GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts
|
|
|
- Shauna Morton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts Wei Zhou, Jin Chang, Xin Wang, Masha G. Savelieff, Yinyin Zhao, Shanshan Ke, and Bing Ye
2 Supplemental Figures
3 Figure S1. Golgi compartments in Drosophila larval epithelial cells, Drosophila da neurons, and cultured cortical neurons from mouse embryos. (Related to Figure 1) (A and B) Golgi mini-stacks in larval epithelial cells. (A) The Golgi were labeled by the transgenic marker ManII-GFP (medial) and immunostained for endogenous dgmap (cis). (B) The Golgi were labeled by ManII-GFP (medial) and GalT-TagRFP (trans). The distinct compartments are juxtaposed to each other in the Golgi mini-stacks, which is visible in the single mini-stacks shown in the insets. (C and D) Somal Golgi in da neurons. (C) The localization of the cis Golgi marker dgmap, trans Golgi markers GalT-YFP and GalNacT2-TagRFP in the soma of class III da neurons. (D) The localization of the medial Golgi markers HA-ManI and ManII-GFP and the trans Golgi marker GalT-TagRFP in the soma of class III da neurons. (E) Golgi compartments are disconnected in dendritic shafts. Whereas the medial Golgi marker ManII-GFP (green) and the trans Golgi marker GalNacT2-TagRFP (magenta) colocalize in the soma (top), they are often disconnected in dendritic shafts (bottom). (F) BFA disperses the Golgi labeled by ManII-GFP and GalT-TagRFP transgenic markers in both soma (top) and dendrites (bottom). Both somal Golgi and dendritic Golgi outposts re-appear after 30 min of wash-out. (G-H) Switching the fluorescent protein tags of the Golgi markers does not change the localizations of the markers. (G) ManII was tagged with TagRFP-T and GalT with YFP. Arrows point to multi-compartment Golgi outposts in dendrites. (H) Quantification of percentage of multi-compartment Golgi outposts in dendritic shafts between ManII- TagRFP/GalT-YFP and ManII-GFP/GalT-TagRFP pairs.
4 (I) Both single and multi-compartment Golgi outposts exist in the dendrites of mouse cortical neurons in culture. Cultured neurons were stained with antibodies against endogenous Golgi proteins: anti-mania for medial Golgi (green) and anti-galt for trans Golgi (red). An anti-map2 antibody (blue) was used to identify dendrites. The arrowhead points to the Golgi in a branch point, and the arrows point to multicompartment Golgi outposts in dendrites. (J) Quantitation of single and multi-compartment Golgi outposts in mouse cultured cortical neurons.
5
6 Figure S2. The roles of dgm130 and dgrasp in organizing Golgi architecture. (Related to Figure 2) (A and B) dgm130 is required for connecting the cis, medial, and trans compartments in the lobula plate tangential cells (A) and epithelial cells (B). Loss of dgm130 function leads to a separation of Golgi compartments. Arrows indicate single Golgi compartments in dgm130 mutant cells. (C) Single and multi-compartment Golgi outposts are present in the dendrites of lobula plate tangential cells in adult brains. Lower panels show the magnified images of the boxed region in the upper panels. Arrows point to multi-compartment Golgi outposts. (D) Loss of dgm130 decreases the percentage of multi-compartment Golgi outposts in the distal, but not, proximal dendrites. Arrows point to multi-compartment Golgi outposts. (E-G) dgrasp mutant da neurons do not show significant change in Golgi compartmental organization. (E) The P-element excision sites in the mutant lines were identified by DNA sequencing of PCR-amplified genomic DNA. (F) A schematic showing the deleted regions in the imprecise excision lines based on results from sequencing of the genomic DNA. In the dgrasp 129 line, the promoter and coding region except for the last 34 amino acids were deleted. In the dgrasp 102 and dgrasp 302 lines, the entire coding region was deleted. (G) The compartmental organization of somal Golgi in dgrasp 302 is similar to that in wild-type neurons. As we discussed in the main text, this is possibly due to maternal contribution of wild-type dgrasp.
7 Figure S3. Compartmental organization of somal and dendritic Golgi in mutant neurons with decreased or increased dendritic branching. (Related to Figure 3) (A) dar1 null mutant class III da neurons, which dramatically reduces dendritic branching, displayed a significantly reduced percentage of multi-compartment of Golgi outposts in dendrites, although somal Golgi appeared to be normal. MARCM analysis was used. Arrows point to multi-compartment Golgi outposts. (B) Quantification of percentage of multi-compartment Golgi outposts in the dendrites of wild type and dar1 mutant neurons. (C) Overexpressing Knot in class III da neurons, which increases dendritic branching, does not change the compartmental organization of somal and dendritic Golgi.
8 (D) Quantification of percentage of multi-compartment Golgi outposts in the dendrites of wild type and Knot-overexpressing neurons.
9 Figure S4. dgm130 regulates dendritic branching. (Related to Figure 4) (A-B) Loss of dgmap does not change the number of microtubule initiation sites in dendrites. (A) Kymographs representing the movement of EB1 comets in control and
10 dgmap null mutants. (B) Quantification of total initiation events of EB1 comets between control and dgmap null mutant. (C) The morphologies of the class III da neuron ddaas that are wild-type (wt), dgm130 mutant (dgm130 -/- ), and dgm130-overexpression (O/E dgm130). Cyan arrowheads point to the soma and red arrows point to the branch points that are higher than the 4 th order. (D) Tracings of the microtubule-based dendritic branches. The numerous F-actin-based dendritic spikes of class III da neurons were not included in the tracings. (E) Quantification of the number of branch points in different orders. The F-actin-based dendritic spikes were excluded from the quantification.
