Supplement Figure S1:
|
|
|
- Kellie Kelley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
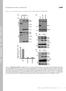
1 Supplement Figure S1: A, Sequence of Xcadherin-11 Morpholino 1 (Xcad-11MO) and 2 (Xcad-11 MO2) and control morpholino in comparison to the Xcadherin-11 sequence. The Xcad-11MO binding sequence spans the start codon while Xcad-11MO2 binds in the 5 UTR. B, Function of Xcad-11MO. The function of the chosen Xcad-11MO was demonstrated by in vitro transcription and translation. The TNT was performed according to manufacturer s description (Promega). For detection of synthesized protein S 35 -labelled methionine was incorporated. The addition of Xcad-11MO to the reaction mix resulted in a strong decrease of detectable protein whereas the addition of control morpholino had no influence (left panel). Xcad-11MO was not able to suppress protein production of murine cadherin-6 or XB-cadherin (right panel). C, Endogenous function of Xcad-11MO and Xcad-11MO2. After injection of 2 pmol Xcad- 11MO and Xcad-11MO2 a strong decrease of protein was detected in embryo lysates in comparison to wildtype embryos. Endogenous XB-cadherin was not affected by Xcad-11Mo and Xcad-11MO2 injection. For detection, αcad-11 and 6D5 αxb-cadherin antibody were used. D, Specificity of Xcadherin-11 function. The impaired invasion of pharyngeal pouches caused by injection of Xcad-11MO could neither be rescued by co-injection of the type1 XB-cadherin nor by type II murine cadherin-6 as demonstrated by whole mount in situ hybridizations with the neural crest marker twist. Instead, human Cadherin-11 was able to rescue twist signal in the pharyngeal pouches (up to 90%). Injected side: middle panel, control side: left panel. Right panel: statistics for rescue experiments. In case of Xcad-11MO injection 28%, and in case of 9 pmol Xcad-11MO2 39% of the embryos showed a normal invasion in the pharyngeal pouches. A rescue with 50 pg XB-cadherin or with 100 pg murine cadherin-6 resulted in only 37% or 31% twist positive cells in the branchial arches, respectively.
2
3 Supplement Movie S2: In vivo migration of control CNC. Transplants of Dextran labelled cranial neural crest were examined from stage 20 to stage 26, when the cells have reached their final destination. Anterior is to the left and dorsal to the top. Note that the migrating CNC enter all pharyngeal arches (see also cell tracking in Fig. 1b). Images captured every 15 minutes over a period of 15 hours using a Leica-DMRE2 microscope with 10 plan NA 0.25 Ph1 objective.
4 Supplement Movie S3: In vivo migration of Xcadherin-11 depleted CNC. Transplants from Xcad-11MO (2 pmol) injected and Dextran labelled CNC were examined from stage 20 to stage 26. Anterior is to the left and dorsal to the top. Note that the hyoidal and branchial cranial neural crest start to delaminate but do not enter the pharyngeal arches (see also cell tracking in Fig. 1b). The migration of the mandibular cranial neural crest is unaffected. Images captured every 15 minutes over a period of 15 hours using a Leica-DMRE2 microscope with 10x plan NA 0.25 Ph1 objective.
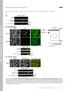
5 Supplement Figure S4: A, Ventral view on Alcian blue-stained wildtype (left panel) and Xcad-11MO (2 pmol) injected embryos (medial panel) at stage 42. Corresponding schematic drawing of the craniofacial cartilage (right panel). Mandibular CNC (green) differentiate into Meckel s cartilage (M), hyoidal CNC (yellow) differentiate into ceratohyale (ch) and branchial CNC (orange, purple) into ceratobranchiale (cb) cartilage. In Xcad-11MO injected embryos cartilage elements derived from hyoidal and branchial CNC are malformed or absent. Asterisk marks injected side. Scale bar: 250 µm. B, In vivo differentiation analysis in CNC transplants. Grafts from Xcad-11 depleted CNC were unable to invade hyoidal and branchial arches (white arrow) and differentiate into melanocytes (black arrow, dorsal view). Control CNC grafts exhibited normal migration and differentiated into cartilage (ventral view). Embryos at stage 42. C, Cranial nerve structures were visualized by 3A10 monoclonal antibody staining in whole embryos at stage 46 (dorsal view). Xcad-11 depleted non-migrating CNC grafts showed increase in melanocytes and thickening of cranial nerves (yellow arrow). Boxed area is enlarged in lower column. Asterisk marks grafted side. D, Depletion of Xcad-11 led to an up-regulation of Trp-2. Xcad-11MO (2 pmol) or CoMO (2 pmol) were injected in one blastomere of 2-cell stage embryo. Dextran was used as lineage tracer. At stage 42, pigmentation was analyzed. Xcad-11 depleted embryos showed increase of melanocytes, whereas injection of CoMO had no influence. Scale bar: 250 µm E, Semi-quantitative RT-PCR of the melanocytes specific marker gene Trp-2. Xcad-11MO (2 pmol) was injected in each blastomere of 2-cell stage embryo and Trp-2 expression from stage 25 to 35 was compared with uninjected embryos. H4 was used as house keeping gene for normalization. -RT, -cdna = negative controls. F, Xcad-11MO injection resulted in increased proliferation in neural crest cells, shown by whole mount ph3 staining (dorsal view, st. 23; n = 30). The number of apoptotic cells in the same region was detected by TUNEL assay and showed no significant difference between injected side (asterix) and uninjected side (n = 23).
6
7 Supplement Movie S5: Analysis of CNC migration in vitro. Control explants of membrane GFP (200 pg mrna) injected embryos were cultured in vitro on fibronectin for several hours. Note that control CNC show extensive protrusive activity and form transient cell-cell contacts. Images captured every 1 minute over a period of 30 minutes using a Leica-DMRE2 microscope with 63x plan apochromat NA 1.32 Ph3 oil objective.
8 Supplement Movie S6: Xcad-11MO. Explants of Xcad-11MO (2 pmol) and membrane GFP (200 pg mrna) injected embryos. Note that Xcadherin-11 depleted CNC are not able to form filopodia and lamellipodia. They have a round cell shape and only show membrane blebbing. Images captured every 1 minute over a period of 30 minutes using a Leica-DMRE2 microscope with 63x plan apochromat NA 1.32 Ph3 oil objective.
