October 24, BIOS 95: Cell Division and Chromosome Dynamics
|
|
|
- Emory Lloyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 October 24, 2008 BIOS 95: Cell Division and Chromosome Dynamics
2 Cancer unregulated cell growth and migration Aneuploidy errors in chromosome segregation and genome maintenance living with an altered genome
3 Aneuploidy can be limited
4 Aneuploidy can Rampant Duplications Translocations
5 Cancer unregulated growth and movement Aneuploidy errors in chromosome segregation and genome maintenance Metastasis cell migration and ignoring cues leaving home without a forwarding address
6 Shape and proximity Love the neighbor Not so close
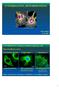
7 Wildtype cells Tumor cells Scratch test Time Tumor cells Show Increased mobility Zhu et al 2004
8 Chromosome Segregation and Cell Migration A. Chromosome segregation - Main points: 1.The essential blue-print of instructions are contained on chromosomes (you have 2 sets of 23 and you need them ALL) 2. Before a cell divides into two the cells must copy each chromosome to obtain to identical sets 3. Cell division is the process by which the chromosomes (and later cell volume) are separated 4. Chromosome segregation requires structural elements, mechanical forces and geometry
9 Phases in the life of a cell and in making another cell Chromosome segregation
10 Chromosome segregation M G2 G1 S DNA Replication
11 Simple scopes - mitosis
12 Polarization scope Inoue et al 1995
13 Fibers required to move chromosomes Inoue et al 1995
14 Cytoskeleton: actin - cell surface shape, cell migration microtubules - internal organelle trafficking, chromosome segregation intermediate filaments - mechanical strength, resist shear
15 The soluble subunit Tubulin (that makes up Microtubules) is really two proteins tightly bound together ALL OF THE TIME Tubulin = heterodimer PEANUT
16 Tubulin heterodimers associate head-to-tail (like actin) but aggregate as 13 protofilaments into a hollow cylinder!
17 The 25 nm cylinder is strong - resists bending and compression Tubulin subunits are distinct β α because of head-to-tail assembly microtubule also has polarity β subunit end α subunit end
18 Addition promotes hydrolysis of underlying tubulin
19 Why microtubules Are not like Rock candy crystals At steady state (no net change in polymer) EACH microtubule randomly switches between growth and shortening -> Dynamic Instability
20 Microtubule plus-ends exhibit Dynamic Instability Random loss/gain of tubulin GTP cap
21 Biochemistry Identifying Mt-associated proteins
22
23 Microtubule tip (plus-end) binding proteins EB1 and Green Fluorescence Protein
24 Microtubule ends are dynamic lattice relatively immobile
25 Microtubules exhibit different rates of catastrophe and rescue throughout the cell cycle
26 Review #1 Microtubules are hollow cylinders made up of tubulin subunits Microtubule ends are biochemically different Microtubules exhibit Dynamic Instability the plus-end (β-tubulin end) randomly switches between growth and shortening Cells regulate microtubule dynamics throughout cell cycle
27 Microtubules are the railway of the cell squid axoplasm...
28
29 Microtubules generate railway system Railway is polarized Melanocyte in + Melanocyte out
30 Microtubules generate railway system Railway is polarized... Melanocyte in + Melanocyte out
31 Polarized railway... You go to the plus-end, and I ll go to the minus-end: Opposing motors
32 Microtubules are nucleated AND organized by the centrosome Notice polarized array
33 Microtubules exhibit dynamic instability plus-ends randomly switching between growth and shortening minus-ends are tethered to a pole foci Nucleation - single site
34
35 Review #2 Microtubules generate a railway system in the cell Microtubules are nucleated from centrosomes Centrosomes seed microtubule growth so that a polarized array is formed β-end (plus-end) points to cell periphery Motors transport cargo along microtubules Kinesins are dedicated plus-end directed motors Dyneins are dedicated minus-end directed motors
36 Cell division Re-organization of the microtubule railway into two polar arrays oppositely oriented Chromosomes capture microtubule ends
37
38 Pericentriolar material (not centrioles) nucleates Microtubules requires a specialized tubulin seed
39 During S-phase, centrosomes duplicate Two sets of polarized Microtubules arrays
40 Two sets of polarized Microtubules arrays Kinesins help Drive poles apart + + Anti-parallel arrays and kinesin complexes
41 Just prior to mitosis entry duplicated chromosomes condense plate of spaghetti model
42 Prophase -> Nuclear Envelope Breakdown -> Prometaphase Cytoplasmic microtubules can now be captured by chromosomes
43
44 Microtubules captured by discrete protein complexes on each Sister chromatids Skibbens et al
45 Centrosomes Microtubules Pulling Forces Kinetochores - protein complex assembled onto centromere DNA Microtubule capturing complex
CHAPTER 16 THE CYTOSKELETON
 CHAPTER 16 THE CYTOSKELETON THE SELF-ASSEMBLY AND DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF CYTOSKELETAL FILAMENTS HOW CELLS REGULATE THEIR CYTOSKELETAL FILAMENTS MOLECULAR MOTORS THE CYTOSKELETON AND CELL BEHAVIOR THE SELF-ASSEMBLY
CHAPTER 16 THE CYTOSKELETON THE SELF-ASSEMBLY AND DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF CYTOSKELETAL FILAMENTS HOW CELLS REGULATE THEIR CYTOSKELETAL FILAMENTS MOLECULAR MOTORS THE CYTOSKELETON AND CELL BEHAVIOR THE SELF-ASSEMBLY
Cell cycle oscillations
 Positive and negative feedback produce a cell cycle Fast Slow Cell cycle oscillations Active Cdk1-Cyclin Inactive Cdk1-Cyclin Active APC 1 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis Glycine Isopeptide bond Lysine
Positive and negative feedback produce a cell cycle Fast Slow Cell cycle oscillations Active Cdk1-Cyclin Inactive Cdk1-Cyclin Active APC 1 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis Glycine Isopeptide bond Lysine
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH CYTOSKELETON AND CELL MOVEMENT.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF THE CYTOSKELETON The cytoskeleton is an intricate of protein filaments that extend throughout the cytoplasm It is a highly organized and dynamic structure (constantly
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF THE CYTOSKELETON The cytoskeleton is an intricate of protein filaments that extend throughout the cytoplasm It is a highly organized and dynamic structure (constantly
MCBII. Points this page
 1. What makes intermediate filaments (IFs) an inefficient track for motor proteins (4 pts)? A. The outer surface of IFs is hydrophobic. B. IFs are nonpolar structures. C. IFs contain coiled coil domains.