11 Supplemental Experimental Procedures Imprecise excision to generate dgm130 and dgrasp mutants Imprecise excision of P{RS3}GM130 CB was performed to generate the dgm130 null mutants. The initial screen for deletion mutants was based on loss of the white transgene. A secondary screen on the candidate lines was performed by using PCR. The exact region deleted in each of the mutants was identified by DNA sequencing. Although null alleles of dgm130 survived to adulthood and were fertile, 18.9% homozygous mutants died at the pupal stage (n=479), compared to 0% in wild-type (n = 836). These results suggest that dgm130 mutant flies are not completely normal. The dgrasp null mutants were generated similarly by imprecise excision of p{epgy2}[ey00794]. Mouse neuronal cultures and immunostaining Cortical neurons were prepared from mouse embryos (embryonic day 17), and plated at 30,000 cells per well on poly-d-lysine coated coverslips placed in the wells of 12-well plates. At 5 days in vitro (D.I.V.), the neurons were fixed in 100% cold methanol (-20 C) at 4 C for 10 min, followed by permeablization and washing in wash buffer (1X PBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100). The neurons were then blocked in wash buffer containing 5% bovine serum albumin, and incubated with the goat anti-β-1,4-galt1 (1:100; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX), rabbit anti-α-1,2-mannosidase IA (1:100; Abcam, Cambridge, MA), and chicken anti-map2 (1:200; Aves Labs, Inc., Tigard, OR). The goat anti- β-1,4-galt1 antibody was pre-absorbed with poly-d-lysine-coated coverslips as this antibody tended to give a background staining on these coverslips. The
12 incubations with primary and secondary antibodies were done at 4 C overnight in the blocking buffer. Image processing and quantification Image processing of somal Golgi and dendritic Golgi outposts was performed with ImageJ. To remove the background, the intensity threshold was set as the mean intensity of background plus three times the standard deviation of background. Threshold levels were determined independently for each data set. Statistical analysis Two-tailed Student s t-test was used throughout the manuscript. P-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < Data are presented as mean s.e.m. Brefeldin A (BFA)-treatment of Drosophila da neurons in situ Third instar larvae were dissected in sylgard-coated dishes and treated with insect saline containing either 10 μg/ml BFA (Cell Signaling Technology, MA) dissolved in DMSO or the same volume of DMSO only as negative control. The BFA-treatment lasted for 30 minutes. In the wash-out experiments, the larval samples were treated with 10 μg/ml BFA for 30 minutes, washed 3 times with insect saline, and then incubated in insect saline for 30 minutes. After the treatments, the larval samples were fixed and immunostained as described above.
Sarker et al. Supplementary Material. Subcellular Fractionation
 Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
Supplemental Figure 1 (Figure S1), related to Figure 1 Figure S1 provides evidence to demonstrate Nfatc1Cre is a mouse line that directed gene
 Developmental Cell, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Brg1 Governs a Positive Feedback Circuit in the Hair Follicle for Tissue Regeneration and Repair Yiqin Xiong, Wei Li, Ching Shang, Richard M. Chen,
Developmental Cell, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Brg1 Governs a Positive Feedback Circuit in the Hair Follicle for Tissue Regeneration and Repair Yiqin Xiong, Wei Li, Ching Shang, Richard M. Chen,
Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Figure S2. Verification of ihog and boi
 Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Extracts from S2R+ cells, embryos, and adults were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with anti-ihog antibody. The Ihog
Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Extracts from S2R+ cells, embryos, and adults were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with anti-ihog antibody. The Ihog
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods MARCM-based forward genetic screen We used ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS) to mutagenize flies carrying FRT 2A and FRT 82B transgenes, which are sites for the FLP-mediated recombination
Supplementary Methods MARCM-based forward genetic screen We used ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS) to mutagenize flies carrying FRT 2A and FRT 82B transgenes, which are sites for the FLP-mediated recombination
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Selective control of inhibitory synapse development by Slitrk3-PTPδ trans-synaptic interaction Hideto Takahashi 1, Kei-ichi Katayama 2, Kazuhiro Sohya 3,4, Hiroyuki Miyamoto 4,5,
Supplementary Information Selective control of inhibitory synapse development by Slitrk3-PTPδ trans-synaptic interaction Hideto Takahashi 1, Kei-ichi Katayama 2, Kazuhiro Sohya 3,4, Hiroyuki Miyamoto 4,5,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/310/5753/1487/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Stem Cell Self-Renewal Controlled by Chromatin Remodeling Factors Rongwen Xi and Ting Xie* *To whom correspondence should
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/310/5753/1487/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Stem Cell Self-Renewal Controlled by Chromatin Remodeling Factors Rongwen Xi and Ting Xie* *To whom correspondence should
DCLK-immunopositive. Bars, 100 µm for B, 50 µm for C.
 Supplementary Figure S1. Characterization of rabbit polyclonal anti-dclk antibody. (A) Immunoblotting of COS7 cells transfected with DCLK1-GFP and DCLK2-GFP expression plasmids probed with anti-dclk antibody
Supplementary Figure S1. Characterization of rabbit polyclonal anti-dclk antibody. (A) Immunoblotting of COS7 cells transfected with DCLK1-GFP and DCLK2-GFP expression plasmids probed with anti-dclk antibody
Cytotoxicity of Botulinum Neurotoxins Reveals a Direct Role of
 Supplementary Information Cytotoxicity of Botulinum Neurotoxins Reveals a Direct Role of Syntaxin 1 and SNAP-25 in Neuron Survival Lisheng Peng, Huisheng Liu, Hongyu Ruan, William H. Tepp, William H. Stoothoff,
Supplementary Information Cytotoxicity of Botulinum Neurotoxins Reveals a Direct Role of Syntaxin 1 and SNAP-25 in Neuron Survival Lisheng Peng, Huisheng Liu, Hongyu Ruan, William H. Tepp, William H. Stoothoff,
Supplemental Figure 1 Human REEP family of proteins can be divided into two distinct subfamilies. Residues (single letter amino acid code) identical
 Supplemental Figure Human REEP family of proteins can be divided into two distinct subfamilies. Residues (single letter amino acid code) identical in all six REEPs are highlighted in green. Additional
Supplemental Figure Human REEP family of proteins can be divided into two distinct subfamilies. Residues (single letter amino acid code) identical in all six REEPs are highlighted in green. Additional
Input. Pulldown GST. GST-Ahi1
 A kd 250 150 100 75 50 37 25 -GST-Ahi1 +GST-Ahi1 kd 148 98 64 50 37 22 GST GST-Ahi1 C kd 250 148 98 64 50 Control Input Hap1A Hap1 Pulldown GST GST-Ahi1 Hap1A Hap1 Hap1A Hap1 Figure S1. (A) Ahi1 western
A kd 250 150 100 75 50 37 25 -GST-Ahi1 +GST-Ahi1 kd 148 98 64 50 37 22 GST GST-Ahi1 C kd 250 148 98 64 50 Control Input Hap1A Hap1 Pulldown GST GST-Ahi1 Hap1A Hap1 Hap1A Hap1 Figure S1. (A) Ahi1 western
