Sn 2+ (aq) + 2
Today! Demonstrations of Redox Chemistry! Electrochemistry! electrons moving about! equilibrium with a control knob! The disappearing Aluminum Rod!
 Today! Electrochemistry! electrons moving about! equilibrium with a control knob! Redox chemistry! oxidation and reduction! Demonstrations of Redox Chemistry! The disappearing Aluminum Rod! Alkali Metals
Today! Electrochemistry! electrons moving about! equilibrium with a control knob! Redox chemistry! oxidation and reduction! Demonstrations of Redox Chemistry! The disappearing Aluminum Rod! Alkali Metals
1. The equation that represents the equilibrium in a saturated solution of Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 is.. The precipitate which forms first is
 CHEMISTRY 12 UNIT 3 - REVIEW Ksp Part A - Multiple Choice 1. The equation that represents the equilibrium in a saturated solution of Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 is A. Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 (s) 3 Fe 2+ (aq) + 2 SO 4 3 (aq)
CHEMISTRY 12 UNIT 3 - REVIEW Ksp Part A - Multiple Choice 1. The equation that represents the equilibrium in a saturated solution of Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 is A. Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 (s) 3 Fe 2+ (aq) + 2 SO 4 3 (aq)
1. What volume of water is required to make a 4.65 M solution from 5.2 g of NaBr (MM = g/mol)?
 CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM II Answer Key March 22, 2013 1. What volume of water is required to make a 4.65 M solution from 5.2 g of NaBr (MM = 102.894 g/mol)? A. 4.65 ml B. 10.9 ml C. 11 ml D. 235 ml E. 240 ml
CHEMISTRY 110 EXAM II Answer Key March 22, 2013 1. What volume of water is required to make a 4.65 M solution from 5.2 g of NaBr (MM = 102.894 g/mol)? A. 4.65 ml B. 10.9 ml C. 11 ml D. 235 ml E. 240 ml
Periodic Properties: Analysis of Group I, II and Transition Metals
 Periodic Properties: Analysis of Group I, II and Transition Metals Procedure All solutions should be mixed thoroughly after any additions. Clearly record all observations (indicating what you did), even
Periodic Properties: Analysis of Group I, II and Transition Metals Procedure All solutions should be mixed thoroughly after any additions. Clearly record all observations (indicating what you did), even
+ 10Cl 2Mn H 2 O + 5Cl 2. Deduce the half-equation for the oxidation of chloride ions to chlorine.
 Q1.Chlorine is an important industrial chemical. (a) Chlorine is formed when KMnO 4 reacts with hydrochloric acid. The ionic equation for this redox reaction is 16H + + 2MnO 4 + 10Cl 2Mn 2+ + 8H 2 O +
Q1.Chlorine is an important industrial chemical. (a) Chlorine is formed when KMnO 4 reacts with hydrochloric acid. The ionic equation for this redox reaction is 16H + + 2MnO 4 + 10Cl 2Mn 2+ + 8H 2 O +
Qualitative Analysis: Group I, II and Transition Metals. Prelab. 2. Refer to the flowcharts on the pages 5 and 6 to answer the following:
 1. What is the purpose of this experiment? Qualitative Analysis: Group I, II and Transition Metals Prelab 2. Refer to the flowcharts on the pages 5 and 6 to answer the following: a. What does a double
1. What is the purpose of this experiment? Qualitative Analysis: Group I, II and Transition Metals Prelab 2. Refer to the flowcharts on the pages 5 and 6 to answer the following: a. What does a double
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS PART I INTRODUCTION
 EXPERIMENT 10 (2 Weeks) Chemistry 100 Laboratory TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS PART I INTRODUCTION It is useful to classify reactions into different types, because products of reactions can be predicted.
EXPERIMENT 10 (2 Weeks) Chemistry 100 Laboratory TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS PART I INTRODUCTION It is useful to classify reactions into different types, because products of reactions can be predicted.
Periodic Properties: Analysis of Group I, II and Transition Metals. Prelab. 2. Refer to the flowcharts on the pages 5 and 6 to answer the following:
 1. What is the purpose of this experiment? Periodic Properties: Analysis of Group I, II and Transition Metals Prelab 2. Refer to the flowcharts on the pages 5 and 6 to answer the following: a. What does
1. What is the purpose of this experiment? Periodic Properties: Analysis of Group I, II and Transition Metals Prelab 2. Refer to the flowcharts on the pages 5 and 6 to answer the following: a. What does
CHEM 1151 Review Chapter 3 and 4 Chapter 3: Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Formulas
 CHEM 1151 Review Chapter 3 and 4 Chapter 3: Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Formulas 1. What are the two different ions present in the compound FeCl3? A) Fe 2+, Cl 3- B) Fe 3+, Cl 3- C) Fe +, Cl - D)
CHEM 1151 Review Chapter 3 and 4 Chapter 3: Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Formulas 1. What are the two different ions present in the compound FeCl3? A) Fe 2+, Cl 3- B) Fe 3+, Cl 3- C) Fe +, Cl - D)
BALANCING EQUATIONS: PRACTICE PROBLEMS - NORTH ALLEGHENY
 BALANCING CHEMICAL EQUATIONS 1 PDF BALANCING EQUATIONS: PRACTICE PROBLEMS - NORTH ALLEGHENY BALANCING CHEMICAL EQUATIONS WORKSHEET 1 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 balancing chemical equations 1 pdf Balancing Equations:
BALANCING CHEMICAL EQUATIONS 1 PDF BALANCING EQUATIONS: PRACTICE PROBLEMS - NORTH ALLEGHENY BALANCING CHEMICAL EQUATIONS WORKSHEET 1 1 / 5 2 / 5 3 / 5 balancing chemical equations 1 pdf Balancing Equations:
Chemical reactions and electrolysis
 Chemical reactions and electrolysis Higher Revision Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 95 minutes Marks: 95 marks Comments: Page of 29 (a) Magnesium metal is shaped to make magnesium ribbon. Explain why
Chemical reactions and electrolysis Higher Revision Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 95 minutes Marks: 95 marks Comments: Page of 29 (a) Magnesium metal is shaped to make magnesium ribbon. Explain why
 Stoichiometric Calculations 1. The weight of calcium carbonate required to produce carbon-dioxide that is sufficient for conversion of one 0.1 mole sodium carbonate to sodium bicarbonate is 1) 1gm 2) 10gm
Stoichiometric Calculations 1. The weight of calcium carbonate required to produce carbon-dioxide that is sufficient for conversion of one 0.1 mole sodium carbonate to sodium bicarbonate is 1) 1gm 2) 10gm
Chapter 12: Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and Solids
 1. Which one of the following substances is expected to have the highest boiling point? A) Br 2 B) Cl 2 C) F 2 D) I 2 3. Which one of the following substances is expected to have the highest boiling point?
1. Which one of the following substances is expected to have the highest boiling point? A) Br 2 B) Cl 2 C) F 2 D) I 2 3. Which one of the following substances is expected to have the highest boiling point?
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9701 CHEMISTRY
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME f the May/June 2012 question paper f the guidance of teachers 9701 CHEMISTRY 9701/21
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME f the May/June 2012 question paper f the guidance of teachers 9701 CHEMISTRY 9701/21
2K CrO H SO K CrO K SO H O potassium dichromate yellow. orange
 Potassium dichromate, (KCrO7) Potassium dichromate is one of the most important compound of chromium, and also among dichromates. In this compound Cr is in the hexavalent (+6) state. Preparation : It can
Potassium dichromate, (KCrO7) Potassium dichromate is one of the most important compound of chromium, and also among dichromates. In this compound Cr is in the hexavalent (+6) state. Preparation : It can
KULLEĠĠ SAN BENEDITTU Boys Secondary, Kirkop
 KULLEĠĠ SAN BENEDITTU Boys Secondary, Kirkop Mark HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATION 2013/2014 Junior Lyceum Programme FORM 4 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Global Mark Max. Mark 10 16 15 11 8 20
KULLEĠĠ SAN BENEDITTU Boys Secondary, Kirkop Mark HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATION 2013/2014 Junior Lyceum Programme FORM 4 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Global Mark Max. Mark 10 16 15 11 8 20
Compiled by Rahul Arora What do you mean by corrosion? How can you prevent it?
 Rahul Arora 12. What do you mean by corrosion? How can you prevent it? 13. MnO2 + 4HCl MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2 In the above equation, name the compound which is oxidized and which is reduced? 14. Match the
Rahul Arora 12. What do you mean by corrosion? How can you prevent it? 13. MnO2 + 4HCl MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2 In the above equation, name the compound which is oxidized and which is reduced? 14. Match the
Flue-Gas Treatment by Methane Tri-Reforming Combined with Lime Carbonation and Syngas Production
 High Temperature Solid Looping Cycles Network, Oviedo, Spain, 15-17 Sept. 2009 Flue-Gas Treatment by Methane Tri-Reforming Combined with Lime Carbonation and Syngas Production M. Halmann 1 and A. Steinfeld
High Temperature Solid Looping Cycles Network, Oviedo, Spain, 15-17 Sept. 2009 Flue-Gas Treatment by Methane Tri-Reforming Combined with Lime Carbonation and Syngas Production M. Halmann 1 and A. Steinfeld
PO 4 NH 4 H + + SO 3
 KEY TO AP CHEMISTRY EQUATIONS BY TYPE 196882, 198588, 199093, 1995 Double Replacement 1. Hydrogen sulfide is bubbled through a solution of silver nitrate. H 2 S + Ag 1+ Ag 2 S + H + 2. An excess of sodium
KEY TO AP CHEMISTRY EQUATIONS BY TYPE 196882, 198588, 199093, 1995 Double Replacement 1. Hydrogen sulfide is bubbled through a solution of silver nitrate. H 2 S + Ag 1+ Ag 2 S + H + 2. An excess of sodium
Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C2 Higher Tier
 Centre Number 71 Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2014 Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C2 Higher Tier GSD52 [GSD52] TUESDAY 10 JUNE 2014, AFTERNOON TIME 1 hour 15 minutes.
Centre Number 71 Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2014 Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C2 Higher Tier GSD52 [GSD52] TUESDAY 10 JUNE 2014, AFTERNOON TIME 1 hour 15 minutes.
NABTEB Past Questions and Answers - Uploaded online QUESTION AND ANSWER
 QUESTION AND ANSWER CHEMISTRY, MAY/JUNE 2009 Section B (Essay 100 marks) Time: 1 hour 40 mins 1. Starting from bauxite, explain how to obtain pure aluminium metal i. Dissolve the impure bauxite in hot
QUESTION AND ANSWER CHEMISTRY, MAY/JUNE 2009 Section B (Essay 100 marks) Time: 1 hour 40 mins 1. Starting from bauxite, explain how to obtain pure aluminium metal i. Dissolve the impure bauxite in hot
Explain whether this process is oxidation or reduction.