1. What makes intermediate filaments (IFs) an inefficient track for motor proteins (4 pts)? A. The outer surface of IFs is hydrophobic. B. IFs are nonpolar structures. C. IFs contain coiled coil domains.
Section 10. Junaid Malek, M.D.
 Section 10 Junaid Malek, M.D. Cell Division Make sure you understand: How do cells know when to divide? (What drives the cell cycle? Why is it important to regulate this?) How is DNA replication regulated?
Section 10 Junaid Malek, M.D. Cell Division Make sure you understand: How do cells know when to divide? (What drives the cell cycle? Why is it important to regulate this?) How is DNA replication regulated?
cell fusion live and fixed imaging genetics biochemistry in vitro systems inhibitors of cellular processes (transcription, replication, microtubules)
 DISCUSSION SECTIONS BY STUDENT NUMBER ENDING IN ODD NUMBERS 2-3, EVEN 3-4 Methods for Studying the Cell Cycle cell fusion live and fixed imaging genetics biochemistry in vitro systems inhibitors of cellular
DISCUSSION SECTIONS BY STUDENT NUMBER ENDING IN ODD NUMBERS 2-3, EVEN 3-4 Methods for Studying the Cell Cycle cell fusion live and fixed imaging genetics biochemistry in vitro systems inhibitors of cellular
Practice Exam 3 MCBII
 1. Which is not a feature of lamin intermediate filaments (IFs)? (4 pts) A. They are protein polymers. B. They are used by motor proteins to traffic cargo. C. They contain coiled coil domains. D. They
1. Which is not a feature of lamin intermediate filaments (IFs)? (4 pts) A. They are protein polymers. B. They are used by motor proteins to traffic cargo. C. They contain coiled coil domains. D. They
Development Team. Molecular Cell Biology Cytoskeleton ZOOLOGY. Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi
 Paper No. : 15 Module : 11 Development Team Principal Investigator: Prof. Neeta Sehgal Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Paper Coordinator: Prof. S. Basu Modak Department of Zoology, University
Paper No. : 15 Module : 11 Development Team Principal Investigator: Prof. Neeta Sehgal Head, Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Paper Coordinator: Prof. S. Basu Modak Department of Zoology, University
Lecture 13. Motor Proteins I
 Lecture 13 Motor Proteins I Introduction: The study of motor proteins has become a major focus in cell and molecular biology. Motor proteins are very interesting because they do what no man-made engines
Lecture 13 Motor Proteins I Introduction: The study of motor proteins has become a major focus in cell and molecular biology. Motor proteins are very interesting because they do what no man-made engines
Prof. R. V. Skibbens. Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 18, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer 4 Stages of the cell cycle: Genome segregation Interphase DNA Microtubules Microtubules
Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 18, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer 4 Stages of the cell cycle: Genome segregation Interphase DNA Microtubules Microtubules
Biophysics of Molecules
 Biophysics of Molecules Cytoskeletal filaments, Actin polymerization and Actin Treadmilling Part 2 (26.11.2012) Dr. Carsten Grashoff MPI of Biochemistry E-mail: cgrasho@biochem.mpg.de Lecture Outline The
Biophysics of Molecules Cytoskeletal filaments, Actin polymerization and Actin Treadmilling Part 2 (26.11.2012) Dr. Carsten Grashoff MPI of Biochemistry E-mail: cgrasho@biochem.mpg.de Lecture Outline The
Microtubules. Forms a sheet of protofilaments that folds to a tube Both tubulins bind GTP
 Microtubules Polymerize from a-tubulin/ß-tubulin dimers Hollow tube of 13 protofilaments In vitro- filament number varies In vivo- always 13 protofilaments Forms a sheet of protofilaments that folds to
Microtubules Polymerize from a-tubulin/ß-tubulin dimers Hollow tube of 13 protofilaments In vitro- filament number varies In vivo- always 13 protofilaments Forms a sheet of protofilaments that folds to
System of protein filaments in the cytoplasm of. eukaryotic cell that gives the cell shape and capacity for
 Cytoskeleton System of protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cell that gives the cell shape and capacity for directed movement. The protein filaments are responsible for the shaping, moving,
Cytoskeleton System of protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cell that gives the cell shape and capacity for directed movement. The protein filaments are responsible for the shaping, moving,
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only) I. Protein Synthesis: creation of new proteins a. Much of the cellular machinery is devoted to synthesizing
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only) I. Protein Synthesis: creation of new proteins a. Much of the cellular machinery is devoted to synthesizing
1. The microtubule wall is composed of globular proteins arranged in longitudinal rows called.
 Name: Quiz name: Quiz 7 ate: 1. The microtubule wall is composed of globular proteins arranged in longitudinal rows called. microfilaments protofilaments prototubules microtubular subunits 2. Which of
Name: Quiz name: Quiz 7 ate: 1. The microtubule wall is composed of globular proteins arranged in longitudinal rows called. microfilaments protofilaments prototubules microtubular subunits 2. Which of
Chapter 17. Microtubules. Chapter 17. Microtubules. Chapter 17. Microtubules. Chapter 17. Microtubules. Chapter 17. Microtubules
 Chapter 15. Mechanism of Vesicle Formation A reminder: two things I said that we should to keep an eye on for each of the components of the cytoskeleton: The role of polymerization and depolymerization
Chapter 15. Mechanism of Vesicle Formation A reminder: two things I said that we should to keep an eye on for each of the components of the cytoskeleton: The role of polymerization and depolymerization
Golgi are located near the MTOC while the ER is spread throughout the cytoplasm, so which of the following is probably true?
