Table of domains participating in Swap events, and listings of the protein isoforms (annotated for Pfam domains) giving rise to Swap events.
|
|
|
- Ilene Rice
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Table of domains participating in Swap events, and listings of the protein isoforms (annotated for Pfam domains) giving rise to Swap events. I. Table of domains participating in Swap events in 65 pairs of protein isoform sequences. Domains participating in Swap Events (D1 <> D2) Domain D1 Domain D2 Description of Domain D1 Description of Domain D2 Hormone_receptor zf C4 Ligand binding domain of nuclear hormone receptor. Steroid hormone receptor activity; transcription factor activity. DNA dependent regulation of transcription. KRAB Zf C2H2 Kruppel associated box. Nucleic Acid binding; DNA dependent regulation of transcription. Zinc finger C4 type. Found in steroid/thyroid hormone receptors; transcription factor activity. Regulation of transcription. Zinc finger. Nucleic acid binding. SCAN zf C2H2 SCAN domain (named after SRE ZBP, CTfin51, AW 1 and Number 18 cdna). Found in several zf C2H2 proteins. DNA dependent regulation of transcription. Zinc finger, C2H2 type. Zinc ion binding; nucleic acid binding. Mito_carr efhand Mitochondrial carrier. Transport CH Plectin Calponin homology domain. Actin binding family. Cytoskeletal / signal transduction sushi CUB Sushi domain (SCR repeat) Complement control protein (CCP) modules, or short consensus repeats (SCR). Complement and adhesion. RGS PDZ Regulator of G protein signaling domain. C2 PDZ Ca2+ dependent membrane targeting module. Signal transduction / EF hand. Calcium ion binding. Signaling. Buffering/transport. Plectin repeat. Found in Plakin proteins. Plasma and nuclear membrances. Structural motif in extracellular and plasma membrane associated proteins. PDZ domain. Protein binding. Signaling PDZ domain. Protein binding. Signaling
2 Domains participating in Swap Events (D1 <> D2) membrane trafficking collagen emi Collagen triple helix repeat. Phosphate transport. Extracellular structural proteins Found in extracellular proteins. Nebulin LIM Nebulin repeat. Found in the thin filaments of striated vertebrate muscle. Actin binding protein. PH Pkinase_Tyr pleckstrin homology. Intracellular signaling / constituent of cytoskeleton. Pkinase_tyr supposed to contain PH domains. LIM domain (Binding protein).zinc ion binding. Interface for protein protein interaction Protein tyrosine kinase. Mediates the response to external stimuli. Tubulin binding MAP2_projctn Tau and MAP protein. Tubulinbinding repeat. FHA BRCT Forkhead associated domain. Phosphopeptide binding motif MAP domain (MHC class II analogue protein) BRCA1 C terminus domain. Phospho protein binding protein. NTP_transf_2 PAP_RNA bind Nucleotidyltransferase domain. Poly(A) polymerase predicted RNA binding domain. Polynucleotide adenyltransferase activity. Ion_trans Ion_trans_2 Ion transport protein Ion channel. Both are of same clan. Orn_Arg_deC_N Orn_DAP_Arg_deC Pyridoxal dependent decarboxylase, pyridoxal binding domain. Catalytic activity MAM ig Adhesive function. Cellular component : membrance Pyridoxal dependent decarboxylase, C terminal sheet domain. Catalytic activity. Immunoglobulin domain ig I set Immunoglobulin Immunoglobulin intermediate. Both are of same clan. I set V set Immunoglobulin I set (intermediate) domain. I set and V set are of same clan. Immunoglobulin V set (variable) domain. EGF_CA EGF Calcium binding EGF domain. EGF like protein. Both are of same clan. Hydrolase E1 E2_ATPase Haloacid dehalogenase like hydrolase. Catalytic activity. Metabolic process Hydrolase activity. ATP binding. Radical_SAM Mob_synth_C Catalytic activity; iron sulfur cluster binding. Molybdenum cofactor synthesis C. iron, sulfur cluster binding Aconitase Aconitase_C Aconitase hydratase. Lyase activity. Aconitase hydratase. Hydro
3 Domains participating in Swap Events (D1 <> D2) lyase activity. Filament Filament_head Intermediate filament protein. Structural molecule activity CNH Pkinase Citron and Citron kinase. Small GTPase regulator activity. PSI Sema Plexin repeat. Membrane. Receptor activity Head region of intermediate filaments. Protein kinase activity. ATP binding. Semaphorins. Secreted and transmembrane proteins. GTP_EFTU_D2 GTP_EFTU Elongation factor GTP binding. Elongation factor PARP WWE Poly(ADP ribose) polymerase. Catalyses covalent attachment of ADP ribose to DNA binding proteins Mediates protein protein interactions in ubiquitin and ADP ribose conjugation system. Sushi An_peroxidase Complement control protein (CCP) modules, or short consensus repeats (SCR). Complement and adhesion Animal haem peroxidase. Peroxidase activity. PH Oxysterol_BP pleckstrin homology. Intracellular signaling / constituent of cytoskeleton Oxysterol binding protein. Steroid metabolic process Ank KH_1 Ankyrin repeat. Protein protein interaction GON TSP_1 Proteinaceous extracellular matrix. Zinc ion binding. Metalloendopeptidase activitiy. K homology domain. RNA binding Thrombospondin type 1 domain. Cell adhesion Thioredoxin DnaJ Participates in redox reactions. Heat shock protein binding Collagen EMI Collagen triple helix repeat. Phosphate transport process. Connective tissue structures. HECT RCC1 HECT domain (ubiquitin transferase) Homologous to the E6 AP Carboxyl terminus. Ubiquitin protein ligase; protein modification process. EMI domain. Participates in multimerization Regulator of chromose condensation. Acts as a guaninenucleotide dissociation simulator (GDS)
