TOG PROTEINS ARE SPATIALLY REGULATED BY RAC-GSK3β TO CONTROL INTERPHASE MICROTUBULE DYNAMICS. Kathryn P. Trogden
|
|
|
- Norah Little
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TOG PROTEINS ARE SPATIALLY REGULATED BY RAC-GSK3β TO CONTROL INTERPHASE MICROTUBULE DYNAMICS Kathryn P. Trogden A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Department of Biology in the College of Arts and Sciences. Chapel Hill 2015 Approved by: Stephen Rogers Victoria Bautch Stephanie Gupton Benjamin Major Kevin Slep
2 2015 Kathryn P. Trogden ALL RIGHTS RESERVED ii
3 ABSTRACT Kathryn P. Trogden: TOG Proteins are spatially regulated by Rac-GSK3β to control interphase microtubule dynamics (Under the direction of Stephen L. Rogers) Within a cell, the ends of individual microtubules switch between three different phases: growth, shrinkage and pause without affecting the total mass of microtubule polymer. This inherent property of microtubules is termed dynamic instability. During interphase, microtubule dynamics are regulated by a class of proteins that interact primarily with the plus end of the microtubule (+TIPs). How these proteins are regulated, either through interactions with each other or through signaling pathways in the cell are poorly understood. Two +TIP protein families, the XMAP215 family, known as Mini spindles (Msps) in Drosophila and the CLASP family, known as Orbit, contain arrays of tubulin binding TOG domains. We show that in Drosophila S2 cells Orbit is phosphorylated by the kinase GSK3β, similar to what has been reported for mammalian CLASPs. At the periphery of the cell, GSK3β is inhibited by the Rho GTPase Rac and Orbit is no longer phosphorylated. Orbit is then able to interact with Msps through their C-termini, allowing Msps to bind to the lattice. Msps lattice binding is important for proper microtubule dynamics as mutations that disrupt this interaction lead to aberrant dynamics. This interaction requires the scaffolding protein Sentin to bring the two proteins into contact at the periphery of the cell. Further work has shown a role for another Rac effector kinase, PAK, in this pathway. This interaction may also be important for migration in Drosophila cells. Depletion of +TIPs leads to changes in cell movement, indicating that microtubule dynamics may play a role in motility. iii
4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I would like to acknowledge my advisor, Steve Rogers, and my committee, Vicki Bautch, Stephanie Gupton, Ben Major, and Kevin Slep, for their creative input and encouragement throughout my dissertation progress. I would also like to thank the members of the Rogers lab, past and present. A special thanks for Josh Currie and Derek Applewhite for continual help and dicussions about my project. Also to Kim Peters for not sugar coating things and providing realistic views on graduate school. A special thanks to the people who made graduate school survivable, Lauren Slevin, Tom Lane, Fatima Manzoor, Jennifer Heppert, Diana Chong and Joy Meserve. Finally, I would like to thank my parents, Jeff and Anita Trogden, for doing my taxes, supporting, if not understanding my choice to stay in school and not get a real job and for making an effort, if not always succeeding, in saying Drosophila. iv
5 PREFACE Chapter 2 is a manuscript in review at MBoC. I performed all of the experiments and anaylsis and drafted the figures. Stephen Rogers and I designed experiments and drafted the manuscript. Trogden, K.P., and Rogers, S.L. (2015). Spatial regulation of Drosophila Mini-spindles by Rac and GSK3β requires its interaction with Orbit. Mol Biol Cell. In review. Chapter 3 describes an ongoing project that is a collaborative effort between Stephen Rogers and me to further explore the pathway described in Chapter 2. I performed all of the experiments and anaylsis. Chapter 4 describes an ongoing project to study the role of the pathway decribed in Chapter 2 in cell migration. All expirements and anaylsis were performed by me. Experimental design was overseen by Derek Applewhite and Steve Rogers. v
6 TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF TABLES... xiii LIST OF FIGURES... xiv LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS AND SYMBOLS... xvi CHAPTER 1 : INTRODUCTION... 1 Summary... 1 Microtubules are inherently dynamic... 1 Dynamic Instability is regulated in cells by Microtubule Associated Proteins... 4 End Binding (EB) Proteins... 5 SLAIN/Sentin Proteins... 9 Cytoplasmic Linker Associated Proteins (CLASPs) Dis1/XMAP215 Proteins Kinesin-13/KinI Depolymerase Motor Proteins The Role of +TIPs in Cell Migration References CHAPTER 2 : SPATIAL REGULATION OF DROSOPHILA MINI-SPINDLES BY RAC AND GSK3Β REQUIRES ITS INTERACTION WITH ORBIT Summary Introduction Results There are two populations of microtubules in Drosophila S2 cells Rac and GSK3β regulate Orbit and Msps localization in S2 cells vii
7 Msps is regulated by GSK3β through Orbit Sentin is necessary for Msps and Orbit to interact The C-termini of Msps and Orbit interact Msps mutants that cannot bind Orbit increase microtubule growth Discussion Experimental Procedues Cell Culture and RNA interference Immunofluorescnece and live cell imaging Immunoprecipitation/Western-blotting Molecular biology and transfection Microtubule and actin retrograde flow measurements References Tables Supplemental Figures CHAPTER 3 : PLK4 PB3 IS A DIVERGENT PB DOMAIN WITH SPECIES- DEPENDENT ROLES AND A VARIABLE STRUCTURE Summary Introduction Results Rac1 regulates Orbit and Mini-spinldes lattice binding, but Mtl does not Orbit and Mini-spindles lattice binding is regulated downstream of Rac by the PAK kinases Discussion Experimental Procedues Cell-Culture and RNA interference Immunofluorescence and live-cell imaging viii
8 Molecular biology and transfection Colocalization analysis References CHAPTER 4 : DROSOPHILA D25 CELLS ARE MOTILE AND REQUIRE PROPER MICROTUBULE DYNAMICS FOR NORMAL CELL MOVEMENT Summary Introduction Results D25 cell have lamellipodia and move in a non-directional manner Pioneer microtubules grow into the lamellipodia at the leading edge of D25 cells Proper microtubule dynamics are important for regular cell migration of D25 cells Msps and Orbit lattice association is regulated by Rac1 in D25 cells Disscussion Experimental Procedures Cell Culture and RNA interference Immunofluorscence and live cell imaging Molecular biology and transfection Measurement of Cell Movement References CHAPTER 5 : CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK TIPs interact at the plus end in a hierarchical, regulated manner TIPs play an important role in cell migration TIPs in Drosophila cell migration Microtubules and +TIPs play a role in Drosophila development Concluding remarks References ix
9 LIST OF TABLES Table 2.1. Microtubule dynamics parameters x
10 LIST OF FIGURES Figure 1.1. Microtubules stochastically switch between three states Figure 1.2. Domain Structure of +TIP Families Figure 1.3. Pathways Downstream of Rac at the Leading Edge of Motile Mammalian Cells Figure 2.1 Orbit and Msps localization is regulated by Rac-GSK3β signaling Figure 2.2. Orbit is phosphorylated by GSK3β in the linker region between TOG2 and TOG Figure 2.3. Orbit and GSK3β levels regulate Msps recruitment to the microtubule lattice Figure 2.4. Sentin expression is required for the Orbit-Msps interaction, but is not regulated by Rac Figure 2.5 Msps interacts with Orbit Figure 2.6 Measurement of microtubule dynamics Figure 2.7. Model Figure 2.S1. Endogenous Orbit and Msps are regulated by Rac-GSK3β signaling Figure 2.S2. Orbit is phosphorylated by GSK3β in the linker region between TOG2 and TOG Figure 2.S3. EB1 is not regulated by Rac and Sentin can interact with Orbit Supplemental Figure 2.S4. Msps interacts with Orbit Figure 2.S5. Rates of actin retrograde flow is altered only by changes in Rac activity Figure 3.1 Rac1, and not Mtl, regulates Orbit and Msps lattice association Figure 3.2 PAK1 and PAK3 regulate the lattice association of Orbit and Msps redundantly Figure 4.1 D25 cells are able to move in a non-directional manner Figure 4.2 Microtubules are important for D25 cell movement xi
11 Figure 4.3 Msps and Orbit localize to microtubules in D25 cells and respond to CA-Rac Figure 5.1 Orbit and KLP10A can co-immunoprecipitate xii
12 LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS AND SYMBOLS CH ConA CA CuSO4 CLASP CLIP EB FBS GFP GEF MAP MTOC +TIP Mtl Msps PAK PBS RNAi TIRF μm calponin homology concanavalin A constitutively active copper sulfate Cytoplasmic linker associated protein Cytoplasmic linker protein End binding fetal bovine serum green fluorescent protein guanine nucleotide exchange factor microtubule associated protein microtubule organizing center microtubule plus end interacting protein Mig2-like protein Mini spindles p21 activated kinase phosphate-buffered saline RNA interference total internal reflection fluorescence micrometer xiii
The microtubule lattice and plus-end association of Drosophila Mini spindles is spatially regulated to fine-tune microtubule dynamics
 MBoC ARTICLE The microtubule lattice and plus-end association of Drosophila Mini spindles is spatially regulated to fine-tune microtubule dynamics Joshua D. Currie a, Shannon Stewman b, Gregory Schimizzi
MBoC ARTICLE The microtubule lattice and plus-end association of Drosophila Mini spindles is spatially regulated to fine-tune microtubule dynamics Joshua D. Currie a, Shannon Stewman b, Gregory Schimizzi
Flag-Rac Vector V12 V12 N17 C40. Vector C40 pakt (T308) Akt1. Myc-DN-PAK1 (N-SP)
 a b FlagRac FlagRac V2 V2 N7 C4 V2 V2 N7 C4 p (T38) p (S99, S24) p Flag (Rac) NIH 3T3 COS c +Serum p (T38) MycDN (NSP) Mycp27 3 6 2 3 6 2 3 6 2 min p Myc ( or p27) Figure S (a) Effects of Rac mutants on
a b FlagRac FlagRac V2 V2 N7 C4 V2 V2 N7 C4 p (T38) p (S99, S24) p Flag (Rac) NIH 3T3 COS c +Serum p (T38) MycDN (NSP) Mycp27 3 6 2 3 6 2 3 6 2 min p Myc ( or p27) Figure S (a) Effects of Rac mutants on
The microtubule lattice and plus-end association of Drosophila Mini spindles is spatially regulated to fine-tune microtubule dynamics
 The microtubule lattice and plus-end association of Drosophila Mini spindles is spatially regulated to fine-tune microtubule dynamics Joshua D. Currie 1, Shannon Stewman 4, Gregory Schimizzi 1, Kevin C.
The microtubule lattice and plus-end association of Drosophila Mini spindles is spatially regulated to fine-tune microtubule dynamics Joshua D. Currie 1, Shannon Stewman 4, Gregory Schimizzi 1, Kevin C.
Golgi are located near the MTOC while the ER is spread throughout the cytoplasm, so which of the following is probably true?
 Golgi are located near the MTOC while the ER is spread throughout the cytoplasm, so which of the following is probably true? A. COPII and COPI vesicles are transported with dynein. B. COPII and COPI vesicles
Golgi are located near the MTOC while the ER is spread throughout the cytoplasm, so which of the following is probably true? A. COPII and COPI vesicles are transported with dynein. B. COPII and COPI vesicles
Practice Exam 3 MCBII
 1. Which is not a feature of lamin intermediate filaments (IFs)? (4 pts) A. They are protein polymers. B. They are used by motor proteins to traffic cargo. C. They contain coiled coil domains. D. They
1. Which is not a feature of lamin intermediate filaments (IFs)? (4 pts) A. They are protein polymers. B. They are used by motor proteins to traffic cargo. C. They contain coiled coil domains. D. They
BME Engineering Molecular Cell Biology. The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament
 BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 09: The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament BME42-620 Lecture 09, September 27, 2011 1 Outline Overviewofcytoskeletal
BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 09: The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament BME42-620 Lecture 09, September 27, 2011 1 Outline Overviewofcytoskeletal
Lecture 13. Motor Proteins I
 Lecture 13 Motor Proteins I Introduction: The study of motor proteins has become a major focus in cell and molecular biology. Motor proteins are very interesting because they do what no man-made engines
Lecture 13 Motor Proteins I Introduction: The study of motor proteins has become a major focus in cell and molecular biology. Motor proteins are very interesting because they do what no man-made engines
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material 1 Figure S1. Phylogenetic analysis of Cep72 and Lrrc36, comparative localization of Cep72 and Lrrc36 and Cep72 antibody characterization (A) Phylogenetic alignment of Cep72 and Lrrc36
Supplemental Material 1 Figure S1. Phylogenetic analysis of Cep72 and Lrrc36, comparative localization of Cep72 and Lrrc36 and Cep72 antibody characterization (A) Phylogenetic alignment of Cep72 and Lrrc36
cell fusion live and fixed imaging genetics biochemistry in vitro systems inhibitors of cellular processes (transcription, replication, microtubules)
 DISCUSSION SECTIONS BY STUDENT NUMBER ENDING IN ODD NUMBERS 2-3, EVEN 3-4 Methods for Studying the Cell Cycle cell fusion live and fixed imaging genetics biochemistry in vitro systems inhibitors of cellular
DISCUSSION SECTIONS BY STUDENT NUMBER ENDING IN ODD NUMBERS 2-3, EVEN 3-4 Methods for Studying the Cell Cycle cell fusion live and fixed imaging genetics biochemistry in vitro systems inhibitors of cellular
System. Dynamic Monitoring of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activation in Living Cells. Application Note No. 4 / March
 System Application Note No. 4 / March 2008 Dynamic Monitoring of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activation in Living Cells www.roche-applied-science.com Dynamic Monitoring of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activation
System Application Note No. 4 / March 2008 Dynamic Monitoring of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activation in Living Cells www.roche-applied-science.com Dynamic Monitoring of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activation
The XMAP215 family drives microtubule polymerization using a structurally diverse TOG array
 MBoC ARTICLE The XMAP215 family drives microtubule polymerization using a structurally diverse TOG array Jaime C. Fox a,b, Amy E. Howard a,b, Joshua D. Currie c, Stephen L. Rogers c,d,e, and Kevin C. Slep
MBoC ARTICLE The XMAP215 family drives microtubule polymerization using a structurally diverse TOG array Jaime C. Fox a,b, Amy E. Howard a,b, Joshua D. Currie c, Stephen L. Rogers c,d,e, and Kevin C. Slep
J. Cell Sci. 128: doi: /jcs : Supplementary Material. Supplemental Figures. Journal of Cell Science Supplementary Material
 Supplemental Figures Figure S1. Trio controls endothelial barrier function. (A) TagRFP-shTrio constructs were expressed in ECs. Western blot shows efficient Trio knockdown in TagRFP-expressing ECs. (B)
Supplemental Figures Figure S1. Trio controls endothelial barrier function. (A) TagRFP-shTrio constructs were expressed in ECs. Western blot shows efficient Trio knockdown in TagRFP-expressing ECs. (B)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2271 Supplementary Figure a! WM266.4 mock WM266.4 #7 sirna WM266.4 #10 sirna SKMEL28 mock SKMEL28 #7 sirna SKMEL28 #10 sirna WM1361 mock WM1361 #7 sirna WM1361 #10 sirna 9 WM266. WM136
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2271 Supplementary Figure a! WM266.4 mock WM266.4 #7 sirna WM266.4 #10 sirna SKMEL28 mock SKMEL28 #7 sirna SKMEL28 #10 sirna WM1361 mock WM1361 #7 sirna WM1361 #10 sirna 9 WM266. WM136
McNair Scholars Journal
 McNair Scholars Journal Volume 10 Issue 1 Article 9 2006 Exploring Important Protein Interactions in the Mammalian Diaphanous-related Formins: A Closer Look at the Relationship between the Intracellular
McNair Scholars Journal Volume 10 Issue 1 Article 9 2006 Exploring Important Protein Interactions in the Mammalian Diaphanous-related Formins: A Closer Look at the Relationship between the Intracellular
Biophysics of Molecules
 Biophysics of Molecules Cytoskeletal filaments, Actin polymerization and Actin Treadmilling Part 2 (26.11.2012) Dr. Carsten Grashoff MPI of Biochemistry E-mail: cgrasho@biochem.mpg.de Lecture Outline The
Biophysics of Molecules Cytoskeletal filaments, Actin polymerization and Actin Treadmilling Part 2 (26.11.2012) Dr. Carsten Grashoff MPI of Biochemistry E-mail: cgrasho@biochem.mpg.de Lecture Outline The
Sarker et al. Supplementary Material. Subcellular Fractionation
 Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion
 Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
Investigating the regulation of mirna biogenesis and Argonaute2 by RNA binding proteins
 Investigating the regulation of mirna biogenesis and Argonaute2 by RNA binding proteins Patrick Peter Connerty Supervisor: Gyorgy Hutvagner Thesis Submitted for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Science)
Investigating the regulation of mirna biogenesis and Argonaute2 by RNA binding proteins Patrick Peter Connerty Supervisor: Gyorgy Hutvagner Thesis Submitted for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Science)
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Rainero et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201109112/dc1 Figure S1. The expression of DGK- is reduced upon transfection
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Rainero et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201109112/dc1 Figure S1. The expression of DGK- is reduced upon transfection
Supplemental Data Length Control of the Metaphase Spindle
 Supplemental Data Length Control of the Metaphase Spindle S1 Gohta Goshima, Roy Wollman, Nico Stuurman, Jonathan M. Scholey, and Ronald D. Vale Supplemental Experimental Procedures Cell Culture, RNA Interference,
Supplemental Data Length Control of the Metaphase Spindle S1 Gohta Goshima, Roy Wollman, Nico Stuurman, Jonathan M. Scholey, and Ronald D. Vale Supplemental Experimental Procedures Cell Culture, RNA Interference,
MCBII. Points this page
 1. What makes intermediate filaments (IFs) an inefficient track for motor proteins (4 pts)? A. The outer surface of IFs is hydrophobic. B. IFs are nonpolar structures. C. IFs contain coiled coil domains.
1. What makes intermediate filaments (IFs) an inefficient track for motor proteins (4 pts)? A. The outer surface of IFs is hydrophobic. B. IFs are nonpolar structures. C. IFs contain coiled coil domains.
Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section B and ONE question from Section C.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-18 CELL BIOLOGY BIO-5005B Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-18 CELL BIOLOGY BIO-5005B Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section
CHAPTER 16 THE CYTOSKELETON
 CHAPTER 16 THE CYTOSKELETON THE SELF-ASSEMBLY AND DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF CYTOSKELETAL FILAMENTS HOW CELLS REGULATE THEIR CYTOSKELETAL FILAMENTS MOLECULAR MOTORS THE CYTOSKELETON AND CELL BEHAVIOR THE SELF-ASSEMBLY
CHAPTER 16 THE CYTOSKELETON THE SELF-ASSEMBLY AND DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF CYTOSKELETAL FILAMENTS HOW CELLS REGULATE THEIR CYTOSKELETAL FILAMENTS MOLECULAR MOTORS THE CYTOSKELETON AND CELL BEHAVIOR THE SELF-ASSEMBLY
October 24, BIOS 95: Cell Division and Chromosome Dynamics
 October 24, 2008 BIOS 95: Cell Division and Chromosome Dynamics Cancer unregulated cell growth and migration Aneuploidy errors in chromosome segregation and genome maintenance living with an altered genome
October 24, 2008 BIOS 95: Cell Division and Chromosome Dynamics Cancer unregulated cell growth and migration Aneuploidy errors in chromosome segregation and genome maintenance living with an altered genome
Supplemental Information Control of apico-basal epithelial polarity by the microtubule minus-end binding protein CAMSAP3 and spectraplakin ACF7
 Supplemental Information Control of apico-basal epithelial polarity by the microtubule minus-end binding protein CAMSAP3 and spectraplakin ACF7 Ivar Noordstra, Qingyang Liu, Wilco Nijenhuis, Shasha Hua,
Supplemental Information Control of apico-basal epithelial polarity by the microtubule minus-end binding protein CAMSAP3 and spectraplakin ACF7 Ivar Noordstra, Qingyang Liu, Wilco Nijenhuis, Shasha Hua,
3'UTR elements inhibit Ras-induced C/EBPß posttranslational activation and senescence in tumor cells
 Manuscript EMBO-2011-77536 3'UTR elements inhibit Ras-induced C/EBPß posttranslational activation and senescence in tumor cells Sandip K. Basu, Radek Malik, Christopher J. Huggins, Sook Lee, Thomas Sebastian,
Manuscript EMBO-2011-77536 3'UTR elements inhibit Ras-induced C/EBPß posttranslational activation and senescence in tumor cells Sandip K. Basu, Radek Malik, Christopher J. Huggins, Sook Lee, Thomas Sebastian,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a 14 12 Densitometry (AU) 1 8 6 4 2 t b 16 NMHC-IIA GAPDH NMHC-IIB Densitometry (AU) 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 1 nm 1 nm 1 nm 1 nm sirna 1 nm 1 nm Figure S1 S4 Quantification of protein levels. (a) The microtubule
a 14 12 Densitometry (AU) 1 8 6 4 2 t b 16 NMHC-IIA GAPDH NMHC-IIB Densitometry (AU) 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 1 nm 1 nm 1 nm 1 nm sirna 1 nm 1 nm Figure S1 S4 Quantification of protein levels. (a) The microtubule
hnrnp C promotes APP translation by competing with FMRP for APP mrna recruitment to P bodies
 hnrnp C promotes APP translation by competing with for APP mrna recruitment to P bodies Eun Kyung Lee 1, Hyeon Ho Kim 1, Yuki Kuwano 1, Kotb Abdelmohsen 1, Subramanya Srikantan 1, Sarah S. Subaran 2, Marc
hnrnp C promotes APP translation by competing with for APP mrna recruitment to P bodies Eun Kyung Lee 1, Hyeon Ho Kim 1, Yuki Kuwano 1, Kotb Abdelmohsen 1, Subramanya Srikantan 1, Sarah S. Subaran 2, Marc
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table.
 Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
EFFECTS OF CYSTEINE MODIFICATION ON MICROTUBULE-MOTOR FUNCTION AND TUBULIN ASSEMBLY. by Kalmia Kniel Phelps
 EFFECTS OF CYSTEINE MODIFICATION ON MICROTUBULE-MOTOR FUNCTION AND TUBULIN ASSEMBLY by Kalmia Kniel Phelps Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in
EFFECTS OF CYSTEINE MODIFICATION ON MICROTUBULE-MOTOR FUNCTION AND TUBULIN ASSEMBLY by Kalmia Kniel Phelps Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in
Sequence of C-terminal tail regions of myosin heavy chains in class XI of Nicotiana benthamiana (Nb
 Fig. S1 Sequence of C-terminal tail regions of myosin heavy chains in class XI of Nicotiana benthamiana (Nb myosin XI-2, -F and K) and BY-2 cell (Nt 170-kD myosin and Nt 175-kD myosin). Amino acids identical
Fig. S1 Sequence of C-terminal tail regions of myosin heavy chains in class XI of Nicotiana benthamiana (Nb myosin XI-2, -F and K) and BY-2 cell (Nt 170-kD myosin and Nt 175-kD myosin). Amino acids identical
7.06 Problem Set #3, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #3, Spring 2005 1. The Drosophila compound eye is composed of about 800 units called ommatidia. Each ommatidium contains eight photoreceptor neurons (R1 through R8), which develop in a
7.06 Problem Set #3, Spring 2005 1. The Drosophila compound eye is composed of about 800 units called ommatidia. Each ommatidium contains eight photoreceptor neurons (R1 through R8), which develop in a
Functional Genomics Research Stream
 Functional Genomics Research Stream Research Meeting: January 19, 2010 Introduction, Policy Discussion & Scientific Writing histone occupancy histone occupancy histone modification histone occupancy histone
Functional Genomics Research Stream Research Meeting: January 19, 2010 Introduction, Policy Discussion & Scientific Writing histone occupancy histone occupancy histone modification histone occupancy histone
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
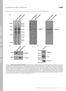 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Bays et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201309092/dc1 Figure S1. Specificity of the phospho-y822 antibody. (A) Total cell
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Bays et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201309092/dc1 Figure S1. Specificity of the phospho-y822 antibody. (A) Total cell
DDA3 associates with microtubule plus ends and orchestrates microtubule dynamics and directional cell migration
 DDA3 associates with microtubule plus ends and orchestrates microtubule dynamics and directional cell migration Liangyu Zhang 1,2,4, Hengyi Shao 1,4, Tongge Zhu, Peng Xia 1, Zhikai Wang 1,2, Lifang Liu
DDA3 associates with microtubule plus ends and orchestrates microtubule dynamics and directional cell migration Liangyu Zhang 1,2,4, Hengyi Shao 1,4, Tongge Zhu, Peng Xia 1, Zhikai Wang 1,2, Lifang Liu
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2743 Figure S1 stabilizes cellular protein level, post-transcriptionally. (a, b) and DDR1 were RNAi-depleted from HEK.293.-CBG cells. Western blots with indicated antibodies (a). RT-PCRs
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2743 Figure S1 stabilizes cellular protein level, post-transcriptionally. (a, b) and DDR1 were RNAi-depleted from HEK.293.-CBG cells. Western blots with indicated antibodies (a). RT-PCRs
ANAT Cell Biology Lecture 11 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales. UNSW Copyright Notice
 ANAT3231 - Cell Biology Lecture 11 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales The actin cytoskeleton Prof Peter Gunning Oncology Research Unit Room 502A Wallace Wurth Building Email:
ANAT3231 - Cell Biology Lecture 11 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales The actin cytoskeleton Prof Peter Gunning Oncology Research Unit Room 502A Wallace Wurth Building Email:
Automated Screening of Microtubule Growth Dynamics Identifies MARK2 as a Regulator of Leading Edge Microtubules Downstream of Rac1 in Migrating Cells
 Automated Screening of Microtubule Growth Dynamics Identifies MARK2 as a Regulator of Leading Edge Microtubules Downstream of Rac1 in Migrating Cells The Harvard community has made this article openly
Automated Screening of Microtubule Growth Dynamics Identifies MARK2 as a Regulator of Leading Edge Microtubules Downstream of Rac1 in Migrating Cells The Harvard community has made this article openly
Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of LRRK1 bind to Grb2.
 Myc- HA-Grb2 Mr(K) 105 IP HA 75 25 105 1-1163 1-595 - + - + - + 1164-1989 Blot Myc HA total lysate 75 25 Myc HA Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of bind to Grb2. COS7 cells were cotransfected
Myc- HA-Grb2 Mr(K) 105 IP HA 75 25 105 1-1163 1-595 - + - + - + 1164-1989 Blot Myc HA total lysate 75 25 Myc HA Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of bind to Grb2. COS7 cells were cotransfected
GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts
 Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts Wei Zhou, Jin Chang, Xin Wang, Masha G. Savelieff, Yinyin Zhao, Shanshan
Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts Wei Zhou, Jin Chang, Xin Wang, Masha G. Savelieff, Yinyin Zhao, Shanshan
Patronin Regulates the Microtubule Network by Protecting Microtubule Minus Ends
 Patronin Regulates the Microtubule Network by Protecting Microtubule Minus Ends Sarah S. Goodwin 1 and Ronald D. Vale 1, * 1 The Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Cellular and Molecular
Patronin Regulates the Microtubule Network by Protecting Microtubule Minus Ends Sarah S. Goodwin 1 and Ronald D. Vale 1, * 1 The Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Cellular and Molecular
MICB688L/MOCB639 Advanced Cell Biology Exam II
 MICB688L/MOCB639 Advanced Cell Biology Exam II May 10, 2001 Name: 1. Briefly describe the four major classes of cell surface receptors and their modes of action (immediate downstream only) (8) 2. Please
MICB688L/MOCB639 Advanced Cell Biology Exam II May 10, 2001 Name: 1. Briefly describe the four major classes of cell surface receptors and their modes of action (immediate downstream only) (8) 2. Please
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF EUKARYOTES 2016 SYLLABUS
 03-442 Lectures: MWF 9:30-10:20 a.m. Doherty Hall 2105 03-742 Advanced Discussion Section: Time and place to be announced Probably Mon 4-6 p.m. or 6-8p.m.? Once we establish who is taking the advanced
03-442 Lectures: MWF 9:30-10:20 a.m. Doherty Hall 2105 03-742 Advanced Discussion Section: Time and place to be announced Probably Mon 4-6 p.m. or 6-8p.m.? Once we establish who is taking the advanced
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1919 Mori et al. Supplementary Figure 1a-b a Characterization of the mdrg cells Anti-NF150 DIC (89%: N=154) 100µm Anti-S100 DIC 100µm b (9.1%: N=144) Characterization of the cortical neurons
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1919 Mori et al. Supplementary Figure 1a-b a Characterization of the mdrg cells Anti-NF150 DIC (89%: N=154) 100µm Anti-S100 DIC 100µm b (9.1%: N=144) Characterization of the cortical neurons
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Clustering of a kinesin-14 motor enables processive retrograde microtubule-based transport in plants NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants 1 2 NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants NATURE PLANTS
Clustering of a kinesin-14 motor enables processive retrograde microtubule-based transport in plants NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants 1 2 NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants NATURE PLANTS
Post-translational modification
 Protein expression Western blotting, is a widely used and accepted technique to detect levels of protein expression in a cell or tissue extract. This technique measures protein levels in a biological sample
Protein expression Western blotting, is a widely used and accepted technique to detect levels of protein expression in a cell or tissue extract. This technique measures protein levels in a biological sample
ANAT Cell Biology Lecture 12 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales
 ANAT3231 - Cell Biology Lecture 12 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales Prof Peter Gunning Microfilaments, 2010 Sllide 1 UNSW Copyright Notice COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright
ANAT3231 - Cell Biology Lecture 12 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales Prof Peter Gunning Microfilaments, 2010 Sllide 1 UNSW Copyright Notice COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright
A Role for CLASPs in the Regulation of the Major Microtubule +TIP Complex Organizers, End-Binding Proteins. Ashley Dyan Grimaldi.
 A Role for CLASPs in the Regulation of the Major Microtubule +TIP Complex Organizers, End-Binding Proteins By Ashley Dyan Grimaldi Dissertation Submitted to the Faulty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt
A Role for CLASPs in the Regulation of the Major Microtubule +TIP Complex Organizers, End-Binding Proteins By Ashley Dyan Grimaldi Dissertation Submitted to the Faulty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
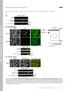 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Nakajima and Tanoue, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201104118/dc1 Figure S1. DLD-1 cells exhibit the characteristic morphology
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Nakajima and Tanoue, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201104118/dc1 Figure S1. DLD-1 cells exhibit the characteristic morphology
Short hairpin RNA (shrna) against MMP14. Lentiviral plasmids containing shrna
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Short hairpin RNA (shrna) against MMP14. Lentiviral plasmids containing shrna (Mission shrna, Sigma) against mouse MMP14 were transfected into HEK293 cells using FuGene6
Supplemental Materials and Methods Short hairpin RNA (shrna) against MMP14. Lentiviral plasmids containing shrna (Mission shrna, Sigma) against mouse MMP14 were transfected into HEK293 cells using FuGene6
Microtubules (MTs) are dynamic cytoskeletal polymers composed of αβ-tubulin that
 Introduction: Microtubules (MTs) are dynamic cytoskeletal polymers composed of αβ-tubulin that define cell structure, establish platforms for the transportation of intracellular cargos, and form the mitotic
Introduction: Microtubules (MTs) are dynamic cytoskeletal polymers composed of αβ-tubulin that define cell structure, establish platforms for the transportation of intracellular cargos, and form the mitotic
Synonymous Modification Results in High Fidelity Gene Expression of Repetitive Protein and Nucleotide Sequences
 Synonymous Modification Results in High Fidelity Gene Expression of Repetitive Protein and Nucleotide Sequences Bin Wu *,1,2, Veronika Miskolci *,1, Hanae Sato 1, Evelina Tutucci 1, Charles A. Kenworthy
Synonymous Modification Results in High Fidelity Gene Expression of Repetitive Protein and Nucleotide Sequences Bin Wu *,1,2, Veronika Miskolci *,1, Hanae Sato 1, Evelina Tutucci 1, Charles A. Kenworthy
Mechanisms of embryonic stem cell division and differentiation
 Mechanisms of embryonic stem cell division and differentiation Josephine Wbite.'.... Department of Molecular Biosciences (Biochemistry) The University of Adelaide Adelaide, South Australia Submitted for
Mechanisms of embryonic stem cell division and differentiation Josephine Wbite.'.... Department of Molecular Biosciences (Biochemistry) The University of Adelaide Adelaide, South Australia Submitted for
Animal Development Regulation of gene expression
 Animal Development Regulation of gene expression Prof. Ilan Davis, Department of Biochemistry. Wellcome Trust Research Senior Fellow Senior Research Fellow, Jesus College ilan.davis@bioch.ox.ac.uk http://www.ilandavis.com
Animal Development Regulation of gene expression Prof. Ilan Davis, Department of Biochemistry. Wellcome Trust Research Senior Fellow Senior Research Fellow, Jesus College ilan.davis@bioch.ox.ac.uk http://www.ilandavis.com
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.18/ncb46 a Damage Fracture s s 7 5 16 1 9 26 5 µm 5 µm b Position of photo-damage site in cells 15 Counts 1 5-14 -12-1 -8-6 -4-2 Distance from damage site to tip (µm) Supplementary Figure 1 Effect
DOI: 1.18/ncb46 a Damage Fracture s s 7 5 16 1 9 26 5 µm 5 µm b Position of photo-damage site in cells 15 Counts 1 5-14 -12-1 -8-6 -4-2 Distance from damage site to tip (µm) Supplementary Figure 1 Effect
Mannen et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Mannen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201601024 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Characterization of SNB components. (A) SNB localization of Venus-tagged
Supplemental material JCB Mannen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201601024 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Characterization of SNB components. (A) SNB localization of Venus-tagged
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Methods Cells and constructs. YT cells were maintained as described in (Lamaze et al., 2001). Hep2 (ATCC) cells were stably transfected with NTβ (Subtil and Dautry-Varsat, 1998),
Supplementary information Methods Cells and constructs. YT cells were maintained as described in (Lamaze et al., 2001). Hep2 (ATCC) cells were stably transfected with NTβ (Subtil and Dautry-Varsat, 1998),
Chromosome Structural Analysis
 Chromosome Structural Analysis A Practical Approach Edited by WENDY A. BICKMORE Cell Genetics Section, MRC Human Genetics Unit, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh OXJORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1999 List of
Chromosome Structural Analysis A Practical Approach Edited by WENDY A. BICKMORE Cell Genetics Section, MRC Human Genetics Unit, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh OXJORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1999 List of
Microtubules. Forms a sheet of protofilaments that folds to a tube Both tubulins bind GTP
 Microtubules Polymerize from a-tubulin/ß-tubulin dimers Hollow tube of 13 protofilaments In vitro- filament number varies In vivo- always 13 protofilaments Forms a sheet of protofilaments that folds to
Microtubules Polymerize from a-tubulin/ß-tubulin dimers Hollow tube of 13 protofilaments In vitro- filament number varies In vivo- always 13 protofilaments Forms a sheet of protofilaments that folds to
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Thompson et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200909067/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Modification-specific antibodies do not detect unmodified
Supplemental material Thompson et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200909067/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Modification-specific antibodies do not detect unmodified
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 01: Introduction to Molecular Cell Biology
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 01: Introduction to Molecular Cell Biology Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement describes how an organism is organized from most simple to most complex? Question
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 01: Introduction to Molecular Cell Biology Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement describes how an organism is organized from most simple to most complex? Question
Genetic Engineering for Biofuels Production
 Genetic Engineering for Biofuels Production WSE 573 Spring 2013 Greeley Beck INTRODUCTION Alternative transportation fuels are needed in the United States because of oil supply insecurity, oil price increases,
Genetic Engineering for Biofuels Production WSE 573 Spring 2013 Greeley Beck INTRODUCTION Alternative transportation fuels are needed in the United States because of oil supply insecurity, oil price increases,
Supplemental Information: Phosphorylation of CLIP-170 by Both Plk1 and CK2 Is Involved in the Timely Formation of Kinetochore-microtubule Attachments
 Supplemental Information: Phosphorylation of CLIP-170 by Both Plk1 and CK2 Is Involved in the Timely Formation of Kinetochore-microtubule Attachments Hongchang Li, X. Shawn Liu, Xiaoming Yang, Yingmin
Supplemental Information: Phosphorylation of CLIP-170 by Both Plk1 and CK2 Is Involved in the Timely Formation of Kinetochore-microtubule Attachments Hongchang Li, X. Shawn Liu, Xiaoming Yang, Yingmin
Regulation of microtubulebased
 Regulation of microtubulebased transport by MAP4 The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Semenova, Irina, Kazuho
Regulation of microtubulebased transport by MAP4 The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Semenova, Irina, Kazuho
Introduction: The eukaryotic cytoskeleton and actin-microtubule coordination
 Chapter 1 Introduction: The eukaryotic cytoskeleton and actin-microtubule coordination In this introductory chapter we first outline the general properties of the three eukaryotic cytoskeletal systems:
Chapter 1 Introduction: The eukaryotic cytoskeleton and actin-microtubule coordination In this introductory chapter we first outline the general properties of the three eukaryotic cytoskeletal systems:
Supplemental Data Supplementary Figure Legends and Scheme Figure S1.
 Supplemental Data Supplementary Figure Legends and Scheme Figure S1. UTK1 inhibits the second EGF-induced wave of lamellipodia formation in TT cells. A and B, EGF-induced lamellipodia formation in TT cells,
Supplemental Data Supplementary Figure Legends and Scheme Figure S1. UTK1 inhibits the second EGF-induced wave of lamellipodia formation in TT cells. A and B, EGF-induced lamellipodia formation in TT cells,
Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity.
 Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity. (A) Amino acid alignment of HDA5, HDA15 and HDA18. The blue line
Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity. (A) Amino acid alignment of HDA5, HDA15 and HDA18. The blue line
Supplement Figure S1:
 Supplement Figure S1: A, Sequence of Xcadherin-11 Morpholino 1 (Xcad-11MO) and 2 (Xcad-11 MO2) and control morpholino in comparison to the Xcadherin-11 sequence. The Xcad-11MO binding sequence spans the
Supplement Figure S1: A, Sequence of Xcadherin-11 Morpholino 1 (Xcad-11MO) and 2 (Xcad-11 MO2) and control morpholino in comparison to the Xcadherin-11 sequence. The Xcad-11MO binding sequence spans the
BIOL 461/ 661 Cell Biology 4 Credits Instructor: Dr. Kristin O Brien. T/TH 11:30-1:00, Irving I 208 Office hours: M 9-10, TH 3-4
 BIOL 461/ 661 Cell Biology 4 Credits Instructor: Dr. Kristin O Brien Prerequisites: BIOL 362 Principals of Genetics Office: 226 Arctic Health CHEM 321 Organic Chemistry Laboratory: 229 Arctic Health T/TH
BIOL 461/ 661 Cell Biology 4 Credits Instructor: Dr. Kristin O Brien Prerequisites: BIOL 362 Principals of Genetics Office: 226 Arctic Health CHEM 321 Organic Chemistry Laboratory: 229 Arctic Health T/TH
Effects of metformin on Sirt1, Nrf2 and AhR expression in cancer cells
 A Dissertation for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy Effects of metformin on Sirt1, Nrf2 and AhR expression in cancer cells Department of Pharmacy Graduate School Chungnam National University By Minh
A Dissertation for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy Effects of metformin on Sirt1, Nrf2 and AhR expression in cancer cells Department of Pharmacy Graduate School Chungnam National University By Minh
Multiple domains of human CLASP contribute to microtubule dynamics and organization in vitro and in Xenopus egg extracts
 Multiple domains of human CLASP contribute to microtubule dynamics and organization in vitro and in Xenopus egg extracts by Kieren Jay Patel A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements
Multiple domains of human CLASP contribute to microtubule dynamics and organization in vitro and in Xenopus egg extracts by Kieren Jay Patel A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements
Supplemental Data. Liu et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. The GFP Tag Does Not Disturb the Physiological Functions of WDL3. (A) RT-PCR analysis of WDL3 expression in wild-type, WDL3-GFP, and WDL3 (without the GFP tag) transgenic seedlings.
Supplemental Figure 1. The GFP Tag Does Not Disturb the Physiological Functions of WDL3. (A) RT-PCR analysis of WDL3 expression in wild-type, WDL3-GFP, and WDL3 (without the GFP tag) transgenic seedlings.
Supporting Online Material for
 Supporting Online Material for Spatiotemporal dynamics of Aurora B-PLK1-MCAK signaling axis orchestrates kinetochore bi-orientation and faithful chromosome segregation Hengyi Shao, Yuejia Huang, Liangyu
Supporting Online Material for Spatiotemporal dynamics of Aurora B-PLK1-MCAK signaling axis orchestrates kinetochore bi-orientation and faithful chromosome segregation Hengyi Shao, Yuejia Huang, Liangyu
Molecular interactions of Polo-like-kinase 1 with the mitotic kinesin-like protein CHO1/MKLP-1
 Research Article 3233 Molecular interactions of Polo-like-kinase 1 with the mitotic kinesin-like protein CHO1/MKLP-1 Xiaoqi Liu 1, *, Tianhua Zhou 1, Ryoko Kuriyama 2 and Raymond L. Erikson 1 1 Department
Research Article 3233 Molecular interactions of Polo-like-kinase 1 with the mitotic kinesin-like protein CHO1/MKLP-1 Xiaoqi Liu 1, *, Tianhua Zhou 1, Ryoko Kuriyama 2 and Raymond L. Erikson 1 1 Department
Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7)
 Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7) I. General Principles (Chapter 7 introduction) a. Morse code distinct series of dots and dashes encode the 26 letters of the
Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7) I. General Principles (Chapter 7 introduction) a. Morse code distinct series of dots and dashes encode the 26 letters of the
Microtubule Minus-End Stabilization by Polymerization-Driven CAMSAP Deposition
 Article Microtubule Minus-End Stabilization by Polymerization-Driven CAMSAP Deposition Kai Jiang, 1 Shasha Hua, 1 Renu Mohan, 1 Ilya Grigoriev, 1 Kah Wai Yau, 1 Qingyang Liu, 1,2 Eugene A. Katrukha, 1
Article Microtubule Minus-End Stabilization by Polymerization-Driven CAMSAP Deposition Kai Jiang, 1 Shasha Hua, 1 Renu Mohan, 1 Ilya Grigoriev, 1 Kah Wai Yau, 1 Qingyang Liu, 1,2 Eugene A. Katrukha, 1
Chapter One. Construction of a Fluorescent α5 Subunit. Elucidation of the unique contribution of the α5 subunit is complicated by several factors
 4 Chapter One Construction of a Fluorescent α5 Subunit The significance of the α5 containing nachr receptor (α5* receptor) has been a challenging question for researchers since its characterization by
4 Chapter One Construction of a Fluorescent α5 Subunit The significance of the α5 containing nachr receptor (α5* receptor) has been a challenging question for researchers since its characterization by
Development Team. Molecular Cell Biology Cytoskeleton ZOOLOGY. Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi
 Paper No. : 15 Module : 11 Development Team Principal Investigator: Prof. Neeta Sehgal Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Paper Coordinator: Prof. S. Basu Modak Department of Zoology, University
Paper No. : 15 Module : 11 Development Team Principal Investigator: Prof. Neeta Sehgal Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Paper Coordinator: Prof. S. Basu Modak Department of Zoology, University
At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Kinesin motors in the transport along microtubules. Dynein Motor
 Molecular Cell Biology Autumn 2014, Michael Pavlov Based on Chapter 17 and 18.(1-4), MCB book Lecture 9: Cytoskeleton Microtubules: Tubulin Structure of tubulin dimer and organization of tubulin dimers
Molecular Cell Biology Autumn 2014, Michael Pavlov Based on Chapter 17 and 18.(1-4), MCB book Lecture 9: Cytoskeleton Microtubules: Tubulin Structure of tubulin dimer and organization of tubulin dimers
MT minus end catastrophe
 DOI: 1.138/ncb3241 MT minus end catastrophe frequency [s -1 ].2.15.1.5 control mgfp- TPX2 * * mgfp- TPX2 mini Supplementary Figure 1. TPX2 reduces catastrophes at the microtubule minus ends. Modified box-and-whiskers
DOI: 1.138/ncb3241 MT minus end catastrophe frequency [s -1 ].2.15.1.5 control mgfp- TPX2 * * mgfp- TPX2 mini Supplementary Figure 1. TPX2 reduces catastrophes at the microtubule minus ends. Modified box-and-whiskers
The Contribution of Human. Capital towards Economic. Growth in China. John Joshua
 The Contribution of Human Capital towards Economic Growth in China John Joshua Contents List offigures ListofTables Preface Acknowledgements x xi xiii xiv Introduction 1 Structural transformational growth
The Contribution of Human Capital towards Economic Growth in China John Joshua Contents List offigures ListofTables Preface Acknowledgements x xi xiii xiv Introduction 1 Structural transformational growth
Polyclonal ARHGAP25 antibody was prepared from rabbit serum after intracutaneous
 Preparation and purification of polyclonal antibodies Polyclonal ARHGAP25 antibody was prepared from rabbit serum after intracutaneous injections of glutathione S-transferase-ARHGAP25-(509-619) (GST-coiled
Preparation and purification of polyclonal antibodies Polyclonal ARHGAP25 antibody was prepared from rabbit serum after intracutaneous injections of glutathione S-transferase-ARHGAP25-(509-619) (GST-coiled
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or
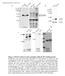 Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
The ends of growing microtubules (MTs) accumulate
 Published Online: 6 June, 2011 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201012179 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on April 21, 2018 JCB: Article SLAIN2 links microtubule plus end tracking proteins and controls
Published Online: 6 June, 2011 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201012179 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on April 21, 2018 JCB: Article SLAIN2 links microtubule plus end tracking proteins and controls
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2156 Figure S1 Depletion of p114rhogef with different sirnas. Caco-2 (a) and HCE (b) cells were transfected with individual sirnas, pools of the two sirnas or the On Target (OnT) sirna
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2156 Figure S1 Depletion of p114rhogef with different sirnas. Caco-2 (a) and HCE (b) cells were transfected with individual sirnas, pools of the two sirnas or the On Target (OnT) sirna
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. Eberly College of Science IDENTIFYING THE FUNCTION OF KINESIN-13 FAMILY MEMBERS AND HOW
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Eberly College of Science IDENTIFYING THE FUNCTION OF KINESIN-13 FAMILY MEMBERS AND HOW THEY CONTRIBUTE TO NEURONAL DEVELOPMENT A Thesis in Cell and
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Eberly College of Science IDENTIFYING THE FUNCTION OF KINESIN-13 FAMILY MEMBERS AND HOW THEY CONTRIBUTE TO NEURONAL DEVELOPMENT A Thesis in Cell and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1: Activation of the ATM pathway by I-PpoI. A. HEK293T cells were either untransfected, vector transfected, transfected with an I-PpoI expression vector, or subjected to 2Gy γ-irradiation. 24 hrs
Figure S1: Activation of the ATM pathway by I-PpoI. A. HEK293T cells were either untransfected, vector transfected, transfected with an I-PpoI expression vector, or subjected to 2Gy γ-irradiation. 24 hrs
The Skap-hom Dimerization and PH Domains Comprise
 Molecular Cell, Volume 32 Supplemental Data The Skap-hom Dimerization and PH Domains Comprise a 3 -Phosphoinositide-Gated Molecular Switch Kenneth D. Swanson, Yong Tang, Derek F. Ceccarelli, Florence Poy,
Molecular Cell, Volume 32 Supplemental Data The Skap-hom Dimerization and PH Domains Comprise a 3 -Phosphoinositide-Gated Molecular Switch Kenneth D. Swanson, Yong Tang, Derek F. Ceccarelli, Florence Poy,
Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells
 Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells Ryosuke Horie. Kagawa University of medecine, Kita-gun, Japan. Disclosures: R. Horie: None.
Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells Ryosuke Horie. Kagawa University of medecine, Kita-gun, Japan. Disclosures: R. Horie: None.
REVIEW SHEET: Units 9 & 10 Cell Cycle, DNA, & Gene Expression
 REVIEW SHEET: Units 9 & 10 Cell Cycle, DNA, & Gene Expression HONORS BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Cell Cycle (Ch. 10.1 and 10.2), DNA (Ch. 12), and Gene Expression (Ch. 13) Handouts:! Online Tutorial: Cell
REVIEW SHEET: Units 9 & 10 Cell Cycle, DNA, & Gene Expression HONORS BIOLOGY Textbook Reading: Cell Cycle (Ch. 10.1 and 10.2), DNA (Ch. 12), and Gene Expression (Ch. 13) Handouts:! Online Tutorial: Cell
Section 10. Junaid Malek, M.D.
 Section 10 Junaid Malek, M.D. Cell Division Make sure you understand: How do cells know when to divide? (What drives the cell cycle? Why is it important to regulate this?) How is DNA replication regulated?
Section 10 Junaid Malek, M.D. Cell Division Make sure you understand: How do cells know when to divide? (What drives the cell cycle? Why is it important to regulate this?) How is DNA replication regulated?
Chapter 17 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
ADAMAS UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE - DEPARTMENT OF BIOTECHNOLOGY BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (Honours) SEMESTER - I
 NEW CHOICE BASED CREDIT SYSTEM (TOTAL CREDIT = 22+22+28+28+26+26 = 152) Type of the Paper Paper Code ADAMAS UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE - DEPARTMENT OF BIOTECHNOLOGY SEMESTER - I / Brief Contents I BT1201
NEW CHOICE BASED CREDIT SYSTEM (TOTAL CREDIT = 22+22+28+28+26+26 = 152) Type of the Paper Paper Code ADAMAS UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE - DEPARTMENT OF BIOTECHNOLOGY SEMESTER - I / Brief Contents I BT1201
Quick Review of Protein Synthesis
 Collin College BIOL. 2401 Quick Review of Protein Synthesis. Proteins and Protein Synthesis Proteins are the molecular units that do most of the work in a cell. They function as molecular catalysts, help
Collin College BIOL. 2401 Quick Review of Protein Synthesis. Proteins and Protein Synthesis Proteins are the molecular units that do most of the work in a cell. They function as molecular catalysts, help
Supplementary data. sienigma. F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM. a-p53
 Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Chapter 17. Microtubules. Chapter 17. Microtubules. Chapter 17. Microtubules. Chapter 17. Microtubules. Chapter 17. Microtubules
 Chapter 15. Mechanism of Vesicle Formation A reminder: two things I said that we should to keep an eye on for each of the components of the cytoskeleton: The role of polymerization and depolymerization
Chapter 15. Mechanism of Vesicle Formation A reminder: two things I said that we should to keep an eye on for each of the components of the cytoskeleton: The role of polymerization and depolymerization
ksierzputowska.com Research Title: Using novel TALEN technology to engineer precise mutations in the genome of D. melanogaster
 Research Title: Using novel TALEN technology to engineer precise mutations in the genome of D. melanogaster Research plan: Specific aims: 1. To successfully engineer transgenic Drosophila expressing TALENs
Research Title: Using novel TALEN technology to engineer precise mutations in the genome of D. melanogaster Research plan: Specific aims: 1. To successfully engineer transgenic Drosophila expressing TALENs
Materials and Methods: All strains were derivatives of SK1 and are listed in Supplemental Table 1.
 Supplemental Online Material: Materials and Methods: All strains were derivatives of SK1 and are listed in Supplemental Table 1. Constructs: pclb2-3ha-cdc5 and pclb2-3ha-cdc2 strains were constructed by
Supplemental Online Material: Materials and Methods: All strains were derivatives of SK1 and are listed in Supplemental Table 1. Constructs: pclb2-3ha-cdc5 and pclb2-3ha-cdc2 strains were constructed by
CytoSelect 24-Well Wound Healing Assay
 Product Manual CytoSelect 24-Well Wound Healing Assay Catalog Number CBA-120 CBA-120-5 24 assays 5 x 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Wounded tissue initiates
Product Manual CytoSelect 24-Well Wound Healing Assay Catalog Number CBA-120 CBA-120-5 24 assays 5 x 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Wounded tissue initiates