9 Supplement Movie S7: Protrusion activity of wildtype CNC in vivo. Transplants of mgfp labelled cranial neural crest were examined at stage 26. Extensive filopodia formation could be observed in several cells. Images captured every two second over a period of 20 minutes using a Perkin Elmer Ultra View ERS spinning disc confocal microscope with 60 plan apo VC NA 1.2 multi-immersion objective.
10 Supplement movie S8: Protrusion activity of Xcad-11MO injected CNC in vivo. Transplants of mgfp and Xcad-11MO labelled cranial neural crest were examined at stage 26. Only blebbings of the cells could be observed. Images were captured every two second over a period of 3.5 minutes using a Perkin Elmer Ultra View ERS spinning disc confocal microscope with 60 plan apo VC NA 1.2 multiimmersion objective.
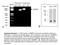
11 Supplement Figure S9: A, Western Blot demonstrating the correct production of all rescue constructs. Translation efficiency and correct size of synthesized proteins was demonstrated by immunoblotting. The myc-tagged proteins were injected in both cells of two-cell stage embryos. The embryos were lysed at stage 12 and protein extraction was performed by NOP buffer. The myc-tagged proteins were enriched by immunoprecipitation with 9E10 antibody (myc) and detected with the same antibody on the Western Blot. Arrows indicate the respective protein band, asterisk marks unspecific band. B, Protein alignment of the different rescue constructs. The different regions (propeptide, EC1-5, QAV motif for homophilic binding, transmembrane domain, intracellular domain, p120 and β- catenin binding site, myc tag and His tag) are marked above the sequence. Predicted molecular masses without glycosylation or other modifications are listed behind the sequences. C, Counting of cell protrusions. Number of stable ( 5 min) and transiently formed filopodia, lamellipodia and membrane blebbings. Injection of CoMo or Xcad-11MO together with Xcadherin-11 RNA, e RNA or ca cdc42 DNA led to equivalent numbers in filopodia and lamellipodia formation and stability per cell as in wildtype cells. In contrast, Xcad-11MO injected cells only showed membrane blebbings, while co-injection of Xcad-11MO with e p120 RNA resulted in an increase of transient filopodia and lamellipodia. Rescue experiments with ca RhoA or Rac1 led to an increase in transient lamellipodia..
12
13 Supplement Movie S10: Ca RhoA rescued CNC in vitro. Explants of Xcad-11MO (2 pmol), ca cdc42 (10 pg DNA) and membrane GFP (200 pg mrna) injected embryos. Note that this CNC co-injected with ca RhoA show extensive protrusive activity. Images captured every 1 minute over a period of 30 minutes using a Leica-DMRE2 microscope with 63x plan apochromat NA 1.32 Ph3 oil objective.
14 Supplement Figure S11: A, Confocal imaging of Xcad-11-EGFP: injected CNC explants after fixation and immunostaining for β-catenin. Co-localization is visible in areas of cell-cell contact (arrowhead). B, Co-localization of Xcad-11-EGFP and β-catenin in filopodia. Scale bar: 20 µm. C, Application of 20 ng/ml Rho GTPases inhibitor Toxin B on mgfp injected neural crest explants led to the formation of cell blebbing after 30 and 45 minutes. Arrows mark blebbings. Scale bar: 10 µm D, Co-immunoprecipitation of Trio with Xcadherin-11 e and XB-cadherin. Precipitation of Trio with HA antibody from transfected COS cells. Trio was detected in Western blot (lower left panel). Western blot for Xcadherin-11 showed successful precipitation of Xcadherin-11 e (upper left). Instead, XB-cadherin could not be co-immunoprecipitated with Trio. Right panels: input. E, Co-immunoprecipitation of β-catenin with different myc-tagged Xcadherin-11 mutants. Precipitation of Xcadherin-11 constructs with 9E10 antibody from transfected COS cells. Western Blot for β-catenin showed co-precipitation of e and e p120 with β-catenin, while e β-catenin mutant was not precipitated. Specific protein bands are marked by asterisks. Xcadherin-11 was detected in Western Blot with 9E10 αmyc antibody. Right panels: input.
15
16 Supplement Figure S12: A, Sequence alignment of XTrio probe with Trio sequences of human, mouse, chicken, zebrafish, and Xenopus tropicalis (upper panel) and graphical structure of human Trio. N-terminally are spectrin repeats followed by 2 complexes of GEF and SH domains. At the C-terminus are an Ig domain and a kinase region. The two arrows indicate the position of the XTrio probe in relation to human full length Trio. The nucleic acid sequence homology between Xenopus laevis XTrio probe and human sequence is 70 %, between X. laevis and mouse 71 %. B, Expression of XTrio. Whole mount in situ hybridization revealed a signal in the neural tube in stage 19. Also, a staining of the neural plate laterally expanding in the CNC region is visible. In stage 25 the staining is found in the migrating CNC (arrow) as well as in brain and eyes. The sense probe in the same stage did not show any staining. In semi-quantitative RT-PCR first transcripts could be detected around stage 16 and were increasing with age until stage 34, the latest stage examined. ODC was used as house-keeping gene for normalization.