4 II. Listings of the protein isoforms (annotated for Pfam domains) giving rise to the observed swap events. II.1. Isoform pairs from ASD data set in all the three instances, the isoforms involve domain repeats. There is a possibility of ambiguity in the alignment due to repeats. 'ENSG _1', 'Tubulin binding', 'Tubulin binding', 'Tubulin binding', 'Tubulin binding' 'ENSG _2', 'MAP2_projctn', 'Tubulin binding', 'Tubulin binding' SWAP : Tubulin binding, MAP2_projctn 'ENSG _2', 'Thioredoxin', 'Thioredoxin' 'ENSG _1', 'DnaJ', 'Thioredoxin' SWAP : Thioredoxin, DnaJ 'ENSG _2', 'CUB', 'Sushi', 'CUB', 'Sushi', 'CUB', 'Sushi', 'CUB', 'Sushi', 'CUB', 'Sushi', 'CUB', 'Sushi', 'CUB' 'ENSG _3', 'Sushi', 'Sushi', 'Sushi', 'Sushi', 'Sushi', Sushi', Sushi', Sushi', 'Sushi', 'Sushi', 'Sushi', SWAP : CUB, Sushi II.2. Isoform pairs from Vega data set II Isoform pairs from Vega data set the isoforms do not show repeating domains and hence the Swap events do not have any ambiguities. 'OTTHUMP ', 'C2', 'RGS' 'OTTHUMP ', 'C2', 'PDZ' SWAP : RGS, PDZ 'OTTHUMP ', 'FHA', 'Nbs1_C' 'OTTHUMP ', 'BRCT', 'Nbs1_C' SWAP : FHA, BRCT 'OTTHUMP ', 'Collagen', 'C1q' 'OTTHUMP ', 'EMI', 'C1q' SWAP : Collagen, EMI 'OTTHUMP ', 'PAP_central', 'NTP_transf_2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'PAP_central', 'PAP_RNA bind' SWAP : NTP_transf_2, PAP_RNA bind 'OTTHUMP ', 'Ion_trans', 'BK_channel_a' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Ion_trans_2', 'BK_channel_a' SWAP : Ion_trans, Ion_trans_2 'OTTHUMP ', 'Ion_trans_2', 'KCNQ_channel' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Ion_trans', 'KCNQ_channel' SWAP : Ion_trans_2, Ion_trans
5 II. Repeating domains. II Isoform pairs from Vega data set the isoforms show repeating domains and hence the Swap events may have ambiguities. 'OTTHUMP ', 'Orn_Arg_deC_N', 'Orn_Arg_deC_N' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Orn_Arg_deC_N', 'Orn_DAP_Arg_deC' SWAP : Orn_Arg_deC_N, Orn_DAP_Arg_deC 'OTTHUMP ', 'ig', 'ig' 'OTTHUMP ', 'I set', 'I set', 'I set', 'ig', 'I set', 'I set', 'V set' SWAP : ig, I set 'OTTHUMP ', 'I set', 'I set', 'I set', 'ig', 'I set', 'I set', 'V set' 'OTTHUMP ', 'I set', 'I set', 'I set', 'I set', 'ig', 'ig' SWAP : I set, ig 'OTTHUMP ', 'EGF_CA', 'EGF_CA', 'GCC2_GCC3', 'GCC2_GCC3', 'GCC2_GCC3', 'CUB' 'OTTHUMP ', 'EGF_CA', 'EGF', 'EGF', 'EGF', 'EGF'] SWAP : EGF_CA, EGF 'OTTHUMP ', 'EGF_CA', 'EGF_CA', 'GCC2_GCC3', 'GCC2_GCC3', 'GCC2_GCC3', 'CUB' 'OTTHUMP ', 'EGF_CA', 'EGF', 'EGF', 'EGF' SWAP : EGF_CA, EGF 'OTTHUMP ', 'Hormone_recep', 'Hormone_recep' 'OTTHUMP ', 'zf C4', 'Hormone_recep' SWAP : Hormone_recep, zf C4 'OTTHUMP ', 'Hydrolase', 'Hydrolase', 'Cation_ATPase_C' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Cation_ATPase_N', 'E1 E2_ATPase', 'Hydrolase', 'Cation_ATPase_C' SWAP : Hydrolase, E1 E2_ATPase 'OTTHUMP ' : 'Plectin', 'Plectin', 'Plectin', 'Plectin' 'OTTHUMP ', 'CH', 'CH', 'Plectin', 'Plectin', 'Plectin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'GAS2' SWAP : Plectin, CH 'OTTHUMP ', 'PH', 'Oxysterol_BP'] (LP) 'OTTHUMP ', 'Oxysterol_BP', 'Oxysterol_BP' SWAP : PH, Oxysterol_BP 'OTTHUMP ', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2'] 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' SWAP : zf C2H2, KRAB 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf
6 C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'SCAN' 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' SWAP : SCAN, zf C2H2 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'SCAN' SWAP : zf C2H2, SCAN 'OTTHUMP ', 'Hormone_recep', 'Hormone_recep' 'OTTHUMP ', 'zf C4', 'Hormone_recep' SWAP : Hormone_recep, zf C4 'OTTHUMP ', 'MAP2_projctn', 'Tubulin binding', 'Tubulin binding', 'Tubulin binding' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Tubulin binding', 'Tubulin binding', 'Tubulin binding', 'Tubulin binding'] SWAP : MAP2_projctn, Tubulin binding 'OTTHUMP ', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'KH_1' SWAP : Ank, KH_1 'OTTHUMP ', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'KH_1'] (LP) SWAP : Ank, KH_1 'OTTHUMP ', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'Ank', 'KH_1' SWAP : Ank, KH_1 'OTTHUMP ', 'Radical_SAM', 'Mob_synth_C', 'MoaC' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Mob_synth_C', 'Mob_synth_C' SWAP : Radical_SAM, Mob_synth_C 'OTTHUMP ', 'Radical_SAM', 'Mob_synth_C', 'MoaC' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Mob_synth_C', 'Mob_synth_C' SWAP : Radical_SAM, Mob_synth_C 'OTTHUMP ', 'TSP_1', 'TSP_1', 'ig', 'I set', 'I set', 'I set', 'TSP_1', 'PLAC' 'OTTHUMP ', V set', 'I set' SWAP : I set, V set 'OTTHUMP ', 'RCC1', 'RCC1', 'RCC1', 'RCC1', 'HECT' 'OTTHUMP ', 'RCC1', 'RCC1', 'RCC1', 'RCC1', 'RCC1', 'RCC1' SWAP : HECT, RCC1 'OTTHUMP ', 'Aconitase', 'Aconitase'
7 'OTTHUMP ', 'Aconitase', 'Aconitase_C' SWAP : Aconitase, Aconitase_C 'OTTHUMP ', 'Filament', 'Filament' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Filament_head', 'Filament' SWAP : Filament, Filament_head 'OTTHUMP ', 'zf C4', 'Hormone_recep' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Hormone_recep', 'Hormone_recep' SWAP : zf C4, Hormone_recep 'OTTHUMP ', 'Nebulin', 'Nebulin', 'Nebulin', 'Nebulin', 'Nebulin', 'Nebulin', 'Nebulin', 'SH3_1' 'OTTHUMP ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', 'LIM', 'Nebulin', 'Nebulin', 'SH3_1' SWAP : Nebulin, LIM 'OTTHUMP ', 'Pkinase', 'CNH' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Pkinase', 'Pkinase' SWAP : CNH, Pkinase 'OTTHUMP ', 'C2', 'C2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'C2', 'C2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'C2', 'C2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'C2', 'C2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'C2', 'C2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'C2', 'C2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' SWAP : zf C2H2, KRAB 'OTTHUMP ', 'Pep_M12B_propep', 'Reprolysin', 'TSP_1', 'ADAM_spacer1', 'GON'
