Figure S1. Schematic representation of the winter VRN-H1 allele from cv. Strider (AY750993) with positions of markers genotyped in this study
|
|
|
- Alexina Johns
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Figure S1. Schematic representation of the winter VRN-H1 allele from cv. Strider (AY750993) with positions of markers genotyped in this study indicated. Exons are denoted by black boxes. SNP1 (T-1,948/C), SNP2 (A-1,881/G) and SNP3 (T-1,655/C) are located in the promoter. SNP4 (T+14,567/C) and SNP5 (G+14,585/A) are located in intron VII, while SNP6 (C+14,828/G) is in the 3 UTR. Primer pair 1 assay for the absence of a deletion in intron I, which Fu et al. (2005) describe as characteristic of winter varieties; primer pair 2 assay for the presence of a 5.2 kb deletion within intron I, characteristic of the spring cv. Morex (Fu et al. 2005); primer pair 3 (HvBM5A-exon2- F1 / HvBM5A-intron1-R13, sequences for which are presented in Table S1) assay for the presence or absence of a 42 bp InDel at the 3 end of intron I (first identified by von Zitzewitz et al. 2005). The positions of the MITE (grey box), Lolaog solo LTR (striped box) and the Morex intron I deletion (boxed by dashed line) within intron I are indicated. All other intron I deletions are illustrated in Figure 2. Primers designed to assay for these additional intron I deletions were designed flanking these breakpoints, and are listed in Table S1.
2 Figure S2. Separation of PCR amplicons by agarose-gel electrophoresis, illustrating differentiation between VRN-H1 haplotypes 1A (winter) / 2 (spring) and 5C (winter) using primers HvBM5A-intron1-F3 / Intr1/H/R3 (VRN-H1 haplotype 1A/2 = 1,438 bp, haplotype 5C = 952 bp; all other spring alleles = no amplification). Haplotype 1A = Igri, haplotype 1B = Etu, haplotype 2 = Varunda, haplotype 3 = Dandy, haplotype 4 A = Optic, haplotype 4B = Prisma, haplotype 5A = Pohto, haplotype 5B = Oriol, haplotype 5C = Express, L = 1 kb ladder. Primer details listed in Table S1.
3 Table S1 Primer name Sequence 5 to 3 Use HvBM5A-promoter-F1 GCAATGCAGCACCTATGCCA Amplify/sequence promoter HvBM5A-promoter-R1 CGTTGCTGCGTGTGGGTTG Amplify/sequence promoter HvBM5A-promoter-F2 CATCGCATGATTCGACGCTG Amplify /sequence promoter HvBM5A-promoter-R2 GCGAGCGAGCGAGCGACCG Amplify /sequence promoter HvBM5A-exon1-F1 CTTCACCCAACCACCTGACAG Amplify/sequence exon I HvBM5A-exon1-R1 GCGGACGCAAATGTCACTTTT Amplify/sequence exon I HvBM5A-intronI-F1 GTTCTCCACCGAGTCATGGT Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-R1 CGCTGGACGAGAATTATTGA Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-F2 GGCGATGGTTCTTGACAAAG Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-R2 TGAGTCGGTTATATGCAGGCTA Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-F3 TTTGTCGGAACTACAACCTTCA Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-R3 GTGTCAGCCTTACGCAAGAA Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-F4 CCAGGGGACCCACAGTAGTA Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-R4 TTTATGTGCACAGGATCTCCA Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-F5 TAACCGTGCGAGATGACGTA Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-R5 CCTTGAGTCATAGCCCACCA Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-F6 CCACACATGCACAGTCACAC Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-R6 AGAAGGTTACCCTGCGAACA Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-F7 AGCACGAGAGGCGAAGATAG Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-R7 GGGCGGAGTACTGCTACAAC Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-F8 AATTTTGCCCGGCGTATAGT Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-R8 GCTACCATTCCACAGCATCA Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-F9 AGCATCACGGCGAAAGAG Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-R9 CGGATGGTTCCTGAGGATATT Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-F10 TCATGAGTGCTTGGAACGTC Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-R10 TGCAGGTCACTCTTTGCATC Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-F11 ATTGGAGGAGAAAGGCAACC Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-R11 AAAGCCCGATGCTGAAAAC Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-F12 CAGGATATTGAGCCCGAAGA Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-R12 GCCAAGGAAAGTCCCTAACC Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-F13 GGTCTGGATCGTGAGGAGAG Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-intronI-R13 CCGTTCAAGAATTTTGTCCA Amplify/sequence intron I HvBM5A-exon2-F1 TCCCAAGAAAACTTGAACAACACCAG Amplify/sequence exon II HvBM5A-exon2-R1 ATTAGGTTACATCATTCGACCA Amplify/sequence exon II HvBM5A-intronII-F1 TCAGTTTCATGTGCTCTTTCTAG Amplify/sequence intron II HvBM5A-intronII-R1 GTGGTGCTTGTGGGTGGT Amplify/sequence intron II HvBM5A-intronII-F2 CACCTACGCGAGTCCATCTC Amplify/sequence intron II HvBM5A-intronII-R2 CAAACATGTCCACCTGGATT Amplify/sequence intron II HvBM5A-intronII-F3 AGAGGGAGGGGAGGGAGT Amplify/sequence intron II HvBM5A-intronII-R3 CCTGGAGCTCGAGTTACAAAA Amplify/sequence intron II HvBM5A-intronII-F4 AGCTTGTCCAAGGCTAACCA Amplify/sequence intron II HvBM5A-intronII-R4 TTCGCTGAACTTCTCTGCAA Amplify/sequence intron II HvBM5A-exon3-8-F1 AGCTTGTCCAAGGCTAACCA Amplify/sequence exon III-VIII HvBM5A-exon3-8-R1 GCCCAGGTGGAAAGGAAAC Amplify/sequence exon III-VIII HvBM5A-T-1,948/C CACACTGCAAAGTTTAGGGA SNP1 extension primer HvBM5A-A-1,881/G CGTCAAAAACTGTGCATCTA SNP2 extension primer HvBM5A-T-1,684/C TTGTACAATAATTATGTCATGGAGGT SNP3 extension primer HvBM5A-T+14,567/C ACTGACTAGTAACAAAATACTCCATCTGTAAA SNP4 extension primer HvBM5A-G+14,585/A ACATTTAAAACACTACTTTAGTAAT SNP5 extension primer HvBM5A-C+14,828/G GACTAAAAGACTGTTCGCAACCGCATGATACA SNP6 extension primer CCAGGCTGGCCG HvBM5A-(CGCT)n-R 6FAM-CTGGCGGTTGATCTTGTTCT (CGCT) n SSR, use with HvBM5A-exon1-F1 HvBM5A-intronI-F1m TAGGCGCTAGAATACTTCGT Haplotype 2A intron I InDel HvFT1-F1 CACTCATCATCACCATTCAC Amplify/sequence HvFT1 HvFT1-R1 TAGTCCGCTAGTGTATATCG Amplify/sequence HvFT1
4 Table S1. Primer details for previously unpublished VRN-H1 genotype assays and sequencing of VRN-H1 and HvFT1. Fragments amplified using VRN-H1-promoter-F1 / VRN-H1-promoter-R1 and VRN-H1-exon3-8-F1 / VRN-H1-exon3-8-R1 were used as the template for SNaPshot single base detection of SNP1/SNP2/SNP3 and SNP4/SNP5/SNP6, respectively. Non-complementary primer tails are underlined. Intron I deletions. HvBM5A-intronI-F1 / HvBM5A-intronI-R6 used to assay for haplotype 1B intron I deletions. HvBM5A-intron1-F1 / HvBM5A-exon1-R1 used to assay for haplotype 2 transposable element insertion; HvBM5A-intronI-F1 / HvBM5A-intronI-R9 used to assay for haplotype 3 intron I deletions. HvBM5A-intronI-F1m / HvBM5A-intronI-R13 used to assay for haplotype 4A intron I deletions. HvBM5A-intronI-F1 / HvBM5A-intronI- R7 used to assay for haplotype 5B/5C deletions. Previously published primers (Fu et al. 2005) were used to detect haplotype 4B and 5A deletions (Intr1/H/F1 / Intr1/H/R1) and the absence of intron I deletions (Intr1/H/F3 / Intr1/H/R3). HvBM5A-intronI-F3 used in combination with primer Intr1/H/R3 (5 -AAAGCTCCTGCCAACTACGA-3, Fu et al. 2005) to identify all known winter VRN-H1 alleles identified in this study (VRN-H1- introni-1a/5c assay). An 879 bp fragment from the VRN-H3 gene, HvFT1 (Yan et al. 2006) was amplified and sequenced in Xenia using the primers shown.