B. ADM: C. D. Apoptosis: 1.68% 2.99% 1.31% Figure.S1,Li et al. number. invaded cells. HuH7 BxPC-3 DLD-1.
 A. - Figure.S1,Li et al. B. : - + - + - + E-cadherin CK19 α-sma vimentin β -actin C. D. Apoptosis: 1.68% 2.99% 1.31% - : - + - + - + Apoptosis: 48.33% 45.32% 44.59% E. invaded cells number 400 300 200
A. - Figure.S1,Li et al. B. : - + - + - + E-cadherin CK19 α-sma vimentin β -actin C. D. Apoptosis: 1.68% 2.99% 1.31% - : - + - + - + Apoptosis: 48.33% 45.32% 44.59% E. invaded cells number 400 300 200
To isolate single GNS 144 cell clones, cells were plated at a density of 1cell/well
 Supplemental Information: Supplemental Methods: Cell culture To isolate single GNS 144 cell clones, cells were plated at a density of 1cell/well in 96 well Primaria plates in GNS media and incubated at
Supplemental Information: Supplemental Methods: Cell culture To isolate single GNS 144 cell clones, cells were plated at a density of 1cell/well in 96 well Primaria plates in GNS media and incubated at
Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity.
 Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity. (A) Amino acid alignment of HDA5, HDA15 and HDA18. The blue line
Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity. (A) Amino acid alignment of HDA5, HDA15 and HDA18. The blue line
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10810 Supplementary Fig. 1: Mutation of the loqs gene leads to shortened lifespan and adult-onset brain degeneration. a. Northern blot of control and loqs f00791 mutant flies. loqs f00791
doi:10.1038/nature10810 Supplementary Fig. 1: Mutation of the loqs gene leads to shortened lifespan and adult-onset brain degeneration. a. Northern blot of control and loqs f00791 mutant flies. loqs f00791
Supplementary Figure 1. APP cleavage assay. HEK293 cells were transfected with various
 Supplementary Figure 1. APP cleavage assay. HEK293 cells were transfected with various GST-tagged N-terminal truncated APP fragments including GST-APP full-length (FL), APP (123-695), APP (189-695), or
Supplementary Figure 1. APP cleavage assay. HEK293 cells were transfected with various GST-tagged N-terminal truncated APP fragments including GST-APP full-length (FL), APP (123-695), APP (189-695), or
A population of Nestin expressing progenitors in the cerebellum exhibits increased tumorigenicity
 A population of Nestin expressing progenitors in the cerebellum exhibits increased tumorigenicity Peng Li 1,2, Fang Du 1, Larra W. Yuelling 1, Tiffany Lin 3, Renata E. Muradimova 1, Rossella Tricarico
A population of Nestin expressing progenitors in the cerebellum exhibits increased tumorigenicity Peng Li 1,2, Fang Du 1, Larra W. Yuelling 1, Tiffany Lin 3, Renata E. Muradimova 1, Rossella Tricarico
bronchial epithelial cells (I). Bronchi are outlined with dashed line. Scale bars = 25 µm, if not
 Supplemental Figure S1: ronchial epithelial cell polarity and integrity is maintained in bronchi. (A-E) Staining for selected markers of bronchial cell differentiation and intracellular compartments is
Supplemental Figure S1: ronchial epithelial cell polarity and integrity is maintained in bronchi. (A-E) Staining for selected markers of bronchial cell differentiation and intracellular compartments is
Short hairpin RNA (shrna) against MMP14. Lentiviral plasmids containing shrna
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Short hairpin RNA (shrna) against MMP14. Lentiviral plasmids containing shrna (Mission shrna, Sigma) against mouse MMP14 were transfected into HEK293 cells using FuGene6
Supplemental Materials and Methods Short hairpin RNA (shrna) against MMP14. Lentiviral plasmids containing shrna (Mission shrna, Sigma) against mouse MMP14 were transfected into HEK293 cells using FuGene6
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Moutin et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110101/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Tagged Homer1a and Homer are functional and display different
Supplemental material Moutin et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110101/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Tagged Homer1a and Homer are functional and display different
Otefin, a Nuclear Membrane Protein, Determines
 Developmental Cell 14 Supplemental Data Otefin, a Nuclear Membrane Protein, Determines the Fate of Germline Stem Cells in Drosophila via Interaction with Smad Complexes Xiaoyong Jiang, Laixin Xia, Dongsheng
Developmental Cell 14 Supplemental Data Otefin, a Nuclear Membrane Protein, Determines the Fate of Germline Stem Cells in Drosophila via Interaction with Smad Complexes Xiaoyong Jiang, Laixin Xia, Dongsheng
JCB. Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY. Paul et al.,
 Supplemental material JCB Paul et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201502040/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Mutant p53-expressing cells display limited retrograde actin flow at
Supplemental material JCB Paul et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201502040/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Mutant p53-expressing cells display limited retrograde actin flow at
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Yamaguchi et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201009126/dc1 S1 Figure S2. The expression levels of GFP-Akt1-PH and localization
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Yamaguchi et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201009126/dc1 S1 Figure S2. The expression levels of GFP-Akt1-PH and localization
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein. complexes during long term depression
 Supplementary Information Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein complexes during long term depression Shinji Matsuda, Wataru Kakegawa, Timotheus Budisantoso, Toshihiro Nomura,
Supplementary Information Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein complexes during long term depression Shinji Matsuda, Wataru Kakegawa, Timotheus Budisantoso, Toshihiro Nomura,
by Neurobasal medium (supplemented with B27, 0.5mM glutamine, and 100 U/mL
 Supplementary Materials and methods Neuronal cultures and transfection The hippocampus was dissected from E8 rat embryos, dissociated, and neurons plated onto glass coverslips coated with poly-ornithine
Supplementary Materials and methods Neuronal cultures and transfection The hippocampus was dissected from E8 rat embryos, dissociated, and neurons plated onto glass coverslips coated with poly-ornithine
AIP1 functions as an endogenous inhibitor of VEGFR2-mediated signaling and inflammatory angiogenesis
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS functions as an endogenous inhibitor of VEGFR2-mediated signaling and inflammatory angiogenesis Haifeng Zhang 1*, Yun He 1*, Shengchuan Dai 1*, Zhe Xu 2*, Yan Luo 2, Ting Wan 2,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS functions as an endogenous inhibitor of VEGFR2-mediated signaling and inflammatory angiogenesis Haifeng Zhang 1*, Yun He 1*, Shengchuan Dai 1*, Zhe Xu 2*, Yan Luo 2, Ting Wan 2,
Supplementary Figure 1. Co-localization of GLUT1 and DNAL4 in BeWo cells cultured
 Supplementary Figure 1. Co-localization of GLUT1 and DNAL4 in BeWo cells cultured under static conditions. Cells were seeded in the chamber area of the device and cultured overnight without medium perfusion.