8 'OTTHUMP ', 'Reprolysin', 'TSP_1', 'ADAM_spacer1', 'TSP_1', 'TSP_1', 'TSP_1', 'TSP_1', 'TSP_1' SWAP : GON, TSP_1 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ','KRAB', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'ig', 'I set', 'ig', 'Pkinase_Tyr' 'OTTHUMP ', 'I set', 'I set', 'Pkinase_Tyr' SWAP : ig, I set 'OTTHUMP ', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' SWAP : zf C2H2, KRAB 'OTTHUMP ', 'Sema', 'PSI' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Sema', 'Sema' SWAP : PSI, Sema 'OTTHUMP ', 'GTP_EFTU', 'GTP_EFTU_D2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'GTP_EFTU', 'GTP_EFTU' SWAP : GTP_EFTU_D2, GTP_EFTU 'OTTHUMP ', 'C1_1', 'C1_1', 'PH', 'Pkinase' 'OTTHUMP ','Pkinase_Tyr', 'Pkinase' SWAP : PH, Pkinase_Tyr 'OTTHUMP ', 'Mito_carr', 'Mito_carr', 'Mito_carr' 'OTTHUMP ', 'efhand', 'Mito_carr' SWAP : Mito_carr, efhand 'OTTHUMP ', 'A1pp', 'A1pp', 'PARP' 'OTTHUMP ', 'A1pp', 'A1pp', 'A1pp', 'WWE' SWAP : PARP, WWE 'OTTHUMP ', 'A1pp', 'A1pp', 'PARP' 'OTTHUMP ', 'A1pp', 'A1pp', 'A1pp', 'WWE'
9 SWAP : PARP, WWE 'OTTHUMP ', 'MAM', 'fn3', 'fn3', 'Y_phosphatase', 'Y_phosphatase'] (LP) 'OTTHUMP ', 'ig', 'fn3' SWAP : MAM, ig 'OTTHUMP ', 'An_peroxidase', 'Sushi', 'EGF_CA' 'OTTHUMP ', 'An_peroxidase', 'An_peroxidase', 'EGF_CA' SWAP : Sushi, An_peroxidase 'OTTHUMP ', 'zf C4', 'Hormone_recep' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Hormone_recep', 'Hormone_recep' SWAP : zf C4, Hormone_recep 'OTTHUMP ', 'CH', 'CH', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'efhand', 'efhand', 'GAS2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Plectin', 'Plectin', 'Plectin', 'Plectin', 'Plectin', 'Plectin', 'Plectin', 'Plectin', ' ', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'Spectrin', 'efhand', 'efhand', 'GAS2' SWAP : CH, Plectin 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'zf C4', 'Hormone_recep' 'OTTHUMP ', 'Hormone_recep', 'Hormone_recep' SWAP : zf C4, Hormone_recep 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'KRAB', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'KRAB', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' 'OTTHUMP ', 'KRAB', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2', 'zf C2H2' SWAP : zf C2H2, KRAB
10 III. The single Swap event observed with PRINTS fingerprints (from ASD data set) ENSG _1 ENSG (LP) ['CACHANNEL', 'LVDCCALPHA1D', 'CACHANNEL'] ENSG _3 ENSG ['LVDCCALPHA1D', 'LVDCCALPHA1'] SWAP CACHANNEL, LVDCCALPHA1 IV. The single reshuffle event observed with PRINTS fingerprints (from Vega data set) OTTHUMP OTTHUMG (LP) [''SH2DOMAIN', 'SH3DOMAIN'] False OTTHUMP OTTHUMG ['SH3DOMAIN', 'SH2DOMAIN'] False RESHUFFLE ['SH2DOMAIN', 'SH3DOMAIN'] ['SH3DOMAIN', 'SH2DOMAIN']
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 01: Introduction to Molecular Cell Biology
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 01: Introduction to Molecular Cell Biology Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement describes how an organism is organized from most simple to most complex? Question
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 01: Introduction to Molecular Cell Biology Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement describes how an organism is organized from most simple to most complex? Question
Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section B and ONE question from Section C.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-18 CELL BIOLOGY BIO-5005B Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2017-18 CELL BIOLOGY BIO-5005B Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section
ENCODE DCC Antibody Validation Document
 ENCODE DCC Antibody Validation Document Date of Submission Name: Email: Lab Antibody Name: Target: Company/ Source: Catalog Number, database ID, laboratory Lot Number Antibody Description: Target Description:
ENCODE DCC Antibody Validation Document Date of Submission Name: Email: Lab Antibody Name: Target: Company/ Source: Catalog Number, database ID, laboratory Lot Number Antibody Description: Target Description:
Inserting genes into plasmids
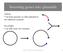 Inserting genes into plasmids GENE cut from genome or other plasmid w/ two different enzymes PLASMID cut with same two enzymes BTEC 120 - Molecular & Cell Biotechnology 18 Inserting genes into plasmids
Inserting genes into plasmids GENE cut from genome or other plasmid w/ two different enzymes PLASMID cut with same two enzymes BTEC 120 - Molecular & Cell Biotechnology 18 Inserting genes into plasmids
Supplemental Material for: A high-throughput RNA-seq approach to profile transcriptional responses
 Supplemental Material for: A high-throughput RNA-seq approach to profile transcriptional responses G. A. Moyerbrailean 1, G. O. Davis 1, C. T. Harvey 1, D. Watza 1, X. Wen 2, R. Pique-Regi 1,3,, F. Luca
Supplemental Material for: A high-throughput RNA-seq approach to profile transcriptional responses G. A. Moyerbrailean 1, G. O. Davis 1, C. T. Harvey 1, D. Watza 1, X. Wen 2, R. Pique-Regi 1,3,, F. Luca
Gene expression DNA RNA. Protein DNA. Replication. Initiation Elongation Processing Export. DNA RNA Protein. Transcription. Degradation.
