CHAPTER II MATERIALS AND METHODS. Cell Culture and Plasmids. Cos-7 cells were maintained in Dulbecco s modified Eagle medium (DMEM,
|
|
|
- Aron Parker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER II MATERIALS AND METHODS Cell Culture and Plasmids Cos-7 cells were maintained in Dulbecco s modified Eagle medium (DMEM, BioWhittaker Inc,Walkersville, MD) containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 50 U/ml penicillin, 50 µg/ml streptomycin, and 2 mm L-glutamine (BioWhittaker). NIH 3T3 cells were maintained in DMEM containing 10% bovine serum. The pcmv5-runx deletion mutant was created by PCR amplification of the and fragments with the inclusion of a unique Nhe I restriction site for cloning using primer sequences listed in Table 1. Table 1. Primer Sequences for Generation of Runx1 Δ Deletion Construct Name CMV30 380Nhe 430Nhe 3 BglII Sequence (5 3 ) AAT GTC GTA ATA ACC CCG CCC CGT TG CCG GCT AGC GGT GTG GTA GCG CGT GGC CGA GCC CGC GCT AGC CCC TGT ACC AAC GCC TCC ACG GGC GCG AGA TCT CAG TAG GGC CGC CAC ACG GCC TC In Vitro Transcription and Translation In vitro purification studies were performed using the bacterially expressed GSTfusion proteins, which were created by subcloning the full length SUV39H1 or the Set and fragments from the GAL4 plasmids into pgex4t. The purified proteins were quantified after SDS-PAGE using Coomassie Brilliant Blue and approximately 51
2 equal amounts of protein were used for each reaction. RUNX1 or RUNX1a were transcribed and translated using the quick coupled system (TnT; Promega, Inc., Madison, WI) in the presence of 35 S-Methionine. An equal amount of the reticulocyte lysate was diluted into PBS containing 0.5% Triton X-100 and added to the glutathione beads and incubated on ice for 4-12 hr. Samples were washed 3 times with PBS containing 0.5% Triton X-100 and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Luciferase Assays NIH 3T3 cells were transfected using the Superfect or Polyfect reagent (Qiagen) with 300 ng WWP-Luciferase (p21 Waf1/Cip1 ), 300 ng pcmv5-runx1 (unless otherwise noted) or deletion constructs, and 300 ng pcmv5-secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) plasmids. Empty pcmv5 was used as a control and pbluescript KS was added to bring the total amount of DNA in each sample to 1.5 µg. Luciferase activity was measured using the Luciferase Assay System (Promega) and normalized to SEAP activity. Co-Immunoprecipitation Cos-7 cells (3 x 10 6 cells in 100 mm dishes) were transfected using lipofectamine or lipofectamine 2000 (Life Technologies) with up to 5 µg of expression plasmids. Cells were extracted with phosphate buffered saline supplemented with 1 mm EDTA, 0.2 mm PMSF, and 0.1 T.I.U/ml aprotinin, and containing 0.5% Triton X-100. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with either anti-flag M2-Agarose Affinity Gel (Sigma) or GAL4 antibody (Sigma) and precipitated using Protein G Sepharose (Sigma). 52
3 Flow Cytometry Analysis Single cell suspensions of hematopoietic tissues were obtained by either flushing the tibia and femur, or mincing the spleen or the thymus of Mx:Hdac3 mice. Following lysis of the red blood cells using the Erythrocyte lysis buffer, 1 X 10 6 to 4 X 10 6 cells were aliquoted into individual tubes. The cells were stained with antibodies against: CD3, CD4, CD8, Ter119, Gr-1, Mac-1, B220, Sca-1, and c-kit. Fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis was performed on a Becton Dickinson FACSCalibur, LSRII, or FACSAria flow cytometer. Methylcellulose Assay (MCA) Single cell suspensions were obtained by flushing cells from the tibia and femur of Mx:Hdac3 mice. The red blood cells were lysed with Erythrocyte lysis buffer (Sigma). The cells were mixed with complete methocult M3434 media (Stem Cell Technologies) and plated on 35mm dishes in duplicate. Colonies were grown at 37C, 5% CO 2 for 12 days and colonies were counted. Antibodies The Runx1 antibody was obtained from EMD Biosciences. The Flag M2 antibody (F-1804) was obtained from Sigma. The following antibodies were obtained from Upstate Cell signaling: Histone H3 (05-928), Histone H4 (07-108), acetyl-histone H4 (Lys5) (07-327), acetyl-histone H4 (Lys8) (06-760), acetyl-histone H4 (Lys12) (06-761), acetyl-histone H4 (Lys16) (07-329), acetyl-histone H3 (Lys9) (06-942), and phospho-histone H2A.X (Ser139), clone JBW301 (05-636). The antibodies for Hdac3 53
4 (ab and ab2379) and GAPDH (clone 6C5, ab8245) were obtained from Abcam. The antibody for Pparγ (sc-7196) was obtained from Santa Cruz. The p70 S6 Kinase (2708) and phospho-p70 S6 Kinase (Thr398) (9206) antibodies were obtained from Cell Signaling Technology. The cytokeratin wide spectrum antibody (Z0622) was obtained from DakoCytomation. The sources of the secondary antibodies are as follows: anti-mouse IgG (Sigma) and anti-rabbit IgG (Promega, Inc. Madison, WI). Generation of Hdac3 Knockout Mice The targeting construct was designed to flank Hdac3 exon 7 with LoxP sites and place a floxed Neo cassette in the intron between exons 7 and 8. The 5 arm of the targeting construct was generated containing a LoxP site by PCR using splicing by overlap extension (SOE). Initially, two PCR products making up the 5 arm were generated using the primers 5 arm fwd, 5 -CGA CTC GAG GTG CAA CTG TAA GCC AGG CAG TGG-3 and 5 arm mid rev, 5 -GAA TTC ACG CGT GGC TGA AAT GTG AGC AGG CAG CA-3 and 5 arm rev, 5 -CGA ATC GAT AAG CCA GCC TGG TCT GTA GCA ATA-3 and 5 arm mid fwd, 5 -CGA CTC GAG CCG CTG CAT GTT CCC TTT CTC CCC-3. TL1 ES cell DNA was used as the template and the PCR conditions were 94 o C, 8 min followed by 30 cycles of 94 o C, 1 min, 58 o C, 1 min, 72 o C, 3 min with a 72 o C, 10 min final extension. These PCR products were used as templates for the SOE. The reaction conditions and the primers, containing a LoxP site (italics) and an internal Mlu1 site (underlined; added for diagnostic purposes), were as follows: first set of reactions used primers 5 arm fwd, and LoxP Rev, 5 -ATA ACT TCG TAT AGC ATA CAT TAT ACG AAG TTA TAC GCG TGG CTG AAA TGT GAG CAG GCA GCA G-3 ; 54
5 5 arm rev, and LoxP Fwd, 5 -ACG CGT ATA ACT TCG TAT AAT GTA TGC TAT ACG AAG TTA TCC GCT GCA TGT TCC CTT TCT CCC C-3. The PCR conditions for the first set of reactions were 94 o C, 8 min followed by 30 cycles of 94 o C, 1 min, 58 o C, 1 min, 72 o C, 3 min with a 72 o C, 10 min final extension. The full-length 5 arm was created by adding the two products of the above reactions together diluted 1:20 with the primers 5 arm fwd and 5 arm rev. PCR reaction conditions were 94 o C, 3 min followed by 30 cycles of 94 o C, 1 min, 60 o C, 45 sec, 72 o C, 3 min with a 72 o C, 10 min final extension. The product of this reaction was sequenced to verify the presence of the LoxP site and MluI sites. The approx. 1.8 kb product was subcloned into the XhoI and ClaI sites of pntk(a)lp2 creating the 5 arm pntk construct. The pntk(a)lp2 vector used for making the targeting construct contains a floxed Neo cassette bounded by multiple cloning sites with HSV TK and was provided by the Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center Transgenic Mouse/Embryonic Stem Cell Shared Resource. The 3 arm was also generated using SOE. The first set of products were generated by the following sets of primers: 3 arm fwd 5 -CGA CTC GAG CTG CTT CTT GAG TGC TGG GAT TAA-3 and 3 arm mid rev 5 -GTG CTG ACA TCT GGA TGG AGT GTG-3. The second product was generated by 3 arm rev 5 -ACA GGA TCC TGG TTC ACT GCT CAG GAC AGA GTA-3 and 3 arm mid fwd 5 -GAT TCA CTC TGG TGT CTC AGC CAT-3. Reaction conditions for the first round of PCR were 94 o C, 3 min, 30 cycles of 94 o C, 1 min, 63 o C, 45 sec, 72 o C, 6 min, with a final extension of 72 o C, 10 min. The full-length 3 arm was generated by adding the above two products together after diluting each 3-fold and 8-fold, respectively, and performing PCR with 55