17
J. Cell Sci. 128: doi: /jcs : Supplementary Material. Supplemental Figures. Journal of Cell Science Supplementary Material
 Supplemental Figures Figure S1. Trio controls endothelial barrier function. (A) TagRFP-shTrio constructs were expressed in ECs. Western blot shows efficient Trio knockdown in TagRFP-expressing ECs. (B)
Supplemental Figures Figure S1. Trio controls endothelial barrier function. (A) TagRFP-shTrio constructs were expressed in ECs. Western blot shows efficient Trio knockdown in TagRFP-expressing ECs. (B)
Supplemental Figure 1 Human REEP family of proteins can be divided into two distinct subfamilies. Residues (single letter amino acid code) identical
 Supplemental Figure Human REEP family of proteins can be divided into two distinct subfamilies. Residues (single letter amino acid code) identical in all six REEPs are highlighted in green. Additional
Supplemental Figure Human REEP family of proteins can be divided into two distinct subfamilies. Residues (single letter amino acid code) identical in all six REEPs are highlighted in green. Additional
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3363 Supplementary Figure 1 Several WNTs bind to the extracellular domains of PKD1. (a) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with indicated plasmids. Flag-tagged proteins were immunoprecipiated
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3363 Supplementary Figure 1 Several WNTs bind to the extracellular domains of PKD1. (a) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with indicated plasmids. Flag-tagged proteins were immunoprecipiated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2271 Supplementary Figure a! WM266.4 mock WM266.4 #7 sirna WM266.4 #10 sirna SKMEL28 mock SKMEL28 #7 sirna SKMEL28 #10 sirna WM1361 mock WM1361 #7 sirna WM1361 #10 sirna 9 WM266. WM136
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2271 Supplementary Figure a! WM266.4 mock WM266.4 #7 sirna WM266.4 #10 sirna SKMEL28 mock SKMEL28 #7 sirna SKMEL28 #10 sirna WM1361 mock WM1361 #7 sirna WM1361 #10 sirna 9 WM266. WM136
Supplementary Information. Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish
 Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
JCB. Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY. Paul et al.,
 Supplemental material JCB Paul et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201502040/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Mutant p53-expressing cells display limited retrograde actin flow at
Supplemental material JCB Paul et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201502040/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Mutant p53-expressing cells display limited retrograde actin flow at
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of
 Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
Chapter One. Construction of a Fluorescent α5 Subunit. Elucidation of the unique contribution of the α5 subunit is complicated by several factors
 4 Chapter One Construction of a Fluorescent α5 Subunit The significance of the α5 containing nachr receptor (α5* receptor) has been a challenging question for researchers since its characterization by
4 Chapter One Construction of a Fluorescent α5 Subunit The significance of the α5 containing nachr receptor (α5* receptor) has been a challenging question for researchers since its characterization by
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2743 Figure S1 stabilizes cellular protein level, post-transcriptionally. (a, b) and DDR1 were RNAi-depleted from HEK.293.-CBG cells. Western blots with indicated antibodies (a). RT-PCRs
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2743 Figure S1 stabilizes cellular protein level, post-transcriptionally. (a, b) and DDR1 were RNAi-depleted from HEK.293.-CBG cells. Western blots with indicated antibodies (a). RT-PCRs
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Rainero et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201109112/dc1 Figure S1. The expression of DGK- is reduced upon transfection
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Rainero et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201109112/dc1 Figure S1. The expression of DGK- is reduced upon transfection
Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Figure S2. Verification of ihog and boi
 Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Extracts from S2R+ cells, embryos, and adults were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with anti-ihog antibody. The Ihog
Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Extracts from S2R+ cells, embryos, and adults were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with anti-ihog antibody. The Ihog
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Han et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201311007/dc1 Figure S1. SIVA1 interacts with PCNA. (A) HEK293T cells were transiently
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Han et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201311007/dc1 Figure S1. SIVA1 interacts with PCNA. (A) HEK293T cells were transiently
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Nakajima and Tanoue, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201104118/dc1 Figure S1. DLD-1 cells exhibit the characteristic morphology
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Nakajima and Tanoue, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201104118/dc1 Figure S1. DLD-1 cells exhibit the characteristic morphology
Fig. S1. Effect of p120-catenin overexpression on the interaction of SCUBE2 with E-cadherin. The expression plasmid encoding FLAG.
 Fig. S1. Effect of p120-catenin overexpression on the interaction of SCUBE2 with E-cadherin. The expression plasmid encoding FLAG.SCUBE2, E-cadherin.Myc, or HA.p120-catenin was transfected in a combination
Fig. S1. Effect of p120-catenin overexpression on the interaction of SCUBE2 with E-cadherin. The expression plasmid encoding FLAG.SCUBE2, E-cadherin.Myc, or HA.p120-catenin was transfected in a combination
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table.
 Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
Methanol fixation allows better visualization of Kal7. To compare methods for
 Supplementary Data Methanol fixation allows better visualization of Kal7. To compare methods for visualizing Kal7 in dendrites, mature cultures of dissociated hippocampal neurons (DIV21) were fixed with
Supplementary Data Methanol fixation allows better visualization of Kal7. To compare methods for visualizing Kal7 in dendrites, mature cultures of dissociated hippocampal neurons (DIV21) were fixed with
At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
-RT RT RT -RT XBMPRII
 Base pairs 2000 1650 1000 850 600 500 400 Marker Primer set 1 Primer set 2 -RT RT RT -RT XBMPRII kda 100 75 50 37 25 20 XAC p-xac A 300 B Supplemental figure 1. PCR analysis of BMPRII expression and western
Base pairs 2000 1650 1000 850 600 500 400 Marker Primer set 1 Primer set 2 -RT RT RT -RT XBMPRII kda 100 75 50 37 25 20 XAC p-xac A 300 B Supplemental figure 1. PCR analysis of BMPRII expression and western
Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 (Supplementary Methods and Materials) GST pull-down assay GST-fusion proteins Fe65 365-533, and Fe65 538-700 were expressed in BL21 bacterial cells and purified with glutathione-agarose beads (Sigma).
(Supplementary Methods and Materials) GST pull-down assay GST-fusion proteins Fe65 365-533, and Fe65 538-700 were expressed in BL21 bacterial cells and purified with glutathione-agarose beads (Sigma).
Supplementary Fig. 1. Multiple five micron sections of liver tissues of rats treated
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. Multiple five micron sections of liver tissues of rats treated with either vehicle (left; n=3) or CCl 4 (right; n=3) were co-immunostained for NRP-1 (green)
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. Multiple five micron sections of liver tissues of rats treated with either vehicle (left; n=3) or CCl 4 (right; n=3) were co-immunostained for NRP-1 (green)
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
embryos. Asterisk represents loss of or reduced expression. Brackets represent
 Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1. tfec expression is highly enriched in tail endothelial cells (A- B) ISH of tfec at 15 and 16hpf in WT embryos. (C- D) ISH of tfec at 36 and 38hpf in WT embryos.
Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1. tfec expression is highly enriched in tail endothelial cells (A- B) ISH of tfec at 15 and 16hpf in WT embryos. (C- D) ISH of tfec at 36 and 38hpf in WT embryos.