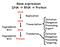 Gene expression DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA Degradation RNA Degradation Protein Replication Transcription Translation Initiation Elongation Processing Export Initiation Elongation Processing Targeting Chapter
Gene expression DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA Degradation RNA Degradation Protein Replication Transcription Translation Initiation Elongation Processing Export Initiation Elongation Processing Targeting Chapter
BME Engineering Molecular Cell Biology. The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament
 BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 09: The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament BME42-620 Lecture 09, September 27, 2011 1 Outline Overviewofcytoskeletal
BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 09: The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament BME42-620 Lecture 09, September 27, 2011 1 Outline Overviewofcytoskeletal
Cell-Extracellular Matrix Interactions
 Cell-Extracellular Matrix Interactions Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Organised network outside of the cell s plasma membrane Between cells Composition varies throughout the ECM Continuous sheet of ECM = Basement
Cell-Extracellular Matrix Interactions Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Organised network outside of the cell s plasma membrane Between cells Composition varies throughout the ECM Continuous sheet of ECM = Basement
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 16 Monday 1 March
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 16 Monday 1 March Review Primary Structure of a portion of a polypeptide chain backbone of Polypeptide chain R-groups of amino acids Native conformation of a dimeric protein,
BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 16 Monday 1 March Review Primary Structure of a portion of a polypeptide chain backbone of Polypeptide chain R-groups of amino acids Native conformation of a dimeric protein,
Section C: The Control of Gene Expression
 Section C: The Control of Gene Expression 1. Each cell of a multicellular eukaryote expresses only a small fraction of its genes 2. The control of gene expression can occur at any step in the pathway from
Section C: The Control of Gene Expression 1. Each cell of a multicellular eukaryote expresses only a small fraction of its genes 2. The control of gene expression can occur at any step in the pathway from
Gut microbial colonization in day old chicks. Henri Woelders DirkJan Schokker Mari A. Smits
 Gut microbial colonization in day old chicks Henri Woelders DirkJan Schokker Mari A. Smits Trends Robustness; Resilience. Ability to keep healthy, or recover from disease (with minimal human intervention).
Gut microbial colonization in day old chicks Henri Woelders DirkJan Schokker Mari A. Smits Trends Robustness; Resilience. Ability to keep healthy, or recover from disease (with minimal human intervention).
Quick Review of Protein Synthesis
 Collin College BIOL. 2401 Quick Review of Protein Synthesis. Proteins and Protein Synthesis Proteins are the molecular units that do most of the work in a cell. They function as molecular catalysts, help
Collin College BIOL. 2401 Quick Review of Protein Synthesis. Proteins and Protein Synthesis Proteins are the molecular units that do most of the work in a cell. They function as molecular catalysts, help
Chemistry 1050 Exam 4 Study Guide
 Chapter 19 Chemistry 1050 Exam 4 Study Guide 19.1 and 19.2 Know there are 20 common amino acids that can polymerize into proteins. Know why amino acids are called alpha amino acids. Identify the charges
Chapter 19 Chemistry 1050 Exam 4 Study Guide 19.1 and 19.2 Know there are 20 common amino acids that can polymerize into proteins. Know why amino acids are called alpha amino acids. Identify the charges
Chemistry 1120 Exam 3 Study Guide
 Chemistry 1120 Exam 3 Study Guide Chapter 9 9.1 and 9.2 Know there are 20 common amino acids that can polymerize into proteins. Know why amino acids are called alpha amino acids. Identify the charges of
Chemistry 1120 Exam 3 Study Guide Chapter 9 9.1 and 9.2 Know there are 20 common amino acids that can polymerize into proteins. Know why amino acids are called alpha amino acids. Identify the charges of
namibia UniVERSITY OF SC IEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES PAPER: THEORY
 namibia UniVERSITY OF SC IEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBBMS LEVEL: 6 COURSE:
namibia UniVERSITY OF SC IEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBBMS LEVEL: 6 COURSE:
Translation. Protein Synthesis
 Protein Structure Translation Protein Synthesis Size and Shape Comparison of Proteins Levels of Protein Structure 1 o 2 o 3 o 4 o Amino Acids Peptide Bonds Proteins are formed by creating peptide bonds
Protein Structure Translation Protein Synthesis Size and Shape Comparison of Proteins Levels of Protein Structure 1 o 2 o 3 o 4 o Amino Acids Peptide Bonds Proteins are formed by creating peptide bonds
Introduction to Proteins
 Introduction to Proteins Lecture 4 Module I: Molecular Structure & Metabolism Molecular Cell Biology Core Course (GSND5200) Matthew Neiditch - Room E450U ICPH matthew.neiditch@umdnj.edu What is a protein?
Introduction to Proteins Lecture 4 Module I: Molecular Structure & Metabolism Molecular Cell Biology Core Course (GSND5200) Matthew Neiditch - Room E450U ICPH matthew.neiditch@umdnj.edu What is a protein?
DNA. Branden & Tooze, Ch. 7 Deoxyribose nucleic acids are made of three parts
 DNA Branden & Tooze, Ch. 7 Deoxyribose nucleic acids are made of three parts base: adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine sugar: deoxyribose phosphate: will form the phosphate backbone wide narrow DNA binding
DNA Branden & Tooze, Ch. 7 Deoxyribose nucleic acids are made of three parts base: adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine sugar: deoxyribose phosphate: will form the phosphate backbone wide narrow DNA binding
The cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton, the motor proteins, the muscle and its regulation. The cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton.
 , the motor proteins, the muscle and its regulation Dept. of Biophysics, University of Pécs Zoltán Ujfalusi January-February 2012 Dynamic framework of the Eukaryotes Three main filament-class: 1. Intermedier
, the motor proteins, the muscle and its regulation Dept. of Biophysics, University of Pécs Zoltán Ujfalusi January-February 2012 Dynamic framework of the Eukaryotes Three main filament-class: 1. Intermedier
DNA Binding Domains: Structural Motifs. Effector Domain. Zinc Fingers. Zinc Fingers, continued. Zif268
 DNA Binding Domains: Structural Motifs Studies of known transcription factors have found several motifs of protein design to allow sequence-specific binding of DNA. We will cover only three of these motifs:
DNA Binding Domains: Structural Motifs Studies of known transcription factors have found several motifs of protein design to allow sequence-specific binding of DNA. We will cover only three of these motifs:
DNA RNA PROTEIN. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted
 DNA RNA PROTEIN Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted DNA Molecule of heredity Contains all the genetic info our cells inherit Determines
DNA RNA PROTEIN Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted DNA Molecule of heredity Contains all the genetic info our cells inherit Determines
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 7 - GENE EXPRESSION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1
 AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.5 Nucleic Acids and their functions Page 1 From the syllabus: 1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1 l. Nucleic
AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.5 Nucleic Acids and their functions Page 1 From the syllabus: 1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1 l. Nucleic
Key Area 1.3: Gene Expression
 Key Area 1.3: Gene Expression RNA There is a second type of nucleic acid in the cell, called RNA. RNA plays a vital role in the production of protein from the code in the DNA. What is gene expression?
Key Area 1.3: Gene Expression RNA There is a second type of nucleic acid in the cell, called RNA. RNA plays a vital role in the production of protein from the code in the DNA. What is gene expression?
BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2008
 BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2008 NAME (printed very legibly) Key UT-EID EXAMINATION 3 Before beginning, check to be sure that this exam contains 7 pages (including front and back) numbered consecutively,
BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2008 NAME (printed very legibly) Key UT-EID EXAMINATION 3 Before beginning, check to be sure that this exam contains 7 pages (including front and back) numbered consecutively,
3.1 Storing Information. Polypeptides. Protein Structure. Helical Secondary Structure. Types of Protein Structure. Molecular Biology Fourth Edition
 Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Molecular Biology Fourth Edition Robert F. Weaver Chapter 3 An Introduction to Gene Function 3.1 Storing Information Producing a protein from DNA information involves both
Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Molecular Biology Fourth Edition Robert F. Weaver Chapter 3 An Introduction to Gene Function 3.1 Storing Information Producing a protein from DNA information involves both
Amino Acids & Proteins
 Chemistry 131 Lecture 13: Protein Function; Amino Acids and Properties, Chirality & Handedness in Amino Acids, Primary Protein Structure Sections 18.1 18.7 in McMurry, Ballantine, et. al. 7 th edition
Chemistry 131 Lecture 13: Protein Function; Amino Acids and Properties, Chirality & Handedness in Amino Acids, Primary Protein Structure Sections 18.1 18.7 in McMurry, Ballantine, et. al. 7 th edition
Gene Expression and Regulation - 1
 Gene Expression and Regulation - 1 We have been discussing the molecular structure of DNA and its function in DNA replication and in transcription. Earlier we discussed how genes interact in transmission
Gene Expression and Regulation - 1 We have been discussing the molecular structure of DNA and its function in DNA replication and in transcription. Earlier we discussed how genes interact in transmission
Chapter 3 An Introduction to Gene Function 3.1 Storing Information 3.2 Replication 3.3 Mutation
 Chapter 3 An Introduction to Gene Function 3.1 Storing Information 3.2 Replication 3.3 Mutation 3.1 Storing Information [Central Dogma] Producing a protein from DNA => by transcription and translation
Chapter 3 An Introduction to Gene Function 3.1 Storing Information 3.2 Replication 3.3 Mutation 3.1 Storing Information [Central Dogma] Producing a protein from DNA => by transcription and translation
Translation Mechanisms
 Translation Mechanisms Biology I Hayder A. Giha Translation The translation is the process of protein synthesis, where information in nucleotides sequences of a mrna is translated into amino acids sequence
Translation Mechanisms Biology I Hayder A. Giha Translation The translation is the process of protein synthesis, where information in nucleotides sequences of a mrna is translated into amino acids sequence
Self-test Quiz for Chapter 12 (From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype)
 Self-test Quiz for Chapter 12 (From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype) Question#1: One-Gene, One-Polypeptide The figure below shows the results of feeding trials with one auxotroph strain of Neurospora
Self-test Quiz for Chapter 12 (From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype) Question#1: One-Gene, One-Polypeptide The figure below shows the results of feeding trials with one auxotroph strain of Neurospora
Chapter 2 Molecules to enzymes - Short answer [72 marks]
![Chapter 2 Molecules to enzymes - Short answer [72 marks] Chapter 2 Molecules to enzymes - Short answer [72 marks]](/thumbs/72/67260206.jpg) Chapter 2 Molecules to enzymes - Short answer [72 marks] 1a. Outline primary and quaternary protein structures. Primary protein structure: Quaternary protein structure: a. (primary structure) is sequence
Chapter 2 Molecules to enzymes - Short answer [72 marks] 1a. Outline primary and quaternary protein structures. Primary protein structure: Quaternary protein structure: a. (primary structure) is sequence
Please sign below if you wish to have your grades posted by the last five digits of your SSN
 BIO 226R EXAM II (Sample) PRINT YOUR NAME SSN Please sign below if you wish to have your grades posted by the last five digits of your SSN Signature BIO 226R Exam II has 6 pages, and 27 questions. There
BIO 226R EXAM II (Sample) PRINT YOUR NAME SSN Please sign below if you wish to have your grades posted by the last five digits of your SSN Signature BIO 226R Exam II has 6 pages, and 27 questions. There
From Gene to Protein. Wednesday, 26th July
 From Gene to Protein Wednesday, 26th July Overview During this session, you will explore the following questions: What are the building blocks of DNA? What are proteins made of? How does genes get translated
From Gene to Protein Wednesday, 26th July Overview During this session, you will explore the following questions: What are the building blocks of DNA? What are proteins made of? How does genes get translated
Bayesian Decomposition
 Bayesian Decomposition Michael Ochs Making Proteins A Closer Look at Translation Post-Translational Modification RNA Splicing mirna Identifying Pathways A 1 2 3 B C D A B C D Bioinformatics www.promega.com
Bayesian Decomposition Michael Ochs Making Proteins A Closer Look at Translation Post-Translational Modification RNA Splicing mirna Identifying Pathways A 1 2 3 B C D A B C D Bioinformatics www.promega.com
The Central Dogma. DNA makes RNA makes Proteins
 The Central Dogma DNA makes RNA makes Proteins TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION OF
The Central Dogma DNA makes RNA makes Proteins TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION OF
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only) I. Protein Synthesis: creation of new proteins a. Much of the cellular machinery is devoted to synthesizing
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit IV Cellular Function Chapter 4, Chapter 27 (meiosis only) I. Protein Synthesis: creation of new proteins a. Much of the cellular machinery is devoted to synthesizing
Mechanism of action-1
 Mechanism of action-1 receptors: mediators of hormone action, membrane associated vs. intracellular receptors: measurements of receptor - ligand interaction, mechanism surface-receptors: kinases, phosphatases,
Mechanism of action-1 receptors: mediators of hormone action, membrane associated vs. intracellular receptors: measurements of receptor - ligand interaction, mechanism surface-receptors: kinases, phosphatases,
Sequence Databases and database scanning
 Sequence Databases and database scanning Marjolein Thunnissen Lund, 2012 Types of databases: Primary sequence databases (proteins and nucleic acids). Composite protein sequence databases. Secondary databases.
Sequence Databases and database scanning Marjolein Thunnissen Lund, 2012 Types of databases: Primary sequence databases (proteins and nucleic acids). Composite protein sequence databases. Secondary databases.
Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points?
 BCH 401G Lecture 37 Andres Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points? RNA processing: Capping, polyadenylation, splicing. Why process mammalian
BCH 401G Lecture 37 Andres Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points? RNA processing: Capping, polyadenylation, splicing. Why process mammalian
Hemidesmosome. Focal adhesion
 BIOLOGY 52 - - CELL AND DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY - - FALL 2002 Third Examination - - November, 2002 -------------------------------------------------- Put your name at the top of each page. Please read each
BIOLOGY 52 - - CELL AND DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY - - FALL 2002 Third Examination - - November, 2002 -------------------------------------------------- Put your name at the top of each page. Please read each
Chapter 11. Gene Expression and Regulation. Lectures by Gregory Ahearn. University of North Florida. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc..
 Chapter 11 Gene Expression and Regulation Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.. 11.1 How Is The Information In DNA Used In A Cell? Most genes contain
Chapter 11 Gene Expression and Regulation Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.. 11.1 How Is The Information In DNA Used In A Cell? Most genes contain
Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
Differential Gene Expression
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Differential Gene Expression October 13, 2005 core transcription initiation site 5 promoter 3 TATAT +1 upstream downstream Basal transcription factors (eukaryotes) TFIID
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Differential Gene Expression October 13, 2005 core transcription initiation site 5 promoter 3 TATAT +1 upstream downstream Basal transcription factors (eukaryotes) TFIID
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology
 Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Spring 2006 Biochemistry 302 Exam 2
 Name Spring 2006 Biochemistry 302 Exam 2 Directions: This exam has 45 questions/problems totaling 110 points. Check to make sure you have seven pages. Some questions have multiple parts so read each one
Name Spring 2006 Biochemistry 302 Exam 2 Directions: This exam has 45 questions/problems totaling 110 points. Check to make sure you have seven pages. Some questions have multiple parts so read each one
Chapter 15. Cytoskeletal Systems. Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Cytoskeletal Systems Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Table 15-1 - Microtubules Table 15-1 - Microfilaments Table 15-1 Intermediate Filaments Table 15-3 Microtubules
Chapter 15 Cytoskeletal Systems Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Table 15-1 - Microtubules Table 15-1 - Microfilaments Table 15-1 Intermediate Filaments Table 15-3 Microtubules
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID sema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin)
Gene Information Gene Name Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID sema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin)
Unit 1 Human cells. 1. Division and differentiation in human cells
 Unit 1 Human cells 1. Division and differentiation in human cells Stem cells Describe the process of differentiation. Explain how differentiation is brought about with reference to genes. Name the two
Unit 1 Human cells 1. Division and differentiation in human cells Stem cells Describe the process of differentiation. Explain how differentiation is brought about with reference to genes. Name the two
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I)
 Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I) Microbial Metabolism Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions that occur within a living organism. These chemical reactions are generally of two types: Catabolic:
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I) Microbial Metabolism Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions that occur within a living organism. These chemical reactions are generally of two types: Catabolic:
Molecular biology WID Masters of Science in Tropical and Infectious Diseases-Transcription Lecture Series RNA I. Introduction and Background:
 Molecular biology WID 602 - Masters of Science in Tropical and Infectious Diseases-Transcription Lecture Series RNA I. Introduction and Background: DNA and RNA each consists of only four different nucleotides.
Molecular biology WID 602 - Masters of Science in Tropical and Infectious Diseases-Transcription Lecture Series RNA I. Introduction and Background: DNA and RNA each consists of only four different nucleotides.
Lecture 11: Metalloproteins - I
 Lecture 11: Metalloproteins - I 1. Introduction A large number of biochemical reactions are known to be catalyzed by proteins. The reason behind their functions as catalysts is attributed to the side chains
Lecture 11: Metalloproteins - I 1. Introduction A large number of biochemical reactions are known to be catalyzed by proteins. The reason behind their functions as catalysts is attributed to the side chains
Highlights Translation I
 Highlights Translation I 1. Prokaryotic ribosomes are a 70S multi-protein, multi-rna complex, consisting of a large 50S subunit (31 proteins + 23S rrna + 5S rrna) and a smaller 30S subunit (21 proteins
Highlights Translation I 1. Prokaryotic ribosomes are a 70S multi-protein, multi-rna complex, consisting of a large 50S subunit (31 proteins + 23S rrna + 5S rrna) and a smaller 30S subunit (21 proteins
Relationship of Gene s Types and Introns
 Chi To BME 230 Final Project Relationship of Gene s Types and Introns Abstract: The relationship in gene ontology classification and the modification of the length of introns through out the evolution
Chi To BME 230 Final Project Relationship of Gene s Types and Introns Abstract: The relationship in gene ontology classification and the modification of the length of introns through out the evolution
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline. Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics
 Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Transcription. By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt
 Transcription By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION 11/26/2010 2 RNA Messenger RNAs (mrnas) encode the amino acid sequence of one or more polypeptides specified by
Transcription By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION 11/26/2010 2 RNA Messenger RNAs (mrnas) encode the amino acid sequence of one or more polypeptides specified by
Gene Expression: Transcription
 Gene Expression: Transcription The majority of genes are expressed as the proteins they encode. The process occurs in two steps: Transcription = DNA RNA Translation = RNA protein Taken together, they make
Gene Expression: Transcription The majority of genes are expressed as the proteins they encode. The process occurs in two steps: Transcription = DNA RNA Translation = RNA protein Taken together, they make
TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA TRANSCRIPTION. Umm AL Qura University. Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose. Bases AUCG ATCG. Strand length Short Long
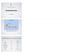 Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
Metabolism BIOL 3702: Chapter 10
 Metabolism BIOL 3702: Chapter 10 Introduction to Metabolism u Metabolism is the sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in a cell u Two major parts of metabolism: v Catabolism Ø Large, more complex
Metabolism BIOL 3702: Chapter 10 Introduction to Metabolism u Metabolism is the sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in a cell u Two major parts of metabolism: v Catabolism Ø Large, more complex
CELL BIOLOGY BIOL3030, 3 credits Fall 2012, Aug 20, Dec 14, 2012 Tuesday/Thursday 8:00 am-9:15 am Bowman-Oddy Laboratories 1049
 INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Song-Tao Liu WO3254B Tel: 419-530-7853 Email: Song-Tao.Liu@utoledo.edu OFFICE HOURS CELL BIOLOGY BIOL3030, 3 credits Fall 2012, Aug 20, 2012 - Dec 14, 2012 Tuesday/Thursday 8:00 am-9:15
INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Song-Tao Liu WO3254B Tel: 419-530-7853 Email: Song-Tao.Liu@utoledo.edu OFFICE HOURS CELL BIOLOGY BIOL3030, 3 credits Fall 2012, Aug 20, 2012 - Dec 14, 2012 Tuesday/Thursday 8:00 am-9:15
CYTOSKELETON, MOTORPROTEINS.
 CYTOSKELETON, MOTORPROTEINS. SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY Tamás Huber 15. 10. 2012. CYTOSKELETON: Dynamic scaffold in eukaryotic cells Three main filament systems: A. Intermediate filaments B. Microtubules C.
CYTOSKELETON, MOTORPROTEINS. SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY Tamás Huber 15. 10. 2012. CYTOSKELETON: Dynamic scaffold in eukaryotic cells Three main filament systems: A. Intermediate filaments B. Microtubules C.
Introduction to genome biology Sandrine Dudoit and Robert Gentleman
 Introduction to genome biology Sandrine Dudoit and Robert Gentleman University of California, Berkeley Outline Cells and cell division DNA structure and replication Proteins Central dogma: transcription,
Introduction to genome biology Sandrine Dudoit and Robert Gentleman University of California, Berkeley Outline Cells and cell division DNA structure and replication Proteins Central dogma: transcription,
2012 GENERAL [5 points]
![2012 GENERAL [5 points] 2012 GENERAL [5 points]](/thumbs/75/72452386.jpg) GENERAL [5 points] 2012 Mark all processes that are part of the 'standard dogma of molecular' [ ] DNA replication [ ] transcription [ ] translation [ ] reverse transposition [ ] DNA restriction [ ] DNA
GENERAL [5 points] 2012 Mark all processes that are part of the 'standard dogma of molecular' [ ] DNA replication [ ] transcription [ ] translation [ ] reverse transposition [ ] DNA restriction [ ] DNA
Biochemistry 302. Exam 2. March 10, Answer Key
 1 Biochemistry 302 Exam 2 March 10, 2004 Answer Key 2 Biochemistry 302, Spring 2004 Exam 2 (100 points) Name I. Short answer 1. Identify the 5 end, 3 end, amino acid acceptor nucleoside, and bases comprising
1 Biochemistry 302 Exam 2 March 10, 2004 Answer Key 2 Biochemistry 302, Spring 2004 Exam 2 (100 points) Name I. Short answer 1. Identify the 5 end, 3 end, amino acid acceptor nucleoside, and bases comprising
2 nd Term Final. Revision Sheet. Students Name: Grade: 12-A/B. Subject: Chemistry. Teacher Signature. Page 1 of 10
 2 nd Term Final Revision Sheet Students Name: Grade: 12-A/B Subject: Chemistry Teacher Signature Page 1 of 10 Chapter-23, Lesson-1 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. How does the number of hydrogen atoms in a carbohydrate
2 nd Term Final Revision Sheet Students Name: Grade: 12-A/B Subject: Chemistry Teacher Signature Page 1 of 10 Chapter-23, Lesson-1 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. How does the number of hydrogen atoms in a carbohydrate
Post-translational modification
 Protein expression Western blotting, is a widely used and accepted technique to detect levels of protein expression in a cell or tissue extract. This technique measures protein levels in a biological sample
Protein expression Western blotting, is a widely used and accepted technique to detect levels of protein expression in a cell or tissue extract. This technique measures protein levels in a biological sample
IB BIO I Replication/Transcription/Translation Van Roekel/Madden. Name Date Period. D. It separates DNA strands. (Total 1 mark)
 Name Date Period 1. What is the function of helicase? A. It forms bonds between DNA nucleotides. B. It adds new nucleotides to the DNA helix. C. It forms the DNA helix. D. It separates DNA strands. 2.
Name Date Period 1. What is the function of helicase? A. It forms bonds between DNA nucleotides. B. It adds new nucleotides to the DNA helix. C. It forms the DNA helix. D. It separates DNA strands. 2.
Switch On Protein-Protein Interactions
 Switch On Protein-Protein Interactions Rapid and specific control of signal transduction pathways, protein activity, protein localization, transcription, and more Dimerizer protein 1 protein 2 Clontech
Switch On Protein-Protein Interactions Rapid and specific control of signal transduction pathways, protein activity, protein localization, transcription, and more Dimerizer protein 1 protein 2 Clontech
Molecular Genetics. The flow of genetic information from DNA. DNA Replication. Two kinds of nucleic acids in cells: DNA and RNA.
 Molecular Genetics DNA Replication Two kinds of nucleic acids in cells: DNA and RNA. DNA function 1: DNA transmits genetic information from parents to offspring. DNA function 2: DNA controls the functions
Molecular Genetics DNA Replication Two kinds of nucleic acids in cells: DNA and RNA. DNA function 1: DNA transmits genetic information from parents to offspring. DNA function 2: DNA controls the functions
Bi 8 Lecture 7. Ellen Rothenberg 26 January Reading: Ch. 3, pp ; panel 3-1
 Bi 8 Lecture 7 PROTEIN STRUCTURE, Functional analysis, and evolution Ellen Rothenberg 26 January 2016 Reading: Ch. 3, pp. 109-134; panel 3-1 (end with free amine) aromatic, hydrophobic small, hydrophilic
Bi 8 Lecture 7 PROTEIN STRUCTURE, Functional analysis, and evolution Ellen Rothenberg 26 January 2016 Reading: Ch. 3, pp. 109-134; panel 3-1 (end with free amine) aromatic, hydrophobic small, hydrophilic
Chapter 25: Regulating Eukaryotic Transcription The Ligand Responsive Activators
 Chapter 25: Regulating Eukaryotic Transcription The Ligand Responsive Activators At least 5 potential gene expression control points Superfamily of Gene Regulators Activation of gene structure Initiation
Chapter 25: Regulating Eukaryotic Transcription The Ligand Responsive Activators At least 5 potential gene expression control points Superfamily of Gene Regulators Activation of gene structure Initiation
Chem 465 Biochemistry II
 Chem 465 Biochemistry II Name: 2 points Multiple choice (4 points apiece): 1. Which of the following is not true of trna molecules? A) The 3'-terminal sequence is -CCA. B) Their anticodons are complementary
Chem 465 Biochemistry II Name: 2 points Multiple choice (4 points apiece): 1. Which of the following is not true of trna molecules? A) The 3'-terminal sequence is -CCA. B) Their anticodons are complementary
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Towards definition of an ECM parts list: An advance on GO categories
 Towards definition of an ECM parts list: An advance on GO categories The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published
Towards definition of an ECM parts list: An advance on GO categories The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published
NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM. Omidiwura, B.R.O
 NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM Omidiwura, B.R.O Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid
NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM Omidiwura, B.R.O Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID FGFR1 Human The protein encoded by this gene
Gene Information Gene Name fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID FGFR1 Human The protein encoded by this gene
Microbial Metabolism. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 5 Microbial Metabolism Big Picture: Metabolism Metabolism is the buildup and breakdown of nutrients
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 5 Microbial Metabolism Big Picture: Metabolism Metabolism is the buildup and breakdown of nutrients
Judy Wieber. Department of Computational Biology. May 28, 2008
 Review III: Cellular Processes Judy Wieber BBSI @ Pitt 2008 Department of Computational Biology University it of Pittsburgh School of Medicine i May 28, 2008 Outline Metabolism Cell cycle Transcription
Review III: Cellular Processes Judy Wieber BBSI @ Pitt 2008 Department of Computational Biology University it of Pittsburgh School of Medicine i May 28, 2008 Outline Metabolism Cell cycle Transcription
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 6: DNA: The Molecule of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 6: DNA: The Molecule of Life Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 6.1 Describe the structure of the DNA molecule and how this structure allows for the storage of information,
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 6: DNA: The Molecule of Life Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 6.1 Describe the structure of the DNA molecule and how this structure allows for the storage of information,
1 Scaffolds. 2 Extracellular matrix
 This lecture describes the components of the extracellular matrix and their influence on the cell properties and functions. 1 Scaffolds One of the key components of the tissue engineering triad is the
This lecture describes the components of the extracellular matrix and their influence on the cell properties and functions. 1 Scaffolds One of the key components of the tissue engineering triad is the
Chapter 4: How Cells Work
 Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: l l l l l Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription:
Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: l l l l l Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription:
Chapter 4: How Cells Work
 Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription: Sending the
Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription: Sending the
Old EXAM 1 BIO409/509 NAME. Please number your answers and write them on the attached, lined paper.
 Old EXAM 1 BIO409/509 NAME Please number your answers and write them on the attached, lined paper. 1) Describe euchromatin and heterochromatin. Which form of chromatin would the insulin gene be found in
Old EXAM 1 BIO409/509 NAME Please number your answers and write them on the attached, lined paper. 1) Describe euchromatin and heterochromatin. Which form of chromatin would the insulin gene be found in
C. Incorrect! Threonine is an amino acid, not a nucleotide base.
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 05: RNA and Protein Biosynthesis Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following bases are only found in RNA? Question #01 (A) Ribose. (B) Uracil. (C) Threonine. (D) Adenine.
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 05: RNA and Protein Biosynthesis Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following bases are only found in RNA? Question #01 (A) Ribose. (B) Uracil. (C) Threonine. (D) Adenine.
Creation of a federated database of blood proteins: a powerful new tool for finding and characterizing biomarkers in serum
 Marshall et al. Clinical Proteomics 2014, 11:3 CLINICAL PROTEOMICS RESEARCH Creation of a federated database of blood proteins: a powerful new tool for finding and characterizing biomarkers in serum John
Marshall et al. Clinical Proteomics 2014, 11:3 CLINICAL PROTEOMICS RESEARCH Creation of a federated database of blood proteins: a powerful new tool for finding and characterizing biomarkers in serum John
From Gene to Protein transcription, messenger RNA (mrna) translation, RNA processing triplet code, template strand, codons,
 From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
Chapter 9 - Protein Translation
 Chapter 9 - Protein Translation Section 1: Introduction Section 2: The Genetic code! 2.1! The Problem! 2.2! The Solution Section 3: The players in Translation! 3.1! mrna! 3.2! trna! 3.3! The Ribosome Section
Chapter 9 - Protein Translation Section 1: Introduction Section 2: The Genetic code! 2.1! The Problem! 2.2! The Solution Section 3: The players in Translation! 3.1! mrna! 3.2! trna! 3.3! The Ribosome Section
Biochemistry, Cell and Molecular Biology Test Practice Book
 GRADUATE RECORD EXAMINATIONS Biochemistry, Cell and Molecular Biology Test Practice Book This practice book contains one actual full-length GRE Biochemistry, Cell and Molecular Biology Test test-taking
GRADUATE RECORD EXAMINATIONS Biochemistry, Cell and Molecular Biology Test Practice Book This practice book contains one actual full-length GRE Biochemistry, Cell and Molecular Biology Test test-taking
Eukaryotic Gene Expression Prof. P. N. Rangarajan Department of Biochemistry Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 Eukaryotic Gene Expression Prof. P. N. Rangarajan Department of Biochemistry Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. # 06 Eukaryotic Transcription Factors: Transcription Activation Domains In
Eukaryotic Gene Expression Prof. P. N. Rangarajan Department of Biochemistry Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. # 06 Eukaryotic Transcription Factors: Transcription Activation Domains In
Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein. Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Gene Expression. Which of the following is the best example of gene expression? Why?
 Slide 1 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Slide 1 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Nucleic Acids and the Encoding of Biological Information. Chapter 3
 Nucleic Acids and the Encoding of Biological Information Chapter 3 GRIFFITH S EXPERIMENT ON THE NATURE OF THE GENETIC MATERIAL In 1928, Frederick Griffith demonstrated that molecules can transfer genetic
Nucleic Acids and the Encoding of Biological Information Chapter 3 GRIFFITH S EXPERIMENT ON THE NATURE OF THE GENETIC MATERIAL In 1928, Frederick Griffith demonstrated that molecules can transfer genetic
Scientific Method. Name: NetID: Exam 1 Version 1 September 12, 2017 Dr. A. Pimentel
 Name: NetID: Exam 1 Version 1 September 12, 2017 Dr. A. Pimentel Each question has a value of 4 points and there is a total of 156 points in the exam. However, the maximum score of this exam will be capped
Name: NetID: Exam 1 Version 1 September 12, 2017 Dr. A. Pimentel Each question has a value of 4 points and there is a total of 156 points in the exam. However, the maximum score of this exam will be capped
DNA Function: Information Transmission
 DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES
 CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES I. Introduction A. No operon structures in eukaryotes B. Regulation of gene expression is frequently tissue specific.
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES I. Introduction A. No operon structures in eukaryotes B. Regulation of gene expression is frequently tissue specific.
Transcription: Synthesis of RNA
 Transcription: Synthesis of RNA The flow of information in the cells (the central dogma of molecular biology): Transcription = RNA synthesis on a DNA template. The mrna will provide the information for
Transcription: Synthesis of RNA The flow of information in the cells (the central dogma of molecular biology): Transcription = RNA synthesis on a DNA template. The mrna will provide the information for
DNA and RNA Structure Guided Notes
 Nucleic acids, especially DNA, are considered as the key biomolecules that guarantee the continuity of life. DNA is the prime genetic molecule which carry all the hereditary information that's passed from
Nucleic acids, especially DNA, are considered as the key biomolecules that guarantee the continuity of life. DNA is the prime genetic molecule which carry all the hereditary information that's passed from
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name sortilin 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID SORT1 Human This gene encodes a protein that is a multi-ligand type-1
Gene Information Gene Name sortilin 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID SORT1 Human This gene encodes a protein that is a multi-ligand type-1
Unit 1: DNA and the Genome. Sub-Topic (1.3) Gene Expression
 Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.3) Gene Expression Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.3) Gene Expression On completion of this subtopic I will be able to State the meanings of the terms genotype,
Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.3) Gene Expression Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.3) Gene Expression On completion of this subtopic I will be able to State the meanings of the terms genotype,
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA
 RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
The cytoskeletal system
 The cytoskeletal system Types, polymerization, characteristics and mechanical properties of cytoskeletal filaments. Associated protein. 24.09.2013. Cytoskeleton The cellular "scaffold" or "skeleton" within
The cytoskeletal system Types, polymerization, characteristics and mechanical properties of cytoskeletal filaments. Associated protein. 24.09.2013. Cytoskeleton The cellular "scaffold" or "skeleton" within