 Golgi are located near the MTOC while the ER is spread throughout the cytoplasm, so which of the following is probably true? A. COPII and COPI vesicles are transported with dynein. B. COPII and COPI vesicles
Golgi are located near the MTOC while the ER is spread throughout the cytoplasm, so which of the following is probably true? A. COPII and COPI vesicles are transported with dynein. B. COPII and COPI vesicles
Chapter 15. Cytoskeletal Systems. Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Cytoskeletal Systems Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Table 15-1 - Microtubules Table 15-1 - Microfilaments Table 15-1 Intermediate Filaments Table 15-3 Microtubules
Chapter 15 Cytoskeletal Systems Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Table 15-1 - Microtubules Table 15-1 - Microfilaments Table 15-1 Intermediate Filaments Table 15-3 Microtubules
1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle.
 Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
CYTOSKELETON, MOTORPROTEINS.
 CYTOSKELETON, MOTORPROTEINS. SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY Tamás Huber 15. 10. 2012. CYTOSKELETON: Dynamic scaffold in eukaryotic cells Three main filament systems: A. Intermediate filaments B. Microtubules C.
CYTOSKELETON, MOTORPROTEINS. SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY Tamás Huber 15. 10. 2012. CYTOSKELETON: Dynamic scaffold in eukaryotic cells Three main filament systems: A. Intermediate filaments B. Microtubules C.
Mathematical Modeling of Dynamic Instability in Microtubules
 Mathematical Modeling of Dynamic Instability in Microtubules Christine Lucille Kuryla 2013 NSF/REU Program Department of Physics, University of Notre Dame Advisors: Mark Alber, Dept. of Applied and Computational
Mathematical Modeling of Dynamic Instability in Microtubules Christine Lucille Kuryla 2013 NSF/REU Program Department of Physics, University of Notre Dame Advisors: Mark Alber, Dept. of Applied and Computational
Three major types of cytoskeleton
 The Cytoskeleton Organizes and stabilizes cells Pulls chromosomes apart Drives intracellular traffic Supports plasma membrane and nuclear envelope Enables cellular movement Guides growth of the plant cell
The Cytoskeleton Organizes and stabilizes cells Pulls chromosomes apart Drives intracellular traffic Supports plasma membrane and nuclear envelope Enables cellular movement Guides growth of the plant cell
Leen hajeer. Odai Bani-Monia. Diala abu-hassan
 17 Leen hajeer Odai Bani-Monia Diala abu-hassan We talked last time about actin filaments as a component of the cytoskeleton. In this sheet we are going to talk about second component which is: Microtubules
17 Leen hajeer Odai Bani-Monia Diala abu-hassan We talked last time about actin filaments as a component of the cytoskeleton. In this sheet we are going to talk about second component which is: Microtubules
Chapter 3. DNA Replication & The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 3 DNA Replication & The Cell Cycle DNA Replication and the Cell Cycle Before cells divide, they must duplicate their DNA // the genetic material DNA is organized into strands called chromosomes
Chapter 3 DNA Replication & The Cell Cycle DNA Replication and the Cell Cycle Before cells divide, they must duplicate their DNA // the genetic material DNA is organized into strands called chromosomes
Kinesin motors in the transport along microtubules. Dynein Motor
 Molecular Cell Biology Autumn 2014, Michael Pavlov Based on Chapter 17 and 18.(1-4), MCB book Lecture 9: Cytoskeleton Microtubules: Tubulin Structure of tubulin dimer and organization of tubulin dimers
Molecular Cell Biology Autumn 2014, Michael Pavlov Based on Chapter 17 and 18.(1-4), MCB book Lecture 9: Cytoskeleton Microtubules: Tubulin Structure of tubulin dimer and organization of tubulin dimers
The cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton, the motor proteins, the muscle and its regulation. The cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton.
 , the motor proteins, the muscle and its regulation Dept. of Biophysics, University of Pécs Zoltán Ujfalusi January-February 2012 Dynamic framework of the Eukaryotes Three main filament-class: 1. Intermedier
, the motor proteins, the muscle and its regulation Dept. of Biophysics, University of Pécs Zoltán Ujfalusi January-February 2012 Dynamic framework of the Eukaryotes Three main filament-class: 1. Intermedier
1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle.
 Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Cell cycle oscillations. Active Cdk1-Cyclin Inactive Cdk1-Cyclin Active APC
 Cell cycle oscillations Active Cdk1-Cyclin Inactive Cdk1-Cyclin Active APC 20 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis Glycine Isopeptide bond Lysine Many biological processes are regulated by controlling the stability
Cell cycle oscillations Active Cdk1-Cyclin Inactive Cdk1-Cyclin Active APC 20 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis Glycine Isopeptide bond Lysine Many biological processes are regulated by controlling the stability
BME Engineering Molecular Cell Biology. The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament
 BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 09: The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament BME42-620 Lecture 09, September 27, 2011 1 Outline Overviewofcytoskeletal
BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 09: The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament BME42-620 Lecture 09, September 27, 2011 1 Outline Overviewofcytoskeletal
Microtubule Cytoskeleton and Cell Patterning
 Microtubule Cytoskeleton and Cell Patterning 10:00 Anna Akhmanova Microtubule Dynamics 11:00 Lukas Kapitein Motors and Transport 12:00 12:30 Microscopy Facility Tour 13:00-14:30 Lunch and Self-study Jacobson
Microtubule Cytoskeleton and Cell Patterning 10:00 Anna Akhmanova Microtubule Dynamics 11:00 Lukas Kapitein Motors and Transport 12:00 12:30 Microscopy Facility Tour 13:00-14:30 Lunch and Self-study Jacobson
C. Incorrect! Second Law: Law of Independent Assortment - Genes for different traits sort independently of one another in the formation of gametes.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 20: Chromosomes and Genetic Technology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed, (3) Pick
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 20: Chromosomes and Genetic Technology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed, (3) Pick
Cytoskeleton. B. Balen
 Cytoskeleton B. Balen structural backbone of the cell supports the fragile plasma membrane provides mechanical linkages that let the cell bear stresses without being ripped apart Importance and function
Cytoskeleton B. Balen structural backbone of the cell supports the fragile plasma membrane provides mechanical linkages that let the cell bear stresses without being ripped apart Importance and function
me239 mechanics of the cell homework biopolymers - motivation 3.1 biopolymers - motivation 3. biopolymers biopolymers biopolymers
 3. biopolymers the inner life of a cell, viel & lue, harvard [2006] me239 mechanics of the cell 1 2 biopolymers Figure 3.1. Biopolymers. Characteristic length scales on the cellular and sucellular level..