Supplementary Figure 1 Phosphorylated tau accumulates in Nrf2 (-/-) mice. Hippocampal tissues obtained from Nrf2 (-/-) (10 months old, 4 male; 2
 Supplementary Figure 1 Phosphorylated tau accumulates in Nrf2 (-/-) mice. Hippocampal tissues obtained from Nrf2 (-/-) (10 months old, 4 male; 2 female) or wild-type (5 months old, 1 male; 11 months old,
Supplementary Figure 1 Phosphorylated tau accumulates in Nrf2 (-/-) mice. Hippocampal tissues obtained from Nrf2 (-/-) (10 months old, 4 male; 2 female) or wild-type (5 months old, 1 male; 11 months old,
Supplementary Figure1: ClustalW comparison between Tll, Dsf and NR2E1.
 P-Box Dsf -----------------MG-TAG--DRLLD-IPCKVCGDRSSGKHYGIYSCDGCSGFFKR 39 NR2E1 -----------------MSKPAGSTSRILD-IPCKVCGDRSSGKHYGVYACDGCSGFFKR 42 Tll MQSSEGSPDMMDQKYNSVRLSPAASSRILYHVPCKVCRDHSSGKHYGIYACDGCAGFFKR
P-Box Dsf -----------------MG-TAG--DRLLD-IPCKVCGDRSSGKHYGIYSCDGCSGFFKR 39 NR2E1 -----------------MSKPAGSTSRILD-IPCKVCGDRSSGKHYGVYACDGCSGFFKR 42 Tll MQSSEGSPDMMDQKYNSVRLSPAASSRILYHVPCKVCRDHSSGKHYGIYACDGCAGFFKR
Supplementary Fig. 1 Identification of Nedd4 as an IRS-2-associated protein in camp-treated FRTL-5 cells.
 Supplementary Fig. 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 Identification of Nedd4 as an IRS-2-associated protein in camp-treated FRTL-5 cells. (a) FRTL-5 cells were treated with 1 mm dibutyryl camp for 24 h, and the lysates
Supplementary Fig. 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 Identification of Nedd4 as an IRS-2-associated protein in camp-treated FRTL-5 cells. (a) FRTL-5 cells were treated with 1 mm dibutyryl camp for 24 h, and the lysates
Figure S1 is related to Figure 1B, showing more details of outer segment of
 Supplemental Information Supplementary Figure legends and Figures Figure S1. Electron microscopic images in Sema4A +/+ and Sema4A / retinas Figure S1 is related to Figure 1B, showing more details of outer
Supplemental Information Supplementary Figure legends and Figures Figure S1. Electron microscopic images in Sema4A +/+ and Sema4A / retinas Figure S1 is related to Figure 1B, showing more details of outer
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Lu et al. 10.1073/pnas.1106801108 Fig. S1. Analysis of spatial localization of mrnas coding for 23 zebrafish Wnt genes by whole mount in situ hybridization to identify those present
Supporting Information Lu et al. 10.1073/pnas.1106801108 Fig. S1. Analysis of spatial localization of mrnas coding for 23 zebrafish Wnt genes by whole mount in situ hybridization to identify those present
Supplemental Material Igreja and Izaurralde 1. CUP promotes deadenylation and inhibits decapping of mrna targets. Catia Igreja and Elisa Izaurralde
 Supplemental Material Igreja and Izaurralde 1 CUP promotes deadenylation and inhibits decapping of mrna targets Catia Igreja and Elisa Izaurralde Supplemental Materials and methods Functional assays and
Supplemental Material Igreja and Izaurralde 1 CUP promotes deadenylation and inhibits decapping of mrna targets Catia Igreja and Elisa Izaurralde Supplemental Materials and methods Functional assays and
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full//59/ra7/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dok-7 ctivates the Muscle Receptor Kinase MuSK and Shapes Synapse Formation kane Inoue, Kiyoko Setoguchi, Yosuke Matsubara,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full//59/ra7/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dok-7 ctivates the Muscle Receptor Kinase MuSK and Shapes Synapse Formation kane Inoue, Kiyoko Setoguchi, Yosuke Matsubara,
Regulation of Acetylcholine Receptor Clustering by ADF/Cofilin- Directed Vesicular Trafficking
 Regulation of Acetylcholine Receptor Clustering by ADF/Cofilin- Directed Vesicular Trafficking Chi Wai Lee, Jianzhong Han, James R. Bamburg, Liang Han, Rachel Lynn, and James Q. Zheng Supplementary Figures
Regulation of Acetylcholine Receptor Clustering by ADF/Cofilin- Directed Vesicular Trafficking Chi Wai Lee, Jianzhong Han, James R. Bamburg, Liang Han, Rachel Lynn, and James Q. Zheng Supplementary Figures
Supplementary data. sienigma. F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM. a-p53
 Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan).
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplemental Materials and Methods Cell proliferation assay Cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan). GCs were plated at 96-well
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplemental Materials and Methods Cell proliferation assay Cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan). GCs were plated at 96-well
Supplementary Figure 1. The Hsp70 acetylation level is related to the co-chaperone binding of Hsp70 under various stress conditions.
 Supplementary Figure 1. The Hsp70 acetylation level is related to the co-chaperone binding of Hsp70 under various stress conditions. 1 (a) Etoposide treatment gradually changes acetylation level and co-chaperone
Supplementary Figure 1. The Hsp70 acetylation level is related to the co-chaperone binding of Hsp70 under various stress conditions. 1 (a) Etoposide treatment gradually changes acetylation level and co-chaperone
Figure legends for supplement
 Figure legends for supplement Supplemental Figure 1 Characterization of purified and recombinant proteins Relevant fractions related the final stage of the purification protocol(bingham et al., 1998; Toba
Figure legends for supplement Supplemental Figure 1 Characterization of purified and recombinant proteins Relevant fractions related the final stage of the purification protocol(bingham et al., 1998; Toba
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Bays et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201309092/dc1 Figure S1. Specificity of the phospho-y822 antibody. (A) Total cell
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Bays et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201309092/dc1 Figure S1. Specificity of the phospho-y822 antibody. (A) Total cell
Figure S1. USP-46 is expressed in several tissues including the nervous system
 Supplemental Figure legends Figure S1. USP-46 is expressed in several tissues including the nervous system Transgenic animals expressing a transcriptional reporter (P::GFP) were imaged using epifluorescence
Supplemental Figure legends Figure S1. USP-46 is expressed in several tissues including the nervous system Transgenic animals expressing a transcriptional reporter (P::GFP) were imaged using epifluorescence
This is the author's accepted version of the manuscript.
 This is the author's accepted version of the manuscript. The definitive version is published in Nature Communications Online Edition: 2015/4/16 (Japan time), doi:10.1038/ncomms7780. The final version published
This is the author's accepted version of the manuscript. The definitive version is published in Nature Communications Online Edition: 2015/4/16 (Japan time), doi:10.1038/ncomms7780. The final version published
Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of LRRK1 bind to Grb2.
 Myc- HA-Grb2 Mr(K) 105 IP HA 75 25 105 1-1163 1-595 - + - + - + 1164-1989 Blot Myc HA total lysate 75 25 Myc HA Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of bind to Grb2. COS7 cells were cotransfected
Myc- HA-Grb2 Mr(K) 105 IP HA 75 25 105 1-1163 1-595 - + - + - + 1164-1989 Blot Myc HA total lysate 75 25 Myc HA Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of bind to Grb2. COS7 cells were cotransfected
Supplementary Figure 1. Drawing of spinal cord open-book preparations and DiI tracing. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.3893
 Supplementary Figure 1 Drawing of spinal cord open-book preparations and DiI tracing. Supplementary Figure 2 In ovo electroporation of dominant-negative PlexinA1 in commissural neurons induces midline
Supplementary Figure 1 Drawing of spinal cord open-book preparations and DiI tracing. Supplementary Figure 2 In ovo electroporation of dominant-negative PlexinA1 in commissural neurons induces midline
A Survey of Genetic Methods
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology A Survey of Genetic Methods January 24, 2008 DNA RNA Hybridization ** * radioactive probe reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction RT PCR DNA
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology A Survey of Genetic Methods January 24, 2008 DNA RNA Hybridization ** * radioactive probe reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction RT PCR DNA
The F-box protein Cdc4/Fbxw7 is a novel regulator of neural crest development in Xenopus laevis
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The F-box protein Cdc4/Fbxw7 is a novel regulator of neural crest development in Xenopus laevis Alexandra D Almeida 1, Helen M Wise 2, Christopher J Hindley 1, Michael K Slevin
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The F-box protein Cdc4/Fbxw7 is a novel regulator of neural crest development in Xenopus laevis Alexandra D Almeida 1, Helen M Wise 2, Christopher J Hindley 1, Michael K Slevin
Figure S1. Figure S2. Figure S3 HB Anti-FSP27 (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab. Anti-GST-FSP27(45-127) Ab.
 / 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
/ 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
Supplemental Figure 1. Alignment of the NbGAPC amino acid sequences with their Arabidopsis homologues.
 Supplemental Figure 1. Alignment of the NbGAPC amino acid sequences with their Arabidopsis homologues. Homologs from N. benthamiana (NbGAPC1, NbGAPC2, NbGAPC3), Arabidopsis (AtGAPC1, AT3G04120; AtGAPC2,
Supplemental Figure 1. Alignment of the NbGAPC amino acid sequences with their Arabidopsis homologues. Homologs from N. benthamiana (NbGAPC1, NbGAPC2, NbGAPC3), Arabidopsis (AtGAPC1, AT3G04120; AtGAPC2,
Sarker et al. Supplementary Material. Subcellular Fractionation
 Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified
 Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified by primers used for mrna expression analysis. Gray
Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified by primers used for mrna expression analysis. Gray
A RRM1 H2AX DAPI. RRM1 H2AX DAPI Merge. Cont. sirna RRM1
 A H2AX DAPI H2AX DAPI Merge Cont sirna Figure S1: Accumulation of RRM1 at DNA damage sites (A) HeLa cells were subjected to in situ detergent extraction without IR irradiation, and immunostained with the
A H2AX DAPI H2AX DAPI Merge Cont sirna Figure S1: Accumulation of RRM1 at DNA damage sites (A) HeLa cells were subjected to in situ detergent extraction without IR irradiation, and immunostained with the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
Supplementary Figure 1. Immunoprecipitation of synthetic SUMOm-remnant peptides using UMO monoclonal antibody. (a) LC-MS analyses of tryptic
 Supplementary Figure 1. Immunoprecipitation of synthetic SUMOm-remnant peptides using UMO 1-7-7 monoclonal antibody. (a) LC-MS analyses of tryptic digest from HEK293 cells spiked with 6 SUMOmremnant peptides
Supplementary Figure 1. Immunoprecipitation of synthetic SUMOm-remnant peptides using UMO 1-7-7 monoclonal antibody. (a) LC-MS analyses of tryptic digest from HEK293 cells spiked with 6 SUMOmremnant peptides
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Kunduri et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405020/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Subcellular localization and interactions of PAPLA1.
Supplemental material Kunduri et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405020/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Subcellular localization and interactions of PAPLA1.