 1 Electroplating steel objects with silver involves a three-step process. step 1 A coating of copper is applied to the object. step 2 A coating of nickel is applied to the object. step 3 The coating of
1 Electroplating steel objects with silver involves a three-step process. step 1 A coating of copper is applied to the object. step 2 A coating of nickel is applied to the object. step 3 The coating of
Chapter 18 Homework Answers
 Chapter 18 Homework Answers 18.19 (a) AgI(s) Ag + + I K sp = [Ag + ][I ] (b) Ag PO (s) Ag + + PO K sp = [Ag + ] [PO ] (c) PbCrO (s) Pb + + CrO K sp = [Pb + ][CrO ] (d) Al(OH) (s) Al + + OH K sp = [Al +
Chapter 18 Homework Answers 18.19 (a) AgI(s) Ag + + I K sp = [Ag + ][I ] (b) Ag PO (s) Ag + + PO K sp = [Ag + ] [PO ] (c) PbCrO (s) Pb + + CrO K sp = [Pb + ][CrO ] (d) Al(OH) (s) Al + + OH K sp = [Al +
27 Co Ni Fe Cu Ag Ru Pd Rh Pt Os Ir 192.
 UW VERSIONA CHEM152,Sp11 1A 1 H 1.008 3 Li 6.941 11 Na 22.99 2A 4 Be 9.012 UsefulConstants: R=8.314J/mol.K=0.08206liter.atm/mol.K Avogadro snumber:n a =6.022x10 23 molecules/mol Boltzmann sconstant:k=1.38x10
UW VERSIONA CHEM152,Sp11 1A 1 H 1.008 3 Li 6.941 11 Na 22.99 2A 4 Be 9.012 UsefulConstants: R=8.314J/mol.K=0.08206liter.atm/mol.K Avogadro snumber:n a =6.022x10 23 molecules/mol Boltzmann sconstant:k=1.38x10
Predicting Reaction Products
 Predicting Reaction Products Once you classify a chemical reaction, write the products and balance the reaction. Review Diatomic Molecules! Elements that exist only as compounds in the natural world: Iodine
Predicting Reaction Products Once you classify a chemical reaction, write the products and balance the reaction. Review Diatomic Molecules! Elements that exist only as compounds in the natural world: Iodine
Thermodynamics and Electrode Potential ME Dr. Zuhair M. Gasem
 Thermodynamics and Electrode Potential ME 472-062 Copyright Dr. Zuhair M. Gasem Corrosion Science and Engineering 2 Corrosion Science Engineering: corrosion forms, and controlling methods Chpater2 Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics and Electrode Potential ME 472-062 Copyright Dr. Zuhair M. Gasem Corrosion Science and Engineering 2 Corrosion Science Engineering: corrosion forms, and controlling methods Chpater2 Thermodynamics
General Certificate of Secondary Education Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C2 Higher Tier [GSD52] TUESDAY 10 JUNE 2014, AFTERNOON
![General Certificate of Secondary Education Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C2 Higher Tier [GSD52] TUESDAY 10 JUNE 2014, AFTERNOON General Certificate of Secondary Education Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C2 Higher Tier [GSD52] TUESDAY 10 JUNE 2014, AFTERNOON](/thumbs/87/96373699.jpg) Centre Number 71 Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2014 Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C2 Higher Tier [GSD52] MV18 TUESDAY 10 JUNE 2014, AFTERNOON TIME 1 hour 15 minutes,
Centre Number 71 Candidate Number General Certificate of Secondary Education 2014 Double Award Science: Chemistry Unit C2 Higher Tier [GSD52] MV18 TUESDAY 10 JUNE 2014, AFTERNOON TIME 1 hour 15 minutes,
Balance the following equations: 1. Al + N 2 AlN. 2. Fe + O 2 Fe 3 O CaCO 3 CaO + CO 2 4. NH 4 NO 3 N 2 O + H 2 O. 5. KI + Cl 2 KCl + I 2
 Balance the following equations: 1. Al + N 2 AlN 2. Fe + O 2 Fe 3 O 4 3. CaCO 3 CaO + CO 2 4. NH 4 NO 3 N 2 O + H 2 O 5. KI + Cl 2 KCl + I 2 6. Pb(NO 3 ) 2 + HCl PbCl 2 + HNO 3 7. BaO 2 BaO + O 2 8. Al
Balance the following equations: 1. Al + N 2 AlN 2. Fe + O 2 Fe 3 O 4 3. CaCO 3 CaO + CO 2 4. NH 4 NO 3 N 2 O + H 2 O 5. KI + Cl 2 KCl + I 2 6. Pb(NO 3 ) 2 + HCl PbCl 2 + HNO 3 7. BaO 2 BaO + O 2 8. Al
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH STD: X SUBJECT- CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 1: CHEMICAL REACTIONS WORKSHEET #1
 INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH STD: X SUBJECT- CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 1: CHEMICAL REACTIONS WORKSHEET #1 I) Very Short Type Questions (1 mark) 1. What is the relationship between decomposition and combustion
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH STD: X SUBJECT- CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 1: CHEMICAL REACTIONS WORKSHEET #1 I) Very Short Type Questions (1 mark) 1. What is the relationship between decomposition and combustion
SOLUBILITY STUDY GUIDE- Multiple Choice Section
 SOLUBILITY STUDY GUIDE- Multiple Choice Section Multiple Choice Section: This study guide is a compilation of questions from provincial exams since 2000. I urge you to become intimately familiar with question
SOLUBILITY STUDY GUIDE- Multiple Choice Section Multiple Choice Section: This study guide is a compilation of questions from provincial exams since 2000. I urge you to become intimately familiar with question
Chem 1120 Pretest 3 Fall 2015
 Chem 1120 Pretest 3 Fall 2015 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following solubility product expressions is incorrect? a. Cu
Chem 1120 Pretest 3 Fall 2015 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following solubility product expressions is incorrect? a. Cu
Chemistry. TOPIC : Redox Reactions. products are PH3 and NaH2PO2. This reaction is an examplee of. (b) Reduction (d) Neutralization
 TOPIC : Redox Reactions Date : Marks : 1 mks Time : ½ hr 1. When P reacts with caustic soda, the products are PH and NaHPO. This reaction is an examplee of (a) Oxidation (c) Oxidation and reduction (redox)
TOPIC : Redox Reactions Date : Marks : 1 mks Time : ½ hr 1. When P reacts with caustic soda, the products are PH and NaHPO. This reaction is an examplee of (a) Oxidation (c) Oxidation and reduction (redox)
3. [7 points] How many significant figures should there be in the answer to the following problem?
![3. [7 points] How many significant figures should there be in the answer to the following problem? 3. [7 points] How many significant figures should there be in the answer to the following problem?](/thumbs/83/87492512.jpg) 1 of 6 10/20/2009 3:52 AM 1. [7 points] What is the correct name for ZnF 2? (a) zinc fluorine (b) zinc (II) fluoride (c) zinc fluoride (d) fluoride zinc 2. [7 points] What is the correct name for P 2 O
1 of 6 10/20/2009 3:52 AM 1. [7 points] What is the correct name for ZnF 2? (a) zinc fluorine (b) zinc (II) fluoride (c) zinc fluoride (d) fluoride zinc 2. [7 points] What is the correct name for P 2 O
Duncan. UNIT 8 - Chemical Equations BALANCING EQUATIONS PRACTICE WORKSHEET 14.) C2H6 + O2 CO2 + H2O. 2.) Na + I2 NaI 3.) N2 + O2 N2O 4.
 BALANCING EQUATIONS PRACTICE WORKSHEET 1.) CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O 2.) Na + I2 NaI 3.) N2 + O2 N2O 4.) N2 + H2 NH3 5.) KI + Cl2 KCl + I2 6.) HCl + Ca(OH)2 CaCl2 + H2O 7.) KClO3 KCl + O2 8.) K3PO4 + HCl KCl
BALANCING EQUATIONS PRACTICE WORKSHEET 1.) CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O 2.) Na + I2 NaI 3.) N2 + O2 N2O 4.) N2 + H2 NH3 5.) KI + Cl2 KCl + I2 6.) HCl + Ca(OH)2 CaCl2 + H2O 7.) KClO3 KCl + O2 8.) K3PO4 + HCl KCl
CHEM J-8 June Answer: THE REMAINDER OF THIS PAGE IS FOR ROUGH WORKING ONLY.
 CHEM1101 2014-J-8 June 2014 A 1.0 kg sample of copper metal is heated to 100.0 C. The copper sample is immersed in a volume of water initially at 25.0 C. What volume of water is required so that the final
CHEM1101 2014-J-8 June 2014 A 1.0 kg sample of copper metal is heated to 100.0 C. The copper sample is immersed in a volume of water initially at 25.0 C. What volume of water is required so that the final
19. H, S, C, and G Diagrams Module
 HSC - HSC Diagrams 15012-ORC-J 1 (8) 19. H, S, C, and G Diagrams Module The diagram module presents the basic thermochemical data for the given species in graphical format. Eight different diagram types
HSC - HSC Diagrams 15012-ORC-J 1 (8) 19. H, S, C, and G Diagrams Module The diagram module presents the basic thermochemical data for the given species in graphical format. Eight different diagram types
McCord CH302 Exam 1 Spring 2017
 112 version last name first name signature McCord CH302 Exam 1 Spring 2017 50375 / 50380 Reminder: Be sure and correctly bubble in your name, uteid, and version number on your bubblesheet. The Periodic
112 version last name first name signature McCord CH302 Exam 1 Spring 2017 50375 / 50380 Reminder: Be sure and correctly bubble in your name, uteid, and version number on your bubblesheet. The Periodic
Total Grade /150 Checked by
 FIRST LETTER OF YOUR LAST NAME CHEMISTRY 1127 EXAM I NAME (PRINT) SECTION SIGNATURE TA PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS Do NOT begin the exam until asked to do so. There are 8 numbered pages, a useful
FIRST LETTER OF YOUR LAST NAME CHEMISTRY 1127 EXAM I NAME (PRINT) SECTION SIGNATURE TA PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS Do NOT begin the exam until asked to do so. There are 8 numbered pages, a useful
Which of these is the formula for disulfur heptoxide? A. S 2 O 7 B. S 7 O 2 C. SO 2 D. N 2 O
 Which of these is the formula for disulfur heptoxide? A. S 2 O 7 B. S 7 O 2 C. SO 2 D. N 2 O Which of these is the correct chemical formula for a molecule of oxygen? A. O B. O -2 C. O +2 D. O 2 Which of
Which of these is the formula for disulfur heptoxide? A. S 2 O 7 B. S 7 O 2 C. SO 2 D. N 2 O Which of these is the correct chemical formula for a molecule of oxygen? A. O B. O -2 C. O +2 D. O 2 Which of
Enthalpy " H o " Entropy "S o " Gibbs energy
 THERMODYNAMIC VALUES AT STANDARD STATE (298K) Data Retrieved From: Kots, Treichal, Weaver Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity (Sixth Edition) COPYRIGHT 2006 Species Name Enthalpy " H o " Entropy "S o " Gibbs
THERMODYNAMIC VALUES AT STANDARD STATE (298K) Data Retrieved From: Kots, Treichal, Weaver Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity (Sixth Edition) COPYRIGHT 2006 Species Name Enthalpy " H o " Entropy "S o " Gibbs
The ion with Vanadium in its oxidation state of 5 exists as a solid compound in the form of a VO 3
 Chemistry of some Transition elements: V, Mn, Co, Cu, Cr and Ag Vanadium Vanadium has four main oxidation states. Each one has a different colour. VO 2 VO 2 V 3 V 2 O.N. 5 yellow O.N. 4 blue O.N. 3 green
Chemistry of some Transition elements: V, Mn, Co, Cu, Cr and Ag Vanadium Vanadium has four main oxidation states. Each one has a different colour. VO 2 VO 2 V 3 V 2 O.N. 5 yellow O.N. 4 blue O.N. 3 green
DURATION: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Our country, our future 545/1 S4 CHEMISTRY Exam 16 PAPER 1 DURATION: 1 hour 30 minutes Instructions This paper consists of fifty (50) objective questions. All questions are compulsory Answer the questions
Our country, our future 545/1 S4 CHEMISTRY Exam 16 PAPER 1 DURATION: 1 hour 30 minutes Instructions This paper consists of fifty (50) objective questions. All questions are compulsory Answer the questions
Thermal decomposition. Metal carbonates
 Decomposition reactions Copy correctly Up to 3% of a workbook Copying or scanning from ESA workbooks is subject to the New Zealand Copyright Act which limits copying to 3% of this workbook. Many compounds
Decomposition reactions Copy correctly Up to 3% of a workbook Copying or scanning from ESA workbooks is subject to the New Zealand Copyright Act which limits copying to 3% of this workbook. Many compounds
Unit F FR (part B) Solubility Equilibrium, Ksp (pg 1 of 16)
 Unit F FR (part B) Solubility Equilibrium, Ksp (pg 1 of 16) 1. Answer the following questions about the solubility of some fluoride salts of alkaline earth metals. (a) A student prepares 100. ml of a saturated
Unit F FR (part B) Solubility Equilibrium, Ksp (pg 1 of 16) 1. Answer the following questions about the solubility of some fluoride salts of alkaline earth metals. (a) A student prepares 100. ml of a saturated
NATIONAL BUSINESS AND TECHNICAL EXAMINATIONS BOARD (GENERAL EDUCATION EXAMINATION) MAY/JUNE 2007 SECTION B CHEMISTRY (ESSAY) TIME: 1 HOUR 40 MINUTES
 NATIONAL BUSINESS AND TECHNICAL EXAMINATIONS BOARD (GENERAL EDUCATION EXAMINATION) MAY/JUNE 2007 SECTION B CHEMISTRY (ESSAY) TIME: 1 HOUR 40 MINUTES 1. (a) Give THREE differences between a physical and
NATIONAL BUSINESS AND TECHNICAL EXAMINATIONS BOARD (GENERAL EDUCATION EXAMINATION) MAY/JUNE 2007 SECTION B CHEMISTRY (ESSAY) TIME: 1 HOUR 40 MINUTES 1. (a) Give THREE differences between a physical and
Solutions Unit Exam Name Date Period
 Name Date Period Ms. Roman Page 1 Regents Chemistry 1. Which mixture can be separated by using the equipment shown below? 6. Which ion, when combined with chloride ions, Cl, forms an insoluble substance
Name Date Period Ms. Roman Page 1 Regents Chemistry 1. Which mixture can be separated by using the equipment shown below? 6. Which ion, when combined with chloride ions, Cl, forms an insoluble substance
Labs Covered. Le Chatelier. Calculating Ka. Kitchen Chemistry Project. Calculating Kc. Redox lab
 Labs Covered Le Chatelier Calculating Kc Calculating Ka Redox lab Kitchen Chemistry Project LeChatelier Sample Questions Fe +3 (aq) + SCN -1 (aq) FeSCN +2 (aq) Light orange colourless red a) To create
Labs Covered Le Chatelier Calculating Kc Calculating Ka Redox lab Kitchen Chemistry Project LeChatelier Sample Questions Fe +3 (aq) + SCN -1 (aq) FeSCN +2 (aq) Light orange colourless red a) To create
Q1.A student investigated the temperature change when zinc reacts with copper sulfate solution.
 Q1.A student investigated the temperature change when zinc reacts with copper sulfate solution. The student used a different concentration of copper sulfate solution for each experiment. The student used
Q1.A student investigated the temperature change when zinc reacts with copper sulfate solution. The student used a different concentration of copper sulfate solution for each experiment. The student used
EXPERIMENT 15C. Qualitative Analysis Scheme of Main Group and Transition Metal Cations without Hazardous Waste
 EXPERIMENT 15C Qualitative Analysis Scheme of Main Group and Transition Metal Cations without Hazardous Waste The following experiment is intended to continue the introduction of qualitative analysis through
EXPERIMENT 15C Qualitative Analysis Scheme of Main Group and Transition Metal Cations without Hazardous Waste The following experiment is intended to continue the introduction of qualitative analysis through
Chemistry Test Paper
 Chemistry Test Paper [Time:1 1 hrs] [M. Marks : 80] 2 Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is
Chemistry Test Paper [Time:1 1 hrs] [M. Marks : 80] 2 Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is
Solubility Equilibrium
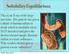 Solubility Equilibrium This is an X-ray of the large intestine. The patient was given a drink of barium sulfate to drink which is insoluble (does NOT dissolve) and gives the doctor a better image. Barium
Solubility Equilibrium This is an X-ray of the large intestine. The patient was given a drink of barium sulfate to drink which is insoluble (does NOT dissolve) and gives the doctor a better image. Barium
What is: (a) aqua fortis, (b) aqua regia (c) Fixation of Nitrogen?
 EXERCISE.1 Question 1: What is: (a) aqua fortis, (b) aqua regia (c) Fixation of Nitrogen? Solution 1: Book Name: Selina concise (a) Aqua fortis: Nitric acid is called aqua fortis. Aqua fortis means strong
EXERCISE.1 Question 1: What is: (a) aqua fortis, (b) aqua regia (c) Fixation of Nitrogen? Solution 1: Book Name: Selina concise (a) Aqua fortis: Nitric acid is called aqua fortis. Aqua fortis means strong
Name: Date: Period: Page: Predicting Products. Predict the products, and balance each reaction. Use the reaction type as a hint.
 Name: Date: Period: Page: Predicting Products Predict the products, and balance each reaction. Use the reaction type as a hint. For reactions with a transition metal, the most likely charge on the metal
Name: Date: Period: Page: Predicting Products Predict the products, and balance each reaction. Use the reaction type as a hint. For reactions with a transition metal, the most likely charge on the metal
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2008
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2008 GCE GCE O Level Chemistry 7081/02 Edexcel Limited. Registered in England and Wales No. 4496750 Registered Office: One90 High Holborn, London WC1V 7BH 7081/02 O-Level Chemistry
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2008 GCE GCE O Level Chemistry 7081/02 Edexcel Limited. Registered in England and Wales No. 4496750 Registered Office: One90 High Holborn, London WC1V 7BH 7081/02 O-Level Chemistry
Chapter 9. Dissolution and Precipitation Equilibria
 Chapter 9 Dissolution and Precipitation Equilibria 9-1 The Nature of Solubility Equilibria 9-2 The Solubility of Ionic Solids 9-3 Precipitation and the Solubility Product 9-4 The Effects of ph on Solubility
Chapter 9 Dissolution and Precipitation Equilibria 9-1 The Nature of Solubility Equilibria 9-2 The Solubility of Ionic Solids 9-3 Precipitation and the Solubility Product 9-4 The Effects of ph on Solubility
Chapter 9 Systematic Equilibrium
 Chapter 9 Systematic Equilibrium 1 What we Skipped Ch. 8 discussed Activity (γ) This is what should be used in equilibrium calculations rather than conc. (molarity) In Ch. 9 in later chapters, you will
Chapter 9 Systematic Equilibrium 1 What we Skipped Ch. 8 discussed Activity (γ) This is what should be used in equilibrium calculations rather than conc. (molarity) In Ch. 9 in later chapters, you will
19. H, S, C, and G Diagrams Module
 HSC 8 - HSC Diagrams November 5, 4 43-ORC-J (8 9. H, S, C, and G Diagrams Module The diagram module presents the basic thermochemical data for the given species in graphical format. Eight different diagram
HSC 8 - HSC Diagrams November 5, 4 43-ORC-J (8 9. H, S, C, and G Diagrams Module The diagram module presents the basic thermochemical data for the given species in graphical format. Eight different diagram
A student investigated the reactivity of three different metals.
 Chemical Changes Q1. A student investigated the reactivity of three different metals. This is the method used. 1. Place 1 g of metal powder in a test tube. 2. Add 10 cm 3 of metal sulfate. 3. Wait 1 minute
Chemical Changes Q1. A student investigated the reactivity of three different metals. This is the method used. 1. Place 1 g of metal powder in a test tube. 2. Add 10 cm 3 of metal sulfate. 3. Wait 1 minute
Batteries. Dry Cell (Flashlight Battery) Self contained electrochemical cell. ! Primary batteries (not rechargeable)
 Batteries Self contained electrochemical cell Dry Cell (Flashlight Battery)! Primary batteries (not rechargeable)! Secondary batteries (rechargeable) Anode: Zn(s)! Research Needed to Improve Batteries:
Batteries Self contained electrochemical cell Dry Cell (Flashlight Battery)! Primary batteries (not rechargeable)! Secondary batteries (rechargeable) Anode: Zn(s)! Research Needed to Improve Batteries:
Tutorial 3 Unit 3 - Solubility
 Tutorial 3 Unit 3 - Solubility The Answer is A Answer A is the primary condition for solubility equilibrium. Remember the solution is also called saturated. B, of course is wrong because these opposing
Tutorial 3 Unit 3 - Solubility The Answer is A Answer A is the primary condition for solubility equilibrium. Remember the solution is also called saturated. B, of course is wrong because these opposing
CHM101 SECOND EXAM 162. Chemistry 101 SECOND Exam (162) Name: Date: 30/4/2017
 Chemistry 101 SECOND Exam (162) Name: Date: 30/4/2017 Student no. Section: Useful Information:Gas Constant R= 0.08206 L.atm/K.mol, Specific heat of H 2 O=4.18 J/g. C 1 atm. = 760 mmhg. H 1 He 2 1.000 4
Chemistry 101 SECOND Exam (162) Name: Date: 30/4/2017 Student no. Section: Useful Information:Gas Constant R= 0.08206 L.atm/K.mol, Specific heat of H 2 O=4.18 J/g. C 1 atm. = 760 mmhg. H 1 He 2 1.000 4
Metallurgy, Industrially important compounds and Noble gases
 Metallurgy, Industrially important compounds and Noble gases Q1. In blast furnace, iron oxide is reduced by a) carbon b) silica c) hot blast of air d) CO Option d In smelting of iron ore, though coke is
Metallurgy, Industrially important compounds and Noble gases Q1. In blast furnace, iron oxide is reduced by a) carbon b) silica c) hot blast of air d) CO Option d In smelting of iron ore, though coke is
JSTSE : PREVIOUS YEARS
 JSTSE : PREVIOUS YEARS CHEMISTRY (2014) 91. In paints dispersed phase and dispersion medium are (1) solid and liquid (2) liquid and solid (3) liquid and liquid (4) gas and liquid 92. Which statement is
JSTSE : PREVIOUS YEARS CHEMISTRY (2014) 91. In paints dispersed phase and dispersion medium are (1) solid and liquid (2) liquid and solid (3) liquid and liquid (4) gas and liquid 92. Which statement is
GCE A level 1095/01 CHEMISTRY CH5
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE A level 1095/01 CHEMISTRY CH5 P.M. TUESDAY, 17 June 2014 1 hour 45 minutes For Examiner s use only ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this examination
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE A level 1095/01 CHEMISTRY CH5 P.M. TUESDAY, 17 June 2014 1 hour 45 minutes For Examiner s use only ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this examination
Batteries. Self contained electrochemical cell. Dry Cell (Flashlight Battery) ! Primary batteries (not rechargeable)
 Batteries Self contained electrochemical cell! Primary batteries (not rechargeable)! Secondary batteries (rechargeable)! Research Needed to Improve Batteries: CHEM112 LRSVDS Batteries and Corrosion 1 Dry
Batteries Self contained electrochemical cell! Primary batteries (not rechargeable)! Secondary batteries (rechargeable)! Research Needed to Improve Batteries: CHEM112 LRSVDS Batteries and Corrosion 1 Dry
The Predom module -O 2. at different temperatures) One-metal
 The Predom module Use Predom to calculate and plot isothermal 1-, 2- and 3-metal predominance area diagrams. Predom makes exclusively use of compound databases. Table of Contents Section 1 Section 2 Section
The Predom module Use Predom to calculate and plot isothermal 1-, 2- and 3-metal predominance area diagrams. Predom makes exclusively use of compound databases. Table of Contents Section 1 Section 2 Section
Carbon dioxide is formed during the complete combustion of octane. + 12½O 2 8CO 2... [1] Why does incomplete combustion sometimes take place?
![Carbon dioxide is formed during the complete combustion of octane. + 12½O 2 8CO 2... [1] Why does incomplete combustion sometimes take place? Carbon dioxide is formed during the complete combustion of octane. + 12½O 2 8CO 2... [1] Why does incomplete combustion sometimes take place?](/thumbs/81/82825046.jpg) 1 Crude oil is a source of hydrocarbons which can be used as fuels or for processing into petrochemicals. Octane, C 8 18, is one of the alkanes present in petrol. Carbon dioxide is formed during the complete
1 Crude oil is a source of hydrocarbons which can be used as fuels or for processing into petrochemicals. Octane, C 8 18, is one of the alkanes present in petrol. Carbon dioxide is formed during the complete
Electrochemistry Written Response
 Electrochemistry Written Response January 1999 7. Balance the following redox reaction in acidic solution: RuO 4 + P Ru(OH) 2 2+ + H 3 PO 3 (acid) (3 marks) 8. A technician tests the concentration of methanol,
Electrochemistry Written Response January 1999 7. Balance the following redox reaction in acidic solution: RuO 4 + P Ru(OH) 2 2+ + H 3 PO 3 (acid) (3 marks) 8. A technician tests the concentration of methanol,
1A End of Lab Questions Notes
 1A End of Lab Questions Notes 11/1/18 Lab 9, Part 1 Lava lamp 1 Ethanol is not soluble in vegetable oil because Ethanol is polar and vegetable oil is non-polar 2 Most lava lamps use water and oil A secret
1A End of Lab Questions Notes 11/1/18 Lab 9, Part 1 Lava lamp 1 Ethanol is not soluble in vegetable oil because Ethanol is polar and vegetable oil is non-polar 2 Most lava lamps use water and oil A secret
ABSORPTION ENHANCED REFORMING OF LIGHT ALCOHOLS (METHANOL AND ETHANOL) FOR THE PRODUCTION OF HYDROGEN: THERMODYNAMIC MODELING
 ABSORPTION ENHANCED REFORMING OF LIGHT ALCOHOLS (METHANOL AND ETHANOL) FOR THE PRODUCTION OF HYDROGEN: THERMODYNAMIC MODELING Miguel A. Escobedo Bretado 1, Manuel D. Delgado Vigil 2, Jesús Salinas Gutiérrez
ABSORPTION ENHANCED REFORMING OF LIGHT ALCOHOLS (METHANOL AND ETHANOL) FOR THE PRODUCTION OF HYDROGEN: THERMODYNAMIC MODELING Miguel A. Escobedo Bretado 1, Manuel D. Delgado Vigil 2, Jesús Salinas Gutiérrez
to water. You add 1 drop of phenolphthalein and the solution turns pink. This observation tells you Na 2
 1A End of Lab Questions Notes 9/11/18 Lab 4 1 You add 100 g of to water You add 1 drop of phenolphthalein and the solution turns pink This observation tells you is a base 2 You add vinegar (09 M acetic
1A End of Lab Questions Notes 9/11/18 Lab 4 1 You add 100 g of to water You add 1 drop of phenolphthalein and the solution turns pink This observation tells you is a base 2 You add vinegar (09 M acetic
85 Q.14 In which of the following substances does nitrogen have the lowest oxidation number?
 Redox and electrolysis / Section 3 / Sect3pp.doc / S. W. Tse / P.1 85 Q.5 The element with an atomic number of 19 is likely to be A. an oxidizing agent. B. a reducing agent. C. a non-metal. D. chemically
Redox and electrolysis / Section 3 / Sect3pp.doc / S. W. Tse / P.1 85 Q.5 The element with an atomic number of 19 is likely to be A. an oxidizing agent. B. a reducing agent. C. a non-metal. D. chemically
PYROMETALLURGY OF IRON
 Kwame Nkrumah University of Science & Technology, Kumasi, Ghana Pyrometallurgy of Iron Common sources of iron-bearing ores: PYROMETALLURGY OF IRON Oxide Ores Stoicheometry Iron Content (wt%) Magnetite
Kwame Nkrumah University of Science & Technology, Kumasi, Ghana Pyrometallurgy of Iron Common sources of iron-bearing ores: PYROMETALLURGY OF IRON Oxide Ores Stoicheometry Iron Content (wt%) Magnetite
Analysis of evolved gases during the thermal decomposition of ammonium diniramide under pressure
 75 Research paper Analysis of evolved gases during the thermal decomposition of ammonium diniramide under pressure Hiroki Matsunaga,HirotoHabu,andAtsumi Miyake Abstract Keywords 1. Introduction 76 ο ο
75 Research paper Analysis of evolved gases during the thermal decomposition of ammonium diniramide under pressure Hiroki Matsunaga,HirotoHabu,andAtsumi Miyake Abstract Keywords 1. Introduction 76 ο ο
CRYSTALLIZATION SOLUBILITY CURVE
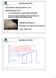 CRYSTALLIZATION saturated solution cooled/evaporated forms crystal important industrially because: i) a crystal formed from an impure solution and itself pure ii) Practical method of obtaining pure chemical
CRYSTALLIZATION saturated solution cooled/evaporated forms crystal important industrially because: i) a crystal formed from an impure solution and itself pure ii) Practical method of obtaining pure chemical
4-10 Using resources Chemistry
 4-0 Using resources Chemistry.0 The picture shows a ring. Photograph supplied by Comstock/Thinkstock. Graph shows the composition of the metals in the ring. Graph The metal in the ring had a mass of 8.5g.
4-0 Using resources Chemistry.0 The picture shows a ring. Photograph supplied by Comstock/Thinkstock. Graph shows the composition of the metals in the ring. Graph The metal in the ring had a mass of 8.5g.
4-10 Using resources Chemistry
 4-0 Using resources Chemistry.0 The picture shows a ring. Photograph supplied by Comstock/Thinkstock. Graph shows the composition of the metals in the ring. Graph The metal in the ring had a mass of 8.5g.
4-0 Using resources Chemistry.0 The picture shows a ring. Photograph supplied by Comstock/Thinkstock. Graph shows the composition of the metals in the ring. Graph The metal in the ring had a mass of 8.5g.
Furnace. 1. (10 points) mol/s 53.5% H2O CO2
 MEEBAL Exam 3 December 2012 Show all work in your blue book. Points will be deducted if steps leading to answers are not shown. No work outside blue books (such as writing on the flow sheets) will be considered.
MEEBAL Exam 3 December 2012 Show all work in your blue book. Points will be deducted if steps leading to answers are not shown. No work outside blue books (such as writing on the flow sheets) will be considered.
Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid to make magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas
 Experiment 1: Magnesium and Hydrochloric acid Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid to make magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas Equation: Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) gas syringe 50 cm 3 dilute
Experiment 1: Magnesium and Hydrochloric acid Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid to make magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas Equation: Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) gas syringe 50 cm 3 dilute
Group I Qualitative Analysis
 Group I Analysis Page 1 Illinois Central College CHEMISTRY 132 Laboratory Section: Group I Qualitative Analysis Name: Equipment 1-tray of dropper bottles 2-micro spatulas 2-wooden test tube blocks 4-medicine
Group I Analysis Page 1 Illinois Central College CHEMISTRY 132 Laboratory Section: Group I Qualitative Analysis Name: Equipment 1-tray of dropper bottles 2-micro spatulas 2-wooden test tube blocks 4-medicine
Written as per the syllabus prescribed by the Central Board of Secondary Education. CBSE CLASS X SCIENCE
 Written as per the syllabus prescribed by the Central Board of Secondary Education. CBSE CLASS X SCIENCE Salient Features Extensive coverage of the syllabus in an effortless and easy to grasp format Neat
Written as per the syllabus prescribed by the Central Board of Secondary Education. CBSE CLASS X SCIENCE Salient Features Extensive coverage of the syllabus in an effortless and easy to grasp format Neat
1. How many moles of calcium chloride are there in a sample containing x particles? l
 1. How many moles of calcium chloride are there in a sample containing 1.0038x 10 22 particles? l 2. A sample of water contains 3.01x10 23 water molecules a. How many moles of water molecules are present
1. How many moles of calcium chloride are there in a sample containing 1.0038x 10 22 particles? l 2. A sample of water contains 3.01x10 23 water molecules a. How many moles of water molecules are present
Table of Contents. Preface...
 Preface... xi Chapter 1. Metallurgical Thermochemistry... 1 1.1. Introduction... 1 1.2. Quantities characterizing the state of a system and its evolution... 3 1.2.1. The types of operations... 3 1.2.2.
Preface... xi Chapter 1. Metallurgical Thermochemistry... 1 1.1. Introduction... 1 1.2. Quantities characterizing the state of a system and its evolution... 3 1.2.1. The types of operations... 3 1.2.2.
Chapter 9 Nitrification
 Chapter 9 Nitrification 9.0 Nitrification - The microbiological oxidation of NH 4+ -N to NO 2- -N and NO 3- -N. NH 4+ -N removal is a mandated process for some wastewaters because i) NH 4 + consumes oxygen
Chapter 9 Nitrification 9.0 Nitrification - The microbiological oxidation of NH 4+ -N to NO 2- -N and NO 3- -N. NH 4+ -N removal is a mandated process for some wastewaters because i) NH 4 + consumes oxygen