Supplementary Figure 1. Co-localization of GLUT1 and DNAL4 in BeWo cells cultured under static conditions. Cells were seeded in the chamber area of the device and cultured overnight without medium perfusion.
Figure S1. USP-46 is expressed in several tissues including the nervous system
 Supplemental Figure legends Figure S1. USP-46 is expressed in several tissues including the nervous system Transgenic animals expressing a transcriptional reporter (P::GFP) were imaged using epifluorescence
Supplemental Figure legends Figure S1. USP-46 is expressed in several tissues including the nervous system Transgenic animals expressing a transcriptional reporter (P::GFP) were imaged using epifluorescence
Supplementary Figure 1. Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Positive selection gates for the collection of LRCs or nonlrcs had to be drawn based on the location and
 Determining positive selection gates for LRCs and nonlrcs Positive selection gates for the collection of LRCs or nonlrcs had to be drawn based on the location and shape of the Gaussian distributions. For
Determining positive selection gates for LRCs and nonlrcs Positive selection gates for the collection of LRCs or nonlrcs had to be drawn based on the location and shape of the Gaussian distributions. For
Supplementary Methods
 Caussinus and Gonzalez Supplementary Methods Mitotic clones Clones of NBs homozygous for numb 03235, mira ZZ176, pros 17 or apkc k06403 were generated by FLP/FRT mediated mitotic recombination (1). As
Caussinus and Gonzalez Supplementary Methods Mitotic clones Clones of NBs homozygous for numb 03235, mira ZZ176, pros 17 or apkc k06403 were generated by FLP/FRT mediated mitotic recombination (1). As
(a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Diaph3 ko mice. (a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for different regions of Diaph3 mrna from WT, heterozygote
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Diaph3 ko mice. (a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for different regions of Diaph3 mrna from WT, heterozygote
Supplemental Information. Plk1/Polo Phosphorylates Sas-4 at the Onset. of Mitosis for an Efficient Recruitment
 Cell Reports, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Plk1/Polo Phosphorylates Sas-4 at the Onset of Mitosis for an Efficient Recruitment of Pericentriolar Material to Centrosomes Anand Ramani, Aruljothi Mariappan,
Cell Reports, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Plk1/Polo Phosphorylates Sas-4 at the Onset of Mitosis for an Efficient Recruitment of Pericentriolar Material to Centrosomes Anand Ramani, Aruljothi Mariappan,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Normalized dorsal trunk length (µm) Normalized dorsal trunk length (TC1-5) (µm) DOI: 1.138/ncb2467 a b c d btl>src64 Src42, btl>src64 e Src64 f g h DT Src64 DT Midgut Src64 Midgut i Src64 Atpα j k l DT
Normalized dorsal trunk length (µm) Normalized dorsal trunk length (TC1-5) (µm) DOI: 1.138/ncb2467 a b c d btl>src64 Src42, btl>src64 e Src64 f g h DT Src64 DT Midgut Src64 Midgut i Src64 Atpα j k l DT
Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured
 Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Polyclonal ARHGAP25 antibody was prepared from rabbit serum after intracutaneous
 Preparation and purification of polyclonal antibodies Polyclonal ARHGAP25 antibody was prepared from rabbit serum after intracutaneous injections of glutathione S-transferase-ARHGAP25-(509-619) (GST-coiled
Preparation and purification of polyclonal antibodies Polyclonal ARHGAP25 antibody was prepared from rabbit serum after intracutaneous injections of glutathione S-transferase-ARHGAP25-(509-619) (GST-coiled
Supplemental Materials and Methods
 Supplemental Materials and Methods In situ hybridization In situ hybridization analysis of HFE2 and genin mrna in rat liver tissues was performed as previously described (1). Briefly, the digoxigenin-labeled
Supplemental Materials and Methods In situ hybridization In situ hybridization analysis of HFE2 and genin mrna in rat liver tissues was performed as previously described (1). Briefly, the digoxigenin-labeled
J. Cell Sci. 128: doi: /jcs : Supplementary Material. Supplemental Figures. Journal of Cell Science Supplementary Material
 Supplemental Figures Figure S1. Trio controls endothelial barrier function. (A) TagRFP-shTrio constructs were expressed in ECs. Western blot shows efficient Trio knockdown in TagRFP-expressing ECs. (B)
Supplemental Figures Figure S1. Trio controls endothelial barrier function. (A) TagRFP-shTrio constructs were expressed in ECs. Western blot shows efficient Trio knockdown in TagRFP-expressing ECs. (B)
- PDI5. - Actin A 300-UTR5. PDI5 lines WT. Arabidopsis Chromosome 1. PDI5 (At1g21750) SALK_ SALK_ SALK_015253
 Supplemental Data. Ondzighi et al. (2008). Arabidopsis Protein Disulfide Isomerase-5 Inhibits ysteine Proteases During Trafficking to Vacuoles Prior to Programmed ell Death of the dothelium in Developing
Supplemental Data. Ondzighi et al. (2008). Arabidopsis Protein Disulfide Isomerase-5 Inhibits ysteine Proteases During Trafficking to Vacuoles Prior to Programmed ell Death of the dothelium in Developing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12119 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND LEGENDS pre-let-7a- 1 +14U pre-let-7a- 1 Ddx3x Dhx30 Dis3l2 Elavl1 Ggt5 Hnrnph 2 Osbpl5 Puf60 Rnpc3 Rpl7 Sf3b3 Sf3b4 Tia1 Triobp U2af1 U2af2 1 6 2 4 3
doi:10.1038/nature12119 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND LEGENDS pre-let-7a- 1 +14U pre-let-7a- 1 Ddx3x Dhx30 Dis3l2 Elavl1 Ggt5 Hnrnph 2 Osbpl5 Puf60 Rnpc3 Rpl7 Sf3b3 Sf3b4 Tia1 Triobp U2af1 U2af2 1 6 2 4 3
Supplemental Material: Rev1 promotes replication through UV lesions in conjunction with DNA
 Supplemental Material: Rev1 promotes replication through UV lesions in conjunction with DNA polymerases,, and, but not with DNA polymerase Jung-Hoon Yoon, Jeseong Park, Juan Conde, Maki Wakamiya, Louise
Supplemental Material: Rev1 promotes replication through UV lesions in conjunction with DNA polymerases,, and, but not with DNA polymerase Jung-Hoon Yoon, Jeseong Park, Juan Conde, Maki Wakamiya, Louise
Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss Yunjong Lee, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Joo-Ho Shin, Yun-Il Lee, Han Seok Ko, Debbie Swing,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss Yunjong Lee, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Joo-Ho Shin, Yun-Il Lee, Han Seok Ko, Debbie Swing,
Figure S1. Specificity of immunofluorescence staining in STC-1 cells. STC-1 cells
 Supplementary Figures and Tables Figure S1. Figure S1. Specificity of immunofluorescence staining in STC-1 cells. STC-1 cells were treated with donkey-anti rabbit antibody conjugated with Dylight488 or
Supplementary Figures and Tables Figure S1. Figure S1. Specificity of immunofluorescence staining in STC-1 cells. STC-1 cells were treated with donkey-anti rabbit antibody conjugated with Dylight488 or
indicated numbers of pups at day of life (DOL) 10, or embryonic day (ED) B. Male mice of
 SUPPLEMENTRY FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1. USP44 loss leads to chromosome missegregation.. Genotypes obtained from the indicated numbers of pups at day of life (DOL) 10, or embryonic day (ED) 13.5.. Male mice
SUPPLEMENTRY FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1. USP44 loss leads to chromosome missegregation.. Genotypes obtained from the indicated numbers of pups at day of life (DOL) 10, or embryonic day (ED) 13.5.. Male mice
Aminoacid change in chromophore. PIN3::PIN3-GFP GFP S65 (no change) (5.9) (Kneen et al., 1998)
 Supplemental Table. Table S1. Fluorophore characteristics of used fluorescent proteins, Related to Figure 2 and 3. Transgenic line Fluprescent marker Aminoacid change in chromophore pk(a) Ref. PIN3::PIN3-GFP
Supplemental Table. Table S1. Fluorophore characteristics of used fluorescent proteins, Related to Figure 2 and 3. Transgenic line Fluprescent marker Aminoacid change in chromophore pk(a) Ref. PIN3::PIN3-GFP
Supplemental Fig. 1. Mcr alleles show defects in tracheal tube size and luminal protein accumulation. (A-F) Confocal projections of living stage 15
 Supplemental Fig. 1. Mcr alleles show defects in tracheal tube size and luminal protein accumulation. (A-F) Confocal projections of living stage 15 embryos expressing GFP and Verm-RFP in tracheal cells
Supplemental Fig. 1. Mcr alleles show defects in tracheal tube size and luminal protein accumulation. (A-F) Confocal projections of living stage 15 embryos expressing GFP and Verm-RFP in tracheal cells
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE S1. Identification of BmCREC. (A) Amino acid sequences of BmCREC show the peptides identified in LC-MS/MS analysis (marked by red letters
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE S1. Identification of BmCREC. (A) Amino acid sequences of BmCREC show the peptides identified in LC-MS/MS analysis (marked by red letters
Chapter 2 Analysis of the C. elegans Germline Stem Cell Region
 Chapter 2 Analysis of the C. elegans Germline Stem Cell Region Sarah L. Crittenden and Judith Kimble Contents 2.1 Introduction... 27 2.2 Materials... 29 2.3 Methods... 30 2.4 Notes... 40 References...
Chapter 2 Analysis of the C. elegans Germline Stem Cell Region Sarah L. Crittenden and Judith Kimble Contents 2.1 Introduction... 27 2.2 Materials... 29 2.3 Methods... 30 2.4 Notes... 40 References...
(A) Schematic depicting morphology of cholinergic DA and DB motor neurons in an L1
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS Supplemental Figure 1 Figure S1. Expression of the non-alpha nachr subunit ACR-2. (A) Schematic depicting morphology of cholinergic DA and DB motor neurons in an L1 animal. Wide-field
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS Supplemental Figure 1 Figure S1. Expression of the non-alpha nachr subunit ACR-2. (A) Schematic depicting morphology of cholinergic DA and DB motor neurons in an L1 animal. Wide-field
from α- to β-cleavage
 Supplementary Information Specific antibody binding to the APP 672-699 region shifts APP processing from α- to β-cleavage Song Li 1,6,8, Juan Deng 1,7,8, Huayan Hou 1,8, Jun Tian 1, Brian Giunta 2,3, Yanjiang
Supplementary Information Specific antibody binding to the APP 672-699 region shifts APP processing from α- to β-cleavage Song Li 1,6,8, Juan Deng 1,7,8, Huayan Hou 1,8, Jun Tian 1, Brian Giunta 2,3, Yanjiang
Supplemental Information. Stratum, a Homolog of the Human GEF Mss4, Partnered with Rab8, Controls the Basal Restriction
 Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Stratum, a Homolog of the Human GEF Mss4, Partnered with Rab8, Controls the Basal Restriction of Basement Membrane Proteins in Epithelial Cells Olivier
Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Stratum, a Homolog of the Human GEF Mss4, Partnered with Rab8, Controls the Basal Restriction of Basement Membrane Proteins in Epithelial Cells Olivier
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Intrinsic protein-protein interaction mediated and chaperonin assisted sequential assembly of a stable Bardet Biedl syndome protein complex, the BBSome * Qihong Zhang 1#, Dahai
Supplemental Information Intrinsic protein-protein interaction mediated and chaperonin assisted sequential assembly of a stable Bardet Biedl syndome protein complex, the BBSome * Qihong Zhang 1#, Dahai
To examine the silencing effects of Celsr3 shrna, we co transfected 293T cells with expression
 Supplemental figures Supplemental Figure. 1. Silencing expression of Celsr3 by shrna. To examine the silencing effects of Celsr3 shrna, we co transfected 293T cells with expression plasmids for the shrna
Supplemental figures Supplemental Figure. 1. Silencing expression of Celsr3 by shrna. To examine the silencing effects of Celsr3 shrna, we co transfected 293T cells with expression plasmids for the shrna
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1919 Mori et al. Supplementary Figure 1a-b a Characterization of the mdrg cells Anti-NF150 DIC (89%: N=154) 100µm Anti-S100 DIC 100µm b (9.1%: N=144) Characterization of the cortical neurons
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1919 Mori et al. Supplementary Figure 1a-b a Characterization of the mdrg cells Anti-NF150 DIC (89%: N=154) 100µm Anti-S100 DIC 100µm b (9.1%: N=144) Characterization of the cortical neurons
Supplemental Information. Pacer Mediates the Function of Class III PI3K. and HOPS Complexes in Autophagosome. Maturation by Engaging Stx17
 Molecular Cell, Volume 65 Supplemental Information Pacer Mediates the Function of Class III PI3K and HOPS Complexes in Autophagosome Maturation by Engaging Stx17 Xiawei Cheng, Xiuling Ma, Xianming Ding,
Molecular Cell, Volume 65 Supplemental Information Pacer Mediates the Function of Class III PI3K and HOPS Complexes in Autophagosome Maturation by Engaging Stx17 Xiawei Cheng, Xiuling Ma, Xianming Ding,
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/9/eaat5401/dc1 Supplementary Materials for GLK-IKKβ signaling induces dimerization and translocation of the AhR-RORγt complex in IL-17A induction and autoimmune
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/9/eaat5401/dc1 Supplementary Materials for GLK-IKKβ signaling induces dimerization and translocation of the AhR-RORγt complex in IL-17A induction and autoimmune
Hoopfer et al., Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure S1. Quantification of ORN axon degeneration
 Hoopfer et al., Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure S1. Quantification of ORN axon degeneration (A) Mean GFP intensity of commissural ORN axons 1 day after antennae removal. 1 day after cutting, wt ORNs
Hoopfer et al., Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure S1. Quantification of ORN axon degeneration (A) Mean GFP intensity of commissural ORN axons 1 day after antennae removal. 1 day after cutting, wt ORNs
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 PCR-genotyping of the three mouse models used in this study and controls for behavioral experiments after semi-chronic Pten inhibition. a-c. DNA from App/Psen1 (a), Pten tg (b) and
Supplementary Figure 1 PCR-genotyping of the three mouse models used in this study and controls for behavioral experiments after semi-chronic Pten inhibition. a-c. DNA from App/Psen1 (a), Pten tg (b) and
Figure legends for supplement
 Figure legends for supplement Supplemental Figure 1 Characterization of purified and recombinant proteins Relevant fractions related the final stage of the purification protocol(bingham et al., 1998; Toba
Figure legends for supplement Supplemental Figure 1 Characterization of purified and recombinant proteins Relevant fractions related the final stage of the purification protocol(bingham et al., 1998; Toba
Supplementary Figure Legends
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 gene targeting strategy for disruption of chicken gene, related to Figure 1 (f)-(i). (a) The locus and the targeting constructs showing HpaI restriction sites. The
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 gene targeting strategy for disruption of chicken gene, related to Figure 1 (f)-(i). (a) The locus and the targeting constructs showing HpaI restriction sites. The
Cell death analysis using the high content bioimager BD PathwayTM 855 instrument (BD
 Supplemental information Materials and Methods: Cell lines, reagents and antibodies: Wild type (A3) and caspase-8 -/- (I9.2) Jurkat cells were cultured in RPMI 164 medium (Life Technologies) supplemented
Supplemental information Materials and Methods: Cell lines, reagents and antibodies: Wild type (A3) and caspase-8 -/- (I9.2) Jurkat cells were cultured in RPMI 164 medium (Life Technologies) supplemented
Supporting information
 Supporting information Construction of strains and plasmids To create ptc67, a PCR product obtained with primers cc2570-162f (gcatgggcaagcttgaggacggcgtcatgt) and cc2570+512f (gaggccgtggtaccatagaggcgggcg),
Supporting information Construction of strains and plasmids To create ptc67, a PCR product obtained with primers cc2570-162f (gcatgggcaagcttgaggacggcgtcatgt) and cc2570+512f (gaggccgtggtaccatagaggcgggcg),
ASPP1 Fw GGTTGGGAATCCACGTGTTG ASPP1 Rv GCCATATCTTGGAGCTCTGAGAG
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
MeCP2. MeCP2/α-tubulin. GFP mir1-1 mir132
 Conservation Figure S1. Schematic showing 3 UTR (top; thick black line), mir132 MRE (arrow) and nucleotide sequence conservation (vertical black lines; http://genome.ucsc.edu). a GFP mir1-1 mir132 b GFP
Conservation Figure S1. Schematic showing 3 UTR (top; thick black line), mir132 MRE (arrow) and nucleotide sequence conservation (vertical black lines; http://genome.ucsc.edu). a GFP mir1-1 mir132 b GFP
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4166
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Haberman et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201108088/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Loss of neurotransmitter release in Drosophila photoreceptors
Supplemental material Haberman et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201108088/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Loss of neurotransmitter release in Drosophila photoreceptors
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) ES and FACS-sorted GFP+/Flk1+ cells were fixed in 1% formaldehyde and sonicated until fragments of an average
 Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) ES and FACS-sorted cells were fixed in % formaldehyde and sonicated until fragments of an average size of 5 bp were obtained. Soluble, sheared chromatin was diluted
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) ES and FACS-sorted cells were fixed in % formaldehyde and sonicated until fragments of an average size of 5 bp were obtained. Soluble, sheared chromatin was diluted
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 )
 Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 ) homologous recombination arm (left) and of the right (3 )
Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 ) homologous recombination arm (left) and of the right (3 )
Flybow genetic multicolor cell labeling for neural circuit analysis in Drosophila melanogaster
 Nature Methods Flybow genetic multicolor cell labeling for neural circuit analysis in Drosophila melanogaster Dafni Hadjieconomou, Shay Rotkopf, Cyrille Alexandre, Donald M Bell, Barry J Dickson & Iris
Nature Methods Flybow genetic multicolor cell labeling for neural circuit analysis in Drosophila melanogaster Dafni Hadjieconomou, Shay Rotkopf, Cyrille Alexandre, Donald M Bell, Barry J Dickson & Iris
Supplementary Figure 1. α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.