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Apoptosis analyses and quantification. Activated caspase3 immunostaining on sections of E9.0 Tcof1 +/ -;p53 +/- (a) and Tcof1 +/ -;p53 -/- (b) littermate embryos
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Apoptosis analyses and quantification. Activated caspase3 immunostaining on sections of E9.0 Tcof1 +/ -;p53 +/- (a) and Tcof1 +/ -;p53 -/- (b) littermate embryos
Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling
 Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling Glendining KA 1, Markie D 2, Gardner RJM 4, Franz EA 3, Robertson SP 4, Jasoni CL 1 Supplementary
Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling Glendining KA 1, Markie D 2, Gardner RJM 4, Franz EA 3, Robertson SP 4, Jasoni CL 1 Supplementary
Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate toward tumor blood vessels Supplementary Information
 Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate toward tumor blood vessels Supplementary Information 1. Supplementary Figure S1-S10: Pages 2-11 2. Supplementary References:
Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate toward tumor blood vessels Supplementary Information 1. Supplementary Figure S1-S10: Pages 2-11 2. Supplementary References:
ASPP1 Fw GGTTGGGAATCCACGTGTTG ASPP1 Rv GCCATATCTTGGAGCTCTGAGAG
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Quantification of western blot analysis of fibroblasts (related to Figure 1) (A-F) Quantification of western blot analysis for control and IR-Mut fibroblasts. Data are expressed
Supplementary Figure 1. Quantification of western blot analysis of fibroblasts (related to Figure 1) (A-F) Quantification of western blot analysis for control and IR-Mut fibroblasts. Data are expressed
Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days,
 Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days, respectively, and their mrnas were quantified by real time
Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days, respectively, and their mrnas were quantified by real time
OmicsLink shrna Clones guaranteed knockdown even in difficult-to-transfect cells
 OmicsLink shrna Clones guaranteed knockdown even in difficult-to-transfect cells OmicsLink shrna clone collections consist of lentiviral, and other mammalian expression vector based small hairpin RNA (shrna)
OmicsLink shrna Clones guaranteed knockdown even in difficult-to-transfect cells OmicsLink shrna clone collections consist of lentiviral, and other mammalian expression vector based small hairpin RNA (shrna)
Supplementary Fig.1 Luton
 Supplementary Fig.1 Luton a 175 Brain Thymus Spleen Small Intestine Kidney Testis HeLa b 250 Lung Kidney MDCK c EFA6B si Control si Mismatch #637 #1564 #1770 83 62 47.5 175 IB: anti-efa6b #B1 130 66 Lysates
Supplementary Fig.1 Luton a 175 Brain Thymus Spleen Small Intestine Kidney Testis HeLa b 250 Lung Kidney MDCK c EFA6B si Control si Mismatch #637 #1564 #1770 83 62 47.5 175 IB: anti-efa6b #B1 130 66 Lysates
Flag-Rac Vector V12 V12 N17 C40. Vector C40 pakt (T308) Akt1. Myc-DN-PAK1 (N-SP)
 a b FlagRac FlagRac V2 V2 N7 C4 V2 V2 N7 C4 p (T38) p (S99, S24) p Flag (Rac) NIH 3T3 COS c +Serum p (T38) MycDN (NSP) Mycp27 3 6 2 3 6 2 3 6 2 min p Myc ( or p27) Figure S (a) Effects of Rac mutants on
a b FlagRac FlagRac V2 V2 N7 C4 V2 V2 N7 C4 p (T38) p (S99, S24) p Flag (Rac) NIH 3T3 COS c +Serum p (T38) MycDN (NSP) Mycp27 3 6 2 3 6 2 3 6 2 min p Myc ( or p27) Figure S (a) Effects of Rac mutants on
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Ho et al. 10.1073/pnas.0808899106 SI Materials and Methods In immunostaining, antibodies from Developmental Studies Hybridoma ank were -FasII (mouse, 1:200), - (mouse, 1:100), and
Supporting Information Ho et al. 10.1073/pnas.0808899106 SI Materials and Methods In immunostaining, antibodies from Developmental Studies Hybridoma ank were -FasII (mouse, 1:200), - (mouse, 1:100), and
Supplemental Data. Sethi et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. MYC2 Binds to the E-box but not the E1-box of the MPK6 Promoter. (A) E1-box and E-box (wild type) containing MPK6 promoter fragment. The region shown in red denotes
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. MYC2 Binds to the E-box but not the E1-box of the MPK6 Promoter. (A) E1-box and E-box (wild type) containing MPK6 promoter fragment. The region shown in red denotes
Supplementary Information for. Regulation of Rev1 by the Fanconi Anemia Core Complex
 Supplementary Information for Regulation of Rev1 by the Fanconi Anemia Core Complex Hyungjin Kim, Kailin Yang, Donniphat Dejsuphong, Alan D. D Andrea* *Corresponding Author: Alan D. D Andrea, M.D. Alan_dandrea@dfci.harvard.edu
Supplementary Information for Regulation of Rev1 by the Fanconi Anemia Core Complex Hyungjin Kim, Kailin Yang, Donniphat Dejsuphong, Alan D. D Andrea* *Corresponding Author: Alan D. D Andrea, M.D. Alan_dandrea@dfci.harvard.edu
Fig Hypoxia causes growth retardation and developmental delay. (A) Morphology of wildtype zebrafish embryos at 48 hours post fertilization
 FIGURES AND TABLES Fig. 1-1. Hypoxia causes growth retardation and developmental delay. (A) Morphology of wildtype zebrafish embryos at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf) after 24 h of normoxia or hypoxia
FIGURES AND TABLES Fig. 1-1. Hypoxia causes growth retardation and developmental delay. (A) Morphology of wildtype zebrafish embryos at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf) after 24 h of normoxia or hypoxia
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Supplementary Methods Cell synchronization. For synchronized cell growth, thymidine was added to 30% confluent U2OS cells to a final concentration of 2.5mM. Cells were incubated
Supplementary Material Supplementary Methods Cell synchronization. For synchronized cell growth, thymidine was added to 30% confluent U2OS cells to a final concentration of 2.5mM. Cells were incubated
supplementary information
 DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4166
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplemental Fig. 1. Mcr alleles show defects in tracheal tube size and luminal protein accumulation. (A-F) Confocal projections of living stage 15
 Supplemental Fig. 1. Mcr alleles show defects in tracheal tube size and luminal protein accumulation. (A-F) Confocal projections of living stage 15 embryos expressing GFP and Verm-RFP in tracheal cells
Supplemental Fig. 1. Mcr alleles show defects in tracheal tube size and luminal protein accumulation. (A-F) Confocal projections of living stage 15 embryos expressing GFP and Verm-RFP in tracheal cells
Supplemental Data. Farmer et al. (2010) Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Amino acid sequence comparison of RAD23 proteins. Identical and similar residues are shown in the black and gray boxes, respectively. Dots denote gaps. The sequence of plant Ub is
Supplemental Figure 1. Amino acid sequence comparison of RAD23 proteins. Identical and similar residues are shown in the black and gray boxes, respectively. Dots denote gaps. The sequence of plant Ub is
Fig. S1. TPL and TPL N176H protein interactions. (A) Semi-in vivo pull-down assays using recombinant GST N-TPL and GST N-TPL N176H fusions and
 Fig. S1. TPL and TPL N176H protein interactions. (A) Semi-in vivo pull-down assays using recombinant GST N-TPL and GST N-TPL N176H fusions and transgenic Arabidopsis TPL-HA lysates. Immunoblotting of input
Fig. S1. TPL and TPL N176H protein interactions. (A) Semi-in vivo pull-down assays using recombinant GST N-TPL and GST N-TPL N176H fusions and transgenic Arabidopsis TPL-HA lysates. Immunoblotting of input
Figure S1. Sequence alignments of ATRIP and ATR TopBP1 interacting regions.
 A H. sapiens 204 TKLQTS--ERANKLAAPSVSH VSPRKNPSVVIKPEACS-PQFGKTSFPTKESFSANMS LP 259 B. taurus 201 TKLQSS--ERANKLAVPTVSH VSPRKSPSVVIKPEACS-PQFGKPSFPTKESFSANKS LP 257 M. musculus 204 TKSQSN--GRTNKPAAPSVSH
A H. sapiens 204 TKLQTS--ERANKLAAPSVSH VSPRKNPSVVIKPEACS-PQFGKTSFPTKESFSANMS LP 259 B. taurus 201 TKLQSS--ERANKLAVPTVSH VSPRKSPSVVIKPEACS-PQFGKPSFPTKESFSANKS LP 257 M. musculus 204 TKSQSN--GRTNKPAAPSVSH
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured
 Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Supplemental Figure 1 (Figure S1), related to Figure 1 Figure S1 provides evidence to demonstrate Nfatc1Cre is a mouse line that directed gene
 Developmental Cell, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Brg1 Governs a Positive Feedback Circuit in the Hair Follicle for Tissue Regeneration and Repair Yiqin Xiong, Wei Li, Ching Shang, Richard M. Chen,
Developmental Cell, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Brg1 Governs a Positive Feedback Circuit in the Hair Follicle for Tissue Regeneration and Repair Yiqin Xiong, Wei Li, Ching Shang, Richard M. Chen,
Supplementary Figure 1 A
 Supplementary Figure A B M. mullata p53, 3 UTR Luciferase activity (%) mir-5b 8 Le et al. Supplementary Information NC-DP - + - - - - - NC-DP - - + - - - - NC-DP3 - - - + - - - 5b-DP - - - - + + + NC-AS
Supplementary Figure A B M. mullata p53, 3 UTR Luciferase activity (%) mir-5b 8 Le et al. Supplementary Information NC-DP - + - - - - - NC-DP - - + - - - - NC-DP3 - - - + - - - 5b-DP - - - - + + + NC-AS
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2116 Figure S1 CDK phosphorylation of EZH2 in cells. (a) Comparison of candidate CDK phosphorylation sites on EZH2 with known CDK substrates by multiple sequence alignments. (b) CDK1 and
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2116 Figure S1 CDK phosphorylation of EZH2 in cells. (a) Comparison of candidate CDK phosphorylation sites on EZH2 with known CDK substrates by multiple sequence alignments. (b) CDK1 and
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Xenopus model of missense mutations. A mutation equivalent to MCIDAS R381H/G355D was introduced in the Xenopus mcidas (R370H, G355D) by PCR, sequenced
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Xenopus model of missense mutations. A mutation equivalent to MCIDAS R381H/G355D was introduced in the Xenopus mcidas (R370H, G355D) by PCR, sequenced
Supplemental Data. Na Xu et al. (2016). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. The weak fluorescence phenotype is not caused by the mutation in At3g60240. (A) A mutation mapped to the gene At3g60240. Map-based cloning strategy was used to map the mutated site
Supplemental Figure 1. The weak fluorescence phenotype is not caused by the mutation in At3g60240. (A) A mutation mapped to the gene At3g60240. Map-based cloning strategy was used to map the mutated site
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
Supplemental Figure Legends:
 Supplemental Figure Legends: Fig S1. GFP-ABRO1 localization. U2OS cells were infected with retrovirus expressing GFP- ABRO1. The cells were fixed with 3.6% formaldehyde and stained with antibodies against
Supplemental Figure Legends: Fig S1. GFP-ABRO1 localization. U2OS cells were infected with retrovirus expressing GFP- ABRO1. The cells were fixed with 3.6% formaldehyde and stained with antibodies against
Cytotoxicity of Botulinum Neurotoxins Reveals a Direct Role of
 Supplementary Information Cytotoxicity of Botulinum Neurotoxins Reveals a Direct Role of Syntaxin 1 and SNAP-25 in Neuron Survival Lisheng Peng, Huisheng Liu, Hongyu Ruan, William H. Tepp, William H. Stoothoff,
Supplementary Information Cytotoxicity of Botulinum Neurotoxins Reveals a Direct Role of Syntaxin 1 and SNAP-25 in Neuron Survival Lisheng Peng, Huisheng Liu, Hongyu Ruan, William H. Tepp, William H. Stoothoff,
Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein. complexes during long term depression
 Supplementary Information Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein complexes during long term depression Shinji Matsuda, Wataru Kakegawa, Timotheus Budisantoso, Toshihiro Nomura,
Supplementary Information Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein complexes during long term depression Shinji Matsuda, Wataru Kakegawa, Timotheus Budisantoso, Toshihiro Nomura,
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material 1 Figure S1. Phylogenetic analysis of Cep72 and Lrrc36, comparative localization of Cep72 and Lrrc36 and Cep72 antibody characterization (A) Phylogenetic alignment of Cep72 and Lrrc36
Supplemental Material 1 Figure S1. Phylogenetic analysis of Cep72 and Lrrc36, comparative localization of Cep72 and Lrrc36 and Cep72 antibody characterization (A) Phylogenetic alignment of Cep72 and Lrrc36
Supplementary Figure 1. Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
JCB. Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY. Hong et al.,
 Supplemental material JCB Hong et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201412127/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Analysis of purified proteins by SDS-PAGE and pull-down assays. (A) Coomassie-stained
Supplemental material JCB Hong et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201412127/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Analysis of purified proteins by SDS-PAGE and pull-down assays. (A) Coomassie-stained
JCB. Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY. Kimura et al.,
 Supplemental material JCB Kimura et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201503023/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. TRIMs regulate IFN-γ induced autophagy. (A and B) HC image analysis
Supplemental material JCB Kimura et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201503023/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. TRIMs regulate IFN-γ induced autophagy. (A and B) HC image analysis
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1: Suv39h1, but not Suv39h2, promotes HP1α sumoylation in vivo. In vivo HP1α sumoylation assay. Top: experimental scheme. Middle: we
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1: Suv39h1, but not Suv39h2, promotes HP1α sumoylation in vivo. In vivo HP1α sumoylation assay. Top: experimental scheme. Middle: we
Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity.
 Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity. (A) Amino acid alignment of HDA5, HDA15 and HDA18. The blue line
Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity. (A) Amino acid alignment of HDA5, HDA15 and HDA18. The blue line
(a) Immunoblotting to show the migration position of Flag-tagged MAVS
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of six MAVS isoforms. (a) Immunoblotting to show the migration position of Flag-tagged MAVS isoforms. HEK293T Mavs -/- cells were transfected with constructs expressing
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of six MAVS isoforms. (a) Immunoblotting to show the migration position of Flag-tagged MAVS isoforms. HEK293T Mavs -/- cells were transfected with constructs expressing
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Suppl. Fig. 1. Notch and myostatin expression is unaffected in the absence of p65 during postnatal development. A & B. Myostatin and Notch-1 expression levels were determined
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Suppl. Fig. 1. Notch and myostatin expression is unaffected in the absence of p65 during postnatal development. A & B. Myostatin and Notch-1 expression levels were determined
Supplement figure legends
 Supplement figure legends Figure S1. Alignments of PRDM16 amino acid sequences of mouse, human, dog, chicken, and Xenopus. Two putative CtBP-binding motifs are indicated in the boxes. Numbers represent
Supplement figure legends Figure S1. Alignments of PRDM16 amino acid sequences of mouse, human, dog, chicken, and Xenopus. Two putative CtBP-binding motifs are indicated in the boxes. Numbers represent
Supplemental Table 1 Gene Symbol FDR corrected p-value PLOD1 CSRP2 PFKP ADFP ADM C10orf10 GPI LOX PLEKHA2 WIPF1
 Supplemental Table 1 Gene Symbol FDR corrected p-value PLOD1 4.52E-18 PDK1 6.77E-18 CSRP2 4.42E-17 PFKP 1.23E-14 MSH2 3.79E-13 NARF_A 5.56E-13 ADFP 5.56E-13 FAM13A1 1.56E-12 FAM29A_A 1.22E-11 CA9 1.54E-11
Supplemental Table 1 Gene Symbol FDR corrected p-value PLOD1 4.52E-18 PDK1 6.77E-18 CSRP2 4.42E-17 PFKP 1.23E-14 MSH2 3.79E-13 NARF_A 5.56E-13 ADFP 5.56E-13 FAM13A1 1.56E-12 FAM29A_A 1.22E-11 CA9 1.54E-11
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Analyses of ECTRs by C-circle and T-circle assays.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analyses of ECTRs by C-circle and T-circle assays. (a) C-circle and (b) T-circle amplification reactions using genomic DNA from different cell lines in the presence (+) or absence
Supplementary Figure 1 Analyses of ECTRs by C-circle and T-circle assays. (a) C-circle and (b) T-circle amplification reactions using genomic DNA from different cell lines in the presence (+) or absence
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature899 Supplementary Figure Suzuki et al. a c p7 -/- / WT ratio (+)/(-) p7 -/- / WT ratio Log X 3. Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) Log X.5 3-3. -. b Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) 8
doi:.38/nature899 Supplementary Figure Suzuki et al. a c p7 -/- / WT ratio (+)/(-) p7 -/- / WT ratio Log X 3. Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) Log X.5 3-3. -. b Fold change by treatment ( (+)/(-)) 8
Supplementary Figure 1 Collision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK2, PPK3 and PPK4 respectively.
 Supplementary Figure 1 lision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK, PPK3 and PPK respectively. % of nuclei with signal / field a 5 c ppif3:gus pppk1:gus 0 35 30 5 0 15 10
Supplementary Figure 1 lision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK, PPK3 and PPK respectively. % of nuclei with signal / field a 5 c ppif3:gus pppk1:gus 0 35 30 5 0 15 10
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2880 Supplementary Figure 1 Sequence alignment of Deup1 and Cep63. The protein sequence alignment was generated by the Clustal X 2.0 multiple sequence alignment program using default parameters.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2880 Supplementary Figure 1 Sequence alignment of Deup1 and Cep63. The protein sequence alignment was generated by the Clustal X 2.0 multiple sequence alignment program using default parameters.
HEK293T. Fig. 1 in the
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Zinc uptake assay of hzip4 and hzip4-δecd transiently expressed in HEK293T cells. The results of one representative e experiment are shown in Fig. 1 in
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Zinc uptake assay of hzip4 and hzip4-δecd transiently expressed in HEK293T cells. The results of one representative e experiment are shown in Fig. 1 in
Contents... vii. List of Figures... xii. List of Tables... xiv. Abbreviatons... xv. Summary... xvii. 1. Introduction In vitro evolution...
 vii Contents Contents... vii List of Figures... xii List of Tables... xiv Abbreviatons... xv Summary... xvii 1. Introduction...1 1.1 In vitro evolution... 1 1.2 Phage Display Technology... 3 1.3 Cell surface
vii Contents Contents... vii List of Figures... xii List of Tables... xiv Abbreviatons... xv Summary... xvii 1. Introduction...1 1.1 In vitro evolution... 1 1.2 Phage Display Technology... 3 1.3 Cell surface
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3556 INTEGRATED SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE TEMPLATE. Supplementary Figure 1
 INTEGRATED SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE TEMPLATE Supplementary Figure 1 REF6 expression in transgenic lines. (a,b) Expression of REF6 in REF6-HA ref6 and REF6ΔZnF-HA ref6 plants detected by RT qpcr (a) and immunoblot
INTEGRATED SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE TEMPLATE Supplementary Figure 1 REF6 expression in transgenic lines. (a,b) Expression of REF6 in REF6-HA ref6 and REF6ΔZnF-HA ref6 plants detected by RT qpcr (a) and immunoblot
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1 sirna and shrna mediated depletion of ATP7A results in loss of melanosomal ATP7A staining. a-h, sirna mediated ATP7A depletion. Immunofluorescence microscopy (IFM) analysis of ATP7A
Supplementary Figure 1 sirna and shrna mediated depletion of ATP7A results in loss of melanosomal ATP7A staining. a-h, sirna mediated ATP7A depletion. Immunofluorescence microscopy (IFM) analysis of ATP7A
Assays for gene expression and protein production
 Assays for gene expression and protein production Module 3, Lecture 5! 20.109 Spring 2011! Topics for Lecture 5 Measuring protein levels! Measuring transcript levels! Imaging assays! 2 Module overview:
Assays for gene expression and protein production Module 3, Lecture 5! 20.109 Spring 2011! Topics for Lecture 5 Measuring protein levels! Measuring transcript levels! Imaging assays! 2 Module overview:
