CHAPTER 9 NATION BUILDING AND NATIONALISM. APUSH Mr. Muller
|
|
|
- Arleen Taylor
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 9 NATION BUILDING AND NATIONALISM APUSH Mr. Muller
2 AIM: HOW DOES THE NATION BEGIN TO EXPAND? Do Now: A high and honorable feeling generally prevails, and the people begin to assume, more and more, a national character; and to look at home for the only means, under divine goodness, of preserving their religion and liberty. -Hezekiah Niles, Niles Weekly Register, September 2, 1815
3
4
5
6 BUILDING NATIONAL UNITY An Era of Good Feelings: - James Monroe is President (Republican) - The arguments between the Republicans and the Federalist began to go away. People of different parties were becoming nice to each other
7 POLITICAL GIANTS John C. Calhoun: (small government) - spoke for the South - did not want to make the central government too powerful Daniel Webster: (large government) - spoke for the North Henry Clay: (large government) - spoke for the West
8
9 AMERICAN SYSTEM: HENRY CLAY Established a better national transportation system to aid trade and national defense. Protective Tariff Encourages American manufacturing Second national bank to promote the necessary financial support.
10 National Bank The charter for the first Bank of the United States expired in With no central bank the U.S. economy was unstable. State banks issued paper money, which led to inflation. Inflation is when the value of money goes down and prices go up. The Republican Party had opposed the first Bank, but now supported chartering a second National Bank in The Bank helped stabilize the currency, although opposition grew to its power and influence. 10
11 COMPETITION FROM ENGLAND In 1815, British goods began pouring into America. Sometimes, British manufactures would sell things in America for less than it cost to make. This practice is called dumping. Dumping is the practice of selling goods in another country for very low prices. British manufactures hoped to put American rivals out of business
12 PROTECTIVE TARIFFS Protective Tariff is a tax meant to protect a country s industries from foreign competition. America wanted to protect factory owners in the North from the British dumping. Southerners did not have many factories, they saw the protective tariff as a tax to help the north and to hurt the south.
13 THE MARSHALL COURT Fletcher v. Peck 1810 States can t invalidate a contract (1 st time Supreme court overruled States) Martin v. Hunter s Lease 1816 Supreme Court had Jurisdiction over State Dartmouth College v. Woodward 1819 Contract by a private corporation couldn t be altered by a state. McCulloch v. Maryland 1819 States cannot tax federal institutions. Cohens v. Virginia 1821 Supreme Court could review a state court s decision involving any of the powers of the federal government. Gibbons v. Ogden 1821 Federal gov t controls interstate commerce
14
15 Expansion created both new free and slave states. It was commonly agreed it would be a good idea if new states did not upset the balance between existing free and slave states. The proposed admission of Missouri in 1819 as a slave state threatened to upset this balance. (from 11 slave and 11 free to 12 slave and 11 free) State year admitted total slave states total free states Ohio Louisiana Indiana Mississippi Illinois Alabama free states Maine
16
17 Northerners were opposed to Missouri's entry as a slave state. There was a storm of protest in the North. For a time Congress was deadlocked on Missouri s admission, but under the leadership of Henry Clay the Missouri Compromise was agreed upon. Under the Compromise, Missouri was admitted as a slave state and Maine came in as a free state. The Missouri Compromise contained a clause which forever prohibited slavery north of 36 30' in all the territory acquired from France by the Louisiana Purchase. In addition, Congress banned slavery from the territory acquired by the Louisiana Purchase north of Missouri's southern boundary. At the time, this provision appeared to be a victory for the Southern states because it was thought unlikely this "Great American Desert" would ever be settled. 1. Admit Missouri as a slave state in accordance with the initial request for statehood. 2. Approve the application for statehood of Maine as a free state. 3. Define the territories in the Louisiana Purchase, which henceforth would be free and slave. 17
18 18
19 19
20
21 Florida becomes part of the U.S. President Madison unsuccessfully tried to take over West Florida from Spain in Many Southerners were angry that Spanish officials protected runaway slaves from coastal South Carolina and Georgia. Many exslaves were allowed to live and work with Seminole Indians in exchange for part of their crops. Black Seminoles In 1816, General Andrew Jackson invaded Florida and destroyed the Negro fort that protected Black Seminole settlements. In 1818, Jackson again invaded Florida and claimed it for the U.S. In 1819, Spain, involved with revolts throughout Latin America, sold Florida to the U.S. for $5 million ($80 million in 2005 dollars) under the Adams-Onis Treaty. 21
22 22
23 Foreign Affairs under President Monroe Latin America Florida Monroe Doctrine John Quincy Adams Serving under President Monroe, Adams was one of America's great Secretaries of State, arranging with England for the joint occupation of the Oregon country, obtaining from Spain the cession of the Florida's, and formulating with the president the Monroe Doctrine. 23
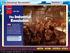
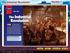
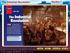
24 The U.S. wanted Latin America to remain free Once Latin America freed itself from Spanish rule, Americans worried other European nations might help Spain re-conquer her lost colonies. Great Britain was also concerned and wanted to partner with the U.S. in issuing a joint document guaranteeing the freedom of the new nations. President Monroe and his Secretary of State John Q. Adams decided to issue a statement from the U.S. alone, rejecting Britain's offer. Britain backed up U.S. efforts with her fleet and army. Mural depicts discussion among the president and members of his Cabinet; from left to right are President James Monroe, Secretary of State John Quincy Adams, Attorney General William Wirt, Secretary of War John Calhoun, and Secretary of the Navy Samuel L. Southard. 24
25 The U.S. issued the Monroe Doctrine which stated: The United States would not get involved in European affairs. The United States would not interfere with existing European colonies in the Western Hemisphere. If a European nation tried to control or interfere with a nation in the Western Hemisphere, the United States would view it as a hostile act. No other nation could form a new colony in the Western Hemisphere. The peoples of the West are henceforth not to be considered as subjects for future colonization by any European powers. Secretary of State John Quincy Adams helped author the document 25
26 NEW TECHNOLOGY Industrial Revolution is a revolution in the ways things are made. Machines replaced people Factories replaced homes Examples of Machines: - Spinning Jenny: a worker could spin several threads at one time, not just one thread on a spinning wheel - Cotton Gin: a machine that would take the seeds out of cotton. Instead of having to take the seeds out by hand.