5 Variety VRN-H1 haplotype Recorded growth habit Accession Determined region Arra 1B Spring EF Promoter /partial 5 UTR / partial intron I/ exon II / partial intron II/ exon III VIII, partial Dandy 3 Spring EF Promoter /partial 5 UTR / exon I / intron I/ exon Golden Promise 5A Spring EF Promoter /partial 5 UTR / exon I /intron I/ exon Golf 5A Spring EF Promoter /partial 5 UTR / exon I / partial intron I/ Optic 4A Spring EF Promoter /partial 5 UTR / exon I / intron I/ exon Pohto 5A Spring EF Promoter /partial 5 UTR / exon I / partial intron I/ Prisma 4B Spring EF Promoter /partial 5 UTR / exon I / intron I/ exon Triumph 4A Spring EF Promoter /partial 5 UTR / exon I / partial intron I/ Igri 1A Winter EF Promoter /partial 5 UTR / exon I / partial intron I/ Panda 1A Winter EF Promoter /partial 5 UTR / exon I / intron I/ exon Pearl 1A Winter EF Promoter /partial 5 UTR / exon I / partial intron I/ Oriol 5B Spring EF Exon I / intron I / exon II Express 5C Winter EF Exon I / intron I / exon II Xenia 1A Spring EF Complete sequence * Etu 1B Spring EF Exon I / intron I / exon II Varunda 2 Spring EF Exon I / intron I / exon II Table S2. Accession numbers and further details for sequenced VRN-H1 (HvBM5A) genomic regions. * Sequence spans from -2,074 to +14,953, relative to the translation start site (+1 bp) in genomic sequence from the Strider winter vrn-h1 allele. The TA repeat region within the promoter could not be completely sequenced across.
6 Table S3. Haplotype groupings (boxed in black) based on polymorphic features identified by sequence comparison of the four genomic fragments amplified in this study with all publicly available genomic H. vulgare ssp. vulgare VRN-H1 sequence (highlighted in grey). Their locations in the promoter (P), 5 UTR (5 UTR), intron I (In I), intron III (In III), exon IV (E IV), intron IV (In IV), intron VII (In VII) and 3 UTR (3 UTR) are indicated. The location of polymorphic features relative to the genomic sequence of the winter cv Strider (AY750993), and their presence in amplicons 1 to 4 (A1 to A4) is indicated. GenBank accession numbers for previously published genomic sequences: Calicucima sib (DQ492702; DQ492704), Dicktoo (AY750994; AY785817; AY785828), Harrington (AY785816), Igri (AY and sequenced in this study), Kompolti korai (AY785824; AY866487), Morex (AY785815; AY785826; AY750995; AY758233), Nure (AY785821), Oregon Wolfe Barley Dominant (DQ492703; AY750996), Strider (AY785823; AY750993), Tremois (AY785819), Triumph (AY and sequenced in this study) and 88Ab536 (AY785818). Where no sequence is available for comparison, missing data is recorded as U. Growth habit coding: S = spring, F = facultative, W = winter. InDel/SSR coding: InDel-1867: 1 = T, 2 = C, 3 = TC, 4 = TTC; InDel-1791: 1 = CATTA present, 2 = CATTA absent; InDel-1215: 1 = TCCTTT present, 2 = TCCTTT absent; SSR-1129: 1 = TAC present, 2 = TAC absent; SSR-1101: 1 = (T) 6, 2 = (T) 8 ; SSR-48: 1 = (CGCT) 2 2 = (CGCT) 4 3 = (CGCT) 5 ; SSR+223: 1 = (C) 6 2 = (C) 7 ; InDel+10878: 1 = 42 bp InDel large allele, 2 = 42 bp InDel small allele.
7 Table S4. Complete raw genotype and phenotype dataset for all 429 barley varieties studied including ten VRN-H1-related and three VRN-H2-related polymorphisms, row number (where available), haplotype designation and predicted and recorded seasonal growth habit. This table is provided as a separate Excel spreadsheet.
Haplotype analysis of vernalization loci in European barley germplasm reveals novel VRN-H1 alleles and a predominant winter VRN-H1/VRN-H2
 DOI 10.1007/s00122-007-0626-x ORIGINAL PAPER Haplotype analysis of vernalization loci in European barley germplasm reveals novel VRN-H1 alleles and a predominant winter VRN-H1/VRN-H2 multi-locus haplotype
DOI 10.1007/s00122-007-0626-x ORIGINAL PAPER Haplotype analysis of vernalization loci in European barley germplasm reveals novel VRN-H1 alleles and a predominant winter VRN-H1/VRN-H2 multi-locus haplotype
Patterns and mechanisms of recombination at the barley VRN- H1 locus. James Cockram
 Patterns and mechanisms of recombination at the barley VRN- H1 locus James Cockram Talk Outline: Project background Genetic markers used Homologous and non-homologous recombination within BM5A Putative
Patterns and mechanisms of recombination at the barley VRN- H1 locus James Cockram Talk Outline: Project background Genetic markers used Homologous and non-homologous recombination within BM5A Putative
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Number and length distributions of the inferred fosmids.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Number and length distributions of the inferred fosmids. Fosmid were inferred by mapping each pool s sequence reads to hg19. We retained only those reads that mapped to within a
Supplementary Figure 1 Number and length distributions of the inferred fosmids. Fosmid were inferred by mapping each pool s sequence reads to hg19. We retained only those reads that mapped to within a
Erhard et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. c1-hbr allele structure. Diagram of the c1-hbr allele found in stocks segregating 1:1 for rpd1-1 and rpd1-2 homozygous mutants showing the presence of a 363 base pair (bp) Heartbreaker
Supplemental Figure 1. c1-hbr allele structure. Diagram of the c1-hbr allele found in stocks segregating 1:1 for rpd1-1 and rpd1-2 homozygous mutants showing the presence of a 363 base pair (bp) Heartbreaker
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Gene replacements and insertions in rice by intron targeting using CRISPR Cas9 Table of Contents Supplementary Figure 1. sgrna-induced targeted mutations in the OsEPSPS gene in rice protoplasts. Supplementary
Gene replacements and insertions in rice by intron targeting using CRISPR Cas9 Table of Contents Supplementary Figure 1. sgrna-induced targeted mutations in the OsEPSPS gene in rice protoplasts. Supplementary
Introduction to some aspects of molecular genetics
 Introduction to some aspects of molecular genetics Julius van der Werf (partly based on notes from Margaret Katz) University of New England, Armidale, Australia Genetic and Physical maps of the genome...