3. biopolymers the inner life of a cell, viel & lue, harvard [2006] me239 mechanics of the cell 1 2 biopolymers Figure 3.1. Biopolymers. Characteristic length scales on the cellular and sucellular level..
The cytoskeletal system
 The cytoskeletal system Types, polymerization, characteristics and mechanical properties of cytoskeletal filaments. Associated protein. 24.09.2013. Cytoskeleton The cellular "scaffold" or "skeleton" within
The cytoskeletal system Types, polymerization, characteristics and mechanical properties of cytoskeletal filaments. Associated protein. 24.09.2013. Cytoskeleton The cellular "scaffold" or "skeleton" within
DNA is the genetic material found in cells Stands for: Deoxyribonucleic Acid Is made up of repeating nucleic acids It s the Unit of Heredity
 What is DNA? DNA is the genetic material found in cells Stands for: Deoxyribonucleic Acid Is made up of repeating nucleic acids It s the Unit of Heredity DNA is found in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and
What is DNA? DNA is the genetic material found in cells Stands for: Deoxyribonucleic Acid Is made up of repeating nucleic acids It s the Unit of Heredity DNA is found in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and
1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA. (from readings, class, TV?)
 1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA (from readings, class, TV?) Before we begin, let s investigate the way DNA molecules are set up! http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/molec ules/builddna/
1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA (from readings, class, TV?) Before we begin, let s investigate the way DNA molecules are set up! http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/molec ules/builddna/
1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA. (from readings, class, TV?)
 1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA (from readings, class, TV?) Before we begin, let s investigate the way DNA molecules are set up! http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/molec ules/builddna/
1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA (from readings, class, TV?) Before we begin, let s investigate the way DNA molecules are set up! http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/molec ules/builddna/
Vocab Word 1: Interphase
 Vocab Word 1: Interphase Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which a typical cell spends most of its life. During this phase, the cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis. Interphase is
Vocab Word 1: Interphase Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which a typical cell spends most of its life. During this phase, the cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis. Interphase is
1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA. (from readings, class, TV?)
 1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA (from readings, class, TV?) Before we begin, let s investigate the way DNA molecules are set up! http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/molec ules/builddna/
1. What is DNA? 2. List anything you know about DNA (from readings, class, TV?) Before we begin, let s investigate the way DNA molecules are set up! http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/molec ules/builddna/
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 2 SI What is the function of the histone proteins that are part of DNA structure?
 BIOL 2457 HPER 3 Part 2 SI 1 1. What is the function of the histone proteins that are part of DN structure? 2. In transcription, acts as a template for synthesis. fter helicase unzips DN, what enzyme adds
BIOL 2457 HPER 3 Part 2 SI 1 1. What is the function of the histone proteins that are part of DN structure? 2. In transcription, acts as a template for synthesis. fter helicase unzips DN, what enzyme adds
Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section B and ONE question from Section C.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-18 CELL BIOLOGY BIO-5005B Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-18 CELL BIOLOGY BIO-5005B Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section
- ex. polarized epithelial cells: certain organelles are arranged in defined order from apical to basal end of cell
 THE CYTOSKELETON - vertebrates: skeleton ; eukaryotic cells: cytoskeleton (analogous) - consists of hardened elements that support soft tissues of body - mediates bodily movements - 3 elements of cytoskeleton
THE CYTOSKELETON - vertebrates: skeleton ; eukaryotic cells: cytoskeleton (analogous) - consists of hardened elements that support soft tissues of body - mediates bodily movements - 3 elements of cytoskeleton
CELLULAR PROCESSES; REPRODUCTION. Unit 5
 CELLULAR PROCESSES; REPRODUCTION Unit 5 Cell Cycle Chromosomes and their make up Crossover Cytokines Diploid (haploid diploid and karyotypes) Mitosis Meiosis What is Cancer? Somatic Cells THE CELL CYCLE
CELLULAR PROCESSES; REPRODUCTION Unit 5 Cell Cycle Chromosomes and their make up Crossover Cytokines Diploid (haploid diploid and karyotypes) Mitosis Meiosis What is Cancer? Somatic Cells THE CELL CYCLE
Cells and Their Housekeeping Functions Nucleus and Other Organelles
 Cells and Their Housekeeping Functions Nucleus and Other Organelles Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/
Cells and Their Housekeeping Functions Nucleus and Other Organelles Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/
Design Principles of Length Control of Cytoskeletal Structures
 Design Principles of Length Control of Cytoskeletal Structures Lishibanya Mohapatra 1, Bruce L. Goode 2, Predrag Jelenkovic 3, Rob Phillips 4, Jane Kondev 5,* 1 Department of Physics, Brandeis University,
Design Principles of Length Control of Cytoskeletal Structures Lishibanya Mohapatra 1, Bruce L. Goode 2, Predrag Jelenkovic 3, Rob Phillips 4, Jane Kondev 5,* 1 Department of Physics, Brandeis University,
Nano-Scale Engineering III Bio-Molecular Motors for Engineering
 Nano-Scale Engineering III Bio-Molecular Motors for Engineering Y. C. Lee Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Colorado Boulder, CO 80309-0427 leeyc@colorado.edu March 4, 2014 1 MLD of Hybrid
Nano-Scale Engineering III Bio-Molecular Motors for Engineering Y. C. Lee Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Colorado Boulder, CO 80309-0427 leeyc@colorado.edu March 4, 2014 1 MLD of Hybrid
Unit 4 Information NUCLEIC ACIDS DNA GENES DOUBLE HELIX REPLICATION MITOSIS
 Unit 4 Information NUCLEIC ACIDS DNA GENES DOUBLE HELIX REPLICATION MITOSIS 1/2/2018 Bell Work What is a Gene? Genes as Medicine As you watch the film, complete the questions on the film guide. When you
Unit 4 Information NUCLEIC ACIDS DNA GENES DOUBLE HELIX REPLICATION MITOSIS 1/2/2018 Bell Work What is a Gene? Genes as Medicine As you watch the film, complete the questions on the film guide. When you
These molecules make up the ladder of the DNA Bound by weak hydrogen bonds. 4 Different Types (2 specific matches) look at the
 B.A.T. Review DNA & Cell Cycle Test is 11/3/16 NAME: PERIOD DNA STRUCTURE VOCABULARY Mitosis Chromosomes Interphase G1,S,G2,M Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis Cleavage Furrow Spindle Fibers
B.A.T. Review DNA & Cell Cycle Test is 11/3/16 NAME: PERIOD DNA STRUCTURE VOCABULARY Mitosis Chromosomes Interphase G1,S,G2,M Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis Cleavage Furrow Spindle Fibers
EFFECTS OF CYSTEINE MODIFICATION ON MICROTUBULE-MOTOR FUNCTION AND TUBULIN ASSEMBLY. by Kalmia Kniel Phelps
 EFFECTS OF CYSTEINE MODIFICATION ON MICROTUBULE-MOTOR FUNCTION AND TUBULIN ASSEMBLY by Kalmia Kniel Phelps Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in
EFFECTS OF CYSTEINE MODIFICATION ON MICROTUBULE-MOTOR FUNCTION AND TUBULIN ASSEMBLY by Kalmia Kniel Phelps Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in
Modeling cytoskeleton self-assembly
 Modeling cytoskeleton self-assembly Dimitrios Vavylonis Department of Physics, Lehigh University BIOS 10 Lehigh University Oct 30, 2009 Cell organization How does the cell achieve internal organization?
Modeling cytoskeleton self-assembly Dimitrios Vavylonis Department of Physics, Lehigh University BIOS 10 Lehigh University Oct 30, 2009 Cell organization How does the cell achieve internal organization?
Y1 Biology 131 Syllabus - Academic Year
 Y1 Biology 131 Syllabus - Academic Year 2016-2017 Monday 28/11/2016 DNA Packaging Week 11 Tuesday 29/11/2016 Regulation of gene expression Wednesday 22/9/2014 Cell cycle Sunday 4/12/2016 Tutorial Monday
Y1 Biology 131 Syllabus - Academic Year 2016-2017 Monday 28/11/2016 DNA Packaging Week 11 Tuesday 29/11/2016 Regulation of gene expression Wednesday 22/9/2014 Cell cycle Sunday 4/12/2016 Tutorial Monday
DNA STRUCTURE. Nucleotides: Nitrogenous Bases (Carry the Genetic Code) Expectation Sheet: DNA & Cell Cycle. I can statements: Basic Information:
 Expectation Sheet: DNA & Cell Cycle NAME: Test is 11/8/17 I can statements: I can discuss how DNA is found in all organisms and that the structure is common to all living things. I can diagram and label
Expectation Sheet: DNA & Cell Cycle NAME: Test is 11/8/17 I can statements: I can discuss how DNA is found in all organisms and that the structure is common to all living things. I can diagram and label
NUCLEUS. Fig. 2. Various stages in the condensation of chromatin
 NUCLEUS Animal cells contain DNA in nucleus (contains ~ 98% of cell DNA) and mitochondrion. Both compartments are surrounded by an envelope (double membrane). Nuclear DNA represents some linear molecules
NUCLEUS Animal cells contain DNA in nucleus (contains ~ 98% of cell DNA) and mitochondrion. Both compartments are surrounded by an envelope (double membrane). Nuclear DNA represents some linear molecules
DNA and GENETICS UNIT NOTES
 DNA and GENETICS UNIT NOTES NAME: DO NOT LOSE! DNA DNA - Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid Shape is called double helix DNA has the information for our cells to make proteins. DNA through transcription makes mrna
DNA and GENETICS UNIT NOTES NAME: DO NOT LOSE! DNA DNA - Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid Shape is called double helix DNA has the information for our cells to make proteins. DNA through transcription makes mrna
The Cell Cycle. Study Guide: Cell Division and DNA Structure
 A. Review Materials 1. Text: Chapter 2, section 3. 2. EOS questions: cell division and DNA (online) 3. Any videos linked from the website 4. Labs: review conclusions and notes (DNA Candy, Flipbooks, Scum)
A. Review Materials 1. Text: Chapter 2, section 3. 2. EOS questions: cell division and DNA (online) 3. Any videos linked from the website 4. Labs: review conclusions and notes (DNA Candy, Flipbooks, Scum)
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1. Questions & Answers
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 1.1 In a DNA double helix each type of base forms a stable base pair with only one type of base. When
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 1.1 In a DNA double helix each type of base forms a stable base pair with only one type of base. When
In Chapter 19, we looked at microfilaments and intermediate MICROTUBULES
 20 MICROTUBULES A 3-second time lapse movie captures the kinesin-powered movement of a vesicle along a microtubule. [From N. Pollack et al., 1999, J. Cell Biol. 147:493 506; courtesy of R. D. Vale.] In
20 MICROTUBULES A 3-second time lapse movie captures the kinesin-powered movement of a vesicle along a microtubule. [From N. Pollack et al., 1999, J. Cell Biol. 147:493 506; courtesy of R. D. Vale.] In
Chapter 17. Molecular Motors. to accompany Biochemistry, 2/e by Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham. Biochemistry 2/e - Garrett & Grisham
 Chapter 17 Molecular Motors to accompany Biochemistry, 2/e by Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:
Chapter 17 Molecular Motors to accompany Biochemistry, 2/e by Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:
UNIT 3: CELL REPRODUCTION
 UNIT 3: CELL REPRODUCTION What are Chromosomes? Cell structures that contain genetic material. Where are they found? Found inside a cell, inside the nucleus. VOCABULARY Somatic cells (body cells) Sex cells
UNIT 3: CELL REPRODUCTION What are Chromosomes? Cell structures that contain genetic material. Where are they found? Found inside a cell, inside the nucleus. VOCABULARY Somatic cells (body cells) Sex cells
Introduction to Medical Genetics: Human Chromosome
 Introduction to Medical Genetics: Human Chromosome Ashley Soosay This OpenCourseWare@UNIMAS and its related course materials are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike 4.0
Introduction to Medical Genetics: Human Chromosome Ashley Soosay This OpenCourseWare@UNIMAS and its related course materials are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike 4.0
Bio Study Guide. What is the structure of a DNA. A nitrogen base (ATCG/AUCG) connected to a sugar and a phosphate. nucleotide?
 What are nucleic acids? The largest organic molecules. Master organisms, they are in control of cell functions. They are found in all living organisms, and they are two types of them- DNA and RNA. They
What are nucleic acids? The largest organic molecules. Master organisms, they are in control of cell functions. They are found in all living organisms, and they are two types of them- DNA and RNA. They
Cell cycle: Cell growth and division (when the replication and segregation of chromosomes occurs). Interphase: Interphase Chromosomes
 Chromosomes exist in different states throughout the life of a cell Cell cycle: Cell growth and division (when the replication and segregation of chromosomes occurs). Interphase: Interphase Chromosomes
Chromosomes exist in different states throughout the life of a cell Cell cycle: Cell growth and division (when the replication and segregation of chromosomes occurs). Interphase: Interphase Chromosomes
EXAMINATION IN MOL4010 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY FOR TECHNOLOGISTS
 Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Biology EXAMINATION IN MOL4010 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY FOR TECHNOLOGISTS Responsible contact during examination: Berit Johansen Phone: 91897000 Date
Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Biology EXAMINATION IN MOL4010 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY FOR TECHNOLOGISTS Responsible contact during examination: Berit Johansen Phone: 91897000 Date
Epigenetics in. Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chapter 4 2/4/14
 Epigenetics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Chapter 4 2/4/14 The budding yeast - Saccharomyces cerevisiae The fission yeast - Schizosaccharomyces pombe The budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the fission
Epigenetics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Chapter 4 2/4/14 The budding yeast - Saccharomyces cerevisiae The fission yeast - Schizosaccharomyces pombe The budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the fission
Cell cycle. Chen Li. Department of cellular and genetic medicine
 Cell cycle Chen Li Department of cellular and genetic medicine 13 223 chenli2008@fudan.edu.cn Outline A. Historical background B. Phases of cell cycle C. DNA replication D. Telomere & telomerase E. DNA
Cell cycle Chen Li Department of cellular and genetic medicine 13 223 chenli2008@fudan.edu.cn Outline A. Historical background B. Phases of cell cycle C. DNA replication D. Telomere & telomerase E. DNA
Cell Division. Use Target Reading Skills. This section explains how cells grow and divide.
 Name Date Class Cell Processes Guided Reading and Study Cell Division This section explains how cells grow and divide. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, make a cycle diagram that shows the events
Name Date Class Cell Processes Guided Reading and Study Cell Division This section explains how cells grow and divide. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, make a cycle diagram that shows the events
Answers will be posted on WebCT on October 22. Which of the following images of chromosomes was made by fluorescence light microscopy?
 October 2007 Biology 022 Sample Questions Page 1 of 7 This is not a practice test ; these questions illustrate the style of questions used in Biology 022 but do not necessarily reflect the expectations
October 2007 Biology 022 Sample Questions Page 1 of 7 This is not a practice test ; these questions illustrate the style of questions used in Biology 022 but do not necessarily reflect the expectations
Topic 11 Introduction to the Cytoskeleton and Actin
 BIOL 201 Cell Biology and Metabolism C. Aikins Notes II: Topic 11-15 (Cell Cycle) Winter 2011 Topic 11 Introduction to the Cytoskeleton and Actin Overview Cells come in many shapes Ex. muscle cells are
BIOL 201 Cell Biology and Metabolism C. Aikins Notes II: Topic 11-15 (Cell Cycle) Winter 2011 Topic 11 Introduction to the Cytoskeleton and Actin Overview Cells come in many shapes Ex. muscle cells are
Dynamics of Mitotic Microtubules in Fission Yeast
 University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Undergraduate Honors Theses Honors Program Spring 2017 Dynamics of Mitotic Microtubules in Fission Yeast Patrick Flynn pafl9640@colorado.edu Follow this and additional
University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Undergraduate Honors Theses Honors Program Spring 2017 Dynamics of Mitotic Microtubules in Fission Yeast Patrick Flynn pafl9640@colorado.edu Follow this and additional
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2996
 Supplementary Figure 1 Negative-stain EM of native cytoplasmic dynein. (a) A representative micrograph of negatively stained dynein, with the flexible dimeric molecules circled in white. (b) Reference-free
Supplementary Figure 1 Negative-stain EM of native cytoplasmic dynein. (a) A representative micrograph of negatively stained dynein, with the flexible dimeric molecules circled in white. (b) Reference-free
Cell Cycle. Trends in Cell Biology
 Cell Cycle Trends in Cell Biology Cyclic proteolysis Two distinct enzyme complexes proteolysis of cyclin-cdk complexes SCF (Skp1-Cul1-F box) Ubiquitylation and destruction of G1/S-cyclins and CKI proteins
Cell Cycle Trends in Cell Biology Cyclic proteolysis Two distinct enzyme complexes proteolysis of cyclin-cdk complexes SCF (Skp1-Cul1-F box) Ubiquitylation and destruction of G1/S-cyclins and CKI proteins
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SIXTH EDITION. CHAPTER 18 Cell Organization and Movement II: Microtubules and Intermediate Filaments
 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger Scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SIXTH EDITION CHAPTER 18 Cell Organization and Movement II: Microtubules and Intermediate Filaments 2008 W. H. Freeman
Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger Scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SIXTH EDITION CHAPTER 18 Cell Organization and Movement II: Microtubules and Intermediate Filaments 2008 W. H. Freeman
Movement at the Molecular Level
 Movement at the Molecular Level Diffusion: = 6 D t (D 6 π µ a) Typical numbers: 10 nm protein in water D= 10-10 m 2 /s.in cells D= 10-12 m 2 /s (D= 10-14 m 2 /s lipids) [] 1/2 =1 µm, t ~0.2
Movement at the Molecular Level Diffusion: = 6 D t (D 6 π µ a) Typical numbers: 10 nm protein in water D= 10-10 m 2 /s.in cells D= 10-12 m 2 /s (D= 10-14 m 2 /s lipids) [] 1/2 =1 µm, t ~0.2
Lecture 4 04/12/2018
 Lecture 4 04/12/2018 Communicating cells may be close (local) or far (distant) Local signaling: a chemical signal which communicates between 2 nearby cells. Paracrine signaling: a cell secretes the signal
Lecture 4 04/12/2018 Communicating cells may be close (local) or far (distant) Local signaling: a chemical signal which communicates between 2 nearby cells. Paracrine signaling: a cell secretes the signal
Biosensors. DNA Microarrays (for chemical analysis) Protein Sensors (for identifying viruses)
 Biosensors DNA Microarrays (for chemical analysis) Protein Sensors (for identifying viruses) DNA Microarrays 40 000 detectors in parallel, each detecting a specific DNA sequence. Combinatorial Chemistry
Biosensors DNA Microarrays (for chemical analysis) Protein Sensors (for identifying viruses) DNA Microarrays 40 000 detectors in parallel, each detecting a specific DNA sequence. Combinatorial Chemistry
Cell Division. embryo: an early stage of development in organisms
 Over the past several years, a debate has been brewing over the use of stem cells. Stem cells can be used to treat certain diseases and conditions such as spinal cord injuries, diabetes, arthritis, and
Over the past several years, a debate has been brewing over the use of stem cells. Stem cells can be used to treat certain diseases and conditions such as spinal cord injuries, diabetes, arthritis, and
Microtubule Assembly Dynamics at the Nanoscale
 Microtubule Assembly Dynamics at the Nanoscale Melissa K. Gardner, Henry T. Schek III*, Alan J. Hunt, and David J. Odde Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455
Microtubule Assembly Dynamics at the Nanoscale Melissa K. Gardner, Henry T. Schek III*, Alan J. Hunt, and David J. Odde Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455
Molecular Communication: Simulation of a Molecular Motor Communication System
 Molecular Communication: Simulation of a Molecular Motor Communication System Michael Moore, Akihiro Enomoto, Tadashi Nakano, Tatsuya Suda Department of Computer Science Donald Bren School of Information
Molecular Communication: Simulation of a Molecular Motor Communication System Michael Moore, Akihiro Enomoto, Tadashi Nakano, Tatsuya Suda Department of Computer Science Donald Bren School of Information
ANAT Cell Biology Lecture 6 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales
 ANAT3231 - Cell Biology Lecture 6 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales Dr Thomas Fath Department of Anatomy Room 502 Wallace Wurth Building Email: t.fath@unsw.edu.au Lecture Designed
ANAT3231 - Cell Biology Lecture 6 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales Dr Thomas Fath Department of Anatomy Room 502 Wallace Wurth Building Email: t.fath@unsw.edu.au Lecture Designed
Docking Studies of the Binding Mode of Dictyostatin and Its Analogues to the Taxoid Binding Site on Tubulin
 Docking Studies of the Binding Mode of Dictyostatin and Its Analogues to the Taxoid Binding Site on Tubulin Christopher B. Hackmeyer Spring Hill College Billy W. Day, Ph.D. Department of Pharmaceutical
Docking Studies of the Binding Mode of Dictyostatin and Its Analogues to the Taxoid Binding Site on Tubulin Christopher B. Hackmeyer Spring Hill College Billy W. Day, Ph.D. Department of Pharmaceutical
Cell Nucleus. Chen Li. Department of Cellular and Genetic Medicine
 Cell Nucleus Chen Li Department of Cellular and Genetic Medicine 13 223 chenli2008@fudan.edu.cn Outline A. Historical background B. Structure of the nucleus: nuclear pore complex (NPC), lamina, nucleolus,
Cell Nucleus Chen Li Department of Cellular and Genetic Medicine 13 223 chenli2008@fudan.edu.cn Outline A. Historical background B. Structure of the nucleus: nuclear pore complex (NPC), lamina, nucleolus,
7.06 Problem Set Four, 2006
 7.06 Problem Set Four, 2006 1. Explain the molecular mechanism behind each of the following events that occur during the cell cycle, making sure to discuss specific proteins that are involved in making
7.06 Problem Set Four, 2006 1. Explain the molecular mechanism behind each of the following events that occur during the cell cycle, making sure to discuss specific proteins that are involved in making
Molecular Cell Biology
 Molecular Cell Biology Biophysics of Helical Polymers Intermediate Filaments Michael Greenberg Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics greenberg@biochem.wustl.edu Intermediate Filaments Diversity
Molecular Cell Biology Biophysics of Helical Polymers Intermediate Filaments Michael Greenberg Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics greenberg@biochem.wustl.edu Intermediate Filaments Diversity
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 06: Genes and Chromosomes
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 06: Genes and Chromosomes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about genes is correct? Question #1 (A) Genes carry the information for protein
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 06: Genes and Chromosomes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about genes is correct? Question #1 (A) Genes carry the information for protein
Page 1. Name: 1) Which letter indicates a cell structure that directly controls the movement of molecules into and out of the cell?
 Name: 1) Which letter indicates a cell structure that directly controls the movement of molecules into and out of the cell? A) A B) B C) C D) D 2) A single-celled organism is represented in the diagram
Name: 1) Which letter indicates a cell structure that directly controls the movement of molecules into and out of the cell? A) A B) B C) C D) D 2) A single-celled organism is represented in the diagram
1. Carry the microscope in an upright position with both hands and place the base of the microscope 5cm from the edge of the bench
 The Microscope Operating the compound light microscope 1. Carry the microscope in an upright position with both hands and place the base of the microscope 5cm from the edge of the bench 2. Check that lenses
The Microscope Operating the compound light microscope 1. Carry the microscope in an upright position with both hands and place the base of the microscope 5cm from the edge of the bench 2. Check that lenses
DNA, Cell Cycles and Genetics! Mrs. Stahl Biology
 DNA, Cell Cycles and Genetics! Mrs. Stahl Biology Let s Think!!!! What does DNA stand for? Where is DNA located in the cell? What is DNA to you? Where do we find DNA? 1928- Fredrick Griffith s Experiment
DNA, Cell Cycles and Genetics! Mrs. Stahl Biology Let s Think!!!! What does DNA stand for? Where is DNA located in the cell? What is DNA to you? Where do we find DNA? 1928- Fredrick Griffith s Experiment
A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY. Alexei Olegovich Demchouk
 Microtubule Tip Tracking and Tip Structures at the Nanometer Scale Using Digital Fluorescence Microscopy A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Alexei
Microtubule Tip Tracking and Tip Structures at the Nanometer Scale Using Digital Fluorescence Microscopy A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Alexei
Lesson Overview DNA Replication
 12.3 THINK ABOUT IT Before a cell divides, its DNA must first be copied. How might the double-helix structure of DNA make that possible? Copying the Code What role does DNA polymerase play in copying DNA?
12.3 THINK ABOUT IT Before a cell divides, its DNA must first be copied. How might the double-helix structure of DNA make that possible? Copying the Code What role does DNA polymerase play in copying DNA?
MICB688L/MOCB639 Advanced Cell Biology Exam II
 MICB688L/MOCB639 Advanced Cell Biology Exam II May 10, 2001 Name: 1. Briefly describe the four major classes of cell surface receptors and their modes of action (immediate downstream only) (8) 2. Please
MICB688L/MOCB639 Advanced Cell Biology Exam II May 10, 2001 Name: 1. Briefly describe the four major classes of cell surface receptors and their modes of action (immediate downstream only) (8) 2. Please
Unit 4: Cell Development and Replication, Part I: The Cell Cycle
 Name: Block: PACKET #9 Reading: Unit 4: Cell Development and Replication, Part I: The Cell Cycle Objectives: By the conclusion of this unit you will be able to: Date: Introduction to the cell cycle 1.
Name: Block: PACKET #9 Reading: Unit 4: Cell Development and Replication, Part I: The Cell Cycle Objectives: By the conclusion of this unit you will be able to: Date: Introduction to the cell cycle 1.
Biochemistry and Cell Biology
 Biochemistry and Cell Biology Monomersare simple molecules that can be linked into chains. (Nucleotides, Amino acids, monosaccharides) Polymersare the long chains of monomers. (DNA, RNA, Cellulose, Protein,
Biochemistry and Cell Biology Monomersare simple molecules that can be linked into chains. (Nucleotides, Amino acids, monosaccharides) Polymersare the long chains of monomers. (DNA, RNA, Cellulose, Protein,
EFFECT OF MICROTUBULE MOTORS ON MICROTUBULE MECHANICS
 EFFECT OF MICROTUBULE MOTORS ON MICROTUBULE MECHANICS By PARAG S. RANE A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
EFFECT OF MICROTUBULE MOTORS ON MICROTUBULE MECHANICS By PARAG S. RANE A DISSERTATION PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURECELLBIOLOGY 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURECELLBIOLOGY SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURECELLBIOLOGY 3 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURECELLBIOLOGY 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURECELLBIOLOGY SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURECELLBIOLOGY 3 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
Chromosomes. M.Sc. Biotechnology. Hawler Medical University, Iraq
 Chromosomes Bashdar Mahmud Hussen M.Sc. Biotechnology Hawler Medical University, Iraq bashdar@res.hmu.edu.iq bmhscience@yahoo.com History of Chromosome Karl Nagali (1842) E. Russow (1872) first description
Chromosomes Bashdar Mahmud Hussen M.Sc. Biotechnology Hawler Medical University, Iraq bashdar@res.hmu.edu.iq bmhscience@yahoo.com History of Chromosome Karl Nagali (1842) E. Russow (1872) first description
Unit 5 Part B: Day 1 Cell Growth, Division & Reproduction
 Name Test Date Period Unit 5 Part B: Day 1 Cell Growth, Division & Reproduction CELL SIZE LIMITATIONS Cells that are will have diffusing materials through the cell. -,, and must enter cell at an efficient
Name Test Date Period Unit 5 Part B: Day 1 Cell Growth, Division & Reproduction CELL SIZE LIMITATIONS Cells that are will have diffusing materials through the cell. -,, and must enter cell at an efficient
Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section B and ONE question from Section C.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 CELL BIOLOGY BIO-2B06 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 CELL BIOLOGY BIO-2B06 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in
Human Biology 175 Lecture Notes: Cells. Section 1 Introduction
 Human Biology 175 Lecture Notes: Cells Section 1 Introduction A) 1) All organisms are composed of at least one cell. a) Unicellular example: b) Multicellular example(s): 2) All cells are similar in their
Human Biology 175 Lecture Notes: Cells Section 1 Introduction A) 1) All organisms are composed of at least one cell. a) Unicellular example: b) Multicellular example(s): 2) All cells are similar in their
Functional characterization of the mitotic kinesin like protein Kif18A
 Functional characterization of the mitotic kinesin like protein Kif18A Dissertation zur Erlangung des akademischen Grades eines Doktors der Naturwissenschaften (Dr. rer. nat.) des Fachbereiches Biologie
Functional characterization of the mitotic kinesin like protein Kif18A Dissertation zur Erlangung des akademischen Grades eines Doktors der Naturwissenschaften (Dr. rer. nat.) des Fachbereiches Biologie
General Biology 115, Summer 2014 Exam II: Form B June 23, Name Student Number
 General Biology 115, Summer 2014 Exam II: Form B June 23, 2014 Name Student Number For questions 1 2, use the following information. A particular plasmid (pbr322) has two unique gene sequences that confer
General Biology 115, Summer 2014 Exam II: Form B June 23, 2014 Name Student Number For questions 1 2, use the following information. A particular plasmid (pbr322) has two unique gene sequences that confer