27 FACTORIES Factories are built by rivers. The water from the river would turn a large wheel. The wheel would run the machines. Factories are expensive to build. Most factories were owned by capitalists. People with money to invest in business to make a profit.
28 SECRETS Britain tries to keep inventions a secret Samuel Slater memorizes the design of a factory in Britain and builds one in America Samuel Slater builds the first factory in the United States Factory System
29 FROM WORKSHOPS TO FACTORIES Lowell Factories - Francis Cabot Lowell builds the first textile factory in Lowell Massachusetts - Lowell joins with several partners to pay for the factory. The partners are called the Boston Associates. - The Boston Associates hire young women from nearby farms to work in the factories. These girls are called Lowell girls.
30
31 CHILD LABOR Children have small hands that can fit inside the machines Children work long hours Children work for low pay Children are easily replaced.
32
33 ELI WHITNEY Eli Whitney invents the cotton gin Eli Whitney invents the idea of interchangeable parts. Interchangeable parts: all machine parts are made the same so that broken parts can be replaced quickly and cheap.
34
35
36 AMERICANS ON THE MOVE GO WEST YOUNG MAN!! People moved west to find free land. Settlers needed better roads when moving to the West. Types of Roads: Turnpikes: A road where the driver would pay a toll (money) to continued traveling on the road Corduroy Roads: Roads made in swampy (wet) areas. Logs would be placed next to each other to form a road. The lines of logs would look like Corduroy cloth. This was a very bumpy ride.
37 TYPES OF TRANSPORTATION Steam Transport: Robert Fulton, makes a boat that is powered by a steam engine. The steam engine permits a boat to travel without having to wait on the current of the water or the wind in the air. Robert Fulton s steamboat is called the Clermont Transcontinental Railroad: Will connect East and West once completed.
38
39 Cumberland Road Referred to as the National Road or Cumberland Road One of the first major improved highways in the U.S. built by the federal government Construction began in 1811 at Cumberland, Maryland Reached Wheeling, West Virginia, in 1818 Although the road was planned to end in Jefferson City, Missouri, funding ran out and it stopped at Vandalia, Illinois, in
40 Cumberland Road 40
41 CANAL BOOM A Canal is a channel dug by people, then filled with water to allow boats to cross a stretch of land Most famous canal built during this time period is the Erie Canal. The Erie Canal connects Lake Erie to the Hudson River. Benefits : reduced travel time lowered the cost of shipping goods helped make New York the center of commerce (trade) linked western farms with eastern cities
42 Erie Canal A canal is a man-made waterway The Erie Canal connects the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean from Lake Erie to the Hudson River Construction took eight years The system works with locks, where a boat goes into a gated area which fills with water so the boat can travel to the next higher water level Made transportation of goods faster and cheaper Encouraged settlement along the route and in the western territory 42
43 The canal runs from Buffalo to the Hudson River 43
44 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN NEW YORK THE ERIE CANAL Erie Canal - Complete in Connected the Hudson River to Lake Erie. - Made shipments of goods easier. - The canal contributed to the growth of upstate New York and New York City.
45
46
47 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION VIDEO QUESTIONS Directions: Complete questions based on the video clip. 1. Describe life before the industrial revolution? 2. List the 2 new textile machines that caused a revolution. 3. What is a factory? 4. When did work begin in the Lowell mills? 5. What day of the week did workers get off? 6. Who harvested cotton? In what region of American did they work? 7. Describe working conditions in factories. 8. Why is coal mining dangerous?
48
49
Industrial Revolution PowerPoint Notes
 Name: Date: Industrial Revolution PowerPoint Notes The Industrial Revolution Begins 1. 1700 s most people were farmers making cloth, tools, furniture by 2. 1800 s people began making cloth and other goods
Name: Date: Industrial Revolution PowerPoint Notes The Industrial Revolution Begins 1. 1700 s most people were farmers making cloth, tools, furniture by 2. 1800 s people began making cloth and other goods
Listen to the Erie Canal Song as you listen, answer the following questions: 1.Why might someone write a song about a canal? 2.What is an important
 Listen to the Erie Canal Song as you listen, answer the following questions: 1.Why might someone write a song about a canal? 2.What is an important effect of this new canal? How did the original Erie Canal
Listen to the Erie Canal Song as you listen, answer the following questions: 1.Why might someone write a song about a canal? 2.What is an important effect of this new canal? How did the original Erie Canal
Why did the Industrial Rev. begin in New England? Define Capitalism- Define Free Enterprise-
 Warm Up 1/14 What city on the east coast were the British successful at attacking? What city on the east coast were they unsuccessful at attacking? What did the British decide after they lost at the Battle
Warm Up 1/14 What city on the east coast were the British successful at attacking? What city on the east coast were they unsuccessful at attacking? What did the British decide after they lost at the Battle
The Industrial Revolution Section 1
 Preview A New Kind of Revolution Starting Points Map: Resources of Great Britain Main Idea / Reading Focus A Revolution in Great Britain A Revolution in Textiles Steam Powers the Revolution Faces of History:
Preview A New Kind of Revolution Starting Points Map: Resources of Great Britain Main Idea / Reading Focus A Revolution in Great Britain A Revolution in Textiles Steam Powers the Revolution Faces of History:
The Industrial Revolution Section 1
 Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Main Idea A New Kind of Revolution In the 1700s conditions in Great Britain led to the rapid growth
Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Main Idea A New Kind of Revolution In the 1700s conditions in Great Britain led to the rapid growth
The Industrial Revolution Section 1
 Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Main Idea A New Kind of Revolution In the 1700s conditions in Great Britain led to the rapid growth
Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Main Idea A New Kind of Revolution In the 1700s conditions in Great Britain led to the rapid growth
I. Create an episode map on westward expansion
 I. Create an episode map on westward expansion A. What is a market?? What do people do at markets?? What is an example of a market?? What are some markets that we use frequently?? I. The Industrial Revolution
I. Create an episode map on westward expansion A. What is a market?? What do people do at markets?? What is an example of a market?? What are some markets that we use frequently?? I. The Industrial Revolution
THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
 THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION 1700-1900 WHAT IS THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION? The Industrial Revolution refers to the time period when there was a huge increase of machine-made goods Images of Industrialization
THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION 1700-1900 WHAT IS THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION? The Industrial Revolution refers to the time period when there was a huge increase of machine-made goods Images of Industrialization
In the mid-1700s, an Industrial Revolution began in England that transformed the way work was done Rather than making goods by hand, new machines
 In the mid-1700s, an Industrial Revolution began in England that transformed the way work was done Rather than making goods by hand, new machines mass-produced products which lowered costs, increased profits,
In the mid-1700s, an Industrial Revolution began in England that transformed the way work was done Rather than making goods by hand, new machines mass-produced products which lowered costs, increased profits,
Economic Growth: Chapter 8, Section 1
 Economic Growth: Chapter 8, Section 1 Geography shapes the physical, economic, and political challenges a region faces. New technology produced the Industrial Revolution. The Growth of Industry Main Idea:
Economic Growth: Chapter 8, Section 1 Geography shapes the physical, economic, and political challenges a region faces. New technology produced the Industrial Revolution. The Growth of Industry Main Idea:
World History Agenda for Unit 10 #3:
 Essential Question: What caused an Industrial Revolution in England in the 1800s? World History Agenda for Unit 10 #3: Industrial Revolution notes Unit 10 Test: Tuesday, March 5 In the mid-1700s, an Industrial
Essential Question: What caused an Industrial Revolution in England in the 1800s? World History Agenda for Unit 10 #3: Industrial Revolution notes Unit 10 Test: Tuesday, March 5 In the mid-1700s, an Industrial
The Industrial Revolution. Learning Goal 1: Describe the causes of industrialization and explain the role technology played in industrialization.
 The Industrial Revolution Learning Goal 1: Describe the causes of industrialization and explain the role technology played in industrialization. THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION 1730-1830 What do you own that
The Industrial Revolution Learning Goal 1: Describe the causes of industrialization and explain the role technology played in industrialization. THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION 1730-1830 What do you own that
THE MARKET REVOLUTION AND AMERICA S REGIONAL IDENTITY ( )
 REGIONAL IDENTITY (1790 1850) Industrial North Western Frontier Southern Agriculture THE RISE OF SECTIONALISM IN THE U.S. The Role of Transportation (1806 1853) Native resistance slowed, but did not stop
REGIONAL IDENTITY (1790 1850) Industrial North Western Frontier Southern Agriculture THE RISE OF SECTIONALISM IN THE U.S. The Role of Transportation (1806 1853) Native resistance slowed, but did not stop
Essential Question: How did the Industrial Revolution impact society?
 Essential Question: How did the Industrial Revolution impact society? The Industrial Revolution Begins in Britain Inventions Spur Industrialization Improvements in Transportation The Railway Age Begins
Essential Question: How did the Industrial Revolution impact society? The Industrial Revolution Begins in Britain Inventions Spur Industrialization Improvements in Transportation The Railway Age Begins
T H E I N D U S T R I A L R E V O L U T I O N
 1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! When and where did the Industrial Revolution begin? Why did it begin in this country? How was work organized before the Industrial Revolution?
1 1 A N S W E R T H E Q U E S T I O N S I N Y O U R O W N W O R D S! When and where did the Industrial Revolution begin? Why did it begin in this country? How was work organized before the Industrial Revolution?
World History Review for AP Human Geography
 World History Review for AP Human Geography Age of European Discovery, Exploration, and Colonization The geographical knowledge acquired was crucial to the expansion of European political and economic
World History Review for AP Human Geography Age of European Discovery, Exploration, and Colonization The geographical knowledge acquired was crucial to the expansion of European political and economic
The Industrial Revolution. Cizj5c
 The Industrial Revolution https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zhl5d Cizj5c What was the Industrial Revolution? a shift from an agricultural (farming) economy to one based on industry (manufacturing) Agricultural
The Industrial Revolution https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zhl5d Cizj5c What was the Industrial Revolution? a shift from an agricultural (farming) economy to one based on industry (manufacturing) Agricultural
I. Create an episode map on westward expansion
 I. Create an episode map on westward expansion I. The Industrial Revolution led to an increased production by machines instead of humans or animals. A. The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain
I. Create an episode map on westward expansion I. The Industrial Revolution led to an increased production by machines instead of humans or animals. A. The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain
Southern Cotton Kingdom: Chapter 9, Section 1
 Southern Cotton Kingdom: Chapter 9, Section 1 Geography shapes the physical, economic, and political challenges a region faces. Cotton was vital to the economy of the South. Rise of the Cotton Kingdom
Southern Cotton Kingdom: Chapter 9, Section 1 Geography shapes the physical, economic, and political challenges a region faces. Cotton was vital to the economy of the South. Rise of the Cotton Kingdom
Industrial Revolution. Great Britain: How and Why It Happened
 Industrial Revolution Great Britain: How and Why It Happened Birth of the Industrial Revolution, Part One THE SEEDS Early 1700s: Great Britain What do you notice about this woman? Imagine how she might
Industrial Revolution Great Britain: How and Why It Happened Birth of the Industrial Revolution, Part One THE SEEDS Early 1700s: Great Britain What do you notice about this woman? Imagine how she might
Travel and Transportation
 Travel and Transportation Early 19th-century Americans were a people on the move. Many were heading west. The small roads and trails could not hold the heavy traffic. Travel was slow and hard, so America
Travel and Transportation Early 19th-century Americans were a people on the move. Many were heading west. The small roads and trails could not hold the heavy traffic. Travel was slow and hard, so America
The Market Revolution. The Americans, Chapter 9.1, Pages
 The Market Revolution The Americans, Chapter 9.1, Pages 274-279. U.S. Markets Expand Early 19 th Century Workers produce own goods Farms self-sufficient Trade surplus at local markets Purchase luxuries
The Market Revolution The Americans, Chapter 9.1, Pages 274-279. U.S. Markets Expand Early 19 th Century Workers produce own goods Farms self-sufficient Trade surplus at local markets Purchase luxuries
The Industrial Revolution ( )
 Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain in the 1750s? Objective: Explain the causes of Industrial Revolution in Great Britain. The Industrial Revolution (1750-1850) The Industrial Revolution
Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain in the 1750s? Objective: Explain the causes of Industrial Revolution in Great Britain. The Industrial Revolution (1750-1850) The Industrial Revolution
All of this was about to change. Industrialization was coming!!
 England in 1700: Was a rural, agricultural society. Most people lived on farms. They grew their own food, made their own clothing and worked hard Most people were poor and, if harvest failed, they risked
England in 1700: Was a rural, agricultural society. Most people lived on farms. They grew their own food, made their own clothing and worked hard Most people were poor and, if harvest failed, they risked
3 Economic Sectors Serve as the Basis of the Infrastructure: Agriculture Factories Transportation/Communication
 The Rise of Industrial America Circa 1790-1900 *Stuff between stars is not part of power point, only talk* Part One; The First Industrial Revolution 1790-1860 Background: -Circa 1750 Europe s industrial
The Rise of Industrial America Circa 1790-1900 *Stuff between stars is not part of power point, only talk* Part One; The First Industrial Revolution 1790-1860 Background: -Circa 1750 Europe s industrial
The Agricultural or (Agrarian) Revolution
 The Agricultural or (Agrarian) Revolution What was the Agrarian Revolution? An increase in food production from a change in the methods of farming. Enclosure Movement Taking over and fencing off land that
The Agricultural or (Agrarian) Revolution What was the Agrarian Revolution? An increase in food production from a change in the methods of farming. Enclosure Movement Taking over and fencing off land that
AN OHIO WATER MILL. Learning Objective. Video Synopsis. Teacher Background
 Learning Objective Students will be able to analyze primary source documents and conduct research to make inferences about technological innovations made during the nineteenth century. Video Synopsis In
Learning Objective Students will be able to analyze primary source documents and conduct research to make inferences about technological innovations made during the nineteenth century. Video Synopsis In
Exam 3 - Fall 2014 Code Name:
 Exam 3 - Fall 2014 Code Name: Part 1: The details (70 points. Each question is worth 2 pts each unless noted.) # s 1 4: Miguel is touring an historical site, one of the earliest factories to be built in
Exam 3 - Fall 2014 Code Name: Part 1: The details (70 points. Each question is worth 2 pts each unless noted.) # s 1 4: Miguel is touring an historical site, one of the earliest factories to be built in
The Industrial Revolution in Britain. AP World History
 The Industrial Revolution in Britain AP World History Today s main idea: What does it mean for a country to experience an Industrial Revolution? Why was Britain the first? Industrialization fundamentally
The Industrial Revolution in Britain AP World History Today s main idea: What does it mean for a country to experience an Industrial Revolution? Why was Britain the first? Industrialization fundamentally
The Industrial Revolution Begins ( )
 World History: Connection to Today Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 20 The Industrial Revolution Begins (1750
World History: Connection to Today Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 20 The Industrial Revolution Begins (1750
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #100 Aims: SWBAT explain how cotton production was an economic incentive for slavery in the South SWBAT identify the different
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #100 Aims: SWBAT explain how cotton production was an economic incentive for slavery in the South SWBAT identify the different
The Industrial Revolution
 1760-1910 The Industrial Revolution Biggest change in human lifestyles since the development of farming during the Neolithic Revolution!!! (New Stone Age) It will all begin with an Agricultural Revolution
1760-1910 The Industrial Revolution Biggest change in human lifestyles since the development of farming during the Neolithic Revolution!!! (New Stone Age) It will all begin with an Agricultural Revolution
Chapter Three FEDERALISM
 Chapter Three FEDERALISM Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Learning Outcomes 1. Define federalism and contrast the federal system of government with the unitary and confederal systems in explaining where
Chapter Three FEDERALISM Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Learning Outcomes 1. Define federalism and contrast the federal system of government with the unitary and confederal systems in explaining where
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
 Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 04/02/2014 Generated By: Cheryl Shelton Title: Grade 6 - Geography Japan is a small island nation with few natural resources.
Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 04/02/2014 Generated By: Cheryl Shelton Title: Grade 6 - Geography Japan is a small island nation with few natural resources.
DBQ 12: THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION: BEGINNINGS
 Document 1 This map shows the resources and canals of England in the eighteenth century. Canals began in 1756 England resources and canals circa 1700 Cotton Lead Tin Lead According to the map, what resources
Document 1 This map shows the resources and canals of England in the eighteenth century. Canals began in 1756 England resources and canals circa 1700 Cotton Lead Tin Lead According to the map, what resources
Land Distribution. Land Purchases. Nature of Settlement Post-Revolution to the Civil War Changing Shape of New York
 Historical Geography of NYS Nature of Settlement Post-Revolution to the Civil War 1780-1865 Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2014 Settlement Sequence New York State Revolutionary War ends in 1781. New York colony
Historical Geography of NYS Nature of Settlement Post-Revolution to the Civil War 1780-1865 Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2014 Settlement Sequence New York State Revolutionary War ends in 1781. New York colony
INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION CH. 9.1 THE BEGINNINGS OF INDUSTRIALIZATION Objectives 1. List two reasons why Industrialization began in England. 2. List one invention created to speed up industry. 3. List four
INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION CH. 9.1 THE BEGINNINGS OF INDUSTRIALIZATION Objectives 1. List two reasons why Industrialization began in England. 2. List one invention created to speed up industry. 3. List four
CORRELATION GUIDE Level 1
 We the People The Citizen and the Constitution Published by the Center for Civic Education Funded by the U.S. Department of Education by act of Congress CORRELATION GUIDE Level 1 For Michigan Social Studies
We the People The Citizen and the Constitution Published by the Center for Civic Education Funded by the U.S. Department of Education by act of Congress CORRELATION GUIDE Level 1 For Michigan Social Studies
Name: Group: 404- Date: Chapter 1: The Formation of the Canadian Federation Section 6: The First Phase of Industrialization
 Name: Group: 404- Date: Notes 1.6 Chapter 1: The Formation of the Canadian Federation Section 6: The First Phase of Industrialization Pages that correspond to this presentation: The First Phase of Industrialization:
Name: Group: 404- Date: Notes 1.6 Chapter 1: The Formation of the Canadian Federation Section 6: The First Phase of Industrialization Pages that correspond to this presentation: The First Phase of Industrialization:
Study Questions for the Hughes & Cain Chapter 8 Readings
 Study Questions for the Hughes & Cain Chapter 8 Readings Objective/Short answer questions 1. (6 points) Farmer Mike and his wife Mildred are living Sharon, PA (indicated by X) in 1835. Mike, Mildred, and
Study Questions for the Hughes & Cain Chapter 8 Readings Objective/Short answer questions 1. (6 points) Farmer Mike and his wife Mildred are living Sharon, PA (indicated by X) in 1835. Mike, Mildred, and
Miss Elliott & Mrs. Hunt Shiloh Christian School
 Miss Elliott & Mrs. Hunt Shiloh Christian School 1 Acts 10:34-35 (34) God shows no partiality. (35) But in every nation whoever fears Him and works righteousness is accepted by Him. 2 A. The first Americans
Miss Elliott & Mrs. Hunt Shiloh Christian School 1 Acts 10:34-35 (34) God shows no partiality. (35) But in every nation whoever fears Him and works righteousness is accepted by Him. 2 A. The first Americans
Chapter 2: THE EVOLUTION OF THE BRITISH EMPIRE
 Chapter 2: THE EVOLUTION OF THE BRITISH EMPIRE OBJECTIVES: We will study about the reorganization of the British colonies. We will see how the Glorious Revolution in Great Britain impacted the colonies.
Chapter 2: THE EVOLUTION OF THE BRITISH EMPIRE OBJECTIVES: We will study about the reorganization of the British colonies. We will see how the Glorious Revolution in Great Britain impacted the colonies.
Foundations of American Government
 Foundations of American Government Why Do We Need Government? Maintain social order Ensure domestic tranquility Establish justice Provide for the common defense Promote the general welfare Secure liberty
Foundations of American Government Why Do We Need Government? Maintain social order Ensure domestic tranquility Establish justice Provide for the common defense Promote the general welfare Secure liberty
Learning Goal: I will understand the economic differences between the North and South in the years leading up to the Civil War.
 HOOK HOOK What conclusions can you make about the impact of the railway development in the U.S.? What impact will this make on the nation before and during the Civil War? North and South Benchmark: SS.8.A.4.10
HOOK HOOK What conclusions can you make about the impact of the railway development in the U.S.? What impact will this make on the nation before and during the Civil War? North and South Benchmark: SS.8.A.4.10
1. Time period where machines were used to create most of the goods in the world instead of by hand. 2. Began in Great Britain due to their abundance
 Ultimate Review 1. Time period where machines were used to create most of the goods in the world instead of by hand. 2. Began in Great Britain due to their abundance of natural resources and large population
Ultimate Review 1. Time period where machines were used to create most of the goods in the world instead of by hand. 2. Began in Great Britain due to their abundance of natural resources and large population
Industrial production began long before the Industrial Revolution
 Industrial production began long before the Industrial Revolution Goods and products were made in numerous places Most interesting relationship was Britain & India (their colony) India s products became
Industrial production began long before the Industrial Revolution Goods and products were made in numerous places Most interesting relationship was Britain & India (their colony) India s products became
Chapter 1 Constitutional Democracy. Constitutional Democracy. Constitutional Democracy. The peaceful transfer of political power through elections
 Chapter 1 A student from Chicago casts an early vote in the 2008 Illinois presidential primary. The peaceful transfer of political power through elections In 2000, Democrat Al Gore won the popular vote,
Chapter 1 A student from Chicago casts an early vote in the 2008 Illinois presidential primary. The peaceful transfer of political power through elections In 2000, Democrat Al Gore won the popular vote,
The Lake Erie Canal. Reading Practice
 Reading Practice The Lake Erie Canal Begun in 1817 and opened in its entirety in 1825, the Erie Canal is considered by some to be the engineering marvel of the nineteenth century. When the federal government
Reading Practice The Lake Erie Canal Begun in 1817 and opened in its entirety in 1825, the Erie Canal is considered by some to be the engineering marvel of the nineteenth century. When the federal government
A Profile of the United States CHAPTER 6
 A Profile of the United States CHAPTER 6 US Wealth The USA is the world s 4 th largest country in area and 3 rd most populous. Very wealthy. Highest Gross National Product (GNP) in the world. GNP is the
A Profile of the United States CHAPTER 6 US Wealth The USA is the world s 4 th largest country in area and 3 rd most populous. Very wealthy. Highest Gross National Product (GNP) in the world. GNP is the
In the Good Old Days Inventory Activity Sheet
 In the Good Old Days Inventory Activity Sheet Find someone who has: Myself (Checkmark) 1. Carded and/or spun wool 2. Made a pie 3. Fed a pig, chicken or cow 4. Gathered eggs 5. Gone barefoot for a week
In the Good Old Days Inventory Activity Sheet Find someone who has: Myself (Checkmark) 1. Carded and/or spun wool 2. Made a pie 3. Fed a pig, chicken or cow 4. Gathered eggs 5. Gone barefoot for a week
World Events leading to formation of United Nations
 History PART A Std VIII 2017-2018 World Events leading to formation of United Nations Q1. When did the First World War break out? The First World War broke out in the year 1914. Q2. Why is the war fought
History PART A Std VIII 2017-2018 World Events leading to formation of United Nations Q1. When did the First World War break out? The First World War broke out in the year 1914. Q2. Why is the war fought
North Climate and Geography
 Comparing the North & South Directions: Read the following passages and complete the graphic organizer comparing the North and South. As you read, highlight important information. North Climate and Geography
Comparing the North & South Directions: Read the following passages and complete the graphic organizer comparing the North and South. As you read, highlight important information. North Climate and Geography
Transportation, Communication, and Technology/Agricultural Technology in the North. By: Kiara Whyte and Destiny Jimenez
 Transportation, Communication, and Technology/Agricultural Technology in the North By: Kiara Whyte and Destiny Jimenez TRANSPORTATION Advanced transportation in the Americas did not begin to flourish up
Transportation, Communication, and Technology/Agricultural Technology in the North By: Kiara Whyte and Destiny Jimenez TRANSPORTATION Advanced transportation in the Americas did not begin to flourish up
ECON European Economic History II, 2018 John Lovett. Code Name: Part 1: (70. points. Answer on this paper. 2.5 pts each unless noted.
 ECON 30733 European Economic History II, 2018 John Lovett Code Name: Part 1: (70. points. Answer on this paper. 2.5 pts each unless noted.) 1. According to lecture, which change in agriculture will lead
ECON 30733 European Economic History II, 2018 John Lovett Code Name: Part 1: (70. points. Answer on this paper. 2.5 pts each unless noted.) 1. According to lecture, which change in agriculture will lead
Chapter 2 Economy & Development
 Chapter 2 Economy & Development Chapter 2 Economy & Development Section 3: The British Regime (1760-1867) Part 1: Fur Trade & Timber Trade The British take over the fur trade After the CONQUEST in 1760
Chapter 2 Economy & Development Chapter 2 Economy & Development Section 3: The British Regime (1760-1867) Part 1: Fur Trade & Timber Trade The British take over the fur trade After the CONQUEST in 1760
Grade 8 History Teacher s Guide Confederation
 Grade 8 History Teacher s Guide Confederation Overall Expectations Describe the internal and external political factors, key personalities, significant events, and geographical realities that led to the
Grade 8 History Teacher s Guide Confederation Overall Expectations Describe the internal and external political factors, key personalities, significant events, and geographical realities that led to the
Birth of the Republic
 Birth of the Republic 1 2 The American Colonists Mainly of English descent Scotch-Irish / Germans --> Pennsylvania Black Africans --> the South Believed they were preserving the true traditions of English
Birth of the Republic 1 2 The American Colonists Mainly of English descent Scotch-Irish / Germans --> Pennsylvania Black Africans --> the South Believed they were preserving the true traditions of English
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution What is a government? A government is a person, or group, who has the power to provide law, order, services, and security within a country. Government gives organization and structure
Creating the Constitution What is a government? A government is a person, or group, who has the power to provide law, order, services, and security within a country. Government gives organization and structure
STUDY GUIDE. Living in Europe. Chapter 13, Section 1. Europe Today. Terms to Know DRAWING FROM EXPERIENCE ORGANIZING YOUR THOUGHTS
 Chapter 13, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 313 319. Living in Europe Terms to Know European Union (EU) A trading community that unites much of western Europe (page 313) Maastricht Treaty The treaty
Chapter 13, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 313 319. Living in Europe Terms to Know European Union (EU) A trading community that unites much of western Europe (page 313) Maastricht Treaty The treaty
Tennessee Academic Standards Science Grade: 4 - Adopted: Technology and Engineering
 Main Criteria: Tennessee Academic Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 4 Correlation Options: Show Correlated TN.T/E. CS.T/E. GQ.T/E. Tennessee Academic Standards Science
Main Criteria: Tennessee Academic Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 4 Correlation Options: Show Correlated TN.T/E. CS.T/E. GQ.T/E. Tennessee Academic Standards Science
Modern US History Ch. 18, Section 3 Farming and Populism
 Modern US History Ch. 18, Section 3 Farming and Populism New Lives on the Plains Homestead Act 1862 US law that gave 160 acres of govt. owned land to people who would move to the land and farm it for 5
Modern US History Ch. 18, Section 3 Farming and Populism New Lives on the Plains Homestead Act 1862 US law that gave 160 acres of govt. owned land to people who would move to the land and farm it for 5
Life in the American Colonies (4-5 Lexile : 800L)
 Name Teacher /5 ER.DFA2.5.R.RI.03 Explain the relationship or interactions between two or more individuals, events, ideas, or concepts in a historical, scientific, or technical text based on specific information
Name Teacher /5 ER.DFA2.5.R.RI.03 Explain the relationship or interactions between two or more individuals, events, ideas, or concepts in a historical, scientific, or technical text based on specific information
What is left of it today/ how is it used in pop culture? (Think branding, Hollywood, sports teams, clothing, etc.)
 What are some myths of the American West? What is left of it today/ how is it used in pop culture? (Think branding, Hollywood, sports teams, clothing, etc.) How have these symbols of the past become both
What are some myths of the American West? What is left of it today/ how is it used in pop culture? (Think branding, Hollywood, sports teams, clothing, etc.) How have these symbols of the past become both
Georgia Milestones Grade 6 EOG Study/Resource Guide for Students and Parents Page 201 of 218
 Unit 8: Canada Today In this unit, you will examine our neighbor to the north, Canada. You will learn about its forms of government, including presidential, unitary, monarchy, and parliamentary systems
Unit 8: Canada Today In this unit, you will examine our neighbor to the north, Canada. You will learn about its forms of government, including presidential, unitary, monarchy, and parliamentary systems
INDUSTRIAL POWER SHIFT
 CHAPTER 11 INDUSTRY INDUSTRIAL POWER SHIFT The recent success of Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and other Asian countries is a dramatic change from the historic dominance of world industry by Western countries.
CHAPTER 11 INDUSTRY INDUSTRIAL POWER SHIFT The recent success of Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and other Asian countries is a dramatic change from the historic dominance of world industry by Western countries.
Articles of Confederation 4 Square Key
 Articles of Confederation 4 Square Key Our 1 st Change in Style of Government 1. Definition 1 st Constitution of U.S. Blueprint for the new government (John Hanson actually became our first president but
Articles of Confederation 4 Square Key Our 1 st Change in Style of Government 1. Definition 1 st Constitution of U.S. Blueprint for the new government (John Hanson actually became our first president but
OHIO RIVERBOATS. Learning Objective. Video Synopsis. Teacher Background
 Learning Objective Students will be able to explain how innovations in transportation and important transportation routes like the Ohio River contributed to the development of the state. Students will
Learning Objective Students will be able to explain how innovations in transportation and important transportation routes like the Ohio River contributed to the development of the state. Students will
Economic History of the US
 Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #4 Peter Allen Econ 120 1 Mercantilism: Gold flows only to London Economic subordination Parliament did not allow colonies to bop surplus
Economic History of the US The Colonial Era, 1607-1776 Lecture #4 Peter Allen Econ 120 1 Mercantilism: Gold flows only to London Economic subordination Parliament did not allow colonies to bop surplus
CHAPTER 3 FEDERALISM CHAPTER OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 3 FEDERALISM CHAPTER OUTLINE I. Defining Federalism (pp. 70-74) A. What Is Federalism? 1. Federalism is a way of organizing a nation so that two or more levels of government have formal authority
CHAPTER 3 FEDERALISM CHAPTER OUTLINE I. Defining Federalism (pp. 70-74) A. What Is Federalism? 1. Federalism is a way of organizing a nation so that two or more levels of government have formal authority
BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas
 BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas 1690 LOCKE S TWO TREATISES ON GOVERNMENT STATE: Man has three things in nature: Life, Liberty & Property which can never be taken away or given
BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas 1690 LOCKE S TWO TREATISES ON GOVERNMENT STATE: Man has three things in nature: Life, Liberty & Property which can never be taken away or given
New England Colonies
 New England Colonies Connecticut Connecticut Founded: 1636 by Thomas Hooker Reason for Founding: believed government should be based on free consent Economy: small subsistence farms - growing enough to
New England Colonies Connecticut Connecticut Founded: 1636 by Thomas Hooker Reason for Founding: believed government should be based on free consent Economy: small subsistence farms - growing enough to
Module 3: Change In Empire
 Population and settlement: Module 3: Change In Empire 1756-1791 As a result of the Treaty of Paris in 1763, Great Britain officially took possession of all French Territories in North America except for
Population and settlement: Module 3: Change In Empire 1756-1791 As a result of the Treaty of Paris in 1763, Great Britain officially took possession of all French Territories in North America except for
Analyze the ideological, military, social, and diplomatic aspects of the American Revolution.
 Analyze the ideological, military, social, and diplomatic aspects of the American Revolution. The Proclamation of 1763 When the French and Indian War ended, the French LEFT But the Indians remained And
Analyze the ideological, military, social, and diplomatic aspects of the American Revolution. The Proclamation of 1763 When the French and Indian War ended, the French LEFT But the Indians remained And
Key areas to pay attention to for the CBA 2
 Sequencing Key areas to pay attention to for the CBA 2 There are four fundamental documents that are created in America and that lead to our system of government now. In sequential order they are Fundamental
Sequencing Key areas to pay attention to for the CBA 2 There are four fundamental documents that are created in America and that lead to our system of government now. In sequential order they are Fundamental
6/28/2011. The Glorious Constitution The Anti-Democratic Constitution
 The Glorious Constitution The Anti-Democratic Constitution 1 2 We hold these truths to be self-evident: That all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable rights;
The Glorious Constitution The Anti-Democratic Constitution 1 2 We hold these truths to be self-evident: That all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable rights;
The French Revolution
 The French Revolution Using your notes, complete the following paragraph. The Enlightenment is also known as the. During this time, people began to reject the teachings of the and the and question traditional
The French Revolution Using your notes, complete the following paragraph. The Enlightenment is also known as the. During this time, people began to reject the teachings of the and the and question traditional
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 1 Government in Colonial America ESSENTIAL QUESTION What influenced the development of our government institutions? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary establish to create or set up levy to charge
Lesson 1 Government in Colonial America ESSENTIAL QUESTION What influenced the development of our government institutions? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary establish to create or set up levy to charge
Careers Note Sheet and Timeline. Agrarian Trades a trade involving farming or natural resources:
 1700 s Careers Note Sheet and Timeline Artisan Trades a skilled trade, a job requiring the creation of a product Blacksmith Silversmith Wheelwright Cooper Carpenter Cabinetmaker Milliner Printer Shoemaker
1700 s Careers Note Sheet and Timeline Artisan Trades a skilled trade, a job requiring the creation of a product Blacksmith Silversmith Wheelwright Cooper Carpenter Cabinetmaker Milliner Printer Shoemaker
Industrial Revolution
 Industrial Revolution Industrial Revolution Causes Agricultural Revolution ENCLOSURES Forced small farmers off land to create large farms Done to INCREASE PRODUCTION as population increased Forced small
Industrial Revolution Industrial Revolution Causes Agricultural Revolution ENCLOSURES Forced small farmers off land to create large farms Done to INCREASE PRODUCTION as population increased Forced small
Industry, Revolution, and and Imperialism: Creating the Modern World, CE
 Industry, Revolution, and and Imperialism: Creating the Modern World, 1750-1914 CE 6 Major Changes Population Growth Energy Communication and Transportation Industry Liberalism Imperialism 1: Population
Industry, Revolution, and and Imperialism: Creating the Modern World, 1750-1914 CE 6 Major Changes Population Growth Energy Communication and Transportation Industry Liberalism Imperialism 1: Population
Map of North and South America
 PASS Social Studies Grade 7 Test 1 Map of North and South America (drawn around the year 1700) SC07SS070101 1. Judging from the above map, it is clear that Europeans in the year 1700 knew the least about
PASS Social Studies Grade 7 Test 1 Map of North and South America (drawn around the year 1700) SC07SS070101 1. Judging from the above map, it is clear that Europeans in the year 1700 knew the least about
The planters group consists of 10 Planter Families of the following make up:
 UTOPIA EXERCISE A natural resources exercise was developed for the Freedom s Frontier partnership meeting in September, 2008. The purpose of this exercise was to go through a decision-making exercise for
UTOPIA EXERCISE A natural resources exercise was developed for the Freedom s Frontier partnership meeting in September, 2008. The purpose of this exercise was to go through a decision-making exercise for
AP U.S. History HOMEWORK Review Activities
 2012-2013 AP U.S. History HOMEWORK Review Activities Due Date Calendar Tuesday, April Mock Test Analysis 9 th American Diversity Thematic Timeline Monday, April American Identity Thematic Timeline 15th
2012-2013 AP U.S. History HOMEWORK Review Activities Due Date Calendar Tuesday, April Mock Test Analysis 9 th American Diversity Thematic Timeline Monday, April American Identity Thematic Timeline 15th
Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy
 Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy FOQ #1: Did the English Civil War help or hurt Democracy? Explain. FOQ #2: What were the causes of the American Revolutionary War? How did it end? FOQ #3: What were the
Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy FOQ #1: Did the English Civil War help or hurt Democracy? Explain. FOQ #2: What were the causes of the American Revolutionary War? How did it end? FOQ #3: What were the
THE COLD WAR
 THE COLD WAR 1945-1990 The Cold War Declared Cold War a state of increased tension and hostility without armed conflict End of WWII saw this sate occurring between the two new superpowers the US and USSR
THE COLD WAR 1945-1990 The Cold War Declared Cold War a state of increased tension and hostility without armed conflict End of WWII saw this sate occurring between the two new superpowers the US and USSR
Ch. 19 Reading Guide: Agriculture and the Land (1 of 4)
 Ch. 19 Reading Guide: Agriculture and the Land (1 of 4) You re largely on your own for this chapter, but email me if you need help or have concerns. There are more questions than normal, but they re shorter
Ch. 19 Reading Guide: Agriculture and the Land (1 of 4) You re largely on your own for this chapter, but email me if you need help or have concerns. There are more questions than normal, but they re shorter
All men are created equal. Certain inalienable rights Life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness
 Rhetoric inspired Americans and the world. It still does. Declaration Of Independence All men are created equal. Certain inalienable rights Life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness In 1781 1789 these
Rhetoric inspired Americans and the world. It still does. Declaration Of Independence All men are created equal. Certain inalienable rights Life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness In 1781 1789 these
A. Abundance of natural resources (oil, timber, iron, gold, cattle, copper)
 History 271 Devine Spring 2015 INDUSTRIALIZATION IN THE LATE NINETEENTH CENTURY An Incredible Economic Expansion 1860-1900 $3 billion in manufactures (1869) $13 billion (1900) Iron ore production quadruples
History 271 Devine Spring 2015 INDUSTRIALIZATION IN THE LATE NINETEENTH CENTURY An Incredible Economic Expansion 1860-1900 $3 billion in manufactures (1869) $13 billion (1900) Iron ore production quadruples
Napoleon s Rise and Fall. AP Euro SAHS 2017
 Napoleon s Rise and Fall AP Euro SAHS 2017 Napoleon Gains Power Napoleon became a hero when he saved the National Assembly from the Royalist Napoleon was a fairly successful military leader He was able
Napoleon s Rise and Fall AP Euro SAHS 2017 Napoleon Gains Power Napoleon became a hero when he saved the National Assembly from the Royalist Napoleon was a fairly successful military leader He was able
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 4 The American Revolution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Why do new ideas often spark change? How do new ways of thinking affect the way people respond to their surroundings? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary
Lesson 4 The American Revolution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Why do new ideas often spark change? How do new ways of thinking affect the way people respond to their surroundings? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary
Industrialization and Urbanization. Standard 5-3.4
 Industrialization and Urbanization Standard 5-3.4 Signs of Change 1 in 6 or 16% of people lived in cities by 1860 1 in 3 or 33% of people lived in cities by 1900 People were moving from farms to cities
Industrialization and Urbanization Standard 5-3.4 Signs of Change 1 in 6 or 16% of people lived in cities by 1860 1 in 3 or 33% of people lived in cities by 1900 People were moving from farms to cities
E & D- British Regime Notes: Part 1
 Name: Group: 406- Date: E & D- British Regime Notes: Part 1 Chapter 2 Economy & Development Section 2: The French Regime (1608-1760) Part 1: The Fur Trade & the Timber Trade After the CONQUEST in 1760
Name: Group: 406- Date: E & D- British Regime Notes: Part 1 Chapter 2 Economy & Development Section 2: The French Regime (1608-1760) Part 1: The Fur Trade & the Timber Trade After the CONQUEST in 1760
Between the end of the Civil War (1865) and World War I (1914), the United States was transformed from an agricultural to an industrial nation
 1865-1914 Between the end of the Civil War (1865) and World War I (1914), the United States was transformed from an agricultural to an industrial nation 1865-1914 Manufacturing areas were created near
1865-1914 Between the end of the Civil War (1865) and World War I (1914), the United States was transformed from an agricultural to an industrial nation 1865-1914 Manufacturing areas were created near
1. Can you name a major North American city not on a river or with access to an ocean?? Where is the clothing you are wearing made? (check!
 1. Can you name a major North American city not on a river or with access to an ocean?? Where is the clothing you are wearing made? (check!) Agenda Weekend Recap Vocab Quiz KI 1-2 due today Ppt on Industry
1. Can you name a major North American city not on a river or with access to an ocean?? Where is the clothing you are wearing made? (check!) Agenda Weekend Recap Vocab Quiz KI 1-2 due today Ppt on Industry
Idaho s Forest Products Business Sector:
 Policy Analysis Group College of Natural Resources Report No. 26 August 2006 Idaho s Forest Products Business Sector: Jobs, Wages and Salaries, Direct and Indirect Effects Linkages, Multipliers, and Economic
Policy Analysis Group College of Natural Resources Report No. 26 August 2006 Idaho s Forest Products Business Sector: Jobs, Wages and Salaries, Direct and Indirect Effects Linkages, Multipliers, and Economic
Land Distribution. Land Purchases. Nature of Settlement Post-Revolution to the Civil War Changing Shape of New York
 Historical Geography of NYS Nature of Settlement Post-Revolution to the Civil War 1780-1865 Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2013 Settlement Sequence New York State Revolutionary War ends in 1781. New York colony
Historical Geography of NYS Nature of Settlement Post-Revolution to the Civil War 1780-1865 Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2013 Settlement Sequence New York State Revolutionary War ends in 1781. New York colony
The Commercial Revolution Most of Europe remained agricultural. Fastest growing part of the economy was trade of goods. Those manufactured in Europe
 13. The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment People to Know 1. Henry VIII 2. Thomas Hobbes 3. Louis XIV 4. John Locke 5. William Blackstone 6. Sir Isaac Newton 7. Robert Boyle 8. Thomas Jefferson 9.
13. The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment People to Know 1. Henry VIII 2. Thomas Hobbes 3. Louis XIV 4. John Locke 5. William Blackstone 6. Sir Isaac Newton 7. Robert Boyle 8. Thomas Jefferson 9.
correlated to Indiana s Academic Standards Social Studies United States Government
 correlated to Indiana s Academic Standards Social Studies United States Government 6/2002 2001 American Government, eighth edition correlated to Indiana's Academic Standards Social Studies United States
correlated to Indiana s Academic Standards Social Studies United States Government 6/2002 2001 American Government, eighth edition correlated to Indiana's Academic Standards Social Studies United States
CIVICS & ECONOMICS EXAM STUDY GUIDE Name
 CIVICS & ECONOMICS EXAM STUDY GUIDE Name GOAL 1: Foundations of American Political System & Values & Principles of American Democracy Objective 1.01: How did geographic diversity influence the economic,
CIVICS & ECONOMICS EXAM STUDY GUIDE Name GOAL 1: Foundations of American Political System & Values & Principles of American Democracy Objective 1.01: How did geographic diversity influence the economic,