Introduction to some aspects of molecular genetics Julius van der Werf (partly based on notes from Margaret Katz) University of New England, Armidale, Australia Genetic and Physical maps of the genome...
GENOTYPING BY PCR PROTOCOL FORM MUTANT MOUSE REGIONAL RESOURCE CENTER North America, International
 Please provide the following information required for genetic analysis of your mutant mice. Please fill in form electronically by tabbing through the text fields. The first 2 pages are protected with gray
Please provide the following information required for genetic analysis of your mutant mice. Please fill in form electronically by tabbing through the text fields. The first 2 pages are protected with gray
Supplementary Information. Optimization of the production of knock-in alleles by CRISPR/Cas9 microinjection into the mouse zygote
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures S1 to S5 and Tables S1 to S3. Optimization of the production of knock-in alleles by CRISPR/Cas9 microinjection into the mouse zygote Aurélien Raveux, Sandrine
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures S1 to S5 and Tables S1 to S3. Optimization of the production of knock-in alleles by CRISPR/Cas9 microinjection into the mouse zygote Aurélien Raveux, Sandrine
CHAPTER THREE RESULTS
 CHAPTER THREE RESULTS 3.1 PCR-SSP In this study, the PCR SSP technique was used to amplify the GYP hybrid gene from the genomic DNA samples and detect GP.Mur, GP.Bun, GP.Hop (148 bp), GP.HF and GP.Hut
CHAPTER THREE RESULTS 3.1 PCR-SSP In this study, the PCR SSP technique was used to amplify the GYP hybrid gene from the genomic DNA samples and detect GP.Mur, GP.Bun, GP.Hop (148 bp), GP.HF and GP.Hut
Map-Based Cloning of Qualitative Plant Genes
 Map-Based Cloning of Qualitative Plant Genes Map-based cloning using the genetic relationship between a gene and a marker as the basis for beginning a search for a gene Chromosome walking moving toward
Map-Based Cloning of Qualitative Plant Genes Map-based cloning using the genetic relationship between a gene and a marker as the basis for beginning a search for a gene Chromosome walking moving toward
Biol 321 Spring 2013 Quiz 4 25 pts NAME
 Biol 321 Spring 2013 Quiz 4 25 pts NAME 1. (3 pts.) a. What is the name of this compound? BE EXPLICIT deoxyribose 5 b. Number the carbons on this structure: 4 1 3 2 2. (4 pts.) Circle True or False. If
Biol 321 Spring 2013 Quiz 4 25 pts NAME 1. (3 pts.) a. What is the name of this compound? BE EXPLICIT deoxyribose 5 b. Number the carbons on this structure: 4 1 3 2 2. (4 pts.) Circle True or False. If
Authors: Vivek Sharma and Ram Kunwar
 Molecular markers types and applications A genetic marker is a gene or known DNA sequence on a chromosome that can be used to identify individuals or species. Why we need Molecular Markers There will be
Molecular markers types and applications A genetic marker is a gene or known DNA sequence on a chromosome that can be used to identify individuals or species. Why we need Molecular Markers There will be
Reading Lecture 8: Lecture 9: Lecture 8. DNA Libraries. Definition Types Construction
 Lecture 8 Reading Lecture 8: 96-110 Lecture 9: 111-120 DNA Libraries Definition Types Construction 142 DNA Libraries A DNA library is a collection of clones of genomic fragments or cdnas from a certain
Lecture 8 Reading Lecture 8: 96-110 Lecture 9: 111-120 DNA Libraries Definition Types Construction 142 DNA Libraries A DNA library is a collection of clones of genomic fragments or cdnas from a certain
BENG 183 Trey Ideker. Genotyping. To be covered in one 1.5 hr lecture
 BENG 183 Trey Ideker Genotyping To be covered in one 1.5 hr lecture Genetic variation: Some basic definitions Allele Alternative form of a genetic locus inherited separately from each parent Polymorphism
BENG 183 Trey Ideker Genotyping To be covered in one 1.5 hr lecture Genetic variation: Some basic definitions Allele Alternative form of a genetic locus inherited separately from each parent Polymorphism
GDMS Templates Documentation GDMS Templates Release 1.0
 GDMS Templates Documentation GDMS Templates Release 1.0 1 Table of Contents 1. SSR Genotyping Template 03 2. DArT Genotyping Template... 05 3. SNP Genotyping Template.. 08 4. QTL Template.. 09 5. Map Template..
GDMS Templates Documentation GDMS Templates Release 1.0 1 Table of Contents 1. SSR Genotyping Template 03 2. DArT Genotyping Template... 05 3. SNP Genotyping Template.. 08 4. QTL Template.. 09 5. Map Template..
Marker types. Potato Association of America Frederiction August 9, Allen Van Deynze
 Marker types Potato Association of America Frederiction August 9, 2009 Allen Van Deynze Use of DNA Markers in Breeding Germplasm Analysis Fingerprinting of germplasm Arrangement of diversity (clustering,
Marker types Potato Association of America Frederiction August 9, 2009 Allen Van Deynze Use of DNA Markers in Breeding Germplasm Analysis Fingerprinting of germplasm Arrangement of diversity (clustering,
Novel alleles of the VERNALIZATION1 genes in wheat are associated with modulation of DNA curvature and flexibility in the promoter region
 Muterko et al. BMC Plant Biology 2016, 16(Suppl 1):9 DOI 10.1186/s12870-015-0691-2 RESEARCH Open Access Novel alleles of the VERNALIZATION1 genes in wheat are associated with modulation of DNA curvature
Muterko et al. BMC Plant Biology 2016, 16(Suppl 1):9 DOI 10.1186/s12870-015-0691-2 RESEARCH Open Access Novel alleles of the VERNALIZATION1 genes in wheat are associated with modulation of DNA curvature
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
Ramp1 EPD0843_4_B11. EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping
 EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
Usp14 EPD0582_2_G09. EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping
 EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
 http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/direct_detection_of_genotype.html 1 Like most other model organism Arabidopsis thaliana has a sequenced genome? What do we mean by sequenced genome? What sort of info
http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/direct_detection_of_genotype.html 1 Like most other model organism Arabidopsis thaliana has a sequenced genome? What do we mean by sequenced genome? What sort of info
Barley Vulnerability to Wheat Stem Rust: Enhancing our Limited Resistance Sources
 Barley Vulnerability to Wheat Stem Rust: Enhancing our Limited Resistance Sources Maricelis Acevedo Plant Pathology Department North Dakota State University Dr. Robert Brueggeman, NDSU, Barley Pathologist
Barley Vulnerability to Wheat Stem Rust: Enhancing our Limited Resistance Sources Maricelis Acevedo Plant Pathology Department North Dakota State University Dr. Robert Brueggeman, NDSU, Barley Pathologist
Microsatellite markers
 Microsatellite markers Review of repetitive sequences 25% 45% 8% 21% 13% 3% Mobile genetic elements: = dispersed repeat included: transposition: moving in the form of DNA by element coding for transposases.
Microsatellite markers Review of repetitive sequences 25% 45% 8% 21% 13% 3% Mobile genetic elements: = dispersed repeat included: transposition: moving in the form of DNA by element coding for transposases.
Kerkel et al., Supplementary Tables and Figures
 Kerkel et al., Supplementary Tables and Figures Table S1. Summary of 16 SNP tagged loci from the combined 50K and 250K MSNP screens with independently validated ASM. PBL, total peripheral blood leukocytes;
Kerkel et al., Supplementary Tables and Figures Table S1. Summary of 16 SNP tagged loci from the combined 50K and 250K MSNP screens with independently validated ASM. PBL, total peripheral blood leukocytes;
Characterization of specific DNA markers at VRN-H1 and VRN-H2 loci for Growth Habit in Barley Genotypes
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Characterization of specific DNA markers at VRN-H1 and VRN-H2 loci for Growth Habit in Barley Genotypes Zahra Sadat Taheripourfard 1 - Ali Izadi- Darbandi* 2 - Habibollah Ghazvini 3 -
RESEARCH ARTICLE Characterization of specific DNA markers at VRN-H1 and VRN-H2 loci for Growth Habit in Barley Genotypes Zahra Sadat Taheripourfard 1 - Ali Izadi- Darbandi* 2 - Habibollah Ghazvini 3 -
Chapter 5. Structural Genomics
 Chapter 5. Structural Genomics Contents 5. Structural Genomics 5.1. DNA Sequencing Strategies 5.1.1. Map-based Strategies 5.1.2. Whole Genome Shotgun Sequencing 5.2. Genome Annotation 5.2.1. Using Bioinformatic
Chapter 5. Structural Genomics Contents 5. Structural Genomics 5.1. DNA Sequencing Strategies 5.1.1. Map-based Strategies 5.1.2. Whole Genome Shotgun Sequencing 5.2. Genome Annotation 5.2.1. Using Bioinformatic
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
Factors affecting PCR
 Lec. 11 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Factors affecting PCR The sequences of the primers are critical to the success of the experiment, as are the precise temperatures used in the heating and cooling stages of the
Lec. 11 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Factors affecting PCR The sequences of the primers are critical to the success of the experiment, as are the precise temperatures used in the heating and cooling stages of the
INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA
 E BMT Guidelines (proj.4) ORIGINAL: English DATE: December 21, 2005 INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA GUIDELINES FOR DNA-PROFILING: MOLECULAR MARKER SELECTION AND
E BMT Guidelines (proj.4) ORIGINAL: English DATE: December 21, 2005 INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA GUIDELINES FOR DNA-PROFILING: MOLECULAR MARKER SELECTION AND
Solution key. c) Consider the following perturbations in different components of this signaling pathway in cells.
 Solution key Question 1 During a summer hike you suddenly spy a grizzly bear. This triggers a fight or flight response activating the signaling pathway that is shown on last Page. a) Circle the best option.
Solution key Question 1 During a summer hike you suddenly spy a grizzly bear. This triggers a fight or flight response activating the signaling pathway that is shown on last Page. a) Circle the best option.
Analysis of structural variation. Alistair Ward USTAR Center for Genetic Discovery University of Utah
 Analysis of structural variation Alistair Ward USTAR Center for Genetic Discovery University of Utah What is structural variation? What differentiates SV from short variants? What are the major SV types?
Analysis of structural variation Alistair Ward USTAR Center for Genetic Discovery University of Utah What is structural variation? What differentiates SV from short variants? What are the major SV types?
Structural Variation CYP2D6
 reference gene locus The gene locus contains three genes,, CYP and CYP, of which only is functional. CYP and CYP are considered pseudogenes. All three genes are composed of nine exons and share a high
reference gene locus The gene locus contains three genes,, CYP and CYP, of which only is functional. CYP and CYP are considered pseudogenes. All three genes are composed of nine exons and share a high
Figure S1. Unrearranged locus. Rearranged locus. Concordant read pairs. Region1. Region2. Cluster of discordant read pairs, bundle
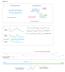 Figure S1 a Unrearranged locus Rearranged locus Concordant read pairs Region1 Concordant read pairs Cluster of discordant read pairs, bundle Region2 Concordant read pairs b Physical coverage 5 4 3 2 1
Figure S1 a Unrearranged locus Rearranged locus Concordant read pairs Region1 Concordant read pairs Cluster of discordant read pairs, bundle Region2 Concordant read pairs b Physical coverage 5 4 3 2 1
Antisense RNA Targeting the First Periplasmic Domain of YidC in Escherichia coli Appears to Induce Filamentation but Does Not Affect Cell Viability
 Antisense RNA Targeting the First Periplasmic Domain of YidC in Escherichia coli Appears to Induce Filamentation but Does Not Affect Cell Viability Riaaz Lalani, Nathaniel Susilo, Elisa Xiao, Andrea Xu
Antisense RNA Targeting the First Periplasmic Domain of YidC in Escherichia coli Appears to Induce Filamentation but Does Not Affect Cell Viability Riaaz Lalani, Nathaniel Susilo, Elisa Xiao, Andrea Xu
HLA typing techniques
 HLA typing techniques D R. S A R A A S S A D I A S L M D. P H D O F I M M U N O L O G Y A S S I S TA N T P R O F E S S O R T E H R A N U N I V E R S I T Y O F M E D I C A L S C I E N C E M O L E C U L
HLA typing techniques D R. S A R A A S S A D I A S L M D. P H D O F I M M U N O L O G Y A S S I S TA N T P R O F E S S O R T E H R A N U N I V E R S I T Y O F M E D I C A L S C I E N C E M O L E C U L
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.20 - BIOTECHNOLOGY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: DNA CLONING DNA cloning is a technique that inserts a foreign gene into a living host to replicate the gene and produce gene products. Transformation the process by which
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: DNA CLONING DNA cloning is a technique that inserts a foreign gene into a living host to replicate the gene and produce gene products. Transformation the process by which
Mutations during meiosis and germ line division lead to genetic variation between individuals
 Mutations during meiosis and germ line division lead to genetic variation between individuals Types of mutations: point mutations indels (insertion/deletion) copy number variation structural rearrangements
Mutations during meiosis and germ line division lead to genetic variation between individuals Types of mutations: point mutations indels (insertion/deletion) copy number variation structural rearrangements
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Park et al. 10.1073/pnas.1410555111 5 -TCAAGTCCATCTACATGGCC-3 5 -CAGCTGCCCGGCTACTACTA-3 5 -TGCAGCTGCCCGGCTACTAC-3 5 -AAGCTGGACATCACCTCCCA-3 5 -TGACAGGAACACCTACAAGT-3 5 -AAGGCACCTTTCTGTCTCCA-3
Supporting Information Park et al. 10.1073/pnas.1410555111 5 -TCAAGTCCATCTACATGGCC-3 5 -CAGCTGCCCGGCTACTACTA-3 5 -TGCAGCTGCCCGGCTACTAC-3 5 -AAGCTGGACATCACCTCCCA-3 5 -TGACAGGAACACCTACAAGT-3 5 -AAGGCACCTTTCTGTCTCCA-3
Isothermal amplification system based on template-dependent extension
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Isothermal amplification system based on template-dependent extension 1. Experimental Section The molecular beacon (Takara Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Dalian, China)
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Isothermal amplification system based on template-dependent extension 1. Experimental Section The molecular beacon (Takara Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Dalian, China)
CHAPTER FOUR. Characterization of parasporal genes in. Paenibacillus popilliae and Paenibacillus lentimorbus. Abstract
 CHAPTER FOUR Characterization of parasporal genes in Paenibacillus popilliae and Paenibacillus lentimorbus Abstract The parasporal gene, cry18aa1, was cloned and sequenced by Zhang et al. (4) from the
CHAPTER FOUR Characterization of parasporal genes in Paenibacillus popilliae and Paenibacillus lentimorbus Abstract The parasporal gene, cry18aa1, was cloned and sequenced by Zhang et al. (4) from the
SolCAP. Executive Commitee : David Douches Walter De Jong Robin Buell David Francis Alexandra Stone Lukas Mueller AllenVan Deynze
 SolCAP Solanaceae Coordinated Agricultural Project Supported by the National Research Initiative Plant Genome Program of USDA CSREES for the Improvement of Potato and Tomato Executive Commitee : David
SolCAP Solanaceae Coordinated Agricultural Project Supported by the National Research Initiative Plant Genome Program of USDA CSREES for the Improvement of Potato and Tomato Executive Commitee : David
Using Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) to Predict Bitter Tasting Ability
 Using Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) to Predict Bitter Tasting Ability Part II:! Digestion and Analysis of an Amplified Region of the Bitter Taste Receptor TAS2R38 Gene In The Last Lab:! You sampled
Using Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) to Predict Bitter Tasting Ability Part II:! Digestion and Analysis of an Amplified Region of the Bitter Taste Receptor TAS2R38 Gene In The Last Lab:! You sampled
Technical University of Denmark. Written examination, 29 May 2012 Course name: Life Science. Course number: Aids allowed: Written material
 1 Technical University of Denmark Written examination, 29 May 2012 Course name: Life Science Course number: 27008 Aids allowed: Written material Exam duration: 4 hours Weighting: The exam set consists
1 Technical University of Denmark Written examination, 29 May 2012 Course name: Life Science Course number: 27008 Aids allowed: Written material Exam duration: 4 hours Weighting: The exam set consists
Analysis of structural variation. Alistair Ward - Boston College
 Analysis of structural variation Alistair Ward - Boston College What is structural variation? What differentiates SV from short variants? What are the major SV types? Summary of MEI detection What is an
Analysis of structural variation Alistair Ward - Boston College What is structural variation? What differentiates SV from short variants? What are the major SV types? Summary of MEI detection What is an
Supplemental Figure 1: Nisoldipine Concentration-Response Relationship on ipsc- CMs. Supplemental Figure 2: Exome Sequencing Prioritization Strategy
 9 10 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 19 0 1 9 0 1 Supplementary Appendix Table of Contents Figures: Supplemental Figure 1: Nisoldipine Concentration-Response Relationship on ipsc- CMs Supplemental Figure : Exome Sequencing
9 10 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 19 0 1 9 0 1 Supplementary Appendix Table of Contents Figures: Supplemental Figure 1: Nisoldipine Concentration-Response Relationship on ipsc- CMs Supplemental Figure : Exome Sequencing
Biotechnology Chapter 20
 Biotechnology Chapter 20 DNA Cloning DNA Cloning AKA Plasmid-based transformation or molecular cloning First off-let s sum up what happens. A plasmid is taken from a bacteria A gene is inserted into the
Biotechnology Chapter 20 DNA Cloning DNA Cloning AKA Plasmid-based transformation or molecular cloning First off-let s sum up what happens. A plasmid is taken from a bacteria A gene is inserted into the
PCR-SSP primer mixes for KIR3DL3 non-synonymous polymorphism, and SNP linkage (L) reactions.
 PCR-SSP primer mixes for KIR3DL3 non-synonymous polymorphism, and SNP linkage (L) reactions. Reaction KIR3DL3 Polymorphism Sense primers Antisense primers Amplicon Control no size (bp) Product 1 b Exon
PCR-SSP primer mixes for KIR3DL3 non-synonymous polymorphism, and SNP linkage (L) reactions. Reaction KIR3DL3 Polymorphism Sense primers Antisense primers Amplicon Control no size (bp) Product 1 b Exon
INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS
 ORIGINAL: English DATE: October 21, 2010 INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA E GUIDELINES FOR DNA-PROFILING: MOLECULAR MARKER SELECTION AND DATABASE CONSTRUCTION (
ORIGINAL: English DATE: October 21, 2010 INTERNATIONAL UNION FOR THE PROTECTION OF NEW VARIETIES OF PLANTS GENEVA E GUIDELINES FOR DNA-PROFILING: MOLECULAR MARKER SELECTION AND DATABASE CONSTRUCTION (
SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS FOR CURTIN,
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS FOR CURTIN, et al. Validating genome-wide association candidates: Selecting, testing, and characterizing
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS FOR CURTIN, et al. Validating genome-wide association candidates: Selecting, testing, and characterizing
Structural variation. Marta Puig Institut de Biotecnologia i Biomedicina Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
 Structural variation Marta Puig Institut de Biotecnologia i Biomedicina Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona Genetic variation How much genetic variation is there between individuals? What type of variants
Structural variation Marta Puig Institut de Biotecnologia i Biomedicina Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona Genetic variation How much genetic variation is there between individuals? What type of variants
Genetic characterization and polymorphism detection of casein genes in Egyptian sheep breeds
 Genetic characterization and polymorphism detection of casein genes in Egyptian sheep breeds Othman E. Othman and Samia A. El-Fiky Cell Biology Department - National Research Center - Dokki - Egypt Corresponding
Genetic characterization and polymorphism detection of casein genes in Egyptian sheep breeds Othman E. Othman and Samia A. El-Fiky Cell Biology Department - National Research Center - Dokki - Egypt Corresponding
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Secondary mutations as a mechanism of cisplatin resistance in BRCA2-mutated cancers Wataru Sakai, Elizabeth M. Swisher, Beth Y. Karlan, Mukesh K. Agarwal, Jake Higgins, Cynthia Friedman, Emily Villegas,
Secondary mutations as a mechanism of cisplatin resistance in BRCA2-mutated cancers Wataru Sakai, Elizabeth M. Swisher, Beth Y. Karlan, Mukesh K. Agarwal, Jake Higgins, Cynthia Friedman, Emily Villegas,
Testing GM crops. Mitesh Shrestha
 Testing GM crops Mitesh Shrestha GMO food/feed testing is based on some fundamental principles of genetic engineering and cellular physiology: DNA: The introduction of foreign DNA into a recipient plant
Testing GM crops Mitesh Shrestha GMO food/feed testing is based on some fundamental principles of genetic engineering and cellular physiology: DNA: The introduction of foreign DNA into a recipient plant
1
 1 2 3 4 5 Cosmids are plasmid vectors that contain cos sites. The cos site is the only requirement for DNA to be packaged into a phage particle 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 For de novo sequencing using
1 2 3 4 5 Cosmids are plasmid vectors that contain cos sites. The cos site is the only requirement for DNA to be packaged into a phage particle 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 For de novo sequencing using
BIOLOGY Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
 BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
rjlflemmers, LUMC, Leiden, The Netherlands 6/3/2010
 Genotyping of the SSLP The simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) 3.5 kb proximal to D4Z4 is studied by PCR and the sequence is localized between positions 1532 and 1694 of AF117653 (see figure below).
Genotyping of the SSLP The simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) 3.5 kb proximal to D4Z4 is studied by PCR and the sequence is localized between positions 1532 and 1694 of AF117653 (see figure below).
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Generation of TSPOΔ/Δ murine embryonic fibroblasts Embryos were harvested from 13.5-day pregnant TSPOfl/fl mice. After dissection to eviscerate and remove the
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Generation of TSPOΔ/Δ murine embryonic fibroblasts Embryos were harvested from 13.5-day pregnant TSPOfl/fl mice. After dissection to eviscerate and remove the
BIO 202 Midterm Exam Winter 2007
 BIO 202 Midterm Exam Winter 2007 Mario Chevrette Lectures 10-14 : Question 1 (1 point) Which of the following statements is incorrect. a) In contrast to prokaryotic DNA, eukaryotic DNA contains many repetitive
BIO 202 Midterm Exam Winter 2007 Mario Chevrette Lectures 10-14 : Question 1 (1 point) Which of the following statements is incorrect. a) In contrast to prokaryotic DNA, eukaryotic DNA contains many repetitive
High-throughput genotyping of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutants using fluorescent
 High-throughput genotyping of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutants using fluorescent PCR-capillary gel electrophoresis Muhammad Khairul RAMLEE, Tingdong YAN, Alice M. S. CHEUNG, Charles CHUAH, Shang LI Figure
High-throughput genotyping of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutants using fluorescent PCR-capillary gel electrophoresis Muhammad Khairul RAMLEE, Tingdong YAN, Alice M. S. CHEUNG, Charles CHUAH, Shang LI Figure
PlantDirect TM Multiplex PCR System
 PlantDirect TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0178 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 3 IV Shipping and Storage. 3 V Simplified Procedures. 3 VI Detailed
PlantDirect TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0178 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 3 IV Shipping and Storage. 3 V Simplified Procedures. 3 VI Detailed
Do Donors With Non-Deletional Blood Group O Allels Boost Anti-A and Anti-B Titers in Blood Group O Recipients?
 Do Donors With Non-Deletional Blood Group O Allels Boost Anti-A and Anti-B Titers in Blood Group O Recipients? E. A. Scharberg, S. Seyboth, K. Panter, A. Ernst, J. Hagel, E. Richter, G. Rink, K. Janetzko,
Do Donors With Non-Deletional Blood Group O Allels Boost Anti-A and Anti-B Titers in Blood Group O Recipients? E. A. Scharberg, S. Seyboth, K. Panter, A. Ernst, J. Hagel, E. Richter, G. Rink, K. Janetzko,
Multiplex PCR Assay Kit Ver.2
 Cat. # RR062A For Research Use Multiplex PCR Assay Kit Ver.2 Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 3 IV. Precautions... 3 V. Designing Primers for Multiplex
Cat. # RR062A For Research Use Multiplex PCR Assay Kit Ver.2 Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 3 IV. Precautions... 3 V. Designing Primers for Multiplex
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name integrin, alpha 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID ITGA1 Human This gene encodes the alpha 1 subunit of integrin
Gene Information Gene Name integrin, alpha 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID ITGA1 Human This gene encodes the alpha 1 subunit of integrin
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name keratin 78 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID KRT78 Human This gene is a member of the type II keratin gene family
Gene Information Gene Name keratin 78 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID KRT78 Human This gene is a member of the type II keratin gene family
Gene mutation and DNA polymorphism
 Gene mutation and DNA polymorphism Outline of this chapter Gene Mutation DNA Polymorphism Gene Mutation Definition Major Types Definition A gene mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence that composes
Gene mutation and DNA polymorphism Outline of this chapter Gene Mutation DNA Polymorphism Gene Mutation Definition Major Types Definition A gene mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence that composes
This Product Description is only valid for Lot No. 36V.
 HLA Wipe Test Negative Control Product Insert Page 1 of 8 Olerup SSP HLA Wipe Test Negative Control Product number: 102.101-01 including Taq polymerase Product number: 102.101-01u without Taq polymerase
HLA Wipe Test Negative Control Product Insert Page 1 of 8 Olerup SSP HLA Wipe Test Negative Control Product number: 102.101-01 including Taq polymerase Product number: 102.101-01u without Taq polymerase
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.15 GENOMES AND GENOMICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF GENOMICS Genomics is the study of genomes in their entirety Bioinformatics is the analysis of the information content of genomes - Genes, regulatory sequences,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF GENOMICS Genomics is the study of genomes in their entirety Bioinformatics is the analysis of the information content of genomes - Genes, regulatory sequences,
Supplementary Table 3d: PCR primers for genomic sequencing-based phasereconstruction
 Supplementary Table 3: Detailed lists of grnas, primers, donor constructs, antibodies, Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) identifiers for Chip-seq and DHSs datasets and CRISPR/Cas9 genome edited cell lines
Supplementary Table 3: Detailed lists of grnas, primers, donor constructs, antibodies, Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) identifiers for Chip-seq and DHSs datasets and CRISPR/Cas9 genome edited cell lines
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID HLA-DRB1 Human HLA-DRB1 belongs
Gene Information Gene Name major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID HLA-DRB1 Human HLA-DRB1 belongs
A multiplex panel of short-amplicon insertion-deletion DNA polymorphisms for forensic analysis
 A multiplex panel of short-amplicon insertion-deletion DNA polymorphisms for forensic analysis V.R.D. Santos 1,2, H.B. Pena 1 and S.D.J. Pena 1,3 1 GENE - Núcleo de Genética Médica, Belo Horizonte, MG,
A multiplex panel of short-amplicon insertion-deletion DNA polymorphisms for forensic analysis V.R.D. Santos 1,2, H.B. Pena 1 and S.D.J. Pena 1,3 1 GENE - Núcleo de Genética Médica, Belo Horizonte, MG,
Existing potato markers and marker conversions. Walter De Jong PAA Workshop August 2009
 Existing potato markers and marker conversions Walter De Jong PAA Workshop August 2009 1 What makes for a good marker? diagnostic for trait of interest robust works even with DNA of poor quality or low
Existing potato markers and marker conversions Walter De Jong PAA Workshop August 2009 1 What makes for a good marker? diagnostic for trait of interest robust works even with DNA of poor quality or low
Puro. Knockout Detection (KOD) Kit
 Puro Knockout Detection (KOD) Kit Cat. No. CC-03 18 Oct. 2016 Contents I. Kit Contents and Storage II. Product Overview III. Methods Experimental Outline Genomic DNA Preparation Obtain Hybrid DNA Digest
Puro Knockout Detection (KOD) Kit Cat. No. CC-03 18 Oct. 2016 Contents I. Kit Contents and Storage II. Product Overview III. Methods Experimental Outline Genomic DNA Preparation Obtain Hybrid DNA Digest
Exam 2 CSS/Hort 430/
 1 Exam 2 CSS/Hort 430/530 2012 1. In a deoxyribonucleotide, 5 and 3 refer to the a. start site for transcription. b. start site for translation. c. carbons where (respectively) the pyrimidine and purine
1 Exam 2 CSS/Hort 430/530 2012 1. In a deoxyribonucleotide, 5 and 3 refer to the a. start site for transcription. b. start site for translation. c. carbons where (respectively) the pyrimidine and purine
PCR-based technologies Latest strategies
 Using molecular marker technology in studies on plant genetic diversity DNA-based technologies PCR-based technologies Latest strategies (DNA sequencing, ESTs, microarrays, DArT, SNPs) Copyright: IPGRI
Using molecular marker technology in studies on plant genetic diversity DNA-based technologies PCR-based technologies Latest strategies (DNA sequencing, ESTs, microarrays, DArT, SNPs) Copyright: IPGRI
Pharmacogenetics: A SNPshot of the Future. Ani Khondkaryan Genomics, Bioinformatics, and Medicine Spring 2001
 Pharmacogenetics: A SNPshot of the Future Ani Khondkaryan Genomics, Bioinformatics, and Medicine Spring 2001 1 I. What is pharmacogenetics? It is the study of how genetic variation affects drug response
Pharmacogenetics: A SNPshot of the Future Ani Khondkaryan Genomics, Bioinformatics, and Medicine Spring 2001 1 I. What is pharmacogenetics? It is the study of how genetic variation affects drug response
Supplementary Figure 1 An overview of pirna biogenesis during fetal mouse reprogramming. (a) (b)
 Supplementary Figure 1 An overview of pirna biogenesis during fetal mouse reprogramming. (a) A schematic overview of the production and amplification of a single pirna from a transposon transcript. The
Supplementary Figure 1 An overview of pirna biogenesis during fetal mouse reprogramming. (a) A schematic overview of the production and amplification of a single pirna from a transposon transcript. The
Structure, Measurement & Analysis of Genetic Variation
 Structure, Measurement & Analysis of Genetic Variation Sven Cichon, PhD Professor of Medical Genetics, Director, Division of Medcial Genetics, University of Basel Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine
Structure, Measurement & Analysis of Genetic Variation Sven Cichon, PhD Professor of Medical Genetics, Director, Division of Medcial Genetics, University of Basel Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine
2. (So) get (fragments with gene) R / required gene. Accept: allele for gene / same gene 2
 M.(a). Cut (DNA) at same (base) sequence / (recognition) sequence; Accept: cut DNA at same place. (So) get (fragments with gene) R / required gene. Accept: allele for gene / same gene (b). Each has / they
M.(a). Cut (DNA) at same (base) sequence / (recognition) sequence; Accept: cut DNA at same place. (So) get (fragments with gene) R / required gene. Accept: allele for gene / same gene (b). Each has / they
Construction of plant complementation vector and generation of transgenic plants
 MATERIAL S AND METHODS Plant materials and growth conditions Arabidopsis ecotype Columbia (Col0) was used for this study. SALK_072009, SALK_076309, and SALK_027645 were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological
MATERIAL S AND METHODS Plant materials and growth conditions Arabidopsis ecotype Columbia (Col0) was used for this study. SALK_072009, SALK_076309, and SALK_027645 were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological
HiPer Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Teaching Kit
 HiPer Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM031 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 3.5 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis:
HiPer Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM031 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 3.5 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis:
Figure S1 Correlation in size of analogous introns in mouse and teleost Piccolo genes. Mouse intron size was plotted against teleost intron size for t
 Figure S1 Correlation in size of analogous introns in mouse and teleost Piccolo genes. Mouse intron size was plotted against teleost intron size for the pcloa genes of zebrafish, green spotted puffer (listed
Figure S1 Correlation in size of analogous introns in mouse and teleost Piccolo genes. Mouse intron size was plotted against teleost intron size for the pcloa genes of zebrafish, green spotted puffer (listed
Ultra-dense SNP genetic map construction and identification of SiDt gene controlling the
 Ultra-dense SNP genetic map construction and identification of SiDt gene controlling the determinate growth habit in Sesamum indicum L. Haiyang Zhang*, Hongmei Miao, Chun Li, Libin Wei, Yinghui Duan, Qin
Ultra-dense SNP genetic map construction and identification of SiDt gene controlling the determinate growth habit in Sesamum indicum L. Haiyang Zhang*, Hongmei Miao, Chun Li, Libin Wei, Yinghui Duan, Qin
previously. co and fca-9 alleles were isolated from the Col background. Plants were
 Supporting Online Material Materials and Methods Plant Growth Conditions The flc-3, FRI Sf2 -Col (S1), fve-4 (S2), ld-1 (S3) and fpa (S4) lines were described previously. co and fca-9 alleles were isolated
Supporting Online Material Materials and Methods Plant Growth Conditions The flc-3, FRI Sf2 -Col (S1), fve-4 (S2), ld-1 (S3) and fpa (S4) lines were described previously. co and fca-9 alleles were isolated
Successful gene expression studies using validated qpcr assays. Jan Hellemans, CEO Biogazelle webinar October 28 th, 2015
 Successful gene expression studies using validated qpcr assays Jan Hellemans, CEO Biogazelle webinar October 28 th, 2015 Agenda Requirements for high quality qpcr assays Approaches for qpcr assay validation
Successful gene expression studies using validated qpcr assays Jan Hellemans, CEO Biogazelle webinar October 28 th, 2015 Agenda Requirements for high quality qpcr assays Approaches for qpcr assay validation
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures A B Supplementary Figure 1. Examples of discrepancies in predicted and validated breakpoint coordinates. A) Most frequently, predicted breakpoints were shifted relative to those derived
Supplementary Figures A B Supplementary Figure 1. Examples of discrepancies in predicted and validated breakpoint coordinates. A) Most frequently, predicted breakpoints were shifted relative to those derived
Read count-based method for high-throughput allelic genotyping of transposable elements and structural variants
 Kuhn et al. BMC Genomics (2015) 16:508 DOI 10.1186/s12864-015-1700-4 METHODOLOGY ARTICLE Open Access Read count-based method for high-throughput allelic genotyping of transposable elements and structural
Kuhn et al. BMC Genomics (2015) 16:508 DOI 10.1186/s12864-015-1700-4 METHODOLOGY ARTICLE Open Access Read count-based method for high-throughput allelic genotyping of transposable elements and structural
High-Resolution Melting Interactive Workshop AACC, July 25 th, 2006 Assay Description
 AACC, July 25 th, 2006 Assay Description List of Example Assays Page Technique Example assay 2 Unlabeled probe genotyping HR-1 Factor V Leiden mutation 6 Unlabeled probe genotyping - LightScanner Factor
AACC, July 25 th, 2006 Assay Description List of Example Assays Page Technique Example assay 2 Unlabeled probe genotyping HR-1 Factor V Leiden mutation 6 Unlabeled probe genotyping - LightScanner Factor
Human Genetic Variation. Ricardo Lebrón Dpto. Genética UGR
 Human Genetic Variation Ricardo Lebrón rlebron@ugr.es Dpto. Genética UGR What is Genetic Variation? Origins of Genetic Variation Genetic Variation is the difference in DNA sequences between individuals.
Human Genetic Variation Ricardo Lebrón rlebron@ugr.es Dpto. Genética UGR What is Genetic Variation? Origins of Genetic Variation Genetic Variation is the difference in DNA sequences between individuals.
Methods in virus diagnosis PCR techniques
 Methods in virus diagnosis PCR techniques 450 MBIO PRACTICAL LESSON 5 Molecular Methods Methods based on the detection of viral genome are also commonly known as molecular methods. It is often said that
Methods in virus diagnosis PCR techniques 450 MBIO PRACTICAL LESSON 5 Molecular Methods Methods based on the detection of viral genome are also commonly known as molecular methods. It is often said that
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name collagen, type IV, alpha 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID COL4A1 Human This gene encodes the major type IV alpha
Gene Information Gene Name collagen, type IV, alpha 1 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID COL4A1 Human This gene encodes the major type IV alpha
Supplementary Figure S1: Initial PrimerDimer primer pairs analysed using bisulfite PCR
 Supplementary Figure S1: Initial PrimerDimer primer pairs analysed using bisulfite PCR. Amplicons produced using PrimerSuite primers were observed to produce bands of the expected size (approximately 110-120base
Supplementary Figure S1: Initial PrimerDimer primer pairs analysed using bisulfite PCR. Amplicons produced using PrimerSuite primers were observed to produce bands of the expected size (approximately 110-120base
The Human Genome Project has always been something of a misnomer, implying the existence of a single human genome
 The Human Genome Project has always been something of a misnomer, implying the existence of a single human genome Of course, every person on the planet with the exception of identical twins has a unique
The Human Genome Project has always been something of a misnomer, implying the existence of a single human genome Of course, every person on the planet with the exception of identical twins has a unique
HCS806 Summer 2010 Methods in Plant Biology: Breeding with Molecular Markers.
 HCS806 Summer 2010 Methods in Plant Biology: Breeding with Molecular Markers. DNA, the stuff of life. We can think of DNA as a biochemical entity or as a data string. With the advent of high throughput
HCS806 Summer 2010 Methods in Plant Biology: Breeding with Molecular Markers. DNA, the stuff of life. We can think of DNA as a biochemical entity or as a data string. With the advent of high throughput
Identification and characterization of a pathogenicity-related gene VdCYP1 from Verticillium dahliae
 Identification and characterization of a pathogenicity-related gene VdCYP1 from Verticillium dahliae Dan-Dan Zhang*, Xin-Yan Wang*, Jie-Yin Chen*, Zhi-Qiang Kong, Yue-Jing Gui, Nan-Yang Li, Yu-Ming Bao,
Identification and characterization of a pathogenicity-related gene VdCYP1 from Verticillium dahliae Dan-Dan Zhang*, Xin-Yan Wang*, Jie-Yin Chen*, Zhi-Qiang Kong, Yue-Jing Gui, Nan-Yang Li, Yu-Ming Bao,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Vidigal and Ventura a wt locus 5 region 3 region CCTCTGCCACTGCGAGGGCGTCCAATGGTGCTTG(...)AACAGGTGGAATATCCCTACTCTA predicted deletion clone 1 clone 2 clone 3 CCTCTGCCACTGCGAGGGCGTC-AGGTGGAATATCCCTACTCTA
Supplementary Information Vidigal and Ventura a wt locus 5 region 3 region CCTCTGCCACTGCGAGGGCGTCCAATGGTGCTTG(...)AACAGGTGGAATATCCCTACTCTA predicted deletion clone 1 clone 2 clone 3 CCTCTGCCACTGCGAGGGCGTC-AGGTGGAATATCCCTACTCTA
PCR Techniques. By Ahmad Mansour Mohamed Alzohairy. Department of Genetics, Zagazig University,Zagazig, Egypt
 PCR Techniques By Ahmad Mansour Mohamed Alzohairy Department of Genetics, Zagazig University,Zagazig, Egypt 2005 PCR Techniques ISSR PCR Inter-Simple Sequence Repeats (ISSRs) By Ahmad Mansour Mohamed Alzohairy
PCR Techniques By Ahmad Mansour Mohamed Alzohairy Department of Genetics, Zagazig University,Zagazig, Egypt 2005 PCR Techniques ISSR PCR Inter-Simple Sequence Repeats (ISSRs) By Ahmad Mansour Mohamed Alzohairy
POPULATION GENETICS studies the genetic. It includes the study of forces that induce evolution (the
 POPULATION GENETICS POPULATION GENETICS studies the genetic composition of populations and how it changes with time. It includes the study of forces that induce evolution (the change of the genetic constitution)
POPULATION GENETICS POPULATION GENETICS studies the genetic composition of populations and how it changes with time. It includes the study of forces that induce evolution (the change of the genetic constitution)
CSS451 Spring 2010 Polymerase Chain Reaction Laboratory
 CSS451 Spring 2010 Polymerase Chain Reaction Laboratory The purpose of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is to amplify specific segments of DNA. If one knows the DNA sequence of regions of DNA that flank
CSS451 Spring 2010 Polymerase Chain Reaction Laboratory The purpose of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is to amplify specific segments of DNA. If one knows the DNA sequence of regions of DNA that flank