 Supplementary Figure 1 α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. (a) Specificity of anti-n103 antibody. Anti-N103 antibody was coated on an ELISA plate and different concentrations of full-length
Supplementary Figure 1 α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. (a) Specificity of anti-n103 antibody. Anti-N103 antibody was coated on an ELISA plate and different concentrations of full-length
SensoLyte Anti-alpha-Synuclein Quantitative ELISA Kit (Human/Mouse/Rat) *Colorimetric*
 Catalog # Kit Size SensoLyte Anti-alpha-Synuclein Quantitative ELISA Kit (Human/Mouse/Rat) *Colorimetric* AS-55550 One 96-well strip plate This kit is optimized to detect human/mouse/rat alpha-synuclein
Catalog # Kit Size SensoLyte Anti-alpha-Synuclein Quantitative ELISA Kit (Human/Mouse/Rat) *Colorimetric* AS-55550 One 96-well strip plate This kit is optimized to detect human/mouse/rat alpha-synuclein
MEFs were treated with the indicated concentrations of LLOMe for three hours, washed
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell Fractionation MEFs were treated with the indicated concentrations of LLOMe for three hours, washed with ice-cold PBS, collected by centrifugation, and then homogenized
Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell Fractionation MEFs were treated with the indicated concentrations of LLOMe for three hours, washed with ice-cold PBS, collected by centrifugation, and then homogenized
JCB. Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY. Hong et al.,
 Supplemental material JCB Hong et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201412127/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Analysis of purified proteins by SDS-PAGE and pull-down assays. (A) Coomassie-stained
Supplemental material JCB Hong et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201412127/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Analysis of purified proteins by SDS-PAGE and pull-down assays. (A) Coomassie-stained
Supplemental Information Control of apico-basal epithelial polarity by the microtubule minus-end binding protein CAMSAP3 and spectraplakin ACF7
 Supplemental Information Control of apico-basal epithelial polarity by the microtubule minus-end binding protein CAMSAP3 and spectraplakin ACF7 Ivar Noordstra, Qingyang Liu, Wilco Nijenhuis, Shasha Hua,
Supplemental Information Control of apico-basal epithelial polarity by the microtubule minus-end binding protein CAMSAP3 and spectraplakin ACF7 Ivar Noordstra, Qingyang Liu, Wilco Nijenhuis, Shasha Hua,
Supplemental Data. The Survival Advantage of Olfaction. in a Competitive Environment. Supplemental Experimental Procedures
 Supplemental Data The Survival Advantage of Olfaction in a Competitive Environment Kenta Asahina, Viktoryia Pavlenkovich, and Leslie B. Vosshall Supplemental Experimental Procedures Experimental animals
Supplemental Data The Survival Advantage of Olfaction in a Competitive Environment Kenta Asahina, Viktoryia Pavlenkovich, and Leslie B. Vosshall Supplemental Experimental Procedures Experimental animals
ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit
 ab110417 ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit Instructions for Use For the Immunocytochemistry analysis of cytochrome c and a mitochondrial marker (Complex Vα) in apoptotic cells and non-apoptotic
ab110417 ApoTrack Cytochrome c Apoptosis ICC Antibody Kit Instructions for Use For the Immunocytochemistry analysis of cytochrome c and a mitochondrial marker (Complex Vα) in apoptotic cells and non-apoptotic
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 3. Supplememtary Note 3, Wehr et al., Monitoring Regulated Protein-Protein Interactions Using Split-TEV 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 3 Fluorescent Proteolysis-only TEV-Reporters We generated TEV reporter that allow visualizing TEV activity at the membrane and in the cytosol of living cells not relying on the addition
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 3 Fluorescent Proteolysis-only TEV-Reporters We generated TEV reporter that allow visualizing TEV activity at the membrane and in the cytosol of living cells not relying on the addition
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
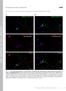 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Kanaani et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200912101/dc1 Figure S1. The K2 rabbit polyclonal antibody is specific for GAD67,
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Kanaani et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200912101/dc1 Figure S1. The K2 rabbit polyclonal antibody is specific for GAD67,
Figure S1. Figure S2. Figure S3 HB Anti-FSP27 (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab. Anti-GST-FSP27(45-127) Ab.
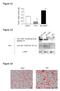 / 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
/ 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
fga phenotypes were also analyzed in the tracheal system, the organ responsible for
 SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT Tracheal defects fga phenotypes were also analyzed in the tracheal system, the organ responsible for oxygen delivery in the fly. In fga homozygous mutant alleles, we observed defects
SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT Tracheal defects fga phenotypes were also analyzed in the tracheal system, the organ responsible for oxygen delivery in the fly. In fga homozygous mutant alleles, we observed defects
Supplementary Figure 1: Derivation and characterization of RN ips cell lines. (a) RN ips cells maintain expression of pluripotency markers OCT4 and
 Supplementary Figure 1: Derivation and characterization of RN ips cell lines. (a) RN ips cells maintain expression of pluripotency markers OCT4 and SSEA4 after 10 passages in mtesr 1 medium. (b) Schematic
Supplementary Figure 1: Derivation and characterization of RN ips cell lines. (a) RN ips cells maintain expression of pluripotency markers OCT4 and SSEA4 after 10 passages in mtesr 1 medium. (b) Schematic
X-gal Staining of Wholemount Drosophila Embryos. 3.7 % formaldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (ph 7.2) 0.1M Phosphate buffer (ph 7.2) and 0.
 X-gal Staining of Wholemount Drosophila Embryos Modified from The Little Blue Book (Gehring lab) Solutions 1. NaCl+TX: 3. PBT: 4. Fe/NaP Buffer: 0.7% NaCl and 0.3% Triton 3.7 % formaldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate
X-gal Staining of Wholemount Drosophila Embryos Modified from The Little Blue Book (Gehring lab) Solutions 1. NaCl+TX: 3. PBT: 4. Fe/NaP Buffer: 0.7% NaCl and 0.3% Triton 3.7 % formaldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. lev-9 mutants are resistant to levamisole. The levamisole dose-response curves indicate that lev-9 mutants are partially resistant to levamisole similar to lev-10(kr26) mutants. unc-29(x29)
Figure S1. lev-9 mutants are resistant to levamisole. The levamisole dose-response curves indicate that lev-9 mutants are partially resistant to levamisole similar to lev-10(kr26) mutants. unc-29(x29)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Ca 2+ /calmodulin Regulates Salicylic Acid-mediated Plant Immunity Liqun Du, Gul S. Ali, Kayla A. Simons, Jingguo Hou, Tianbao Yang, A.S.N. Reddy and B. W. Poovaiah * *To whom correspondence should be
Ca 2+ /calmodulin Regulates Salicylic Acid-mediated Plant Immunity Liqun Du, Gul S. Ali, Kayla A. Simons, Jingguo Hou, Tianbao Yang, A.S.N. Reddy and B. W. Poovaiah * *To whom correspondence should be
To assess the localization of Citrine fusion proteins, we performed antibody staining to
 Trinh et al 1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL FlipTraps recapitulate endogenous protein localization To assess the localization of Citrine fusion proteins, we performed antibody staining to compare the expression
Trinh et al 1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL FlipTraps recapitulate endogenous protein localization To assess the localization of Citrine fusion proteins, we performed antibody staining to compare the expression
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAY INOMATION igure S1 Knockdown of endogenous HI-1α by short-interference NA (sina) reverts EMT and metastatic phenotypes in H1299 cells and in ADU or MC-7 cells undergoing hypoxia. a. Western
SUPPLEMENTAY INOMATION igure S1 Knockdown of endogenous HI-1α by short-interference NA (sina) reverts EMT and metastatic phenotypes in H1299 cells and in ADU or MC-7 cells undergoing hypoxia. a. Western
Figure S1. Related to Figure 1, to show 3-D images of nerve/vessel patterning.
 Supplemental Information Inventory of Supplemental Information Figure S1. Related to Figure 1, to show 3-D images of nerve/vessel patterning. Figure S2. Related to Figure 4, to validate Npn-1 signaling
Supplemental Information Inventory of Supplemental Information Figure S1. Related to Figure 1, to show 3-D images of nerve/vessel patterning. Figure S2. Related to Figure 4, to validate Npn-1 signaling
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Thompson et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200909067/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Modification-specific antibodies do not detect unmodified
Supplemental material Thompson et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200909067/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Modification-specific antibodies do not detect unmodified
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.2558
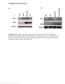 Supplementary. Fig. 1. (a) Sirt1 and mutant HTT (detected by HTT 81-90 antibody) protein levels were detected by Western blotting in cerebral cortex of N171-82Q mice. (b) Sirt1 and mutant HTT (detected
Supplementary. Fig. 1. (a) Sirt1 and mutant HTT (detected by HTT 81-90 antibody) protein levels were detected by Western blotting in cerebral cortex of N171-82Q mice. (b) Sirt1 and mutant HTT (detected
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. (A) UCSC Genome Browser view of region immediately downstream of the NEUROG3 start codon. All candidate grna target sites which meet the G(N 19 )NGG constraint are aligned to illustrate
Supplementary Figure 1. (A) UCSC Genome Browser view of region immediately downstream of the NEUROG3 start codon. All candidate grna target sites which meet the G(N 19 )NGG constraint are aligned to illustrate
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Prolyl isomerase Pin1 and protein kinase HIPK2 cooperate to promote
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Prolyl isomerase Pin1 and protein kinase HIPK2 cooperate to promote cortical neurogenesis by suppressing Groucho/TLE:Hes1-mediated inhibition of neuronal differentiation Running
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Prolyl isomerase Pin1 and protein kinase HIPK2 cooperate to promote cortical neurogenesis by suppressing Groucho/TLE:Hes1-mediated inhibition of neuronal differentiation Running
Single-Cell Knockout Analysis of NMDA Receptor 2B
 Neuron, Volume 62 Supplemental Data Uncoupling Dendrite Growth and Patterning: Single-Cell Knockout Analysis of NMDA Receptor 2B J. Sebastian Espinosa, Damian G. Wheeler, Richard W. Tsien, and Liqun Luo
Neuron, Volume 62 Supplemental Data Uncoupling Dendrite Growth and Patterning: Single-Cell Knockout Analysis of NMDA Receptor 2B J. Sebastian Espinosa, Damian G. Wheeler, Richard W. Tsien, and Liqun Luo
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
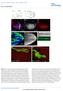 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2806 Supplemental Material: Figure S1 Wnt4 PCP phenotypes are not mediated through canonical Wnt signaling. (a-a ) Illustration of wg, dwnt4 and dwnt6 expression patterns in wing (a) and
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2806 Supplemental Material: Figure S1 Wnt4 PCP phenotypes are not mediated through canonical Wnt signaling. (a-a ) Illustration of wg, dwnt4 and dwnt6 expression patterns in wing (a) and
Supplemental Data. Hachez et al. Plant Cell (2014) /tpc Suppl. Figure 1A
 Suppl. Figure 1A Suppl. Figure 1B Supplemental Figure 1: Results of the commercial screening of interactants using split ubiquitin technique. (A) Isolated preys (192) using the bait construct pbt3-n- as
Suppl. Figure 1A Suppl. Figure 1B Supplemental Figure 1: Results of the commercial screening of interactants using split ubiquitin technique. (A) Isolated preys (192) using the bait construct pbt3-n- as
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material Supplemental Methods Hepatocyte ploidy analysis Kidney immunostaining Plasma and urine chemistry analysis Plasma and urine amino acid analysis Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure
Supplemental Material Supplemental Methods Hepatocyte ploidy analysis Kidney immunostaining Plasma and urine chemistry analysis Plasma and urine amino acid analysis Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure
