Transcription is the first step of gene expression, in which a particular segment of DNA is copied into RNA by the enzyme, RNA polymerase.
|
|
|
- Shawn Carroll
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Transcription in Bacteria
2 Transcription in Bacteria
3 Transcription in Bacteria Transcription is the first step of gene expression, in which a particular segment of DNA is copied into RNA by the enzyme, RNA polymerase. If the gene transcribed encodes a protein, the result of transcription is messenger RNA (mrna), which then will be used to create that protein via the process of translation. Alternatively, the transcribed gene may encode for either noncoding RNA genes (such as microrna) or ribosomal RNA (rrna) or transfer RNA (trna), other components of the proteinassembly process, or other ribozymes.
4 Mechanism of transcription RNA polymerase is the enzyme that catalyzes RNA synthesis. Using DNA as a template, RNA polymerase joins, or polymerizes, nucleoside triphosphates (NTPs) by phosphodiester bonds from 5' to 3'. In bacteria there is one type of RNA polymerase and transcription and translation are coupled (they occur within a single cellular compartment). As soon as transcription of the mrna begins, ribosomes initiate protein synthesis. The whole process occurs within minutes.
5 Transcription in E. coli and in Eucaryotes Procaryotes Genes are grouped into operons Eucaryotes Genes are not grouped in operons mrna may contain transcript of several genes (poly-cistronic) each mrna contains only transcript of a single gene (mono-cistronic) Transcription and translation are coupled. Transcript is translated already during transcription. Transcription and translation are NOT coupled. Transcription takes place in nucleus, translation in cytosol. Gene regulation takes place by modification of transcription rate Gene regulation via transcription and by RNA-processing, RNA stability etc. mrnas are not processed in prokaryotes mrnas are processed in in eukaryotes (splicing, CAP, poly-a tail) rrna and trna are processed both in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
6 Transcription and translation is coupled in prokaryotes Initiation of transcription Sense strand nontemplate strand = mrna Antisense strand template strand As soon the growing mrna chain separates from DNA, ribosomes attach to it and begin translation on the 5 end of the molecule following right behind the RNA polymerase while it is transcribing 3 1 2
7 How does transcription get started? RNA polymerase binds to a region on DNA called a PROMOTER Bacterial promoter structure Bacterial promoters are not absolutely conserved but they do have a consensus sequence. Conserved sequence: When sequences of DNA have exactly the same series of nucleotides in a given region. Consensus sequence Consensus sequence: there is some variation in the sequence but certain nucleotides are present at high frequency.
8 Bacterial promoter structure It is convention to indicate the start of transcription by the number +1 and to use positive numbers to count farther down the DNA in the direction of transcription (downstream). If transcription is proceeding to the right, then the direction to the left is called upstream with the bases indicated by negative numbers. For the majority of E. coli genes, the promoter consensus sequence consists of two hexamer sequences. Centered at 10 is the consensus sequence TATAAT, which is also known as the TATA box or Pribnow box. (capital letters indicate bases found in those positions in more than 50% of promoters analyzed; small letters = less than 50%).
9 Bacterial promoter structure Another region with similar sequences among many promoters is centered at 35. The consensus sequence at 35 is TTGACA. The spacing between the 10 and 35 sequences and the start point for transcription is important, and deletions or insertions that change the spacing are deleterious.
10 How does RNA polymerase recognize and bind to the promoter? Structure of bacterial RNA polymerase Comprised of a core enzyme plus a transcription factor called the sigma factor (σ). Together they form the complete, fully functional enzyme complex called the holoenzyme.
11 Structure of bacterial RNA polymerase The core enzyme The core enzyme is the component of the holoenzyme that catalyzes polymerization. It is 400 kd in size and has five subunits: two copies of the α-subunit (αi, αii), and one copy each of the β-, β -, and ω-subunits. X-ray crystallographic studies revealed a crab claw shape. Subunits α I, α II, and ω form the base of the claw, and subunits β and β form the pincers. These pincers form an internal channel (2.7 nm wide). The enzyme active site is located at this internal channel where an essential Mg 2+ ion is bound. The core enzyme has high affinity for most DNA. In the absence of σ, it can initiate synthesis anywhere on a DNA template in vitro. The σ factor is responsible for decreasing the nonspecific binding affinity of the RNA polymerase. The sequence, structure, and function are evolutionarily conserved from bacteria to humans.
12 Structure of bacterial RNA polymerase Sigma factor In bacteria there are many different σ factors. In E. coli the most abundant σ factor is σ 70. It has a higher binding affinity for the RNA polymerase core enzyme than other σ factors. Most of the σ factors share four regions of amino acid sequence homology that play a role in recognizing the promoter These four regions are further divided into subdomains with specific functions. In the holoenzyme the globular domain of the σ factors are spread out across the face of the crab claw.
13 Structure of bacterial RNA polymerase Sigma factor σ 70 is required for specific binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter of the majority of genes in E. coli. It stimulates a change in shape of the internal channel where transcription takes place. The 35 and the 10 sequences are necessary for recognition by the σ 70 factor The 10 sequence is the region of contact for the core enzyme. In addition, the 10 sequence is necessary for the initial melting of the DNA to expose the template strand. A domain of the σ 70 factor binds to the nontemplate strand of the 10 sequence in a sequence-specific manner that stabilizes the initial transcription bubble.
14 The sigma factor, σ 70 (MW = 72000) Fragments 2.1 and 2.2of σ 70 bind strongly to β'. Adjacent helical segments located in fragments 2.3 and 2.4are involved in recognition of the -10 regionof the promoter. The 2.3 region is required for melting. In addition, sequences near the N-terminal(1.1 and 1.2) of σ 70 were found to be inhibitory to DNA binding. The addition of σto the polymerase core gives the RNA polymerase holoenzymerecognizing a site at -10to form the closed complex. In the holoenzymeform, an additional DNA binding domain of σ, the region 4.2, become unmasked, and this recognizes a second site at -35, approximately 2 helical turns of DNA away. If the -35 site is recognized, the holoenzymemelts the region -11 to +3in the DNA, giving the open complex, and the bubble is stabilized by the ssdnabinding domain of σat region 2.3. The region 2.5 interactswith dsdnafrom -11 to 17(spacer region). Melting of the transcription bubble admits the template strand to the catalytic site, allowing initiation to proceed.
15 Alternative sigma factors respond to general environmental changes E. Coli sigma factors recognize promoters with different consensus sequences Sigma70 (rpod) (-35)TTGACA (-10)TATAAT Primary sigma factor, or housekeeping sigma factor. Sigma54 (rpon) (-35)CTGGCAC (-10)TTGCA Alternative sigma factor involved in transcribing nitrogen-regulated genes (among others). Sigma32 (rpoh) (-35)TNNCNCCCTTGAA (-10)CCCATNT Heat shock factor involved in activation of genes after heat shock. SigmaS (rpos) intrinsic curvature (-10)TGNCCATA(C/A)T Alternative sigma factor transcribing genes of stationary phase of growth. Note the extended -10 element.
16 DNAse I Footprinting 1. Prepare end-labeled DNA. 2. Bind protein. 3. Mild digestion with DNAse I (randomly cleaves ds DNA on each strand) 4. Separate DNA fragments on denaturing acrylamide gels.
17 DNase I footprint performed on an end-labeled DNA fragment FIS Footprint Samples in lanes 2-4 had increasing amounts of the DNA-binding protein (lambda protein cii); lane 1 had no protein.
18 DNA-protein complex Partially DNase I digested DNA is subjected to linear PCR DNase I Products of DNase I digestion are primer extended by linear PCR using a 5 end-labeled oligonucleotide Sequencing gel
19 Gel retardation assay Gel Shift Electro Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Band Shift Incubating a purified protein, or a complex mixture of proteins e.g. nuclear or cell extract, with a 32 P end-labelled DNA fragment containing the putative protein binding site (from promoter region). Reaction products are then analysed on a nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel. The specificity of the DNA-binding protein for the putative binding site is established by competition experiments using DNA fragments or oligonucleotides containing a binding site for the protein of interest, or other unrelated DNA sequences. No protein add protein Non-denaturing PAGE * * Free DNA probe Retarded mobility due to protein binding
20 virb virf virg Bound DNA EMSA Free DNA Evaluating the Binding Affinity
21 Primer extension mrna 5 3 annealing + primer- 32 P G A T C Early-log Mid-log Late-log 37 C 10 C 37 C 10 C 37 C 10 C mrna 5 primer - 32 P 3 reverse transcriptase mrna 5 3 primer - 32 P cdna run on denaturating gel +77 cspa mrna
22 The transcription process consists of three stages: Initiation Elongation Termination
23 Initiation
24 Initiation of transcription The RNA polymerase holoenzyme initially binds to the promoter at nucleotide positions 35 and 10 relative to the transcription start site (+1) to form a closed promoter complex. The term closed indicates that the DNA remains doublestranded and the complex is reversible.
25 Initiation of transcription The complex then undergoes a structural transition to the open form in which approximately 18 bp around the transcription start site are melted to expose the template strand of the DNA. Transcription is aided by negative supercoiling of the promoter region of some genes. Formation of the open complex is generally irreversible and transcription initiated in the presence of NTPs. No primer is required for initiation by RNA polymerase.
26 Initiation of transcription During initial transcription, RNA polymerase produces and releases short RNA transcripts of less then ten ribonucleotides (abortive synthesis) before escaping the promoter (promotor clearance). It is not clear why RNA polymerase must undergo this period of abortive initiation before achieving escape, but a region of the σ factor appear to be involved. Infact, in this step there is sequential displacement of some domains of σ that would otherwise act as a barrier to the extension of the nascent RNA as it emerges from the RNA exit channel.
27 Elongation
28 Elongation After about 9-12 nt of RNA have been synthesized, the initiation complex enters the elongation stage. As RNA polymerase moves during elongation, it holds the DNA strands apart, forming a transcription bubble. The moving polymerase protects a footprint of ~30 bp along the DNA against nuclease digestion. Within the transcription bubble, one strand of DNA acts as the template for RNA synthesis by complementary base pairing. Transcription always proceeds in the 5 3 direction.
29 Proofreading E. coli RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA with remarkable fidelity in vivo. Its low error rate may be achieved by two proofreading mechanisms. Pyrophosphorolytic editing The RNA polymerase use its active site in a simple back-reaction, to catalyze the removal of an incorrectly inserted ribonucleotide by reincorporation of Ppi. Hydrolytic editing The polymerase backtracks by one or more nucleotides and cleaves the RNA product, removing the error-containing sequence. Hydrolytic editing is stimulated by Gre factors, which both enhance hydrolytic function and serve as elongation stimulating factor. Gre factors ensure that polymerase elongates efficiently and help overcome arrest in presence of a mismatch.
30 Termination
31 Termination of transcription The RNA polymerase core enzyme moves down the DNA until a stop signal or terminator sequence is reached by the RNA polymerase. There are two types of terminators recognized, Rho-dependent Rho-independent terminators E. coli uses both kinds of transcript terminators.
32 Termination of transcription Rho-independent termination Also called intrinsic terminators because they cause termination of transcription in the absence of any external factors. Terminator is characterized by a consensus sequence that is an inverted repeat. Stem-loop structures can form within the mrna just before the last base transcribed, by the pairing of complementary bases within the inverted repeat. The inverted repeat sequence in the mrna is followed by seven to eight uracilcontaining nucleotides. A hybrid helix of U in the RNA base paired with A in the DNA is less stable than other complementary base pairs. This property, combined with formation of the stem loop in the exit channel of RNA polymerase, is sufficient to cause the enzyme to pause, resulting in transcript release.
33 Termination of transcription Rho-dependent termination Rho-dependent termination is controlled by the ability of the Rho protein to gain access to the mrna. Terminator is an inverted repeat with no simple consensus sequence and no string of Ts in the nontemplate strand. Rho is a ring-shaped, hexameric helicase protein with a distinct RNAbinding domain and an ATP-binding domain. Rho binds specifically to a C-rich site called a Rho utilization (or rut site) at the 5 end of the newly formed RNA, as it emerges from the exit site of RNA polymerase. Temporary release of one subunit of the hexamer allows the 3 segment of the nascent transcript to enter the central channel of the Rho ring.
34 Termination of transcription Rho-dependent termination In an ATP-dependent process, Rho travels along the RNA, chasing the RNA polymerase. When the polymerase stalls at the terminator stemloop structure, Rho catches up and unwinds the weak DNA RNA hybrid. This causes termination of RNA synthesis and release of all the components.
35 Bacterial gene expression
DNA Transcription. Dr Aliwaini
 DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA
 RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
Transcription in Prokaryotes. Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone:
 Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
Expression of the genome. Books: 1. Molecular biology of the gene: Watson et al 2. Genetics: Peter J. Russell
 Expression of the genome Books: 1. Molecular biology of the gene: Watson et al 2. Genetics: Peter J. Russell 1 Transcription 1. Francis Crick (1956) named the flow of information from DNA RNA protein the
Expression of the genome Books: 1. Molecular biology of the gene: Watson et al 2. Genetics: Peter J. Russell 1 Transcription 1. Francis Crick (1956) named the flow of information from DNA RNA protein the
Chapters 31-32: Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
 Chapters 31-32: Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Short segments from the transcription, processing and translation sections of each chapter Slide 1 RNA In comparison with DNA RNA utilizes uracil in place of thymine
Chapters 31-32: Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Short segments from the transcription, processing and translation sections of each chapter Slide 1 RNA In comparison with DNA RNA utilizes uracil in place of thymine
The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function
 Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
Transcription. By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt
 Transcription By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION 11/26/2010 2 RNA Messenger RNAs (mrnas) encode the amino acid sequence of one or more polypeptides specified by
Transcription By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION 11/26/2010 2 RNA Messenger RNAs (mrnas) encode the amino acid sequence of one or more polypeptides specified by
Mechanisms of Transcription. School of Life Science Shandong University
 Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302. February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm
 RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302 February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm Overview of RNA classes Messenger RNA (mrna) Encodes protein Relatively short half-life ( 3 min in E. coli, 30 min in eukaryotic
RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302 February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm Overview of RNA classes Messenger RNA (mrna) Encodes protein Relatively short half-life ( 3 min in E. coli, 30 min in eukaryotic
Chapter 11. Transcription. The biochemistry and molecular biology department of CMU
 Chapter 11 Transcription The biochemistry and molecular biology department of CMU Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be
Chapter 11 Transcription The biochemistry and molecular biology department of CMU Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be
Basi s c i Fea e tu t re r s s of f R NA N Sy S nth t esi s s i s
 Transcription Dr.H.B.Mahesha, Yuvaraja s College, University of Mysore, Mysuru. It is the process of transcribing or making a copy of Genetic information stored in a DNA strand into a Complementary strand
Transcription Dr.H.B.Mahesha, Yuvaraja s College, University of Mysore, Mysuru. It is the process of transcribing or making a copy of Genetic information stored in a DNA strand into a Complementary strand
Biochemistry 111. Carl Parker x A Braun
 Biochemistry 111 Carl Parker x6368 101A Braun csp@caltech.edu Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Requires a DNA Template Synthesizes RNA in a 5 to 3 direction Requires ribonucleoside
Biochemistry 111 Carl Parker x6368 101A Braun csp@caltech.edu Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Requires a DNA Template Synthesizes RNA in a 5 to 3 direction Requires ribonucleoside
30 Gene expression: Transcription
 30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 12 Transcription
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 12 Transcription 2 3 4 5 Are You Getting It?? Which are general characteristics of transcription? (multiple answers) a) An entire DNA molecule is transcribed
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 12 Transcription 2 3 4 5 Are You Getting It?? Which are general characteristics of transcription? (multiple answers) a) An entire DNA molecule is transcribed
Transcription & post transcriptional modification
 Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
Transcription. The sugar molecule found in RNA is ribose, rather than the deoxyribose found in DNA.
 Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
Transcription is the first stage of gene expression
 Transcription is the first stage of gene expression RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides The RNA is complementary to the
Transcription is the first stage of gene expression RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides The RNA is complementary to the
M1 - Biochemistry. Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I
 M1 - Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I PH Ratz, PhD (Resources: Lehninger et al., 5th ed., Chapters 8, 24 & 26) 1 Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I Learning Objectives: 1.
M1 - Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I PH Ratz, PhD (Resources: Lehninger et al., 5th ed., Chapters 8, 24 & 26) 1 Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I Learning Objectives: 1.
RNA: Structure & Synthesis. Amr S. Moustafa, M.D.; Ph.D.
 RNA: Structure & Synthesis By Amr S. Moustafa, M.D.; Ph.D. Objectives The differences between DNA and RNA The structure and functions of RNAs RNA synthesis (Transcription) Post-transcriptional events (modifications)
RNA: Structure & Synthesis By Amr S. Moustafa, M.D.; Ph.D. Objectives The differences between DNA and RNA The structure and functions of RNAs RNA synthesis (Transcription) Post-transcriptional events (modifications)
Overview of Transcription
 Overview of Transcription The general process is similar in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Three phases: - Initiation The word gene was coined in 1909 (W. Johannsen). The central dogma (1950s). - Elongation
Overview of Transcription The general process is similar in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Three phases: - Initiation The word gene was coined in 1909 (W. Johannsen). The central dogma (1950s). - Elongation
Chapter 11 Part A: Metabolism: The synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins
 Chapter 11 Part A: Metabolism: The synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins I. Synthesis of DNA = REPLICATION A. Components of DNA (Fig. 11-1) 1. Composed of 4 different nucleotides that are joined by the
Chapter 11 Part A: Metabolism: The synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins I. Synthesis of DNA = REPLICATION A. Components of DNA (Fig. 11-1) 1. Composed of 4 different nucleotides that are joined by the
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.10 TRANSCRIPTION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF TRANSCRIPTION Transcription is the process of using DNA as a template to RNA RNA polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes DNA - There are many different types
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF TRANSCRIPTION Transcription is the process of using DNA as a template to RNA RNA polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes DNA - There are many different types
DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork
 DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork Tw 1) T w : # of turns around the central axis 2) W r : # of times the double helix crosses itself 3) Linking Number: L k = T w + W
DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork Tw 1) T w : # of turns around the central axis 2) W r : # of times the double helix crosses itself 3) Linking Number: L k = T w + W
Fig Ch 17: From Gene to Protein
 Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code
 Lecture 28-29 Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code Central dogma of molecular biology During transcription, the information in a DNA sequence (a gene) is copied into a
Lecture 28-29 Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code Central dogma of molecular biology During transcription, the information in a DNA sequence (a gene) is copied into a
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat
 SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline. Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics
 Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Feedback D. Incorrect! No, although this is a correct characteristic of RNA, this is not the best response to the questions.
 Biochemistry - Problem Drill 23: RNA No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements best describes the structural highlights of RNA? (A) RNA can be single or double stranded. (B) G-C pairs have 3 hydrogen
Biochemistry - Problem Drill 23: RNA No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements best describes the structural highlights of RNA? (A) RNA can be single or double stranded. (B) G-C pairs have 3 hydrogen
Proofreading, post-replication modification of DNA. Mitesh Shrestha
 Proofreading, post-replication modification of DNA Mitesh Shrestha Proofreading During DNA replication (copying), most DNA polymerases can check their work with each base that they add. This process is
Proofreading, post-replication modification of DNA Mitesh Shrestha Proofreading During DNA replication (copying), most DNA polymerases can check their work with each base that they add. This process is
Nucleic Acids and the Encoding of Biological Information. Chapter 3
 Nucleic Acids and the Encoding of Biological Information Chapter 3 GRIFFITH S EXPERIMENT ON THE NATURE OF THE GENETIC MATERIAL In 1928, Frederick Griffith demonstrated that molecules can transfer genetic
Nucleic Acids and the Encoding of Biological Information Chapter 3 GRIFFITH S EXPERIMENT ON THE NATURE OF THE GENETIC MATERIAL In 1928, Frederick Griffith demonstrated that molecules can transfer genetic
Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins. From DNA to RNA
 From DNA to RNA Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins I. After the discovery of the structure of DNA, the major question remaining was how does the stored in the 4 letter code of DNA direct the and of
From DNA to RNA Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins I. After the discovery of the structure of DNA, the major question remaining was how does the stored in the 4 letter code of DNA direct the and of
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.17 - GENE EXPRESSION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENES Beadle and Tatum develop the one gene one enzyme hypothesis through their work with Neurospora (bread mold). This idea was later revised as the one gene one polypeptide
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENES Beadle and Tatum develop the one gene one enzyme hypothesis through their work with Neurospora (bread mold). This idea was later revised as the one gene one polypeptide
produces an RNA copy of the coding region of a gene
 1. Transcription Gene Expression The expression of a gene into a protein occurs by: 1) Transcription of a gene into RNA produces an RNA copy of the coding region of a gene the RNA transcript may be the
1. Transcription Gene Expression The expression of a gene into a protein occurs by: 1) Transcription of a gene into RNA produces an RNA copy of the coding region of a gene the RNA transcript may be the
5. Which of the following enzymes catalyze the attachment of an amino acid to trna in the formation of aminoacyl trna?
 Sample Examination Questions for Exam 3 Material Biology 3300 / Dr. Jerald Hendrix Warning! These questions are posted solely to provide examples of past test questions. There is no guarantee that any
Sample Examination Questions for Exam 3 Material Biology 3300 / Dr. Jerald Hendrix Warning! These questions are posted solely to provide examples of past test questions. There is no guarantee that any
Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang
 Today s Agenda: I. DNA Structure II. DNA Replication III. DNA Proofreading and Repair IV. The Central Dogma V. Transcription VI. Post-transcriptional Modifications Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11
Today s Agenda: I. DNA Structure II. DNA Replication III. DNA Proofreading and Repair IV. The Central Dogma V. Transcription VI. Post-transcriptional Modifications Delve AP Biology Lecture 7: 10/30/11
DNA Transcription. Visualizing Transcription. The Transcription Process
 DNA Transcription By: Suzanne Clancy, Ph.D. 2008 Nature Education Citation: Clancy, S. (2008) DNA transcription. Nature Education 1(1) If DNA is a book, then how is it read? Learn more about the DNA transcription
DNA Transcription By: Suzanne Clancy, Ph.D. 2008 Nature Education Citation: Clancy, S. (2008) DNA transcription. Nature Education 1(1) If DNA is a book, then how is it read? Learn more about the DNA transcription
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
 TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
Principle 2. Overview of Central. 3. Nucleic Acid Structure 4. The Organization of
 Central dogma I and II the flow of genetic information 1. The Transforming Principle 2. Overview of Central Dogma 3. Nucleic Acid Structure 4. The Organization of DNA in Cells 5. DNA Replication 6. Gene
Central dogma I and II the flow of genetic information 1. The Transforming Principle 2. Overview of Central Dogma 3. Nucleic Acid Structure 4. The Organization of DNA in Cells 5. DNA Replication 6. Gene
Transcription. Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally
 Transcription Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally manzursir@gmail.com RNA transcription is actively regulated Not all DNA is transcribed in a given cell (less than 50% even in prokaryotes) For
Transcription Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally manzursir@gmail.com RNA transcription is actively regulated Not all DNA is transcribed in a given cell (less than 50% even in prokaryotes) For
Answers to Module 1. An obligate aerobe is an organism that has an absolute requirement of oxygen for growth.
 Answers to Module 1 Short Answers 1) What is an obligate aerobe? An obligate aerobe is an organism that has an absolute requirement of oxygen for growth. What about facultative anaerobe? 2) Distinguish
Answers to Module 1 Short Answers 1) What is an obligate aerobe? An obligate aerobe is an organism that has an absolute requirement of oxygen for growth. What about facultative anaerobe? 2) Distinguish
Student name ID # Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores Total
 Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Total 1 1. Matching (7 pts). Each answer is used exactly once Helicase
Second Mid Term Exam, Biology 2020, Spring 2002 Scores 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Total 1 1. Matching (7 pts). Each answer is used exactly once Helicase
Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
 Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 4. Transcription Gene Expression Regulatory region (promoter) 5 flanking region Upstream region Coding region 3 flanking region Downstream region Transcription
Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 4. Transcription Gene Expression Regulatory region (promoter) 5 flanking region Upstream region Coding region 3 flanking region Downstream region Transcription
Lecture for Wednesday. Dr. Prince BIOL 1408
 Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells
 Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
DNA. Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
 Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
 I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Central Dogma: Gene Expression: RNA Structure RNA nucleotides contain the pentose sugar Ribose instead of deoxyribose. Contain the bases
I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Central Dogma: Gene Expression: RNA Structure RNA nucleotides contain the pentose sugar Ribose instead of deoxyribose. Contain the bases
DNA Function: Information Transmission
 DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA
 1 We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA molecules; in transcription, information passes from DNA
1 We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA molecules; in transcription, information passes from DNA
DNA Replication and Repair
 DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
Recitation CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies
 Recitation CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies DNA Cloning: General Scheme A cloning vector and eukaryotic chromosomes are separately cleaved with the same restriction endonuclease. (A single chromosome is shown
Recitation CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies DNA Cloning: General Scheme A cloning vector and eukaryotic chromosomes are separately cleaved with the same restriction endonuclease. (A single chromosome is shown
Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of..
 Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Molecular Biology: General Theory
 Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory
 Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Molecular Biology: General Theory Author: Dr Darshana Morar Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process of duplicating the DNA sequence in the
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Chapter 12: Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Biology Textbook Notes Chapter 12: Molecular Biology of the Gene p. 214-219 The Genetic Material (12.1) - Genetic Material must: 1. Be able to store information that pertains to the development, structure,
Biology Textbook Notes Chapter 12: Molecular Biology of the Gene p. 214-219 The Genetic Material (12.1) - Genetic Material must: 1. Be able to store information that pertains to the development, structure,
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II.
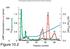 Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
Protein Synthesis Notes
 Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4)
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY. Transcription
 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Transcription U. N. Dwivedi Department of Biochemistry University of Lucknow, Lucknow-226007 and Smita Rastogi Department of Biotechnology, Integral University, Lucknow 20-Jul-2006 (Revised
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Transcription U. N. Dwivedi Department of Biochemistry University of Lucknow, Lucknow-226007 and Smita Rastogi Department of Biotechnology, Integral University, Lucknow 20-Jul-2006 (Revised
Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level
 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level Two levels tied together since the molecular level affects the structure and function of cells which determines
Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level Two levels tied together since the molecular level affects the structure and function of cells which determines
Bis2A 12.0 Transcription *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56068 1 Bis2A 12.0 Transcription * Mitch Singer Based on Transcription by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
OpenStax-CNX module: m56068 1 Bis2A 12.0 Transcription * Mitch Singer Based on Transcription by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Section 3: DNA Replication
 Section 3: DNA Replication Main Idea: Replication- process by which DNA is copied during the cell cycle DNA Polymerase- a group of enzymes that bond the new nucleotides together 1 DNA Replication Replication
Section 3: DNA Replication Main Idea: Replication- process by which DNA is copied during the cell cycle DNA Polymerase- a group of enzymes that bond the new nucleotides together 1 DNA Replication Replication
DNA, RNA, Replication and Transcription
 Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College DNA, RNA, Replication and Transcription The metabolic processes described earlier (glycolysis, cellular respiration, photophosphorylation,
Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College DNA, RNA, Replication and Transcription The metabolic processes described earlier (glycolysis, cellular respiration, photophosphorylation,
Prokaryotic Physiology. March 3, 2017
 1. (10 pts) Explain the replication of both strands of DNA in prokaryotes. At a minimum explain the direction of synthesis, synthesis of the leading and lagging strand, separation of the strands and the
1. (10 pts) Explain the replication of both strands of DNA in prokaryotes. At a minimum explain the direction of synthesis, synthesis of the leading and lagging strand, separation of the strands and the
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Transcription & RNA Processing
 Chapter 10. Transcription & RNA Processing 1. Transfer of Genetic Information: the Central Dogma 2. The Process of Gene Expression 3. Transcription & RNA Processing in Eukaryotes 4. Interrupted Genes in
Chapter 10. Transcription & RNA Processing 1. Transfer of Genetic Information: the Central Dogma 2. The Process of Gene Expression 3. Transcription & RNA Processing in Eukaryotes 4. Interrupted Genes in
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes
 Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
Winter Quarter Midterm Exam
 1. For a science fair project, two students decided to repeat the Hershey and Chase experiment, with modifications. They decided to label the nitrogen of the DNA, rather than the phosphate. They reasoned
1. For a science fair project, two students decided to repeat the Hershey and Chase experiment, with modifications. They decided to label the nitrogen of the DNA, rather than the phosphate. They reasoned
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein
 CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
Nucleic Acid Structure:
 Nucleic Acid Structure: Purine and Pyrimidine nucleotides can be combined to form nucleic acids: 1. Deoxyribonucliec acid (DNA) is composed of deoxyribonucleosides of! Adenine! Guanine! Cytosine! Thymine
Nucleic Acid Structure: Purine and Pyrimidine nucleotides can be combined to form nucleic acids: 1. Deoxyribonucliec acid (DNA) is composed of deoxyribonucleosides of! Adenine! Guanine! Cytosine! Thymine
Transcription. Dr. Mahesha H B Associate Professor and Head Department of Sericulture Yuvaraja scollege University of Mysore, Mysuru, India
 Transcription Dr. Mahesha H B Associate Professor and Head Department of Sericulture Yuvaraja scollege University of Mysore, Mysuru, India 3 September 2017 www.hbmahesh.weebly.com 1 Transcription It is
Transcription Dr. Mahesha H B Associate Professor and Head Department of Sericulture Yuvaraja scollege University of Mysore, Mysuru, India 3 September 2017 www.hbmahesh.weebly.com 1 Transcription It is
Chapter 13. From DNA to Protein
 Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination
 Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination Copyright Copyright 2009 Pearson 2009 Pearson Education, Education, Inc. Inc. 11.1 DNA is reproduced by Semiconservative Replication The complementarity of
Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination Copyright Copyright 2009 Pearson 2009 Pearson Education, Education, Inc. Inc. 11.1 DNA is reproduced by Semiconservative Replication The complementarity of
Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation
 Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation Copyright 2013 Pearson Canada Inc. 27-1 DNA as the Template for RNA Synthesis Enzymology of RNA Synthesis: RNA Polymerase
Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation Copyright 2013 Pearson Canada Inc. 27-1 DNA as the Template for RNA Synthesis Enzymology of RNA Synthesis: RNA Polymerase
وراثة األحياء الدقيقة Microbial Genetics
 وراثة األحياء الدقيقة Microbial Genetics د. تركي محمد الداود مكتب 2 ب 45 أساسيات في علم الوراثة Fundamentals of Genetics Lecture 4 Physical Chemistry of Nucleic Acids DNA and RNA molecules can appear in
وراثة األحياء الدقيقة Microbial Genetics د. تركي محمد الداود مكتب 2 ب 45 أساسيات في علم الوراثة Fundamentals of Genetics Lecture 4 Physical Chemistry of Nucleic Acids DNA and RNA molecules can appear in
Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology
 Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated to synthesize
Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated to synthesize
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr.
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
DNA REPLICATION. DNA structure. Semiconservative replication. DNA structure. Origin of replication. Replication bubbles and forks.
 DNA REPLICATION 5 4 Phosphate 3 DNA structure Nitrogenous base 1 Deoxyribose 2 Nucleotide DNA strand = DNA polynucleotide 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program 2 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program
DNA REPLICATION 5 4 Phosphate 3 DNA structure Nitrogenous base 1 Deoxyribose 2 Nucleotide DNA strand = DNA polynucleotide 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program 2 2004 Biology Olympiad Preparation Program
TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA TRANSCRIPTION. Umm AL Qura University. Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose. Bases AUCG ATCG. Strand length Short Long
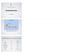 Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
Chapter 2. An Introduction to Genes and Genomes
 PowerPoint Lectures for Introduction to Biotechnology, Second Edition William J.Thieman and Michael A.Palladino Chapter 2 An Introduction to Genes and Genomes Lectures by Lara Dowland Chapter Contents
PowerPoint Lectures for Introduction to Biotechnology, Second Edition William J.Thieman and Michael A.Palladino Chapter 2 An Introduction to Genes and Genomes Lectures by Lara Dowland Chapter Contents
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process.
 Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra
 Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology
 Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Replication Review. 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place in eukaryotic cells?
 Replication Review 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place in eukaryotic cells? 3. Where does DNA Replication take place in the cell cycle? 4. 4. What guides DNA Replication?
Replication Review 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place in eukaryotic cells? 3. Where does DNA Replication take place in the cell cycle? 4. 4. What guides DNA Replication?
Exam 2 Key - Spring 2008 A#: Please see us if you have any questions!
 Page 1 of 5 Exam 2 Key - Spring 2008 A#: Please see us if you have any questions! 1. A mutation in which parts of two nonhomologous chromosomes change places is called a(n) A. translocation. B. transition.
Page 1 of 5 Exam 2 Key - Spring 2008 A#: Please see us if you have any questions! 1. A mutation in which parts of two nonhomologous chromosomes change places is called a(n) A. translocation. B. transition.
Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein
 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein Overview: The Flow of Genetic Information The information content of DNA is in the form of specific sequences of nucleotides The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein Overview: The Flow of Genetic Information The information content of DNA is in the form of specific sequences of nucleotides The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific
Transcription: Synthesis of RNA
 Transcription: Synthesis of RNA The flow of information in the cells (the central dogma of molecular biology): Transcription = RNA synthesis on a DNA template. The mrna will provide the information for
Transcription: Synthesis of RNA The flow of information in the cells (the central dogma of molecular biology): Transcription = RNA synthesis on a DNA template. The mrna will provide the information for
Lesson 8. DNA: The Molecule of Heredity. Gene Expression and Regulation. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 8 DNA: The Molecule of Heredity Gene Expression and Regulation Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Genes and DNA Hereditary information is found in discrete units called genes Genes are segments
Lesson 8 DNA: The Molecule of Heredity Gene Expression and Regulation Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Genes and DNA Hereditary information is found in discrete units called genes Genes are segments
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins. The Central Dogma
 DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points
 Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the back of the
Bio 366: Biological Chemistry II Test #3, 100 points READ THIS: Take a numbered test and sit in the seat with that number on it. Remove the numbered sticker from the desk, and stick it on the back of the
RNA metabolism. DNA dependent synthesis of RNA RNA processing RNA dependent synthesis of RNA and DNA.
 RNA metabolism DNA dependent synthesis of RNA RNA processing RNA dependent synthesis of RNA and DNA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ovc8nxobxmq DNA dependent synthesis of RNA : production of an RNA molecule
RNA metabolism DNA dependent synthesis of RNA RNA processing RNA dependent synthesis of RNA and DNA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ovc8nxobxmq DNA dependent synthesis of RNA : production of an RNA molecule
8/21/2014. From Gene to Protein
 From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
Regulation of bacterial gene expression
 Regulation of bacterial gene expression Gene Expression Gene Expression: RNA and protein synthesis DNA ----------> RNA ----------> Protein transcription translation! DNA replication only occurs in cells
Regulation of bacterial gene expression Gene Expression Gene Expression: RNA and protein synthesis DNA ----------> RNA ----------> Protein transcription translation! DNA replication only occurs in cells
Genes and How They Work. Chapter 15
 Genes and How They Work Chapter 15 The Nature of Genes They proposed the one gene one enzyme hypothesis. Today we know this as the one gene one polypeptide hypothesis. 2 The Nature of Genes The central
Genes and How They Work Chapter 15 The Nature of Genes They proposed the one gene one enzyme hypothesis. Today we know this as the one gene one polypeptide hypothesis. 2 The Nature of Genes The central
Chapter Fundamental Molecular Genetic Mechanisms
 Chapter 5-1 - Fundamental Molecular Genetic Mechanisms 5.1 Structure of Nucleic Acids 5.2 Transcription of Protein-Coding Genes and Formation of Functional mrna 5.3 The Decoding of mrna by trnas 5.4 Stepwise
Chapter 5-1 - Fundamental Molecular Genetic Mechanisms 5.1 Structure of Nucleic Acids 5.2 Transcription of Protein-Coding Genes and Formation of Functional mrna 5.3 The Decoding of mrna by trnas 5.4 Stepwise
SCBC203 Gene Expression. Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318
 SCBC203 Gene Expression Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318 Rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th 1 Gene Expression Gene expression is a process where by the genetic
SCBC203 Gene Expression Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318 Rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th 1 Gene Expression Gene expression is a process where by the genetic
Fermentation. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview 13.1 RNA
 13.1 RNA THINK ABOUT IT DNA is the genetic material of cells. The sequence of nucleotide bases in the strands of DNA carries some sort of code. In order for that code to work, the cell must be able to
13.1 RNA THINK ABOUT IT DNA is the genetic material of cells. The sequence of nucleotide bases in the strands of DNA carries some sort of code. In order for that code to work, the cell must be able to
Protein Synthesis
 HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
DNA RNA. Protein. Enzymes in the central dogma. Cellular enzymes (Mostly) RNA virus enzymes. DNA polymerase. Reverse transcriptase.
 Enzymes in the central dogma Cellular enzymes (Mostly) RNA virus enzymes DNA DNA polymerase Reverse transcriptase RNA polymerase RNA-dependent RNA polymerase RNA Ribosome Protein The process of transcription
Enzymes in the central dogma Cellular enzymes (Mostly) RNA virus enzymes DNA DNA polymerase Reverse transcriptase RNA polymerase RNA-dependent RNA polymerase RNA Ribosome Protein The process of transcription
