Overview of Transcription
|
|
|
- Alexandrina Cornelia Rice
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Overview of Transcription The general process is similar in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Three phases: - Initiation The word gene was coined in 1909 (W. Johannsen). The central dogma (1950s). - Elongation - Termination In prokaryotes a singe RNA polymerase transcribes genes encoding mrna, rrna and trna.
2 Transcription and translation is coupled in prokaryotes 1) mrna are processed in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes 2) rrna and trna are processed both in eukaryotes and prokaryotes Initiation of transcription Sense strand nontemplate strand = mrna As soon the growing mrna chain separates from DNA, ribosomes attach to it and begin translation on the 5 end of the molecule following right behind the RNA polymerase while it is transcribing the mrna. Antisense strand template strand 1 2 3
3 Conserved sequences in prokaryotic promoters Pribnow box (TATA box) Startpoint in most E. coli genes is an A (the distance of the startpoint from the TATA box may vary from 5 to 9 nucleotides). D. Pribnow (1975) P.N.A.S. -10 sequence double-stranded DNA separation. -35 sequence initial binding of RNA polymerase. spacer region (16-19 bp) it is important in maintaining the appropriate positions of the -10 and -35 elements.
4 Promoter quality has a strong influence on the level of expression. Some examples of σ 70 promoters are shown (red indicates positions which are conserved). The moderately matched lacz promoter has about 1% initiation efficiency compared with ideal, and effective expression is strongly dependent on activation by CAP. The poorly matched laci promoter is even less efficient (LacI repressor is present only at few copy per cell). Conserved sequences in eukaryotic promoters T T G A C A T A T A A T Promoter consensus sequences
5 The effects of mutations in the promoters region on transcription for the mouse β-globin gene. not recovered mutations (the relative transcription level was not determined) * more than one mutation was recovered for the corresponding nucleotide Upstream of the CAAT box most eukaryotic promoters (genes encoding mrna) have additional conserved sequences: CG box (GGGCGG) and CACCC box (GCCACACCC). Their role is still unclear.
6 DNaseI Footprinting DNase I footprint performed on end-labelled DNA fragment FIS
7 Primer extension mrna 5 3 annealing + primer- 32 P G A T C Early-log Mid-log Late-log 37 C 10 C 37 C 10 C 37 C 10 C mrna 5 primer - 32 P 3 reverse transcriptase mrna 5 3 primer - 32 P cdna run on denaturating gel +77 cspa mrna
8 S1 Mapping La nucleasi S1 digerisce DNA o RNA a singolo filamento [#] [*] Il sito d inizio della trascrizione si trova a 300 basi dall estremità 5 marcata del frammento di DNA usato come sonda [#] [*]
9 Bacterial RNA polymerase The overall reaction rate is ~40 nucleotides/second at 37 C (for the bacterial RNA polymerase); this is about the same as the rate of translation (15 amino acids/sec). One mistake occurs every nucleotides added. About 7000 RNA polymerase molecules are present in an E. coli cell. Many of them are engaged in transcription; probably enzymes are synthesizing RNA at any one time. The typical eubacterial RNA polymerase consists of an essential four-subunit core enzyme organized as ααββ'. A fifth subunit ω interacts with and stabilizes β'. Deletion of the rpoz gene expressing ω results in a slow- growth phenotype. The α subunit (36.5 kda, rpoa gene) is organized in two domains, with the N-terminal (1-235) in contact with β or β' subunits. A flexible linker connects to the C-terminal domain ( , α-ctd) which lies outside the core polymerase and is the target for interaction both exit with activating factors such as Catabolite Activator Protein (CAP) and entry site site cis up-elements. The β subunit (150 kda, rpob gene) contains nine highly conserved regions and crosslinks to the 5'-end of nascent RNA. The β' subunit (155 kda, rpoc gene) contains eight conserved regions, contains the catalytic site, cross linking to the 3'-end of nascent RNA. The rudder is a projecting loop of the β' subunit which is proposed to act to separate the nascent RNA from the DNA template.
10 RNA polymerase passes through several steps prior elongation. 1) The enzyme remains at the promoter while it synthesizes the first ~10 nucleotide bonds. The initiation phase is protracted by the occurrence of abortive events, in which the enzyme makes short transcripts (< 10 nucleotides), releases them, and then starts synthesis of RNA again. 15 bp 2) The initiation phase ends when the enzyme succeeds in extending the chain and escapes from the promoter. Transition to the elongation complex involves partial dissociation of the holoenzyme. The sigma factor is left at the promoter complex, and the core RNA polymerase proceeds downstream. Conformational changes in the core enzyme result in the flap segment of subunit β clamping around the DNA, so that the polymerase never leaves the template. This is critical for processive transcription, since RNA polymerase can't resume synthesis of an incompletely transcribed gene, and must be assured of remaining bound for reaction cycles. The hybrid DNA-RNA is only 8-9 nt long.
11 Initiation requires tight binding only to particular sequences (promoters), while elongation requires close association with all sequences that the enzyme encounters during transcription. 1) The core enzyme has a general affinity for DNA, (electrostatic attraction between the basic protein and the nucleic acid). The complex core enzyme-dna is stable, with a half-life for dissociation of the enzyme from DNA ~60 minutes. Core enzyme does not distinguish between promoters and other sequences of DNA. 2) The affinity of RNA polymerase for DNA is reduced by a factor of ~10 4, and the half-life of the complex is <1 second when sigma factor is bound to core enzyme. 3) In the presence of sigma factor, the holoenzyme binds to promoters very tightly, with an association constant increased from that of core enzyme by (on average) 1000 times and with a half-life of several hours. 4) There is wide variation in the rate at which the holoenzyme binds to different promoter sequences. The binding constants extend from ~10 12 to ~10 6 M -1, reflecting promoter strengths that support initiation frequencies of ~1/sec (rrna genes) to ~1/30 min (the laci promoter).
12 Transition in shape and size identifies three forms of complex The RNA polymerase directly recognizes the promoter The most likely model is to suppose that the bound sequence is directly displaced by another sequence. The enzyme continues to exchange sequences until a promoter is found. The RNA polymerase moves along DNA
13 RNA polymerase approaches DNA from one side and recognizes that face of the DNA Prior modification experiments identify all those sites that the enzyme must recognize in order to bind. Protection experiments recognize all those sites that actually make contact in the binary complex The regions at 35 and 10 contain most of the contact points for the enzyme. Within these regions, the same sets of positions tend both to prevent binding if previously modified, and to show increased or decreased susceptibility to modification after RNA polymerase binding.
14 Sigma factor (MW = 72000) Fragments 2.1 and 2.2, which map to a small helical region in σ 70, bind strongly to β'. Adjacent helical segments located in fragments 2.3 and 2.4 are involved in recognition of the -10 region of the promoter and binding the single stranded region of the transcription bubble. In addition, sequences near the N-terminal (1.1 and 1.2) of σ 70 were found to be inhibitory to DNA binding. The addition of σ to the polymerase core gives the RNA polymerase holoenzyme recognizing a site at -10 to form the closed complex. In the holoenzyme form, an additional DNA binding domain at the C- terminal end of σ, region 4.2, become unmasked, and this recognizes a second site at -35, approximately 2 helical turns of DNA away. If the -35 site is recognized, the holoenzyme melts the region -11 to +3 in the DNA, giving the open complex, and the bubble is stabilized by the ssdna binding domain of σ at region 2.3, which binds to the non-template strand. Region 2.4 interacts with the upstream fork, and region 2.5 with dsdna from -11 to 17 (spacer region). Melting of the transcription bubble admits the template strand to the catalytic site, allowing initiation to proceed.
15 Cambiamenti strutturali che avvengono nella RNA polimerasi durante l isomerizzazione (transizione complesso chiuso-complesso-aperto) -11 (template) (non template) +3 - Le pinze (pincers) bloccano il DNA nel complesso chiuso. - Cambiamento di posizione della regione 1.1 del fattore sigma sigma. Quando l oloenzima non è legato ad un promotore la regione σ 1.1 impegna il sito attivo bloccando l accesso al DNA. Quando si forma il complesso aperto la regione σ 1.1 è spostata 50 A fuori dall enzima permettendo l ingresso del DNA nel sito attivo. La regione σ 1.1 mina il DNA in quanto è carica negativamente. Il sito attivo sull enzima che interagisce alternativamente con il DNA o con σ 1.1, è carico positivamente. Alternative sigma factors respond to general environmental changes. Intrinsic DNA curvature TGNCCATA(C/A)T -10
16 The production of new sigma factors occurs during infection of B. subtilis by bacteriophage SPO1. α 2 ββ σ 43 gp28 gp33 gp34
17 Elongation 1) The antisense strand of DNA is used as template. 2) Transcription proceeds in direction. 3) The double stranded RNA-DNA hybrid is very transient. At any given time during transcription, the number of nucleotides of RNA that remain paired with the DNA template may vary between 8 and 10. Several proteins can affect the rate of elongation. NusA slows elongation when RNA polymerase encounters certain sequences keeping the rate of transcription similar to the rate of translation so that the ribosomes are able to follow on RNA molecule right behind the RNA polymerase. TFIIS avoids that RNA polymerase II stalls at certain nucleotide sequences.
18 Termination in prokaryotes 1) Core enzyme can terminate in vitro at certain sites in the absence of any other factor. These sites are called intrinsic terminators. 2) Rho-dependent terminators are defined by the need for addition of rho factor in vitro transcription assay. 1) Intrinsic terminator loop stem The importance of the run of U bases is confirmed by making deletions that shorten this stretch; although the polymerase still pauses at the hairpin, it no longer terminates.
19 2) Rho dependent termination. -rho factor is an essential protein in E. coli (~275 kd) hexamer of identical subunits). -Mutations in rpob gene (β subunit of RNA polymerase) can reduce termination at a rho-dependent site. A consensus sequence for rho-dependent terminators cannot be defined (high C and low G content). - E. coli has relatively few rhodependent terminators; most of the known rho-dependent terminators are found in phage genomes. - rho has a 5-3 helicase action that can cause an RNA-DNA hybrid to separate; hydrolysis of ATP is used to provide energy for the reaction. - The idea that rho moves along RNA leads to an important prediction about the relationship between transcription and translation. The RNA polymerase pauses when it reaches a terminator, and termination occurs if rho catches it there. Stop codon
20 In some cases, a nonsense mutation in one gene of a transcription unit prevents the expression of subsequent genes in the unit. This effect is called polarity. Rho and NusA create a link between transcription and translation. UAA UGA UAG
Transcription is the first step of gene expression, in which a particular segment of DNA is copied into RNA by the enzyme, RNA polymerase.
 Transcription in Bacteria Transcription in Bacteria Transcription in Bacteria Transcription is the first step of gene expression, in which a particular segment of DNA is copied into RNA by the enzyme,
Transcription in Bacteria Transcription in Bacteria Transcription in Bacteria Transcription is the first step of gene expression, in which a particular segment of DNA is copied into RNA by the enzyme,
DNA Transcription. Dr Aliwaini
 DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302. February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm
 RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302 February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm Overview of RNA classes Messenger RNA (mrna) Encodes protein Relatively short half-life ( 3 min in E. coli, 30 min in eukaryotic
RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302 February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm Overview of RNA classes Messenger RNA (mrna) Encodes protein Relatively short half-life ( 3 min in E. coli, 30 min in eukaryotic
Transcription & post transcriptional modification
 Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
Transcription in Prokaryotes. Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone:
 Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
Mechanisms of Transcription. School of Life Science Shandong University
 Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
Answers to Module 1. An obligate aerobe is an organism that has an absolute requirement of oxygen for growth.
 Answers to Module 1 Short Answers 1) What is an obligate aerobe? An obligate aerobe is an organism that has an absolute requirement of oxygen for growth. What about facultative anaerobe? 2) Distinguish
Answers to Module 1 Short Answers 1) What is an obligate aerobe? An obligate aerobe is an organism that has an absolute requirement of oxygen for growth. What about facultative anaerobe? 2) Distinguish
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis
 Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes
 Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
2. From the first paragraph in this section, find three ways in which RNA differs from DNA.
 Name Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein Begin reading at page 328 Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours
Name Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein Begin reading at page 328 Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours
DNA Transcription. Visualizing Transcription. The Transcription Process
 DNA Transcription By: Suzanne Clancy, Ph.D. 2008 Nature Education Citation: Clancy, S. (2008) DNA transcription. Nature Education 1(1) If DNA is a book, then how is it read? Learn more about the DNA transcription
DNA Transcription By: Suzanne Clancy, Ph.D. 2008 Nature Education Citation: Clancy, S. (2008) DNA transcription. Nature Education 1(1) If DNA is a book, then how is it read? Learn more about the DNA transcription
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat
 SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline. Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics
 Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Fig Ch 17: From Gene to Protein
 Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
BEADLE & TATUM EXPERIMENT
 FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
Protein Synthesis Notes
 Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
 TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra
 Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells
 Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II.
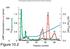 Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
7.1 The lac Operon 7-1
 7.1 The lac Operon The lac operon was the first operon discovered It contains 3 genes coding for E. coli proteins that permit the bacteria to use the sugar lactose Galactoside permease (lacy) which transports
7.1 The lac Operon The lac operon was the first operon discovered It contains 3 genes coding for E. coli proteins that permit the bacteria to use the sugar lactose Galactoside permease (lacy) which transports
DNA Replication and Repair
 DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
Chapter Fundamental Molecular Genetic Mechanisms
 Chapter 5-1 - Fundamental Molecular Genetic Mechanisms 5.1 Structure of Nucleic Acids 5.2 Transcription of Protein-Coding Genes and Formation of Functional mrna 5.3 The Decoding of mrna by trnas 5.4 Stepwise
Chapter 5-1 - Fundamental Molecular Genetic Mechanisms 5.1 Structure of Nucleic Acids 5.2 Transcription of Protein-Coding Genes and Formation of Functional mrna 5.3 The Decoding of mrna by trnas 5.4 Stepwise
DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork
 DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork Tw 1) T w : # of turns around the central axis 2) W r : # of times the double helix crosses itself 3) Linking Number: L k = T w + W
DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork Tw 1) T w : # of turns around the central axis 2) W r : # of times the double helix crosses itself 3) Linking Number: L k = T w + W
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Chapter 10 - Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Bio 100 - Molecular Genetics 1 A. Bacterial Transformation Chapter 10 - Molecular Biology of the Gene Researchers found that they could transfer an inherited characteristic (e.g. the ability to cause pneumonia),
Bio 100 - Molecular Genetics 1 A. Bacterial Transformation Chapter 10 - Molecular Biology of the Gene Researchers found that they could transfer an inherited characteristic (e.g. the ability to cause pneumonia),
GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL. Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function
GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function
Protein Synthesis. Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy
 Protein Synthesis Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy STRUCTURE OF RNA RNA, adenine forms a base pair with
Protein Synthesis Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy STRUCTURE OF RNA RNA, adenine forms a base pair with
Microbiology: The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to protein
 Microbiology: The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to protein I. Overview A. DNA ultimately determines every aspect of a cell from shape to function 1. DNA = 2. Nucleotides of DNA have three units a. A nitrogen-containing
Microbiology: The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to protein I. Overview A. DNA ultimately determines every aspect of a cell from shape to function 1. DNA = 2. Nucleotides of DNA have three units a. A nitrogen-containing
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA
 Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7)
 Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7) I. General Principles (Chapter 7 introduction) a. Morse code distinct series of dots and dashes encode the 26 letters of the
Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7) I. General Principles (Chapter 7 introduction) a. Morse code distinct series of dots and dashes encode the 26 letters of the
Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription. RNA polymerases
 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
 Name Period This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours to truly master
Name Period This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours to truly master
Protein Synthesis
 HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
Module 7: The Central Dogma. CSE590: Molecular programming and neural computation. All slides by Eric Klavins.
 Module 7: The Central Dogma CSE590: Molecular programming and neural computation. All slides by Eric Klavins. 1 The Central Dogma RNA Polymerase The Ribosome m Note: We will look mainly at prokaryo=c (e.g.
Module 7: The Central Dogma CSE590: Molecular programming and neural computation. All slides by Eric Klavins. 1 The Central Dogma RNA Polymerase The Ribosome m Note: We will look mainly at prokaryo=c (e.g.
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation
 Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
 The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
Problem Set 8. Answer Key
 MCB 102 University of California, Berkeley August 11, 2009 Isabelle Philipp Online Document Problem Set 8 Answer Key 1. The Genetic Code (a) Are all amino acids encoded by the same number of codons? no
MCB 102 University of California, Berkeley August 11, 2009 Isabelle Philipp Online Document Problem Set 8 Answer Key 1. The Genetic Code (a) Are all amino acids encoded by the same number of codons? no
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 2 2/20/15
 Name: TRASK Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 2 2/20/15 Answer each of the following short and longer answer questions in the space provided; circle the BEST answer or answers for each multiple choice question
Name: TRASK Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 2 2/20/15 Answer each of the following short and longer answer questions in the space provided; circle the BEST answer or answers for each multiple choice question
Name 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene Test Date Study Guide You must know: The structure of DNA. The major steps to replication.
 Name 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene Test Date Study Guide You must know: The structure of DNA. The major steps to replication. The difference between replication, transcription, and translation. How
Name 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene Test Date Study Guide You must know: The structure of DNA. The major steps to replication. The difference between replication, transcription, and translation. How
Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein
 Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect
Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4)
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
C. Incorrect! Threonine is an amino acid, not a nucleotide base.
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 05: RNA and Protein Biosynthesis Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following bases are only found in RNA? Question #01 (A) Ribose. (B) Uracil. (C) Threonine. (D) Adenine.
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 05: RNA and Protein Biosynthesis Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following bases are only found in RNA? Question #01 (A) Ribose. (B) Uracil. (C) Threonine. (D) Adenine.
Chapter 13. From DNA to Protein
 Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
The Genetic Code and Transcription. Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot
 The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION
 M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 7 Microbial Genetics Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville The Structure and Replication
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 7 Microbial Genetics Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville The Structure and Replication
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins. The Central Dogma
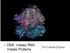 DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotide
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of..
 Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Quiz Submissions Quiz 4
 Quiz Submissions Quiz 4 Attempt 1 Written: Nov 1, 2015 17:35 Nov 1, 2015 22:19 Submission View Released: Nov 4, 2015 20:24 Question 1 0 / 1 point Three RNA polymerases synthesize most of the RNA present
Quiz Submissions Quiz 4 Attempt 1 Written: Nov 1, 2015 17:35 Nov 1, 2015 22:19 Submission View Released: Nov 4, 2015 20:24 Question 1 0 / 1 point Three RNA polymerases synthesize most of the RNA present
Bio11 Announcements. Ch 21: DNA Biology and Technology. DNA Functions. DNA and RNA Structure. How do DNA and RNA differ? What are genes?
 Bio11 Announcements TODAY Genetics (review) and quiz (CP #4) Structure and function of DNA Extra credit due today Next week in lab: Case study presentations Following week: Lab Quiz 2 Ch 21: DNA Biology
Bio11 Announcements TODAY Genetics (review) and quiz (CP #4) Structure and function of DNA Extra credit due today Next week in lab: Case study presentations Following week: Lab Quiz 2 Ch 21: DNA Biology
RNA : functional role
 RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
Eukaryotic Transcription
 Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation
 Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation Copyright 2013 Pearson Canada Inc. 27-1 DNA as the Template for RNA Synthesis Enzymology of RNA Synthesis: RNA Polymerase
Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation Copyright 2013 Pearson Canada Inc. 27-1 DNA as the Template for RNA Synthesis Enzymology of RNA Synthesis: RNA Polymerase
Prokaryotic Transcription
 Prokaryotic Transcription Transcription Basics DNA is the genetic material Nucleic acid Capable of self-replication and synthesis of RNA RNA is the middle man Nucleic acid Structure and base sequence are
Prokaryotic Transcription Transcription Basics DNA is the genetic material Nucleic acid Capable of self-replication and synthesis of RNA RNA is the middle man Nucleic acid Structure and base sequence are
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. copyright cmassengale
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
Themes: RNA and RNA Processing. Messenger RNA (mrna) What is a gene? RNA is very versatile! RNA-RNA interactions are very important!
 Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
8/21/2014. From Gene to Protein
 From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
Chapter 4: How Cells Work
 Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: l l l l l Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription:
Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: l l l l l Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription:
DNA. Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
 Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
DNA. translation. base pairing rules for DNA Replication. thymine. cytosine. amino acids. The building blocks of proteins are?
 2 strands, has the 5-carbon sugar deoxyribose, and has the nitrogen base Thymine. The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? DNA translation Adenine pairs with Thymine, Thymine
2 strands, has the 5-carbon sugar deoxyribose, and has the nitrogen base Thymine. The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? DNA translation Adenine pairs with Thymine, Thymine
Protein Synthesis & Gene Expression
 DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
Chromosomes. Chromosomes. Genes. Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce
 Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
Pauling/Itano Experiment
 Chapter 12 Pauling/Itano Experiment Linus Pauling and Harvey Itano knew that hemoglobin, a molecule in red blood cells, contained an electrical charge. They wanted to see if the hemoglobin in normal RBC
Chapter 12 Pauling/Itano Experiment Linus Pauling and Harvey Itano knew that hemoglobin, a molecule in red blood cells, contained an electrical charge. They wanted to see if the hemoglobin in normal RBC
CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS
 CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS A. Promoters and Polymerases (RNA pols): 1. General characteristics - Initiation of transcription requires a. Transcription factors
CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS A. Promoters and Polymerases (RNA pols): 1. General characteristics - Initiation of transcription requires a. Transcription factors
Protein Synthesis. DNA to RNA to Protein
 Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
DNA replication: Enzymes link the aligned nucleotides by phosphodiester bonds to form a continuous strand.
 DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
5 -GAC-3 5 -GTC-3 5 -CAG Which of these are NOT important for RNA Polymerase interacting with DNA?
 Name This exam is schedule for 75 minutes and I anticipate it to take the full time allotted. You are free to leave if you finish. The exam is split into two sections. Part 1 is multiple choice select
Name This exam is schedule for 75 minutes and I anticipate it to take the full time allotted. You are free to leave if you finish. The exam is split into two sections. Part 1 is multiple choice select
1. The diagram below shows an error in the transcription of a DNA template to messenger RNA (mrna).
 1. The diagram below shows an error in the transcription of a DNA template to messenger RNA (mrna). Which statement best describes the error shown in the diagram? (A) The mrna strand contains the uracil
1. The diagram below shows an error in the transcription of a DNA template to messenger RNA (mrna). Which statement best describes the error shown in the diagram? (A) The mrna strand contains the uracil
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN. Section C: The Synthesis of Protein
 CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
Biochemistry Eukaryotic Transcription
 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 1. Understand and have an overview of eucaryotic transcriptional regulation. 2. Explain
1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 1. Understand and have an overview of eucaryotic transcriptional regulation. 2. Explain
GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES
 GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES Prepared by Brenda Leady, University of Toledo Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene regulation refers to
GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES Prepared by Brenda Leady, University of Toledo Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene regulation refers to
RNA metabolism. DNA dependent synthesis of RNA RNA processing RNA dependent synthesis of RNA and DNA.
 RNA metabolism DNA dependent synthesis of RNA RNA processing RNA dependent synthesis of RNA and DNA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ovc8nxobxmq DNA dependent synthesis of RNA : production of an RNA molecule
RNA metabolism DNA dependent synthesis of RNA RNA processing RNA dependent synthesis of RNA and DNA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ovc8nxobxmq DNA dependent synthesis of RNA : production of an RNA molecule
What happens after DNA Replication??? Transcription, translation, gene expression/protein synthesis!!!!
 What happens after DNA Replication??? Transcription, translation, gene expression/protein synthesis!!!! Protein Synthesis/Gene Expression Why do we need to make proteins? To build parts for our body as
What happens after DNA Replication??? Transcription, translation, gene expression/protein synthesis!!!! Protein Synthesis/Gene Expression Why do we need to make proteins? To build parts for our body as
RNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Chapter 13
 RNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Chapter 13 DNA Double stranded Thymine Sugar is RNA Single stranded Uracil Sugar is Ribose Deoxyribose Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries copies of instructions from
RNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Chapter 13 DNA Double stranded Thymine Sugar is RNA Single stranded Uracil Sugar is Ribose Deoxyribose Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries copies of instructions from
From Gene to Protein. Chapter 17. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Transcription. Dr. Mahesha H B Associate Professor and Head Department of Sericulture Yuvaraja scollege University of Mysore, Mysuru, India
 Transcription Dr. Mahesha H B Associate Professor and Head Department of Sericulture Yuvaraja scollege University of Mysore, Mysuru, India 3 September 2017 www.hbmahesh.weebly.com 1 Transcription It is
Transcription Dr. Mahesha H B Associate Professor and Head Department of Sericulture Yuvaraja scollege University of Mysore, Mysuru, India 3 September 2017 www.hbmahesh.weebly.com 1 Transcription It is
From Gene to Protein transcription, messenger RNA (mrna) translation, RNA processing triplet code, template strand, codons,
 From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
MOLECULAR GENETICS PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Replication Review. 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place in eukaryotic cells?
 Replication Review 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place in eukaryotic cells? 3. Where does DNA Replication take place in the cell cycle? 4. 4. What guides DNA Replication?
Replication Review 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place in eukaryotic cells? 3. Where does DNA Replication take place in the cell cycle? 4. 4. What guides DNA Replication?
TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA TRANSCRIPTION. Umm AL Qura University. Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose. Bases AUCG ATCG. Strand length Short Long
 Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
KEY CONCEPT DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. Found live S with R bacteria and injected
 Section 1: Identifying DNA as the Genetic Material KEY CONCEPT DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. VOCABULARY bacteriophage MAIN IDEA: Griffith finds a transforming
Section 1: Identifying DNA as the Genetic Material KEY CONCEPT DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. VOCABULARY bacteriophage MAIN IDEA: Griffith finds a transforming
Chapter 13 - Concept Mapping
 Chapter 13 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the discovery of DNA structure. amount of base pairs five-carbon sugar purine DNA polymerases Franklin
Chapter 13 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the discovery of DNA structure. amount of base pairs five-carbon sugar purine DNA polymerases Franklin
WORKING WITH THE FIGURES. 1. In Figure 8-3, why are the arrows for genes 1 and 2 pointing in opposite directions?
 8 RNA: Transcription and Processing WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. In Figure 8-3, why are the arrows for genes 1 and 2 pointing in opposite directions? The arrows for genes 1 and 2 indicate the direction
8 RNA: Transcription and Processing WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. In Figure 8-3, why are the arrows for genes 1 and 2 pointing in opposite directions? The arrows for genes 1 and 2 indicate the direction
DNA & Protein Synthesis UNIT D & E
 DNA & Protein Synthesis UNIT D & E How this Unit is broken down Chapter 10.1 10.3 The structure of the genetic material Chapter 10.4 & 10.5 DNA replication Chapter 10.6 10.15 The flow of genetic information
DNA & Protein Synthesis UNIT D & E How this Unit is broken down Chapter 10.1 10.3 The structure of the genetic material Chapter 10.4 & 10.5 DNA replication Chapter 10.6 10.15 The flow of genetic information
Biological information flow
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Biological information flow Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors
BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Biological information flow Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors
PUC Vikasana Program- 2012
 Chromosome Nucleus DNA PUC Vikasana Program- 2012 Introduction Molecular biology is the study of biology at a molecular level. Macromolecules and the macromolecular mechanisms. Interactions between the
Chromosome Nucleus DNA PUC Vikasana Program- 2012 Introduction Molecular biology is the study of biology at a molecular level. Macromolecules and the macromolecular mechanisms. Interactions between the
Chapter 31. Transcription and RNA processing
 Chapter 31 Transcription and RNA processing RNA polymerase (RNAP) E. coli promoters Components of E. coli RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme (α 2 ββ'ωσ) Structure of prokaryotic RNAP The closed and open state of
Chapter 31 Transcription and RNA processing RNA polymerase (RNAP) E. coli promoters Components of E. coli RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme (α 2 ββ'ωσ) Structure of prokaryotic RNAP The closed and open state of
Biological information flow
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors mrna processing Biological
BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors mrna processing Biological
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process.
 Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Biological information flow
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Biological information flow Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors
BCMB 3100 Chapters 36-38 Transcription & RNA Processing Biological information flow Definition of gene RNA Polymerase Gene coding vs template strand Promoter Transcription in E. coli Transcription factors
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 10-1 Discovery of DNA
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 10-1 Discovery of DNA Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. The virulent strain of the bacterium S. pneumoniae causes disease because it a. has
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 10-1 Discovery of DNA Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. The virulent strain of the bacterium S. pneumoniae causes disease because it a. has
Neurospora mutants. Beadle & Tatum: Neurospora molds. Mutant A: Mutant B: HOW? Neurospora mutants
 Chapter 10: Central Dogma Gene Expression and Regulation Mutant A: Neurospora mutants Mutant B: Not made Not made Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are
Chapter 10: Central Dogma Gene Expression and Regulation Mutant A: Neurospora mutants Mutant B: Not made Not made Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are
CHAPTER 20 DNA TECHNOLOGY AND GENOMICS. Section A: DNA Cloning
 Section A: DNA Cloning 1. DNA technology makes it possible to clone genes for basic research and commercial applications: an overview 2. Restriction enzymes are used to make recombinant DNA 3. Genes can
Section A: DNA Cloning 1. DNA technology makes it possible to clone genes for basic research and commercial applications: an overview 2. Restriction enzymes are used to make recombinant DNA 3. Genes can
Chapter 12. DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION
 Chapter 12 DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis WARM UP What are proteins? Where do they come from? From DNA to RNA to Protein DNA in our cells carry the instructions for making
Chapter 12 DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis WARM UP What are proteins? Where do they come from? From DNA to RNA to Protein DNA in our cells carry the instructions for making
Adv Biology: DNA and RNA Study Guide
 Adv Biology: DNA and RNA Study Guide Chapter 12 Vocabulary -Notes What experiments led up to the discovery of DNA being the hereditary material? o The discovery that DNA is the genetic code involved many
Adv Biology: DNA and RNA Study Guide Chapter 12 Vocabulary -Notes What experiments led up to the discovery of DNA being the hereditary material? o The discovery that DNA is the genetic code involved many
Transcription in Escherichia coli DNA. Nucleoside 3'
 BIMM 122 Lecture Notes #5 Transcription in Escherichia coli Dr. Milton Saier bubble C 2 B 2 C 2 B 1 : olymerase adds nucleotides to the of the chain. coding : Nucleoside non-coding Copy either strand;
BIMM 122 Lecture Notes #5 Transcription in Escherichia coli Dr. Milton Saier bubble C 2 B 2 C 2 B 1 : olymerase adds nucleotides to the of the chain. coding : Nucleoside non-coding Copy either strand;