6 3 arm fwd and 3 arm rev with the following reaction conditions: 94 o C, 3 min, 30 cycles of 94 o C, 1 min, 65 o C, 45 sec, 72 o C, 7 min, with a final extension of 72 o C, 10 min. The approx. 3.7 kb product was subcloned into PCR-Script for sequencing. The product was released by XhoI and BamHI digest and subcloned into the SalI and BamHI digested 5 arm pntk. The targeting construct was restricted with NotI for electroporation into TL1 ES cells. Primers for the 3 probe included: 3 probe fwd 5 -CTG AGC AGT GAA CCA GTA GAC CAC-3 and 3 probe rev 5 -TCA CAG CAA CTC GAG TGG TCT CAG-3 with reaction conditions 94 o C, 3 min, 30 cycles of 94 o C, 1 min, 65 o C, 45 sec, 72 o C, 7 min, with a final extension of 72 o C, 10 min. TL1 DNA was used as a template for the reactions. The 3 probe was used to hybridize a Southern blot of NheI digested ES cell DNA to identify clones that had undergone homologous recombination. Potential positives were identified and a PCR screen examining the 5 end of the targeting construct was performed to ensure proper homologous recombination. This screen used the following primers: 5 outside, 5 -TTA GCC CCA AGC AGC TGT TGA TCT G-3 fwd (outside of the arm of the targeting construct) and Hdac rev, 5 -GGA CAC AGT CAT GAC CCG GTC-3 (inside the arm of the targeting construct). This PCR product spans the LoxP site and the MluI site that was incorporated with the SOE reaction for diagnostic purposes. The PCR products were cut with MluI to identify the positive clones. Two positive clones were expanded and injected into C57BL/6 blastocysts. The resulting chimeric mice were bred to heterozygosity and crossed with transgenic mice expressing Cre ubiquitously from the EIIA promoter. Mice that had lost the Neo sequences but that retained LoxP sites 56
7 flanking exon 7 were identified and used for these studies. Mice that had lost both the Neo and exon 7 on one allele (heterozygous) were also identified and bred. Generation of Liver-specific Hdac3 Knockout Mice Mice harboring a conditional allele (fl) or a null allele (-) of Hdac3 were crossed to transgenic mice expressing Mx1-Cre recombinase (318) or Albumin-Cre recombinase (319, 320). The offspring from these mice were then bred to yield mice with a conditional allele in conjunction with either a wild-type (fl/+) or null allele (fl/-), and Cre. To induce Cre expression in the Mx1-Cre expressing mice, 5-week old animals received an intraperitoneal (IP) injection of 500 µg polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (pipc) in PBS every other day for 13 days, for a total of 7 injections, with the last day of injection being denoted as Day 0. Mice were sacrificed at 1 day, 2 day, and 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 weeks after the last injection. In vivo Inhibitor Treatment Three-week old Alb:Hdac3 mice were used in both the GW9662 (Cayman Chemicals) and rapamycin (LC Laboratories) studies. Inhibitors were diluted to a working stock in vehicle solution (5% Tween-80, 5% PEG-400). For the GW9662 experiments, mice were injected with either vehicle or 2mg/kg GW9662, daily for 4 weeks. For the rapamycin experiments, mice were injected with vehicle or 10mg/kg rapamycin, daily for 3 weeks. 57
8 Genotyping of Transgenic and Conditional Hdac3 Deletion Mice Genomic DNA was extracted by incubating mouse tail piece in Jeffer s mix (0.1M Tris, ph 8.0, 5mM EDTA, 0.2% SDS, 0.2M NaCl) plus 250 µg Proteinase K at 55 C for 3 hours-o/n, followed by centrifugation, decanting solution to a new tube, and precipitating with ice cold isopropanol at -20 C for 30 minutes. DNA was pelleted by centrifugation, washed 1-2 times with 100% ethanol, air dried, and resuspended in nuclease-free water. One-2 microliters of DNA was used for PCR screening to identify mice carrying a floxed exon 7, wild-type exon 7 and a deleted exon 7 of the Hdac3 allele with primer set 1263T/2158B, or a floxed exon 7 and wild-type exon 7 of the Hdac3 allele with primer set 1133T/1597B (Table 2). Transgenic mice expressing Mx1-Cre recombinase or Albumin-Cre recombinase were genotyped using the Cre 685/Cre1054 primer set, with the Mtg16-48/Mtg16-49 primer set (Table 2) as a positive control. The Rosa26 reporter allele was identified using the WildRosa/TransRosa/CommonRosa primer set (Table 2). Table 2. Transgenic and knockout mouse genotyping primer sequences. Name 1263T 2158B 1133T 1597B Cre 645 Cre 1054 Mtg16-48 Mtg16-49 WildRosa TransRosa CommonRosa Sequence (5 3 ) CCA CTG GCT TCT CCT AAG TTC CCC AGG TTA GCT TTG AAC TCT CTC TGG CTT CTG CTA TGT CAA TG GGA CAC AGT CAT GAC CCG GTC ACC TGA AGA TGT TCG CGATTA TCT ACC GTC AGT ACG TGA GAT ATC TT CAC ACG TGT ATA TTA GGT TGC CTG CCC CAC GTA GCC TGT TCG TAG CAG ACA GCC GGA GCG GGA GAA ATG GAT ATG GCG AAG AGT TTG TCC TCA ACC AAA GTC GCT CTG AGT TGT TAT 58
9 Preparation of Bone Marrow and Liver Lysates Whole cell lysates (WCL) of total bone marrow were made by homogenizing in PBS plus 0.5% Triton X-100, 0.1% DOC, and 0.1% SDS, sonicated and cleared by centrifugation. To make cellular fractions of liver, fresh or frozen liver tissue was homogenized in Buffer A (PBS plus 1.5 mm MgCl 2, 10 mm NaF, 0.1 mm NaVO 3, 0.2 mm PMSF, 5µg/mL leupeptin, 1 mm EDTA, 0.5 mm DTT), centrifuged at 850 g, and the supernatent was collected as the cytoplasmic fraction. The remaining pellet was washed twice with Buffer A, resuspsended in Buffer B (Buffer A plus 270 mm NaCl, for a final concentration of 0.4 M NaCl), incubated on ice for 30 minutes with frequent, gentle vortexing, then centrifuged at g for 15 minutes at 4. Supernatent was collected as the nuclear fraction. The remaining pellet was washed twice with Buffer B, resuspended in Buffer C (Buffer B plus 0.5% Triton X-100, 0.1% DOC, 0.1% SDS), and sonicated until no longer viscous. All fractions were centrifuged at g to clear lysates. WCL were made by homogenizing in Buffer A plus 0.5% Triton X-100, 0.1% DOC, and 0.1% SDS, sonicated and cleared by centrifugation. Histology and Immunohistochemistry Tissue was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at 4, dehydrated and embedded in paraffin. 5µm sections were stained with hemotoxylin and eosin (H&E) and periodic acid Schiff (PAS). Apoptotic cells were detected by TUNEL using the ApopTag Plus Kit (Chemicon International). Cycling cells were detected by injecting the mice IP with 100µg/g BrdU in PBS 1 hour prior to sacrifice. BrdU was detected using anti-brdu for immunohistochemistry and BrdU positive cells were counted per 100 nuclei in control 59
10 and Hdac3-null liver sections. Frozen sections were prepared by fixing tissue in 4% paraformaldehyde at 4 for 2 hours, then 30% sucrose for 3-12 hrs. Tissue was then embedded in OCT, frozen on dry ice, and 10µm sections were stained with Oil Red O and counterstained with hematoxylin. For immunofluorescence, 5µm sections were cut, permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 for 5 minutes, washed 3 times with PBS, and blocked with 10% normal goat serum in PBS for 30 minutes, followed by 3 washes in PBS. Primary antibody was diluted in 10% normal goat serum in PBS, and tissue sections were incubated for 1 hour at RT, followed by 3 washes in PBS. Tissue was then incubated with secondary antibody diluted in 10% normal goat serum, for 45 minutes at RT, in the dark, followed by 3 washes with PBS. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst dye (B-1155, Sigma) at RT for 10 minutes, washed 3 times with PBS, and sections were mounted with coverslips using Permamount (Fisher). Liver DNA and RNA Extraction, Q-RT-PCR and Microarray Analysis Liver DNA was purified using Qiagen DNeasy Tissue Kit. Liver RNA was extracted using Versagene RNA Tissue Kit (Gentra Systems). cdna was prepared from 2-3 µg RNA using random hexanucleotide primers (Applied Biosystems) and M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase (Promega). For Q-RT-PCR, cdna was analyzed using iq SYBR Green Supermix (Biorad). Primer sequences are listed in Table 3. For the microarray analysis, pools of RNA were prepared from a total of 10 control and 10 Alb:Hdac3 fl/- mice at P17 and P28. Briefly, RNA was prepared from individual whole livers, tested for quality, and high quality RNA was pooled into 2 groups of 5 to normalize for biological variability between animals prior to being 60
11 hybridized to Applied Biosystems 1700 Mouse Expression Array System chips for analysis in the Vanderbilt Microarray Shared Resource. Data was analyzed using GeneSpring (Agilent Technologies), and genes whose expression changed at least 2-fold in 2 of 2 Alb:Hdac3 fl/- biological replicates (determined using a T-test) were included in the data sets. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis software (Ingenuity Systems, Mountain View, CA) and Panther Classification System software (321, 322) were used to group the regulated genes into ontology groups. Chromatin Immunoprecipiation (ChIP) The ChIP assay was performed following the standard protocol provided in the Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay Kit from Upstate Cell Signaling, with slight modifications. Antibodies for immunoprecipitation of protein/dna crosslinks included Histone H3, acetyl-histone H3K9, acetyl-histone H4 K5, K8, K12 or K16 (Upstate). Liver tissue was minced using a razor blade for formaldehyde crosslinking. DNA was purified using the Qiagen PCR Purification kit after uncrosslinking for 4 hours. Primers designed to the designated promoter sequences were used for quantification of histone acetylation using Q-PCR and are listed in Table 4. Histone H3 and input sonicated DNA were used as reference controls. 61
12 Table 3. Q-RT-PCR primer sets Primer Name ACoACarb B-actin Cby Cd36 Cyp51 DopaDC Ehhadh Fasn Gapdh Ggt1 Glut4 Hdac1RT Hdac2RT Hdac3RT Hmgcr Hmgcs Igf2 Lss Mouse 18S Pcsk9 Pdk4 Sequences (5 3 ) 5 - GAA TCT CAC GCG CCT ACT ATG 3 - ACG GTG AAA TCT CTG TGC AGG 5 - GAC GGC CAG GTC ATC ACT ATT G 3 - AGG AAG GCT GGA AAA GAG CC 5 - CGT TTC CTC ACT GAG TTA GG 3 - TAG TCT GCT AAT CTG ACG GG 5 - CCG AGG ACC ACA CTG TGT C 3 - AAC CCC ACA AGA GTT CTT TCA AA 5 - GGA GCG AAA AGT CCA CCA CAT 3 - GGT AAG GCT AAA CAC AGG TCC 5 - TAC CCA GCT ATG CTT GCA GAC 3 - GCG GAT AAC TTT AGT CCG AGC 5 - GGC TTT AAA TCT CCC ACT GGC 3 - CAG GAA GAA TTC CCA GCA TCA C 5 - AGA GAT CCC GAG ACG CTT CT 3 - GCC TGG TAG GCA TTC TGT AGT 5 - GCC TTC CGT GTT CCT ACC C 3 - TGC CTG CTT CAC CAC CTT C 5 - TCC TAC AGG AAG GTG GTT CCG 3 - CGG GCA TTG ATA ACC TCA ACT T 5 - GGA AGG AAA AGG GCT ATG CTG 3 - TGA GGA ACC GTC CAA GAA TGA 5 - TCT ACC GCC CTC ACA AAG C 3 - ACA GAA CTC AAA CAA GCC ATC A 5 - GGA GAT GAG GAT GGA GAA GAC C 3 - GTC CTT GGA TTT GTC TTC TTC C 5 - CGG GTG CTC TAC ATT GAT ATC GAC AT 3 -TAC CAG GAG AGG GAT ATT GAA ACT CT 5 - TCG TCA TTC ATT TCC TCG ACA AA 3 - GAT TGC CAT TCC ACG AGC TAT 5 - AAC TGG TGC AGA AAT CTC TAG C 3 - GGT TGA ATA GCT CAG AAC TAG CC 5 - GGG ACG TGT CTA CCT CTC AGG 3 - GAC GAT GAC GTT TGG CCT CTC 5 - GGA CTG CCC TGA ACT ATG TGG 3 - GGA CAG CCA GCC AGA ACT T 5 - TCG GCG TCC CCC AAC TTC TTA 3 - GGT AGT AGC GAC GGG CGG TGT 5 - CCC CAT GTG GAG TAC ATT GAG G 3 - CAC GCT GTT GAA GTC GGT GA 5 - AGG GAG GTC GAG CTG TTC TC 3 - GGA GTG TTC ACT AAG CGG TCA 62
13 Table 3 continued Ppara Pparb/d Pparg Pparg1mRNA Pparg2mRNA PpargmRNA-Common Sqle 5 - AAC ATC GAG TGT CGA ATA TGT GG 3 - AGC CGA ATA GTT CGC CGA AAG 5 - CCT CCA TCG TCA ACA AAG ACG GG 3 - GTC CTG GAT GGC TTC TAC CTG G 5 - TGT GGG GAT AAA GCA TCA GGC 3 - CCG GCA GTT AAG ATC ACA CCT AT 5 - CAG GAG CCT GTG AGA CCA ACA G 5 - GGT GAA ACT CTG GGA GAT TCT CC 3 - GTG TGG AGC AGA AAT GCT GGA G 5 - CGC TGC CTT CTC GGA TAT TCT 3 - ATG TCG TTT CTG AAA GAC CGA TT 63
14 Table 4. Primer sets used for amplification of designated promoter regions analyzed in ChIP assay. Primer Name Acacb Apoa4 Cyp17a1 Cyp7a1Distal Cyp7a1Proximal Cyp Cyp51-2kb Cyp51 Ex5 Cyp51 Txn G0/G1Prom GkPPRE HexCREB HexPPRE NCoR Pparg1Promoter Pparg2Promoter Saa2 SqleMinus2kb SqleSRE Sequences (5 3 ) 5 - GCA CTG GTT GCT CTT GCA GAG 3 - CTG AAC ACA CTA GCA GCA TCG AC 5 - GTG GAA CTG TAG CTG AGA TGT CC 3 - GAT TCT GTG AGA TAG TCT GGC TCC 5 - GCC CAT TCA AGA GAA TGT ACC TAG 3 -CTC CCA GAG GCA AAT GCT ATC AG 5 -GAG ACT GAC CCA CTA GAG ATG CAC 3 - GCC TTT CTC TCA CTC TCT GTC AC 5 - GAC AGA CCT TCG GCT TAT CGA C 3 - GCT TAG CAA AGC AAG ACG GTC 5 - CGA AGG GCT GGT CTC ACA AAG CCC AG 3 - CTC AGG ACC AGA TTG GTG GCG GAC AGC 5 - GGG CTG GCT GTG ATG GCA TAT ATC TTG G 3 - CAG CTG GTG CAA CCA ACC TTG TCT AC 5 - GCA CTG TCT GAG CTC ATA ATT TTG ACA GC 3 - CTG AAA CTT GGC AGA GGC AGC C 5 - CGG GCC AGA CTA AGC CAT CAG GCC GG 3 - CTG CTC CAT CGC CTG TCC GAG CAC C 5 - GTG ATC AGC ACC TTC TGA GTC TAG CAG 3 - GCT GTG GCT ATC GGT GTA CCT G 5 - CCA GCC ACT TCA TCA ACC TCT CCA CAG 3 - GGC TGA GTG TTG CAA AAG ACA GGC AGC C 5 - CTC TAG CCA CGG AAC ACA CGT CCC AAC 3 - GCA GAA CAA CTC CGG GTA GCC TGT GG 5 - CTC TCC AGC CTT TGC TGG CTT CAA G 3 - CTC AAC GAG TCA GCG GAT CCC TG 5 - GGA GCA AAG AAC ATG GCT TCA TCG 3 - GAA GTT TCC ACG CTA GAC CAC GAA TC 5 - TGT CTA TCA TGT GGG CTT CAG GCT 3 - TTG TGT GTG TAT GCA CGT GAA CGG 5 - TGG CCA AAT ACG TTT ATC TGG TGT 3 - AAT GCT GTC TGC TGC TTT GGC AAG 5 - GGA CAC ACA GCA TGA TGT CAC ATC 3 - GGA TTA GAG GTG TGA GCC ACC ATG 5 - CTT CCC AAT ACT GTG ACT GTA GCC TG 3 - GCA CAG AAC ATA GGA TGA GAT CTT GGT GG 5 - CCA GGA GCC ACC AAG AGT TCC TCC AG 3 - CGG TAG GCT AAG ATG GCG CTA TAG AGC 64
15 Metabolic Analysis Serum levels of alanine transaminase (ALT) were measured using the ALT (SGPT) Reagent Colorimetric, Endpoint Method (Teco Diagnostics) following the standard protocol with slight modifications to scale down the reactions. Glucose levels were measured in whole blood using the Free Style Flash glucose monitor, courtesy of Dr. William Russell. Insulin and glucagon levels were measured in serum using a double antibody radioimmunoassay, with all primary reagents supplied by Linco Research, Inc. (St. Charles, MO). Hormone levels were determined by the Vanderbilt Diabetes Center Hormone Assay Core. To perform the glucose tolerance test, 10-week old mice were fasted for 6 hours, and injected IP with glucose at 1.5 mg/g of body weight. Blood glucose levels were measured through the tail tip using the Free Style Flash glucose monitor during the indicated time course. Total plasma cholesterol and triglycerides were measured by standard enzymatic assays. Liver tissue extraction and analysis of lipids and cholesterol were performed by the Vanderbilt Mouse Metabolic Phenotyping Center (MMPC) Analytical Resources Core, as previously described (323). Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Liver tissue was minced to fine pieces using razor blades and fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde in 0.1M cacodylate buffer at RT for 1-2 hours, then stored at 4 until processing. Samples were washed in 0.1M cacodylate buffer then postfixed in 1% aqueous osmium tetroxide. After postfixation, the tissues were washed, dehydrated through a graded series of ethanols and embedding in Spurr resin. Thin sections (100 nm) were viewed with an FEI CM-12 transmission electron microscope operated at 80 KeV. 65
Hes6. PPARα. PPARγ HNF4 CD36
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Table Positions and Sequences of ChIP primers -63 AGGTCACTGCCA -79 AGGTCTGCTGTG Hes6-0067 GGGCAaAGTTCA ACOT -395 GGGGCAgAGTTCA PPARα -309 GGCTCAaAGTTCAaGTTCA CPTa
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Table Positions and Sequences of ChIP primers -63 AGGTCACTGCCA -79 AGGTCTGCTGTG Hes6-0067 GGGCAaAGTTCA ACOT -395 GGGGCAgAGTTCA PPARα -309 GGCTCAaAGTTCAaGTTCA CPTa
Supplementary Figure 1A A404 Cells +/- Retinoic Acid
 Supplementary Figure 1A A44 Cells +/- Retinoic Acid 1 1 H3 Lys4 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA 14 1 1 8 6 4 H3 Lys79 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Figure 1A A44 Cells +/- Retinoic Acid 1 1 H3 Lys4 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA 14 1 1 8 6 4 H3 Lys79 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA Supplementary Figure
Supplementary. Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids. complementary to positions from 77 of the SRα '- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C
 Supplementary Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids 913954 5'- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C 913955 5'- CCC AAG CTT ACA GTG TGG CCA TTC TGC TG 223396 5'- CGA CGC GTA CAG TGT GGC CAT TCT GCT G
Supplementary Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids 913954 5'- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C 913955 5'- CCC AAG CTT ACA GTG TGG CCA TTC TGC TG 223396 5'- CGA CGC GTA CAG TGT GGC CAT TCT GCT G
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC
 Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Supplemental Information. Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids. Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites. to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination
 Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 42 Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination Konstantina Skourti-Stathaki, Nicholas
Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 42 Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination Konstantina Skourti-Stathaki, Nicholas
PCR analysis was performed to show the presence and the integrity of the var1csa and var-
 Supplementary information: Methods: Table S1: Primer Name Nucleotide sequence (5-3 ) DBL3-F tcc ccg cgg agt gaa aca tca tgt gac tg DBL3-R gac tag ttt ctt tca ata aat cac tcg c DBL5-F cgc cct agg tgc ttc
Supplementary information: Methods: Table S1: Primer Name Nucleotide sequence (5-3 ) DBL3-F tcc ccg cgg agt gaa aca tca tgt gac tg DBL3-R gac tag ttt ctt tca ata aat cac tcg c DBL5-F cgc cct agg tgc ttc
ΔPDD1 x ΔPDD1. ΔPDD1 x wild type. 70 kd Pdd1. Pdd3
 Supplemental Fig. S1 ΔPDD1 x wild type ΔPDD1 x ΔPDD1 70 kd Pdd1 50 kd 37 kd Pdd3 Supplemental Fig. S1. ΔPDD1 strains express no detectable Pdd1 protein. Western blot analysis of whole-protein extracts
Supplemental Fig. S1 ΔPDD1 x wild type ΔPDD1 x ΔPDD1 70 kd Pdd1 50 kd 37 kd Pdd3 Supplemental Fig. S1. ΔPDD1 strains express no detectable Pdd1 protein. Western blot analysis of whole-protein extracts
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR
 Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
Anti-Pim-1 (Cat#3247), anti-met (Cat#3127), anti-ron (Cat#2654), Anti-EGFR
 Supplementary Methods Antibodies Anti-Pim-1 (Cat#3247), anti-met (Cat#3127), anti-ron (Cat#2654), Anti-EGFR (Cat#2646), anti-igf1r (Cat#3018), anti-insr (Cat#3020), anti-akt (pan, Cat#4691), anti-phospho-akt
Supplementary Methods Antibodies Anti-Pim-1 (Cat#3247), anti-met (Cat#3127), anti-ron (Cat#2654), Anti-EGFR (Cat#2646), anti-igf1r (Cat#3018), anti-insr (Cat#3020), anti-akt (pan, Cat#4691), anti-phospho-akt
Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH).
 Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of
 Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
Y-chromosomal haplogroup typing Using SBE reaction
 Schematic of multiplex PCR followed by SBE reaction Multiplex PCR Exo SAP purification SBE reaction 5 A 3 ddatp ddgtp 3 T 5 A G 3 T 5 3 5 G C 5 3 3 C 5 ddttp ddctp 5 T 3 T C 3 A 5 3 A 5 5 C 3 3 G 5 3 G
Schematic of multiplex PCR followed by SBE reaction Multiplex PCR Exo SAP purification SBE reaction 5 A 3 ddatp ddgtp 3 T 5 A G 3 T 5 3 5 G C 5 3 3 C 5 ddttp ddctp 5 T 3 T C 3 A 5 3 A 5 5 C 3 3 G 5 3 G
Supplemental Data. mir156-regulated SPL Transcription. Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering. Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana
 Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Overexpression Normal expression Overexpression Normal expression. 26 (21.1%) N (%) P-value a N (%)
 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Table S1. Alteration of ZNF322A protein expression levels in relation to clinicopathological parameters in 123 Asian and 74 Caucasian lung cancer patients. Asian patients Caucasian
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Table S1. Alteration of ZNF322A protein expression levels in relation to clinicopathological parameters in 123 Asian and 74 Caucasian lung cancer patients. Asian patients Caucasian
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Transfection of DNA Cages into Mammalian Cells Email: a.turberfield@physics.ox.ac.uk Table of Contents Supporting Figure 1 DNA tetrahedra used in transfection experiments 2 Supporting
Supporting Information Transfection of DNA Cages into Mammalian Cells Email: a.turberfield@physics.ox.ac.uk Table of Contents Supporting Figure 1 DNA tetrahedra used in transfection experiments 2 Supporting
Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR
 Supplemental Dataset Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. DNA sequence Amino acid sequence WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR Allele 1 CCTGTC------------------GATAGC
Supplemental Dataset Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. DNA sequence Amino acid sequence WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR Allele 1 CCTGTC------------------GATAGC
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1 Characterization of GSCs. a. Immunostaining of primary GSC spheres from GSC lines. Nestin (neural progenitor marker, red), TLX (green). Merged images of nestin,
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1 Characterization of GSCs. a. Immunostaining of primary GSC spheres from GSC lines. Nestin (neural progenitor marker, red), TLX (green). Merged images of nestin,
MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual
 MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual Shipping and Storage MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kits are shipped on dry ice. Each kit contains a box with cloning reagents and an attached bag with Eco-Blue Competent Cells (optional).
MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual Shipping and Storage MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kits are shipped on dry ice. Each kit contains a box with cloning reagents and an attached bag with Eco-Blue Competent Cells (optional).
PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells
 Supplementary Information for: PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells Ju Hye Jang 1, Hyun Kim 2, Mi Jung Jang 2, Ju Hyun Cho 1,2,* 1 Research Institute
Supplementary Information for: PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells Ju Hye Jang 1, Hyun Kim 2, Mi Jung Jang 2, Ju Hyun Cho 1,2,* 1 Research Institute
Cat. # Product Size DS130 DynaExpress TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1
 Product Name: Kit Component TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) Cat. # Product Size DS130 TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1 2 Ligation Buffer
Product Name: Kit Component TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) Cat. # Product Size DS130 TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1 2 Ligation Buffer
Quantitative reverse-transcription PCR. Transcript levels of flgs, flgr, flia and flha were
 1 Supplemental methods 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 Quantitative reverse-transcription PCR. Transcript levels of flgs, flgr, flia and flha were monitored by quantitative reverse-transcription
1 Supplemental methods 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 Quantitative reverse-transcription PCR. Transcript levels of flgs, flgr, flia and flha were monitored by quantitative reverse-transcription
Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor AtADF4 mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB
 Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB Files in this Data Supplement: Supplemental Table S1 Supplemental Table
Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB Files in this Data Supplement: Supplemental Table S1 Supplemental Table
Luo et al. Supplemental Figures and Materials and Methods
 Luo et al. Supplemental Figures and Materials and Methods The supplemental figures demonstrate that nuclear NFAT is situated at PODs, overexpressed PML does not increase NFAT nuclear localization, and
Luo et al. Supplemental Figures and Materials and Methods The supplemental figures demonstrate that nuclear NFAT is situated at PODs, overexpressed PML does not increase NFAT nuclear localization, and
Disease and selection in the human genome 3
 Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
Dierks Supplementary Fig. S1
 Dierks Supplementary Fig. S1 ITK SYK PH TH K42R wt K42R (kinase deficient) R29C E42K Y323F R29C E42K Y323F (reduced phospholipid binding) (enhanced phospholipid binding) (reduced Cbl binding) E42K Y323F
Dierks Supplementary Fig. S1 ITK SYK PH TH K42R wt K42R (kinase deficient) R29C E42K Y323F R29C E42K Y323F (reduced phospholipid binding) (enhanced phospholipid binding) (reduced Cbl binding) E42K Y323F
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/494/eaan6284/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Activation of master virulence regulator PhoP in acidic ph requires the Salmonella-specific protein UgtL Jeongjoon
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/494/eaan6284/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Activation of master virulence regulator PhoP in acidic ph requires the Salmonella-specific protein UgtL Jeongjoon
hcd1tg/hj1tg/ ApoE-/- hcd1tg/hj1tg/ ApoE+/+
 ApoE+/+ ApoE-/- ApoE-/- H&E (1x) Supplementary Figure 1. No obvious pathology is observed in the colon of diseased ApoE-/me. Colon samples were fixed in 1% formalin and laid out in Swiss rolls for paraffin
ApoE+/+ ApoE-/- ApoE-/- H&E (1x) Supplementary Figure 1. No obvious pathology is observed in the colon of diseased ApoE-/me. Colon samples were fixed in 1% formalin and laid out in Swiss rolls for paraffin
RPA-AB RPA-C Supplemental Figure S1: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification.
 RPA-AB RPA-C (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Supplemental Figure S: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification. (a) RPA; (b) RPA-AB; (c) RPA-CDE; (d) RPA-CDE core; (e) RPA-DE; and (f) RPA-C
RPA-AB RPA-C (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Supplemental Figure S: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification. (a) RPA; (b) RPA-AB; (c) RPA-CDE; (d) RPA-CDE core; (e) RPA-DE; and (f) RPA-C
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for PCR.
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for PCR. Gene Type Primer Sequence Genotyping and semi-quantitative RT-PCR F 5 -TTG CCC GAT CAC CAT CTG TA-3 rwa1-1 R 5 -TGT AGC GAT CAA GGC CTG ATC TAA-3 LB 5 -TAG CAT
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for PCR. Gene Type Primer Sequence Genotyping and semi-quantitative RT-PCR F 5 -TTG CCC GAT CAC CAT CTG TA-3 rwa1-1 R 5 -TGT AGC GAT CAA GGC CTG ATC TAA-3 LB 5 -TAG CAT
Materials Protein synthesis kit. This kit consists of 24 amino acids, 24 transfer RNAs, four messenger RNAs and one ribosome (see below).
 Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
Supplementary Methods Quantitative RT-PCR. For mrna, total RNA was prepared using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) and genomic DNA was eliminated with TURB
 Supplementary Methods Quantitative RT-PCR. For mrna, total RNA was prepared using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) and genomic DNA was eliminated with TURBO DNA-free Kit (Ambion). One µg of total RNA was reverse
Supplementary Methods Quantitative RT-PCR. For mrna, total RNA was prepared using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) and genomic DNA was eliminated with TURBO DNA-free Kit (Ambion). One µg of total RNA was reverse
Converting rabbit hybridoma into recombinant antibodies with effective transient production in an optimized human expression system
 Converting rabbit hybridoma into recombinant antibodies with effective transient production in an optimized human expression system Dr. Tim Welsink Molecular Biology Transient Gene Expression OUTLINE Short
Converting rabbit hybridoma into recombinant antibodies with effective transient production in an optimized human expression system Dr. Tim Welsink Molecular Biology Transient Gene Expression OUTLINE Short
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material Diversity of O-antigen repeat-unit structures can account for the substantial sequence variation of Wzx translocases Yaoqin Hong and Peter R. Reeves School of Molecular Bioscience,
Supplemental material Diversity of O-antigen repeat-unit structures can account for the substantial sequence variation of Wzx translocases Yaoqin Hong and Peter R. Reeves School of Molecular Bioscience,
Supporting Information. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2006
 Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), , DOI: /bi00034a013
 Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), 10807 10815, DOI: 10.1021/bi00034a013 LESNIK 10807-1081 Terms & Conditions Electronic Supporting Information files are available without a subscription
Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), 10807 10815, DOI: 10.1021/bi00034a013 LESNIK 10807-1081 Terms & Conditions Electronic Supporting Information files are available without a subscription
Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures)
 Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures) Strain number Relevant genotype Source or reference 1045 AB1157 Graham Walker (Donnelly and Walker, 1989) 2458 3084 (MG1655)
Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures) Strain number Relevant genotype Source or reference 1045 AB1157 Graham Walker (Donnelly and Walker, 1989) 2458 3084 (MG1655)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature07182 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES Fig. S1. myf5-expressing cells give rise to brown fat depots and skeletal muscle (a) Perirenal BAT from control (cre negative) and myf5-cre:r26r3-yfp
doi: 10.1038/nature07182 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES Fig. S1. myf5-expressing cells give rise to brown fat depots and skeletal muscle (a) Perirenal BAT from control (cre negative) and myf5-cre:r26r3-yfp
Supplementary Information. Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins
 Supplementary Information Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins Chuhan Zong 1, Mikhail O. Maksimov 2, A. James Link 2,3 * Departments of 1 Chemistry, 2 Chemical and Biological Engineering, and
Supplementary Information Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins Chuhan Zong 1, Mikhail O. Maksimov 2, A. James Link 2,3 * Departments of 1 Chemistry, 2 Chemical and Biological Engineering, and
NAME:... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:... Maximum marks: 50. Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer Science, UKZN
 COMP710, Bioinformatics with Julia, Test One, Thursday the 20 th of April, 2017, 09h30-11h30 1 NAME:...... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:...... Maximum marks: 50 Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer
COMP710, Bioinformatics with Julia, Test One, Thursday the 20 th of April, 2017, 09h30-11h30 1 NAME:...... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:...... Maximum marks: 50 Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer
II 0.95 DM2 (RPP1) DM3 (At3g61540) b
 Table S2. F 2 Segregation Ratios at 16 C, Related to Figure 2 Cross n c Phenotype Model e 2 Locus A Locus B Normal F 1 -like Enhanced d Uk-1/Uk-3 149 64 36 49 DM2 (RPP1) DM1 (SSI4) a Bla-1/Hh-0 F 3 111
Table S2. F 2 Segregation Ratios at 16 C, Related to Figure 2 Cross n c Phenotype Model e 2 Locus A Locus B Normal F 1 -like Enhanced d Uk-1/Uk-3 149 64 36 49 DM2 (RPP1) DM1 (SSI4) a Bla-1/Hh-0 F 3 111
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Table S1. Oligonucleotide sequences used in this work Oligo DNA A B C D CpG-A CpG-B CpG-C CpG-D Sequence 5 ACA TTC CTA AGT CTG AAA CAT TAC AGC TTG CTA CAC GAG AAG AGC CGC CAT AGT
Supporting Information Table S1. Oligonucleotide sequences used in this work Oligo DNA A B C D CpG-A CpG-B CpG-C CpG-D Sequence 5 ACA TTC CTA AGT CTG AAA CAT TAC AGC TTG CTA CAC GAG AAG AGC CGC CAT AGT
Legends for supplementary figures 1-3
 High throughput resistance profiling of Plasmodium falciparum infections based on custom dual indexing and Illumina next generation sequencing-technology Sidsel Nag 1,2 *, Marlene D. Dalgaard 3, Poul-Erik
High throughput resistance profiling of Plasmodium falciparum infections based on custom dual indexing and Illumina next generation sequencing-technology Sidsel Nag 1,2 *, Marlene D. Dalgaard 3, Poul-Erik
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature11496 Cl. 8 Cl. E93 Rag1 -/- 3H9 + BM Rag1 -/- BM CD CD c-kit c-kit c-kit wt Spleen c-kit B22 B22 IgM IgM IgM Supplementary Figure 1. FACS analysis of single-cell-derived pre-b cell clones.
doi:1.138/nature11496 Cl. 8 Cl. E93 Rag1 -/- 3H9 + BM Rag1 -/- BM CD CD c-kit c-kit c-kit wt Spleen c-kit B22 B22 IgM IgM IgM Supplementary Figure 1. FACS analysis of single-cell-derived pre-b cell clones.
strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular
![strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular](/thumbs/72/66361212.jpg) Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Supplemental Data. Bennett et al. (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 BRN1 ---------MSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYEKFEMEVIKEVDLNKIEPWDLQDRCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 81 BRN2 --------MGSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYQKFEMEVIREVDLNKLEPWDLQERCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 82 SMB
BRN1 ---------MSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYEKFEMEVIKEVDLNKIEPWDLQDRCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 81 BRN2 --------MGSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYQKFEMEVIREVDLNKLEPWDLQERCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 82 SMB
Supporting Online Information
 Supporting Online Information Isolation of Human Genomic DNA Sequences with Expanded Nucleobase Selectivity Preeti Rathi, Sara Maurer, Grzegorz Kubik and Daniel Summerer* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
Supporting Online Information Isolation of Human Genomic DNA Sequences with Expanded Nucleobase Selectivity Preeti Rathi, Sara Maurer, Grzegorz Kubik and Daniel Summerer* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
Supplemental Information. Target-Mediated Protection of Endogenous. MicroRNAs in C. elegans. Inventory of Supplementary Information
 Developmental Cell, Volume 20 Supplemental Information Target-Mediated Protection of Endogenous MicroRNAs in C. elegans Saibal Chatterjee, Monika Fasler, Ingo Büssing, and Helge Großhans Inventory of Supplementary
Developmental Cell, Volume 20 Supplemental Information Target-Mediated Protection of Endogenous MicroRNAs in C. elegans Saibal Chatterjee, Monika Fasler, Ingo Büssing, and Helge Großhans Inventory of Supplementary
Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification
 Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification Duhee Bang & George M Church Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Dpo4 gene (1.05kb) construction by various methods. Supplementary
Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification Duhee Bang & George M Church Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Dpo4 gene (1.05kb) construction by various methods. Supplementary
Lecture 11: Gene Prediction
 Lecture 11: Gene Prediction Study Chapter 6.11-6.14 1 Gene: A sequence of nucleotides coding for protein Gene Prediction Problem: Determine the beginning and end positions of genes in a genome Where are
Lecture 11: Gene Prediction Study Chapter 6.11-6.14 1 Gene: A sequence of nucleotides coding for protein Gene Prediction Problem: Determine the beginning and end positions of genes in a genome Where are
SUPPORTING INFORMATION FILE
 Intrinsic and extrinsic connections of Tet3 dioxygenase with CXXC zinc finger modules Nan Liu, Mengxi Wang, Wen Deng, Christine S. Schmidt, Weihua Qin, Heinrich Leonhardt and Fabio Spada Department of
Intrinsic and extrinsic connections of Tet3 dioxygenase with CXXC zinc finger modules Nan Liu, Mengxi Wang, Wen Deng, Christine S. Schmidt, Weihua Qin, Heinrich Leonhardt and Fabio Spada Department of
An engineered tryptophan zipper-type peptide as a molecular recognition scaffold
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL An engineered tryptophan zipper-type peptide as a molecular recognition scaffold Zihao Cheng and Robert E. Campbell* Supplementary Methods Library construction for FRET-based screening
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL An engineered tryptophan zipper-type peptide as a molecular recognition scaffold Zihao Cheng and Robert E. Campbell* Supplementary Methods Library construction for FRET-based screening
ORFs and genes. Please sit in row K or forward
 ORFs and genes Please sit in row K or forward https://www.flickr.com/photos/teseum/3231682806/in/photostream/ Question: why do some strains of Vibrio cause cholera and others don t? Methods Mechanisms
ORFs and genes Please sit in row K or forward https://www.flickr.com/photos/teseum/3231682806/in/photostream/ Question: why do some strains of Vibrio cause cholera and others don t? Methods Mechanisms
Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines
 Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, 2007. Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines Project Leader: Dr Douglas C. Hodgins (519-824-4120 Ex 54758, fax 519-824-5930)
Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, 2007. Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines Project Leader: Dr Douglas C. Hodgins (519-824-4120 Ex 54758, fax 519-824-5930)
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Investigation of the Biosynthesis of the Lasso Peptide Chaxapeptin Using an E. coli-based Production System Helena Martin-Gómez, Uwe Linne, Fernando Albericio, Judit Tulla-Puche,*
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Investigation of the Biosynthesis of the Lasso Peptide Chaxapeptin Using an E. coli-based Production System Helena Martin-Gómez, Uwe Linne, Fernando Albericio, Judit Tulla-Puche,*
An evolutionarily conserved negative feedback mechanism in the hippo pathway reflects functional difference between LATS1 and LATS2
 /, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2015 2016 An evolutionarily conserved negative feedback mechanism in the hippo pathway reflects functional difference between LATS1 and LATS2 Supplementary
/, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2015 2016 An evolutionarily conserved negative feedback mechanism in the hippo pathway reflects functional difference between LATS1 and LATS2 Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1. The level of pri-mir-8 gradually decreases while those of BR-C and E74 increase during 3rd instar larval development.
 qrt-pcr RT-PCR Relative pri-mir-8 level 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Early 3rd (72h) Mid 3rd (96h) Late 3rd (119h) BR-C E74 mtl rrna Early 3rd (72h) Mid 3rd (96h) Late 3rd (119h) Supplementary Figure 1.
qrt-pcr RT-PCR Relative pri-mir-8 level 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Early 3rd (72h) Mid 3rd (96h) Late 3rd (119h) BR-C E74 mtl rrna Early 3rd (72h) Mid 3rd (96h) Late 3rd (119h) Supplementary Figure 1.
Supplementary Figure 1 Tmod3 expression and phosphorylation. (a) Expression of Tmod3 in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and differentiated adipocytes.
 1 2 3 1 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Supplementary Figure 1 Tmod3 expression and phosphorylation. (a) Expression of Tmod3 in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and differentiated
1 2 3 1 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Supplementary Figure 1 Tmod3 expression and phosphorylation. (a) Expression of Tmod3 in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and differentiated
Supplemental Data. Lin28 Mediates the Terminal Uridylation. of let-7 Precursor MicroRNA. Molecular Cell, Volume 32
 Molecular Cell, Volume 32 Supplemental Data Lin28 Mediates the Terminal Uridylation of let-7 Precursor MicroRNA Inha Heo, Chirlmin Joo, Jun Cho, Minju Ha, Jinju Han, and V. Narry Kim Figure S1. Endogenous
Molecular Cell, Volume 32 Supplemental Data Lin28 Mediates the Terminal Uridylation of let-7 Precursor MicroRNA Inha Heo, Chirlmin Joo, Jun Cho, Minju Ha, Jinju Han, and V. Narry Kim Figure S1. Endogenous
Multiplexing Genome-scale Engineering
 Multiplexing Genome-scale Engineering Harris Wang, Ph.D. Department of Systems Biology Department of Pathology & Cell Biology http://wanglab.c2b2.columbia.edu Rise of Genomics An Expanding Toolbox Esvelt
Multiplexing Genome-scale Engineering Harris Wang, Ph.D. Department of Systems Biology Department of Pathology & Cell Biology http://wanglab.c2b2.columbia.edu Rise of Genomics An Expanding Toolbox Esvelt
S4B fluorescence (AU)
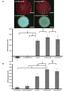 A S4B fluorescence (AU) S4B fluorescence (AU) dsbb csgba csgd dsbb csgba bcsa 5000 * NS NS 4000 * 3000 2000 1000 0 ΔcsgBAΔbcsA ΔcsgDΔdsbBΔbcsA ΔcsgBA ΔdsbBΔcsgBA ΔcsgDΔdsbB B -1000 4000 * * NS 3500 * 3000
A S4B fluorescence (AU) S4B fluorescence (AU) dsbb csgba csgd dsbb csgba bcsa 5000 * NS NS 4000 * 3000 2000 1000 0 ΔcsgBAΔbcsA ΔcsgDΔdsbBΔbcsA ΔcsgBA ΔdsbBΔcsgBA ΔcsgDΔdsbB B -1000 4000 * * NS 3500 * 3000
Total RNA was extracted from ESCs or wild-type MEF using an RNeasy Plus mini kit
 Supplementary information, Data S1 Materials and methods RNA-seq Total RNA was extracted from ESCs or wild-type MEF using an RNeasy Plus mini kit (Qiagen). Poly A+ RNA was purified from the total RNA and
Supplementary information, Data S1 Materials and methods RNA-seq Total RNA was extracted from ESCs or wild-type MEF using an RNeasy Plus mini kit (Qiagen). Poly A+ RNA was purified from the total RNA and
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE S1. Additional descriptions of plasmid constructions and the oligonucleotides used Plasmid or Oligonucleotide
 SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE S1. Additional descriptions of plasmid constructions and the oligonucleotides used Plasmid or Oligonucleotide former/ working Description a designation Plasmids pes213a b pes213-tn5
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE S1. Additional descriptions of plasmid constructions and the oligonucleotides used Plasmid or Oligonucleotide former/ working Description a designation Plasmids pes213a b pes213-tn5
Expression of Recombinant Proteins
 Expression of Recombinant Proteins Uses of Cloned Genes sequencing reagents (eg, probes) protein production insufficient natural quantities modify/mutagenesis library screening Expression Vector Features
Expression of Recombinant Proteins Uses of Cloned Genes sequencing reagents (eg, probes) protein production insufficient natural quantities modify/mutagenesis library screening Expression Vector Features
Supplementary Fig. 1. Isolation and in vitro expansion of EpCAM + cholangiocytes. For collagenase perfusion, enzyme solution was injected from the
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Isolation and in vitro expansion of EpCAM + cholangiocytes. For collagenase perfusion, enzyme solution was injected from the portal vein for digesting adult livers, whereas it was
Supplementary Fig. 1. Isolation and in vitro expansion of EpCAM + cholangiocytes. For collagenase perfusion, enzyme solution was injected from the portal vein for digesting adult livers, whereas it was
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE S1. Identification of BmCREC. (A) Amino acid sequences of BmCREC show the peptides identified in LC-MS/MS analysis (marked by red letters
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE S1. Identification of BmCREC. (A) Amino acid sequences of BmCREC show the peptides identified in LC-MS/MS analysis (marked by red letters
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Microbead-based biomimetic synthetic neighbors enhance survival and function of rat pancreatic β-cells Wei Li, a Samuel Lee, b Minglin Ma, a, f Soo Min Kim, b Patrick Guye, c
Supplementary Information Microbead-based biomimetic synthetic neighbors enhance survival and function of rat pancreatic β-cells Wei Li, a Samuel Lee, b Minglin Ma, a, f Soo Min Kim, b Patrick Guye, c
SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer
 TEACHER S GUIDE SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer SYNOPSIS This activity uses the metaphor of decoding a secret message for the Protein Synthesis process. Students teach themselves
TEACHER S GUIDE SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer SYNOPSIS This activity uses the metaphor of decoding a secret message for the Protein Synthesis process. Students teach themselves
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Material and methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Material and methods Cell culture Human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG) cells and human embryonic kidney (HEK)93 cells were grown in Dulbecco s modified Eagle s medium (Invitrogen
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Material and methods Cell culture Human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG) cells and human embryonic kidney (HEK)93 cells were grown in Dulbecco s modified Eagle s medium (Invitrogen
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Barderas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0801221105 SI Text: Docking of gastrin to Constructed scfv Models Interactive predocking of the 4-WL-5 motif into the central pocket observed in the
Supporting Information Barderas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0801221105 SI Text: Docking of gastrin to Constructed scfv Models Interactive predocking of the 4-WL-5 motif into the central pocket observed in the
evaluated with UAS CLB eliciting UAS CIT -N Libraries increase in the
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Promoter scaffold library assemblies. Many ensembless of libraries were evaluated in this work. As a legend, the box outline color in top half of the figure
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Promoter scaffold library assemblies. Many ensembless of libraries were evaluated in this work. As a legend, the box outline color in top half of the figure
Efficient genome replication of hepatitis B virus using adenovirus vector: a compact pregenomic RNA-expression unit
 Efficient genome replication of hepatitis B virus using adenovirus vector: a compact pregenomic RNA-expression unit Mariko Suzuki 1, Saki Kondo 1, Manabu Yamasaki 2, Norie Matsuda 2, Akio Nomoto 2, Tetsuro
Efficient genome replication of hepatitis B virus using adenovirus vector: a compact pregenomic RNA-expression unit Mariko Suzuki 1, Saki Kondo 1, Manabu Yamasaki 2, Norie Matsuda 2, Akio Nomoto 2, Tetsuro
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplemental Table 1. Magnaporthe oryzae strains generated in this study. Strain background Genotype Strain name Description Guy-11 H1:RFP H1:RFP Strain expressing Histone H1- encoding gene
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplemental Table 1. Magnaporthe oryzae strains generated in this study. Strain background Genotype Strain name Description Guy-11 H1:RFP H1:RFP Strain expressing Histone H1- encoding gene
A Genetically Encoded Toolbox for Glycocalyx Engineering: Tunable Control of Cell Adhesion,
 TITLE A Genetically Encoded Toolbox for Glycocalyx Engineering: Tunable Control of Cell Adhesion, Survival, and Cancer Cell Behaviors AUTHORS Carolyn R. Shurer *, Marshall J. Colville *, Vivek K. Gupta,
TITLE A Genetically Encoded Toolbox for Glycocalyx Engineering: Tunable Control of Cell Adhesion, Survival, and Cancer Cell Behaviors AUTHORS Carolyn R. Shurer *, Marshall J. Colville *, Vivek K. Gupta,
Search for and Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and Establishment of SNP Markers
 DNA Research 9, 163 171 (2002) Search for and Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and Establishment of SNP Markers Shinobu Nasu, Junko Suzuki, Rieko
DNA Research 9, 163 171 (2002) Search for and Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and Establishment of SNP Markers Shinobu Nasu, Junko Suzuki, Rieko
I. Things to keep in mind before you start this protocol
 Inverse PCR and Sequencing Protocol on 5 Fly Preps For recovery of sequences flanking piggybac elements This protocol is an adaptation of "Inverse PCR and Cycle Sequencing Protocols" by E. Jay Rehm Berkeley
Inverse PCR and Sequencing Protocol on 5 Fly Preps For recovery of sequences flanking piggybac elements This protocol is an adaptation of "Inverse PCR and Cycle Sequencing Protocols" by E. Jay Rehm Berkeley
Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis. Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010
 Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010 1 1- What is quick change site directed mutagenesis? 2- An overview of the kit contents. 3- A brief information
Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010 1 1- What is quick change site directed mutagenesis? 2- An overview of the kit contents. 3- A brief information
Lecture 19A. DNA computing
 Lecture 19A. DNA computing What exactly is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? DNA is the material that contains codes for the many physical characteristics of every living creature. Your cells use different
Lecture 19A. DNA computing What exactly is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? DNA is the material that contains codes for the many physical characteristics of every living creature. Your cells use different
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Coding and noncoding transcription at the vg locus. (a,b) qpcr analysis of developmental and tissue-specific vg mrna (a) and PRE/TRE (b) transcription, shown as percentage of TBP
Supplementary Figure 1 Coding and noncoding transcription at the vg locus. (a,b) qpcr analysis of developmental and tissue-specific vg mrna (a) and PRE/TRE (b) transcription, shown as percentage of TBP
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
Supplemental Data. Jones et al. Plant Cell. (2010) /tpc
 IAA synthesis rate Supplemental Data. Jones et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..7856 Supplemental Figure. Root tip specific IAA biosynthesis after induction of the CKX gene. 6 DAG pmdc7:atckx seedling roots
IAA synthesis rate Supplemental Data. Jones et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..7856 Supplemental Figure. Root tip specific IAA biosynthesis after induction of the CKX gene. 6 DAG pmdc7:atckx seedling roots
Nongenetic Reprogramming of the Ligand Specificity. of Growth Factor Receptors by Bispecific DNA Aptamers
 Supporting Information For Nongenetic Reprogramming of the Ligand Specificity of Growth Factor Receptors by Bispecific DNA Aptamers Ryosuke Ueki,* Saki Atsuta, Ayaka Ueki and Shinsuke Sando* Department
Supporting Information For Nongenetic Reprogramming of the Ligand Specificity of Growth Factor Receptors by Bispecific DNA Aptamers Ryosuke Ueki,* Saki Atsuta, Ayaka Ueki and Shinsuke Sando* Department
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS. E. coli strains, plasmids, and growth conditions. Escherichia coli strain P90C (1)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS E. coli strains, plasmids, and growth conditions. Escherichia coli strain P90C (1) dinb::kan (lab stock) derivative was used as wild-type. MG1655 alka tag dinb (2) is
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS E. coli strains, plasmids, and growth conditions. Escherichia coli strain P90C (1) dinb::kan (lab stock) derivative was used as wild-type. MG1655 alka tag dinb (2) is
Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription
 Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription Students must be positive that they understand standard PCR. There is a resource on the web for this purpose. Warn them before this class.
Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription Students must be positive that they understand standard PCR. There is a resource on the web for this purpose. Warn them before this class.
Glutathione (GSH)-Decorated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Binding Glutathione-S-transferase (GST) Fusion Protein and Manipulating Live Cells
 Glutathione (GSH)-Decorated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Binding Glutathione-S-transferase (GST) Fusion Protein and Manipulating Live Cells Yue Pan, Marcus J. C. Long, Xinming Li, Junfeng Shi, Lizbeth Hedstrom,
Glutathione (GSH)-Decorated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Binding Glutathione-S-transferase (GST) Fusion Protein and Manipulating Live Cells Yue Pan, Marcus J. C. Long, Xinming Li, Junfeng Shi, Lizbeth Hedstrom,
Homework. A bit about the nature of the atoms of interest. Project. The role of electronega<vity
 Homework Why cited articles are especially useful. citeulike science citation index When cutting and pasting less is more. Project Your protein: I will mail these out this weekend If you haven t gotten
Homework Why cited articles are especially useful. citeulike science citation index When cutting and pasting less is more. Project Your protein: I will mail these out this weekend If you haven t gotten
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL GENOTYPING WITH MULTIPLEXING TARGETED RESEQUENCING
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL GENOTYPING WITH MULTIPLEXING TARGETED RESEQUENCING All of the patients and control subjects were sequenced and genotyped in the same way. Shotgun libraries of approximately 250 bp
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL GENOTYPING WITH MULTIPLEXING TARGETED RESEQUENCING All of the patients and control subjects were sequenced and genotyped in the same way. Shotgun libraries of approximately 250 bp
PCR-based Markers and Cut Flower Longevity in Carnation
 PCRbased Markers and Cut Flower Longevity in Carnation Laura De Benedetti, Luca Braglia, Simona Bruna, Gianluca Burchi *, Antonio Mercuri and Tito Schiva Istituto Sperimentale per la Floricoltura, Corso
PCRbased Markers and Cut Flower Longevity in Carnation Laura De Benedetti, Luca Braglia, Simona Bruna, Gianluca Burchi *, Antonio Mercuri and Tito Schiva Istituto Sperimentale per la Floricoltura, Corso
G+C content. 1 Introduction. 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts. 3 Genome size. 4 Replichores and gene orientation. 5 Chirochores.
 1 Introduction 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts 3 Genome size 4 Replichores and gene orientation 5 Chirochores 6 7 Codon usage 121 marc.bailly-bechet@univ-lyon1.fr Bacterial genome structures Introduction
1 Introduction 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts 3 Genome size 4 Replichores and gene orientation 5 Chirochores 6 7 Codon usage 121 marc.bailly-bechet@univ-lyon1.fr Bacterial genome structures Introduction
Supplementary data. sienigma. F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM. a-p53
 Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet
 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet Exam in: MBV4010 Arbeidsmetoder i molekylærbiologi og biokjemi I MBV4010 Methods in molecular biology and biochemistry I Day of exam: Friday
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet Exam in: MBV4010 Arbeidsmetoder i molekylærbiologi og biokjemi I MBV4010 Methods in molecular biology and biochemistry I Day of exam: Friday
DNA sentences. How are proteins coded for by DNA? Materials. Teacher instructions. Student instructions. Reflection
 DNA sentences How are proteins coded for by DNA? Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the molecule of life. DNA is one of the most recognizable nucleic acids, a double-stranded helix. The process by which DNA
DNA sentences How are proteins coded for by DNA? Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the molecule of life. DNA is one of the most recognizable nucleic acids, a double-stranded helix. The process by which DNA
11th Meeting of the Science Working Group. Lima, Peru, October 2012 SWG-11-JM-11
 11th Meeting of the Science Working Group Lima, Peru, 15-19 October 2012 Russian population genetics studies of jack mackerel in the South Pacific P.K.Afanasiev M.A.Rabchun A.I.Glubokov Introduction. In
11th Meeting of the Science Working Group Lima, Peru, 15-19 October 2012 Russian population genetics studies of jack mackerel in the South Pacific P.K.Afanasiev M.A.Rabchun A.I.Glubokov Introduction. In
Supporting Information. for. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Z Wiley-VCH 2004
 Supporting Information for Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Z53445 Wiley-VC 2004 69451 Weinheim, Germany Small Interfering RNA Expression in Cells Based on an Efficiently Constructed Dumbbell-shaped DNA Masumi Taki,
Supporting Information for Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Z53445 Wiley-VC 2004 69451 Weinheim, Germany Small Interfering RNA Expression in Cells Based on an Efficiently Constructed Dumbbell-shaped DNA Masumi Taki,
Supporting Information
 upporting Information hiota et al..73/pnas.159218 I Materials and Methods Yeast trains. Yeast strains used in this study are described in Table 1. TOM22FLAG, a yeast haploid strain for expression of C-terminally
upporting Information hiota et al..73/pnas.159218 I Materials and Methods Yeast trains. Yeast strains used in this study are described in Table 1. TOM22FLAG, a yeast haploid strain for expression of C-terminally
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Load-dependent modulation of non-muscle myosin-2a function by tropomyosin 4.2 Nikolas Hundt 1, Walter Steffen 2, Salma Pathan-Chhatbar 1, Manuel H. Taft 1, Dietmar J. Manstein
Supplementary Information Load-dependent modulation of non-muscle myosin-2a function by tropomyosin 4.2 Nikolas Hundt 1, Walter Steffen 2, Salma Pathan-Chhatbar 1, Manuel H. Taft 1, Dietmar J. Manstein
BioInformatics and Computational Molecular Biology. Course Website
 BioInformatics and Computational Molecular Biology Course Website http://bioinformatics.uchc.edu What is Bioinformatics Bioinformatics upgrades the information content of biological measurements. Discovery
BioInformatics and Computational Molecular Biology Course Website http://bioinformatics.uchc.edu What is Bioinformatics Bioinformatics upgrades the information content of biological measurements. Discovery
